FRIEND FUNCTIONS IN CPP
|
|
|
- Sharleen Poole
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 FRIEND FUNCTIONS IN CPP Friend Functions It is possible to grant a nonmember function access to the private members of a class by using a friend. A friend function has access to all private and protected members of the class for which it is a friend. To declare a friend function, include its prototype within the class, preceding it with the keyword friend. Consider this program: #include <iostream> using namespace std; class myclass int a, b; friend int sum(myclass x); void set_ab(int i, int j); ; void myclass::set_ab(int i, int j) a = i; b = j; // Note: sum() is not a member function of any class. int sum(myclass x) /* Because sum() is a friend of myclass, it can directly access a and b. */ return x.a + x.b; int main() myclass n; n.set_ab(3, 4); cout << sum(n);
2 return 0; In this example, the sum( ) function is not a member of myclass. However, it still has full access to its private members. Also, notice that sum( ) is called without the use of the dot operator. Because it is not a member function, it does not need to be (indeed, it may not be) qualified with an object's name. Although there is nothing gained by making sum( ) a friend rather than a member function of myclass, there are some circumstances in which friend functions are quite valuable. First, friends can be useful when you are overloading certain types of operators (see Chapter 14). Second, friend functions make the creation of some types of I/O functions easier (see Chapter 18). The third reason that friend functions may be desirable is that in some cases, two or more classes may contain members that are interrelated relative to other parts of your program. Let's examine this third usage now. To begin, imagine two different classes, each of which displays a pop-up message on the screen when error conditions occur. Other parts of your program may wish to know if a pop-up message is currently being displayed before writing to the screen so that no message is accidentally overwritten. Although you can create member functions in each class that return a value indicating whether a message is active, this means additional overhead when the condition is checked (that is, two function calls, not just one). If the condition needs to be checked frequently, this additional overhead may not be acceptable. However, using a function that is a friend of each class, it is possible to check the status of each object by calling only this one function. Thus, in situations like this, a friend function allows you to generate more efficient code. The following program illustrates this concept: #include <iostream> using namespace std; const int IDLE = 0; const int INUSE = 1; class C2; // forward declaration class C1
3 int status; // IDLE if off, INUSE if on screen friend int idle(c1 a, C2 b); ; class C2 int status; // IDLE if off, INUSE if on screen friend int idle(c1 a, C2 b); ; void C1::set_status(int state) void C2::set_status(int state) int idle(c1 a, C2 b) if(a.status b.status) return 0; else return 1; int main() C1 x; C2 y; x.set_status(idle);
4 y.set_status(idle); if(idle(x, y)) cout << "Screen can be used.\n"; x.set_status(inuse); if(idle(x, y)) cout << "Screen can be used.\n"; return 0; Notice that this program uses a forward declaration (also called a forward reference) for the class C2. This is necessary because the declaration of idle( ) inside C1 refers to C2 before it is declared. To create a forward declaration to a class, simply use the form shown in this program. A friend of one class may be a member of another. For example, here is the preceding program rewritten so that idle( ) is a member of C1: #include <iostream> using namespace std; const int IDLE = 0; const int INUSE = 1; class C2; // forward declaration class C1 int status; // IDLE if off, INUSE if on screen int idle(c2 b); // now a member of C1 ; class C2 int status; // IDLE if off, INUSE if on screen
5 friend int C1::idle(C2 b); ; void C1::set_status(int state) void C2::set_status(int state) // idle() is member of C1, but friend of C2 int C1::idle(C2 b) if(status b.status) return 0; else return 1; int main() C1 x; C2 y; x.set_status(idle); y.set_status(idle); if(x.idle(y)) cout << "Screen can be used.\n"; x.set_status(inuse); if(x.idle(y)) cout << "Screen can be used.\n"; return 0; Because idle( ) is a member of C1, it can access the status variable of objects of type C1 directly. Thus, only objects of type C2 need be passed to idle( ). There are two important
6 restrictions that apply to friend functions. First, a derived class does not inherit friend functions. Second, friend functions may not have a storage-class specifier. That is, they may not be declared as static or extern.
UNIT -1: Introduction to C++
 Object Oriented Programming in C++ 10CS36 UNIT -1: Introduction to C++ JUNE-JULY 2009 1a. Differentiate between procedure oriented and object oriented programming. (06 marks) Procedure oriented programming
Object Oriented Programming in C++ 10CS36 UNIT -1: Introduction to C++ JUNE-JULY 2009 1a. Differentiate between procedure oriented and object oriented programming. (06 marks) Procedure oriented programming
Overloading Operators in C++
 Overloading Operators in C++ C++ allows the programmer to redefine the function of most built-in operators on a class-by-class basis the operator keyword is used to declare a function that specifies what
Overloading Operators in C++ C++ allows the programmer to redefine the function of most built-in operators on a class-by-class basis the operator keyword is used to declare a function that specifies what
PIC 10A. Lecture 17: Classes III, overloading
 PIC 10A Lecture 17: Classes III, overloading Function overloading Having multiple constructors with same name is example of something called function overloading. You are allowed to have functions with
PIC 10A Lecture 17: Classes III, overloading Function overloading Having multiple constructors with same name is example of something called function overloading. You are allowed to have functions with
4. Structure of a C++ program
 4.1 Basic Structure 4. Structure of a C++ program The best way to learn a programming language is by writing programs. Typically, the first program beginners write is a program called "Hello World", which
4.1 Basic Structure 4. Structure of a C++ program The best way to learn a programming language is by writing programs. Typically, the first program beginners write is a program called "Hello World", which
Introduction Of Classes ( OOPS )
 Introduction Of Classes ( OOPS ) Classes (I) A class is an expanded concept of a data structure: instead of holding only data, it can hold both data and functions. An object is an instantiation of a class.
Introduction Of Classes ( OOPS ) Classes (I) A class is an expanded concept of a data structure: instead of holding only data, it can hold both data and functions. An object is an instantiation of a class.
Friends and Overloaded Operators
 Friend Function Friends and Overloaded Operators Class operations are typically implemented as member functions Some operations are better implemented as ordinary (nonmember) functions CSC 330 OO Software
Friend Function Friends and Overloaded Operators Class operations are typically implemented as member functions Some operations are better implemented as ordinary (nonmember) functions CSC 330 OO Software
Friends and Overloaded Operators
 Friends and Overloaded Operators Friend Function Class operations are typically implemented as member functions Some operations are better implemented as ordinary (nonmember) functions CSC 330 OO Software
Friends and Overloaded Operators Friend Function Class operations are typically implemented as member functions Some operations are better implemented as ordinary (nonmember) functions CSC 330 OO Software
Classes. Logical method to organise data and functions in a same structure. Also known as abstract data type (ADT).
 UNITII Classes Logical method to organise data and functions in a same structure. Also known as abstract data type (ADT). It s a User Defined Data-type. The Data declared in a Class are called Data- Members
UNITII Classes Logical method to organise data and functions in a same structure. Also known as abstract data type (ADT). It s a User Defined Data-type. The Data declared in a Class are called Data- Members
AN OVERVIEW OF C++ 1
 AN OVERVIEW OF C++ 1 OBJECTIVES Introduction What is object-oriented programming? Two versions of C++ C++ console I/O C++ comments Classes: A first look Some differences between C and C++ Introducing function
AN OVERVIEW OF C++ 1 OBJECTIVES Introduction What is object-oriented programming? Two versions of C++ C++ console I/O C++ comments Classes: A first look Some differences between C and C++ Introducing function
Abstract Data Types (ADTs) 1. Legal Values. Client Code for Rational ADT. ADT Design. CS 247: Software Engineering Principles
 Abstract Data Types (ADTs) CS 247: Software Engineering Principles ADT Design An abstract data type (ADT) is a user-defined type that bundles together: the range of values that variables of that type can
Abstract Data Types (ADTs) CS 247: Software Engineering Principles ADT Design An abstract data type (ADT) is a user-defined type that bundles together: the range of values that variables of that type can
CS 247: Software Engineering Principles. ADT Design
 CS 247: Software Engineering Principles ADT Design Readings: Eckel, Vol. 1 Ch. 7 Function Overloading & Default Arguments Ch. 12 Operator Overloading U Waterloo CS247 (Spring 2017) p.1/17 Abstract Data
CS 247: Software Engineering Principles ADT Design Readings: Eckel, Vol. 1 Ch. 7 Function Overloading & Default Arguments Ch. 12 Operator Overloading U Waterloo CS247 (Spring 2017) p.1/17 Abstract Data
Lecture 7. Log into Linux New documents posted to course webpage
 Lecture 7 Log into Linux New documents posted to course webpage Coding style guideline; part of project grade is following this Homework 4, due on Monday; this is a written assignment Project 1, due next
Lecture 7 Log into Linux New documents posted to course webpage Coding style guideline; part of project grade is following this Homework 4, due on Monday; this is a written assignment Project 1, due next
Object Oriented Design
 Object Oriented Design Lecture 3: Introduction to C++ (Continue) Examples using declarations that eliminate the need to repeat the std:: prefix 1 Examples using namespace std; enables a program to use
Object Oriented Design Lecture 3: Introduction to C++ (Continue) Examples using declarations that eliminate the need to repeat the std:: prefix 1 Examples using namespace std; enables a program to use
Basic memory model Using functions Writing functions. Basics Prototypes Parameters Return types Functions and memory Names and namespaces
 Basic memory model Using functions Writing functions Basics Prototypes Parameters Return types Functions and memory Names and namespaces When a program runs it requires main memory (RAM) space for Program
Basic memory model Using functions Writing functions Basics Prototypes Parameters Return types Functions and memory Names and namespaces When a program runs it requires main memory (RAM) space for Program
Short Notes of CS201
 #includes: Short Notes of CS201 The #include directive instructs the preprocessor to read and include a file into a source code file. The file name is typically enclosed with < and > if the file is a system
#includes: Short Notes of CS201 The #include directive instructs the preprocessor to read and include a file into a source code file. The file name is typically enclosed with < and > if the file is a system
G52CPP C++ Programming Lecture 13
 G52CPP C++ Programming Lecture 13 Dr Jason Atkin http://www.cs.nott.ac.uk/~jaa/cpp/ g52cpp.html 1 Last lecture Function pointers Arrays of function pointers Virtual and non-virtual functions vtable and
G52CPP C++ Programming Lecture 13 Dr Jason Atkin http://www.cs.nott.ac.uk/~jaa/cpp/ g52cpp.html 1 Last lecture Function pointers Arrays of function pointers Virtual and non-virtual functions vtable and
NAMESPACES IN C++ You can refer the Programming with ANSI C++ by Bhushan Trivedi for Understanding Namespaces Better(Chapter 14)
 NAMESPACES IN C++ You can refer the Programming with ANSI C++ by Bhushan Trivedi for Understanding Namespaces Better(Chapter 14) Some Material for your reference: Consider following C++ program. // A program
NAMESPACES IN C++ You can refer the Programming with ANSI C++ by Bhushan Trivedi for Understanding Namespaces Better(Chapter 14) Some Material for your reference: Consider following C++ program. // A program
C++ For Science and Engineering Lecture 15
 C++ For Science and Engineering Lecture 15 John Chrispell Tulane University Wednesday September 29, 2010 Function Review Recall the basics you already know about functions. Provide a function definition.
C++ For Science and Engineering Lecture 15 John Chrispell Tulane University Wednesday September 29, 2010 Function Review Recall the basics you already know about functions. Provide a function definition.
CS201 - Introduction to Programming Glossary By
 CS201 - Introduction to Programming Glossary By #include : The #include directive instructs the preprocessor to read and include a file into a source code file. The file name is typically enclosed with
CS201 - Introduction to Programming Glossary By #include : The #include directive instructs the preprocessor to read and include a file into a source code file. The file name is typically enclosed with
Recharge (int, int, int); //constructor declared void disply();
 Constructor and destructors in C++ Constructor Constructor is a special member function of the class which is invoked automatically when new object is created. The purpose of constructor is to initialize
Constructor and destructors in C++ Constructor Constructor is a special member function of the class which is invoked automatically when new object is created. The purpose of constructor is to initialize
III. Classes (Chap. 3)
 III. Classes III-1 III. Classes (Chap. 3) As we have seen, C++ data types can be classified as: Fundamental (or simple or scalar): A data object of one of these types is a single object. int, double, char,
III. Classes III-1 III. Classes (Chap. 3) As we have seen, C++ data types can be classified as: Fundamental (or simple or scalar): A data object of one of these types is a single object. int, double, char,
Time(int h, int m, int s) { hrs = h; mins = m; secs = s; } void set(int h, int m, int s) { hrs = h; mins = m; secs = s; }
 Inheritance The following class implements time in hh:mm::ss format: class { public: () { = 0; = 0; = 0; (int h, int m, int s) { = h; = m; = s; void set(int h, int m, int s) { = h; = m; = s; void tick()
Inheritance The following class implements time in hh:mm::ss format: class { public: () { = 0; = 0; = 0; (int h, int m, int s) { = h; = m; = s; void set(int h, int m, int s) { = h; = m; = s; void tick()
3.Constructors and Destructors. Develop cpp program to implement constructor and destructor.
 3.Constructors and Destructors Develop cpp program to implement constructor and destructor. Constructors A constructor is a special member function whose task is to initialize the objects of its class.
3.Constructors and Destructors Develop cpp program to implement constructor and destructor. Constructors A constructor is a special member function whose task is to initialize the objects of its class.
Object Oriented Design
 Object Oriented Design Chapter 6 Example Activity Diagram 1 Outline Chapter 6 Topics 6.6 C++ Standard Library Header Files 6.14 Inline Functions 6.16 Default Arguments 6.17 Unary Scope Resolution Operator
Object Oriented Design Chapter 6 Example Activity Diagram 1 Outline Chapter 6 Topics 6.6 C++ Standard Library Header Files 6.14 Inline Functions 6.16 Default Arguments 6.17 Unary Scope Resolution Operator
Friend Functions and Friend Classes
 Friend Functions and Friend Classes C++ allows you to declare another class to be a friend of the current class to make it easier to access variables. OOP purists have criticized this feature as weakening
Friend Functions and Friend Classes C++ allows you to declare another class to be a friend of the current class to make it easier to access variables. OOP purists have criticized this feature as weakening
VARIABLES & ASSIGNMENTS
 Fall 2018 CS150 - Intro to CS I 1 VARIABLES & ASSIGNMENTS Sections 2.1, 2.2, 2.3, 2.4 Fall 2018 CS150 - Intro to CS I 2 Variables Named storage location for holding data named piece of memory You need
Fall 2018 CS150 - Intro to CS I 1 VARIABLES & ASSIGNMENTS Sections 2.1, 2.2, 2.3, 2.4 Fall 2018 CS150 - Intro to CS I 2 Variables Named storage location for holding data named piece of memory You need
Use the dot operator to access a member of a specific object.
 Lab 16 Class A class is a data type that can contain several parts, which are called members. There are two types of members, data member and functions. An object is an instance of a class, and each object
Lab 16 Class A class is a data type that can contain several parts, which are called members. There are two types of members, data member and functions. An object is an instance of a class, and each object
mywbut.com Inheritance
 Inheritance 1 Inheritance is one of the cornerstones of OOP because it allows the creation of hierarchical classifications. Using inheritance, you can create a general class that defines traits common
Inheritance 1 Inheritance is one of the cornerstones of OOP because it allows the creation of hierarchical classifications. Using inheritance, you can create a general class that defines traits common
Paytm Programming Sample paper: 1) A copy constructor is called. a. when an object is returned by value
 Paytm Programming Sample paper: 1) A copy constructor is called a. when an object is returned by value b. when an object is passed by value as an argument c. when compiler generates a temporary object
Paytm Programming Sample paper: 1) A copy constructor is called a. when an object is returned by value b. when an object is passed by value as an argument c. when compiler generates a temporary object
Chapter 16. Templates. Copyright 2010 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved
 Chapter 16 Templates Copyright 2010 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved Learning Objectives Function Templates Syntax, defining Compiler complications Class Templates Syntax Example: array template
Chapter 16 Templates Copyright 2010 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved Learning Objectives Function Templates Syntax, defining Compiler complications Class Templates Syntax Example: array template
Object-Oriented Programming
 - oriented - iuliana@cs.ubbcluj.ro Babes-Bolyai University 2018 1 / 56 Overview - oriented 1 2 -oriented 3 4 5 6 7 8 Static and friend elements 9 Summary 2 / 56 I - oriented was initially created by Bjarne
- oriented - iuliana@cs.ubbcluj.ro Babes-Bolyai University 2018 1 / 56 Overview - oriented 1 2 -oriented 3 4 5 6 7 8 Static and friend elements 9 Summary 2 / 56 I - oriented was initially created by Bjarne
Recap: Pointers. int* int& *p &i &*&* ** * * * * IFMP 18, M. Schwerhoff
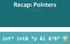 Recap: Pointers IFMP 18, M. Schwerhoff int* int& *p &i &*&* ** * * * * A 0 A 1 A 2 A 3 A 4 A 5 A 0 A 1 A 2 A 3 A 4 A 5 5 i int* p; A 0 A 1 A 2 A 3 A 4 A 5 5 i p int* p; p = &i; A 0 A 1 A 2 A 3 A 4 A 5
Recap: Pointers IFMP 18, M. Schwerhoff int* int& *p &i &*&* ** * * * * A 0 A 1 A 2 A 3 A 4 A 5 A 0 A 1 A 2 A 3 A 4 A 5 5 i int* p; A 0 A 1 A 2 A 3 A 4 A 5 5 i p int* p; p = &i; A 0 A 1 A 2 A 3 A 4 A 5
Modern C++ for Computer Vision and Image Processing. Igor Bogoslavskyi
 Modern C++ for Computer Vision and Image Processing Igor Bogoslavskyi Outline Move semantics Classes Operator overloading Making your class copyable Making your class movable Rule of all or nothing Inheritance
Modern C++ for Computer Vision and Image Processing Igor Bogoslavskyi Outline Move semantics Classes Operator overloading Making your class copyable Making your class movable Rule of all or nothing Inheritance
CSCE 110 PROGRAMMING FUNDAMENTALS
 CSCE 110 PROGRAMMING FUNDAMENTALS WITH C++ Prof. Amr Goneid AUC Part 15. Dictionaries (1): A Key Table Class Prof. amr Goneid, AUC 1 Dictionaries(1): A Key Table Class Prof. Amr Goneid, AUC 2 A Key Table
CSCE 110 PROGRAMMING FUNDAMENTALS WITH C++ Prof. Amr Goneid AUC Part 15. Dictionaries (1): A Key Table Class Prof. amr Goneid, AUC 1 Dictionaries(1): A Key Table Class Prof. Amr Goneid, AUC 2 A Key Table
Inheritance, and Polymorphism.
 Inheritance and Polymorphism by Yukong Zhang Object-oriented programming languages are the most widely used modern programming languages. They model programming based on objects which are very close to
Inheritance and Polymorphism by Yukong Zhang Object-oriented programming languages are the most widely used modern programming languages. They model programming based on objects which are very close to
Exceptions, Case Study-Exception handling in C++.
 PART III: Structuring of Computations- Structuring the computation, Expressions and statements, Conditional execution and iteration, Routines, Style issues: side effects and aliasing, Exceptions, Case
PART III: Structuring of Computations- Structuring the computation, Expressions and statements, Conditional execution and iteration, Routines, Style issues: side effects and aliasing, Exceptions, Case
Chapter 9: Pointers Co C pyr py igh i t gh Pear ea so s n n E ducat ca io i n, n Inc. n c.
 Chapter 9: Pointers 9.1 Getting the Address of a Variable C++ Variables [ not in book ] A Variable has all of the following attributes: 1. name 2. type 3. size 4. value 5. storage class static or automatic
Chapter 9: Pointers 9.1 Getting the Address of a Variable C++ Variables [ not in book ] A Variable has all of the following attributes: 1. name 2. type 3. size 4. value 5. storage class static or automatic
Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) Fundamental Principles of OOP
 Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) O b j e c t O r i e n t e d P r o g r a m m i n g 1 Object-oriented programming is the successor of procedural programming. The problem with procedural programming is
Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) O b j e c t O r i e n t e d P r o g r a m m i n g 1 Object-oriented programming is the successor of procedural programming. The problem with procedural programming is
COSC 320 Exam 2 Key Spring Part 1: Hash Functions
 COSC 320 Exam 2 Key Spring 2011 Part 1: Hash s 1. (5 Points) Create the templated function object lessthan, you may assume that the templated data type T has overloaded the < operator. template
COSC 320 Exam 2 Key Spring 2011 Part 1: Hash s 1. (5 Points) Create the templated function object lessthan, you may assume that the templated data type T has overloaded the < operator. template
Module Operator Overloading and Type Conversion. Table of Contents
 1 Module - 33 Operator Overloading and Type Conversion Table of Contents 1. Introduction 2. Operator Overloading 3. this pointer 4. Overloading Unary Operators 5. Overloading Binary Operators 6. Overloading
1 Module - 33 Operator Overloading and Type Conversion Table of Contents 1. Introduction 2. Operator Overloading 3. this pointer 4. Overloading Unary Operators 5. Overloading Binary Operators 6. Overloading
CSCE Practice Midterm. Data Types
 CSCE 2004 - Practice Midterm This midterm exam was given in class several years ago. Work each of the following questions on your own. Once you are done, check your answers. For any questions whose answers
CSCE 2004 - Practice Midterm This midterm exam was given in class several years ago. Work each of the following questions on your own. Once you are done, check your answers. For any questions whose answers
CSE 374 Programming Concepts & Tools. Hal Perkins Spring 2010
 CSE 374 Programming Concepts & Tools Hal Perkins Spring 2010 Lecture 19 Introduction ti to C++ C++ C++ is an enormous language: g All of C Classes and objects (kind of like Java, some crucial differences)
CSE 374 Programming Concepts & Tools Hal Perkins Spring 2010 Lecture 19 Introduction ti to C++ C++ C++ is an enormous language: g All of C Classes and objects (kind of like Java, some crucial differences)
University of Technology. Laser & Optoelectronics Engineering Department. C++ Lab.
 University of Technology Laser & Optoelectronics Engineering Department C++ Lab. Fifth week Control Structures A program is usually not limited to a linear sequence of instructions. During its process
University of Technology Laser & Optoelectronics Engineering Department C++ Lab. Fifth week Control Structures A program is usually not limited to a linear sequence of instructions. During its process
G52CPP C++ Programming Lecture 14. Dr Jason Atkin
 G52CPP C++ Programming Lecture 14 Dr Jason Atkin 1 Last Lecture Automatically created methods: A default constructor so that objects can be created without defining a constructor A copy constructor used
G52CPP C++ Programming Lecture 14 Dr Jason Atkin 1 Last Lecture Automatically created methods: A default constructor so that objects can be created without defining a constructor A copy constructor used
System Design and Programming II
 System Design and Programming II CSCI 194 Section 01 CRN: 20220 Spring 2016 David L. Sylvester, Sr., Assistant Professor Chapter 15 Inheritance, Polymorphism, And Virtual Functions What is Inheritance?
System Design and Programming II CSCI 194 Section 01 CRN: 20220 Spring 2016 David L. Sylvester, Sr., Assistant Professor Chapter 15 Inheritance, Polymorphism, And Virtual Functions What is Inheritance?
Distributed Real-Time Control Systems. Lecture 14 Intro to C++ Part III
 Distributed Real-Time Control Systems Lecture 14 Intro to C++ Part III 1 Class Hierarchies The human brain is very efficient in finding common properties to different entities and classify them according
Distributed Real-Time Control Systems Lecture 14 Intro to C++ Part III 1 Class Hierarchies The human brain is very efficient in finding common properties to different entities and classify them according
Exercises with Linked Lists CS 16: Solving Problems with Computers I Lecture #15
 Exercises with Linked Lists CS 16: Solving Problems with Computers I Lecture #15 Ziad Matni Dept. of Computer Science, UCSB The head of a List The box labeled head, in Display 13.1, is not a node, but
Exercises with Linked Lists CS 16: Solving Problems with Computers I Lecture #15 Ziad Matni Dept. of Computer Science, UCSB The head of a List The box labeled head, in Display 13.1, is not a node, but
CE221 Programming in C++ Part 2 References and Pointers, Arrays and Strings
 CE221 Programming in C++ Part 2 References and Pointers, Arrays and Strings 19/10/2017 CE221 Part 2 1 Variables and References 1 In Java a variable of primitive type is associated with a memory location
CE221 Programming in C++ Part 2 References and Pointers, Arrays and Strings 19/10/2017 CE221 Part 2 1 Variables and References 1 In Java a variable of primitive type is associated with a memory location
Ch 8. Operator Overloading, Friends, and References
 2014-1 Ch 8. Operator Overloading, Friends, and References May 28, 2014 Advanced Networking Technology Lab. (YU-ANTL) Dept. of Information & Comm. Eng, Graduate School, Yeungnam University, KOREA (Tel
2014-1 Ch 8. Operator Overloading, Friends, and References May 28, 2014 Advanced Networking Technology Lab. (YU-ANTL) Dept. of Information & Comm. Eng, Graduate School, Yeungnam University, KOREA (Tel
CMSC 202 Midterm Exam 1 Fall 2015
 1. (15 points) There are six logic or syntax errors in the following program; find five of them. Circle each of the five errors you find and write the line number and correction in the space provided below.
1. (15 points) There are six logic or syntax errors in the following program; find five of them. Circle each of the five errors you find and write the line number and correction in the space provided below.
University of Technology. Laser & Optoelectronics Engineering Department. C++ Lab.
 University of Technology Laser & Optoelectronics Engineering Department C++ Lab. Second week Variables Data Types. The usefulness of the "Hello World" programs shown in the previous section is quite questionable.
University of Technology Laser & Optoelectronics Engineering Department C++ Lab. Second week Variables Data Types. The usefulness of the "Hello World" programs shown in the previous section is quite questionable.
Chapter 15 - C++ As A "Better C"
 Chapter 15 - C++ As A "Better C" Outline 15.1 Introduction 15.2 C++ 15.3 A Simple Program: Adding Two Integers 15.4 C++ Standard Library 15.5 Header Files 15.6 Inline Functions 15.7 References and Reference
Chapter 15 - C++ As A "Better C" Outline 15.1 Introduction 15.2 C++ 15.3 A Simple Program: Adding Two Integers 15.4 C++ Standard Library 15.5 Header Files 15.6 Inline Functions 15.7 References and Reference
Reference Parameters A reference parameter is an alias for its corresponding argument in the function call. Use the ampersand (&) to indicate that
 Reference Parameters There are two ways to pass arguments to functions: pass-by-value and pass-by-reference. pass-by-value A copy of the argument s value is made and passed to the called function. Changes
Reference Parameters There are two ways to pass arguments to functions: pass-by-value and pass-by-reference. pass-by-value A copy of the argument s value is made and passed to the called function. Changes
Introduction to C++ Systems Programming
 Introduction to C++ Systems Programming Introduction to C++ Syntax differences between C and C++ A Simple C++ Example C++ Input/Output C++ Libraries C++ Header Files Another Simple C++ Example Inline Functions
Introduction to C++ Systems Programming Introduction to C++ Syntax differences between C and C++ A Simple C++ Example C++ Input/Output C++ Libraries C++ Header Files Another Simple C++ Example Inline Functions
CSCE 206: Structured Programming in C++
 CSCE 206: Structured Programming in C++ 2017 Spring Exam 2 Monday, March 20, 2017 Total - 100 Points B Instructions: Total of 13 pages, including this cover and the last page. Before starting the exam,
CSCE 206: Structured Programming in C++ 2017 Spring Exam 2 Monday, March 20, 2017 Total - 100 Points B Instructions: Total of 13 pages, including this cover and the last page. Before starting the exam,
Fast Introduction to Object Oriented Programming and C++
 Fast Introduction to Object Oriented Programming and C++ Daniel G. Aliaga Note: a compilation of slides from Jacques de Wet, Ohio State University, Chad Willwerth, and Daniel Aliaga. Outline Programming
Fast Introduction to Object Oriented Programming and C++ Daniel G. Aliaga Note: a compilation of slides from Jacques de Wet, Ohio State University, Chad Willwerth, and Daniel Aliaga. Outline Programming
Programming Fundamentals. With C++ Variable Declaration, Evaluation and Assignment 1
 300580 Programming Fundamentals 3 With C++ Variable Declaration, Evaluation and Assignment 1 Today s Topics Variable declaration Assignment to variables Typecasting Counting Mathematical functions Keyboard
300580 Programming Fundamentals 3 With C++ Variable Declaration, Evaluation and Assignment 1 Today s Topics Variable declaration Assignment to variables Typecasting Counting Mathematical functions Keyboard
C++ Basics. Data Processing Course, I. Hrivnacova, IPN Orsay
 C++ Basics Data Processing Course, I. Hrivnacova, IPN Orsay The First Program Comments Function main() Input and Output Namespaces Variables Fundamental Types Operators Control constructs 1 C++ Programming
C++ Basics Data Processing Course, I. Hrivnacova, IPN Orsay The First Program Comments Function main() Input and Output Namespaces Variables Fundamental Types Operators Control constructs 1 C++ Programming
A506 / C201 Computer Programming II Placement Exam Sample Questions. For each of the following, choose the most appropriate answer (2pts each).
 A506 / C201 Computer Programming II Placement Exam Sample Questions For each of the following, choose the most appropriate answer (2pts each). 1. Which of the following functions is causing a temporary
A506 / C201 Computer Programming II Placement Exam Sample Questions For each of the following, choose the most appropriate answer (2pts each). 1. Which of the following functions is causing a temporary
Object Oriented Design Final Exam (From 3:30 pm to 4:45 pm) Name:
 Object Oriented Design Final Exam (From 3:30 pm to 4:45 pm) Name: Section 1 Multiple Choice Questions (40 pts total, 2 pts each): Q1: Employee is a base class and HourlyWorker is a derived class, with
Object Oriented Design Final Exam (From 3:30 pm to 4:45 pm) Name: Section 1 Multiple Choice Questions (40 pts total, 2 pts each): Q1: Employee is a base class and HourlyWorker is a derived class, with
pointers + memory double x; string a; int x; main overhead int y; main overhead
 pointers + memory computer have memory to store data. every program gets a piece of it to use as we create and use more variables, more space is allocated to a program memory int x; double x; string a;
pointers + memory computer have memory to store data. every program gets a piece of it to use as we create and use more variables, more space is allocated to a program memory int x; double x; string a;
The American University in Cairo Department of Computer Science & Engineering CSCI &09 Dr. KHALIL Exam-I Fall 2011
 The American University in Cairo Department of Computer Science & Engineering CSCI 106-07&09 Dr. KHALIL Exam-I Fall 2011 Last Name :... ID:... First Name:... Form I Section No.: EXAMINATION INSTRUCTIONS
The American University in Cairo Department of Computer Science & Engineering CSCI 106-07&09 Dr. KHALIL Exam-I Fall 2011 Last Name :... ID:... First Name:... Form I Section No.: EXAMINATION INSTRUCTIONS
Review Questions for Final Exam
 CS 102 / ECE 206 Spring 11 Review Questions for Final Exam The following review questions are similar to the kinds of questions you will be expected to answer on the Final Exam, which will cover LCR, chs.
CS 102 / ECE 206 Spring 11 Review Questions for Final Exam The following review questions are similar to the kinds of questions you will be expected to answer on the Final Exam, which will cover LCR, chs.
Constructor - example
 Constructors A constructor is a special member function whose task is to initialize the objects of its class. It is special because its name is same as the class name. The constructor is invoked whenever
Constructors A constructor is a special member function whose task is to initialize the objects of its class. It is special because its name is same as the class name. The constructor is invoked whenever
Name Section: M/W or T/TH. True or False (14 Points)
 Name Section: M/W or T/TH True or False (14 Points) 1. (14 pts) Circle T for true and F for false: T F a) In C++, a function definition should not be nested within another function definition. T F b) Static
Name Section: M/W or T/TH True or False (14 Points) 1. (14 pts) Circle T for true and F for false: T F a) In C++, a function definition should not be nested within another function definition. T F b) Static
1. (25 pts) Short Answer. Provide brief (1-3 sentence) answers to the following:
 CSCE A211 Sample Midterm 2 Name: 1. (25 pts) Short Answer. Provide brief (1-3 sentence) answers to the following: a) When defining a class, why is it considered a good practice to declare class variable
CSCE A211 Sample Midterm 2 Name: 1. (25 pts) Short Answer. Provide brief (1-3 sentence) answers to the following: a) When defining a class, why is it considered a good practice to declare class variable
Object-Oriented Programming in C++
 Object-Oriented Programming in C++ Pre-Lecture 9: Advanced topics Prof Niels Walet (Niels.Walet@manchester.ac.uk) Room 7.07, Schuster Building March 24, 2015 Prelecture 9 Outline This prelecture largely
Object-Oriented Programming in C++ Pre-Lecture 9: Advanced topics Prof Niels Walet (Niels.Walet@manchester.ac.uk) Room 7.07, Schuster Building March 24, 2015 Prelecture 9 Outline This prelecture largely
C++_ MARKS 40 MIN
 C++_16.9.2018 40 MARKS 40 MIN https://tinyurl.com/ya62ayzs 1) Declaration of a pointer more than once may cause A. Error B. Abort C. Trap D. Null 2Whice is not a correct variable type in C++? A. float
C++_16.9.2018 40 MARKS 40 MIN https://tinyurl.com/ya62ayzs 1) Declaration of a pointer more than once may cause A. Error B. Abort C. Trap D. Null 2Whice is not a correct variable type in C++? A. float
Lecture 23: Pointer Arithmetic
 Lecture 23: Pointer Arithmetic Wai L. Khoo Department of Computer Science City College of New York November 29, 2011 Wai L. Khoo (CS@CCNY) Lecture 23 November 29, 2011 1 / 14 Pointer Arithmetic Pointer
Lecture 23: Pointer Arithmetic Wai L. Khoo Department of Computer Science City College of New York November 29, 2011 Wai L. Khoo (CS@CCNY) Lecture 23 November 29, 2011 1 / 14 Pointer Arithmetic Pointer
CSE 374 Programming Concepts & Tools. Hal Perkins Fall 2015 Lecture 19 Introduction to C++
 CSE 374 Programming Concepts & Tools Hal Perkins Fall 2015 Lecture 19 Introduction to C++ C++ C++ is an enormous language: All of C Classes and objects (kind of like Java, some crucial differences) Many
CSE 374 Programming Concepts & Tools Hal Perkins Fall 2015 Lecture 19 Introduction to C++ C++ C++ is an enormous language: All of C Classes and objects (kind of like Java, some crucial differences) Many
CAAM 420 Fall 2012 Lecture 29. Duncan Eddy
 CAAM 420 Fall 2012 Lecture 29 Duncan Eddy November 7, 2012 Table of Contents 1 Templating in C++ 3 1.1 Motivation.............................................. 3 1.2 Templating Functions........................................
CAAM 420 Fall 2012 Lecture 29 Duncan Eddy November 7, 2012 Table of Contents 1 Templating in C++ 3 1.1 Motivation.............................................. 3 1.2 Templating Functions........................................
(5-1) Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) and C++ Instructor - Andrew S. O Fallon CptS 122 (February 4, 2019) Washington State University
 (5-1) Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) and C++ Instructor - Andrew S. O Fallon CptS 122 (February 4, 2019) Washington State University Key Concepts 2 Object-Oriented Design Object-Oriented Programming
(5-1) Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) and C++ Instructor - Andrew S. O Fallon CptS 122 (February 4, 2019) Washington State University Key Concepts 2 Object-Oriented Design Object-Oriented Programming
OBJECT ORIENTED PROGRAMMING USING C++
 OBJECT ORIENTED PROGRAMMING USING C++ 1 Slide 2 Chapter 9 Separate Compilation and Namespaces Created by David Mann, North Idaho College Slide 3 Overview Separate Compilation (9.1) Namespaces (9.2) Slide
OBJECT ORIENTED PROGRAMMING USING C++ 1 Slide 2 Chapter 9 Separate Compilation and Namespaces Created by David Mann, North Idaho College Slide 3 Overview Separate Compilation (9.1) Namespaces (9.2) Slide
Data Structures using OOP C++ Lecture 3
 References: th 1. E Balagurusamy, Object Oriented Programming with C++, 4 edition, McGraw-Hill 2008. 2. Robert L. Kruse and Alexander J. Ryba, Data Structures and Program Design in C++, Prentice-Hall 2000.
References: th 1. E Balagurusamy, Object Oriented Programming with C++, 4 edition, McGraw-Hill 2008. 2. Robert L. Kruse and Alexander J. Ryba, Data Structures and Program Design in C++, Prentice-Hall 2000.
CSE 303: Concepts and Tools for Software Development
 CSE 303: Concepts and Tools for Software Development Hal Perkins Autumn 2008 Lecture 24 Introduction to C++ CSE303 Autumn 2008, Lecture 24 1 C++ C++ is an enormous language: All of C Classes and objects
CSE 303: Concepts and Tools for Software Development Hal Perkins Autumn 2008 Lecture 24 Introduction to C++ CSE303 Autumn 2008, Lecture 24 1 C++ C++ is an enormous language: All of C Classes and objects
Due Date: See Blackboard
 Source File: ~/2315/45/lab45.(C CPP cpp c++ cc cxx cp) Input: under control of main function Output: under control of main function Value: 4 Integer data is usually represented in a single word on a computer.
Source File: ~/2315/45/lab45.(C CPP cpp c++ cc cxx cp) Input: under control of main function Output: under control of main function Value: 4 Integer data is usually represented in a single word on a computer.
Functions, Arrays & Structs
 Functions, Arrays & Structs Unit 1 Chapters 6-7, 11 Function Definitions! Function definition pattern: datatype identifier (parameter1, parameter2,...) { statements... Where a parameter is: datatype identifier
Functions, Arrays & Structs Unit 1 Chapters 6-7, 11 Function Definitions! Function definition pattern: datatype identifier (parameter1, parameter2,...) { statements... Where a parameter is: datatype identifier
Fundamentals of Programming. Lecture 19 Hamed Rasifard
 Fundamentals of Programming Lecture 19 Hamed Rasifard 1 Outline C++ Object-Oriented Programming Class 2 C++ C++ began as an expanded version of C. C++ improves on many of C s features and provides object-oriented-programming
Fundamentals of Programming Lecture 19 Hamed Rasifard 1 Outline C++ Object-Oriented Programming Class 2 C++ C++ began as an expanded version of C. C++ improves on many of C s features and provides object-oriented-programming
moretosearch = (location < length);
 Chapter 3(6th edition): Exercises 1,2,3,9,10,11,12,18-28 (due: 25/10/2017) Solution: 1. (a) Boolean IsThere(ItemType item) Function: Determines if item is in the list. Precondition: List has been initialized.
Chapter 3(6th edition): Exercises 1,2,3,9,10,11,12,18-28 (due: 25/10/2017) Solution: 1. (a) Boolean IsThere(ItemType item) Function: Determines if item is in the list. Precondition: List has been initialized.
Sample Final Exam. 1) (24 points) Show what is printed by the following segments of code (assume all appropriate header files, etc.
 Name: Sample Final Exam 1) (24 points) Show what is printed by the following segments of code (assume all appropriate header files, etc. are included): a) int start = 10, end = 21; while (start < end &&
Name: Sample Final Exam 1) (24 points) Show what is printed by the following segments of code (assume all appropriate header files, etc. are included): a) int start = 10, end = 21; while (start < end &&
W3101: Programming Languages C++ Ramana Isukapalli
 Lecture-6 Operator overloading Namespaces Standard template library vector List Map Set Casting in C++ Operator Overloading Operator overloading On two objects of the same class, can we perform typical
Lecture-6 Operator overloading Namespaces Standard template library vector List Map Set Casting in C++ Operator Overloading Operator overloading On two objects of the same class, can we perform typical
Linked List using a Sentinel
 Linked List using a Sentinel Linked List.h / Linked List.h Using a sentinel for search Created by Enoch Hwang on 2/1/10. Copyright 2010 La Sierra University. All rights reserved. / #include
Linked List using a Sentinel Linked List.h / Linked List.h Using a sentinel for search Created by Enoch Hwang on 2/1/10. Copyright 2010 La Sierra University. All rights reserved. / #include
Chapter 8. Operator Overloading, Friends, and References. Copyright 2010 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved
 Chapter 8 Operator Overloading, Friends, and References Copyright 2010 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved Learning Objectives Basic Operator Overloading Unary operators As member functions Friends
Chapter 8 Operator Overloading, Friends, and References Copyright 2010 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved Learning Objectives Basic Operator Overloading Unary operators As member functions Friends
Wentworth Institute of Technology COMP201 Computer Science II Spring 2015 Derbinsky. C++ Kitchen Sink. Lecture 14.
 Lecture 14 1 Exceptions Iterators Random numbers Casting Enumerations Pairs The Big Three Outline 2 Error Handling It is often easier to write a program by first assuming that nothing incorrect will happen
Lecture 14 1 Exceptions Iterators Random numbers Casting Enumerations Pairs The Big Three Outline 2 Error Handling It is often easier to write a program by first assuming that nothing incorrect will happen
STUDY NOTES UNIT 1 - INTRODUCTION TO OBJECT ORIENTED PROGRAMMING
 OBJECT ORIENTED PROGRAMMING STUDY NOTES UNIT 1 - INTRODUCTION TO OBJECT ORIENTED PROGRAMMING 1. Object Oriented Programming Paradigms 2. Comparison of Programming Paradigms 3. Basic Object Oriented Programming
OBJECT ORIENTED PROGRAMMING STUDY NOTES UNIT 1 - INTRODUCTION TO OBJECT ORIENTED PROGRAMMING 1. Object Oriented Programming Paradigms 2. Comparison of Programming Paradigms 3. Basic Object Oriented Programming
Implementing Abstract Data Types (ADT) using Classes
 Implementing Abstract Data Types (ADT) using Classes Class Definition class classname { public: //public member functions private: //private data members and member functions }; // Note the semicolon!
Implementing Abstract Data Types (ADT) using Classes Class Definition class classname { public: //public member functions private: //private data members and member functions }; // Note the semicolon!
VIRTUAL FUNCTIONS Chapter 10
 1 VIRTUAL FUNCTIONS Chapter 10 OBJECTIVES Polymorphism in C++ Pointers to derived classes Important point on inheritance Introduction to virtual functions Virtual destructors More about virtual functions
1 VIRTUAL FUNCTIONS Chapter 10 OBJECTIVES Polymorphism in C++ Pointers to derived classes Important point on inheritance Introduction to virtual functions Virtual destructors More about virtual functions
AP Computer Science Chapter 10 Implementing and Using Classes Study Guide
 AP Computer Science Chapter 10 Implementing and Using Classes Study Guide 1. A class that uses a given class X is called a client of X. 2. Private features of a class can be directly accessed only within
AP Computer Science Chapter 10 Implementing and Using Classes Study Guide 1. A class that uses a given class X is called a client of X. 2. Private features of a class can be directly accessed only within
Note 12/1/ Review of Inheritance Practice: Please write down 10 most important facts you know about inheritance...
 CISC 2000 Computer Science II Fall, 2014 Note 12/1/2014 1 Review of Inheritance Practice: Please write down 10 most important facts you know about inheritance... (a) What s the purpose of inheritance?
CISC 2000 Computer Science II Fall, 2014 Note 12/1/2014 1 Review of Inheritance Practice: Please write down 10 most important facts you know about inheritance... (a) What s the purpose of inheritance?
Week 4 EECS 183 MAXIM ALEKSA. maximal.io
 Week 4 EECS 183 MAXIM ALEKSA maximal.io Agenda Functions Scope Conditions Boolean Expressions Lab 2 Project 2 Q&A Lectures 15% 36% 19% 8:30am 10:00am with Bill Arthur 10:00am 11:30am with Mary Lou Dorf
Week 4 EECS 183 MAXIM ALEKSA maximal.io Agenda Functions Scope Conditions Boolean Expressions Lab 2 Project 2 Q&A Lectures 15% 36% 19% 8:30am 10:00am with Bill Arthur 10:00am 11:30am with Mary Lou Dorf
Object Oriented Programming. Assistant Lecture Omar Al Khayat 2 nd Year
 Object Oriented Programming Assistant Lecture Omar Al Khayat 2 nd Year Syllabus Overview of C++ Program Principles of object oriented programming including classes Introduction to Object-Oriented Paradigm:Structures
Object Oriented Programming Assistant Lecture Omar Al Khayat 2 nd Year Syllabus Overview of C++ Program Principles of object oriented programming including classes Introduction to Object-Oriented Paradigm:Structures
The American University in Cairo Department of Computer Science & Engineeringt CSCI &09 Dr. KHALIL Exam-I Fall 2009
 The American University in Cairo Department of Computer Science & Engineeringt CSCI 106-05&09 Dr. KHALIL Exam-I Fall 2009 Last Name :... ID:... First Name:... Form I Section No.: EXAMINATION INSTRUCTIONS
The American University in Cairo Department of Computer Science & Engineeringt CSCI 106-05&09 Dr. KHALIL Exam-I Fall 2009 Last Name :... ID:... First Name:... Form I Section No.: EXAMINATION INSTRUCTIONS
C++ 8. Constructors and Destructors
 8. Constructors and Destructors C++ 1. When an instance of a class comes into scope, the function that executed is. a) Destructors b) Constructors c) Inline d) Friend 2. When a class object goes out of
8. Constructors and Destructors C++ 1. When an instance of a class comes into scope, the function that executed is. a) Destructors b) Constructors c) Inline d) Friend 2. When a class object goes out of
As an example using arrays, let s write some code to get started with the Upthrust game. We can use a 2D array to represent the game board.
 Array Example Upthrust Board As an example using arrays, let s write some code to get started with the Upthrust game. We can use a 2D array to represent the game board. First, note that the game board
Array Example Upthrust Board As an example using arrays, let s write some code to get started with the Upthrust game. We can use a 2D array to represent the game board. First, note that the game board
CE221 Programming in C++ Part 1 Introduction
 CE221 Programming in C++ Part 1 Introduction 06/10/2017 CE221 Part 1 1 Module Schedule There are two lectures (Monday 13.00-13.50 and Tuesday 11.00-11.50) each week in the autumn term, and a 2-hour lab
CE221 Programming in C++ Part 1 Introduction 06/10/2017 CE221 Part 1 1 Module Schedule There are two lectures (Monday 13.00-13.50 and Tuesday 11.00-11.50) each week in the autumn term, and a 2-hour lab
Week 3. Function Definitions. Example: Function. Function Call, Return Statement. Functions & Arrays. Gaddis: Chapters 6 and 7. CS 5301 Spring 2018
 Week 3 Functions & Arrays Gaddis: Chapters 6 and 7 CS 5301 Spring 2018 Jill Seaman 1 Function Definitions l Function definition pattern: datatype identifier (parameter1, parameter2,...) { statements...
Week 3 Functions & Arrays Gaddis: Chapters 6 and 7 CS 5301 Spring 2018 Jill Seaman 1 Function Definitions l Function definition pattern: datatype identifier (parameter1, parameter2,...) { statements...
ME240 Computation for Mechanical Engineering. Lecture 4. C++ Data Types
 ME240 Computation for Mechanical Engineering Lecture 4 C++ Data Types Introduction In this lecture we will learn some fundamental elements of C++: Introduction Data Types Identifiers Variables Constants
ME240 Computation for Mechanical Engineering Lecture 4 C++ Data Types Introduction In this lecture we will learn some fundamental elements of C++: Introduction Data Types Identifiers Variables Constants
C++ Scope Resolution Operator ::
 C++ Scope Resolution Operator :: C++The :: (scope resolution) operator is used to qualify hidden names so that you can still use them. You can use the unary scope operator if a namespace scope or global
C++ Scope Resolution Operator :: C++The :: (scope resolution) operator is used to qualify hidden names so that you can still use them. You can use the unary scope operator if a namespace scope or global
Review. What is const member data? By what mechanism is const enforced? How do we initialize it? How do we initialize it?
 Review Describe pass-by-value and pass-by-reference Why do we use pass-by-reference? What does the term calling object refer to? What is a const member function? What is a const object? How do we initialize
Review Describe pass-by-value and pass-by-reference Why do we use pass-by-reference? What does the term calling object refer to? What is a const member function? What is a const object? How do we initialize
TEMPLATES AND EXCEPTION HANDLING
 CONTENTS: Function template Class template Exception handling Try-Catch-Throw paradigm Exception specification Terminate functions Unexcepted functions Uncaught exception UNIT-III TEMPLATES AND EXCEPTION
CONTENTS: Function template Class template Exception handling Try-Catch-Throw paradigm Exception specification Terminate functions Unexcepted functions Uncaught exception UNIT-III TEMPLATES AND EXCEPTION
