Log1 Contest Round 2 Theta Circles, Parabolas and Polygons. 4 points each
|
|
|
- Claude Bernard Kelly
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Name: Units do not have to be included Log1 Contest Round Theta Circles, Parabolas and Polygons 4 points each 1 Find the value of x given that 8 x 30 Find the area of a triangle given that it has side lengths 15, 0, 5. 3 Given that the two shapes are similar, find the perimeter of the larger rectangle. m 5 m P 1 = 10 m P =??? 4 How many sides does a regular polygon have if one measure of its interior angle is 179 degrees? 5 How many sides does a heptadecagon have? 5 points each 6 Find the minimum distance from the point (, 5) to the circle (x 10) + (y + 11) = 49 7 A rectangle is constructed such that its diagonals are 5 inches. Given that the side lengths are integers that are relatively prime, what is the perimeter of the rectangle. 8 How many sides does a convex polygon have if the sum of its interior angles is equal to 10 straight angles? 9 If a regular polygon has 819 diagonals, how many side does this regular polygon have? 10 A circle circumscribes a triangle with side lengths 8,96, and 100. Determine the area of the circle.
2 6 points each 11 A wheel with a radius of 8 π meters rolls directly down a smooth 5 meter path. How many revolutions does the wheel make on the path? 1 Consider the parabola given by the equation y = 1 1 x x + 7. An ellipse is drawn with its 3 3 center located at the focus of the parabola. The minor axis of the ellipse is the latus rectum of the parabola, which is the line segment formed by the points of intersection of the parabola and a horizontal line that passes through its focus. The semi-major axis is the vertical line segment joining the parabola s focus and its reflection point through its directrix. Calculate the area of this ellipse. 13 What is the surface area of a regular icosahedron with side length 10? 14 What is the area, in square meters, of an isosceles right triangle that has a 14 meter hypotenuse? 15 A cube has side length 8. Four distinct points are chosen from the centers of the cube s faces, not all coplanar. What is the volume of the tetrahedron whose vertices are these points?
3 Name: Units do not have to be included. 1 Find the value of x given that Log1 Contest Round Alpha Circles, Parabolas and Polygons 8 4 points each x 30 Find the area of a triangle given that it has side lengths 15, 0, 5. 3 Given that the two shapes are similar, find the perimeter of the larger rectangle. m 5 m 4 How many diagonals does a regular nonagon have? P 1 = 10 m P =??? 5 How many sides does a heptadecagon have? 5 points each 6 Find the minimum distance from the point (, 5) to the circle (x 10) + (y + 11) = 49 7 A rectangle is constructed such that its diagonals are 5 inches. Given that the side lengths are integers that are relatively prime, what is the perimeter of the rectangle. 8 How many sides does a convex polygon have if the sum of its interior angles is equal to 10 straight angles? 9 What is the area of a regular hexagon that is inscribed in a circle if this circle also circumscribes a right triangle with legs of length 6 and 8? 10 A circle circumscribes a triangle with side lengths 8,96, and 100. Determine the area of the circle.
4 6 points each 11 A wheel with a radius of 8 π meters rolls directly down a smooth 5 meter path. How many revolutions does the wheel make on the path? 1 Consider the parabola given by the equation y = 1 1 x x + 7. An ellipse is drawn with its 3 3 center located at the focus of the parabola. The minor axis of the ellipse is the latus rectum of the parabola, which is the line segment formed by the points of intersection of the parabola and a horizontal line that passes through its focus. The semi-major axis is the vertical line segment joining the parabola s focus and its reflection point through its directrix. Calculate the area of this ellipse. 13 What is the surface area of a regular icosahedron with side length 10? 14 Find the area of the circle that circumscribes an equilateral triangle with a side of 48. Leave your answer in terms of pi. 15 A cube has side length 8. Four distinct points are chosen from the centers of the cube s faces, not all coplanar. What is the volume of the tetrahedron whose vertices are these points?
5 Name: Units do not have to be included. 1 Find the value of x given that Log1 Contest Round Mu Circles, Parabolas and Polygons 8 4 points each x 30 Find the area of a triangle given that it has side lengths 15, 0, 5. 3 Given that the two shapes are similar, find the perimeter of the larger rectangle. m 5 m 4 How many diagonals does a regular nonagon have? P 1 = 10 m P =??? 5 What is the area enclosed by the graph of y = f( x ) and the x-axis from x = 3 to x = +3 given that f(x) = 4x 3? 5 points each 6 Find the minimum distance from the point (, 5) to the circle (x 10) + (y + 11) = 49 7 A rectangle is constructed such that its diagonals are 5 inches. Given that the side lengths are integers that are relatively prime, what is the perimeter of the rectangle. 8 How many sides does a convex polygon have if the sum of its interior angles is equal to 10 straight angles? 9 What is the area of a regular hexagon that is inscribed in a circle if this circle also circumscribes a right triangle with legs of length 6 and 8? 10 The region bounded by the coordinate axes and the portion of the line y = x + 4 in the first quadrant is rotated around the y-axis. What is the volume of the resulting solid?
6 6 points each 11 A wheel with a radius of 8 π meters rolls directly down a smooth 5 meter path. How many revolutions does the wheel make on the path? 1 Consider the parabola given by the equation y = 1 1 x x + 7. An ellipse is drawn with its center 3 3 located at the focus of the parabola. The minor axis of the ellipse is the latus rectum of the parabola, which is the line segment formed by the points of intersection of the parabola and a horizontal line that passes through its focus. The semi-major axis is the vertical line segment joining the parabola s focus and its reflection point through its directrix. Calculate the area of this ellipse. 13 What is the surface area of a regular icosahedron with side length 10? 14 Find the area of the circle that circumscribes an equilateral triangle with a side of 48. Leave your answer in terms of pi The definite integral π ( 16 x ) dx represents the volume of a sphere. What 4 is the surface area of the sphere?
7 Log1 Contest Round Theta Circles, Parabolas and Polygons Answer Key Name: Units do not have to be included. 4 points each 1 Find the value of x given that 16 8 x 30 Find the area of a triangle given that it has side lengths 15, 0, Given that the two shapes are similar, find the perimeter of the larger rectangle. m 5 m P 1 = 10 m P =??? 5 4 How many sides does a regular polygon have if one measure of its interior angle is 179 degrees? How many sides does a heptadecagon have? 17 5 points each 6 Find the minimum distance from the point (, 5) to the circle (x 10) + (y + 11) = A rectangle is constructed such that its diagonals are 5 inches. Given that the side lengths are integers that are relatively prime, what is the perimeter of the rectangle. 6 8 How many sides does a convex polygon have if the sum of its interior angles is equal to 10 straight angles? 1 9 If a regular polygon has 819 diagonals, how many side does this regular polygon have? 4 10 A circle circumscribes a triangle with side lengths 8,96, and 100. Determine the area of the circle. 500π
8 11 6 points each A wheel with a radius of 8 π meters rolls directly down a smooth 5 meter path. How many revolutions does the wheel make on the path? 1 Consider the parabola given by the equation 7π y = 1 1 x x + 7. An ellipse is drawn with its center 3 3 located at the focus of the parabola. The minor axis of the ellipse is the latus rectum of the parabola, which is the line segment formed by the points of intersection of the parabola and a horizontal line that passes through its focus. The semi-major axis is the vertical line segment joining the parabola s focus and its reflection point through its directrix. Calculate the area of this ellipse. 13 What is the surface area of a regular icosahedron with side length 10? What is the area, in square meters, of an isosceles right triangle that has a 14 meter hypotenuse? A cube has side length 8. Four distinct points are chosen from the centers of the cube s faces, not all coplanar. What is the volume of the tetrahedron whose vertices are these points? 64 3
9 Log1 Contest Round Alpha Circles, Parabolas and Polygons Answer Key Name: Units do not have to be included. 4 points each 1 Find the value of x given that 16 8 x 30 Find the area of a triangle given that it has side lengths 15, 0, Given that the two shapes are similar, find the perimeter of the larger rectangle. m 5 m P 1 = 10 m P =??? 5 4 How many diagonals does a regular nonagon have? 7 5 How many sides does a heptadecagon have? 17 5 points each 6 Find the minimum distance from the point (, 5) to the circle (x 10) + (y + 11) = A rectangle is constructed such that its diagonals are 5 inches. Given that the side lengths are integers that are relatively prime, what is the perimeter of the rectangle. 6 8 How many sides does a convex polygon have if the sum of its interior angles is equal to 10 straight angles? 1 9 What is the area of a regular hexagon that is inscribed in a circle if this circle also circumscribes a right triangle with legs of length 6 and 8? A circle circumscribes a triangle with side lengths 8,96, and 100. Determine the area of the circle. 500π
10 11 6 points each A wheel with a radius of 8 π meters rolls directly down a smooth 5 meter path. How many revolutions does the wheel make on the path? 1 Consider the parabola given by the equation 7π y = 1 1 x x + 7. An ellipse is drawn with its 3 3 center located at the focus of the parabola. The minor axis of the ellipse is the latus rectum of the parabola, which is the line segment formed by the points of intersection of the parabola and a horizontal line that passes through its focus. The semi-major axis is the vertical line segment joining the parabola s focus and its reflection point through its directrix. Calculate the area of this ellipse. 13 What is the surface area of a regular icosahedron with side length 10? Find the area of the circle that circumscribes an equilateral triangle with a side of 48. Leave your answer in terms of pi. 768π 15 A cube has side length 8. Four distinct points are chosen from the centers of the cube s faces, not all coplanar. What is the volume of the tetrahedron whose vertices are these points? 64 3
11 Log1 Contest Round Mu Circles, Parabolas and Polygons Answer Key Name: Units do not have to be included. 4 points each 1 Find the value of x given that 16 8 x 30 Find the area of a triangle given that it has side lengths 15, 0, Given that the two shapes are similar, find the perimeter of the larger rectangle. m 5 m P 1 = 10 m P =??? 5 4 How many diagonals does a regular nonagon have? 7 5 What is the area enclosed by the graph of y = f( x ) and the x-axis from x = 3 to x = +3 given that f(x) = 4x 3? 16 5 points each 6 Find the minimum distance from the point (, 5) to the circle (x 10) + (y + 11) = 49 7 A rectangle is constructed such that its diagonals are 5 inches. Given that the side lengths are integers that are relatively prime, what is the perimeter of the rectangle. 8 How many sides does a convex polygon have if the sum of its interior angles is equal to 10 straight angles? 9 What is the area of the region that is outside a regular hexagon AND inside the circle that circumscribes it if the circle has a circumference of 16 3π? 10 The region bounded by the coordinate axes and the portion of the line y = x + 4 in the first quadrant is rotated around the y-axis. What is the volume of the resulting solid? π 3
12 11 6 points each A wheel with a radius of 8 π meters rolls directly down a smooth 5 meter path. How many revolutions does the wheel make on the path? 1 Consider the parabola given by the equation 7π y = 1 1 x x + 7. An ellipse is drawn with its center 3 3 located at the focus of the parabola. The minor axis of the ellipse is the latus rectum of the parabola, which is the line segment formed by the points of intersection of the parabola and a horizontal line that passes through its focus. The semi-major axis is the vertical line segment joining the parabola s focus and its reflection point through its directrix. Calculate the area of this ellipse. 13 What is the surface area of a regular icosahedron with side length 10? Find the area of the circle that circumscribes an equilateral triangle with a side of 48. Leave your answer in terms of pi. 768π 15 4 The definite integral π ( 16 x ) dx represents the volume of a sphere. What 4 is the surface area of the sphere? 64π
13 Log1 Contest Round Circles, Parabolas and Polygons Solutions Mu Al Th Solution sin 30 = 1 Therefore, sin 30 = 8 x So, 1 = 8 x x = 8() x = 16 Using Heron s formula s(s a)(s b)(s c) Where s = a+b+c the side perimeters. s = = 30 A = 30(30 15)(30 0)(30 5) A = 500 = P 1 = 10, so 10 (+) = 3, 3 is the missing side length With that information we can set up a relationship 5 = 3 x x = 15, x = 7.5, P = ( ) = The general formula for solving for diagonals is n(n 3), where n is the number of sides. 9(9 3) = 7 4 The adjacent exterior angle is 1 since the polygon is regular the number of sides is found by = 360.
14 5 Evaluate the integral of the function f(x) from x = 0 to x = x 3 dx = = 81 0 For x < 0, f( x ) generates a graph that is the reflection over the y-axis of the function f(x)for x > 0. Therefore, the area is (81) = A heptadecagon has 17 sides The center of the circle is (10, -11) D = (x x 1 ) + (y + y 1 ) Using the point give (, 5) We can plug it into the equation. D = (10 ( )) + ( 11 5) D = D = 400 D = 0 Then we subtract 7 for the radius and the answer is D = l + w, 5 = l + w, 65 = l + w, There is only one possible pair that could work which is the side lengths being 7 and 4. So the Perimeter is P = (7 + 4) = Sum of interior angles = (n )180; 1800 = (n )180; 10 = n ; n = 1
15 9 9 The right triangle inscribed in the circle has a hypotenuse of 10. This implies that the hypotenuse is also the diameter of the circumscribing circle. For a regular hexagon inscribed in a circle, the line segments that connect directly opposing vertices are also diameters of this circle. Each line segment connecting opposing vertices bisects each 10 angle of the hexagon, thus forming 6 identical, equilateral triangles of side length 5, which corresponds to ½ the diameter of the circle. Therefore, A H = 6 ( ) = Number of diagonals = 819 = n(n 3) 1638 = n(n 3) n = 4 n(n 3) 10 The x-intercept is at (,0), and the y-intercept is at (0,4). The figure is a cone of radius and height 4, which has volume 1 3 πr h = 16π Note that this triangle is right (if you divide the sides by 4, you get 7-4-5, a well-known right triangle with integer side lengths). The right angle subtends an arc of 180 degrees, so the hypotenuse goes through the center of the circle. So the radius of the circle is 100/ = 50, so the area of the circle is 500π
16 The wheel s circumference is πr = π 8 π = 16 = 4 ; 5 4 = 1 = Thus, the wheel makes revolutions Rewrite the equation for the parabola in standard form, (x h) = 4p(y k) 1y = x 8x + 8 1y 1 = x 8x (y 1) = (x 4) 4(3)(y 1) = (x 4) Focus: F = (h, k + p) = (4,1 + 3) = (4,4) Vertex: V = (h, k) = (4,1) Directrix: y = k p = 1 3 = ; y = Latus Rectum: LR = 4p = 4(3) = 1 Semi minor axis: a = 1 LR = 1 (1) = 6 Semi major axis: b = (4 ( )) = (6) = 1 Area of an Ellipse: A = πab = π(6)(1) = 7π SA = 5(a²)( 3) Where a = side length. So 5(10 )( 3) = 500 3
17 14 14 We are given that the sides are 48 units. Draw the perpendicular bisector from one of the vertices of the triangle. Also, draw a line from another vertex of the triangle to its circumcenter. This forms a right triangle with a base equal to 4 and a hypotenuse that is the radius of the circumscribed circle. Since the triangle is equilateral, its circumcenter and incenter are concurrent. Thus, the radius bisects the vertex angle. Consequently, the right triangle is a right triangle with a base angle formed at the vertex of the inscribed triangle equal to 30 degrees. The ratio of the base to the hypotenuse must be 3. Therefore, 3 = 4 c c = 48 3 The area of the circumscribed circle is A = π ( 4() 3 ) = 768π a c 4 14 Given that the triangle is an isosceles right triangle we know that its two legs must be equal in length. Set these lengths equal to x and use the Pythagorean Theorem. 14 = x + x 196 = x x = 98 For this triangle, the legs correspond to its base and height. Thus x = Base x Height. Since the area of a triangle is A = 1 Bh, x = x Area. Therefore, Area = The quantity squared comes from equation y = 16 x which is the top half of a circle of radius 4. The sphere would have surface area 4π(4 )
18 15 15 Note that any tetrahedron satisfying these properties is the same. To see this, since we have 6 faces and 4 points to choose from, by the Pigeonhole Principle, two points must be on opposite faces. Choosing a third point always yields the same resulting triangle, and the fourth point cannot be opposite the third point. This leaves two possible points, and both yield identical tetrahedrons. Now orient the tetrahedron so that there is a right triangle in the middle layer and a point on the top face. The right triangle is isosceles and has legs of length 4, yielding a base of area 16. The height is half the length of the cube, or 4. The volume of a pyramid is 1 Ah, A = area of base, h = height, so the volume of the tetrahedron 3 is 1 64 (16)(4) = 3 3
3. Radius of incenter, C. 4. The centroid is the point that corresponds to the center of gravity in a triangle. B
 1. triangle that contains one side that has the same length as the diameter of its circumscribing circle must be a right triangle, which cannot be acute, obtuse, or equilateral. 2. 3. Radius of incenter,
1. triangle that contains one side that has the same length as the diameter of its circumscribing circle must be a right triangle, which cannot be acute, obtuse, or equilateral. 2. 3. Radius of incenter,
Hustle Geometry SOLUTIONS MAΘ National Convention 2018 Answers:
 Hustle Geometry SOLUTIONS MAΘ National Convention 08 Answers:. 50.. 4. 8 4. 880 5. 6. 6 7 7. 800π 8. 6 9. 8 0. 58. 5.. 69 4. 0 5. 57 6. 66 7. 46 8. 6 9. 0.. 75. 00. 80 4. 8 5 5. 7 8 6+6 + or. Hustle Geometry
Hustle Geometry SOLUTIONS MAΘ National Convention 08 Answers:. 50.. 4. 8 4. 880 5. 6. 6 7 7. 800π 8. 6 9. 8 0. 58. 5.. 69 4. 0 5. 57 6. 66 7. 46 8. 6 9. 0.. 75. 00. 80 4. 8 5 5. 7 8 6+6 + or. Hustle Geometry
Moore Catholic High School Math Department
 Moore Catholic High School Math Department Geometry Vocabulary The following is a list of terms and properties which are necessary for success in a Geometry class. You will be tested on these terms during
Moore Catholic High School Math Department Geometry Vocabulary The following is a list of terms and properties which are necessary for success in a Geometry class. You will be tested on these terms during
Suggested List of Mathematical Language. Geometry
 Suggested List of Mathematical Language Geometry Problem Solving A additive property of equality algorithm apply constraints construct discover explore generalization inductive reasoning parameters reason
Suggested List of Mathematical Language Geometry Problem Solving A additive property of equality algorithm apply constraints construct discover explore generalization inductive reasoning parameters reason
MANHATTAN HUNTER SCIENCE HIGH SCHOOL GEOMETRY CURRICULUM
 COORDINATE Geometry Plotting points on the coordinate plane. Using the Distance Formula: Investigate, and apply the Pythagorean Theorem as it relates to the distance formula. (G.GPE.7, 8.G.B.7, 8.G.B.8)
COORDINATE Geometry Plotting points on the coordinate plane. Using the Distance Formula: Investigate, and apply the Pythagorean Theorem as it relates to the distance formula. (G.GPE.7, 8.G.B.7, 8.G.B.8)
Geometry Vocabulary Math Fundamentals Reference Sheet Page 1
 Math Fundamentals Reference Sheet Page 1 Acute Angle An angle whose measure is between 0 and 90 Acute Triangle A that has all acute Adjacent Alternate Interior Angle Two coplanar with a common vertex and
Math Fundamentals Reference Sheet Page 1 Acute Angle An angle whose measure is between 0 and 90 Acute Triangle A that has all acute Adjacent Alternate Interior Angle Two coplanar with a common vertex and
Theta Circles & Polygons 2015 Answer Key 11. C 2. E 13. D 4. B 15. B 6. C 17. A 18. A 9. D 10. D 12. C 14. A 16. D
 Theta Circles & Polygons 2015 Answer Key 1. C 2. E 3. D 4. B 5. B 6. C 7. A 8. A 9. D 10. D 11. C 12. C 13. D 14. A 15. B 16. D 17. A 18. A 19. A 20. B 21. B 22. C 23. A 24. C 25. C 26. A 27. C 28. A 29.
Theta Circles & Polygons 2015 Answer Key 1. C 2. E 3. D 4. B 5. B 6. C 7. A 8. A 9. D 10. D 11. C 12. C 13. D 14. A 15. B 16. D 17. A 18. A 19. A 20. B 21. B 22. C 23. A 24. C 25. C 26. A 27. C 28. A 29.
Indiana State Math Contest Geometry
 Indiana State Math Contest 018 Geometry This test was prepared by faculty at Indiana University - Purdue University Columbus Do not open this test booklet until you have been advised to do so by the test
Indiana State Math Contest 018 Geometry This test was prepared by faculty at Indiana University - Purdue University Columbus Do not open this test booklet until you have been advised to do so by the test
Index COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL. Symbols & Numerics
 Symbols & Numerics. (dot) character, point representation, 37 symbol, perpendicular lines, 54 // (double forward slash) symbol, parallel lines, 54, 60 : (colon) character, ratio of quantity representation
Symbols & Numerics. (dot) character, point representation, 37 symbol, perpendicular lines, 54 // (double forward slash) symbol, parallel lines, 54, 60 : (colon) character, ratio of quantity representation
Geometry. Geometry is one of the most important topics of Quantitative Aptitude section.
 Geometry Geometry is one of the most important topics of Quantitative Aptitude section. Lines and Angles Sum of the angles in a straight line is 180 Vertically opposite angles are always equal. If any
Geometry Geometry is one of the most important topics of Quantitative Aptitude section. Lines and Angles Sum of the angles in a straight line is 180 Vertically opposite angles are always equal. If any
Angles. An angle is: the union of two rays having a common vertex.
 Angles An angle is: the union of two rays having a common vertex. Angles can be measured in both degrees and radians. A circle of 360 in radian measure is equal to 2π radians. If you draw a circle with
Angles An angle is: the union of two rays having a common vertex. Angles can be measured in both degrees and radians. A circle of 360 in radian measure is equal to 2π radians. If you draw a circle with
Glossary of dictionary terms in the AP geometry units
 Glossary of dictionary terms in the AP geometry units affine linear equation: an equation in which both sides are sums of terms that are either a number times y or a number times x or just a number [SlL2-D5]
Glossary of dictionary terms in the AP geometry units affine linear equation: an equation in which both sides are sums of terms that are either a number times y or a number times x or just a number [SlL2-D5]
Unit Number of Days Dates. 1 Angles, Lines and Shapes 14 8/2 8/ Reasoning and Proof with Lines and Angles 14 8/22 9/9
 8 th Grade Geometry Curriculum Map Overview 2016-2017 Unit Number of Days Dates 1 Angles, Lines and Shapes 14 8/2 8/19 2 - Reasoning and Proof with Lines and Angles 14 8/22 9/9 3 - Congruence Transformations
8 th Grade Geometry Curriculum Map Overview 2016-2017 Unit Number of Days Dates 1 Angles, Lines and Shapes 14 8/2 8/19 2 - Reasoning and Proof with Lines and Angles 14 8/22 9/9 3 - Congruence Transformations
Log1 Contest Round 1 Theta Circles & Polygons. 4 points each. 5 points each
 014 015 Log1 Contest Round 1 Theta Circles & Polygons 1 Find the area, in square inches, enclosed by a circle whose diameter is 8 inches. A rectangle has sides of length 4 and 6. Find the area enclosed
014 015 Log1 Contest Round 1 Theta Circles & Polygons 1 Find the area, in square inches, enclosed by a circle whose diameter is 8 inches. A rectangle has sides of length 4 and 6. Find the area enclosed
Moore Catholic High School Math Department
 Moore Catholic High School Math Department Geometry Vocabulary The following is a list of terms and properties which are necessary for success in a Geometry class. You will be tested on these terms during
Moore Catholic High School Math Department Geometry Vocabulary The following is a list of terms and properties which are necessary for success in a Geometry class. You will be tested on these terms during
Geometry Vocabulary. Name Class
 Geometry Vocabulary Name Class Definition/Description Symbol/Sketch 1 point An exact location in space. In two dimensions, an ordered pair specifies a point in a coordinate plane: (x,y) 2 line 3a line
Geometry Vocabulary Name Class Definition/Description Symbol/Sketch 1 point An exact location in space. In two dimensions, an ordered pair specifies a point in a coordinate plane: (x,y) 2 line 3a line
Chapter 10 Similarity
 Chapter 10 Similarity Def: The ratio of the number a to the number b is the number. A proportion is an equality between ratios. a, b, c, and d are called the first, second, third, and fourth terms. The
Chapter 10 Similarity Def: The ratio of the number a to the number b is the number. A proportion is an equality between ratios. a, b, c, and d are called the first, second, third, and fourth terms. The
Postulates, Theorems, and Corollaries. Chapter 1
 Chapter 1 Post. 1-1-1 Through any two points there is exactly one line. Post. 1-1-2 Through any three noncollinear points there is exactly one plane containing them. Post. 1-1-3 If two points lie in a
Chapter 1 Post. 1-1-1 Through any two points there is exactly one line. Post. 1-1-2 Through any three noncollinear points there is exactly one plane containing them. Post. 1-1-3 If two points lie in a
Acknowledgement: Scott, Foresman. Geometry. SIMILAR TRIANGLES. 1. Definition: A ratio represents the comparison of two quantities.
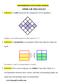 1 cknowledgement: Scott, Foresman. Geometry. SIMILR TRINGLS 1. efinition: ratio represents the comparison of two quantities. In figure, ratio of blue squares to white squares is 3 : 5 2. efinition: proportion
1 cknowledgement: Scott, Foresman. Geometry. SIMILR TRINGLS 1. efinition: ratio represents the comparison of two quantities. In figure, ratio of blue squares to white squares is 3 : 5 2. efinition: proportion
Geometry Learning Targets
 Geometry Learning Targets 2015 2016 G0. Algebra Prior Knowledge G0a. Simplify algebraic expressions. G0b. Solve a multi-step equation. G0c. Graph a linear equation or find the equation of a line. G0d.
Geometry Learning Targets 2015 2016 G0. Algebra Prior Knowledge G0a. Simplify algebraic expressions. G0b. Solve a multi-step equation. G0c. Graph a linear equation or find the equation of a line. G0d.
Definition / Postulates / Theorems Checklist
 3 undefined terms: point, line, plane Definition / Postulates / Theorems Checklist Section Definition Postulate Theorem 1.2 Space Collinear Non-collinear Coplanar Non-coplanar Intersection 1.3 Segment
3 undefined terms: point, line, plane Definition / Postulates / Theorems Checklist Section Definition Postulate Theorem 1.2 Space Collinear Non-collinear Coplanar Non-coplanar Intersection 1.3 Segment
Perimeter. Area. Surface Area. Volume. Circle (circumference) C = 2πr. Square. Rectangle. Triangle. Rectangle/Parallelogram A = bh
 Perimeter Circle (circumference) C = 2πr Square P = 4s Rectangle P = 2b + 2h Area Circle A = πr Triangle A = bh Rectangle/Parallelogram A = bh Rhombus/Kite A = d d Trapezoid A = b + b h A area a apothem
Perimeter Circle (circumference) C = 2πr Square P = 4s Rectangle P = 2b + 2h Area Circle A = πr Triangle A = bh Rectangle/Parallelogram A = bh Rhombus/Kite A = d d Trapezoid A = b + b h A area a apothem
1. AREAS. Geometry 199. A. Rectangle = base altitude = bh. B. Parallelogram = base altitude = bh. C. Rhombus = 1 product of the diagonals = 1 dd
 Geometry 199 1. AREAS A. Rectangle = base altitude = bh Area = 40 B. Parallelogram = base altitude = bh Area = 40 Notice that the altitude is different from the side. It is always shorter than the second
Geometry 199 1. AREAS A. Rectangle = base altitude = bh Area = 40 B. Parallelogram = base altitude = bh Area = 40 Notice that the altitude is different from the side. It is always shorter than the second
Shortcuts, Formulas & Tips
 & present Shortcuts, Formulas & Tips For MBA, Banking, Civil Services & Other Entrance Examinations Vol. 3: Geometry Lines and Angles Sum of the angles in a straight line is 180 Vertically opposite angles
& present Shortcuts, Formulas & Tips For MBA, Banking, Civil Services & Other Entrance Examinations Vol. 3: Geometry Lines and Angles Sum of the angles in a straight line is 180 Vertically opposite angles
Geometry Foundations Planning Document
 Geometry Foundations Planning Document Unit 1: Chromatic Numbers Unit Overview A variety of topics allows students to begin the year successfully, review basic fundamentals, develop cooperative learning
Geometry Foundations Planning Document Unit 1: Chromatic Numbers Unit Overview A variety of topics allows students to begin the year successfully, review basic fundamentals, develop cooperative learning
Videos, Constructions, Definitions, Postulates, Theorems, and Properties
 Videos, Constructions, Definitions, Postulates, Theorems, and Properties Videos Proof Overview: http://tinyurl.com/riehlproof Modules 9 and 10: http://tinyurl.com/riehlproof2 Module 9 Review: http://tinyurl.com/module9livelesson-recording
Videos, Constructions, Definitions, Postulates, Theorems, and Properties Videos Proof Overview: http://tinyurl.com/riehlproof Modules 9 and 10: http://tinyurl.com/riehlproof2 Module 9 Review: http://tinyurl.com/module9livelesson-recording
Geometry: Semester 2 Practice Final Unofficial Worked Out Solutions by Earl Whitney
 Geometry: Semester 2 Practice Final Unofficial Worked Out Solutions by Earl Whitney 1. Wrapping a string around a trash can measures the circumference of the trash can. Assuming the trash can is circular,
Geometry: Semester 2 Practice Final Unofficial Worked Out Solutions by Earl Whitney 1. Wrapping a string around a trash can measures the circumference of the trash can. Assuming the trash can is circular,
Course: Geometry Level: Regular Date: 11/2016. Unit 1: Foundations for Geometry 13 Days 7 Days. Unit 2: Geometric Reasoning 15 Days 8 Days
 Geometry Curriculum Chambersburg Area School District Course Map Timeline 2016 Units *Note: unit numbers are for reference only and do not indicate the order in which concepts need to be taught Suggested
Geometry Curriculum Chambersburg Area School District Course Map Timeline 2016 Units *Note: unit numbers are for reference only and do not indicate the order in which concepts need to be taught Suggested
Math Vocabulary Grades K 12
 I < > a. m. Above Abscissa Absolute value Acute angle Acute angle Acute triangle Acute triangle Add Addends Addition Addition sentence Adjacent angles After Altitude Analog clock Angle Angle Apothem Arc
I < > a. m. Above Abscissa Absolute value Acute angle Acute angle Acute triangle Acute triangle Add Addends Addition Addition sentence Adjacent angles After Altitude Analog clock Angle Angle Apothem Arc
NEW YORK GEOMETRY TABLE OF CONTENTS
 NEW YORK GEOMETRY TABLE OF CONTENTS CHAPTER 1 POINTS, LINES, & PLANES {G.G.21, G.G.27} TOPIC A: Concepts Relating to Points, Lines, and Planes PART 1: Basic Concepts and Definitions...1 PART 2: Concepts
NEW YORK GEOMETRY TABLE OF CONTENTS CHAPTER 1 POINTS, LINES, & PLANES {G.G.21, G.G.27} TOPIC A: Concepts Relating to Points, Lines, and Planes PART 1: Basic Concepts and Definitions...1 PART 2: Concepts
Ohio s Learning Standards-Extended. Mathematics. Congruence Standards Complexity a Complexity b Complexity c
 Ohio s Learning Standards-Extended Mathematics Congruence Standards Complexity a Complexity b Complexity c Most Complex Least Complex Experiment with transformations in the plane G.CO.1 Know precise definitions
Ohio s Learning Standards-Extended Mathematics Congruence Standards Complexity a Complexity b Complexity c Most Complex Least Complex Experiment with transformations in the plane G.CO.1 Know precise definitions
Common Core Specifications for Geometry
 1 Common Core Specifications for Geometry Examples of how to read the red references: Congruence (G-Co) 2-03 indicates this spec is implemented in Unit 3, Lesson 2. IDT_C indicates that this spec is implemented
1 Common Core Specifications for Geometry Examples of how to read the red references: Congruence (G-Co) 2-03 indicates this spec is implemented in Unit 3, Lesson 2. IDT_C indicates that this spec is implemented
2015 Theta Geometry Topic Test Answer Key 13. A 12. D 23. C 24. D 15. A 26. B 17. B 8. A 29. B 10. C 11. D 14. B 16. A
 2015 Theta Geometry Topic Test Answer Key 1. A 2. D 3. C 4. D 5. A 6. B 7. B 8. A 9. B 10. C 11. D 12. D 13. A 14. B 15. A 16. A 17. B 18. E (9) 19. A 20. D 21. A 22. C 23. C 24. D 25. C 26. B 27. C 28.
2015 Theta Geometry Topic Test Answer Key 1. A 2. D 3. C 4. D 5. A 6. B 7. B 8. A 9. B 10. C 11. D 12. D 13. A 14. B 15. A 16. A 17. B 18. E (9) 19. A 20. D 21. A 22. C 23. C 24. D 25. C 26. B 27. C 28.
Chapter 1. acute angle (A), (G) An angle whose measure is greater than 0 and less than 90.
 hapter 1 acute angle (), (G) n angle whose measure is greater than 0 and less than 90. adjacent angles (), (G), (2T) Two coplanar angles that share a common vertex and a common side but have no common
hapter 1 acute angle (), (G) n angle whose measure is greater than 0 and less than 90. adjacent angles (), (G), (2T) Two coplanar angles that share a common vertex and a common side but have no common
The radius for a regular polygon is the same as the radius of the circumscribed circle.
 Perimeter and Area The perimeter and area of geometric shapes are basic properties that we need to know. The more complex a shape is, the more complex the process can be in finding its perimeter and area.
Perimeter and Area The perimeter and area of geometric shapes are basic properties that we need to know. The more complex a shape is, the more complex the process can be in finding its perimeter and area.
Geometry. Cluster: Experiment with transformations in the plane. G.CO.1 G.CO.2. Common Core Institute
 Geometry Cluster: Experiment with transformations in the plane. G.CO.1: Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and line segment, based on the undefined notions of
Geometry Cluster: Experiment with transformations in the plane. G.CO.1: Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and line segment, based on the undefined notions of
High School Geometry. Correlation of the ALEKS course High School Geometry to the ACT College Readiness Standards for Mathematics
 High School Geometry Correlation of the ALEKS course High School Geometry to the ACT College Readiness Standards for Mathematics Standard 5 : Graphical Representations = ALEKS course topic that addresses
High School Geometry Correlation of the ALEKS course High School Geometry to the ACT College Readiness Standards for Mathematics Standard 5 : Graphical Representations = ALEKS course topic that addresses
Common Core Cluster. Experiment with transformations in the plane. Unpacking What does this standard mean that a student will know and be able to do?
 Congruence G.CO Experiment with transformations in the plane. G.CO.1 Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and line segment, based on the undefined notions of point,
Congruence G.CO Experiment with transformations in the plane. G.CO.1 Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and line segment, based on the undefined notions of point,
Aim: How do we find the volume of a figure with a given base? Get Ready: The region R is bounded by the curves. y = x 2 + 1
 Get Ready: The region R is bounded by the curves y = x 2 + 1 y = x + 3. a. Find the area of region R. b. The region R is revolved around the horizontal line y = 1. Find the volume of the solid formed.
Get Ready: The region R is bounded by the curves y = x 2 + 1 y = x + 3. a. Find the area of region R. b. The region R is revolved around the horizontal line y = 1. Find the volume of the solid formed.
Grade IX. Mathematics Geometry Notes. #GrowWithGreen
 Grade IX Mathematics Geometry Notes #GrowWithGreen The distance of a point from the y - axis is called its x -coordinate, or abscissa, and the distance of the point from the x -axis is called its y-coordinate,
Grade IX Mathematics Geometry Notes #GrowWithGreen The distance of a point from the y - axis is called its x -coordinate, or abscissa, and the distance of the point from the x -axis is called its y-coordinate,
Standards to Topics. Common Core State Standards 2010 Geometry
 Standards to Topics G-CO.01 Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and line segment, based on the undefined notions of point, line, distance along a line, and distance
Standards to Topics G-CO.01 Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and line segment, based on the undefined notions of point, line, distance along a line, and distance
Geometry: Angle Relationships
 Geometry: Angle Relationships I. Define the following angles (in degrees) and draw an example of each. 1. Acute 3. Right 2. Obtuse 4. Straight Complementary angles: Supplementary angles: a + b = c + d
Geometry: Angle Relationships I. Define the following angles (in degrees) and draw an example of each. 1. Acute 3. Right 2. Obtuse 4. Straight Complementary angles: Supplementary angles: a + b = c + d
2 Formula (given): Volume of a Pyramid V = 1/3 BH What does B represent? Formula: Area of a Trapezoid. 3 Centroid. 4 Midsegment of a triangle
 1 Formula: Area of a Trapezoid 2 Formula (given): Volume of a Pyramid V = 1/3 BH What does B represent? 3 Centroid 4 Midsegment of a triangle 5 Slope formula 6 Point Slope Form of Linear Equation *can
1 Formula: Area of a Trapezoid 2 Formula (given): Volume of a Pyramid V = 1/3 BH What does B represent? 3 Centroid 4 Midsegment of a triangle 5 Slope formula 6 Point Slope Form of Linear Equation *can
CHAPTER 2 REVIEW COORDINATE GEOMETRY MATH Warm-Up: See Solved Homework questions. 2.2 Cartesian coordinate system
 CHAPTER 2 REVIEW COORDINATE GEOMETRY MATH6 2.1 Warm-Up: See Solved Homework questions 2.2 Cartesian coordinate system Coordinate axes: Two perpendicular lines that intersect at the origin O on each line.
CHAPTER 2 REVIEW COORDINATE GEOMETRY MATH6 2.1 Warm-Up: See Solved Homework questions 2.2 Cartesian coordinate system Coordinate axes: Two perpendicular lines that intersect at the origin O on each line.
Honors Geometry Pacing Guide Honors Geometry Pacing First Nine Weeks
 Unit Topic To recognize points, lines and planes. To be able to recognize and measure segments and angles. To classify angles and name the parts of a degree To recognize collinearity and betweenness of
Unit Topic To recognize points, lines and planes. To be able to recognize and measure segments and angles. To classify angles and name the parts of a degree To recognize collinearity and betweenness of
MATH DICTIONARY. Number Sense. Number Families. Operations. Counting (Natural) Numbers The numbers we say when we count. Example: {0, 1, 2, 3, 4 }
 Number Sense Number Families MATH DICTIONARY Counting (Natural) Numbers The numbers we say when we count Example: {1, 2, 3, 4 } Whole Numbers The counting numbers plus zero Example: {0, 1, 2, 3, 4 } Positive
Number Sense Number Families MATH DICTIONARY Counting (Natural) Numbers The numbers we say when we count Example: {1, 2, 3, 4 } Whole Numbers The counting numbers plus zero Example: {0, 1, 2, 3, 4 } Positive
MADISON ACADEMY GEOMETRY PACING GUIDE
 MADISON ACADEMY GEOMETRY PACING GUIDE 2018-2019 Standards (ACT included) ALCOS#1 Know the precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and line segment based on the undefined
MADISON ACADEMY GEOMETRY PACING GUIDE 2018-2019 Standards (ACT included) ALCOS#1 Know the precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and line segment based on the undefined
3 Identify shapes as two-dimensional (lying in a plane, flat ) or three-dimensional ( solid ).
 Geometry Kindergarten Identify and describe shapes (squares, circles, triangles, rectangles, hexagons, cubes, cones, cylinders, and spheres). 1 Describe objects in the environment using names of shapes,
Geometry Kindergarten Identify and describe shapes (squares, circles, triangles, rectangles, hexagons, cubes, cones, cylinders, and spheres). 1 Describe objects in the environment using names of shapes,
STANDARDS OF LEARNING CONTENT REVIEW NOTES HONORS GEOMETRY. 3 rd Nine Weeks,
 STANDARDS OF LEARNING CONTENT REVIEW NOTES HONORS GEOMETRY 3 rd Nine Weeks, 2016-2017 1 OVERVIEW Geometry Content Review Notes are designed by the High School Mathematics Steering Committee as a resource
STANDARDS OF LEARNING CONTENT REVIEW NOTES HONORS GEOMETRY 3 rd Nine Weeks, 2016-2017 1 OVERVIEW Geometry Content Review Notes are designed by the High School Mathematics Steering Committee as a resource
WAYNESBORO AREA SCHOOL DISTRICT CURRICULUM ACCELERATED GEOMETRY (June 2014)
 UNIT: Chapter 1 Essentials of Geometry UNIT : How do we describe and measure geometric figures? Identify Points, Lines, and Planes (1.1) How do you name geometric figures? Undefined Terms Point Line Plane
UNIT: Chapter 1 Essentials of Geometry UNIT : How do we describe and measure geometric figures? Identify Points, Lines, and Planes (1.1) How do you name geometric figures? Undefined Terms Point Line Plane
Triangles. Leg = s. Hypotenuse = s 2
 Honors Geometry Second Semester Final Review This review is designed to give the student a BASIC outline of what needs to be reviewed for the second semester final exam in Honors Geometry. It is up to
Honors Geometry Second Semester Final Review This review is designed to give the student a BASIC outline of what needs to be reviewed for the second semester final exam in Honors Geometry. It is up to
Geometry Common Core State Standard (CCSS) Math
 = ntroduced R=Reinforced/Reviewed HGH SCHOOL GEOMETRY MATH STANDARDS 1 2 3 4 Congruence Experiment with transformations in the plane G.CO.1 Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line,
= ntroduced R=Reinforced/Reviewed HGH SCHOOL GEOMETRY MATH STANDARDS 1 2 3 4 Congruence Experiment with transformations in the plane G.CO.1 Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line,
Geometry Practice. 1. Angles located next to one another sharing a common side are called angles.
 Geometry Practice Name 1. Angles located next to one another sharing a common side are called angles. 2. Planes that meet to form right angles are called planes. 3. Lines that cross are called lines. 4.
Geometry Practice Name 1. Angles located next to one another sharing a common side are called angles. 2. Planes that meet to form right angles are called planes. 3. Lines that cross are called lines. 4.
K-12 Geometry Standards
 Geometry K.G Identify and describe shapes (squares, circles, triangles, rectangles, hexagons, cubes, cones, cylinders, and spheres). 1. Describe objects in the environment using names of shapes, and describe
Geometry K.G Identify and describe shapes (squares, circles, triangles, rectangles, hexagons, cubes, cones, cylinders, and spheres). 1. Describe objects in the environment using names of shapes, and describe
Mathematics High School Geometry An understanding of the attributes and relationships of geometric objects can be applied in diverse contexts
 Mathematics High School Geometry An understanding of the attributes and relationships of geometric objects can be applied in diverse contexts interpreting a schematic drawing, estimating the amount of
Mathematics High School Geometry An understanding of the attributes and relationships of geometric objects can be applied in diverse contexts interpreting a schematic drawing, estimating the amount of
Lines Plane A flat surface that has no thickness and extends forever.
 Lines Plane A flat surface that has no thickness and extends forever. Point an exact location Line a straight path that has no thickness and extends forever in opposite directions Ray Part of a line that
Lines Plane A flat surface that has no thickness and extends forever. Point an exact location Line a straight path that has no thickness and extends forever in opposite directions Ray Part of a line that
(1) Find the area of an equilateral triangle if each side is 8. (2) Given the figure to the right with measures as marked, find: mab, m BAF, m.
 (1) ind the area of an equilateral triangle if each side is 8. (2) Given the figure to the right with measures as marked, find: m, m, m, m 100 9 90 (3) ind the length of the arc of a sector of in a circle
(1) ind the area of an equilateral triangle if each side is 8. (2) Given the figure to the right with measures as marked, find: m, m, m, m 100 9 90 (3) ind the length of the arc of a sector of in a circle
Grade VIII. Mathematics Geometry Notes. #GrowWithGreen
 Grade VIII Mathematics Geometry Notes #GrowWithGreen Polygons can be classified according to their number of sides (or vertices). The sum of all the interior angles of an n -sided polygon is given by,
Grade VIII Mathematics Geometry Notes #GrowWithGreen Polygons can be classified according to their number of sides (or vertices). The sum of all the interior angles of an n -sided polygon is given by,
Point A location in geometry. A point has no dimensions without any length, width, or depth. This is represented by a dot and is usually labelled.
 Test Date: November 3, 2016 Format: Scored out of 100 points. 8 Multiple Choice (40) / 8 Short Response (60) Topics: Points, Angles, Linear Objects, and Planes Recognizing the steps and procedures for
Test Date: November 3, 2016 Format: Scored out of 100 points. 8 Multiple Choice (40) / 8 Short Response (60) Topics: Points, Angles, Linear Objects, and Planes Recognizing the steps and procedures for
YEAR AT A GLANCE Student Learning Outcomes by Marking Period
 2014-2015 Term 1 Overarching/general themes: Tools to Build and Analyze Points, Lines and Angles Dates Textual References To Demonstrate Proficiency by the End of the Term Students Will : Marking Period
2014-2015 Term 1 Overarching/general themes: Tools to Build and Analyze Points, Lines and Angles Dates Textual References To Demonstrate Proficiency by the End of the Term Students Will : Marking Period
algebraic representation algorithm alternate interior angles altitude analytical geometry x x x analytical proof x x angle
 Words PS R Comm CR Geo R Proof Trans Coor Catogoriers Key AA triangle similarity Constructed Response AAA triangle similarity Problem Solving AAS triangle congruence Resoning abscissa Communication absolute
Words PS R Comm CR Geo R Proof Trans Coor Catogoriers Key AA triangle similarity Constructed Response AAA triangle similarity Problem Solving AAS triangle congruence Resoning abscissa Communication absolute
Geometry Geometry Grade Grade Grade
 Grade Grade Grade 6.G.1 Find the area of right triangles, special quadrilaterals, and polygons by composing into rectangles or decomposing into triangles and other shapes; apply these techniques in the
Grade Grade Grade 6.G.1 Find the area of right triangles, special quadrilaterals, and polygons by composing into rectangles or decomposing into triangles and other shapes; apply these techniques in the
Madison County Schools Suggested Geometry Pacing Guide,
 Madison County Schools Suggested Geometry Pacing Guide, 2016 2017 Domain Abbreviation Congruence G-CO Similarity, Right Triangles, and Trigonometry G-SRT Modeling with Geometry *G-MG Geometric Measurement
Madison County Schools Suggested Geometry Pacing Guide, 2016 2017 Domain Abbreviation Congruence G-CO Similarity, Right Triangles, and Trigonometry G-SRT Modeling with Geometry *G-MG Geometric Measurement
Grade 9 Math Terminology
 Unit 1 Basic Skills Review BEDMAS a way of remembering order of operations: Brackets, Exponents, Division, Multiplication, Addition, Subtraction Collect like terms gather all like terms and simplify as
Unit 1 Basic Skills Review BEDMAS a way of remembering order of operations: Brackets, Exponents, Division, Multiplication, Addition, Subtraction Collect like terms gather all like terms and simplify as
Example: The following is an example of a polyhedron. Fill the blanks with the appropriate answer. Vertices:
 11.1: Space Figures and Cross Sections Polyhedron: solid that is bounded by polygons Faces: polygons that enclose a polyhedron Edge: line segment that faces meet and form Vertex: point or corner where
11.1: Space Figures and Cross Sections Polyhedron: solid that is bounded by polygons Faces: polygons that enclose a polyhedron Edge: line segment that faces meet and form Vertex: point or corner where
Introduction to Geometry
 Introduction to Geometry This course covers the topics outlined below. You can customize the scope and sequence of this course to meet your curricular needs. Curriculum (211 topics + 6 additional topics)
Introduction to Geometry This course covers the topics outlined below. You can customize the scope and sequence of this course to meet your curricular needs. Curriculum (211 topics + 6 additional topics)
High School Geometry
 High School Geometry This course covers the topics shown below. Students navigate learning paths based on their level of readiness. Institutional users may customize the scope and sequence to meet curricular
High School Geometry This course covers the topics shown below. Students navigate learning paths based on their level of readiness. Institutional users may customize the scope and sequence to meet curricular
Course: Geometry Year: Teacher(s): various
 Course: Geometry Year: 2015-2016 Teacher(s): various Unit 1: Coordinates and Transformations Standards Essential Questions Enduring Understandings G-CO.1. Know 1) How is coordinate Geometric precise definitions
Course: Geometry Year: 2015-2016 Teacher(s): various Unit 1: Coordinates and Transformations Standards Essential Questions Enduring Understandings G-CO.1. Know 1) How is coordinate Geometric precise definitions
a B. 3a D. 0 E. NOTA m RVS a. DB is parallel to EC and AB=3, DB=5, and
 Geometry Individual Test NO LULTOR!!! Middleton Invitational February 18, 006 The abbreviation "NOT" denotes "None of These nswers." iagrams are not necessarily drawn to scale. 1. Which set does not always
Geometry Individual Test NO LULTOR!!! Middleton Invitational February 18, 006 The abbreviation "NOT" denotes "None of These nswers." iagrams are not necessarily drawn to scale. 1. Which set does not always
Mathematics High School Geometry
 Mathematics High School Geometry An understanding of the attributes and relationships of geometric objects can be applied in diverse contexts interpreting a schematic drawing, estimating the amount of
Mathematics High School Geometry An understanding of the attributes and relationships of geometric objects can be applied in diverse contexts interpreting a schematic drawing, estimating the amount of
, y 2. ), then PQ = - y 1 ) 2. x 1 + x 2
 Tools of Geometry Chapter 1 Undefined Terms (p. 5) A point is a location. It has neither shape nor size. A line is made up of points and has no thickness or width. A plane is a flat surface made up of
Tools of Geometry Chapter 1 Undefined Terms (p. 5) A point is a location. It has neither shape nor size. A line is made up of points and has no thickness or width. A plane is a flat surface made up of
The triangle
 The Unit Circle The unit circle is without a doubt the most critical topic a student must understand in trigonometry. The unit circle is the foundation on which trigonometry is based. If someone were to
The Unit Circle The unit circle is without a doubt the most critical topic a student must understand in trigonometry. The unit circle is the foundation on which trigonometry is based. If someone were to
STANDARDS OF LEARNING CONTENT REVIEW NOTES GEOMETRY. 3 rd Nine Weeks,
 STANDARDS OF LEARNING CONTENT REVIEW NOTES GEOMETRY 3 rd Nine Weeks, 2016-2017 1 OVERVIEW Geometry Content Review Notes are designed by the High School Mathematics Steering Committee as a resource for
STANDARDS OF LEARNING CONTENT REVIEW NOTES GEOMETRY 3 rd Nine Weeks, 2016-2017 1 OVERVIEW Geometry Content Review Notes are designed by the High School Mathematics Steering Committee as a resource for
12 m. 30 m. The Volume of a sphere is 36 cubic units. Find the length of the radius.
 NAME DATE PER. REVIEW #18: SPHERES, COMPOSITE FIGURES, & CHANGING DIMENSIONS PART 1: SURFACE AREA & VOLUME OF SPHERES Find the measure(s) indicated. Answers to even numbered problems should be rounded
NAME DATE PER. REVIEW #18: SPHERES, COMPOSITE FIGURES, & CHANGING DIMENSIONS PART 1: SURFACE AREA & VOLUME OF SPHERES Find the measure(s) indicated. Answers to even numbered problems should be rounded
2. A circle is inscribed in a square of diagonal length 12 inches. What is the area of the circle?
 March 24, 2011 1. When a square is cut into two congruent rectangles, each has a perimeter of P feet. When the square is cut into three congruent rectangles, each has a perimeter of P 6 feet. Determine
March 24, 2011 1. When a square is cut into two congruent rectangles, each has a perimeter of P feet. When the square is cut into three congruent rectangles, each has a perimeter of P 6 feet. Determine
Answer Key: Three-Dimensional Cross Sections
 Geometry A Unit Answer Key: Three-Dimensional Cross Sections Name Date Objectives In this lesson, you will: visualize three-dimensional objects from different perspectives be able to create a projection
Geometry A Unit Answer Key: Three-Dimensional Cross Sections Name Date Objectives In this lesson, you will: visualize three-dimensional objects from different perspectives be able to create a projection
Curriki Geometry Glossary
 Curriki Geometry Glossary The following terms are used throughout the Curriki Geometry projects and represent the core vocabulary and concepts that students should know to meet Common Core State Standards.
Curriki Geometry Glossary The following terms are used throughout the Curriki Geometry projects and represent the core vocabulary and concepts that students should know to meet Common Core State Standards.
Course Number: Course Title: Geometry
 Course Number: 1206310 Course Title: Geometry RELATED GLOSSARY TERM DEFINITIONS (89) Altitude The perpendicular distance from the top of a geometric figure to its opposite side. Angle Two rays or two line
Course Number: 1206310 Course Title: Geometry RELATED GLOSSARY TERM DEFINITIONS (89) Altitude The perpendicular distance from the top of a geometric figure to its opposite side. Angle Two rays or two line
Properties of a Circle Diagram Source:
 Properties of a Circle Diagram Source: http://www.ricksmath.com/circles.html Definitions: Circumference (c): The perimeter of a circle is called its circumference Diameter (d): Any straight line drawn
Properties of a Circle Diagram Source: http://www.ricksmath.com/circles.html Definitions: Circumference (c): The perimeter of a circle is called its circumference Diameter (d): Any straight line drawn
Birkdale High School - Higher Scheme of Work
 Birkdale High School - Higher Scheme of Work Module 1 - Integers and Decimals Understand and order integers (assumed) Use brackets and hierarchy of operations (BODMAS) Add, subtract, multiply and divide
Birkdale High School - Higher Scheme of Work Module 1 - Integers and Decimals Understand and order integers (assumed) Use brackets and hierarchy of operations (BODMAS) Add, subtract, multiply and divide
Geometry Rules. Triangles:
 Triangles: Geometry Rules 1. Types of Triangles: By Sides: Scalene - no congruent sides Isosceles - 2 congruent sides Equilateral - 3 congruent sides By Angles: Acute - all acute angles Right - one right
Triangles: Geometry Rules 1. Types of Triangles: By Sides: Scalene - no congruent sides Isosceles - 2 congruent sides Equilateral - 3 congruent sides By Angles: Acute - all acute angles Right - one right
Carnegie Learning High School Math Series: Geometry Indiana Standards Worktext Correlations
 Carnegie Learning High School Math Series: Logic and Proofs G.LP.1 Understand and describe the structure of and relationships within an axiomatic system (undefined terms, definitions, axioms and postulates,
Carnegie Learning High School Math Series: Logic and Proofs G.LP.1 Understand and describe the structure of and relationships within an axiomatic system (undefined terms, definitions, axioms and postulates,
DEFINITIONS. Perpendicular Two lines are called perpendicular if they form a right angle.
 DEFINITIONS Degree A degree is the 1 th part of a straight angle. 180 Right Angle A 90 angle is called a right angle. Perpendicular Two lines are called perpendicular if they form a right angle. Congruent
DEFINITIONS Degree A degree is the 1 th part of a straight angle. 180 Right Angle A 90 angle is called a right angle. Perpendicular Two lines are called perpendicular if they form a right angle. Congruent
Correlation of Discovering Geometry 5th Edition to Florida State Standards
 Correlation of 5th Edition to Florida State s MAFS content is listed under three headings: Introduced (I), Developed (D), and Applied (A). Developed standards are the focus of the lesson, and are being
Correlation of 5th Edition to Florida State s MAFS content is listed under three headings: Introduced (I), Developed (D), and Applied (A). Developed standards are the focus of the lesson, and are being
Name Date Period. Worksheet 6.3 Volumes Show all work. No calculator unless stated. Multiple Choice
 Name Date Period Worksheet 6. Volumes Show all work. No calculator unless stated. Multiple Choice. (Calculator Permitted) The base of a solid S is the region enclosed by the graph of y ln x, the line x
Name Date Period Worksheet 6. Volumes Show all work. No calculator unless stated. Multiple Choice. (Calculator Permitted) The base of a solid S is the region enclosed by the graph of y ln x, the line x
Geometry 10 and 11 Notes
 Geometry 10 and 11 Notes Area and Volume Name Per Date 10.1 Area is the amount of space inside of a two dimensional object. When working with irregular shapes, we can find its area by breaking it up into
Geometry 10 and 11 Notes Area and Volume Name Per Date 10.1 Area is the amount of space inside of a two dimensional object. When working with irregular shapes, we can find its area by breaking it up into
FORMULAS to UNDERSTAND & MEMORIZE
 1 of 6 FORMULAS to UNDERSTAND & MEMORIZE Now we come to the part where you need to just bear down and memorize. To make the process a bit simpler, I am providing all of the key info that they re going
1 of 6 FORMULAS to UNDERSTAND & MEMORIZE Now we come to the part where you need to just bear down and memorize. To make the process a bit simpler, I am providing all of the key info that they re going
Geometry. Geometry. Domain Cluster Standard. Congruence (G CO)
 Domain Cluster Standard 1. Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and line segment, based on the undefined notions of point, line, distance along a line, and distance
Domain Cluster Standard 1. Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and line segment, based on the undefined notions of point, line, distance along a line, and distance
West Windsor-Plainsboro Regional School District Basic Geometry Grades 9-12
 West Windsor-Plainsboro Regional School District Basic Geometry Grades 9-12 Unit 1: Basics of Geometry Content Area: Mathematics Course & Grade Level: Basic Geometry, 9 12 Summary and Rationale This unit
West Windsor-Plainsboro Regional School District Basic Geometry Grades 9-12 Unit 1: Basics of Geometry Content Area: Mathematics Course & Grade Level: Basic Geometry, 9 12 Summary and Rationale This unit
Killingly Public Schools. Grades Draft Sept. 2002
 Killingly Public Schools Grades 10-12 Draft Sept. 2002 ESSENTIALS OF GEOMETRY Grades 10-12 Language of Plane Geometry CONTENT STANDARD 10-12 EG 1: The student will use the properties of points, lines,
Killingly Public Schools Grades 10-12 Draft Sept. 2002 ESSENTIALS OF GEOMETRY Grades 10-12 Language of Plane Geometry CONTENT STANDARD 10-12 EG 1: The student will use the properties of points, lines,
Make geometric constructions. (Formalize and explain processes)
 Standard 5: Geometry Pre-Algebra Plus Algebra Geometry Algebra II Fourth Course Benchmark 1 - Benchmark 1 - Benchmark 1 - Part 3 Draw construct, and describe geometrical figures and describe the relationships
Standard 5: Geometry Pre-Algebra Plus Algebra Geometry Algebra II Fourth Course Benchmark 1 - Benchmark 1 - Benchmark 1 - Part 3 Draw construct, and describe geometrical figures and describe the relationships
Pearson Mathematics Geometry Common Core 2015
 A Correlation of Pearson Mathematics Geometry Common Core 2015 to the Common Core State Standards for Bid Category 13-040-10 A Correlation of Pearson, Common Core Pearson Geometry Congruence G-CO Experiment
A Correlation of Pearson Mathematics Geometry Common Core 2015 to the Common Core State Standards for Bid Category 13-040-10 A Correlation of Pearson, Common Core Pearson Geometry Congruence G-CO Experiment
SHAPE AND STRUCTURE. Shape and Structure. An explanation of Mathematical terminology
 Shape and Structure An explanation of Mathematical terminology 2005 1 POINT A dot Dots join to make lines LINE A line is 1 dimensional (length) A line is a series of points touching each other and extending
Shape and Structure An explanation of Mathematical terminology 2005 1 POINT A dot Dots join to make lines LINE A line is 1 dimensional (length) A line is a series of points touching each other and extending
Achievement Level Descriptors Geometry
 Achievement Level Descriptors Geometry ALD Stard Level 2 Level 3 Level 4 Level 5 Policy MAFS Students at this level demonstrate a below satisfactory level of success with the challenging Students at this
Achievement Level Descriptors Geometry ALD Stard Level 2 Level 3 Level 4 Level 5 Policy MAFS Students at this level demonstrate a below satisfactory level of success with the challenging Students at this
11.3 Surface Area of Pyramids and Cones
 11.3 Surface Area of Pyramids and Cones Learning Objectives Find the surface area of a pyramid. Find the surface area of a cone. Review Queue 1. A rectangular prism has sides of 5 cm, 6 cm, and 7 cm. What
11.3 Surface Area of Pyramids and Cones Learning Objectives Find the surface area of a pyramid. Find the surface area of a cone. Review Queue 1. A rectangular prism has sides of 5 cm, 6 cm, and 7 cm. What
Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Geometry 2015 correlated to the New York Common Core Learning Standards for Mathematics Geometry
 Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Geometry 2015 correlated to the New York Common Core Learning Standards for Mathematics Geometry Standards for Mathematical Practice SMP.1 Make sense of problems and persevere
Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Geometry 2015 correlated to the New York Common Core Learning Standards for Mathematics Geometry Standards for Mathematical Practice SMP.1 Make sense of problems and persevere
Geometry. Oklahoma Math Day INSTRUCTIONS:
 Oklahoma Math Day November 16, 016 Geometry INSTRUCTIONS: 1. Do not begin the test until told to do so.. Calculators are not permitted. 3. Be sure to enter your name and high school code on the answer
Oklahoma Math Day November 16, 016 Geometry INSTRUCTIONS: 1. Do not begin the test until told to do so.. Calculators are not permitted. 3. Be sure to enter your name and high school code on the answer
Select the best answer. Bubble the corresponding choice on your scantron. Team 13. Geometry
 Team Geometry . What is the sum of the interior angles of an equilateral triangle? a. 60 b. 90 c. 80 d. 60. The sine of angle A is. What is the cosine of angle A? 6 4 6 a. b. c.. A parallelogram has all
Team Geometry . What is the sum of the interior angles of an equilateral triangle? a. 60 b. 90 c. 80 d. 60. The sine of angle A is. What is the cosine of angle A? 6 4 6 a. b. c.. A parallelogram has all
Modified and Animated By Chris Headlee Apr SSM: Super Second-grader Methods
 Modified and Animated By Chris Headlee Apr 2014 Super Second-grader Methods Ch 2 match up like variables If then is symbolically, and two angles are congruent is q, and angles are vertical angles is p
Modified and Animated By Chris Headlee Apr 2014 Super Second-grader Methods Ch 2 match up like variables If then is symbolically, and two angles are congruent is q, and angles are vertical angles is p
2 nd Semester Final Exam Review
 2 nd Semester Final xam Review I. Vocabulary hapter 7 cross products proportion scale factor dilation ratio similar extremes scale similar polygons indirect measurements scale drawing similarity ratio
2 nd Semester Final xam Review I. Vocabulary hapter 7 cross products proportion scale factor dilation ratio similar extremes scale similar polygons indirect measurements scale drawing similarity ratio
