Basics of Multiple Sequence Alignment
|
|
|
- Louisa Chandler
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Basics of Multiple Sequence Alignment Tandy Warnow February 10, 2018
2 Basics of Multiple Sequence Alignment Tandy Warnow
3 Basic issues What is a multiple sequence alignment? Evolutionary processes operating on sequences Using profile HMMs to model multiple sequence alignment Optimization problems Basic techniques of standard methods Fundamental limitations of nearly all multiple sequence alignment methods How to evaluate alignments Performance studies of multiple sequence alignment methods operate on data
4 -HMM alignment strategies: the underlying alignments that A multiple sequence alignment rofile HMMs are not modified during the process. final multiple sequence alignment A of {s 1,s 2,...,s 8 } obta d A 2 from Table 9.7, computing their profiles P 1 and P 2 (see s T A C s A T A C s 3 C - A - - G s 4 C - A A T G s 5 C - - T - G s 6 C T - - A C s 7 C - A T A C s 8 G - A - A T
5 Homology Two letters in two sequences are homologous if they descend from a letter in a common ancestor. Deletion Substitution ACGGTGCAGTTACCA Insertion ACCAGTCACCTA ACGGTGCAGTTACC-A AC----CAGTCACCTA The true mul*ple alignment Reflects historical substitution, insertion, and deletion events Defined using transitive closure of pairwise alignments computed on edges of the true tree Evolutionary multiple sequence alignment seeks to create a matrix in which the input sequences are the rows and each column has letters that are all homologous to each other.
6 Evolutionary processes operating on sequences Substitutions Insertions and deletions of strings (indels) Rearrangements (inversions and transpositions) Duplications of regions Note: most alignment methods stretch out sequences so that the line up well, and so only address substitutions and indels.
7 ith A 1 and A 2. Hence, during this profile-profile alignment the Building alignments a profile A 1 HMM and Afor 2. an This MSA is a property of profile-pr -HMM alignment strategies: the underlying alignments that For the MSA below, the standard technique for building profile rofile HMMs are not modified during the process. HMMs would use an insertion state for position 2 (because more than 50% of the sequences are gapped in that position). s T A C s A T A C s 3 C - A - - G s 4 C - A A T G s 5 C - - T - G s 6 C T - - A C s 7 C - A T A C s 8 G - A - A T
8 Optimization criteria Sum-of-pairs (sum of edit distances on induced pairwise alignments) Tree alignment (sum of costs of edges) Maximum likelihood under a statistical model of sequence evolution All three are NP-hard, even if the tree is given.
9 Basic techniques Multiple sequence alignment methods generally use one or more of the following techniques to align a set S of sequences: Align all sequences in S to a single sequence s or to a profile HMM (or some other model) Progressive alignment: compute a guide tree, and then align sequences from the bottom up Consistency: infer support for homology between two letters using third sequences Divide-and-conquer (especially based on a tree) Iteration between tree estimation and alignment estimation
10 Adding a sequence s to an alignment A We are given an alignment A and its profile HMM, H, and we are also given s = s 1 s 2... s n, which is homologous to the sequences in A. To add s to A, we: 1. Find the maximum likelihood path through H for s 2. Use that path to add s into A. Details for Step 2: Align s to the profile HMM, and note which states emit the letters of s. If letter s i is emitted by match state j, put s i in the column for this match state (might not be j). If letter s i is emitted by an insertion state, put s i in its own column after s i 1. (Don t put two letters in the same column if either is emitted by an insertion state.)
11 Aligning a set S of sequences Suppose S is a set of unaligned sequences and we are told they are all homologous (i.e., share a common evolutionary history) with the sequences in a family F. How shall we compute a multiple sequence alignment for S?
12 Aligning a set S of homologous sequences Compute an MSA A for the sequences in F. Build the profile HMM H for the alignment A. Add all the sequences in S to A, independently. The alignment produced will contain all the sequences of F S; you can then restrict to just the sequences in S.
13 Progressive Alignment Build a guide tree from the sequences Align the sequences from the bottom-up (aligning alignments as you go up) Multiple sequence alignment Figure 2.7 Outline of the progressive alignment approach. For a given set of input sequences (a), a distance matrix is computed (b), and from this a phylogenetic guide tree is derived (c). Then, sequences at the leaves of the tree are aligned to produce profiles at the internal
14 Aligning alignments In a progressive alignment, alignments on disjoint sets are aligned together, to make an alignment on the combined set of sequences. To do this, the two alignments are first represented by profiles, and then these profiles are aligned to each other. This is performed using dynamic programming, similar to Needleman-Wunsch. Examples of methods that can align two alignments include Opal and Muscle. However, another approach is to represent each of the alignments as profile HMMs, and then align the two profile HMMs.
15 Using libraries of pairwise alignments, part 1 Suppose we have a set S of sequences, and a library L of pairwise alignments for the sequences in S. For each pair x, y of letters (one from each of two sequences), you have the frequency with which the two letters are aligned in L (i.e., the support for the homology pair x, y). Given a library of pairwise alignments, we can define the support for all homology pairs, and then seek the best MSA for these support values.
16 Using libraries of pairwise alignments, part 2 The consistency technique is another way of using a library L of pairwise alignments. Another way of defining the support for the homology pair is the number of letters z (in a third sequence) such that x and z and y and z are aligned in some pairwise alignments in P. This is how consistency is defined support via a third sequence. Many of the best MSA methods (e.g., T-Coffee and ProbCons) use the consistency technique in some way, and differ mainly in how they construct the library.
17 Statistical alignment estimation Some alignment methods are based on explicit parametric models of sequence evolution that include insertions and deletions (indels) as well as substitutions. Examples: BAli-Phy StatAlign Prank PAGAN These likelihood-based methods tend to be more computationally intensive than standard MSA methods, but have appealing statistical properties.
18 Divide-and-conquer using trees, cont. The main objective of divide-and-conquer is to scale good MSA methods to larger datasets, so that they are more accurate or can analyze larger datasets. Build a guide tree (perhaps by computing pairwise edit distances and then a tree based on the distances) Divide sequence dataset into disjoint subsets using the guide tree Align subsets 9.13 Co-estimation of alignments and trees 217 Align alignments together (e.g., profile-profile alignment)
19 One PASTA iteration
20 Iteration between MSA and tree estimation
21 How to evaluate methods Given an estimated and true (or reference alignment), we can compute various statistics, many of which are based on homology pairs : SPFN: sum of the false negative homology pairs SPFP: sum of the false positive homology pairs TC: total column score Compression: ratio of the estimated alignment length to true alignment length Distance between gap length distributions
22 Issues to consider Most methods can only handle indels and substitutions (i.e., no rearrangements or duplications). Most methods assume full-length sequences. Statistical methods are all based on models of sequence evolution, and the models are limited. Mosts methods cannot analyze very large datasets. Evaluation of methods is tricky.
Profiles and Multiple Alignments. COMP 571 Luay Nakhleh, Rice University
 Profiles and Multiple Alignments COMP 571 Luay Nakhleh, Rice University Outline Profiles and sequence logos Profile hidden Markov models Aligning profiles Multiple sequence alignment by gradual sequence
Profiles and Multiple Alignments COMP 571 Luay Nakhleh, Rice University Outline Profiles and sequence logos Profile hidden Markov models Aligning profiles Multiple sequence alignment by gradual sequence
Supplementary Online Material PASTA: ultra-large multiple sequence alignment
 Supplementary Online Material PASTA: ultra-large multiple sequence alignment Siavash Mirarab, Nam Nguyen, and Tandy Warnow University of Texas at Austin - Department of Computer Science {smirarab,bayzid,tandy}@cs.utexas.edu
Supplementary Online Material PASTA: ultra-large multiple sequence alignment Siavash Mirarab, Nam Nguyen, and Tandy Warnow University of Texas at Austin - Department of Computer Science {smirarab,bayzid,tandy}@cs.utexas.edu
Multiple sequence alignment. November 20, 2018
 Multiple sequence alignment November 20, 2018 Why do multiple alignment? Gain insight into evolutionary history Can assess time of divergence by looking at the number of mutations needed to change one
Multiple sequence alignment November 20, 2018 Why do multiple alignment? Gain insight into evolutionary history Can assess time of divergence by looking at the number of mutations needed to change one
Sequence alignment algorithms
 Sequence alignment algorithms Bas E. Dutilh Systems Biology: Bioinformatic Data Analysis Utrecht University, February 23 rd 27 After this lecture, you can decide when to use local and global sequence alignments
Sequence alignment algorithms Bas E. Dutilh Systems Biology: Bioinformatic Data Analysis Utrecht University, February 23 rd 27 After this lecture, you can decide when to use local and global sequence alignments
PROTEIN MULTIPLE ALIGNMENT MOTIVATION: BACKGROUND: Marina Sirota
 Marina Sirota MOTIVATION: PROTEIN MULTIPLE ALIGNMENT To study evolution on the genetic level across a wide range of organisms, biologists need accurate tools for multiple sequence alignment of protein
Marina Sirota MOTIVATION: PROTEIN MULTIPLE ALIGNMENT To study evolution on the genetic level across a wide range of organisms, biologists need accurate tools for multiple sequence alignment of protein
Chapter 8 Multiple sequence alignment. Chaochun Wei Spring 2018
 1896 1920 1987 2006 Chapter 8 Multiple sequence alignment Chaochun Wei Spring 2018 Contents 1. Reading materials 2. Multiple sequence alignment basic algorithms and tools how to improve multiple alignment
1896 1920 1987 2006 Chapter 8 Multiple sequence alignment Chaochun Wei Spring 2018 Contents 1. Reading materials 2. Multiple sequence alignment basic algorithms and tools how to improve multiple alignment
Stephen Scott.
 1 / 33 sscott@cse.unl.edu 2 / 33 Start with a set of sequences In each column, residues are homolgous Residues occupy similar positions in 3D structure Residues diverge from a common ancestral residue
1 / 33 sscott@cse.unl.edu 2 / 33 Start with a set of sequences In each column, residues are homolgous Residues occupy similar positions in 3D structure Residues diverge from a common ancestral residue
Lecture 5: Multiple sequence alignment
 Lecture 5: Multiple sequence alignment Introduction to Computational Biology Teresa Przytycka, PhD (with some additions by Martin Vingron) Why do we need multiple sequence alignment Pairwise sequence alignment
Lecture 5: Multiple sequence alignment Introduction to Computational Biology Teresa Przytycka, PhD (with some additions by Martin Vingron) Why do we need multiple sequence alignment Pairwise sequence alignment
Algorithms for Ultra-large Multiple Sequence Alignment and Phylogeny Estimation
 Algorithms for Ultra-large Multiple Sequence Alignment and Phylogeny Estimation Tandy Warnow Department of Computer Science The University of Texas at Austin Phylogeny (evolutionary tree) Orangutan Gorilla
Algorithms for Ultra-large Multiple Sequence Alignment and Phylogeny Estimation Tandy Warnow Department of Computer Science The University of Texas at Austin Phylogeny (evolutionary tree) Orangutan Gorilla
Chapter 6. Multiple sequence alignment (week 10)
 Course organization Introduction ( Week 1,2) Part I: Algorithms for Sequence Analysis (Week 1-11) Chapter 1-3, Models and theories» Probability theory and Statistics (Week 3)» Algorithm complexity analysis
Course organization Introduction ( Week 1,2) Part I: Algorithms for Sequence Analysis (Week 1-11) Chapter 1-3, Models and theories» Probability theory and Statistics (Week 3)» Algorithm complexity analysis
Evolutionary tree reconstruction (Chapter 10)
 Evolutionary tree reconstruction (Chapter 10) Early Evolutionary Studies Anatomical features were the dominant criteria used to derive evolutionary relationships between species since Darwin till early
Evolutionary tree reconstruction (Chapter 10) Early Evolutionary Studies Anatomical features were the dominant criteria used to derive evolutionary relationships between species since Darwin till early
Multiple sequence alignment. November 2, 2017
 Multiple sequence alignment November 2, 2017 Why do multiple alignment? Gain insight into evolutionary history Can assess time of divergence by looking at the number of mutations needed to change one sequence
Multiple sequence alignment November 2, 2017 Why do multiple alignment? Gain insight into evolutionary history Can assess time of divergence by looking at the number of mutations needed to change one sequence
GLOBEX Bioinformatics (Summer 2015) Multiple Sequence Alignment
 GLOBEX Bioinformatics (Summer 2015) Multiple Sequence Alignment Scoring Dynamic Programming algorithms Heuristic algorithms CLUSTAL W Courtesy of jalview Motivations Collective (or aggregate) statistic
GLOBEX Bioinformatics (Summer 2015) Multiple Sequence Alignment Scoring Dynamic Programming algorithms Heuristic algorithms CLUSTAL W Courtesy of jalview Motivations Collective (or aggregate) statistic
Scaling species tree estimation methods to large datasets using NJMerge
 Scaling species tree estimation methods to large datasets using NJMerge Erin Molloy and Tandy Warnow {emolloy2, warnow}@illinois.edu University of Illinois at Urbana Champaign 2018 Phylogenomics Software
Scaling species tree estimation methods to large datasets using NJMerge Erin Molloy and Tandy Warnow {emolloy2, warnow}@illinois.edu University of Illinois at Urbana Champaign 2018 Phylogenomics Software
HIDDEN MARKOV MODELS AND SEQUENCE ALIGNMENT
 HIDDEN MARKOV MODELS AND SEQUENCE ALIGNMENT - Swarbhanu Chatterjee. Hidden Markov models are a sophisticated and flexible statistical tool for the study of protein models. Using HMMs to analyze proteins
HIDDEN MARKOV MODELS AND SEQUENCE ALIGNMENT - Swarbhanu Chatterjee. Hidden Markov models are a sophisticated and flexible statistical tool for the study of protein models. Using HMMs to analyze proteins
Sequence length requirements. Tandy Warnow Department of Computer Science The University of Texas at Austin
 Sequence length requirements Tandy Warnow Department of Computer Science The University of Texas at Austin Part 1: Absolute Fast Convergence DNA Sequence Evolution AAGGCCT AAGACTT TGGACTT -3 mil yrs -2
Sequence length requirements Tandy Warnow Department of Computer Science The University of Texas at Austin Part 1: Absolute Fast Convergence DNA Sequence Evolution AAGGCCT AAGACTT TGGACTT -3 mil yrs -2
Biochemistry 324 Bioinformatics. Multiple Sequence Alignment (MSA)
 Biochemistry 324 Bioinformatics Multiple Sequence Alignment (MSA) Big- Οh notation Greek omicron symbol Ο The Big-Oh notation indicates the complexity of an algorithm in terms of execution speed and storage
Biochemistry 324 Bioinformatics Multiple Sequence Alignment (MSA) Big- Οh notation Greek omicron symbol Ο The Big-Oh notation indicates the complexity of an algorithm in terms of execution speed and storage
1. R. Durbin, S. Eddy, A. Krogh und G. Mitchison: Biological sequence analysis, Cambridge, 1998
 7 Multiple Sequence Alignment The exposition was prepared by Clemens Gröpl, based on earlier versions by Daniel Huson, Knut Reinert, and Gunnar Klau. It is based on the following sources, which are all
7 Multiple Sequence Alignment The exposition was prepared by Clemens Gröpl, based on earlier versions by Daniel Huson, Knut Reinert, and Gunnar Klau. It is based on the following sources, which are all
PASTA: Ultra-Large Multiple Sequence Alignment
 PASTA: Ultra-Large Multiple Sequence Alignment Siavash Mirarab, Nam Nguyen, and Tandy Warnow University of Texas at Austin - Department of Computer Science 2317 Speedway, Stop D9500 Austin, TX 78712 {smirarab,namphuon,tandy}@cs.utexas.edu
PASTA: Ultra-Large Multiple Sequence Alignment Siavash Mirarab, Nam Nguyen, and Tandy Warnow University of Texas at Austin - Department of Computer Science 2317 Speedway, Stop D9500 Austin, TX 78712 {smirarab,namphuon,tandy}@cs.utexas.edu
CS273: Algorithms for Structure Handout # 4 and Motion in Biology Stanford University Thursday, 8 April 2004
 CS273: Algorithms for Structure Handout # 4 and Motion in Biology Stanford University Thursday, 8 April 2004 Lecture #4: 8 April 2004 Topics: Sequence Similarity Scribe: Sonil Mukherjee 1 Introduction
CS273: Algorithms for Structure Handout # 4 and Motion in Biology Stanford University Thursday, 8 April 2004 Lecture #4: 8 April 2004 Topics: Sequence Similarity Scribe: Sonil Mukherjee 1 Introduction
Multiple Sequence Alignment Gene Finding, Conserved Elements
 Multiple Sequence Alignment Gene Finding, Conserved Elements Definition Given N sequences x 1, x 2,, x N : Insert gaps (-) in each sequence x i, such that All sequences have the same length L Score of
Multiple Sequence Alignment Gene Finding, Conserved Elements Definition Given N sequences x 1, x 2,, x N : Insert gaps (-) in each sequence x i, such that All sequences have the same length L Score of
Multiple Sequence Alignment II
 Multiple Sequence Alignment II Lectures 20 Dec 5, 2011 CSE 527 Computational Biology, Fall 2011 Instructor: Su-In Lee TA: Christopher Miles Monday & Wednesday 12:00-1:20 Johnson Hall (JHN) 022 1 Outline
Multiple Sequence Alignment II Lectures 20 Dec 5, 2011 CSE 527 Computational Biology, Fall 2011 Instructor: Su-In Lee TA: Christopher Miles Monday & Wednesday 12:00-1:20 Johnson Hall (JHN) 022 1 Outline
Designing parallel algorithms for constructing large phylogenetic trees on Blue Waters
 Designing parallel algorithms for constructing large phylogenetic trees on Blue Waters Erin Molloy University of Illinois at Urbana Champaign General Allocation (PI: Tandy Warnow) Exploratory Allocation
Designing parallel algorithms for constructing large phylogenetic trees on Blue Waters Erin Molloy University of Illinois at Urbana Champaign General Allocation (PI: Tandy Warnow) Exploratory Allocation
Brief review from last class
 Sequence Alignment Brief review from last class DNA is has direction, we will use only one (5 -> 3 ) and generate the opposite strand as needed. DNA is a 3D object (see lecture 1) but we will model it
Sequence Alignment Brief review from last class DNA is has direction, we will use only one (5 -> 3 ) and generate the opposite strand as needed. DNA is a 3D object (see lecture 1) but we will model it
Alignment ABC. Most slides are modified from Serafim s lectures
 Alignment ABC Most slides are modified from Serafim s lectures Complete genomes Evolution Evolution at the DNA level C ACGGTGCAGTCACCA ACGTTGCAGTCCACCA SEQUENCE EDITS REARRANGEMENTS Sequence conservation
Alignment ABC Most slides are modified from Serafim s lectures Complete genomes Evolution Evolution at the DNA level C ACGGTGCAGTCACCA ACGTTGCAGTCCACCA SEQUENCE EDITS REARRANGEMENTS Sequence conservation
Principles of Bioinformatics. BIO540/STA569/CSI660 Fall 2010
 Principles of Bioinformatics BIO540/STA569/CSI660 Fall 2010 Lecture 11 Multiple Sequence Alignment I Administrivia Administrivia The midterm examination will be Monday, October 18 th, in class. Closed
Principles of Bioinformatics BIO540/STA569/CSI660 Fall 2010 Lecture 11 Multiple Sequence Alignment I Administrivia Administrivia The midterm examination will be Monday, October 18 th, in class. Closed
Multiple Sequence Alignment. With thanks to Eric Stone and Steffen Heber, North Carolina State University
 Multiple Sequence Alignment With thanks to Eric Stone and Steffen Heber, North Carolina State University Definition: Multiple sequence alignment Given a set of sequences, a multiple sequence alignment
Multiple Sequence Alignment With thanks to Eric Stone and Steffen Heber, North Carolina State University Definition: Multiple sequence alignment Given a set of sequences, a multiple sequence alignment
Molecular Evolution & Phylogenetics Complexity of the search space, distance matrix methods, maximum parsimony
 Molecular Evolution & Phylogenetics Complexity of the search space, distance matrix methods, maximum parsimony Basic Bioinformatics Workshop, ILRI Addis Ababa, 12 December 2017 Learning Objectives understand
Molecular Evolution & Phylogenetics Complexity of the search space, distance matrix methods, maximum parsimony Basic Bioinformatics Workshop, ILRI Addis Ababa, 12 December 2017 Learning Objectives understand
3.4 Multiple sequence alignment
 3.4 Multiple sequence alignment Why produce a multiple sequence alignment? Using more than two sequences results in a more convincing alignment by revealing conserved regions in ALL of the sequences Aligned
3.4 Multiple sequence alignment Why produce a multiple sequence alignment? Using more than two sequences results in a more convincing alignment by revealing conserved regions in ALL of the sequences Aligned
Genome 559: Introduction to Statistical and Computational Genomics. Lecture15a Multiple Sequence Alignment Larry Ruzzo
 Genome 559: Introduction to Statistical and Computational Genomics Lecture15a Multiple Sequence Alignment Larry Ruzzo 1 Multiple Alignment: Motivations Common structure, function, or origin may be only
Genome 559: Introduction to Statistical and Computational Genomics Lecture15a Multiple Sequence Alignment Larry Ruzzo 1 Multiple Alignment: Motivations Common structure, function, or origin may be only
CISC 889 Bioinformatics (Spring 2003) Multiple Sequence Alignment
 CISC 889 Bioinformatics (Spring 2003) Multiple Sequence Alignment Courtesy of jalview 1 Motivations Collective statistic Protein families Identification and representation of conserved sequence features
CISC 889 Bioinformatics (Spring 2003) Multiple Sequence Alignment Courtesy of jalview 1 Motivations Collective statistic Protein families Identification and representation of conserved sequence features
Dynamic Programming User Manual v1.0 Anton E. Weisstein, Truman State University Aug. 19, 2014
 Dynamic Programming User Manual v1.0 Anton E. Weisstein, Truman State University Aug. 19, 2014 Dynamic programming is a group of mathematical methods used to sequentially split a complicated problem into
Dynamic Programming User Manual v1.0 Anton E. Weisstein, Truman State University Aug. 19, 2014 Dynamic programming is a group of mathematical methods used to sequentially split a complicated problem into
Biology 644: Bioinformatics
 Find the best alignment between 2 sequences with lengths n and m, respectively Best alignment is very dependent upon the substitution matrix and gap penalties The Global Alignment Problem tries to find
Find the best alignment between 2 sequences with lengths n and m, respectively Best alignment is very dependent upon the substitution matrix and gap penalties The Global Alignment Problem tries to find
Multiple Sequence Alignment (MSA)
 I519 Introduction to Bioinformatics, Fall 2013 Multiple Sequence Alignment (MSA) Yuzhen Ye (yye@indiana.edu) School of Informatics & Computing, IUB Outline Multiple sequence alignment (MSA) Generalize
I519 Introduction to Bioinformatics, Fall 2013 Multiple Sequence Alignment (MSA) Yuzhen Ye (yye@indiana.edu) School of Informatics & Computing, IUB Outline Multiple sequence alignment (MSA) Generalize
Biology 644: Bioinformatics
 A statistical Markov model in which the system being modeled is assumed to be a Markov process with unobserved (hidden) states in the training data. First used in speech and handwriting recognition In
A statistical Markov model in which the system being modeled is assumed to be a Markov process with unobserved (hidden) states in the training data. First used in speech and handwriting recognition In
Today s Lecture. Edit graph & alignment algorithms. Local vs global Computational complexity of pairwise alignment Multiple sequence alignment
 Today s Lecture Edit graph & alignment algorithms Smith-Waterman algorithm Needleman-Wunsch algorithm Local vs global Computational complexity of pairwise alignment Multiple sequence alignment 1 Sequence
Today s Lecture Edit graph & alignment algorithms Smith-Waterman algorithm Needleman-Wunsch algorithm Local vs global Computational complexity of pairwise alignment Multiple sequence alignment 1 Sequence
AlignMe Manual. Version 1.1. Rene Staritzbichler, Marcus Stamm, Kamil Khafizov and Lucy R. Forrest
 AlignMe Manual Version 1.1 Rene Staritzbichler, Marcus Stamm, Kamil Khafizov and Lucy R. Forrest Max Planck Institute of Biophysics Frankfurt am Main 60438 Germany 1) Introduction...3 2) Using AlignMe
AlignMe Manual Version 1.1 Rene Staritzbichler, Marcus Stamm, Kamil Khafizov and Lucy R. Forrest Max Planck Institute of Biophysics Frankfurt am Main 60438 Germany 1) Introduction...3 2) Using AlignMe
Multiple Sequence Alignment. Mark Whitsitt - NCSA
 Multiple Sequence Alignment Mark Whitsitt - NCSA What is a Multiple Sequence Alignment (MA)? GMHGTVYANYAVDSSDLLLAFGVRFDDRVTGKLEAFASRAKIVHIDIDSAEIGKNKQPHV GMHGTVYANYAVEHSDLLLAFGVRFDDRVTGKLEAFASRAKIVHIDIDSAEIGKNKTPHV
Multiple Sequence Alignment Mark Whitsitt - NCSA What is a Multiple Sequence Alignment (MA)? GMHGTVYANYAVDSSDLLLAFGVRFDDRVTGKLEAFASRAKIVHIDIDSAEIGKNKQPHV GMHGTVYANYAVEHSDLLLAFGVRFDDRVTGKLEAFASRAKIVHIDIDSAEIGKNKTPHV
1. R. Durbin, S. Eddy, A. Krogh und G. Mitchison: Biological sequence analysis, Cambridge, 1998
 7 Multiple Sequence Alignment The exposition was prepared by Clemens GrÃP pl, based on earlier versions by Daniel Huson, Knut Reinert, and Gunnar Klau. It is based on the following sources, which are all
7 Multiple Sequence Alignment The exposition was prepared by Clemens GrÃP pl, based on earlier versions by Daniel Huson, Knut Reinert, and Gunnar Klau. It is based on the following sources, which are all
Sequence Comparison: Dynamic Programming. Genome 373 Genomic Informatics Elhanan Borenstein
 Sequence omparison: Dynamic Programming Genome 373 Genomic Informatics Elhanan Borenstein quick review: hallenges Find the best global alignment of two sequences Find the best global alignment of multiple
Sequence omparison: Dynamic Programming Genome 373 Genomic Informatics Elhanan Borenstein quick review: hallenges Find the best global alignment of two sequences Find the best global alignment of multiple
Lecture 10. Sequence alignments
 Lecture 10 Sequence alignments Alignment algorithms: Overview Given a scoring system, we need to have an algorithm for finding an optimal alignment for a pair of sequences. We want to maximize the score
Lecture 10 Sequence alignments Alignment algorithms: Overview Given a scoring system, we need to have an algorithm for finding an optimal alignment for a pair of sequences. We want to maximize the score
Reconstructing long sequences from overlapping sequence fragment. Searching databases for related sequences and subsequences
 SEQUENCE ALIGNMENT ALGORITHMS 1 Why compare sequences? Reconstructing long sequences from overlapping sequence fragment Searching databases for related sequences and subsequences Storing, retrieving and
SEQUENCE ALIGNMENT ALGORITHMS 1 Why compare sequences? Reconstructing long sequences from overlapping sequence fragment Searching databases for related sequences and subsequences Storing, retrieving and
Sequence alignment is an essential concept for bioinformatics, as most of our data analysis and interpretation techniques make use of it.
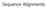 Sequence Alignments Overview Sequence alignment is an essential concept for bioinformatics, as most of our data analysis and interpretation techniques make use of it. Sequence alignment means arranging
Sequence Alignments Overview Sequence alignment is an essential concept for bioinformatics, as most of our data analysis and interpretation techniques make use of it. Sequence alignment means arranging
Comparison of Phylogenetic Trees of Multiple Protein Sequence Alignment Methods
 Comparison of Phylogenetic Trees of Multiple Protein Sequence Alignment Methods Khaddouja Boujenfa, Nadia Essoussi, and Mohamed Limam International Science Index, Computer and Information Engineering waset.org/publication/482
Comparison of Phylogenetic Trees of Multiple Protein Sequence Alignment Methods Khaddouja Boujenfa, Nadia Essoussi, and Mohamed Limam International Science Index, Computer and Information Engineering waset.org/publication/482
Sequence analysis Pairwise sequence alignment
 UMF11 Introduction to bioinformatics, 25 Sequence analysis Pairwise sequence alignment 1. Sequence alignment Lecturer: Marina lexandersson 12 September, 25 here are two types of sequence alignments, global
UMF11 Introduction to bioinformatics, 25 Sequence analysis Pairwise sequence alignment 1. Sequence alignment Lecturer: Marina lexandersson 12 September, 25 here are two types of sequence alignments, global
Introduction to Triangulated Graphs. Tandy Warnow
 Introduction to Triangulated Graphs Tandy Warnow Topics for today Triangulated graphs: theorems and algorithms (Chapters 11.3 and 11.9) Examples of triangulated graphs in phylogeny estimation (Chapters
Introduction to Triangulated Graphs Tandy Warnow Topics for today Triangulated graphs: theorems and algorithms (Chapters 11.3 and 11.9) Examples of triangulated graphs in phylogeny estimation (Chapters
Multiple Sequence Alignment
 . Multiple Sequence lignment utorial #4 Ilan ronau Multiple Sequence lignment Reminder S = S = S = Possible alignment Possible alignment Multiple Sequence lignment Reminder Input: Sequences S, S,, S over
. Multiple Sequence lignment utorial #4 Ilan ronau Multiple Sequence lignment Reminder S = S = S = Possible alignment Possible alignment Multiple Sequence lignment Reminder Input: Sequences S, S,, S over
MULTIPLE SEQUENCE ALIGNMENT SOLUTIONS AND APPLICATIONS
 MULTIPLE SEQUENCE ALIGNMENT SOLUTIONS AND APPLICATIONS By XU ZHANG A DISSERTATION PRESENTED TO THE GRADUATE SCHOOL OF THE UNIVERSITY OF FLORIDA IN PARTIAL FULFILLMENT OF THE REQUIREMENTS FOR THE DEGREE
MULTIPLE SEQUENCE ALIGNMENT SOLUTIONS AND APPLICATIONS By XU ZHANG A DISSERTATION PRESENTED TO THE GRADUATE SCHOOL OF THE UNIVERSITY OF FLORIDA IN PARTIAL FULFILLMENT OF THE REQUIREMENTS FOR THE DEGREE
On the Efficacy of Haskell for High Performance Computational Biology
 On the Efficacy of Haskell for High Performance Computational Biology Jacqueline Addesa Academic Advisors: Jeremy Archuleta, Wu chun Feng 1. Problem and Motivation Biologists can leverage the power of
On the Efficacy of Haskell for High Performance Computational Biology Jacqueline Addesa Academic Advisors: Jeremy Archuleta, Wu chun Feng 1. Problem and Motivation Biologists can leverage the power of
EECS730: Introduction to Bioinformatics
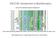 EECS730: Introduction to Bioinformatics Lecture 06: Multiple Sequence Alignment https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/7/79/rplp0_90_clustalw_aln.gif/575px-rplp0_90_clustalw_aln.gif Slides
EECS730: Introduction to Bioinformatics Lecture 06: Multiple Sequence Alignment https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/7/79/rplp0_90_clustalw_aln.gif/575px-rplp0_90_clustalw_aln.gif Slides
Tutorial: Phylogenetic Analysis on BioHealthBase Written by: Catherine A. Macken Version 1: February 2009
 Tutorial: Phylogenetic Analysis on BioHealthBase Written by: Catherine A. Macken Version 1: February 2009 BioHealthBase provides multiple functions for inferring phylogenetic trees, through the Phylogenetic
Tutorial: Phylogenetic Analysis on BioHealthBase Written by: Catherine A. Macken Version 1: February 2009 BioHealthBase provides multiple functions for inferring phylogenetic trees, through the Phylogenetic
Introduction to Trees
 Introduction to Trees Tandy Warnow December 28, 2016 Introduction to Trees Tandy Warnow Clades of a rooted tree Every node v in a leaf-labelled rooted tree defines a subset of the leafset that is below
Introduction to Trees Tandy Warnow December 28, 2016 Introduction to Trees Tandy Warnow Clades of a rooted tree Every node v in a leaf-labelled rooted tree defines a subset of the leafset that is below
MULTIPLE SEQUENCE ALIGNMENT
 MULTIPLE SEQUENCE ALIGNMENT Multiple Alignment versus Pairwise Alignment Up until now we have only tried to align two sequences. What about more than two? A faint similarity between two sequences becomes
MULTIPLE SEQUENCE ALIGNMENT Multiple Alignment versus Pairwise Alignment Up until now we have only tried to align two sequences. What about more than two? A faint similarity between two sequences becomes
The Simplex Algorithm
 The Simplex Algorithm April 25, 2005 We seek x 1,..., x n 0 which mini- Problem. mizes C(x 1,..., x n ) = c 1 x 1 + + c n x n, subject to the constraint Ax b, where A is m n, b = m 1. Through the introduction
The Simplex Algorithm April 25, 2005 We seek x 1,..., x n 0 which mini- Problem. mizes C(x 1,..., x n ) = c 1 x 1 + + c n x n, subject to the constraint Ax b, where A is m n, b = m 1. Through the introduction
Dynamic Programming in 3-D Progressive Alignment Profile Progressive Alignment (ClustalW) Scoring Multiple Alignments Entropy Sum of Pairs Alignment
 Dynamic Programming in 3-D Progressive Alignment Profile Progressive Alignment (ClustalW) Scoring Multiple Alignments Entropy Sum of Pairs Alignment Partial Order Alignment (POA) A-Bruijin (ABA) Approach
Dynamic Programming in 3-D Progressive Alignment Profile Progressive Alignment (ClustalW) Scoring Multiple Alignments Entropy Sum of Pairs Alignment Partial Order Alignment (POA) A-Bruijin (ABA) Approach
24 Grundlagen der Bioinformatik, SS 10, D. Huson, April 26, This lecture is based on the following papers, which are all recommended reading:
 24 Grundlagen der Bioinformatik, SS 10, D. Huson, April 26, 2010 3 BLAST and FASTA This lecture is based on the following papers, which are all recommended reading: D.J. Lipman and W.R. Pearson, Rapid
24 Grundlagen der Bioinformatik, SS 10, D. Huson, April 26, 2010 3 BLAST and FASTA This lecture is based on the following papers, which are all recommended reading: D.J. Lipman and W.R. Pearson, Rapid
Event-based Phylogeny Inference and Multiple Sequence Alignment
 Event-based Phylogeny Inference and Multiple Sequence Alignment Phong Nguyen Duc Computer Science Department Brown University Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the Degree of Master
Event-based Phylogeny Inference and Multiple Sequence Alignment Phong Nguyen Duc Computer Science Department Brown University Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the Degree of Master
Computational Biology Lecture 4: Overlap detection, Local Alignment, Space Efficient Needleman-Wunsch Saad Mneimneh
 Computational Biology Lecture 4: Overlap detection, Local Alignment, Space Efficient Needleman-Wunsch Saad Mneimneh Overlap detection: Semi-Global Alignment An overlap of two sequences is considered an
Computational Biology Lecture 4: Overlap detection, Local Alignment, Space Efficient Needleman-Wunsch Saad Mneimneh Overlap detection: Semi-Global Alignment An overlap of two sequences is considered an
Computational Molecular Biology
 Computational Molecular Biology Erwin M. Bakker Lecture 3, mainly from material by R. Shamir [2] and H.J. Hoogeboom [4]. 1 Pairwise Sequence Alignment Biological Motivation Algorithmic Aspect Recursive
Computational Molecular Biology Erwin M. Bakker Lecture 3, mainly from material by R. Shamir [2] and H.J. Hoogeboom [4]. 1 Pairwise Sequence Alignment Biological Motivation Algorithmic Aspect Recursive
Sequence clustering. Introduction. Clustering basics. Hierarchical clustering
 Sequence clustering Introduction Data clustering is one of the key tools used in various incarnations of data-mining - trying to make sense of large datasets. It is, thus, natural to ask whether clustering
Sequence clustering Introduction Data clustering is one of the key tools used in various incarnations of data-mining - trying to make sense of large datasets. It is, thus, natural to ask whether clustering
Biological Sequence Matching Using Fuzzy Logic
 International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research Volume 2, Issue 7, July-2011 1 Biological Sequence Matching Using Fuzzy Logic Nivit Gill, Shailendra Singh Abstract: Sequence alignment is the
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research Volume 2, Issue 7, July-2011 1 Biological Sequence Matching Using Fuzzy Logic Nivit Gill, Shailendra Singh Abstract: Sequence alignment is the
Sequence Alignment 1
 Sequence Alignment 1 Nucleotide and Base Pairs Purine: A and G Pyrimidine: T and C 2 DNA 3 For this course DNA is double-helical, with two complementary strands. Complementary bases: Adenine (A) - Thymine
Sequence Alignment 1 Nucleotide and Base Pairs Purine: A and G Pyrimidine: T and C 2 DNA 3 For this course DNA is double-helical, with two complementary strands. Complementary bases: Adenine (A) - Thymine
Sequence comparison: Local alignment
 Sequence comparison: Local alignment Genome 559: Introuction to Statistical an Computational Genomics Prof. James H. Thomas http://faculty.washington.eu/jht/gs559_217/ Review global alignment en traceback
Sequence comparison: Local alignment Genome 559: Introuction to Statistical an Computational Genomics Prof. James H. Thomas http://faculty.washington.eu/jht/gs559_217/ Review global alignment en traceback
A multiple alignment tool in 3D
 Outline Department of Computer Science, Bioinformatics Group University of Leipzig TBI Winterseminar Bled, Slovenia February 2005 Outline Outline 1 Multiple Alignments Problems Goal Outline Outline 1 Multiple
Outline Department of Computer Science, Bioinformatics Group University of Leipzig TBI Winterseminar Bled, Slovenia February 2005 Outline Outline 1 Multiple Alignments Problems Goal Outline Outline 1 Multiple
Dynamic Programming for Phylogenetic Estimation
 1 / 45 Dynamic Programming for Phylogenetic Estimation CS598AGB Pranjal Vachaspati University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign 2 / 45 Coalescent-based Species Tree Estimation Find evolutionary tree for
1 / 45 Dynamic Programming for Phylogenetic Estimation CS598AGB Pranjal Vachaspati University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign 2 / 45 Coalescent-based Species Tree Estimation Find evolutionary tree for
Representation is Everything: Towards Efficient and Adaptable Similarity Measures for Biological Data
 Representation is Everything: Towards Efficient and Adaptable Similarity Measures for Biological Data Charu C. Aggarwal IBM T. J. Watson Research Center charu@us.ibm.com Abstract Distance function computation
Representation is Everything: Towards Efficient and Adaptable Similarity Measures for Biological Data Charu C. Aggarwal IBM T. J. Watson Research Center charu@us.ibm.com Abstract Distance function computation
CS 581. Tandy Warnow
 CS 581 Tandy Warnow This week Maximum parsimony: solving it on small datasets Maximum Likelihood optimization problem Felsenstein s pruning algorithm Bayesian MCMC methods Research opportunities Maximum
CS 581 Tandy Warnow This week Maximum parsimony: solving it on small datasets Maximum Likelihood optimization problem Felsenstein s pruning algorithm Bayesian MCMC methods Research opportunities Maximum
Multiple alignment. Multiple alignment. Computational complexity. Multiple sequence alignment. Consensus. 2 1 sec sec sec
 Introduction to Bioinformatics Iosif Vaisman Email: ivaisman@gmu.edu VTISCTGSSSNIGAG-NHVKWYQQLPG VTISCTGTSSNIGS--ITVNWYQQLPG LRLSCSSSGFIFSS--YAMYWVRQAPG LSLTCTVSGTSFDD--YYSTWVRQPPG PEVTCVVVDVSHEDPQVKFNWYVDG--
Introduction to Bioinformatics Iosif Vaisman Email: ivaisman@gmu.edu VTISCTGSSSNIGAG-NHVKWYQQLPG VTISCTGTSSNIGS--ITVNWYQQLPG LRLSCSSSGFIFSS--YAMYWVRQAPG LSLTCTVSGTSFDD--YYSTWVRQPPG PEVTCVVVDVSHEDPQVKFNWYVDG--
Phylogenetics on CUDA (Parallel) Architectures Bradly Alicea
 Descent w/modification Descent w/modification Descent w/modification Descent w/modification CPU Descent w/modification Descent w/modification Phylogenetics on CUDA (Parallel) Architectures Bradly Alicea
Descent w/modification Descent w/modification Descent w/modification Descent w/modification CPU Descent w/modification Descent w/modification Phylogenetics on CUDA (Parallel) Architectures Bradly Alicea
Machine Learning. Computational biology: Sequence alignment and profile HMMs
 10-601 Machine Learning Computational biology: Sequence alignment and profile HMMs Central dogma DNA CCTGAGCCAACTATTGATGAA transcription mrna CCUGAGCCAACUAUUGAUGAA translation Protein PEPTIDE 2 Growth
10-601 Machine Learning Computational biology: Sequence alignment and profile HMMs Central dogma DNA CCTGAGCCAACTATTGATGAA transcription mrna CCUGAGCCAACUAUUGAUGAA translation Protein PEPTIDE 2 Growth
Pairwise Sequence Alignment. Zhongming Zhao, PhD
 Pairwise Sequence Alignment Zhongming Zhao, PhD Email: zhongming.zhao@vanderbilt.edu http://bioinfo.mc.vanderbilt.edu/ Sequence Similarity match mismatch A T T A C G C G T A C C A T A T T A T G C G A T
Pairwise Sequence Alignment Zhongming Zhao, PhD Email: zhongming.zhao@vanderbilt.edu http://bioinfo.mc.vanderbilt.edu/ Sequence Similarity match mismatch A T T A C G C G T A C C A T A T T A T G C G A T
15-780: Graduate Artificial Intelligence. Computational biology: Sequence alignment and profile HMMs
 5-78: Graduate rtificial Intelligence omputational biology: Sequence alignment and profile HMMs entral dogma DN GGGG transcription mrn UGGUUUGUG translation Protein PEPIDE 2 omparison of Different Organisms
5-78: Graduate rtificial Intelligence omputational biology: Sequence alignment and profile HMMs entral dogma DN GGGG transcription mrn UGGUUUGUG translation Protein PEPIDE 2 omparison of Different Organisms
A Layer-Based Approach to Multiple Sequences Alignment
 A Layer-Based Approach to Multiple Sequences Alignment Tianwei JIANG and Weichuan YU Laboratory for Bioinformatics and Computational Biology, Department of Electronic and Computer Engineering, The Hong
A Layer-Based Approach to Multiple Sequences Alignment Tianwei JIANG and Weichuan YU Laboratory for Bioinformatics and Computational Biology, Department of Electronic and Computer Engineering, The Hong
Lecture 3: February Local Alignment: The Smith-Waterman Algorithm
 CSCI1820: Sequence Alignment Spring 2017 Lecture 3: February 7 Lecturer: Sorin Istrail Scribe: Pranavan Chanthrakumar Note: LaTeX template courtesy of UC Berkeley EECS dept. Notes are also adapted from
CSCI1820: Sequence Alignment Spring 2017 Lecture 3: February 7 Lecturer: Sorin Istrail Scribe: Pranavan Chanthrakumar Note: LaTeX template courtesy of UC Berkeley EECS dept. Notes are also adapted from
One report (in pdf format) addressing each of following questions.
 MSCBIO 2070/02-710: Computational Genomics, Spring 2016 HW1: Sequence alignment and Evolution Due: 24:00 EST, Feb 15, 2016 by autolab Your goals in this assignment are to 1. Complete a genome assembler
MSCBIO 2070/02-710: Computational Genomics, Spring 2016 HW1: Sequence alignment and Evolution Due: 24:00 EST, Feb 15, 2016 by autolab Your goals in this assignment are to 1. Complete a genome assembler
Giri Narasimhan. CAP 5510: Introduction to Bioinformatics. ECS 254; Phone: x3748
 CAP 5510: Introduction to Bioinformatics Giri Narasimhan ECS 254; Phone: x3748 giri@cis.fiu.edu www.cis.fiu.edu/~giri/teach/bioinfs07.html 1/30/07 CAP5510 1 BLAST & FASTA FASTA [Lipman, Pearson 85, 88]
CAP 5510: Introduction to Bioinformatics Giri Narasimhan ECS 254; Phone: x3748 giri@cis.fiu.edu www.cis.fiu.edu/~giri/teach/bioinfs07.html 1/30/07 CAP5510 1 BLAST & FASTA FASTA [Lipman, Pearson 85, 88]
Special course in Computer Science: Advanced Text Algorithms
 Special course in Computer Science: Advanced Text Algorithms Lecture 8: Multiple alignments Elena Czeizler and Ion Petre Department of IT, Abo Akademi Computational Biomodelling Laboratory http://www.users.abo.fi/ipetre/textalg
Special course in Computer Science: Advanced Text Algorithms Lecture 8: Multiple alignments Elena Czeizler and Ion Petre Department of IT, Abo Akademi Computational Biomodelling Laboratory http://www.users.abo.fi/ipetre/textalg
Chordal Graphs and Evolutionary Trees. Tandy Warnow
 Chordal Graphs and Evolutionary Trees Tandy Warnow Possible Indo-European tree (Ringe, Warnow and Taylor 2000) Anatolian Vedic Iranian Greek Italic Celtic Tocharian Armenian Germanic Baltic Slavic Albanian
Chordal Graphs and Evolutionary Trees Tandy Warnow Possible Indo-European tree (Ringe, Warnow and Taylor 2000) Anatolian Vedic Iranian Greek Italic Celtic Tocharian Armenian Germanic Baltic Slavic Albanian
Recent Research Results. Evolutionary Trees Distance Methods
 Recent Research Results Evolutionary Trees Distance Methods Indo-European Languages After Tandy Warnow What is the purpose? Understand evolutionary history (relationship between species). Uderstand how
Recent Research Results Evolutionary Trees Distance Methods Indo-European Languages After Tandy Warnow What is the purpose? Understand evolutionary history (relationship between species). Uderstand how
BLAST & Genome assembly
 BLAST & Genome assembly Solon P. Pissis Tomáš Flouri Heidelberg Institute for Theoretical Studies May 15, 2014 1 BLAST What is BLAST? The algorithm 2 Genome assembly De novo assembly Mapping assembly 3
BLAST & Genome assembly Solon P. Pissis Tomáš Flouri Heidelberg Institute for Theoretical Studies May 15, 2014 1 BLAST What is BLAST? The algorithm 2 Genome assembly De novo assembly Mapping assembly 3
DNA Alignment With Affine Gap Penalties
 DNA Alignment With Affine Gap Penalties Laurel Schuster Why Use Affine Gap Penalties? When aligning two DNA sequences, one goal may be to infer the mutations that made them different. Though it s impossible
DNA Alignment With Affine Gap Penalties Laurel Schuster Why Use Affine Gap Penalties? When aligning two DNA sequences, one goal may be to infer the mutations that made them different. Though it s impossible
Research Article Aligning Sequences by Minimum Description Length
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation EURASIP Journal on Bioinformatics and Systems Biology Volume 2007, Article ID 72936, 14 pages doi:10.1155/2007/72936 Research Article Aligning Sequences by Minimum Description
Hindawi Publishing Corporation EURASIP Journal on Bioinformatics and Systems Biology Volume 2007, Article ID 72936, 14 pages doi:10.1155/2007/72936 Research Article Aligning Sequences by Minimum Description
Computational Molecular Biology
 Computational Molecular Biology Erwin M. Bakker Lecture 2 Materials used from R. Shamir [2] and H.J. Hoogeboom [4]. 1 Molecular Biology Sequences DNA A, T, C, G RNA A, U, C, G Protein A, R, D, N, C E,
Computational Molecular Biology Erwin M. Bakker Lecture 2 Materials used from R. Shamir [2] and H.J. Hoogeboom [4]. 1 Molecular Biology Sequences DNA A, T, C, G RNA A, U, C, G Protein A, R, D, N, C E,
Inverse Sequence Alignment from Partial Examples
 Inverse Sequence Alignment from Partial Examples Eagu Kim and John Kececioglu Department of Computer Science The University of Arizona, Tucson AZ 85721, USA {egkim,kece}@cs.arizona.edu Abstract. When aligning
Inverse Sequence Alignment from Partial Examples Eagu Kim and John Kececioglu Department of Computer Science The University of Arizona, Tucson AZ 85721, USA {egkim,kece}@cs.arizona.edu Abstract. When aligning
CAP BLAST. BIOINFORMATICS Su-Shing Chen CISE. 8/20/2005 Su-Shing Chen, CISE 1
 CAP 5510-6 BLAST BIOINFORMATICS Su-Shing Chen CISE 8/20/2005 Su-Shing Chen, CISE 1 BLAST Basic Local Alignment Prof Search Su-Shing Chen Tool A Fast Pair-wise Alignment and Database Searching Tool 8/20/2005
CAP 5510-6 BLAST BIOINFORMATICS Su-Shing Chen CISE 8/20/2005 Su-Shing Chen, CISE 1 BLAST Basic Local Alignment Prof Search Su-Shing Chen Tool A Fast Pair-wise Alignment and Database Searching Tool 8/20/2005
Finding data. HMMER Answer key
 Finding data HMMER Answer key HMMER input is prepared using VectorBase ClustalW, which runs a Java application for the graphical representation of the results. If you get an error message that blocks this
Finding data HMMER Answer key HMMER input is prepared using VectorBase ClustalW, which runs a Java application for the graphical representation of the results. If you get an error message that blocks this
Machine Learning Techniques for Bacteria Classification
 Machine Learning Techniques for Bacteria Classification Massimo La Rosa Riccardo Rizzo Alfonso M. Urso S. Gaglio ICAR-CNR University of Palermo Workshop on Hardware Architectures Beyond 2020: Challenges
Machine Learning Techniques for Bacteria Classification Massimo La Rosa Riccardo Rizzo Alfonso M. Urso S. Gaglio ICAR-CNR University of Palermo Workshop on Hardware Architectures Beyond 2020: Challenges
Codon models. In reality we use codon model Amino acid substitution rates meet nucleotide models Codon(nucleotide triplet)
 Phylogeny Codon models Last lecture: poor man s way of calculating dn/ds (Ka/Ks) Tabulate synonymous/non- synonymous substitutions Normalize by the possibilities Transform to genetic distance K JC or K
Phylogeny Codon models Last lecture: poor man s way of calculating dn/ds (Ka/Ks) Tabulate synonymous/non- synonymous substitutions Normalize by the possibilities Transform to genetic distance K JC or K
Phylogenetics. Introduction to Bioinformatics Dortmund, Lectures: Sven Rahmann. Exercises: Udo Feldkamp, Michael Wurst
 Phylogenetics Introduction to Bioinformatics Dortmund, 16.-20.07.2007 Lectures: Sven Rahmann Exercises: Udo Feldkamp, Michael Wurst 1 Phylogenetics phylum = tree phylogenetics: reconstruction of evolutionary
Phylogenetics Introduction to Bioinformatics Dortmund, 16.-20.07.2007 Lectures: Sven Rahmann Exercises: Udo Feldkamp, Michael Wurst 1 Phylogenetics phylum = tree phylogenetics: reconstruction of evolutionary
Sequence alignment theory and applications Session 3: BLAST algorithm
 Sequence alignment theory and applications Session 3: BLAST algorithm Introduction to Bioinformatics online course : IBT Sonal Henson Learning Objectives Understand the principles of the BLAST algorithm
Sequence alignment theory and applications Session 3: BLAST algorithm Introduction to Bioinformatics online course : IBT Sonal Henson Learning Objectives Understand the principles of the BLAST algorithm
Visual Representations for Machine Learning
 Visual Representations for Machine Learning Spectral Clustering and Channel Representations Lecture 1 Spectral Clustering: introduction and confusion Michael Felsberg Klas Nordberg The Spectral Clustering
Visual Representations for Machine Learning Spectral Clustering and Channel Representations Lecture 1 Spectral Clustering: introduction and confusion Michael Felsberg Klas Nordberg The Spectral Clustering
Mismatch String Kernels for SVM Protein Classification
 Mismatch String Kernels for SVM Protein Classification by C. Leslie, E. Eskin, J. Weston, W.S. Noble Athina Spiliopoulou Morfoula Fragopoulou Ioannis Konstas Outline Definitions & Background Proteins Remote
Mismatch String Kernels for SVM Protein Classification by C. Leslie, E. Eskin, J. Weston, W.S. Noble Athina Spiliopoulou Morfoula Fragopoulou Ioannis Konstas Outline Definitions & Background Proteins Remote
Leaning Graphical Model Structures using L1-Regularization Paths (addendum)
 Leaning Graphical Model Structures using -Regularization Paths (addendum) Mark Schmidt and Kevin Murphy Computer Science Dept. University of British Columbia {schmidtm,murphyk}@cs.ubc.ca 1 Introduction
Leaning Graphical Model Structures using -Regularization Paths (addendum) Mark Schmidt and Kevin Murphy Computer Science Dept. University of British Columbia {schmidtm,murphyk}@cs.ubc.ca 1 Introduction
Introduction to Computational Phylogenetics
 Introduction to Computational Phylogenetics Tandy Warnow The University of Texas at Austin No Institute Given This textbook is a draft, and should not be distributed. Much of what is in this textbook appeared
Introduction to Computational Phylogenetics Tandy Warnow The University of Texas at Austin No Institute Given This textbook is a draft, and should not be distributed. Much of what is in this textbook appeared
IMPROVING THE QUALITY OF MULTIPLE SEQUENCE ALIGNMENT. A Dissertation YUE LU
 IMPROVING THE QUALITY OF MULTIPLE SEQUENCE ALIGNMENT A Dissertation by YUE LU Submitted to the Office of Graduate Studies of Texas A&M University in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree
IMPROVING THE QUALITY OF MULTIPLE SEQUENCE ALIGNMENT A Dissertation by YUE LU Submitted to the Office of Graduate Studies of Texas A&M University in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree
A New Approach For Tree Alignment Based on Local Re-Optimization
 A New Approach For Tree Alignment Based on Local Re-Optimization Feng Yue and Jijun Tang Department of Computer Science and Engineering University of South Carolina Columbia, SC 29063, USA yuef, jtang
A New Approach For Tree Alignment Based on Local Re-Optimization Feng Yue and Jijun Tang Department of Computer Science and Engineering University of South Carolina Columbia, SC 29063, USA yuef, jtang
Blast2GO User Manual. Blast2GO Ortholog Group Annotation May, BioBam Bioinformatics S.L. Valencia, Spain
 Blast2GO User Manual Blast2GO Ortholog Group Annotation May, 2016 BioBam Bioinformatics S.L. Valencia, Spain Contents 1 Clusters of Orthologs 2 2 Orthologous Group Annotation Tool 2 3 Statistics for NOG
Blast2GO User Manual Blast2GO Ortholog Group Annotation May, 2016 BioBam Bioinformatics S.L. Valencia, Spain Contents 1 Clusters of Orthologs 2 2 Orthologous Group Annotation Tool 2 3 Statistics for NOG
Lecture Overview. Sequence search & alignment. Searching sequence databases. Sequence Alignment & Search. Goals: Motivations:
 Lecture Overview Sequence Alignment & Search Karin Verspoor, Ph.D. Faculty, Computational Bioscience Program University of Colorado School of Medicine With credit and thanks to Larry Hunter for creating
Lecture Overview Sequence Alignment & Search Karin Verspoor, Ph.D. Faculty, Computational Bioscience Program University of Colorado School of Medicine With credit and thanks to Larry Hunter for creating
PFstats User Guide. Aspartate/ornithine carbamoyltransferase Case Study. Neli Fonseca
 PFstats User Guide Aspartate/ornithine carbamoyltransferase Case Study 1 Contents Overview 3 Obtaining An Alignment 3 Methods 4 Alignment Filtering............................................ 4 Reference
PFstats User Guide Aspartate/ornithine carbamoyltransferase Case Study 1 Contents Overview 3 Obtaining An Alignment 3 Methods 4 Alignment Filtering............................................ 4 Reference
Cost Partitioning Techniques for Multiple Sequence Alignment. Mirko Riesterer,
 Cost Partitioning Techniques for Multiple Sequence Alignment Mirko Riesterer, 10.09.18 Agenda. 1 Introduction 2 Formal Definition 3 Solving MSA 4 Combining Multiple Pattern Databases 5 Cost Partitioning
Cost Partitioning Techniques for Multiple Sequence Alignment Mirko Riesterer, 10.09.18 Agenda. 1 Introduction 2 Formal Definition 3 Solving MSA 4 Combining Multiple Pattern Databases 5 Cost Partitioning
