Math Introduction to Advanced Mathematics
|
|
|
- Alvin Young
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Math Introduction to Advanced Mathematics Number Theory Fall 2017 The following introductory guide to number theory is borrowed from Drew Shulman and is used in a couple of other Math 215 classes. Over the next 2-3 weeks our goal as a class is to prove all of the propositions, lemmas, and theorems listed here simply by using the definitions provided. All of these should be thought of as your current problem set for this part of the course. I will take all 5 quiz-exam questions directly from this guide. Assumptions: For these problems, we assume the existence of the set of natural numbers N = {1, 2, 3,...} and the set of integers Z = {..., 2, 1, 0, 1, 2,...}. We also assume the following basic properties: If a, b are integers, then a + b, a b, and ab are integers. If a, b are natural numbers, then a + b and ab are natural numbers. If a, b are integers, then exactly one of the following is true: a < b, b < a, or a = b. The operations addition and multiplication on the integers are associative, commutative, and distributive. Definition 1 Let a, b be integers. We say that a divides b if there exists an integer k such that ak = b. If a divides b, we write a b. Remark 2 If a divides b, we can also say that a is a divisor of b, or that b is a multiple of a. Proposition 3 Let a, b, c be integers. If a b and a c, then a (b + c). Proposition 4 Let a, b, c be integers. If a b and a c, then a (b c). Conjecture 5 Let a, b, c be integers. If a (b + c), then a b and a c. Proposition 6 Let a, b, c be integers. If a b and a c, then a bc. Proposition 7 Let a, b, c be integers. If a b, then a bc. Proposition 8 Let a, b, c be integers. If a b and b c, then a c. Proposition 9 If n is an integer, then n 0. 1
2 Corollary 10 If n and a are integers, then n (a a). Proposition 11 Let n, a, b be integers. If n (a b), then n (b a). Proposition 12 Let n, a, b, c be integers. If n (a b) and n (b c), then n (a c). Definition 13 Let a, b be integers and n a natural number. If n (a b), then we say that a is congruent to b modulo n and write a b mod n. Remark 14 Consider two statements P and Q. We write P if and only if Q to mean the combination of the statements If P, then Q AND If Q, then P. Proposition 15 Let a be an integer and n a natural number. n a if and only if a 0 mod n. Note: In the above proposition, the statement P is n a and the statement Q is a 0 mod n. Proposition 16 Let a be an integer and n a natural number. Then a a mod n. Proposition 17 Let a, b be integers and n a natural number. If a b mod n, then b a mod n. Proposition 18 Let a, b, c be integers and n a natural number. If a b mod n and b c mod n, then a c mod n. Proposition 19 Let a, b, c, d be integers and n a natural number. d mod n, then a + c b + d mod n. Proposition 20 Let a, b, c, d be integers and n a natural number. d mod n, then a c b d mod n. Proposition 21 Let a, b, c, d be integers and n a natural number. d mod n, then ac bd mod n. Notation 22 If a does not divide b, we notate this by a b. Proposition Proposition 24 Let a, b be natural numbers. If a > b, then a b. Definition 25 Let S be a set of integers and let l be an element of S. We say that l is a least element of S if l s for every s in S. Proposition 26 Let S be a set of integers and assume that l is a least element of S. If l is some other least element of S, then l = l. Note: Proposition 26 says that the least element of a set (if it exists) is unique. Conjecture 27 Every non-empty set of integers has a least element.
3 Axiom 28 If S is a non-empty set of non-negative integers, then S has a least element. Note: An axiom is something we assume to be true without proof. Challenge 29 Let a be an integer and n a natural number. Show that there exists a unique integer r such that a r mod n and 0 r < n. Hints: Consider the set S = {a kn : k is an integer and a kn 0}. Show that S only contains non-negative integers and is non-empty. Use Axiom 28 to find the smallest element of S and call it r. Show that a r mod n and explain why 0 r < n. Question 30 Why have we labeled the unique integer in Challenge 29 with the letter r? What does this number represent? Remark 31 Let a be an integer and n a natural number. Let r be the unique integer as in Challenge 29. Define the (unique) integer q by the formula a = nq + r. (Why have we chosen to use the letter q?) Given the integer a and the natural number n, finding the unique integers q, r such that a = nq + r where 0 r < n is called the division algorithm. Proposition 32 Let a, b be integers and n a natural number. If a b mod n, then a 2 b 2 mod n. Proposition 33 Let a, b be integers and n a natural number. If a b mod n, then a 3 b 3 mod n. Proposition 34 Let a, b be integers and n a natural number. If a b mod n, then a k b k mod n for every natural number k. Problem 35 For the following pairs of integers a and n, find q and r in the division algorithm. a = 5, n = 2 a = 72, n = 5 a = 94, n = 100 a = 7814, n = 1124 Definition 36 Let a and b be positive integers and d an integer such that d a and d b. Then we say that d is a common divisor of a and b. Definition 37 Let a and b be integers such that not both of a and b are zero. We say an integer d is a greatest common divisor of a and b if the following two statements are true: 1. d a and d b; and 2. if c is any integer such that c a and c b, then c d. Proposition 38 Let a and b be integers such that not both are zero. Let D = {am + bn : m and n are integers, and am + bn > 0}. Then the following statements are true:
4 1. D is a non-empty set of positive integers. 2. D has a least element. Call that least element d. 3. There exists integers x and y such that d = ax + by. 4. d a and d b. [Hint: Use the division algorithm.] 5. If c is any integer such that c a and c b, then c d. 6. If c is any integer such that c a and c b, then c d. 7. d is a greatest common divisor of a and b. 8. The greatest common divisor is unique. Notation 39 The greatest common divisor of a and b is denoted gcd(a, b). Lemma 40 Let a, b be natural numbers, and let r be the unique integer as defined by a = bq +r where 0 r < b. If d is a natural number, then d a and d b if and only if d b and d r. Proposition 41 Let a, b be natural numbers, and let r be the unique integer as defined by a = bq + r where 0 r < b. Then gcd(a, b) = gcd(b, r). Proposition 42 Let a be a natural number. Then gcd(a, 0) = a. Problem 43 Using the previous two propositions, find the greatest common divisor of the following pairs of natural numbers. gcd(7, 2) gcd(52, 16) gcd(1492, 2014) gcd(528740, ) Remark 44 The process of finding the greatest common divisor of two natural numbers using the previous two propositions is referred to as the Euclidean Algorithm. Problem 45 For each part, find integers m, n such that gcd(a, b) = am + bn. gcd(7, 2) gcd(52, 16) gcd(1492, 2014) gcd(528740, ) Definition 46 Two integers a and b are called relatively prime (or coprime) if gcd(a, b) = 1.
5 Proposition 47 Two integers a and b are relatively prime if and only if there exists integers m, n such that am + bn = 1. Proposition 48 Let a, b be relatively prime integers. If a c and b c, then ab c. If a bc, then a c. Definition 49 An integer p > 1 is prime if the only positive divisors of p are 1 and p. Proposition 50 Let p be a prime, and let a be an integer. Then either p a or p and a are relatively prime. Proposition 51 Let p be a prime, and let a, b be integers. If p ab, then p a or p b. Corollary 52 If p is prime, and p a 1 a 2 a k 1 a k, then p a i for some i = 1, 2,..., k. Theorem 53 (Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic) Let n be an integer greater than 1. Then n = p e 1 1 pe k k where the primes p 1 < p 2 < < p k are distinct and the exponents e i are positive integers. This prime-factorization is unique. Theorem 54 (Euclid s Theorem) There are infinitely many primes. Hint: There are MANY proofs that there are an infinite number of primes, but Euclid s proof is the most beautiful (it is short and sweet). It is perhaps the prettiest proof in all of mathematics. To arrive at a contradiction, assume that there are only finitely many primes. Call those primes p 1, p 2,..., p k, and consider the integer n = p 1 p 2 p k + 1.
1 Elementary number theory
 Math 215 - Introduction to Advanced Mathematics Spring 2019 1 Elementary number theory We assume the existence of the natural numbers and the integers N = {1, 2, 3,...} Z = {..., 3, 2, 1, 0, 1, 2, 3,...},
Math 215 - Introduction to Advanced Mathematics Spring 2019 1 Elementary number theory We assume the existence of the natural numbers and the integers N = {1, 2, 3,...} Z = {..., 3, 2, 1, 0, 1, 2, 3,...},
1 Elementary number theory
 1 Elementary number theory We assume the existence of the natural numbers and the integers N = {1, 2, 3,...} Z = {..., 3, 2, 1, 0, 1, 2, 3,...}, along with their most basic arithmetical and ordering properties.
1 Elementary number theory We assume the existence of the natural numbers and the integers N = {1, 2, 3,...} Z = {..., 3, 2, 1, 0, 1, 2, 3,...}, along with their most basic arithmetical and ordering properties.
Know the Well-ordering principle: Any set of positive integers which has at least one element contains a smallest element.
 The first exam will be on Wednesday, September 22, 2010. The syllabus will be sections 1.1 and 1.2 in Lax, and the number theory handout found on the class web site, plus the handout on the method of successive
The first exam will be on Wednesday, September 22, 2010. The syllabus will be sections 1.1 and 1.2 in Lax, and the number theory handout found on the class web site, plus the handout on the method of successive
Integers and Mathematical Induction
 IT Program, NTUT, Fall 07 Integers and Mathematical Induction Chuan-Ming Liu Computer Science and Information Engineering National Taipei University of Technology TAIWAN 1 Learning Objectives Learn about
IT Program, NTUT, Fall 07 Integers and Mathematical Induction Chuan-Ming Liu Computer Science and Information Engineering National Taipei University of Technology TAIWAN 1 Learning Objectives Learn about
Algorithmic number theory Cryptographic hardness assumptions. Table of contents
 Algorithmic number theory Cryptographic hardness assumptions Foundations of Cryptography Computer Science Department Wellesley College Fall 2016 Table of contents Introduction Primes and Divisibility Modular
Algorithmic number theory Cryptographic hardness assumptions Foundations of Cryptography Computer Science Department Wellesley College Fall 2016 Table of contents Introduction Primes and Divisibility Modular
Math 302 Introduction to Proofs via Number Theory. Robert Jewett (with small modifications by B. Ćurgus)
 Math 30 Introduction to Proofs via Number Theory Robert Jewett (with small modifications by B. Ćurgus) March 30, 009 Contents 1 The Integers 3 1.1 Axioms of Z...................................... 3 1.
Math 30 Introduction to Proofs via Number Theory Robert Jewett (with small modifications by B. Ćurgus) March 30, 009 Contents 1 The Integers 3 1.1 Axioms of Z...................................... 3 1.
Discrete Mathematics Lecture 4. Harper Langston New York University
 Discrete Mathematics Lecture 4 Harper Langston New York University Sequences Sequence is a set of (usually infinite number of) ordered elements: a 1, a 2,, a n, Each individual element a k is called a
Discrete Mathematics Lecture 4 Harper Langston New York University Sequences Sequence is a set of (usually infinite number of) ordered elements: a 1, a 2,, a n, Each individual element a k is called a
Chapter 4. Number Theory. 4.1 Factors and multiples
 Chapter 4 Number Theory We ve now covered most of the basic techniques for writing proofs. So we re going to start applying them to specific topics in mathematics, starting with number theory. Number theory
Chapter 4 Number Theory We ve now covered most of the basic techniques for writing proofs. So we re going to start applying them to specific topics in mathematics, starting with number theory. Number theory
Number System. Introduction. Natural Numbers (N) Whole Numbers (W) Integers (Z) Prime Numbers (P) Face Value. Place Value
 1 Number System Introduction In this chapter, we will study about the number system and number line. We will also learn about the four fundamental operations on whole numbers and their properties. Natural
1 Number System Introduction In this chapter, we will study about the number system and number line. We will also learn about the four fundamental operations on whole numbers and their properties. Natural
Introduction to Programming in C Department of Computer Science and Engineering\ Lecture No. #02 Introduction: GCD
 Introduction to Programming in C Department of Computer Science and Engineering\ Lecture No. #02 Introduction: GCD In this session, we will write another algorithm to solve a mathematical problem. If you
Introduction to Programming in C Department of Computer Science and Engineering\ Lecture No. #02 Introduction: GCD In this session, we will write another algorithm to solve a mathematical problem. If you
Euclid's Algorithm. MA/CSSE 473 Day 06. Student Questions Odd Pie Fight Euclid's algorithm (if there is time) extended Euclid's algorithm
 MA/CSSE 473 Day 06 Euclid's Algorithm MA/CSSE 473 Day 06 Student Questions Odd Pie Fight Euclid's algorithm (if there is time) extended Euclid's algorithm 1 Quick look at review topics in textbook REVIEW
MA/CSSE 473 Day 06 Euclid's Algorithm MA/CSSE 473 Day 06 Student Questions Odd Pie Fight Euclid's algorithm (if there is time) extended Euclid's algorithm 1 Quick look at review topics in textbook REVIEW
36 Modular Arithmetic
 36 Modular Arithmetic Tom Lewis Fall Term 2010 Tom Lewis () 36 Modular Arithmetic Fall Term 2010 1 / 10 Outline 1 The set Z n 2 Addition and multiplication 3 Modular additive inverse 4 Modular multiplicative
36 Modular Arithmetic Tom Lewis Fall Term 2010 Tom Lewis () 36 Modular Arithmetic Fall Term 2010 1 / 10 Outline 1 The set Z n 2 Addition and multiplication 3 Modular additive inverse 4 Modular multiplicative
4&5 Binary Operations and Relations. The Integers. (part I)
 c Oksana Shatalov, Spring 2016 1 4&5 Binary Operations and Relations. The Integers. (part I) 4.1: Binary Operations DEFINITION 1. A binary operation on a nonempty set A is a function from A A to A. Addition,
c Oksana Shatalov, Spring 2016 1 4&5 Binary Operations and Relations. The Integers. (part I) 4.1: Binary Operations DEFINITION 1. A binary operation on a nonempty set A is a function from A A to A. Addition,
Lecture 7 Number Theory Euiseong Seo
 Lecture 7 Number Theory Euiseong Seo (euiseong@skku.edu) 1 Number Theory God created the integers. All else is the work of man Leopold Kronecker Study of the property of the integers Specifically, integer
Lecture 7 Number Theory Euiseong Seo (euiseong@skku.edu) 1 Number Theory God created the integers. All else is the work of man Leopold Kronecker Study of the property of the integers Specifically, integer
AXIOMS FOR THE INTEGERS
 AXIOMS FOR THE INTEGERS BRIAN OSSERMAN We describe the set of axioms for the integers which we will use in the class. The axioms are almost the same as what is presented in Appendix A of the textbook,
AXIOMS FOR THE INTEGERS BRIAN OSSERMAN We describe the set of axioms for the integers which we will use in the class. The axioms are almost the same as what is presented in Appendix A of the textbook,
Lemma (x, y, z) is a Pythagorean triple iff (y, x, z) is a Pythagorean triple.
 Chapter Pythagorean Triples.1 Introduction. The Pythagorean triples have been known since the time of Euclid and can be found in the third century work Arithmetica by Diophantus [9]. An ancient Babylonian
Chapter Pythagorean Triples.1 Introduction. The Pythagorean triples have been known since the time of Euclid and can be found in the third century work Arithmetica by Diophantus [9]. An ancient Babylonian
Computable Euclidean Domains
 Computable Euclidean Domains Asher M. Kach (Joint Work with Rod Downey and with Paul Ellis and Reed Solomon) Southern Wisconsin Logic Colloquium 9 October 2012 Asher M. Kach Computable Euclidean Domains
Computable Euclidean Domains Asher M. Kach (Joint Work with Rod Downey and with Paul Ellis and Reed Solomon) Southern Wisconsin Logic Colloquium 9 October 2012 Asher M. Kach Computable Euclidean Domains
UCT Algorithm Circle: Number Theory
 UCT Algorithm Circle: 7 April 2011 Outline Primes and Prime Factorisation 1 Primes and Prime Factorisation 2 3 4 Some revision (hopefully) What is a prime number? An integer greater than 1 whose only factors
UCT Algorithm Circle: 7 April 2011 Outline Primes and Prime Factorisation 1 Primes and Prime Factorisation 2 3 4 Some revision (hopefully) What is a prime number? An integer greater than 1 whose only factors
COP 4516: Math for Programming Contest Notes
 COP 4516: Math for Programming Contest Notes Euclid's Algorithm Euclid's Algorithm is the efficient way to determine the greatest common divisor between two integers. Given two positive integers a and
COP 4516: Math for Programming Contest Notes Euclid's Algorithm Euclid's Algorithm is the efficient way to determine the greatest common divisor between two integers. Given two positive integers a and
CSE 20 DISCRETE MATH. Fall
 CSE 20 DISCRETE MATH Fall 2017 http://cseweb.ucsd.edu/classes/fa17/cse20-ab/ Final exam The final exam is Saturday December 16 11:30am-2:30pm. Lecture A will take the exam in Lecture B will take the exam
CSE 20 DISCRETE MATH Fall 2017 http://cseweb.ucsd.edu/classes/fa17/cse20-ab/ Final exam The final exam is Saturday December 16 11:30am-2:30pm. Lecture A will take the exam in Lecture B will take the exam
2. Draw a non-isosceles triangle. Now make a template of this triangle out of cardstock or cardboard.
 Tessellations The figure at the left shows a tiled floor. Because the floor is entirely covered by the tiles we call this arrangement a tessellation of the plane. A regular tessellation occurs when: The
Tessellations The figure at the left shows a tiled floor. Because the floor is entirely covered by the tiles we call this arrangement a tessellation of the plane. A regular tessellation occurs when: The
r=1 The Binomial Theorem. 4 MA095/98G Revision
 Revision Read through the whole course once Make summary sheets of important definitions and results, you can use the following pages as a start and fill in more yourself Do all assignments again Do the
Revision Read through the whole course once Make summary sheets of important definitions and results, you can use the following pages as a start and fill in more yourself Do all assignments again Do the
ELEMENTARY NUMBER THEORY AND METHODS OF PROOF
 CHAPTER 4 ELEMENTARY NUMBER THEORY AND METHODS OF PROOF Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. SECTION 4.8 Application: Algorithms Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Application:
CHAPTER 4 ELEMENTARY NUMBER THEORY AND METHODS OF PROOF Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. SECTION 4.8 Application: Algorithms Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Application:
9.5 Equivalence Relations
 9.5 Equivalence Relations You know from your early study of fractions that each fraction has many equivalent forms. For example, 2, 2 4, 3 6, 2, 3 6, 5 30,... are all different ways to represent the same
9.5 Equivalence Relations You know from your early study of fractions that each fraction has many equivalent forms. For example, 2, 2 4, 3 6, 2, 3 6, 5 30,... are all different ways to represent the same
A Communications Network???
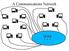 A Communications Network??? A Communications Network What are the desirable properties of the switching box? 1. Every two users must be connected at a switch. 2. Every switch must "look alike". 3. The
A Communications Network??? A Communications Network What are the desirable properties of the switching box? 1. Every two users must be connected at a switch. 2. Every switch must "look alike". 3. The
COMPSCI 230 Discrete Math Prime Numbers January 24, / 15
 COMPSCI 230 Discrete Math January 24, 2017 COMPSCI 230 Discrete Math Prime Numbers January 24, 2017 1 / 15 Outline 1 Prime Numbers The Sieve of Eratosthenes Python Implementations GCD and Co-Primes COMPSCI
COMPSCI 230 Discrete Math January 24, 2017 COMPSCI 230 Discrete Math Prime Numbers January 24, 2017 1 / 15 Outline 1 Prime Numbers The Sieve of Eratosthenes Python Implementations GCD and Co-Primes COMPSCI
Introduction to Sets and Logic (MATH 1190)
 Introduction to Sets and Logic () Instructor: Email: shenlili@yorku.ca Department of Mathematics and Statistics York University Dec 4, 2014 Outline 1 2 3 4 Definition A relation R from a set A to a set
Introduction to Sets and Logic () Instructor: Email: shenlili@yorku.ca Department of Mathematics and Statistics York University Dec 4, 2014 Outline 1 2 3 4 Definition A relation R from a set A to a set
CHAPTER 8. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
 CHAPTER 8 RELATIONS Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. SECTION 8.3 Equivalence Relations Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. The Relation Induced by a Partition 3 The Relation
CHAPTER 8 RELATIONS Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. SECTION 8.3 Equivalence Relations Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. The Relation Induced by a Partition 3 The Relation
Interpretations and Models. Chapter Axiomatic Systems and Incidence Geometry
 Interpretations and Models Chapter 2.1-2.4 - Axiomatic Systems and Incidence Geometry Axiomatic Systems in Mathematics The gold standard for rigor in an area of mathematics Not fully achieved in most areas
Interpretations and Models Chapter 2.1-2.4 - Axiomatic Systems and Incidence Geometry Axiomatic Systems in Mathematics The gold standard for rigor in an area of mathematics Not fully achieved in most areas
Problem. Prove that the square of any whole number n is a multiple of 4 or one more than a multiple of 4.
 CHAPTER 8 Integers Problem. Prove that the square of any whole number n is a multiple of 4 or one more than a multiple of 4. Strategy 13 Use cases. This strategy may be appropriate when A problem can be
CHAPTER 8 Integers Problem. Prove that the square of any whole number n is a multiple of 4 or one more than a multiple of 4. Strategy 13 Use cases. This strategy may be appropriate when A problem can be
On Jeśmanowicz Conjecture Concerning Pythagorean Triples
 Journal of Mathematical Research with Applications Mar., 2015, Vol. 35, No. 2, pp. 143 148 DOI:10.3770/j.issn:2095-2651.2015.02.004 Http://jmre.dlut.edu.cn On Jeśmanowicz Conjecture Concerning Pythagorean
Journal of Mathematical Research with Applications Mar., 2015, Vol. 35, No. 2, pp. 143 148 DOI:10.3770/j.issn:2095-2651.2015.02.004 Http://jmre.dlut.edu.cn On Jeśmanowicz Conjecture Concerning Pythagorean
Chapter 3: Theory of Modular Arithmetic 1. Chapter 3: Theory of Modular Arithmetic
 Chapter 3: Theory of Modular Arithmetic 1 Chapter 3: Theory of Modular Arithmetic SECTION A Introduction to Congruences By the end of this section you will be able to deduce properties of large positive
Chapter 3: Theory of Modular Arithmetic 1 Chapter 3: Theory of Modular Arithmetic SECTION A Introduction to Congruences By the end of this section you will be able to deduce properties of large positive
Assertions & Verification & Example Loop Invariants Example Exam Questions
 2014 November 27 1. Assertions & Verification & Example Loop Invariants Example Exam Questions 2. A B C Give a general template for refining an operation into a sequence and state what questions a designer
2014 November 27 1. Assertions & Verification & Example Loop Invariants Example Exam Questions 2. A B C Give a general template for refining an operation into a sequence and state what questions a designer
Ch 3.4 The Integers and Division
 Integers and Division 1 Ch 3.4 The Integers and Division This area of discrete mathematics belongs to the area of Number Theory. Some applications of the concepts in this section include generating pseudorandom
Integers and Division 1 Ch 3.4 The Integers and Division This area of discrete mathematics belongs to the area of Number Theory. Some applications of the concepts in this section include generating pseudorandom
Pick s Theorem and Lattice Point Geometry
 Pick s Theorem and Lattice Point Geometry 1 Lattice Polygon Area Calculations Lattice points are points with integer coordinates in the x, y-plane. A lattice line segment is a line segment that has 2 distinct
Pick s Theorem and Lattice Point Geometry 1 Lattice Polygon Area Calculations Lattice points are points with integer coordinates in the x, y-plane. A lattice line segment is a line segment that has 2 distinct
SEQUENCES, MATHEMATICAL INDUCTION, AND RECURSION
 CHAPTER 5 SEQUENCES, MATHEMATICAL INDUCTION, AND RECURSION Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. SECTION 5.5 Application: Correctness of Algorithms Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
CHAPTER 5 SEQUENCES, MATHEMATICAL INDUCTION, AND RECURSION Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. SECTION 5.5 Application: Correctness of Algorithms Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
Assertions & Verification Example Exam Questions
 2009 November 23 Assertions & Verification Example Exam Questions 1. 2. A B C Give a general template for refining an operation into a sequence and state what questions a designer must answer to verify
2009 November 23 Assertions & Verification Example Exam Questions 1. 2. A B C Give a general template for refining an operation into a sequence and state what questions a designer must answer to verify
SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING & BUILT ENVIRONMENT. Mathematics. Numbers & Number Systems
 SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING & BUILT ENVIRONMENT Mathematics Numbers & Number Systems Introduction Numbers and Their Properties Multiples and Factors The Division Algorithm Prime and Composite Numbers Prime Factors
SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING & BUILT ENVIRONMENT Mathematics Numbers & Number Systems Introduction Numbers and Their Properties Multiples and Factors The Division Algorithm Prime and Composite Numbers Prime Factors
CSE 20 DISCRETE MATH. Winter
 CSE 20 DISCRETE MATH Winter 2017 http://cseweb.ucsd.edu/classes/wi17/cse20-ab/ Final exam The final exam is Saturday March 18 8am-11am. Lecture A will take the exam in GH 242 Lecture B will take the exam
CSE 20 DISCRETE MATH Winter 2017 http://cseweb.ucsd.edu/classes/wi17/cse20-ab/ Final exam The final exam is Saturday March 18 8am-11am. Lecture A will take the exam in GH 242 Lecture B will take the exam
CMSC Honors Discrete Mathematics
 CMSC 27130 Honors Discrete Mathematics Lectures by Alexander Razborov Notes by Justin Lubin The University of Chicago, Autumn 2017 1 Contents I Number Theory 4 1 The Euclidean Algorithm 4 2 Mathematical
CMSC 27130 Honors Discrete Mathematics Lectures by Alexander Razborov Notes by Justin Lubin The University of Chicago, Autumn 2017 1 Contents I Number Theory 4 1 The Euclidean Algorithm 4 2 Mathematical
Introduction to Modular Arithmetic
 Randolph High School Math League 2014-2015 Page 1 1 Introduction Introduction to Modular Arithmetic Modular arithmetic is a topic residing under Number Theory, which roughly speaking is the study of integers
Randolph High School Math League 2014-2015 Page 1 1 Introduction Introduction to Modular Arithmetic Modular arithmetic is a topic residing under Number Theory, which roughly speaking is the study of integers
Chapter 1 An Introduction to Computer Science. INVITATION TO Computer Science 1
 Chapter 1 An Introduction to Computer Science INVITATION TO Computer Science 1 Q8. Under what conditions would the well-known quadratic formula not be effectively computable? (Assume that you are working
Chapter 1 An Introduction to Computer Science INVITATION TO Computer Science 1 Q8. Under what conditions would the well-known quadratic formula not be effectively computable? (Assume that you are working
Star Decompositions of the Complete Split Graph
 University of Dayton ecommons Honors Theses University Honors Program 4-016 Star Decompositions of the Complete Split Graph Adam C. Volk Follow this and additional works at: https://ecommons.udayton.edu/uhp_theses
University of Dayton ecommons Honors Theses University Honors Program 4-016 Star Decompositions of the Complete Split Graph Adam C. Volk Follow this and additional works at: https://ecommons.udayton.edu/uhp_theses
1 / 43. Today. Finish Euclid. Bijection/CRT/Isomorphism. Fermat s Little Theorem. Review for Midterm.
 1 / 43 Today Finish Euclid. Bijection/CRT/Isomorphism. Fermat s Little Theorem. Review for Midterm. 2 / 43 Finding an inverse? We showed how to efficiently tell if there is an inverse. Extend euclid to
1 / 43 Today Finish Euclid. Bijection/CRT/Isomorphism. Fermat s Little Theorem. Review for Midterm. 2 / 43 Finding an inverse? We showed how to efficiently tell if there is an inverse. Extend euclid to
Discrete Math: Selected Homework Problems
 Discrete Math: Selected Homework Problems 2006 2.1 Prove: if d is a common divisor of a and b and d is also a linear combination of a and b then d is a greatest common divisor of a and b. (5 3.1 Prove:
Discrete Math: Selected Homework Problems 2006 2.1 Prove: if d is a common divisor of a and b and d is also a linear combination of a and b then d is a greatest common divisor of a and b. (5 3.1 Prove:
Line Graphs and Circulants
 Line Graphs and Circulants Jason Brown and Richard Hoshino Department of Mathematics and Statistics Dalhousie University Halifax, Nova Scotia, Canada B3H 3J5 Abstract The line graph of G, denoted L(G),
Line Graphs and Circulants Jason Brown and Richard Hoshino Department of Mathematics and Statistics Dalhousie University Halifax, Nova Scotia, Canada B3H 3J5 Abstract The line graph of G, denoted L(G),
Chapter Summary. Mathematical Induction Recursive Definitions Structural Induction Recursive Algorithms
 Chapter Summary Mathematical Induction Recursive Definitions Structural Induction Recursive Algorithms Section 5.1 Sec.on Summary Mathematical Induction Examples of Proof by Mathematical Induction Mistaken
Chapter Summary Mathematical Induction Recursive Definitions Structural Induction Recursive Algorithms Section 5.1 Sec.on Summary Mathematical Induction Examples of Proof by Mathematical Induction Mistaken
Calculation of extended gcd by normalization
 SCIREA Journal of Mathematics http://www.scirea.org/journal/mathematics August 2, 2018 Volume 3, Issue 3, June 2018 Calculation of extended gcd by normalization WOLF Marc, WOLF François, LE COZ Corentin
SCIREA Journal of Mathematics http://www.scirea.org/journal/mathematics August 2, 2018 Volume 3, Issue 3, June 2018 Calculation of extended gcd by normalization WOLF Marc, WOLF François, LE COZ Corentin
9/19/12. Why Study Discrete Math? What is discrete? Sets (Rosen, Chapter 2) can be described by discrete math TOPICS
 What is discrete? Sets (Rosen, Chapter 2) TOPICS Discrete math Set Definition Set Operations Tuples Consisting of distinct or unconnected elements, not continuous (calculus) Helps us in Computer Science
What is discrete? Sets (Rosen, Chapter 2) TOPICS Discrete math Set Definition Set Operations Tuples Consisting of distinct or unconnected elements, not continuous (calculus) Helps us in Computer Science
ELEMENTARY NUMBER THEORY AND METHODS OF PROOF
 CHAPTER 4 ELEMENTARY NUMBER THEORY AND METHODS OF PROOF Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. SECTION 4.3 Direct Proof and Counterexample III: Divisibility Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights
CHAPTER 4 ELEMENTARY NUMBER THEORY AND METHODS OF PROOF Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. SECTION 4.3 Direct Proof and Counterexample III: Divisibility Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights
ELEMENTARY NUMBER THEORY AND METHODS OF PROOF
 CHAPTER 4 ELEMENTARY NUMBER THEORY AND METHODS OF PROOF Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. SECTION 4.3 Direct Proof and Counterexample III: Divisibility Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights
CHAPTER 4 ELEMENTARY NUMBER THEORY AND METHODS OF PROOF Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. SECTION 4.3 Direct Proof and Counterexample III: Divisibility Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights
Section 5.5. Greatest common factors
 Section 5.5 Greatest common factors Definition GCF The greatest common factor (GCF) is the largest factor common to both of the specified numbers. Ex. GCF(36,84) List factors 36:1,2,3,4,6,9,12,18,36 84:1,2,3,4,6,7,9,12,14,21,28,42,84
Section 5.5 Greatest common factors Definition GCF The greatest common factor (GCF) is the largest factor common to both of the specified numbers. Ex. GCF(36,84) List factors 36:1,2,3,4,6,9,12,18,36 84:1,2,3,4,6,7,9,12,14,21,28,42,84
SPERNER S LEMMA MOOR XU
 SPERNER S LEMMA MOOR XU Abstract. Is it possible to dissect a square into an odd number of triangles of equal area? This question was first answered by Paul Monsky in 970, and the solution requires elements
SPERNER S LEMMA MOOR XU Abstract. Is it possible to dissect a square into an odd number of triangles of equal area? This question was first answered by Paul Monsky in 970, and the solution requires elements
Section A Arithmetic ( 5) Exercise A
 Section A Arithmetic In the non-calculator section of the examination there might be times when you need to work with quite awkward numbers quickly and accurately. In particular you must be very familiar
Section A Arithmetic In the non-calculator section of the examination there might be times when you need to work with quite awkward numbers quickly and accurately. In particular you must be very familiar
Modular Arithmetic. is just the set of remainders we can get when we divide integers by n
 20181004 Modular Arithmetic We are accustomed to performing arithmetic on infinite sets of numbers. But sometimes we need to perform arithmetic on a finite set, and we need it to make sense and be consistent
20181004 Modular Arithmetic We are accustomed to performing arithmetic on infinite sets of numbers. But sometimes we need to perform arithmetic on a finite set, and we need it to make sense and be consistent
Definition MATH Benjamin V.C. Collins, James A. Swenson MATH 2730
 MATH 2730 Benjamin V.C. Collins James A. Swenson s and undefined terms The importance of definition s matter! may be more important in Discrete Math than in any math course that you have had previously.
MATH 2730 Benjamin V.C. Collins James A. Swenson s and undefined terms The importance of definition s matter! may be more important in Discrete Math than in any math course that you have had previously.
CS 310 Advanced Data Structures and Algorithms
 CS 310 Advanced Data Structures and Algorithms Recursion June 27, 2017 Tong Wang UMass Boston CS 310 June 27, 2017 1 / 20 Recursion Recursion means defining something, such as a function, in terms of itself
CS 310 Advanced Data Structures and Algorithms Recursion June 27, 2017 Tong Wang UMass Boston CS 310 June 27, 2017 1 / 20 Recursion Recursion means defining something, such as a function, in terms of itself
Today. Finish Euclid. Bijection/CRT/Isomorphism. Review for Midterm.
 Today Finish Euclid. Bijection/CRT/Isomorphism. Review for Midterm. Finding an inverse? We showed how to efficiently tell if there is an inverse. Extend euclid to find inverse. Euclid s GCD algorithm.
Today Finish Euclid. Bijection/CRT/Isomorphism. Review for Midterm. Finding an inverse? We showed how to efficiently tell if there is an inverse. Extend euclid to find inverse. Euclid s GCD algorithm.
Digital Logic Design: a rigorous approach c
 Digital Logic Design: a rigorous approach c Chapter 5: Binary Representation Guy Even Moti Medina School of Electrical Engineering Tel-Aviv Univ. November 7, 2017 Book Homepage: http://www.eng.tau.ac.il/~guy/even-medina
Digital Logic Design: a rigorous approach c Chapter 5: Binary Representation Guy Even Moti Medina School of Electrical Engineering Tel-Aviv Univ. November 7, 2017 Book Homepage: http://www.eng.tau.ac.il/~guy/even-medina
Excerpt from "Art of Problem Solving Volume 1: the Basics" 2014 AoPS Inc.
 Chapter 5 Using the Integers In spite of their being a rather restricted class of numbers, the integers have a lot of interesting properties and uses. Math which involves the properties of integers is
Chapter 5 Using the Integers In spite of their being a rather restricted class of numbers, the integers have a lot of interesting properties and uses. Math which involves the properties of integers is
Topic 10 Part 2 [474 marks]
![Topic 10 Part 2 [474 marks] Topic 10 Part 2 [474 marks]](/thumbs/89/97991710.jpg) Topic Part 2 [474 marks] The complete graph H has the following cost adjacency matrix Consider the travelling salesman problem for H a By first finding a minimum spanning tree on the subgraph of H formed
Topic Part 2 [474 marks] The complete graph H has the following cost adjacency matrix Consider the travelling salesman problem for H a By first finding a minimum spanning tree on the subgraph of H formed
2. Sets. 2.1&2.2: Sets and Subsets. Combining Sets. c Dr Oksana Shatalov, Fall
 c Dr Oksana Shatalov, Fall 2014 1 2. Sets 2.1&2.2: Sets and Subsets. Combining Sets. Set Terminology and Notation DEFINITIONS: Set is well-defined collection of objects. Elements are objects or members
c Dr Oksana Shatalov, Fall 2014 1 2. Sets 2.1&2.2: Sets and Subsets. Combining Sets. Set Terminology and Notation DEFINITIONS: Set is well-defined collection of objects. Elements are objects or members
Lecture Notes, CSE 232, Fall 2014 Semester
 Lecture Notes, CSE 232, Fall 2014 Semester Dr. Brett Olsen Week 11 - Number Theory Number theory is the study of the integers. The most basic concept in number theory is divisibility. We say that b divides
Lecture Notes, CSE 232, Fall 2014 Semester Dr. Brett Olsen Week 11 - Number Theory Number theory is the study of the integers. The most basic concept in number theory is divisibility. We say that b divides
Definition. A Taylor series of a function f is said to represent function f, iff the error term converges to 0 for n going to infinity.
 Definition A Taylor series of a function f is said to represent function f, iff the error term converges to 0 for n going to infinity. 120202: ESM4A - Numerical Methods 32 f(x) = e x at point c = 0. Taylor
Definition A Taylor series of a function f is said to represent function f, iff the error term converges to 0 for n going to infinity. 120202: ESM4A - Numerical Methods 32 f(x) = e x at point c = 0. Taylor
CPSC 121: Models of Computation Assignment #4, due Thursday, March 16 th,2017at16:00
 CPSC 121: Models of Computation Assignment #4, due Thursday, March 16 th,2017at16:00 [18] 1. Consider the following predicate logic statement: 9x 2 A, 8y 2 B,9z 2 C, P(x, y, z)! Q(x, y, z), where A, B,
CPSC 121: Models of Computation Assignment #4, due Thursday, March 16 th,2017at16:00 [18] 1. Consider the following predicate logic statement: 9x 2 A, 8y 2 B,9z 2 C, P(x, y, z)! Q(x, y, z), where A, B,
CHAPTER TWO. . Therefore the oblong number n(n + 1) is double the triangular number T n. , and the summands are the triangular numbers T n 1 and T n.
 CHAPTER TWO 1. Since AB BC; since the two angles at B are equal; and since the angles at A and C are both right angles, it follows by the angle-side-angle theorem that EBC is congruent to SBA and therefore
CHAPTER TWO 1. Since AB BC; since the two angles at B are equal; and since the angles at A and C are both right angles, it follows by the angle-side-angle theorem that EBC is congruent to SBA and therefore
Scan Scheduling Specification and Analysis
 Scan Scheduling Specification and Analysis Bruno Dutertre System Design Laboratory SRI International Menlo Park, CA 94025 May 24, 2000 This work was partially funded by DARPA/AFRL under BAE System subcontract
Scan Scheduling Specification and Analysis Bruno Dutertre System Design Laboratory SRI International Menlo Park, CA 94025 May 24, 2000 This work was partially funded by DARPA/AFRL under BAE System subcontract
Solutions to the Second Midterm Exam
 CS/Math 240: Intro to Discrete Math 3/27/2011 Instructor: Dieter van Melkebeek Solutions to the Second Midterm Exam Problem 1 This question deals with the following implementation of binary search. Function
CS/Math 240: Intro to Discrete Math 3/27/2011 Instructor: Dieter van Melkebeek Solutions to the Second Midterm Exam Problem 1 This question deals with the following implementation of binary search. Function
Unit 7 Number System and Bases. 7.1 Number System. 7.2 Binary Numbers. 7.3 Adding and Subtracting Binary Numbers. 7.4 Multiplying Binary Numbers
 Contents STRAND B: Number Theory Unit 7 Number System and Bases Student Text Contents Section 7. Number System 7.2 Binary Numbers 7.3 Adding and Subtracting Binary Numbers 7.4 Multiplying Binary Numbers
Contents STRAND B: Number Theory Unit 7 Number System and Bases Student Text Contents Section 7. Number System 7.2 Binary Numbers 7.3 Adding and Subtracting Binary Numbers 7.4 Multiplying Binary Numbers
Binary Relations McGraw-Hill Education
 Binary Relations A binary relation R from a set A to a set B is a subset of A X B Example: Let A = {0,1,2} and B = {a,b} {(0, a), (0, b), (1,a), (2, b)} is a relation from A to B. We can also represent
Binary Relations A binary relation R from a set A to a set B is a subset of A X B Example: Let A = {0,1,2} and B = {a,b} {(0, a), (0, b), (1,a), (2, b)} is a relation from A to B. We can also represent
CUT VERTICES IN ZERO-DIVISOR GRAPHS OF FINITE COMMUTATIVE RINGS
 CUT VERTICES IN ZERO-DIVISOR GRAPHS OF FINITE COMMUTATIVE RINGS M. AXTELL, N. BAETH, AND J. STICKLES Abstract. A cut vertex of a connected graph is a vertex whose removal would result in a graph having
CUT VERTICES IN ZERO-DIVISOR GRAPHS OF FINITE COMMUTATIVE RINGS M. AXTELL, N. BAETH, AND J. STICKLES Abstract. A cut vertex of a connected graph is a vertex whose removal would result in a graph having
MITOCW watch?v=kvtlwgctwn4
 MITOCW watch?v=kvtlwgctwn4 PROFESSOR: The idea of congruence was introduced to the world by Gauss in the early 18th century. You've heard of him before, I think. He's responsible for some work on magnetism
MITOCW watch?v=kvtlwgctwn4 PROFESSOR: The idea of congruence was introduced to the world by Gauss in the early 18th century. You've heard of him before, I think. He's responsible for some work on magnetism
Mathematics. Jaehyun Park. CS 97SI Stanford University. June 29, 2015
 Mathematics Jaehyun Park CS 97SI Stanford University June 29, 2015 Outline Algebra Number Theory Combinatorics Geometry Algebra 2 Sum of Powers n k=1 k 3 k 2 = 1 n(n + 1)(2n + 1) 6 = ( k ) 2 = ( 1 2 n(n
Mathematics Jaehyun Park CS 97SI Stanford University June 29, 2015 Outline Algebra Number Theory Combinatorics Geometry Algebra 2 Sum of Powers n k=1 k 3 k 2 = 1 n(n + 1)(2n + 1) 6 = ( k ) 2 = ( 1 2 n(n
Content Development for Distance Education in Advanced University Mathematics Using Mizar
 Content Development for Distance Education in Advanced University Mathematics Using Mizar Takaya IDO 1, Hiroyuki OKAZAKI 1, Hiroshi YAMAZAKI 1, Pauline Naomi KAWAMOTO 1, Katsumi WASAKI 1, and Yasunari
Content Development for Distance Education in Advanced University Mathematics Using Mizar Takaya IDO 1, Hiroyuki OKAZAKI 1, Hiroshi YAMAZAKI 1, Pauline Naomi KAWAMOTO 1, Katsumi WASAKI 1, and Yasunari
Discrete Mathematics SECOND EDITION OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS. Norman L. Biggs. Professor of Mathematics London School of Economics University of London
 Discrete Mathematics SECOND EDITION Norman L. Biggs Professor of Mathematics London School of Economics University of London OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents PART I FOUNDATIONS Statements and proofs. 1
Discrete Mathematics SECOND EDITION Norman L. Biggs Professor of Mathematics London School of Economics University of London OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents PART I FOUNDATIONS Statements and proofs. 1
Conditionals !
 Conditionals 02-201! Computing GCD GCD Problem: Compute the greatest common divisor of two integers. Input: Two integers a and b. Output: The greatest common divisor of a and b. Exercise: Design an algorithm
Conditionals 02-201! Computing GCD GCD Problem: Compute the greatest common divisor of two integers. Input: Two integers a and b. Output: The greatest common divisor of a and b. Exercise: Design an algorithm
The Further Mathematics Support Programme
 Degree Topics in Mathematics Groups A group is a mathematical structure that satisfies certain rules, which are known as axioms. Before we look at the axioms, we will consider some terminology. Elements
Degree Topics in Mathematics Groups A group is a mathematical structure that satisfies certain rules, which are known as axioms. Before we look at the axioms, we will consider some terminology. Elements
A.1 Numbers, Sets and Arithmetic
 522 APPENDIX A. MATHEMATICS FOUNDATIONS A.1 Numbers, Sets and Arithmetic Numbers started as a conceptual way to quantify count objects. Later, numbers were used to measure quantities that were extensive,
522 APPENDIX A. MATHEMATICS FOUNDATIONS A.1 Numbers, Sets and Arithmetic Numbers started as a conceptual way to quantify count objects. Later, numbers were used to measure quantities that were extensive,
One of the most important areas where quantifier logic is used is formal specification of computer programs.
 Section 5.2 Formal specification of computer programs One of the most important areas where quantifier logic is used is formal specification of computer programs. Specification takes place on several levels
Section 5.2 Formal specification of computer programs One of the most important areas where quantifier logic is used is formal specification of computer programs. Specification takes place on several levels
COMPUTER SCIENCE TRIPOS
 CST.2000.1.1 COMPUTER SCIENCE TRIPOS Part IA Monday 5 June 2000 1.30 to 4.30 Paper 1 Answer two questions from Section A, and one question from each of Sections B, C, D and E. Submit the answers in six
CST.2000.1.1 COMPUTER SCIENCE TRIPOS Part IA Monday 5 June 2000 1.30 to 4.30 Paper 1 Answer two questions from Section A, and one question from each of Sections B, C, D and E. Submit the answers in six
Math 55 - Spring 04 - Lecture notes # 1 - Jan 20 (Tuesday)
 Math 55 - Spring 04 - Lecture notes # 1 - Jan 20 (Tuesday) Name, class, URL (www.cs.berkeley.edu/~demmel/ma55) on board Head TA Mike West speaks on bureaucracy Advertise CS 70 (T Th 2-3:30) as an "honors"
Math 55 - Spring 04 - Lecture notes # 1 - Jan 20 (Tuesday) Name, class, URL (www.cs.berkeley.edu/~demmel/ma55) on board Head TA Mike West speaks on bureaucracy Advertise CS 70 (T Th 2-3:30) as an "honors"
Ramsey s Theorem on Graphs
 Ramsey s Theorem on Graphs 1 Introduction Exposition by William Gasarch Imagine that you have 6 people at a party. We assume that, for every pair of them, either THEY KNOW EACH OTHER or NEITHER OF THEM
Ramsey s Theorem on Graphs 1 Introduction Exposition by William Gasarch Imagine that you have 6 people at a party. We assume that, for every pair of them, either THEY KNOW EACH OTHER or NEITHER OF THEM
Math 126 Number Theory
 Math 16 Number Theory Prof. D. Joyce, Clark University 8 Mar 006 Due Friday. Page 155: exercises 1,, 7. Choose one of the three and write it up completely. Whichever one you choose, find all those solutions
Math 16 Number Theory Prof. D. Joyce, Clark University 8 Mar 006 Due Friday. Page 155: exercises 1,, 7. Choose one of the three and write it up completely. Whichever one you choose, find all those solutions
1.1 - Introduction to Sets
 1.1 - Introduction to Sets Math 166-502 Blake Boudreaux Department of Mathematics Texas A&M University January 18, 2018 Blake Boudreaux (Texas A&M University) 1.1 - Introduction to Sets January 18, 2018
1.1 - Introduction to Sets Math 166-502 Blake Boudreaux Department of Mathematics Texas A&M University January 18, 2018 Blake Boudreaux (Texas A&M University) 1.1 - Introduction to Sets January 18, 2018
Primes and Codes. Dr Bill Lionheart, Department of Mathematics, UMIST. October 4, 2001
 Primes and Codes Dr Bill Lionheart, Department of Mathematics, UMIST October 4, 2001 1 Introduction Codes have been used since ancient times to send secret messages. Today they are even more important.
Primes and Codes Dr Bill Lionheart, Department of Mathematics, UMIST October 4, 2001 1 Introduction Codes have been used since ancient times to send secret messages. Today they are even more important.
Prepared by Sa diyya Hendrickson. Package Summary
 Introduction Prepared by Sa diyya Hendrickson Name: Date: Package Summary Exponent Form and Basic Properties Order of Operations Using Divisibility Rules Finding Factors and Common Factors Primes, Prime
Introduction Prepared by Sa diyya Hendrickson Name: Date: Package Summary Exponent Form and Basic Properties Order of Operations Using Divisibility Rules Finding Factors and Common Factors Primes, Prime
Lectures on Order and Topology
 Lectures on Order and Topology Antonino Salibra 17 November 2014 1 Topology: main definitions and notation Definition 1.1 A topological space X is a pair X = ( X, OX) where X is a nonempty set and OX is
Lectures on Order and Topology Antonino Salibra 17 November 2014 1 Topology: main definitions and notation Definition 1.1 A topological space X is a pair X = ( X, OX) where X is a nonempty set and OX is
Hashing. Yufei Tao. Department of Computer Science and Engineering Chinese University of Hong Kong
 Department of Computer Science and Engineering Chinese University of Hong Kong In this lecture, we will revisit the dictionary search problem, where we want to locate an integer v in a set of size n or
Department of Computer Science and Engineering Chinese University of Hong Kong In this lecture, we will revisit the dictionary search problem, where we want to locate an integer v in a set of size n or
Lecture 1. 1 Notation
 Lecture 1 (The material on mathematical logic is covered in the textbook starting with Chapter 5; however, for the first few lectures, I will be providing some required background topics and will not be
Lecture 1 (The material on mathematical logic is covered in the textbook starting with Chapter 5; however, for the first few lectures, I will be providing some required background topics and will not be
CSC Discrete Math I, Spring Sets
 CSC 125 - Discrete Math I, Spring 2017 Sets Sets A set is well-defined, unordered collection of objects The objects in a set are called the elements, or members, of the set A set is said to contain its
CSC 125 - Discrete Math I, Spring 2017 Sets Sets A set is well-defined, unordered collection of objects The objects in a set are called the elements, or members, of the set A set is said to contain its
Test 1, Spring 2013 ( Solutions): Provided by Jeff Collins and Anil Patel. 1. Axioms for a finite AFFINE plane of order n.
 Math 532, 736I: Modern Geometry Test 1, Spring 2013 ( Solutions): Provided by Jeff Collins and Anil Patel Part 1: 1. Axioms for a finite AFFINE plane of order n. AA1: There exist at least 4 points, no
Math 532, 736I: Modern Geometry Test 1, Spring 2013 ( Solutions): Provided by Jeff Collins and Anil Patel Part 1: 1. Axioms for a finite AFFINE plane of order n. AA1: There exist at least 4 points, no
Connecting Statements. Today. First there was logic jumping forward.. ..and then proofs and then induction...
 Today Review for Midterm. First there was logic... A statement is a true or false. Statements? 3 = 4 1? Statement! 3 = 5? Statement! 3? Not a statement! n = 3? Not a statement...but a predicate. Predicate:
Today Review for Midterm. First there was logic... A statement is a true or false. Statements? 3 = 4 1? Statement! 3 = 5? Statement! 3? Not a statement! n = 3? Not a statement...but a predicate. Predicate:
Heron Quadrilaterals with Sides in Arithmetic or Geometric Progression
 Heron Quadrilaterals with Sides in Arithmetic or Geometric Progression R.H.Buchholz & J.A.MacDougall Abstract We study triangles and cyclic quadrilaterals which have rational area and whose sides form
Heron Quadrilaterals with Sides in Arithmetic or Geometric Progression R.H.Buchholz & J.A.MacDougall Abstract We study triangles and cyclic quadrilaterals which have rational area and whose sides form
Unit 1 Geometric Fundamentals
 Honors Geometry Unit 1 Geometric Fundamentals Date Target Assignment Done! R 8-17 1.1a 1.1a Worksheet F 8-18 1.1b Pre-Assessment / 1.1b Worksheet M 8-21 1.1 1.2a Worksheet T 8-22 1.2a 1.2b Worksheet W
Honors Geometry Unit 1 Geometric Fundamentals Date Target Assignment Done! R 8-17 1.1a 1.1a Worksheet F 8-18 1.1b Pre-Assessment / 1.1b Worksheet M 8-21 1.1 1.2a Worksheet T 8-22 1.2a 1.2b Worksheet W
The statement implies that any three intersection points of two distinct planes lie on a line.
 Math 3181 Dr. Franz Rothe February 23, 2015 All3181\3181_spr15ts1.tex 1 Solution of Test Name: Problem 1.1. The second part of Hilbert s Proposition 1 states: Any two different planes have either no point
Math 3181 Dr. Franz Rothe February 23, 2015 All3181\3181_spr15ts1.tex 1 Solution of Test Name: Problem 1.1. The second part of Hilbert s Proposition 1 states: Any two different planes have either no point
CS 97SI: INTRODUCTION TO PROGRAMMING CONTESTS. Jaehyun Park
 CS 97SI: INTRODUCTION TO PROGRAMMING CONTESTS Jaehyun Park Today s Lecture Algebra Number Theory Combinatorics (non-computational) Geometry Emphasis on how to compute Sum of Powers n k=1 k 2 = 1 6 n(n
CS 97SI: INTRODUCTION TO PROGRAMMING CONTESTS Jaehyun Park Today s Lecture Algebra Number Theory Combinatorics (non-computational) Geometry Emphasis on how to compute Sum of Powers n k=1 k 2 = 1 6 n(n
Odd-Numbered Answers to Exercise Set 1.1: Numbers
 Odd-Numbered Answers to Exercise Set.: Numbers. (a) Composite;,,, Prime Neither (d) Neither (e) Composite;,,,,,. (a) 0. 0. 0. (d) 0. (e) 0. (f) 0. (g) 0. (h) 0. (i) 0.9 = (j). (since = ) 9 9 (k). (since
Odd-Numbered Answers to Exercise Set.: Numbers. (a) Composite;,,, Prime Neither (d) Neither (e) Composite;,,,,,. (a) 0. 0. 0. (d) 0. (e) 0. (f) 0. (g) 0. (h) 0. (i) 0.9 = (j). (since = ) 9 9 (k). (since
Uncharted Territory of Zero Divisor Graphs and Their Complements
 Uncharted Territory of Zero Divisor Graphs and Their Complements Amanda Phillips, Julie Rogers, Kevin Tolliver, and Frances Worek July, 004 Abstract Let Γ(Z n ) be a zero divisor graph whose vertices are
Uncharted Territory of Zero Divisor Graphs and Their Complements Amanda Phillips, Julie Rogers, Kevin Tolliver, and Frances Worek July, 004 Abstract Let Γ(Z n ) be a zero divisor graph whose vertices are
DISCRETE MATHEMATICS
 DISCRETE MATHEMATICS WITH APPLICATIONS THIRD EDITION SUSANNA S. EPP DePaul University THOIVISON * BROOKS/COLE Australia Canada Mexico Singapore Spain United Kingdom United States CONTENTS Chapter 1 The
DISCRETE MATHEMATICS WITH APPLICATIONS THIRD EDITION SUSANNA S. EPP DePaul University THOIVISON * BROOKS/COLE Australia Canada Mexico Singapore Spain United Kingdom United States CONTENTS Chapter 1 The
Chapter 18 out of 37 from Discrete Mathematics for Neophytes: Number Theory, Probability, Algorithms, and Other Stuff by J. M. Cargal.
 Chapter 8 out of 7 from Discrete Mathematics for Neophytes: Number Theory, Probability, Algorithms, and Other Stuff by J. M. Cargal 8 Matrices Definitions and Basic Operations Matrix algebra is also known
Chapter 8 out of 7 from Discrete Mathematics for Neophytes: Number Theory, Probability, Algorithms, and Other Stuff by J. M. Cargal 8 Matrices Definitions and Basic Operations Matrix algebra is also known
