CCured. One-Slide Summary. Lecture Outline. Type-Safe Retrofitting of C Programs
|
|
|
- Frederica McDonald
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CCured Type-Safe Retrofitting of C Programs [Necula, McPeak,, Weimer, Condit, Harren] #1 One-Slide Summary CCured enforces memory safety and type safety in legacy C programs. CCured analyzes how you use pointers and either proves the usage safe statically or inserts run-time checks. Along the way we ll see cameo appearances by just about every CS 415 topic. #2 Lecture Outline Type and Memory Safety CCured Motivation SAFE Pointers SEQuence Pointers WILD Pointers Experimental Results Analysis #3 1
2 Why Now, Brown Cow? Type Systems [ Type Safety ] Language Security [ Memory Safety ] Static and Dynamic Types [ Run-Time Type Info ] Runtime Organization [ Pointer Layout ] Subtyping [ Convertibility ] Garbage Collection [ Tag Bits ] Dataflow Analysis [ Pointer-Kind Inference ] Object-Oriented Programming [ OOP in C ] Aspect-Oriented Programming [ Checks Everywhere ] Libraries [ Library Compatibility ] Debuggers and Profilers [ Purify and Valgrind ] #4 Two Kinds of Safety Type safety is a property of a programming language that prevents certain errors (type errors) that result from attempts to perform an operation on a value of the wrong type. Type safety prevents: hello + 3 Not Type safe: 3 + (int) hello Some languages allow unsafe casts between types. Memory safety: if a value of type T 1 is read from address A, then the most recent store to A had type T 2 with T 2 T 1 Store a Dog in memory, read an Animal later #5 We Need Them Both You cannot have true Type Safety without Memory Safety Why? Hint: an unsafe cast defeats type safety #6 2
3 We Need Them Both You cannot have true Type Safety without Memory Safety Why? Example: table * t = new table(); char buf[10]; buf[10] = buf[11] = buf[12] = buf[13] = 55; t->countlegs(); Buffer overrun! #7 Memory Safety Essential component of a security infrastructure Prevents interference 50% of reported attacks are due to buffer overruns Software engineering advantages Memory bugs are hard to find (why?) Memory safety ensures component isolation Required for soundness of many program analyses (why? hint: aliasing) Does not even need an explicit specification #8 C and Memory Safety C was designed for flexibility and efficiency Many operators can be used unsafely Memory safety is sacrificed! In practice, many C programs use those operators safely Only a small portion of the pointers and operators are responsible for the unsafe behavior #9 3
4 CCured Idea 1. Devise a sound type system and a type inference algorithm that handles most C programs Combination of static and dynamic types 2. Insert run-time checks (e.g. array-bounds checks and dynamic type checking) in those places where safety cannot be verified statically This way we sacrifice performance instead of safety Makes sense for more and more applications every day Hardware progress improves performance but not safety #10 CCured Goals Compatibility: support existing C code Source-to-source transformation Handle GCC/MSVC source, Makefiles All that is needed is a recompilation: make CC=ccured Efficiency: 0-50% overhead rather than 1000% Other research: 10x, Purify: 20x, BoundsChecker: 150x More effective and more efficient than Purify Because it leverages existing type information in source Use for production code not just during testing #11 Diseases We Want to Cure Focus on pointer usage Is it lupus? Dereferencing a non-pointer (or NULL) Invoking a non-function Complicated by casts and union types It s never lupus! Dereferencing outside of object bounds Buffer overruns Complicated by pointer arithmetic Not always caught by Purify Freeing non-pointers, using freed memory #12 4
5 Example Pointer Usage in C Consider an implementation of a hash table struct list {void * data; struct list * next} * * hash; Cast allowed Arith allowed Yes Yes No No No Yes #13 SAFE Pointer Invariants and Representation T * safe Can be 0 or a pointer to storage containing a T All aliases agree on the type of the referenced storage Must do null-check before dereference Inexpensive to store and to use Prototypical example: FILE * p T statically typed home area #14 Quiz How many pointers in an average C program are SAFE according to the previous definition? Answer: between 40-95% of the declared pointers #15 5
6 Typing Rules for SAFE Pointers e : T * safe 0 : T * safe * e : T e 1 : T * safe e 2 : T * e 1 = e 2 : T e : T * safe T * safe T 1 * safe (T 1 * safe) e : T 1 * safe T * safe T 1 * safe means that a pointer of the first kind is convertible to a pointer of second kind #16 Convertibility of Pointers The convertibility relation is based on the physical layout of types (flatten structures and arrays) Examples: struct { int x, y; int *p;} * int * struct { int x; struct { int y; int *p;} s; } * struct { int x, y; } * It s like an upcast in OOP #17 SEQ Pointer Invariants and Representation T * seq Can be 0 Can be involved in pointer arithmetic Null check and bounds check before use Carries the bounds of a home area consisting of a sequence of T s All SAFE or SEQ aliases agree on the type of the referenced area base p end T T T statically typed home area #18 6
7 Typing Rules for SEQUENCE Pointers e : T * seq e : T * seq e + e : T * seq e : int T * seq T 1 * seq (T 1 * seq) e : T 1 * seq Before dereferencing a SEQ pointer it must be converted to SAFE (with a bounds check and with dropping the base and the end fields) e : T * seq (T * safe) e : T * safe #19 Forward SEQUENCE Pointers Often a sequence pointer is only advanced We call it a Forward Sequence (FSEQ) Needs to carry only the end and needs only an upper bound check p end T T Pointer arithmetic must be checked to advance A SEQ is converted to FSEQ via a lower-bound check and dropping the lower-bound field #20 Quiz How many forward-thinking Cylon characters are in a typical Battlestar episode? Answer: Six or Eight #21 7
8 Quiz How many forward sequence and sequence pointers are in a typical C program? Answer: about 25% FSEQ, 1% SEQ #22 The WILD West So far we have not faced the really ugly pointers Those that are cast to incompatible types We call them WILD pointers For these we cannot count on the static type! We must keep run-time type tags (cf. Python, Ruby) Operations allowed: read/write assign an integer pointer arithmetic cast to other WILD pointers #23 WILD Pointer Invariants and Representation T * wild Can be a non-pointer (any integer) Carries the bounds of a dynamic home area (containing only integers and dynamic pointers) Has only WILD pointer aliases Must do a non-pointer and a bounds check Must maintain the tags when writing (1 bit per word) base end p dynamically typed home area Just like in garbage collection! tag bits #24 8
9 WILD Complications What if we have a SAFE alias for a WILD? T * safe s; T * wild w = s; // w is an alias for s base w s T *(T * wild)w = random_stuff_of_type_t ; For Safety: WILD pointers can only alias other WILD pointers! #25 WILD Complications What if we have a WILD pointer to a SAFE ptr? base p base q T * safe The type system cannot ensure that all writes through the WILD pointer will write a compatible SAFE pointer For Safety: WILD pointers must point to areas containing only WILD pointers! #26 WILD Pointers are Highly Contagious A WILD pointer will force other pointers to be WILD as well: All pointers to which it is assigned All pointers from which it is assigned All pointers that it points to We need ways to reduce the number of WILD pointers Better understanding of casts #27 9
10 Handling Downcasts 10-20% of the pointers are void* Cast from void* to T* is unsafe! This is a special case of a downcast Downcasts are frequent in C programs (50-90% of bad casts) We introduce pointers that carry run-time type info Each downcast is checked at run-time (like in Java) T 1 * RTTI p; p rtti(t) T Invariant: T is a subtype of T 1 #28 Programming OO-Style in C With RTTI pointers we can program safely in a object oriented style (e.g. dynamic dispatch): struct Figure { double (*area)(struct Figure * RTTI ); } struct Circle { double (*area)(struct Figure * RTTI ); double radius; } double circle_area(struct Figure* RTTI fig) { struct Circle *circ = (struct Circle*)fig; return PI * circ->radius * circ->radius; } ; struct Figure * RTTI fig; fig->area(fig) Other places where RTTI helps Heterogeneous data structures Polymorphic code and data structures #29 Pointer-Kind Inference For every pointer in the program Try to infer the fastest sound representation We construct a whole-program data flow graph We collect constraints about pointer kinds Then linear-time constraint solving Analysis can be modularized if the interfaces are annotated with pointer kind Extremely simple, fast and predictable #30 10
11 Example: SAFE/SEQ int *a =... ; int *b = a ; int *c = b ; print(*c) ; b = b + 1 ; so a is FSEQ too bounds check here but c can be SAFE arithmetic: b must be FSEQ #31 Example: WILD pointer to a pointer int foo(int **p) { int *q = (int *)p; return *q; } cast to incompatible type: both p and q are WILD (so is the caller's argument!) #32 Experience Using CCured CCured handles all of C: vararg, function pointers, union types, GCC extensions CCured works on low-level code Apache modules, Linux device drivers CCured scales to large programs sendmail, openssl, ssh, bind (>= 100K lines) ACE infrastructure (>= 1M lines) CCured often requires manual intervention must change between 1/100 to 1/300 lines of code #33 11
12 CCured Purify Experimental Results Slowdown of CCured and Purify vs. C (low numbers = good) ijpeg compress go li bh tsp % slowdown % of pointers are statically known to be type safe Found bugs in SPEC95 benchmarks #34 The GOOD, the UGLY, and the BAD Standard techniques from type theory can be used to understand the type safety of existing C programs CCured works automatically in most cases Most pointers are SAFE and some are SEQUENCE The slowdown is minimal in many cases The uglier your program the slower it will be #35 The GOOD, the UGLY, and the BAD Occasional significant slowdown Typically due to either large number of WILD or SEQUENCE pointers Increased memory footprint Larger code size Some pointers take 64-bits and some even 96-bits CCured is confused by custom-memory allocators Forced to treat them WILD Or to trust the allocator (as in the experiments) #36 12
13 The GOOD, the UGLY, and the BAD Incompatibilities with some libraries Due to different layout of data structures Solved by writing wrappers Some programs require changes Those that store addresses of locals in the heap Those that cast pointers to integers and then back Some (non-portable) programs are terminally-ill Self-modifying programs Those that depend on the size of pointers Those that intentionally skip from one field to another #37 Future Work Allow the programmer to define new pointer kinds Derived from the existing ones Maybe even brand new ones? Open the door to type-safe interoperability with C Type-safe Java native methods Type-safe inline C in C# programs Check it out at #38 Homework PA5 Due Friday April 27 (tomorrow) Final Examination Block 4 Thursday May MEC 214 #39 13
CCured in the Real World
 CCured in the Real World Jeremy Condit Matthew Harren Scott McPeak George C. Necula Westley Weimer University of California, Berkeley {jcondit,matth,smcpeak,necula,weimer}@cs.berkeley.edu ABSTRACT CCured
CCured in the Real World Jeremy Condit Matthew Harren Scott McPeak George C. Necula Westley Weimer University of California, Berkeley {jcondit,matth,smcpeak,necula,weimer}@cs.berkeley.edu ABSTRACT CCured
Today Program Analysis for finding bugs, especially security bugs problem specification motivation approaches remaining issues
 Finding Bugs Last time Run-time reordering transformations Today Program Analysis for finding bugs, especially security bugs problem specification motivation approaches remaining issues CS553 Lecture Finding
Finding Bugs Last time Run-time reordering transformations Today Program Analysis for finding bugs, especially security bugs problem specification motivation approaches remaining issues CS553 Lecture Finding
Type Checking Systems Code
 Type Checking Systems Code Greg Morrisett Cornell University Abstract. Our critical computing systems are coded in low-level, typeunsafe languages such as C, and it is unlikely that they will be re-coded
Type Checking Systems Code Greg Morrisett Cornell University Abstract. Our critical computing systems are coded in low-level, typeunsafe languages such as C, and it is unlikely that they will be re-coded
CCured: Type-Safe Retrofitting of Legacy Software
 CCured: Type-Safe Retrofitting of Legacy Software GEORGE C. NECULA, JEREMY CONDIT, MATTHEW HARREN, SCOTT McPEAK, and WESTLEY WEIMER University of California, Berkeley This paper describes CCured, a program
CCured: Type-Safe Retrofitting of Legacy Software GEORGE C. NECULA, JEREMY CONDIT, MATTHEW HARREN, SCOTT McPEAK, and WESTLEY WEIMER University of California, Berkeley This paper describes CCured, a program
One-Slide Summary. Lecture Outline. Language Security
 Language Security Or: bringing a knife to a gun fight #1 One-Slide Summary A language s design principles and features have a strong influence on the security of programs written in that language. C s
Language Security Or: bringing a knife to a gun fight #1 One-Slide Summary A language s design principles and features have a strong influence on the security of programs written in that language. C s
CS 430 Spring Mike Lam, Professor. Data Types and Type Checking
 CS 430 Spring 2015 Mike Lam, Professor Data Types and Type Checking Type Systems Type system Rules about valid types, type compatibility, and how data values can be used Benefits of a robust type system
CS 430 Spring 2015 Mike Lam, Professor Data Types and Type Checking Type Systems Type system Rules about valid types, type compatibility, and how data values can be used Benefits of a robust type system
Short Notes of CS201
 #includes: Short Notes of CS201 The #include directive instructs the preprocessor to read and include a file into a source code file. The file name is typically enclosed with < and > if the file is a system
#includes: Short Notes of CS201 The #include directive instructs the preprocessor to read and include a file into a source code file. The file name is typically enclosed with < and > if the file is a system
CS201 - Introduction to Programming Glossary By
 CS201 - Introduction to Programming Glossary By #include : The #include directive instructs the preprocessor to read and include a file into a source code file. The file name is typically enclosed with
CS201 - Introduction to Programming Glossary By #include : The #include directive instructs the preprocessor to read and include a file into a source code file. The file name is typically enclosed with
In Java we have the keyword null, which is the value of an uninitialized reference type
 + More on Pointers + Null pointers In Java we have the keyword null, which is the value of an uninitialized reference type In C we sometimes use NULL, but its just a macro for the integer 0 Pointers are
+ More on Pointers + Null pointers In Java we have the keyword null, which is the value of an uninitialized reference type In C we sometimes use NULL, but its just a macro for the integer 0 Pointers are
Dependant Type Systems (saying what you are) Data Abstraction (hiding what you are) Review. Dependent Types. Dependent Type Notation
 Dependant Type Systems (saying what you are) Data Abstraction (hiding what you are) #1 Recount We re now reaching the point where you have all of the tools and background to understand advanced topics.
Dependant Type Systems (saying what you are) Data Abstraction (hiding what you are) #1 Recount We re now reaching the point where you have all of the tools and background to understand advanced topics.
CCured: Type-Safe Retrofitting of Legacy Code
 Published in the Proceedings of the Principles of Programming Languages, 2002, pages 128 139 CCured: Type-Safe Retrofitting of Legacy Code George C. Necula Scott McPeak Westley Weimer University of California,
Published in the Proceedings of the Principles of Programming Languages, 2002, pages 128 139 CCured: Type-Safe Retrofitting of Legacy Code George C. Necula Scott McPeak Westley Weimer University of California,
Ironclad C++ A Library-Augmented Type-Safe Subset of C++
 Ironclad C++ A Library-Augmented Type-Safe Subset of C++ Christian DeLozier, Richard Eisenberg, Peter-Michael Osera, Santosh Nagarakatte*, Milo M. K. Martin, and Steve Zdancewic October 30, 2013 University
Ironclad C++ A Library-Augmented Type-Safe Subset of C++ Christian DeLozier, Richard Eisenberg, Peter-Michael Osera, Santosh Nagarakatte*, Milo M. K. Martin, and Steve Zdancewic October 30, 2013 University
HW1 due Monday by 9:30am Assignment online, submission details to come
 inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c CS61CL : Machine Structures Lecture #2 - C Pointers and Arrays Administrivia Buggy Start Lab schedule, lab machines, HW0 due tomorrow in lab 2009-06-24 HW1 due Monday by 9:30am
inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c CS61CL : Machine Structures Lecture #2 - C Pointers and Arrays Administrivia Buggy Start Lab schedule, lab machines, HW0 due tomorrow in lab 2009-06-24 HW1 due Monday by 9:30am
CMPSC 497 Other Memory Vulnerabilities
 Systems and Internet Infrastructure Security Network and Security Research Center Department of Computer Science and Engineering Pennsylvania State University, University Park PA CMPSC 497 Other Memory
Systems and Internet Infrastructure Security Network and Security Research Center Department of Computer Science and Engineering Pennsylvania State University, University Park PA CMPSC 497 Other Memory
Hacking in C. Pointers. Radboud University, Nijmegen, The Netherlands. Spring 2019
 Hacking in C Pointers Radboud University, Nijmegen, The Netherlands Spring 2019 Allocation of multiple variables Consider the program main(){ char x; int i; short s; char y;... } What will the layout of
Hacking in C Pointers Radboud University, Nijmegen, The Netherlands Spring 2019 Allocation of multiple variables Consider the program main(){ char x; int i; short s; char y;... } What will the layout of
Pointer Basics. Lecture 13 COP 3014 Spring March 28, 2018
 Pointer Basics Lecture 13 COP 3014 Spring 2018 March 28, 2018 What is a Pointer? A pointer is a variable that stores a memory address. Pointers are used to store the addresses of other variables or memory
Pointer Basics Lecture 13 COP 3014 Spring 2018 March 28, 2018 What is a Pointer? A pointer is a variable that stores a memory address. Pointers are used to store the addresses of other variables or memory
CS527 Software Security
 Security Policies Purdue University, Spring 2018 Security Policies A policy is a deliberate system of principles to guide decisions and achieve rational outcomes. A policy is a statement of intent, and
Security Policies Purdue University, Spring 2018 Security Policies A policy is a deliberate system of principles to guide decisions and achieve rational outcomes. A policy is a statement of intent, and
Memory Safety for Embedded Devices with nescheck
 Memory Safety for Embedded Devices with nescheck Daniele MIDI, Mathias PAYER, Elisa BERTINO Purdue University AsiaCCS 2017 Ubiquitous Computing and Security Sensors and WSNs are pervasive Small + cheap
Memory Safety for Embedded Devices with nescheck Daniele MIDI, Mathias PAYER, Elisa BERTINO Purdue University AsiaCCS 2017 Ubiquitous Computing and Security Sensors and WSNs are pervasive Small + cheap
Language Security. Lecture 40
 Language Security Lecture 40 (from notes by G. Necula) Prof. Hilfinger CS 164 Lecture 40 1 Lecture Outline Beyond compilers Looking at other issues in programming language design and tools C Arrays Exploiting
Language Security Lecture 40 (from notes by G. Necula) Prof. Hilfinger CS 164 Lecture 40 1 Lecture Outline Beyond compilers Looking at other issues in programming language design and tools C Arrays Exploiting
Lectures 5-6: Introduction to C
 Lectures 5-6: Introduction to C Motivation: C is both a high and a low-level language Very useful for systems programming Faster than Java This intro assumes knowledge of Java Focus is on differences Most
Lectures 5-6: Introduction to C Motivation: C is both a high and a low-level language Very useful for systems programming Faster than Java This intro assumes knowledge of Java Focus is on differences Most
A program execution is memory safe so long as memory access errors never occur:
 A program execution is memory safe so long as memory access errors never occur: Buffer overflows, null pointer dereference, use after free, use of uninitialized memory, illegal free Memory safety categories
A program execution is memory safe so long as memory access errors never occur: Buffer overflows, null pointer dereference, use after free, use of uninitialized memory, illegal free Memory safety categories
Outline. Java Models for variables Types and type checking, type safety Interpretation vs. compilation. Reasoning about code. CSCI 2600 Spring
 Java Outline Java Models for variables Types and type checking, type safety Interpretation vs. compilation Reasoning about code CSCI 2600 Spring 2017 2 Java Java is a successor to a number of languages,
Java Outline Java Models for variables Types and type checking, type safety Interpretation vs. compilation Reasoning about code CSCI 2600 Spring 2017 2 Java Java is a successor to a number of languages,
CS 161 Computer Security
 Wagner Spring 2014 CS 161 Computer Security 1/27 Reasoning About Code Often functions make certain assumptions about their arguments, and it is the caller s responsibility to make sure those assumptions
Wagner Spring 2014 CS 161 Computer Security 1/27 Reasoning About Code Often functions make certain assumptions about their arguments, and it is the caller s responsibility to make sure those assumptions
Semantic Analysis. Outline. The role of semantic analysis in a compiler. Scope. Types. Where we are. The Compiler Front-End
 Outline Semantic Analysis The role of semantic analysis in a compiler A laundry list of tasks Scope Static vs. Dynamic scoping Implementation: symbol tables Types Static analyses that detect type errors
Outline Semantic Analysis The role of semantic analysis in a compiler A laundry list of tasks Scope Static vs. Dynamic scoping Implementation: symbol tables Types Static analyses that detect type errors
CS61C Machine Structures. Lecture 3 Introduction to the C Programming Language. 1/23/2006 John Wawrzynek. www-inst.eecs.berkeley.
 CS61C Machine Structures Lecture 3 Introduction to the C Programming Language 1/23/2006 John Wawrzynek (www.cs.berkeley.edu/~johnw) www-inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c/ CS 61C L03 Introduction to C (1) Administrivia
CS61C Machine Structures Lecture 3 Introduction to the C Programming Language 1/23/2006 John Wawrzynek (www.cs.berkeley.edu/~johnw) www-inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c/ CS 61C L03 Introduction to C (1) Administrivia
COS 320. Compiling Techniques
 Topic 5: Types COS 320 Compiling Techniques Princeton University Spring 2016 Lennart Beringer 1 Types: potential benefits (I) 2 For programmers: help to eliminate common programming mistakes, particularly
Topic 5: Types COS 320 Compiling Techniques Princeton University Spring 2016 Lennart Beringer 1 Types: potential benefits (I) 2 For programmers: help to eliminate common programming mistakes, particularly
An Efficient and Backwards-Compatible Transformation to Ensure Memory Safety of C Programs
 An Efficient and Backwards-Compatible Transformation to Ensure Memory Safety of C Programs Wei Xu, Daniel C. DuVarney, and R. Sekar Department of Computer Science, Stony Brook University Stony Brook, NY
An Efficient and Backwards-Compatible Transformation to Ensure Memory Safety of C Programs Wei Xu, Daniel C. DuVarney, and R. Sekar Department of Computer Science, Stony Brook University Stony Brook, NY
Simply-Typed Lambda Calculus
 #1 Simply-Typed Lambda Calculus #2 Back to School What is operational semantics? When would you use contextual (small-step) semantics? What is denotational semantics? What is axiomatic semantics? What
#1 Simply-Typed Lambda Calculus #2 Back to School What is operational semantics? When would you use contextual (small-step) semantics? What is denotational semantics? What is axiomatic semantics? What
The role of semantic analysis in a compiler
 Semantic Analysis Outline The role of semantic analysis in a compiler A laundry list of tasks Scope Static vs. Dynamic scoping Implementation: symbol tables Types Static analyses that detect type errors
Semantic Analysis Outline The role of semantic analysis in a compiler A laundry list of tasks Scope Static vs. Dynamic scoping Implementation: symbol tables Types Static analyses that detect type errors
Runtime Defenses against Memory Corruption
 CS 380S Runtime Defenses against Memory Corruption Vitaly Shmatikov slide 1 Reading Assignment Cowan et al. Buffer overflows: Attacks and defenses for the vulnerability of the decade (DISCEX 2000). Avijit,
CS 380S Runtime Defenses against Memory Corruption Vitaly Shmatikov slide 1 Reading Assignment Cowan et al. Buffer overflows: Attacks and defenses for the vulnerability of the decade (DISCEX 2000). Avijit,
QUIZ. Write the following for the class Bar: Default constructor Constructor Copy-constructor Overloaded assignment oper. Is a destructor needed?
 QUIZ Write the following for the class Bar: Default constructor Constructor Copy-constructor Overloaded assignment oper. Is a destructor needed? Or Foo(x), depending on how we want the initialization
QUIZ Write the following for the class Bar: Default constructor Constructor Copy-constructor Overloaded assignment oper. Is a destructor needed? Or Foo(x), depending on how we want the initialization
Class Information ANNOUCEMENTS
 Class Information ANNOUCEMENTS Third homework due TODAY at 11:59pm. Extension? First project has been posted, due Monday October 23, 11:59pm. Midterm exam: Friday, October 27, in class. Don t forget to
Class Information ANNOUCEMENTS Third homework due TODAY at 11:59pm. Extension? First project has been posted, due Monday October 23, 11:59pm. Midterm exam: Friday, October 27, in class. Don t forget to
Information Flow Analysis and Type Systems for Secure C Language (VITC Project) Jun FURUSE. The University of Tokyo
 Information Flow Analysis and Type Systems for Secure C Language (VITC Project) Jun FURUSE The University of Tokyo furuse@yl.is.s.u-tokyo.ac.jp e-society MEXT project toward secure and reliable software
Information Flow Analysis and Type Systems for Secure C Language (VITC Project) Jun FURUSE The University of Tokyo furuse@yl.is.s.u-tokyo.ac.jp e-society MEXT project toward secure and reliable software
CSolve: Verifying C With Liquid Types
 CSolve: Verifying C With Liquid Types Patrick Rondon, Alexander Bakst, Ming Kawaguchi, and Ranjit Jhala University of California, San Diego {prondon, abakst, mwookawa, jhala@cs.ucsd.edu Abstract. We present
CSolve: Verifying C With Liquid Types Patrick Rondon, Alexander Bakst, Ming Kawaguchi, and Ranjit Jhala University of California, San Diego {prondon, abakst, mwookawa, jhala@cs.ucsd.edu Abstract. We present
Software Security: Vulnerability Analysis
 Computer Security Course. Software Security: Vulnerability Analysis Program Verification Program Verification How to prove a program free of buffer overflows? Precondition Postcondition Loop invariants
Computer Security Course. Software Security: Vulnerability Analysis Program Verification Program Verification How to prove a program free of buffer overflows? Precondition Postcondition Loop invariants
CS 330 Lecture 18. Symbol table. C scope rules. Declarations. Chapter 5 Louden Outline
 CS 0 Lecture 8 Chapter 5 Louden Outline The symbol table Static scoping vs dynamic scoping Symbol table Dictionary associates names to attributes In general: hash tables, tree and lists (assignment ) can
CS 0 Lecture 8 Chapter 5 Louden Outline The symbol table Static scoping vs dynamic scoping Symbol table Dictionary associates names to attributes In general: hash tables, tree and lists (assignment ) can
CS61C : Machine Structures
 Get your clickers ready...! inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c CS61C : Machine Structures Lecture 3 Introduction to the C Programming Language (pt 1) 2013-01-28! Hello to Nishant Varma watching from India!!!Senior
Get your clickers ready...! inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c CS61C : Machine Structures Lecture 3 Introduction to the C Programming Language (pt 1) 2013-01-28! Hello to Nishant Varma watching from India!!!Senior
Topics Covered Thus Far CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages
 Topics Covered Thus Far CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages Names & Binding, Type Systems Programming languages Ruby Ocaml Lambda calculus Syntax specification Regular expressions Context free
Topics Covered Thus Far CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages Names & Binding, Type Systems Programming languages Ruby Ocaml Lambda calculus Syntax specification Regular expressions Context free
Dynamic Memory Allocation: Advanced Concepts
 Dynamic Memory Allocation: Advanced Concepts Keeping Track of Free Blocks Method 1: Implicit list using length links all blocks 5 4 6 Method : Explicit list among the free blocks using pointers 5 4 6 Kai
Dynamic Memory Allocation: Advanced Concepts Keeping Track of Free Blocks Method 1: Implicit list using length links all blocks 5 4 6 Method : Explicit list among the free blocks using pointers 5 4 6 Kai
Operational Semantics. One-Slide Summary. Lecture Outline
 Operational Semantics #1 One-Slide Summary Operational semantics are a precise way of specifying how to evaluate a program. A formal semantics tells you what each expression means. Meaning depends on context:
Operational Semantics #1 One-Slide Summary Operational semantics are a precise way of specifying how to evaluate a program. A formal semantics tells you what each expression means. Meaning depends on context:
QUIZ How do we implement run-time constants and. compile-time constants inside classes?
 QUIZ How do we implement run-time constants and compile-time constants inside classes? Compile-time constants in classes The static keyword inside a class means there s only one instance, regardless of
QUIZ How do we implement run-time constants and compile-time constants inside classes? Compile-time constants in classes The static keyword inside a class means there s only one instance, regardless of
Lecture 27. Pros and Cons of Pointers. Basics Design Options Pointer Analysis Algorithms Pointer Analysis Using BDDs Probabilistic Pointer Analysis
 Pros and Cons of Pointers Lecture 27 Pointer Analysis Basics Design Options Pointer Analysis Algorithms Pointer Analysis Using BDDs Probabilistic Pointer Analysis Many procedural languages have pointers
Pros and Cons of Pointers Lecture 27 Pointer Analysis Basics Design Options Pointer Analysis Algorithms Pointer Analysis Using BDDs Probabilistic Pointer Analysis Many procedural languages have pointers
CMSC 313 COMPUTER ORGANIZATION & ASSEMBLY LANGUAGE PROGRAMMING
 CMSC 313 COMPUTER ORGANIZATION & ASSEMBLY LANGUAGE PROGRAMMING LECTURE 16, SPRING 2013 TOPICS TODAY Project 6 Perils & Pitfalls of Memory Allocation C Function Call Conventions in Assembly Language PERILS
CMSC 313 COMPUTER ORGANIZATION & ASSEMBLY LANGUAGE PROGRAMMING LECTURE 16, SPRING 2013 TOPICS TODAY Project 6 Perils & Pitfalls of Memory Allocation C Function Call Conventions in Assembly Language PERILS
Lecture 20 Pointer Analysis
 Lecture 20 Pointer Analysis Basics Design Options Pointer Analysis Algorithms Pointer Analysis Using BDDs Probabilistic Pointer Analysis (Slide content courtesy of Greg Steffan, U. of Toronto) 15-745:
Lecture 20 Pointer Analysis Basics Design Options Pointer Analysis Algorithms Pointer Analysis Using BDDs Probabilistic Pointer Analysis (Slide content courtesy of Greg Steffan, U. of Toronto) 15-745:
Lecture 14 Pointer Analysis
 Lecture 14 Pointer Analysis Basics Design Options Pointer Analysis Algorithms Pointer Analysis Using BDDs Probabilistic Pointer Analysis [ALSU 12.4, 12.6-12.7] Phillip B. Gibbons 15-745: Pointer Analysis
Lecture 14 Pointer Analysis Basics Design Options Pointer Analysis Algorithms Pointer Analysis Using BDDs Probabilistic Pointer Analysis [ALSU 12.4, 12.6-12.7] Phillip B. Gibbons 15-745: Pointer Analysis
CS61C : Machine Structures
 Get your clickers ready...! inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c CS61C : Machine Structures Lecture 3 Introduction to the C Programming Language (pt 1)!!Senior Lecturer SOE Dan Garcia!!!www.cs.berkeley.edu/~ddgarcia
Get your clickers ready...! inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c CS61C : Machine Structures Lecture 3 Introduction to the C Programming Language (pt 1)!!Senior Lecturer SOE Dan Garcia!!!www.cs.berkeley.edu/~ddgarcia
Region-Based Memory Management in Cyclone
 Region-Based Memory Management in Cyclone Dan Grossman Cornell University June 2002 Joint work with: Greg Morrisett, Trevor Jim (AT&T), Michael Hicks, James Cheney, Yanling Wang Cyclone A safe C-level
Region-Based Memory Management in Cyclone Dan Grossman Cornell University June 2002 Joint work with: Greg Morrisett, Trevor Jim (AT&T), Michael Hicks, James Cheney, Yanling Wang Cyclone A safe C-level
CPSC 3740 Programming Languages University of Lethbridge. Data Types
 Data Types A data type defines a collection of data values and a set of predefined operations on those values Some languages allow user to define additional types Useful for error detection through type
Data Types A data type defines a collection of data values and a set of predefined operations on those values Some languages allow user to define additional types Useful for error detection through type
CSE 303 Concepts and Tools for Software Development. Magdalena Balazinska Winter 2010 Lecture 27 Final Exam Revision
 CSE 303 Concepts and Tools for Software Development Magdalena Balazinska Winter 2010 Lecture 27 Final Exam Revision Today Final review session! The final is not yet written, but you know roughly what it
CSE 303 Concepts and Tools for Software Development Magdalena Balazinska Winter 2010 Lecture 27 Final Exam Revision Today Final review session! The final is not yet written, but you know roughly what it
Java and C CSE 351 Spring
 Java and C CSE 351 Spring 2018 https://xkcd.com/801/ Roadmap C: car *c = malloc(sizeof(car)); c->miles = 100; c->gals = 17; float mpg = get_mpg(c); free(c); Assembly language: Machine code: get_mpg: pushq
Java and C CSE 351 Spring 2018 https://xkcd.com/801/ Roadmap C: car *c = malloc(sizeof(car)); c->miles = 100; c->gals = 17; float mpg = get_mpg(c); free(c); Assembly language: Machine code: get_mpg: pushq
Dynamic Memory Allocation
 Dynamic Memory Allocation CS61, Lecture 11 Prof. Stephen Chong October 6, 2011 Announcements 1/2 Reminder: No section on Monday Monday sections have been rescheduled See website for details Please attend
Dynamic Memory Allocation CS61, Lecture 11 Prof. Stephen Chong October 6, 2011 Announcements 1/2 Reminder: No section on Monday Monday sections have been rescheduled See website for details Please attend
QUIZ. What is wrong with this code that uses default arguments?
 QUIZ What is wrong with this code that uses default arguments? Solution The value of the default argument should be placed in either declaration or definition, not both! QUIZ What is wrong with this code
QUIZ What is wrong with this code that uses default arguments? Solution The value of the default argument should be placed in either declaration or definition, not both! QUIZ What is wrong with this code
Types and Type Inference
 Types and Type Inference Mooly Sagiv Slides by Kathleen Fisher and John Mitchell Reading: Concepts in Programming Languages, Revised Chapter 6 - handout on the course homepage Outline General discussion
Types and Type Inference Mooly Sagiv Slides by Kathleen Fisher and John Mitchell Reading: Concepts in Programming Languages, Revised Chapter 6 - handout on the course homepage Outline General discussion
Types and Type Inference
 CS 242 2012 Types and Type Inference Notes modified from John Mitchell and Kathleen Fisher Reading: Concepts in Programming Languages, Revised Chapter 6 - handout on Web!! Outline General discussion of
CS 242 2012 Types and Type Inference Notes modified from John Mitchell and Kathleen Fisher Reading: Concepts in Programming Languages, Revised Chapter 6 - handout on Web!! Outline General discussion of
Lecture 16 Pointer Analysis
 Pros and Cons of Pointers Lecture 16 Pointer Analysis Basics Design Options Pointer Analysis Algorithms Pointer Analysis Using BDDs Probabilistic Pointer Analysis Many procedural languages have pointers
Pros and Cons of Pointers Lecture 16 Pointer Analysis Basics Design Options Pointer Analysis Algorithms Pointer Analysis Using BDDs Probabilistic Pointer Analysis Many procedural languages have pointers
CS-527 Software Security
 CS-527 Software Security Memory Safety Asst. Prof. Mathias Payer Department of Computer Science Purdue University TA: Kyriakos Ispoglou https://nebelwelt.net/teaching/17-527-softsec/ Spring 2017 Eternal
CS-527 Software Security Memory Safety Asst. Prof. Mathias Payer Department of Computer Science Purdue University TA: Kyriakos Ispoglou https://nebelwelt.net/teaching/17-527-softsec/ Spring 2017 Eternal
Contents. I. Classes, Superclasses, and Subclasses. Topic 04 - Inheritance
 Contents Topic 04 - Inheritance I. Classes, Superclasses, and Subclasses - Inheritance Hierarchies Controlling Access to Members (public, no modifier, private, protected) Calling constructors of superclass
Contents Topic 04 - Inheritance I. Classes, Superclasses, and Subclasses - Inheritance Hierarchies Controlling Access to Members (public, no modifier, private, protected) Calling constructors of superclass
CS152: Programming Languages. Lecture 23 Advanced Concepts in Object-Oriented Programming. Dan Grossman Spring 2011
 CS152: Programming Languages Lecture 23 Advanced Concepts in Object-Oriented Programming Dan Grossman Spring 2011 So far... The difference between OOP and records of functions with shared private state
CS152: Programming Languages Lecture 23 Advanced Concepts in Object-Oriented Programming Dan Grossman Spring 2011 So far... The difference between OOP and records of functions with shared private state
The Compiler So Far. CSC 4181 Compiler Construction. Semantic Analysis. Beyond Syntax. Goals of a Semantic Analyzer.
 The Compiler So Far CSC 4181 Compiler Construction Scanner - Lexical analysis Detects inputs with illegal tokens e.g.: main 5 (); Parser - Syntactic analysis Detects inputs with ill-formed parse trees
The Compiler So Far CSC 4181 Compiler Construction Scanner - Lexical analysis Detects inputs with illegal tokens e.g.: main 5 (); Parser - Syntactic analysis Detects inputs with ill-formed parse trees
The Java Language Implementation
 CS 242 2012 The Java Language Implementation Reading Chapter 13, sections 13.4 and 13.5 Optimizing Dynamically-Typed Object-Oriented Languages With Polymorphic Inline Caches, pages 1 5. Outline Java virtual
CS 242 2012 The Java Language Implementation Reading Chapter 13, sections 13.4 and 13.5 Optimizing Dynamically-Typed Object-Oriented Languages With Polymorphic Inline Caches, pages 1 5. Outline Java virtual
The Mercury project. Zoltan Somogyi
 The Mercury project Zoltan Somogyi The University of Melbourne Linux Users Victoria 7 June 2011 Zoltan Somogyi (Linux Users Victoria) The Mercury project June 15, 2011 1 / 23 Introduction Mercury: objectives
The Mercury project Zoltan Somogyi The University of Melbourne Linux Users Victoria 7 June 2011 Zoltan Somogyi (Linux Users Victoria) The Mercury project June 15, 2011 1 / 23 Introduction Mercury: objectives
A brief introduction to C programming for Java programmers
 A brief introduction to C programming for Java programmers Sven Gestegård Robertz September 2017 There are many similarities between Java and C. The syntax in Java is basically
A brief introduction to C programming for Java programmers Sven Gestegård Robertz September 2017 There are many similarities between Java and C. The syntax in Java is basically
Topic 9: Type Checking
 Recommended Exercises and Readings Topic 9: Type Checking From Haskell: The craft of functional programming (3 rd Ed.) Exercises: 13.17, 13.18, 13.19, 13.20, 13.21, 13.22 Readings: Chapter 13.5, 13.6 and
Recommended Exercises and Readings Topic 9: Type Checking From Haskell: The craft of functional programming (3 rd Ed.) Exercises: 13.17, 13.18, 13.19, 13.20, 13.21, 13.22 Readings: Chapter 13.5, 13.6 and
Topic 9: Type Checking
 Topic 9: Type Checking 1 Recommended Exercises and Readings From Haskell: The craft of functional programming (3 rd Ed.) Exercises: 13.17, 13.18, 13.19, 13.20, 13.21, 13.22 Readings: Chapter 13.5, 13.6
Topic 9: Type Checking 1 Recommended Exercises and Readings From Haskell: The craft of functional programming (3 rd Ed.) Exercises: 13.17, 13.18, 13.19, 13.20, 13.21, 13.22 Readings: Chapter 13.5, 13.6
Inheritance, Polymorphism and the Object Memory Model
 Inheritance, Polymorphism and the Object Memory Model 1 how objects are stored in memory at runtime? compiler - operations such as access to a member of an object are compiled runtime - implementation
Inheritance, Polymorphism and the Object Memory Model 1 how objects are stored in memory at runtime? compiler - operations such as access to a member of an object are compiled runtime - implementation
CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages. Ownership, References, and Lifetimes in Rust
 CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages Ownership, References, and Lifetimes in Rust CMSC330 Spring 2018 1 Memory: the Stack and the Heap The stack constant-time, automatic (de)allocation Data
CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages Ownership, References, and Lifetimes in Rust CMSC330 Spring 2018 1 Memory: the Stack and the Heap The stack constant-time, automatic (de)allocation Data
CSE 351, Spring 2010 Lab 7: Writing a Dynamic Storage Allocator Due: Thursday May 27, 11:59PM
 CSE 351, Spring 2010 Lab 7: Writing a Dynamic Storage Allocator Due: Thursday May 27, 11:59PM 1 Instructions In this lab you will be writing a dynamic storage allocator for C programs, i.e., your own version
CSE 351, Spring 2010 Lab 7: Writing a Dynamic Storage Allocator Due: Thursday May 27, 11:59PM 1 Instructions In this lab you will be writing a dynamic storage allocator for C programs, i.e., your own version
CS 314 Principles of Programming Languages. Lecture 11
 CS 314 Principles of Programming Languages Lecture 11 Zheng Zhang Department of Computer Science Rutgers University Wednesday 12 th October, 2016 Zheng Zhang 1 eddy.zhengzhang@cs.rutgers.edu Class Information
CS 314 Principles of Programming Languages Lecture 11 Zheng Zhang Department of Computer Science Rutgers University Wednesday 12 th October, 2016 Zheng Zhang 1 eddy.zhengzhang@cs.rutgers.edu Class Information
Memory Safety (cont d) Software Security
 Memory Safety (cont d) Software Security CS 161: Computer Security Prof. Raluca Ada Popa January 17, 2016 Some slides credit to David Wagner and Nick Weaver Announcements Discussion sections and office
Memory Safety (cont d) Software Security CS 161: Computer Security Prof. Raluca Ada Popa January 17, 2016 Some slides credit to David Wagner and Nick Weaver Announcements Discussion sections and office
CS61C Machine Structures. Lecture 4 C Pointers and Arrays. 1/25/2006 John Wawrzynek. www-inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c/
 CS61C Machine Structures Lecture 4 C Pointers and Arrays 1/25/2006 John Wawrzynek (www.cs.berkeley.edu/~johnw) www-inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c/ CS 61C L04 C Pointers (1) Common C Error There is a difference
CS61C Machine Structures Lecture 4 C Pointers and Arrays 1/25/2006 John Wawrzynek (www.cs.berkeley.edu/~johnw) www-inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c/ CS 61C L04 C Pointers (1) Common C Error There is a difference
CSE 307: Principles of Programming Languages
 CSE 307: Principles of Programming Languages Variables and Constants R. Sekar 1 / 22 Topics 2 / 22 Variables and Constants Variables are stored in memory, whereas constants need not be. Value of variables
CSE 307: Principles of Programming Languages Variables and Constants R. Sekar 1 / 22 Topics 2 / 22 Variables and Constants Variables are stored in memory, whereas constants need not be. Value of variables
Lectures 5-6: Introduction to C
 Lectures 5-6: Introduction to C Motivation: C is both a high and a low-level language Very useful for systems programming Faster than Java This intro assumes knowledge of Java Focus is on differences Most
Lectures 5-6: Introduction to C Motivation: C is both a high and a low-level language Very useful for systems programming Faster than Java This intro assumes knowledge of Java Focus is on differences Most
Java and C I. CSE 351 Spring Instructor: Ruth Anderson
 Java and C I CSE 351 Spring 2017 Instructor: Ruth Anderson Teaching Assistants: Dylan Johnson Kevin Bi Linxing Preston Jiang Cody Ohlsen Yufang Sun Joshua Curtis Administrivia Homework 5 Due TONIGHT Wed
Java and C I CSE 351 Spring 2017 Instructor: Ruth Anderson Teaching Assistants: Dylan Johnson Kevin Bi Linxing Preston Jiang Cody Ohlsen Yufang Sun Joshua Curtis Administrivia Homework 5 Due TONIGHT Wed
Organization of Programming Languages CS320/520N. Lecture 06. Razvan C. Bunescu School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science
 Organization of Programming Languages CS320/520N Razvan C. Bunescu School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science bunescu@ohio.edu Data Types A data type defines a collection of data objects and
Organization of Programming Languages CS320/520N Razvan C. Bunescu School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science bunescu@ohio.edu Data Types A data type defines a collection of data objects and
Types. What is a type?
 Types What is a type? Type checking Type conversion Aggregates: strings, arrays, structures Enumeration types Subtypes Types, CS314 Fall 01 BGRyder 1 What is a type? A set of values and the valid operations
Types What is a type? Type checking Type conversion Aggregates: strings, arrays, structures Enumeration types Subtypes Types, CS314 Fall 01 BGRyder 1 What is a type? A set of values and the valid operations
 https://lambda.mines.edu A pointer is a value that indicates location in memory. When we change the location the pointer points to, we say we assign the pointer a value. When we look at the data the pointer
https://lambda.mines.edu A pointer is a value that indicates location in memory. When we change the location the pointer points to, we say we assign the pointer a value. When we look at the data the pointer
CSE 431S Type Checking. Washington University Spring 2013
 CSE 431S Type Checking Washington University Spring 2013 Type Checking When are types checked? Statically at compile time Compiler does type checking during compilation Ideally eliminate runtime checks
CSE 431S Type Checking Washington University Spring 2013 Type Checking When are types checked? Statically at compile time Compiler does type checking during compilation Ideally eliminate runtime checks
CS 31: Intro to Systems Pointers and Memory. Martin Gagne Swarthmore College February 16, 2016
 CS 31: Intro to Systems Pointers and Memory Martin Gagne Swarthmore College February 16, 2016 So we declared a pointer How do we make it point to something? 1. Assign it the address of an existing variable
CS 31: Intro to Systems Pointers and Memory Martin Gagne Swarthmore College February 16, 2016 So we declared a pointer How do we make it point to something? 1. Assign it the address of an existing variable
G52CPP C++ Programming Lecture 3. Dr Jason Atkin
 G52CPP C++ Programming Lecture 3 Dr Jason Atkin E-Mail: jaa@cs.nott.ac.uk 1 Revision so far C/C++ designed for speed, Java for catching errors Java hides a lot of the details (so can C++) Much of C, C++
G52CPP C++ Programming Lecture 3 Dr Jason Atkin E-Mail: jaa@cs.nott.ac.uk 1 Revision so far C/C++ designed for speed, Java for catching errors Java hides a lot of the details (so can C++) Much of C, C++
CS558 Programming Languages
 CS558 Programming Languages Fall 2016 Lecture 3a Andrew Tolmach Portland State University 1994-2016 Formal Semantics Goal: rigorous and unambiguous definition in terms of a wellunderstood formalism (e.g.
CS558 Programming Languages Fall 2016 Lecture 3a Andrew Tolmach Portland State University 1994-2016 Formal Semantics Goal: rigorous and unambiguous definition in terms of a wellunderstood formalism (e.g.
Lecture 14. No in-class files today. Homework 7 (due on Wednesday) and Project 3 (due in 10 days) posted. Questions?
 Lecture 14 No in-class files today. Homework 7 (due on Wednesday) and Project 3 (due in 10 days) posted. Questions? Friday, February 11 CS 215 Fundamentals of Programming II - Lecture 14 1 Outline Static
Lecture 14 No in-class files today. Homework 7 (due on Wednesday) and Project 3 (due in 10 days) posted. Questions? Friday, February 11 CS 215 Fundamentals of Programming II - Lecture 14 1 Outline Static
Functions in C C Programming and Software Tools
 Functions in C C Programming and Software Tools N.C. State Department of Computer Science Functions in C Functions are also called subroutines or procedures One part of a program calls (or invokes the
Functions in C C Programming and Software Tools N.C. State Department of Computer Science Functions in C Functions are also called subroutines or procedures One part of a program calls (or invokes the
High Performance Computing and Programming, Lecture 3
 High Performance Computing and Programming, Lecture 3 Memory usage and some other things Ali Dorostkar Division of Scientific Computing, Department of Information Technology, Uppsala University, Sweden
High Performance Computing and Programming, Lecture 3 Memory usage and some other things Ali Dorostkar Division of Scientific Computing, Department of Information Technology, Uppsala University, Sweden
CS6202: Advanced Topics in Programming Languages and Systems Lecture 0 : Overview
 CS6202: Advanced Topics in Programming Languages and Systems Lecture 0 : Overview Advanced Language Features and Foundations Lecturer : Chin Wei Ngan Email : chinwn@comp.nus.edu.sg Office : S15 06-01 CS6202
CS6202: Advanced Topics in Programming Languages and Systems Lecture 0 : Overview Advanced Language Features and Foundations Lecturer : Chin Wei Ngan Email : chinwn@comp.nus.edu.sg Office : S15 06-01 CS6202
Simple Overflow. #include <stdio.h> int main(void){ unsigned int num = 0xffffffff;
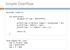 Simple Overflow 1 #include int main(void){ unsigned int num = 0xffffffff; printf("num is %d bits long\n", sizeof(num) * 8); printf("num = 0x%x\n", num); printf("num + 1 = 0x%x\n", num + 1); }
Simple Overflow 1 #include int main(void){ unsigned int num = 0xffffffff; printf("num is %d bits long\n", sizeof(num) * 8); printf("num = 0x%x\n", num); printf("num + 1 = 0x%x\n", num + 1); }
Introduction Primitive Data Types Character String Types User-Defined Ordinal Types Array Types. Record Types. Pointer and Reference Types
 Chapter 6 Topics WEEK E FOUR Data Types Introduction Primitive Data Types Character String Types User-Defined Ordinal Types Array Types Associative Arrays Record Types Union Types Pointer and Reference
Chapter 6 Topics WEEK E FOUR Data Types Introduction Primitive Data Types Character String Types User-Defined Ordinal Types Array Types Associative Arrays Record Types Union Types Pointer and Reference
Ch. 3: The C in C++ - Continued -
 Ch. 3: The C in C++ - Continued - QUIZ What are the 3 ways a reference can be passed to a C++ function? QUIZ True or false: References behave like constant pointers with automatic dereferencing. QUIZ What
Ch. 3: The C in C++ - Continued - QUIZ What are the 3 ways a reference can be passed to a C++ function? QUIZ True or false: References behave like constant pointers with automatic dereferencing. QUIZ What
Announcements. assign0 due tonight. Labs start this week. No late submissions. Very helpful for assign1
 Announcements assign due tonight No late submissions Labs start this week Very helpful for assign1 Goals for Today Pointer operators Allocating memory in the heap malloc and free Arrays and pointer arithmetic
Announcements assign due tonight No late submissions Labs start this week Very helpful for assign1 Goals for Today Pointer operators Allocating memory in the heap malloc and free Arrays and pointer arithmetic
Agenda CS121/IS223. Reminder. Object Declaration, Creation, Assignment. What is Going On? Variables in Java
 CS121/IS223 Object Reference Variables Dr Olly Gotel ogotel@pace.edu http://csis.pace.edu/~ogotel Having problems? -- Come see me or call me in my office hours -- Use the CSIS programming tutors Agenda
CS121/IS223 Object Reference Variables Dr Olly Gotel ogotel@pace.edu http://csis.pace.edu/~ogotel Having problems? -- Come see me or call me in my office hours -- Use the CSIS programming tutors Agenda
377 Student Guide to C++
 377 Student Guide to C++ c Mark Corner January 21, 2004 1 Introduction In this course you will be using the C++ language to complete several programming assignments. Up to this point we have only provided
377 Student Guide to C++ c Mark Corner January 21, 2004 1 Introduction In this course you will be using the C++ language to complete several programming assignments. Up to this point we have only provided
Organization of Programming Languages CS3200 / 5200N. Lecture 06
 Organization of Programming Languages CS3200 / 5200N Razvan C. Bunescu School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science bunescu@ohio.edu Data Types A data type defines a collection of data objects
Organization of Programming Languages CS3200 / 5200N Razvan C. Bunescu School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science bunescu@ohio.edu Data Types A data type defines a collection of data objects
Secure Software Development: Theory and Practice
 Secure Software Development: Theory and Practice Suman Jana MW 2:40-3:55pm 415 Schapiro [SCEP] *Some slides are borrowed from Dan Boneh and John Mitchell Software Security is a major problem! Why writing
Secure Software Development: Theory and Practice Suman Jana MW 2:40-3:55pm 415 Schapiro [SCEP] *Some slides are borrowed from Dan Boneh and John Mitchell Software Security is a major problem! Why writing
Chapter 10. Improving the Runtime Type Checker Type-Flow Analysis
 122 Chapter 10 Improving the Runtime Type Checker The runtime overhead of the unoptimized RTC is quite high, because it instruments every use of a memory location in the program and tags every user-defined
122 Chapter 10 Improving the Runtime Type Checker The runtime overhead of the unoptimized RTC is quite high, because it instruments every use of a memory location in the program and tags every user-defined
Limitations of the stack
 The heap hic 1 Limitations of the stack int *table_of(int num, int len) { int table[len+1]; for (int i=0; i
The heap hic 1 Limitations of the stack int *table_of(int num, int len) { int table[len+1]; for (int i=0; i
Week 7. Statically-typed OO languages: C++ Closer look at subtyping
 C++ & Subtyping Week 7 Statically-typed OO languages: C++ Closer look at subtyping Why talk about C++? C++ is an OO extension of C Efficiency and flexibility from C OO program organization from Simula
C++ & Subtyping Week 7 Statically-typed OO languages: C++ Closer look at subtyping Why talk about C++? C++ is an OO extension of C Efficiency and flexibility from C OO program organization from Simula
QUIZ. What are 3 differences between C and C++ const variables?
 QUIZ What are 3 differences between C and C++ const variables? Solution QUIZ Source: http://stackoverflow.com/questions/17349387/scope-of-macros-in-c Solution The C/C++ preprocessor substitutes mechanically,
QUIZ What are 3 differences between C and C++ const variables? Solution QUIZ Source: http://stackoverflow.com/questions/17349387/scope-of-macros-in-c Solution The C/C++ preprocessor substitutes mechanically,
Identifying Memory Corruption Bugs with Compiler Instrumentations. 이병영 ( 조지아공과대학교
 Identifying Memory Corruption Bugs with Compiler Instrumentations 이병영 ( 조지아공과대학교 ) blee@gatech.edu @POC2014 How to find bugs Source code auditing Fuzzing Source Code Auditing Focusing on specific vulnerability
Identifying Memory Corruption Bugs with Compiler Instrumentations 이병영 ( 조지아공과대학교 ) blee@gatech.edu @POC2014 How to find bugs Source code auditing Fuzzing Source Code Auditing Focusing on specific vulnerability
CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages
 CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages Type Systems, Names and Binding CMSC 330 - Spring 2013 1 Topics Covered Thus Far! Programming languages Ruby OCaml! Syntax specification Regular expressions
CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages Type Systems, Names and Binding CMSC 330 - Spring 2013 1 Topics Covered Thus Far! Programming languages Ruby OCaml! Syntax specification Regular expressions
Pierce Ch. 3, 8, 11, 15. Type Systems
 Pierce Ch. 3, 8, 11, 15 Type Systems Goals Define the simple language of expressions A small subset of Lisp, with minor modifications Define the type system of this language Mathematical definition using
Pierce Ch. 3, 8, 11, 15 Type Systems Goals Define the simple language of expressions A small subset of Lisp, with minor modifications Define the type system of this language Mathematical definition using
Memory Allocation III
 Memory Allocation III CSE 351 Winter 2018 Instructor: Mark Wyse Teaching Assistants: Kevin Bi Parker DeWilde Emily Furst Sarah House Waylon Huang Vinny Palaniappan https://xkcd.com/835/ Administrivia Homework
Memory Allocation III CSE 351 Winter 2018 Instructor: Mark Wyse Teaching Assistants: Kevin Bi Parker DeWilde Emily Furst Sarah House Waylon Huang Vinny Palaniappan https://xkcd.com/835/ Administrivia Homework
