Data Organization and Processing
|
|
|
- Bernadette Lyons
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Data Organization and Processing Spatial Join (NDBI007) David Hoksza
2 Outline Spatial join basics Relational join Spatial join
3 Spatial join definition (1) Given two sets of multi-dimensional objects in Euclidean space, a spatial join finds all pairs of objects satisfying a given spatial relation between the objects, such as intersection. Simplified spatial join Given two sets of rectangles, R and S, find all of the pairs of intersecting rectangles between the two sets, i.e. { r, s : r s, r R, s S}
4 Spatial join definition (2) Spatial overlay join (general spatial join) the data set can consist of general spatial objects (points, lines, polygons) the data sets can have more than two dimensions the relation between pairs of spatial objects can be any spatial relation (nearness, enclosure, direction, ) there can be more sets in the relation (multiway spatial join) or one set joined with itself (self spatial join)
5 Spatial join examples Find all pair of rivers and cities that intersect. Find all of the rural areas that are below sea level, given an elevation and land use map. Find the houses inside the areas with poor slope stability.
6 Non-spatial join There exist algorithms for standard relational join only equi-joins (the join predicate is equality) considered here nested loop join (hnízděné cykly) sort-merge join (setřídění-slévání) hash join (hashované spojení) most of the standard relational join algorithms are not suitable for spatial data because the join condition involves multidimensional spatial attribute
7 Non-spatial nested loop join Nested loop join checks one by one for each element of a relation R all elements in relation in S FOREACH r R DO FOREACH s S DO IF cond(r,s) THEN REPORT(r,s) In its basic version, the nested loop join is the least efficient algorithm from the relational joins algorithms The only of the standard relational join algorithms applicable also to spatial data Therefore special spatial join algorithms had to be developed
8 Non-spatial sort-merge join Two-phase algorithm sort both relations R, S independently scan both relations at once in the same order and join Multi-dimensional data do not preserve proximity so this method (used as is) is not applicable to spatial data
9 Non-spatial hash join Hash join One of the relations (R) is hashed with a hash function h (the assumption that R fits into main memory) The other relation (S) is processed one by one and the elements ids are hashed with h If for two elements r R, s S: h r = h(s) then r and s are checked for r. cmpr_attributes = s. cmpr_attributes Equijoins rely on grouping objects with the same value which is not possible for spatial objects since these have an extent
10 Filter-refine policy The objects to be searched for can be very complex testing of the join condition (spatial predicate) itself can be highly time demanding not many objects fit into main memory filter-refine strategy Spatial objects are approximated using simple spatial objects Filter-refine filter - the spatial join is conducted using the objects approximations candidate set refine pairs which pass the filter are tested for the spatial predicate using their full spatial representation
11 Approximations (1) The most common approximation is minimum bounding rectangle (MBR) the smallest rectangle fully enclosing given object whose sides are parallel to the axes Dead space the amount of space covered by the approximation but not the approximated object the approximation should aim to minimize dead space large dead space areas can lead to higher false hit rate in the filtering stage Large dead area False hit
12 Approximations (2) Conservative every point of the object is also point of the approximation concave convex MBR most common minimum bounding polygon minimum bounding circle/ellipse Progressive every point of the approximation is also point of the object maximum nested rectangles, circles,
13 Approximations (3) Object decomposition minimizes dead space by decomposing an object into disjoint fragments with their own MBRs after refine step and extra filtering stage is needed to remove duplicities
14 Spatial join methods Internal Memory Methods Nested loop join External Memory Methods Hierarchical traversal Index nested loop join Plane Sweep Partitioning-based methods Z-order
15 Internal memory methods Nested loop join Index nested loop join Plane Sweep Z-order
16 Nested loop join The algorithm is identical to the standard relational one works with arbitrary object type and join condition Given datasets A and B the join takes O( A B ) time suitable for small datasets NESTED_LOOP_JOIN(setA, setb, joincondition) INPUT: Sets to join and condition based on which the join happens OUTPUT: Pairs of objects satisfying the join condition FOREACH a seta FOREACH b setb IF Satisfied(a, b, joincondition) THEN REPORT(a, b);
17 Index nested loop join Variant of nested loop join where first a spatial index is created over one of the sets The indexed set is queried by each of the objects from the second set for intersection (window query) Given datasets A and B the join takes O(log A B ) time (not including time needed for building the index) INDEX_NESTED_LOOP_JOIN(setA, setb) INPUT: Sets to join OUTPUT: Pairs of intersecting objects ix := CreateSpatialIndex(setA) FOREACH b setb REPORT(ix.Search(b));
18 Plane sweep Two-phase algorithm for identification of intersecting rectangles sorting the rectangles in ascending order on the basis of their left sides (x-axis) sweeping a vertical scan line through the sorted list from left to right, halting at each of the rectangles lower x coordinates and identification of rectangles intersecting (vertical line) with the current rectangle and checking for intersection based on the y-axis Similar to non-spatial sort-merge join
19 Plane sweep algorithm (1) PLANE_SWEEP(setA, setb) INPUT: Sets of rectangles to join OUTPUT: Pairs of intersecting rectangles lista SortByLeftSide(setA); listb SortByLeftSide(setB); sweepstructa CreateSweepStructure(); sweepstructb CreateSweepStructure(); WHILE NOT(listA.End()) NOT (listb.end()) DO IF lista.first() < listb.first() THEN sweepstructa.insert(lista.first()); sweepstructb.removeinactive(lista.first()); sweepstructb.search(lista.first()); lista.next(); ELSE sweepstructb.insert(listb.first ()); sweepstructa.removeinactive(listb.first()); sweepstructa.search(listb.first()); listb.next();
20 Plane sweep algorithm (2) Sweep structure tracks active rectangles and has to support three operations Insert insert a rectangle into the active set RemoveInactive removes from the active set all rectangles that do not overlap a given rectangle (line) Search searches for all active rectangles that intersect a given rectangle and outputs them if the data are sorted, only the data in the sweep structures need to be kept in internal memory Given datasets A and B the algorithm takes O(log n n) where n = A + B, including the list sort time.
21 Z-ordering Z-order methods are based on representing an object using a set of continuous segments corresponding to Z-ordering object o { z 1, o, z n, o } The z-order-based representation can be processed in different ways sort-merge standard relational sort-merge but the sets are z-ordered plane-sweep the active set, instead of being the objects that intersect the sweep line, are the enclosing cells of the objects that intersect the current Z-order grid cell the sweep structure can be represented by a stack where each object in the stack intersects the query object
22 External memory methods Hierarchical traversal Partitioning-based methods
23 Hierarchical traversal Assumption - both datasets are indexed using a hierarchical index such as R-tree Synchronized traversal can be used to test the join condition the algorithm traverses the two trees in a synchronized fashion and compares bounding objects at given levels for indexes of different heights, the join of a leaf of one index with a sub-tree of the other can be accomplished using a window query, or handling leaf-to-node comparison as special cases if a node corresponding to a part of the space does not match the condition it can be excluded from the traversal iterative filter and refine approach reading a node usually corresponds to reading one memory page
24 General synchronized traversal INDEXED_TRAVERSAL_JOIN(rootA, rootb) INPUT: Roots of the structures representing the sets to be joined OUTPUT: Pairs of intersecting rectangles queue CreateQueue(); queue.add(pair(roota, rootb)); WHILE NOT(queue.Empty()) DO nodepair queue.pop(); pairs IdentifyIntersectingPairs(nodePair); FOREACH p pairs DO IF p is leaf THEN ReportIntersection(p); ELSE queue.add(p);
25 Partitioning Often applied when neither of the sets to be joined is indexed Resulting partitions should be small enough to fit in internal memory Once the data are partitioned, each pair of overlapping partitions is read into internal memory and internal memory techniques are used
26 Partition join of uniform data GRID_JOIN(setA, setb) INPUT: Sets of objects to be joined OUTPUT: Pairs of intersecting objects m AvailableInternalMemory(); mbrsize BytesToStoreMBR(); minnrofpartitions (seta.size() + setb.size())*mbrsize() / m; partlist DeterminePartitions(minNrOfPartitions); partitionpointersa PartitionData(partList, SetA); {object appears in every partition it intersects} partitionpointersb PartitionData(partList, SetB); FOREACH part partlist DO partitiona ReadPartition(partitionPointersA, part); partitionb ReadPartition(partitionPointersB, part); PLANE_SWEEP(partitionA, partitionb);
27 Avoiding duplicate results Space partitioning can lead to object duplication which can, in turn, lead to duplication of results partition border Deduplication sort and remove duplicates requires sorting which implies increased computational demands reference point method a consistently chosen reference point is selected from the intersecting region intersection is reported only if the reference point lies within given partition
28 Grid partitioning skewed distributions Basic grid algorithm is rarely used since the objects distribution is often not uniform [Patel & DeWitt; 1996] proposed to group partitions using a mapping function to minimize skew by creating partitions having similar number of items
29 Size-based partitioning [Koudas & Sevcik; 1997] Partitioning of data using a series of finer and finer grids level i grid contains 4 i 1 partitions (i horizontal and i vertical splitting axis) each object is placed into the partition associated with the grid in which the object does not intersect the grid lines in second-level grid are objects which cross level 3 partition borders (16 cells) but not level 2 partition borders (4 cells) each partition is a filter and objects fall through to the lowest level partition where a partition boundary is crossed Associated with level 2. Associated with level 1. Associated with level > 2.
30 Searching in size-based partitioning Given two spatial data sets A and B Scan data sets A and B and for each entity: 1. Compute the Hilbert (Z) value of the entity 2. Determine the level at which the entity belongs and place its entity descriptor in the corresponding level file For each level file 1. Sort by Hilbert (Z) value Perform a synchronized scan over the pages of level files Each page of each level file is read just once Entries in page A l (l-th level) need to be checked only against actual pages B m (m l)
Spatial Join Techniques
 Spatial Join Techniques EDWIN H. JACOX and HANAN SAMET Computer Science Department Center for Automation Research Institute for Advanced Computer Studies University of Maryland College Park, Maryland 20742
Spatial Join Techniques EDWIN H. JACOX and HANAN SAMET Computer Science Department Center for Automation Research Institute for Advanced Computer Studies University of Maryland College Park, Maryland 20742
Introduction to Spatial Database Systems
 Introduction to Spatial Database Systems by Cyrus Shahabi from Ralf Hart Hartmut Guting s VLDB Journal v3, n4, October 1994 Data Structures & Algorithms 1. Implementation of spatial algebra in an integrated
Introduction to Spatial Database Systems by Cyrus Shahabi from Ralf Hart Hartmut Guting s VLDB Journal v3, n4, October 1994 Data Structures & Algorithms 1. Implementation of spatial algebra in an integrated
Multidimensional Data and Modelling - DBMS
 Multidimensional Data and Modelling - DBMS 1 DBMS-centric approach Summary: l Spatial data is considered as another type of data beside conventional data in a DBMS. l Enabling advantages of DBMS (data
Multidimensional Data and Modelling - DBMS 1 DBMS-centric approach Summary: l Spatial data is considered as another type of data beside conventional data in a DBMS. l Enabling advantages of DBMS (data
Extending Rectangle Join Algorithms for Rectilinear Polygons
 Extending Rectangle Join Algorithms for Rectilinear Polygons Hongjun Zhu, Jianwen Su, and Oscar H. Ibarra University of California at Santa Barbara Abstract. Spatial joins are very important but costly
Extending Rectangle Join Algorithms for Rectilinear Polygons Hongjun Zhu, Jianwen Su, and Oscar H. Ibarra University of California at Santa Barbara Abstract. Spatial joins are very important but costly
An Introduction to Spatial Databases
 An Introduction to Spatial Databases R. H. Guting VLDB Journal v3, n4, October 1994 Speaker: Giovanni Conforti Outline: a rather old (but quite complete) survey on Spatial DBMS Introduction & definition
An Introduction to Spatial Databases R. H. Guting VLDB Journal v3, n4, October 1994 Speaker: Giovanni Conforti Outline: a rather old (but quite complete) survey on Spatial DBMS Introduction & definition
Introduction to Indexing R-trees. Hong Kong University of Science and Technology
 Introduction to Indexing R-trees Dimitris Papadias Hong Kong University of Science and Technology 1 Introduction to Indexing 1. Assume that you work in a government office, and you maintain the records
Introduction to Indexing R-trees Dimitris Papadias Hong Kong University of Science and Technology 1 Introduction to Indexing 1. Assume that you work in a government office, and you maintain the records
Multidimensional (spatial) Data and Modelling (2)
 Multidimensional (spatial) Data and Modelling (2) 1 Representative operations on maps l l l l l are operations on layers used in maps (all 2-d). Synonyms f. map: layer, spatial partition Def. properties:
Multidimensional (spatial) Data and Modelling (2) 1 Representative operations on maps l l l l l are operations on layers used in maps (all 2-d). Synonyms f. map: layer, spatial partition Def. properties:
CMPUT 391 Database Management Systems. Spatial Data Management. University of Alberta 1. Dr. Jörg Sander, 2006 CMPUT 391 Database Management Systems
 CMPUT 391 Database Management Systems Spatial Data Management University of Alberta 1 Spatial Data Management Shortcomings of Relational Databases and ORDBMS Modeling Spatial Data Spatial Queries Space-Filling
CMPUT 391 Database Management Systems Spatial Data Management University of Alberta 1 Spatial Data Management Shortcomings of Relational Databases and ORDBMS Modeling Spatial Data Spatial Queries Space-Filling
Course Content. Objectives of Lecture? CMPUT 391: Spatial Data Management Dr. Jörg Sander & Dr. Osmar R. Zaïane. University of Alberta
 Database Management Systems Winter 2002 CMPUT 39: Spatial Data Management Dr. Jörg Sander & Dr. Osmar. Zaïane University of Alberta Chapter 26 of Textbook Course Content Introduction Database Design Theory
Database Management Systems Winter 2002 CMPUT 39: Spatial Data Management Dr. Jörg Sander & Dr. Osmar. Zaïane University of Alberta Chapter 26 of Textbook Course Content Introduction Database Design Theory
A Real Time GIS Approximation Approach for Multiphase Spatial Query Processing Using Hierarchical-Partitioned-Indexing Technique
 International Journal of Scientific Research in Computer Science, Engineering and Information Technology 2017 IJSRCSEIT Volume 2 Issue 6 ISSN : 2456-3307 A Real Time GIS Approximation Approach for Multiphase
International Journal of Scientific Research in Computer Science, Engineering and Information Technology 2017 IJSRCSEIT Volume 2 Issue 6 ISSN : 2456-3307 A Real Time GIS Approximation Approach for Multiphase
CMSC 754 Computational Geometry 1
 CMSC 754 Computational Geometry 1 David M. Mount Department of Computer Science University of Maryland Fall 2005 1 Copyright, David M. Mount, 2005, Dept. of Computer Science, University of Maryland, College
CMSC 754 Computational Geometry 1 David M. Mount Department of Computer Science University of Maryland Fall 2005 1 Copyright, David M. Mount, 2005, Dept. of Computer Science, University of Maryland, College
Polygon Partitioning. Lecture03
 1 Polygon Partitioning Lecture03 2 History of Triangulation Algorithms 3 Outline Monotone polygon Triangulation of monotone polygon Trapezoidal decomposition Decomposition in monotone mountain Convex decomposition
1 Polygon Partitioning Lecture03 2 History of Triangulation Algorithms 3 Outline Monotone polygon Triangulation of monotone polygon Trapezoidal decomposition Decomposition in monotone mountain Convex decomposition
CSE 512 Course Project Operation Requirements
 CSE 512 Course Project Operation Requirements 1. Operation Checklist 1) Geometry union 2) Geometry convex hull 3) Geometry farthest pair 4) Geometry closest pair 5) Spatial range query 6) Spatial join
CSE 512 Course Project Operation Requirements 1. Operation Checklist 1) Geometry union 2) Geometry convex hull 3) Geometry farthest pair 4) Geometry closest pair 5) Spatial range query 6) Spatial join
What we have covered?
 What we have covered? Indexing and Hashing Data warehouse and OLAP Data Mining Information Retrieval and Web Mining XML and XQuery Spatial Databases Transaction Management 1 Lecture 6: Spatial Data Management
What we have covered? Indexing and Hashing Data warehouse and OLAP Data Mining Information Retrieval and Web Mining XML and XQuery Spatial Databases Transaction Management 1 Lecture 6: Spatial Data Management
Spatial Data Management
 Spatial Data Management [R&G] Chapter 28 CS432 1 Types of Spatial Data Point Data Points in a multidimensional space E.g., Raster data such as satellite imagery, where each pixel stores a measured value
Spatial Data Management [R&G] Chapter 28 CS432 1 Types of Spatial Data Point Data Points in a multidimensional space E.g., Raster data such as satellite imagery, where each pixel stores a measured value
Multidimensional Indexing The R Tree
 Multidimensional Indexing The R Tree Module 7, Lecture 1 Database Management Systems, R. Ramakrishnan 1 Single-Dimensional Indexes B+ trees are fundamentally single-dimensional indexes. When we create
Multidimensional Indexing The R Tree Module 7, Lecture 1 Database Management Systems, R. Ramakrishnan 1 Single-Dimensional Indexes B+ trees are fundamentally single-dimensional indexes. When we create
Spatial Data Management
 Spatial Data Management Chapter 28 Database management Systems, 3ed, R. Ramakrishnan and J. Gehrke 1 Types of Spatial Data Point Data Points in a multidimensional space E.g., Raster data such as satellite
Spatial Data Management Chapter 28 Database management Systems, 3ed, R. Ramakrishnan and J. Gehrke 1 Types of Spatial Data Point Data Points in a multidimensional space E.g., Raster data such as satellite
Intersection Acceleration
 Advanced Computer Graphics Intersection Acceleration Matthias Teschner Computer Science Department University of Freiburg Outline introduction bounding volume hierarchies uniform grids kd-trees octrees
Advanced Computer Graphics Intersection Acceleration Matthias Teschner Computer Science Department University of Freiburg Outline introduction bounding volume hierarchies uniform grids kd-trees octrees
Multidimensional Indexes [14]
![Multidimensional Indexes [14] Multidimensional Indexes [14]](/thumbs/88/117268268.jpg) CMSC 661, Principles of Database Systems Multidimensional Indexes [14] Dr. Kalpakis http://www.csee.umbc.edu/~kalpakis/courses/661 Motivation Examined indexes when search keys are in 1-D space Many interesting
CMSC 661, Principles of Database Systems Multidimensional Indexes [14] Dr. Kalpakis http://www.csee.umbc.edu/~kalpakis/courses/661 Motivation Examined indexes when search keys are in 1-D space Many interesting
Cost Models for Query Processing Strategies in the Active Data Repository
 Cost Models for Query rocessing Strategies in the Active Data Repository Chialin Chang Institute for Advanced Computer Studies and Department of Computer Science University of Maryland, College ark 272
Cost Models for Query rocessing Strategies in the Active Data Repository Chialin Chang Institute for Advanced Computer Studies and Department of Computer Science University of Maryland, College ark 272
External-Memory Algorithms with Applications in GIS - (L. Arge) Enylton Machado Roberto Beauclair
 External-Memory Algorithms with Applications in GIS - (L. Arge) Enylton Machado Roberto Beauclair {machado,tron}@visgraf.impa.br Theoretical Models Random Access Machine Memory: Infinite Array. Access
External-Memory Algorithms with Applications in GIS - (L. Arge) Enylton Machado Roberto Beauclair {machado,tron}@visgraf.impa.br Theoretical Models Random Access Machine Memory: Infinite Array. Access
Spatial Data Structures
 CSCI 420 Computer Graphics Lecture 17 Spatial Data Structures Jernej Barbic University of Southern California Hierarchical Bounding Volumes Regular Grids Octrees BSP Trees [Angel Ch. 8] 1 Ray Tracing Acceleration
CSCI 420 Computer Graphics Lecture 17 Spatial Data Structures Jernej Barbic University of Southern California Hierarchical Bounding Volumes Regular Grids Octrees BSP Trees [Angel Ch. 8] 1 Ray Tracing Acceleration
Page 1. Area-Subdivision Algorithms z-buffer Algorithm List Priority Algorithms BSP (Binary Space Partitioning Tree) Scan-line Algorithms
 Visible Surface Determination Visibility Culling Area-Subdivision Algorithms z-buffer Algorithm List Priority Algorithms BSP (Binary Space Partitioning Tree) Scan-line Algorithms Divide-and-conquer strategy:
Visible Surface Determination Visibility Culling Area-Subdivision Algorithms z-buffer Algorithm List Priority Algorithms BSP (Binary Space Partitioning Tree) Scan-line Algorithms Divide-and-conquer strategy:
R-Trees. Accessing Spatial Data
 R-Trees Accessing Spatial Data In the beginning The B-Tree provided a foundation for R- Trees. But what s a B-Tree? A data structure for storing sorted data with amortized run times for insertion and deletion
R-Trees Accessing Spatial Data In the beginning The B-Tree provided a foundation for R- Trees. But what s a B-Tree? A data structure for storing sorted data with amortized run times for insertion and deletion
Spatial Data Structures
 CSCI 480 Computer Graphics Lecture 7 Spatial Data Structures Hierarchical Bounding Volumes Regular Grids BSP Trees [Ch. 0.] March 8, 0 Jernej Barbic University of Southern California http://www-bcf.usc.edu/~jbarbic/cs480-s/
CSCI 480 Computer Graphics Lecture 7 Spatial Data Structures Hierarchical Bounding Volumes Regular Grids BSP Trees [Ch. 0.] March 8, 0 Jernej Barbic University of Southern California http://www-bcf.usc.edu/~jbarbic/cs480-s/
Orthogonal range searching. Orthogonal range search
 CG Lecture Orthogonal range searching Orthogonal range search. Problem definition and motiation. Space decomposition: techniques and trade-offs 3. Space decomposition schemes: Grids: uniform, non-hierarchical
CG Lecture Orthogonal range searching Orthogonal range search. Problem definition and motiation. Space decomposition: techniques and trade-offs 3. Space decomposition schemes: Grids: uniform, non-hierarchical
Introduction to Spatial Database Systems. Outline
 Introduction to Spatial Database Systems by Cyrus Shahabi from Ralf Hart Hartmut Guting s VLDB Journal v3, n4, October 1994 1 Outline Introduction & definition Modeling Querying Data structures and algorithms
Introduction to Spatial Database Systems by Cyrus Shahabi from Ralf Hart Hartmut Guting s VLDB Journal v3, n4, October 1994 1 Outline Introduction & definition Modeling Querying Data structures and algorithms
Computational Geometry
 Windowing queries Windowing Windowing queries Zoom in; re-center and zoom in; select by outlining Windowing Windowing queries Windowing Windowing queries Given a set of n axis-parallel line segments, preprocess
Windowing queries Windowing Windowing queries Zoom in; re-center and zoom in; select by outlining Windowing Windowing queries Windowing Windowing queries Given a set of n axis-parallel line segments, preprocess
Evaluating Queries. Query Processing: Overview. Query Processing: Example 6/2/2009. Query Processing
 Evaluating Queries Query Processing Query Processing: Overview Query Processing: Example select lname from employee where ssn = 123456789 ; query expression tree? π lname σ ssn= 123456789 employee physical
Evaluating Queries Query Processing Query Processing: Overview Query Processing: Example select lname from employee where ssn = 123456789 ; query expression tree? π lname σ ssn= 123456789 employee physical
Announcements. Written Assignment2 is out, due March 8 Graded Programming Assignment2 next Tuesday
 Announcements Written Assignment2 is out, due March 8 Graded Programming Assignment2 next Tuesday 1 Spatial Data Structures Hierarchical Bounding Volumes Grids Octrees BSP Trees 11/7/02 Speeding Up Computations
Announcements Written Assignment2 is out, due March 8 Graded Programming Assignment2 next Tuesday 1 Spatial Data Structures Hierarchical Bounding Volumes Grids Octrees BSP Trees 11/7/02 Speeding Up Computations
Potentials for Improving Query Processing in Spatial Database Systems
 Potentials for Improving Query Processing in Spatial Database Systems Hans-Peter Kriegel, Ralf Schneider, Thomas Brinkhoff Institute for Computer Science, University of Munich Leopoldstr. 11 B, W-8000
Potentials for Improving Query Processing in Spatial Database Systems Hans-Peter Kriegel, Ralf Schneider, Thomas Brinkhoff Institute for Computer Science, University of Munich Leopoldstr. 11 B, W-8000
Experimental Evaluation of Spatial Indices with FESTIval
 Experimental Evaluation of Spatial Indices with FESTIval Anderson Chaves Carniel 1, Ricardo Rodrigues Ciferri 2, Cristina Dutra de Aguiar Ciferri 1 1 Department of Computer Science University of São Paulo
Experimental Evaluation of Spatial Indices with FESTIval Anderson Chaves Carniel 1, Ricardo Rodrigues Ciferri 2, Cristina Dutra de Aguiar Ciferri 1 1 Department of Computer Science University of São Paulo
Computational Geometry
 Motivation Motivation Polygons and visibility Visibility in polygons Triangulation Proof of the Art gallery theorem Two points in a simple polygon can see each other if their connecting line segment is
Motivation Motivation Polygons and visibility Visibility in polygons Triangulation Proof of the Art gallery theorem Two points in a simple polygon can see each other if their connecting line segment is
Planar Point Location
 C.S. 252 Prof. Roberto Tamassia Computational Geometry Sem. II, 1992 1993 Lecture 04 Date: February 15, 1993 Scribe: John Bazik Planar Point Location 1 Introduction In range searching, a set of values,
C.S. 252 Prof. Roberto Tamassia Computational Geometry Sem. II, 1992 1993 Lecture 04 Date: February 15, 1993 Scribe: John Bazik Planar Point Location 1 Introduction In range searching, a set of values,
Spatial Queries. Nearest Neighbor Queries
 Spatial Queries Nearest Neighbor Queries Spatial Queries Given a collection of geometric objects (points, lines, polygons,...) organize them on disk, to answer efficiently point queries range queries k-nn
Spatial Queries Nearest Neighbor Queries Spatial Queries Given a collection of geometric objects (points, lines, polygons,...) organize them on disk, to answer efficiently point queries range queries k-nn
Polygon Triangulation. (slides partially by Daniel Vlasic )
 Polygon Triangulation (slides partially by Daniel Vlasic ) Triangulation: Definition Triangulation of a simple polygon P: decomposition of P into triangles by a maximal set of non-intersecting diagonals
Polygon Triangulation (slides partially by Daniel Vlasic ) Triangulation: Definition Triangulation of a simple polygon P: decomposition of P into triangles by a maximal set of non-intersecting diagonals
A Minimalist s Implementation of the 3-d Divide-and-Conquer Convex Hull Algorithm
 A Minimalist s Implementation of the 3-d Divide-and-Conquer Convex Hull Algorithm Timothy M. Chan Presented by Dana K. Jansens Carleton University Simple Polygons Polygon = A consecutive set of vertices
A Minimalist s Implementation of the 3-d Divide-and-Conquer Convex Hull Algorithm Timothy M. Chan Presented by Dana K. Jansens Carleton University Simple Polygons Polygon = A consecutive set of vertices
Principles of Data Management. Lecture #14 (Spatial Data Management)
 Principles of Data Management Lecture #14 (Spatial Data Management) Instructor: Mike Carey mjcarey@ics.uci.edu Database Management Systems 3ed, R. Ramakrishnan and J. Gehrke 1 Today s Notable News v Project
Principles of Data Management Lecture #14 (Spatial Data Management) Instructor: Mike Carey mjcarey@ics.uci.edu Database Management Systems 3ed, R. Ramakrishnan and J. Gehrke 1 Today s Notable News v Project
Parallel Physically Based Path-tracing and Shading Part 3 of 2. CIS565 Fall 2012 University of Pennsylvania by Yining Karl Li
 Parallel Physically Based Path-tracing and Shading Part 3 of 2 CIS565 Fall 202 University of Pennsylvania by Yining Karl Li Jim Scott 2009 Spatial cceleration Structures: KD-Trees *Some portions of these
Parallel Physically Based Path-tracing and Shading Part 3 of 2 CIS565 Fall 202 University of Pennsylvania by Yining Karl Li Jim Scott 2009 Spatial cceleration Structures: KD-Trees *Some portions of these
Computational Geometry
 Windowing queries Windowing Windowing queries Zoom in; re-center and zoom in; select by outlining Windowing Windowing queries Windowing Windowing queries Given a set of n axis-parallel line segments, preprocess
Windowing queries Windowing Windowing queries Zoom in; re-center and zoom in; select by outlining Windowing Windowing queries Windowing Windowing queries Given a set of n axis-parallel line segments, preprocess
Chap4: Spatial Storage and Indexing. 4.1 Storage:Disk and Files 4.2 Spatial Indexing 4.3 Trends 4.4 Summary
 Chap4: Spatial Storage and Indexing 4.1 Storage:Disk and Files 4.2 Spatial Indexing 4.3 Trends 4.4 Summary Learning Objectives Learning Objectives (LO) LO1: Understand concept of a physical data model
Chap4: Spatial Storage and Indexing 4.1 Storage:Disk and Files 4.2 Spatial Indexing 4.3 Trends 4.4 Summary Learning Objectives Learning Objectives (LO) LO1: Understand concept of a physical data model
CSE 530A. B+ Trees. Washington University Fall 2013
 CSE 530A B+ Trees Washington University Fall 2013 B Trees A B tree is an ordered (non-binary) tree where the internal nodes can have a varying number of child nodes (within some range) B Trees When a key
CSE 530A B+ Trees Washington University Fall 2013 B Trees A B tree is an ordered (non-binary) tree where the internal nodes can have a varying number of child nodes (within some range) B Trees When a key
External Memory Algorithms for Geometric Problems. Piotr Indyk (slides partially by Lars Arge and Jeff Vitter)
 External Memory for Geometric Problems Piotr Indyk (slides partially by Lars Arge and Jeff Vitter) Compared to Previous Lectures Another way to tackle large data sets Exact solutions (no more embeddings)
External Memory for Geometric Problems Piotr Indyk (slides partially by Lars Arge and Jeff Vitter) Compared to Previous Lectures Another way to tackle large data sets Exact solutions (no more embeddings)
Database Management Systems. Objectives of Lecture 10. The Need for a DBMS
 Database Management Systems Winter 2004 CMPUT 391: Spatial Data Management Dr. Osmar. Zaïane University of Alberta Objectives of Lecture 10 Spatial Data Management Discuss limitations of the relational
Database Management Systems Winter 2004 CMPUT 391: Spatial Data Management Dr. Osmar. Zaïane University of Alberta Objectives of Lecture 10 Spatial Data Management Discuss limitations of the relational
Computer Graphics. Bing-Yu Chen National Taiwan University The University of Tokyo
 Computer Graphics Bing-Yu Chen National Taiwan University The University of Tokyo Hidden-Surface Removal Back-Face Culling The Depth-Sort Algorithm Binary Space-Partitioning Trees The z-buffer Algorithm
Computer Graphics Bing-Yu Chen National Taiwan University The University of Tokyo Hidden-Surface Removal Back-Face Culling The Depth-Sort Algorithm Binary Space-Partitioning Trees The z-buffer Algorithm
layers in a raster model
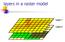 layers in a raster model Layer 1 Layer 2 layers in an vector-based model (1) Layer 2 Layer 1 layers in an vector-based model (2) raster versus vector data model Raster model Vector model Simple data structure
layers in a raster model Layer 1 Layer 2 layers in an vector-based model (1) Layer 2 Layer 1 layers in an vector-based model (2) raster versus vector data model Raster model Vector model Simple data structure
Solid Modeling. Thomas Funkhouser Princeton University C0S 426, Fall Represent solid interiors of objects
 Solid Modeling Thomas Funkhouser Princeton University C0S 426, Fall 2000 Solid Modeling Represent solid interiors of objects Surface may not be described explicitly Visible Human (National Library of Medicine)
Solid Modeling Thomas Funkhouser Princeton University C0S 426, Fall 2000 Solid Modeling Represent solid interiors of objects Surface may not be described explicitly Visible Human (National Library of Medicine)
Foundations of Multidimensional and Metric Data Structures
 Foundations of Multidimensional and Metric Data Structures Hanan Samet University of Maryland, College Park ELSEVIER AMSTERDAM BOSTON HEIDELBERG LONDON NEW YORK OXFORD PARIS SAN DIEGO SAN FRANCISCO SINGAPORE
Foundations of Multidimensional and Metric Data Structures Hanan Samet University of Maryland, College Park ELSEVIER AMSTERDAM BOSTON HEIDELBERG LONDON NEW YORK OXFORD PARIS SAN DIEGO SAN FRANCISCO SINGAPORE
Spatial Data Structures
 15-462 Computer Graphics I Lecture 17 Spatial Data Structures Hierarchical Bounding Volumes Regular Grids Octrees BSP Trees Constructive Solid Geometry (CSG) April 1, 2003 [Angel 9.10] Frank Pfenning Carnegie
15-462 Computer Graphics I Lecture 17 Spatial Data Structures Hierarchical Bounding Volumes Regular Grids Octrees BSP Trees Constructive Solid Geometry (CSG) April 1, 2003 [Angel 9.10] Frank Pfenning Carnegie
Lecture 24: Image Retrieval: Part II. Visual Computing Systems CMU , Fall 2013
 Lecture 24: Image Retrieval: Part II Visual Computing Systems Review: K-D tree Spatial partitioning hierarchy K = dimensionality of space (below: K = 2) 3 2 1 3 3 4 2 Counts of points in leaf nodes Nearest
Lecture 24: Image Retrieval: Part II Visual Computing Systems Review: K-D tree Spatial partitioning hierarchy K = dimensionality of space (below: K = 2) 3 2 1 3 3 4 2 Counts of points in leaf nodes Nearest
Efficient Processing of Spatial Joins Using R-trees
 Efficient Processing of Spatial Joins Using R-trees Thomas Brinkhoff Hans-Peter Kriegel Bernhard Seeger Institute of Computer Science, University of Munich Leopoldstr. 11 B, W- München 4, Germany e-mail:
Efficient Processing of Spatial Joins Using R-trees Thomas Brinkhoff Hans-Peter Kriegel Bernhard Seeger Institute of Computer Science, University of Munich Leopoldstr. 11 B, W- München 4, Germany e-mail:
January 10-12, NIT Surathkal Introduction to Graph and Geometric Algorithms
 Geometric data structures Sudebkumar Prasant Pal Department of Computer Science and Engineering IIT Kharagpur, 721302. email: spp@cse.iitkgp.ernet.in January 10-12, 2012 - NIT Surathkal Introduction to
Geometric data structures Sudebkumar Prasant Pal Department of Computer Science and Engineering IIT Kharagpur, 721302. email: spp@cse.iitkgp.ernet.in January 10-12, 2012 - NIT Surathkal Introduction to
Hierarchical Representation of 2-D Shapes using Convex Polygons: a Contour-Based Approach
 Hierarchical Representation of 2-D Shapes using Convex Polygons: a Contour-Based Approach O. El Badawy, M. S. Kamel Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence Laboratory, Department of Systems Design Engineering,
Hierarchical Representation of 2-D Shapes using Convex Polygons: a Contour-Based Approach O. El Badawy, M. S. Kamel Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence Laboratory, Department of Systems Design Engineering,
Spatial Data Structures and Speed-Up Techniques. Tomas Akenine-Möller Department of Computer Engineering Chalmers University of Technology
 Spatial Data Structures and Speed-Up Techniques Tomas Akenine-Möller Department of Computer Engineering Chalmers University of Technology Spatial data structures What is it? Data structure that organizes
Spatial Data Structures and Speed-Up Techniques Tomas Akenine-Möller Department of Computer Engineering Chalmers University of Technology Spatial data structures What is it? Data structure that organizes
Spatial Data Structures
 15-462 Computer Graphics I Lecture 17 Spatial Data Structures Hierarchical Bounding Volumes Regular Grids Octrees BSP Trees Constructive Solid Geometry (CSG) March 28, 2002 [Angel 8.9] Frank Pfenning Carnegie
15-462 Computer Graphics I Lecture 17 Spatial Data Structures Hierarchical Bounding Volumes Regular Grids Octrees BSP Trees Constructive Solid Geometry (CSG) March 28, 2002 [Angel 8.9] Frank Pfenning Carnegie
Collision detection. Piotr Fulma«ski. 1 grudnia
 Collision detection Piotr Fulma«ski piotr@fulmanski.pl 1 grudnia 2016 Table of contents Collision in games Algorithms to detect collision in games depend on the type of shapes that can collide (e.g. rectangle
Collision detection Piotr Fulma«ski piotr@fulmanski.pl 1 grudnia 2016 Table of contents Collision in games Algorithms to detect collision in games depend on the type of shapes that can collide (e.g. rectangle
26 The closest pair problem
 The closest pair problem 1 26 The closest pair problem Sweep algorithms solve many kinds of proximity problems efficiently. We present a simple sweep that solves the two-dimensional closest pair problem
The closest pair problem 1 26 The closest pair problem Sweep algorithms solve many kinds of proximity problems efficiently. We present a simple sweep that solves the two-dimensional closest pair problem
The Unified Segment Tree and its Application to the Rectangle Intersection Problem
 CCCG 2013, Waterloo, Ontario, August 10, 2013 The Unified Segment Tree and its Application to the Rectangle Intersection Problem David P. Wagner Abstract In this paper we introduce a variation on the multidimensional
CCCG 2013, Waterloo, Ontario, August 10, 2013 The Unified Segment Tree and its Application to the Rectangle Intersection Problem David P. Wagner Abstract In this paper we introduce a variation on the multidimensional
Collision and Proximity Queries
 Collision and Proximity Queries Dinesh Manocha (based on slides from Ming Lin) COMP790-058 Fall 2013 Geometric Proximity Queries l Given two object, how would you check: If they intersect with each other
Collision and Proximity Queries Dinesh Manocha (based on slides from Ming Lin) COMP790-058 Fall 2013 Geometric Proximity Queries l Given two object, how would you check: If they intersect with each other
Speeding Up Ray Tracing. Optimisations. Ray Tracing Acceleration
 Speeding Up Ray Tracing nthony Steed 1999, eline Loscos 2005, Jan Kautz 2007-2009 Optimisations Limit the number of rays Make the ray test faster for shadow rays the main drain on resources if there are
Speeding Up Ray Tracing nthony Steed 1999, eline Loscos 2005, Jan Kautz 2007-2009 Optimisations Limit the number of rays Make the ray test faster for shadow rays the main drain on resources if there are
Clustering Algorithm (DBSCAN) VISHAL BHARTI Computer Science Dept. GC, CUNY
 Clustering Algorithm (DBSCAN) VISHAL BHARTI Computer Science Dept. GC, CUNY Clustering Algorithm Clustering is an unsupervised machine learning algorithm that divides a data into meaningful sub-groups,
Clustering Algorithm (DBSCAN) VISHAL BHARTI Computer Science Dept. GC, CUNY Clustering Algorithm Clustering is an unsupervised machine learning algorithm that divides a data into meaningful sub-groups,
Chap4: Spatial Storage and Indexing
 Chap4: Spatial Storage and Indexing 4.1 Storage:Disk and Files 4.2 Spatial Indexing 4.3 Trends 4.4 Summary Learning Objectives Learning Objectives (LO) LO1: Understand concept of a physical data model
Chap4: Spatial Storage and Indexing 4.1 Storage:Disk and Files 4.2 Spatial Indexing 4.3 Trends 4.4 Summary Learning Objectives Learning Objectives (LO) LO1: Understand concept of a physical data model
Ray-tracing Acceleration. Acceleration Data Structures for Ray Tracing. Shadows. Shadows & Light Sources. Antialiasing Supersampling.
 Ray-tracing Acceleration Acceleration Data Structures for Ray Tracing Thanks to Fredo Durand and Barb Cutler Soft shadows Antialiasing (getting rid of jaggies) Glossy reflection Motion blur Depth of field
Ray-tracing Acceleration Acceleration Data Structures for Ray Tracing Thanks to Fredo Durand and Barb Cutler Soft shadows Antialiasing (getting rid of jaggies) Glossy reflection Motion blur Depth of field
CS 532: 3D Computer Vision 14 th Set of Notes
 1 CS 532: 3D Computer Vision 14 th Set of Notes Instructor: Philippos Mordohai Webpage: www.cs.stevens.edu/~mordohai E-mail: Philippos.Mordohai@stevens.edu Office: Lieb 215 Lecture Outline Triangulating
1 CS 532: 3D Computer Vision 14 th Set of Notes Instructor: Philippos Mordohai Webpage: www.cs.stevens.edu/~mordohai E-mail: Philippos.Mordohai@stevens.edu Office: Lieb 215 Lecture Outline Triangulating
Lecture 3: Art Gallery Problems and Polygon Triangulation
 EECS 396/496: Computational Geometry Fall 2017 Lecture 3: Art Gallery Problems and Polygon Triangulation Lecturer: Huck Bennett In this lecture, we study the problem of guarding an art gallery (specified
EECS 396/496: Computational Geometry Fall 2017 Lecture 3: Art Gallery Problems and Polygon Triangulation Lecturer: Huck Bennett In this lecture, we study the problem of guarding an art gallery (specified
Computer Graphics. The Two-Dimensional Viewing. Somsak Walairacht, Computer Engineering, KMITL
 Computer Graphics Chapter 6 The Two-Dimensional Viewing Somsak Walairacht, Computer Engineering, KMITL Outline The Two-Dimensional Viewing Pipeline The Clipping Window Normalization and Viewport Transformations
Computer Graphics Chapter 6 The Two-Dimensional Viewing Somsak Walairacht, Computer Engineering, KMITL Outline The Two-Dimensional Viewing Pipeline The Clipping Window Normalization and Viewport Transformations
External Memory Algorithms and Data Structures Fall Project 3 A GIS system
 External Memory Algorithms and Data Structures Fall 2003 1 Project 3 A GIS system GSB/RF November 17, 2003 1 Introduction The goal of this project is to implement a rudimentary Geographical Information
External Memory Algorithms and Data Structures Fall 2003 1 Project 3 A GIS system GSB/RF November 17, 2003 1 Introduction The goal of this project is to implement a rudimentary Geographical Information
Simulation in Computer Graphics Space Subdivision. Matthias Teschner
 Simulation in Computer Graphics Space Subdivision Matthias Teschner Outline Introduction Uniform grid Octree and k-d tree BSP tree University of Freiburg Computer Science Department 2 Model Partitioning
Simulation in Computer Graphics Space Subdivision Matthias Teschner Outline Introduction Uniform grid Octree and k-d tree BSP tree University of Freiburg Computer Science Department 2 Model Partitioning
Computation Geometry Exercise Range Searching II
 Computation Geometry Exercise Range Searching II LEHRSTUHL FÜR ALGORITHMIK I INSTITUT FÜR THEORETISCHE INFORMATIK FAKULTÄT FÜR INFORMATIK Guido Brückner 20.07.2018 1 Object types in range queries y0 y
Computation Geometry Exercise Range Searching II LEHRSTUHL FÜR ALGORITHMIK I INSTITUT FÜR THEORETISCHE INFORMATIK FAKULTÄT FÜR INFORMATIK Guido Brückner 20.07.2018 1 Object types in range queries y0 y
Data Warehousing & Data Mining
 Data Warehousing & Data Mining Wolf-Tilo Balke Kinda El Maarry Institut für Informationssysteme Technische Universität Braunschweig http://www.ifis.cs.tu-bs.de Summary Last week: Logical Model: Cubes,
Data Warehousing & Data Mining Wolf-Tilo Balke Kinda El Maarry Institut für Informationssysteme Technische Universität Braunschweig http://www.ifis.cs.tu-bs.de Summary Last week: Logical Model: Cubes,
Accelerating Geometric Queries. Computer Graphics CMU /15-662, Fall 2016
 Accelerating Geometric Queries Computer Graphics CMU 15-462/15-662, Fall 2016 Geometric modeling and geometric queries p What point on the mesh is closest to p? What point on the mesh is closest to p?
Accelerating Geometric Queries Computer Graphics CMU 15-462/15-662, Fall 2016 Geometric modeling and geometric queries p What point on the mesh is closest to p? What point on the mesh is closest to p?
Last Time: Acceleration Data Structures for Ray Tracing. Schedule. Today. Shadows & Light Sources. Shadows
 Last Time: Acceleration Data Structures for Ray Tracing Modeling Transformations Illumination (Shading) Viewing Transformation (Perspective / Orthographic) Clipping Projection (to Screen Space) Scan Conversion
Last Time: Acceleration Data Structures for Ray Tracing Modeling Transformations Illumination (Shading) Viewing Transformation (Perspective / Orthographic) Clipping Projection (to Screen Space) Scan Conversion
Query Processing and Advanced Queries. Advanced Queries (2): R-TreeR
 Query Processing and Advanced Queries Advanced Queries (2): R-TreeR Review: PAM Given a point set and a rectangular query, find the points enclosed in the query We allow insertions/deletions online Query
Query Processing and Advanced Queries Advanced Queries (2): R-TreeR Review: PAM Given a point set and a rectangular query, find the points enclosed in the query We allow insertions/deletions online Query
TOUCH: In-Memory Spatial Join by Hierarchical Data-Oriented Partitioning
 : In-Memory Spatial Join by Hierarchical Data-Oriented Partitioning Sadegh Nobari Farhan Tauheed Thomas Heinis Panagiotis Karras Stéphane Bressan Anastasia Ailamaki National University of Singapore, Singapore
: In-Memory Spatial Join by Hierarchical Data-Oriented Partitioning Sadegh Nobari Farhan Tauheed Thomas Heinis Panagiotis Karras Stéphane Bressan Anastasia Ailamaki National University of Singapore, Singapore
Algorithms for GIS:! Quadtrees
 Algorithms for GIS: Quadtrees Quadtree A data structure that corresponds to a hierarchical subdivision of the plane Start with a square (containing inside input data) Divide into 4 equal squares (quadrants)
Algorithms for GIS: Quadtrees Quadtree A data structure that corresponds to a hierarchical subdivision of the plane Start with a square (containing inside input data) Divide into 4 equal squares (quadrants)
CoE4TN4 Image Processing
 CoE4TN4 Image Processing Chapter 11 Image Representation & Description Image Representation & Description After an image is segmented into regions, the regions are represented and described in a form suitable
CoE4TN4 Image Processing Chapter 11 Image Representation & Description Image Representation & Description After an image is segmented into regions, the regions are represented and described in a form suitable
Prof. Gill Barequet. Center for Graphics and Geometric Computing, Technion. Dept. of Computer Science The Technion Haifa, Israel
 Computational Geometry (CS 236719) http://www.cs.tufts.edu/~barequet/teaching/cg Chapter 1 Introduction 1 Copyright 2002-2009 2009 Prof. Gill Barequet Center for Graphics and Geometric Computing Dept.
Computational Geometry (CS 236719) http://www.cs.tufts.edu/~barequet/teaching/cg Chapter 1 Introduction 1 Copyright 2002-2009 2009 Prof. Gill Barequet Center for Graphics and Geometric Computing Dept.
kd-trees Idea: Each level of the tree compares against 1 dimension. Let s us have only two children at each node (instead of 2 d )
 kd-trees Invented in 1970s by Jon Bentley Name originally meant 3d-trees, 4d-trees, etc where k was the # of dimensions Now, people say kd-tree of dimension d Idea: Each level of the tree compares against
kd-trees Invented in 1970s by Jon Bentley Name originally meant 3d-trees, 4d-trees, etc where k was the # of dimensions Now, people say kd-tree of dimension d Idea: Each level of the tree compares against
8. Hidden Surface Elimination
 8. Hidden Surface Elimination Identification and Removal of parts of picture that are not visible from a chosen viewing position. 1 8. Hidden Surface Elimination Basic idea: Overwriting Paint things in
8. Hidden Surface Elimination Identification and Removal of parts of picture that are not visible from a chosen viewing position. 1 8. Hidden Surface Elimination Basic idea: Overwriting Paint things in
K-structure, Separating Chain, Gap Tree, and Layered DAG
 K-structure, Separating Chain, Gap Tree, and Layered DAG Presented by Dave Tahmoush Overview Improvement on Gap Tree and K-structure Faster point location Encompasses Separating Chain Better storage Designed
K-structure, Separating Chain, Gap Tree, and Layered DAG Presented by Dave Tahmoush Overview Improvement on Gap Tree and K-structure Faster point location Encompasses Separating Chain Better storage Designed
I/O-Algorithms Lars Arge Aarhus University
 I/O-Algorithms Aarhus University April 10, 2008 I/O-Model Block I/O D Parameters N = # elements in problem instance B = # elements that fits in disk block M = # elements that fits in main memory M T =
I/O-Algorithms Aarhus University April 10, 2008 I/O-Model Block I/O D Parameters N = # elements in problem instance B = # elements that fits in disk block M = # elements that fits in main memory M T =
Collision detection. Piotr Fulma«ski. 19 pa¹dziernika Wydziaª Matematyki i Informatyki, Uniwersytet Šódzki, Polska
 Collision detection Piotr Fulma«ski Wydziaª Matematyki i Informatyki, Uniwersytet Šódzki, Polska 19 pa¹dziernika 2015 Table of contents Collision in games Algorithms to detect collision in games depend
Collision detection Piotr Fulma«ski Wydziaª Matematyki i Informatyki, Uniwersytet Šódzki, Polska 19 pa¹dziernika 2015 Table of contents Collision in games Algorithms to detect collision in games depend
Advanced Ray Tracing
 Advanced Ray Tracing Thanks to Fredo Durand and Barb Cutler The Ray Tree Ni surface normal Ri reflected ray Li shadow ray Ti transmitted (refracted) ray 51 MIT EECS 6.837, Cutler and Durand 1 Ray Tree
Advanced Ray Tracing Thanks to Fredo Durand and Barb Cutler The Ray Tree Ni surface normal Ri reflected ray Li shadow ray Ti transmitted (refracted) ray 51 MIT EECS 6.837, Cutler and Durand 1 Ray Tree
Collision Detection based on Spatial Partitioning
 Simulation in Computer Graphics Collision Detection based on Spatial Partitioning Matthias Teschner Computer Science Department University of Freiburg Outline introduction uniform grid Octree and k-d tree
Simulation in Computer Graphics Collision Detection based on Spatial Partitioning Matthias Teschner Computer Science Department University of Freiburg Outline introduction uniform grid Octree and k-d tree
Computational geometry
 Computational geometry Inge Li Gørtz CLRS Chapter 33.0, 33.1, 33.3. Computational Geometry Geometric problems (this course Euclidean plane). Does a set of line segments intersect, dividing plane into regions,
Computational geometry Inge Li Gørtz CLRS Chapter 33.0, 33.1, 33.3. Computational Geometry Geometric problems (this course Euclidean plane). Does a set of line segments intersect, dividing plane into regions,
Computational Geometry
 Orthogonal Range Searching omputational Geometry hapter 5 Range Searching Problem: Given a set of n points in R d, preprocess them such that reporting or counting the k points inside a d-dimensional axis-parallel
Orthogonal Range Searching omputational Geometry hapter 5 Range Searching Problem: Given a set of n points in R d, preprocess them such that reporting or counting the k points inside a d-dimensional axis-parallel
CEng 477 Introduction to Computer Graphics Fall 2007
 Visible Surface Detection CEng 477 Introduction to Computer Graphics Fall 2007 Visible Surface Detection Visible surface detection or hidden surface removal. Realistic scenes: closer objects occludes the
Visible Surface Detection CEng 477 Introduction to Computer Graphics Fall 2007 Visible Surface Detection Visible surface detection or hidden surface removal. Realistic scenes: closer objects occludes the
Today. Acceleration Data Structures for Ray Tracing. Cool results from Assignment 2. Last Week: Questions? Schedule
 Today Acceleration Data Structures for Ray Tracing Cool results from Assignment 2 Last Week: koi seantek Ray Tracing Shadows Reflection Refraction Local Illumination Bidirectional Reflectance Distribution
Today Acceleration Data Structures for Ray Tracing Cool results from Assignment 2 Last Week: koi seantek Ray Tracing Shadows Reflection Refraction Local Illumination Bidirectional Reflectance Distribution
Polygon decomposition. Motivation: Art gallery problem
 CG Lecture 3 Polygon decomposition 1. Polygon triangulation Triangulation theory Monotone polygon triangulation 2. Polygon decomposition into monotone pieces 3. Trapezoidal decomposition 4. Convex decomposition
CG Lecture 3 Polygon decomposition 1. Polygon triangulation Triangulation theory Monotone polygon triangulation 2. Polygon decomposition into monotone pieces 3. Trapezoidal decomposition 4. Convex decomposition
CS6100: Topics in Design and Analysis of Algorithms
 CS6100: Topics in Design and Analysis of Algorithms Guarding and Triangulating Polygons John Augustine CS6100 (Even 2012): Guarding and Triangulating Polygons The Art Gallery Problem A simple polygon is
CS6100: Topics in Design and Analysis of Algorithms Guarding and Triangulating Polygons John Augustine CS6100 (Even 2012): Guarding and Triangulating Polygons The Art Gallery Problem A simple polygon is
Sorting a file in RAM. External Sorting. Why Sort? 2-Way Sort of N pages Requires Minimum of 3 Buffers Pass 0: Read a page, sort it, write it.
 Sorting a file in RAM External Sorting Chapter 13 Three steps: Read the entire file from disk into RAM Sort the records using a standard sorting procedure, such as Shell sort, heap sort, bubble sort, Write
Sorting a file in RAM External Sorting Chapter 13 Three steps: Read the entire file from disk into RAM Sort the records using a standard sorting procedure, such as Shell sort, heap sort, bubble sort, Write
Computer Graphics. Bing-Yu Chen National Taiwan University
 Computer Graphics Bing-Yu Chen National Taiwan University Visible-Surface Determination Back-Face Culling The Depth-Sort Algorithm Binary Space-Partitioning Trees The z-buffer Algorithm Scan-Line Algorithm
Computer Graphics Bing-Yu Chen National Taiwan University Visible-Surface Determination Back-Face Culling The Depth-Sort Algorithm Binary Space-Partitioning Trees The z-buffer Algorithm Scan-Line Algorithm
Advanced Data Types and New Applications
 Advanced Data Types and New Applications These slides are a modified version of the slides of the book Database System Concepts (Chapter 24), 5th Ed., McGraw-Hill, by Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan.
Advanced Data Types and New Applications These slides are a modified version of the slides of the book Database System Concepts (Chapter 24), 5th Ed., McGraw-Hill, by Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan.
Lesson 05. Mid Phase. Collision Detection
 Lesson 05 Mid Phase Collision Detection Lecture 05 Outline Problem definition and motivations Generic Bounding Volume Hierarchy (BVH) BVH construction, fitting, overlapping Metrics and Tandem traversal
Lesson 05 Mid Phase Collision Detection Lecture 05 Outline Problem definition and motivations Generic Bounding Volume Hierarchy (BVH) BVH construction, fitting, overlapping Metrics and Tandem traversal
Chapter 12: Query Processing. Chapter 12: Query Processing
 Chapter 12: Query Processing Database System Concepts, 6 th Ed. See www.db-book.com for conditions on re-use Chapter 12: Query Processing Overview Measures of Query Cost Selection Operation Sorting Join
Chapter 12: Query Processing Database System Concepts, 6 th Ed. See www.db-book.com for conditions on re-use Chapter 12: Query Processing Overview Measures of Query Cost Selection Operation Sorting Join
Outline. Motivation. Traditional Database Systems. A Distributed Indexing Scheme for Multi-dimensional Range Queries in Sensor Networks
 A Distributed Indexing Scheme for Multi-dimensional Range Queries in Sensor Networks Tingjian Ge Outline Introduction and Overview Concepts and Technology Inserting Events into the Index Querying the Index
A Distributed Indexing Scheme for Multi-dimensional Range Queries in Sensor Networks Tingjian Ge Outline Introduction and Overview Concepts and Technology Inserting Events into the Index Querying the Index
Geometric and Thematic Integration of Spatial Data into Maps
 Geometric and Thematic Integration of Spatial Data into Maps Mark McKenney Department of Computer Science, Texas State University mckenney@txstate.edu Abstract The map construction problem (MCP) is defined
Geometric and Thematic Integration of Spatial Data into Maps Mark McKenney Department of Computer Science, Texas State University mckenney@txstate.edu Abstract The map construction problem (MCP) is defined
Implementing Relational Operators: Selection, Projection, Join. Database Management Systems, R. Ramakrishnan and J. Gehrke 1
 Implementing Relational Operators: Selection, Projection, Join Database Management Systems, R. Ramakrishnan and J. Gehrke 1 Readings [RG] Sec. 14.1-14.4 Database Management Systems, R. Ramakrishnan and
Implementing Relational Operators: Selection, Projection, Join Database Management Systems, R. Ramakrishnan and J. Gehrke 1 Readings [RG] Sec. 14.1-14.4 Database Management Systems, R. Ramakrishnan and
8. Hidden Surface Elimination
 -04-8 Hidden Surface Elimination To eliminate edges and surfaces not visible to the viewer Two categories: Object space methods: Image space methods: deal with object definitions directly Order the surfaces
-04-8 Hidden Surface Elimination To eliminate edges and surfaces not visible to the viewer Two categories: Object space methods: Image space methods: deal with object definitions directly Order the surfaces
CPSC / Sonny Chan - University of Calgary. Collision Detection II
 CPSC 599.86 / 601.86 Sonny Chan - University of Calgary Collision Detection II Outline Broad phase collision detection: - Problem definition and motivation - Bounding volume hierarchies - Spatial partitioning
CPSC 599.86 / 601.86 Sonny Chan - University of Calgary Collision Detection II Outline Broad phase collision detection: - Problem definition and motivation - Bounding volume hierarchies - Spatial partitioning
