(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,327,388 B1. Zhou et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 4, 2001
|
|
|
- Kristin Jenkins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
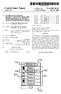
1 USOO B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,327,388 B1 Zhou et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 4, 2001 (54) IDENTIFICATION OF LOGOS FROM 5,748,865 5/1998 Yamamoto et al.. DOCUMENT IMAGES 5,751,849 5/1998 Ikeda. 5,757,957 5/1998 Tachikawa. (75) Inventors: Jiangying Zhou, Columbia, SC (US); 5,767,978 6/1998 Revankar et al.. Daniel P. Lopresti, Hopewell, NJ (US); 5,774,579 6/1998 Wang et al.. Prateek Sarkar, Briarcliff Manor, NY OTHER PUBLICATIONS (US) A. Lawrence Spitz, "Logotype Detection in Compressed (73) Assignee: Matsushita Electric Industrial Co., Images using Alignment Signatures', Daimler Benz Ltd., Osaka (JP) Research and Technology Center, pp M.Y. Jaisimha, Wavelet Features for Similarity based (*) Notice: Subject to any disclaimer, the term of this Retrieval of Logo Images, Apr. 1996, vol. 2660, pp. patent is extended or adjusted under U.S.C. 154(b) by 0 days. David Doermann et al., Logo Recognition, Center for Automation Research, University of Maryland, Oct. 1993, (21) Appl. No.: 09/134,143 pp (22) Filed: Aug. 14, 1998 * cited by examiner 7 Primary Examiner Andrew W. Johns s 82.2set is Assistant Examiner Seyed Azarian -rr s (74) Attorney, Agent, or Firm-Harness, Dickey & Pierce, (58) Field of Search /204, 205, P.L.C. 382/206, 219, 229, 180, 203, 209, 215, 216, 217, 218, 227,317, 394, 296, 298 (57) ABSTRACT (56) References Cited The method and apparatus enables any user to Search for logos in document images Stored in a bitmap format. The U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS Search efficiently compares bitmap or image data by extract 4, /1980 Moulton ing a Series of connected components. These connected /1984 Okubo. components are grouped according to region where each 4817,166 3/1989 Gonzalez et al.. region may be a potential logo. Shape and density param 4,972,499 11/1990 Kurosawa. eters of a region are determined and compared to the 5, /1994 Kimura. parameters of the Stored logo image. If a region is Success 5,351,314 9/1994 Vaezi. fully matched then that region is aligned and Scaled to the 5,414,781 * 5/1995 Spitz et al /296 corresponding Stored logo image. Thereafter, a bitwise com 5,436,983 * 7/1995 Bernzott et al /229 parison is then performed between the Scaled and aligned 5,438,628 * 8/1995 Spitz et al /181 region and the logo image. A match Score is assigned to each 5:39: : 3.E. EN f al.. tal 382/592 region along with other pertinent information about the 5,555,362 9/1996 NE region, and is Stored in a ranked logo list database. The 5, /1996 Wang. ranked logo list database represents a list of logos found in 5,680,479 10/1997 Wang et al.. the document image. 5,699,453 12/1997 Ozaki. 5, /1997 Niki et al.. 22 Claims, 8 Drawing Sheets Dris Document image Connected Component H Parameter Data Structure Module 36 Logo Bit Patters and Pafaeig's Database Logo Image Comparison Module Align and Scale Module Bitvise Compare Module logo... watch - Candidates Data Structure 34 s: 1 Adjusted Bitratterr sk CataStructure Ranked Logo List 40 Database b
2 U.S. Patent Dec. 4, 2001 Sheet 1 of 8 US 6,327,388 B1 Document Image Connected Component Module 28 Parameter al-ya Data Structure Logo Bit Patterns and Comparison 3O Module Logo Match N-Y32 Candidates Parameters 34 Database Align and Scale Module Data Structure Logo Image Adjusted N-Y Bit Pattern Data Structure Bitwise Compare Module Ranked Logo List Database FIGURE 1
3 U.S. Patent Dec. 4, 2001 Sheet 2 of 8 US 6,327,388 B1 FIGURE 2 Parameter Data Structure Connected Mean Aspect H Component Area Density eight Width Ratio Region 1 FIGURE 3
4 U.S. Patent Dec. 4, 2001 Sheet 3 of 8 US 6,327,388 B1 DOCument Region DOCument Region GOOd Match Bad Match FIGURE 4
5 U.S. Patent Dec. 4, 2001 Sheet 4 of 8 US 6,327,388 B1 Before ROtation After Rotation FIGURE 5
6 U.S. Patent Dec. 4, 2001 Sheet 5 of 8 US 6,327,388 B1-7 t W / a \ / Y. A / - \. / W A. V first All MIT MIT FIGURE 6A FIGURE 6B FIGURE 6C f
7 U.S. Patent Dec. 4, 2001 Sheet 6 of 8 US 6,327,388 B1 FIGURE 7A A MT FIGURE 7B
8 U.S. Patent Dec. 4, 2001 Sheet 7 of 8 US 6,327,388 B1 t Panasonic LOgOS For a Mac lover it's a wish COme title Document Basic Solution Block (legiatel, y Y Ranked D- O Sort by Score List of --> LOgOS FIGURE 8
9 U.S. Patent Dec. 4, 2001 Sheet 8 of 8 US 6,327,388 B1 For a lac lover it's a wish COee Basic SOlution Block (LOgO Label, SCOre) Sort by Score Ranked - > List Of Documents FIGURE 9
10 1 IDENTIFICATION OF LOGOS FROM DOCUMENT IMAGES BACKGROUND AND SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION The present invention relates generally to image analysis and electronic information identification. More particularly, the invention relates to a computerized System for locating and identifying logos in document images. In this information age, we are constantly bombarded with electronic files and information. Some call this the information explosion. Much of this information derives from image-based Systems that generate bitmapped images. To help cope with the information explosion we need many tools, including ones to distinguish electronic files and documents based on information contained in bitmapped images. Image-based Systems present a major challenge to infor mation retrieval because the data is difficult to Search. Whereas information retrieval technology is fairly well advanced in coded character-based Systems, these retrieval techniques do not work in image-based Systems. That is because image-based Systems Store information as bitmap data that correspond to the appearance of the printed page and not the information content of that page. Traditional techniques require the conversion of bitmap data into text data, through optical character recognition (OCR) Software, before information retrieval Systems can go to work. Unfortunately, optical character recognition Software is computationally expensive, and the recognition process is rather slow. In addition, often important information may be encoded graphically, in a form that cannot be readily converted into text. Corporate logos represent an important example of Such information. While Some corporate logos do include letters that can be converted using OCR, many do not. It would therefore be quite helpful to be able to identify logos, regardless of whether they contain recognizable letters, to allow the computer to Search and retrieve information based on the presence of the logo. This would allow one to organize documents and files by logo, if desired. Organizing information on this basis can be quite helpful, even if character-based organization is also possible. For example, Suppose a user wanted to locate any docu ment received from ABC Corporation. Normally this would be performed as a text search for the letters ABC, and this text search would yield any three letters ABC that are connected together as a Single entity. However, if ABC Corporation uses a highly Stylized logo instead of easily recognizable letters, the text Search technique may be of little value. Conversely, Such a text Search would also uncover other instances of the letters ABC, possibly having nothing to do with a document received from ABC corporation. A text Search would also retrieve newspaper articles about ABC corporation, for example. In this example a logo Search would be highly desirable. It could locate the document of interest without the foregoing prob lems. The present invention recognizes that there will be vast amounts of data that are in bitmap or image format, and that users will want to Search this information, just as they now Search text-based Systems. Instead of converting the entire document from image format to text format, the present invention analyzes the bitmap data in its native format, to extract regions within the image data that correspond to the most likely candidates for logos. The invention recognizes US 6,327,388 B that the logos may be in any position in the document and at different skew angles. The invention Scans the document, Seeking a bitmap that is similar to the bitmap of the logo in question. In accordance with the invention, a document image is matched with a database of logo images Stored in a computer readable memory as a logo bit pattern and as predefined Sets of parameters. The predefined Sets of parameters are indica tive of shape and mean density. Connected component analysis is performed on the bit pattern of a document image to identify a plurality of regions of connected components in the document image and to generate region parameter data that include parameters indicative of Shape and mean den sity. The parameters of a document region are compared with the parameters of a database of logo images to identify a plurality of logo match candidates. The document regions are then Scaled and aligned to correspond to the size and skew of the logo match candidates. The result of the document regions being Scaled and aligned is to create a number of adjusted regions that also have corresponding adjusted bit patterns. A bitwise comparison is performed between the adjusted bit patterns with their corresponding adjusted regions and the bit patterns of the logo match candidates to Select a best match and Store the best match Selections in a ranked logo list database. For a more complete understanding of the invention, reference may be had to the following Specification and to the accompanying drawings. BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS FIG. 1 is a Software block diagram of the presently preferred embodiment of the invention; FIG. 2 is an enlarged Sample view of three separate connected components, FIG. 3 is a diagram of the connected component data Structure used by the presently preferred embodiment; FIG. 4 is an illustration of Scaling and aligning of logos, FIG. 5 is a diagram illustrating the minimum and maxi mum limits to the aspect ratio of the presently preferred embodiment of the invention; FIG. 6A illustrates the difference image that results from the mathematical combination of the bits of FIGS. 6B and 6C; FIG. 7A is an illustration of the region of interest for its corresponding FIG. 7B logo image. FIG. 8 is an illustration of using the invention to identify all logos within a document image. FIG. 9 is an illustration of using the invention to locate all documents in a database that contain the same logo. DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE PREFERRED EMBODIMENT Referring now to FIG. 1, an overall software block diagram of an entire logo recognition System in accordance with the preferred embodiment of the present invention is shown. This particular System is designed to input a docu ment image in the form of a bitmap and utilizing a logo image in the form of bit pattern and parameter data in the logo database it is designed to Search for a logo in the document image and if there is a match it is Suppose to identify and rank each adjusted document region according to their matched Scores. Generally, the overall System com prises a document image bitmap 20, a bitmap buffer 22, a
11 3 connected component module 24, a parameter data structure 26, a comparison module 28, a logo bit pattern and param eter database 30, a logo match candidate data Structure 32, an align and Scale module 34, a adjusted bit pattern data structure 36, a bitwise compare module 38, and a ranked logo list database 40. Referring to FIG. 1, a document image 20 stored as a bit pattern in a bitmap buffer 22 such that individual black or white pixels of the image are Stored as binary numbers. The document image can come from a wide variety of Sources including optical Scanners, fax machines, copiers, graphics Software, Video data, world wide web pages and the like. The processor of the computer System on which the invention is implemented maintains a bitmap buffer 22 within the random access memory of the computer System. The bitmap buffer 22 is preferably of a size sufficient to hold all of the bitmap data associated with a given page or image. If desired, the bitmap buffer 22 can be made larger, to hold multiple pages. In general, the size of the bitmap buffer 22 will depend upon the resolution of the image. Each indi vidual picture element or pixel is Stored in a Separate memory location within the buffer 22. Regarding the bit pattern data, the present description will describe the invention in the context of black and white image data. In other words, for purposes of this description, the bitmap buffer 22 data comprises simple binary data representing black and white dots or pixels that make up the overall image. Of course, the techniques described herein can be readily extended to other forms of image data, including multiple bit grayscale data and multiple bit color data. Binary black and white data is used here to simplify the explanation, and illustrate one possible configuration. The computer implemented Software System employs a group of processing modules, each designed to perform different data manipulation functions. These processing modules have been illustrated in FIG. 1 by enclosed rect angles. These modules operate upon data Stored in memory according to predefined data Structures that will be described more fully below. In FIG. 1 the data structures have been illustrated using open-ended rectangles, to distinguish them from the processing modules. Also, to aid in understanding the invention, the processing modules of the invention have been arranged in FIG. 1 in a top down order, showing the Sequence in which various modules are placed in Service. First, a connected component extraction process is per formed by module 24 upon the document image bitmap pattern in the bitmap buffer 22. This connected component extraction process essentially populates the connected com ponent data Structure 26 that is used to Store much of the geometric data associated with the bitmap image. A con nected component in a binary image is a maximal Set of touching black pixels. ESSentially, the connected component extraction process Starts with a given data element within a bitmap buffer 22 and analyzes the adjacent data elements to determine whether they comprise a part of a connected component, as the black dots that make up a rectangle are all connected together. Refer to FIG. 2 for an example. Note that there are three rectangles in the region in FIG. 2. Each rectangle is made up of a collection of connected black dots. The connected component analysis will consider each rect angle a separate connected component. In the preferred embodiment the connected component analysis is performed in a raster-scan fashion whereby contiguous black pixels lying in the same horizontal line are treated as a Single unit, called a Segment. The connected component is in turn made up of one or more of Such Segments and may therefore be expressed as a linked list of Segments. US 6,327,388 B The connected component extraction module 24 identifies individual connected components and identifies and extracts various geometric features that are used by other modules later within the program. FIG. 3 graphically shows the configuration of connected component data structure 26. Referring to FIG. 3, the connected component data structure 26 maintains a record of the number of geometric features for each connected component. These features include: the location, width and height of the bounding box that defines the connected component, area of component, aspect ratio, and mean density. Mean density is the ratio of the number of black pixels of the component to the number of pixels in the bounding box. A bounding box is defined as the mini mum rectangle enclosing a connected component. The pres ently preferred embodiment eliminates, from further analyses, connected components which are comparable or Smaller in size than 10 point text. The connected component data Structure 26 is essentially configured as a list, with each connected component being represented as a separate element in the list belonging to a particular region, refer to FIG. 3. In the presently preferred embodiment a region represents a linked list of all compo nents that are at a detected minimal distance from the component's neighbor. The distance between neighbors is measured as the minimum distance between the Sides of the bounding boxes of the connected components. ESSentially, a region is a potential logo that must be verified through further analyses. After the data structure 26 has been populated by the connected component extraction process 24 the comparison module 28 is then called upon to operate on the data in the parameter data Structure 26 and the parameter data of the logo image database 30. For each region, in the parameter data Structure 26, the comparison module 28 will arrange each connected component in decreasing order of area. The comparison module 28 then pairs a connected component of the region with a connected component of the logo image. The aspect ratio and the mean density of the logo connected component is compared to the aspect ratio and the mean density of the document region connected component. Aspect ratios computed from different images of a pattern may vary within a close range owing to a Sampling variation, skew and a host of other printing and Scanning imperfec tions. Therefore, in order to decide whether aspect ratios of two bounding boxes are close enough to warrant further matching of the connected components, we have to Set an allowable range of variation. The above motivates the fol lowing procedure. Since the logo image in the logo image database has no skew by assumption, the comparison module Starts with the bounding box of the logo image. The next Step rotates the diagonal of the box through +2.5 and obtains the maximum and minimum limits to the aspect ratio, see FIG. 5. If the aspect ratio of the connected component of the document region falls within the above limits then the aspect ratios are considered matched. If the aspect ratio and the mean density of the connected components of a region from the document image 20 match the aspect ratio and mean density of the connected components from the logo image bitmap 30 then We Store the logo bit pattern and its associated parameters with the document region and its associated parameters in a logo matched candidate data Structure 32. After the logo match candidate data Structure 32 has been populated, by the comparison module 28, the align and Scale module 34 is called upon to operate on the data in the data structure 32. The align and scale module 34 is responsible to
12 S ensure that each logo match candidate is aligned and Scaled relative to the logo bit pattern Stored in the logo image bitmap database 30. When logos are printed at different sizes a Scaling factor needs to be used to Size one logo relative to the other. Since logos are Scaled uniformly in all directions the Scaling factor between two different matching compo nents can be estimated using one of the following: 1. the ratio of widths of their bounding boxes, S. 2. the ratio of heights of their bounding boxes, S, 3. the square root of the ratio of the number of black pixels in each component, S. When one component is a scaled version of the other, all three methods should give equal estimates. However, images may be thinned or thickened around the edges due to ink spread or improper Setting of threshold during digitiza tion. When the images are thinned or thickened around the edges the three methods do not give equal results if used Separately. This observation motivated a heuristic correction Scheme for the Scale estimates. The Scaling factor for sizing a logo match candidate is then calculated as S=S+S-S. The Scaling factor is then applied to the bit pattern of the document region So that the resulting Scale of the adjusted bit pattern of the document region matches that of the logo match candidate. For aligning, the bit pattern of the document region is anchored to a reference point relative to that of the logo match candidate. FIG. 4 illustrates how the Scaling and aligning process takes place. After the Scaling and aligning of the document image region associated with the logo candidate the resultant adjusted bit pattern of the adjusted document image region is Stored in the adjusted bit pattern data structure 36. In the next step, the bitwise comparison module 38 treats the logo bit pattern from the logo bit pattern database 30 as a template and examines how well the template matches the adjusted bit pattern of the document region from the adjusted bit pattern data Structure 36 at the Specified align ment. The bitwise comparison module 38 treats the logo bit pattern as the template and examines how well the template matches the adjusted bit pattern of the document region at the Specified alignment. In the preferred embodiment a bitwise exclusive-or operation is performed between the two bit patterns yielding a difference image. Each non-zero pixel in the difference image represents a point where the colors of the logo bit pattern 30 and the document image 20 are different. In other words, each non-zero pixel corresponds to a pixel mismatch. A large number of mismatch pixels thus indicates a bad match. FIG. 6 shows a difference image, refer to FIG. 6A, between the region of a document image, refer to FIG. 6B, and a logo image, refer to FIG. 6C. A mismatch Score is then calculated. In the current embodiment, the mismatch Score is computed only in the region-of-interest. In the preferred embodiment, a mis match Score is computed for each region of interest. In the preferred embodiment we define the region of interest as the region between the outermost black pixels of the Outermost logo edges plus a fixed-width buffer region, refer to FIG. 7A. This is based on the understanding that logos are printed to be visually conspicuous and readily recognizable. If the logo is printed along with Several extraneous black components intruding into its territory it becomes more difficult to distinguish the logo. An illustration of the region of interest concept is in referring to FIG. 6A where the difference image in FIG. 6A returns a good match because the jutting tip of the extraneous component lies outside the region of interest and therefore does not contribute to the mismatch Score. Since logos and match regions can vary in size, it is necessary to normalize the mismatch count. In the preferred embodiment the match count is defined as: US 6,327,388 B1 1O match score=1-(imismatch count)/(number of pixels in the region of interest) So for each document image region that is fed into the bitwise compare module 38 from the adjusted bit pattern data Structure 36 a Score is generated corresponding to the respective match count. In the preferred embodiment a threshold match Score is used to discard match Scores that are too low. Also generated for each adjusted document image region are the coordinates of the matching region on the page, and the number of pixels that are matched. The above Set of match Score, coordinates, and number of pixels are associated with their adjusted document image region and are Stored in a ranked logo list database 40. From the foregoing it will be understood that the inven tion analyzes a document image for logo patterns and returns a ranked list of logos, each with a match Score that reflects the Systems confidence in the match. The invention matches logo images to document images by using connected com ponent analysis, and Subsequent data processing operations. A logo recognition System can be used for at least two classes of tasks. Given the document image the task may be to identify and recognize logos in the image. We shall call this the problem of document annotation. On the other hand, given a logo image we may have to find all documents in the database with the same logo on it. We can call this the problem of document retrieval. To illustrate the invention in operation, consider the examples illustrated in FIGS. 8 and 9. FIG. 8 illustrates using the invention to identify a logo within a document image. FIG. 9 illustrates using the invention to locate all documents in a database that contain the same logo. Logo images are Stored in a computer-readable memory as a logo bit pattern and as a predefined Set of parameters. The document image is Stored in a bitmap buffer. This document image is Stored in the form of a bitmap pattern. The System processes the document image by finding the black components in each document image via the con nected component module. For each black connected com ponent that is found, the connected component module calculates features Such as location, height and width of each component's bounding box and the area or number of black pixels in the component. Furthermore, the connected com ponent module also calculates the aspect ratio and mean density of each connected component. The connected components are then grouped according to region. The connected components belong to the same region if each connected component is within a Set distance from any other connected component in that Same region. The connected components and their corresponding param eters are then Stored in a parameter data structure where each member is grouped according to region. Following the connected component analysis, a compari Son module then compares the connected components and their corresponding parameters from the parameter data Structure to the predefined logo connected components and its corresponding predefined parameters that are Stored in the logo image database. For each region, the connected components are then arranged in decreasing order of area. Pairs of connected components are then picked, one each from the predefined logo and the document region. If there is a good match of aspect ratios and the mean densities between the connected components of a document region and a predefined logo then we store the logo bit pattern and its associated parameters with the document region and its associated parameters in a logo matched candidate data Structure. Since the document region can be a different size than the logo match candidate, the bit pattern from the document
13 7 region must be adjusted to match the Scale of the logo match candidate. Similarly, Since the bit pattern of the document region may be aligned differently than the logo match candidate, the bit pattern from the document region must be adjusted to match the alignment of the logo match candidate. For the bit pattern from the document region a Scaling factor is estimated and applied to the bit pattern of the document region So that the resulting Scale of the bit pattern of the document region matches that of the logo match candidate. Then, the bit pattern of the document region is anchored to match the alignment of the logo match candidate. After the bit pattern of the document region is Scaled and aligned the resultant adjusted bit pattern of the document region and the connected components of the document region are Stored in an adjusted bit pattern data structure. Thereafter, a bitwise comparison module treats the logo match candidate from the logo match candidate database as a template and examines how well the template matches the adjusted bit pattern of the document region at the Specified alignment. The two images are first aligned as Specified and a logical bitwise operation is performed to yield a difference image. Each non-zero pixel in the difference image repre Sents a point where the colors of the logo and the document images are different. In other words, each non-zero pixel corresponds to a pixel mismatch. A high number of mis matched pixels thus indicates a bad match. If desired, further refinement of the analysis can be performed by creating a region of interest around a Specified Zone inside the template thereby reducing false pixel mismatches. A match Score is calculated based on the number of mismatches that the comparison creates. The match Score is used to create a ranked logo list where for any given document image a list of all the logos found on the document are listed. While the invention has been described in its presently preferred embodiment, it will be understood that the inven tion is capable of certain modifications without departing from the Spirit of the invention as Set forth in the appended claims. What is claimed is: 1. A method for matching a bit pattern of a document image with a database of logo images Stored in a computer readable memory as a logo bit pattern and as a predefined Sets of parameters including parameters indicative of the shape and mean density of each logo image, comprising the Steps of: performing connected component analysis on the bit pattern of Said document image to identify at least one region of connected components within Said document image and to generate for Said region parameter data that includes a parameter indicative of shape and a parameter indicative of mean density; comparing Said parameters of Said region with Said parameters of Said database of logo images to identify a plurality of logo match candidates having associated logo bit patterns as Stored in Said database; Scaling and aligning at least one Said region to correspond to the size and skew of Said logo match candidates and to thereby generate a plurality of adjusted regions having corresponding adjusted bit patterns Such that the resulting Scale of the adjusted bit pattern matches that of the logo match candidates, and performing a bitwise comparison between the adjusted bit patterns of Said adjusted region and the bit patterns of Said logo match candidates to Select the best match and Store Said best match Selections in a ranked logo list database. US 6,327,388 B The method of claim 1 wherein said region is further defined by a minimum predetermined distance Separating each Said connected component. 3. The method of claim 1 wherein said connected com ponents of Said region of Said document further include a predetermined minimum size. 4. The method of claim 1 wherein Said region parameter data further includes location, height, width and area of Said connected component. 5. The method of claim 1 further comprising arranging each connected component by decreasing order of area. 6. The method of claim 1 wherein said comparison of said parameters of Said region and Said parameters of Said database of logo images further include comparing at least one parameter indicative of aspect ratio and Said parameter indicative of mean density. 7. The method of claim 1 further comprising a Scaling factor for Sizing Said logo match candidates. 8. The method of claim 7 wherein said scaling factor corresponds to a calculation utilizing the ratio of widths of Said region, the ratio of heights of Said region, and the Square root of the ratio of the number of black pixels in said connected component. 9. The method of claim 1 further including a region of interest within a fixed area that encompasses the Outermost black pixels of Said logo image So that Said adjusted region corresponds to Said region of interest. 10. The method of claim 1 wherein said best match corresponds to a calculation utilizing the mismatch count and the number of pixels in Said region of interest. 11. The method of claim 10 wherein said best match further includes a predetermined minimum threshold Score. 12. An apparatus for locating and identifying logos on document images, comprising: a computer readable memory for storing a database of logo images So that Said database consists of a logo bit pattern and a predefined set of parameters, a bitmap buffer for Storing Said document images So that said bitmap buffer consists of at least one bit pattern of Said document image; a connected component module connected to Said bitmap buffer for identifying at least one region of connected components within Said document image and to gen erate for Said region parameter data that includes a parameter indicative of shape and a parameter indica tive of mean density; a comparison module connected to Said parameter data and Said database of log images for comparing Said parameters of Said region with Said database of logo images to identify a plurality of logo match candidates having associated log bit patterns as Stored in Said database; a Scale and align module connected to Said plurality of logo match candidates and Said parameter data bit patterns for Scaling and aligning Said at least one region to correspond to the Size and skew of Said logo match candidates and to thereby generate a plurality of adjusted regions having corresponding bit patterns. Such that the resulting Scale of the adjusted bit pattern matches that of the logo match candidates, and a bitwise comparison connected to Said adjusted bit pattern data and Said logo match candidates for per forming a bitwise comparison between the adjusted bit patterns of Said adjusted region and the bit patterns of Said logo match candidates to Select the best match. 13. The apparatus of claim 1 wherein Said region is further defined by a minimum predetermined distance Separating each Said connected component.
14 9 14. The apparatus of claim 1 wherein Said connected components of Said region of Said document further include a predetermined minimum size. 15. The apparatus of claim 1 wherein Said region param eter data further includes location, height, width and area of Said connected component. 16. The apparatus of claim 1 further comprising arranging Said connected components and Said region parameter data associated with Said connected components by decreasing order of area. 17. The apparatus of claim 1 wherein Said comparison of Said parameters of Said region and Said parameters of Said database of logo images further includes at least one param eter indicative of aspect ratio and Said parameter indicative of mean density. 18. The apparatus of claim 1 further comprising a Scale factor for Sizing Said logo match candidates. US 6,327,388 B The apparatus of claim 18 wherein said scale factor corresponds to a calculation utilizing the ratio of widths of Said region, the ratio of heights of Said region, and the Square root of the ratio of the number of black pixels in said connected component. 20. The apparatus of claim 1 further including a region of interest within a fixed area that encompasses the Outermost black pixels of Said logo image So that Said adjusted region corresponds to Said region of interest. 21. The apparatus of claim 1 wherein said best match corresponds to a calculation utilizing the mismatch count and the number of pixels in Said region of interest. 22. The apparatus of claim 21 wherein Said best match further includes a predetermined minimum threshold Score.
15 UNITED STATES PATENT AND TRADEMARK OFFICE CERTIFICATE OF CORRECTION PATENT NO. : 6, Bl Page 1 of DATED : December 4, 2001 INVENTOR(S) : Jiangying Zhou et al. it is certified that error appears in the above-identified patent and that said Letters Patent is hereby corrected as shown below: Title page, Item 56 under References Cited, U.S. PATENT DOCUMENT 5,588,027 should be -- 5,588, Column 8 Line 47, "log" should be -- logo --. Line 50, "log" should be - logo --. Signed and Sealed this Twenty-eighth Day of May, 2002 Attesting Officer JAMESEROGAN Director of the United States Patent and Trademark Office
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,731,259 B2
 USOO6731259B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,731,259 B2 Yer et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 4, 2004 (54) DRIVING CIRCUIT OF A LIQUID CRYSTAL 6,121.950 A * 9/2000 Zavracky et al.... 34.5/101
USOO6731259B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,731,259 B2 Yer et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 4, 2004 (54) DRIVING CIRCUIT OF A LIQUID CRYSTAL 6,121.950 A * 9/2000 Zavracky et al.... 34.5/101
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,739,050 B2
 USOO773905OB2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,739,050 B2 Tatro (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 15, 2010 (54) SOFTWARE-BASED QUALITY CONTROL (56) References Cited ANALYSIS OF WELL LOG DATA U.S.
USOO773905OB2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,739,050 B2 Tatro (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 15, 2010 (54) SOFTWARE-BASED QUALITY CONTROL (56) References Cited ANALYSIS OF WELL LOG DATA U.S.
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,002,560 B2
 USOO700256OB2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,002,560 B2 Graham (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 21, 2006 (54) METHOD OF COMBINING DATA ENTRY OF 6,049,329 A * 4/2000 Zetts et al.... 345/179 HANDWRITTEN
USOO700256OB2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,002,560 B2 Graham (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 21, 2006 (54) METHOD OF COMBINING DATA ENTRY OF 6,049,329 A * 4/2000 Zetts et al.... 345/179 HANDWRITTEN
58 Field of Search /341,123, NEE"E", "E.
 USOO597.7975A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Mugura et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 2, 1999 54) ARRAY OF DISPLAYED GRAPHIC IMAGES 5,233,333 8/1993 Borsuk... 345/127 FOR ENABLING SELECTION
USOO597.7975A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Mugura et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 2, 1999 54) ARRAY OF DISPLAYED GRAPHIC IMAGES 5,233,333 8/1993 Borsuk... 345/127 FOR ENABLING SELECTION
III. United States Patent Patent Number: 5,748,253. Chatinsky et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 5, 1998
 III USO05748253A United States Patent 19 11 Patent Number: 5,748,253 Chatinsky et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 5, 1998 54 DIRECT KEYBOARD ACCESS TO WIDEO 5,001,473 3/1991 Ritter et al.... 340/825.52 EDTING
III USO05748253A United States Patent 19 11 Patent Number: 5,748,253 Chatinsky et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 5, 1998 54 DIRECT KEYBOARD ACCESS TO WIDEO 5,001,473 3/1991 Ritter et al.... 340/825.52 EDTING
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,199,163 B1
 USOO6199163B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,199,163 B1 Dumas et al. 45) Date of Patent: Mar. 6, 2001 9 (54) HARD DISK PASSWORD LOCK 5,231,662 * 7/1993 van Rumpt et al.... 380/9 5,283,828
USOO6199163B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,199,163 B1 Dumas et al. 45) Date of Patent: Mar. 6, 2001 9 (54) HARD DISK PASSWORD LOCK 5,231,662 * 7/1993 van Rumpt et al.... 380/9 5,283,828
231 age sins N3 : as a. (12) United States Patent US 8,194,335 B2. Jun. 5, (45) Date of Patent: (10) Patent No.
 USOO8194,335B2 (12) United States Patent Hsueh (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 8,194,335 B2 Jun. 5, 2012 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (51) (52) (58) OPTICAL LENS ON WAFER LEVEL AND RELATED
USOO8194,335B2 (12) United States Patent Hsueh (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 8,194,335 B2 Jun. 5, 2012 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (51) (52) (58) OPTICAL LENS ON WAFER LEVEL AND RELATED
SCSI routing table (90) and a SCSI to Fibre Channel routing table (92). The system receives a cross bus transfer of data
 US00604.1381A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 6,041,381 Hoese (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 21, 2000 54 FIBRE CHANNEL TO SCSI ADDRESSING OTHER PUBLICATIONS METHOD AND SYSTEM Hoese, Geoffrey B.,
US00604.1381A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 6,041,381 Hoese (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 21, 2000 54 FIBRE CHANNEL TO SCSI ADDRESSING OTHER PUBLICATIONS METHOD AND SYSTEM Hoese, Geoffrey B.,
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,467,088 B1
 USOO6467088B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,467,088 B1 alsafadi et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 15, 2002 (54) RECONFIGURATION MANAGER FOR WO WO9015394 6/1990... GO6F/15/46 CONTROLLING
USOO6467088B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,467,088 B1 alsafadi et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 15, 2002 (54) RECONFIGURATION MANAGER FOR WO WO9015394 6/1990... GO6F/15/46 CONTROLLING
United States Patent (19) Jones et al.
 United States Patent (19) Jones et al. 11 Patent Number: () Date of Patent: 4,764,129 Aug. 16, 1988 54 ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR ASSEMBLIES (75) Inventors: Brian Jones; Graeme S. Allan, both of Solihull, England
United States Patent (19) Jones et al. 11 Patent Number: () Date of Patent: 4,764,129 Aug. 16, 1988 54 ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR ASSEMBLIES (75) Inventors: Brian Jones; Graeme S. Allan, both of Solihull, England
US 7.663,338 B2. Feb. 16, (45) Date of Patent: (10) Patent No.: Guthrie et al. used to receive a USB bus voltage from the USB interface and (51)
 USOO7663338B2 (12) United States Patent Guthrie et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7.663,338 B2 Feb. 16, 2010 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (60) (51) (52) (58) (56) METHOD AND APPARATUS
USOO7663338B2 (12) United States Patent Guthrie et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7.663,338 B2 Feb. 16, 2010 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (60) (51) (52) (58) (56) METHOD AND APPARATUS
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1. Choi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 27, 2006
 US 20060090088A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0090088 A1 Choi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 27, 2006 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR Publication Classification
US 20060090088A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0090088 A1 Choi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 27, 2006 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR Publication Classification
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,208,340 B1. Amin et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 27, 2001
 USOO620834OB1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,208,340 B1 Amin et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 27, 2001 (54) GRAPHICAL USER INTERFACE 5,317,687 5/1994 Torres... 395/159 INCLUDING A DROP-DOWN
USOO620834OB1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,208,340 B1 Amin et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 27, 2001 (54) GRAPHICAL USER INTERFACE 5,317,687 5/1994 Torres... 395/159 INCLUDING A DROP-DOWN
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,657,548 B2. Dai (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 2, 2003
 USOO6657548B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,657,548 B2 Dai (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 2, 2003 (54) SYSTEMSTATUS LIGHT INDICATOR 6,501,897 B1 * 12/2002 German et al.... 385/134 DEVICE EMBEDDED
USOO6657548B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,657,548 B2 Dai (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 2, 2003 (54) SYSTEMSTATUS LIGHT INDICATOR 6,501,897 B1 * 12/2002 German et al.... 385/134 DEVICE EMBEDDED
-Gorse III IEEEEEEEEE OFF-TIM -17B is 12 L=y 3 14 KB/Mouse 16- DSP-CONT. United States Patent 19 Yoshida 0 T 1 O LEVEL I LEVEL 10
 United States Patent 19 Yoshida 54 DISPLAY CONTROL METHOD AND DISPLAY CONTROLAPPARATUSADAPTED TO PORTABLE DATA PROCESSING EQUIPMENT PROVIDED WITH A BATTERY. DRIVABLE FLAT PANEL DISPLAY 75) Inventor: Norio
United States Patent 19 Yoshida 54 DISPLAY CONTROL METHOD AND DISPLAY CONTROLAPPARATUSADAPTED TO PORTABLE DATA PROCESSING EQUIPMENT PROVIDED WITH A BATTERY. DRIVABLE FLAT PANEL DISPLAY 75) Inventor: Norio
(12) United States Patent
 US007107617B2 (12) United States Patent Hursey et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 12, 2006 (54) MALWARE SCANNING OF COMPRESSED COMPUTER S (75) Inventors: Nell John Hursey, Hertfordshire
US007107617B2 (12) United States Patent Hursey et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 12, 2006 (54) MALWARE SCANNING OF COMPRESSED COMPUTER S (75) Inventors: Nell John Hursey, Hertfordshire
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8.131,217 B2
 US008131217B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8.131,217 B2 Srinivasa et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 6, 2012 (54) IDENTIFICATION OF MAKE AND MODEL 2004/0266347 A1* 12/2004 Palin et al....
US008131217B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8.131,217 B2 Srinivasa et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 6, 2012 (54) IDENTIFICATION OF MAKE AND MODEL 2004/0266347 A1* 12/2004 Palin et al....
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,159,495 B2
 US0089495 B2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: Carter-Schwendler et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 17, 2012 (54) REMOTING SUB-PIXEL RESOLVED 6.2,671 B1* 6/2001 Peng et al.... 358,111 CHARACTERS 6,356,278
US0089495 B2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: Carter-Schwendler et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 17, 2012 (54) REMOTING SUB-PIXEL RESOLVED 6.2,671 B1* 6/2001 Peng et al.... 358,111 CHARACTERS 6,356,278
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 (19) United States US 2004O231004A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0231004 A1 Seo (43) Pub. Date: (54) HTTP BASED VIDEO STREAMING APPARATUS AND METHOD IN MOBILE COMMUNICATION
(19) United States US 2004O231004A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0231004 A1 Seo (43) Pub. Date: (54) HTTP BASED VIDEO STREAMING APPARATUS AND METHOD IN MOBILE COMMUNICATION
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7, B2
 USOO7941.543B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,941.543 B2 Moussallam et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 10, 2011 (54) SYSTEMAND METHOD FOR MIGRATING 2002/0169781 A1* 11/2002 Poole et al....
USOO7941.543B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,941.543 B2 Moussallam et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 10, 2011 (54) SYSTEMAND METHOD FOR MIGRATING 2002/0169781 A1* 11/2002 Poole et al....
(12) (10) Patent No.: US 7,330,395 B2. Ichijo (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 12, 2008
 United States Patent USOO7330395 B2 (12) (10) Patent No.: US 7,330,395 B2 Ichijo (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 12, 2008 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR 2002fOO67835 A1 6/2002 Vatter... 381.58 AUTOMATICALLY CALIBRATING
United States Patent USOO7330395 B2 (12) (10) Patent No.: US 7,330,395 B2 Ichijo (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 12, 2008 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR 2002fOO67835 A1 6/2002 Vatter... 381.58 AUTOMATICALLY CALIBRATING
(12) United States Patent
 USOO9729447B2 (12) United States Patent Wang et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9,729.447 B2 *Aug. 8, 2017 (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (63) (60) (51) (52)
USOO9729447B2 (12) United States Patent Wang et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9,729.447 B2 *Aug. 8, 2017 (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (63) (60) (51) (52)
Is more than one finger placed on touchpad surface?
 USOO776O189B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Cheston et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 20, 2010 (54) TOUCHPAD DIAGONAL SCROLLING 6,043,809 A 3/2000 Holehan 6,707.449 B2 3/2004 Hinckley et al.
USOO776O189B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Cheston et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 20, 2010 (54) TOUCHPAD DIAGONAL SCROLLING 6,043,809 A 3/2000 Holehan 6,707.449 B2 3/2004 Hinckley et al.
Wireless devices supports in a simple environment
 USOO8868690B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,868,690 B2 Tsao (45) Date of Patent: *Oct. 21, 2014 (54) SYSTEMAND METHOD FOR SUPPORT (52) U.S. Cl. (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (63)
USOO8868690B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,868,690 B2 Tsao (45) Date of Patent: *Oct. 21, 2014 (54) SYSTEMAND METHOD FOR SUPPORT (52) U.S. Cl. (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (63)
(10) Patent No.: US 8,169,449 B2 (56) 7,528,890 B2 * 2007/ A2 * 2009/ A1 * * cited by examiner
 111111 1111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111 US8169449B2 c12) United States Patent Turcotte et al. (1) Patent o.: US 8,169,449 B2 (45) Date of Patent: May 1, 212 (54) SYSTEM COMPOSITIG
111111 1111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111 US8169449B2 c12) United States Patent Turcotte et al. (1) Patent o.: US 8,169,449 B2 (45) Date of Patent: May 1, 212 (54) SYSTEM COMPOSITIG
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,172,601 B1. Wada et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 9, 2001
 USOO61726O1B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Wada et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 9, 2001 (54) THREE-DIMENSIONAL SCOPE SYSTEM 5,646,614 * 7/1997 Abersfelder et al.... 340/932.2 WITH A SINGLE
USOO61726O1B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Wada et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 9, 2001 (54) THREE-DIMENSIONAL SCOPE SYSTEM 5,646,614 * 7/1997 Abersfelder et al.... 340/932.2 WITH A SINGLE
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Matsuda USOO6211649B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 3, 2001 (54) USB CABLE AND METHOD FOR CHARGING BATTERY OF EXTERNAL APPARATUS BY USING USB CABLE (75) Inventor:
(12) United States Patent Matsuda USOO6211649B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 3, 2001 (54) USB CABLE AND METHOD FOR CHARGING BATTERY OF EXTERNAL APPARATUS BY USING USB CABLE (75) Inventor:
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Xiao US006663420B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 16, 2003 (54) ADAPTER FOR EXCHANGING DATA AND TRANSMITTING POWER BETWEEN PC AND PORTABLE DEVICE (75) Inventor: Hui
(12) United States Patent Xiao US006663420B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 16, 2003 (54) ADAPTER FOR EXCHANGING DATA AND TRANSMITTING POWER BETWEEN PC AND PORTABLE DEVICE (75) Inventor: Hui
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,377,725 B1
 USOO6377725B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Stevens et al. 45) Date of Patent: Apr. 23, 2002 9 (54) OPTICAL WAVELENGTH DIVISION 5,907,551 A * 5/1999 Nishio et al. MULTIPLEXED INTERCONNECT
USOO6377725B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Stevens et al. 45) Date of Patent: Apr. 23, 2002 9 (54) OPTICAL WAVELENGTH DIVISION 5,907,551 A * 5/1999 Nishio et al. MULTIPLEXED INTERCONNECT
336w 330 FPGA / 330 MW} Compgnenf _/14 / 38 US 7,774,801 B1. Aug. 10, 2010 (56) (10) Patent N0.: (45) Date of Patent: (12) United States Patent Fitkin
 US007774801B1 (12) United States Patent Fitkin (10) Patent N0.: (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 10, 2010 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (51) (52) (58) (56) CORBA FIELD PROGRAMMABLE GATE ARRAY/DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSOR
US007774801B1 (12) United States Patent Fitkin (10) Patent N0.: (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 10, 2010 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (51) (52) (58) (56) CORBA FIELD PROGRAMMABLE GATE ARRAY/DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSOR
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,199,058 B1
 USOO6199058B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,199,058 B1 Wong et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 6, 2001 (54) REPORT SERVER CACHING 5,168,444 12/1992 Cukor et al.... 705/1 5,625,818 4/1997
USOO6199058B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,199,058 B1 Wong et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 6, 2001 (54) REPORT SERVER CACHING 5,168,444 12/1992 Cukor et al.... 705/1 5,625,818 4/1997
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent USOO6941277B2 (10) Patent No.: Imag0 (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 6, 2005 (54) METHODS AND SYSTEMS FOR PROVIDING (56) References Cited ONLINE INFORMATION FOR NETWORKED DEVICES U.S.
(12) United States Patent USOO6941277B2 (10) Patent No.: Imag0 (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 6, 2005 (54) METHODS AND SYSTEMS FOR PROVIDING (56) References Cited ONLINE INFORMATION FOR NETWORKED DEVICES U.S.
(12) (10) Patent No.: US 7,103,736 B2. Sachs (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 5, 2006
 United States Patent US007103736B2 (12) (10) Patent No.: Sachs (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 5, 2006 (54) SYSTEM FOR REPAIR OF ROM 5.325,504 A * 6/1994 Tipley et al.... T11/128 PROGRAMMING ERRORS ORDEFECTS
United States Patent US007103736B2 (12) (10) Patent No.: Sachs (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 5, 2006 (54) SYSTEM FOR REPAIR OF ROM 5.325,504 A * 6/1994 Tipley et al.... T11/128 PROGRAMMING ERRORS ORDEFECTS
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent US007 140922B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,140,922 B2 Lulu et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 28, 2006 (54) MULTI-OUTLET AC/DC ADAPTER (56) References Cited (75) Inventors: Daniel V.
(12) United States Patent US007 140922B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,140,922 B2 Lulu et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 28, 2006 (54) MULTI-OUTLET AC/DC ADAPTER (56) References Cited (75) Inventors: Daniel V.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States US 20110149932A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0149932 A1 KM et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) ZIGBEE GATEWAY AND MESSAGE Publication Classification IDENTIFICATION
(19) United States US 20110149932A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0149932 A1 KM et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) ZIGBEE GATEWAY AND MESSAGE Publication Classification IDENTIFICATION
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7, B2
 USOO7561411 B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,561.411 B2 Johnson, Jr. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 14, 2009 (54) UNINTERRUPTIBLE POWER DISTRIBUTION 7,400,066 B2 * 7/2008 Tassitino et al....
USOO7561411 B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,561.411 B2 Johnson, Jr. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 14, 2009 (54) UNINTERRUPTIBLE POWER DISTRIBUTION 7,400,066 B2 * 7/2008 Tassitino et al....
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,399,323 B1
 US0093.99323B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Lu et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 26, 2016 (54) THREE-DIMENSIONAL PRINTING USPC... 425/470; 264/401, 497, 212, 308 STRUCTURE See application
US0093.99323B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Lu et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 26, 2016 (54) THREE-DIMENSIONAL PRINTING USPC... 425/470; 264/401, 497, 212, 308 STRUCTURE See application
US A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 6,058,048 KWOn (45) Date of Patent: May 2, 2000
 US006058048A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 6,058,048 KWOn (45) Date of Patent: May 2, 2000 54) FLASH MEMORY DEVICE USED ASA 56) References Cited BOOT-UP MEMORY IN A COMPUTER SYSTEM U.S. PATENT
US006058048A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 6,058,048 KWOn (45) Date of Patent: May 2, 2000 54) FLASH MEMORY DEVICE USED ASA 56) References Cited BOOT-UP MEMORY IN A COMPUTER SYSTEM U.S. PATENT
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0317029 A1 TASAK et al. US 20080317029A1 (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 25, 2008 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (60) UNICAST/MULTICAST SYSTEM
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0317029 A1 TASAK et al. US 20080317029A1 (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 25, 2008 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (60) UNICAST/MULTICAST SYSTEM
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent USOO7506087B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,506,087 B2 H0 et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 17, 2009 (54) METHOD FOR CONFIGURING A (56) References Cited PERPHERAL COMPONENT INTERCONNECT
(12) United States Patent USOO7506087B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,506,087 B2 H0 et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 17, 2009 (54) METHOD FOR CONFIGURING A (56) References Cited PERPHERAL COMPONENT INTERCONNECT
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent USOO7366822B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,366,822 B2 KWalk et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 29, 2008 (54) SEMICONDUCTOR MEMORY DEVICE (56) References Cited CAPABLE OF READING AND WRITING
(12) United States Patent USOO7366822B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,366,822 B2 KWalk et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 29, 2008 (54) SEMICONDUCTOR MEMORY DEVICE (56) References Cited CAPABLE OF READING AND WRITING
31553, ,660, EEE,
 USOO65494OOB1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Medin et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 15, 2003 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR QUICKLY 5,301,346 A 4/1994 Notarianni et al.... 361/686 CONNECTING A
USOO65494OOB1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Medin et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 15, 2003 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR QUICKLY 5,301,346 A 4/1994 Notarianni et al.... 361/686 CONNECTING A
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,253,777 B2
 US008253777B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,253,777 B2 Lin (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 28, 2012 (54) PANORAMIC CAMERA WITH A PLURALITY 7,424,218 B2 * 9/2008 Baudisch et al.... 396,322 OF
US008253777B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,253,777 B2 Lin (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 28, 2012 (54) PANORAMIC CAMERA WITH A PLURALITY 7,424,218 B2 * 9/2008 Baudisch et al.... 396,322 OF
(73) Assignee: Nokia Networks Oy (FI) Wii: 12: 'We (*) Notice: Subject to any disclaimer, the term of this * cited by examiner
 USOO6246871B1 12) United States Patent 10) Patent No.: US 6,246,871 B1 9 9 Ala-Laurila (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 12, 2001 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR 5,941,946 8/1999 Baldwin et al.. PROVIDING ACCESS
USOO6246871B1 12) United States Patent 10) Patent No.: US 6,246,871 B1 9 9 Ala-Laurila (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 12, 2001 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR 5,941,946 8/1999 Baldwin et al.. PROVIDING ACCESS
(12) United States Patent
 USOO9442667B2 (12) United States Patent Drosch (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9.442,667 B2 Sep. 13, 2016 (54) (71) (72) (*) (21) (22) (86) (87) (65) (60) (30) (51) (52) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR
USOO9442667B2 (12) United States Patent Drosch (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9.442,667 B2 Sep. 13, 2016 (54) (71) (72) (*) (21) (22) (86) (87) (65) (60) (30) (51) (52) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 US 20160364902A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0364902 A1 Hong et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) HIGH QUALITY EMBEDDED GRAPHICS (52) U.S. Cl. FOR REMOTE VISUALIZATION
US 20160364902A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0364902 A1 Hong et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) HIGH QUALITY EMBEDDED GRAPHICS (52) U.S. Cl. FOR REMOTE VISUALIZATION
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent N0.: US 6,446,174 B1 Dow (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 3, 2002
 US006446174B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent N0.: US 6,446,174 B1 Dow (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 3, 2002 (54) COMPUTER SYSTEM WITH DRAM BUS 5,969,728 A 10/1999 Dye et al...... 345/515 6,003,121 A
US006446174B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent N0.: US 6,446,174 B1 Dow (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 3, 2002 (54) COMPUTER SYSTEM WITH DRAM BUS 5,969,728 A 10/1999 Dye et al...... 345/515 6,003,121 A
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,446,087 B1. Lai (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 3, 2002
 USOO6446087B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Lai (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 3, 2002 (54) SYSTEM FOR MAINTAINING THE (74) Attorney, Agent, or Firm-Patton Boggs, LLP INTEGRITY OF APPLICATION DATA
USOO6446087B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Lai (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 3, 2002 (54) SYSTEM FOR MAINTAINING THE (74) Attorney, Agent, or Firm-Patton Boggs, LLP INTEGRITY OF APPLICATION DATA
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,917,832 B2
 US007.917832B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,917,832 B2 Hsieh et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 29, 2011 (54) APPARATUS FOR IMPROVING DATA 6,725,321 B1 4/2004 Sinclair et al.... T11 103
US007.917832B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,917,832 B2 Hsieh et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 29, 2011 (54) APPARATUS FOR IMPROVING DATA 6,725,321 B1 4/2004 Sinclair et al.... T11 103
6,000,859 Dec. 14, 1999
 United States Patent [19] Mulcahy et al. US006000859A [11] Patent Number: [45] Date of Patent: 6,000,859 Dec. 14, 1999 [54] CAMERA AND FLASH UNIT POSITIONING DEVICE [76] Inventors: Timothy G. Mulcahy,
United States Patent [19] Mulcahy et al. US006000859A [11] Patent Number: [45] Date of Patent: 6,000,859 Dec. 14, 1999 [54] CAMERA AND FLASH UNIT POSITIONING DEVICE [76] Inventors: Timothy G. Mulcahy,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 20050281269A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0281269 A1 Choi (43) Pub. Date: (54) MOBILE TELECOMMUNICATION SYSTEM (30) Foreign Application Priority Data
(19) United States US 20050281269A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0281269 A1 Choi (43) Pub. Date: (54) MOBILE TELECOMMUNICATION SYSTEM (30) Foreign Application Priority Data
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,642,750 B1
 USOO664275OB1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,642,750 B1 Egan (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 4, 2003 (54) SEQUENCING CIRCUIT FOR APPLYING A 5,886,561. A 3/1999 Eitan et al.... 327/408 HIGHEST
USOO664275OB1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,642,750 B1 Egan (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 4, 2003 (54) SEQUENCING CIRCUIT FOR APPLYING A 5,886,561. A 3/1999 Eitan et al.... 327/408 HIGHEST
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,640,289 B2
 USOO7640289B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Chen (45) Date of Patent: *Dec. 29, 2009 (54) INTELLIGENT COMPUTER SWITCH 6,388,658 B1 5/2002 Ahern et al. 6,567,869 B2 5/2003 Shirley (75) Inventor:
USOO7640289B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Chen (45) Date of Patent: *Dec. 29, 2009 (54) INTELLIGENT COMPUTER SWITCH 6,388,658 B1 5/2002 Ahern et al. 6,567,869 B2 5/2003 Shirley (75) Inventor:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1. Lin et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 30, 2004
 (19) United States US 20040189577A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Lin et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 30, 2004 (54) PIXEL CIRCUIT FOR LIQUID CRYSTAL (30) Foreign Application Priority Data
(19) United States US 20040189577A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Lin et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 30, 2004 (54) PIXEL CIRCUIT FOR LIQUID CRYSTAL (30) Foreign Application Priority Data
US 9,531,657 B2. 1 of 8. I lllll llllllll Ill lllll lllll lllll lllll lllll
 I lllll llllllll Ill lllll lllll lllll lllll lllll 111111111111111111111111111111111 US009531657B2 c12) United States Patent Ratnakar US 9,531,657 B2 (IO) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: *Dec. 27, 2016
I lllll llllllll Ill lllll lllll lllll lllll lllll 111111111111111111111111111111111 US009531657B2 c12) United States Patent Ratnakar US 9,531,657 B2 (IO) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: *Dec. 27, 2016
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,643,021 B2. Pai et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 5, 2010
 USOO7643021B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,643,021 B2 Pai et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 5, 2010 (54) DRIVING SYSTEMAND DRIVING METHOD 6,215,468 B1 * 4/2001 Van Mourik... 345 605 FORMOTION
USOO7643021B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,643,021 B2 Pai et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 5, 2010 (54) DRIVING SYSTEMAND DRIVING METHOD 6,215,468 B1 * 4/2001 Van Mourik... 345 605 FORMOTION
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 (19) United States US 2003.0109252A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0109252 A1 Prentice et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 12, 2003 (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD OF CODEC EMPLOYMENT INA CELLULAR
(19) United States US 2003.0109252A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0109252 A1 Prentice et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 12, 2003 (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD OF CODEC EMPLOYMENT INA CELLULAR
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 20050044179A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0044179 A1 Hunter (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 24, 2005 (54) AUTOMATIC ACCESS OF INTERNET CONTENT WITH A CAMERA-ENABLED
(19) United States US 20050044179A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0044179 A1 Hunter (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 24, 2005 (54) AUTOMATIC ACCESS OF INTERNET CONTENT WITH A CAMERA-ENABLED
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent USOO731.9457B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,319.457 B2 Lin et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 15, 2008 (54) METHOD OF SCROLLING WINDOW (56) References Cited SCREEN BY MEANS OF CONTROLLING
(12) United States Patent USOO731.9457B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,319.457 B2 Lin et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 15, 2008 (54) METHOD OF SCROLLING WINDOW (56) References Cited SCREEN BY MEANS OF CONTROLLING
wo W /1997 * cited by examiner
 111111 1111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111 US006963980Bl (12) United States Patent Matts son (10) Patent No.: US 6,963,980 Bl (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 8, 2005 (54) COMBINED HARDWARE
111111 1111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111 US006963980Bl (12) United States Patent Matts son (10) Patent No.: US 6,963,980 Bl (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 8, 2005 (54) COMBINED HARDWARE
is is a self United States Patent (19) Ogawa et al. I75 Inventors: Takashi Ogawa, Yokohama; Masaaki 13 Claims, 6 Drawing Sheets ) -
 United States Patent (19) Ogawa et al. 54 DISK CARTRIDGE DRVNGAPPARATUS I75 Inventors: Takashi Ogawa, Yokohama; Masaaki Sofue, Hadano: Hideo Inuzuka, Yokohama, all of Japan 73 Assignee: Ricoh Company,
United States Patent (19) Ogawa et al. 54 DISK CARTRIDGE DRVNGAPPARATUS I75 Inventors: Takashi Ogawa, Yokohama; Masaaki Sofue, Hadano: Hideo Inuzuka, Yokohama, all of Japan 73 Assignee: Ricoh Company,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States US 20110239111A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0239111A1 GROVER (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 29, 2011 (54) SPELL CHECKER INTERFACE (52) U.S. Cl.... 715/257; 715/764;
(19) United States US 20110239111A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0239111A1 GROVER (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 29, 2011 (54) SPELL CHECKER INTERFACE (52) U.S. Cl.... 715/257; 715/764;
United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,509,092 Hirayama et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 16, 1996
 III US005509092A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,509,092 Hirayama et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 16, 1996 54 METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR 5,093,868 3/1992 Tanaka et al.... 382/9 GENERATING
III US005509092A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,509,092 Hirayama et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 16, 1996 54 METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR 5,093,868 3/1992 Tanaka et al.... 382/9 GENERATING
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,418,453 B1
 USOO6418453B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Kraft et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 9, 2002 (54) NETWORK REPOSITORY SERVICE FOR 6.295,529 B1 * 9/2001 Corston-Oliver et al.... 707/3 EFFICIENT
USOO6418453B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Kraft et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 9, 2002 (54) NETWORK REPOSITORY SERVICE FOR 6.295,529 B1 * 9/2001 Corston-Oliver et al.... 707/3 EFFICIENT
(12) (10) Patent N0.: US 6,879,518 B1. Curry (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 12, 2005
 United States Patent US006879518B1 (12) (10) Patent N0.: Curry (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 12, 2005 (54) EMBEDDED MEMORY WITH SECURITY 6,076,149 A * 6/2000 Usami et a1...... 711/163 ROW LOCK PROTECTION 6,088,262
United States Patent US006879518B1 (12) (10) Patent N0.: Curry (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 12, 2005 (54) EMBEDDED MEMORY WITH SECURITY 6,076,149 A * 6/2000 Usami et a1...... 711/163 ROW LOCK PROTECTION 6,088,262
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0024764 A1 LOu et al. US 2013 OO24764A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 24, 2013 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (86) (30) METHOD FORTRANSFORMINGWEB
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0024764 A1 LOu et al. US 2013 OO24764A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 24, 2013 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (86) (30) METHOD FORTRANSFORMINGWEB
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Yadav et al. USOO6868062B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Mar., 2005 (54) MANAGING DATA TRAFFICON MULTIPLE PORTS (75) Inventors: Satyendra Yadav, Portland, OR (US); Puqi
(12) United States Patent Yadav et al. USOO6868062B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Mar., 2005 (54) MANAGING DATA TRAFFICON MULTIPLE PORTS (75) Inventors: Satyendra Yadav, Portland, OR (US); Puqi
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States US 2014025631 7A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0256317 A1 ZHAO et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (63) (30) METHOD, APPARATUS, AND SYSTEM
(19) United States US 2014025631 7A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0256317 A1 ZHAO et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (63) (30) METHOD, APPARATUS, AND SYSTEM
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States US 2016037 1322A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0371322 A1 GUNTI et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 22, 2016 (54) EFFICIENT MANAGEMENT OF LARGE (52) U.S. Cl. NUMBER
(19) United States US 2016037 1322A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0371322 A1 GUNTI et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 22, 2016 (54) EFFICIENT MANAGEMENT OF LARGE (52) U.S. Cl. NUMBER
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1. Hsu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 26, 2012
 US 20120023517A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0023517 A1 Hsu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 26, 2012 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR MEASURING AN INTERNET PROTOCOL
US 20120023517A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0023517 A1 Hsu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 26, 2012 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR MEASURING AN INTERNET PROTOCOL
(12) (10) Patent No.: US 7,017,055 B1. H0 (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 21, 2006
 United States Patent USOO701.7055B1 (12) (10) Patent No.: H0 (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 21, 2006 (54) HUB THAT CAN SUPPLY POWER FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS ACTIVELY JP 20020945.45 A * 3/2002 : (75) Inventor:
United States Patent USOO701.7055B1 (12) (10) Patent No.: H0 (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 21, 2006 (54) HUB THAT CAN SUPPLY POWER FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS ACTIVELY JP 20020945.45 A * 3/2002 : (75) Inventor:
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7423,692 B2
 USOO7423692B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7423,692 B2 Chen (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 9, 2008 (54) DE-INTERLACE METHOD AND METHOD 6,930,729 B2 * 8/2005 Min... 348/607 FOR GENERATING DE-INTERLACE
USOO7423692B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7423,692 B2 Chen (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 9, 2008 (54) DE-INTERLACE METHOD AND METHOD 6,930,729 B2 * 8/2005 Min... 348/607 FOR GENERATING DE-INTERLACE
US A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 6,055,373 McElroy et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 25, 2000
 US006055373A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 6,055,373 McElroy et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 25, 2000 54) COMPUTER SYSTEM INCLUDING A 5,291,614 3/1994 Baker et al.... 395/800 DIGITAL SIGNAL
US006055373A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 6,055,373 McElroy et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 25, 2000 54) COMPUTER SYSTEM INCLUDING A 5,291,614 3/1994 Baker et al.... 395/800 DIGITAL SIGNAL
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,845,158 B2
 USOO684.5158B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,845,158 B2 KOester et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 18, 2005 (54) RETRACTABLE-REMOVABLE HEADPHONE 5,136,446 A 8/1992 Yamamoto et al. MODULE
USOO684.5158B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,845,158 B2 KOester et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 18, 2005 (54) RETRACTABLE-REMOVABLE HEADPHONE 5,136,446 A 8/1992 Yamamoto et al. MODULE
(12) (10) Patent No.: US 7.263,017 B2. VOShe (45) Date of Patent: *Aug. 28, 2007
 United States Patent USOO7263017B2 (12) (10) Patent No.: US 7.263,017 B2 VOShe (45) Date of Patent: *Aug. 28, 2007 (54) AC SENSING FOR A RESISTIVE MEMORY 5,881,007 A 3/1999 Jeong et al. 6,226,222 B1 5,
United States Patent USOO7263017B2 (12) (10) Patent No.: US 7.263,017 B2 VOShe (45) Date of Patent: *Aug. 28, 2007 (54) AC SENSING FOR A RESISTIVE MEMORY 5,881,007 A 3/1999 Jeong et al. 6,226,222 B1 5,
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Beck et al. USOO6842611B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 11, 2005 (54) RECEIVED DATA PROCESSING METHOD IN COMMUNICATION DEVICE FOR SUPPORTING WIRELESS COMMUNICATION
(12) United States Patent Beck et al. USOO6842611B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 11, 2005 (54) RECEIVED DATA PROCESSING METHOD IN COMMUNICATION DEVICE FOR SUPPORTING WIRELESS COMMUNICATION
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States US 2008.0036860A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/003.6860 A1 Addy (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 14, 2008 (54) PTZ PRESETS CONTROL ANALYTIUCS CONFIGURATION (76) Inventor:
(19) United States US 2008.0036860A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/003.6860 A1 Addy (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 14, 2008 (54) PTZ PRESETS CONTROL ANALYTIUCS CONFIGURATION (76) Inventor:
HLR/HLR-T. (12) United States Patent US 8,331,990 B2. Dec. 11, (45) Date of Patent: AUCIAUC-T. (10) Patent No.:
 USOO8331990B2 (12) United States Patent LarssOn (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 11, 2012 (54) METHOD FORACTIVATING SIM CARDS (75) Inventor: Thomas Larsson, Alvsjo (SE) (73) Assignee: Giesecke
USOO8331990B2 (12) United States Patent LarssOn (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 11, 2012 (54) METHOD FORACTIVATING SIM CARDS (75) Inventor: Thomas Larsson, Alvsjo (SE) (73) Assignee: Giesecke
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1. Zhou et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 29, 2006
 US 2006O1394.94A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/01394.94 A1 Zhou et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 29, 2006 (54) METHOD OF TEMPORAL NOISE (52) U.S. Cl.... 348/607;
US 2006O1394.94A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/01394.94 A1 Zhou et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 29, 2006 (54) METHOD OF TEMPORAL NOISE (52) U.S. Cl.... 348/607;
(12) (10) Patent No.: US 7, B2. Peng (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 20, 2007
 United States Patent US007194291B2 (12) (10) Patent No.: US 7,194.291 B2 Peng (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 20, 2007 (54) PROTECTIVE MASK OF MOBILE PHONE 6,591,088 B1* 7/2003 Watanabe... 455/90.3 6,594,472
United States Patent US007194291B2 (12) (10) Patent No.: US 7,194.291 B2 Peng (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 20, 2007 (54) PROTECTIVE MASK OF MOBILE PHONE 6,591,088 B1* 7/2003 Watanabe... 455/90.3 6,594,472
Gammalcode. Frame 1, Frame 2. drive signal. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1. Timing code.
 (19) United States US 20160104.405A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0104405 A1 Fang et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 14, 2016 (54) DRIVE CIRCUIT AND DISPLAY DEVICE (71) Applicant:
(19) United States US 20160104.405A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0104405 A1 Fang et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 14, 2016 (54) DRIVE CIRCUIT AND DISPLAY DEVICE (71) Applicant:
(12) United States Patent
 USOO7370164B1 (12) United States Patent Nagarkar et al. (54) BACKUP OF VIRTUAL MACHINES FROM THE BASE MACHINE (75) Inventors: Kuldeep Sureshrao Nagarkar, Pune (IN); Sinh Dang Nguyen, Eden Prairie, MN (US);
USOO7370164B1 (12) United States Patent Nagarkar et al. (54) BACKUP OF VIRTUAL MACHINES FROM THE BASE MACHINE (75) Inventors: Kuldeep Sureshrao Nagarkar, Pune (IN); Sinh Dang Nguyen, Eden Prairie, MN (US);
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9.295,288 B1
 US00929.5288B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9.295,288 B1 Goff (45) Date of Patent: *Mar. 29, 2016 (54) POCKET BRASYSTEM 4,263,678 A * 4/1981 Off... 2.247 4,699,144. A * 10/1987 Sherwood...
US00929.5288B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9.295,288 B1 Goff (45) Date of Patent: *Mar. 29, 2016 (54) POCKET BRASYSTEM 4,263,678 A * 4/1981 Off... 2.247 4,699,144. A * 10/1987 Sherwood...
Accot (43) Pub. Date: May 5, (54) SPIRAL SCROLLBAR (52) U.S. Cl /772; 715/786; 715/856;
 (19) United States US 20050097.474A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0097.474A1 Accot (43) Pub. Date: (54) SPIRAL SCROLLBAR (52) U.S. Cl.... 715/772; 715/786; 715/856; 715/863
(19) United States US 20050097.474A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0097.474A1 Accot (43) Pub. Date: (54) SPIRAL SCROLLBAR (52) U.S. Cl.... 715/772; 715/786; 715/856; 715/863
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Ramaswamy USOO6480717B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 12, 2002 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (51) (52) (58) (56) TUNNELING OF NON-GSM SIGNALNG MESSAGES IN A GSM BASED
(12) United States Patent Ramaswamy USOO6480717B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 12, 2002 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (51) (52) (58) (56) TUNNELING OF NON-GSM SIGNALNG MESSAGES IN A GSM BASED
/ client computer. \ single sign-on. application program server (AP) network. server (SS0) (12) United States Patent Hsieh et a].
![/ client computer. \ single sign-on. application program server (AP) network. server (SS0) (12) United States Patent Hsieh et a]. / client computer. \ single sign-on. application program server (AP) network. server (SS0) (12) United States Patent Hsieh et a].](/thumbs/90/103929709.jpg) US007278155B2 (12) United States Patent Hsieh et a]. (10) Patent N0.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,278,155 B2 Oct. 2, 2007 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (30) Foreign Application Priority Data Oct. 22,
US007278155B2 (12) United States Patent Hsieh et a]. (10) Patent N0.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,278,155 B2 Oct. 2, 2007 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (30) Foreign Application Priority Data Oct. 22,
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,526,272 B1
 USOO6526272B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Bansal et al. (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 25, 2003 (54) REDUCING CALLING COSTS FOR 6,167,250 A * 12/2000 Rahman et al... 455/408 WIRELESS PHONES USING
USOO6526272B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Bansal et al. (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 25, 2003 (54) REDUCING CALLING COSTS FOR 6,167,250 A * 12/2000 Rahman et al... 455/408 WIRELESS PHONES USING
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,263,771 B1
 USOO6263771B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,263,771 B1 Strauch (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 24, 2001 (54) FORCE TRANSMISSIONSTRUCTURE 5,873,290 2/1999 Chaconas... 81/436 ESPECIALLY FOR A
USOO6263771B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,263,771 B1 Strauch (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 24, 2001 (54) FORCE TRANSMISSIONSTRUCTURE 5,873,290 2/1999 Chaconas... 81/436 ESPECIALLY FOR A
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Margalit et al. USOO6554621B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 29, 2003 (54) CABLE APPARATUS (75) Inventors: Yanki Margalit, Ramat Gan (IL); Dany Margalit, Ramat Gan
(12) United States Patent Margalit et al. USOO6554621B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 29, 2003 (54) CABLE APPARATUS (75) Inventors: Yanki Margalit, Ramat Gan (IL); Dany Margalit, Ramat Gan
(10) Patent No.: US 8,358,981 Bl. (56) References Cited
 111111 1111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111 US008358981Bl c12) United States Patent Gitlin et al. (10) Patent No.: US 8,358,981 Bl (45) Date of Patent: Jan.22,2013 (54) MINIMALLY
111111 1111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111 US008358981Bl c12) United States Patent Gitlin et al. (10) Patent No.: US 8,358,981 Bl (45) Date of Patent: Jan.22,2013 (54) MINIMALLY
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1. (51) Int. Cl. (52) U.S. Cl COMMUNICATIONS
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0036568 A1 HWANG US 2015.0036568A1 (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 5, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONSTERMINAL
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0036568 A1 HWANG US 2015.0036568A1 (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 5, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONSTERMINAL
(12) (10) Patent No.: US 7,017,113 B2. Bourbakis et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 21, 2006
 United States Patent USOO7017113B2 (12) (10) Patent No.: Bourbakis et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 21, 2006 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR 6,275,610 B1* 8/2001 Hall et al.... 382/18O REMOVING REDUNDANT
United States Patent USOO7017113B2 (12) (10) Patent No.: Bourbakis et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 21, 2006 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR 6,275,610 B1* 8/2001 Hall et al.... 382/18O REMOVING REDUNDANT
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States US 2008.0068375A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0068375 A1 Min et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 20, 2008 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR EARLY Z (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 2008.0068375A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0068375 A1 Min et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 20, 2008 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR EARLY Z (30) Foreign Application
(FSN JSO (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1. (19) United States
 (19) United States US 2005O146349A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0146349 A1 Lai et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 7, 2005 (54) TESTINGAPPARATUS FOR FLAT-PANEL DISPLAY (76) Inventors:
(19) United States US 2005O146349A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0146349 A1 Lai et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 7, 2005 (54) TESTINGAPPARATUS FOR FLAT-PANEL DISPLAY (76) Inventors:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 US 2016O128237A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0128237 A1 SZEREMETA (43) Pub. Date: May 5, 2016 (54) SERVER WITH STORAGE DRIVE COOLING (52) U.S. Cl. SYSTEM
US 2016O128237A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0128237 A1 SZEREMETA (43) Pub. Date: May 5, 2016 (54) SERVER WITH STORAGE DRIVE COOLING (52) U.S. Cl. SYSTEM
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Priddy et al. 54 75 (73 21 22 (51) (52) (58) (56) DYNAMICALLY WARIABLEMACHINE READABLE BINARY CODE AND METHOD FOR READING AND PRODUCING THEREOF - - - Dennis G. Priddy, Safety
United States Patent (19) Priddy et al. 54 75 (73 21 22 (51) (52) (58) (56) DYNAMICALLY WARIABLEMACHINE READABLE BINARY CODE AND METHOD FOR READING AND PRODUCING THEREOF - - - Dennis G. Priddy, Safety
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,181,053 B2
 US007 181053B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,181,053 B2 Wang et al. (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 20, 2007 (54) USB DRIVE MASS STORAGE DEVICE WITH 6,886,104 B1 * 4/2005 McClurg et al....
US007 181053B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,181,053 B2 Wang et al. (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 20, 2007 (54) USB DRIVE MASS STORAGE DEVICE WITH 6,886,104 B1 * 4/2005 McClurg et al....
(12) United States Patent
 US00795391 OB2 (12) United States Patent Kakish (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: May 31, 2011 (54) ALL-IN-ONE PERSONAL COMPUTER WITH EXTERNAL VIDEO INPUT (75) Inventor: Musa Ibrahim Kakish, Anaheim,
US00795391 OB2 (12) United States Patent Kakish (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: May 31, 2011 (54) ALL-IN-ONE PERSONAL COMPUTER WITH EXTERNAL VIDEO INPUT (75) Inventor: Musa Ibrahim Kakish, Anaheim,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005O125217A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0125217 A1 MaZOr (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 9, 2005 (54) SERVER-BASED SPELL CHECK ENGINE (52) U.S. Cl.... 704/1
(19) United States US 2005O125217A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0125217 A1 MaZOr (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 9, 2005 (54) SERVER-BASED SPELL CHECK ENGINE (52) U.S. Cl.... 704/1
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,237,112 B1
 USOO62371.12B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Yo0 et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 22, 2001 (54) SCSI DEVICE AVAILABLE FOR BREAKDOWN PREDICTION AND 5,966,510 * 10/1999 Carbonneau et al.... 714/44
USOO62371.12B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Yo0 et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 22, 2001 (54) SCSI DEVICE AVAILABLE FOR BREAKDOWN PREDICTION AND 5,966,510 * 10/1999 Carbonneau et al.... 714/44
