Calculate the area of each figure. Each square on the grid represents a square that is one meter long and one meter wide.
|
|
|
- Dwain Griffin
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CH 3 Test Review Boundary Lines: Area of Parallelograms and Triangles Calculate the area of each figure Each square on the grid represents a square that is one meter long and one meter wide 1 You are making a kite out of nylon fabric The height of the kite will be 36 inches and the widest part of the kite will be 24 inches as shown in the diagram How much nylon fabric will you need to make the kite? Write the answer in square inches and square feet The Keystone Effect: Area of a Trapezoid Calculate the area of each trapezoid Each square on the grid represents a square that is one inch long and one inch wide 2 The area of a trapezoid is 209 square yards and the bases are 15 yards and 23 yards What is the height of the trapezoid? 3 The area of a trapezoid is 150 square meters The height is 10 meters and one base is two meters longer than the other base What is each base? 1
2 Signs, Signs, Every Place There Are Signs!: Area of Regular Polygons Calculate the area of each regular polygon A regular heptagon has a side length of 24 inches and an apothem of 249 inches What is the area of the regular heptagon? 7 A stop sign has a perimeter of 160 inches and an apothem of 241 inches What is the area of the stop sign? 8 A regular nonagon has an area of 378 square yards and an apothem of 105 yards What is the length of a side of the regular nonagon 2
3 9 A regular polygon has an area of 10,080 square meters The length of a side of the polygon is 30 meters and the apothem is 56 meters What type of regular polygon is this? Say Cheese!: Area and Circumference of a Circle Calculate the circumference and area of each circle Use 314 to approximate π Each square on the grid represents a square that is one centimeter long and one centimeter wide 10 What is the area of the annulus shown? Use 314 to approximate π Boundary Lines: Area of Parallelograms and Triangles Define each term in your own words 11 parallelogram 12 altitude of a parallelogram 3
4 13 height of a parallelogram 14 altitude of a triangle 15 height of a triangle Boundary Lines:Area of Parallelograms and Triangles Calculate the area of each parallelogram EXAMPLE: 16 A = 8(4) = 32 mi 2 4
5 17 Boundary Lines: Area of Parallelograms and Triangles In each parallelogram, the base, height, or area is unknown Calculate the value of the unknown measure EXAMPLE: A = bh 63 = 9h 7 = h The height is 7 meters 18 5
6 Boundary Lines: Area of Parallelograms and Triangles The base of each triangle is labeled Draw a segment that represents the height of the triangle EXAMPLE:
7 Boundary Lines: Area of Parallelograms and Triangles Calculate the area of each triangle EXAMPLE: A = 1 2 (6)(8) = 1 2 (48) = 24 in
8 Boundary Lines: Area of Parallelograms and Triangles In each triangle, the base, height, or area is unknown Calculate the value of the unknown measure EXAMPLE: A = 1 2 bh 30 = 1 2 (15)h 60 = 15h 4 = h The height of the triangle is 4 meters
9 The Keystone Effect: Area of a Trapezoid Problem Set Calculate the area of each trapezoid Each square on the grid represents a square that is two inches long and two inches wide EXAMPLE: A = 1 2 (8 + 16)10 = 1 (24)(10) = square inches 25 9
10 26 The Keystone Effect: Area of a Trapezoid Calculate the area of each trapezoid with the given dimensions, where h represents the height, b 1 represents the length of a base, and b 2 represents the length of the other base EXAMPLE: h = 2,b 1 = 4,b 2 = 3 A = 1 2 (4 + 3)2 = 1 2 (7)(2) = 7 The area is 7 square units 27 h = 6, b 1 = 5, b 2 = 3 28 h = 5, b 1 = 9, b 2 = 1 29 h = 4, b 1 = 2 3, b 2 =
11 The Keystone Effect: Area of a Trapezoid In each trapezoid, one base, height, or area is unknown Calculate the value of the unknown measure EXAMPLE: A = 1 2 (2 + 4)3 = 1 2 (6)(3) = 9 The trapezoid has an area of 9 square feet
12
13 Signs, Signs, Every Place There Are Signs!: Area of Regular Polygons Calculate the area of each regular polygon EXAMPLE: A = 1 2 (8)(63)(6) A = 1512 The area is 1512 square centimeters
14 Say Cheese!: Area and Circumference of a Circle Write the term that best completes each statement concentric circles diameter radius circle irrational number circumference annulus 38 The is the distance around a circle 39 The distance that is equal to one half the diameter of a circle is the 40 The distance across a circle through the center is the 41 A decimal that never repeats or terminates is a(n) 42 are circles that share the same center 43 The is the region bounded by two concentric circles Say Cheese!: Area and Circumference of a Circle Problem Set: Calculate the diameter of each circle EXAMPLE: 44 d = 2r = 2(6) = 12cm 14
15 45 Say Cheese!:Area and Circumference of a Circle Calculate the radius of each circle r = d 2 = 18 2 = 9ft
16 Say Cheese!: Area and Circumference of a Circle Calculate the circumference of each circle given the radius r of the circle Write your answers in terms of π EXAMPLE: r = 8 cm C = 2πr = 2(π)(8) = 16π cm 48 r = 2 cm 49 r = 10 ft 50 r = 42 cm Say Cheese!: Area and Circumference of a Circle Calculate the area of each circle given the radius r of the circle Write your answers in terms of π EXAMPLE: r = 6 m A = πr 2 = π(6 2 ) = 36π m 2 51 r = 4 in 16
17 52 r = 12 cm 53 r = 98 yd Say Cheese!: Area and Circumference of a Circle Calculate the radius of each circle given the circumference C of the circle Write your answers in terms of π EXAMPLE: C = 90π mm C = 2πr 90π = 2πr 45 = r r = 45 mm 54 C = 220π ft 55 C = 13π cm 56 C = 108π mi 17
18 Say Cheese!: Area and Circumference of a Circle Calculate the radius of each circle given the area A of the circle Write your answers in terms of π EXAMPLE: A = 9π cm 2 A = πr 2 9π = r 2 9 = r 2 3 = r r = 3 cm 57 A = 16π m 2 58 A = 49π yd 2 59 A = 1 4 π m2 18
19 Say Cheese!: Area and Circumference of a Circle Use the given information to answer each question EXAMPLE: If a circle has a circumference of 6π inches, what is its area? C = 2πr 6π = 2πr 3 = r A = πr 2 A = π(3 2 ) A = 9π The area of the circle is 9π square inches 60 If a circle has a circumference of 3π feet, what is its area? 61 If a circle has an area of 25π square feet, what is its circumference? 19
20 Say Cheese!: Area and Circumference of a Circle Calculate the area of each annulus shown Use 314 to approximate π EXAMPLE: Area of larger circle: A = πr 2 = π(12 2 ) = 144π in 2 Area of smaller circle: A = πr 2 = π(8 2 ) = 64π in 2 Area of annulus: A = 2512 in
21 Installing Carpeting and Tile: Area and Perimeter of Composite Figures Calculate the area of each figure All measurements are in centimeters Use 314 for π and round decimal answers to the nearest hundredth EXAMPLE: A = 14(2) + 7(3) = = 49 cm
22 66 Installing Carpeting and Tile: Area and Perimeter of Composite Figures Calculate the area of the shaded portion of each figure All measurements are in inches Use 314 for π and round decimal answers to the nearest hundredth EXAMPLE: A 3 4 (314)(32 ) = 3 4 (314)(9) = 2120 in
23 All of the line segments in the figure are either vertical or horizontal Determine the perimeter of the figure 23
24 Determine the area of the region bounded by the line segments All of the line segments in the figure shown are either vertical or horizontal What is the perimeter of the figure? 73 All of the line segments in the diagram of the bathroom floor shown are either vertical or horizontal How many one-inch square tiles would it take to tile the entire floor? 24
25 ID: A CH 3 Test Review Answer Section 1 ANS: Area of left triangle = 1 (36)(12) = 216 square inches 2 Area of right triangle = 1 (36)(12) = 216 square inches 2 Totalarea of kite = = 432 square inches 432 square inches 1 square foot 144 square inches = 3 square feet You will need 432 square inches, or 3 square feet, of nylon fabric to make the kite PTS: 1 REF: Ch32 TOP: Assignment 2 ANS: 209 = 1 ( )h = 19h 11 = h The height of the trapezoid is 11 yards PTS: 1 REF: Ch33 TOP: Assignment 3 ANS: Let x represent one base Then x + 2 represents the other base 150 = 1 (x + x + 2)(10) = 5(2x + 2) 150 = 10x = 10x 14 = x One base is 14 meters and the other base is = 16 meters PTS: 1 REF: Ch33 TOP: Assignment 4 ANS: A = 1 2 (18)(124)(5) = 558 square feet PTS: 1 REF: Ch34 TOP: Assignment 1
26 ID: A 5 ANS: A = 1 2 (35)(539)(10) = square centimeters PTS: 1 REF: Ch34 TOP: Assignment 6 ANS: A = 1 2 (24)(249)(7) = The area of the regular heptagon is square inches PTS: 1 REF: Ch34 TOP: Assignment 7 ANS: A = 1 2 (160)(241) = 1928 The area of the stop sign is 1928 square inches PTS: 1 REF: Ch34 TOP: Assignment 8 ANS: 378 = 1 2 ( )(105)(9) 378 = = The length of a side of the regular nonagon is 8 yards PTS: 1 REF: Ch34 TOP: Assignment 9 ANS: 10,080 = 1 2 (30)(56)(n) 10,080 = 840n 12 = n The regular polygon has 12 sides Therefore, the polygon is a regular 12-gon PTS: 1 REF: Ch34 TOP: Assignment 2
27 ID: A 10 ANS: Area of larger circle: A = πr 2 = π(10 2 ) = 100π 314 m 2 Area of smaller circle: A = πr 2 = π(75 2 ) = 5625π m 2 Area of annulus: A = m 2 The area of the annulus is approximately square meters PTS: 1 REF: Ch35 TOP: Assignment 11 ANS: A parallelogram is a quadrilateral in which both pairs of opposite sides are parallel PTS: 1 REF: Ch32 TOP: Skills Practice 12 ANS: An altitude of a parallelogram is a line segment drawn from a vertex, perpendicular to the line containing the opposite side PTS: 1 REF: Ch32 TOP: Skills Practice 13 ANS: A height of a parallelogram is the perpendicular distance from any point on one side to the line containing the opposite side PTS: 1 REF: Ch32 TOP: Skills Practice 14 ANS: An altitude of a triangle is a line segment drawn from a vertex perpendicular to the line containing the opposite side PTS: 1 REF: Ch32 TOP: Skills Practice 15 ANS: A height of a triangle is the perpendicular distance from a vertex to the line containing the base of the triangle PTS: 1 REF: Ch32 TOP: Skills Practice 16 ANS: A = 11(6) = 66 mi 2 PTS: 1 REF: Ch32 TOP: Skills Practice 17 ANS: A = 7(16) = 112 yd 2 PTS: 1 REF: Ch32 TOP: Skills Practice 3
28 ID: A 18 ANS: A = bh 96 = 12b 8 = b The base is 8 feet PTS: 1 REF: Ch32 TOP: Skills Practice 19 ANS: PTS: 1 REF: Ch32 TOP: Skills Practice 20 ANS: PTS: 1 REF: Ch32 TOP: Skills Practice 21 ANS: A = 1 2 (7)(7) = 1 (49) = 245 ft2 2 PTS: 1 REF: Ch32 TOP: Skills Practice 4
29 ID: A 22 ANS: A = 1 2 (45)(4) = 1 (18) = 9 m2 2 PTS: 1 REF: Ch32 TOP: Skills Practice 23 ANS: A = 1 2 bh A = 1 2 (3)(2) A = 1 2 (6) A = 3 The area of the triangle is 3 square feet PTS: 1 REF: Ch32 TOP: Skills Practice 24 ANS: A = 1 2 bh 6 = 1 2 b(3) 12 = 3b 4 = b The base of the triangle is 4 yards PTS: 1 REF: Ch32 TOP: Skills Practice 25 ANS: A = 1 2 (4 + 8)6 = 1 (12)(6) = square inches PTS: 1 REF: Ch33 TOP: Skills Practice 26 ANS: A = 1 2 ( )14 = 1 (30)(14) = square inches PTS: 1 REF: Ch33 TOP: Skills Practice 5
30 ID: A 27 ANS: A = 1 2 (5 + 3)6 = 1 (8)(6) = 24 2 The area is 24 square units PTS: 1 REF: Ch33 TOP: Skills Practice 28 ANS: A = 1 2 (9 + 1)5 = 1 (10)(5) = 25 2 The area is 25 square units PTS: 1 REF: Ch33 TOP: Skills Practice 29 ANS: A = 1 Ê ˆ Ë Á 3 4 = 1 2 (2)(4) = 4 The area is 4 square units PTS: 1 REF: Ch33 TOP: Skills Practice 30 ANS: 1 2 (b + 3)2 = 8 1 b = 8 b 1 = 5 The trapezoid has a base of 5 centimeters PTS: 1 REF: Ch33 TOP: Skills Practice 31 ANS: 1 2 (b 1 + 8)5 = 25 b = 10 b 1 = 2 The trapezoid has a base of 2 yards PTS: 1 REF: Ch33 TOP: Skills Practice 32 ANS: 1 (5 + 15)h = h = 70 h = 7 The trapezoid has a height of 7 yards PTS: 1 REF: Ch33 TOP: Skills Practice 6
31 ID: A 33 ANS: A = 1 2 ( )5 = 1 (35)(5) = The trapezoid has an area of 875 square feet PTS: 1 REF: Ch33 TOP: Skills Practice 34 ANS: 1 2 (b )7 = 98 b = 28 b 1 = 15 The trapezoid has a base of 15 meters PTS: 1 REF: Ch33 TOP: Skills Practice 35 ANS: A = 1 2 (12)(83)(5) = 249 The area is 249 square feet PTS: 1 REF: Ch34 TOP: Skills Practice 36 ANS: A = 1 2 (10)(104)(7) = 364 The area is 364 square yards PTS: 1 REF: Ch34 TOP: Skills Practice 37 ANS: A = 1 2 (4)(75)(12) = 180 The area is 180 square inches PTS: 1 REF: Ch34 TOP: Skills Practice 38 ANS: circumference PTS: 1 REF: Ch35 TOP: Skills Practice 39 ANS: radius PTS: 1 REF: Ch35 TOP: Skills Practice 40 ANS: diameter PTS: 1 REF: Ch35 TOP: Skills Practice 7
32 ID: A 41 ANS: irrational number PTS: 1 REF: Ch35 TOP: Skills Practice 42 ANS: concentric circles PTS: 1 REF: Ch35 TOP: Skills Practice 43 ANS: annulus PTS: 1 REF: Ch35 TOP: Skills Practice 44 ANS: d = 2r = 2(22) = 44ft PTS: 1 REF: Ch35 TOP: Skills Practice 45 ANS: d = 2r = 2(975) = 195 in PTS: 1 REF: Ch35 TOP: Skills Practice 46 ANS: r = d 2 = = 50m PTS: 1 REF: Ch35 TOP: Skills Practice 47 ANS: r = d 2 = 105 = 525 yd 2 PTS: 1 REF: Ch35 TOP: Skills Practice 48 ANS: C = 2πr = 2(π)(2) = 4π cm PTS: 1 REF: Ch35 TOP: Skills Practice 49 ANS: C = 2πr = 2(π)(10) = 20π ft PTS: 1 REF: Ch35 TOP: Skills Practice 50 ANS: C = 2πr = 2(π)(42) = 84π cm PTS: 1 REF: Ch35 TOP: Skills Practice 51 ANS: A = πr 2 = π(4 2 ) = 16π in 2 PTS: 1 REF: Ch35 TOP: Skills Practice 52 ANS: A = πr 2 = π(12 2 ) = 144π cm 2 PTS: 1 REF: Ch35 TOP: Skills Practice 8
33 ID: A 53 ANS: A = πr 2 = π(98 2 ) = 9604π yd 2 PTS: 1 REF: Ch35 TOP: Skills Practice 54 ANS: C = 2πr 220π = 2πr 110 = r r = 110 ft PTS: 1 REF: Ch35 TOP: Skills Practice 55 ANS: C = 2πr 13π = 2πr 65 = r r = 65 cm PTS: 1 REF: Ch35 TOP: Skills Practice 56 ANS: C = 2πr 108π = 2πr 54 = r r = 54 mi PTS: 1 REF: Ch35 TOP: Skills Practice 57 ANS: A = πr 2 16π = πr 2 16 = r 2 4 = r r = 4 m PTS: 1 REF: Ch35 TOP: Skills Practice 9
34 ID: A 58 ANS: A = πr 2 49π = πr 2 49 = r 2 7 = r r = 7 yd PTS: 1 REF: Ch35 TOP: Skills Practice 59 ANS: A = πr π = πr = r2 1 2 = r r = 1 2 m PTS: 1 REF: Ch35 TOP: Skills Practice 60 ANS: C = 2πr A = πr 2 3π = 2πr A = π(15 2 ) 15 = r A = 225π The area of the circle is 225π square feet PTS: 1 REF: Ch35 TOP: Skills Practice 61 ANS: A = πr 2 C = 2πr 25π = πr 2 25 = r 2 C = 2π(5) C = 10π 5 = r The circumference of the circle is 10π feet PTS: 1 REF: Ch35 TOP: Skills Practice 10
35 ID: A 62 ANS: Area of larger circle: A = πr 2 = π(22 2 ) = 484π ft 2 Area of smaller circle: A = πr 2 = π(11 2 ) = 121π ft 2 Area of annulus: A = ft 2 PTS: 1 REF: Ch35 TOP: Skills Practice 63 ANS: Area of larger circle: A = πr 2 = π(34 2 ) = 1156π m 2 Area of smaller circle: A = πr 2 = π(272 2 ) = 73984π m 2 Area of annulus: A = m 2 PTS: 1 REF: Ch35 TOP: Skills Practice 64 ANS: A = 1 2 ( )(15) (20)(15) = = 4875 cm 2 PTS: 1 REF: Ch36 TOP: Skills Practice 65 ANS: Ê A = 2 1 ˆ + 4(1) Ë Á 2 (1)(2) = = 6 cm 2 PTS: 1 REF: Ch36 TOP: Skills Practice 66 ANS: A = 1 2 (6)(4) (5)(10) = = 37 cm 2 PTS: 1 REF: Ch36 TOP: Skills Practice 11
36 ID: A 67 ANS: A 8(5) 1 2 (314)(252 ) = = 3019 in 2 PTS: 1 REF: Ch36 TOP: Skills Practice 68 ANS: A = 3 Ê (32)(277) ˆ Ë Á = 3 4 (4432) = 3324 in 2 PTS: 1 REF: Ch36 TOP: Skills Practice 69 ANS: A 20(20) (314)(10 2 ) = = 86 in 2 PTS: 1 REF: Ch36 TOP: Skills Practice 70 ANS: The perimeter is = 40 centimeters PTS: 1 REF: Ch36 TOP: Mid Ch Test 71 ANS: To determine the area, you can add the areas of the two rectangles One rectangle is 11 units by 12 units and the other rectangle is 10 units by 6 units Total area = 11(12) + 10(6) = = 192 The area of the region bounded by the line segments is 192 square units PTS: 1 REF: Ch36 TOP: End Ch Test 72 ANS: The sum of the shorter horizontal segments is 20 yards, and the sum of the shorter vertical segments is 18 yards So, = 76 The perimeter is 76 yards PTS: 1 REF: Ch36 TOP: End Ch Test 12
37 ID: A 73 ANS: First, calculate the sum of the areas of the two rectangles:7(6) + 5(9) = = 89 square feet Then, multiply the number of square feet by 144, the number of square inches in one square foot: = 12,816 So, 12,816 one-inch square tiles are needed to tile the entire floor PTS: 1 REF: Ch36 TOP: End Ch Test 13
Area of Polygons And Circles
 Name: Date: Geometry 2011-2012 Area of Polygons And Circles Name: Teacher: Pd: Table of Contents DAY 1: SWBAT: Calculate the area and perimeter of Parallelograms and Triangles Pgs: 1-5 HW: Pgs: 6-7 DAY
Name: Date: Geometry 2011-2012 Area of Polygons And Circles Name: Teacher: Pd: Table of Contents DAY 1: SWBAT: Calculate the area and perimeter of Parallelograms and Triangles Pgs: 1-5 HW: Pgs: 6-7 DAY
Chapter Test Form A. 173 Holt Geometry. Name Date Class. 1. Find the area of the triangle.
 Form A 1. Find the area of the triangle. 6. A square has a perimeter of 8 inches. Find the area of the square. cm 7. Find the circumference of C in terms of.. Find the area of the parallelogram. 11 cm
Form A 1. Find the area of the triangle. 6. A square has a perimeter of 8 inches. Find the area of the square. cm 7. Find the circumference of C in terms of.. Find the area of the parallelogram. 11 cm
TEST REVIEW: UNIT 8 Surface Area 2018
 Class: Date: TEST REVIEW: UNIT 8 Surface Area 2018 Find the area. The figure is not drawn to scale. 1. 5. Find the area. All lengths are in centimeters. Round answer to the nearest tenth. 2. 6. A can of
Class: Date: TEST REVIEW: UNIT 8 Surface Area 2018 Find the area. The figure is not drawn to scale. 1. 5. Find the area. All lengths are in centimeters. Round answer to the nearest tenth. 2. 6. A can of
Area. Domain 4 Lesson 25. Getting the Idea
 Domain 4 Lesson 5 Area Common Core Standard: 7.G.6 Getting the Idea The area of a figure is the number of square units inside the figure. Below are some formulas that can be used to find the areas of common
Domain 4 Lesson 5 Area Common Core Standard: 7.G.6 Getting the Idea The area of a figure is the number of square units inside the figure. Below are some formulas that can be used to find the areas of common
Chapter 8 Review. 1. Find both the perimeter and the area 2. Find both the perimeter and the area
 Name: Block: 8a. Find the perimeter and the area of polygons. 1. Find both the perimeter and the area 2. Find both the perimeter and the area of parallelogram QRST. (Don t forget UNITS!) of rectangle JKLM.
Name: Block: 8a. Find the perimeter and the area of polygons. 1. Find both the perimeter and the area 2. Find both the perimeter and the area of parallelogram QRST. (Don t forget UNITS!) of rectangle JKLM.
Geometry 10 and 11 Notes
 Geometry 10 and 11 Notes Area and Volume Name Per Date 10.1 Area is the amount of space inside of a two dimensional object. When working with irregular shapes, we can find its area by breaking it up into
Geometry 10 and 11 Notes Area and Volume Name Per Date 10.1 Area is the amount of space inside of a two dimensional object. When working with irregular shapes, we can find its area by breaking it up into
Areas of Rectangles and Parallelograms
 CONDENSED LESSON 8.1 Areas of Rectangles and Parallelograms In this lesson, you Review the formula for the area of a rectangle Use the area formula for rectangles to find areas of other shapes Discover
CONDENSED LESSON 8.1 Areas of Rectangles and Parallelograms In this lesson, you Review the formula for the area of a rectangle Use the area formula for rectangles to find areas of other shapes Discover
Practice Test - Chapter 11. Find the area and perimeter of each figure. Round to the nearest tenth if necessary.
 Find the area and perimeter of each figure. Round to the nearest tenth if necessary. 1. Use the Pythagorean Theorem to find the height h, of the parallelogram. 2. Use the Pythagorean Theorem to find the
Find the area and perimeter of each figure. Round to the nearest tenth if necessary. 1. Use the Pythagorean Theorem to find the height h, of the parallelogram. 2. Use the Pythagorean Theorem to find the
Circular Reasoning. Solving Area and Circumference. Problems. WARM UP Determine the area of each circle. Use 3.14 for π.
 Circular Reasoning Solving Area and Circumference 3 Problems WARM UP Determine the area of each circle. Use 3.14 for π. 1. 4 in. 2. 3.8 cm LEARNING GOALS Use the area and circumference formulas for a circle
Circular Reasoning Solving Area and Circumference 3 Problems WARM UP Determine the area of each circle. Use 3.14 for π. 1. 4 in. 2. 3.8 cm LEARNING GOALS Use the area and circumference formulas for a circle
Free Response. Test A. 1. What is the estimated area of the figure?
 Test A 1. What is the estimated area of the 6. An 8.5 in. by 11 in. sheet of paper is enlarged to make a poster by doubling its length and width. What is the new perimeter? 7. How does the area of a square
Test A 1. What is the estimated area of the 6. An 8.5 in. by 11 in. sheet of paper is enlarged to make a poster by doubling its length and width. What is the new perimeter? 7. How does the area of a square
11-1 Study Guide and Intervention
 11-1 Study Guide and Intervention reas of Parallelograms reas of Parallelograms parallelogram is a quadrilateral with both pairs of opposite sides parallel. ny side of a parallelogram can be called a base.
11-1 Study Guide and Intervention reas of Parallelograms reas of Parallelograms parallelogram is a quadrilateral with both pairs of opposite sides parallel. ny side of a parallelogram can be called a base.
Chapter 11 Review. Period:
 Chapter 11 Review Name: Period: 1. Find the sum of the measures of the interior angles of a pentagon. 6. Find the area of an equilateral triangle with side 1.. Find the sum of the measures of the interior
Chapter 11 Review Name: Period: 1. Find the sum of the measures of the interior angles of a pentagon. 6. Find the area of an equilateral triangle with side 1.. Find the sum of the measures of the interior
Review: What is the definition of a parallelogram? What are the properties of a parallelogram? o o o o o o
 Geometry CP Lesson 11-1: Areas of Parallelograms Page 1 of 2 Objectives: Find perimeters and areas of parallelograms Determine whether points on a coordinate plane define a parallelogram CA Geometry Standard:
Geometry CP Lesson 11-1: Areas of Parallelograms Page 1 of 2 Objectives: Find perimeters and areas of parallelograms Determine whether points on a coordinate plane define a parallelogram CA Geometry Standard:
Vocabulary. Term Page Definition Clarifying Example. apothem. center of a circle. center of a regular polygon. central angle of a regular polygon
 CHAPTER 9 Vocabulary The table contains important vocabulary terms from Chapter 9. As you work through the chapter, fill in the page number, definition, and a clarifying example. apothem Term Page Definition
CHAPTER 9 Vocabulary The table contains important vocabulary terms from Chapter 9. As you work through the chapter, fill in the page number, definition, and a clarifying example. apothem Term Page Definition
Geometry SIA #3. Name: Class: Date: Short Answer. 1. Find the perimeter of parallelogram ABCD with vertices A( 2, 2), B(4, 2), C( 6, 1), and D(0, 1).
 Name: Class: Date: ID: A Geometry SIA #3 Short Answer 1. Find the perimeter of parallelogram ABCD with vertices A( 2, 2), B(4, 2), C( 6, 1), and D(0, 1). 2. If the perimeter of a square is 72 inches, what
Name: Class: Date: ID: A Geometry SIA #3 Short Answer 1. Find the perimeter of parallelogram ABCD with vertices A( 2, 2), B(4, 2), C( 6, 1), and D(0, 1). 2. If the perimeter of a square is 72 inches, what
Area rectangles & parallelograms
 Area rectangles & parallelograms Rectangles One way to describe the size of a room is by naming its dimensions. So a room that measures 12 ft. by 10 ft. could be described by saying its a 12 by 10 foot
Area rectangles & parallelograms Rectangles One way to describe the size of a room is by naming its dimensions. So a room that measures 12 ft. by 10 ft. could be described by saying its a 12 by 10 foot
Chapter 11 Areas of Polygons and Circles
 Section 11-1: Areas of Parallelograms and Triangles SOL: G.14 The student will use similar geometric objects in two- or three-dimensions to a) compare ratios between side lengths, perimeters, areas, and
Section 11-1: Areas of Parallelograms and Triangles SOL: G.14 The student will use similar geometric objects in two- or three-dimensions to a) compare ratios between side lengths, perimeters, areas, and
NAME DATE PERIOD. Areas of Parallelograms and Triangles. Review Vocabulary Define parallelogram in your own words. (Lesson 6-2)
 11-1 Areas of Parallelograms and Triangles What You ll Learn Skim Lesson 11-1. Predict two things you expect to learn based on the headings and the Key Concept box. 1. Active Vocabulary 2. Review Vocabulary
11-1 Areas of Parallelograms and Triangles What You ll Learn Skim Lesson 11-1. Predict two things you expect to learn based on the headings and the Key Concept box. 1. Active Vocabulary 2. Review Vocabulary
Any questions about the material so far? About the exercises?
 Any questions about the material so far? About the exercises? Here is a question for you. In the diagram on the board, DE is parallel to AC, DB = 4, AB = 9 and BE = 8. What is the length EC? Polygons Definitions:
Any questions about the material so far? About the exercises? Here is a question for you. In the diagram on the board, DE is parallel to AC, DB = 4, AB = 9 and BE = 8. What is the length EC? Polygons Definitions:
Pre-Algebra Notes Unit 10: Geometric Figures & Their Properties; Volume
 Pre-Algebra Notes Unit 0: Geometric Figures & Their Properties; Volume Triangles, Quadrilaterals, and Polygons Syllabus Objectives: (4.6) The student will validate conclusions about geometric figures and
Pre-Algebra Notes Unit 0: Geometric Figures & Their Properties; Volume Triangles, Quadrilaterals, and Polygons Syllabus Objectives: (4.6) The student will validate conclusions about geometric figures and
Chapter 10 Practice Test
 Chapter 10 Practice Test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Find the area. The figure is not drawn to scale. 7.6 cm 3.7 cm a. b. c. d. 2.
Chapter 10 Practice Test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Find the area. The figure is not drawn to scale. 7.6 cm 3.7 cm a. b. c. d. 2.
NAME DATE PERIOD. Angle and Line Relationships. Classify the pairs of angles shown. Then find the value of x in each figure
 11-1 Skills Practice Angle and Line Relationships In the figure at the right, c d and p is a transversal. If m 5 = 110, find the measure of each angle. 1. 6 2. 8 3. 2 4. 4 c 1 2 5 6 d 3 4 7 8 p In the
11-1 Skills Practice Angle and Line Relationships In the figure at the right, c d and p is a transversal. If m 5 = 110, find the measure of each angle. 1. 6 2. 8 3. 2 4. 4 c 1 2 5 6 d 3 4 7 8 p In the
Name: Target 12.2: Find and apply surface of Spheres and Composites 12.2a: Surface Area of Spheres 12.2b: Surface Area of Composites Solids
 Unit 12: Surface Area and Volume of Solids Target 12.0: Euler s Formula and Introduction to Solids Target 12.1: Find and apply surface area of solids 12.1a: Surface Area of Prisms and Cylinders 12.1b:
Unit 12: Surface Area and Volume of Solids Target 12.0: Euler s Formula and Introduction to Solids Target 12.1: Find and apply surface area of solids 12.1a: Surface Area of Prisms and Cylinders 12.1b:
heptagon; not regular; hexagon; not regular; quadrilateral; convex concave regular; convex
 10 1 Naming Polygons A polygon is a plane figure formed by a finite number of segments. In a convex polygon, all of the diagonals lie in the interior. A regular polygon is a convex polygon that is both
10 1 Naming Polygons A polygon is a plane figure formed by a finite number of segments. In a convex polygon, all of the diagonals lie in the interior. A regular polygon is a convex polygon that is both
Math 6 Unit 9 Notes: Measurement and Geometry, Area/Volume
 Math 6 Unit 9 Notes: Measurement and Geometry, rea/volume erimeter Objectives: (5.5) The student will model formulas to find the perimeter, circumference and area of plane figures. (5.6) The student will
Math 6 Unit 9 Notes: Measurement and Geometry, rea/volume erimeter Objectives: (5.5) The student will model formulas to find the perimeter, circumference and area of plane figures. (5.6) The student will
9 Find the area of the figure. Round to the. 11 Find the area of the figure. Round to the
 Name: Period: Date: Show all work for full credit. Provide exact answers and decimal (rounded to nearest tenth, unless instructed differently). Ch 11 Retake Test Review 1 Find the area of a regular octagon
Name: Period: Date: Show all work for full credit. Provide exact answers and decimal (rounded to nearest tenth, unless instructed differently). Ch 11 Retake Test Review 1 Find the area of a regular octagon
Pre-Algebra, Unit 10: Measurement, Area, and Volume Notes
 Pre-Algebra, Unit 0: Measurement, Area, and Volume Notes Triangles, Quadrilaterals, and Polygons Objective: (4.6) The student will classify polygons. Take this opportunity to review vocabulary and previous
Pre-Algebra, Unit 0: Measurement, Area, and Volume Notes Triangles, Quadrilaterals, and Polygons Objective: (4.6) The student will classify polygons. Take this opportunity to review vocabulary and previous
Someone else might choose to describe the closet by determining how many square tiles it would take to cover the floor. 6 ft.
 Areas Rectangles One way to describe the size of a room is by naming its dimensions. So a room that measures 12 ft. by 10 ft. could be described by saying its a 12 by 10 foot room. In fact, that is how
Areas Rectangles One way to describe the size of a room is by naming its dimensions. So a room that measures 12 ft. by 10 ft. could be described by saying its a 12 by 10 foot room. In fact, that is how
Math 8: Identify Shapes and Surface Area
 Name: Class: Date: Math 8: Identify Shapes and Surface Area 1. Name the solid according to its description: The figure has one base that is a rectangle and four lateral surfaces that are triangles. 2.
Name: Class: Date: Math 8: Identify Shapes and Surface Area 1. Name the solid according to its description: The figure has one base that is a rectangle and four lateral surfaces that are triangles. 2.
11.4 Volume of Prisms and Cylinders
 11.4 Volume of Prisms and Cylinders Learning Objectives Find the volume of a prism. Find the volume of a cylinder. Review Queue 1. Define volume in your own words. 2. What is the surface area of a cube
11.4 Volume of Prisms and Cylinders Learning Objectives Find the volume of a prism. Find the volume of a cylinder. Review Queue 1. Define volume in your own words. 2. What is the surface area of a cube
Ready To Go On? Skills Intervention 9-1 Developing Formulas for Triangles and Quadrilaterals
 9A Ready To Go On? Skills Intervention 9-1 Developing Formulas for Triangles and Quadrilaterals Finding Measurements of Parallelograms Find each measurement. A. the area of the parallelogram A b Use the
9A Ready To Go On? Skills Intervention 9-1 Developing Formulas for Triangles and Quadrilaterals Finding Measurements of Parallelograms Find each measurement. A. the area of the parallelogram A b Use the
Geometry. Geometry is the study of shapes and sizes. The next few pages will review some basic geometry facts. Enjoy the short lesson on geometry.
 Geometry Introduction: We live in a world of shapes and figures. Objects around us have length, width and height. They also occupy space. On the job, many times people make decision about what they know
Geometry Introduction: We live in a world of shapes and figures. Objects around us have length, width and height. They also occupy space. On the job, many times people make decision about what they know
Properties of a Circle Diagram Source:
 Properties of a Circle Diagram Source: http://www.ricksmath.com/circles.html Definitions: Circumference (c): The perimeter of a circle is called its circumference Diameter (d): Any straight line drawn
Properties of a Circle Diagram Source: http://www.ricksmath.com/circles.html Definitions: Circumference (c): The perimeter of a circle is called its circumference Diameter (d): Any straight line drawn
Formative Assessment Area Unit 5
 Area Unit 5 Administer the formative assessment and select contrasting student responses to create further opportunities for learning about area measure, especially the difference between units of length
Area Unit 5 Administer the formative assessment and select contrasting student responses to create further opportunities for learning about area measure, especially the difference between units of length
HS Pre-Algebra Notes Unit 10: Measurement, Area, and Volume
 HS Pre-Algebra Notes Unit 0: Measurement, Area, and Volume Triangles, Quadrilaterals, and Polygons Syllabus Objectives: (5.6) The student will classify polygons. (5.5) The student will validate conclusions
HS Pre-Algebra Notes Unit 0: Measurement, Area, and Volume Triangles, Quadrilaterals, and Polygons Syllabus Objectives: (5.6) The student will classify polygons. (5.5) The student will validate conclusions
Additional Practice. Name Date Class
 Additional Practice Investigation 1 1. The four nets below will fold into rectangular boxes. Net iii folds into an open box. The other nets fold into closed boxes. Answer the following questions for each
Additional Practice Investigation 1 1. The four nets below will fold into rectangular boxes. Net iii folds into an open box. The other nets fold into closed boxes. Answer the following questions for each
Appendix E. Plane Geometry
 Appendix E Plane Geometry A. Circle A circle is defined as a closed plane curve every point of which is equidistant from a fixed point within the curve. Figure E-1. Circle components. 1. Pi In mathematics,
Appendix E Plane Geometry A. Circle A circle is defined as a closed plane curve every point of which is equidistant from a fixed point within the curve. Figure E-1. Circle components. 1. Pi In mathematics,
Perimeter and Area. Slide 1 / 183. Slide 2 / 183. Slide 3 / 183. Table of Contents. New Jersey Center for Teaching and Learning
 New Jersey Center for Teaching and Learning Slide 1 / 183 Progressive Mathematics Initiative This material is made freely available at www.njctl.org and is intended for the non-commercial use of students
New Jersey Center for Teaching and Learning Slide 1 / 183 Progressive Mathematics Initiative This material is made freely available at www.njctl.org and is intended for the non-commercial use of students
CCBC Math 081 Geometry Section 2.2
 2.2 Geometry Geometry is the study of shapes and their mathematical properties. In this section, we will learn to calculate the perimeter, area, and volume of a few basic geometric shapes. Perimeter We
2.2 Geometry Geometry is the study of shapes and their mathematical properties. In this section, we will learn to calculate the perimeter, area, and volume of a few basic geometric shapes. Perimeter We
Part I Multiple Choice
 Oregon Focus on Surface Area and Volume Practice Test ~ Surface Area Name Period Date Long/Short Term Learning Targets MA.MS.07.ALT.05: I can solve problems and explain formulas involving surface area
Oregon Focus on Surface Area and Volume Practice Test ~ Surface Area Name Period Date Long/Short Term Learning Targets MA.MS.07.ALT.05: I can solve problems and explain formulas involving surface area
Area and Perimeter. Perimeter Class Work Find the perimeter of the following figures
 Area and Perimeter Perimeter Find the perimeter of the following figures. 1. 2. 3. 4. The length of a rectangle is 7 cm and its width is 5 cm, what is the rectangles perimeter? 5. An equilateral triangle
Area and Perimeter Perimeter Find the perimeter of the following figures. 1. 2. 3. 4. The length of a rectangle is 7 cm and its width is 5 cm, what is the rectangles perimeter? 5. An equilateral triangle
Geometry Unit 10 Note Sheets Date Name of Lesson. 1.6 Two-Dimensional Figures Areas of Circles and Sectors
 Date Name of Lesson 1.6 Two-Dimensional Figures 11.3 Areas of Circles and Sectors Quiz 11.1 Areas of Parallelograms and Triangles 11.2 Areas of Trapezoids, Rhombi and Kites 11.4 Areas of Regular Polygons
Date Name of Lesson 1.6 Two-Dimensional Figures 11.3 Areas of Circles and Sectors Quiz 11.1 Areas of Parallelograms and Triangles 11.2 Areas of Trapezoids, Rhombi and Kites 11.4 Areas of Regular Polygons
UNIT 3 - MEASUREMENT & PROPORTIONAL REASONING TEST
 Class: Date: UNIT 3 - MEASUREMENT & PROPORTIONAL REASONING TEST Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. When designing a building, you must be
Class: Date: UNIT 3 - MEASUREMENT & PROPORTIONAL REASONING TEST Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. When designing a building, you must be
10-2. Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz. Holt McDougal Geometry
 Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz Geometry Warm Up Find the unknown side lengths in each special right triangle. 1. a 30-60 -90 triangle with hypotenuse 2 ft 2. a 45-45 -90 triangle with leg length
Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz Geometry Warm Up Find the unknown side lengths in each special right triangle. 1. a 30-60 -90 triangle with hypotenuse 2 ft 2. a 45-45 -90 triangle with leg length
GEOMETRY B: CHAPTER 10 PRACTICE TEST
 Name: Class: Date: GEOMETRY B: CHAPTER 10 PRACTICE TEST Short Answer 1. An isosceles triangle has area of 15 ft. If the base is 14 ft, what is the length of the legs? Round your answer to the nearest tenth.
Name: Class: Date: GEOMETRY B: CHAPTER 10 PRACTICE TEST Short Answer 1. An isosceles triangle has area of 15 ft. If the base is 14 ft, what is the length of the legs? Round your answer to the nearest tenth.
2014 Geometry ACTM State Exam
 2014 eometry TM State xam In each of the following choose the best answer and place the corresponding letter on the Scantron Sheet. If you erase on the answer sheet, be sure to erase completely. nswer
2014 eometry TM State xam In each of the following choose the best answer and place the corresponding letter on the Scantron Sheet. If you erase on the answer sheet, be sure to erase completely. nswer
11.1 Understanding Area
 /6/05. Understanding rea Counting squares is neither the easiest or the best way to find the area of a region. Let s investigate how to find the areas of rectangles and squares Objective: fter studying
/6/05. Understanding rea Counting squares is neither the easiest or the best way to find the area of a region. Let s investigate how to find the areas of rectangles and squares Objective: fter studying
Answer Section. Honors Geometry Final Study Guide 2013 Solutions and Section References 1. ANS: 900
 Honors Geometry Final Study Guide 2013 Solutions and Section References Answer Section 1. ANS: 900 2. ANS: 6300 3. ANS: B 4. ANS: x = 111, y = 64 5. ANS: 45 6. ANS: 110 7. ANS: REF: 6-2 Properties of Parallelograms
Honors Geometry Final Study Guide 2013 Solutions and Section References Answer Section 1. ANS: 900 2. ANS: 6300 3. ANS: B 4. ANS: x = 111, y = 64 5. ANS: 45 6. ANS: 110 7. ANS: REF: 6-2 Properties of Parallelograms
Note Sheets Chapter 8: Area
 Ch 8 Notesheet L Key V3 Note Sheets Chapter 8: rea In General ON LL PROBLEMS!!. State the relationship (or the formula).. Sustitute in known values. 3. Simplify or Solve the equation. Use the order of
Ch 8 Notesheet L Key V3 Note Sheets Chapter 8: rea In General ON LL PROBLEMS!!. State the relationship (or the formula).. Sustitute in known values. 3. Simplify or Solve the equation. Use the order of
12-3 Area of Composite Figures
 Find the area of each figure. Round to the nearest tenth, if necessary. 1. 5. The Jamesons hired a landscaper to brick their walkway. One case of bricks costs $25 and covers 6 square feet. 2. 38.4 cm 2
Find the area of each figure. Round to the nearest tenth, if necessary. 1. 5. The Jamesons hired a landscaper to brick their walkway. One case of bricks costs $25 and covers 6 square feet. 2. 38.4 cm 2
For full credit, show all work. Label all answers. For all problems involving a formula you must show the formula and each step. LABEL!
 Accelerated Review 0: Polygons and Circles Name: For full credit, show all work. Label all answers. For all problems involving a formula you must show the formula and each step. LABEL! Find the area and
Accelerated Review 0: Polygons and Circles Name: For full credit, show all work. Label all answers. For all problems involving a formula you must show the formula and each step. LABEL! Find the area and
10-3 Composite Figures
 10-3 Composite Figures Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz Geometry Warm Up Find the area of each figure. 1. a rectangle in which b = 14 cm and h = 5 cm A = 70 cm 2 2. a triangle in which b = 6 in.
10-3 Composite Figures Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz Geometry Warm Up Find the area of each figure. 1. a rectangle in which b = 14 cm and h = 5 cm A = 70 cm 2 2. a triangle in which b = 6 in.
Study Guide and Review
 State whether each sentence is or false. If false, replace the underlined term to make a sentence. 1. The center of a trapezoid is the perpendicular distance between the bases. false; height false; height
State whether each sentence is or false. If false, replace the underlined term to make a sentence. 1. The center of a trapezoid is the perpendicular distance between the bases. false; height false; height
SPRINGBOARD UNIT 5 GEOMETRY
 SPRINGBOARD UNIT 5 GEOMETRY 5.1 Area and Perimeter Perimeter the distance around an object. To find perimeter, add all sides. Area the amount of space inside a 2 dimensional object. Measurements for area
SPRINGBOARD UNIT 5 GEOMETRY 5.1 Area and Perimeter Perimeter the distance around an object. To find perimeter, add all sides. Area the amount of space inside a 2 dimensional object. Measurements for area
Chapter 11. Area of Polygons and Circles
 Chapter 11 Area of Polygons and Circles 11.1 & 11.2 Area of Parallelograms, Triangles, Trapezoids, Rhombi, and Kites Use your formula chart to find the formula for the Areas of the following Polygons
Chapter 11 Area of Polygons and Circles 11.1 & 11.2 Area of Parallelograms, Triangles, Trapezoids, Rhombi, and Kites Use your formula chart to find the formula for the Areas of the following Polygons
1. AREAS. Geometry 199. A. Rectangle = base altitude = bh. B. Parallelogram = base altitude = bh. C. Rhombus = 1 product of the diagonals = 1 dd
 Geometry 199 1. AREAS A. Rectangle = base altitude = bh Area = 40 B. Parallelogram = base altitude = bh Area = 40 Notice that the altitude is different from the side. It is always shorter than the second
Geometry 199 1. AREAS A. Rectangle = base altitude = bh Area = 40 B. Parallelogram = base altitude = bh Area = 40 Notice that the altitude is different from the side. It is always shorter than the second
Unit Lesson Plan: Measuring Length and Area: Area of shapes
 Unit Lesson Plan: Measuring Length and Area: Area of shapes Day 1: Area of Square, Rectangles, and Parallelograms Day 2: Area of Triangles Trapezoids, Rhombuses, and Kites Day 3: Quiz over Area of those
Unit Lesson Plan: Measuring Length and Area: Area of shapes Day 1: Area of Square, Rectangles, and Parallelograms Day 2: Area of Triangles Trapezoids, Rhombuses, and Kites Day 3: Quiz over Area of those
Study Guide and Intervention
 Study Guide and Intervention Areas of Regular Polygons In a regular polygon, the segment drawn from the center of the polygon perpendicular to the opposite side is called the apothem. In the figure at
Study Guide and Intervention Areas of Regular Polygons In a regular polygon, the segment drawn from the center of the polygon perpendicular to the opposite side is called the apothem. In the figure at
9-1. Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz. Holt Geometry
 9-1 9-1 Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz Warm Up Find the unknown side length in each right triangle with legs a and b and hypotenuse c. 1. a = 20, b = 21 2. b = 21, c = 35 3. a = 20, c = 52 c =
9-1 9-1 Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz Warm Up Find the unknown side length in each right triangle with legs a and b and hypotenuse c. 1. a = 20, b = 21 2. b = 21, c = 35 3. a = 20, c = 52 c =
Ch. 11 Worksheet #3 Honors Geometry
 Ch. 11 Worksheet #3 1) Find the area of the trapezoid. 2) Find the area (BC). 8 30 C 12 2 B 4 3) Given: rea (BCE) = 78 sq. units, Find the length of C E 135 C 5 2 5 2 B 4) Given: Parallelogram BC; M, N
Ch. 11 Worksheet #3 1) Find the area of the trapezoid. 2) Find the area (BC). 8 30 C 12 2 B 4 3) Given: rea (BCE) = 78 sq. units, Find the length of C E 135 C 5 2 5 2 B 4) Given: Parallelogram BC; M, N
Length and Area. Charles Delman. April 20, 2010
 Length and Area Charles Delman April 20, 2010 What is the length? Unit Solution Unit 5 (linear) units What is the length? Unit Solution Unit 5 2 = 2 1 2 (linear) units What is the perimeter of the shaded
Length and Area Charles Delman April 20, 2010 What is the length? Unit Solution Unit 5 (linear) units What is the length? Unit Solution Unit 5 2 = 2 1 2 (linear) units What is the perimeter of the shaded
10.6 Area and Perimeter of Regular Polygons
 10.6. Area and Perimeter of Regular Polygons www.ck12.org 10.6 Area and Perimeter of Regular Polygons Learning Objectives Calculate the area and perimeter of a regular polygon. Review Queue 1. What is
10.6. Area and Perimeter of Regular Polygons www.ck12.org 10.6 Area and Perimeter of Regular Polygons Learning Objectives Calculate the area and perimeter of a regular polygon. Review Queue 1. What is
Math 2 Plane Geometry part 1 Unit Updated January 13, 2017
 Complementary angles (two angles whose sum is 90 ) and supplementary angles (two angles whose sum is 180. A straight line = 180. In the figure below and to the left, angle EFH and angle HFG form a straight
Complementary angles (two angles whose sum is 90 ) and supplementary angles (two angles whose sum is 180. A straight line = 180. In the figure below and to the left, angle EFH and angle HFG form a straight
A. 180 B. 108 C. 360 D. 540
 Part I - Multiple Choice - Circle your answer: REVIEW FOR FINAL EXAM - GEOMETRY 2 1. Find the area of the shaded sector. Q O 8 P A. 2 π B. 4 π C. 8 π D. 16 π 2. An octagon has sides. A. five B. six C.
Part I - Multiple Choice - Circle your answer: REVIEW FOR FINAL EXAM - GEOMETRY 2 1. Find the area of the shaded sector. Q O 8 P A. 2 π B. 4 π C. 8 π D. 16 π 2. An octagon has sides. A. five B. six C.
10 Perimeter and Area
 CHAPTER 10 Perimeter and Area Chapter Outline 10.1 TRIANGLES AND PARALLELOGRAMS 10.2 TRAPEZOIDS, RHOMBI, AND KITES 10.3 AREAS OF SIMILAR POLYGONS 10.4 CIRCUMFERENCE AND ARC LENGTH 10.5 AREAS OF CIRCLES
CHAPTER 10 Perimeter and Area Chapter Outline 10.1 TRIANGLES AND PARALLELOGRAMS 10.2 TRAPEZOIDS, RHOMBI, AND KITES 10.3 AREAS OF SIMILAR POLYGONS 10.4 CIRCUMFERENCE AND ARC LENGTH 10.5 AREAS OF CIRCLES
Geometry Term 2 Final Exam Review
 Geometry Term Final Eam Review 1. If X(5,4) is reflected in the line y =, then find X.. (5,). (5,0). (-1,) D. (-1,4) Name 6. Find the tangent of angle X. Round your answer to four decimal places. X. 0.5
Geometry Term Final Eam Review 1. If X(5,4) is reflected in the line y =, then find X.. (5,). (5,0). (-1,) D. (-1,4) Name 6. Find the tangent of angle X. Round your answer to four decimal places. X. 0.5
Name: Second semester Exam Honors geometry Agan and Mohyuddin. May 13, 2014
 Name: Second semester Exam Honors geometry Agan and Mohyuddin May 13, 2014 1. A circular pizza has a diameter of 14 inches and is cut into 8 equal slices. To the nearest tenth of a square inch, which answer
Name: Second semester Exam Honors geometry Agan and Mohyuddin May 13, 2014 1. A circular pizza has a diameter of 14 inches and is cut into 8 equal slices. To the nearest tenth of a square inch, which answer
The radius for a regular polygon is the same as the radius of the circumscribed circle.
 Perimeter and Area The perimeter and area of geometric shapes are basic properties that we need to know. The more complex a shape is, the more complex the process can be in finding its perimeter and area.
Perimeter and Area The perimeter and area of geometric shapes are basic properties that we need to know. The more complex a shape is, the more complex the process can be in finding its perimeter and area.
Practice Geometry Semester 2 Exam
 Practice Geometry Semester 2 Exam Short Answer 1. Explain why the triangles are similar. Then find the value of x. 6 2 11 > > x The polygons are similar, but not necessarily drawn to scale. Find the values
Practice Geometry Semester 2 Exam Short Answer 1. Explain why the triangles are similar. Then find the value of x. 6 2 11 > > x The polygons are similar, but not necessarily drawn to scale. Find the values
Geometry Spring Final Exam Review 1. Find the sum of the measures of the interior angles of a convex hexagon.
 Geometry Spring Final Exam Review 1. Find the sum of the measures of the interior angles of a convex hexagon. 2. Find the value of x. 68 110 135 x 3. Find the values of x and y in the parallelogram when,,
Geometry Spring Final Exam Review 1. Find the sum of the measures of the interior angles of a convex hexagon. 2. Find the value of x. 68 110 135 x 3. Find the values of x and y in the parallelogram when,,
Math 1 Plane Geometry Part 1
 Math 1 Plane Geometry Part 1 1 Intersecting lines: When two lines intersect, adjacent angles are supplementary (they make a line and add up to 180 degrees, and vertical angles (angles across from each
Math 1 Plane Geometry Part 1 1 Intersecting lines: When two lines intersect, adjacent angles are supplementary (they make a line and add up to 180 degrees, and vertical angles (angles across from each
Honors Geometry Final Study Guide 2014
 Honors Geometry Final Study Guide 2014 1. Find the sum of the measures of the angles of the figure. 2. What is the sum of the angle measures of a 37-gon? 3. Complete this statement: A polygon with all
Honors Geometry Final Study Guide 2014 1. Find the sum of the measures of the angles of the figure. 2. What is the sum of the angle measures of a 37-gon? 3. Complete this statement: A polygon with all
Geometry Unit 11 Practice Test
 Name: Class: Date: ID: X Geometry Unit 11 Practice Test Short Answer 1. 2. What is the volume of the cylinder in terms of x? 3. What is the height of a square pyramid that has a side length of and a volume
Name: Class: Date: ID: X Geometry Unit 11 Practice Test Short Answer 1. 2. What is the volume of the cylinder in terms of x? 3. What is the height of a square pyramid that has a side length of and a volume
Unit 9 Study Guide. Multiple Choice (2 points) Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Unit 9 Study Guide Multiple hoice (2 points) Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. Find the perimeter of each rectangle. 1. 38 m 18 m a. 684 m c. 56 m b. 94 m d.
Unit 9 Study Guide Multiple hoice (2 points) Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. Find the perimeter of each rectangle. 1. 38 m 18 m a. 684 m c. 56 m b. 94 m d.
Chapters 11 and 12 Study Guide Name: Length, Area, Surface Area, Block: and Volume of Solids
 Page 1 of 15 Chapters 11 and 12 Study Guide Name: Length, Area, Surface Area, Block: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 and Volume of Solids SOL G.13 The student will use formulas for surface area and volume of three-dimensional
Page 1 of 15 Chapters 11 and 12 Study Guide Name: Length, Area, Surface Area, Block: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 and Volume of Solids SOL G.13 The student will use formulas for surface area and volume of three-dimensional
To find the surface area of a pyramid and a cone
 11-3 Surface Areas of Pyramids and Cones Common Core State Standards G-MG.A.1 Use geometric shapes, their measures, and their properties to describe objects. MP 1, MP 3, MP 4, MP 6, MP 7 Objective To find
11-3 Surface Areas of Pyramids and Cones Common Core State Standards G-MG.A.1 Use geometric shapes, their measures, and their properties to describe objects. MP 1, MP 3, MP 4, MP 6, MP 7 Objective To find
Geometry Test Review. π. a. A = π cm cm 2 b. A = 63.2π cm cm 2 c. A = 31.6π cm cm 2 d. A = π cm
 Name: _ Date: Period: _ Score: Geometry Test Review 1. The distance between two cities is 600 miles. On a map, they are 4 inches apart. What is the scale of the map? a. 4 in.:100 mi b. 1 in.:600 mi c.
Name: _ Date: Period: _ Score: Geometry Test Review 1. The distance between two cities is 600 miles. On a map, they are 4 inches apart. What is the scale of the map? a. 4 in.:100 mi b. 1 in.:600 mi c.
9.2. Polygons. Copyright 2005 Pearson Education, Inc.
 9.2 Polygons Polygons Polygons are names according to their number of sides. Number of Sides Name Number of Sides Name 3 Triangle 8 Octagon 4 Quadrilateral 9 Nonagon 5 Pentagon 10 Decagon 6 Hexagon 12
9.2 Polygons Polygons Polygons are names according to their number of sides. Number of Sides Name Number of Sides Name 3 Triangle 8 Octagon 4 Quadrilateral 9 Nonagon 5 Pentagon 10 Decagon 6 Hexagon 12
A plane that is to the base of the figure will create a cross section that is the same shape as the base.
 Objective: 9.1 3 Notes: Surface Area of Solids Name Cross Sections: A cuts through a solid figure to create a cross section. Depending on the way in which the plane cuts through the figure will determine
Objective: 9.1 3 Notes: Surface Area of Solids Name Cross Sections: A cuts through a solid figure to create a cross section. Depending on the way in which the plane cuts through the figure will determine
Name: Date: Period: Mrs. K. Williams ID: A
 Name: Date: Period: Mrs. K. Williams ID: A Review Assignment: Chapters 1-7 CHAPTER 1- solve each equation. 6. 1. 12x 7 67 x = 2. 6 m 12 18 m = 3. 5.4x 13 121 7. x = 4. 22.8 2p 44.4 5. p = CHAPTER 2- Determine
Name: Date: Period: Mrs. K. Williams ID: A Review Assignment: Chapters 1-7 CHAPTER 1- solve each equation. 6. 1. 12x 7 67 x = 2. 6 m 12 18 m = 3. 5.4x 13 121 7. x = 4. 22.8 2p 44.4 5. p = CHAPTER 2- Determine
Polygons. 5 sides 5 angles. pentagon. Name
 Lesson 11.1 Reteach Polygons A polygon is a closed plane figure formed by three or more line segments that meet at points called vertices. You can classify a polygon by the number of sides and the number
Lesson 11.1 Reteach Polygons A polygon is a closed plane figure formed by three or more line segments that meet at points called vertices. You can classify a polygon by the number of sides and the number
Lesson 1 - Area Review Shape Words Formula
 Lesson 1 - Area Review Shape Words Formula Rectangle The area A of a rectangle is the product of the length and the width w. A = w Parallelogram The area A of a parallelogram is the product of any base
Lesson 1 - Area Review Shape Words Formula Rectangle The area A of a rectangle is the product of the length and the width w. A = w Parallelogram The area A of a parallelogram is the product of any base
Areas of Triangles and Parallelograms. There is no substitute for hard work. Thomas Edison
 Areas of Triangles and Parallelograms There is no substitute for hard work. Thomas Edison Concept 1: Postulate 24-26 Postulate 24: Area of a Square Postulate The area of a square is the square of the length
Areas of Triangles and Parallelograms There is no substitute for hard work. Thomas Edison Concept 1: Postulate 24-26 Postulate 24: Area of a Square Postulate The area of a square is the square of the length
Math 10 C Measurement Unit
 Math 10 C Measurement Unit Name: Class: Date: ID: A Chapter Test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which imperial unit is most appropriate
Math 10 C Measurement Unit Name: Class: Date: ID: A Chapter Test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which imperial unit is most appropriate
NAME DATE PERIOD. Name each polygon by its number of sides and then classify it as convex or concave and regular or irregular.
 Skills Practice Name each polygon by its number of sides and then classify it as convex or concave and regular or irregular. Lesson Find the perimeter or circumference of each figure. Round to the nearest
Skills Practice Name each polygon by its number of sides and then classify it as convex or concave and regular or irregular. Lesson Find the perimeter or circumference of each figure. Round to the nearest
Unit 7: 3D Figures 10.1 & D formulas & Area of Regular Polygon
 Unit 7: 3D Figures 10.1 & 10.2 2D formulas & Area of Regular Polygon NAME Name the polygon with the given number of sides: 3-sided: 4-sided: 5-sided: 6-sided: 7-sided: 8-sided: 9-sided: 10-sided: Find
Unit 7: 3D Figures 10.1 & 10.2 2D formulas & Area of Regular Polygon NAME Name the polygon with the given number of sides: 3-sided: 4-sided: 5-sided: 6-sided: 7-sided: 8-sided: 9-sided: 10-sided: Find
Unit 4 End-of-Unit Assessment Study Guide
 Circles Unit 4 End-of-Unit Assessment Study Guide Definitions Radius (r) = distance from the center of a circle to the circle s edge Diameter (d) = distance across a circle, from edge to edge, through
Circles Unit 4 End-of-Unit Assessment Study Guide Definitions Radius (r) = distance from the center of a circle to the circle s edge Diameter (d) = distance across a circle, from edge to edge, through
Volume of Cylinders. Volume of Cones. Example Find the volume of the cylinder. Round to the nearest tenth.
 Volume of Cylinders As with prisms, the area of the base of a cylinder tells the number of cubic units in one layer. The height tells how many layers there are in the cylinder. The volume V of a cylinder
Volume of Cylinders As with prisms, the area of the base of a cylinder tells the number of cubic units in one layer. The height tells how many layers there are in the cylinder. The volume V of a cylinder
17-18 ACP Geometry Final Exam REVIEW
 17-18 ACP Geometry Final Exam REVIEW Chapter 7 Similarity 1. Given ABC DEF. Find the value of x. Justify your answer. Are the following triangles similar? If so, justify your answer, and write a similarity
17-18 ACP Geometry Final Exam REVIEW Chapter 7 Similarity 1. Given ABC DEF. Find the value of x. Justify your answer. Are the following triangles similar? If so, justify your answer, and write a similarity
Areas of Triangles and Quadrilaterals. Mrs. Poland January 5, 2010
 Areas of Triangles and Quadrilaterals Mrs. Poland January 5, 2010 Review 1! A polygon with 7 sides is called a. A) nonagon B) dodecagon C) heptagon D) hexagon E) decagon Review 2! Find m
Areas of Triangles and Quadrilaterals Mrs. Poland January 5, 2010 Review 1! A polygon with 7 sides is called a. A) nonagon B) dodecagon C) heptagon D) hexagon E) decagon Review 2! Find m
Volume of Prisms and Cylinders
 Volume of Prisms and Cylinders Say Thanks to the Authors Click http://www.ck12.org/saythanks (No sign in required) To access a customizable version of this book, as well as other interactive content, visit
Volume of Prisms and Cylinders Say Thanks to the Authors Click http://www.ck12.org/saythanks (No sign in required) To access a customizable version of this book, as well as other interactive content, visit
Additional Practice. Name Date Class. 1. Find the area and the perimeter of each of the four shapes below. a. b. c. d. Covering and Surrounding
 Additional Practice. Find the area and the perimeter of each of the four shapes below. Investigation a. b. c. d. 52 cm 6 cm 52 cm 34 cm 93 Investigation 2. Susan is helping her father measure the living
Additional Practice. Find the area and the perimeter of each of the four shapes below. Investigation a. b. c. d. 52 cm 6 cm 52 cm 34 cm 93 Investigation 2. Susan is helping her father measure the living
Write Euler s Theorem. Solving Problems Using Surface Area and Volume. Figure Surface Area Volume. Cl V 5 1 } 3
 CHAPTER SUMMARY Big Idea 1 BIG IDEAS Exploring Solids and Their Properties For Your Notebook Euler s Theorem is useful when finding the number of faces, edges, or vertices on a polyhedron, especially when
CHAPTER SUMMARY Big Idea 1 BIG IDEAS Exploring Solids and Their Properties For Your Notebook Euler s Theorem is useful when finding the number of faces, edges, or vertices on a polyhedron, especially when
Sample: Do Not Reproduce GEO1 STUDENT PAGES. GEOMETRY AND MEASUREMENT Student Pages for Packet 1: Length and Area.
 Name Period Date GEOMETRY AND MEASUREMENT Student Pages for Packet 1: GEO1.1 Congruence Plot simple figures on coordinate graphs, and determine their lengths and areas. Make conjectures about perimeters
Name Period Date GEOMETRY AND MEASUREMENT Student Pages for Packet 1: GEO1.1 Congruence Plot simple figures on coordinate graphs, and determine their lengths and areas. Make conjectures about perimeters
Chapter 10 Polygons and Area
 Geometry Concepts Chapter 10 Polygons and Area Name polygons according to sides and angles Find measures of interior angles Find measures of exterior angles Estimate and find areas of polygons Estimate
Geometry Concepts Chapter 10 Polygons and Area Name polygons according to sides and angles Find measures of interior angles Find measures of exterior angles Estimate and find areas of polygons Estimate
EOC Review: Practice: 1. In the circle below, AB = 2BC. What is the probability of hitting the shaded region with a random dart?
 EOC Review: Focus Areas: Trigonometric Ratios Area and Volume including Changes in Area/Volume Geometric Probability Proofs and Deductive Reasoning including Conditionals Properties of Polygons and Circles
EOC Review: Focus Areas: Trigonometric Ratios Area and Volume including Changes in Area/Volume Geometric Probability Proofs and Deductive Reasoning including Conditionals Properties of Polygons and Circles
NAME DATE PERIOD. Find the perimeter and area of each parallelogram. Round to the nearest tenth if necessary. 4 ft. 22 in. 45.
 - Skills Practice Area of Parallelograms Find the perimeter and area of each parallelogram Round to the nearest tenth if necessary 0 cm 0 0 cm 4 ft 55 ft 0 4 yd 4 7 yd 45 in 45 in Lesson - 5 4 m 5 km 9
- Skills Practice Area of Parallelograms Find the perimeter and area of each parallelogram Round to the nearest tenth if necessary 0 cm 0 0 cm 4 ft 55 ft 0 4 yd 4 7 yd 45 in 45 in Lesson - 5 4 m 5 km 9
Q3 Exam Review Date: Per:
 Geometry Name: Q3 Exam Review Date: Per: Show all your work. Box or circle your final answer. When appropriate, write your answers in simplest radical form, as a simplified improper fraction, AND as a
Geometry Name: Q3 Exam Review Date: Per: Show all your work. Box or circle your final answer. When appropriate, write your answers in simplest radical form, as a simplified improper fraction, AND as a
Algebra Area of Parallelograms
 Lesson 10.1 Reteach Algebra Area of Parallelograms The formula for the area of a parallelogram is the product of the base and height. The formula for the area of a square is the square of one of its sides.
Lesson 10.1 Reteach Algebra Area of Parallelograms The formula for the area of a parallelogram is the product of the base and height. The formula for the area of a square is the square of one of its sides.
Geometry 2: 2D and 3D shapes Review
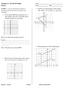 Geometry 2: 2D and 3D shapes Review G-GPE.7 I can use the distance formula to compute perimeter and area of triangles and rectangles. Name Period Date 3. Find the area and perimeter of the triangle with
Geometry 2: 2D and 3D shapes Review G-GPE.7 I can use the distance formula to compute perimeter and area of triangles and rectangles. Name Period Date 3. Find the area and perimeter of the triangle with
