Lecture 05: Methods. AITI Nigeria Summer 2012 University of Lagos.
|
|
|
- Francis Gordon
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Lecture 05: Methods AITI Nigeria Summer 2012 University of Lagos.
2 Agenda What a method is Why we use methods How to declare a method The four parts of a method How to use (invoke) a method The purpose of the main method
3 The Concept of a Method Methods are a way of organizing a sequence of statements into a named unit. Reusable Parameterizable (can accept inputs) Organize code into smaller units Easier to understand Any complex process that can exist on its own should be a method Better to have more methods, even if they are not reused.
4 The Concept of a Method Methods can accept inputs (called arguments) They can then perform some operations with the arguments And can output a value (called a return value) that is the result of the computations inputs method outputs
5 Square Root Method The square root method accepts a single number as an argument and returns the square root of that number. (argument) number Square Root Method number (return value)
6 Square Root Method (con t) The computation of square roots involves many intermediate steps between input and output. When we use square root, we don t care about these steps or details. All we need is to get the correct output. Hiding the internal workings of a method and providing the correct answer is known as abstraction 4 Square Root +2,-2 Black Box
7 Declaring Methods A method has 4 parts: the return type, the name, the arguments, and the body: type name arguments body double sqrt(double num) { // a set of operations that compute // the square root of a number The type, name and arguments together is referred to as the signature of the method Methods with same names must have unique signature
8 Return Type of a Method The return type of a method may be any data type... inputs method int,double, OR string... The return type of a method is a promise for what data type the output will be A method can return different outputs than inputs A method cannot return multiple types, returns one type Methods can also return nothing in which case they are declared void.
9 Return Statements The return statement is used in a method to output the result of the method computation. It has the form: return expression-value; The type of the expression_value must be the same as the type of the method: double sqrt(double num) { double answer; // Compute the square root of num // and store in answer return answer; What is the return type of this method?
10 Return Statements A method exits immediately after it executes the return statement double sqrt(double num) { double answer; // Compute the square root of num // and store in answer return answer; answer = 5 + 4; //never executed, illegal
11 Multiple Returns An example using multiple returns: int absolutevalue (int num) { if (num < 0) return num; else return num;
12 void Methods A method of type void does not return a value inputs Used often in practice. method Perform some computation that does not produce a value Affect system state, ex: System.out.println() A void method can have a return statement without any specified value. i.e. return; If no return statement is used in a method of type void, it automatically returns at the end
13 Method Arguments Methods can take input in the form of arguments. Arguments are used as variables inside the method body. Like variables, arguments must have their type specified. Arguments are specified inside the parentheses that follow the name of the method.
14 Example Method Here is an example of a method that divides two doubles: double divide(double a, double b) { double answer; answer = a / b; return answer; a,b divide answer = a/b
15 Method Arguments Multiple method arguments are separated by commas: double divide(double a, double b) { double answer; answer = a / b; return answer; Arguments may be of different types (double/int) double divide(int a, int b) When calling method, exact sequence of input types must be applied
16 The Method Body The body of a method is a block specified by curly brackets i.e {. The body defines the actions of the method. The method arguments can be used anywhere inside of the body. All methods must have curly brackets to specify the body even if the body contains only one statement or no statements. double divide( double a, double b) { double answer; answer = a / b; return answer;
17 Invoking Methods To call a method, specify the name of the method followed by a list of comma separated arguments in parentheses: divide(10, 2); //Computes 10/2 If the method has no arguments, you still need to follow the method name with empty parentheses: int size() { //Compute and return size size(); //Calls size
18 Method Variable Scoping For now, methods can only access their own arguments and local variables. A method cannot access arguments/locals from other methods Even if one method calls another Example 18
19 Recursive Methods A method can also call itself! When a method calls itself, it needs a stopping condition, called the base case Or else it would call itself without end Example Factorial: Factorial of n, denoted n!: n (n 1) (n 2) 0 0! = 1 (base case)
20 Factorial Implementation int factorial(int n) { if (n==0) return 1; else { return n * factorial (n-1); 20
21 Static Methods For now, all the methods we write in lab will be static. static double divide(double a, double b) { return a / b; We'll learn what it means for a method to be static in a later lecture
22 main A Special Method The only method that we have used in lab up until this point is the main method. The main method is where a Java program always starts when you run a class file (entry point) The main method is static and has a strict signature which must be followed: public static void main(string[] args) {...
23 main Method (con t) class SayHi { public static void main(string[] args) { System.out.println("Hi, " + args[0]); If you were to type java Program arg1 arg2 argn on the command line, anything after the name of the class file is automatically entered into the args array: java SayHi Sonia In this example args[0] will contain the String "Sonia", and the output of the program will be "Hi, Sonia".
24 Methods Review What are the four parts of a method and what are their functions? 1.Return type data type returned by the method 2. Name name of the method 3. Arguments inputs to the method 4. Body sequence of instructions executed by the method
25 What is wrong with the following? static double addsometimes(num1, num2){ double sum; if (num1 < num2){ sum = num1 + num2; String completed = completed ; return completed; Types for the arguments num1 and num2 are not specified String completed does not match the correct double return type Method addsometimes does not always return an answer. This will cause an error in Java because we specified that addsometimes would always return a double.
26 Example class Max { public static void main(string args[]) { if (args.length == 0) return; int max = Integer.parseInt(args[0]); for (int i=1; i < args.length; i++) { if (Integer.parseInt(args[i]) > max) { max = Integer.parseInt(args[i]); System.out.println(max); After compiling, if you type java Max the program will print out 9
27 Important Points Covered. Methods capture a piece of computation we wish to perform repeatedly into a single abstraction Methods in Java have 4 parts: return type, name, arguments, body. The return type and arguments may be either primitive data types (i.e. int) or complex data types (i.e. Objects), which we will cover next lecture main is a special Java method which the java interpreter looks for when you try to run a class file main has a strict signature that must be followed: public static void main(string args[])
Lecture 5: Methods CS2301
 Lecture 5: Methods NADA ALZAHRANI CS2301 1 Opening Problem Find the sum of integers from 1 to 10, from 20 to 30, and from 35 to 45, respectively. 2 Solution public static int sum(int i1, int i2) { int
Lecture 5: Methods NADA ALZAHRANI CS2301 1 Opening Problem Find the sum of integers from 1 to 10, from 20 to 30, and from 35 to 45, respectively. 2 Solution public static int sum(int i1, int i2) { int
Announcements. PS 3 is due Thursday, 10/6. Midterm Exam 1: 10/14 (Fri), 9:00am-10:53am
 Announcements PS 3 is due Thursday, 10/6 Midterm Exam 1: 10/14 (Fri), 9:00am-10:53am Room TBD Scope: Lecture 1 to Lecture 9 (Chapters 1 to 6 of text) You may bring a sheet of paper (A4, both sides) Tutoring
Announcements PS 3 is due Thursday, 10/6 Midterm Exam 1: 10/14 (Fri), 9:00am-10:53am Room TBD Scope: Lecture 1 to Lecture 9 (Chapters 1 to 6 of text) You may bring a sheet of paper (A4, both sides) Tutoring
CS-201 Introduction to Programming with Java
 CS-201 Introduction to Programming with Java California State University, Los Angeles Computer Science Department Lecture X: Methods II Passing Arguments Passing Arguments methods can accept outside information
CS-201 Introduction to Programming with Java California State University, Los Angeles Computer Science Department Lecture X: Methods II Passing Arguments Passing Arguments methods can accept outside information
Chapter 5 Methods. Liang, Introduction to Java Programming, Eighth Edition, (c) 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 5 Methods 1 Opening Problem Find the sum of integers from 1 to 10, from 20 to 30, and from 35 to 45, respectively. 2 Problem int sum = 0; for (int i = 1; i
Chapter 5 Methods 1 Opening Problem Find the sum of integers from 1 to 10, from 20 to 30, and from 35 to 45, respectively. 2 Problem int sum = 0; for (int i = 1; i
Java Methods. Lecture 8 COP 3252 Summer May 23, 2017
 Java Methods Lecture 8 COP 3252 Summer 2017 May 23, 2017 Java Methods In Java, the word method refers to the same kind of thing that the word function is used for in other languages. Specifically, a method
Java Methods Lecture 8 COP 3252 Summer 2017 May 23, 2017 Java Methods In Java, the word method refers to the same kind of thing that the word function is used for in other languages. Specifically, a method
Lecture 1: Introduction to Java
 Accelerating Information Technology Innovation http://aiti.mit.edu Lecture 1: Introduction to Java AITI Nigeria Summer 2012 University of Lagos. Agenda First Lab.. Class is Hands on remember? Recap Previously
Accelerating Information Technology Innovation http://aiti.mit.edu Lecture 1: Introduction to Java AITI Nigeria Summer 2012 University of Lagos. Agenda First Lab.. Class is Hands on remember? Recap Previously
Opening Problem. Find the sum of integers from 1 to 10, from 20 to 30, and from 35 to 45, respectively.
 Chapter 6 Methods 1 Opening Problem Find the sum of integers from 1 to 10, from 20 to 30, and from 35 to 45, respectively. 2 A Solution int sum = 0; for (int i = 1; i
Chapter 6 Methods 1 Opening Problem Find the sum of integers from 1 to 10, from 20 to 30, and from 35 to 45, respectively. 2 A Solution int sum = 0; for (int i = 1; i
CS110: PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE I
 CS110: PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE I Computer Science Department Lecture 8: Methods Lecture Contents: 2 Introduction Program modules in java Defining Methods Calling Methods Scope of local variables Passing Parameters
CS110: PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE I Computer Science Department Lecture 8: Methods Lecture Contents: 2 Introduction Program modules in java Defining Methods Calling Methods Scope of local variables Passing Parameters
COP3502 Programming Fundamentals for CIS Majors 1. Instructor: Parisa Rashidi
 COP3502 Programming Fundamentals for CIS Majors 1 Instructor: Parisa Rashidi Chapter 4 Loops for while do-while Last Week Chapter 5 Methods Input arguments Output Overloading Code reusability Scope of
COP3502 Programming Fundamentals for CIS Majors 1 Instructor: Parisa Rashidi Chapter 4 Loops for while do-while Last Week Chapter 5 Methods Input arguments Output Overloading Code reusability Scope of
Methods. CSE 114, Computer Science 1 Stony Brook University
 Methods CSE 114, Computer Science 1 Stony Brook University http://www.cs.stonybrook.edu/~cse114 1 Opening Problem Find multiple sums of integers: - from 1 to 10, - from 20 to 30, - from 35 to 45,... 2
Methods CSE 114, Computer Science 1 Stony Brook University http://www.cs.stonybrook.edu/~cse114 1 Opening Problem Find multiple sums of integers: - from 1 to 10, - from 20 to 30, - from 35 to 45,... 2
Chapter 5 Methods / Functions
 Chapter 5 Methods / Functions 1 Motivations A method is a construct for grouping statements together to perform a function. Using a method, you can write the code once for performing the function in a
Chapter 5 Methods / Functions 1 Motivations A method is a construct for grouping statements together to perform a function. Using a method, you can write the code once for performing the function in a
Object-oriented programming. and data-structures CS/ENGRD 2110 SUMMER 2018
 Object-oriented programming 1 and data-structures CS/ENGRD 2110 SUMMER 2018 Lecture 1: Types and Control Flow http://courses.cs.cornell.edu/cs2110/2018su Lecture 1 Outline 2 Languages Overview Imperative
Object-oriented programming 1 and data-structures CS/ENGRD 2110 SUMMER 2018 Lecture 1: Types and Control Flow http://courses.cs.cornell.edu/cs2110/2018su Lecture 1 Outline 2 Languages Overview Imperative
To define methods, invoke methods, and pass arguments to a method ( ). To develop reusable code that is modular, easy-toread, easy-to-debug,
 1 To define methods, invoke methods, and pass arguments to a method ( 5.2-5.5). To develop reusable code that is modular, easy-toread, easy-to-debug, and easy-to-maintain. ( 5.6). To use method overloading
1 To define methods, invoke methods, and pass arguments to a method ( 5.2-5.5). To develop reusable code that is modular, easy-toread, easy-to-debug, and easy-to-maintain. ( 5.6). To use method overloading
Lecture 06: Classes and Objects
 Accelerating Information Technology Innovation http://aiti.mit.edu Lecture 06: Classes and Objects AITI Nigeria Summer 2012 University of Lagos. What do we know so far? Primitives: int, float, double,
Accelerating Information Technology Innovation http://aiti.mit.edu Lecture 06: Classes and Objects AITI Nigeria Summer 2012 University of Lagos. What do we know so far? Primitives: int, float, double,
AP CS Unit 3: Control Structures Notes
 AP CS Unit 3: Control Structures Notes The if and if-else Statements. These statements are called control statements because they control whether a particular block of code is executed or not. Some texts
AP CS Unit 3: Control Structures Notes The if and if-else Statements. These statements are called control statements because they control whether a particular block of code is executed or not. Some texts
Opening Problem. Find the sum of integers from 1 to 10, from 20 to 30, and from 35 to 45, respectively.
 Chapter 6 Methods 1 Opening Problem Find the sum of integers from 1 to 10, from 20 to 30, and from 35 to 45, respectively. 2 A Solution int sum = 0; for (int i = 1; i
Chapter 6 Methods 1 Opening Problem Find the sum of integers from 1 to 10, from 20 to 30, and from 35 to 45, respectively. 2 A Solution int sum = 0; for (int i = 1; i
Lab 9: Creating a Reusable Class
 Lab 9: Creating a Reusable Class Objective This will introduce the student to creating custom, reusable classes This will introduce the student to using the custom, reusable class This will reinforce programming
Lab 9: Creating a Reusable Class Objective This will introduce the student to creating custom, reusable classes This will introduce the student to using the custom, reusable class This will reinforce programming
( &% class MyClass { }
 Recall! $! "" # ' ' )' %&! ( &% class MyClass { $ Individual things that differentiate one object from another Determine the appearance, state or qualities of objects Represents any variables needed for
Recall! $! "" # ' ' )' %&! ( &% class MyClass { $ Individual things that differentiate one object from another Determine the appearance, state or qualities of objects Represents any variables needed for
Functions. CS111 Lab Queens College, CUNY Instructor: Kent Chin
 Functions CS111 Lab Queens College, CUNY Instructor: Kent Chin Functions They're everywhere! Input: x Function: f Output: f(x) Input: Sheets of Paper Function: Staple Output: Stapled Sheets of Paper C++
Functions CS111 Lab Queens College, CUNY Instructor: Kent Chin Functions They're everywhere! Input: x Function: f Output: f(x) Input: Sheets of Paper Function: Staple Output: Stapled Sheets of Paper C++
Static Methods. Why use methods?
 Static Methods A method is just a collection of code. They are also called functions or procedures. It provides a way to break a larger program up into smaller, reusable chunks. This also has the benefit
Static Methods A method is just a collection of code. They are also called functions or procedures. It provides a way to break a larger program up into smaller, reusable chunks. This also has the benefit
CS-201 Introduction to Programming with Java
 CS-201 Introduction to Programming with Java California State University, Los Angeles Computer Science Department Lecture IX: Methods Introduction method: construct for grouping statements together to
CS-201 Introduction to Programming with Java California State University, Los Angeles Computer Science Department Lecture IX: Methods Introduction method: construct for grouping statements together to
Lesson 05 Methods. MIT 12043, Fundamentals of Programming By: S. Sabraz Nawaz Senior Lecturer in MIT Department of MIT FMC, SEUSL
 Lesson 05 Methods MIT 12043, Fundamentals of Programming By: S. Sabraz Nawaz Senior Lecturer in MIT Department of MIT FMC, SEUSL Why Write Methods? Methods are commonly used to break a problem down into
Lesson 05 Methods MIT 12043, Fundamentals of Programming By: S. Sabraz Nawaz Senior Lecturer in MIT Department of MIT FMC, SEUSL Why Write Methods? Methods are commonly used to break a problem down into
Lecture 08: Static Fields and Methods
 Accelerating Information Technology Innovation http://aiti.mit.edu Lecture 08: Static Fields and Methods AITI Nigeria Summer 2012 University of Lagos. What You Know So Far Each object has its own copy
Accelerating Information Technology Innovation http://aiti.mit.edu Lecture 08: Static Fields and Methods AITI Nigeria Summer 2012 University of Lagos. What You Know So Far Each object has its own copy
Sequence structure. The computer executes java statements one after the other in the order in which they are written. Total = total +grade;
 Control Statements Control Statements All programs could be written in terms of only one of three control structures: Sequence Structure Selection Structure Repetition Structure Sequence structure The
Control Statements Control Statements All programs could be written in terms of only one of three control structures: Sequence Structure Selection Structure Repetition Structure Sequence structure The
Lecture 04 FUNCTIONS AND ARRAYS
 Lecture 04 FUNCTIONS AND ARRAYS 1 Motivations Divide hug tasks to blocks: divide programs up into sets of cooperating functions. Define new functions with function calls and parameter passing. Use functions
Lecture 04 FUNCTIONS AND ARRAYS 1 Motivations Divide hug tasks to blocks: divide programs up into sets of cooperating functions. Define new functions with function calls and parameter passing. Use functions
CSCI 135 Exam #0 Fundamentals of Computer Science I Fall 2013
 CSCI 135 Exam #0 Fundamentals of Computer Science I Fall 2013 Name: This exam consists of 7 problems on the following 6 pages. You may use your single- side hand- written 8 ½ x 11 note sheet during the
CSCI 135 Exam #0 Fundamentals of Computer Science I Fall 2013 Name: This exam consists of 7 problems on the following 6 pages. You may use your single- side hand- written 8 ½ x 11 note sheet during the
COMP 250: Java Programming I. Carlos G. Oliver, Jérôme Waldispühl January 17-18, 2018 Slides adapted from M. Blanchette
 COMP 250: Java Programming I Carlos G. Oliver, Jérôme Waldispühl January 17-18, 2018 Slides adapted from M. Blanchette Variables and types [Downey Ch 2] Variable: temporary storage location in memory.
COMP 250: Java Programming I Carlos G. Oliver, Jérôme Waldispühl January 17-18, 2018 Slides adapted from M. Blanchette Variables and types [Downey Ch 2] Variable: temporary storage location in memory.
Functions. Lecture 6 COP 3014 Spring February 11, 2018
 Functions Lecture 6 COP 3014 Spring 2018 February 11, 2018 Functions A function is a reusable portion of a program, sometimes called a procedure or subroutine. Like a mini-program (or subprogram) in its
Functions Lecture 6 COP 3014 Spring 2018 February 11, 2018 Functions A function is a reusable portion of a program, sometimes called a procedure or subroutine. Like a mini-program (or subprogram) in its
A Foundation for Programming
 2.1 Functions A Foundation for Programming any program you might want to write objects functions and modules build bigger programs and reuse code graphics, sound, and image I/O arrays conditionals and
2.1 Functions A Foundation for Programming any program you might want to write objects functions and modules build bigger programs and reuse code graphics, sound, and image I/O arrays conditionals and
Review. Primitive Data Types & Variables. String Mathematical operators: + - * / % Comparison: < > <= >= == int, long float, double boolean char
 Review Primitive Data Types & Variables int, long float, double boolean char String Mathematical operators: + - * / % Comparison: < > = == 1 1.3 Conditionals and Loops Introduction to Programming in
Review Primitive Data Types & Variables int, long float, double boolean char String Mathematical operators: + - * / % Comparison: < > = == 1 1.3 Conditionals and Loops Introduction to Programming in
COMP-202. Recursion. COMP Recursion, 2011 Jörg Kienzle and others
 COMP-202 Recursion Recursion Recursive Definitions Run-time Stacks Recursive Programming Recursion vs. Iteration Indirect Recursion Lecture Outline 2 Recursive Definitions (1) A recursive definition is
COMP-202 Recursion Recursion Recursive Definitions Run-time Stacks Recursive Programming Recursion vs. Iteration Indirect Recursion Lecture Outline 2 Recursive Definitions (1) A recursive definition is
Chapter 6 Methods. Dr. Hikmat Jaber
 Chapter 6 Methods Dr. Hikmat Jaber 1 Opening Problem Find the sum of integers from 1 to 10, from 20 to 30, and from 35 to 45, respectively. 2 Problem int sum = 0; for (int i = 1; i
Chapter 6 Methods Dr. Hikmat Jaber 1 Opening Problem Find the sum of integers from 1 to 10, from 20 to 30, and from 35 to 45, respectively. 2 Problem int sum = 0; for (int i = 1; i
Review Chapter 6 in Bravaco. Short Answers 1. This type of method does not return a value. a. null b. void c. empty d. anonymous
 Assignment 3 Methods Review CSC 123 Fall 2018 Notes: All homework must be submitted via e-mail. All parts of assignment must be submitted in a single e-mail with multiple attachments when required. Notes:
Assignment 3 Methods Review CSC 123 Fall 2018 Notes: All homework must be submitted via e-mail. All parts of assignment must be submitted in a single e-mail with multiple attachments when required. Notes:
CS 106 Introduction to Computer Science I
 CS 106 Introduction to Computer Science I 06 / 10 / 2015 Instructor: Michael Eckmann Today s Topics Questions / comments? Method terminology and Programmer defined methods Michael Eckmann - Skidmore College
CS 106 Introduction to Computer Science I 06 / 10 / 2015 Instructor: Michael Eckmann Today s Topics Questions / comments? Method terminology and Programmer defined methods Michael Eckmann - Skidmore College
CT 229 Methods Continued
 CT 229 Methods Continued 13/10/2006 CT229 Lab Assignments Due Date for current lab assignment : Oct 20 th In Part 1 of Assignment you can declare a constant 3.14 to use as PI or you can use Math.PI Formula
CT 229 Methods Continued 13/10/2006 CT229 Lab Assignments Due Date for current lab assignment : Oct 20 th In Part 1 of Assignment you can declare a constant 3.14 to use as PI or you can use Math.PI Formula
Tutorials. Inf1-OP. Learning Outcomes for this week. A Foundation for Programming. Conditionals and Loops 1
 Tutorials Inf1-OP Conditionals and Loops 1 Volker Seeker, adapting earlier version by Perdita Stevens and Ewan Klein Start this week please let the ITO know if you need to switch tutorial groups. Labs
Tutorials Inf1-OP Conditionals and Loops 1 Volker Seeker, adapting earlier version by Perdita Stevens and Ewan Klein Start this week please let the ITO know if you need to switch tutorial groups. Labs
Unit 7. Functions. Need of User Defined Functions
 Unit 7 Functions Functions are the building blocks where every program activity occurs. They are self contained program segments that carry out some specific, well defined task. Every C program must have
Unit 7 Functions Functions are the building blocks where every program activity occurs. They are self contained program segments that carry out some specific, well defined task. Every C program must have
Methods. Every Java application must have a main method.
 Methods Every Java application must have a main method. The JVM calls main when it runs your program. When main finishes control goes back to the JVM. Up to now, we have always coded public static void
Methods Every Java application must have a main method. The JVM calls main when it runs your program. When main finishes control goes back to the JVM. Up to now, we have always coded public static void
Java Identifiers, Data Types & Variables
 Java Identifiers, Data Types & Variables 1. Java Identifiers: Identifiers are name given to a class, variable or a method. public class TestingShastra { //TestingShastra is an identifier for class char
Java Identifiers, Data Types & Variables 1. Java Identifiers: Identifiers are name given to a class, variable or a method. public class TestingShastra { //TestingShastra is an identifier for class char
CS115 Principles of Computer Science
 CS115 Principles of Computer Science Chapter 5 Methods Prof. Joe X. Zhou Department of Computer Science CS115 Methods.1 Re: Objectives in Loops Sequence and selection aside, we need repetition (loops)
CS115 Principles of Computer Science Chapter 5 Methods Prof. Joe X. Zhou Department of Computer Science CS115 Methods.1 Re: Objectives in Loops Sequence and selection aside, we need repetition (loops)
Methods. Contents Anatomy of a Method How to design a Method Static methods Additional Reading. Anatomy of a Method
 Methods Objectives: 1. create a method with arguments 2. create a method with return value 3. use method arguments 4. use the return keyword 5. use the static keyword 6. write and invoke static methods
Methods Objectives: 1. create a method with arguments 2. create a method with return value 3. use method arguments 4. use the return keyword 5. use the static keyword 6. write and invoke static methods
Condi(onals and Loops
 Condi(onals and Loops 1 Review Primi(ve Data Types & Variables int, long float, double boolean char String Mathema(cal operators: + - * / % Comparison: < > = == 2 A Founda(on for Programming any program
Condi(onals and Loops 1 Review Primi(ve Data Types & Variables int, long float, double boolean char String Mathema(cal operators: + - * / % Comparison: < > = == 2 A Founda(on for Programming any program
Java+- Language Reference Manual
 Fall 2016 COMS4115 Programming Languages & Translators Java+- Language Reference Manual Authors Ashley Daguanno (ad3079) - Manager Anna Wen (aw2802) - Tester Tin Nilar Hlaing (th2520) - Systems Architect
Fall 2016 COMS4115 Programming Languages & Translators Java+- Language Reference Manual Authors Ashley Daguanno (ad3079) - Manager Anna Wen (aw2802) - Tester Tin Nilar Hlaing (th2520) - Systems Architect
CS113: Lecture 4. Topics: Functions. Function Activation Records
 CS113: Lecture 4 Topics: Functions Function Activation Records 1 Why functions? Functions add no expressive power to the C language in a formal sense. Why have them? Breaking tasks into smaller ones make
CS113: Lecture 4 Topics: Functions Function Activation Records 1 Why functions? Functions add no expressive power to the C language in a formal sense. Why have them? Breaking tasks into smaller ones make
Chapter 5 Methods. Liang, Introduction to Java Programming, Ninth Edition, (c) 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 5 Methods 1 Opening Problem Find the sum of integers from 1 to 10, from 20 to 30, and from 35 to 45, respectively. 2 Problem int sum = 0; for (int i = 1; i
Chapter 5 Methods 1 Opening Problem Find the sum of integers from 1 to 10, from 20 to 30, and from 35 to 45, respectively. 2 Problem int sum = 0; for (int i = 1; i
CONDITIONAL EXECUTION
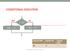 CONDITIONAL EXECUTION yes x > y? no max = x; max = y; logical AND logical OR logical NOT &&! Fundamentals of Computer Science I Outline Conditional Execution if then if then Nested if then statements Comparisons
CONDITIONAL EXECUTION yes x > y? no max = x; max = y; logical AND logical OR logical NOT &&! Fundamentals of Computer Science I Outline Conditional Execution if then if then Nested if then statements Comparisons
News and information! Review: Java Programs! Feedback after Lecture 2! Dead-lines for the first two lab assignment have been posted.!
 True object-oriented programming: Dynamic Objects Reference Variables D0010E Object-Oriented Programming and Design Lecture 3 Static Object-Oriented Programming UML" knows-about Eckel: 30-31, 41-46, 107-111,
True object-oriented programming: Dynamic Objects Reference Variables D0010E Object-Oriented Programming and Design Lecture 3 Static Object-Oriented Programming UML" knows-about Eckel: 30-31, 41-46, 107-111,
Functions. Lab 4. Introduction: A function : is a collection of statements that are grouped together to perform an operation.
 Lab 4 Functions Introduction: A function : is a collection of statements that are grouped together to perform an operation. The following is its format: type name ( parameter1, parameter2,...) { statements
Lab 4 Functions Introduction: A function : is a collection of statements that are grouped together to perform an operation. The following is its format: type name ( parameter1, parameter2,...) { statements
Functions. x y z. f (x, y, z) Take in input arguments (zero or more) Perform some computation - May have side-effects (such as drawing)
 2.1 Functions Functions Take in input arguments (zero or more) Perform some computation - May have side-effects (such as drawing) Return one output value Input Arguments x y z f Return Value f (x, y, z)
2.1 Functions Functions Take in input arguments (zero or more) Perform some computation - May have side-effects (such as drawing) Return one output value Input Arguments x y z f Return Value f (x, y, z)
Faculty of Engineering Computer Engineering Department Islamic University of Gaza C++ Programming Language Lab # 6 Functions
 Faculty of Engineering Computer Engineering Department Islamic University of Gaza 2013 C++ Programming Language Lab # 6 Functions C++ Programming Language Lab # 6 Functions Objective: To be familiar with
Faculty of Engineering Computer Engineering Department Islamic University of Gaza 2013 C++ Programming Language Lab # 6 Functions C++ Programming Language Lab # 6 Functions Objective: To be familiar with
Chapter 6 Methods. Liang, Introduction to Java Programming, Tenth Edition, Global Edition. Pearson Education Limited
 Chapter 6 Methods Liang, Introduction to Java Programming, Tenth Edition, Global Edition. Pearson Education Limited 2015 1 Opening Problem Find the sum of integers from 1 to 10, from 20 to 30, and from
Chapter 6 Methods Liang, Introduction to Java Programming, Tenth Edition, Global Edition. Pearson Education Limited 2015 1 Opening Problem Find the sum of integers from 1 to 10, from 20 to 30, and from
Advanced Computer Programming
 Programming in the Large I: Methods (Subroutines) 188230 Advanced Computer Programming Asst. Prof. Dr. Kanda Runapongsa Saikaew (krunapon@kku.ac.th) Department of Computer Engineering Khon Kaen University
Programming in the Large I: Methods (Subroutines) 188230 Advanced Computer Programming Asst. Prof. Dr. Kanda Runapongsa Saikaew (krunapon@kku.ac.th) Department of Computer Engineering Khon Kaen University
Methods and Data (Savitch, Chapter 5)
 Methods and Data (Savitch, Chapter 5) TOPICS Invoking Methods Return Values Local Variables Method Parameters Public versus Private 2 public class Temperature { public static void main(string[] args) {
Methods and Data (Savitch, Chapter 5) TOPICS Invoking Methods Return Values Local Variables Method Parameters Public versus Private 2 public class Temperature { public static void main(string[] args) {
CSE 114 Computer Science I
 CSE 114 Computer Science I Iteration Cape Breton, Nova Scotia What is Iteration? Repeating a set of instructions a specified number of times or until a specific result is achieved How do we repeat steps?
CSE 114 Computer Science I Iteration Cape Breton, Nova Scotia What is Iteration? Repeating a set of instructions a specified number of times or until a specific result is achieved How do we repeat steps?
PROGRAMMING FUNDAMENTALS
 PROGRAMMING FUNDAMENTALS Q1. Name any two Object Oriented Programming languages? Q2. Why is java called a platform independent language? Q3. Elaborate the java Compilation process. Q4. Why do we write
PROGRAMMING FUNDAMENTALS Q1. Name any two Object Oriented Programming languages? Q2. Why is java called a platform independent language? Q3. Elaborate the java Compilation process. Q4. Why do we write
Computer Programming, I. Laboratory Manual. Experiment #7. Methods
 Think Twice Code Once The Islamic University of Gaza Engineering Faculty Department of Computer Engineering Fall 2017 ECOM 2005 Khaleel I. Shaheen Computer Programming, I Laboratory Manual Experiment #7
Think Twice Code Once The Islamic University of Gaza Engineering Faculty Department of Computer Engineering Fall 2017 ECOM 2005 Khaleel I. Shaheen Computer Programming, I Laboratory Manual Experiment #7
Chapter 5 Methods. Lecture notes for computer programming 1 Faculty of Engineering and Information Technology Prepared by: Iyad Albayouk
 Chapter 5 Methods Lecture notes for computer programming 1 Faculty of Engineering and Information Technology Prepared by: Iyad Albayouk ١ Introducing Methods A method is a collection of statements that
Chapter 5 Methods Lecture notes for computer programming 1 Faculty of Engineering and Information Technology Prepared by: Iyad Albayouk ١ Introducing Methods A method is a collection of statements that
JAVA GUI PROGRAMMING REVISION TOUR III
 1. In java, methods reside in. (a) Function (b) Library (c) Classes (d) Object JAVA GUI PROGRAMMING REVISION TOUR III 2. The number and type of arguments of a method are known as. (a) Parameter list (b)
1. In java, methods reside in. (a) Function (b) Library (c) Classes (d) Object JAVA GUI PROGRAMMING REVISION TOUR III 2. The number and type of arguments of a method are known as. (a) Parameter list (b)
1 class Lecture5 { 2 3 "Methods" / References 8 [1] Ch. 5 in YDL 9 [1] Ch. 20 in YDL 0 / Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 176 / 199
![1 class Lecture5 { 2 3 Methods / References 8 [1] Ch. 5 in YDL 9 [1] Ch. 20 in YDL 0 / Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 176 / 199 1 class Lecture5 { 2 3 Methods / References 8 [1] Ch. 5 in YDL 9 [1] Ch. 20 in YDL 0 / Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 176 / 199](/thumbs/77/74905821.jpg) 1 class Lecture5 { 2 3 "Methods" 4 5 } 6 7 / References 8 [1] Ch. 5 in YDL 9 [1] Ch. 20 in YDL 0 / Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 176 / 199 Methods 2 Methods can be used to define reusable code, and organize
1 class Lecture5 { 2 3 "Methods" 4 5 } 6 7 / References 8 [1] Ch. 5 in YDL 9 [1] Ch. 20 in YDL 0 / Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 176 / 199 Methods 2 Methods can be used to define reusable code, and organize
Pace University. Fundamental Concepts of CS121 1
 Pace University Fundamental Concepts of CS121 1 Dr. Lixin Tao http://csis.pace.edu/~lixin Computer Science Department Pace University October 12, 2005 This document complements my tutorial Introduction
Pace University Fundamental Concepts of CS121 1 Dr. Lixin Tao http://csis.pace.edu/~lixin Computer Science Department Pace University October 12, 2005 This document complements my tutorial Introduction
CSCI 135 Exam #1 Fundamentals of Computer Science I Fall 2014
 CSCI 135 Exam #1 Fundamentals of Computer Science I Fall 2014 Name: This exam consists of 8 problems on the following 8 pages. You may use your two- sided hand- written 8 ½ x 11 note sheet during the exam.
CSCI 135 Exam #1 Fundamentals of Computer Science I Fall 2014 Name: This exam consists of 8 problems on the following 8 pages. You may use your two- sided hand- written 8 ½ x 11 note sheet during the exam.
Building Java Programs
 Building Java Programs Chapter 5 Lecture 5-1: while Loops, Fencepost Loops, and Sentinel Loops reading: 4.1, 5.1 self-check: Ch. 4 #2; Ch. 5 # 1-10 exercises: Ch. 4 #2, 4, 5, 8; Ch. 5 # 1-2 Copyright 2009
Building Java Programs Chapter 5 Lecture 5-1: while Loops, Fencepost Loops, and Sentinel Loops reading: 4.1, 5.1 self-check: Ch. 4 #2; Ch. 5 # 1-10 exercises: Ch. 4 #2, 4, 5, 8; Ch. 5 # 1-2 Copyright 2009
AN OVERVIEW OF C, PART 3. CSE 130: Introduction to Programming in C Stony Brook University
 AN OVERVIEW OF C, PART 3 CSE 130: Introduction to Programming in C Stony Brook University FANCIER OUTPUT FORMATTING Recall that you can insert a text field width value into a printf() format specifier:
AN OVERVIEW OF C, PART 3 CSE 130: Introduction to Programming in C Stony Brook University FANCIER OUTPUT FORMATTING Recall that you can insert a text field width value into a printf() format specifier:
CS/IT 114 Introduction to Java, Part 1 FALL 2016 CLASS 10: OCT. 6TH INSTRUCTOR: JIAYIN WANG
 CS/IT 114 Introduction to Java, Part 1 FALL 2016 CLASS 10: OCT. 6TH INSTRUCTOR: JIAYIN WANG 1 Notice Assignments Reading Assignment: Chapter 3: Introduction to Parameters and Objects The Class 10 Exercise
CS/IT 114 Introduction to Java, Part 1 FALL 2016 CLASS 10: OCT. 6TH INSTRUCTOR: JIAYIN WANG 1 Notice Assignments Reading Assignment: Chapter 3: Introduction to Parameters and Objects The Class 10 Exercise
Chapter 1. Section 1.4 Subprograms or functions. CS 50 - Hathairat Rattanasook
 Chapter 1 Section 1.4 Subprograms or functions 0 Functions Functions are essential in writing structured and well-organized code. Functions help for code to be reused. Functions help to reduce errors and
Chapter 1 Section 1.4 Subprograms or functions 0 Functions Functions are essential in writing structured and well-organized code. Functions help for code to be reused. Functions help to reduce errors and
Language Reference Manual
 ALACS Language Reference Manual Manager: Gabriel Lopez (gal2129) Language Guru: Gabriel Kramer-Garcia (glk2110) System Architect: Candace Johnson (crj2121) Tester: Terence Jacobs (tj2316) Table of Contents
ALACS Language Reference Manual Manager: Gabriel Lopez (gal2129) Language Guru: Gabriel Kramer-Garcia (glk2110) System Architect: Candace Johnson (crj2121) Tester: Terence Jacobs (tj2316) Table of Contents
Learning Outcomes for this week. Inf1-OP. A Foundation for Programming. A Foundation for Programming
 Learning Outcomes for this week Inf1-OP Conditionals and Loops 1 Perdita Stevens, adapting earlier version by Ewan Klein School of Informatics January 9, 2016 Use if and if-else statements to execute a
Learning Outcomes for this week Inf1-OP Conditionals and Loops 1 Perdita Stevens, adapting earlier version by Ewan Klein School of Informatics January 9, 2016 Use if and if-else statements to execute a
public class Foo { private int var; public int Method1() { // var accessible anywhere here } public int MethodN() {
 Scoping, Static Variables, Overloading, Packages In this lecture, we will examine in more detail the notion of scope for variables. We ve already indicated that variables only exist within the block they
Scoping, Static Variables, Overloading, Packages In this lecture, we will examine in more detail the notion of scope for variables. We ve already indicated that variables only exist within the block they
Lecture 10: Interfaces
 Accelerating Information Technology Innovation http://aiti.mit.edu Lecture 10: Interfaces AITI Nigeria Summer 2012 University of Lagos. Interfaces An interface in Java is special type A class with only
Accelerating Information Technology Innovation http://aiti.mit.edu Lecture 10: Interfaces AITI Nigeria Summer 2012 University of Lagos. Interfaces An interface in Java is special type A class with only
CS110D: PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE I
 CS110D: PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE I Computer Science department Lecture 7&8: Methods Lecture Contents What is a method? Static methods Declaring and using methods Parameters Scope of declaration Overloading
CS110D: PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE I Computer Science department Lecture 7&8: Methods Lecture Contents What is a method? Static methods Declaring and using methods Parameters Scope of declaration Overloading
Chapter 5: Methods. by Tony Gaddis. Starting Out with Java: From Control Structures through Objects. Fourth Edition
 Chapter 5: Methods Starting Out with Java: From Control Structures through Objects Fourth Edition by Tony Gaddis Addison Wesley is an imprint of 2010 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved. Reading
Chapter 5: Methods Starting Out with Java: From Control Structures through Objects Fourth Edition by Tony Gaddis Addison Wesley is an imprint of 2010 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved. Reading
Notes - Recursion. A geeky definition of recursion is as follows: Recursion see Recursion.
 Notes - Recursion So far we have only learned how to solve problems iteratively using loops. We will now learn how to solve problems recursively by having a method call itself. A geeky definition of recursion
Notes - Recursion So far we have only learned how to solve problems iteratively using loops. We will now learn how to solve problems recursively by having a method call itself. A geeky definition of recursion
CS171:Introduction to Computer Science II
 CS171:Introduction to Computer Science II Department of Mathematics and Computer Science Li Xiong 9/7/2012 1 Announcement Introductory/Eclipse Lab, Friday, Sep 7, 2-3pm (today) Hw1 to be assigned Monday,
CS171:Introduction to Computer Science II Department of Mathematics and Computer Science Li Xiong 9/7/2012 1 Announcement Introductory/Eclipse Lab, Friday, Sep 7, 2-3pm (today) Hw1 to be assigned Monday,
CT 229 Arrays Continued
 CT 229 Arrays Continued 20/10/2006 CT229 Lab Assignments Current lab assignment is due today: Oct 20 th Before submission make sure that the name of each.java file matches the name given in the assignment
CT 229 Arrays Continued 20/10/2006 CT229 Lab Assignments Current lab assignment is due today: Oct 20 th Before submission make sure that the name of each.java file matches the name given in the assignment
Constants. Why Use Constants? main Method Arguments. CS256 Computer Science I Kevin Sahr, PhD. Lecture 25: Miscellaneous
 CS256 Computer Science I Kevin Sahr, PhD Lecture 25: Miscellaneous 1 main Method Arguments recall the method header of the main method note the argument list public static void main (String [] args) we
CS256 Computer Science I Kevin Sahr, PhD Lecture 25: Miscellaneous 1 main Method Arguments recall the method header of the main method note the argument list public static void main (String [] args) we
Lecture 04 FUNCTIONS AND ARRAYS
 Lecture 04 FUNCTIONS AND ARRAYS 1 Motivations Divide hug tasks to blocks: divide programs up into sets of cooperating functions. Define new functions with function calls and parameter passing. Use functions
Lecture 04 FUNCTIONS AND ARRAYS 1 Motivations Divide hug tasks to blocks: divide programs up into sets of cooperating functions. Define new functions with function calls and parameter passing. Use functions
Comments are almost like C++
 UMBC CMSC 331 Java Comments are almost like C++ The javadoc program generates HTML API documentation from the javadoc style comments in your code. /* This kind of comment can span multiple lines */ //
UMBC CMSC 331 Java Comments are almost like C++ The javadoc program generates HTML API documentation from the javadoc style comments in your code. /* This kind of comment can span multiple lines */ //
3.Constructors and Destructors. Develop cpp program to implement constructor and destructor.
 3.Constructors and Destructors Develop cpp program to implement constructor and destructor. Constructors A constructor is a special member function whose task is to initialize the objects of its class.
3.Constructors and Destructors Develop cpp program to implement constructor and destructor. Constructors A constructor is a special member function whose task is to initialize the objects of its class.
Overview. Lab 5 Methods and Parameters
 Lab 5 Methods and Parameters Overview At this point in the course, you should have a set of skills which allow you to create functionality at the level of using control structures like if statements and
Lab 5 Methods and Parameters Overview At this point in the course, you should have a set of skills which allow you to create functionality at the level of using control structures like if statements and
Chapter 5 Methods. Modifier returnvaluetype methodname(list of parameters) { // method body; }
 Chapter 5 Methods 5.1 Introduction A method is a collection of statements that are grouped together to perform an operation. You will learn how to: o create your own mthods with or without return values,
Chapter 5 Methods 5.1 Introduction A method is a collection of statements that are grouped together to perform an operation. You will learn how to: o create your own mthods with or without return values,
Introduction to Computer Science Unit 2. Notes
 Introduction to Computer Science Unit 2. Notes Name: Objectives: By the completion of this packet, students should be able to describe the difference between.java and.class files and the JVM. create and
Introduction to Computer Science Unit 2. Notes Name: Objectives: By the completion of this packet, students should be able to describe the difference between.java and.class files and the JVM. create and
Functions CMPE-013/L. Functions. Functions What is a function? Functions Remember Algebra Class? Gabriel Hugh Elkaim Winter 2014.
 CMPE-013/L Program Structure Gabriel Hugh Elkaim Winter 2014 main()... eat();... drink();... eat()... return; drink()... be_merry(); return; be_merry()... return; Definition What is a function? are self
CMPE-013/L Program Structure Gabriel Hugh Elkaim Winter 2014 main()... eat();... drink();... eat()... return; drink()... be_merry(); return; be_merry()... return; Definition What is a function? are self
Functions. Prof. Indranil Sen Gupta. Dept. of Computer Science & Engg. Indian Institute t of Technology Kharagpur. Introduction
 Functions Prof. Indranil Sen Gupta Dept. of Computer Science & Engg. Indian Institute t of Technology Kharagpur Programming and Data Structure 1 Function Introduction A self-contained program segment that
Functions Prof. Indranil Sen Gupta Dept. of Computer Science & Engg. Indian Institute t of Technology Kharagpur Programming and Data Structure 1 Function Introduction A self-contained program segment that
Chapter 4 Defining Classes I
 Chapter 4 Defining Classes I This chapter introduces the idea that students can create their own classes and therefore their own objects. Introduced is the idea of methods and instance variables as the
Chapter 4 Defining Classes I This chapter introduces the idea that students can create their own classes and therefore their own objects. Introduced is the idea of methods and instance variables as the
Computer Programming: C++
 The Islamic University of Gaza Engineering Faculty Department of Computer Engineering Fall 2017 ECOM 2003 Muath i.alnabris Computer Programming: C++ Experiment #7 Arrays Part II Passing Array to a Function
The Islamic University of Gaza Engineering Faculty Department of Computer Engineering Fall 2017 ECOM 2003 Muath i.alnabris Computer Programming: C++ Experiment #7 Arrays Part II Passing Array to a Function
1.00 Lecture 6. Java Methods
 1.00 Lecture 6 Methods and Scope Reading for next time: Big Java: sections 2.6-2.10, 3.1-3.8 Java Methods Methods are the interface or communications between program components They provide a way to invoke
1.00 Lecture 6 Methods and Scope Reading for next time: Big Java: sections 2.6-2.10, 3.1-3.8 Java Methods Methods are the interface or communications between program components They provide a way to invoke
Administration. Classes. Objects Part II. Agenda. Review: Object References. Object Aliases. CS 99 Summer 2000 Michael Clarkson Lecture 7
 Administration Classes CS 99 Summer 2000 Michael Clarkson Lecture 7 Lab 7 due tomorrow Question: Lab 6.equals( SquareRoot )? Lab 8 posted today Prelim 2 in six days! Covers two weeks of material: lectures
Administration Classes CS 99 Summer 2000 Michael Clarkson Lecture 7 Lab 7 due tomorrow Question: Lab 6.equals( SquareRoot )? Lab 8 posted today Prelim 2 in six days! Covers two weeks of material: lectures
Defining Program Syntax. Chapter Two Modern Programming Languages, 2nd ed. 1
 Defining Program Syntax Chapter Two Modern Programming Languages, 2nd ed. 1 Syntax And Semantics Programming language syntax: how programs look, their form and structure Syntax is defined using a kind
Defining Program Syntax Chapter Two Modern Programming Languages, 2nd ed. 1 Syntax And Semantics Programming language syntax: how programs look, their form and structure Syntax is defined using a kind
University of Palestine. Mid Exam Total Grade: 100
 First Question No. of Branches (5) A) Choose the correct answer: 1. If we type: system.out.println( a ); in the main() method, what will be the result? int a=12; //in the global space... void f() { int
First Question No. of Branches (5) A) Choose the correct answer: 1. If we type: system.out.println( a ); in the main() method, what will be the result? int a=12; //in the global space... void f() { int
Introduction to Programming (Java) 4/12
 Introduction to Programming (Java) 4/12 Michal Krátký Department of Computer Science Technical University of Ostrava Introduction to Programming (Java) 2008/2009 c 2006 2008 Michal Krátký Introduction
Introduction to Programming (Java) 4/12 Michal Krátký Department of Computer Science Technical University of Ostrava Introduction to Programming (Java) 2008/2009 c 2006 2008 Michal Krátký Introduction
Lexical Considerations
 Massachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 6.035, Fall 2005 Handout 6 Decaf Language Wednesday, September 7 The project for the course is to write a
Massachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 6.035, Fall 2005 Handout 6 Decaf Language Wednesday, September 7 The project for the course is to write a
All copyrights reserved - KV NAD, Aluva. Dinesh Kumar Ram PGT(CS) KV NAD Aluva
 All copyrights reserved - KV NAD, Aluva Dinesh Kumar Ram PGT(CS) KV NAD Aluva Overview Looping Introduction While loops Syntax Examples Points to Observe Infinite Loops Examples using while loops do..
All copyrights reserved - KV NAD, Aluva Dinesh Kumar Ram PGT(CS) KV NAD Aluva Overview Looping Introduction While loops Syntax Examples Points to Observe Infinite Loops Examples using while loops do..
COMP 202. More on OO. CONTENTS: static revisited this reference class dependencies method parameters variable scope method overloading
 COMP 202 CONTENTS: static revisited this reference class dependencies method parameters variable scope method overloading More on OO COMP 202 - Week 7 1 Static member variables So far: Member variables
COMP 202 CONTENTS: static revisited this reference class dependencies method parameters variable scope method overloading More on OO COMP 202 - Week 7 1 Static member variables So far: Member variables
Computer Science 210 Data Structures Siena College Fall Topic Notes: Methods
 Computer Science 210 Data Structures Siena College Fall 2017 Topic Notes: Methods As programmers, we often find ourselves writing the same or similar code over and over. We learned that we can place code
Computer Science 210 Data Structures Siena College Fall 2017 Topic Notes: Methods As programmers, we often find ourselves writing the same or similar code over and over. We learned that we can place code
JAVA PROGRAMMING LAB. ABSTRACT In this Lab you will learn to define and invoke void and return java methods
 Islamic University of Gaza Faculty of Engineering Computer Engineering Dept. Computer Programming Lab (ECOM 2114) ABSTRACT In this Lab you will learn to define and invoke void and return java methods JAVA
Islamic University of Gaza Faculty of Engineering Computer Engineering Dept. Computer Programming Lab (ECOM 2114) ABSTRACT In this Lab you will learn to define and invoke void and return java methods JAVA
Methods. Bok, Jong Soon
 Methods Bok, Jong Soon javaexpert@nate.com www.javaexpert.co.kr Methods Enable you to separate statements into code blocks. Can be called whenever appropriate. Can invoke each other. Can call themselves(recursion)
Methods Bok, Jong Soon javaexpert@nate.com www.javaexpert.co.kr Methods Enable you to separate statements into code blocks. Can be called whenever appropriate. Can invoke each other. Can call themselves(recursion)
Admin. CS 112 Introduction to Programming. Recap: Exceptions. Summary: for loop. Recap: CaesarFile using Loop. Summary: Flow Control Statements
 Admin. CS 112 Introduction to Programming q Puzzle Day from Friday to Monday Arrays; Loop Patterns (break) Yang (Richard) Yang Computer Science Department Yale University 308A Watson, Phone: 432-6400 Email:
Admin. CS 112 Introduction to Programming q Puzzle Day from Friday to Monday Arrays; Loop Patterns (break) Yang (Richard) Yang Computer Science Department Yale University 308A Watson, Phone: 432-6400 Email:
CS 302: INTRODUCTION TO PROGRAMMING IN JAVA. Chapter 5: Methods. Lecture 10
 CS 302: INTRODUCTION TO PROGRAMMING IN JAVA Chapter 5: Methods Lecture 10 1 PROBLEM What if I was using a lot of different arrays and often wanted to print out their contents? I would have to have that
CS 302: INTRODUCTION TO PROGRAMMING IN JAVA Chapter 5: Methods Lecture 10 1 PROBLEM What if I was using a lot of different arrays and often wanted to print out their contents? I would have to have that
Methods. Methods. Mysteries Revealed
 Methods Methods and Data (Savitch, Chapter 5) TOPICS Invoking Methods Return Values Local Variables Method Parameters Public versus Private A method (a.k.a. func2on, procedure, rou2ne) is a piece of code
Methods Methods and Data (Savitch, Chapter 5) TOPICS Invoking Methods Return Values Local Variables Method Parameters Public versus Private A method (a.k.a. func2on, procedure, rou2ne) is a piece of code
Lecture 8 Classes and Objects Part 2. MIT AITI June 15th, 2005
 Lecture 8 Classes and Objects Part 2 MIT AITI June 15th, 2005 1 What is an object? A building (Strathmore university) A desk A laptop A car Data packets through the internet 2 What is an object? Objects
Lecture 8 Classes and Objects Part 2 MIT AITI June 15th, 2005 1 What is an object? A building (Strathmore university) A desk A laptop A car Data packets through the internet 2 What is an object? Objects
