Computer Graphics (CS 543) Lecture 3b: Shader Setup & GLSL Introduction
|
|
|
- Charity Casey
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Computer Graphics (CS 543) Lecture 3b: Shader Setup & GLSL Introduction Prof Emmanuel Agu Computer Science Dept. Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI)
2 OpenGL function format function name gluniform3f(x,y,z) Number of arguments belongs to GL library x,y,z are floats gluniform3fv(p) Argument is array of values p is a pointer to array
3 Lack of Object Orientation OpenGL is not object oriented Multiple versions for each command gluniform3f gluniform2i gluniform3dv
4 OpenGL Data Types C++ Signed char Short Int Float Double Unsigned char Unsigned short Unsigned int OpenGL GLByte GLShort GLInt GLFloat GLDouble GLubyte GLushort GLuint Example: Integer is 32-bits on 32-bit machine but 64-bits on a 64-bit machine Good to define OpenGL data type: same number of bits on all machines
5 Recall: Single Buffering If display mode set to single framebuffers Any drawing into framebuffer is seen by user. How? glutinitdisplaymode(glut_single GLUT_RGB); Single buffering with RGB colors Drawing may not be drawn to screen until call to glflush( ) void mydisplay(void){ glclear(gl_color_buffer_bit); // clear screen gldrawarrays(gl_points, 0, N); glflush( ); } Drawing sent to screen Single Frame buffer
6 Double Buffering Set display mode to double buffering (create front and back framebuffers) Double buffering is good for animations, avoids tearing artifacts glutinitdisplaymode(glut_double GLUT_RGB); Double buffering with RGB colors Front buffer displayed on screen, back buffers not displayed Drawing into back buffers (not displayed) until swapped in using glutswapbuffers( ) void mydisplay(void){ } glclear(gl_color_buffer_bit); // clear screen gldrawarrays(gl_points, 0, N); glutswapbuffers( ); Back buffer drawing swapped in, becomes visible here Back Front Double Frame buffer
7 Recall: OpenGL Skeleton void main(int argc, char** argv){ glutinit(&argc, argv); // initialize toolkit glutinitdisplaymode(glut_single GLUT_RGB); glutinitwindowsize(640, 480); glutinitwindowposition(100, 150); glutcreatewindow( my first attempt ); glewinit( ); // now register callback functions glutdisplayfunc(mydisplay); glutreshapefunc(myreshape); glutmousefunc(mymouse); glutkeyboardfunc(mykeyboard); void shadersetup( void ) { // Load shaders and use the resulting shader program program = InitShader( "vshader1.glsl", "fshader1.glsl" ); gluseprogram( program ); glewinit( ); generategeometry( ); initgpubuffers( ); void shadersetup( ); // Initialize vertex position attribute from vertex shader GLuint loc = glgetattriblocation( program, "vposition" ); glenablevertexattribarray( loc ); glvertexattribpointer( loc, 2, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, 0, BUFFER_OFFSET(0) ); } glutmainloop( ); } // sets white as color used to clear screen glclearcolor( 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0 );
8 Recall: OpenGL Program: Shader Setup initshader( ): our homegrown shader initialization Used in main program, connects and link vertex, fragment shaders Shader sources read in, compiled and linked Gluint = program; GLuint program = InitShader( "vshader1.glsl", "fshader1.glsl" ); gluseprogram(program); example.cpp Main Program What s inside initshader?? Next! Vertex shader vshader1.glsl Fragment Shader fshader1.glsl
9 Coupling Shaders to Application (initshader function) 1. Create a program object 2. Read shaders 3. Add + Compile shaders 4. Link program (everything together) 5. Link variables in application with variables in shaders Vertex attributes Uniform variables
10 Step 1. Create Program Object Container for shaders Can contain multiple shaders, other GLSL functions GLuint myprogobj; myprogobj = glcreateprogram(); Create container called Program Object Main Program
11 Step 2: Read a Shader Shaders compiled and added to program object example.cpp Main Program Passed in as string Vertex shader vshader1.glsl Fragment Shader Fshader1.glsl Passed in as string Shader file code passed in as null-terminated string using the function glshadersource Shaders in files (vshader.glsl, fshader.glsl), write function readshadersource to convert shader file to string Shader file name (e.g. vshader.glsl) readshadersource String of entire shader code
12 Shader Reader Code? #include <stdio.h> static char* readshadersource(const char* shaderfile) { FILE* fp = fopen(shaderfile, "r"); if ( fp == NULL ) { return NULL; } fseek(fp, 0L, SEEK_END); long size = ftell(fp); fseek(fp, 0L, SEEK_SET); char* buf = new char[size + 1]; fread(buf, 1, size, fp); buf[size] = '\0'; fclose(fp); } return buf; Shader file name (e.g. vshader.glsl) readshadersource String of entire shader code
13 Step 3: Adding + Compiling Shaders GLuint myvertexobj; Gluint myfragmentobj; Declare shader object (container for shader) GLchar* vsource = readshadersource( vshader1.glsl ); GLchar* fsource = readshadersource( fshader1.glsl ); myvertexobj = glcreateshader(gl_vertex_shader); myfragmentobj = glcreateshader(gl_fragment_shader); Read shader files, Convert code to string Create empty Shader objects example.cpp Main Program Vertex shader vshader1.glsl Fragment Shader fshader1.glsl
14 Step 3: Adding + Compiling Shaders Step 4: Link Program glshadersource(myvertexobj, 1, vsource, NULL); glshadersource(myfragmentobj, 1, fsource, NULL); Read shader code strings into shader objects glcompileshader(myvertexobj); glcompileshader(myfragmentobj); Compile shader objects glattachshader(myprogobj, myvertexobj); glattachshader(myprogobj, myfragmentobj); Attach shader objects to program object gllinkprogram(myprogobj); Link Program example.cpp Main Program Attach shader objects to program object Vertex shader vshader1.glsl Fragment Shader fshader1.glsl
15 Uniform Variables Variables that are constant for an entire primitive Can be changed in application and sent to shaders Cannot be changed in shader Used to pass information to shader Example: bounding box of a primitive Bounding Box
16 Uniform variables Sometimes want to connect uniform variable in OpenGL application to uniform variable in shader Example? Check elapsed time variable (etime) in OpenGL application Use elapsed time variable (time) in shader for calculations etime OpenGL application time Shader application
17 Uniform variables First declare etime variable in OpenGL application, get time float etime; Elapsed time since program started etime = 0.001*glutGet(GLUT_ELAPSED_TIME); Use corresponding variable time in shader uniform float time; attribute vec4 vposition; main( ){ vposition.x += (1+sin(time)); gl_position = vposition; } etime time Need to connect etime in application and time in shader!!
18 Connecting etime and time Linker forms table of shader variables, each with an address In application, find address of shader time variable in linker table Tie address of time to application variable etime Glint timeloc; timeloc = glgetuniformlocation(program, time ); 423 time Connect: location of shader variable time to etime! gluniform1(timeloc, etime); Location of shader variable time Application variable, etime
19 GL Shading Language (GLSL) GLSL: high level C-like language Main program (e.g. example1.cpp) program written in C/C++ Vertex and Fragment shaders written in GLSL From OpenGL 3.1, application must use shaders What does keyword out mean? const vec4 red = vec4(1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0); out vec3 color_out; void main(void){ gl_position = vposition; color_out = red; } Example code of vertex shader gl_position not declared Built-in types (already declared, just use)
20 Passing values Variable declared out in vertex shader can be declared as in in fragment shader and used Why? To pass result of vertex shader calculation to fragment shader const vec4 red = vec4(1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0); out vec3 color_out; in From main program Vertex Shader out To fragment shader void main(void){ gl_position = vposition; color_out = red; } in vec3 color_out; void main(void){ // can use color_out here. } Vertex shader Fragment shader From Vertex shader in Fragment Shader out To framebuffer
21 Data Types C types: int, float, bool GLSL types: float vec2: e.g. (x,y) // vector of 2 floats float vec3: e.g. (x,y,z) or (R,G,B) // vector of 3 floats float vec4: e.g. (x,y,z,w) // vector of 4 floats Const float vec4 red = vec4(1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0); out float vec3 color_out; void main(void){ gl_position = vposition; color_out = red; } Vertex shader C++ style constructors (initialize values) Also: int (ivec2, ivec3, ivec4) and boolean (bvec2, bvec3,bvec4)
22 Data Types Matrices: mat2, mat3, mat4 Stored by columns Standard referencing m[row][column] Matrices and vectors are basic types can be passed in and out from GLSL functions E.g mat3 func(mat3 a) No pointers in GLSL Can use C structs that are copied back from functions
23 Operators and Functions Standard C functions Trigonometric: cos, sin, tan, etc Arithmetic: log, min, max, abs, etc Normalize, reflect, length Overloading of vector and matrix types mat4 a; vec4 b, c, d; c = b*a; // a column vector stored as a 1d array d = a*b; // a row vector stored as a 1d array
24 Swizzling and Selection Selection: Can refer to array elements by element using [] or selection (.) operator with x, y, z, w r, g, b, a s, t, p, q vec4 a; a[2], a.b, a.z, a.p are the same Swizzling operator lets us manipulate components a.yz = vec2(1.0, 2.0);
25 References Angel and Shreiner, Interactive Computer Graphics, 6 th edition, Chapter 2 Hill and Kelley, Computer Graphics using OpenGL, 3 rd edition, Chapter 2
Computer Graphics (CS 4731) & 2D Graphics Systems
 Computer Graphics (CS 4731) Lecture 4: Shader Setup & 2D Graphics Systems Prof Emmanuel Agu Computer Science Dept. Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI) Recall: OpenGL Program: Shader Setup initshader(
Computer Graphics (CS 4731) Lecture 4: Shader Setup & 2D Graphics Systems Prof Emmanuel Agu Computer Science Dept. Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI) Recall: OpenGL Program: Shader Setup initshader(
Comp 410/510 Computer Graphics Spring Programming with OpenGL Part 3: Shaders
 Comp 410/510 Computer Graphics Spring 2018 Programming with OpenGL Part 3: Shaders Objectives Basic shaders - Vertex shader - Fragment shader Programming shaders with GLSL Finish first program void init(void)
Comp 410/510 Computer Graphics Spring 2018 Programming with OpenGL Part 3: Shaders Objectives Basic shaders - Vertex shader - Fragment shader Programming shaders with GLSL Finish first program void init(void)
CS 543 Lecture 1 (Part 3) Prof Emmanuel Agu. Computer Science Dept. Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI)
 Computer Graphics CS 543 Lecture 1 (Part 3) Prof Emmanuel Agu Computer Science Dept. Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI) Recall: OpenGL Skeleton void main(int argc, char** argv){ // First initialize
Computer Graphics CS 543 Lecture 1 (Part 3) Prof Emmanuel Agu Computer Science Dept. Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI) Recall: OpenGL Skeleton void main(int argc, char** argv){ // First initialize
Programming with OpenGL Part 5: More GLSL. Ed Angel Professor Emeritus of Computer Science University of New Mexico
 Programming with OpenGL Part 5: More GLSL Ed Angel Professor Emeritus of Computer Science University of New Mexico 1 Objectives Coupling shaders to applications - Reading - Compiling - Linking Vertex Attributes
Programming with OpenGL Part 5: More GLSL Ed Angel Professor Emeritus of Computer Science University of New Mexico 1 Objectives Coupling shaders to applications - Reading - Compiling - Linking Vertex Attributes
Computer Graphics (CS 4731) OpenGL/GLUT (Part 2)
 Computer Graphics (CS 4731) Lecture 3: Introduction to OpenGL/GLUT (Part 2) Prof Emmanuel Agu Computer Science Dept. Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI) Triangulation Generally OpenGL breaks polygonsdownintotriangles
Computer Graphics (CS 4731) Lecture 3: Introduction to OpenGL/GLUT (Part 2) Prof Emmanuel Agu Computer Science Dept. Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI) Triangulation Generally OpenGL breaks polygonsdownintotriangles
Programming with OpenGL Part 3: Shaders. Ed Angel Professor of Emeritus of Computer Science University of New Mexico
 Programming with OpenGL Part 3: Shaders Ed Angel Professor of Emeritus of Computer Science University of New Mexico 1 Objectives Simple Shaders - Vertex shader - Fragment shaders Programming shaders with
Programming with OpenGL Part 3: Shaders Ed Angel Professor of Emeritus of Computer Science University of New Mexico 1 Objectives Simple Shaders - Vertex shader - Fragment shaders Programming shaders with
Computer Graphics (CS 543) Lecture 1 (Part 2): Introduction to OpenGL/GLUT (Part 1)
 Computer Graphics (CS 543) Lecture 1 (Part 2): Introduction to OpenGL/GLUT (Part 1) Prof Emmanuel Agu Computer Science Dept. Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI) OpenGL/GLUT Installation OpenGL: Specific
Computer Graphics (CS 543) Lecture 1 (Part 2): Introduction to OpenGL/GLUT (Part 1) Prof Emmanuel Agu Computer Science Dept. Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI) OpenGL/GLUT Installation OpenGL: Specific
Today s Agenda. Shaders fundamentals. Programming with shader-based OpenGL
 Today s Agenda Shaders fundamentals Programming with shader-based OpenGL Shaders Like a function call data are passed in, processed, and passed back out -- Shreiner et al, OpenGL Programming Guide GLSL
Today s Agenda Shaders fundamentals Programming with shader-based OpenGL Shaders Like a function call data are passed in, processed, and passed back out -- Shreiner et al, OpenGL Programming Guide GLSL
Objectives. Programming with OpenGL Part 5: More GLSL. Program Object. Reading a Shader. Shader Reader. Linking Shaders with Application
 Objectives Programming with OpenGL Part : More GLSL CS Interactive Computer Graphics Prof. David E. Breen Department of Computer Science Coupling shaders to applications - Reading - Compiling - Linking
Objectives Programming with OpenGL Part : More GLSL CS Interactive Computer Graphics Prof. David E. Breen Department of Computer Science Coupling shaders to applications - Reading - Compiling - Linking
Computer Graphics (4731) Lecture 4: 2D Graphics Systems (Drawing Polylines, tiling, & Aspect Ratio)
 Computer Graphics (4731) Lecture 4: 2D Graphics Systems (Drawing Polylines, tiling, & Aspect Ratio) Prof Emmanuel Agu Computer Science Dept. Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI) Screen Coordinate System
Computer Graphics (4731) Lecture 4: 2D Graphics Systems (Drawing Polylines, tiling, & Aspect Ratio) Prof Emmanuel Agu Computer Science Dept. Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI) Screen Coordinate System
Lecture 3. Programming with OpenGL GLUT + GLEW. CS 354 Computer Graphics Sunday, January 20, 13
 Lecture 3 Programming with OpenGL 3.1 + GLUT + GLEW OpenGL The success of GL lead to OpenGL (1992), a platform-independent API that was - Easy to use - Close enough to the hardware to get excellent performance
Lecture 3 Programming with OpenGL 3.1 + GLUT + GLEW OpenGL The success of GL lead to OpenGL (1992), a platform-independent API that was - Easy to use - Close enough to the hardware to get excellent performance
Supplement to Lecture 22
 Supplement to Lecture 22 Programmable GPUs Programmable Pipelines Introduce programmable pipelines - Vertex shaders - Fragment shaders Introduce shading languages - Needed to describe shaders - RenderMan
Supplement to Lecture 22 Programmable GPUs Programmable Pipelines Introduce programmable pipelines - Vertex shaders - Fragment shaders Introduce shading languages - Needed to describe shaders - RenderMan
Lecture 5 Vertex and Fragment Shaders-1. CITS3003 Graphics & Animation
 Lecture 5 Vertex and Fragment Shaders-1 CITS3003 Graphics & Animation E. Angel and D. Shreiner: Interactive Computer Graphics 6E Addison-Wesley 2012 Objectives The rendering pipeline and the shaders Data
Lecture 5 Vertex and Fragment Shaders-1 CITS3003 Graphics & Animation E. Angel and D. Shreiner: Interactive Computer Graphics 6E Addison-Wesley 2012 Objectives The rendering pipeline and the shaders Data
Programming with OpenGL Shaders I. Adapted From: Ed Angel Professor of Emeritus of Computer Science University of New Mexico
 Programming with OpenGL Shaders I Adapted From: Ed Angel Professor of Emeritus of Computer Science University of New Mexico 0 Objectives Shader Basics Simple Shaders Vertex shader Fragment shaders 1 Vertex
Programming with OpenGL Shaders I Adapted From: Ed Angel Professor of Emeritus of Computer Science University of New Mexico 0 Objectives Shader Basics Simple Shaders Vertex shader Fragment shaders 1 Vertex
Programming with OpenGL Shaders I. Adapted From: Ed Angel Professor of Emeritus of Computer Science University of New Mexico
 Programming with OpenGL Shaders I Adapted From: Ed Angel Professor of Emeritus of Computer Science University of New Mexico Objectives Shader Programming Basics Simple Shaders Vertex shader Fragment shaders
Programming with OpenGL Shaders I Adapted From: Ed Angel Professor of Emeritus of Computer Science University of New Mexico Objectives Shader Programming Basics Simple Shaders Vertex shader Fragment shaders
Objectives. Open GL Shading Language (GLSL)
 Open GL Shading Language (GLSL) Objectives Shader applications Vertex shaders Fragment shaders Programming shaders Cg GLSL Coupling GLSL to Applications Example applications 1 Vertex Shader Applications
Open GL Shading Language (GLSL) Objectives Shader applications Vertex shaders Fragment shaders Programming shaders Cg GLSL Coupling GLSL to Applications Example applications 1 Vertex Shader Applications
Computer Graphics (CS 4731) OpenGL/GLUT(Part 1)
 Computer Graphics (CS 4731) Lecture 2: Introduction to OpenGL/GLUT(Part 1) Prof Emmanuel Agu Computer Science Dept. Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI) Recall: OpenGL GLBasics OpenGL s function Rendering
Computer Graphics (CS 4731) Lecture 2: Introduction to OpenGL/GLUT(Part 1) Prof Emmanuel Agu Computer Science Dept. Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI) Recall: OpenGL GLBasics OpenGL s function Rendering
CS 4731 Lecture 3: Introduction to OpenGL and GLUT: Part II. Emmanuel Agu
 CS 4731 Lecture 3: Introduction to OpenGL and GLUT: Part II Emmanuel Agu Recall: OpenGL Skeleton void main(int argc, char** argv){ // First initialize toolkit, set display mode and create window glutinit(&argc,
CS 4731 Lecture 3: Introduction to OpenGL and GLUT: Part II Emmanuel Agu Recall: OpenGL Skeleton void main(int argc, char** argv){ // First initialize toolkit, set display mode and create window glutinit(&argc,
CS 432 Interactive Computer Graphics
 CS 432 Interactive Computer Graphics Lecture 2 Part 2 Introduction to Shaders Matt Burlick - Drexel University - CS 432 1 Shaders To understand shaders, let s look at the graphics pipeline again The job
CS 432 Interactive Computer Graphics Lecture 2 Part 2 Introduction to Shaders Matt Burlick - Drexel University - CS 432 1 Shaders To understand shaders, let s look at the graphics pipeline again The job
Comp 410/510 Computer Graphics Spring Programming with OpenGL Part 2: First Program
 Comp 410/510 Computer Graphics Spring 2017 Programming with OpenGL Part 2: First Program Objectives Refine the first program Introduce a standard program structure - Initialization Program Structure Most
Comp 410/510 Computer Graphics Spring 2017 Programming with OpenGL Part 2: First Program Objectives Refine the first program Introduce a standard program structure - Initialization Program Structure Most
Computer Graphics (CS 543) Lecture 2b: 2D Graphics Systems (Drawing Polylines, tiling, & Aspect Ratio)
 Computer Graphics (CS 543) Lecture 2b: 2D Graphics Systems (Drawing Polylines, tiling, & Aspect Ratio) Prof Emmanuel Agu Computer Science Dept. Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI) Announcements All code
Computer Graphics (CS 543) Lecture 2b: 2D Graphics Systems (Drawing Polylines, tiling, & Aspect Ratio) Prof Emmanuel Agu Computer Science Dept. Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI) Announcements All code
OPEN GL BACKGROUND. Objectives. Early History of APIs. SGI and GL. PHIGS and X. Modified from Angel 6e book slides
 OPEN GL Modified from Angel 6e book slides BACKGROUND Objectives Early History of APIs Development of the OpenGL API OpenGL Architecture OpenGL as a state machine OpenGL as a data flow machine Functions
OPEN GL Modified from Angel 6e book slides BACKGROUND Objectives Early History of APIs Development of the OpenGL API OpenGL Architecture OpenGL as a state machine OpenGL as a data flow machine Functions
Computer Graphics (CS 4731) Lecture 11: Implementing Transformations. Prof Emmanuel Agu. Computer Science Dept. Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI)
 Computer Graphics (CS 47) Lecture : Implementing Transformations Prof Emmanuel Agu Computer Science Dept. Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI) Objectives Learn how to implement transformations in OpenGL
Computer Graphics (CS 47) Lecture : Implementing Transformations Prof Emmanuel Agu Computer Science Dept. Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI) Objectives Learn how to implement transformations in OpenGL
CS Computer Graphics: OpenGL, Continued
 CS 543 - Computer Graphics: OpenGL, Continued by Robert W. Lindeman gogo@wpi.edu (with help from Emmanuel Agu ;-) Last time. OpenGL set up Basic structure OpenGL skeleton Callback functions, etc. R.W.
CS 543 - Computer Graphics: OpenGL, Continued by Robert W. Lindeman gogo@wpi.edu (with help from Emmanuel Agu ;-) Last time. OpenGL set up Basic structure OpenGL skeleton Callback functions, etc. R.W.
CS Computer Graphics: OpenGL, Continued
 CS 543 - Computer Graphics: OpenGL, Continued by Robert W. Lindeman gogo@wpi.edu (with help from Emmanuel Agu ;-) Last time. OpenGL set up Basic structure OpenGL skeleton Callback functions, etc. R.W.
CS 543 - Computer Graphics: OpenGL, Continued by Robert W. Lindeman gogo@wpi.edu (with help from Emmanuel Agu ;-) Last time. OpenGL set up Basic structure OpenGL skeleton Callback functions, etc. R.W.
Information Coding / Computer Graphics, ISY, LiTH. OpenGL! ! where it fits!! what it contains!! how you work with it 11(40)
 11(40) Information Coding / Computer Graphics, ISY, LiTH OpenGL where it fits what it contains how you work with it 11(40) OpenGL The cross-platform graphics library Open = Open specification Runs everywhere
11(40) Information Coding / Computer Graphics, ISY, LiTH OpenGL where it fits what it contains how you work with it 11(40) OpenGL The cross-platform graphics library Open = Open specification Runs everywhere
OpenGL pipeline Evolution and OpenGL Shading Language (GLSL) Part 2/3 Vertex and Fragment Shaders
 OpenGL pipeline Evolution and OpenGL Shading Language (GLSL) Part 2/3 Vertex and Fragment Shaders Prateek Shrivastava CS12S008 shrvstv@cse.iitm.ac.in 1 GLSL Data types Scalar types: float, int, bool Vector
OpenGL pipeline Evolution and OpenGL Shading Language (GLSL) Part 2/3 Vertex and Fragment Shaders Prateek Shrivastava CS12S008 shrvstv@cse.iitm.ac.in 1 GLSL Data types Scalar types: float, int, bool Vector
GLSL 1: Basics. J.Tumblin-Modified SLIDES from:
 GLSL 1: Basics J.Tumblin-Modified SLIDES from: Ed Angel Professor of Computer Science, Electrical and Computer Engineering, and Media Arts Director, Arts Technology Center University of New Mexico and
GLSL 1: Basics J.Tumblin-Modified SLIDES from: Ed Angel Professor of Computer Science, Electrical and Computer Engineering, and Media Arts Director, Arts Technology Center University of New Mexico and
Computer Graphics (CS 4731) Lecture 11: Implementing Transformations. Prof Emmanuel Agu. Computer Science Dept. Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI)
 Computer Graphics (CS 47) Lecture : Implementing Transformations Prof Emmanuel Agu Computer Science Dept. Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI) Objectives Learn how to implement transformations in OpenGL
Computer Graphics (CS 47) Lecture : Implementing Transformations Prof Emmanuel Agu Computer Science Dept. Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI) Objectives Learn how to implement transformations in OpenGL
CS 543 Lecture 1 (Part II): Intro to OpenGL and GLUT (Part I) Emmanuel Agu
 CS 543 Lecture 1 (Part II): Intro to OpenGL and GLUT (Part I) Emmanuel Agu OpenGL Basics OpenGL s function Rendering Rendering? Convert geometric/mathematical object descriptions into images OpenGL can
CS 543 Lecture 1 (Part II): Intro to OpenGL and GLUT (Part I) Emmanuel Agu OpenGL Basics OpenGL s function Rendering Rendering? Convert geometric/mathematical object descriptions into images OpenGL can
Philip Calderon CSE 520 Lab 3 Color Shader
 Philip Calderon CSE 520 Lab 3 Color Shader Summary: The purpose of lab 4 is to produce a pyramid tetrahedron that we are able to rotate it when clicked. Part 1: Color Tetrahedron Part 2: Rotation to show
Philip Calderon CSE 520 Lab 3 Color Shader Summary: The purpose of lab 4 is to produce a pyramid tetrahedron that we are able to rotate it when clicked. Part 1: Color Tetrahedron Part 2: Rotation to show
Computer Graphics. Making Pictures. Computer Graphics CSC470 1
 Computer Graphics Making Pictures Computer Graphics CSC470 1 Getting Started Making Pictures Graphics display: Entire screen (a); windows system (b); [both have usual screen coordinates, with y-axis y
Computer Graphics Making Pictures Computer Graphics CSC470 1 Getting Started Making Pictures Graphics display: Entire screen (a); windows system (b); [both have usual screen coordinates, with y-axis y
Computer Graphics CS 543 Lecture 4 (Part 2) Building 3D Models (Part 2)
 Computer Graphics CS 543 Lecture 4 (Part 2) Building 3D Models (Part 2) Prof Emmanuel Agu Computer Science Dept. Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI) Modeling a Cube In 3D, declare vertices as (x,y,z)
Computer Graphics CS 543 Lecture 4 (Part 2) Building 3D Models (Part 2) Prof Emmanuel Agu Computer Science Dept. Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI) Modeling a Cube In 3D, declare vertices as (x,y,z)
Erik Anchondo cse 520 lab 4
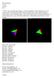 Erik Anchondo 2-6-19 cse 520 lab 4 1. Wrote a glsl program that displays a colored tetrahedron. The tetrahedron starts to rotate on the x axis when the mouse button is clicked once. If the mouse button
Erik Anchondo 2-6-19 cse 520 lab 4 1. Wrote a glsl program that displays a colored tetrahedron. The tetrahedron starts to rotate on the x axis when the mouse button is clicked once. If the mouse button
2a. The triangles scale increases (expands) when the 'e' key is pressed and decreases (contracts) when the 'c' key is pressed.
 Erik Anchondo 1-29-19 cse 520 lab 3 1. Wrote a shader program to display three colored triangles, with one of each triangle being red, green, and blue. The colors change which triangle they are applied
Erik Anchondo 1-29-19 cse 520 lab 3 1. Wrote a shader program to display three colored triangles, with one of each triangle being red, green, and blue. The colors change which triangle they are applied
CS 432 Interactive Computer Graphics
 CS 432 Interactive Computer Graphics Lecture 1 Part 3 Anatomy of OpenGL Programs Matt Burlick - Drexel University - CS 432 1 Reading Angel Chapter 2 Red Book Chapter 4 Matt Burlick - Drexel University
CS 432 Interactive Computer Graphics Lecture 1 Part 3 Anatomy of OpenGL Programs Matt Burlick - Drexel University - CS 432 1 Reading Angel Chapter 2 Red Book Chapter 4 Matt Burlick - Drexel University
OpenGL and GLUT. COMP413 Computer Graphics. School of Computer Sci. & Eng. Kyungpook National University, Korea. Spring Semester, 2016
 OpenGL and GLUT COMP413 Computer Graphics School of Computer Sci. & Eng. Kyungpook National University, Korea Spring Semester, 2016 2007-2016 N Baek 1 Contents OpenGL Libraries OpenGL functions naming
OpenGL and GLUT COMP413 Computer Graphics School of Computer Sci. & Eng. Kyungpook National University, Korea Spring Semester, 2016 2007-2016 N Baek 1 Contents OpenGL Libraries OpenGL functions naming
GLSL II. Objectives. Coupling GLSL to Applications Example applications
 GLSL II Ed Angel Professor of Computer Science, Electrical and Computer Engineering, and Media Arts Director, Arts Technology Center University of New Mexico Objectives Coupling GLSL to Applications Example
GLSL II Ed Angel Professor of Computer Science, Electrical and Computer Engineering, and Media Arts Director, Arts Technology Center University of New Mexico Objectives Coupling GLSL to Applications Example
Information Coding / Computer Graphics, ISY, LiTH GLSL. OpenGL Shading Language. Language with syntax similar to C
 GLSL OpenGL Shading Language Language with syntax similar to C Syntax somewhere between C och C++ No classes. Straight ans simple code. Remarkably understandable and obvious! Avoids most of the bad things
GLSL OpenGL Shading Language Language with syntax similar to C Syntax somewhere between C och C++ No classes. Straight ans simple code. Remarkably understandable and obvious! Avoids most of the bad things
2D graphics with WebGL
 2D graphics with WebGL Some material contained here is adapted from the book s slides. September 7, 2015 (Dr. Mihail) 2D graphics September 7, 2015 1 / 22 Graphics Pipeline (Dr. Mihail) 2D graphics September
2D graphics with WebGL Some material contained here is adapted from the book s slides. September 7, 2015 (Dr. Mihail) 2D graphics September 7, 2015 1 / 22 Graphics Pipeline (Dr. Mihail) 2D graphics September
Comp 410/510 Computer Graphics Spring Programming with OpenGL Part 4: Three Dimensions
 Comp 410/510 Computer Graphics Spring 2018 Programming with OpenGL Part 4: Three Dimensions Objectives Develop a bit more sophisticated three-dimensional example - Rotating cube Introduce hidden-surface
Comp 410/510 Computer Graphics Spring 2018 Programming with OpenGL Part 4: Three Dimensions Objectives Develop a bit more sophisticated three-dimensional example - Rotating cube Introduce hidden-surface
to OpenGL Introduction Pipeline Graphics pipeline OpenGL pipeline OpenGL syntax Modeling Arrays Conclusion 1 Introduction Introduction to OpenGL
 to to ning Lecture : introduction to Lab : first steps in and - 25/02/2009 Lecture/Lab : transformations and hierarchical - 04/03/2009 to Lecture : lights and materials in - 11/03/2009 Lab : lights and
to to ning Lecture : introduction to Lab : first steps in and - 25/02/2009 Lecture/Lab : transformations and hierarchical - 04/03/2009 to Lecture : lights and materials in - 11/03/2009 Lab : lights and
WebGL A quick introduction. J. Madeira V. 0.2 September 2017
 WebGL A quick introduction J. Madeira V. 0.2 September 2017 1 Interactive Computer Graphics Graphics library / package is intermediary between application and display hardware Application program maps
WebGL A quick introduction J. Madeira V. 0.2 September 2017 1 Interactive Computer Graphics Graphics library / package is intermediary between application and display hardware Application program maps
API Background. Prof. George Wolberg Dept. of Computer Science City College of New York
 API Background Prof. George Wolberg Dept. of Computer Science City College of New York Objectives Graphics API history OpenGL API OpenGL function format Immediate Mode vs Retained Mode Examples The Programmer
API Background Prof. George Wolberg Dept. of Computer Science City College of New York Objectives Graphics API history OpenGL API OpenGL function format Immediate Mode vs Retained Mode Examples The Programmer
Today s Agenda. Basic design of a graphics system. Introduction to OpenGL
 Today s Agenda Basic design of a graphics system Introduction to OpenGL Image Compositing Compositing one image over another is most common choice can think of each image drawn on a transparent plastic
Today s Agenda Basic design of a graphics system Introduction to OpenGL Image Compositing Compositing one image over another is most common choice can think of each image drawn on a transparent plastic
Objectives. Coupling GLSL to Applications Example applications
 GLSL II Ed Angel Professor of Computer Science, Electrical and Computer Engineering, and Media Arts Director, Arts Technology Center University of New Mexico Objectives Coupling GLSL to Applications Example
GLSL II Ed Angel Professor of Computer Science, Electrical and Computer Engineering, and Media Arts Director, Arts Technology Center University of New Mexico Objectives Coupling GLSL to Applications Example
Drawing Primitives. OpenGL basics
 CSC 706 Computer Graphics / Dr. N. Gueorguieva 1 OpenGL Libraries Drawing Primitives OpenGL basics OpenGL core library OpenGL32 on Windows GL on most unix/linux systems (libgl.a) OpenGL Utility Library
CSC 706 Computer Graphics / Dr. N. Gueorguieva 1 OpenGL Libraries Drawing Primitives OpenGL basics OpenGL core library OpenGL32 on Windows GL on most unix/linux systems (libgl.a) OpenGL Utility Library
Lecture 2 CISC440/640 Spring Department of Computer and Information Science
 Lecture 2 CISC440/640 Spring 2015 Department of Computer and Information Science Today s Topic The secrets of Glut-tony 2 So let s do some graphics! For the next week or so this is your world: -1 1-1 1
Lecture 2 CISC440/640 Spring 2015 Department of Computer and Information Science Today s Topic The secrets of Glut-tony 2 So let s do some graphics! For the next week or so this is your world: -1 1-1 1
CSE 167: Introduction to Computer Graphics Lecture #7: GLSL. Jürgen P. Schulze, Ph.D. University of California, San Diego Spring Quarter 2016
 CSE 167: Introduction to Computer Graphics Lecture #7: GLSL Jürgen P. Schulze, Ph.D. University of California, San Diego Spring Quarter 2016 Announcements Project 2 due Friday 4/22 at 2pm Midterm #1 on
CSE 167: Introduction to Computer Graphics Lecture #7: GLSL Jürgen P. Schulze, Ph.D. University of California, San Diego Spring Quarter 2016 Announcements Project 2 due Friday 4/22 at 2pm Midterm #1 on
Announcement. Homework 1 has been posted in dropbox and course website. Due: 1:15 pm, Monday, September 12
 Announcement Homework 1 has been posted in dropbox and course website Due: 1:15 pm, Monday, September 12 Today s Agenda Primitives Programming with OpenGL OpenGL Primitives Polylines GL_POINTS GL_LINES
Announcement Homework 1 has been posted in dropbox and course website Due: 1:15 pm, Monday, September 12 Today s Agenda Primitives Programming with OpenGL OpenGL Primitives Polylines GL_POINTS GL_LINES
Computer Graphics (CS 543) Lecture 4a: Linear Algebra for Graphics (Points, Scalars, Vectors)
 Computer Graphics (CS 543) Lecture 4a: Linear Algebra for Graphics (Points, Scalars, Vectors) Prof Emmanuel Agu Computer Science Dept. Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI) Announcements Sample exam 1
Computer Graphics (CS 543) Lecture 4a: Linear Algebra for Graphics (Points, Scalars, Vectors) Prof Emmanuel Agu Computer Science Dept. Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI) Announcements Sample exam 1
Shader Programs. Lecture 30 Subsections 2.8.2, Robb T. Koether. Hampden-Sydney College. Wed, Nov 16, 2011
 Shader Programs Lecture 30 Subsections 2.8.2, 2.8.3 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Nov 16, 2011 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Shader Programs Wed, Nov 16, 2011 1 / 43 Outline 1
Shader Programs Lecture 30 Subsections 2.8.2, 2.8.3 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Nov 16, 2011 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Shader Programs Wed, Nov 16, 2011 1 / 43 Outline 1
Computer Graphics CS 543 Lecture 5 (Part 2) Implementing Transformations
 Computer Graphics CS 543 Lecture 5 (Part 2) Implementing Transformations Prof Emmanuel Agu Computer Science Dept. Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI) Objectives Learn how to implement transformations
Computer Graphics CS 543 Lecture 5 (Part 2) Implementing Transformations Prof Emmanuel Agu Computer Science Dept. Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI) Objectives Learn how to implement transformations
2. OpenGL -I. 2.1 What is OpenGL? Things OpenGL can do: -23-
 2.1 What is OpenGL? -23-2. OpenGL -I - Device-independent, application program interface (API) to graphics hardware - 3D-oriented - Event-driven Things OpenGL can do: - wireframe models - depth-cuing effect
2.1 What is OpenGL? -23-2. OpenGL -I - Device-independent, application program interface (API) to graphics hardware - 3D-oriented - Event-driven Things OpenGL can do: - wireframe models - depth-cuing effect
COMPUTER GRAPHICS LAB # 3
 COMPUTER GRAPHICS LAB # 3 Chapter 2: COMPUTER GRAPHICS by F.S HILLs. Initial steps in drawing figures (polygon, rectangle etc) Objective: Basic understanding of simple code in OpenGL and initial steps
COMPUTER GRAPHICS LAB # 3 Chapter 2: COMPUTER GRAPHICS by F.S HILLs. Initial steps in drawing figures (polygon, rectangle etc) Objective: Basic understanding of simple code in OpenGL and initial steps
An Introduction to 3D Computer Graphics, Stereoscopic Image, and Animation in OpenGL and C/C++ Fore June
 An Introduction to 3D Computer Graphics, Stereoscopic Image, and Animation in OpenGL and C/C++ Fore June Appendix D OpenGL Shading Language (GLSL) D.1 Extending OpenGL The OpenGL architecture we have presented
An Introduction to 3D Computer Graphics, Stereoscopic Image, and Animation in OpenGL and C/C++ Fore June Appendix D OpenGL Shading Language (GLSL) D.1 Extending OpenGL The OpenGL architecture we have presented
CMSC 425: Lecture 4 More about OpenGL and GLUT Tuesday, Feb 5, 2013
 CMSC 425: Lecture 4 More about OpenGL and GLUT Tuesday, Feb 5, 2013 Reading: See any standard reference on OpenGL or GLUT. Basic Drawing: In the previous lecture, we showed how to create a window in GLUT,
CMSC 425: Lecture 4 More about OpenGL and GLUT Tuesday, Feb 5, 2013 Reading: See any standard reference on OpenGL or GLUT. Basic Drawing: In the previous lecture, we showed how to create a window in GLUT,
Lecture 09: Shaders (Part 1)
 Lecture 09: Shaders (Part 1) CSE 40166 Computer Graphics Peter Bui University of Notre Dame, IN, USA November 9, 2010 OpenGL Rendering Pipeline OpenGL Rendering Pipeline (Pseudo-Code) 1 f o r gl_vertex
Lecture 09: Shaders (Part 1) CSE 40166 Computer Graphics Peter Bui University of Notre Dame, IN, USA November 9, 2010 OpenGL Rendering Pipeline OpenGL Rendering Pipeline (Pseudo-Code) 1 f o r gl_vertex
Models and Architectures. Angel and Shreiner: Interactive Computer Graphics 7E Addison-Wesley 2015
 Models and Architectures 1 Objectives Learn the basic design of a graphics system Introduce pipeline architecture Examine software components for an interactive graphics system 2 Image Formation Revisited
Models and Architectures 1 Objectives Learn the basic design of a graphics system Introduce pipeline architecture Examine software components for an interactive graphics system 2 Image Formation Revisited
3D Game Programming Programmable Pipelines. Ming-Te Chi Department of Computer Science, National Chengchi University
 3D Game Programming Programmable Pipelines Ming-Te Chi Department of Computer Science, National Chengchi University Outline Programmable Pipelines(4ed CH15) (5th CH5) Vertex shaders Fragment shaders Introduce
3D Game Programming Programmable Pipelines Ming-Te Chi Department of Computer Science, National Chengchi University Outline Programmable Pipelines(4ed CH15) (5th CH5) Vertex shaders Fragment shaders Introduce
Computer Graphics. Bing-Yu Chen National Taiwan University
 Computer Graphics Bing-Yu Chen National Taiwan University Introduction to OpenGL General OpenGL Introduction An Example OpenGL Program Drawing with OpenGL Transformations Animation and Depth Buffering
Computer Graphics Bing-Yu Chen National Taiwan University Introduction to OpenGL General OpenGL Introduction An Example OpenGL Program Drawing with OpenGL Transformations Animation and Depth Buffering
Introduction to Computer Graphics. Hardware Acceleration Review
 Introduction to Computer Graphics Hardware Acceleration Review OpenGL Project Setup Create a command-line style project in Xcode 4 Select the project file and click Build Phases tab Add OpenGL.framework
Introduction to Computer Graphics Hardware Acceleration Review OpenGL Project Setup Create a command-line style project in Xcode 4 Select the project file and click Build Phases tab Add OpenGL.framework
Lecture 3. Understanding of OPenGL programming
 Lecture 3 Understanding of OPenGL programming What is OpenGL GL: stands for Graphic Library Software interface for rendering purposes for 2D or 3D geometric data objects. Various Pieces gl: The basic libraries.
Lecture 3 Understanding of OPenGL programming What is OpenGL GL: stands for Graphic Library Software interface for rendering purposes for 2D or 3D geometric data objects. Various Pieces gl: The basic libraries.
1. Write a shader program that animates the morphing of Figure 'A' to Figure 'B' and back.
 Karl Zachary Maier CSE 520 Homework 1 1. Write a shader program that animates the morphing of Figure 'A' to Figure 'B' and back. /* morph.cpp */ #include #include #include
Karl Zachary Maier CSE 520 Homework 1 1. Write a shader program that animates the morphing of Figure 'A' to Figure 'B' and back. /* morph.cpp */ #include #include #include
Lecture 2 2D transformations Introduction to OpenGL
 Lecture 2 2D transformations Introduction to OpenGL OpenGL where it fits what it contains how you work with it OpenGL parts: GL = Graphics Library (core lib) GLU = GL Utilities (always present) GLX, AGL,
Lecture 2 2D transformations Introduction to OpenGL OpenGL where it fits what it contains how you work with it OpenGL parts: GL = Graphics Library (core lib) GLU = GL Utilities (always present) GLX, AGL,
Building Models. Prof. George Wolberg Dept. of Computer Science City College of New York
 Building Models Prof. George Wolberg Dept. of Computer Science City College of New York Objectives Introduce simple data structures for building polygonal models - Vertex lists - Edge lists Deprecated
Building Models Prof. George Wolberg Dept. of Computer Science City College of New York Objectives Introduce simple data structures for building polygonal models - Vertex lists - Edge lists Deprecated
Fog example. Fog is atmospheric effect. Better realism, helps determine distances
 Fog example Fog is atmospheric effect Better realism, helps determine distances Fog Fog was part of OpenGL fixed function pipeline Programming fixed function fog Parameters: Choose fog color, fog model
Fog example Fog is atmospheric effect Better realism, helps determine distances Fog Fog was part of OpenGL fixed function pipeline Programming fixed function fog Parameters: Choose fog color, fog model
VR-programming tools (procedural) More VRML later in this course! (declarative)
 Realtime 3D Computer Graphics & Virtual Reality OpenGL Introduction VR-programming Input and display devices are the main hardware interface to users Immersion embeds users through the generation of live-like
Realtime 3D Computer Graphics & Virtual Reality OpenGL Introduction VR-programming Input and display devices are the main hardware interface to users Immersion embeds users through the generation of live-like
CS380: Computer Graphics Screen Space & World Space. Sung-Eui Yoon ( 윤성의 ) Course URL:
 CS380: Computer Graphics Screen Space & World Space Sung-Eui Yoon ( 윤성의 ) Course URL: http://sglab.kaist.ac.kr/~sungeui/cg Class Objectives Understand different spaces and basic OpenGL commands Understand
CS380: Computer Graphics Screen Space & World Space Sung-Eui Yoon ( 윤성의 ) Course URL: http://sglab.kaist.ac.kr/~sungeui/cg Class Objectives Understand different spaces and basic OpenGL commands Understand
LECTURE 02 OPENGL API
 COMPUTER GRAPHICS LECTURE 02 OPENGL API Still from Pixar s Inside Out, 2015 IMRAN IHSAN ASSISTANT PROFESSOR WWW.IMRANIHSAN.COM EARLY HISTORY OF APIS IFIPS (1973) formed two committees to come up with a
COMPUTER GRAPHICS LECTURE 02 OPENGL API Still from Pixar s Inside Out, 2015 IMRAN IHSAN ASSISTANT PROFESSOR WWW.IMRANIHSAN.COM EARLY HISTORY OF APIS IFIPS (1973) formed two committees to come up with a
1)Write a shader program that renders a regular pentagon with textured image like the one shown below.
 Andrew Yenalavitch CSE520 Winter 2015 Quiz 2 Report 1)Write a shader program that renders a regular pentagon with textured image like the one shown below. Use the following provided image for the texture:
Andrew Yenalavitch CSE520 Winter 2015 Quiz 2 Report 1)Write a shader program that renders a regular pentagon with textured image like the one shown below. Use the following provided image for the texture:
CS559: Computer Graphics. Lecture 12: OpenGL Li Zhang Spring 2008
 CS559: Computer Graphics Lecture 12: OpenGL Li Zhang Spring 2008 Reading Redbook Ch 1 & 2 So far: 3D Geometry Pipeline Model Space (Object Space) Rotation Translation Resizing World Space M Rotation Translation
CS559: Computer Graphics Lecture 12: OpenGL Li Zhang Spring 2008 Reading Redbook Ch 1 & 2 So far: 3D Geometry Pipeline Model Space (Object Space) Rotation Translation Resizing World Space M Rotation Translation
Computer Graphics (CS 543) Lecture 8c: Environment Mapping (Reflections and Refractions)
 Computer Graphics (CS 543) Lecture 8c: Environment Mapping (Reflections and Refractions) Prof Emmanuel Agu (Adapted from slides by Ed Angel) Computer Science Dept. Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI)
Computer Graphics (CS 543) Lecture 8c: Environment Mapping (Reflections and Refractions) Prof Emmanuel Agu (Adapted from slides by Ed Angel) Computer Science Dept. Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI)
An Overview GLUT GLSL GLEW
 OpenGL, GLUT, GLEW, GLSL An Overview GLUT GLEW GLSL Objectives Give you an overview of the software that you will be using this semester OpenGL, GLUT, GLEW, GLSL What are they? How do you use them? What
OpenGL, GLUT, GLEW, GLSL An Overview GLUT GLEW GLSL Objectives Give you an overview of the software that you will be using this semester OpenGL, GLUT, GLEW, GLSL What are they? How do you use them? What
- Surface Rendering -
 Programmable Shaders II - Surface Rendering - 12 th Week, 2008 Sun-Jeong Kim Downloading 2 GLEW OpenGL Extension Wrangler Library http://glew.sourceforge.net/ Cross-platform open-source C/C++ extension
Programmable Shaders II - Surface Rendering - 12 th Week, 2008 Sun-Jeong Kim Downloading 2 GLEW OpenGL Extension Wrangler Library http://glew.sourceforge.net/ Cross-platform open-source C/C++ extension
CS475/CS675 - Computer Graphics. OpenGL Drawing
 CS475/CS675 - Computer Graphics OpenGL Drawing What is OpenGL? Open Graphics Library API to specify geometric objects in 2D/3D and to control how they are rendered into the framebuffer. A software interface
CS475/CS675 - Computer Graphics OpenGL Drawing What is OpenGL? Open Graphics Library API to specify geometric objects in 2D/3D and to control how they are rendered into the framebuffer. A software interface
Tutorial 04. Harshavardhan Kode. September 14, 2015
 Tutorial 04 Harshavardhan Kode September 14, 2015 1 About This tutorial an extension of the Tutorial 03. So you might see quite a lot similarities. The following things are new. A Plane is added underneath
Tutorial 04 Harshavardhan Kode September 14, 2015 1 About This tutorial an extension of the Tutorial 03. So you might see quite a lot similarities. The following things are new. A Plane is added underneath
Some advantages come from the limited environment! No classes. Stranight ans simple code. Remarkably. Avoids most of the bad things with C/C++.
 GLSL OpenGL Shading Language Language with syntax similar to C Syntax somewhere between C och C++ No classes. Stranight ans simple code. Remarkably understandable and obvious! Avoids most of the bad things
GLSL OpenGL Shading Language Language with syntax similar to C Syntax somewhere between C och C++ No classes. Stranight ans simple code. Remarkably understandable and obvious! Avoids most of the bad things
Teacher Assistant : Tamir Grossinger Reception hours: by - Building 37 / office -102 Assignments: 4 programing using
 Teacher Assistant : Tamir Grossinger email: tamirgr@gmail.com Reception hours: by email - Building 37 / office -102 Assignments: 4 programing using C++ 1 theoretical You can find everything you need in
Teacher Assistant : Tamir Grossinger email: tamirgr@gmail.com Reception hours: by email - Building 37 / office -102 Assignments: 4 programing using C++ 1 theoretical You can find everything you need in
Duc Nguyen CSE 420 Computer Graphics 10/10/2018 Homework 1
 Duc Nguyen CSE 420 Computer Graphics 10/10/2018 Homework 1 1. The endpoints of a given line are (0, 0) and (18, 6). Compute the first 4 values of y manually using Bresenham's Line Algorithm as x steps
Duc Nguyen CSE 420 Computer Graphics 10/10/2018 Homework 1 1. The endpoints of a given line are (0, 0) and (18, 6). Compute the first 4 values of y manually using Bresenham's Line Algorithm as x steps
Shaders. Slide credit to Prof. Zwicker
 Shaders Slide credit to Prof. Zwicker 2 Today Shader programming 3 Complete model Blinn model with several light sources i diffuse specular ambient How is this implemented on the graphics processor (GPU)?
Shaders Slide credit to Prof. Zwicker 2 Today Shader programming 3 Complete model Blinn model with several light sources i diffuse specular ambient How is this implemented on the graphics processor (GPU)?
Computer Graphics Anatomy of GUI. Computer Graphics CSC470 1
 Computer Graphics Anatomy of GUI 1 Anatomy of GLUT keyboard mouse OpenGL Application if (key == f key == F ) { glutfullscreen(); } else if(key == w key == W ) { glutreshapewindow(640,480); } display reshape
Computer Graphics Anatomy of GUI 1 Anatomy of GLUT keyboard mouse OpenGL Application if (key == f key == F ) { glutfullscreen(); } else if(key == w key == W ) { glutreshapewindow(640,480); } display reshape
Assignment 1. Simple Graphics program using OpenGL
 Assignment 1 Simple Graphics program using OpenGL In this assignment we will use basic OpenGL functions to draw some basic graphical figures. Example: Consider following program to draw a point on screen.
Assignment 1 Simple Graphics program using OpenGL In this assignment we will use basic OpenGL functions to draw some basic graphical figures. Example: Consider following program to draw a point on screen.
COMP371 COMPUTER GRAPHICS
 COMP371 COMPUTER GRAPHICS SESSION 12 PROGRAMMABLE SHADERS Announcement Programming Assignment #2 deadline next week: Session #7 Review of project proposals 2 Lecture Overview GPU programming 3 GPU Pipeline
COMP371 COMPUTER GRAPHICS SESSION 12 PROGRAMMABLE SHADERS Announcement Programming Assignment #2 deadline next week: Session #7 Review of project proposals 2 Lecture Overview GPU programming 3 GPU Pipeline
Programming with WebGL Part 1: Background. CS 432 Interactive Computer Graphics Prof. David E. Breen Department of Computer Science
 Programming with WebGL Part 1: Background CS 432 Interactive Computer Graphics Prof. David E. Breen Department of Computer Science E. Angel and D. Shreiner: Interactive Computer Graphics 6E Addison-Wesley
Programming with WebGL Part 1: Background CS 432 Interactive Computer Graphics Prof. David E. Breen Department of Computer Science E. Angel and D. Shreiner: Interactive Computer Graphics 6E Addison-Wesley
2/3/16. Interaction. Triangles (Clarification) Choice of Programming Language. Buffer Objects. The CPU-GPU bus. CSCI 420 Computer Graphics Lecture 3
 CSCI 420 Computer Graphics Lecture 3 Interaction Jernej Barbic University of Southern California [Angel Ch. 2] Triangles (Clarification) Can be any shape or size Well-shaped triangles have advantages for
CSCI 420 Computer Graphics Lecture 3 Interaction Jernej Barbic University of Southern California [Angel Ch. 2] Triangles (Clarification) Can be any shape or size Well-shaped triangles have advantages for
Building Models. CS 537 Interactive Computer Graphics Prof. David E. Breen Department of Computer Science
 Building Models CS 537 Interactive Computer Graphics Prof. David E. Breen Department of Computer Science 1 Objectives Introduce simple data structures for building polygonal models - Vertex lists - Edge
Building Models CS 537 Interactive Computer Graphics Prof. David E. Breen Department of Computer Science 1 Objectives Introduce simple data structures for building polygonal models - Vertex lists - Edge
CS452/552; EE465/505. Image Processing Frame Buffer Objects
 CS452/552; EE465/505 Image Processing Frame Buffer Objects 3-12 15 Outline! Image Processing: Examples! Render to Texture Read: Angel, Chapter 7, 7.10-7.13 Lab3 new due date: Friday, Mar. 13 th Project#1
CS452/552; EE465/505 Image Processing Frame Buffer Objects 3-12 15 Outline! Image Processing: Examples! Render to Texture Read: Angel, Chapter 7, 7.10-7.13 Lab3 new due date: Friday, Mar. 13 th Project#1
Interaction. CSCI 420 Computer Graphics Lecture 3
 CSCI 420 Computer Graphics Lecture 3 Interaction Jernej Barbic University of Southern California Client/Server Model Callbacks Double Buffering Hidden Surface Removal Simple Transformations [Angel Ch.
CSCI 420 Computer Graphics Lecture 3 Interaction Jernej Barbic University of Southern California Client/Server Model Callbacks Double Buffering Hidden Surface Removal Simple Transformations [Angel Ch.
Announcements OpenGL. Computer Graphics. Autumn 2009 CS4815
 Computer Graphics Autumn 2009 Outline 1 Labs 2 Labs Outline 1 Labs 2 Labs Labs Week02 lab Marking 8 10 labs in total each lab worth 2 3% of overall grade marked on attendance and completion of lab completed
Computer Graphics Autumn 2009 Outline 1 Labs 2 Labs Outline 1 Labs 2 Labs Labs Week02 lab Marking 8 10 labs in total each lab worth 2 3% of overall grade marked on attendance and completion of lab completed
CS452/552; EE465/505. Image Formation
 CS452/552; EE465/505 Image Formation 1-15-15 Outline! Image Formation! Introduction to WebGL, continued Draw a colored triangle using WebGL Read: Angel, Chapters 2 & 3 Homework #1 will be available on
CS452/552; EE465/505 Image Formation 1-15-15 Outline! Image Formation! Introduction to WebGL, continued Draw a colored triangle using WebGL Read: Angel, Chapters 2 & 3 Homework #1 will be available on
by modifying the glutinitwindowsize() function you can change the screen size to whatever you please.
 Zoe Veale Lab 2 Draw2 part 1: I edited the glutinitwindowsize() function tom change the size of my screen window. int main(int argc, char** argv) glutinit(&argc, argv); //initialize toolkit glutinitdisplaymode
Zoe Veale Lab 2 Draw2 part 1: I edited the glutinitwindowsize() function tom change the size of my screen window. int main(int argc, char** argv) glutinit(&argc, argv); //initialize toolkit glutinitdisplaymode
Introduction to OpenGL: Part 2
 Introduction to OpenGL: Part 2 Introduction to OpenGL: Part 2 A more complex example recursive refinement Introduction to OpenGL: Part 2 A more complex example recursive refinement Can OpenGL draw continuous
Introduction to OpenGL: Part 2 Introduction to OpenGL: Part 2 A more complex example recursive refinement Introduction to OpenGL: Part 2 A more complex example recursive refinement Can OpenGL draw continuous
Computer Graphics Course 2005
 Computer Graphics Course 2005 Introduction to GLUT, GLU and OpenGL Administrative Stuff Teaching Assistant: Rony Goldenthal Reception Hour: Wed. 18:00 19:00 Room 31 (Ross 1) Questions: E-mail: cg@cs Newsgroups:
Computer Graphics Course 2005 Introduction to GLUT, GLU and OpenGL Administrative Stuff Teaching Assistant: Rony Goldenthal Reception Hour: Wed. 18:00 19:00 Room 31 (Ross 1) Questions: E-mail: cg@cs Newsgroups:
Copyright Khronos Group 2012 Page 1. Teaching GL. Dave Shreiner Director, Graphics and GPU Computing, ARM 1 December 2012
 Copyright Khronos Group 2012 Page 1 Teaching GL Dave Shreiner Director, Graphics and GPU Computing, ARM 1 December 2012 Copyright Khronos Group 2012 Page 2 Agenda Overview of OpenGL family of APIs Comparison
Copyright Khronos Group 2012 Page 1 Teaching GL Dave Shreiner Director, Graphics and GPU Computing, ARM 1 December 2012 Copyright Khronos Group 2012 Page 2 Agenda Overview of OpenGL family of APIs Comparison
Announcements OpenGL. Computer Graphics. Spring CS4815
 Computer Graphics Spring 2017-2018 Outline 1 2 Tutes and Labs Tute02, vector review (see matrix) Week02 lab Lab Marking 10 labs in total each lab worth 3% of overall grade marked on attendance and completion
Computer Graphics Spring 2017-2018 Outline 1 2 Tutes and Labs Tute02, vector review (see matrix) Week02 lab Lab Marking 10 labs in total each lab worth 3% of overall grade marked on attendance and completion
Computer Graphics (CS 543) Lecture 8a: Per-Vertex lighting, Shading and Per-Fragment lighting
 Computer Graphics (CS 543) Lecture 8a: Per-Vertex lighting, Shading and Per-Fragment lighting Prof Emmanuel Agu Computer Science Dept. Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI) Computation of Vectors To calculate
Computer Graphics (CS 543) Lecture 8a: Per-Vertex lighting, Shading and Per-Fragment lighting Prof Emmanuel Agu Computer Science Dept. Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI) Computation of Vectors To calculate
This Lecture. Why OpenGL? Introduction to OpenGL. Programmer s View
 Foundations of Computer Graphics Overview and Motivation This Lecture Introduction to OpenGL and simple demo code mytest1.cpp ; you compiled mytest3.cpp for HW 0 I am going to show (and write) actual code
Foundations of Computer Graphics Overview and Motivation This Lecture Introduction to OpenGL and simple demo code mytest1.cpp ; you compiled mytest3.cpp for HW 0 I am going to show (and write) actual code
Programmable Graphics Hardware
 CSCI 480 Computer Graphics Lecture 14 Programmable Graphics Hardware [Ch. 9] March 2, 2011 Jernej Barbic University of Southern California OpenGL Extensions Shading Languages Vertex Program Fragment Program
CSCI 480 Computer Graphics Lecture 14 Programmable Graphics Hardware [Ch. 9] March 2, 2011 Jernej Barbic University of Southern California OpenGL Extensions Shading Languages Vertex Program Fragment Program
GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT, GL_PROJECTION, GL_MODELVIEW
 OpenGL Syntax Functions have prefix gl and initial capital letters for each word glclearcolor(), glenable(), glpushmatrix() glu for GLU functions glulookat(), gluperspective() constants begin with GL_,
OpenGL Syntax Functions have prefix gl and initial capital letters for each word glclearcolor(), glenable(), glpushmatrix() glu for GLU functions glulookat(), gluperspective() constants begin with GL_,
