The Normal Distribution
|
|
|
- Annabella Shepherd
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The Normal Distribution Lecture 20 Section Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Sep 28, 2011 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) The Normal Distribution Wed, Sep 28, / 41
2 Outline 1 Density Functions Uniform Distributions 2 The Normal Distribution Examples 3 The Rule 4 The Standard Normal Distribution Standard Normal Areas TI-83 Standard Normal Areas 5 Areas under Other Normal Curves 6 IQ Scores 7 Assignment 8 Answers to Even-numbered Exercises Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) The Normal Distribution Wed, Sep 28, / 41
3 Outline 1 Density Functions Uniform Distributions 2 The Normal Distribution Examples 3 The Rule 4 The Standard Normal Distribution Standard Normal Areas TI-83 Standard Normal Areas 5 Areas under Other Normal Curves 6 IQ Scores 7 Assignment 8 Answers to Even-numbered Exercises Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) The Normal Distribution Wed, Sep 28, / 41
4 Density Functions Definition (Density Function) A density function is a function whose graph shows the distribution of a population A density function is scaled so that its total area is 1. Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) The Normal Distribution Wed, Sep 28, / 41
5 Density Functions Definition (Density Function) A density function is a function whose graph shows the distribution of a population Area = A density function is scaled so that its total area is 1. Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) The Normal Distribution Wed, Sep 28, / 41
6 Density Functions AREA = PROPORTION = PROBABILITY This is the fundamental property that connects the graph of a continuous model to the population that it represents, namely: The area under the graph between two points on the x-axis represents the proportion of the population that lies between those two points. Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) The Normal Distribution Wed, Sep 28, / 41
7 Density Functions Density Consider an arbitrary continuous distribution. Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) The Normal Distribution Wed, Sep 28, / 41
8 Density Functions Density The area under the curve between 2 and 5 is the proportion of the values of x that lie between 2 and 5. Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) The Normal Distribution Wed, Sep 28, / 41
9 Density Functions Density The area under the curve between 2 and 5 is the proportion of the values of x that lie between 2 and 5. Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) The Normal Distribution Wed, Sep 28, / 41
10 Density Functions Density The area under the curve between 2 and 5 is the proportion of the values of x that lie between 2 and 5. Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) The Normal Distribution Wed, Sep 28, / 41
11 Density Functions Density Area = Proportion The area under the curve between 2 and 5 is the proportion of the values of x that lie between 2 and 5. Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) The Normal Distribution Wed, Sep 28, / 41
12 Outline 1 Density Functions Uniform Distributions 2 The Normal Distribution Examples 3 The Rule 4 The Standard Normal Distribution Standard Normal Areas TI-83 Standard Normal Areas 5 Areas under Other Normal Curves 6 IQ Scores 7 Assignment 8 Answers to Even-numbered Exercises Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) The Normal Distribution Wed, Sep 28, / 41
13 Uniform Distributions The simplest of all density functions is the uniform density function. The graph is horizontal. We will learn more about uniform distributions later Area = Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) The Normal Distribution Wed, Sep 28, / 41
14 Outline 1 Density Functions Uniform Distributions 2 The Normal Distribution Examples 3 The Rule 4 The Standard Normal Distribution Standard Normal Areas TI-83 Standard Normal Areas 5 Areas under Other Normal Curves 6 IQ Scores 7 Assignment 8 Answers to Even-numbered Exercises Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) The Normal Distribution Wed, Sep 28, / 41
15 The Normal Distribution Definition (Normal distribution) The normal distribution is the statistician s name for the bell curve. It is a density function in the shape of a bell. Symmetric. Unimodal. Extends over the entire real line (no endpoints). Main part lies within ±3σ of the mean. Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) The Normal Distribution Wed, Sep 28, / 41
16 The Normal Distribution The curve has a bell shape, with infinitely long tails in both directions. Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) The Normal Distribution Wed, Sep 28, / 41
17 The Normal Distribution The mean µ is located in the center, at the peak. µ Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) The Normal Distribution Wed, Sep 28, / 41
18 The Normal Distribution The width of the main part of the curve is 6 standard deviations wide (3 standard deviations each way from the mean). σ µ 3σ µ µ + 3σ Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) The Normal Distribution Wed, Sep 28, / 41
19 The Normal Distribution The area under the entire curve is 1. (The area outside of µ ± 3σ is approx ) Area = 1 µ 3σ µ µ + 3σ Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) The Normal Distribution Wed, Sep 28, / 41
20 The Normal Distribution The normal distribution with mean µ and standard deviation σ is denoted N(µ, σ). For example, if X is a variable whose distribution is normal with mean 30 and standard deviation 5, then we say that X is N(30, 5). Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) The Normal Distribution Wed, Sep 28, / 41
21 Outline 1 Density Functions Uniform Distributions 2 The Normal Distribution Examples 3 The Rule 4 The Standard Normal Distribution Standard Normal Areas TI-83 Standard Normal Areas 5 Areas under Other Normal Curves 6 IQ Scores 7 Assignment 8 Answers to Even-numbered Exercises Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) The Normal Distribution Wed, Sep 28, / 41
22 The Normal Distribution If X is N(30, 5), then the distribution of X looks like this: Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) The Normal Distribution Wed, Sep 28, / 41
23 Some Normal Distributions Some other examples: N(3, 1) Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) The Normal Distribution Wed, Sep 28, / 41
24 Some Normal Distributions Some other examples: N(5, 1) Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) The Normal Distribution Wed, Sep 28, / 41
25 Some Normal Distributions Some other examples: N ( 2, 1 2) Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) The Normal Distribution Wed, Sep 28, / 41
26 Some Normal Distributions Some other examples: N ( 3 1 2, 1 1 2) Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) The Normal Distribution Wed, Sep 28, / 41
27 Outline 1 Density Functions Uniform Distributions 2 The Normal Distribution Examples 3 The Rule 4 The Standard Normal Distribution Standard Normal Areas TI-83 Standard Normal Areas 5 Areas under Other Normal Curves 6 IQ Scores 7 Assignment 8 Answers to Even-numbered Exercises Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) The Normal Distribution Wed, Sep 28, / 41
28 The Rule The Rule For any normal distribution, Approximately 68% of the values lie within one standard deviation of the mean. Approximately 95% of the values lie within two standard deviations of the mean. Approximately 99.7% of the values lie within three standard deviations of the mean. Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) The Normal Distribution Wed, Sep 28, / 41
29 The Empirical Rule The Empirical Rule For any mound-shaped distribution, Approximately 68% lie within one standard deviation of the mean. Approximately 95% lie within two standard deviations of the mean. Nearly all lie within three standard deviations of the mean. The well-known Empirical Rule is somewhat more general than the Rule. Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) The Normal Distribution Wed, Sep 28, / 41
30 Outline 1 Density Functions Uniform Distributions 2 The Normal Distribution Examples 3 The Rule 4 The Standard Normal Distribution Standard Normal Areas TI-83 Standard Normal Areas 5 Areas under Other Normal Curves 6 IQ Scores 7 Assignment 8 Answers to Even-numbered Exercises Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) The Normal Distribution Wed, Sep 28, / 41
31 The Standard Normal Distribution Definition (Standard normal distribution) The standard normal distribution is the normal distribution with mean 0 and standard deviation 1. It is denoted by the letter Z. That is, Z is N(0, 1). Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) The Normal Distribution Wed, Sep 28, / 41
32 The Standard Normal Distribution Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) The Normal Distribution Wed, Sep 28, / 41
33 Outline 1 Density Functions Uniform Distributions 2 The Normal Distribution Examples 3 The Rule 4 The Standard Normal Distribution Standard Normal Areas TI-83 Standard Normal Areas 5 Areas under Other Normal Curves 6 IQ Scores 7 Assignment 8 Answers to Even-numbered Exercises Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) The Normal Distribution Wed, Sep 28, / 41
34 Areas Under the Standard Normal Curve Easy questions: What is the total area under the curve? What proportion of values of Z will fall below 0? What proportion of values of Z will fall above 0? Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) The Normal Distribution Wed, Sep 28, / 41
35 Areas Under the Standard Normal Curve What proportion of values will fall below +1? Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) The Normal Distribution Wed, Sep 28, / 41
36 Areas Under the Standard Normal Curve It turns out that the area to the left of +1 is Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) The Normal Distribution Wed, Sep 28, / 41
37 Areas Under the Standard Normal Curve What is the area to the right of +1? Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) The Normal Distribution Wed, Sep 28, / 41
38 Areas Under the Standard Normal Curve What is the area between 1 and 1? Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) The Normal Distribution Wed, Sep 28, / 41
39 Areas Under the Standard Normal Curve What is the area between 0 and 1? Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) The Normal Distribution Wed, Sep 28, / 41
40 Areas Under the Standard Normal Curve There are two methods to finding standard normal areas: The TI-83 function normalcdf. Standard normal table. We will use the TI-83 (unless you want to use the table). Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) The Normal Distribution Wed, Sep 28, / 41
41 Outline 1 Density Functions Uniform Distributions 2 The Normal Distribution Examples 3 The Rule 4 The Standard Normal Distribution Standard Normal Areas TI-83 Standard Normal Areas 5 Areas under Other Normal Curves 6 IQ Scores 7 Assignment 8 Answers to Even-numbered Exercises Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) The Normal Distribution Wed, Sep 28, / 41
42 TI-83 - Standard Normal Areas TI-83 Standard Normal Areas Press 2nd DISTR. Select normalcdf (Item #2). Enter the lower and upper bounds of the interval. If the interval is infinite to the left, enter E99 as the lower bound. If the interval is infinite to the right, enter E99 as the upper bound. Press ENTER. The area appears in the display. Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) The Normal Distribution Wed, Sep 28, / 41
43 Standard Normal Areas Practice Use the TI-83 to find the following. The area between 1 and 1. The area to the right of 1. The area to the left of What standard normal percentile is 1.645? Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) The Normal Distribution Wed, Sep 28, / 41
44 Outline 1 Density Functions Uniform Distributions 2 The Normal Distribution Examples 3 The Rule 4 The Standard Normal Distribution Standard Normal Areas TI-83 Standard Normal Areas 5 Areas under Other Normal Curves 6 IQ Scores 7 Assignment 8 Answers to Even-numbered Exercises Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) The Normal Distribution Wed, Sep 28, / 41
45 Other Normal Curves If we are working with a different normal distribution, say N(30, 5), then how can we find areas under the curve? Use the same procedure as before, except enter the mean and standard deviation as the 3rd and 4th parameters of the normalcdf function. Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) The Normal Distribution Wed, Sep 28, / 41
46 TI-83 - Area Under Normal Curves Example (TI-83 Normal Areas) Find area between 25 and 38 in the distribution N(30, 5). In the TI-83, enter normalcdf(25,38,30,5). Press ENTER. The answer appears. Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) The Normal Distribution Wed, Sep 28, / 41
47 Outline 1 Density Functions Uniform Distributions 2 The Normal Distribution Examples 3 The Rule 4 The Standard Normal Distribution Standard Normal Areas TI-83 Standard Normal Areas 5 Areas under Other Normal Curves 6 IQ Scores 7 Assignment 8 Answers to Even-numbered Exercises Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) The Normal Distribution Wed, Sep 28, / 41
48 IQ Scores Read the article Understanding and Interpreting IQ. IQ scores are normalized to have a mean of 100 and a standard deviation of 15. Psychologists often assume a normal distribution of IQ scores as well. Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) The Normal Distribution Wed, Sep 28, / 41
49 IQ Scores Practice What percentage of the population has an IQ above 120? above 140? What percentage of the population has an IQ between 75 and 125? Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) The Normal Distribution Wed, Sep 28, / 41
50 Outline 1 Density Functions Uniform Distributions 2 The Normal Distribution Examples 3 The Rule 4 The Standard Normal Distribution Standard Normal Areas TI-83 Standard Normal Areas 5 Areas under Other Normal Curves 6 IQ Scores 7 Assignment 8 Answers to Even-numbered Exercises Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) The Normal Distribution Wed, Sep 28, / 41
51 Assignment Homework Read Section , pages Let s Do It! 6.1, 6.2, 6.3, 6.4, 6.5, 6.6. Exercises 1-9, 11, 12, 15, 16, 18,, 32, page 376. Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) The Normal Distribution Wed, Sep 28, / 41
52 Outline 1 Density Functions Uniform Distributions 2 The Normal Distribution Examples 3 The Rule 4 The Standard Normal Distribution Standard Normal Areas TI-83 Standard Normal Areas 5 Areas under Other Normal Curves 6 IQ Scores 7 Assignment 8 Answers to Even-numbered Exercises Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) The Normal Distribution Wed, Sep 28, / 41
53 Answers to Even-numbered Exercises Page 376, Exercises 4, 6, 8, 12, 16, A score at the mean. 6.6 µ = 5 and σ = 1. The Rule says that about 95% lie between µ 2σ and µ + 2σ, which is the interval from 1 to (a) Stats: 0.41; Logic: 0.70; Verbal: (b) Stats. (c) 65.82%. (d) 24.15%. (e) 2.83%. Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) The Normal Distribution Wed, Sep 28, / 41
54 Answers to Even-numbered Exercises Page 376, Exercises 4, 6, 8, 12, 16, (a) (b) Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) The Normal Distribution Wed, Sep 28, / 41
55 Answers to Even-numbered Exercises Page 376, Exercises 4, 6, 8, 12, 16, The means are the same, but the standard deviation for men is larger than the standard deviation for women Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) The Normal Distribution Wed, Sep 28, / 41
56 Answers to Even-numbered Exercises Page 376, Exercises 4, 6, 8, 12, 16, (a) (b) minutes. (c) minutes. Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) The Normal Distribution Wed, Sep 28, / 41
Density Curves Sections
 Density Curves Sections 3.1-3.2 Lecture 8 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Jan 27, 2016 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Density CurvesSections 3.1-3.2 Wed, Jan 27, 2016 1 / 18 Outline
Density Curves Sections 3.1-3.2 Lecture 8 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Jan 27, 2016 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Density CurvesSections 3.1-3.2 Wed, Jan 27, 2016 1 / 18 Outline
Sampling Distribution Examples Sections 15.4, 15.5
 Sampling Distribution Examples Sections 15.4, 15.5 Lecture 27 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Mar 2, 2016 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College)Sampling Distribution ExamplesSections 15.4,
Sampling Distribution Examples Sections 15.4, 15.5 Lecture 27 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Mar 2, 2016 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College)Sampling Distribution ExamplesSections 15.4,
Lecture 21 Section Fri, Oct 3, 2008
 Lecture 21 Section 6.3.1 Hampden-Sydney College Fri, Oct 3, 2008 Outline 1 2 3 4 5 6 Exercise 6.15, page 378. A young woman needs a 15-ampere fuse for the electrical system in her apartment and has decided
Lecture 21 Section 6.3.1 Hampden-Sydney College Fri, Oct 3, 2008 Outline 1 2 3 4 5 6 Exercise 6.15, page 378. A young woman needs a 15-ampere fuse for the electrical system in her apartment and has decided
Displaying Distributions - Quantitative Variables
 Displaying Distributions - Quantitative Variables Lecture 13 Sections 4.4.1-4.4.3 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Feb 8, 2012 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College)Displaying Distributions
Displaying Distributions - Quantitative Variables Lecture 13 Sections 4.4.1-4.4.3 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Feb 8, 2012 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College)Displaying Distributions
Boxplots. Lecture 17 Section Robb T. Koether. Hampden-Sydney College. Wed, Feb 10, 2010
 Boxplots Lecture 17 Section 5.3.3 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Feb 10, 2010 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Boxplots Wed, Feb 10, 2010 1 / 34 Outline 1 Boxplots TI-83 Boxplots 2
Boxplots Lecture 17 Section 5.3.3 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Feb 10, 2010 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Boxplots Wed, Feb 10, 2010 1 / 34 Outline 1 Boxplots TI-83 Boxplots 2
Chapter 6. THE NORMAL DISTRIBUTION
 Chapter 6. THE NORMAL DISTRIBUTION Introducing Normally Distributed Variables The distributions of some variables like thickness of the eggshell, serum cholesterol concentration in blood, white blood cells
Chapter 6. THE NORMAL DISTRIBUTION Introducing Normally Distributed Variables The distributions of some variables like thickness of the eggshell, serum cholesterol concentration in blood, white blood cells
Learning Objectives. Continuous Random Variables & The Normal Probability Distribution. Continuous Random Variable
 Learning Objectives Continuous Random Variables & The Normal Probability Distribution 1. Understand characteristics about continuous random variables and probability distributions 2. Understand the uniform
Learning Objectives Continuous Random Variables & The Normal Probability Distribution 1. Understand characteristics about continuous random variables and probability distributions 2. Understand the uniform
The Critical-Path Algorithm
 The Critical-Path Algorithm Lecture 32 Sections 8.3-8.4 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Nov 19, 2014 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) The Critical-Path Algorithm Wed, Nov 19, 2014 1
The Critical-Path Algorithm Lecture 32 Sections 8.3-8.4 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Nov 19, 2014 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) The Critical-Path Algorithm Wed, Nov 19, 2014 1
Data Analysis & Probability
 Unit 5 Probability Distributions Name: Date: Hour: Section 7.2: The Standard Normal Distribution (Area under the curve) Notes By the end of this lesson, you will be able to Find the area under the standard
Unit 5 Probability Distributions Name: Date: Hour: Section 7.2: The Standard Normal Distribution (Area under the curve) Notes By the end of this lesson, you will be able to Find the area under the standard
Chapter 6. THE NORMAL DISTRIBUTION
 Chapter 6. THE NORMAL DISTRIBUTION Introducing Normally Distributed Variables The distributions of some variables like thickness of the eggshell, serum cholesterol concentration in blood, white blood cells
Chapter 6. THE NORMAL DISTRIBUTION Introducing Normally Distributed Variables The distributions of some variables like thickness of the eggshell, serum cholesterol concentration in blood, white blood cells
Minimal Spanning Trees
 Minimal Spanning Trees Lecture 33 Sections 7.1-7.3 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Apr 11, 20 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Minimal Spanning Trees Wed, Apr 11, 20 1 / 17 1 Networks
Minimal Spanning Trees Lecture 33 Sections 7.1-7.3 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Apr 11, 20 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Minimal Spanning Trees Wed, Apr 11, 20 1 / 17 1 Networks
MAT 102 Introduction to Statistics Chapter 6. Chapter 6 Continuous Probability Distributions and the Normal Distribution
 MAT 102 Introduction to Statistics Chapter 6 Chapter 6 Continuous Probability Distributions and the Normal Distribution 6.2 Continuous Probability Distributions Characteristics of a Continuous Probability
MAT 102 Introduction to Statistics Chapter 6 Chapter 6 Continuous Probability Distributions and the Normal Distribution 6.2 Continuous Probability Distributions Characteristics of a Continuous Probability
STA Module 4 The Normal Distribution
 STA 2023 Module 4 The Normal Distribution Learning Objectives Upon completing this module, you should be able to 1. Explain what it means for a variable to be normally distributed or approximately normally
STA 2023 Module 4 The Normal Distribution Learning Objectives Upon completing this module, you should be able to 1. Explain what it means for a variable to be normally distributed or approximately normally
STA /25/12. Module 4 The Normal Distribution. Learning Objectives. Let s Look at Some Examples of Normal Curves
 STA 2023 Module 4 The Normal Distribution Learning Objectives Upon completing this module, you should be able to 1. Explain what it means for a variable to be normally distributed or approximately normally
STA 2023 Module 4 The Normal Distribution Learning Objectives Upon completing this module, you should be able to 1. Explain what it means for a variable to be normally distributed or approximately normally
The Coefficient of Determination
 The Coefficient of Determination Lecture 46 Section 13.9 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Apr 17, 2012 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) The Coefficient of Determination Wed, Apr 17,
The Coefficient of Determination Lecture 46 Section 13.9 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Apr 17, 2012 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) The Coefficient of Determination Wed, Apr 17,
CHAPTER 2 Modeling Distributions of Data
 CHAPTER 2 Modeling Distributions of Data 2.2 Density Curves and Normal Distributions The Practice of Statistics, 5th Edition Starnes, Tabor, Yates, Moore Bedford Freeman Worth Publishers HW 34. Sketch
CHAPTER 2 Modeling Distributions of Data 2.2 Density Curves and Normal Distributions The Practice of Statistics, 5th Edition Starnes, Tabor, Yates, Moore Bedford Freeman Worth Publishers HW 34. Sketch
The Pairwise-Comparison Method
 The Pairwise-Comparison Method Lecture 10 Section 1.5 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Mon, Sep 11, 2017 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) The Pairwise-Comparison Method Mon, Sep 11, 2017
The Pairwise-Comparison Method Lecture 10 Section 1.5 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Mon, Sep 11, 2017 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) The Pairwise-Comparison Method Mon, Sep 11, 2017
Chapter 2: The Normal Distribution
 Chapter 2: The Normal Distribution 2.1 Density Curves and the Normal Distributions 2.2 Standard Normal Calculations 1 2 Histogram for Strength of Yarn Bobbins 15.60 16.10 16.60 17.10 17.60 18.10 18.60
Chapter 2: The Normal Distribution 2.1 Density Curves and the Normal Distributions 2.2 Standard Normal Calculations 1 2 Histogram for Strength of Yarn Bobbins 15.60 16.10 16.60 17.10 17.60 18.10 18.60
while Loops Lecture 13 Sections Robb T. Koether Wed, Sep 26, 2018 Hampden-Sydney College
 while Loops Lecture 13 Sections 5.8-5.9 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Sep 26, 2018 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) while Loops Wed, Sep 26, 2018 1 / 25 1 while Loops 2 Input Loops
while Loops Lecture 13 Sections 5.8-5.9 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Sep 26, 2018 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) while Loops Wed, Sep 26, 2018 1 / 25 1 while Loops 2 Input Loops
Chapter 2 Modeling Distributions of Data
 Chapter 2 Modeling Distributions of Data Section 2.1 Describing Location in a Distribution Describing Location in a Distribution Learning Objectives After this section, you should be able to: FIND and
Chapter 2 Modeling Distributions of Data Section 2.1 Describing Location in a Distribution Describing Location in a Distribution Learning Objectives After this section, you should be able to: FIND and
Recursive Sequences. Lecture 24 Section 5.6. Robb T. Koether. Hampden-Sydney College. Wed, Feb 27, 2013
 Recursive Sequences Lecture 24 Section 5.6 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Feb 27, 2013 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Recursive Sequences Wed, Feb 27, 2013 1 / 21 1 Recursive Sequences
Recursive Sequences Lecture 24 Section 5.6 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Feb 27, 2013 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Recursive Sequences Wed, Feb 27, 2013 1 / 21 1 Recursive Sequences
Introduction to the Practice of Statistics Fifth Edition Moore, McCabe
 Introduction to the Practice of Statistics Fifth Edition Moore, McCabe Section 1.3 Homework Answers Assignment 5 1.80 If you ask a computer to generate "random numbers between 0 and 1, you uniform will
Introduction to the Practice of Statistics Fifth Edition Moore, McCabe Section 1.3 Homework Answers Assignment 5 1.80 If you ask a computer to generate "random numbers between 0 and 1, you uniform will
Math 14 Lecture Notes Ch. 6.1
 6.1 Normal Distribution What is normal? a 10-year old boy that is 4' tall? 5' tall? 6' tall? a 25-year old woman with a shoe size of 5? 7? 9? an adult alligator that weighs 200 pounds? 500 pounds? 800
6.1 Normal Distribution What is normal? a 10-year old boy that is 4' tall? 5' tall? 6' tall? a 25-year old woman with a shoe size of 5? 7? 9? an adult alligator that weighs 200 pounds? 500 pounds? 800
The Decreasing-Time Algorithm
 The Decreasing-Time Algorithm Lecture 36 Sections 8.4 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Apr 18, 2018 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) The Decreasing-Time Algorithm Wed, Apr 18, 2018 1
The Decreasing-Time Algorithm Lecture 36 Sections 8.4 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Apr 18, 2018 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) The Decreasing-Time Algorithm Wed, Apr 18, 2018 1
Lecture 3 Questions that we should be able to answer by the end of this lecture:
 Lecture 3 Questions that we should be able to answer by the end of this lecture: Which is the better exam score? 67 on an exam with mean 50 and SD 10 or 62 on an exam with mean 40 and SD 12 Is it fair
Lecture 3 Questions that we should be able to answer by the end of this lecture: Which is the better exam score? 67 on an exam with mean 50 and SD 10 or 62 on an exam with mean 40 and SD 12 Is it fair
CHAPTER 2 Modeling Distributions of Data
 CHAPTER 2 Modeling Distributions of Data 2.2 Density Curves and Normal Distributions The Practice of Statistics, 5th Edition Starnes, Tabor, Yates, Moore Bedford Freeman Worth Publishers Density Curves
CHAPTER 2 Modeling Distributions of Data 2.2 Density Curves and Normal Distributions The Practice of Statistics, 5th Edition Starnes, Tabor, Yates, Moore Bedford Freeman Worth Publishers Density Curves
Lecture 6: Chapter 6 Summary
 1 Lecture 6: Chapter 6 Summary Z-score: Is the distance of each data value from the mean in standard deviation Standardizes data values Standardization changes the mean and the standard deviation: o Z
1 Lecture 6: Chapter 6 Summary Z-score: Is the distance of each data value from the mean in standard deviation Standardizes data values Standardization changes the mean and the standard deviation: o Z
Density Curve (p52) Density curve is a curve that - is always on or above the horizontal axis.
 1.3 Density curves p50 Some times the overall pattern of a large number of observations is so regular that we can describe it by a smooth curve. It is easier to work with a smooth curve, because the histogram
1.3 Density curves p50 Some times the overall pattern of a large number of observations is so regular that we can describe it by a smooth curve. It is easier to work with a smooth curve, because the histogram
The Plurality-with-Elimination Method
 The Plurality-with-Elimination Method Lecture 9 Section 1.4 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Fri, Sep 8, 2017 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) The Plurality-with-Elimination Method Fri, Sep
The Plurality-with-Elimination Method Lecture 9 Section 1.4 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Fri, Sep 8, 2017 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) The Plurality-with-Elimination Method Fri, Sep
Normal Distribution. 6.4 Applications of Normal Distribution
 Normal Distribution 6.4 Applications of Normal Distribution 1 /20 Homework Read Sec 6-4. Discussion question p316 Do p316 probs 1-10, 16-22, 31, 32, 34-37, 39 2 /20 3 /20 Objective Find the probabilities
Normal Distribution 6.4 Applications of Normal Distribution 1 /20 Homework Read Sec 6-4. Discussion question p316 Do p316 probs 1-10, 16-22, 31, 32, 34-37, 39 2 /20 3 /20 Objective Find the probabilities
Lecture 3 Questions that we should be able to answer by the end of this lecture:
 Lecture 3 Questions that we should be able to answer by the end of this lecture: Which is the better exam score? 67 on an exam with mean 50 and SD 10 or 62 on an exam with mean 40 and SD 12 Is it fair
Lecture 3 Questions that we should be able to answer by the end of this lecture: Which is the better exam score? 67 on an exam with mean 50 and SD 10 or 62 on an exam with mean 40 and SD 12 Is it fair
Rotations and Translations
 Rotations and Translations Lecture 33 Sections 11.3-11.4 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Nov 20, 2013 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Rotations and Translations Wed, Nov 20, 2013 1
Rotations and Translations Lecture 33 Sections 11.3-11.4 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Nov 20, 2013 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Rotations and Translations Wed, Nov 20, 2013 1
Recursive Sequences. Lecture 24 Section 5.6. Robb T. Koether. Hampden-Sydney College. Wed, Feb 26, 2014
 Recursive Sequences Lecture 24 Section 5.6 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Feb 26, 2014 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Recursive Sequences Wed, Feb 26, 2014 1 / 26 1 Recursive Sequences
Recursive Sequences Lecture 24 Section 5.6 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Feb 26, 2014 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Recursive Sequences Wed, Feb 26, 2014 1 / 26 1 Recursive Sequences
Section 2.2 Normal Distributions
 Section 2.2 Mrs. Daniel AP Statistics We abbreviate the Normal distribution with mean µ and standard deviation σ as N(µ,σ). Any particular Normal distribution is completely specified by two numbers: its
Section 2.2 Mrs. Daniel AP Statistics We abbreviate the Normal distribution with mean µ and standard deviation σ as N(µ,σ). Any particular Normal distribution is completely specified by two numbers: its
Student Learning Objectives
 Student Learning Objectives A. Understand that the overall shape of a distribution of a large number of observations can be summarized by a smooth curve called a density curve. B. Know that an area under
Student Learning Objectives A. Understand that the overall shape of a distribution of a large number of observations can be summarized by a smooth curve called a density curve. B. Know that an area under
Chapter 2: The Normal Distributions
 Chapter 2: The Normal Distributions Measures of Relative Standing & Density Curves Z-scores (Measures of Relative Standing) Suppose there is one spot left in the University of Michigan class of 2014 and
Chapter 2: The Normal Distributions Measures of Relative Standing & Density Curves Z-scores (Measures of Relative Standing) Suppose there is one spot left in the University of Michigan class of 2014 and
CHAPTER 2 Modeling Distributions of Data
 CHAPTER 2 Modeling Distributions of Data 2.2 Density Curves and Normal Distributions The Practice of Statistics, 5th Edition Starnes, Tabor, Yates, Moore Bedford Freeman Worth Publishers Density Curves
CHAPTER 2 Modeling Distributions of Data 2.2 Density Curves and Normal Distributions The Practice of Statistics, 5th Edition Starnes, Tabor, Yates, Moore Bedford Freeman Worth Publishers Density Curves
Ch6: The Normal Distribution
 Ch6: The Normal Distribution Introduction Review: A continuous random variable can assume any value between two endpoints. Many continuous random variables have an approximately normal distribution, which
Ch6: The Normal Distribution Introduction Review: A continuous random variable can assume any value between two endpoints. Many continuous random variables have an approximately normal distribution, which
Street-Routing Problems
 Street-Routing Problems Lecture 26 Sections 5.1-5.2 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Oct 25, 2017 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Street-Routing Problems Wed, Oct 25, 2017 1 / 21 1
Street-Routing Problems Lecture 26 Sections 5.1-5.2 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Oct 25, 2017 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Street-Routing Problems Wed, Oct 25, 2017 1 / 21 1
Key: 5 9 represents a team with 59 wins. (c) The Kansas City Royals and Cleveland Indians, who both won 65 games.
 AP statistics Chapter 2 Notes Name Modeling Distributions of Data Per Date 2.1A Distribution of a variable is the a variable takes and it takes that value. When working with quantitative data we can calculate
AP statistics Chapter 2 Notes Name Modeling Distributions of Data Per Date 2.1A Distribution of a variable is the a variable takes and it takes that value. When working with quantitative data we can calculate
The Normal Distribution
 Chapter 6 The Normal Distribution Continuous random variables are used to approximate probabilities where there are many possibilities or an infinite number of possibilities on a given trial. One of the
Chapter 6 The Normal Distribution Continuous random variables are used to approximate probabilities where there are many possibilities or an infinite number of possibilities on a given trial. One of the
Stack Applications. Lecture 27 Sections Robb T. Koether. Hampden-Sydney College. Wed, Mar 29, 2017
 Stack Applications Lecture 27 Sections 18.7-18.8 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Mar 29, 2017 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College) Stack Applications Wed, Mar 29, 2017 1 / 27 1 Function
Stack Applications Lecture 27 Sections 18.7-18.8 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Mar 29, 2017 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College) Stack Applications Wed, Mar 29, 2017 1 / 27 1 Function
Measures of Position
 Measures of Position In this section, we will learn to use fractiles. Fractiles are numbers that partition, or divide, an ordered data set into equal parts (each part has the same number of data entries).
Measures of Position In this section, we will learn to use fractiles. Fractiles are numbers that partition, or divide, an ordered data set into equal parts (each part has the same number of data entries).
Lecture 31 Sections 9.4. Tue, Mar 17, 2009
 s for s for Lecture 31 Sections 9.4 Hampden-Sydney College Tue, Mar 17, 2009 Outline s for 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 s for Exercise 9.17, page 582. It is believed that 20% of all university faculty would be willing
s for s for Lecture 31 Sections 9.4 Hampden-Sydney College Tue, Mar 17, 2009 Outline s for 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 s for Exercise 9.17, page 582. It is believed that 20% of all university faculty would be willing
BIOL Gradation of a histogram (a) into the normal curve (b)
 (التوزيع الطبيعي ( Distribution Normal (Gaussian) One of the most important distributions in statistics is a continuous distribution called the normal distribution or Gaussian distribution. Consider the
(التوزيع الطبيعي ( Distribution Normal (Gaussian) One of the most important distributions in statistics is a continuous distribution called the normal distribution or Gaussian distribution. Consider the
Scheduling and Digraphs
 Scheduling and Digraphs Lecture 35 Sections 8.1, 8.2 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Mon, Nov 21, 2016 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Scheduling and Digraphs Mon, Nov 21, 2016 1 / 25 1
Scheduling and Digraphs Lecture 35 Sections 8.1, 8.2 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Mon, Nov 21, 2016 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Scheduling and Digraphs Mon, Nov 21, 2016 1 / 25 1
Lecture Slides. Elementary Statistics Twelfth Edition. by Mario F. Triola. and the Triola Statistics Series. Section 6.2-1
 Lecture Slides Elementary Statistics Twelfth Edition and the Triola Statistics Series by Mario F. Triola Section 6.2-1 Chapter 6 Normal Probability Distributions 6-1 Review and Preview 6-2 The Standard
Lecture Slides Elementary Statistics Twelfth Edition and the Triola Statistics Series by Mario F. Triola Section 6.2-1 Chapter 6 Normal Probability Distributions 6-1 Review and Preview 6-2 The Standard
6-1 THE STANDARD NORMAL DISTRIBUTION
 6-1 THE STANDARD NORMAL DISTRIBUTION The major focus of this chapter is the concept of a normal probability distribution, but we begin with a uniform distribution so that we can see the following two very
6-1 THE STANDARD NORMAL DISTRIBUTION The major focus of this chapter is the concept of a normal probability distribution, but we begin with a uniform distribution so that we can see the following two very
The Traveling Salesman Problem Brute Force Method
 The Traveling Salesman Problem Brute Force Method Lecture 30 Sections 6.1, 6.3 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Fri, Nov 3, 2017 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College)The Traveling Salesman Problem
The Traveling Salesman Problem Brute Force Method Lecture 30 Sections 6.1, 6.3 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Fri, Nov 3, 2017 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College)The Traveling Salesman Problem
Prepare a stem-and-leaf graph for the following data. In your final display, you should arrange the leaves for each stem in increasing order.
 Chapter 2 2.1 Descriptive Statistics A stem-and-leaf graph, also called a stemplot, allows for a nice overview of quantitative data without losing information on individual observations. It can be a good
Chapter 2 2.1 Descriptive Statistics A stem-and-leaf graph, also called a stemplot, allows for a nice overview of quantitative data without losing information on individual observations. It can be a good
Regular Expressions. Lecture 10 Sections Robb T. Koether. Hampden-Sydney College. Wed, Sep 14, 2016
 Regular Expressions Lecture 10 Sections 3.1-3.2 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Sep 14, 2016 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Regular Expressions Wed, Sep 14, 2016 1 / 23 Outline 1
Regular Expressions Lecture 10 Sections 3.1-3.2 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Sep 14, 2016 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Regular Expressions Wed, Sep 14, 2016 1 / 23 Outline 1
IT 403 Practice Problems (1-2) Answers
 IT 403 Practice Problems (1-2) Answers #1. Using Tukey's Hinges method ('Inclusionary'), what is Q3 for this dataset? 2 3 5 7 11 13 17 a. 7 b. 11 c. 12 d. 15 c (12) #2. How do quartiles and percentiles
IT 403 Practice Problems (1-2) Answers #1. Using Tukey's Hinges method ('Inclusionary'), what is Q3 for this dataset? 2 3 5 7 11 13 17 a. 7 b. 11 c. 12 d. 15 c (12) #2. How do quartiles and percentiles
Boolean Expressions. Lecture 31 Sections 6.6, 6.7. Robb T. Koether. Hampden-Sydney College. Wed, Apr 8, 2015
 Boolean Expressions Lecture 31 Sections 6.6, 6.7 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Apr 8, 2015 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Boolean Expressions Wed, Apr 8, 2015 1 / 22 1 Relational
Boolean Expressions Lecture 31 Sections 6.6, 6.7 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Apr 8, 2015 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Boolean Expressions Wed, Apr 8, 2015 1 / 22 1 Relational
Chapter 2: Modeling Distributions of Data
 Chapter 2: Modeling Distributions of Data Section 2.2 The Practice of Statistics, 4 th edition - For AP* STARNES, YATES, MOORE Chapter 2 Modeling Distributions of Data 2.1 Describing Location in a Distribution
Chapter 2: Modeling Distributions of Data Section 2.2 The Practice of Statistics, 4 th edition - For AP* STARNES, YATES, MOORE Chapter 2 Modeling Distributions of Data 2.1 Describing Location in a Distribution
XPath Lecture 34. Robb T. Koether. Hampden-Sydney College. Wed, Apr 11, 2012
 XPath Lecture 34 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Apr 11, 2012 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) XPathLecture 34 Wed, Apr 11, 2012 1 / 20 1 XPath Functions 2 Predicates 3 Axes Robb T.
XPath Lecture 34 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Apr 11, 2012 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) XPathLecture 34 Wed, Apr 11, 2012 1 / 20 1 XPath Functions 2 Predicates 3 Axes Robb T.
Section 10.4 Normal Distributions
 Section 10.4 Normal Distributions Random Variables Suppose a bank is interested in improving its services to customers. The manager decides to begin by finding the amount of time tellers spend on each
Section 10.4 Normal Distributions Random Variables Suppose a bank is interested in improving its services to customers. The manager decides to begin by finding the amount of time tellers spend on each
Solving Recursive Sequences by Iteration
 Solving Recursive Sequences by Iteration Lecture 25 Section 5.7 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Thu, Feb 28, 2013 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Solving Recursive Sequences by Iteration
Solving Recursive Sequences by Iteration Lecture 25 Section 5.7 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Thu, Feb 28, 2013 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Solving Recursive Sequences by Iteration
Chapter 5: The standard deviation as a ruler and the normal model p131
 Chapter 5: The standard deviation as a ruler and the normal model p131 Which is the better exam score? 67 on an exam with mean 50 and SD 10 62 on an exam with mean 40 and SD 12? Is it fair to say: 67 is
Chapter 5: The standard deviation as a ruler and the normal model p131 Which is the better exam score? 67 on an exam with mean 50 and SD 10 62 on an exam with mean 40 and SD 12? Is it fair to say: 67 is
Recursive Descent Parsers
 Recursive Descent Parsers Lecture 7 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Jan 28, 2015 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Recursive Descent Parsers Wed, Jan 28, 2015 1 / 18 1 Parsing 2 LL Parsers
Recursive Descent Parsers Lecture 7 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Jan 28, 2015 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Recursive Descent Parsers Wed, Jan 28, 2015 1 / 18 1 Parsing 2 LL Parsers
Distributions of random variables
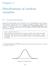 Chapter 3 Distributions of random variables 31 Normal distribution Among all the distributions we see in practice, one is overwhelmingly the most common The symmetric, unimodal, bell curve is ubiquitous
Chapter 3 Distributions of random variables 31 Normal distribution Among all the distributions we see in practice, one is overwhelmingly the most common The symmetric, unimodal, bell curve is ubiquitous
Probability and Statistics. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
 Probability and Statistics Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 14.6 Descriptive Statistics (Graphical) Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Objectives Data in Categories Histograms
Probability and Statistics Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 14.6 Descriptive Statistics (Graphical) Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Objectives Data in Categories Histograms
The Traveling Salesman Problem Nearest-Neighbor Algorithm
 The Traveling Salesman Problem Nearest-Neighbor Algorithm Lecture 31 Sections 6.4 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Fri, Apr 6, 2018 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College)The Traveling Salesman
The Traveling Salesman Problem Nearest-Neighbor Algorithm Lecture 31 Sections 6.4 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Fri, Apr 6, 2018 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College)The Traveling Salesman
Magnification and Minification
 Magnification and Minification Lecture 30 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Fri, Nov 6, 2015 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Magnification and Minification Fri, Nov 6, 2015 1 / 17 Outline
Magnification and Minification Lecture 30 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Fri, Nov 6, 2015 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Magnification and Minification Fri, Nov 6, 2015 1 / 17 Outline
The Class Construct Part 1
 The Class Construct Part 1 Lecture 23 Sections 7.5-7.6 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Fri, Oct 26, 2018 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) The Class Construct Part 1 Fri, Oct 26, 2018 1 /
The Class Construct Part 1 Lecture 23 Sections 7.5-7.6 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Fri, Oct 26, 2018 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) The Class Construct Part 1 Fri, Oct 26, 2018 1 /
23.2 Normal Distributions
 1_ Locker LESSON 23.2 Normal Distributions Common Core Math Standards The student is expected to: S-ID.4 Use the mean and standard deviation of a data set to fit it to a normal distribution and to estimate
1_ Locker LESSON 23.2 Normal Distributions Common Core Math Standards The student is expected to: S-ID.4 Use the mean and standard deviation of a data set to fit it to a normal distribution and to estimate
Chapter 6 Normal Probability Distributions
 Chapter 6 Normal Probability Distributions 6-1 Review and Preview 6-2 The Standard Normal Distribution 6-3 Applications of Normal Distributions 6-4 Sampling Distributions and Estimators 6-5 The Central
Chapter 6 Normal Probability Distributions 6-1 Review and Preview 6-2 The Standard Normal Distribution 6-3 Applications of Normal Distributions 6-4 Sampling Distributions and Estimators 6-5 The Central
Chapter 1. Looking at Data-Distribution
 Chapter 1. Looking at Data-Distribution Statistics is the scientific discipline that provides methods to draw right conclusions: 1)Collecting the data 2)Describing the data 3)Drawing the conclusions Raw
Chapter 1. Looking at Data-Distribution Statistics is the scientific discipline that provides methods to draw right conclusions: 1)Collecting the data 2)Describing the data 3)Drawing the conclusions Raw
Shading Triangles. Lecture 37. Robb T. Koether. Hampden-Sydney College. Mon, Nov 30, 2015
 Shading Triangles Lecture 37 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Mon, Nov 30, 2015 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Shading Triangles Mon, Nov 30, 2015 1 / 35 Outline 1 Shading Triangles Barycentric
Shading Triangles Lecture 37 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Mon, Nov 30, 2015 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Shading Triangles Mon, Nov 30, 2015 1 / 35 Outline 1 Shading Triangles Barycentric
CHAPTER 2: SAMPLING AND DATA
 CHAPTER 2: SAMPLING AND DATA This presentation is based on material and graphs from Open Stax and is copyrighted by Open Stax and Georgia Highlands College. OUTLINE 2.1 Stem-and-Leaf Graphs (Stemplots),
CHAPTER 2: SAMPLING AND DATA This presentation is based on material and graphs from Open Stax and is copyrighted by Open Stax and Georgia Highlands College. OUTLINE 2.1 Stem-and-Leaf Graphs (Stemplots),
Implementing Linked Lists
 Implementing Linked Lists Lecture 16 Sections 17.1-17.3 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Feb 27, 2013 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Implementing Linked Lists Wed, Feb 27, 2013 1 /
Implementing Linked Lists Lecture 16 Sections 17.1-17.3 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Feb 27, 2013 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Implementing Linked Lists Wed, Feb 27, 2013 1 /
Pointers. Lecture 1 Sections Robb T. Koether. Hampden-Sydney College. Wed, Jan 14, 2015
 Pointers Lecture 1 Sections 10.1-10.2 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Jan 14, 2015 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Pointers Wed, Jan 14, 2015 1 / 23 1 Pointers 2 Pointer Initialization
Pointers Lecture 1 Sections 10.1-10.2 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Jan 14, 2015 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Pointers Wed, Jan 14, 2015 1 / 23 1 Pointers 2 Pointer Initialization
3.5 Applying the Normal Distribution: Z-Scores
 3.5 Applying the Normal Distribution: Z-Scores In the previous section, you learned about the normal curve and the normal distribution. You know that the area under any normal curve is 1, and that 68%
3.5 Applying the Normal Distribution: Z-Scores In the previous section, you learned about the normal curve and the normal distribution. You know that the area under any normal curve is 1, and that 68%
Chapter 6. The Normal Distribution. McGraw-Hill, Bluman, 7 th ed., Chapter 6 1
 Chapter 6 The Normal Distribution McGraw-Hill, Bluman, 7 th ed., Chapter 6 1 Bluman, Chapter 6 2 Chapter 6 Overview Introduction 6-1 Normal Distributions 6-2 Applications of the Normal Distribution 6-3
Chapter 6 The Normal Distribution McGraw-Hill, Bluman, 7 th ed., Chapter 6 1 Bluman, Chapter 6 2 Chapter 6 Overview Introduction 6-1 Normal Distributions 6-2 Applications of the Normal Distribution 6-3
MATH 1070 Introductory Statistics Lecture notes Descriptive Statistics and Graphical Representation
 MATH 1070 Introductory Statistics Lecture notes Descriptive Statistics and Graphical Representation Objectives: 1. Learn the meaning of descriptive versus inferential statistics 2. Identify bar graphs,
MATH 1070 Introductory Statistics Lecture notes Descriptive Statistics and Graphical Representation Objectives: 1. Learn the meaning of descriptive versus inferential statistics 2. Identify bar graphs,
a. divided by the. 1) Always round!! a) Even if class width comes out to a, go up one.
 Probability and Statistics Chapter 2 Notes I Section 2-1 A Steps to Constructing Frequency Distributions 1 Determine number of (may be given to you) a Should be between and classes 2 Find the Range a The
Probability and Statistics Chapter 2 Notes I Section 2-1 A Steps to Constructing Frequency Distributions 1 Determine number of (may be given to you) a Should be between and classes 2 Find the Range a The
LR Parsing - Conflicts
 LR Parsing - Conflicts Lecture 15 Sections 4.5, 4.6 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Fri, Feb 20, 2015 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) LR Parsing - Conflicts Fri, Feb 20, 2015 1 / 15 1 Shift/Reduce
LR Parsing - Conflicts Lecture 15 Sections 4.5, 4.6 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Fri, Feb 20, 2015 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) LR Parsing - Conflicts Fri, Feb 20, 2015 1 / 15 1 Shift/Reduce
UNIT 1A EXPLORING UNIVARIATE DATA
 A.P. STATISTICS E. Villarreal Lincoln HS Math Department UNIT 1A EXPLORING UNIVARIATE DATA LESSON 1: TYPES OF DATA Here is a list of important terms that we must understand as we begin our study of statistics
A.P. STATISTICS E. Villarreal Lincoln HS Math Department UNIT 1A EXPLORING UNIVARIATE DATA LESSON 1: TYPES OF DATA Here is a list of important terms that we must understand as we begin our study of statistics
XPath. Lecture 36. Robb T. Koether. Wed, Apr 16, Hampden-Sydney College. Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) XPath Wed, Apr 16, / 28
 XPath Lecture 36 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Apr 16, 2014 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) XPath Wed, Apr 16, 2014 1 / 28 1 XPath 2 Executing XPath Expressions 3 XPath Expressions
XPath Lecture 36 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Apr 16, 2014 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) XPath Wed, Apr 16, 2014 1 / 28 1 XPath 2 Executing XPath Expressions 3 XPath Expressions
Sections 4.3 and 4.4
 Sections 4.3 and 4.4 Timothy Hanson Department of Statistics, University of South Carolina Stat 205: Elementary Statistics for the Biological and Life Sciences 1 / 32 4.3 Areas under normal densities Every
Sections 4.3 and 4.4 Timothy Hanson Department of Statistics, University of South Carolina Stat 205: Elementary Statistics for the Biological and Life Sciences 1 / 32 4.3 Areas under normal densities Every
Programming Languages
 Programming Languages Lecture 3 Section 1.3 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Mon, Sep 2, 2013 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Programming Languages Mon, Sep 2, 2013 1 / 25 1 Programming
Programming Languages Lecture 3 Section 1.3 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Mon, Sep 2, 2013 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Programming Languages Mon, Sep 2, 2013 1 / 25 1 Programming
Scope and Parameter Passing
 Scope and Parameter Passing Lecture 16 Sections 6.5, 6.10, 6.13 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Mon, Oct 7, 2013 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Scope and Parameter Passing Mon, Oct 7,
Scope and Parameter Passing Lecture 16 Sections 6.5, 6.10, 6.13 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Mon, Oct 7, 2013 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Scope and Parameter Passing Mon, Oct 7,
appstats6.notebook September 27, 2016
 Chapter 6 The Standard Deviation as a Ruler and the Normal Model Objectives: 1.Students will calculate and interpret z scores. 2.Students will compare/contrast values from different distributions using
Chapter 6 The Standard Deviation as a Ruler and the Normal Model Objectives: 1.Students will calculate and interpret z scores. 2.Students will compare/contrast values from different distributions using
Section 2.2 Normal Distributions. Normal Distributions
 Section 2.2 Normal Distributions Normal Distributions One particularly important class of density curves are the Normal curves, which describe Normal distributions. All Normal curves are symmetric, single-peaked,
Section 2.2 Normal Distributions Normal Distributions One particularly important class of density curves are the Normal curves, which describe Normal distributions. All Normal curves are symmetric, single-peaked,
Unit 7 Statistics. AFM Mrs. Valentine. 7.1 Samples and Surveys
 Unit 7 Statistics AFM Mrs. Valentine 7.1 Samples and Surveys v Obj.: I will understand the different methods of sampling and studying data. I will be able to determine the type used in an example, and
Unit 7 Statistics AFM Mrs. Valentine 7.1 Samples and Surveys v Obj.: I will understand the different methods of sampling and studying data. I will be able to determine the type used in an example, and
The Normal Distribution
 14-4 OBJECTIVES Use the normal distribution curve. The Normal Distribution TESTING The class of 1996 was the first class to take the adjusted Scholastic Assessment Test. The test was adjusted so that the
14-4 OBJECTIVES Use the normal distribution curve. The Normal Distribution TESTING The class of 1996 was the first class to take the adjusted Scholastic Assessment Test. The test was adjusted so that the
The Graphics Pipeline
 The Graphics Pipeline Lecture 2 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Aug 23, 2017 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) The Graphics Pipeline Wed, Aug 23, 2017 1 / 19 Outline 1 Vertices 2 The
The Graphics Pipeline Lecture 2 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Aug 23, 2017 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) The Graphics Pipeline Wed, Aug 23, 2017 1 / 19 Outline 1 Vertices 2 The
The Normal Distribution & z-scores
 & z-scores Distributions: Who needs them? Why are we interested in distributions? Important link between distributions and probabilities of events If we know the distribution of a set of events, then we
& z-scores Distributions: Who needs them? Why are we interested in distributions? Important link between distributions and probabilities of events If we know the distribution of a set of events, then we
Frequency Distributions
 Displaying Data Frequency Distributions After collecting data, the first task for a researcher is to organize and summarize the data so that it is possible to get a general overview of the results. Remember,
Displaying Data Frequency Distributions After collecting data, the first task for a researcher is to organize and summarize the data so that it is possible to get a general overview of the results. Remember,
7.2. The Standard Normal Distribution
 7.2 The Standard Normal Distribution Standard Normal The standard normal curve is the one with mean μ = 0 and standard deviation σ = 1 We have related the general normal random variable to the standard
7.2 The Standard Normal Distribution Standard Normal The standard normal curve is the one with mean μ = 0 and standard deviation σ = 1 We have related the general normal random variable to the standard
Chapter 6: Continuous Random Variables & the Normal Distribution. 6.1 Continuous Probability Distribution
 Chapter 6: Continuous Random Variables & the Normal Distribution 6.1 Continuous Probability Distribution and the Normal Probability Distribution 6.2 Standardizing a Normal Distribution 6.3 Applications
Chapter 6: Continuous Random Variables & the Normal Distribution 6.1 Continuous Probability Distribution and the Normal Probability Distribution 6.2 Standardizing a Normal Distribution 6.3 Applications
The string Class. Lecture 21 Sections 2.9, 3.9, Robb T. Koether. Wed, Oct 17, Hampden-Sydney College
 The string Class Lecture 21 Sections 2.9, 3.9, 3.10 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Oct 17, 2018 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) The string Class Wed, Oct 17, 2018 1 / 18 1 The String
The string Class Lecture 21 Sections 2.9, 3.9, 3.10 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Oct 17, 2018 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) The string Class Wed, Oct 17, 2018 1 / 18 1 The String
Chapter 6 The Standard Deviation as Ruler and the Normal Model
 ST 305 Chapter 6 Reiland The Standard Deviation as Ruler and the Normal Model Chapter Objectives: At the end of this chapter you should be able to: 1) describe how adding or subtracting the same value
ST 305 Chapter 6 Reiland The Standard Deviation as Ruler and the Normal Model Chapter Objectives: At the end of this chapter you should be able to: 1) describe how adding or subtracting the same value
Goals. The Normal Probability Distribution. A distribution. A Discrete Probability Distribution. Results of Tossing Two Dice. Probabilities involve
 Goals The Normal Probability Distribution Chapter 7 Dr. Richard Jerz Understand the difference between discrete and continuous distributions. Compute the mean, standard deviation, and probabilities for
Goals The Normal Probability Distribution Chapter 7 Dr. Richard Jerz Understand the difference between discrete and continuous distributions. Compute the mean, standard deviation, and probabilities for
Recursion. Lecture 2 Sections Robb T. Koether. Hampden-Sydney College. Wed, Jan 17, 2018
 Recursion Lecture 2 Sections 20.1-20.4 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Jan 17, 2018 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Recursion Wed, Jan 17, 2018 1 / 18 1 Recursion 2 Advantages and
Recursion Lecture 2 Sections 20.1-20.4 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Jan 17, 2018 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Recursion Wed, Jan 17, 2018 1 / 18 1 Recursion 2 Advantages and
CHAPTER 2: Describing Location in a Distribution
 CHAPTER 2: Describing Location in a Distribution 2.1 Goals: 1. Compute and use z-scores given the mean and sd 2. Compute and use the p th percentile of an observation 3. Intro to density curves 4. More
CHAPTER 2: Describing Location in a Distribution 2.1 Goals: 1. Compute and use z-scores given the mean and sd 2. Compute and use the p th percentile of an observation 3. Intro to density curves 4. More
Chapters 5-6: Statistical Inference Methods
 Chapters 5-6: Statistical Inference Methods Chapter 5: Estimation (of population parameters) Ex. Based on GSS data, we re 95% confident that the population mean of the variable LONELY (no. of days in past
Chapters 5-6: Statistical Inference Methods Chapter 5: Estimation (of population parameters) Ex. Based on GSS data, we re 95% confident that the population mean of the variable LONELY (no. of days in past
The Normal Probability Distribution. Goals. A distribution 2/27/16. Chapter 7 Dr. Richard Jerz
 The Normal Probability Distribution Chapter 7 Dr. Richard Jerz 1 2016 rjerz.com Goals Understand the difference between discrete and continuous distributions. Compute the mean, standard deviation, and
The Normal Probability Distribution Chapter 7 Dr. Richard Jerz 1 2016 rjerz.com Goals Understand the difference between discrete and continuous distributions. Compute the mean, standard deviation, and
Lab 4: Distributions of random variables
 Lab 4: Distributions of random variables In this lab we ll investigate the probability distribution that is most central to statistics: the normal distribution If we are confident that our data are nearly
Lab 4: Distributions of random variables In this lab we ll investigate the probability distribution that is most central to statistics: the normal distribution If we are confident that our data are nearly
Specular Reflection. Lecture 19. Robb T. Koether. Hampden-Sydney College. Wed, Oct 4, 2017
 Specular Reflection Lecture 19 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Oct 4, 2017 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Specular Reflection Wed, Oct 4, 2017 1 / 22 Outline 1 Specular Reflection
Specular Reflection Lecture 19 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Oct 4, 2017 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Specular Reflection Wed, Oct 4, 2017 1 / 22 Outline 1 Specular Reflection
Mipmaps. Lecture 35. Robb T. Koether. Hampden-Sydney College. Wed, Nov 18, 2015
 Mipmaps Lecture 35 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Nov 18, 2015 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Mipmaps Wed, Nov 18, 2015 1 / 31 Outline 1 Discrete Sampling 2 Mipmaps 3 Generating
Mipmaps Lecture 35 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Nov 18, 2015 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Mipmaps Wed, Nov 18, 2015 1 / 31 Outline 1 Discrete Sampling 2 Mipmaps 3 Generating
