Final Examination. Winter Problem Points Score. Total 180
|
|
|
- Lindsay Ellis
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CS243 Winter You have 3 hours to work on this exam. The examination has 180 points. Please budget your time accordingly. Write your answers in the space provided on the exam. If you use additional scratch paper, please turn that in as well. Your Name: In accordance with both the letter and spirit of the Honor Code, I have neither given nor received assistance on this examination. Signature: Problem Points Score Total 180 Winter 2003 Page 1 of 13
2 1. (10 points) Suppose you have a machine with 3 registers. Can you find a register allocation for the following interference graph such that no spilling is necessary? Your answer may be one of: yes, no, I don t know. If the answer is yes, specify a register assignment. If the answer is no, explain why Winter 2003 Page 2 of 13
3 2. (20 points) Briefly give one important advantage and disadvantage for each of the following styles of garbage collection. a. Reference counting Advantage: Disadvantage: b. Copying garbage collection Advantage: Disadvantage: c. Generational garbage collection Advantage: Disadvantage: d. Incremental garbage collection Advantage: Disadvantage: Winter 2003 Page 3 of 13
4 3. (30 points) Consider the following control flow graph: Entry A B C D F E G H I J K Exit L a. Give a reverse post-ordering for this flow graph. Winter 2003 Page 4 of 13
5 b. Draw the dominator tree for this graph. c. Find the natural loops in this graph. d. Is the flow graph reducible? Explain. Winter 2003 Page 5 of 13
6 e. Consider a data-flow solver that sweeps through all the nodes in reverse post-order until there are no more changes. Assume that the solver needs to iterate through the nodes once after the final answer is reached to detect convergence. If we apply the solver to the dataflow problem of finding dominators, what is the maximum number of times this solver has to iterate before it converges for the above program. Justify your answer. f. What is the maximum number of times a reverse post-order solver has to iterate to find reaching definitions in this program? To justify the answer to part (e), show an example that requires the maximum number of iterations. You may do so by placing one definition in the program and identifying a program point whose value is not correct until the last but one iteration. Winter 2003 Page 6 of 13
7 4. (20 points) Show the result of applying lazy code motion to the following program. Show the result of the optimization -- it is not necessary to show any intermediate steps. (Introduce new basic blocks as necessary). B 1 ENTRY u=a+b B 2 B 3 B 4 v=a+b B 5 B 6 EXIT B 7 w=a+b B 8 B 9 B 10 b=read() B 11 Winter 2003 Page 7 of 13
8 *** Extra page for answers *** Winter 2003 Page 8 of 13
9 5. (30 points) Design a monotone iterative data flow analysis algorithm to find the signs of variables in a program. Your algorithm must determine, for each basic block, if each variable in the program is positive, non-positive, equal to zero, negative, non-negative, or unknown. The instructions in the program are: assignments, additions, subtractions, squares (square(x)=x*x), conditional and unconditional branches. You do not need to optimize the branch operations. a. What is the direction of your data flow analysis? b. Draw a diagram of the semi-lattice for one variable, identifying the top and bottom elements clearly. c. How do you initialize the iterative algorithm? d. Define the transfer function of a basic block. e. Is your transfer function distributive? f. Will your algorithm converge? If so, why? Winter 2003 Page 9 of 13
10 6. (30 points) Consider an architecture that can issue one memory operation (LOD, STR), one arithmetic operation (ADD, MUL), and one control flow operation simultaneously. Addresses are of the form A[r+c], where r is a register, A is a base address, and c is a constant. LOD, STR, and ADD have latency 1; MUL has latency 2 (and is perfectly pipelined). All registers that are read in a cycle are read at the beginning of the cycle; all registers that are written are written at the end of the clock cycle. a. The following code is handed to a scheduler: (1) LOD r1 = A[r2+0] (2) MUL r3 = r3 * r4 (3) ADD r3 = r4 + r1 (4) STR B[r2+0] = r3 List all dependencies in the following code and classify them as true, anti-, or output dependencies. b. Consider the following code: L: (1) LOD r2 = A[r1+0] (2) LOD r3 = B[r1+0] (3) MUL r3 = r3 * r3 (4) ADD r2 = r2 + r3 (5) STR C[r1+0] = r2 (6) LOOP L, r1, 1, 1000 i. Give a lower bound on the initiation interval for a software pipelined version of this code? Justify your answer by showing the modulo resource reservation table. ii. Show the steady state of the software pipelined code. Use modulo variable expansion if necessary. Assume as many registers as necessary are available. Winter 2003 Page 10 of 13
11 *** Extra page for answers *** Winter 2003 Page 11 of 13
12 7. (40 points) Consider a small programming language defined as follows: A program is a statement. A statement is a sequence of primitive or loop statements separated by semi-colons. Let u, v, w below represent variables. A primitive statement can be one of: a. constant assignments: u = <constant> b. copy operations: u = v c. additions: u = v + w, u = v + <constant> A loop statement: Loop <constant> times { <statement> } where the constant is a positive number. Devise a general region-based constant propagation algorithm that can, for example, find the constant value of variable d in the following program: a = 1 b = 2 c = a + b; Loop 10 times { b = b + 1; loop 100 times { a = a + c; } b = b + 4; } d = a + b Winter 2003 Page 12 of 13
13 *** Extra page for answers *** Winter 2003 Page 13 of 13
CS143 Final Spring 2016
 CS143 Final Spring 2016 Please read all instructions (including these) carefully. There are 5 questions on the exam, all with multiple parts. This exam is designed to take 2 hours, but you have the full
CS143 Final Spring 2016 Please read all instructions (including these) carefully. There are 5 questions on the exam, all with multiple parts. This exam is designed to take 2 hours, but you have the full
CS243 Homework 1. Winter Due: January 23, 2019 at 4:30 pm
 CS243 Homework 1 Winter 2019 Due: January 23, 2019 at 4:30 pm Directions: Submit via Gradescope. You may use up to two of your remaining late days for this assignment, for a late deadline of January 25,
CS243 Homework 1 Winter 2019 Due: January 23, 2019 at 4:30 pm Directions: Submit via Gradescope. You may use up to two of your remaining late days for this assignment, for a late deadline of January 25,
CS143 Final Fall 2009
 CS143 Final Fall 2009 Please read all instructions (including these) carefully. There are 4 questions on the exam, all with multiple parts. You have 2 hours to work on the exam. The exam is closed book,
CS143 Final Fall 2009 Please read all instructions (including these) carefully. There are 4 questions on the exam, all with multiple parts. You have 2 hours to work on the exam. The exam is closed book,
Name: CIS 341 Final Examination 10 December 2008
 Name: CIS 341 Final Examination 10 December 2008 1 /8 2 /12 3 /18 4 /18 5 /14 Total /70 Do not begin the exam until you are told to do so. You have 120 minutes to complete the exam. There are 11 pages
Name: CIS 341 Final Examination 10 December 2008 1 /8 2 /12 3 /18 4 /18 5 /14 Total /70 Do not begin the exam until you are told to do so. You have 120 minutes to complete the exam. There are 11 pages
CIS 341 Final Examination 3 May 2011
 CIS 341 Final Examination 3 May 2011 1 /16 2 /20 3 /40 4 /28 5 /16 Total /120 Do not begin the exam until you are told to do so. You have 120 minutes to complete the exam. There are 12 pages in this exam.
CIS 341 Final Examination 3 May 2011 1 /16 2 /20 3 /40 4 /28 5 /16 Total /120 Do not begin the exam until you are told to do so. You have 120 minutes to complete the exam. There are 12 pages in this exam.
This test is not formatted for your answers. Submit your answers via to:
 Page 1 of 7 Computer Science 320: Final Examination May 17, 2017 You have as much time as you like before the Monday May 22 nd 3:00PM ET deadline to answer the following questions. For partial credit,
Page 1 of 7 Computer Science 320: Final Examination May 17, 2017 You have as much time as you like before the Monday May 22 nd 3:00PM ET deadline to answer the following questions. For partial credit,
CIS 341 Final Examination 30 April 2013
 CIS 341 Final Examination 30 April 2013 1 /40 2 /30 3 /30 4 /20 Total /120 Do not begin the exam until you are told to do so. You have 120 minutes to complete the exam. There are 12 pages in this exam.
CIS 341 Final Examination 30 April 2013 1 /40 2 /30 3 /30 4 /20 Total /120 Do not begin the exam until you are told to do so. You have 120 minutes to complete the exam. There are 12 pages in this exam.
Lecture 19. Software Pipelining. I. Example of DoAll Loops. I. Introduction. II. Problem Formulation. III. Algorithm.
 Lecture 19 Software Pipelining I. Introduction II. Problem Formulation III. Algorithm I. Example of DoAll Loops Machine: Per clock: 1 read, 1 write, 1 (2-stage) arithmetic op, with hardware loop op and
Lecture 19 Software Pipelining I. Introduction II. Problem Formulation III. Algorithm I. Example of DoAll Loops Machine: Per clock: 1 read, 1 write, 1 (2-stage) arithmetic op, with hardware loop op and
Computer Science 320: Final Examination
 Computer Science 320: Final Examination May 17, 2001 You have 3 hours to answer the following questions. This midterm is closed book/closed notes. For partial credit, show all work. State all assumptions.
Computer Science 320: Final Examination May 17, 2001 You have 3 hours to answer the following questions. This midterm is closed book/closed notes. For partial credit, show all work. State all assumptions.
EECS 470 Midterm Exam Winter 2015
 EECS 470 Midterm Exam Winter 2015 Name: unique name: Sign the honor code: I have neither given nor received aid on this exam nor observed anyone else doing so. Scores: Page # Points 2 /20 3 /15 4 /9 5
EECS 470 Midterm Exam Winter 2015 Name: unique name: Sign the honor code: I have neither given nor received aid on this exam nor observed anyone else doing so. Scores: Page # Points 2 /20 3 /15 4 /9 5
CS140 Operating Systems and Systems Programming Midterm Exam
 CS140 Operating Systems and Systems Programming Midterm Exam October 28 th, 2005 (Total time = 50 minutes, Total Points = 50) Name: (please print) In recognition of and in the spirit of the Stanford University
CS140 Operating Systems and Systems Programming Midterm Exam October 28 th, 2005 (Total time = 50 minutes, Total Points = 50) Name: (please print) In recognition of and in the spirit of the Stanford University
CS144: Intro to Computer Networks Homework 1 Scan and submit your solution online. Due Friday January 30, 4pm
 CS144: Intro to Computer Networks Homework 1 Scan and submit your solution online. Due Friday January 30, 2015 @ 4pm Your Name: SUNet ID: @stanford.edu Check if you would like exam routed back via SCPD:
CS144: Intro to Computer Networks Homework 1 Scan and submit your solution online. Due Friday January 30, 2015 @ 4pm Your Name: SUNet ID: @stanford.edu Check if you would like exam routed back via SCPD:
Problem Score Max Score 1 Syntax directed translation & type
 CMSC430 Spring 2014 Midterm 2 Name Instructions You have 75 minutes for to take this exam. This exam has a total of 100 points. An average of 45 seconds per point. This is a closed book exam. No notes
CMSC430 Spring 2014 Midterm 2 Name Instructions You have 75 minutes for to take this exam. This exam has a total of 100 points. An average of 45 seconds per point. This is a closed book exam. No notes
Calculus II (Math 122) Final Exam, 11 December 2013
 Name ID number Sections B Calculus II (Math 122) Final Exam, 11 December 2013 This is a closed book exam. Notes and calculators are not allowed. A table of trigonometric identities is attached. To receive
Name ID number Sections B Calculus II (Math 122) Final Exam, 11 December 2013 This is a closed book exam. Notes and calculators are not allowed. A table of trigonometric identities is attached. To receive
University of Waterloo Midterm Examination Solution
 University of Waterloo Midterm Examination Solution Winter, 2011 1. (6 total marks) The diagram below shows an extensible hash table with four hash buckets. Each number x in the buckets represents an entry
University of Waterloo Midterm Examination Solution Winter, 2011 1. (6 total marks) The diagram below shows an extensible hash table with four hash buckets. Each number x in the buckets represents an entry
Structure of Computer Systems
 288 between this new matrix and the initial collision matrix M A, because the original forbidden latencies for functional unit A still have to be considered in later initiations. Figure 5.37. State diagram
288 between this new matrix and the initial collision matrix M A, because the original forbidden latencies for functional unit A still have to be considered in later initiations. Figure 5.37. State diagram
CS140 Operating Systems and Systems Programming Final Exam
 CS140 Operating Systems and Systems Programming Final Exam December 11, 2003 (Total time = 165 minutes, Total Points = 165) Name: (please print) In recognition of and in the spirit of the Stanford University
CS140 Operating Systems and Systems Programming Final Exam December 11, 2003 (Total time = 165 minutes, Total Points = 165) Name: (please print) In recognition of and in the spirit of the Stanford University
CS140 Operating Systems and Systems Programming Midterm Exam
 CS140 Operating Systems and Systems Programming Midterm Exam October 31 st, 2003 (Total time = 50 minutes, Total Points = 50) Name: (please print) In recognition of and in the spirit of the Stanford University
CS140 Operating Systems and Systems Programming Midterm Exam October 31 st, 2003 (Total time = 50 minutes, Total Points = 50) Name: (please print) In recognition of and in the spirit of the Stanford University
Lecture 21. Software Pipelining & Prefetching. I. Software Pipelining II. Software Prefetching (of Arrays) III. Prefetching via Software Pipelining
 Lecture 21 Software Pipelining & Prefetching I. Software Pipelining II. Software Prefetching (of Arrays) III. Prefetching via Software Pipelining [ALSU 10.5, 11.11.4] Phillip B. Gibbons 15-745: Software
Lecture 21 Software Pipelining & Prefetching I. Software Pipelining II. Software Prefetching (of Arrays) III. Prefetching via Software Pipelining [ALSU 10.5, 11.11.4] Phillip B. Gibbons 15-745: Software
6.034 Quiz 1, Spring 2004 Solutions
 6.034 Quiz 1, Spring 2004 Solutions Open Book, Open Notes 1 Tree Search (12 points) Consider the tree shown below. The numbers on the arcs are the arc lengths. Assume that the nodes are expanded in alphabetical
6.034 Quiz 1, Spring 2004 Solutions Open Book, Open Notes 1 Tree Search (12 points) Consider the tree shown below. The numbers on the arcs are the arc lengths. Assume that the nodes are expanded in alphabetical
CS144: Intro to Computer Networks Homework 1 Scan and submit your solution online. Due Friday January 30, 4pm
 CS144: Intro to Computer Networks Homework 1 Scan and submit your solution online. Due Friday January 30, 2015 @ 4pm Your Name: Answers SUNet ID: root @stanford.edu Check if you would like exam routed
CS144: Intro to Computer Networks Homework 1 Scan and submit your solution online. Due Friday January 30, 2015 @ 4pm Your Name: Answers SUNet ID: root @stanford.edu Check if you would like exam routed
COS 471A,COS 471B/ELE 375 Midterm
 COS 471A,COS 471B/ELE 375 Midterm Prof: David August TAs : Jonathan Chang Junwen Lai Neil Vachharajani Fall 2004 Please write your answers clearly in the space provided. For partial credit, show all work.
COS 471A,COS 471B/ELE 375 Midterm Prof: David August TAs : Jonathan Chang Junwen Lai Neil Vachharajani Fall 2004 Please write your answers clearly in the space provided. For partial credit, show all work.
Homework #6 (Constraint Satisfaction, Non-Deterministic Uncertainty and Adversarial Search) Out: 2/21/11 Due: 2/29/11 (at noon)
 CS121 Introduction to Artificial Intelligence Winter 2011 Homework #6 (Constraint Satisfaction, Non-Deterministic Uncertainty and Adversarial Search) Out: 2/21/11 Due: 2/29/11 (at noon) How to complete
CS121 Introduction to Artificial Intelligence Winter 2011 Homework #6 (Constraint Satisfaction, Non-Deterministic Uncertainty and Adversarial Search) Out: 2/21/11 Due: 2/29/11 (at noon) How to complete
ˆ The exam is closed book, closed calculator, and closed notes except your one-page crib sheet.
 CS Summer Introduction to Artificial Intelligence Midterm ˆ You have approximately minutes. ˆ The exam is closed book, closed calculator, and closed notes except your one-page crib sheet. ˆ Mark your answers
CS Summer Introduction to Artificial Intelligence Midterm ˆ You have approximately minutes. ˆ The exam is closed book, closed calculator, and closed notes except your one-page crib sheet. ˆ Mark your answers
EECS 492 Midterm #1. Example Questions. Note: Not a complete exam!
 EECS 492 Midterm #1 Example Questions Note: Not a complete exam! General Instructions This exam is closed book, except that you are allowed to refer to a single sheet of paper. You may use a calculator
EECS 492 Midterm #1 Example Questions Note: Not a complete exam! General Instructions This exam is closed book, except that you are allowed to refer to a single sheet of paper. You may use a calculator
Computer Architecture CS372 Exam 3
 Name: Computer Architecture CS372 Exam 3 This exam has 7 pages. Please make sure you have all of them. Write your name on this page and initials on every other page now. You may only use the green card
Name: Computer Architecture CS372 Exam 3 This exam has 7 pages. Please make sure you have all of them. Write your name on this page and initials on every other page now. You may only use the green card
CS6303 Computer Architecture Regulation 2013 BE-Computer Science and Engineering III semester 2 MARKS
 CS6303 Computer Architecture Regulation 2013 BE-Computer Science and Engineering III semester 2 MARKS UNIT-I OVERVIEW & INSTRUCTIONS 1. What are the eight great ideas in computer architecture? The eight
CS6303 Computer Architecture Regulation 2013 BE-Computer Science and Engineering III semester 2 MARKS UNIT-I OVERVIEW & INSTRUCTIONS 1. What are the eight great ideas in computer architecture? The eight
The exam is closed book, closed calculator, and closed notes except your one-page crib sheet.
 CS Summer Introduction to Artificial Intelligence Midterm You have approximately minutes. The exam is closed book, closed calculator, and closed notes except your one-page crib sheet. Mark your answers
CS Summer Introduction to Artificial Intelligence Midterm You have approximately minutes. The exam is closed book, closed calculator, and closed notes except your one-page crib sheet. Mark your answers
ENGR 100 Midterm (CSE Part) Winter 2014
 ENGR 100 Midterm (CSE Part) Winter 2014 There are two parts in this midterm. This part focuses on the CSE aspects of the course. You will have 80 minutes to work on the exam. We recommend you spend about
ENGR 100 Midterm (CSE Part) Winter 2014 There are two parts in this midterm. This part focuses on the CSE aspects of the course. You will have 80 minutes to work on the exam. We recommend you spend about
Spring 2 Spring Loop Optimizations
 Spring 2010 Loop Optimizations Instruction Scheduling 5 Outline Scheduling for loops Loop unrolling Software pipelining Interaction with register allocation Hardware vs. Compiler Induction Variable Recognition
Spring 2010 Loop Optimizations Instruction Scheduling 5 Outline Scheduling for loops Loop unrolling Software pipelining Interaction with register allocation Hardware vs. Compiler Induction Variable Recognition
Math 52 Final Exam March 16, 2009
 Math 52 Final Exam March 16, 2009 Name : Section Leader: Josh Lan Xiannan (Circle one) Genauer Huang Li Section Time: 10:00 11:00 1:15 2:15 (Circle one) This is a closed-book, closed-notes exam. No calculators
Math 52 Final Exam March 16, 2009 Name : Section Leader: Josh Lan Xiannan (Circle one) Genauer Huang Li Section Time: 10:00 11:00 1:15 2:15 (Circle one) This is a closed-book, closed-notes exam. No calculators
CS140 Operating Systems and Systems Programming Final Exam
 CS140 Operating Systems and Systems Programming Final Exam December 12, 2005 Name: (please print) In recognition of and in the spirit of the Stanford University Honor Code, I certify that I will neither
CS140 Operating Systems and Systems Programming Final Exam December 12, 2005 Name: (please print) In recognition of and in the spirit of the Stanford University Honor Code, I certify that I will neither
CS143 Midterm Spring 2014
 CS143 Midterm Spring 2014 Please read all instructions (including these) carefully. There are 5 questions on the exam, most with multiple parts. You have 75 minutes to work on the exam. The exam is open
CS143 Midterm Spring 2014 Please read all instructions (including these) carefully. There are 5 questions on the exam, most with multiple parts. You have 75 minutes to work on the exam. The exam is open
1 Tree Search (12 points)
 1 Tree Search (12 points) Consider the tree shown below. The numbers on the arcs are the arc lengths. Assume that the nodes are expanded in alphabetical order when no other order is specified by the search,
1 Tree Search (12 points) Consider the tree shown below. The numbers on the arcs are the arc lengths. Assume that the nodes are expanded in alphabetical order when no other order is specified by the search,
What Compilers Can and Cannot Do. Saman Amarasinghe Fall 2009
 What Compilers Can and Cannot Do Saman Amarasinghe Fall 009 Optimization Continuum Many examples across the compilation pipeline Static Dynamic Program Compiler Linker Loader Runtime System Optimization
What Compilers Can and Cannot Do Saman Amarasinghe Fall 009 Optimization Continuum Many examples across the compilation pipeline Static Dynamic Program Compiler Linker Loader Runtime System Optimization
EXAM #1. CS 2410 Graduate Computer Architecture. Spring 2016, MW 11:00 AM 12:15 PM
 EXAM #1 CS 2410 Graduate Computer Architecture Spring 2016, MW 11:00 AM 12:15 PM Directions: This exam is closed book. Put all materials under your desk, including cell phones, smart phones, smart watches,
EXAM #1 CS 2410 Graduate Computer Architecture Spring 2016, MW 11:00 AM 12:15 PM Directions: This exam is closed book. Put all materials under your desk, including cell phones, smart phones, smart watches,
EECS 373 Midterm Winter 2013
 EECS 373 Midterm Winter 2013 Name: unique name: Sign the honor code: I have neither given nor received aid on this exam nor observed anyone else doing so. Scores: # Page Points 2 /15 3 /20 4 /12 5 /13
EECS 373 Midterm Winter 2013 Name: unique name: Sign the honor code: I have neither given nor received aid on this exam nor observed anyone else doing so. Scores: # Page Points 2 /15 3 /20 4 /12 5 /13
MATH 1075 Final Exam
 Autumn 2018 Form C Name: Signature: OSU name.#: Lecturer: Recitation Instructor: Recitation Time: MATH 1075 Final Exam Instructions: You will have 1 hour and 45 minutes to take the exam. Show ALL work
Autumn 2018 Form C Name: Signature: OSU name.#: Lecturer: Recitation Instructor: Recitation Time: MATH 1075 Final Exam Instructions: You will have 1 hour and 45 minutes to take the exam. Show ALL work
EXAM 1 SOLUTIONS. Midterm Exam. ECE 741 Advanced Computer Architecture, Spring Instructor: Onur Mutlu
 Midterm Exam ECE 741 Advanced Computer Architecture, Spring 2009 Instructor: Onur Mutlu TAs: Michael Papamichael, Theodoros Strigkos, Evangelos Vlachos February 25, 2009 EXAM 1 SOLUTIONS Problem Points
Midterm Exam ECE 741 Advanced Computer Architecture, Spring 2009 Instructor: Onur Mutlu TAs: Michael Papamichael, Theodoros Strigkos, Evangelos Vlachos February 25, 2009 EXAM 1 SOLUTIONS Problem Points
Fall Compiler Principles Lecture 12: Register Allocation. Roman Manevich Ben-Gurion University
 Fall 2014-2015 Compiler Principles Lecture 12: Register Allocation Roman Manevich Ben-Gurion University Syllabus Front End Intermediate Representation Optimizations Code Generation Scanning Lowering Local
Fall 2014-2015 Compiler Principles Lecture 12: Register Allocation Roman Manevich Ben-Gurion University Syllabus Front End Intermediate Representation Optimizations Code Generation Scanning Lowering Local
CS 2506 Computer Organization II Test 2
 Instructions: Print your name in the space provided below. This examination is closed book and closed notes, aside from the permitted one-page formula sheet. No calculators or other computing devices may
Instructions: Print your name in the space provided below. This examination is closed book and closed notes, aside from the permitted one-page formula sheet. No calculators or other computing devices may
Note that there are questions printed on both sides of each page!
 Math 1001 Name: Fall 2007 Test 1 Student ID: 10/5/07 Time allowed: 50 minutes Section: 10:10 11:15 12:20 This exam includes 7 pages, including this one and a sheet for scratch work. There are a total of
Math 1001 Name: Fall 2007 Test 1 Student ID: 10/5/07 Time allowed: 50 minutes Section: 10:10 11:15 12:20 This exam includes 7 pages, including this one and a sheet for scratch work. There are a total of
G Programming Languages - Fall 2012
 G22.2110-003 Programming Languages - Fall 2012 Lecture 3 Thomas Wies New York University Review Last week Names and Bindings Lifetimes and Allocation Garbage Collection Scope Outline Control Flow Sequencing
G22.2110-003 Programming Languages - Fall 2012 Lecture 3 Thomas Wies New York University Review Last week Names and Bindings Lifetimes and Allocation Garbage Collection Scope Outline Control Flow Sequencing
CS433 Midterm. Prof Josep Torrellas. October 16, Time: 1 hour + 15 minutes
 CS433 Midterm Prof Josep Torrellas October 16, 2014 Time: 1 hour + 15 minutes Name: Alias: Instructions: 1. This is a closed-book, closed-notes examination. 2. The Exam has 4 Questions. Please budget your
CS433 Midterm Prof Josep Torrellas October 16, 2014 Time: 1 hour + 15 minutes Name: Alias: Instructions: 1. This is a closed-book, closed-notes examination. 2. The Exam has 4 Questions. Please budget your
6.034 QUIZ 1. Fall 2002
 6.034 QUIZ Fall 2002 Name E-mail Problem Number Maximum Score Problem 30 Problem 2 30 Problem 3 0 Problem 4 30 Total 00 Problem : Rule-Based Book Recommendations (30 points) Part A: Forward chaining (5
6.034 QUIZ Fall 2002 Name E-mail Problem Number Maximum Score Problem 30 Problem 2 30 Problem 3 0 Problem 4 30 Total 00 Problem : Rule-Based Book Recommendations (30 points) Part A: Forward chaining (5
CS 5803 Introduction to High Performance Computer Architecture: Arithmetic Logic Unit. A.R. Hurson 323 CS Building, Missouri S&T
 CS 5803 Introduction to High Performance Computer Architecture: Arithmetic Logic Unit A.R. Hurson 323 CS Building, Missouri S&T hurson@mst.edu 1 Outline Motivation Design of a simple ALU How to design
CS 5803 Introduction to High Performance Computer Architecture: Arithmetic Logic Unit A.R. Hurson 323 CS Building, Missouri S&T hurson@mst.edu 1 Outline Motivation Design of a simple ALU How to design
Do not start the test until instructed to do so!
 Instructions: Print your name in the space provided below. This examination is closed book and closed notes, aside from the permitted one-page formula sheet. No calculators or other electronic devices
Instructions: Print your name in the space provided below. This examination is closed book and closed notes, aside from the permitted one-page formula sheet. No calculators or other electronic devices
4 Search Problem formulation (23 points)
 4 Search Problem formulation (23 points) Consider a Mars rover that has to drive around the surface, collect rock samples, and return to the lander. We want to construct a plan for its exploration. It
4 Search Problem formulation (23 points) Consider a Mars rover that has to drive around the surface, collect rock samples, and return to the lander. We want to construct a plan for its exploration. It
CS145 Midterm Examination
 CS145 Midterm Examination Autumn 2005, Prof. Widom Please read all instructions (including these) carefully. There are 8 problems on the exam, with a varying number of points for each problem and subproblem
CS145 Midterm Examination Autumn 2005, Prof. Widom Please read all instructions (including these) carefully. There are 8 problems on the exam, with a varying number of points for each problem and subproblem
CS-171, Intro to A.I. Mid-term Exam Winter Quarter, 2016
 CS-171, Intro to A.I. Mid-term Exam Winter Quarter, 016 YOUR NAME: YOUR ID: ID TO RIGHT: ROW: SEAT: The exam will begin on the next page. Please, do not turn the page until told. When you are told to begin
CS-171, Intro to A.I. Mid-term Exam Winter Quarter, 016 YOUR NAME: YOUR ID: ID TO RIGHT: ROW: SEAT: The exam will begin on the next page. Please, do not turn the page until told. When you are told to begin
Math 124 Final Examination Winter 2016 !!! READ...INSTRUCTIONS...READ!!!
 Math 124 Final Examination Winter 2016 Print Your Name Signature Student ID Number Quiz Section Professor s Name TA s Name!!! READ...INSTRUCTIONS...READ!!! 1. Your exam contains 7 problems and 9 pages;
Math 124 Final Examination Winter 2016 Print Your Name Signature Student ID Number Quiz Section Professor s Name TA s Name!!! READ...INSTRUCTIONS...READ!!! 1. Your exam contains 7 problems and 9 pages;
CS 2504 Intro Computer Organization Test 1
 Instructions: Print your name in the space provided below. This examination is closed book and closed notes, aside from the permitted one-page formula sheet and the MIPS reference card. No calculators
Instructions: Print your name in the space provided below. This examination is closed book and closed notes, aside from the permitted one-page formula sheet and the MIPS reference card. No calculators
CS3330 Fall 2014 Exam 2 Page 1 of 6 ID:
 S3330 Fall 2014 xam 2 Page 1 of 6 mail I: S3330 xam 2 Spring 2014 Name: irections: Put the letter of your selection or the short answer requested in the box. Write clearly: if we are unsure what you wrote
S3330 Fall 2014 xam 2 Page 1 of 6 mail I: S3330 xam 2 Spring 2014 Name: irections: Put the letter of your selection or the short answer requested in the box. Write clearly: if we are unsure what you wrote
MIT Spring 2011 Quiz 3
 MIT 6.035 Spring 2011 Quiz 3 Full Name: MIT ID: Athena ID: Run L A TEX again to produce the table 1. Consider a simple machine with one ALU and one memory unit. The machine can execute an ALU operation
MIT 6.035 Spring 2011 Quiz 3 Full Name: MIT ID: Athena ID: Run L A TEX again to produce the table 1. Consider a simple machine with one ALU and one memory unit. The machine can execute an ALU operation
CS 3330 Exam 2 Fall 2017 Computing ID:
 S 3330 Fall 2017 Exam 2 Variant page 1 of 8 Email I: S 3330 Exam 2 Fall 2017 Name: omputing I: Letters go in the boxes unless otherwise specified (e.g., for 8 write not 8 ). Write Letters clearly: if we
S 3330 Fall 2017 Exam 2 Variant page 1 of 8 Email I: S 3330 Exam 2 Fall 2017 Name: omputing I: Letters go in the boxes unless otherwise specified (e.g., for 8 write not 8 ). Write Letters clearly: if we
Code Generation. CS 540 George Mason University
 Code Generation CS 540 George Mason University Compiler Architecture Intermediate Language Intermediate Language Source language Scanner (lexical analysis) tokens Parser (syntax analysis) Syntactic structure
Code Generation CS 540 George Mason University Compiler Architecture Intermediate Language Intermediate Language Source language Scanner (lexical analysis) tokens Parser (syntax analysis) Syntactic structure
MCS-378 Intraterm Exam 1 Serial #:
 MCS-378 Intraterm Exam 1 Serial #: This exam is closed-book and mostly closed-notes. You may, however, use a single 8 1/2 by 11 sheet of paper with hand-written notes for reference. (Both sides of the
MCS-378 Intraterm Exam 1 Serial #: This exam is closed-book and mostly closed-notes. You may, however, use a single 8 1/2 by 11 sheet of paper with hand-written notes for reference. (Both sides of the
Compiler Architecture
 Code Generation 1 Compiler Architecture Source language Scanner (lexical analysis) Tokens Parser (syntax analysis) Syntactic structure Semantic Analysis (IC generator) Intermediate Language Code Optimizer
Code Generation 1 Compiler Architecture Source language Scanner (lexical analysis) Tokens Parser (syntax analysis) Syntactic structure Semantic Analysis (IC generator) Intermediate Language Code Optimizer
CS244 Advanced Topics in Computer Networks Midterm Exam Monday, May 2, 2016 OPEN BOOK, OPEN NOTES, INTERNET OFF
 CS244 Advanced Topics in Computer Networks Midterm Exam Monday, May 2, 2016 OPEN BOOK, OPEN NOTES, INTERNET OFF Your Name: Answers SUNet ID: root @stanford.edu In accordance with both the letter and the
CS244 Advanced Topics in Computer Networks Midterm Exam Monday, May 2, 2016 OPEN BOOK, OPEN NOTES, INTERNET OFF Your Name: Answers SUNet ID: root @stanford.edu In accordance with both the letter and the
CS140 Operating Systems and Systems Programming Final Exam
 CS140 Operating Systems and Systems Programming Final Exam March 19, 2008 Name: (please print) In recognition of and in the spirit of the Stanford University Honor Code, I certify that I will neither give
CS140 Operating Systems and Systems Programming Final Exam March 19, 2008 Name: (please print) In recognition of and in the spirit of the Stanford University Honor Code, I certify that I will neither give
CS 3114 Data Structures and Algorithms Test 1 READ THIS NOW!
 READ THIS NOW! Print your name in the space provided below. There are 7 short-answer questions, priced as marked. The maximum score is 100. This examination is closed book and closed notes, aside from
READ THIS NOW! Print your name in the space provided below. There are 7 short-answer questions, priced as marked. The maximum score is 100. This examination is closed book and closed notes, aside from
Binary Adders. Ripple-Carry Adder
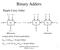 Ripple-Carry Adder Binary Adders x n y n x y x y c n FA c n - c 2 FA c FA c s n MSB position Longest delay (Critical-path delay): d c(n) = n d carry = 2n gate delays d s(n-) = (n-) d carry +d sum = 2n
Ripple-Carry Adder Binary Adders x n y n x y x y c n FA c n - c 2 FA c FA c s n MSB position Longest delay (Critical-path delay): d c(n) = n d carry = 2n gate delays d s(n-) = (n-) d carry +d sum = 2n
NAME: Problem Points Score. 7 (bonus) 15. Total
 Midterm Exam ECE 741 Advanced Computer Architecture, Spring 2009 Instructor: Onur Mutlu TAs: Michael Papamichael, Theodoros Strigkos, Evangelos Vlachos February 25, 2009 NAME: Problem Points Score 1 40
Midterm Exam ECE 741 Advanced Computer Architecture, Spring 2009 Instructor: Onur Mutlu TAs: Michael Papamichael, Theodoros Strigkos, Evangelos Vlachos February 25, 2009 NAME: Problem Points Score 1 40
CS 2506 Computer Organization II
 Instructions: Print your name in the space provided below. This examination is closed book and closed notes, aside from the permitted one-page formula sheet. No calculators or other computing devices may
Instructions: Print your name in the space provided below. This examination is closed book and closed notes, aside from the permitted one-page formula sheet. No calculators or other computing devices may
Updated Exercises by Diana Franklin
 C-82 Appendix C Pipelining: Basic and Intermediate Concepts Updated Exercises by Diana Franklin C.1 [15/15/15/15/25/10/15] Use the following code fragment: Loop: LD R1,0(R2) ;load R1 from address
C-82 Appendix C Pipelining: Basic and Intermediate Concepts Updated Exercises by Diana Franklin C.1 [15/15/15/15/25/10/15] Use the following code fragment: Loop: LD R1,0(R2) ;load R1 from address
COMPUTATIONAL PROPERIES OF DSP ALGORITHMS
 COMPUTATIONAL PROPERIES OF DSP ALGORITHMS 1 DSP Algorithms A DSP algorithm is a computational rule, f, that maps an ordered input sequence, x(nt), to an ordered output sequence, y(nt), according to xnt
COMPUTATIONAL PROPERIES OF DSP ALGORITHMS 1 DSP Algorithms A DSP algorithm is a computational rule, f, that maps an ordered input sequence, x(nt), to an ordered output sequence, y(nt), according to xnt
Flow Graph Theory. Depth-First Ordering Efficiency of Iterative Algorithms Reducible Flow Graphs
 Flow Graph Theory Depth-First Ordering Efficiency of Iterative Algorithms Reducible Flow Graphs 1 Roadmap Proper ordering of nodes of a flow graph speeds up the iterative algorithms: depth-first ordering.
Flow Graph Theory Depth-First Ordering Efficiency of Iterative Algorithms Reducible Flow Graphs 1 Roadmap Proper ordering of nodes of a flow graph speeds up the iterative algorithms: depth-first ordering.
CS 155 Final Exam. CS 155: Spring 2005 June 2005
 CS 155: Spring 2005 June 2005 CS 155 Final Exam This exam is open books and open notes, but you may not use a laptop. You have 2 hours. Make sure you print your name legibly and sign the honor code below.
CS 155: Spring 2005 June 2005 CS 155 Final Exam This exam is open books and open notes, but you may not use a laptop. You have 2 hours. Make sure you print your name legibly and sign the honor code below.
FAMILY NAME: (Print in ink) GIVEN NAME(S): (Print in ink) STUDENT NUMBER: SIGNATURE: (in ink) (I understand that cheating is a serious offense)
 TITLE PAGE FAMILY NAME: (Print in ink) GIVEN NAME(S): (Print in ink) STUDENT NUMBER: SIGNATURE: (in ink) (I understand that cheating is a serious offense) INSTRUCTIONS TO STUDENTS: This is a 2 hour exam.
TITLE PAGE FAMILY NAME: (Print in ink) GIVEN NAME(S): (Print in ink) STUDENT NUMBER: SIGNATURE: (in ink) (I understand that cheating is a serious offense) INSTRUCTIONS TO STUDENTS: This is a 2 hour exam.
To earn the extra credit, one of the following has to hold true. Please circle and sign.
 CS 188 Spring 2011 Introduction to Artificial Intelligence Practice Final Exam To earn the extra credit, one of the following has to hold true. Please circle and sign. A I spent 3 or more hours on the
CS 188 Spring 2011 Introduction to Artificial Intelligence Practice Final Exam To earn the extra credit, one of the following has to hold true. Please circle and sign. A I spent 3 or more hours on the
Spring 2017 CS 1110/1111 Exam 1
 CS 1110/1111 Spring 2017 Exam 1 page 1 of 6 Spring 2017 CS 1110/1111 Exam 1 Bubble in your computing ID in the footer of this page. We use an optical scanner to read it, so fill in the bubbles darkly.
CS 1110/1111 Spring 2017 Exam 1 page 1 of 6 Spring 2017 CS 1110/1111 Exam 1 Bubble in your computing ID in the footer of this page. We use an optical scanner to read it, so fill in the bubbles darkly.
EECS 470 Midterm Exam
 EECS 470 Midterm Exam Winter 2014 Name: unique name: Sign the honor code: I have neither given nor received aid on this exam nor observed anyone else doing so. Scores: NOTES: # Points Page 2 /12 Page 3
EECS 470 Midterm Exam Winter 2014 Name: unique name: Sign the honor code: I have neither given nor received aid on this exam nor observed anyone else doing so. Scores: NOTES: # Points Page 2 /12 Page 3
CS 140 Midterm Examination Winter Quarter, 2012
 CS 140 Midterm Examination Winter Quarter, 2012 You have 1.5 hours (90 minutes) for this examination; the number of points for each question indicates roughly how many minutes you should spend on that
CS 140 Midterm Examination Winter Quarter, 2012 You have 1.5 hours (90 minutes) for this examination; the number of points for each question indicates roughly how many minutes you should spend on that
CS 6353 Compiler Construction, Homework #3
 CS 6353 Compiler Construction, Homework #3 1. Consider the following attribute grammar for code generation regarding array references. (Note that the attribute grammar is the same as the one in the notes.
CS 6353 Compiler Construction, Homework #3 1. Consider the following attribute grammar for code generation regarding array references. (Note that the attribute grammar is the same as the one in the notes.
CSE 401 Final Exam. March 14, 2017 Happy π Day! (3/14) This exam is closed book, closed notes, closed electronics, closed neighbors, open mind,...
 CSE 401 Final Exam March 14, 2017 Happy π Day! (3/14) Name This exam is closed book, closed notes, closed electronics, closed neighbors, open mind,.... Please wait to turn the page until everyone has their
CSE 401 Final Exam March 14, 2017 Happy π Day! (3/14) Name This exam is closed book, closed notes, closed electronics, closed neighbors, open mind,.... Please wait to turn the page until everyone has their
University of California at Berkeley College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences. Spring 2010 May 10, 2010
 University of California at Berkeley College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences EECS150 J. Wawrzynek Spring 2010 May 10, 2010 Final Exam Name: ID number: This is
University of California at Berkeley College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences EECS150 J. Wawrzynek Spring 2010 May 10, 2010 Final Exam Name: ID number: This is
CS 2506 Computer Organization II
 Instructions: Print your name in the space provided below. This examination is closed book and closed notes, aside from the permitted one-page formula sheet. No calculators or other computing devices may
Instructions: Print your name in the space provided below. This examination is closed book and closed notes, aside from the permitted one-page formula sheet. No calculators or other computing devices may
Lecture 31: Building a Runnable Program
 The University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill Spring 2002 Lecture 31: Building a Runnable Program April 10 1 From Source Code to Executable Code program gcd(input, output); var i, j: integer; begin read(i,
The University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill Spring 2002 Lecture 31: Building a Runnable Program April 10 1 From Source Code to Executable Code program gcd(input, output); var i, j: integer; begin read(i,
TSEA 26 exam page 1 of Examination. Design of Embedded DSP Processors, TSEA26 Date 8-12, G34, G32, FOI hus G
 TSEA 26 exam page 1 of 10 20171019 Examination Design of Embedded DSP Processors, TSEA26 Date 8-12, 2017-10-19 Room G34, G32, FOI hus G Time 08-12AM Course code TSEA26 Exam code TEN1 Design of Embedded
TSEA 26 exam page 1 of 10 20171019 Examination Design of Embedded DSP Processors, TSEA26 Date 8-12, 2017-10-19 Room G34, G32, FOI hus G Time 08-12AM Course code TSEA26 Exam code TEN1 Design of Embedded
Supplement for MIPS (Section 4.14 of the textbook)
 Supplement for MIPS (Section 44 of the textbook) Section 44 does a good job emphasizing that MARIE is a toy architecture that lacks key feature of real-world computer architectures Most noticable, MARIE
Supplement for MIPS (Section 44 of the textbook) Section 44 does a good job emphasizing that MARIE is a toy architecture that lacks key feature of real-world computer architectures Most noticable, MARIE
CS 540: Introduction to Artificial Intelligence
 CS 540: Introduction to Artificial Intelligence Midterm Exam: 7:15-9:15 pm, October, 014 Room 140 CS Building CLOSED BOOK (one sheet of notes and a calculator allowed) Write your answers on these pages
CS 540: Introduction to Artificial Intelligence Midterm Exam: 7:15-9:15 pm, October, 014 Room 140 CS Building CLOSED BOOK (one sheet of notes and a calculator allowed) Write your answers on these pages
CSE331 Winter 2014, Midterm Examination February 12, 2014
 CSE331 Winter 2014, Midterm Examination February 12, 2014 Please do not turn the page until 10:30. Rules: The exam is closed-book, closed-note, etc. Please stop promptly at 11:20. There are 100 points
CSE331 Winter 2014, Midterm Examination February 12, 2014 Please do not turn the page until 10:30. Rules: The exam is closed-book, closed-note, etc. Please stop promptly at 11:20. There are 100 points
Stanford University Computer Science Department CS 295 midterm. May 14, (45 points) (30 points) total
 Stanford University Computer Science Department CS 295 midterm May 14, 2008 This is an open-book exam. You have 75 minutes. Write all of your answers directly on the paper. Make your answers as concise
Stanford University Computer Science Department CS 295 midterm May 14, 2008 This is an open-book exam. You have 75 minutes. Write all of your answers directly on the paper. Make your answers as concise
Instruction Scheduling
 Instruction Scheduling Michael O Boyle February, 2014 1 Course Structure Introduction and Recap Course Work Scalar optimisation and dataflow L5 Code generation L6 Instruction scheduling Next register allocation
Instruction Scheduling Michael O Boyle February, 2014 1 Course Structure Introduction and Recap Course Work Scalar optimisation and dataflow L5 Code generation L6 Instruction scheduling Next register allocation
You have 45 minutes to work on this exam. It is a "closed-book/closed-notes" test.
 NAME (as it appears on your UF ID): (Please PRINT) UF Student ID#: ----------------------------- CEN 5035 - Software Engineering --------------------------- Exam 3 Fall 2014 You have 45 minutes to work
NAME (as it appears on your UF ID): (Please PRINT) UF Student ID#: ----------------------------- CEN 5035 - Software Engineering --------------------------- Exam 3 Fall 2014 You have 45 minutes to work
CPSC 313, 04w Term 2 Midterm Exam 2 Solutions
 1. (10 marks) Short answers. CPSC 313, 04w Term 2 Midterm Exam 2 Solutions Date: March 11, 2005; Instructor: Mike Feeley 1a. Give an example of one important CISC feature that is normally not part of a
1. (10 marks) Short answers. CPSC 313, 04w Term 2 Midterm Exam 2 Solutions Date: March 11, 2005; Instructor: Mike Feeley 1a. Give an example of one important CISC feature that is normally not part of a
EECS 470 Midterm Exam
 EECS 470 Midterm Exam Fall 2009 Name: unique name: Sign the honor code: I have neither given nor received aid on this exam nor observed anyone else doing so. Scores: NOTES: # Points Page 2 /18 Page 3 /15
EECS 470 Midterm Exam Fall 2009 Name: unique name: Sign the honor code: I have neither given nor received aid on this exam nor observed anyone else doing so. Scores: NOTES: # Points Page 2 /18 Page 3 /15
CS 3114 Data Structures and Algorithms READ THIS NOW!
 READ THIS NOW! Print your name in the space provided below. There are 9 short-answer questions, priced as marked. The maximum score is 100. When you have finished, sign the pledge at the bottom of this
READ THIS NOW! Print your name in the space provided below. There are 9 short-answer questions, priced as marked. The maximum score is 100. When you have finished, sign the pledge at the bottom of this
CS4411 Intro. to Operating Systems Final Fall points 12 pages
 CS44 Intro. to Operating Systems Final Exam Fall 5 CS44 Intro. to Operating Systems Final Fall 5 points pages Name: Most of the following questions only require very short answers. Usually a few sentences
CS44 Intro. to Operating Systems Final Exam Fall 5 CS44 Intro. to Operating Systems Final Fall 5 points pages Name: Most of the following questions only require very short answers. Usually a few sentences
ECE 341 Midterm Exam
 ECE 341 Midterm Exam Time allowed: 75 minutes Total Points: 75 Points Scored: Name: Problem No. 1 (8 points) For each of the following statements, indicate whether the statement is TRUE or FALSE: (a) A
ECE 341 Midterm Exam Time allowed: 75 minutes Total Points: 75 Points Scored: Name: Problem No. 1 (8 points) For each of the following statements, indicate whether the statement is TRUE or FALSE: (a) A
Midterm II CS164, Spring 2006
 Midterm II CS164, Spring 2006 April 11, 2006 Please read all instructions (including these) carefully. Write your name, login, SID, and circle the section time. There are 10 pages in this exam and 4 questions,
Midterm II CS164, Spring 2006 April 11, 2006 Please read all instructions (including these) carefully. Write your name, login, SID, and circle the section time. There are 10 pages in this exam and 4 questions,
CS 351 Exam 2, Fall 2012
 CS 351 Exam 2, Fall 2012 Your name: Rules You may use one handwritten 8.5 x 11 cheat sheet (front and back). This is the only resource you may consult during this exam. Include explanations and comments
CS 351 Exam 2, Fall 2012 Your name: Rules You may use one handwritten 8.5 x 11 cheat sheet (front and back). This is the only resource you may consult during this exam. Include explanations and comments
The x-intercept can be found by setting y = 0 and solving for x: 16 3, 0
 y=-3/4x+4 and y=2 x I need to graph the functions so I can clearly describe the graphs Specifically mention any key points on the graphs, including intercepts, vertex, or start/end points. What is the
y=-3/4x+4 and y=2 x I need to graph the functions so I can clearly describe the graphs Specifically mention any key points on the graphs, including intercepts, vertex, or start/end points. What is the
EECS 470 Midterm Exam Winter 2009
 EECS 70 Midterm Exam Winter 2009 Name: unique name: Sign the honor code: I have neither given nor received aid on this exam nor observed anyone else doing so. Scores: # Points 1 / 18 2 / 12 3 / 29 / 21
EECS 70 Midterm Exam Winter 2009 Name: unique name: Sign the honor code: I have neither given nor received aid on this exam nor observed anyone else doing so. Scores: # Points 1 / 18 2 / 12 3 / 29 / 21
CS 1301 Exam 1 Fall 2010
 CS 1301 Exam 1 Fall 2010 Name : Grading TA: Integrity: By taking this exam, you pledge that this is your work and you have neither given nor received inappropriate help during the taking of this exam in
CS 1301 Exam 1 Fall 2010 Name : Grading TA: Integrity: By taking this exam, you pledge that this is your work and you have neither given nor received inappropriate help during the taking of this exam in
Cornell University Computer Science 211 Second Preliminary Examination 18 April 2006
 Cornell University Computer Science 211 Second Preliminary Examination 18 April 2006 There are 4 problems on this exam. It is 8 pages long, so make sure you have the whole exam. You will have 1 1 hours
Cornell University Computer Science 211 Second Preliminary Examination 18 April 2006 There are 4 problems on this exam. It is 8 pages long, so make sure you have the whole exam. You will have 1 1 hours
Fall 2011 PhD Qualifier Exam
 Computer Architecture Area Fall 2011 PhD Qualifier Exam November 18 th 2011 This exam has six (6) equally- weighted problems. You must submit your answers to all six problems. Write your answers/solutions
Computer Architecture Area Fall 2011 PhD Qualifier Exam November 18 th 2011 This exam has six (6) equally- weighted problems. You must submit your answers to all six problems. Write your answers/solutions
Final Exam. If you plan to solve a problem using a standard graph algorithm then you should clearly
 NAME: CS 241 Algorithms and Data Structures Spring Semester, 2003 Final Exam May 2, 2003 Do not spend too much time on any problem. The point value approximates the time I expect you to need for the problem.
NAME: CS 241 Algorithms and Data Structures Spring Semester, 2003 Final Exam May 2, 2003 Do not spend too much time on any problem. The point value approximates the time I expect you to need for the problem.
ECE 341 Final Exam Solution
 ECE 341 Final Exam Solution Time allowed: 110 minutes Total Points: 100 Points Scored: Name: Problem No. 1 (10 points) For each of the following statements, indicate whether the statement is TRUE or FALSE.
ECE 341 Final Exam Solution Time allowed: 110 minutes Total Points: 100 Points Scored: Name: Problem No. 1 (10 points) For each of the following statements, indicate whether the statement is TRUE or FALSE.
CS 5565 Final Exam. Name (printed)
 CS 5565 This is a closed-book, closed-internet, closed-cellphone and closed-computer exam. However, you may refer to your 2 sheets of prepared notes. Your exam should have 11 pages with 6 questions totaling
CS 5565 This is a closed-book, closed-internet, closed-cellphone and closed-computer exam. However, you may refer to your 2 sheets of prepared notes. Your exam should have 11 pages with 6 questions totaling
