Computation of Velocity, Pressure and Temperature Distributions near a Stagnation Point in Planar Laminar Viscous Incompressible Flow
|
|
|
- Percival Bridges
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Excerpt from the Proceedings of the COMSOL Conference 8 Boston Computation of Velocity, Pressure and Temperature Distributions near a Stagnation Point in Planar Laminar Viscous Incompressible Flow E. Kaufman 1 and E. Gutierrez-Miravete *, 1 Pratt and Whitney, Rensselaer at Hartford *Corresponding author: 75 Windsor Street, Hartford, CT 61, gutiee@rpi.edu Abstract: As gas turbine engine turbine temperatures and component life requirements continue to rise, it becomes increasingly important to have a good understanding of the operating temperatures of turbine components. Recent work has explored the possibility of approximating the leading edge stagnation heat transfer coefficient through analogy with the Hiemenz flow solution for stagnating plane flow in front of a flat wall. The objective of this study was to set the framework for an exploration into whether a Hiemenz flow approximation based on measured static pressures near an airfoil leading edge can provide a good estimate of the leading edge heat transfer coefficient. To achieve the stated objective, the Hiemenz solution was reproduced using MATLAB in order to obtain a reliable baseline for comparison. Finite element and finite volume CFD solvers COMSOL and FLUENT, respectively, were each used to produce numerical solutions of the same problem and the results compared. Keywords: Stagnation flow, laminar, incompressible, viscous fluid. 1. Introduction The two-dimensional plane flow of an inviscid incompressible fluid approaching a wall is shown in Figure 1. The wall is located at y=, while x= is a symmetry plane. The stagnation point is at the origin. The fluid moves towards the wall from the positive y-direction and is then deflected by it and moves along the positive x- direction. Figure 1. Velocity field near a stagnation point for the planar laminar flow of an inviscid incompressible fluid. This flow can be solved analytically and the solution, in terms of the stream function is given by ψ = axy [1]. This solution for inviscid flow in the vicinity of a stagnation point is the basis for the derivation of the similarity flow solution for the flow of a viscous fluid in the same situation. As outlined in [,3], the inviscid stream function is modified so that the no-slip condition at the wall can be satisfied and one writes instead ψ ( y) viscous = axf, where the function f depends only on the coordinate y. Hence, once values for f(y) have been determined, the velocity and pressure distributions for the viscous case can be determined. The velocity components can be described in terms of the function f: df u= ax dy v= af y ( )
2 The pressure distribution can be described as follows, introducing the function F(y): 1 p p= a + ρ [ x F( y) ] If the stagnation pressure p is taken as the pressure at the stagnation point, where x=y=, we can extract the condition: F ( y) = y= The incorporation of the above together with the no-slip condition and the Navier-Stokes equations yields Hiemenz equation for the dimensionless function φ (η ) : Where and φ ''' + φφ'' φ ' φ + 1= ( η) = f ( y ) / aν η = a y ν Here ν is the kinematic viscosity of the fluid. Hiemenz equation is a third order, non-linear ordinary differential equation that must be solved subject to the following boundary conditions: φ ' = η= φ = η= φ ' = 1 η No analytical solution of the above problem is possible; therefore a numerical method must be used as described below. combined with shooting within the MATLAB environment [4]. The results obtained using this procedure were in excellent agreement with previously published results and are used as our baseline for comparison against predictions using COMSOL and the CFD program FLUENT. Utmost care had to be used to ensure the far-field conditions in these simulations matched those used in the original method. Both COMSOL and FLUENT [5] flow solvers were used to develop models of the viscous flow field in the case of a -dimensional, steady, incompressible viscous flow with constant properties. Selection of appropriate domain and boundary conditions are essential to obtaining a solution consistent with the results obtained from the Hiemenz equation. Several variations on the geometry and boundary conditions were investigated. Each of these cases resulted in streamlines and pressures that were qualitatively consistent with the analytical solutions. However, pressure magnitudes did not generally agree well with the Hiemenz solution. The most successful case for the purposes of comparison was one in which the domain was 6 meters by 6 meters, and inlet and exit boundary conditions were specified so as to be consistent with the boundary conditions used in the analytical case. The domain size of 6 was sufficient to ensure that the boundaries were effectively at far field; i.e. the velocities should have asymptotically achieved their far-field character by the boundaries of the domain. This was established based on the viscous exact solution, for which 99% of far-field conditions are achieved at 3 units from the wall. The COMSOL and FLUENT meshes used are shown in Figures a and b, respectively.. Methodology The boundary value problem described in the previous section is solved by first transforming the original equation into a system of first order ordinary differential equations than are then solved using a fourth order Runge-Kutta method
3 prediction at x=6, given a reference pressure p of 1 Pa. 3. Results Figure a. Mesh used in the COMSOL model. The velocity fields computed using COMSOL and FLUENT are shown in Figures 3a and 3b, respectively. The velocity fields predicted by these codes are nearly identical, with a maximum value of 8.4 m/s in each case. This maximum value is also consistent with the viscous analytical solution, which is (u,v)=(6, ) at the corner (x,y)=(6,6). This velocity magnitude of 8.4 m/s is slightly lower than that predicted by the inviscid solution, 8.49 m/s. Figure b. Mesh used in the FLUENT model. For the computations, the inlet velocity was set such that U = x and V= (m/s). The inlet x-velocity comes from the boundary condition U = ax far from the wall, and the inlet y- velocity was based on the results of the viscous (Hiemenz) solution. The specified inlet x- velocity defines the final parameter, a, required to ensure that the case is properly nondimensionalized ( a= 1s -1 ). The inlet y-velocity is equal to the analytical prediction at y=η=6. The density was set to 1 kgm -3 and viscosity was set equal to 1 kgm -1 s -1. These values simplify the comparison between the analytical and numerical results. Selecting this set of initial conditions and material properties ensures that the numerical values of the dimensionless function φ (η) are equivalent to those of the dimensional function f(y), and that the values of the dimensionless coordinate η and the dimensional y are also equal. (The dimensions of both y and f(y) are meters). The exit pressure was specified so as to be consistent with the analytical Figure 3a. Velocity field computed with COMSOL. Figure 3b. Velocity field computed with FLUENT. The pressure fields computed by COMSOL and FLUENT are shown in Figures 4a and 4b,
4 respectively. They are both close in shape to the analytical solution, and in each case indicate a stagnation pressure very close to the specified value of 1 Pa. The contours are, however, slightly different between the codes. This could be attributable to several factors, including differences in mesh density (which is visible in Figures a and b); the discretization of applied boundary condition profiles, which was comparable to the mesh density in the FLUENT case but finer than the COMSOL case, or perhaps to solver differences. Y coordinate (m) Pressure Profile at Symmetry Plane (X=) COMSOL FLUENT Hiemenz Inviscid Pressure (Pa) Figure 5. Pressure distributions computed along the symmetry line, near the stagnation point for all four cases considered. Figure 4a. Pressure field computed with COMSOL. Temperature Profile COMSOL FLUENT Hiemenz Inviscid Y coordinate (m) Figure 4b. Pressure field computed with FLUENT. Figure 5, shows the computed pressure distributions along the symmetry line and in close proximity to the wall for the four models considered (namely, the inviscid case, Hiemenz, COMSOL and FLUENT). The figure shows that there is very good agreement between the Hiemenz and COMSOL results and small, but not negligible differences are obtained between the COMSOL and FLUENT results. Finally, Figure 6 shows computed results for the temperature profiles along the symmetry line for the same four cases considered. The agreement is excellent for the three viscous methods Normalized Temp (T-Twall)/(Tinf-Twall) Figure 6. Temperature distributions computed along the symmetry line, near the stagnation point for all four cases considered. 4. Conclusions We have investigated the planar laminar flow of an incompressible viscous fluid in the vicinity of a stagnation point. The solution first obtained by Hiemenz was reproduced and used as a baseline for comparison. Finite element (using COMSOL) and finite volume (using FLUENT)
5 models of the problem were developed to investigate their performance against the baseline. Both, the COMSOL and FLUENT simulations were shown to be reliable for predicting the velocity, pressure and temperature distributions in this case. 8. References 1. F. B. Hildebrand, Advanced Calculus for Applications, nd ed. Prentice-Hall, Inc. 1976, p H. Schlichting and K. Gersten, Boundary Layer Theory, 8 th ed., Springer, NY,, p Holly, Brian M. and Lee S. Langston, Analytical Modeling of Turbine Cascade Leading Edge Heat Transfer using Skin Friction and Pressure Measurements, GT7-81, Proceedings of GT AMSE Turbo Expo 7: Power for Land, Sea and Air, May 14-17, Montréal, Canada. 4. R. Burden and J.D. Faires, Numerical Analysis, 7 th ed. Brooks-Cole, CA, 1, chapters 5 and FLUENT Website (
Studies of the Continuous and Discrete Adjoint Approaches to Viscous Automatic Aerodynamic Shape Optimization
 Studies of the Continuous and Discrete Adjoint Approaches to Viscous Automatic Aerodynamic Shape Optimization Siva Nadarajah Antony Jameson Stanford University 15th AIAA Computational Fluid Dynamics Conference
Studies of the Continuous and Discrete Adjoint Approaches to Viscous Automatic Aerodynamic Shape Optimization Siva Nadarajah Antony Jameson Stanford University 15th AIAA Computational Fluid Dynamics Conference
SPC 307 Aerodynamics. Lecture 1. February 10, 2018
 SPC 307 Aerodynamics Lecture 1 February 10, 2018 Sep. 18, 2016 1 Course Materials drahmednagib.com 2 COURSE OUTLINE Introduction to Aerodynamics Review on the Fundamentals of Fluid Mechanics Euler and
SPC 307 Aerodynamics Lecture 1 February 10, 2018 Sep. 18, 2016 1 Course Materials drahmednagib.com 2 COURSE OUTLINE Introduction to Aerodynamics Review on the Fundamentals of Fluid Mechanics Euler and
Module D: Laminar Flow over a Flat Plate
 Module D: Laminar Flow over a Flat Plate Summary... Problem Statement Geometry and Mesh Creation Problem Setup Solution. Results Validation......... Mesh Refinement.. Summary This ANSYS FLUENT tutorial
Module D: Laminar Flow over a Flat Plate Summary... Problem Statement Geometry and Mesh Creation Problem Setup Solution. Results Validation......... Mesh Refinement.. Summary This ANSYS FLUENT tutorial
Strömningslära Fluid Dynamics. Computer laboratories using COMSOL v4.4
 UMEÅ UNIVERSITY Department of Physics Claude Dion Olexii Iukhymenko May 15, 2015 Strömningslära Fluid Dynamics (5FY144) Computer laboratories using COMSOL v4.4!! Report requirements Computer labs must
UMEÅ UNIVERSITY Department of Physics Claude Dion Olexii Iukhymenko May 15, 2015 Strömningslära Fluid Dynamics (5FY144) Computer laboratories using COMSOL v4.4!! Report requirements Computer labs must
Verification and Validation of Turbulent Flow around a Clark-Y Airfoil
 Verification and Validation of Turbulent Flow around a Clark-Y Airfoil 1. Purpose 58:160 Intermediate Mechanics of Fluids CFD LAB 2 By Tao Xing and Fred Stern IIHR-Hydroscience & Engineering The University
Verification and Validation of Turbulent Flow around a Clark-Y Airfoil 1. Purpose 58:160 Intermediate Mechanics of Fluids CFD LAB 2 By Tao Xing and Fred Stern IIHR-Hydroscience & Engineering The University
TUTORIAL#4. Marek Jaszczur. Turbulent Thermal Boundary Layer on a Flat Plate W1-1 AGH 2018/2019
 TUTORIAL#4 Turbulent Thermal Boundary Layer on a Flat Plate Marek Jaszczur AGH 2018/2019 W1-1 Problem specification TUTORIAL#4 Turbulent Thermal Boundary Layer - on a flat plate Goal: Solution for Non-isothermal
TUTORIAL#4 Turbulent Thermal Boundary Layer on a Flat Plate Marek Jaszczur AGH 2018/2019 W1-1 Problem specification TUTORIAL#4 Turbulent Thermal Boundary Layer - on a flat plate Goal: Solution for Non-isothermal
Simulation of Turbulent Flow in an Asymmetric Diffuser
 Simulation of Turbulent Flow in an Asymmetric Diffuser 1. Purpose 58:160 Intermediate Mechanics of Fluids CFD LAB 3 By Tao Xing and Fred Stern IIHR-Hydroscience & Engineering The University of Iowa C.
Simulation of Turbulent Flow in an Asymmetric Diffuser 1. Purpose 58:160 Intermediate Mechanics of Fluids CFD LAB 3 By Tao Xing and Fred Stern IIHR-Hydroscience & Engineering The University of Iowa C.
TUTORIAL#3. Marek Jaszczur. Boundary Layer on a Flat Plate W1-1 AGH 2018/2019
 TUTORIAL#3 Boundary Layer on a Flat Plate Marek Jaszczur AGH 2018/2019 W1-1 Problem specification TUTORIAL#3 Boundary Layer - on a flat plate Goal: Solution for boudary layer 1. Creating 2D simple geometry
TUTORIAL#3 Boundary Layer on a Flat Plate Marek Jaszczur AGH 2018/2019 W1-1 Problem specification TUTORIAL#3 Boundary Layer - on a flat plate Goal: Solution for boudary layer 1. Creating 2D simple geometry
Introduction to ANSYS CFX
 Workshop 03 Fluid flow around the NACA0012 Airfoil 16.0 Release Introduction to ANSYS CFX 2015 ANSYS, Inc. March 13, 2015 1 Release 16.0 Workshop Description: The flow simulated is an external aerodynamics
Workshop 03 Fluid flow around the NACA0012 Airfoil 16.0 Release Introduction to ANSYS CFX 2015 ANSYS, Inc. March 13, 2015 1 Release 16.0 Workshop Description: The flow simulated is an external aerodynamics
Compressible Flow in a Nozzle
 SPC 407 Supersonic & Hypersonic Fluid Dynamics Ansys Fluent Tutorial 1 Compressible Flow in a Nozzle Ahmed M Nagib Elmekawy, PhD, P.E. Problem Specification Consider air flowing at high-speed through a
SPC 407 Supersonic & Hypersonic Fluid Dynamics Ansys Fluent Tutorial 1 Compressible Flow in a Nozzle Ahmed M Nagib Elmekawy, PhD, P.E. Problem Specification Consider air flowing at high-speed through a
Introduction to CFX. Workshop 2. Transonic Flow Over a NACA 0012 Airfoil. WS2-1. ANSYS, Inc. Proprietary 2009 ANSYS, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Workshop 2 Transonic Flow Over a NACA 0012 Airfoil. Introduction to CFX WS2-1 Goals The purpose of this tutorial is to introduce the user to modelling flow in high speed external aerodynamic applications.
Workshop 2 Transonic Flow Over a NACA 0012 Airfoil. Introduction to CFX WS2-1 Goals The purpose of this tutorial is to introduce the user to modelling flow in high speed external aerodynamic applications.
Flow and Heat Transfer in a Mixing Elbow
 Flow and Heat Transfer in a Mixing Elbow Objectives The main objectives of the project are to learn (i) how to set up and perform flow simulations with heat transfer and mixing, (ii) post-processing and
Flow and Heat Transfer in a Mixing Elbow Objectives The main objectives of the project are to learn (i) how to set up and perform flow simulations with heat transfer and mixing, (ii) post-processing and
Computational Simulation of the Wind-force on Metal Meshes
 16 th Australasian Fluid Mechanics Conference Crown Plaza, Gold Coast, Australia 2-7 December 2007 Computational Simulation of the Wind-force on Metal Meshes Ahmad Sharifian & David R. Buttsworth Faculty
16 th Australasian Fluid Mechanics Conference Crown Plaza, Gold Coast, Australia 2-7 December 2007 Computational Simulation of the Wind-force on Metal Meshes Ahmad Sharifian & David R. Buttsworth Faculty
Simulation of Turbulent Flow around an Airfoil
 Simulation of Turbulent Flow around an Airfoil ENGR:2510 Mechanics of Fluids and Transfer Processes CFD Pre-Lab 2 (ANSYS 17.1; Last Updated: Nov. 7, 2016) By Timur Dogan, Michael Conger, Andrew Opyd, Dong-Hwan
Simulation of Turbulent Flow around an Airfoil ENGR:2510 Mechanics of Fluids and Transfer Processes CFD Pre-Lab 2 (ANSYS 17.1; Last Updated: Nov. 7, 2016) By Timur Dogan, Michael Conger, Andrew Opyd, Dong-Hwan
SimCafe. ANSYS WB - Airfoil - Setup (Physics) Added by Benjamin J Mullen, last edited by Benjamin J Mullen on Apr 29, :18
 Page 1 of 5 Search Cornell SimCafe Home Edit Browse/Manage Login Simulation > > ANSYS WB - Airfoil - Setup (Physics) Search ANSYS WB - Airfoil - Setup (Physics) Added by Benjamin J Mullen, last edited
Page 1 of 5 Search Cornell SimCafe Home Edit Browse/Manage Login Simulation > > ANSYS WB - Airfoil - Setup (Physics) Search ANSYS WB - Airfoil - Setup (Physics) Added by Benjamin J Mullen, last edited
Simulation of Flow Development in a Pipe
 Tutorial 4. Simulation of Flow Development in a Pipe Introduction The purpose of this tutorial is to illustrate the setup and solution of a 3D turbulent fluid flow in a pipe. The pipe networks are common
Tutorial 4. Simulation of Flow Development in a Pipe Introduction The purpose of this tutorial is to illustrate the setup and solution of a 3D turbulent fluid flow in a pipe. The pipe networks are common
An Introduction to SolidWorks Flow Simulation 2010
 An Introduction to SolidWorks Flow Simulation 2010 John E. Matsson, Ph.D. SDC PUBLICATIONS www.sdcpublications.com Schroff Development Corporation Chapter 2 Flat Plate Boundary Layer Objectives Creating
An Introduction to SolidWorks Flow Simulation 2010 John E. Matsson, Ph.D. SDC PUBLICATIONS www.sdcpublications.com Schroff Development Corporation Chapter 2 Flat Plate Boundary Layer Objectives Creating
Analysis of an airfoil
 UNDERGRADUATE RESEARCH FALL 2010 Analysis of an airfoil using Computational Fluid Dynamics Tanveer Chandok 12/17/2010 Independent research thesis at the Georgia Institute of Technology under the supervision
UNDERGRADUATE RESEARCH FALL 2010 Analysis of an airfoil using Computational Fluid Dynamics Tanveer Chandok 12/17/2010 Independent research thesis at the Georgia Institute of Technology under the supervision
Simulation of Turbulent Flow around an Airfoil
 1. Purpose Simulation of Turbulent Flow around an Airfoil ENGR:2510 Mechanics of Fluids and Transfer Processes CFD Lab 2 (ANSYS 17.1; Last Updated: Nov. 7, 2016) By Timur Dogan, Michael Conger, Andrew
1. Purpose Simulation of Turbulent Flow around an Airfoil ENGR:2510 Mechanics of Fluids and Transfer Processes CFD Lab 2 (ANSYS 17.1; Last Updated: Nov. 7, 2016) By Timur Dogan, Michael Conger, Andrew
ANSYS AIM Tutorial Turbulent Flow Over a Backward Facing Step
 ANSYS AIM Tutorial Turbulent Flow Over a Backward Facing Step Author(s): Sebastian Vecchi, ANSYS Created using ANSYS AIM 18.1 Problem Specification Pre-Analysis & Start Up Governing Equation Start-Up Geometry
ANSYS AIM Tutorial Turbulent Flow Over a Backward Facing Step Author(s): Sebastian Vecchi, ANSYS Created using ANSYS AIM 18.1 Problem Specification Pre-Analysis & Start Up Governing Equation Start-Up Geometry
Middle East Technical University Mechanical Engineering Department ME 485 CFD with Finite Volume Method Fall 2017 (Dr. Sert)
 Middle East Technical University Mechanical Engineering Department ME 485 CFD with Finite Volume Method Fall 2017 (Dr. Sert) ANSYS Fluent Tutorial Developing Laminar Flow in a 2D Channel 1 How to use This
Middle East Technical University Mechanical Engineering Department ME 485 CFD with Finite Volume Method Fall 2017 (Dr. Sert) ANSYS Fluent Tutorial Developing Laminar Flow in a 2D Channel 1 How to use This
Debojyoti Ghosh. Adviser: Dr. James Baeder Alfred Gessow Rotorcraft Center Department of Aerospace Engineering
 Debojyoti Ghosh Adviser: Dr. James Baeder Alfred Gessow Rotorcraft Center Department of Aerospace Engineering To study the Dynamic Stalling of rotor blade cross-sections Unsteady Aerodynamics: Time varying
Debojyoti Ghosh Adviser: Dr. James Baeder Alfred Gessow Rotorcraft Center Department of Aerospace Engineering To study the Dynamic Stalling of rotor blade cross-sections Unsteady Aerodynamics: Time varying
Inviscid Flows. Introduction. T. J. Craft George Begg Building, C41. The Euler Equations. 3rd Year Fluid Mechanics
 Contents: Navier-Stokes equations Inviscid flows Boundary layers Transition, Reynolds averaging Mixing-length models of turbulence Turbulent kinetic energy equation One- and Two-equation models Flow management
Contents: Navier-Stokes equations Inviscid flows Boundary layers Transition, Reynolds averaging Mixing-length models of turbulence Turbulent kinetic energy equation One- and Two-equation models Flow management
Microwell Mixing with Surface Tension
 Microwell Mixing with Surface Tension Nick Cox Supervised by Professor Bruce Finlayson University of Washington Department of Chemical Engineering June 6, 2007 Abstract For many applications in the pharmaceutical
Microwell Mixing with Surface Tension Nick Cox Supervised by Professor Bruce Finlayson University of Washington Department of Chemical Engineering June 6, 2007 Abstract For many applications in the pharmaceutical
Terminal Falling Velocity of a Sand Grain
 Terminal Falling Velocity of a Sand Grain Introduction The first stop for polluted water entering a water work is normally a large tank, where large particles are left to settle. More generally, gravity
Terminal Falling Velocity of a Sand Grain Introduction The first stop for polluted water entering a water work is normally a large tank, where large particles are left to settle. More generally, gravity
Simulation of Laminar Pipe Flows
 Simulation of Laminar Pipe Flows 57:020 Mechanics of Fluids and Transport Processes CFD PRELAB 1 By Timur Dogan, Michael Conger, Maysam Mousaviraad, Tao Xing and Fred Stern IIHR-Hydroscience & Engineering
Simulation of Laminar Pipe Flows 57:020 Mechanics of Fluids and Transport Processes CFD PRELAB 1 By Timur Dogan, Michael Conger, Maysam Mousaviraad, Tao Xing and Fred Stern IIHR-Hydroscience & Engineering
The viscous forces on the cylinder are proportional to the gradient of the velocity field at the
 Fluid Dynamics Models : Flow Past a Cylinder Flow Past a Cylinder Introduction The flow of fluid behind a blunt body such as an automobile is difficult to compute due to the unsteady flows. The wake behind
Fluid Dynamics Models : Flow Past a Cylinder Flow Past a Cylinder Introduction The flow of fluid behind a blunt body such as an automobile is difficult to compute due to the unsteady flows. The wake behind
Driven Cavity Example
 BMAppendixI.qxd 11/14/12 6:55 PM Page I-1 I CFD Driven Cavity Example I.1 Problem One of the classic benchmarks in CFD is the driven cavity problem. Consider steady, incompressible, viscous flow in a square
BMAppendixI.qxd 11/14/12 6:55 PM Page I-1 I CFD Driven Cavity Example I.1 Problem One of the classic benchmarks in CFD is the driven cavity problem. Consider steady, incompressible, viscous flow in a square
Verification of Laminar and Validation of Turbulent Pipe Flows
 1 Verification of Laminar and Validation of Turbulent Pipe Flows 1. Purpose ME:5160 Intermediate Mechanics of Fluids CFD LAB 1 (ANSYS 18.1; Last Updated: Aug. 1, 2017) By Timur Dogan, Michael Conger, Dong-Hwan
1 Verification of Laminar and Validation of Turbulent Pipe Flows 1. Purpose ME:5160 Intermediate Mechanics of Fluids CFD LAB 1 (ANSYS 18.1; Last Updated: Aug. 1, 2017) By Timur Dogan, Michael Conger, Dong-Hwan
Calculate a solution using the pressure-based coupled solver.
 Tutorial 19. Modeling Cavitation Introduction This tutorial examines the pressure-driven cavitating flow of water through a sharpedged orifice. This is a typical configuration in fuel injectors, and brings
Tutorial 19. Modeling Cavitation Introduction This tutorial examines the pressure-driven cavitating flow of water through a sharpedged orifice. This is a typical configuration in fuel injectors, and brings
SolidWorks Flow Simulation 2014
 An Introduction to SolidWorks Flow Simulation 2014 John E. Matsson, Ph.D. SDC PUBLICATIONS Better Textbooks. Lower Prices. www.sdcpublications.com Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org) Visit the following websites
An Introduction to SolidWorks Flow Simulation 2014 John E. Matsson, Ph.D. SDC PUBLICATIONS Better Textbooks. Lower Prices. www.sdcpublications.com Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org) Visit the following websites
and to the following students who assisted in the creation of the Fluid Dynamics tutorials:
 Fluid Dynamics CAx Tutorial: Channel Flow Basic Tutorial # 4 Deryl O. Snyder C. Greg Jensen Brigham Young University Provo, UT 84602 Special thanks to: PACE, Fluent, UGS Solutions, Altair Engineering;
Fluid Dynamics CAx Tutorial: Channel Flow Basic Tutorial # 4 Deryl O. Snyder C. Greg Jensen Brigham Young University Provo, UT 84602 Special thanks to: PACE, Fluent, UGS Solutions, Altair Engineering;
FEMLAB Exercise 1 for ChE366
 FEMLAB Exercise 1 for ChE366 Problem statement Consider a spherical particle of radius r s moving with constant velocity U in an infinitely long cylinder of radius R that contains a Newtonian fluid. Let
FEMLAB Exercise 1 for ChE366 Problem statement Consider a spherical particle of radius r s moving with constant velocity U in an infinitely long cylinder of radius R that contains a Newtonian fluid. Let
Stream Function-Vorticity CFD Solver MAE 6263
 Stream Function-Vorticity CFD Solver MAE 66 Charles O Neill April, 00 Abstract A finite difference CFD solver was developed for transient, two-dimensional Cartesian viscous flows. Flow parameters are solved
Stream Function-Vorticity CFD Solver MAE 66 Charles O Neill April, 00 Abstract A finite difference CFD solver was developed for transient, two-dimensional Cartesian viscous flows. Flow parameters are solved
Using a Single Rotating Reference Frame
 Tutorial 9. Using a Single Rotating Reference Frame Introduction This tutorial considers the flow within a 2D, axisymmetric, co-rotating disk cavity system. Understanding the behavior of such flows is
Tutorial 9. Using a Single Rotating Reference Frame Introduction This tutorial considers the flow within a 2D, axisymmetric, co-rotating disk cavity system. Understanding the behavior of such flows is
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY. Analyzing wind flow around the square plate using ADINA Project. Ankur Bajoria
 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Analyzing wind flow around the square plate using ADINA 2.094 - Project Ankur Bajoria May 1, 2008 Acknowledgement I would like to thank ADINA R & D, Inc for the full
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Analyzing wind flow around the square plate using ADINA 2.094 - Project Ankur Bajoria May 1, 2008 Acknowledgement I would like to thank ADINA R & D, Inc for the full
Application of Wray-Agarwal Turbulence Model for Accurate Numerical Simulation of Flow Past a Three-Dimensional Wing-body
 Washington University in St. Louis Washington University Open Scholarship Mechanical Engineering and Materials Science Independent Study Mechanical Engineering & Materials Science 4-28-2016 Application
Washington University in St. Louis Washington University Open Scholarship Mechanical Engineering and Materials Science Independent Study Mechanical Engineering & Materials Science 4-28-2016 Application
and to the following students who assisted in the creation of the Fluid Dynamics tutorials:
 Fluid Dynamics CAx Tutorial: Pressure Along a Streamline Basic Tutorial #3 Deryl O. Snyder C. Greg Jensen Brigham Young University Provo, UT 84602 Special thanks to: PACE, Fluent, UGS Solutions, Altair
Fluid Dynamics CAx Tutorial: Pressure Along a Streamline Basic Tutorial #3 Deryl O. Snyder C. Greg Jensen Brigham Young University Provo, UT 84602 Special thanks to: PACE, Fluent, UGS Solutions, Altair
Verification and Validation of Turbulent Flow around a Clark-Y Airfoil
 1 Verification and Validation of Turbulent Flow around a Clark-Y Airfoil 1. Purpose ME:5160 Intermediate Mechanics of Fluids CFD LAB 2 (ANSYS 19.1; Last Updated: Aug. 7, 2018) By Timur Dogan, Michael Conger,
1 Verification and Validation of Turbulent Flow around a Clark-Y Airfoil 1. Purpose ME:5160 Intermediate Mechanics of Fluids CFD LAB 2 (ANSYS 19.1; Last Updated: Aug. 7, 2018) By Timur Dogan, Michael Conger,
Comparisons of Compressible and Incompressible Solvers: Flat Plate Boundary Layer and NACA airfoils
 Comparisons of Compressible and Incompressible Solvers: Flat Plate Boundary Layer and NACA airfoils Moritz Kompenhans 1, Esteban Ferrer 2, Gonzalo Rubio, Eusebio Valero E.T.S.I.A. (School of Aeronautics)
Comparisons of Compressible and Incompressible Solvers: Flat Plate Boundary Layer and NACA airfoils Moritz Kompenhans 1, Esteban Ferrer 2, Gonzalo Rubio, Eusebio Valero E.T.S.I.A. (School of Aeronautics)
COMPUTATIONAL FLUID DYNAMICS ANALYSIS OF ORIFICE PLATE METERING SITUATIONS UNDER ABNORMAL CONFIGURATIONS
 COMPUTATIONAL FLUID DYNAMICS ANALYSIS OF ORIFICE PLATE METERING SITUATIONS UNDER ABNORMAL CONFIGURATIONS Dr W. Malalasekera Version 3.0 August 2013 1 COMPUTATIONAL FLUID DYNAMICS ANALYSIS OF ORIFICE PLATE
COMPUTATIONAL FLUID DYNAMICS ANALYSIS OF ORIFICE PLATE METERING SITUATIONS UNDER ABNORMAL CONFIGURATIONS Dr W. Malalasekera Version 3.0 August 2013 1 COMPUTATIONAL FLUID DYNAMICS ANALYSIS OF ORIFICE PLATE
Isotropic Porous Media Tutorial
 STAR-CCM+ User Guide 3927 Isotropic Porous Media Tutorial This tutorial models flow through the catalyst geometry described in the introductory section. In the porous region, the theoretical pressure drop
STAR-CCM+ User Guide 3927 Isotropic Porous Media Tutorial This tutorial models flow through the catalyst geometry described in the introductory section. In the porous region, the theoretical pressure drop
Ashwin Shridhar et al. Int. Journal of Engineering Research and Applications ISSN : , Vol. 5, Issue 6, ( Part - 5) June 2015, pp.
 RESEARCH ARTICLE OPEN ACCESS Conjugate Heat transfer Analysis of helical fins with airfoil crosssection and its comparison with existing circular fin design for air cooled engines employing constant rectangular
RESEARCH ARTICLE OPEN ACCESS Conjugate Heat transfer Analysis of helical fins with airfoil crosssection and its comparison with existing circular fin design for air cooled engines employing constant rectangular
Tutorial 2. Modeling Periodic Flow and Heat Transfer
 Tutorial 2. Modeling Periodic Flow and Heat Transfer Introduction: Many industrial applications, such as steam generation in a boiler or air cooling in the coil of an air conditioner, can be modeled as
Tutorial 2. Modeling Periodic Flow and Heat Transfer Introduction: Many industrial applications, such as steam generation in a boiler or air cooling in the coil of an air conditioner, can be modeled as
Lab 9: FLUENT: Transient Natural Convection Between Concentric Cylinders
 Lab 9: FLUENT: Transient Natural Convection Between Concentric Cylinders Objective: The objective of this laboratory is to introduce how to use FLUENT to solve both transient and natural convection problems.
Lab 9: FLUENT: Transient Natural Convection Between Concentric Cylinders Objective: The objective of this laboratory is to introduce how to use FLUENT to solve both transient and natural convection problems.
Modeling and Simulation of Single Phase Fluid Flow and Heat Transfer in Packed Beds
 Modeling and Simulation of Single Phase Fluid Flow and Heat Transfer in Packed Beds by:- Balaaji Mahadevan Shaurya Sachdev Subhanshu Pareek Amol Deshpande Birla Institute of Technology and Science, Pilani
Modeling and Simulation of Single Phase Fluid Flow and Heat Transfer in Packed Beds by:- Balaaji Mahadevan Shaurya Sachdev Subhanshu Pareek Amol Deshpande Birla Institute of Technology and Science, Pilani
NUMERICAL 3D TRANSONIC FLOW SIMULATION OVER A WING
 Review of the Air Force Academy No.3 (35)/2017 NUMERICAL 3D TRANSONIC FLOW SIMULATION OVER A WING Cvetelina VELKOVA Department of Technical Mechanics, Naval Academy Nikola Vaptsarov,Varna, Bulgaria (cvetelina.velkova1985@gmail.com)
Review of the Air Force Academy No.3 (35)/2017 NUMERICAL 3D TRANSONIC FLOW SIMULATION OVER A WING Cvetelina VELKOVA Department of Technical Mechanics, Naval Academy Nikola Vaptsarov,Varna, Bulgaria (cvetelina.velkova1985@gmail.com)
Supersonic Flow Over a Wedge
 SPC 407 Supersonic & Hypersonic Fluid Dynamics Ansys Fluent Tutorial 2 Supersonic Flow Over a Wedge Ahmed M Nagib Elmekawy, PhD, P.E. Problem Specification A uniform supersonic stream encounters a wedge
SPC 407 Supersonic & Hypersonic Fluid Dynamics Ansys Fluent Tutorial 2 Supersonic Flow Over a Wedge Ahmed M Nagib Elmekawy, PhD, P.E. Problem Specification A uniform supersonic stream encounters a wedge
Non-Newtonian Transitional Flow in an Eccentric Annulus
 Tutorial 8. Non-Newtonian Transitional Flow in an Eccentric Annulus Introduction The purpose of this tutorial is to illustrate the setup and solution of a 3D, turbulent flow of a non-newtonian fluid. Turbulent
Tutorial 8. Non-Newtonian Transitional Flow in an Eccentric Annulus Introduction The purpose of this tutorial is to illustrate the setup and solution of a 3D, turbulent flow of a non-newtonian fluid. Turbulent
MESHLESS SOLUTION OF INCOMPRESSIBLE FLOW OVER BACKWARD-FACING STEP
 Vol. 12, Issue 1/2016, 63-68 DOI: 10.1515/cee-2016-0009 MESHLESS SOLUTION OF INCOMPRESSIBLE FLOW OVER BACKWARD-FACING STEP Juraj MUŽÍK 1,* 1 Department of Geotechnics, Faculty of Civil Engineering, University
Vol. 12, Issue 1/2016, 63-68 DOI: 10.1515/cee-2016-0009 MESHLESS SOLUTION OF INCOMPRESSIBLE FLOW OVER BACKWARD-FACING STEP Juraj MUŽÍK 1,* 1 Department of Geotechnics, Faculty of Civil Engineering, University
3D Modeling of Urban Areas for Built Environment CFD Applications
 3D Modeling of Urban Areas for Built Environment CFD Applications using C A.W.M. (Jos) van Schijndel Eindhoven University of Technology P.O. Box 513; 5600 MB Eindhoven; Netherlands, A.W.M.v.Schijndel@tue.nl
3D Modeling of Urban Areas for Built Environment CFD Applications using C A.W.M. (Jos) van Schijndel Eindhoven University of Technology P.O. Box 513; 5600 MB Eindhoven; Netherlands, A.W.M.v.Schijndel@tue.nl
Modeling External Compressible Flow
 Tutorial 3. Modeling External Compressible Flow Introduction The purpose of this tutorial is to compute the turbulent flow past a transonic airfoil at a nonzero angle of attack. You will use the Spalart-Allmaras
Tutorial 3. Modeling External Compressible Flow Introduction The purpose of this tutorial is to compute the turbulent flow past a transonic airfoil at a nonzero angle of attack. You will use the Spalart-Allmaras
Optimizing Bio-Inspired Flow Channel Design on Bipolar Plates of PEM Fuel Cells
 Excerpt from the Proceedings of the COMSOL Conference 2010 Boston Optimizing Bio-Inspired Flow Channel Design on Bipolar Plates of PEM Fuel Cells James A. Peitzmeier *1, Steven Kapturowski 2 and Xia Wang
Excerpt from the Proceedings of the COMSOL Conference 2010 Boston Optimizing Bio-Inspired Flow Channel Design on Bipolar Plates of PEM Fuel Cells James A. Peitzmeier *1, Steven Kapturowski 2 and Xia Wang
Steady Flow: Lid-Driven Cavity Flow
 STAR-CCM+ User Guide Steady Flow: Lid-Driven Cavity Flow 2 Steady Flow: Lid-Driven Cavity Flow This tutorial demonstrates the performance of STAR-CCM+ in solving a traditional square lid-driven cavity
STAR-CCM+ User Guide Steady Flow: Lid-Driven Cavity Flow 2 Steady Flow: Lid-Driven Cavity Flow This tutorial demonstrates the performance of STAR-CCM+ in solving a traditional square lid-driven cavity
Precise FEM solution of corner singularity using adjusted mesh applied to 2D flow
 Precise FEM solution of corner singularity using adjusted mesh applied to 2D flow Jakub Šístek, Pavel Burda, Jaroslav Novotný Department of echnical Mathematics, Czech echnical University in Prague, Faculty
Precise FEM solution of corner singularity using adjusted mesh applied to 2D flow Jakub Šístek, Pavel Burda, Jaroslav Novotný Department of echnical Mathematics, Czech echnical University in Prague, Faculty
Abstract. Die Geometry. Introduction. Mesh Partitioning Technique for Coextrusion Simulation
 OPTIMIZATION OF A PROFILE COEXTRUSION DIE USING A THREE-DIMENSIONAL FLOW SIMULATION SOFTWARE Kim Ryckebosh 1 and Mahesh Gupta 2, 3 1. Deceuninck nv, BE-8830 Hooglede-Gits, Belgium 2. Michigan Technological
OPTIMIZATION OF A PROFILE COEXTRUSION DIE USING A THREE-DIMENSIONAL FLOW SIMULATION SOFTWARE Kim Ryckebosh 1 and Mahesh Gupta 2, 3 1. Deceuninck nv, BE-8830 Hooglede-Gits, Belgium 2. Michigan Technological
Simulation and Validation of Turbulent Pipe Flows
 Simulation and Validation of Turbulent Pipe Flows ENGR:2510 Mechanics of Fluids and Transport Processes CFD LAB 1 (ANSYS 17.1; Last Updated: Oct. 10, 2016) By Timur Dogan, Michael Conger, Dong-Hwan Kim,
Simulation and Validation of Turbulent Pipe Flows ENGR:2510 Mechanics of Fluids and Transport Processes CFD LAB 1 (ANSYS 17.1; Last Updated: Oct. 10, 2016) By Timur Dogan, Michael Conger, Dong-Hwan Kim,
ANSYS AIM Tutorial Steady Flow Past a Cylinder
 ANSYS AIM Tutorial Steady Flow Past a Cylinder Author(s): Sebastian Vecchi, ANSYS Created using ANSYS AIM 18.1 Problem Specification Pre-Analysis & Start Up Solution Domain Boundary Conditions Start-Up
ANSYS AIM Tutorial Steady Flow Past a Cylinder Author(s): Sebastian Vecchi, ANSYS Created using ANSYS AIM 18.1 Problem Specification Pre-Analysis & Start Up Solution Domain Boundary Conditions Start-Up
Numerical and theoretical analysis of shock waves interaction and reflection
 Fluid Structure Interaction and Moving Boundary Problems IV 299 Numerical and theoretical analysis of shock waves interaction and reflection K. Alhussan Space Research Institute, King Abdulaziz City for
Fluid Structure Interaction and Moving Boundary Problems IV 299 Numerical and theoretical analysis of shock waves interaction and reflection K. Alhussan Space Research Institute, King Abdulaziz City for
Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) Simulation in Air Duct Channels Using STAR CCM+
 Available onlinewww.ejaet.com European Journal of Advances in Engineering and Technology, 2017,4 (3): 216-220 Research Article ISSN: 2394-658X Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) Simulation in Air Duct
Available onlinewww.ejaet.com European Journal of Advances in Engineering and Technology, 2017,4 (3): 216-220 Research Article ISSN: 2394-658X Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) Simulation in Air Duct
NUMERICAL METHOD FOR FREE SURFACE VISCOUS FLOWS
 STUDIA UNIV. BABEŞ BOLYAI, MATHEMATICA, Volume LIII, Number 3, September 2008 NUMERICAL METHOD FOR FREE SURFACE VISCOUS FLOWS TIBERIU IOANA AND TITUS PETRILA Abstract. In this paper we present a new algorithm
STUDIA UNIV. BABEŞ BOLYAI, MATHEMATICA, Volume LIII, Number 3, September 2008 NUMERICAL METHOD FOR FREE SURFACE VISCOUS FLOWS TIBERIU IOANA AND TITUS PETRILA Abstract. In this paper we present a new algorithm
Wall-bounded laminar sink flows
 Aeta Meehanica 125, 211-215 (1997) ACTA MECHANICA 9 Springer-Verlag 1997 Wall-bounded laminar sink flows S. Haas and W. Schneider, Vienna, Austria Dedicated to Prof. Dr. Dr. h. c. Franz Ziegler on the
Aeta Meehanica 125, 211-215 (1997) ACTA MECHANICA 9 Springer-Verlag 1997 Wall-bounded laminar sink flows S. Haas and W. Schneider, Vienna, Austria Dedicated to Prof. Dr. Dr. h. c. Franz Ziegler on the
Simulation of Turbulent Flow over the Ahmed Body
 1 Simulation of Turbulent Flow over the Ahmed Body ME:5160 Intermediate Mechanics of Fluids CFD LAB 4 (ANSYS 18.1; Last Updated: Aug. 18, 2016) By Timur Dogan, Michael Conger, Dong-Hwan Kim, Maysam Mousaviraad,
1 Simulation of Turbulent Flow over the Ahmed Body ME:5160 Intermediate Mechanics of Fluids CFD LAB 4 (ANSYS 18.1; Last Updated: Aug. 18, 2016) By Timur Dogan, Michael Conger, Dong-Hwan Kim, Maysam Mousaviraad,
Solution Recording and Playback: Vortex Shedding
 STAR-CCM+ User Guide 6663 Solution Recording and Playback: Vortex Shedding This tutorial demonstrates how to use the solution recording and playback module for capturing the results of transient phenomena.
STAR-CCM+ User Guide 6663 Solution Recording and Playback: Vortex Shedding This tutorial demonstrates how to use the solution recording and playback module for capturing the results of transient phenomena.
ANSYS FLUENT. Airfoil Analysis and Tutorial
 ANSYS FLUENT Airfoil Analysis and Tutorial ENGR083: Fluid Mechanics II Terry Yu 5/11/2017 Abstract The NACA 0012 airfoil was one of the earliest airfoils created. Its mathematically simple shape and age
ANSYS FLUENT Airfoil Analysis and Tutorial ENGR083: Fluid Mechanics II Terry Yu 5/11/2017 Abstract The NACA 0012 airfoil was one of the earliest airfoils created. Its mathematically simple shape and age
Shape optimisation using breakthrough technologies
 Shape optimisation using breakthrough technologies Compiled by Mike Slack Ansys Technical Services 2010 ANSYS, Inc. All rights reserved. 1 ANSYS, Inc. Proprietary Introduction Shape optimisation technologies
Shape optimisation using breakthrough technologies Compiled by Mike Slack Ansys Technical Services 2010 ANSYS, Inc. All rights reserved. 1 ANSYS, Inc. Proprietary Introduction Shape optimisation technologies
Research and Design working characteristics of orthogonal turbine Nguyen Quoc Tuan (1), Chu Dinh Do (2), Quach Thi Son (2)
 GSJ: VOLUME 6, ISSUE 6, JUNE 018 116 Research and Design working characteristics of orthogonal turbine Nguyen Quoc Tuan (1), Chu Dinh Do (), Quach Thi Son () (1) Institute for hydro power and renewable
GSJ: VOLUME 6, ISSUE 6, JUNE 018 116 Research and Design working characteristics of orthogonal turbine Nguyen Quoc Tuan (1), Chu Dinh Do (), Quach Thi Son () (1) Institute for hydro power and renewable
CFD Analysis on Heat Transfer Through Different Extended Surfaces
 CFD Analysis on Heat Transfer Through Different Extended Surfaces Ravindra Kondaguli 1 1 Department of Mechanical Engineering BLDECET Vijayapur Abstract: The present work includes CFD analysis and comparison
CFD Analysis on Heat Transfer Through Different Extended Surfaces Ravindra Kondaguli 1 1 Department of Mechanical Engineering BLDECET Vijayapur Abstract: The present work includes CFD analysis and comparison
APPLIED COMPUTATIONAL FLUID DYNAMICS-PROJECT-3
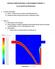 APPLIED COMPUTATIONAL FLUID DYNAMICS-PROJECT-3 BY SAI CHAITANYA MANGAVELLI Common Setup Data: 1) Mesh Proximity and Curvature with Refinement of 2. 2) Double Precision and second order for methods in Solver.
APPLIED COMPUTATIONAL FLUID DYNAMICS-PROJECT-3 BY SAI CHAITANYA MANGAVELLI Common Setup Data: 1) Mesh Proximity and Curvature with Refinement of 2. 2) Double Precision and second order for methods in Solver.
Effect of Position of Wall Mounted Surface Protrusion in Drag Characteristics At Low Reynolds Number
 ISSN (e): 2250 3005 Volume, 07 Issue, 11 November 2017 International Journal of Computational Engineering Research (IJCER) Effect of Position of Wall Mounted Surface Protrusion in Drag Characteristics
ISSN (e): 2250 3005 Volume, 07 Issue, 11 November 2017 International Journal of Computational Engineering Research (IJCER) Effect of Position of Wall Mounted Surface Protrusion in Drag Characteristics
FAST ALGORITHMS FOR CALCULATIONS OF VISCOUS INCOMPRESSIBLE FLOWS USING THE ARTIFICIAL COMPRESSIBILITY METHOD
 TASK QUARTERLY 12 No 3, 273 287 FAST ALGORITHMS FOR CALCULATIONS OF VISCOUS INCOMPRESSIBLE FLOWS USING THE ARTIFICIAL COMPRESSIBILITY METHOD ZBIGNIEW KOSMA Institute of Applied Mechanics, Technical University
TASK QUARTERLY 12 No 3, 273 287 FAST ALGORITHMS FOR CALCULATIONS OF VISCOUS INCOMPRESSIBLE FLOWS USING THE ARTIFICIAL COMPRESSIBILITY METHOD ZBIGNIEW KOSMA Institute of Applied Mechanics, Technical University
Modeling & Simulation of Supersonic Flow Using McCormack s Technique
 Modeling & Simulation of Supersonic Flow Using McCormack s Technique M. Saif Ullah Khalid*, Afzaal M. Malik** Abstract In this work, two-dimensional inviscid supersonic flow around a wedge has been investigated
Modeling & Simulation of Supersonic Flow Using McCormack s Technique M. Saif Ullah Khalid*, Afzaal M. Malik** Abstract In this work, two-dimensional inviscid supersonic flow around a wedge has been investigated
Influence of mesh quality and density on numerical calculation of heat exchanger with undulation in herringbone pattern
 Influence of mesh quality and density on numerical calculation of heat exchanger with undulation in herringbone pattern Václav Dvořák, Jan Novosád Abstract Research of devices for heat recovery is currently
Influence of mesh quality and density on numerical calculation of heat exchanger with undulation in herringbone pattern Václav Dvořák, Jan Novosád Abstract Research of devices for heat recovery is currently
Computational Study of Laminar Flowfield around a Square Cylinder using Ansys Fluent
 MEGR 7090-003, Computational Fluid Dynamics :1 7 Spring 2015 Computational Study of Laminar Flowfield around a Square Cylinder using Ansys Fluent Rahul R Upadhyay Master of Science, Dept of Mechanical
MEGR 7090-003, Computational Fluid Dynamics :1 7 Spring 2015 Computational Study of Laminar Flowfield around a Square Cylinder using Ansys Fluent Rahul R Upadhyay Master of Science, Dept of Mechanical
1.2 Numerical Solutions of Flow Problems
 1.2 Numerical Solutions of Flow Problems DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS OF MOTION FOR A SIMPLIFIED FLOW PROBLEM Continuity equation for incompressible flow: 0 Momentum (Navier-Stokes) equations for a Newtonian
1.2 Numerical Solutions of Flow Problems DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS OF MOTION FOR A SIMPLIFIED FLOW PROBLEM Continuity equation for incompressible flow: 0 Momentum (Navier-Stokes) equations for a Newtonian
Solved with COMSOL Multiphysics 4.2
 Backstep Introduction This tutorial model solves the incompressible Navier-Stokes equations in a backstep geometry. A characteristic feature of fluid flow in geometries of this kind is the recirculation
Backstep Introduction This tutorial model solves the incompressible Navier-Stokes equations in a backstep geometry. A characteristic feature of fluid flow in geometries of this kind is the recirculation
Lisa Michelle Dahl June 04, 2008 CHEM E Finlayson Mixing Properties of an Optimized SAR Mixer (2D and 3D Models)
 Mixing Properties of an Optimized SAR Mixer (2D and 3D Models) I. Introduction While mixing is the most common unit-operation in chemical industrial processes, optimizing mixing in microchemical processes
Mixing Properties of an Optimized SAR Mixer (2D and 3D Models) I. Introduction While mixing is the most common unit-operation in chemical industrial processes, optimizing mixing in microchemical processes
CFD MODELING FOR PNEUMATIC CONVEYING
 CFD MODELING FOR PNEUMATIC CONVEYING Arvind Kumar 1, D.R. Kaushal 2, Navneet Kumar 3 1 Associate Professor YMCAUST, Faridabad 2 Associate Professor, IIT, Delhi 3 Research Scholar IIT, Delhi e-mail: arvindeem@yahoo.co.in
CFD MODELING FOR PNEUMATIC CONVEYING Arvind Kumar 1, D.R. Kaushal 2, Navneet Kumar 3 1 Associate Professor YMCAUST, Faridabad 2 Associate Professor, IIT, Delhi 3 Research Scholar IIT, Delhi e-mail: arvindeem@yahoo.co.in
SOLIDWORKS Flow Simulation 2015
 An Introduction to SOLIDWORKS Flow Simulation 2015 John E. Matsson, Ph.D. SDC PUBLICATIONS Better Textbooks. Lower Prices. www.sdcpublications.com Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org) Visit the following websites
An Introduction to SOLIDWORKS Flow Simulation 2015 John E. Matsson, Ph.D. SDC PUBLICATIONS Better Textbooks. Lower Prices. www.sdcpublications.com Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org) Visit the following websites
Application of A Priori Error Estimates for Navier-Stokes Equations to Accurate Finite Element Solution
 Application of A Priori Error Estimates for Navier-Stokes Equations to Accurate Finite Element Solution P. BURDA a,, J. NOVOTNÝ b,, J. ŠÍSTE a, a Department of Mathematics Czech University of Technology
Application of A Priori Error Estimates for Navier-Stokes Equations to Accurate Finite Element Solution P. BURDA a,, J. NOVOTNÝ b,, J. ŠÍSTE a, a Department of Mathematics Czech University of Technology
CFD modelling of thickened tailings Final project report
 26.11.2018 RESEM Remote sensing supporting surveillance and operation of mines CFD modelling of thickened tailings Final project report Lic.Sc.(Tech.) Reeta Tolonen and Docent Esa Muurinen University of
26.11.2018 RESEM Remote sensing supporting surveillance and operation of mines CFD modelling of thickened tailings Final project report Lic.Sc.(Tech.) Reeta Tolonen and Docent Esa Muurinen University of
1 Thomas Chengattu MAE 494 November Project # 2: Transient Simulation using VOF Methods
 1 Thomas Chengattu Project # 2: Transient Simulation using VOF Methods INITIAL SET UP The initial set-up for all the geometries varied with respect to each tasks. The common similarities between these
1 Thomas Chengattu Project # 2: Transient Simulation using VOF Methods INITIAL SET UP The initial set-up for all the geometries varied with respect to each tasks. The common similarities between these
FLUENT Secondary flow in a teacup Author: John M. Cimbala, Penn State University Latest revision: 26 January 2016
 FLUENT Secondary flow in a teacup Author: John M. Cimbala, Penn State University Latest revision: 26 January 2016 Note: These instructions are based on an older version of FLUENT, and some of the instructions
FLUENT Secondary flow in a teacup Author: John M. Cimbala, Penn State University Latest revision: 26 January 2016 Note: These instructions are based on an older version of FLUENT, and some of the instructions
Coupled Analysis of FSI
 Coupled Analysis of FSI Qin Yin Fan Oct. 11, 2008 Important Key Words Fluid Structure Interface = FSI Computational Fluid Dynamics = CFD Pressure Displacement Analysis = PDA Thermal Stress Analysis = TSA
Coupled Analysis of FSI Qin Yin Fan Oct. 11, 2008 Important Key Words Fluid Structure Interface = FSI Computational Fluid Dynamics = CFD Pressure Displacement Analysis = PDA Thermal Stress Analysis = TSA
Lab 8: FLUENT: Turbulent Boundary Layer Flow with Convection
 Lab 8: FLUENT: Turbulent Boundary Layer Flow with Convection Objective: The objective of this laboratory is to use FLUENT to solve for the total drag and heat transfer rate for external, turbulent boundary
Lab 8: FLUENT: Turbulent Boundary Layer Flow with Convection Objective: The objective of this laboratory is to use FLUENT to solve for the total drag and heat transfer rate for external, turbulent boundary
Computational Flow Analysis of Para-rec Bluff Body at Various Reynold s Number
 International Journal of Engineering Research and Technology. ISSN 0974-3154 Volume 6, Number 5 (2013), pp. 667-674 International Research Publication House http://www.irphouse.com Computational Flow Analysis
International Journal of Engineering Research and Technology. ISSN 0974-3154 Volume 6, Number 5 (2013), pp. 667-674 International Research Publication House http://www.irphouse.com Computational Flow Analysis
A Verification Study of ABAQUS AC3D8R Elements for Acoustic Wave Propagation
 A Verification Study of ABAQUS AC3D8R Elements for Acoustic Wave Propagation by Michael Robert Hubenthal A Project Submitted to the Graduate Faculty of Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute in Partial Fulfillment
A Verification Study of ABAQUS AC3D8R Elements for Acoustic Wave Propagation by Michael Robert Hubenthal A Project Submitted to the Graduate Faculty of Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute in Partial Fulfillment
How to Enter and Analyze a Wing
 How to Enter and Analyze a Wing Entering the Wing The Stallion 3-D built-in geometry creation tool can be used to model wings and bodies of revolution. In this example, a simple rectangular wing is modeled
How to Enter and Analyze a Wing Entering the Wing The Stallion 3-D built-in geometry creation tool can be used to model wings and bodies of revolution. In this example, a simple rectangular wing is modeled
Backward facing step Homework. Department of Fluid Mechanics. For Personal Use. Budapest University of Technology and Economics. Budapest, 2010 autumn
 Backward facing step Homework Department of Fluid Mechanics Budapest University of Technology and Economics Budapest, 2010 autumn Updated: October 26, 2010 CONTENTS i Contents 1 Introduction 1 2 The problem
Backward facing step Homework Department of Fluid Mechanics Budapest University of Technology and Economics Budapest, 2010 autumn Updated: October 26, 2010 CONTENTS i Contents 1 Introduction 1 2 The problem
Modeling Flow Through Porous Media
 Tutorial 7. Modeling Flow Through Porous Media Introduction Many industrial applications involve the modeling of flow through porous media, such as filters, catalyst beds, and packing. This tutorial illustrates
Tutorial 7. Modeling Flow Through Porous Media Introduction Many industrial applications involve the modeling of flow through porous media, such as filters, catalyst beds, and packing. This tutorial illustrates
A B C D E. Settings Choose height, H, free stream velocity, U, and fluid (dynamic viscosity and density ) so that: Reynolds number
 Individual task Objective To derive the drag coefficient for a 2D object, defined as where D (N/m) is the aerodynamic drag force (per unit length in the third direction) acting on the object. The object
Individual task Objective To derive the drag coefficient for a 2D object, defined as where D (N/m) is the aerodynamic drag force (per unit length in the third direction) acting on the object. The object
Numerical Investigation of Non-Newtonian Laminar Flow in Curved Tube with Insert
 Numerical Investigation of Non-Newtonian Laminar Flow in Curved Tube with Insert A. Kadyyrov 1 1 Research center for power engineering problems Federal government budgetary institution of science Kazan
Numerical Investigation of Non-Newtonian Laminar Flow in Curved Tube with Insert A. Kadyyrov 1 1 Research center for power engineering problems Federal government budgetary institution of science Kazan
Analysis of Flow Dynamics of an Incompressible Viscous Fluid in a Channel
 Analysis of Flow Dynamics of an Incompressible Viscous Fluid in a Channel Deepak Kumar Assistant Professor, Department of Mechanical Engineering, Amity University Gurgaon, India E-mail: deepak209476@gmail.com
Analysis of Flow Dynamics of an Incompressible Viscous Fluid in a Channel Deepak Kumar Assistant Professor, Department of Mechanical Engineering, Amity University Gurgaon, India E-mail: deepak209476@gmail.com
ISSN(PRINT): ,(ONLINE): ,VOLUME-1,ISSUE-1,
 NUMERICAL ANALYSIS OF THE TUBE BANK PRESSURE DROP OF A SHELL AND TUBE HEAT EXCHANGER Kartik Ajugia, Kunal Bhavsar Lecturer, Mechanical Department, SJCET Mumbai University, Maharashtra Assistant Professor,
NUMERICAL ANALYSIS OF THE TUBE BANK PRESSURE DROP OF A SHELL AND TUBE HEAT EXCHANGER Kartik Ajugia, Kunal Bhavsar Lecturer, Mechanical Department, SJCET Mumbai University, Maharashtra Assistant Professor,
Modeling Unsteady Compressible Flow
 Tutorial 4. Modeling Unsteady Compressible Flow Introduction In this tutorial, FLUENT s density-based implicit solver is used to predict the timedependent flow through a two-dimensional nozzle. As an initial
Tutorial 4. Modeling Unsteady Compressible Flow Introduction In this tutorial, FLUENT s density-based implicit solver is used to predict the timedependent flow through a two-dimensional nozzle. As an initial
Development of Hybrid Fluid Jet / Float Polishing Process
 COMSOL Conference - Tokyo 2013 Development of Hybrid Fluid Jet / Float Polishing Process A. Beaucamp, Y. Namba Dept. of Mechanical Engineering, Chubu University, Japan Zeeko LTD, United Kingdom Research
COMSOL Conference - Tokyo 2013 Development of Hybrid Fluid Jet / Float Polishing Process A. Beaucamp, Y. Namba Dept. of Mechanical Engineering, Chubu University, Japan Zeeko LTD, United Kingdom Research
Possibility of Implicit LES for Two-Dimensional Incompressible Lid-Driven Cavity Flow Based on COMSOL Multiphysics
 Possibility of Implicit LES for Two-Dimensional Incompressible Lid-Driven Cavity Flow Based on COMSOL Multiphysics Masanori Hashiguchi 1 1 Keisoku Engineering System Co., Ltd. 1-9-5 Uchikanda, Chiyoda-ku,
Possibility of Implicit LES for Two-Dimensional Incompressible Lid-Driven Cavity Flow Based on COMSOL Multiphysics Masanori Hashiguchi 1 1 Keisoku Engineering System Co., Ltd. 1-9-5 Uchikanda, Chiyoda-ku,
Faculty of Mechanical and Manufacturing Engineering, University Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia (UTHM), Parit Raja, Batu Pahat, Johor, Malaysia
 Applied Mechanics and Materials Vol. 393 (2013) pp 305-310 (2013) Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/amm.393.305 The Implementation of Cell-Centred Finite Volume Method
Applied Mechanics and Materials Vol. 393 (2013) pp 305-310 (2013) Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/amm.393.305 The Implementation of Cell-Centred Finite Volume Method
Tutorial 17. Using the Mixture and Eulerian Multiphase Models
 Tutorial 17. Using the Mixture and Eulerian Multiphase Models Introduction: This tutorial examines the flow of water and air in a tee junction. First you will solve the problem using the less computationally-intensive
Tutorial 17. Using the Mixture and Eulerian Multiphase Models Introduction: This tutorial examines the flow of water and air in a tee junction. First you will solve the problem using the less computationally-intensive
A NURBS-BASED APPROACH FOR SHAPE AND TOPOLOGY OPTIMIZATION OF FLOW DOMAINS
 6th European Conference on Computational Mechanics (ECCM 6) 7th European Conference on Computational Fluid Dynamics (ECFD 7) 11 15 June 2018, Glasgow, UK A NURBS-BASED APPROACH FOR SHAPE AND TOPOLOGY OPTIMIZATION
6th European Conference on Computational Mechanics (ECCM 6) 7th European Conference on Computational Fluid Dynamics (ECFD 7) 11 15 June 2018, Glasgow, UK A NURBS-BASED APPROACH FOR SHAPE AND TOPOLOGY OPTIMIZATION
