Generation of a Disparity Map Using Piecewise Linear Transformation
|
|
|
- Emily Sanders
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Proceedings of the 5th WSEAS Int. Conf. on COMPUTATIONAL INTELLIGENCE, MAN-MACHINE SYSTEMS AND CYBERNETICS, Venice, Italy, November 2-22, 26 4 Generation of a Disparity Map Using Piecewise Linear Transformation HYEJIN KIM, JAEWAN CHOI, HOWOOK CHANG, KIYUN YU School of Civil, Urban & Geo-System Engineering Seoul National University Shinrim-Dong, Gwana-Ku, Seoul KOREA Abstract: - The generation of a disparity map usually requires a pair of precisely rectified stereo images, which implies that the images have epipolar geometry. In many practical cases, it is not easy to obtain a rectified stereo pair without using specialized stereo camera systems. We have proposed a new approach for generating a disparity map from a random stereo pair, called a segment- based piecewise linear transformation. The basic concept relies on the fact that displacements from piecewise image to image registration approximate to the disparity. Using this approach, segmentation of the left image is carried out first, followed by extraction of conjugate points from the stereo pair. Finally, a set of linear transformation functions is determined using least squares method. By applying these functions, the displacement for each pixel is calculated to allow for the generation of a disparity map. To estimate the quality of the resulting disparity map, two stereo anaglyphs, one from the disparity map and the other from the original stereo pair, were produced and compared visually. The results show that the disparity map wors well on both uniform and slanted disparity surfaces. An advantage of this approach is that it does not necessarily require stereo rectification, and that it is applicable to any set of stereo images that are not in epipolar geometry. Key-Words: - Disparity map, Piecewise linear transformation, Segmentation, Mean-shift algorithm, Conjugate points, SIFT detector, Anaglyph 1 Introduction Generation of disparity maps is one of the most active research topics in computer vision. The disparity indicates the difference in location of the conjugate pixels from a pair of stereo images, and it is represented as an inverse depth. Generating a disparity map implies solving the many problems that occur in textureless regions, disparity discontinuous boundaries, and occluded areas. Therefore, many techniques have been developed, and the major part of previous related wors has been devoted to local window based algorithms, which have estimated the disparity at a given pixel, only depending on its intensity within a finite neighboring window [8, 13]. Recently, global algorithms using various energy minimization techniques, such as graph cuts, have attracted much attention [1, 7, 9, 12]. Regardless of the algorithms introduced in previous research efforts, there has been the assumption that precise rectified stereo images are available. This implies that the images are in epipolar geometry. However, in many practical applications, it is not always easy to obtain a pair of rectified stereo images without employing specially designed camera systems. This hinders the wider applications of the previously proposed algorithms [1, 11]. Therefore, we have proposed a new approach consisting of three steps.
2 Proceedings of the 5th WSEAS Int. Conf. on COMPUTATIONAL INTELLIGENCE, MAN-MACHINE SYSTEMS AND CYBERNETICS, Venice, Italy, November 2-22, First, segmentation of the left image is carried out to generate a series of small segments. Then, extraction of the conjugate points from the stereo pair is conducted, and a set of linear transformation functions is determined using the least squares technique. Once these functions are produced, the displacement for each pixel is calculated after applying the functions to the small segments that have been generated. This generates a disparity map. To examine the quality of the disparity map, two stereo anaglyphs, one from the disparity map and the other from the original stereo pair, are produced and compared visually. The entire worflow is illustrated in Figure 1. Fig.3 Flowchart of the proposed algorithm 2 Color Segmentation Our approach is built on the assumption that large disparity discontinuities only occur at the boundaries of homogeneous color segments [7, 9]. For a qualified result, the number of segments must be handled carefully, because too many segments maes it difficult to obtain enough conjugate points, and too small number of segments result in ill merging between separate objects. A mean shift color segmentation algorithm was used in our implementation, as mean shift based segmentation is one of the most powerful and generally used segmentation techniques [6, 9]. 3 Conjugate Point Extractions To extract conjugate points from the left and right images, we detected feature points in two images using Scale-Invariant Feature Transform (SIFT) [3, 4, 5]. In the SIFT technique, the local image gradient orientation around the detected features was used as a feature descriptor. Two points with the most similar feature descriptors were selected as a corresponding pair. SIFT has some advantages over other matching algorithms for our experiments because it extracts a large number of ey points and even small segments can include at least three matched ey points as discussed in [3]. In addition, SIFT is invariant to scale change, translation, and rotation. It also yields the correct matching results despite illumination change and affine distortions. Moreover, it removes any ey points located along the edges. Considering that the edges usually coincided with the segments boundaries, rejecting the ey points around the edges has a favorable effect. Because points located along an edge are highly liely to be included in a wrong segment, then removing the ey points along the edges enhances the accuracy of depth calculation in each segment. 4 Piecewise Linear Transformation Throughout the procedures described above, a set of matched points for each segment was obtained for the
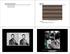
3 Proceedings of the 5th WSEAS Int. Conf. on COMPUTATIONAL INTELLIGENCE, MAN-MACHINE SYSTEMS AND CYBERNETICS, Venice, Italy, November 2-22, piecewise linear transformation. Because the left image was the reference image, we estimated the linear transformational functions after registering the left image (x, y) to right image (x, y ) using the least square method. The piecewise linear transformation function is expressed by the following equations : x ' = a + bx + cy, y' = d + ex + fy (1) x' 1 x' n y' 1 y' n 1 1 = x x 1 n y y 1 n 1 x1 y1 1 xn yn a b c d e f (2) where is the segment index, (x i, y i ) is conjugate point coordinates of left image, (x i, y i ) is conjugate point coordinates of right image, and n is the number of matched points within segment Equation (2) can be rewritten in brief : L = A X (3) Therefore, the coefficients matrix, X, can be solved using the least squares method as follows : X = ( A T A ) 1 A T L (4) Then, the displacement value, v, of each pixel in the entire image can be estimated using the transformation function of each segment : v xy = 2 ( x x') + ( y y ') 2 (5) vij where is the displacement value at (x, y), (x, y) is the coordinates of left image, and (x, y ) is the transformed coordinates. Obtaining the affine transformation coefficients requires at least three points that are matched correctly in each segment. If a given segment contains fewer than three matched points, then we substitute the mean displacement values between the conjugate points for the displacement value in that segment to prevent a null-type value occurring. 5 Experimental Results 5.1 Data acquisition To evaluate our approach, we too two stereo pair images of different scene using Nion Coolpix 37 digital camera, set to manual exposure and focus. The first scene taen was of a paring area, and the second scene taen was of a des. The distance between the camera centers in each stereo pair was adjusted to be about 1/3 of the distance between the camera and the nearest object. The image size was 64 Î48 pixels and the color depth was 24bits. 5.2 Algorithm applications We executed segmentation of the left image in each test pair. The number of segments in the left image of the first and second pairs was 42 and 3, respectively. Figure 2 shows the test images and segmentation results of these left images. Through extraction of the conjugate points, we obtained 422 and 413 matched points for each pair, respectively. The disparity maps were then generated using the piecewise linear transformation. 5.3 Result evaluation
4 Proceedings of the 5th WSEAS Int. Conf. on COMPUTATIONAL INTELLIGENCE, MAN-MACHINE SYSTEMS AND CYBERNETICS, Venice, Italy, November 2-22, Figure 3 shows the results of our experiment. Figures 3(a) and 3(d) show the disparity maps generated from the two test pairs, 3(b) and 3(e) show the anaglyphs from the disparity maps that we produced and their corresponding left images, and 3(c) and 3(f) show the reference anaglyph images obtained from the original stereo pairs. Our proposed algorithm generated the disparity relatively well within the entire scene, not only in the uniform plane, but also in the slanted disparity surfaces, such as along the sides of cars, along the ground, and around the surface of the des. In addition, the discontinuous boundaries were expressed clearly. Fig. 3. Images (a), (b), and (c) show the left, right, and segmentation images of the first test pair ; images (d), (e), and (f) show the left, right, and segmentation images of the second test pair. 1
5 Proceedings of the 5th WSEAS Int. Conf. on COMPUTATIONAL INTELLIGENCE, MAN-MACHINE SYSTEMS AND CYBERNETICS, Venice, Italy, November 2-22, Fig. 3 Images (a) and (d) show the disparity maps for each test pair, images (b) and (e) show the anaglyphs from the disparity maps, and images (c) and (f) show the reference anaglyphs. However, in the areas that had indefinite boundaries, such as mountains and trees, or few corresponding points, such as side of the telephone, satisfactory results were not obtained. To evaluate the generated disparity map, we compared our results with the original stereo pair by viewing the 3D stereo anaglyphs. Through this evaluation, the anaglyphs constructed using our proposed approach could express depth as well as the reference anaglyphs do, especially the close objects. 6 Conclusions We have proposed a new approach that enables the generation of a disparity map from a random stereo pair where the stereo pair is not necessarily required to be in epipolar geometry. This approach adopts the piecewise linear transformation for the generation of a disparity map. In experiments, the resulting disparity map was shown to be suitable for expressing the uniform disparity plane and the slanted disparity surfaces. The advantages of this approach are that it does not necessarily require stereo rectification, and that it is applicable to any set of stereo images that are not in epipolar geometry. Apart from these advantages, it s not appropriate to express a curved surface, and the areas that had indefinite boundaries. Our proposed approach was affected by the quality of the segmentation and corresponding point pair extraction, so it is important to determine the number of segments and matched points properly. This is now the topic of our ongoing research. Acnowledgments The authors gratefully acnowledge financial support form Seoul Research and Business Development (154).
6 Proceedings of the 5th WSEAS Int. Conf. on COMPUTATIONAL INTELLIGENCE, MAN-MACHINE SYSTEMS AND CYBERNETICS, Venice, Italy, November 2-22, References: [1] Andreas Klaus, Mario Sormann and Konrad Karner, Segment Based Stereo Matching Using Belief Propagation and a Self Adapting Dissimilarity Measure, Pattern Recognition. ICPR 26, Vol.3, 26, pp [2] Bogdan Georgescu, Point Matching under Large Image Deformations and Illumination Changes, IEEE Transactions On Pattern Analysis And Machine Intelligence, Vol.26, 24, pp [3] David G. Lowe, Distinctive Image Features from Scale-Invariant Keypoints, International Journal of Computer Vision, Vol.6, 24, pp [4] David G. Lowe, Local Feature View Clustering for 3D Object Recognition, IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vol.1, 21, pp [5] David G. Lowe, Object Recognition from Local Scale-Invariant Features, International Conference on Computer Vision, Vol.2, 1999, pp [6] Dorin Comaniciu and Peter Meer, Robust Analysis of Feature Spaces: Color Image Segmentation, Proceedings of the 26 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 1997, pp [7] Hai Tao, Harpreet S. Sawhney and Raesh Kumar, A Global Matching Framewor for Stereo Computation, Eighth International Conference on Computer Vision, Vol.1, 21, p. 532 [8] Ku-Jin Yoon and In-So Kweon, Locally Adaptive Support-Weight Approach for Visual Correspondence Search, Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vol.2, 25, pp [9] Li Hong and George Chen, Segment-based Stereo Matching Using Graph Cuts, IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vol.1, 24, pp [1] Marc Pollefeys, Reinhard Koch and Luc Van Gool, A Simple and Efficient Rectification Method for General Motion, International Conference on Computer Vision, Vol.2, 1999, pp [11] Pravin Bhat, Ke Colin Zheng, Noah Snavely and Aseem Agarwala, Piecewise Image Registration in the Presence of Multiple Large Motions, Proceedings of the 26 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vol.2, 26, pp [12] Qingxiong Yang, Liang Wang, Ruigang Yang, Henri Stewénius and David Nistér, Stereo Matching with Color-Weighted Correlation, Hierarchical Belief Propagation and Occlusion Handling, Proceedings of the 26 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vol.2, 26, pp [13] Vladimir Kolmogorov and Ramin Zabith, Multi Camera Scene Reconstruction via Graph Cuts, Lecture Notes in Computer Science, Vol.2532, 22, pp
A novel 3D torso image reconstruction procedure using a pair of digital stereo back images
 Modelling in Medicine and Biology VIII 257 A novel 3D torso image reconstruction procedure using a pair of digital stereo back images A. Kumar & N. Durdle Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering,
Modelling in Medicine and Biology VIII 257 A novel 3D torso image reconstruction procedure using a pair of digital stereo back images A. Kumar & N. Durdle Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering,
Robot localization method based on visual features and their geometric relationship
 , pp.46-50 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/astl.2015.85.11 Robot localization method based on visual features and their geometric relationship Sangyun Lee 1, Changkyung Eem 2, and Hyunki Hong 3 1 Department
, pp.46-50 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/astl.2015.85.11 Robot localization method based on visual features and their geometric relationship Sangyun Lee 1, Changkyung Eem 2, and Hyunki Hong 3 1 Department
segments. The geometrical relationship of adjacent planes such as parallelism and intersection is employed for determination of whether two planes sha
 A New Segment-based Stereo Matching using Graph Cuts Daolei Wang National University of Singapore EA #04-06, Department of Mechanical Engineering Control and Mechatronics Laboratory, 10 Kent Ridge Crescent
A New Segment-based Stereo Matching using Graph Cuts Daolei Wang National University of Singapore EA #04-06, Department of Mechanical Engineering Control and Mechatronics Laboratory, 10 Kent Ridge Crescent
Colour Segmentation-based Computation of Dense Optical Flow with Application to Video Object Segmentation
 ÖGAI Journal 24/1 11 Colour Segmentation-based Computation of Dense Optical Flow with Application to Video Object Segmentation Michael Bleyer, Margrit Gelautz, Christoph Rhemann Vienna University of Technology
ÖGAI Journal 24/1 11 Colour Segmentation-based Computation of Dense Optical Flow with Application to Video Object Segmentation Michael Bleyer, Margrit Gelautz, Christoph Rhemann Vienna University of Technology
Chaplin, Modern Times, 1936
 Chaplin, Modern Times, 1936 [A Bucket of Water and a Glass Matte: Special Effects in Modern Times; bonus feature on The Criterion Collection set] Multi-view geometry problems Structure: Given projections
Chaplin, Modern Times, 1936 [A Bucket of Water and a Glass Matte: Special Effects in Modern Times; bonus feature on The Criterion Collection set] Multi-view geometry problems Structure: Given projections
Dense 3D Reconstruction. Christiano Gava
 Dense 3D Reconstruction Christiano Gava christiano.gava@dfki.de Outline Previous lecture: structure and motion II Structure and motion loop Triangulation Today: dense 3D reconstruction The matching problem
Dense 3D Reconstruction Christiano Gava christiano.gava@dfki.de Outline Previous lecture: structure and motion II Structure and motion loop Triangulation Today: dense 3D reconstruction The matching problem
CS 4495 Computer Vision A. Bobick. Motion and Optic Flow. Stereo Matching
 Stereo Matching Fundamental matrix Let p be a point in left image, p in right image l l Epipolar relation p maps to epipolar line l p maps to epipolar line l p p Epipolar mapping described by a 3x3 matrix
Stereo Matching Fundamental matrix Let p be a point in left image, p in right image l l Epipolar relation p maps to epipolar line l p maps to epipolar line l p p Epipolar mapping described by a 3x3 matrix
Segmentation and Tracking of Partial Planar Templates
 Segmentation and Tracking of Partial Planar Templates Abdelsalam Masoud William Hoff Colorado School of Mines Colorado School of Mines Golden, CO 800 Golden, CO 800 amasoud@mines.edu whoff@mines.edu Abstract
Segmentation and Tracking of Partial Planar Templates Abdelsalam Masoud William Hoff Colorado School of Mines Colorado School of Mines Golden, CO 800 Golden, CO 800 amasoud@mines.edu whoff@mines.edu Abstract
Dense 3D Reconstruction. Christiano Gava
 Dense 3D Reconstruction Christiano Gava christiano.gava@dfki.de Outline Previous lecture: structure and motion II Structure and motion loop Triangulation Wide baseline matching (SIFT) Today: dense 3D reconstruction
Dense 3D Reconstruction Christiano Gava christiano.gava@dfki.de Outline Previous lecture: structure and motion II Structure and motion loop Triangulation Wide baseline matching (SIFT) Today: dense 3D reconstruction
What have we leaned so far?
 What have we leaned so far? Camera structure Eye structure Project 1: High Dynamic Range Imaging What have we learned so far? Image Filtering Image Warping Camera Projection Model Project 2: Panoramic
What have we leaned so far? Camera structure Eye structure Project 1: High Dynamic Range Imaging What have we learned so far? Image Filtering Image Warping Camera Projection Model Project 2: Panoramic
Segmentation-based Disparity Plane Fitting using PSO
 , pp.141-145 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/astl.2014.47.33 Segmentation-based Disparity Plane Fitting using PSO Hyunjung, Kim 1, Ilyong, Weon 2, Youngcheol, Jang 3, Changhun, Lee 4 1,4 Department of Computer
, pp.141-145 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/astl.2014.47.33 Segmentation-based Disparity Plane Fitting using PSO Hyunjung, Kim 1, Ilyong, Weon 2, Youngcheol, Jang 3, Changhun, Lee 4 1,4 Department of Computer
Stereo Vision. MAN-522 Computer Vision
 Stereo Vision MAN-522 Computer Vision What is the goal of stereo vision? The recovery of the 3D structure of a scene using two or more images of the 3D scene, each acquired from a different viewpoint in
Stereo Vision MAN-522 Computer Vision What is the goal of stereo vision? The recovery of the 3D structure of a scene using two or more images of the 3D scene, each acquired from a different viewpoint in
CHAPTER 3 DISPARITY AND DEPTH MAP COMPUTATION
 CHAPTER 3 DISPARITY AND DEPTH MAP COMPUTATION In this chapter we will discuss the process of disparity computation. It plays an important role in our caricature system because all 3D coordinates of nodes
CHAPTER 3 DISPARITY AND DEPTH MAP COMPUTATION In this chapter we will discuss the process of disparity computation. It plays an important role in our caricature system because all 3D coordinates of nodes
A Comparison of SIFT, PCA-SIFT and SURF
 A Comparison of SIFT, PCA-SIFT and SURF Luo Juan Computer Graphics Lab, Chonbuk National University, Jeonju 561-756, South Korea qiuhehappy@hotmail.com Oubong Gwun Computer Graphics Lab, Chonbuk National
A Comparison of SIFT, PCA-SIFT and SURF Luo Juan Computer Graphics Lab, Chonbuk National University, Jeonju 561-756, South Korea qiuhehappy@hotmail.com Oubong Gwun Computer Graphics Lab, Chonbuk National
Lecture 10: Multi view geometry
 Lecture 10: Multi view geometry Professor Fei Fei Li Stanford Vision Lab 1 What we will learn today? Stereo vision Correspondence problem (Problem Set 2 (Q3)) Active stereo vision systems Structure from
Lecture 10: Multi view geometry Professor Fei Fei Li Stanford Vision Lab 1 What we will learn today? Stereo vision Correspondence problem (Problem Set 2 (Q3)) Active stereo vision systems Structure from
SUMMARY: DISTINCTIVE IMAGE FEATURES FROM SCALE- INVARIANT KEYPOINTS
 SUMMARY: DISTINCTIVE IMAGE FEATURES FROM SCALE- INVARIANT KEYPOINTS Cognitive Robotics Original: David G. Lowe, 004 Summary: Coen van Leeuwen, s1460919 Abstract: This article presents a method to extract
SUMMARY: DISTINCTIVE IMAGE FEATURES FROM SCALE- INVARIANT KEYPOINTS Cognitive Robotics Original: David G. Lowe, 004 Summary: Coen van Leeuwen, s1460919 Abstract: This article presents a method to extract
Fundamentals of Stereo Vision Michael Bleyer LVA Stereo Vision
 Fundamentals of Stereo Vision Michael Bleyer LVA Stereo Vision What Happened Last Time? Human 3D perception (3D cinema) Computational stereo Intuitive explanation of what is meant by disparity Stereo matching
Fundamentals of Stereo Vision Michael Bleyer LVA Stereo Vision What Happened Last Time? Human 3D perception (3D cinema) Computational stereo Intuitive explanation of what is meant by disparity Stereo matching
Final project bits and pieces
 Final project bits and pieces The project is expected to take four weeks of time for up to four people. At 12 hours per week per person that comes out to: ~192 hours of work for a four person team. Capstone:
Final project bits and pieces The project is expected to take four weeks of time for up to four people. At 12 hours per week per person that comes out to: ~192 hours of work for a four person team. Capstone:
A novel point matching method for stereovision measurement using RANSAC affine transformation
 A novel point matching method for stereovision measurement using RANSAC affine transformation Naiguang Lu, Peng Sun, Wenyi Deng, Lianqing Zhu, Xiaoping Lou School of Optoelectronic Information & Telecommunication
A novel point matching method for stereovision measurement using RANSAC affine transformation Naiguang Lu, Peng Sun, Wenyi Deng, Lianqing Zhu, Xiaoping Lou School of Optoelectronic Information & Telecommunication
Project 3 code & artifact due Tuesday Final project proposals due noon Wed (by ) Readings Szeliski, Chapter 10 (through 10.5)
 Announcements Project 3 code & artifact due Tuesday Final project proposals due noon Wed (by email) One-page writeup (from project web page), specifying:» Your team members» Project goals. Be specific.
Announcements Project 3 code & artifact due Tuesday Final project proposals due noon Wed (by email) One-page writeup (from project web page), specifying:» Your team members» Project goals. Be specific.
Recap from Previous Lecture
 Recap from Previous Lecture Tone Mapping Preserve local contrast or detail at the expense of large scale contrast. Changing the brightness within objects or surfaces unequally leads to halos. We are now
Recap from Previous Lecture Tone Mapping Preserve local contrast or detail at the expense of large scale contrast. Changing the brightness within objects or surfaces unequally leads to halos. We are now
A Novel Segment-based Stereo Matching Algorithm for Disparity Map Generation
 2011 International Conference on Computer and Software Modeling IPCSIT vol.14 (2011) (2011) IACSIT Press, Singapore A Novel Segment-based Stereo Matching Algorithm for Disparity Map Generation Viral H.
2011 International Conference on Computer and Software Modeling IPCSIT vol.14 (2011) (2011) IACSIT Press, Singapore A Novel Segment-based Stereo Matching Algorithm for Disparity Map Generation Viral H.
Piecewise Image Registration in the Presence of Multiple Large Motions
 Piecewise Image Registration in the Presence of Multiple Large Motions Pravin Bhat 1, Ke Colin Zheng 1, Noah Snavely 1, Aseem Agarwala 1, Maneesh Agrawala 2, Michael F. Cohen 3, Brian Curless 1 1 University
Piecewise Image Registration in the Presence of Multiple Large Motions Pravin Bhat 1, Ke Colin Zheng 1, Noah Snavely 1, Aseem Agarwala 1, Maneesh Agrawala 2, Michael F. Cohen 3, Brian Curless 1 1 University
Topics to be Covered in the Rest of the Semester. CSci 4968 and 6270 Computational Vision Lecture 15 Overview of Remainder of the Semester
 Topics to be Covered in the Rest of the Semester CSci 4968 and 6270 Computational Vision Lecture 15 Overview of Remainder of the Semester Charles Stewart Department of Computer Science Rensselaer Polytechnic
Topics to be Covered in the Rest of the Semester CSci 4968 and 6270 Computational Vision Lecture 15 Overview of Remainder of the Semester Charles Stewart Department of Computer Science Rensselaer Polytechnic
Stereo Wrap + Motion. Computer Vision I. CSE252A Lecture 17
 Stereo Wrap + Motion CSE252A Lecture 17 Some Issues Ambiguity Window size Window shape Lighting Half occluded regions Problem of Occlusion Stereo Constraints CONSTRAINT BRIEF DESCRIPTION 1-D Epipolar Search
Stereo Wrap + Motion CSE252A Lecture 17 Some Issues Ambiguity Window size Window shape Lighting Half occluded regions Problem of Occlusion Stereo Constraints CONSTRAINT BRIEF DESCRIPTION 1-D Epipolar Search
Accurate and Dense Wide-Baseline Stereo Matching Using SW-POC
 Accurate and Dense Wide-Baseline Stereo Matching Using SW-POC Shuji Sakai, Koichi Ito, Takafumi Aoki Graduate School of Information Sciences, Tohoku University, Sendai, 980 8579, Japan Email: sakai@aoki.ecei.tohoku.ac.jp
Accurate and Dense Wide-Baseline Stereo Matching Using SW-POC Shuji Sakai, Koichi Ito, Takafumi Aoki Graduate School of Information Sciences, Tohoku University, Sendai, 980 8579, Japan Email: sakai@aoki.ecei.tohoku.ac.jp
CS 4495 Computer Vision A. Bobick. Motion and Optic Flow. Stereo Matching
 Stereo Matching Fundamental matrix Let p be a point in left image, p in right image l l Epipolar relation p maps to epipolar line l p maps to epipolar line l p p Epipolar mapping described by a 3x3 matrix
Stereo Matching Fundamental matrix Let p be a point in left image, p in right image l l Epipolar relation p maps to epipolar line l p maps to epipolar line l p p Epipolar mapping described by a 3x3 matrix
Real-Time Disparity Map Computation Based On Disparity Space Image
 Real-Time Disparity Map Computation Based On Disparity Space Image Nadia Baha and Slimane Larabi Computer Science Department, University of Science and Technology USTHB, Algiers, Algeria nbahatouzene@usthb.dz,
Real-Time Disparity Map Computation Based On Disparity Space Image Nadia Baha and Slimane Larabi Computer Science Department, University of Science and Technology USTHB, Algiers, Algeria nbahatouzene@usthb.dz,
A virtual tour of free viewpoint rendering
 A virtual tour of free viewpoint rendering Cédric Verleysen ICTEAM institute, Université catholique de Louvain, Belgium cedric.verleysen@uclouvain.be Organization of the presentation Context Acquisition
A virtual tour of free viewpoint rendering Cédric Verleysen ICTEAM institute, Université catholique de Louvain, Belgium cedric.verleysen@uclouvain.be Organization of the presentation Context Acquisition
Viewpoint Invariant Features from Single Images Using 3D Geometry
 Viewpoint Invariant Features from Single Images Using 3D Geometry Yanpeng Cao and John McDonald Department of Computer Science National University of Ireland, Maynooth, Ireland {y.cao,johnmcd}@cs.nuim.ie
Viewpoint Invariant Features from Single Images Using 3D Geometry Yanpeng Cao and John McDonald Department of Computer Science National University of Ireland, Maynooth, Ireland {y.cao,johnmcd}@cs.nuim.ie
Computer Vision Lecture 17
 Computer Vision Lecture 17 Epipolar Geometry & Stereo Basics 13.01.2015 Bastian Leibe RWTH Aachen http://www.vision.rwth-aachen.de leibe@vision.rwth-aachen.de Announcements Seminar in the summer semester
Computer Vision Lecture 17 Epipolar Geometry & Stereo Basics 13.01.2015 Bastian Leibe RWTH Aachen http://www.vision.rwth-aachen.de leibe@vision.rwth-aachen.de Announcements Seminar in the summer semester
Computer Vision Lecture 17
 Announcements Computer Vision Lecture 17 Epipolar Geometry & Stereo Basics Seminar in the summer semester Current Topics in Computer Vision and Machine Learning Block seminar, presentations in 1 st week
Announcements Computer Vision Lecture 17 Epipolar Geometry & Stereo Basics Seminar in the summer semester Current Topics in Computer Vision and Machine Learning Block seminar, presentations in 1 st week
Stereo. 11/02/2012 CS129, Brown James Hays. Slides by Kristen Grauman
 Stereo 11/02/2012 CS129, Brown James Hays Slides by Kristen Grauman Multiple views Multi-view geometry, matching, invariant features, stereo vision Lowe Hartley and Zisserman Why multiple views? Structure
Stereo 11/02/2012 CS129, Brown James Hays Slides by Kristen Grauman Multiple views Multi-view geometry, matching, invariant features, stereo vision Lowe Hartley and Zisserman Why multiple views? Structure
TWO-DIMENSIONAL REGULARIZED DISPARITY ESTIMATION BASED ON THE GABOR TRANSFORM. Xiaodong Huang and Eric Dubois
 TWO-DIMENSIONAL REGULARIZED DISPARITY ESTIMATION BASED ON THE GABOR TRANSFORM Xiaodong Huang and Eric Dubois School of Information Technology and Engineering (SITE) University of Ottawa, Ottawa, ON, KN
TWO-DIMENSIONAL REGULARIZED DISPARITY ESTIMATION BASED ON THE GABOR TRANSFORM Xiaodong Huang and Eric Dubois School of Information Technology and Engineering (SITE) University of Ottawa, Ottawa, ON, KN
Lecture 14: Basic Multi-View Geometry
 Lecture 14: Basic Multi-View Geometry Stereo If I needed to find out how far point is away from me, I could use triangulation and two views scene point image plane optical center (Graphic from Khurram
Lecture 14: Basic Multi-View Geometry Stereo If I needed to find out how far point is away from me, I could use triangulation and two views scene point image plane optical center (Graphic from Khurram
Segment-based Stereo Matching Using Graph Cuts
 Segment-based Stereo Matching Using Graph Cuts Li Hong George Chen Advanced System Technology San Diego Lab, STMicroelectronics, Inc. li.hong@st.com george-qian.chen@st.com Abstract In this paper, we present
Segment-based Stereo Matching Using Graph Cuts Li Hong George Chen Advanced System Technology San Diego Lab, STMicroelectronics, Inc. li.hong@st.com george-qian.chen@st.com Abstract In this paper, we present
A Novel Extreme Point Selection Algorithm in SIFT
 A Novel Extreme Point Selection Algorithm in SIFT Ding Zuchun School of Electronic and Communication, South China University of Technolog Guangzhou, China zucding@gmail.com Abstract. This paper proposes
A Novel Extreme Point Selection Algorithm in SIFT Ding Zuchun School of Electronic and Communication, South China University of Technolog Guangzhou, China zucding@gmail.com Abstract. This paper proposes
An Overview of Matchmoving using Structure from Motion Methods
 An Overview of Matchmoving using Structure from Motion Methods Kamyar Haji Allahverdi Pour Department of Computer Engineering Sharif University of Technology Tehran, Iran Email: allahverdi@ce.sharif.edu
An Overview of Matchmoving using Structure from Motion Methods Kamyar Haji Allahverdi Pour Department of Computer Engineering Sharif University of Technology Tehran, Iran Email: allahverdi@ce.sharif.edu
Stereo imaging ideal geometry
 Stereo imaging ideal geometry (X,Y,Z) Z f (x L,y L ) f (x R,y R ) Optical axes are parallel Optical axes separated by baseline, b. Line connecting lens centers is perpendicular to the optical axis, and
Stereo imaging ideal geometry (X,Y,Z) Z f (x L,y L ) f (x R,y R ) Optical axes are parallel Optical axes separated by baseline, b. Line connecting lens centers is perpendicular to the optical axis, and
III. VERVIEW OF THE METHODS
 An Analytical Study of SIFT and SURF in Image Registration Vivek Kumar Gupta, Kanchan Cecil Department of Electronics & Telecommunication, Jabalpur engineering college, Jabalpur, India comparing the distance
An Analytical Study of SIFT and SURF in Image Registration Vivek Kumar Gupta, Kanchan Cecil Department of Electronics & Telecommunication, Jabalpur engineering college, Jabalpur, India comparing the distance
Stereo Matching.
 Stereo Matching Stereo Vision [1] Reduction of Searching by Epipolar Constraint [1] Photometric Constraint [1] Same world point has same intensity in both images. True for Lambertian surfaces A Lambertian
Stereo Matching Stereo Vision [1] Reduction of Searching by Epipolar Constraint [1] Photometric Constraint [1] Same world point has same intensity in both images. True for Lambertian surfaces A Lambertian
Adaptive Zoom Distance Measuring System of Camera Based on the Ranging of Binocular Vision
 Adaptive Zoom Distance Measuring System of Camera Based on the Ranging of Binocular Vision Zhiyan Zhang 1, Wei Qian 1, Lei Pan 1 & Yanjun Li 1 1 University of Shanghai for Science and Technology, China
Adaptive Zoom Distance Measuring System of Camera Based on the Ranging of Binocular Vision Zhiyan Zhang 1, Wei Qian 1, Lei Pan 1 & Yanjun Li 1 1 University of Shanghai for Science and Technology, China
Global localization from a single feature correspondence
 Global localization from a single feature correspondence Friedrich Fraundorfer and Horst Bischof Institute for Computer Graphics and Vision Graz University of Technology {fraunfri,bischof}@icg.tu-graz.ac.at
Global localization from a single feature correspondence Friedrich Fraundorfer and Horst Bischof Institute for Computer Graphics and Vision Graz University of Technology {fraunfri,bischof}@icg.tu-graz.ac.at
Features Points. Andrea Torsello DAIS Università Ca Foscari via Torino 155, Mestre (VE)
 Features Points Andrea Torsello DAIS Università Ca Foscari via Torino 155, 30172 Mestre (VE) Finding Corners Edge detectors perform poorly at corners. Corners provide repeatable points for matching, so
Features Points Andrea Torsello DAIS Università Ca Foscari via Torino 155, 30172 Mestre (VE) Finding Corners Edge detectors perform poorly at corners. Corners provide repeatable points for matching, so
Computational Optical Imaging - Optique Numerique. -- Multiple View Geometry and Stereo --
 Computational Optical Imaging - Optique Numerique -- Multiple View Geometry and Stereo -- Winter 2013 Ivo Ihrke with slides by Thorsten Thormaehlen Feature Detection and Matching Wide-Baseline-Matching
Computational Optical Imaging - Optique Numerique -- Multiple View Geometry and Stereo -- Winter 2013 Ivo Ihrke with slides by Thorsten Thormaehlen Feature Detection and Matching Wide-Baseline-Matching
Structure from Motion. Introduction to Computer Vision CSE 152 Lecture 10
 Structure from Motion CSE 152 Lecture 10 Announcements Homework 3 is due May 9, 11:59 PM Reading: Chapter 8: Structure from Motion Optional: Multiple View Geometry in Computer Vision, 2nd edition, Hartley
Structure from Motion CSE 152 Lecture 10 Announcements Homework 3 is due May 9, 11:59 PM Reading: Chapter 8: Structure from Motion Optional: Multiple View Geometry in Computer Vision, 2nd edition, Hartley
A New Approach For 3D Image Reconstruction From Multiple Images
 International Journal of Electronics Engineering Research. ISSN 0975-6450 Volume 9, Number 4 (2017) pp. 569-574 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com A New Approach For 3D Image Reconstruction
International Journal of Electronics Engineering Research. ISSN 0975-6450 Volume 9, Number 4 (2017) pp. 569-574 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com A New Approach For 3D Image Reconstruction
arxiv: v1 [cs.cv] 28 Sep 2018
![arxiv: v1 [cs.cv] 28 Sep 2018 arxiv: v1 [cs.cv] 28 Sep 2018](/thumbs/93/113542646.jpg) Camera Pose Estimation from Sequence of Calibrated Images arxiv:1809.11066v1 [cs.cv] 28 Sep 2018 Jacek Komorowski 1 and Przemyslaw Rokita 2 1 Maria Curie-Sklodowska University, Institute of Computer Science,
Camera Pose Estimation from Sequence of Calibrated Images arxiv:1809.11066v1 [cs.cv] 28 Sep 2018 Jacek Komorowski 1 and Przemyslaw Rokita 2 1 Maria Curie-Sklodowska University, Institute of Computer Science,
Computational Optical Imaging - Optique Numerique. -- Single and Multiple View Geometry, Stereo matching --
 Computational Optical Imaging - Optique Numerique -- Single and Multiple View Geometry, Stereo matching -- Autumn 2015 Ivo Ihrke with slides by Thorsten Thormaehlen Reminder: Feature Detection and Matching
Computational Optical Imaging - Optique Numerique -- Single and Multiple View Geometry, Stereo matching -- Autumn 2015 Ivo Ihrke with slides by Thorsten Thormaehlen Reminder: Feature Detection and Matching
Multiple View Geometry
 Multiple View Geometry CS 6320, Spring 2013 Guest Lecture Marcel Prastawa adapted from Pollefeys, Shah, and Zisserman Single view computer vision Projective actions of cameras Camera callibration Photometric
Multiple View Geometry CS 6320, Spring 2013 Guest Lecture Marcel Prastawa adapted from Pollefeys, Shah, and Zisserman Single view computer vision Projective actions of cameras Camera callibration Photometric
Feature Detection and Matching
 and Matching CS4243 Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Leow Wee Kheng Department of Computer Science School of Computing National University of Singapore Leow Wee Kheng (CS4243) Camera Models 1 /
and Matching CS4243 Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Leow Wee Kheng Department of Computer Science School of Computing National University of Singapore Leow Wee Kheng (CS4243) Camera Models 1 /
A Summary of Projective Geometry
 A Summary of Projective Geometry Copyright 22 Acuity Technologies Inc. In the last years a unified approach to creating D models from multiple images has been developed by Beardsley[],Hartley[4,5,9],Torr[,6]
A Summary of Projective Geometry Copyright 22 Acuity Technologies Inc. In the last years a unified approach to creating D models from multiple images has been developed by Beardsley[],Hartley[4,5,9],Torr[,6]
Moving Object Segmentation Method Based on Motion Information Classification by X-means and Spatial Region Segmentation
 IJCSNS International Journal of Computer Science and Network Security, VOL.13 No.11, November 2013 1 Moving Object Segmentation Method Based on Motion Information Classification by X-means and Spatial
IJCSNS International Journal of Computer Science and Network Security, VOL.13 No.11, November 2013 1 Moving Object Segmentation Method Based on Motion Information Classification by X-means and Spatial
TERM PAPER REPORT ROBUST VIDEO STABILIZATION BASED ON PARTICLE FILTER TRACKING OF PROJECTED CAMERA MOTION
 TERM PAPER REPORT ROBUST VIDEO STABILIZATION BASED ON PARTICLE FILTER TRACKING OF PROJECTED CAMERA MOTION EE 608A DIGITAL VIDEO PROCESSING : TERM PAPER REPORT ROBUST VIDEO STABILIZATION BASED ON PARTICLE
TERM PAPER REPORT ROBUST VIDEO STABILIZATION BASED ON PARTICLE FILTER TRACKING OF PROJECTED CAMERA MOTION EE 608A DIGITAL VIDEO PROCESSING : TERM PAPER REPORT ROBUST VIDEO STABILIZATION BASED ON PARTICLE
Using temporal seeding to constrain the disparity search range in stereo matching
 Using temporal seeding to constrain the disparity search range in stereo matching Thulani Ndhlovu Mobile Intelligent Autonomous Systems CSIR South Africa Email: tndhlovu@csir.co.za Fred Nicolls Department
Using temporal seeding to constrain the disparity search range in stereo matching Thulani Ndhlovu Mobile Intelligent Autonomous Systems CSIR South Africa Email: tndhlovu@csir.co.za Fred Nicolls Department
Fundamental matrix. Let p be a point in left image, p in right image. Epipolar relation. Epipolar mapping described by a 3x3 matrix F
 Fundamental matrix Let p be a point in left image, p in right image l l Epipolar relation p maps to epipolar line l p maps to epipolar line l p p Epipolar mapping described by a 3x3 matrix F Fundamental
Fundamental matrix Let p be a point in left image, p in right image l l Epipolar relation p maps to epipolar line l p maps to epipolar line l p p Epipolar mapping described by a 3x3 matrix F Fundamental
Implementation and Comparison of Feature Detection Methods in Image Mosaicing
 IOSR Journal of Electronics and Communication Engineering (IOSR-JECE) e-issn: 2278-2834,p-ISSN: 2278-8735 PP 07-11 www.iosrjournals.org Implementation and Comparison of Feature Detection Methods in Image
IOSR Journal of Electronics and Communication Engineering (IOSR-JECE) e-issn: 2278-2834,p-ISSN: 2278-8735 PP 07-11 www.iosrjournals.org Implementation and Comparison of Feature Detection Methods in Image
An Improved Image Resizing Approach with Protection of Main Objects
 An Improved Image Resizing Approach with Protection of Main Objects Chin-Chen Chang National United University, Miaoli 360, Taiwan. *Corresponding Author: Chun-Ju Chen National United University, Miaoli
An Improved Image Resizing Approach with Protection of Main Objects Chin-Chen Chang National United University, Miaoli 360, Taiwan. *Corresponding Author: Chun-Ju Chen National United University, Miaoli
Announcements. Stereo Vision Wrapup & Intro Recognition
 Announcements Stereo Vision Wrapup & Intro Introduction to Computer Vision CSE 152 Lecture 17 HW3 due date postpone to Thursday HW4 to posted by Thursday, due next Friday. Order of material we ll first
Announcements Stereo Vision Wrapup & Intro Introduction to Computer Vision CSE 152 Lecture 17 HW3 due date postpone to Thursday HW4 to posted by Thursday, due next Friday. Order of material we ll first
Target Tracking Based on Mean Shift and KALMAN Filter with Kernel Histogram Filtering
 Target Tracking Based on Mean Shift and KALMAN Filter with Kernel Histogram Filtering Sara Qazvini Abhari (Corresponding author) Faculty of Electrical, Computer and IT Engineering Islamic Azad University
Target Tracking Based on Mean Shift and KALMAN Filter with Kernel Histogram Filtering Sara Qazvini Abhari (Corresponding author) Faculty of Electrical, Computer and IT Engineering Islamic Azad University
EE795: Computer Vision and Intelligent Systems
 EE795: Computer Vision and Intelligent Systems Spring 2012 TTh 17:30-18:45 FDH 204 Lecture 14 130307 http://www.ee.unlv.edu/~b1morris/ecg795/ 2 Outline Review Stereo Dense Motion Estimation Translational
EE795: Computer Vision and Intelligent Systems Spring 2012 TTh 17:30-18:45 FDH 204 Lecture 14 130307 http://www.ee.unlv.edu/~b1morris/ecg795/ 2 Outline Review Stereo Dense Motion Estimation Translational
Stereo matching. Francesco Isgrò. 3D Reconstruction and Stereo p.1/21
 Stereo matching Francesco Isgrò 3D Reconstruction and Stereo p.1/21 Structure of a stereo vision system Extract interesting point from each image Determine a set of matching points Compute the fundamental
Stereo matching Francesco Isgrò 3D Reconstruction and Stereo p.1/21 Structure of a stereo vision system Extract interesting point from each image Determine a set of matching points Compute the fundamental
BUILDING MODEL RECONSTRUCTION FROM DATA INTEGRATION INTRODUCTION
 BUILDING MODEL RECONSTRUCTION FROM DATA INTEGRATION Ruijin Ma Department Of Civil Engineering Technology SUNY-Alfred Alfred, NY 14802 mar@alfredstate.edu ABSTRACT Building model reconstruction has been
BUILDING MODEL RECONSTRUCTION FROM DATA INTEGRATION Ruijin Ma Department Of Civil Engineering Technology SUNY-Alfred Alfred, NY 14802 mar@alfredstate.edu ABSTRACT Building model reconstruction has been
Improved depth map estimation in Stereo Vision
 Improved depth map estimation in Stereo Vision Hajer Fradi and and Jean-Luc Dugelay EURECOM, Sophia Antipolis, France ABSTRACT In this paper, we present a new approach for dense stereo matching which is
Improved depth map estimation in Stereo Vision Hajer Fradi and and Jean-Luc Dugelay EURECOM, Sophia Antipolis, France ABSTRACT In this paper, we present a new approach for dense stereo matching which is
Local Features Tutorial: Nov. 8, 04
 Local Features Tutorial: Nov. 8, 04 Local Features Tutorial References: Matlab SIFT tutorial (from course webpage) Lowe, David G. Distinctive Image Features from Scale Invariant Features, International
Local Features Tutorial: Nov. 8, 04 Local Features Tutorial References: Matlab SIFT tutorial (from course webpage) Lowe, David G. Distinctive Image Features from Scale Invariant Features, International
Image de-fencing using RGB-D data
 Image de-fencing using RGB-D data Vikram Voleti IIIT-Hyderabad, India Supervisor: Masters thesis at IIT Kharagpur, India (2013-2014) Prof. Rajiv Ranjan Sahay Associate Professor, Electrical Engineering,
Image de-fencing using RGB-D data Vikram Voleti IIIT-Hyderabad, India Supervisor: Masters thesis at IIT Kharagpur, India (2013-2014) Prof. Rajiv Ranjan Sahay Associate Professor, Electrical Engineering,
CONTENTS. High-Accuracy Stereo Depth Maps Using Structured Light. Yeojin Yoon
 [Paper Seminar 7] CVPR2003, Vol.1, pp.195-202 High-Accuracy Stereo Depth Maps Using Structured Light Daniel Scharstein Middlebury College Richard Szeliski Microsoft Research 2012. 05. 30. Yeojin Yoon Introduction
[Paper Seminar 7] CVPR2003, Vol.1, pp.195-202 High-Accuracy Stereo Depth Maps Using Structured Light Daniel Scharstein Middlebury College Richard Szeliski Microsoft Research 2012. 05. 30. Yeojin Yoon Introduction
The SIFT (Scale Invariant Feature
 The SIFT (Scale Invariant Feature Transform) Detector and Descriptor developed by David Lowe University of British Columbia Initial paper ICCV 1999 Newer journal paper IJCV 2004 Review: Matt Brown s Canonical
The SIFT (Scale Invariant Feature Transform) Detector and Descriptor developed by David Lowe University of British Columbia Initial paper ICCV 1999 Newer journal paper IJCV 2004 Review: Matt Brown s Canonical
BSB663 Image Processing Pinar Duygulu. Slides are adapted from Selim Aksoy
 BSB663 Image Processing Pinar Duygulu Slides are adapted from Selim Aksoy Image matching Image matching is a fundamental aspect of many problems in computer vision. Object or scene recognition Solving
BSB663 Image Processing Pinar Duygulu Slides are adapted from Selim Aksoy Image matching Image matching is a fundamental aspect of many problems in computer vision. Object or scene recognition Solving
Feature Detection. Raul Queiroz Feitosa. 3/30/2017 Feature Detection 1
 Feature Detection Raul Queiroz Feitosa 3/30/2017 Feature Detection 1 Objetive This chapter discusses the correspondence problem and presents approaches to solve it. 3/30/2017 Feature Detection 2 Outline
Feature Detection Raul Queiroz Feitosa 3/30/2017 Feature Detection 1 Objetive This chapter discusses the correspondence problem and presents approaches to solve it. 3/30/2017 Feature Detection 2 Outline
Visual Tracking (1) Tracking of Feature Points and Planar Rigid Objects
 Intelligent Control Systems Visual Tracking (1) Tracking of Feature Points and Planar Rigid Objects Shingo Kagami Graduate School of Information Sciences, Tohoku University swk(at)ic.is.tohoku.ac.jp http://www.ic.is.tohoku.ac.jp/ja/swk/
Intelligent Control Systems Visual Tracking (1) Tracking of Feature Points and Planar Rigid Objects Shingo Kagami Graduate School of Information Sciences, Tohoku University swk(at)ic.is.tohoku.ac.jp http://www.ic.is.tohoku.ac.jp/ja/swk/
IMAGE-BASED 3D ACQUISITION TOOL FOR ARCHITECTURAL CONSERVATION
 IMAGE-BASED 3D ACQUISITION TOOL FOR ARCHITECTURAL CONSERVATION Joris Schouteden, Marc Pollefeys, Maarten Vergauwen, Luc Van Gool Center for Processing of Speech and Images, K.U.Leuven, Kasteelpark Arenberg
IMAGE-BASED 3D ACQUISITION TOOL FOR ARCHITECTURAL CONSERVATION Joris Schouteden, Marc Pollefeys, Maarten Vergauwen, Luc Van Gool Center for Processing of Speech and Images, K.U.Leuven, Kasteelpark Arenberg
Stereo Matching: An Outlier Confidence Approach
 Stereo Matching: An Outlier Confidence Approach Li Xu and Jiaya Jia Department of Computer Science and Engineering The Chinese University of Hong Kong {xuli,leojia}@cse.cuhk.edu.hk Abstract. One of the
Stereo Matching: An Outlier Confidence Approach Li Xu and Jiaya Jia Department of Computer Science and Engineering The Chinese University of Hong Kong {xuli,leojia}@cse.cuhk.edu.hk Abstract. One of the
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 14 FIFO 2 and SIFT. Recap and Outline
 EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 14 FIFO 2 and SIFT Oct. 15, 2013 Prof. Ronald Fearing Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California, Berkeley (slides courtesy of Prof. John Wawrzynek)
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 14 FIFO 2 and SIFT Oct. 15, 2013 Prof. Ronald Fearing Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California, Berkeley (slides courtesy of Prof. John Wawrzynek)
Image Matching Using SIFT, SURF, BRIEF and ORB: Performance Comparison for Distorted Images
 Image Matching Using SIFT, SURF, BRIEF and ORB: Performance Comparison for Distorted Images Ebrahim Karami, Siva Prasad, and Mohamed Shehata Faculty of Engineering and Applied Sciences, Memorial University,
Image Matching Using SIFT, SURF, BRIEF and ORB: Performance Comparison for Distorted Images Ebrahim Karami, Siva Prasad, and Mohamed Shehata Faculty of Engineering and Applied Sciences, Memorial University,
EECS 442 Computer vision. Stereo systems. Stereo vision Rectification Correspondence problem Active stereo vision systems
 EECS 442 Computer vision Stereo systems Stereo vision Rectification Correspondence problem Active stereo vision systems Reading: [HZ] Chapter: 11 [FP] Chapter: 11 Stereo vision P p p O 1 O 2 Goal: estimate
EECS 442 Computer vision Stereo systems Stereo vision Rectification Correspondence problem Active stereo vision systems Reading: [HZ] Chapter: 11 [FP] Chapter: 11 Stereo vision P p p O 1 O 2 Goal: estimate
Epipolar Geometry and Stereo Vision
 Epipolar Geometry and Stereo Vision Computer Vision Jia-Bin Huang, Virginia Tech Many slides from S. Seitz and D. Hoiem Last class: Image Stitching Two images with rotation/zoom but no translation. X x
Epipolar Geometry and Stereo Vision Computer Vision Jia-Bin Huang, Virginia Tech Many slides from S. Seitz and D. Hoiem Last class: Image Stitching Two images with rotation/zoom but no translation. X x
Illumination-Robust Face Recognition based on Gabor Feature Face Intrinsic Identity PCA Model
 Illumination-Robust Face Recognition based on Gabor Feature Face Intrinsic Identity PCA Model TAE IN SEOL*, SUN-TAE CHUNG*, SUNHO KI**, SEONGWON CHO**, YUN-KWANG HONG*** *School of Electronic Engineering
Illumination-Robust Face Recognition based on Gabor Feature Face Intrinsic Identity PCA Model TAE IN SEOL*, SUN-TAE CHUNG*, SUNHO KI**, SEONGWON CHO**, YUN-KWANG HONG*** *School of Electronic Engineering
Determinant of homography-matrix-based multiple-object recognition
 Determinant of homography-matrix-based multiple-object recognition 1 Nagachetan Bangalore, Madhu Kiran, Anil Suryaprakash Visio Ingenii Limited F2-F3 Maxet House Liverpool Road Luton, LU1 1RS United Kingdom
Determinant of homography-matrix-based multiple-object recognition 1 Nagachetan Bangalore, Madhu Kiran, Anil Suryaprakash Visio Ingenii Limited F2-F3 Maxet House Liverpool Road Luton, LU1 1RS United Kingdom
Stereo Epipolar Geometry for General Cameras. Sanja Fidler CSC420: Intro to Image Understanding 1 / 33
 Stereo Epipolar Geometry for General Cameras Sanja Fidler CSC420: Intro to Image Understanding 1 / 33 Stereo Epipolar geometry Case with two cameras with parallel optical axes General case Now this Sanja
Stereo Epipolar Geometry for General Cameras Sanja Fidler CSC420: Intro to Image Understanding 1 / 33 Stereo Epipolar geometry Case with two cameras with parallel optical axes General case Now this Sanja
Stereo. Outline. Multiple views 3/29/2017. Thurs Mar 30 Kristen Grauman UT Austin. Multi-view geometry, matching, invariant features, stereo vision
 Stereo Thurs Mar 30 Kristen Grauman UT Austin Outline Last time: Human stereopsis Epipolar geometry and the epipolar constraint Case example with parallel optical axes General case with calibrated cameras
Stereo Thurs Mar 30 Kristen Grauman UT Austin Outline Last time: Human stereopsis Epipolar geometry and the epipolar constraint Case example with parallel optical axes General case with calibrated cameras
Introduction to Computer Vision
 Introduction to Computer Vision Michael J. Black Nov 2009 Perspective projection and affine motion Goals Today Perspective projection 3D motion Wed Projects Friday Regularization and robust statistics
Introduction to Computer Vision Michael J. Black Nov 2009 Perspective projection and affine motion Goals Today Perspective projection 3D motion Wed Projects Friday Regularization and robust statistics
Motion Estimation and Optical Flow Tracking
 Image Matching Image Retrieval Object Recognition Motion Estimation and Optical Flow Tracking Example: Mosiacing (Panorama) M. Brown and D. G. Lowe. Recognising Panoramas. ICCV 2003 Example 3D Reconstruction
Image Matching Image Retrieval Object Recognition Motion Estimation and Optical Flow Tracking Example: Mosiacing (Panorama) M. Brown and D. G. Lowe. Recognising Panoramas. ICCV 2003 Example 3D Reconstruction
Multiple-Choice Questionnaire Group C
 Family name: Vision and Machine-Learning Given name: 1/28/2011 Multiple-Choice naire Group C No documents authorized. There can be several right answers to a question. Marking-scheme: 2 points if all right
Family name: Vision and Machine-Learning Given name: 1/28/2011 Multiple-Choice naire Group C No documents authorized. There can be several right answers to a question. Marking-scheme: 2 points if all right
Multi-stable Perception. Necker Cube
 Multi-stable Perception Necker Cube Spinning dancer illusion, Nobuyuki Kayahara Multiple view geometry Stereo vision Epipolar geometry Lowe Hartley and Zisserman Depth map extraction Essential matrix
Multi-stable Perception Necker Cube Spinning dancer illusion, Nobuyuki Kayahara Multiple view geometry Stereo vision Epipolar geometry Lowe Hartley and Zisserman Depth map extraction Essential matrix
Fast and Robust 3D Terrain Surface Reconstruction of Construction Site Using Stereo Camera
 33 rd International Symposium on Automation and Robotics in Construction (ISARC 2016) Fast and Robust 3D Terrain Surface Reconstruction of Construction Site Using Stereo Camera Changhun Sung a, Sang Hoon
33 rd International Symposium on Automation and Robotics in Construction (ISARC 2016) Fast and Robust 3D Terrain Surface Reconstruction of Construction Site Using Stereo Camera Changhun Sung a, Sang Hoon
CS 4495/7495 Computer Vision Frank Dellaert, Fall 07. Dense Stereo Some Slides by Forsyth & Ponce, Jim Rehg, Sing Bing Kang
 CS 4495/7495 Computer Vision Frank Dellaert, Fall 07 Dense Stereo Some Slides by Forsyth & Ponce, Jim Rehg, Sing Bing Kang Etymology Stereo comes from the Greek word for solid (στερεο), and the term can
CS 4495/7495 Computer Vision Frank Dellaert, Fall 07 Dense Stereo Some Slides by Forsyth & Ponce, Jim Rehg, Sing Bing Kang Etymology Stereo comes from the Greek word for solid (στερεο), and the term can
Project 2 due today Project 3 out today. Readings Szeliski, Chapter 10 (through 10.5)
 Announcements Stereo Project 2 due today Project 3 out today Single image stereogram, by Niklas Een Readings Szeliski, Chapter 10 (through 10.5) Public Library, Stereoscopic Looking Room, Chicago, by Phillips,
Announcements Stereo Project 2 due today Project 3 out today Single image stereogram, by Niklas Een Readings Szeliski, Chapter 10 (through 10.5) Public Library, Stereoscopic Looking Room, Chicago, by Phillips,
Dynamic Pushbroom Stereo Mosaics for Moving Target Extraction
 Dynamic Pushbroom Stereo Mosaics for Moving Target Extraction Paper ID #413 Abstract Our goal is to rapidly acquire panoramic mosaicing maps with information of all 3D (moving) targets as a light aerial
Dynamic Pushbroom Stereo Mosaics for Moving Target Extraction Paper ID #413 Abstract Our goal is to rapidly acquire panoramic mosaicing maps with information of all 3D (moving) targets as a light aerial
ACEEE Int. J. on Information Technology, Vol. 02, No. 01, March 2012
 Feature Tracking of Objects in Underwater Video Sequences Prabhakar C J & Praveen Kumar P U Department of P.G. Studies and Research in Computer Science Kuvempu University, Shankaraghatta - 577451 Karnataka,
Feature Tracking of Objects in Underwater Video Sequences Prabhakar C J & Praveen Kumar P U Department of P.G. Studies and Research in Computer Science Kuvempu University, Shankaraghatta - 577451 Karnataka,
A Comparison of SIFT and SURF
 A Comparison of SIFT and SURF P M Panchal 1, S R Panchal 2, S K Shah 3 PG Student, Department of Electronics & Communication Engineering, SVIT, Vasad-388306, India 1 Research Scholar, Department of Electronics
A Comparison of SIFT and SURF P M Panchal 1, S R Panchal 2, S K Shah 3 PG Student, Department of Electronics & Communication Engineering, SVIT, Vasad-388306, India 1 Research Scholar, Department of Electronics
CS5670: Computer Vision
 CS5670: Computer Vision Noah Snavely, Zhengqi Li Stereo Single image stereogram, by Niklas Een Mark Twain at Pool Table", no date, UCR Museum of Photography Stereo Given two images from different viewpoints
CS5670: Computer Vision Noah Snavely, Zhengqi Li Stereo Single image stereogram, by Niklas Een Mark Twain at Pool Table", no date, UCR Museum of Photography Stereo Given two images from different viewpoints
School of Computing University of Utah
 School of Computing University of Utah Presentation Outline 1 2 3 4 Main paper to be discussed David G. Lowe, Distinctive Image Features from Scale-Invariant Keypoints, IJCV, 2004. How to find useful keypoints?
School of Computing University of Utah Presentation Outline 1 2 3 4 Main paper to be discussed David G. Lowe, Distinctive Image Features from Scale-Invariant Keypoints, IJCV, 2004. How to find useful keypoints?
Stereo Image Rectification for Simple Panoramic Image Generation
 Stereo Image Rectification for Simple Panoramic Image Generation Yun-Suk Kang and Yo-Sung Ho Gwangju Institute of Science and Technology (GIST) 261 Cheomdan-gwagiro, Buk-gu, Gwangju 500-712 Korea Email:{yunsuk,
Stereo Image Rectification for Simple Panoramic Image Generation Yun-Suk Kang and Yo-Sung Ho Gwangju Institute of Science and Technology (GIST) 261 Cheomdan-gwagiro, Buk-gu, Gwangju 500-712 Korea Email:{yunsuk,
EE368 Project Report CD Cover Recognition Using Modified SIFT Algorithm
 EE368 Project Report CD Cover Recognition Using Modified SIFT Algorithm Group 1: Mina A. Makar Stanford University mamakar@stanford.edu Abstract In this report, we investigate the application of the Scale-Invariant
EE368 Project Report CD Cover Recognition Using Modified SIFT Algorithm Group 1: Mina A. Makar Stanford University mamakar@stanford.edu Abstract In this report, we investigate the application of the Scale-Invariant
Chapter 3 Image Registration. Chapter 3 Image Registration
 Chapter 3 Image Registration Distributed Algorithms for Introduction (1) Definition: Image Registration Input: 2 images of the same scene but taken from different perspectives Goal: Identify transformation
Chapter 3 Image Registration Distributed Algorithms for Introduction (1) Definition: Image Registration Input: 2 images of the same scene but taken from different perspectives Goal: Identify transformation
K-Means Based Matching Algorithm for Multi-Resolution Feature Descriptors
 K-Means Based Matching Algorithm for Multi-Resolution Feature Descriptors Shao-Tzu Huang, Chen-Chien Hsu, Wei-Yen Wang International Science Index, Electrical and Computer Engineering waset.org/publication/0007607
K-Means Based Matching Algorithm for Multi-Resolution Feature Descriptors Shao-Tzu Huang, Chen-Chien Hsu, Wei-Yen Wang International Science Index, Electrical and Computer Engineering waset.org/publication/0007607
arxiv: v1 [cs.cv] 28 Sep 2018
![arxiv: v1 [cs.cv] 28 Sep 2018 arxiv: v1 [cs.cv] 28 Sep 2018](/thumbs/91/106305353.jpg) Extrinsic camera calibration method and its performance evaluation Jacek Komorowski 1 and Przemyslaw Rokita 2 arxiv:1809.11073v1 [cs.cv] 28 Sep 2018 1 Maria Curie Sklodowska University Lublin, Poland jacek.komorowski@gmail.com
Extrinsic camera calibration method and its performance evaluation Jacek Komorowski 1 and Przemyslaw Rokita 2 arxiv:1809.11073v1 [cs.cv] 28 Sep 2018 1 Maria Curie Sklodowska University Lublin, Poland jacek.komorowski@gmail.com
A Novel Real-Time Feature Matching Scheme
 Sensors & Transducers, Vol. 165, Issue, February 01, pp. 17-11 Sensors & Transducers 01 by IFSA Publishing, S. L. http://www.sensorsportal.com A Novel Real-Time Feature Matching Scheme Ying Liu, * Hongbo
Sensors & Transducers, Vol. 165, Issue, February 01, pp. 17-11 Sensors & Transducers 01 by IFSA Publishing, S. L. http://www.sensorsportal.com A Novel Real-Time Feature Matching Scheme Ying Liu, * Hongbo
Augmenting Reality, Naturally:
 Augmenting Reality, Naturally: Scene Modelling, Recognition and Tracking with Invariant Image Features by Iryna Gordon in collaboration with David G. Lowe Laboratory for Computational Intelligence Department
Augmenting Reality, Naturally: Scene Modelling, Recognition and Tracking with Invariant Image Features by Iryna Gordon in collaboration with David G. Lowe Laboratory for Computational Intelligence Department
