Ch. 26: Geometrical Optics
|
|
|
- Kenneth Waters
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Sec. 6-1: The Reflection of Light Wave Fronts and Rays Ch. 6: Geometrical Optics Wave front: a surface on which E is a maximum. Figure 5-3: Plane Wave *For this wave, the wave fronts are a series of planes. Rays: lines drawn in the direction of propagation. Figure 6- point source Law of reflection: angle of incidence = angle of reflection Figure 6-3 Plane wave *At great distances, point source looks like plane wave. Angle of incidence: angle that incident ray makes with normal. Angle of reflection: angle that reflected ray makes with normal. 1
2 Figure 6-8 Figure 6-9 Spherical mirrors: shaped like a section of a sphere. mirror Figure 6-10 kinds of spherical mirrors: convex, concave Convex spherical mirror Concave spherical mirror Figure 6-11 Convex mirror Paraxial rays parallel to principal axis extend back to single point called focal point. Paraxial: near the principal axis Focal length: f = R (convex mirror) Sign convention: Distances behind mirror negative. Distances in front of mirror positive.
3 Figure 6-1 Concave mirror Sec. 6-4: Ray Tracing and Mirror Equation 3 important rays called principal rays: Paraxial rays parallel to principal axis now reflect back through focal point on same side of mirror. Focal length: f = R (concave mirror) 1. Parallel ray ( P ray ): ray coming in parallel to principal axis. Reflects through focal point.. Focal ray ( F ray ): ray drawn through focal point. Reflects parallel to principal axis. 3. Center-of-curvature ray ( C ray ): ray drawn through center of curvature. Reflects back along line of incidence. These rays determine the size and orientation of the image! Figure 6-14 Figure 6-15 Convex mirror 3
4 observer Figure 6-16 Figure 6-17 light rays appear to diverge from here Virtual image: no light rays really emanating from the image (no light at the location of the image). Summary: Convex mirrors Figure 6-18 Concave mirror (object distance d o > f) Behind mirrror Right-side up Smaller than object Virtual observer Object distance d o > R observer Object distance d o < R Inverted Smaller than object In front of mirror (closer to mirror than object is) real Inverted larger than object In front of mirror (farther away than object is) real 4
5 Example 6-3 Concave mirror (object distance d o < f) Figure 6-19 Deriving the Mirror Equation observer Right-side up larger than object behind mirror virtual ho = do hi di Mirror Equation: = 1 do di f Magnification: h m i h o d m= i d o Sec. 6-5: Refraction of Light Saw in Ch. 5 that speed of light in vacuum is c = m/s When light travels through a different material, it slows down: v= c n n is called the index of refraction of the material n vacuum = 1 (exactly) n air = n water = 1.33 n 1.5 glass Table 6-, p. 864 Light also bends (changes direction), when entering different material. This bending called refraction. 5
6 Figure 6-4 Exercise 6-4 Snell s Law: n sinθ = n sinθ 1 1 normal Willebrord Snell (161) normal nair 1.00 nair 1.00 nwater = 1.33 nglass 1.5 nglass =1.5 angles θ1 &θ measured relative to normal. when going from low n to high n, bends toward normal when going from high n to low n, bends away from normal Sec. 6-6: Ray Tracing for Lenses midline Thin lens approximation: In limit as slab gets thinner and thinner, can say that all refraction takes place pretty much at center (midline). Converging and Diverging Lenses: A First Look Figure 6-9 Figure 6-31 Figure 6-30 Two Basic Categories of Lenses: converging: focuses parallel rays so that they converge to a point on other side. diverging: bends parallel rays outward so that they diverge on other side. Converging (convex) Diverging (concave) nglass =1.5 nglass =1.5 focal point focal point 6
7 As with mirrors, can determine size and orientation of image by considering three important rays called principal rays: 1. Parallel ray ( P ray ): ray drawn parallel to principal axis. Focal ray ( F ray ): ray drawn through focal point 3. Midpoint ray ( M ray ): ray drawn through midpoint Diverging Lenses A Closer Look Parallel ray ( P ray ): parallel to principal axis. Refracted ray extrapolates back through focal point. Focal-point Ray ( F ray ): ray directed toward focal point on other side of lens. Refracts parallel to principal axis. Midpoint Ray ( M ray ): ray from object through midpoint of lens. Goes through undeflected. Figure 6-33 Figure 6-34 P P observer To find image, find intersection of all three principal rays on same side of lens as object Right-side up Smaller than object closer to lens than object is Virtual (there s no light really emanating from point P ) 7
8 Converging Lenses A Closer Look Figure 6-3 Locating image for converging lens is a bit more complicated than for diverging lens. Depends on where the object is located. Parallel ray ( P ray ): parallel to principal axis. Refracts through focal point on other side of lens. Focal-point Ray ( F ray ): passes through focal point on left side of lens (before hitting lens). Refracts parallel to principal axis. Midpoint Ray ( M ray ): passes through midpoint of lens undeflected. Figure 6-35 Sec. 6-7: The Thin-lens Equation Figure 6-36 ho h = i f di f (1) object farther away than focal point Image: on other side of lens inverted real can be smaller than object or larger than it object closer than focal point Image: on same side of lens as object right-side up virtual larger than object ho h = i do di () 1 = f do di (Thin-lens eq.) 8
9 Magnification: h m i h o d m= i d o p. 874: Sign conventions. Don t worry about virtual objects in last line. Read: Sec 6-1 Sec 6- Sec 6-3 Sec 6-4 Sec 6-5 (skip Total Internal Reflection, Total Polarization ) Sec 6-6 Sec 6-7 Skip: Sec 6-8 HW #8 (Chapter 6): CQ: 7, 13, 8 Probs: 3, 5, 11, 13, 18, 19, 1,, 37, 46, 47, 57, 59 (also calculate the image location), 74, 90 Take-home Quiz (Due Mon., Nov. 9): Prob. #7, Ch. 5 (end of chapter) 9
Algebra Based Physics
 Slide 1 / 66 Slide 2 / 66 Algebra Based Physics Geometric Optics 2015-12-01 www.njctl.org Table of ontents Slide 3 / 66 lick on the topic to go to that section Reflection Spherical Mirror Refraction and
Slide 1 / 66 Slide 2 / 66 Algebra Based Physics Geometric Optics 2015-12-01 www.njctl.org Table of ontents Slide 3 / 66 lick on the topic to go to that section Reflection Spherical Mirror Refraction and
Chapter 26 Geometrical Optics
 Chapter 26 Geometrical Optics 1 Overview of Chapter 26 The Reflection of Light Forming Images with a Plane Mirror Spherical Mirrors Ray Tracing and the Mirror Equation The Refraction of Light Ray Tracing
Chapter 26 Geometrical Optics 1 Overview of Chapter 26 The Reflection of Light Forming Images with a Plane Mirror Spherical Mirrors Ray Tracing and the Mirror Equation The Refraction of Light Ray Tracing
AP Physics: Curved Mirrors and Lenses
 The Ray Model of Light Light often travels in straight lines. We represent light using rays, which are straight lines emanating from an object. This is an idealization, but is very useful for geometric
The Ray Model of Light Light often travels in straight lines. We represent light using rays, which are straight lines emanating from an object. This is an idealization, but is very useful for geometric
Outline The Refraction of Light Forming Images with a Plane Mirror 26-3 Spherical Mirror 26-4 Ray Tracing and the Mirror Equation
 Chapter 6 Geometrical Optics Outline 6-1 The Reflection of Light 6- Forming Images with a Plane Mirror 6-3 Spherical Mirror 6-4 Ray Tracing and the Mirror Equation 6-5 The Refraction of Light 6-6 Ray Tracing
Chapter 6 Geometrical Optics Outline 6-1 The Reflection of Light 6- Forming Images with a Plane Mirror 6-3 Spherical Mirror 6-4 Ray Tracing and the Mirror Equation 6-5 The Refraction of Light 6-6 Ray Tracing
Light: Geometric Optics
 Light: Geometric Optics 23.1 The Ray Model of Light Light very often travels in straight lines. We represent light using rays, which are straight lines emanating from an object. This is an idealization,
Light: Geometric Optics 23.1 The Ray Model of Light Light very often travels in straight lines. We represent light using rays, which are straight lines emanating from an object. This is an idealization,
Geometric Optics. The Law of Reflection. Physics Waves & Oscillations 3/20/2016. Spring 2016 Semester Matthew Jones
 Physics 42200 Waves & Oscillations Lecture 27 Propagation of Light Hecht, chapter 5 Spring 2016 Semester Matthew Jones Geometric Optics Typical problems in geometric optics: Given an optical system, what
Physics 42200 Waves & Oscillations Lecture 27 Propagation of Light Hecht, chapter 5 Spring 2016 Semester Matthew Jones Geometric Optics Typical problems in geometric optics: Given an optical system, what
LIGHT. Speed of light Law of Reflection Refraction Snell s Law Mirrors Lenses
 LIGHT Speed of light Law of Reflection Refraction Snell s Law Mirrors Lenses Light = Electromagnetic Wave Requires No Medium to Travel Oscillating Electric and Magnetic Field Travel at the speed of light
LIGHT Speed of light Law of Reflection Refraction Snell s Law Mirrors Lenses Light = Electromagnetic Wave Requires No Medium to Travel Oscillating Electric and Magnetic Field Travel at the speed of light
Chapter 26 Geometrical Optics
 Chapter 26 Geometrical Optics The Reflection of Light: Mirrors: Mirrors produce images because the light that strikes them is reflected, rather than absorbed. Reflected light does much more than produce
Chapter 26 Geometrical Optics The Reflection of Light: Mirrors: Mirrors produce images because the light that strikes them is reflected, rather than absorbed. Reflected light does much more than produce
Light: Geometric Optics (Chapter 23)
 Light: Geometric Optics (Chapter 23) Units of Chapter 23 The Ray Model of Light Reflection; Image Formed by a Plane Mirror Formation of Images by Spherical Index of Refraction Refraction: Snell s Law 1
Light: Geometric Optics (Chapter 23) Units of Chapter 23 The Ray Model of Light Reflection; Image Formed by a Plane Mirror Formation of Images by Spherical Index of Refraction Refraction: Snell s Law 1
General Physics II. Mirrors & Lenses
 General Physics II Mirrors & Lenses Nothing New! For the next several lectures we will be studying geometrical optics. You already know the fundamentals of what is going on!!! Reflection: θ 1 = θ r incident
General Physics II Mirrors & Lenses Nothing New! For the next several lectures we will be studying geometrical optics. You already know the fundamentals of what is going on!!! Reflection: θ 1 = θ r incident
Lecture Outline Chapter 26. Physics, 4 th Edition James S. Walker. Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Lecture Outline Chapter 26 Physics, 4 th Edition James S. Walker Chapter 26 Geometrical Optics Units of Chapter 26 The Reflection of Light Forming Images with a Plane Mirror Spherical Mirrors Ray Tracing
Lecture Outline Chapter 26 Physics, 4 th Edition James S. Walker Chapter 26 Geometrical Optics Units of Chapter 26 The Reflection of Light Forming Images with a Plane Mirror Spherical Mirrors Ray Tracing
Ray Optics. Physics 11. Sources of Light Rays: Self-Luminous Objects. The Ray Model of Light
 Physics 11 Ray Optics Ray Model of Light Reflection Plane Mirrors Spherical Mirrors Ray Tracing Images from a Concave Mirror Images from a Convex Mirror Slide 18-3 The Ray Model of Light Sources of Light
Physics 11 Ray Optics Ray Model of Light Reflection Plane Mirrors Spherical Mirrors Ray Tracing Images from a Concave Mirror Images from a Convex Mirror Slide 18-3 The Ray Model of Light Sources of Light
GEOMETRIC OPTICS. LENSES refract light, so we need to know how light bends when entering and exiting a lens and how that interaction forms an image.
 I. What is GEOMTERIC OPTICS GEOMETRIC OPTICS In geometric optics, LIGHT is treated as imaginary rays. How these rays interact with at the interface of different media, including lenses and mirrors, is
I. What is GEOMTERIC OPTICS GEOMETRIC OPTICS In geometric optics, LIGHT is treated as imaginary rays. How these rays interact with at the interface of different media, including lenses and mirrors, is
Chapter 3: Mirrors and Lenses
 Chapter 3: Mirrors and Lenses Chapter 3: Mirrors and Lenses Lenses Refraction Converging rays Diverging rays Converging Lens Ray tracing rules Image formation Diverging Lens Ray tracing Image formation
Chapter 3: Mirrors and Lenses Chapter 3: Mirrors and Lenses Lenses Refraction Converging rays Diverging rays Converging Lens Ray tracing rules Image formation Diverging Lens Ray tracing Image formation
Waves & Oscillations
 Physics 42200 Waves & Oscillations Lecture 26 Propagation of Light Hecht, chapter 5 Spring 2015 Semester Matthew Jones Geometric Optics Typical problems in geometric optics: Given an optical system, what
Physics 42200 Waves & Oscillations Lecture 26 Propagation of Light Hecht, chapter 5 Spring 2015 Semester Matthew Jones Geometric Optics Typical problems in geometric optics: Given an optical system, what
Chapter 26 Geometrical Optics
 Chapter 26 Geometrical Optics 26.1 The Reflection of Light 26.2 Forming Images With a Plane Mirror 26.3 Spherical Mirrors 26.4 Ray Tracing and the Mirror Equation 26.5 The Refraction of Light 26.6 Ray
Chapter 26 Geometrical Optics 26.1 The Reflection of Light 26.2 Forming Images With a Plane Mirror 26.3 Spherical Mirrors 26.4 Ray Tracing and the Mirror Equation 26.5 The Refraction of Light 26.6 Ray
Light: Geometric Optics
 Light: Geometric Optics The Ray Model of Light Light very often travels in straight lines. We represent light using rays, which are straight lines emanating from an object. This is an idealization, but
Light: Geometric Optics The Ray Model of Light Light very often travels in straight lines. We represent light using rays, which are straight lines emanating from an object. This is an idealization, but
Physics 102: Lecture 17 Reflection and Refraction of Light
 Physics 102: Lecture 17 Reflection and Refraction of Light Physics 102: Lecture 17, Slide 1 Today Last Time Recall from last time. Reflection: q i = q r Flat Mirror: image equidistant behind Spherical
Physics 102: Lecture 17 Reflection and Refraction of Light Physics 102: Lecture 17, Slide 1 Today Last Time Recall from last time. Reflection: q i = q r Flat Mirror: image equidistant behind Spherical
M = h' h = #i. n = c v
 Name: Physics Chapter 14 Study Guide ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Useful Information: c = 3 "10 8 m s 1 i + 1 o = 1 f M = h' h =
Name: Physics Chapter 14 Study Guide ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Useful Information: c = 3 "10 8 m s 1 i + 1 o = 1 f M = h' h =
LECTURE 25 Spherical Refracting Surfaces. Geometric Optics
 LECTURE 25 Spherical Refracting Surfaces Geometric ptics When length scales are >> than the light s wavelength, light propagates as rays incident ray reflected ray θ θ r θ 2 refracted ray Reflection: Refraction:
LECTURE 25 Spherical Refracting Surfaces Geometric ptics When length scales are >> than the light s wavelength, light propagates as rays incident ray reflected ray θ θ r θ 2 refracted ray Reflection: Refraction:
Refraction and Lenses. Honors Physics
 Refraction and Lenses Honors Physics Refraction Refraction is based on the idea that LIGHT is passing through one MEDIUM into another. The question is, WHAT HAPPENS? Suppose you are running on the beach
Refraction and Lenses Honors Physics Refraction Refraction is based on the idea that LIGHT is passing through one MEDIUM into another. The question is, WHAT HAPPENS? Suppose you are running on the beach
Physics 1C Lecture 26A. Beginning of Chapter 26
 Physics 1C Lecture 26A Beginning of Chapter 26 Mirrors and Lenses! As we have noted before, light rays can be diverted by optical systems to fool your eye into thinking an object is somewhere that it is
Physics 1C Lecture 26A Beginning of Chapter 26 Mirrors and Lenses! As we have noted before, light rays can be diverted by optical systems to fool your eye into thinking an object is somewhere that it is
Physics 102: Lecture 17 Reflection and Refraction of Light
 Physics 102: Lecture 17 Reflection and Refraction of Light Physics 102: Lecture 17, Slide 1 Recall from last time. Today Last Time Reflection: θ i = θ r Flat Mirror: image equidistant behind Spherical
Physics 102: Lecture 17 Reflection and Refraction of Light Physics 102: Lecture 17, Slide 1 Recall from last time. Today Last Time Reflection: θ i = θ r Flat Mirror: image equidistant behind Spherical
Nicholas J. Giordano. Chapter 24. Geometrical Optics. Marilyn Akins, PhD Broome Community College
 Nicholas J. Giordano www.cengage.com/physics/giordano Chapter 24 Geometrical Optics Marilyn Akins, PhD Broome Community College Optics The study of light is called optics Some highlights in the history
Nicholas J. Giordano www.cengage.com/physics/giordano Chapter 24 Geometrical Optics Marilyn Akins, PhD Broome Community College Optics The study of light is called optics Some highlights in the history
Announcement on HW 8. HW 8 originally due this Wednesday, Mar. 13 Now due FRIDAY, Mar. 15 at 8:00am. Physics 102: Lecture 16, Slide 1
 Announcement on HW 8 HW 8 originally due this Wednesday, Mar. 13 Now due FRIDAY, Mar. 15 at 8:00am Physics 102: Lecture 16, Slide 1 Physics 102: Lecture 16 Introduction to Mirrors Physics 102: Lecture
Announcement on HW 8 HW 8 originally due this Wednesday, Mar. 13 Now due FRIDAY, Mar. 15 at 8:00am Physics 102: Lecture 16, Slide 1 Physics 102: Lecture 16 Introduction to Mirrors Physics 102: Lecture
Chapter 23. Geometrical Optics (lecture 1: mirrors) Dr. Armen Kocharian
 Chapter 23 Geometrical Optics (lecture 1: mirrors) Dr. Armen Kocharian Reflection and Refraction at a Plane Surface The light radiate from a point object in all directions The light reflected from a plane
Chapter 23 Geometrical Optics (lecture 1: mirrors) Dr. Armen Kocharian Reflection and Refraction at a Plane Surface The light radiate from a point object in all directions The light reflected from a plane
Ch. 25 The Reflection of Light
 Ch. 25 The Reflection of Light 25. Wave fronts and rays We are all familiar with mirrors. We see images because some light is reflected off the surface of the mirror and into our eyes. In order to describe
Ch. 25 The Reflection of Light 25. Wave fronts and rays We are all familiar with mirrors. We see images because some light is reflected off the surface of the mirror and into our eyes. In order to describe
The Law of Reflection
 If the surface off which the light is reflected is smooth, then the light undergoes specular reflection (parallel rays will all be reflected in the same directions). If, on the other hand, the surface
If the surface off which the light is reflected is smooth, then the light undergoes specular reflection (parallel rays will all be reflected in the same directions). If, on the other hand, the surface
Today s Topic: Ray Diagrams Intro to & Converging
 Today s Topic: Ray Diagrams Intro to & Converging Learning Goal: Students will be able to describe the resulting image of light once it passes through a converging lens. What is a focal point? What happens
Today s Topic: Ray Diagrams Intro to & Converging Learning Goal: Students will be able to describe the resulting image of light once it passes through a converging lens. What is a focal point? What happens
Phys102 Lecture 21/22 Light: Reflection and Refraction
 Phys102 Lecture 21/22 Light: Reflection and Refraction Key Points The Ray Model of Light Reflection and Mirrors Refraction, Snell s Law Total internal Reflection References 23-1,2,3,4,5,6. The Ray Model
Phys102 Lecture 21/22 Light: Reflection and Refraction Key Points The Ray Model of Light Reflection and Mirrors Refraction, Snell s Law Total internal Reflection References 23-1,2,3,4,5,6. The Ray Model
Today s Topic: Refraction / Snell s Law
 Today s Topic: Refraction / Snell s Law Learning Goal: Students will be able to calculate the angle of reflection of a bent light wave. Take out your notes from yesterday as we learn about Snell s Law.
Today s Topic: Refraction / Snell s Law Learning Goal: Students will be able to calculate the angle of reflection of a bent light wave. Take out your notes from yesterday as we learn about Snell s Law.
Chapter 34: Geometrical Optics
 Chapter 34: Geometrical Optics Mirrors Plane Spherical (convex or concave) Lenses The lens equation Lensmaker s equation Combination of lenses E! Phys Phys 2435: 22: Chap. 34, 3, Pg Mirrors New Topic Phys
Chapter 34: Geometrical Optics Mirrors Plane Spherical (convex or concave) Lenses The lens equation Lensmaker s equation Combination of lenses E! Phys Phys 2435: 22: Chap. 34, 3, Pg Mirrors New Topic Phys
Optics II. Reflection and Mirrors
 Optics II Reflection and Mirrors Geometric Optics Using a Ray Approximation Light travels in a straight-line path in a homogeneous medium until it encounters a boundary between two different media The
Optics II Reflection and Mirrors Geometric Optics Using a Ray Approximation Light travels in a straight-line path in a homogeneous medium until it encounters a boundary between two different media The
1. What is the law of reflection?
 Name: Skill Sheet 7.A The Law of Reflection The law of reflection works perfectly with light and the smooth surface of a mirror. However, you can apply this law to other situations. For example, how would
Name: Skill Sheet 7.A The Law of Reflection The law of reflection works perfectly with light and the smooth surface of a mirror. However, you can apply this law to other situations. For example, how would
Chapter 7: Geometrical Optics. The branch of physics which studies the properties of light using the ray model of light.
 Chapter 7: Geometrical Optics The branch of physics which studies the properties of light using the ray model of light. Overview Geometrical Optics Spherical Mirror Refraction Thin Lens f u v r and f 2
Chapter 7: Geometrical Optics The branch of physics which studies the properties of light using the ray model of light. Overview Geometrical Optics Spherical Mirror Refraction Thin Lens f u v r and f 2
Optics Course (Phys 311) Geometrical Optics Refraction through Lenses
 Optics Course (Phys ) Geometrical Optics Refraction through Lenses Lecturer: Dr Zeina Hashim Slide 1 Objectives covered in this lesson : 1. Refraction through single spherical refracting surfaces. 2. Lenses:
Optics Course (Phys ) Geometrical Optics Refraction through Lenses Lecturer: Dr Zeina Hashim Slide 1 Objectives covered in this lesson : 1. Refraction through single spherical refracting surfaces. 2. Lenses:
Light, Photons, and MRI
 Light, Photons, and MRI When light hits an object, some of it will be reflected. The reflected light can form an image. We usually want to be able to characterize the image given what we know about the
Light, Photons, and MRI When light hits an object, some of it will be reflected. The reflected light can form an image. We usually want to be able to characterize the image given what we know about the
P06 ray diagrams with concave mirrors and intro to problem solving.notebook
 Ray Diagrams Concave Mirror A concave mirror is a converging mirror because parallel rays will. For any object, millions and millions of rays are reflected in all directions. Some of these rays hit the
Ray Diagrams Concave Mirror A concave mirror is a converging mirror because parallel rays will. For any object, millions and millions of rays are reflected in all directions. Some of these rays hit the
Optics. a- Before the beginning of the nineteenth century, light was considered to be a stream of particles.
 Optics 1- Light Nature: a- Before the beginning of the nineteenth century, light was considered to be a stream of particles. The particles were either emitted by the object being viewed or emanated from
Optics 1- Light Nature: a- Before the beginning of the nineteenth century, light was considered to be a stream of particles. The particles were either emitted by the object being viewed or emanated from
Light & Optical Systems Reflection & Refraction. Notes
 Light & Optical Systems Reflection & Refraction Notes What is light? Light is electromagnetic radiation Ultra-violet + visible + infra-red Behavior of Light Light behaves in 2 ways particles (photons)
Light & Optical Systems Reflection & Refraction Notes What is light? Light is electromagnetic radiation Ultra-violet + visible + infra-red Behavior of Light Light behaves in 2 ways particles (photons)
Optics and Images. Lenses and Mirrors. Matthew W. Milligan
 Optics and Images Lenses and Mirrors Light: Interference and Optics I. Light as a Wave - wave basics review - electromagnetic radiation II. Diffraction and Interference - diffraction, Huygen s principle
Optics and Images Lenses and Mirrors Light: Interference and Optics I. Light as a Wave - wave basics review - electromagnetic radiation II. Diffraction and Interference - diffraction, Huygen s principle
P H Y L A B 1 : G E O M E T R I C O P T I C S
 P H Y 1 4 3 L A B 1 : G E O M E T R I C O P T I C S Introduction Optics is the study of the way light interacts with other objects. This behavior can be extremely complicated. However, if the objects in
P H Y 1 4 3 L A B 1 : G E O M E T R I C O P T I C S Introduction Optics is the study of the way light interacts with other objects. This behavior can be extremely complicated. However, if the objects in
Chapter 32 Light: Reflection and Refraction. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 32 Light: Reflection and Refraction Units of Chapter 32 The Ray Model of Light Reflection; Image Formation by a Plane Mirror Formation of Images by Spherical Mirrors Index of Refraction Refraction:
Chapter 32 Light: Reflection and Refraction Units of Chapter 32 The Ray Model of Light Reflection; Image Formation by a Plane Mirror Formation of Images by Spherical Mirrors Index of Refraction Refraction:
Chapter 12 Notes: Optics
 Chapter 12 Notes: Optics How can the paths traveled by light rays be rearranged in order to form images? In this chapter we will consider just one form of electromagnetic wave: visible light. We will be
Chapter 12 Notes: Optics How can the paths traveled by light rays be rearranged in order to form images? In this chapter we will consider just one form of electromagnetic wave: visible light. We will be
LIGHT & OPTICS. Fundamentals of Physics 2112 Chapter 34 1
 LIGHT & OPTICS Fundamentals of Physics 22 Chapter 34 Chapter 34 Images. Two Types of Images 2. Plane Mirrors 3. Spherical Mirrors 4. Images from Spherical Mirrors 5. Spherical Refracting Surfaces 6. Thin
LIGHT & OPTICS Fundamentals of Physics 22 Chapter 34 Chapter 34 Images. Two Types of Images 2. Plane Mirrors 3. Spherical Mirrors 4. Images from Spherical Mirrors 5. Spherical Refracting Surfaces 6. Thin
Chapter 23. Images and Mirrors 3/23/11. Mirrors and Lenses QUESTIONS? PLEASE ASK! Types of Images for Mirrors and Lenses.
 3/23/ LIGO mirror Announcements LIGO mirror Two exams down, one to go! No HW this week. Credit: LIGO Laboratory, Caltech Office hours: My office hours today from 2-3 pm (or make an appointment) Chapter
3/23/ LIGO mirror Announcements LIGO mirror Two exams down, one to go! No HW this week. Credit: LIGO Laboratory, Caltech Office hours: My office hours today from 2-3 pm (or make an appointment) Chapter
Light and Lenses Notes
 Light and Lenses Notes Refraction The change in speed and direction of a wave Due to change in medium Must cross boundary at an angle other than 90 o, otherwise no change in direction I R (unlike reflection)
Light and Lenses Notes Refraction The change in speed and direction of a wave Due to change in medium Must cross boundary at an angle other than 90 o, otherwise no change in direction I R (unlike reflection)
PHY 171 Lecture 6 (January 18, 2012)
 PHY 171 Lecture 6 (January 18, 2012) Light Throughout most of the next 2 weeks, we will be concerned with the wave properties of light, and phenomena based on them (interference & diffraction). Light also
PHY 171 Lecture 6 (January 18, 2012) Light Throughout most of the next 2 weeks, we will be concerned with the wave properties of light, and phenomena based on them (interference & diffraction). Light also
The Ray model of Light. Reflection. Class 18
 The Ray model of Light Over distances of a terrestrial scale light travels in a straight line. The path of a laser is now the best way we have of defining a straight line. The model of light which assumes
The Ray model of Light Over distances of a terrestrial scale light travels in a straight line. The path of a laser is now the best way we have of defining a straight line. The model of light which assumes
PHYSICS. Chapter 34 Lecture FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS A STRATEGIC APPROACH 4/E RANDALL D. KNIGHT
 PHYSICS FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS A STRATEGIC APPROACH 4/E Chapter 34 Lecture RANDALL D. KNIGHT Chapter 34 Ray Optics IN THIS CHAPTER, you will learn about and apply the ray model of light Slide 34-2
PHYSICS FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS A STRATEGIC APPROACH 4/E Chapter 34 Lecture RANDALL D. KNIGHT Chapter 34 Ray Optics IN THIS CHAPTER, you will learn about and apply the ray model of light Slide 34-2
Figure 27a3See Answer T5. A convex lens used as a magnifying glass.
 F1 Figure 27a (in Answer T5) shows a diagram similar to that required, but with different dimensions. The object is between the first focus and the lens. The image is erect and virtual. The lateral magnification
F1 Figure 27a (in Answer T5) shows a diagram similar to that required, but with different dimensions. The object is between the first focus and the lens. The image is erect and virtual. The lateral magnification
Winmeen Tnpsc Group 1 & 2 Self Preparation Course Physics UNIT 9. Ray Optics. surface at the point of incidence, all lie in the same plane.
 Laws of reflection Physics UNIT 9 Ray Optics The incident ray, the reflected ray and the normal drawn to the reflecting surface at the point of incidence, all lie in the same plane. The angle of incidence
Laws of reflection Physics UNIT 9 Ray Optics The incident ray, the reflected ray and the normal drawn to the reflecting surface at the point of incidence, all lie in the same plane. The angle of incidence
Physics 11 Chapter 18: Ray Optics
 Physics 11 Chapter 18: Ray Optics "... Everything can be taken from a man but one thing; the last of the human freedoms to choose one s attitude in any given set of circumstances, to choose one s own way.
Physics 11 Chapter 18: Ray Optics "... Everything can be taken from a man but one thing; the last of the human freedoms to choose one s attitude in any given set of circumstances, to choose one s own way.
Physics 1202: Lecture 17 Today s Agenda
 Physics 1202: Lecture 17 Today s Agenda Announcements: Team problems today Team 10, 11 & 12: this Thursday Homework #8: due Friday Midterm 2: Tuesday April 10 Office hours if needed (M-2:30-3:30 or TH
Physics 1202: Lecture 17 Today s Agenda Announcements: Team problems today Team 10, 11 & 12: this Thursday Homework #8: due Friday Midterm 2: Tuesday April 10 Office hours if needed (M-2:30-3:30 or TH
Chapter 34. Images. In this chapter we define and classify images, and then classify several basic ways in which they can be produced.
 Chapter 34 Images One of the most important uses of the basic laws governing light is the production of images. Images are critical to a variety of fields and industries ranging from entertainment, security,
Chapter 34 Images One of the most important uses of the basic laws governing light is the production of images. Images are critical to a variety of fields and industries ranging from entertainment, security,
Refraction of Light. This bending of the ray is called refraction
 Refraction & Lenses Refraction of Light When a ray of light traveling through a transparent medium encounters a boundary leading into another transparent medium, part of the ray is reflected and part of
Refraction & Lenses Refraction of Light When a ray of light traveling through a transparent medium encounters a boundary leading into another transparent medium, part of the ray is reflected and part of
Recap: Refraction. Amount of bending depends on: - angle of incidence - refractive index of medium. (n 2 > n 1 ) n 2
 Amount of bending depends on: - angle of incidence - refractive index of medium Recap: Refraction λ 1 (n 2 > n 1 ) Snell s Law: When light passes from one transparent medium to another, the rays will be
Amount of bending depends on: - angle of incidence - refractive index of medium Recap: Refraction λ 1 (n 2 > n 1 ) Snell s Law: When light passes from one transparent medium to another, the rays will be
Lecture Notes (Geometric Optics)
 Lecture Notes (Geometric Optics) Intro: - plane mirrors are flat, smooth surfaces from which light is reflected by regular reflection - light rays are reflected with equal angles of incidence and reflection
Lecture Notes (Geometric Optics) Intro: - plane mirrors are flat, smooth surfaces from which light is reflected by regular reflection - light rays are reflected with equal angles of incidence and reflection
normal angle of incidence increases special angle no light is reflected
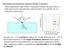 Reflection from transparent materials (Chapt. 33 last part) When unpolarized light strikes a transparent surface like glass there is both transmission and reflection, obeying Snell s law and the law of
Reflection from transparent materials (Chapt. 33 last part) When unpolarized light strikes a transparent surface like glass there is both transmission and reflection, obeying Snell s law and the law of
Physics 102: Lecture 16 Introduction to Mirrors
 Physics 102: Lecture 16 Introduction to Mirrors Physics 102: Lecture 16, Slide 1 Exam II Tuesday April 1st! What will exam cover? Lectures 8 15 (Magnetic fields Polarization) What do you need to bring?
Physics 102: Lecture 16 Introduction to Mirrors Physics 102: Lecture 16, Slide 1 Exam II Tuesday April 1st! What will exam cover? Lectures 8 15 (Magnetic fields Polarization) What do you need to bring?
PHYS 219 General Physics: Electricity, Light and Modern Physics
 PHYS 219 General Physics: Electricity, Light and Modern Physics Exam 2 is scheduled on Tuesday, March 26 @ 8 10 PM In Physics 114 It will cover four Chapters 21, 22, 23, and 24. Start reviewing lecture
PHYS 219 General Physics: Electricity, Light and Modern Physics Exam 2 is scheduled on Tuesday, March 26 @ 8 10 PM In Physics 114 It will cover four Chapters 21, 22, 23, and 24. Start reviewing lecture
Part Images Formed by Flat Mirrors. This Chapter. Phys. 281B Geometric Optics. Chapter 2 : Image Formation. Chapter 2: Image Formation
 Phys. 281B Geometric Optics This Chapter 3 Physics Department Yarmouk University 21163 Irbid Jordan 1- Images Formed by Flat Mirrors 2- Images Formed by Spherical Mirrors 3- Images Formed by Refraction
Phys. 281B Geometric Optics This Chapter 3 Physics Department Yarmouk University 21163 Irbid Jordan 1- Images Formed by Flat Mirrors 2- Images Formed by Spherical Mirrors 3- Images Formed by Refraction
The path of light is bent. Refraction and Lenses 5/3/2018. The angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection. Not so for refraction.
 The path of light is bent. Refraction and Lenses Unit 11 These are not photographs, but rather computer generated graphics based on the artist s understanding of the index of refraction. The angle of incidence
The path of light is bent. Refraction and Lenses Unit 11 These are not photographs, but rather computer generated graphics based on the artist s understanding of the index of refraction. The angle of incidence
Unit 11 Light and Optics Holt Chapter 14 Student Outline Light and Refraction
 Holt Chapter 14 Student Outline Light and Refraction Variables introduced or used in chapter: Quantity Symbol Units Speed of light frequency wavelength angle Object Distance Image Distance Radius of Curvature
Holt Chapter 14 Student Outline Light and Refraction Variables introduced or used in chapter: Quantity Symbol Units Speed of light frequency wavelength angle Object Distance Image Distance Radius of Curvature
INTRODUCTION REFLECTION AND REFRACTION AT BOUNDARIES. Introduction. Reflection and refraction at boundaries. Reflection at a single surface
 Chapter 8 GEOMETRICAL OPTICS Introduction Reflection and refraction at boundaries. Reflection at a single surface Refraction at a single boundary Dispersion Summary INTRODUCTION It has been shown that
Chapter 8 GEOMETRICAL OPTICS Introduction Reflection and refraction at boundaries. Reflection at a single surface Refraction at a single boundary Dispersion Summary INTRODUCTION It has been shown that
Chapter 33 Continued Properties of Light. Law of Reflection Law of Refraction or Snell s Law Chromatic Dispersion Brewsters Angle
 Chapter 33 Continued Properties of Light Law of Reflection Law of Refraction or Snell s Law Chromatic Dispersion Brewsters Angle Dispersion: Different wavelengths have different velocities and therefore
Chapter 33 Continued Properties of Light Law of Reflection Law of Refraction or Snell s Law Chromatic Dispersion Brewsters Angle Dispersion: Different wavelengths have different velocities and therefore
Optics INTRODUCTION DISCUSSION OF PRINCIPLES. Reflection by a Plane Mirror
 Optics INTRODUCTION Geometric optics is one of the oldest branches of physics, dealing with the laws of reflection and refraction. Reflection takes place on the surface of an object, and refraction occurs
Optics INTRODUCTION Geometric optics is one of the oldest branches of physics, dealing with the laws of reflection and refraction. Reflection takes place on the surface of an object, and refraction occurs
Reflections. I feel pretty, oh so pretty
 Reflections I feel pretty, oh so pretty Objectives By the end of the lesson, you should be able to: Draw an accurate reflective angle Determine the focal length of a spherical mirror Light Review Light
Reflections I feel pretty, oh so pretty Objectives By the end of the lesson, you should be able to: Draw an accurate reflective angle Determine the focal length of a spherical mirror Light Review Light
What is it? How does it work? How do we use it?
 What is it? How does it work? How do we use it? Dual Nature http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dfpeprq7ogc o Electromagnetic Waves display wave behavior o Created by oscillating electric and magnetic fields
What is it? How does it work? How do we use it? Dual Nature http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dfpeprq7ogc o Electromagnetic Waves display wave behavior o Created by oscillating electric and magnetic fields
PHYS 202 Notes, Week 9
 PHYS 202 Notes, Week 9 Greg Christian March 22 & 24, 206 Last updated: 03/24/206 at 2:23:56 This week we learn about images by mirrors, refraction, and thin lenses. Images Spherical Mirrors First let s
PHYS 202 Notes, Week 9 Greg Christian March 22 & 24, 206 Last updated: 03/24/206 at 2:23:56 This week we learn about images by mirrors, refraction, and thin lenses. Images Spherical Mirrors First let s
Physics 1202: Lecture 18 Today s Agenda
 Physics 1202: Lecture 18 Today s Agenda Announcements: Team problems today Team 10: Alisha Kumar, Adam Saxton, Alanna Forsberg Team 11: Riley Burns, Deanne Edwards, Shauna Bolton Team 12: Kervell Baird,
Physics 1202: Lecture 18 Today s Agenda Announcements: Team problems today Team 10: Alisha Kumar, Adam Saxton, Alanna Forsberg Team 11: Riley Burns, Deanne Edwards, Shauna Bolton Team 12: Kervell Baird,
All forms of EM waves travel at the speed of light in a vacuum = 3.00 x 10 8 m/s This speed is constant in air as well
 Pre AP Physics Light & Optics Chapters 14-16 Light is an electromagnetic wave Electromagnetic waves: Oscillating electric and magnetic fields that are perpendicular to the direction the wave moves Difference
Pre AP Physics Light & Optics Chapters 14-16 Light is an electromagnetic wave Electromagnetic waves: Oscillating electric and magnetic fields that are perpendicular to the direction the wave moves Difference
Chapter 5 Mirror and Lenses
 Chapter 5 Mirror and Lenses Name: 5.1 Ray Model of Light Another model for light is that it is made up of tiny particles called. Photons travel in perfect, lines from a light source This model helps us
Chapter 5 Mirror and Lenses Name: 5.1 Ray Model of Light Another model for light is that it is made up of tiny particles called. Photons travel in perfect, lines from a light source This model helps us
Chapter 7: Geometrical Optics
 Chapter 7: Geometrical Optics 7. Reflection at a Spherical Surface L.O 7.. State laws of reflection Laws of reflection state: L.O The incident ray, the reflected ray and the normal all lie in the same
Chapter 7: Geometrical Optics 7. Reflection at a Spherical Surface L.O 7.. State laws of reflection Laws of reflection state: L.O The incident ray, the reflected ray and the normal all lie in the same
Ray Optics. Ray model Reflection Refraction, total internal reflection Color dispersion Lenses Image formation Magnification Spherical mirrors
 Ray Optics Ray model Reflection Refraction, total internal reflection Color dispersion Lenses Image formation Magnification Spherical mirrors 1 Ray optics Optical imaging and color in medicine Integral
Ray Optics Ray model Reflection Refraction, total internal reflection Color dispersion Lenses Image formation Magnification Spherical mirrors 1 Ray optics Optical imaging and color in medicine Integral
Reflection and Image Formation by Mirrors
 Purpose Theory a. To study the reflection of light Reflection and Image Formation by Mirrors b. To study the formation and characteristics of images formed by different types of mirrors. When light (wave)
Purpose Theory a. To study the reflection of light Reflection and Image Formation by Mirrors b. To study the formation and characteristics of images formed by different types of mirrors. When light (wave)
Physics 1C. Lecture 23A. "If Dracula can t see his reflection in the mirror, how come his hair is always so neatly combed?
 Physics 1C Lecture 23A "If Dracula can t see his reflection in the mirror, how come his hair is always so neatly combed?" --Steven Wright Mirror Equation You can mathematically relate the object distance,
Physics 1C Lecture 23A "If Dracula can t see his reflection in the mirror, how come his hair is always so neatly combed?" --Steven Wright Mirror Equation You can mathematically relate the object distance,
A concave mirror is a converging mirror because parallel rays will. A convex mirror is a diverging mirror because parallel rays will
 Ray Diagrams Convex Mirror A concave mirror is a converging mirror because parallel rays will. A convex mirror is a diverging mirror because parallel rays will. Quick Activity obtain a ray box and a curved
Ray Diagrams Convex Mirror A concave mirror is a converging mirror because parallel rays will. A convex mirror is a diverging mirror because parallel rays will. Quick Activity obtain a ray box and a curved
Optics Course (Phys 311) Geometrical Optics Refraction through Lenses
 Optics Course (Phys ) Geometrical Optics Refraction through Lenses Lecturer: Dr Zeina Hashim Slide 1 Objectives covered in this lesson : 1. The refracting power of a thin lens. 2. Thin lens combinations.
Optics Course (Phys ) Geometrical Optics Refraction through Lenses Lecturer: Dr Zeina Hashim Slide 1 Objectives covered in this lesson : 1. The refracting power of a thin lens. 2. Thin lens combinations.
Refraction at a single curved spherical surface
 Refraction at a single curved spherical surface This is the beginning of a sequence of classes which will introduce simple and complex lens systems We will start with some terminology which will become
Refraction at a single curved spherical surface This is the beginning of a sequence of classes which will introduce simple and complex lens systems We will start with some terminology which will become
PHY 112: Light, Color and Vision. Lecture 11. Prof. Clark McGrew Physics D 134. Review for Exam. Lecture 11 PHY 112 Lecture 1
 PHY 112: Light, Color and Vision Lecture 11 Prof. Clark McGrew Physics D 134 Review for Exam Lecture 11 PHY 112 Lecture 1 From Last Time Lenses Ray tracing a Convex Lens Announcements The midterm is Thursday
PHY 112: Light, Color and Vision Lecture 11 Prof. Clark McGrew Physics D 134 Review for Exam Lecture 11 PHY 112 Lecture 1 From Last Time Lenses Ray tracing a Convex Lens Announcements The midterm is Thursday
Geometrical Optics INTRODUCTION. Wave Fronts and Rays
 Geometrical Optics INTRODUCTION In this experiment, the optical characteristics of mirrors, lenses, and prisms will be studied based on using the following physics definitions and relationships plus simple
Geometrical Optics INTRODUCTION In this experiment, the optical characteristics of mirrors, lenses, and prisms will be studied based on using the following physics definitions and relationships plus simple
Chapter 34. Thin Lenses
 Chapter 34 Thin Lenses Thin Lenses Mirrors Lenses Optical Instruments MFMcGraw-PHY 2426 Chap34a-Lenses-Revised: 7/13/2013 2 Inversion A right-handed coordinate system becomes a left-handed coordinate system
Chapter 34 Thin Lenses Thin Lenses Mirrors Lenses Optical Instruments MFMcGraw-PHY 2426 Chap34a-Lenses-Revised: 7/13/2013 2 Inversion A right-handed coordinate system becomes a left-handed coordinate system
Light travels in straight lines, this is referred to as... this means that light does not bend...
 SNC 2DI - 10.2 Properties of Light and Reflection Light travels in straight lines, this is referred to as... this means that light does not bend... Reflection : Light travels in a straight line as long
SNC 2DI - 10.2 Properties of Light and Reflection Light travels in straight lines, this is referred to as... this means that light does not bend... Reflection : Light travels in a straight line as long
Lecture Outlines Chapter 26
 Lecture Outlines Chapter 26 11/18/2013 2 Chapter 26 Geometrical Optics Objectives: After completing this module, you should be able to: Explain and discuss with diagrams, reflection and refraction of light
Lecture Outlines Chapter 26 11/18/2013 2 Chapter 26 Geometrical Optics Objectives: After completing this module, you should be able to: Explain and discuss with diagrams, reflection and refraction of light
IJSO Training: Light and Colour Mini-experiment Refractive Index and Snell s Law
 IJSO Training: Light and Colour Mini-experiment Refractive Index and Snell s Law Objective In this experiment, you are required to determine the refractive index of an acrylic trapezoid (or any block with
IJSO Training: Light and Colour Mini-experiment Refractive Index and Snell s Law Objective In this experiment, you are required to determine the refractive index of an acrylic trapezoid (or any block with
Reflection and Mirrors
 Reflection and Mirrors 1 The Law of Reflection The angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection. 2 The Law of Reflection When light strikes a surface it is reflected. The light ray striking the surface
Reflection and Mirrors 1 The Law of Reflection The angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection. 2 The Law of Reflection When light strikes a surface it is reflected. The light ray striking the surface
Section 2 Flat Mirrors. Distinguish between specular and diffuse reflection of light. Apply the law of reflection for flat mirrors.
 Section 2 Flat Mirrors Objectives Distinguish between specular and diffuse reflection of light. Apply the law of reflection for flat mirrors. Describe the nature of images formed by flat mirrors. Section
Section 2 Flat Mirrors Objectives Distinguish between specular and diffuse reflection of light. Apply the law of reflection for flat mirrors. Describe the nature of images formed by flat mirrors. Section
LECTURE 17 MIRRORS AND THIN LENS EQUATION. Instructor: Kazumi Tolich
 LECTURE 17 MIRRORS AND THIN LENS EQUATION Instructor: Kazumi Tolich Lecture 17 2 18.6 Image formation with spherical mirrors Concave mirrors Convex mirrors 18.7 The thin-lens equation Sign conventions
LECTURE 17 MIRRORS AND THIN LENS EQUATION Instructor: Kazumi Tolich Lecture 17 2 18.6 Image formation with spherical mirrors Concave mirrors Convex mirrors 18.7 The thin-lens equation Sign conventions
PSC20 - Properties of Waves 3
 PSC20 - Properties of Waves 3 The speed of light is in a vacuum. it travels 299 972 458 m/s. (rounded to m/s). Speed of light is given the symbol comes from the word meaning. How far do you think light
PSC20 - Properties of Waves 3 The speed of light is in a vacuum. it travels 299 972 458 m/s. (rounded to m/s). Speed of light is given the symbol comes from the word meaning. How far do you think light
Dispersion (23.5) Neil Alberding (SFU Physics) Physics 121: Optics, Electricity & Magnetism Spring / 17
 Neil Alberding (SFU Physics) Physics 121: Optics, Electricity & Magnetism Spring 2010 1 / 17 Dispersion (23.5) The speed of light in a material depends on its wavelength White light is a mixture of wavelengths
Neil Alberding (SFU Physics) Physics 121: Optics, Electricity & Magnetism Spring 2010 1 / 17 Dispersion (23.5) The speed of light in a material depends on its wavelength White light is a mixture of wavelengths
Ray Diagrams. Ray Diagrams Used for determining location, size, orientation, and type of image
 Ray Diagrams Reflection for concave mirror: Any incident ray traveling parallel to the principal axis on the way to the mirror will pass through the focal point upon reflection. Any incident ray passing
Ray Diagrams Reflection for concave mirror: Any incident ray traveling parallel to the principal axis on the way to the mirror will pass through the focal point upon reflection. Any incident ray passing
LIGHT CLASS X STUDY MATERIAL & QUESTION BANK:
 LIGHT CLASS X STUDY MATERIAL & QUESTION BANK: 1. REFLECTION OF LIGHT: The phenomenon of light coming back into the same medium after it strikes a smooth surface is called reflection. 2. LAWS OF REFLECTION:
LIGHT CLASS X STUDY MATERIAL & QUESTION BANK: 1. REFLECTION OF LIGHT: The phenomenon of light coming back into the same medium after it strikes a smooth surface is called reflection. 2. LAWS OF REFLECTION:
Reflection & Mirrors
 Reflection & Mirrors Geometric Optics Using a Ray Approximation Light travels in a straight-line path in a homogeneous medium until it encounters a boundary between two different media A ray of light is
Reflection & Mirrors Geometric Optics Using a Ray Approximation Light travels in a straight-line path in a homogeneous medium until it encounters a boundary between two different media A ray of light is
Video: The Mirror. Unit #3 - Optics. Geometric Optics. A) The Law of Reflection. applications Mirrors.
 Video: The Mirror http://vimeo.com/6212004 Unit #3 - Optics 11.1 - Mirrors Geometric Optics the science of how light reflects and bends optical device is any technology that uses light A) The Law of Reflection
Video: The Mirror http://vimeo.com/6212004 Unit #3 - Optics 11.1 - Mirrors Geometric Optics the science of how light reflects and bends optical device is any technology that uses light A) The Law of Reflection
Geometrical Optics. 1 st year physics laboratories. University of Ottawa
 Geometrical Optics 1 st year physics laboratories University of Ottawa https://uottawa.brightspace.com/d2l/home INTRODUCTION Geometrical optics deals with light as a ray that can be bounced (reflected)
Geometrical Optics 1 st year physics laboratories University of Ottawa https://uottawa.brightspace.com/d2l/home INTRODUCTION Geometrical optics deals with light as a ray that can be bounced (reflected)
Chapter 36. Image Formation
 Chapter 36 Image Formation Apr 22, 2012 Light from distant things We learn about a distant thing from the light it generates or redirects. The lenses in our eyes create images of objects our brains can
Chapter 36 Image Formation Apr 22, 2012 Light from distant things We learn about a distant thing from the light it generates or redirects. The lenses in our eyes create images of objects our brains can
1. (25pts) Answer the following questions. Justify your answers. (Use the space provided below and the next page)
 . (25pts) Answer the following questions. Justify your answers. (Use the space provided below and the next page) a). An object (an arrow) is placed as shown in front of each of the following optical instruments.
. (25pts) Answer the following questions. Justify your answers. (Use the space provided below and the next page) a). An object (an arrow) is placed as shown in front of each of the following optical instruments.
Chapter 5 Mirrors and Lenses
 Chapter 5 Notes: Mirrors and Lenses Name: Block: The Ray Model of Light The ray model of light represents light as a line, or ray, indicating the path of a beam of light. Light travels in straight lines
Chapter 5 Notes: Mirrors and Lenses Name: Block: The Ray Model of Light The ray model of light represents light as a line, or ray, indicating the path of a beam of light. Light travels in straight lines
Chapter 23. Geometrical Optics: Mirrors and Lenses and other Instruments
 Chapter 23 Geometrical Optics: Mirrors and Lenses and other Instruments HITT1 A small underwater pool light is 1 m below the surface of a swimming pool. What is the radius of the circle of light on the
Chapter 23 Geometrical Optics: Mirrors and Lenses and other Instruments HITT1 A small underwater pool light is 1 m below the surface of a swimming pool. What is the radius of the circle of light on the
