1. SETS AND FUNCTIONS
|
|
|
- Louise Pierce
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Two marks: 1. SETS AND FUNCTIONS 1. If A C B show that A U B =B (use Venn diagram). 2. If AC B, then find A B and A\ B (use Venn diagram). 3. Let P = = {a, b, c}, Q = {g, h, x, y} and R = {a, e, f, s}. Find R\ (P Q). 4.If A = {4,6,7,8,9}, B = {2,4,6} and C = {1,2,3,4,5,6}, then find AU(B C). 5.If A = {4,6,7,8,9}, B = {2,4,6} and C = {1,2,3,4,5,6}, then find A (BUC). 6.If A = {4,6,7,8,9}, B = {2,4,6} and C = {1,2,3,4,5,6}, then find A\(C\B). 7. Given A = {a, x, y, r s}, B = {1, 3, 5, 7, - 10}, verify the commutative property of set union. 8. Verify the commutative property of set intersection for A = {l, m, n, o 2, 3, 4, 7} and B = {2, 5, 3, -2, m, n, o, p). 9. Use Venn diagram to verify (A B) U (A\B) = A. ǀ 10.Let U = { 4, 8, 12,16, 20, 24,28 }, A = { 8,16 24 } and B = { 4,16, 20, 28}. Find (AUB) ǀ 11.Let U = { 4, 8, 12,16, 20, 24,28 }, A = { 8,16 24 } and B = { 4,16, 20, 28}. Find (A B) 12. Given n (A) = = 285, n (B) = 195, n (U) = 500, n (AUB) = 410, find n (A ǀ U B ǀ ). 13. Let A = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}, B = N and f: A B be defined by f (x) = x 2. Find the range of f. Identify the type of function. 14. For the given function F= {(1, 3), (2, 5), (4, 7), (5, 9), (3, 1)}, write the domain and range. 15. If R= {(a, 2), (-5, b), (8, c), (d, - 1)} represents the identity function, find the values of a, b, c and d. 16. Write the pre-images of 2 and 3 in the function f = {(12, 2), (13, 3), (15, 3), (14, 2), (17, 17)}. 17. A = { 2, 1, 1, 2} and f = {(x, 1/x), x A}.Write down the range of f. Is f a function from A to A? Five Marks: ǀ 1. Use Venn diagrams to verify (AUB) = A ǀ B ǀ ǀ 2. Use Venn diagrams to verify (A B) = A ǀ U B ǀ 3. Use Venn diagrams to verify De Morgan s law for set difference A\ (B C) = (A \ B) U (A \ C). 4. Use Venn diagrams to verify De Morgan s law for set difference A\ (BUC) = (A \ B) (A \ C). 5. Use Venn diagrams to verify AU(B C)= (AUB) (AUC)
2 6. Use Venn diagrams to verify A (BUC)= (A B)U(A C) 7. Let U = { -2, -1 -, 0,1, 2, 3,..10}, A = { -2, 2,3,4,5} and B = {1,3,5, 8,9}. Verify De Morgan s laws of complementation 8. Let A = {a, b, c, d, e, f, g, x, y,z}, B = {1,2, c d, e} and C = {d,e, f, g, 2, y}. Verify A\ (BU C) = (A \ B) (A \ C). 9. Let A = {10,15, 20, 25, 30, 35, 40, 45,50}, B = { 1, 5,10,15, 20, 30} and C = { 7, 8, 15, 20, 35, 45, 48}. Verify A\ (B C) = (A \ B) U (A \ C). 10. In a town 85% of the people speak Tamil, 40% speak English and 20% speak Hindi. Also, 32% speak English and Tamil, 13% speak Tamil and Hindi and 10% speak English and Hindi, find the percentage of people who can speak all the three languages. 11. In a village of 120 families, 93 families use firewood for cooking, 63 families use kerosene, 45 families use cooking gas, 45 families use firewood and kerosene, 24 families use kerosene and cooking gas, 27 families use cooking gas and firewood. Find how many use firewood, kerosene and cooking gas. 12. In a survey of university students, 64 had taken mathematics course, 94 had taken computer science course, 58 had taken physics course, 28 had taken mathematics and physics, 26 had taken mathematics and computer science, 22 had taken computer science and physics course, and 14 had taken all the three courses. Find the number of students who were surveyed. Find how many had taken one course only. 13. An advertising agency finds that, of its 170 clients, 115 use Television, 110 use Radio and 130 use Magazines. Also, 85 use Television and Magazines, 75 use Television and Radio, 95 use Radio and Magazines, 70 use all the three. Draw Venn diagram to represent these data. Find (i) how many use only Radio? (ii) how many use only Television? (iii) how many use Television and magazine but not radio? 14. Let A= {0, 1, 2, 3} and B = {1, 3, 5, 7, 9 } be two sets. Let f :A B be a function given by f(x ) = 2x+1. Represent this function as (i) a set of ordered pairs (ii) a table (iii) an arrow diagram and (iv) a graph. 15. Let A = {6, 9, 15, 18, 21}; B = { 1, 2, 4, 5, 6 } and f :A B be defined by f(x) = x-3. 3 Represent f by (i) an arrow diagram (ii) a set of ordered pairs (iii) a table (iv) a graph. 16. Let A = {4, 6, 8, 10} and B = { 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 }. If f :A B is defined by f(x)= 1 x then represent f by (i) an arrow diagram (ii) a set of ordered pairs and (iii) a table. 17. A function f : [1, 6) R is defined as follows 1+x ; 1 x <2 f(x)= 2x-1 ; 2 x <4 3x 2-10 ; 4 x <6
3 Find the value of (i) f(5) (ii) f( 3) (iii) f(1 ) (iv) f (2) f( 4) (v) 2 f(5) 3f(1) 16. A function f: [-3, 7) R is defined as follows 4x x <2 f(x)= 3x 2 2 x 4 2x 3 4 < x< 7 Find (i) f (5) + f (6) (ii) f(1) f(-3) (iii) f (-2) f (4) (iv) f (3) + f (-1) 17. A function f: [-7, 6) R is defined as follows 2 f (6) f (1) X 2 +2x+1-7 x< -5 f(x)= x+5-5 x 2 x 1 2 < x < 6 Find (i) 2 f (-4) + 3 f (2) (ii) f (-7) f (-3) (iii) 4 f (-3) + 2 f (4) f (-6) 3 f(1) Prepared by S.Murugavel M.Sc., B.Ed., T.G.T in Maths murugavel213@gmail.com
4 2. SEQUENCES AND SERIES OF REAL NUMBERS Two Marks: 1. Find the common difference and 15th term of the A.P. 125, 120, 115, Find the 17th term of the A.P. 4, 9, Which term of the arithmetic sequence 24, 23 1/4, 22 ½. is 3? 4. How many terms are there in the following Arithmetic Progressions 7, 13, 19,, If a, b, c are in A.P. then prove that (a-c) 2 =4(b 2 -ac) 6. If a, b, c are in A.P. then prove that 1/bc, 1/ca, 1/ab are also in A.P. 7. How many two digit numbers are divisible by 13? 8. Which term of the geometric sequence1, 2, 4, 8,.., is 1024? 9. Find the sum of the arithmetic series Find the sum of the first 25 terms of the geometric series Find the sum of the series to 25 terms. 12. Find the sum of the series Find the sum of the series Find the sum of the series If n 3 =36100 then find n Five Marks: 1. The 10 th and 18 th terms of an A.P. are 41 and 73 respectively. Find the 27 th term. 2. The sum of three consecutive terms in an A.P. is 6 and their product is 120. Find the three numbers. 3. Find the three consecutive terms in an A. P. whose sum is 18 and the sum of their squares is The 4th term of a geometric sequence is 2/3 and the seventh term is 16/81. Find the geometric sequence. 5. If the 4 th and 7th terms of a G.P. are 54 and 1458 respectively, find the G.P. 6. The sum of first three terms of a geometric sequence is 13/12 and their product is -1. Find the common ratio and the terms. 7. If a, b, c, d are in geometric sequence, then prove that (b c) 2 +(c a) 2 +(d b) 2 =(a d) 2 8. Find the sum of the first 2n terms of the following series
5 9. In an arithmetic series, the sum of first 14 terms is -203 and the sum of the next 11 terms is 572. Find the arithmetic series. 10. Find the sum of all 3 digit natural numbers, which are divisible by Find the sum of all 3 digit natural numbers, which are divisible by Find the sum of all natural numbers between 300 and 500 which are divisible by Find the sum to n terms of the series Find the sum to n terms of the series If S1, S2,and S3 are the sum of first n, 2n and 3n terms of a geometric series respectively, then prove t6at S1(S3-S2) = (S2- S1) Find the sum of the series Find the sum of the series Find the total area of 14 squares whose sides are 11 cm, 12 cm,.., 24 cm, respectively. 20.Find the total area of 12 squares whose sides are 12 cm, 13cm,, 23cm. respectively. 21. Find the sum of the series Find the sum of the series Find the total volume of 15 cubes whose edges are 16 cm, 17 cm, 18 cm,., 30 cm respectively. Prepared by S.Murugavel M.Sc., B.Ed., T.G.T in Maths murugavel213@gmail.com
6 5. COORDINATE GEOMETRY Two Marks: 1. Find the midpoint of the line segment joining the points (3, 0) and (-1, 4). 2. The center of a circle is at (-6, 4). If one end of a diameter of the circle is at the origin, then find the other end. 3. Find the point which divides the line segment joining the points (3, 5) and (8, 10) internally in the ratio 2: Find the coordinates of the point which divides the line segment joining (3, 4) and ( 6, 2) in the ratio 3: 2 externally. 5. Find the centroid of the triangle whose vertices are A(4, -6), B(3,-2) and C(5, 2). 6. If the centroid of a triangle is at (1, 3) and two of its vertices are (-7, 6) and (8, 5) then find the third vertex of the triangle. 7. Show that the points A (2, 3), B(4, 0) and C(6, -3) are collinear. 8. If P(x, y) is any point on the line segment joining the points (a, 0) and (0, b) then prove that a/ x +b/y = 1, where a, b Find the slope of the straight line passing through the points (3, -2) and (-1, 4). 10. Find the equation of straight line whose angle of inclination is 45 and y-intercept is 2/ Find the equation of the straight line passing through the points (-1, 1) and (2,-4). 12. Find the equation of the straight line passing through the point (-2, 3) with slope 1/ If the x-intercept and y-intercept of a straight line are 2/3 and 3/4 respectively, then find the equation of the straight line. 14. Find the x and y intercepts of the straight line (i) 5x+3y - 15 = 0 (ii) 2x -y +16 = 0 (iii) 3x+10 y+ 4 = Show that the straight lines 3x+2 y- 12 = 0 and 6x +4y + 8 = are parallel. 16. Prove that the straight lines x + 2y+ 1 = 0 and 2x- y +5 = 0 are perpendicular to each other. 17. Find the equation of the straight line parallel to the line x 8y+ 13 =0 and passing through the point (2, 5). Five Marks: 1. Find the points of trisection of the line segment joining (4, - 1) and (-2, - 3). 2. Find the length of the medians of the triangle whose vertices are (1, -1), (0, 4) and (-5, 3). 3. Find the area of the triangle whose vertices are (1, 2), (-3, 4), and (-5,-6). 4. If the area of the ABC is 68 sq. units and the vertices are A (6, 7), B (-4, 1) and C (a, 9) taken in order, then find the value of a. 5. Find the area of the quadrilateral formed by the points (-4, -2), (-3, -5), (3, -2) and (2, 3). 6. Using the concept of slope, show that the points A (5, -2), B(4, -1) and C(1, 2) are collinear.
7 7. Using the concept of slope, show that the points (-2, -1), (4, 0), (3, 3) and (-3, 2) taken in order form a parallelogram. 8. Show that the opposite sides of a quadrilateral with vertices A (-2,-4), B(5, -1), C(6, 4) and D(-1, 1) taken in order are parallel. 10. Using the concept of slope, show that the vertices (1, 2), (-2, 2), (-4, -3) and (-1, -3) taken in order form a parallelogram. 8. The vertices of a ABC are A(1, 2), B(-4, 5) and C(0, 1). Find the slopes of the altitudes of the triangle. 9. The vertices of ABC are A(1, 8), B(-2, 4), C(8, -5). If M and N are the midpoints of AB and AC respectively, find the slope of MN and hence verify that MN is parallel to BC. 11. The vertices of a ABC are A(2, 1), B(-2, 3) and C(4, 5). Find the equation of the median through the vertex A. 12. Find the equations of the straight lines each passing through the point (6, -2) and whose sum of the intercepts is Find the equation of the straight lines passing through the point (2, 2) and the sum of the intercepts is Find the equation of the line whose gradient is 3/2 and which passes through P, where P divides the line segment joining A(-2, 6) and B (3, -4) in the ratio 2 : 3 internally. 15. The vertices of ABC are A(2, 1), B(6, 1) and C(4, 11). Find the equation of the straight line along the altitude from the vertex A. 16. If the vertices of a ABC are A(2, -4), B(3, 3) and C(-1, 5). Find the equation of the straight line along the altitude from the vertex B. 17. Find the equation of the perpendicular bisector of the straight line segment joining the points (3, 4) and (-1, 2). 18. Find the equation of the straight line passing through the point of intersection of the lines 2x +y -3 = 0 and 5x+y -6 = 0 and parallel to the line joining the points (1, 2) and (2, 1). 19. Find the equation of the straight line segment whose end points are the point of intersection of the straight lines 2x-3y + 4=0, x -2y +3 = 0 and the midpoint of the line joining the points (3, -2) and (-5, 8). 20. Find the equation of the straight line which passes through the point of intersection of the straight lines 5x-6 y =1 and 3x+2 y+ 5 =0and is perpendicular to the straight line 3x+5y - 11 = Find the equation of the straight line joining the point of intersection of the lines 3x-y+9 = 0 and x + 2y=4 and the point of intersection of the lines 2x+y-4=0 and x-2y+3=0 Prepared by S.Murugavel M.Sc., B.Ed., murugavel213@gmail.com
8 8. MENSURATION Two marks: 1. A solid right circular cylinder has radius 7 cm and height 20 cm. Find its curved surface area. 2. A solid right circular cylinder has radius 7 cm and height 20 cm. Find its total surface area. 3. Radius and slant height of a solid right circular cone are 35 cm and 37 cm respectively. Find the curved surface area 4. Radius and slant height of a solid right circular cone are 35 cm and 37 cm respectively. Find the total surface area of the cone. 5. Total surface area of a solid hemisphere is 675 π sq.cm. Find the curved surface area of the solid hemisphere. 6. If the circumference of the base of a solid right circular cone is 236 cm and its slant height is 12 cm, find its curved surface area. 7. If the curved surface area of solid a sphere is cm, then find the radius of the sphere. 8. Find the volume of a sphere-shaped metallic shot-put having diameter of 8.4 cm 9. If the volume of a solid sphere is /7 cu.cm, then find its radius. 10. Find the volume of a solid cylinder whose radius is 14 cm and height 30 cm. 11. The radii of two right circular cylinders are in the ratio 2: 3. Find the ratio of their volumes if their heights are in the ratio 5: Radius and slant height of a cone are 20 cm and 29 cm respectively. Find its volume 13. The circumference of the base of a 12 m high wooden solid cone is 44 m. Find the volume. 14. The volume of a cone with circular base is 216 π cu.cm. If the base radius is 9 cm, then find the height of the cone. 15. The volume of a solid hemisphere is 1152π cu.cm. Find its curved surface area Five Marks: 1. If the total surface area of a solid right circular cylinder is 880sq.cm and its radius is 10 cm, find its curved surface area. 2. The diameter of a road roller of length 120 cm is 84 cm. If it takes 500 complete revolutions to level a playground, then find the cost of levelling it at the cost of 75 paise per square metre.
9 3. A sector containing an angle of 120 is cut off from a circle of radius 21 cm and folded into a cone. Find the curved surface area of the cone. 4. The total surface area of a solid right circular cylinder is 231 cm 2. Its curved surface area is two thirds of the total surface area. Find the radius and height of the cylinder. 5. The total surface area of a solid right circular cylinder is 1540 cm 2. If the height is four times the radius of the base, then find the height of the cylinder. 6. The radii of two circular ends of a frustum shaped bucket are 15 cm and 8 cm. If its depth is 63 cm, find the capacity of the bucket in litres. 7. Volume of a hollow sphere is 11352/7 cm 3. If the outer radius is 8 cm, find the inner radius of the sphere. 8. A lead pencil is in the shape of right circular cylinder. The pencil is 28 cm long and its radius is 3 mm. If the lead is of radius 1 mm, then find the volume of the wood used in the pencil. 9. A vessel is in the form of a frustum of a cone. Its radius at one end and the height are 8 cm and 14 cm respectively. If its volume is 5676/3 cm 3, then find the radius at the other end. 10. The perimeter of the ends of a frustum of a cone is 44 cm and 8.4πcm. If the depth is 14 cm, then find its volume. 11. A solid wooden toy is in the form of a cone surmounted on a hemisphere. If the radii of the hemisphere and the base of the cone are 3.5 cm each and the total height of the toy is 17.5 cm, then find the volume of wood used in the toy. 12. A cup is in the form of a hemisphere surmounted by a cylinder. The height of the cylindrical portion is 8 cm and the total height of the cup is 11.5 cm. Find the total surface area of the cup. 13. A circus tent is to be erected in the form of a cone surmounted on a cylinder. The total height of the tent is 49 m. Diameter of the base is 42 m and height of the cylinder is 21 m. Find the cost of canvas needed to make the tent, if the cost of canvas is 12.50/m A hollow sphere of external and internal diameters of 8 cm and 4 cm respectively is melted and made into another solid in the shape of a right circular cone of base diameter of 8 cm. Find the height of the cone. 15. Spherical shaped marbles of diameter 1.4 cm each, are dropped into a cylindrical beaker of diameter 7 cm containing some water. Find the number of marbles that should be dropped into the beaker so that the water level rises by 5.6 cm. 16. Using clay, a student made a right circular cone of height 48 cm and base radius 12 cm. Another student reshapes it in the form of a sphere. Find the radius of the sphere. 17. A spherical solid material of radius 18 cm is melted and recast into three small solid spherical spheres of different sizes. If the radii of two spheres are 2cm and 12 cm, find the radius of the third sphere. 18. An iron right circular cone of diameter 8 cm and height 12 cm is melted and recast into spherical lead shots each of radius 4 mm. How many lead shots can be made?
10 19. A right circular cylinder having diameter 12 cm and height 15 cm is full of ice cream. The ice cream is to be filled in cones of height 12 cm and diameter 6 cm, having a hemispherical shape on top. Find the number of such cones which can be filled with the ice cream available. 20. A cylindrical bucket of height 32 cm and radius 18 cm is filled with sand. The bucket is emptied on the ground and a conical heap of sand is formed. If the height of the conical heap is 24 cm, find the radius and slant height of the heap. 21. A cylindrical shaped well of depth 20 m and diameter 14 m is dug. The dug out soil is evenly spread to form a cuboid-platform with base dimension 20 m X 14 m. Find the height of the platform. Prepared by
11 11. STATISTICS Two Marks: 1. Find the range and the coefficient of range of 43, 24, 38, 56, 22, 39, The largest value in a collection of data is If the range is 2.26, then find the smallest value in the collection. 3. The smallest value of a collection of data is 12 and the range is 59. Find the largest value of the collection of data. 4. Find the standard deviation of the first 10 natural numbers. 5. Calculate the standard deviation of the first 13 natural numbers. 6. If the coefficient of variation of a collection of data is 57 and its S.D is 6.84, then find the mean. 7. A group of 100 candidates have their average height cm with coefficient of variation 3.2. What is the standard deviation of their heights? Five Marks: 1. Find the standard deviation of the numbers 62, 58, 53, 50, 63, 52, Calculate the standard deviation of the following data. (i) 10, 20, 15, 8, 3, 4 (ii) 38, 40, 34, 31, 28, 26, Find the coefficient of variation of the following data. 18, 20, 15, 12, Find the coefficient of variation of the following data. 20, 18, 32, 24, Calculate the standard deviation of the following data. x f Find the standard deviation of the following distribution. x f
12 7. Find the variance of the following distribution. Class interval Frequency The time (in seconds) taken by a group of people to walk across a pedestrian crossing is given in the table below. Time (in sec.) No. of people Calculate the variance and standard deviation of the data. 9. A group of 45 house owners contributed money towards green environment of their street. The amount of money collected is shown in the table below. Amount (Rs) No. of house owners Calculate the variance and standard deviation. 10. Find the variance of the following distribution Class interval Frequency Prove that the standard deviation of the first n natural numbers is = n 2-1 Prepared by 12
13 12. PROBABILITY Two Marks: 1. An integer is chosen from the first twenty natural numbers. What is the probability that it is a prime number? 2. There are 7 defective items in a sample of 35 items. Find the probability that an item chosen at random is non-defective. 3. A ticket is drawn from a bag containing 100 tickets. The tickets are numbered from one to hundred. What is the probability of getting a ticket with a number divisible by 10? 4. A die is thrown twice. Find the probability of getting a total of 9. 5.Three dice are thrown simultaneously. Find the probability of getting the same number on all the three dice. 6. Three rotten eggs are mixed with 12 good ones. One egg is chosen at random. What is the probability of choosing a rotten egg? 7. Two coins are tossed together. What is the probability of getting at most one head cards are numbered from 1 to 20. One card is drawn at random. What is the probability that the number on the card is (i) a multiple of 4 (ii) not a multiple of 6. 9.A two digit number is formed with the digits 3, 5 and 7. Find the probability that the number so formed is greater than Find the probability that a leap year selected at random will have 53 Fridays. 11. Find the probability that a leap year selected at random will have only 52 Fridays. 12. Find the probability that a leap year selected at random will have only 52 Fridays. 13. If A is an event of a random experiment such that P (A): P (A) = 7: 12,then find P(A). 14. If A and B are mutually exclusive events such that P (A) = 3/5 P (B) =1/5then find P (AUB). 15. If A and B are two events such that find P (A) = 1/4 P (B) =2/5 and P (AUB) =1/2 then find P (A B). Five Marks: 1. Two unbiased dice are rolled once. Find the probability of getting (i) a sum 8 (ii) a doublet (iii) a sum greater than Three coins are tossed simultaneously. Using addition theorem on probability, find the probability that either exactly two tails or at least one head turn up. 3. A die is thrown twice. Find the probability that at least one of the two throws comes up with the number A card is drawn from a deck of 52 cards. Find the probability of getting a King or a Heart or a Red card.
14 5. A bag contains 10 white, 5 black, 3 green and 2 red balls. One ball is drawn at random. Find the probability that the ball drawn is white or black or green. 6. If a die is rolled twice, find the probability of getting an even number in the first time or a total of 8 7. Two dice are rolled simultaneously. Find the probability that the sum of the numbers on the faces is neither divisible by 3 nor by The probability that a girl will be selected for admission in a medical college is The probability that she will be selected for admission in an engineering college is 0.24 and the probability that she will be selected in both, is The probability that a new car will get an award for its design is 0.25, the probability that it will get an award for efficient use of fuel is 0.35 and the probability that it will get both the awards is Find the probability that (i) it will get atleast one of the two awards (ii) it will get only one of the awards 10. The probability that A, B and C can solve a problem are 4/5, 2/3, 3/7and respectively. The probability of the problem being solved by A and B is 8/15, B and C is 2/7, A and C is 12/35. The probability of the problem being solved by all the three is 8/35. Find the probability that the problem can be solved by atleast one of them. Prepared by
1. SETS AND FUNCTIONS
 1. SETS AND FUNCTIONS Two marks: 1. If A C B show that A U B =B (use Venn diagram). 2. If AC B, then find A B and A\ B (use Venn diagram). 3. Let P = = {a, b c }, Q ={g, h, x, y}and R = { a,e, f,s}. FindR\
1. SETS AND FUNCTIONS Two marks: 1. If A C B show that A U B =B (use Venn diagram). 2. If AC B, then find A B and A\ B (use Venn diagram). 3. Let P = = {a, b c }, Q ={g, h, x, y}and R = { a,e, f,s}. FindR\
S.S.L.C MATHS IMPORTANT FIVE MARKS COMPULSORY QUESTIONS
 S.S.L.C MATHS IMPORTANT FIVE MARKS COMPULSORY QUESTIONS 1. The 10 th and 18 th terms of an A.P. are 41 and 73 respectively. Find the 27 th term. 2. The sum of three consecutive terms in an A.P. is 6 and
S.S.L.C MATHS IMPORTANT FIVE MARKS COMPULSORY QUESTIONS 1. The 10 th and 18 th terms of an A.P. are 41 and 73 respectively. Find the 27 th term. 2. The sum of three consecutive terms in an A.P. is 6 and
I. SETS AND FUNCTIONS. 3. Which of the following relations are function from A = { 1,4,9,16 } to B = { -1,2,-3,-4,5,6 }?.
 TWO MARK QUESTIONS I. SETS AND FUNCTIONS 1. If A ={4,6.7.8.9}, B = {2,4,6} and C= {1,2,3,4,5,6 } then find i. A U (B C) ii. A \ (C \ B) 2. Draw venn diagram for the following. i. (A B)' ii. A (BUC) iii.
TWO MARK QUESTIONS I. SETS AND FUNCTIONS 1. If A ={4,6.7.8.9}, B = {2,4,6} and C= {1,2,3,4,5,6 } then find i. A U (B C) ii. A \ (C \ B) 2. Draw venn diagram for the following. i. (A B)' ii. A (BUC) iii.
 Chapter 14 Mensuration Surface Area and Volume Conversion of one solid into another solid Some time we have to melt one solid and convert it to another shap. For example we have to convert a metallic sphere
Chapter 14 Mensuration Surface Area and Volume Conversion of one solid into another solid Some time we have to melt one solid and convert it to another shap. For example we have to convert a metallic sphere
Time: 3 hour Total Marks: 90
 Time: 3 hour Total Marks: 90 General Instructions: 1. All questions are compulsory. 2. The question paper consists of 34 questions divided into four sections A, B, C, and D. 3. Section A contains of 8
Time: 3 hour Total Marks: 90 General Instructions: 1. All questions are compulsory. 2. The question paper consists of 34 questions divided into four sections A, B, C, and D. 3. Section A contains of 8
INTERNATIONAL INDIAN SCHOOL, RIYADH SUBJECT: MATHEMATICS PT III
 \ CLASS: X INTERNATIONAL INDIAN SCHOOL, RIYADH SUBJECT: MATHEMATICS PT III ❶ SOME APPLICATIONS OF TRIGONOMETRY 1. A 1.6 m tall girl stands at a distance of 3.2m from a lamp post and casts a shadow of 4.8
\ CLASS: X INTERNATIONAL INDIAN SCHOOL, RIYADH SUBJECT: MATHEMATICS PT III ❶ SOME APPLICATIONS OF TRIGONOMETRY 1. A 1.6 m tall girl stands at a distance of 3.2m from a lamp post and casts a shadow of 4.8
Arithmetic Sequence
 Arithmetic Sequence 1) Write an arithmetic sequence with common difference 7 Write it s algebraic form Can 150 is a term of this sequence Can the difference between any two terms of this sequence be 75?
Arithmetic Sequence 1) Write an arithmetic sequence with common difference 7 Write it s algebraic form Can 150 is a term of this sequence Can the difference between any two terms of this sequence be 75?
13. Surface Areas and Volumes. Q 2 The diameter of a garden roller is 1.4 m and it is 2 m long. How much area will it cover in 5 revolutions?
 13. Surface Areas and Volumes Q 1 Find the area enclosed between two concentric circles of radii 4 cm and 3 cm. Q 2 The diameter of a garden roller is 1.4 m and it is 2 m long. How much area will it cover
13. Surface Areas and Volumes Q 1 Find the area enclosed between two concentric circles of radii 4 cm and 3 cm. Q 2 The diameter of a garden roller is 1.4 m and it is 2 m long. How much area will it cover
CBSE CLASS X MATHS , 1 2p
 CBSE CLASS X MATHS -2013 General Instructions: (i) All questions are compulsory. (ii) The question paper consists of 34 questions divided into four sections A,B,C and D. (iii) Sections A contains 8 questions
CBSE CLASS X MATHS -2013 General Instructions: (i) All questions are compulsory. (ii) The question paper consists of 34 questions divided into four sections A,B,C and D. (iii) Sections A contains 8 questions
Mathematics Class 10 Board Sample paper-1
 1 Mathematics Class 10 Board Sample paper-1 Time allowed: 3 hours Maximum Marks: 80 General Instructions: a) All questions are compulsory. b) The question paper consists of 30 questions divided into four
1 Mathematics Class 10 Board Sample paper-1 Time allowed: 3 hours Maximum Marks: 80 General Instructions: a) All questions are compulsory. b) The question paper consists of 30 questions divided into four
EXERCISE NO:13.1. If cubes are joined end to end, the dimensions of the resulting cuboid will be 4 cm, 4cm, 8 cm. 2 lb bh lh.
 Class X - NCERT Maths EXERCISE NO:1.1 Question 1: cubes each of volume 64 cm are joined end to end. Find the surface area of the resulting cuboids. Solution 1: Given that, Volume of cubes = 64 cm (Edge)
Class X - NCERT Maths EXERCISE NO:1.1 Question 1: cubes each of volume 64 cm are joined end to end. Find the surface area of the resulting cuboids. Solution 1: Given that, Volume of cubes = 64 cm (Edge)
LEARNING MATERIAL CLASS - X
 MINIMUM TARGET 40 LEARNING MATERIAL CLASS - X Kindly select 10 units as per choice of the student Topics Marks 1. Irrationality of numbers (5 questions) 3. Polynomials(long division) (5 questions) 4 3.
MINIMUM TARGET 40 LEARNING MATERIAL CLASS - X Kindly select 10 units as per choice of the student Topics Marks 1. Irrationality of numbers (5 questions) 3. Polynomials(long division) (5 questions) 4 3.
2. The next term of. 3. If the n th term of an A.P is t n = 3-5n, then the sum of the first n terms is. (a)
 4. For a collection of data if x = 99, n = 9, (x 0) = 79 then find x and (x x) 44. A card is drawn from a deck of 5 cards. Find the probability of getting a King or a Heart or a Red card. 45. A circus
4. For a collection of data if x = 99, n = 9, (x 0) = 79 then find x and (x x) 44. A card is drawn from a deck of 5 cards. Find the probability of getting a King or a Heart or a Red card. 45. A circus
KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA, AFS,Bagdogra ( )
 KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA, AFS,Bagdogra (2017-18) SUBJECT: MATHEMATICS(041) Class - X 1. Show that 12 n cannot end with the digit 0 or 5 for any natural number n. 2. Find the value of k for which the quadratic
KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA, AFS,Bagdogra (2017-18) SUBJECT: MATHEMATICS(041) Class - X 1. Show that 12 n cannot end with the digit 0 or 5 for any natural number n. 2. Find the value of k for which the quadratic
Sarvaakarshak classes
 Sarvaakarshak classes Revision_Test_2 The best way to learn SECTION-A Question numbers 1 to 8 carry 2 marks each. 1. If the equation kx 2-2kx + 6 = 0 has equal roots, then find the value of k. 2. Which
Sarvaakarshak classes Revision_Test_2 The best way to learn SECTION-A Question numbers 1 to 8 carry 2 marks each. 1. If the equation kx 2-2kx + 6 = 0 has equal roots, then find the value of k. 2. Which
13. surface areas and volumes
 13. surface areas and volumes Important Terms, Definitions and Results Cuboid : (a) Lateral surface area = 2h(l + b) (b) Surface area = 2(lb + bh + lh) (c) Volume = lbh (d) Length of diagonal = where l,
13. surface areas and volumes Important Terms, Definitions and Results Cuboid : (a) Lateral surface area = 2h(l + b) (b) Surface area = 2(lb + bh + lh) (c) Volume = lbh (d) Length of diagonal = where l,
Q-1 The first three terms of an AP respectively are 3y 1, 3y +5 and 5y +1. Then y equals
 CBSE CLASS X Math Paper-2014 Q-1 The first three terms of an AP respectively are 3y 1, 3y +5 and 5y +1. Then y equals (A) -3 (B) 4 (C) 5 (D) 2 Q-2 In Fig. 1, QR is a common tangent to the given circles,
CBSE CLASS X Math Paper-2014 Q-1 The first three terms of an AP respectively are 3y 1, 3y +5 and 5y +1. Then y equals (A) -3 (B) 4 (C) 5 (D) 2 Q-2 In Fig. 1, QR is a common tangent to the given circles,
LESSON Verify the commutative property of set intersection for A = {l,m,n,o,2,3,4,7} and B ={ 2,5,3-2,m,n,o,p}.
 LESSON 1 2 MARKS 1. If A B, then show that A B = B (use Venn diagram). 2. If A B, then find A B and A\B(use Venn diagram). 3.Let P={a,b,c},Q={g,h,x,y} and R={a,e,f,s}. Then find (i) R \ (P Q) 4. 4.If A={4,6,7,8,9},B={2,4,6}
LESSON 1 2 MARKS 1. If A B, then show that A B = B (use Venn diagram). 2. If A B, then find A B and A\B(use Venn diagram). 3.Let P={a,b,c},Q={g,h,x,y} and R={a,e,f,s}. Then find (i) R \ (P Q) 4. 4.If A={4,6,7,8,9},B={2,4,6}
MENSURATION. 8.1 Introduction. 8.2 Surface Area. Measure what is measurable, and make measurable what is not so -Galileo Galilei
 8 Introduction Surface area and volume Cylinder Cone Sphere Combined figures and invariant volumes Archimedes (8 BC - BC) Greece Archimedes is remembered as the greatest mathematician of the ancient era.
8 Introduction Surface area and volume Cylinder Cone Sphere Combined figures and invariant volumes Archimedes (8 BC - BC) Greece Archimedes is remembered as the greatest mathematician of the ancient era.
Area of Circle, Sector and Segment
 1 P a g e m a t h s c l a s s x 1. Find the circumference and area of a circle of radius 10.5 cm. 2. Find the area of a circle whose circumference is 52.8 cm. 3. Afield is in the form of a circle. The
1 P a g e m a t h s c l a s s x 1. Find the circumference and area of a circle of radius 10.5 cm. 2. Find the area of a circle whose circumference is 52.8 cm. 3. Afield is in the form of a circle. The
Mathematics
 Mathematics Total Score 80 Time 2 ½ hours Instructions Read the instructions against each question before answering them Logical explanations should be given wherever necessary If two questions have OR
Mathematics Total Score 80 Time 2 ½ hours Instructions Read the instructions against each question before answering them Logical explanations should be given wherever necessary If two questions have OR
Class X. Mathematics (Revision Assignment) Applications of Trigonometry
 Class X Mathematics (Revision Assignment) Applications of Trigonometry 1. If the angle of elevation of a cloud from a point h meters above a lake is α and the angle of depression of its reflection in the
Class X Mathematics (Revision Assignment) Applications of Trigonometry 1. If the angle of elevation of a cloud from a point h meters above a lake is α and the angle of depression of its reflection in the
CBSE Board Paper 2011 (Set-3) Class X
 L.K.Gupta (Mathematic Classes) Ph: 981551, 1-4611 CBSE Board Paper 11 (Set-3) Class X General Instructions 1. All questions are compulsory.. The question paper consists of 34 questions divided into four
L.K.Gupta (Mathematic Classes) Ph: 981551, 1-4611 CBSE Board Paper 11 (Set-3) Class X General Instructions 1. All questions are compulsory.. The question paper consists of 34 questions divided into four
Buds Public School, Dubai
 Buds Public School, Dubai Subject: Maths Grade: 11 AB Topic: Statistics, Probability, Trigonometry, 3D, Conic Section, Straight lines and Limits and Derivatives Statistics and Probability: 1. Find the
Buds Public School, Dubai Subject: Maths Grade: 11 AB Topic: Statistics, Probability, Trigonometry, 3D, Conic Section, Straight lines and Limits and Derivatives Statistics and Probability: 1. Find the
SECONDARY DRAFT SYLLABUS. 2. Representation of functions. 3. Types of functions. 4. Composition of functions (two and three)
 et et et CLASS IX Topic :Set Language et et 1. Describing and representing sets SECONDARY DRAFT SYLLABUS Able to describe a set in Descriptive, Set- builder and roster forms and through Venn diagram. Use
et et et CLASS IX Topic :Set Language et et 1. Describing and representing sets SECONDARY DRAFT SYLLABUS Able to describe a set in Descriptive, Set- builder and roster forms and through Venn diagram. Use
DELHI PUBLIC SCHOOL BOKARO STEEL CITY
 DELHI PUBLIC SCHOOL BOKARO STEEL CITY ASSIGNMENT FOR THE SESSION 2015-2016 Class: X Subject : Mathematics Assignment No. 3 QUADRATIC EQUATIONS 1. Solve by completing the square 2x 2 + x 4 = 0. 2. Solve
DELHI PUBLIC SCHOOL BOKARO STEEL CITY ASSIGNMENT FOR THE SESSION 2015-2016 Class: X Subject : Mathematics Assignment No. 3 QUADRATIC EQUATIONS 1. Solve by completing the square 2x 2 + x 4 = 0. 2. Solve
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 SA2 Maths Solved 2016 (Set 3)
 CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 SA2 Maths Solved 2016 (Set 3) Code-LNCBSE Roll No. Please check that this question paper contains 5 printed pages. Code number given on the right hand side of the question
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 SA2 Maths Solved 2016 (Set 3) Code-LNCBSE Roll No. Please check that this question paper contains 5 printed pages. Code number given on the right hand side of the question
SURFACE AREAS AND VOLUMES
 CHAPTER 1 SURFACE AREAS AND VOLUMES (A) Main Concepts and Results Cuboid whose length l, breadth b and height h (a) Volume of cuboid lbh (b) Total surface area of cuboid 2 ( lb + bh + hl ) (c) Lateral
CHAPTER 1 SURFACE AREAS AND VOLUMES (A) Main Concepts and Results Cuboid whose length l, breadth b and height h (a) Volume of cuboid lbh (b) Total surface area of cuboid 2 ( lb + bh + hl ) (c) Lateral
SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT II, II, MATHEMATICS / Class X /
 Page 1 of 10 SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT II, II, MATHEMATICS / Class X / X Time allowed : 3 hours Maximum Marks : 80 3 80 General Instructions : (i) All questions are compulsory. (ii) The question paper consists
Page 1 of 10 SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT II, II, MATHEMATICS / Class X / X Time allowed : 3 hours Maximum Marks : 80 3 80 General Instructions : (i) All questions are compulsory. (ii) The question paper consists
CBSE SAMPLE PAPERS SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT-II (MATHS) CLASS 10
 CBSE SAMPLE PAPERS SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT-II (MATHS) CLASS 10 Time: 3 Hrs Max Marks: 90 General Instructions: A) All questions are compulsory. B) The question paper consists of 34 questions divided into
CBSE SAMPLE PAPERS SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT-II (MATHS) CLASS 10 Time: 3 Hrs Max Marks: 90 General Instructions: A) All questions are compulsory. B) The question paper consists of 34 questions divided into
BOARD PAPER - MARCH 2014
 BOARD PAPER - MARCH 2014 Time : 2 Hours Marks : 40 Notes : (i) Solve all questions. Draw diagrams wherever necessary. Use of calculator is not allowed. Figures to the right indicate full marks. Marks of
BOARD PAPER - MARCH 2014 Time : 2 Hours Marks : 40 Notes : (i) Solve all questions. Draw diagrams wherever necessary. Use of calculator is not allowed. Figures to the right indicate full marks. Marks of
MATHS WORKSHOP NTSE MENSURATION (SURFACE AREA AND VOLUME) A Pre-Foundation Program PAGE# 1. A Pre-Foundation Program
 MATHS WORKSHOP NTSE MENSURATION (SURFACE AREA AND VOLUME) PAGE# PAGE# VOLUME AND SURFACE AREA OF A FRUSTUM OF A RIGHT CIRCULAR CONE Total surface area of the frustum = curved surface area + surface area
MATHS WORKSHOP NTSE MENSURATION (SURFACE AREA AND VOLUME) PAGE# PAGE# VOLUME AND SURFACE AREA OF A FRUSTUM OF A RIGHT CIRCULAR CONE Total surface area of the frustum = curved surface area + surface area
Q.7 The probability that leap year has 53 sunday, is
 Agyat gupta (TARGET MATHEMATICS) Resi.: D-79 Vasant Vihar ; Office : 89-Laxmi bai colony Ph.: 400685,6060(O)Mobile : 9450960; 9450860 PREMIER INSTITUTE for X, XI & XII. General Instructions :. All questions
Agyat gupta (TARGET MATHEMATICS) Resi.: D-79 Vasant Vihar ; Office : 89-Laxmi bai colony Ph.: 400685,6060(O)Mobile : 9450960; 9450860 PREMIER INSTITUTE for X, XI & XII. General Instructions :. All questions
X Std. Topic Content Expected Learning Outcomes Mode of Transaction
 X Std COMMON SYLLABUS 2009 - MATHEMATICS I. Theory of Sets ii. Properties of operations on sets iii. De Morgan s lawsverification using example Venn diagram iv. Formula for n( AÈBÈ C) v. Functions To revise
X Std COMMON SYLLABUS 2009 - MATHEMATICS I. Theory of Sets ii. Properties of operations on sets iii. De Morgan s lawsverification using example Venn diagram iv. Formula for n( AÈBÈ C) v. Functions To revise
KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA SANGATHAN, ERNAKULAM REGION. SECTION A (8 x 1 = 8)
 This question paper contains 06 pages KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA SANGATHAN, ERNAKULAM REGION Class: X SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT - II Max. Marks : 90 Sub: Mathematics 2013-14 Time: 3 hrs General Instructions i) All
This question paper contains 06 pages KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA SANGATHAN, ERNAKULAM REGION Class: X SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT - II Max. Marks : 90 Sub: Mathematics 2013-14 Time: 3 hrs General Instructions i) All
IX MATHEMATICS WORK SHEETS
 ownloaded from IX MTHEMTIS WRK SHEETS LINER EQUTINS IN TW VRILES hoose the correct answer from the given four options(1 to 5): 1. If the point (2,-3) lies on the graph of the linear equation 5x kk = 1,
ownloaded from IX MTHEMTIS WRK SHEETS LINER EQUTINS IN TW VRILES hoose the correct answer from the given four options(1 to 5): 1. If the point (2,-3) lies on the graph of the linear equation 5x kk = 1,
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 SA2 Maths Solved 2016 (Set 2)
 CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 SA2 Maths Solved 2016 (Set 2) Code-LNCBSE Roll No. Please check that this question paper contains 5 printed pages. Code number given on the right hand side of the question
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 SA2 Maths Solved 2016 (Set 2) Code-LNCBSE Roll No. Please check that this question paper contains 5 printed pages. Code number given on the right hand side of the question
Chapter - 13 (Surface areas and Volumes)
 Chapter - 13 (Surface areas and Volumes) Key Concepts SN. Name Figure Lateral/curved surface area 1 Cuboid Total surface area TSA Volume (V) Symbols use for b = breadth 2. Cube 4s 2 6s 2 s 3 s = side 3.
Chapter - 13 (Surface areas and Volumes) Key Concepts SN. Name Figure Lateral/curved surface area 1 Cuboid Total surface area TSA Volume (V) Symbols use for b = breadth 2. Cube 4s 2 6s 2 s 3 s = side 3.
KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA SANGATHAN, HYDERABAD REGION
 KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA SANGATHAN, HYDERABAD REGION SAMPLE PAPER 06 (017-18) SUBJECT: MATHEMATICS(041) BLUE PRINT : CLASS X Unit Chapter VSA (1 mark) SA I ( marks) SA II (3 marks) LA (4 marks) Total Unit Total
KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA SANGATHAN, HYDERABAD REGION SAMPLE PAPER 06 (017-18) SUBJECT: MATHEMATICS(041) BLUE PRINT : CLASS X Unit Chapter VSA (1 mark) SA I ( marks) SA II (3 marks) LA (4 marks) Total Unit Total
Section A. 3. The number of solid spheres, each of diameter that could be moulded to form a solid metal cylinder of height and diameter is:
 Class X Mathematics Section A 1. If the equation has real and distinct roots, then: 2. The from the end of the A.P. is: 3. The number of solid spheres, each of diameter that could be moulded to form a
Class X Mathematics Section A 1. If the equation has real and distinct roots, then: 2. The from the end of the A.P. is: 3. The number of solid spheres, each of diameter that could be moulded to form a
Mathematics. Time Allowed: 3 hours Maximum : The question paper consists of 31 questions divided into four sections A, B, C and D.
 Sample Paper (CBSE) Series SC/SP Code No. SP-16 Mathematics Time Allowed: 3 hours Maximum : 90 General Instructions: 1. All questions are compulsory. 2. The question paper consists of 31 questions divided
Sample Paper (CBSE) Series SC/SP Code No. SP-16 Mathematics Time Allowed: 3 hours Maximum : 90 General Instructions: 1. All questions are compulsory. 2. The question paper consists of 31 questions divided
SECTION A / 1. Any point where graph of linear equation in two variables cuts x-axis is of the form. (a) (x, y) (b) (0, y) (c) (x, 0) (d) (y, x)
 SECTION A / Question numbers 1 to 8 carry 1 mark each. For each question, four alternative choices have been provided, of which only one is correct. You have to select the correct choice. 1 8 1 1. Any
SECTION A / Question numbers 1 to 8 carry 1 mark each. For each question, four alternative choices have been provided, of which only one is correct. You have to select the correct choice. 1 8 1 1. Any
2009 Fall Startup Event Thursday, September 24th, 2009
 009 Fall Startup Event This test consists of 00 problems to be solved in 0 minutes. All answers must be exact, complete, and in simplest form. To ensure consistent grading, if you get a decimal, mixed
009 Fall Startup Event This test consists of 00 problems to be solved in 0 minutes. All answers must be exact, complete, and in simplest form. To ensure consistent grading, if you get a decimal, mixed
120 cm respectively. Its base is a rectangle with
 [ In this exercise, give your answers correct to significant figures if necessary. ] 1. The base of a pyramid is an isosceles right-angled triangle where the lengths of the two equal sides are. The height
[ In this exercise, give your answers correct to significant figures if necessary. ] 1. The base of a pyramid is an isosceles right-angled triangle where the lengths of the two equal sides are. The height
Cutoff.Guru. Recruitment16.in. Recruitment16.in copyright Geometry and Mensuration. Some important mensuration formulas are:
 Geometry and Mensuration Mensuration: Mensuration is the branch of mathematics which deals with the study of Geometric shapes, Their area, Volume and different parameters in geometric objects. Some important
Geometry and Mensuration Mensuration: Mensuration is the branch of mathematics which deals with the study of Geometric shapes, Their area, Volume and different parameters in geometric objects. Some important
MATHEMATICS. Unit 1. Part 2 of 2. Expressions and Formulae
 MATHEMATICS Unit 1 Part 2 of 2 Expressions and Formulae Gradient Exercise 1 1) Work out the gradient of all the lines in the diagram. Write your answers in 1 y the form m AB T B 10 2 G H 8 6 4 F A C D
MATHEMATICS Unit 1 Part 2 of 2 Expressions and Formulae Gradient Exercise 1 1) Work out the gradient of all the lines in the diagram. Write your answers in 1 y the form m AB T B 10 2 G H 8 6 4 F A C D
cbsemath.com: Bathinda based website since Feb 2006.
 Attempt option 1 for challenging questions and 2 for easy-moderate questions Section A 1 Mark Each 1. If a + b + c = 0, a 0 and a, b, c are real numbers then roots of equation ax 2 +bx + c = 0 are (A)
Attempt option 1 for challenging questions and 2 for easy-moderate questions Section A 1 Mark Each 1. If a + b + c = 0, a 0 and a, b, c are real numbers then roots of equation ax 2 +bx + c = 0 are (A)
K.S.E.E.B., Malleshwaram, Bangalore SSLC Model Question Paper-2 (2015) MATHEMATICS
 Max Marks: 80 No. of Questions: 40 K.S.E.E.B., Malleshwaram, Bangalore SSLC Model Question Paper- (015) MATHEMATICS 81E Time: Hours 45 minutes Code No. : 81E Four alternatives are given for the each question.
Max Marks: 80 No. of Questions: 40 K.S.E.E.B., Malleshwaram, Bangalore SSLC Model Question Paper- (015) MATHEMATICS 81E Time: Hours 45 minutes Code No. : 81E Four alternatives are given for the each question.
Find the volume of one tennis ball. (2)
 1. Tennis balls are sold in cylindrical tubes that contain four balls. The radius of each tennis ball is 3.15 cm and the radius of the tube is 3.2 cm. The length of the tube is 26 cm. (a) Find the volume
1. Tennis balls are sold in cylindrical tubes that contain four balls. The radius of each tennis ball is 3.15 cm and the radius of the tube is 3.2 cm. The length of the tube is 26 cm. (a) Find the volume
11. Mensuration. Q 2 Find the altitude of a trapezium, the sum of the lengths of whose bases is 6.5 cm and whose area is 26 cm 2.
 11. Mensuration Q 1 Find the volume of a cuboid whose length is 8 cm, breadth 6 cm and height 3.5 cm. Q 2 Find the altitude of a trapezium, the sum of the lengths of whose bases is 6.5 cm and whose area
11. Mensuration Q 1 Find the volume of a cuboid whose length is 8 cm, breadth 6 cm and height 3.5 cm. Q 2 Find the altitude of a trapezium, the sum of the lengths of whose bases is 6.5 cm and whose area
Mathematics Class 10 Board Sample paper-2
 1 Mathematics Class 10 Board Sample paper-2 Time allowed: 3 hours Maximum Marks: 80 General Instructions: a) All questions are compulsory. b) The question paper consists of 30 questions divided into four
1 Mathematics Class 10 Board Sample paper-2 Time allowed: 3 hours Maximum Marks: 80 General Instructions: a) All questions are compulsory. b) The question paper consists of 30 questions divided into four
Maths Year 11 Mock Revision list
 Maths Year 11 Mock Revision list F = Foundation Tier = Foundation and igher Tier = igher Tier Number Tier Topic know and use the word integer and the equality and inequality symbols use fractions, decimals
Maths Year 11 Mock Revision list F = Foundation Tier = Foundation and igher Tier = igher Tier Number Tier Topic know and use the word integer and the equality and inequality symbols use fractions, decimals
CBSE X Mathematics 2012 Solution (SET 1) Section C
 CBSE X Mathematics 01 Solution (SET 1) Q19. Solve for x : 4x 4ax + (a b ) = 0 Section C The given quadratic equation is x ax a b 4x 4ax a b 0 4x 4ax a b a b 0 4 4 0. 4 x [ a a b b] x ( a b)( a b) 0 4x
CBSE X Mathematics 01 Solution (SET 1) Q19. Solve for x : 4x 4ax + (a b ) = 0 Section C The given quadratic equation is x ax a b 4x 4ax a b 0 4x 4ax a b a b 0 4 4 0. 4 x [ a a b b] x ( a b)( a b) 0 4x
KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA GACHIBOWLI, HYDERABAD 32
 KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA GACHIBOWLI, HYDERABAD 32 SAMPLE PAPER 04 FOR SA II (2015-16) SUBJECT: MATHEMATICS BLUE PRINT : SA-II CLASS X Unit/Topic Algebra Quadratic Equations & Arithmetic Progression Geometry
KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA GACHIBOWLI, HYDERABAD 32 SAMPLE PAPER 04 FOR SA II (2015-16) SUBJECT: MATHEMATICS BLUE PRINT : SA-II CLASS X Unit/Topic Algebra Quadratic Equations & Arithmetic Progression Geometry
CBSE - Class X Math. General Instructions:
 CBSE - Class X Math General Instructions: (I) (II) (III) (IV) All questions are compulsory. The question paper consists of 31 questions divided into four sections A,B, C and D Section A contains 4 questions
CBSE - Class X Math General Instructions: (I) (II) (III) (IV) All questions are compulsory. The question paper consists of 31 questions divided into four sections A,B, C and D Section A contains 4 questions
STRAND E: Measurement. UNIT 13 Areas Student Text Contents. Section Squares, Rectangles and Triangles Area and Circumference of Circles
 UNIT 13 Areas Student Text Contents STRAND E: Measurement Unit 13 Areas Student Text Contents Section 13.1 Squares, Rectangles and Triangles 13. Area and Circumference of Circles 13.3 Sector Areas and
UNIT 13 Areas Student Text Contents STRAND E: Measurement Unit 13 Areas Student Text Contents Section 13.1 Squares, Rectangles and Triangles 13. Area and Circumference of Circles 13.3 Sector Areas and
Section A. 1. If the two roots are and of a quadratic equation, then the quadratic equation is formed in:
 Class X Mathematics GENERAL INSTRUCTIONS: 1. All questions are compulsory. 2. The question paper consists of thirty four questions divided into four sections A, B, C & D. Section A comprises of ten questions
Class X Mathematics GENERAL INSTRUCTIONS: 1. All questions are compulsory. 2. The question paper consists of thirty four questions divided into four sections A, B, C & D. Section A comprises of ten questions
Chapter 11. Q8. Find the area of a rhombus having each side equal to 13 cm and one of whose diagonal is 24cm.
 Chapter 11 Q1. The length and breadth of a rectangular field are in the ration 3:2. If the area of the field is 3456 m 2, find the cost of fencing the field at Rs.3.50 per meter. Q2. The cost of turfing
Chapter 11 Q1. The length and breadth of a rectangular field are in the ration 3:2. If the area of the field is 3456 m 2, find the cost of fencing the field at Rs.3.50 per meter. Q2. The cost of turfing
Sample Question Paper
 Time : 3hrs. MM : 90 Sample Question Paper Term - II General Instructions: (i) (ii) All questions are compulsory. The question paper consists of 34 questions divided into 4 sections. A, B, C and D. Section
Time : 3hrs. MM : 90 Sample Question Paper Term - II General Instructions: (i) (ii) All questions are compulsory. The question paper consists of 34 questions divided into 4 sections. A, B, C and D. Section
Geometry: Unit 11 Rectangular Prism Notes Rectangular Prism:
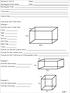 : Unit 11 Rectangular Prism Notes Date: Rectangular Prism: How do we find Total Area? Example 1 Find the area of each face: 6cm Front: Back: Top: 8cm Bottom: Left Side: Right Side: 10cm Total: How do you
: Unit 11 Rectangular Prism Notes Date: Rectangular Prism: How do we find Total Area? Example 1 Find the area of each face: 6cm Front: Back: Top: 8cm Bottom: Left Side: Right Side: 10cm Total: How do you
MATHEMATICS (SYLLABUS D) 4024/02
 CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS General Certificate of Education Ordinary Level MATHEMATICS (SYLLABUS D) 4024/02 Paper 2 Additional Materials: Answer Booklet/Paper Electronic calculator Geometrical
CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS General Certificate of Education Ordinary Level MATHEMATICS (SYLLABUS D) 4024/02 Paper 2 Additional Materials: Answer Booklet/Paper Electronic calculator Geometrical
Indiana State Math Contest Geometry
 Indiana State Math Contest 018 Geometry This test was prepared by faculty at Indiana University - Purdue University Columbus Do not open this test booklet until you have been advised to do so by the test
Indiana State Math Contest 018 Geometry This test was prepared by faculty at Indiana University - Purdue University Columbus Do not open this test booklet until you have been advised to do so by the test
Class 9 Mathematics SA2 (Sample Paper-1) SECTION A
 Class 9 Mathematics SA2 (Sample Paper-1) Max. Marks 80 General Guidelines: The question paper consists of 30 questions divided into four sections A, B, C and D. All the questions are compulsory Section
Class 9 Mathematics SA2 (Sample Paper-1) Max. Marks 80 General Guidelines: The question paper consists of 30 questions divided into four sections A, B, C and D. All the questions are compulsory Section
Assignment Volume and Surface Area of Solids
 Assignment Volume and Surface Area of Solids 1. (a) The diagonal of a cube is 16 3 cm. Find its surface area and volume. (b) The capacity of a cylindrical tank is 1848 m 3 and the diameter of its base
Assignment Volume and Surface Area of Solids 1. (a) The diagonal of a cube is 16 3 cm. Find its surface area and volume. (b) The capacity of a cylindrical tank is 1848 m 3 and the diameter of its base
Sample Question Paper. Time : 3hrs. MM : 90. Time allowed: 3 hours Maximum Marks: 90
 Sample Question Paper SOLVED SAMPLE Term QUESTION - II PAPER Time : 3hrs. MM : 90 General Instructions: (i) (ii) (iii) All questions are compulsory. The question paper consists of 34 questions divided
Sample Question Paper SOLVED SAMPLE Term QUESTION - II PAPER Time : 3hrs. MM : 90 General Instructions: (i) (ii) (iii) All questions are compulsory. The question paper consists of 34 questions divided
KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA GACHIBOWLI, HYDERABAD 32
 KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA GACHIBOWLI, HYDERABAD 32 SAMPLE PAPER 02 FOR SA II (2015-16) SUBJECT: MATHEMATICS BLUE PRINT : SA-II CLASS IX Unit/Topic Algebra Linear Equations in two variables Geometry Quadrilaterals,
KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA GACHIBOWLI, HYDERABAD 32 SAMPLE PAPER 02 FOR SA II (2015-16) SUBJECT: MATHEMATICS BLUE PRINT : SA-II CLASS IX Unit/Topic Algebra Linear Equations in two variables Geometry Quadrilaterals,
Fdaytalk.com. Acute angle The angle which is less than Right angle The angle which is equal to 90 0
 Acute angle The angle which is less than 90 0 Right angle The angle which is equal to 90 0 Obtuse angle The angle which is greater than 90 0 Straight angle The angle which is 180 0 Reflexive angle The
Acute angle The angle which is less than 90 0 Right angle The angle which is equal to 90 0 Obtuse angle The angle which is greater than 90 0 Straight angle The angle which is 180 0 Reflexive angle The
Geometry Final Exam - Study Guide
 Geometry Final Exam - Study Guide 1. Solve for x. True or False? (questions 2-5) 2. All rectangles are rhombuses. 3. If a quadrilateral is a kite, then it is a parallelogram. 4. If two parallel lines are
Geometry Final Exam - Study Guide 1. Solve for x. True or False? (questions 2-5) 2. All rectangles are rhombuses. 3. If a quadrilateral is a kite, then it is a parallelogram. 4. If two parallel lines are
Geometry 10 and 11 Notes
 Geometry 10 and 11 Notes Area and Volume Name Per Date 10.1 Area is the amount of space inside of a two dimensional object. When working with irregular shapes, we can find its area by breaking it up into
Geometry 10 and 11 Notes Area and Volume Name Per Date 10.1 Area is the amount of space inside of a two dimensional object. When working with irregular shapes, we can find its area by breaking it up into
Surface Areas and Volumes
 Exercise. Question. A plastic box.5 m long,.5 m wide and 65 cm deep is to be made. It is opened at the top. Ignoring the thickness of the plastic sheet, determine (i) The area of the sheet required for
Exercise. Question. A plastic box.5 m long,.5 m wide and 65 cm deep is to be made. It is opened at the top. Ignoring the thickness of the plastic sheet, determine (i) The area of the sheet required for
S.S.L.C REVISION PACK FOR ENGLISH MEDIUM STUDENTS CHAPTER-1 ARITHMETIC PROGRESSION
 S.S.L.C REVISION PACK FOR ENGLISH MEDIUM STUDENTS CHAPTER-1 ARITHMETIC PROGRESSION 1)Prove that 2n²+3 cannot be the n th term of an arithmetic progression? 2)The sum of three consecutive terms of an A.P
S.S.L.C REVISION PACK FOR ENGLISH MEDIUM STUDENTS CHAPTER-1 ARITHMETIC PROGRESSION 1)Prove that 2n²+3 cannot be the n th term of an arithmetic progression? 2)The sum of three consecutive terms of an A.P
Name: Date: Period: Chapter 11: Coordinate Geometry Proofs Review Sheet
 Name: Date: Period: Chapter 11: Coordinate Geometry Proofs Review Sheet Complete the entire review sheet (on here, or separate paper as indicated) h in on test day for 5 bonus points! Part 1 The Quadrilateral
Name: Date: Period: Chapter 11: Coordinate Geometry Proofs Review Sheet Complete the entire review sheet (on here, or separate paper as indicated) h in on test day for 5 bonus points! Part 1 The Quadrilateral
Mensuration: Basic Concepts and Important Formulas
 Equilateral Triangle: All the three sides are equal and each angle is equal to. Height (Altitude) = 3(side) Isosceles Triangle: Two sides and two angles are equal and altitude drawn on nonequal side bisects
Equilateral Triangle: All the three sides are equal and each angle is equal to. Height (Altitude) = 3(side) Isosceles Triangle: Two sides and two angles are equal and altitude drawn on nonequal side bisects
Shortcuts, Formulas & Tips
 & present Shortcuts, Formulas & Tips For MBA, Banking, Civil Services & Other Entrance Examinations Vol. 3: Geometry Lines and Angles Sum of the angles in a straight line is 180 Vertically opposite angles
& present Shortcuts, Formulas & Tips For MBA, Banking, Civil Services & Other Entrance Examinations Vol. 3: Geometry Lines and Angles Sum of the angles in a straight line is 180 Vertically opposite angles
Surface Area and Volume
 Surface Area and Volume Level 1 2 1. Calculate the surface area and volume of each shape. Use metres for all lengths. Write your answers to 4 decimal places: a) 0.8 m Surface Area: Volume: b) 1 m 0.2 m
Surface Area and Volume Level 1 2 1. Calculate the surface area and volume of each shape. Use metres for all lengths. Write your answers to 4 decimal places: a) 0.8 m Surface Area: Volume: b) 1 m 0.2 m
Moore Catholic High School Math Department
 Moore Catholic High School Math Department Geometry Vocabulary The following is a list of terms and properties which are necessary for success in a Geometry class. You will be tested on these terms during
Moore Catholic High School Math Department Geometry Vocabulary The following is a list of terms and properties which are necessary for success in a Geometry class. You will be tested on these terms during
100+ Mensuration Questions With Solution
 100+ Mensuration Questions With Solution GovernmentAdda.com Governmentadda.com IBPS SSC SBI RBI SBI FCI RRB RAILWAYS 1 1. What will be the area of trapezium whose parallel sides are 22 cm and 16 cm long,
100+ Mensuration Questions With Solution GovernmentAdda.com Governmentadda.com IBPS SSC SBI RBI SBI FCI RRB RAILWAYS 1 1. What will be the area of trapezium whose parallel sides are 22 cm and 16 cm long,
SURFACE AREAS AND VOLUMES OF SOLID FIGURES
 Surface Areas and Volumes of Solid Figures MODULE - 4 1 SURFACE AREAS AND VOLUMES OF SOLID FIGURES In the previous lesson, you have studied about perimeters and areas of plane figures like rectangles,
Surface Areas and Volumes of Solid Figures MODULE - 4 1 SURFACE AREAS AND VOLUMES OF SOLID FIGURES In the previous lesson, you have studied about perimeters and areas of plane figures like rectangles,
11 cm. A rectangular container is 12 cm long, 11 cm wide and 10 cm high. The container is filled with water to a depth of 8 cm.
 Diagram NOT accurately drawn 10 cm 11 cm 12 cm 3.5 cm A rectangular container is 12 cm long, 11 cm wide and 10 cm high. The container is filled with water to a depth of 8 cm. A metal sphere of radius 3.5
Diagram NOT accurately drawn 10 cm 11 cm 12 cm 3.5 cm A rectangular container is 12 cm long, 11 cm wide and 10 cm high. The container is filled with water to a depth of 8 cm. A metal sphere of radius 3.5
Grade IX. Mathematics Geometry Notes. #GrowWithGreen
 Grade IX Mathematics Geometry Notes #GrowWithGreen The distance of a point from the y - axis is called its x -coordinate, or abscissa, and the distance of the point from the x -axis is called its y-coordinate,
Grade IX Mathematics Geometry Notes #GrowWithGreen The distance of a point from the y - axis is called its x -coordinate, or abscissa, and the distance of the point from the x -axis is called its y-coordinate,
1. Area of (i) a trapezium = half of the sum of the lengths of parallel sides perpendicular distance between them.
 Mensuration. Area of (i) a trapezium = half of the sum of the lengths of parallel sides perpendicular distance between them. A D E B C The area of rectangle ABCD and areas of triangles AEB and DCF will
Mensuration. Area of (i) a trapezium = half of the sum of the lengths of parallel sides perpendicular distance between them. A D E B C The area of rectangle ABCD and areas of triangles AEB and DCF will
8 40. Mark your answers in the M.C. answer sheet. 1. Simplify 5 5 C. 5. D Factorize 8a 3 27b 3. A. 2a 3b 4a 2 6ab 9b 2. B. 2a 3b 4a 2 6ab 9b 2
 Section. Simplify.. 5. 5 5.. 5. D. 5. Multiple hoice: Mark your answers in the M.. answer sheet. 8 40.. Factorize 8a 7b.. a b 4a 6ab 9b.. a b 4a 6ab 9b.. a b 4a 6ab 9b. D. a b 4a 6ab 9b.. 0000000 =. 5
Section. Simplify.. 5. 5 5.. 5. D. 5. Multiple hoice: Mark your answers in the M.. answer sheet. 8 40.. Factorize 8a 7b.. a b 4a 6ab 9b.. a b 4a 6ab 9b.. a b 4a 6ab 9b. D. a b 4a 6ab 9b.. 0000000 =. 5
MATH-G Geometry SOL Test 2015 Exam not valid for Paper Pencil Test Sessions
 MATH-G Geometry SOL Test 2015 Exam not valid for Paper Pencil Test Sessions [Exam ID:2LKRLG 1 Which Venn diagram accurately represents the information in the following statement? If a triangle is equilateral,
MATH-G Geometry SOL Test 2015 Exam not valid for Paper Pencil Test Sessions [Exam ID:2LKRLG 1 Which Venn diagram accurately represents the information in the following statement? If a triangle is equilateral,
AREA OF PLANE FIGURES
 AREA OF PLANE FIGURES 1. Triangle Area of triangle = 1 x base x height Area of an equilateral triangle = 4 ( side) If the length of the sides of a triangle are a, b and c and if the semiperimeter s = (
AREA OF PLANE FIGURES 1. Triangle Area of triangle = 1 x base x height Area of an equilateral triangle = 4 ( side) If the length of the sides of a triangle are a, b and c and if the semiperimeter s = (
MAHESH TUTORIALS I.C.S.E.
 MAHESH TUTORIALS I.C.S.E. GRADE - X (2017-2018) Exam No. : MT/ICSE/SEMI PRELIM - I - SET - B 005 Value Added Tax, Banking, Shares and Dividend, Matrices, Reflection, Section and Mid-Point Formula, Equation
MAHESH TUTORIALS I.C.S.E. GRADE - X (2017-2018) Exam No. : MT/ICSE/SEMI PRELIM - I - SET - B 005 Value Added Tax, Banking, Shares and Dividend, Matrices, Reflection, Section and Mid-Point Formula, Equation
Name Honors Geometry Final Exam Review
 2014-2015 Name Honors Geometry Final Eam Review Chapter 5 Use the picture at the right to answer the following questions. 1. AC= 2. m BFD = 3. m CAE = A 29 C B 71⁰ 19 D 16 F 65⁰ E 4. Find the equation
2014-2015 Name Honors Geometry Final Eam Review Chapter 5 Use the picture at the right to answer the following questions. 1. AC= 2. m BFD = 3. m CAE = A 29 C B 71⁰ 19 D 16 F 65⁰ E 4. Find the equation
SAMPLE PAPER 2 (SA II) Mathematics CLASS : X. Time: 3hrs Max. Marks: 90
 SAMPLE PAPER 2 (SA II) Mathematics MR SANDESH KUMAR BHAT KV 1 JAMMU CLASS : X Time: 3hrs Max. Marks: 90 General Instruction:- 1. All questions are Compulsory. 1. The question paper consists of 34 questions
SAMPLE PAPER 2 (SA II) Mathematics MR SANDESH KUMAR BHAT KV 1 JAMMU CLASS : X Time: 3hrs Max. Marks: 90 General Instruction:- 1. All questions are Compulsory. 1. The question paper consists of 34 questions
General Certificate of Secondary Education Higher Tier November Time allowed 1 hour 30 minutes
 Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials Pages Mark Mathematics General Certificate of Secondary Education Higher Tier November 2014
Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials Pages Mark Mathematics General Certificate of Secondary Education Higher Tier November 2014
Grade 9 Math Terminology
 Unit 1 Basic Skills Review BEDMAS a way of remembering order of operations: Brackets, Exponents, Division, Multiplication, Addition, Subtraction Collect like terms gather all like terms and simplify as
Unit 1 Basic Skills Review BEDMAS a way of remembering order of operations: Brackets, Exponents, Division, Multiplication, Addition, Subtraction Collect like terms gather all like terms and simplify as
If three points A (h, 0), P (a, b) and B (0, k) lie on a line, show that: a b 1.
 ASSIGNMENT ON STRAIGHT LINES LEVEL 1 (CBSE/NCERT/STATE BOARDS) 1 Find the angle between the lines joining the points (0, 0), (2, 3) and the points (2, 2), (3, 5). 2 What is the value of y so that the line
ASSIGNMENT ON STRAIGHT LINES LEVEL 1 (CBSE/NCERT/STATE BOARDS) 1 Find the angle between the lines joining the points (0, 0), (2, 3) and the points (2, 2), (3, 5). 2 What is the value of y so that the line
Grade 10 Surface Area and Volume
 ID : ae-10-surface-area-and-volume [1] Grade 10 Surface Area and Volume For more such worksheets visit www.edugain.com Choose correct answer(s) from the given choices (1) The perimeters of the ends of
ID : ae-10-surface-area-and-volume [1] Grade 10 Surface Area and Volume For more such worksheets visit www.edugain.com Choose correct answer(s) from the given choices (1) The perimeters of the ends of
SOLID SHAPES M.K. HOME TUITION. Mathematics Revision Guides. Level: GCSE Foundation Tier
 Mathematics Revision Guides Solid Shapes Page 1 of 15 M.K. HOME TUITION Mathematics Revision Guides Level: GCSE Foundation Tier SOLID SHAPES Version: 1. Date: 10-11-2015 Mathematics Revision Guides Solid
Mathematics Revision Guides Solid Shapes Page 1 of 15 M.K. HOME TUITION Mathematics Revision Guides Level: GCSE Foundation Tier SOLID SHAPES Version: 1. Date: 10-11-2015 Mathematics Revision Guides Solid
KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA GACHIBOWLI, HYDERABAD 32
 KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA GACHIBOWLI, HYDERABAD 32 SAMPLE PAPER 02 FOR SA II (2016-17) SUBJECT: MATHEMATICS BLUE PRINT : SA-II CLASS IX Unit/Topic Algebra Linear Equations in two variables Geometry Quadrilaterals,
KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA GACHIBOWLI, HYDERABAD 32 SAMPLE PAPER 02 FOR SA II (2016-17) SUBJECT: MATHEMATICS BLUE PRINT : SA-II CLASS IX Unit/Topic Algebra Linear Equations in two variables Geometry Quadrilaterals,
Scheme of Work Form 4 (Scheme A)
 Scheme of Work Form 4 (Scheme A) Topic A revision of number work Directed Numbers Content Factors and Multiples Expressing a number as a product of prime factors LCM and HCF Objectives - Core and Paper
Scheme of Work Form 4 (Scheme A) Topic A revision of number work Directed Numbers Content Factors and Multiples Expressing a number as a product of prime factors LCM and HCF Objectives - Core and Paper
General Certificate of Secondary Education Higher Tier June 2014
 Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials Pages Mark Mathematics General Certificate of Secondary Education Higher Tier June 2014 43603H
Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials Pages Mark Mathematics General Certificate of Secondary Education Higher Tier June 2014 43603H
S8.6 Volume. Section 1. Surface area of cuboids: Q1. Work out the surface area of each cuboid shown below:
 Things to Learn (Key words, Notation & Formulae) Complete from your notes Radius- Diameter- Surface Area- Volume- Capacity- Prism- Cross-section- Surface area of a prism- Surface area of a cylinder- Volume
Things to Learn (Key words, Notation & Formulae) Complete from your notes Radius- Diameter- Surface Area- Volume- Capacity- Prism- Cross-section- Surface area of a prism- Surface area of a cylinder- Volume
P1 REVISION EXERCISE: 1
 P1 REVISION EXERCISE: 1 1. Solve the simultaneous equations: x + y = x +y = 11. For what values of p does the equation px +4x +(p 3) = 0 have equal roots? 3. Solve the equation 3 x 1 =7. Give your answer
P1 REVISION EXERCISE: 1 1. Solve the simultaneous equations: x + y = x +y = 11. For what values of p does the equation px +4x +(p 3) = 0 have equal roots? 3. Solve the equation 3 x 1 =7. Give your answer
SURFACE AREA AND VOLUME EXERCISE cubes each of volume 64 cm3 are joined end to end. Find the surface area of the resulting cuboid.
 SURFACE AREA AND VOLUME EXERCISE -13.1 1. 2 cubes each of volume 64 cm3 are joined end to end. Find the surface area of the resulting cuboid. Solution: 1 The volume of each cube = 64 cm 2 3 Sides of each
SURFACE AREA AND VOLUME EXERCISE -13.1 1. 2 cubes each of volume 64 cm3 are joined end to end. Find the surface area of the resulting cuboid. Solution: 1 The volume of each cube = 64 cm 2 3 Sides of each
1. Alicia tosses 3 fair coins. What is the probability that she gets at 1. least 1 head? Express your answer as a common fraction.
 Blitz, Page 1 1. Alicia tosses 3 fair coins. What is the probability that she gets at 1. least 1 head? Express your answer as a common fraction. 2. It took Anita 2.25 hours to walk 12.5 km. At this rate,
Blitz, Page 1 1. Alicia tosses 3 fair coins. What is the probability that she gets at 1. least 1 head? Express your answer as a common fraction. 2. It took Anita 2.25 hours to walk 12.5 km. At this rate,
Papers 1F and 2F (Foundation Tier)
 Papers 1F and 2F (Foundation Tier) Content overview Number Numbers and the number system Algebra Equations, formulae and identities Sequences, functions and graphs Geometry Shape, space and measure Vectors
Papers 1F and 2F (Foundation Tier) Content overview Number Numbers and the number system Algebra Equations, formulae and identities Sequences, functions and graphs Geometry Shape, space and measure Vectors
