CONCURRENCY MODEL. UNIX Programming 2014 Fall by Euiseong Seo
|
|
|
- Alisha Sherman
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CONCURRENCY MODEL UNIX Programming 2014 Fall by Euiseong Seo
2 Echo Server Revisited int main (int argc, char *argv[]) {... listenfd = socket(af_inet, SOCK_STREAM, 0); bzero((char *)&saddr, sizeof(saddr)); saddr.sin_family = AF_INET; saddr.sin_addr.s_addr = htonl(inaddr_any); saddr.sin_port = htons(port); bind(listenfd, (struct sockaddr *)&saddr, sizeof(saddr)); listen(listenfd, 5); while (1) { connfd = accept(listenfd, (struct sockaddr *)&caddr, &clen); while ((n = read(connfd, buf, MAXLINE)) > 0) { printf ( got %d bytes from client.\n, n); write(connfd, buf, n); close(connfd);
3 Iterative Model One request at a time client 1 server client 2 call connect ret connect call read ret read close call accept ret accept write close call accept ret accept write close call connect ret connect call read ret read close
4 Only One Client at a Time call connect ret connect call fgets User goes out to lunch Client 1 blocks wai5ng for user to type in data client 1 server client 2 Server blocks wai5ng for data from Client 1 call accept ret accept call read Solution: use concurrent servers instead call connect Client 2 blocks wai5ng to complete its connec5on request un5l a<er lunch! Use multiple concurrent flows to serve multiple clients at the same time.
5 Creating Concurrent Flows Processes Kernel automatically interleaves multiple logical flows Each flow has its own private address space I/O multiplexing with select() User manually interleaves multiple logical flows Each flow shares the same address space Popular for high-performance server designs Threads Kernel automatically interleaves multiple logical flows Each flow shares the same address space Hybrid of processes and I/O multiplexing
6 Process-based Servers client 1 server client 2 call accept call connect call connect ret connect call fgets User goes out to lunch Client 1 blocks wai5ng for user to type in data call read child 1 fork... ret accept fork call accept ret accept child 2 call read write close ret connect call fgets write call read end read close
7 Echo Server Iterative version int main (int argc, char *argv[]) {... while (1) { connfd = accept (listenfd, (struct sockaddr *)&caddr, &caddrlen)); while ((n = read(connfd, buf, MAXLINE)) > 0) { printf ( got %d bytes from client.\n, n); write(connfd, buf, n); close(connfd);
8 Echo Server: Process-based int main (int argc, char *argv[]) {... signal (SIGCHLD, handler); while (1) { connfd = accept (listenfd, (struct sockaddr *)&caddr, &caddrlen)); if (fork() == 0) { close(listenfd); while ((n = read(connfd, buf, MAXLINE)) > 0) { printf ( got %d bytes from client.\n, n); write(connfd, buf, n); close(connfd); exit(0); close(connfd); void handler(int sig) { pid_t pid; int stat; while ((pid = waitpid(- 1, &stat, WNOHANG)) > 0); return;
9 Implementation Issues Servers should restart accept() if it is interrupted by a transfer of control to SIGCHLD handler Not necessary for systems with POSIX signal handling Required for portability on some older Unix systems Server must reap zombie children to avoid fatal memory leak Server must close its copy of connfd Kernel keeps reference for each socket After fork(), ref. count of connfd becomes 2 Connection will not be closed until ref. count becomes 0
10 Process-based Designs Pros Handles multiple connections concurrently Easy to implement and clear to understand sharing model Simple and straightforward Cons Additional overhead for process control n Process creation and termination n Process switching Nontrivial to share data between processes n Requires IPC (Inter-Process Communication) mechanisms n FIFO, shared memory and semaphores
11 I/O Multiplexing Event-based concurrent servers Maintain a pool of connected descriptors Repeat followings forever n Use select() system call to block until n (a) New connection request arrives on the listening descriptor n (b) New data arrives on an existing connected descriptor n If (a), add new connection to connection descriptor pool n If (b), read any available data from connection n Close connection on EOF and remove it from pool. I/O multiplexing provides more control with less overhead
12 Select on Sockets Prototype #include <sys/select.h>! int select(int nfds, fd_set *readfds, fd_set *writefds,! fd_set *exceptfds, struct timeval *timeout); select() returns number of FDs contained in the three returned descriptor sets select() blocks for timeout waiting for a file descriptor to become ready FDs in readfds will be tested whether they have something to read FDs in writefds will be tested whether they are available for writing
13 Select on Sockets FDs in exceptfds will be watched for exceptions Three given FD sets will be changed accordingly Only FDs in ready will be included in the result sets
14 Macros for FD Sets Macros for manipulating set descriptors void FD_ZERO (fd_set *fdset) n Turn off all bits in fdset void FD_SET (int fd, fd_set *fdset) n Turn on bit fd in fdset void FD_CLR (int fd, fd_set *fdset) n Turn off bit fd in fdset int FD_ISSET (int fd, fd_set *fdset) n Is bit fd in fdset turned on?
15 Echo Server: Event-based (1) typedef struct { int maxfd; // largest descriptor in read_set int nready; // number of ready desc. from select fd_set read_set; // set of all active descriptors fd_set ready_set; // subset of desc. ready for reading pool; int main (int argc, char *argv[]) { int listenfd, connfd, val; pool p;... listenfd =... // socket(), bind(), listen() // initialize pool p.maxfd = listenfd; FD_ZERO(&p.read_set); FD_SET(listenfd, &p.read_set);
16 Echo Server: Event-based (2) while (1) { p.ready_set = p.read_set; p.nready = select(p.maxfd+1, &p.ready_set, NULL, NULL, NULL); if (FD_ISSET(listenfd, &p.ready_set)) { connfd = accept (listenfd, (struct sockaddr *)&caddr, &caddrlen)); FD_SET(connfd, &p.read_set); if (connfd > p.maxfd) p.maxfd = connfd; p.nready- - ; check_clients (listenfd, &p);
17 Echo Server: Event-based (3) void check_clients (int listenfd, pool *p) { int s, n; char buf[maxline]; for (s = 0; s < p- >maxfd+1 && p- >nready > 0; s++) { if (s == listenfd) continue; if (FD_ISSET(s, &p- >read_set) && FD_ISSET(s, &p- >ready_set)) { p- >nready- - ; if ((n = read(s, buf, MAXLINE)) > 0) write(s, buf, n); if (n == 0) { // EOF close(s); FD_CLR(s, &p- >read_set); if (s == p- >maxfd) { p- >maxfd- - ; while (!FD_ISSET(p- >maxfd, &p- >read_set)) p- >maxfd- - ;
18 Event-based Designs Pros One logical control flow Can single-step with a debugger No process or thread control overhead n Design of choice for high-performance Web servers and search engines Cons Significantly more complex to code than process- or thread-based designs Can be vulnerable to Denial-of-Service attack
Concurrent Programming. Jin-Soo Kim Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University
 Concurrent Programming Jin-Soo Kim (jinsookim@skku.edu) Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University http://csl.skku.edu Echo Server Revisited int main (int argc, char *argv[]) {... listenfd = socket(af_inet,
Concurrent Programming Jin-Soo Kim (jinsookim@skku.edu) Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University http://csl.skku.edu Echo Server Revisited int main (int argc, char *argv[]) {... listenfd = socket(af_inet,
Announcement (1) Due date for PA3 is changed (~ next week) PA4 will also be started in the next class. Not submitted. Not scored
 Announcement (1) Due date for PA3 is changed (~ next week) PA4 will also be started in the next class Not submitted Not scored 1 Concurrent Programming Prof. Jin-Soo Kim( jinsookim@skku.edu) TA Sanghoon
Announcement (1) Due date for PA3 is changed (~ next week) PA4 will also be started in the next class Not submitted Not scored 1 Concurrent Programming Prof. Jin-Soo Kim( jinsookim@skku.edu) TA Sanghoon
Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University
 Concurrent Programming Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University http://csl.skku.edu Echo Server Revisited int main (int argc, char *argv[]) {... listenfd = socket(af_inet, SOCK_STREAM, 0); bzero((char
Concurrent Programming Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University http://csl.skku.edu Echo Server Revisited int main (int argc, char *argv[]) {... listenfd = socket(af_inet, SOCK_STREAM, 0); bzero((char
Concurrent Programming
 Concurrent Programming Prof. Jin-Soo Kim( jinsookim@skku.edu) TA Jinhong Kim( jinhong.kim@csl.skku.edu) Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University http://csl.skku.edu Echo Server Revisited int
Concurrent Programming Prof. Jin-Soo Kim( jinsookim@skku.edu) TA Jinhong Kim( jinhong.kim@csl.skku.edu) Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University http://csl.skku.edu Echo Server Revisited int
Concurrent Servers Dec 2, 2009"
 Concurrent Servers Dec 2, 2009" Administrivia" 2! Iterative Servers" client 1! server! client 2! call connect ret connect call read ret read close call accept" ret accept" write close call accept" ret
Concurrent Servers Dec 2, 2009" Administrivia" 2! Iterative Servers" client 1! server! client 2! call connect ret connect call read ret read close call accept" ret accept" write close call accept" ret
call connect call read call connect ret connect call fgets Client 2 blocks waiting to complete its connection request until after lunch!
 15-213 The course that gives CMU its Zip! Concurrent Servers December 4, 2001 Topics Limitations of iterative servers Process-based concurrent servers Threads-based concurrent servers Event-based concurrent
15-213 The course that gives CMU its Zip! Concurrent Servers December 4, 2001 Topics Limitations of iterative servers Process-based concurrent servers Threads-based concurrent servers Event-based concurrent
Total Score is updated. The score of PA4 will be changed! Please check it. Will be changed
 Announcement Total Score is updated Please check it Will be changed The score of PA4 will be changed! 1 Concurrent Programming Prof. Jin-Soo Kim( jinsookim@skku.edu) TA Sanghoon Han(sanghoon.han@csl.skku.edu)
Announcement Total Score is updated Please check it Will be changed The score of PA4 will be changed! 1 Concurrent Programming Prof. Jin-Soo Kim( jinsookim@skku.edu) TA Sanghoon Han(sanghoon.han@csl.skku.edu)
Iterative Servers The course that gives CMU its Zip! Iterative servers process one request at a time. Concurrent Servers
 15-213 The course that gives CMU its Zip! Concurrent Servers Dec 3, 2002 Topics! Limitations of iterative servers! Process-based concurrent servers! Event-based concurrent servers! Threads-based concurrent
15-213 The course that gives CMU its Zip! Concurrent Servers Dec 3, 2002 Topics! Limitations of iterative servers! Process-based concurrent servers! Event-based concurrent servers! Threads-based concurrent
Sockets. Dong-kun Shin Embedded Software Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University Embedded Software Lab.
 1 Sockets Dong-kun Shin Embedded Software Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University http://nyx.skku.ac.kr Echo Client (1) 2 #include #include #include #include
1 Sockets Dong-kun Shin Embedded Software Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University http://nyx.skku.ac.kr Echo Client (1) 2 #include #include #include #include
CONCURRENT PROGRAMMING. Lecture 5
 CONCURRENT PROGRAMMING Lecture 5 Last lecture TCP I/O RIO: buffered I/O. Unix IO Question: difference between send() and write()? MSG_DONTWAIT, MSG_NOSIGNAL 2 Concurrent Programming is Hard! The human
CONCURRENT PROGRAMMING Lecture 5 Last lecture TCP I/O RIO: buffered I/O. Unix IO Question: difference between send() and write()? MSG_DONTWAIT, MSG_NOSIGNAL 2 Concurrent Programming is Hard! The human
Concurrent Programming
 Concurrent Programming Prof. Jinkyu Jeong( jinkyu@skku.edu) TA Jinhong Kim( jinhong.kim@csl.skku.edu) TA Seokha Shin(seokha.shin@csl.skku.edu) Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University http://csl.skku.edu
Concurrent Programming Prof. Jinkyu Jeong( jinkyu@skku.edu) TA Jinhong Kim( jinhong.kim@csl.skku.edu) TA Seokha Shin(seokha.shin@csl.skku.edu) Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University http://csl.skku.edu
Three Basic Mechanisms for Creating Concurrent Flows. Systemprogrammering 2009 Föreläsning 10 Concurrent Servers. Process-Based Concurrent Server
 Systemprogrammering 2009 Föreläsning 10 Concurrent Servers Topics! Limitations of iterative servers! Process-based concurrent servers! Event-based concurrent servers! Threads-based concurrent servers Three
Systemprogrammering 2009 Föreläsning 10 Concurrent Servers Topics! Limitations of iterative servers! Process-based concurrent servers! Event-based concurrent servers! Threads-based concurrent servers Three
Concurrent Programming April 21, 2005
 15-213 The course that gives CMU its Zip! Concurrent Programming April 21, 2005 Topics Limitations of iterative servers Process-based concurrent servers Event-based concurrent servers Threads-based concurrent
15-213 The course that gives CMU its Zip! Concurrent Programming April 21, 2005 Topics Limitations of iterative servers Process-based concurrent servers Event-based concurrent servers Threads-based concurrent
Sockets. Jin-Soo Kim Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University
 Sockets Jin-Soo Kim (jinsookim@skku.edu) Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University http://csl.skku.edu Internet Connections (1) Connection Clients and servers communicate by sending streams of
Sockets Jin-Soo Kim (jinsookim@skku.edu) Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University http://csl.skku.edu Internet Connections (1) Connection Clients and servers communicate by sending streams of
Concurrent Programming November 28, 2007
 15-213 Concurrent Programming November 28, 2007 Topics Limitations of iterative servers Process-based concurrent servers Event-based concurrent servers Threads-based concurrent servers class25.ppt Concurrent
15-213 Concurrent Programming November 28, 2007 Topics Limitations of iterative servers Process-based concurrent servers Event-based concurrent servers Threads-based concurrent servers class25.ppt Concurrent
Hyo-bong Son Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University
 Sockets Hyo-bong Son (proshb@csl.skku.edu) Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University http://csl.skku.edu Client-Server Model Most network application is based on the client-server model: A server
Sockets Hyo-bong Son (proshb@csl.skku.edu) Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University http://csl.skku.edu Client-Server Model Most network application is based on the client-server model: A server
PA #2 Reviews. set_name, get_name, del_name. Questions? Will be modified after PA #4 ~
 Sockets Prof. Jin-Soo Kim( jinsookim@skku.edu) TA Dong-Yun Lee(dylee@csl.skku.edu) Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University http://csl.skku.edu PA #2 Reviews set_name, get_name, del_name Will
Sockets Prof. Jin-Soo Kim( jinsookim@skku.edu) TA Dong-Yun Lee(dylee@csl.skku.edu) Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University http://csl.skku.edu PA #2 Reviews set_name, get_name, del_name Will
I/O Models. Kartik Gopalan
 I/O Models Kartik Gopalan Types of Concurrency True Concurrency (multiple processes or threads) Multi-processor machines Child processes/threads execute in parallel. Multi-process (forking) servers If
I/O Models Kartik Gopalan Types of Concurrency True Concurrency (multiple processes or threads) Multi-processor machines Child processes/threads execute in parallel. Multi-process (forking) servers If
Concurrent Programming
 Concurrent Programming CS 485G-006: Systems Programming Lectures 32 33: 18 20 Apr 2016 1 Concurrent Programming is Hard! The human mind tends to be sequential The notion of time is often misleading Thinking
Concurrent Programming CS 485G-006: Systems Programming Lectures 32 33: 18 20 Apr 2016 1 Concurrent Programming is Hard! The human mind tends to be sequential The notion of time is often misleading Thinking
NETWORK AND SYSTEM PROGRAMMING. I/O Multiplexing: select and poll function
 NETWORK AND SYSTEM PROGRAMMING LAB 15 I/O Multiplexing: select and poll function 15.1 objectives What is a Concurrent server Use of Select System call Use of Poll System call 15.2 What is concurrent server?
NETWORK AND SYSTEM PROGRAMMING LAB 15 I/O Multiplexing: select and poll function 15.1 objectives What is a Concurrent server Use of Select System call Use of Poll System call 15.2 What is concurrent server?
Lecture #23 Concurrent Programming
 Lecture #23 Concurrent Programming Nov. 20, 2017 18-600 Foundations of Computer Systems 1 Concurrent Programming is Hard! The human mind tends to be sequential The notion of time is often misleading Thinking
Lecture #23 Concurrent Programming Nov. 20, 2017 18-600 Foundations of Computer Systems 1 Concurrent Programming is Hard! The human mind tends to be sequential The notion of time is often misleading Thinking
Concurrent Programming is Hard! Concurrent Programming. Reminder: Iterative Echo Server. The human mind tends to be sequential
 Concurrent Programming is Hard! Concurrent Programming 15 213 / 18 213: Introduction to Computer Systems 23 rd Lecture, April 11, 213 Instructors: Seth Copen Goldstein, Anthony Rowe, and Greg Kesden The
Concurrent Programming is Hard! Concurrent Programming 15 213 / 18 213: Introduction to Computer Systems 23 rd Lecture, April 11, 213 Instructors: Seth Copen Goldstein, Anthony Rowe, and Greg Kesden The
Concurrent Programming
 Chapter 13 Concurrent Programming As we learned in Chapter 8, logical control flows are concurrent if they overlap in time. This general phenomenon, known as concurrency, shows up at many different levels
Chapter 13 Concurrent Programming As we learned in Chapter 8, logical control flows are concurrent if they overlap in time. This general phenomenon, known as concurrency, shows up at many different levels
Carnegie Mellon. Bryant and O Hallaron, Computer Systems: A Programmer s Perspective, Third Edition
 Carnegie Mellon 1 Concurrent Programming 15-213: Introduction to Computer Systems 23 rd Lecture, Nov. 13, 2018 2 Concurrent Programming is Hard! The human mind tends to be sequential The notion of time
Carnegie Mellon 1 Concurrent Programming 15-213: Introduction to Computer Systems 23 rd Lecture, Nov. 13, 2018 2 Concurrent Programming is Hard! The human mind tends to be sequential The notion of time
9/13/2007. Motivations for Sockets What s in a Socket? Working g with Sockets Concurrent Network Applications Software Engineering for Project 1
 Daniel Spangenberger 15 441 Computer Networks, Fall 2007 Goal of Networking: Communication Share data Pass Messages Say I want to talk to a friend in Singapore How can I do this? What applications and
Daniel Spangenberger 15 441 Computer Networks, Fall 2007 Goal of Networking: Communication Share data Pass Messages Say I want to talk to a friend in Singapore How can I do this? What applications and
Concurrent Programming
 Concurrent Programming 15-213 / 18-213: Introduc2on to Computer Systems 23 rd Lecture, Nov. 14, 2013 Instructors: Randy Bryant, Dave O Hallaron, and Greg Kesden 1 Concurrent Programming is Hard! The human
Concurrent Programming 15-213 / 18-213: Introduc2on to Computer Systems 23 rd Lecture, Nov. 14, 2013 Instructors: Randy Bryant, Dave O Hallaron, and Greg Kesden 1 Concurrent Programming is Hard! The human
Εργαστήριο 9 I/O Multiplexing
 Εργαστήριο 9 I/O Multiplexing Στοεργαστήριοθαμελετηθούν: Server High Level View I/O Multiplexing Solutions for Concurrency nonblocking I/O Use alarm and signal handler to interrupt slow system calls. Use
Εργαστήριο 9 I/O Multiplexing Στοεργαστήριοθαμελετηθούν: Server High Level View I/O Multiplexing Solutions for Concurrency nonblocking I/O Use alarm and signal handler to interrupt slow system calls. Use
Concurrent Programming
 Concurrent Programming Andrew Case Slides adapted from Mohamed Zahran, Jinyang Li, Clark Barre=, Randy Bryant and Dave O Hallaron 1 Concurrent vs. Parallelism Concurrency: At least two tasks are making
Concurrent Programming Andrew Case Slides adapted from Mohamed Zahran, Jinyang Li, Clark Barre=, Randy Bryant and Dave O Hallaron 1 Concurrent vs. Parallelism Concurrency: At least two tasks are making
Concurrent Programming
 CHAPTER 12 Concurrent Programming 121 Concurrent Programming with Processes 935 122 Concurrent Programming with I/O Multiplexing 939 123 Concurrent Programming with Threads 947 124 Shared Variables in
CHAPTER 12 Concurrent Programming 121 Concurrent Programming with Processes 935 122 Concurrent Programming with I/O Multiplexing 939 123 Concurrent Programming with Threads 947 124 Shared Variables in
Concurrent Programming
 Concurrent Programming 15-213: Introduc0on to Computer Systems 22 nd Lecture, Nov. 11, 2010 Instructors: Randy Bryant and Dave O Hallaron 1 Concurrent Programming is Hard! The human mind tends to be sequen9al
Concurrent Programming 15-213: Introduc0on to Computer Systems 22 nd Lecture, Nov. 11, 2010 Instructors: Randy Bryant and Dave O Hallaron 1 Concurrent Programming is Hard! The human mind tends to be sequen9al
Concurrent programming
 Concurrent programming : Introduc2on to Computer Systems 24th Lecture Sec2ons 12.1-12.3 Instructors: Ian Foster Gordon Kindlmann Slides borrow copiously from materials by Randy Bryant and Dave O Hallaron
Concurrent programming : Introduc2on to Computer Systems 24th Lecture Sec2ons 12.1-12.3 Instructors: Ian Foster Gordon Kindlmann Slides borrow copiously from materials by Randy Bryant and Dave O Hallaron
Sockets. Dong-kun Shin Embedded Software Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University Embedded Software Lab.
 1 Sockets Dong-kun Shin Embedded Software Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University http://nyx.skku.ac.kr Internet Connections (1) 2 Connection Clients and servers communicate by sending streams of bytes over
1 Sockets Dong-kun Shin Embedded Software Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University http://nyx.skku.ac.kr Internet Connections (1) 2 Connection Clients and servers communicate by sending streams of bytes over
Lecture 3 Overview! Last Lecture! TCP/UDP and Sockets introduction!
 Lecture 3 Overview! Last Lecture! TCP/UDP and Sockets introduction! This Lecture! Elementary TCP sockets! TCP Client-Server example! Source: Stevens book(chapters 4,5), Comer s book (Chapters 20, 21)!
Lecture 3 Overview! Last Lecture! TCP/UDP and Sockets introduction! This Lecture! Elementary TCP sockets! TCP Client-Server example! Source: Stevens book(chapters 4,5), Comer s book (Chapters 20, 21)!
Inter-Process Communication. Disclaimer: some slides are adopted from the book authors slides with permission 1
 Inter-Process Communication Disclaimer: some slides are adopted from the book authors slides with permission 1 Today Inter-Process Communication (IPC) What is it? What IPC mechanisms are available? 2 Inter-Process
Inter-Process Communication Disclaimer: some slides are adopted from the book authors slides with permission 1 Today Inter-Process Communication (IPC) What is it? What IPC mechanisms are available? 2 Inter-Process
ECE 650 Systems Programming & Engineering. Spring 2018
 ECE 650 Systems Programming & Engineering Spring 2018 Programming with Network Sockets Tyler Bletsch Duke University Slides are adapted from Brian Rogers (Duke) Sockets We ve looked at shared memory vs.
ECE 650 Systems Programming & Engineering Spring 2018 Programming with Network Sockets Tyler Bletsch Duke University Slides are adapted from Brian Rogers (Duke) Sockets We ve looked at shared memory vs.
CISC2200 Threads Spring 2015
 CISC2200 Threads Spring 2015 Process We learn the concept of process A program in execution A process owns some resources A process executes a program => execution state, PC, We learn that bash creates
CISC2200 Threads Spring 2015 Process We learn the concept of process A program in execution A process owns some resources A process executes a program => execution state, PC, We learn that bash creates
Client-server model The course that gives CMU its Zip! Network programming Nov 27, Using ports to identify services.
 15-213 The course that gives CMU its Zip! Network programming Nov 27, 2001 Topics Client- model Sockets interface Echo and Client- model Every network application is based on the - model: Application is
15-213 The course that gives CMU its Zip! Network programming Nov 27, 2001 Topics Client- model Sockets interface Echo and Client- model Every network application is based on the - model: Application is
Example Questions for Midterm EE122, Fall 2008 EECS Berkeley
 Example Questions for Midterm EE122, Fall 2008 EECS Berkeley Note: The midterm exam will have six problems or more. The five problems below represent around 60-70% of the workload you should expect at
Example Questions for Midterm EE122, Fall 2008 EECS Berkeley Note: The midterm exam will have six problems or more. The five problems below represent around 60-70% of the workload you should expect at
CSC209H Lecture 10. Dan Zingaro. March 18, 2015
 CSC209H Lecture 10 Dan Zingaro March 18, 2015 Creating a Client To create a client that can connect to a server, call the following, in order: socket: create a communication endpoint This is the same as
CSC209H Lecture 10 Dan Zingaro March 18, 2015 Creating a Client To create a client that can connect to a server, call the following, in order: socket: create a communication endpoint This is the same as
ISA 563: Fundamentals of Systems Programming
 ISA 563: Fundamentals of Systems Programming Advanced IO April 9, 2012 Non-blocking IO Data processing can be much faster than data access Waiting for IO to finish can be time consuming, and may not even
ISA 563: Fundamentals of Systems Programming Advanced IO April 9, 2012 Non-blocking IO Data processing can be much faster than data access Waiting for IO to finish can be time consuming, and may not even
Today: VM wrap-up Select (if time) Course wrap-up Final Evaluations
 Today: VM wrap-up Select (if time) Course wrap-up Final Evaluations Program structure int A[1024][1024] ; Each row is stored in one page Ignore code page in this example One frame allocated Program 1 for
Today: VM wrap-up Select (if time) Course wrap-up Final Evaluations Program structure int A[1024][1024] ; Each row is stored in one page Ignore code page in this example One frame allocated Program 1 for
Global Employee Location Server
 S4516 HELP Session 1 Global Employee Location Server Jeff Zhou jeffz@cs.wpi.edu 3/19/2011 Modified based on S4514 B05 slides Objective: Description To implement a simple concurrent server that has four
S4516 HELP Session 1 Global Employee Location Server Jeff Zhou jeffz@cs.wpi.edu 3/19/2011 Modified based on S4514 B05 slides Objective: Description To implement a simple concurrent server that has four
Concurrent Programming
 Concurrent Programming is Hard! Concurrent Programming Kai Shen The human mind tends to be sequential Thinking about all possible sequences of events in a computer system is at least error prone and frequently
Concurrent Programming is Hard! Concurrent Programming Kai Shen The human mind tends to be sequential Thinking about all possible sequences of events in a computer system is at least error prone and frequently
Introduction to Client-Server Model
 Preview Introduction to Client-Server Model Motivation of Client-Server Model Terminologies and Concepts in Client-Server Model Connectionless vs. Connection-Oriented Stateless vs. Stateful Server Identify
Preview Introduction to Client-Server Model Motivation of Client-Server Model Terminologies and Concepts in Client-Server Model Connectionless vs. Connection-Oriented Stateless vs. Stateful Server Identify
socketservertcl a Tcl extension for using SCM_RIGHTS By Shannon Noe - FlightAware
 socketservertcl a Tcl extension for using SCM_RIGHTS By Shannon Noe - FlightAware Presented at the 24th annual Tcl/Tk conference, Houston Texas, October 2017 Abstract: Horizontal scaling is used to distribute
socketservertcl a Tcl extension for using SCM_RIGHTS By Shannon Noe - FlightAware Presented at the 24th annual Tcl/Tk conference, Houston Texas, October 2017 Abstract: Horizontal scaling is used to distribute
Unix Network Programming Chapter 4. Elementary TCP Sockets 광운대학교컴퓨터과학과 정보통신연구실 석사과정안중현
 Unix Network Programming Chapter 4. Elementary TCP Sockets 광운대학교컴퓨터과학과 정보통신연구실 석사과정안중현 4.1 Introduction A Time line of the typical scenario that takes place between a TCP client and server. Describes the
Unix Network Programming Chapter 4. Elementary TCP Sockets 광운대학교컴퓨터과학과 정보통신연구실 석사과정안중현 4.1 Introduction A Time line of the typical scenario that takes place between a TCP client and server. Describes the
Concurrent Programming
 Concurrent Programming is Hard! Concurrent Programming Kai Shen The human mind tends to be sequential Thinking about all possible sequences of events in a computer system is at least error prone and frequently
Concurrent Programming is Hard! Concurrent Programming Kai Shen The human mind tends to be sequential Thinking about all possible sequences of events in a computer system is at least error prone and frequently
Network Programming September 6, 2005
 class03.ppt Network Programming September 6, 2005 Topics 15-441 David Murray Slides based on those of Dave Maltz, Randy Bryant, Geoff Langale, and the 15-213 crew Programmer s view of the Internet Sockets
class03.ppt Network Programming September 6, 2005 Topics 15-441 David Murray Slides based on those of Dave Maltz, Randy Bryant, Geoff Langale, and the 15-213 crew Programmer s view of the Internet Sockets
Network Programming TDC 561
 Network Programming TDC 561 Lecture # 4: Server Design (II) - Concurrent Servers Dr. Ehab S. Al-Shaer School of Computer Science & Telecommunication DePaul University Chicago, IL 1 Unix Signals A signal
Network Programming TDC 561 Lecture # 4: Server Design (II) - Concurrent Servers Dr. Ehab S. Al-Shaer School of Computer Science & Telecommunication DePaul University Chicago, IL 1 Unix Signals A signal
Experiential Learning Workshop on Basics of Socket Programming
 Experiential Learning Workshop on Basics of Socket June 28, 2018 Dr. Ram P Rustagi Professor, CSE Dept KSIT, Bangalore rprustagi@ksit.edu.in Resources https://rprustagi.com/elnt/experiential- Learning.html
Experiential Learning Workshop on Basics of Socket June 28, 2018 Dr. Ram P Rustagi Professor, CSE Dept KSIT, Bangalore rprustagi@ksit.edu.in Resources https://rprustagi.com/elnt/experiential- Learning.html
CSC209: Software tools. Unix files and directories permissions utilities/commands Shell programming quoting wild cards files
 CSC209 Review CSC209: Software tools Unix files and directories permissions utilities/commands Shell programming quoting wild cards files ... and systems programming C basic syntax functions arrays structs
CSC209 Review CSC209: Software tools Unix files and directories permissions utilities/commands Shell programming quoting wild cards files ... and systems programming C basic syntax functions arrays structs
CSC209: Software tools. Unix files and directories permissions utilities/commands Shell programming quoting wild cards files. Compiler vs.
 CSC209 Review CSC209: Software tools Unix files and directories permissions utilities/commands Shell programming quoting wild cards files... and systems programming C basic syntax functions arrays structs
CSC209 Review CSC209: Software tools Unix files and directories permissions utilities/commands Shell programming quoting wild cards files... and systems programming C basic syntax functions arrays structs
Assignment 2 Group 5 Simon Gerber Systems Group Dept. Computer Science ETH Zurich - Switzerland
 Assignment 2 Group 5 Simon Gerber Systems Group Dept. Computer Science ETH Zurich - Switzerland t Your task Write a simple file server Client has to be implemented in Java Server has to be implemented
Assignment 2 Group 5 Simon Gerber Systems Group Dept. Computer Science ETH Zurich - Switzerland t Your task Write a simple file server Client has to be implemented in Java Server has to be implemented
Semester 2, Computer Communication 352 Module 4
 Page 4.1; CRICOS Number: 00301J MODULE 4 References: 1. Stevens, Fenner, Rudoff, UNIX Network Programming, vol. 1, Chapter 5. OBJECTIVE Provide detail description on TCP Client-Server Example. Discuss
Page 4.1; CRICOS Number: 00301J MODULE 4 References: 1. Stevens, Fenner, Rudoff, UNIX Network Programming, vol. 1, Chapter 5. OBJECTIVE Provide detail description on TCP Client-Server Example. Discuss
Network Programming November 3, 2008
 15-213 Network Programming November 3, 2008 Topics Programmer s view of the Internet (review) Sockets interface Writing clients and servers class20.ppt A Client-Server Transaction Most network applications
15-213 Network Programming November 3, 2008 Topics Programmer s view of the Internet (review) Sockets interface Writing clients and servers class20.ppt A Client-Server Transaction Most network applications
Chapter 5. TCP Client-Server
 Chapter 5. TCP Client-Server Example Contents Introduction TCP Echo Server TCP Echo Client Normal Startup and Termination Posix Signal Handling Handling SIGCHLD Signals Data Format and so on... 5.1 Introduction
Chapter 5. TCP Client-Server Example Contents Introduction TCP Echo Server TCP Echo Client Normal Startup and Termination Posix Signal Handling Handling SIGCHLD Signals Data Format and so on... 5.1 Introduction
ECE 650 Systems Programming & Engineering. Spring 2018
 ECE 650 Systems Programming & Engineering Spring 2018 Inter-process Communication (IPC) Tyler Bletsch Duke University Slides are adapted from Brian Rogers (Duke) Recall Process vs. Thread A process is
ECE 650 Systems Programming & Engineering Spring 2018 Inter-process Communication (IPC) Tyler Bletsch Duke University Slides are adapted from Brian Rogers (Duke) Recall Process vs. Thread A process is
COMP/ELEC 429/556 Introduction to Computer Networks
 COMP/ELEC 429/556 Introduction to Computer Networks Creating a Network Application Some slides used with permissions from Edward W. Knightly, T. S. Eugene Ng, Ion Stoica, Hui Zhang 1 How to Programmatically
COMP/ELEC 429/556 Introduction to Computer Networks Creating a Network Application Some slides used with permissions from Edward W. Knightly, T. S. Eugene Ng, Ion Stoica, Hui Zhang 1 How to Programmatically
CSC209 Review. Yeah! We made it!
 CSC209 Review Yeah! We made it! 1 CSC209: Software tools Unix files and directories permissions utilities/commands Shell programming quoting wild cards files 2 ... and C programming... C basic syntax functions
CSC209 Review Yeah! We made it! 1 CSC209: Software tools Unix files and directories permissions utilities/commands Shell programming quoting wild cards files 2 ... and C programming... C basic syntax functions
PLEASE HAND IN UNIVERSITY OF TORONTO Faculty of Arts and Science
 PLEASE HAND IN UNIVERSITY OF TORONTO Faculty of Arts and Science AUGUST 2012 EXAMINATIONS CSC 209H1Y Instructor: Daniel Zingaro Duration three hours PLEASE HAND IN Examination Aids: one two-sided 8.5x11
PLEASE HAND IN UNIVERSITY OF TORONTO Faculty of Arts and Science AUGUST 2012 EXAMINATIONS CSC 209H1Y Instructor: Daniel Zingaro Duration three hours PLEASE HAND IN Examination Aids: one two-sided 8.5x11
Lecture 24. Thursday, November 19 CS 375 UNIX System Programming - Lecture 24 1
 Lecture 24 Log into Linux. Copy directory /home/hwang/cs375/lecture24 Final project posted. Due during finals week. Reminder: No class next Tuesday (11/24) Questions? Thursday, November 19 CS 375 UNIX
Lecture 24 Log into Linux. Copy directory /home/hwang/cs375/lecture24 Final project posted. Due during finals week. Reminder: No class next Tuesday (11/24) Questions? Thursday, November 19 CS 375 UNIX
Network Programming in C: The Berkeley Sockets API. Networked Systems 3 Laboratory Sessions
 Network Programming in C: The Berkeley Sockets API Networked Systems 3 Laboratory Sessions The Berkeley Sockets API Widely used low-level C networking API First introduced in 4.3BSD Unix Now available
Network Programming in C: The Berkeley Sockets API Networked Systems 3 Laboratory Sessions The Berkeley Sockets API Widely used low-level C networking API First introduced in 4.3BSD Unix Now available
CMPSC 311- Introduction to Systems Programming Module: Concurrency
 CMPSC 311- Introduction to Systems Programming Module: Concurrency Professor Patrick McDaniel Fall 2013 Sequential Programming Processing a network connection as it arrives and fulfilling the exchange
CMPSC 311- Introduction to Systems Programming Module: Concurrency Professor Patrick McDaniel Fall 2013 Sequential Programming Processing a network connection as it arrives and fulfilling the exchange
Any of the descriptors in the set {1, 4} have an exception condition pending
 Page 1 of 6 6.3 select Function This function allows the process to instruct the kernel to wait for any one of multiple events to occur and to wake up the process only when one or more of these events
Page 1 of 6 6.3 select Function This function allows the process to instruct the kernel to wait for any one of multiple events to occur and to wake up the process only when one or more of these events
10. I/O System Library
 10. I/O System Library Header File #include // Found in C:\Nburn\include General File Descriptor Functions close --- Close open file descriptors read --- Read data from a file descriptor ReadWithTimeout
10. I/O System Library Header File #include // Found in C:\Nburn\include General File Descriptor Functions close --- Close open file descriptors read --- Read data from a file descriptor ReadWithTimeout
Network Programming / : Introduc2on to Computer Systems 21 st Lecture, April. 4, Instructors: Todd Mowry and Anthony Rowe
 Network Programming 15-213 / 18-213: Introduc2on to Computer Systems 21 st Lecture, April. 4, 2012 Instructors: Todd Mowry and Anthony Rowe 1 A Programmer s View of the Internet Hosts are mapped to a set
Network Programming 15-213 / 18-213: Introduc2on to Computer Systems 21 st Lecture, April. 4, 2012 Instructors: Todd Mowry and Anthony Rowe 1 A Programmer s View of the Internet Hosts are mapped to a set
Contents. IPC (Inter-Process Communication) Representation of open files in kernel I/O redirection Anonymous Pipe Named Pipe (FIFO)
 Pipes and FIFOs Prof. Jin-Soo Kim( jinsookim@skku.edu) TA JinHong Kim( jinhong.kim@csl.skku.edu) Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University http://csl.skku.edu Contents IPC (Inter-Process Communication)
Pipes and FIFOs Prof. Jin-Soo Kim( jinsookim@skku.edu) TA JinHong Kim( jinhong.kim@csl.skku.edu) Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University http://csl.skku.edu Contents IPC (Inter-Process Communication)
Inter-Process Communication. Disclaimer: some slides are adopted from the book authors slides with permission 1
 Inter-Process Communication Disclaimer: some slides are adopted from the book authors slides with permission 1 Today Inter-Process Communication (IPC) What is it? What IPC mechanisms are available? 2 Inter-Process
Inter-Process Communication Disclaimer: some slides are adopted from the book authors slides with permission 1 Today Inter-Process Communication (IPC) What is it? What IPC mechanisms are available? 2 Inter-Process
Network Games Part II. Architecture of Network Game
 Network Games Part II Doron Nussbaum Network Games Part II COMP 5900 1 Architecture of Network Game Client Server Peer to Peer Player 1 Player 2 Player 1 Player 2 Server Player 5 Player 3 Player 5 Player
Network Games Part II Doron Nussbaum Network Games Part II COMP 5900 1 Architecture of Network Game Client Server Peer to Peer Player 1 Player 2 Player 1 Player 2 Server Player 5 Player 3 Player 5 Player
Light-Weight Processes: Dissecting Linux Threads
 Operating Systems (Fall/Winter 2018) Light-Weight Processes: Dissecting Linux Threads Yajin Zhou (http://yajin.org) Zhejiang University source: https://opensourceforu.com/2011/08/light-weight-processes-dissecting-linux-threads/
Operating Systems (Fall/Winter 2018) Light-Weight Processes: Dissecting Linux Threads Yajin Zhou (http://yajin.org) Zhejiang University source: https://opensourceforu.com/2011/08/light-weight-processes-dissecting-linux-threads/
serverbase.txt (1) Server Client1 (3) (2) Client2 Child Process1 Child Process2 Note: each child process keeps a separate copy of the DB.
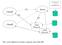 serverbase.txt Client1 (3) (1) (2) Server Client2 Child Process1 Child Process2 Note: each child process keeps a separate copy of the DB. Client APP Layer Server APP Layer NW Layer NW Layer DLL DLL PHL
serverbase.txt Client1 (3) (1) (2) Server Client2 Child Process1 Child Process2 Note: each child process keeps a separate copy of the DB. Client APP Layer Server APP Layer NW Layer NW Layer DLL DLL PHL
CS118 Discussion Week 2. Taqi
 CS118 Discussion Week 2 Taqi Outline Any Questions for Course Project 1? Socket Programming: Non-blocking mode Lecture Review: Application Layer Much of the other related stuff we will only discuss during
CS118 Discussion Week 2 Taqi Outline Any Questions for Course Project 1? Socket Programming: Non-blocking mode Lecture Review: Application Layer Much of the other related stuff we will only discuss during
Inter-process communication (IPC)
 Inter-process communication (IPC) Operating Systems Kartik Gopalan References Chapter 5 of OSTEP book. Unix man pages Advanced Programming in Unix Environment by Richard Stevens http://www.kohala.com/start/apue.html
Inter-process communication (IPC) Operating Systems Kartik Gopalan References Chapter 5 of OSTEP book. Unix man pages Advanced Programming in Unix Environment by Richard Stevens http://www.kohala.com/start/apue.html
Approaches to Concurrency
 PROCESS AND THREADS Approaches to Concurrency Processes Hard to share resources: Easy to avoid unintended sharing High overhead in adding/removing clients Threads Easy to share resources: Perhaps too easy
PROCESS AND THREADS Approaches to Concurrency Processes Hard to share resources: Easy to avoid unintended sharing High overhead in adding/removing clients Threads Easy to share resources: Perhaps too easy
UNIT III - APPLICATION DEVELOPMENT. TCP Echo Server
 UNIT III - APPLICATION DEVELOPMENT TCP Echo Server TCP Echo Client Posix Signal handling Server with multiple clients boundary conditions: Server process Crashes, Server host Crashes, Server Crashes and
UNIT III - APPLICATION DEVELOPMENT TCP Echo Server TCP Echo Client Posix Signal handling Server with multiple clients boundary conditions: Server process Crashes, Server host Crashes, Server Crashes and
Pipes and FIFOs. Woo-Yeong Jeong Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University
 Pipes and FIFOs Woo-Yeong Jeong (wooyeong@csl.skku.edu) Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University http://csl.skku.edu Open Files in Kernel How the Unix kernel represents open files? Two descriptors
Pipes and FIFOs Woo-Yeong Jeong (wooyeong@csl.skku.edu) Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University http://csl.skku.edu Open Files in Kernel How the Unix kernel represents open files? Two descriptors
Operating System Structure
 Operating System Structure CSCI 4061 Introduction to Operating Systems Applications Instructor: Abhishek Chandra Operating System Hardware 2 Questions Operating System Structure How does the OS manage
Operating System Structure CSCI 4061 Introduction to Operating Systems Applications Instructor: Abhishek Chandra Operating System Hardware 2 Questions Operating System Structure How does the OS manage
Socket Programming TCP UDP
 Socket Programming TCP UDP Introduction Computer Network hosts, routers, communication channels Hosts run applications Routers forward information Packets: sequence of bytes contain control information
Socket Programming TCP UDP Introduction Computer Network hosts, routers, communication channels Hosts run applications Routers forward information Packets: sequence of bytes contain control information
Signal Example 1. Signal Example 2
 Signal Example 1 #include #include void ctrl_c_handler(int tmp) { printf("you typed CTL-C, but I don't want to die!\n"); int main(int argc, char* argv[]) { long i; signal(sigint, ctrl_c_handler);
Signal Example 1 #include #include void ctrl_c_handler(int tmp) { printf("you typed CTL-C, but I don't want to die!\n"); int main(int argc, char* argv[]) { long i; signal(sigint, ctrl_c_handler);
CS4514 HELP Session 3. Concurrent Server (in APP) Using Go-Back-N (in DLL)
 CS4514 HELP Session 3 Concurrent Server (in APP) Using Go-Back-N (in DLL) Description! You are supposed to implement a simple concurrent server on top of an emulated network protocol stack (NWL, DLL, PHL).
CS4514 HELP Session 3 Concurrent Server (in APP) Using Go-Back-N (in DLL) Description! You are supposed to implement a simple concurrent server on top of an emulated network protocol stack (NWL, DLL, PHL).
The Berkeley Sockets API. Networked Systems Architecture 3 Lecture 4
 The Berkeley Sockets API Networked Systems Architecture 3 Lecture 4 The Berkeley Sockets API Widely used low-level C networking API First introduced in 4.3BSD Unix Now available on most platforms: Linux,
The Berkeley Sockets API Networked Systems Architecture 3 Lecture 4 The Berkeley Sockets API Widely used low-level C networking API First introduced in 4.3BSD Unix Now available on most platforms: Linux,
CMPSC 311- Introduction to Systems Programming Module: Concurrency
 CMPSC 311- Introduction to Systems Programming Module: Concurrency Professor Patrick McDaniel Fall 2013 Sequential Programming Processing a network connection as it arrives and fulfilling the exchange
CMPSC 311- Introduction to Systems Programming Module: Concurrency Professor Patrick McDaniel Fall 2013 Sequential Programming Processing a network connection as it arrives and fulfilling the exchange
Contents. PA1 review and introduction to PA2. IPC (Inter-Process Communication) Exercise. I/O redirection Pipes FIFOs
 Pipes and FIFOs Prof. Jin-Soo Kim( jinsookim@skku.edu) TA Dong-Yun Lee(dylee@csl.skku.edu) Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University http://csl.skku.edu Contents PA1 review and introduction to
Pipes and FIFOs Prof. Jin-Soo Kim( jinsookim@skku.edu) TA Dong-Yun Lee(dylee@csl.skku.edu) Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University http://csl.skku.edu Contents PA1 review and introduction to
CSC209H Lecture 9. Dan Zingaro. March 11, 2015
 CSC209H Lecture 9 Dan Zingaro March 11, 2015 Socket Programming (Kerrisk Ch 56, 57, 59) Pipes and signals are only useful for processes communicating on the same machine Sockets are a general interprocess
CSC209H Lecture 9 Dan Zingaro March 11, 2015 Socket Programming (Kerrisk Ch 56, 57, 59) Pipes and signals are only useful for processes communicating on the same machine Sockets are a general interprocess
CSCE 313 Introduction to Computer Systems. Instructor: Dezhen Song
 CSCE 313 Introduction to Computer Systems Instructor: Dezhen Song UNIX I/O Files and File Representation Basic operations: Reading / Writing Caching: File Open / Close Multiplexing: Select / Poll File
CSCE 313 Introduction to Computer Systems Instructor: Dezhen Song UNIX I/O Files and File Representation Basic operations: Reading / Writing Caching: File Open / Close Multiplexing: Select / Poll File
CMPSC 311- Introduction to Systems Programming Module: Concurrency
 CMPSC 311- Introduction to Systems Programming Module: Concurrency Professor Patrick McDaniel Fall 2016 Sequential Programming Processing a network connection as it arrives and fulfilling the exchange
CMPSC 311- Introduction to Systems Programming Module: Concurrency Professor Patrick McDaniel Fall 2016 Sequential Programming Processing a network connection as it arrives and fulfilling the exchange
CSE 333 Lecture fork, pthread_create, select
 CSE 333 Lecture 22 -- fork, pthread_create, select Steve Gribble Department of Computer Science & Engineering University of Washington Administrivia HW4 out on Monday - you re gonna love it Final exam
CSE 333 Lecture 22 -- fork, pthread_create, select Steve Gribble Department of Computer Science & Engineering University of Washington Administrivia HW4 out on Monday - you re gonna love it Final exam
Piotr Mielecki Ph. D.
 Piotr Mielecki Ph. D. http://mielecki.ristel.pl/ piotr.mielecki@pwr.edu.pl pmielecki@gmail.com Building blocks of client-server applications: Client, Server, Middleware. Simple client-server application:
Piotr Mielecki Ph. D. http://mielecki.ristel.pl/ piotr.mielecki@pwr.edu.pl pmielecki@gmail.com Building blocks of client-server applications: Client, Server, Middleware. Simple client-server application:
Topics for this Week
 Topics for this Week Layered Network Architecture ISO/OSI Reference Model Internet Protocol Suite Overview Application Programming Interface BSD Socket API Readings Sections 1.1-1.5, 6.1.3 (socket programming),
Topics for this Week Layered Network Architecture ISO/OSI Reference Model Internet Protocol Suite Overview Application Programming Interface BSD Socket API Readings Sections 1.1-1.5, 6.1.3 (socket programming),
CS307 Operating Systems Processes
 CS307 Processes Fan Wu Department of Computer Science and Engineering Shanghai Jiao Tong University Spring 2018 Process Concept Process a program in execution An operating system executes a variety of
CS307 Processes Fan Wu Department of Computer Science and Engineering Shanghai Jiao Tong University Spring 2018 Process Concept Process a program in execution An operating system executes a variety of
Processes. Process Concept. The Process. The Process (Cont.) Process Control Block (PCB) Process State
 CS307 Process Concept Process a program in execution Processes An operating system executes a variety of programs: Batch system jobs Time-shared systems user programs or tasks All these activities are
CS307 Process Concept Process a program in execution Processes An operating system executes a variety of programs: Batch system jobs Time-shared systems user programs or tasks All these activities are
Types (Protocols) Associated functions Styles We will look at using sockets in C Java sockets are conceptually quite similar
 Socket Programming What is a socket? Using sockets Types (Protocols) Associated functions Styles We will look at using sockets in C Java sockets are conceptually quite similar - Advanced Data Communications:
Socket Programming What is a socket? Using sockets Types (Protocols) Associated functions Styles We will look at using sockets in C Java sockets are conceptually quite similar - Advanced Data Communications:
CMPSC 311- Introduction to Systems Programming Module: Network Programming
 CMPSC 311- Introduction to Systems Programming Module: Network Programming Professor Patrick McDaniel Fall 2013 What is a? A is a collection of computing devices that share a transmission media Traditional
CMPSC 311- Introduction to Systems Programming Module: Network Programming Professor Patrick McDaniel Fall 2013 What is a? A is a collection of computing devices that share a transmission media Traditional
Network Programming /18-243: Introduc3on to Computer Systems 22 nd Lecture, 13 April Instructors: Bill Nace and Gregory Kesden
 Network Programming 15-213/18-243: Introduc3on to Computer Systems 22 nd Lecture, 13 April 2010 Instructors: Bill Nace and Gregory Kesden (c) 1998-2010. All Rights Reserved. All work contained herein is
Network Programming 15-213/18-243: Introduc3on to Computer Systems 22 nd Lecture, 13 April 2010 Instructors: Bill Nace and Gregory Kesden (c) 1998-2010. All Rights Reserved. All work contained herein is
Network Programming in C. Networked Systems 3 Laboratory Sessions and Problem Sets
 Network Programming in C Networked Systems 3 Laboratory Sessions and Problem Sets Lab Timetable, Aims, and Objectives Teaching Week Activity 14 Introduction 15 Warm-up exercise 16 17 Web client 18 19 20
Network Programming in C Networked Systems 3 Laboratory Sessions and Problem Sets Lab Timetable, Aims, and Objectives Teaching Week Activity 14 Introduction 15 Warm-up exercise 16 17 Web client 18 19 20
CS118 Discussion 1A, Week 3. Zengwen Yuan Dodd Hall 78, Friday 10:00 11:50 a.m.
 CS118 Discussion 1A, Week 3 Zengwen Yuan Dodd Hall 78, Friday 10:00 11:50 a.m. 1 Outline Application Layer Protocol: DNS, CDN, P2P Transport Layer Protocol: UDP, principles of reliable transport protocol
CS118 Discussion 1A, Week 3 Zengwen Yuan Dodd Hall 78, Friday 10:00 11:50 a.m. 1 Outline Application Layer Protocol: DNS, CDN, P2P Transport Layer Protocol: UDP, principles of reliable transport protocol
Group-A Assignment No. 6
 Group-A Assignment No. 6 R N Oral Total Dated Sign (2) (5) (3) (10) Title : File Transfer using TCP Socket Problem Definition: Use Python for Socket Programming to connect two or more PCs to share a text
Group-A Assignment No. 6 R N Oral Total Dated Sign (2) (5) (3) (10) Title : File Transfer using TCP Socket Problem Definition: Use Python for Socket Programming to connect two or more PCs to share a text
CMPSC 311- Introduction to Systems Programming Module: Network Programming
 CMPSC 311- Introduction to Systems Programming Module: Network Programming Professor Patrick McDaniel Fall 2016 What is a network? A network is a collection of computing devices that share a transmission
CMPSC 311- Introduction to Systems Programming Module: Network Programming Professor Patrick McDaniel Fall 2016 What is a network? A network is a collection of computing devices that share a transmission
Reading Assignment 4. n Chapter 4 Threads, due 2/7. 1/31/13 CSE325 - Processes 1
 Reading Assignment 4 Chapter 4 Threads, due 2/7 1/31/13 CSE325 - Processes 1 What s Next? 1. Process Concept 2. Process Manager Responsibilities 3. Operations on Processes 4. Process Scheduling 5. Cooperating
Reading Assignment 4 Chapter 4 Threads, due 2/7 1/31/13 CSE325 - Processes 1 What s Next? 1. Process Concept 2. Process Manager Responsibilities 3. Operations on Processes 4. Process Scheduling 5. Cooperating
I/O Multiplexing. Dec 2009
 Windows Socket I/O Multiplexing http://icourse.cuc.edu.cn/networkprogramming/ linwei@cuc.edu.cn Dec 2009 Note You should not assume that an example in this presentation is complete. Items may have been
Windows Socket I/O Multiplexing http://icourse.cuc.edu.cn/networkprogramming/ linwei@cuc.edu.cn Dec 2009 Note You should not assume that an example in this presentation is complete. Items may have been
