Laboratory 5 Processor Datapath
|
|
|
- Garey Hall
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Laboratory 5 Processor Datapath Description of HW Instruction Set Architecture 16 bit data bus 8 bit address bus Starting address of every program = 0 (PC initialized to 0 by a reset to begin execution) PC incremented by 2 to move to the next instruction. 16 registers R0 = 0 (constant) R1 =1 (constant) R2-R15 general purpose
2 Instruction Set Instruction Meaning Op Rs Rt Rd 4-bit 4-bit 4-bit 4-bit LW Rs,Rt,offset Rt loaded with word from Data Memory at address(rs + offset) offset SW Rs,Rt,offset Data Memory address(rs + offset) stored with word from Rt offset ADD Rs,Rt,Rd Rd := Rs + Rt SUB Rs,Rt,Rd Rd := Rs - Rt AND Rs,Rt,Rd Rd := Rs AND Rt OR Rs,Rt,Rd Rd := Rs OR Rt BEQ Rs,Rt,offset If Rs=Rt then pc:=pc+2+(offset*2) else pc:=pc offset JMP offset Jump to abs. addr = offset* bit offset-----
3 Instruction Fetch
4 Branch Address Either PC + 2 or PC (2*offset) is the next value of the PC. On a BEQ instruction, BEQ Rs,Rt,offset The offset = number of instructions away from the next value of the PC to branch to, so must be multiplied by 2. Since offset is 4 bits, it must be sign-extended to 8 bits to be added to the PC. A 2x8 multiplexer circuit to selects the next value of the PC. The value of the Branch and Zero bits are used to determine which is used: The Branch control line = 1 if a BEQ instruction is being executed. The Zero bit from the ALU is used to check whether Rs = Rt: it is 1 if Rs Rt = 0 (meaning they re equal). If Branch = 1 and Zero = 1, then the next value of the PC will be the branch address ; otherwise, it will simply be PC + 2:
5 Register File and ALU R-type instructions ADD,SUB,AND,OR,SLT (opcode Rs Rt Rd) read Rs and Rt from register file perform an ALU operation on the contents of the registers write the result to register Rd in register file Memory Access instructions LW,SW (opcode Rs Rt offset) memory address = Rs + sign-extended 4-bit offset if SW, the value to be stored to memory is from Rt. if LW, Rt is loaded with the value read from memory Register written to (Write Register) is Rd or Rt if a LW instruction (chosen by a 2x4 MUX which is controlled by RegDst ) ALU calculates Rs + Rt, or Rs + sign-extended offset. - Input A of the ALU is always Rs - Input B of the ALU is Rt or the offset (chosen by a 2x16 multiplexer, which is controlled by ALUSrc):
6 Data Memory We need an additional memory for values loaded or stored (LW or SW) during execution of the program (the instruction memory is only used to store program instructions). RegDst (chooses whether Rd or Rt goes to the Write data input on the Regfile) If 0, destination is Rd. If 1, destination is Rt. RegWr (control line to RegFile) If 1, writes the value on the Write data input to the register specified by Write register ALUSrc (chooses the source of the second ALU operand) If 0, the operand is the second register file output. If 1, the operand is the sign-extended, lowest 4 bits of the instruction. MemRd (control signal to data memory) If 0, value stored at address in data memory is read from Read data. MemWr (control signal to data memory) If 0, data memory address written with value from Rt on the Write data input. MemtoReg (chooses the value to be written back to the Regfile) If 0, the value comes from the ALU (R-type instruction) If 1, the value comes from data memory (LW ALUop(4 bits) ALU function 0 a AND b 1 a OR b 2 a + b (add) 6 a - b 7 set on less than
7 ALU can perform 5 possible operations: ALUop ALU function 0 a AND b 1 a OR b 2 a + b (add) 6 a - b 7 set on less than
8 Need an ALU Control Unit to select the proper operation for each instruction: Instruction Opcode ALU operation ALUop LW 0 add 2 SW 1 add 2 ADD 2 add 2 SUB 3 sub 6 AND 4 and 0 OR 5 or 1 SLT 6 slt 7 BEQ 7 sub 6 JMP 8 don t care don t care Op3 Op2 Op1 Op0 ALUop3 ALUop2 ALUop1 ALUop Can use a 3x8 decoder to produce the ALUop
9 Control Unit Must provide control signals for all other devices in datapath (MUXs, Regfile, Data Memory) Instruction Opcode RegDst RegWr ALUSrc MemRd MemWr MemtoReg LW SW ADD SUB AND OR SLT BEQ JMP
10 Full Implementation Procedure to Load/Execute a New Program 1. Disconnect the address bus of the Instruction Memory from the CPU 2. Set LOAD = 0 3. Set address and data switches for instruction 4. Set WR = 0, then back to 1 5. Repeat steps 3 and 4 until all instructions are loaded to memory 6. Set LOAD = 1 7. Reconnect address bus to CPU 8. Set Reset = 1, then back to 0 9. Set CLK = 1, then back to 0, for each instruction.
Processor (I) - datapath & control. Hwansoo Han
 Processor (I) - datapath & control Hwansoo Han Introduction CPU performance factors Instruction count - Determined by ISA and compiler CPI and Cycle time - Determined by CPU hardware We will examine two
Processor (I) - datapath & control Hwansoo Han Introduction CPU performance factors Instruction count - Determined by ISA and compiler CPI and Cycle time - Determined by CPU hardware We will examine two
COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND DESIGN. The Hardware/Software Interface. Chapter 4. The Processor: A Based on P&H
 COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND DESIGN The Hardware/Software Interface Chapter 4 The Processor: A Based on P&H Introduction We will examine two MIPS implementations A simplified version A more realistic pipelined
COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND DESIGN The Hardware/Software Interface Chapter 4 The Processor: A Based on P&H Introduction We will examine two MIPS implementations A simplified version A more realistic pipelined
Chapter 4. The Processor. Computer Architecture and IC Design Lab
 Chapter 4 The Processor Introduction CPU performance factors CPI Clock Cycle Time Instruction count Determined by ISA and compiler CPI and Cycle time Determined by CPU hardware We will examine two MIPS
Chapter 4 The Processor Introduction CPU performance factors CPI Clock Cycle Time Instruction count Determined by ISA and compiler CPI and Cycle time Determined by CPU hardware We will examine two MIPS
COMP303 - Computer Architecture Lecture 8. Designing a Single Cycle Datapath
 COMP33 - Computer Architecture Lecture 8 Designing a Single Cycle Datapath The Big Picture The Five Classic Components of a Computer Processor Input Control Memory Datapath Output The Big Picture: The
COMP33 - Computer Architecture Lecture 8 Designing a Single Cycle Datapath The Big Picture The Five Classic Components of a Computer Processor Input Control Memory Datapath Output The Big Picture: The
The MIPS Processor Datapath
 The MIPS Processor Datapath Module Outline MIPS datapath implementation Register File, Instruction memory, Data memory Instruction interpretation and execution. Combinational control Assignment: Datapath
The MIPS Processor Datapath Module Outline MIPS datapath implementation Register File, Instruction memory, Data memory Instruction interpretation and execution. Combinational control Assignment: Datapath
CENG 3420 Lecture 06: Datapath
 CENG 342 Lecture 6: Datapath Bei Yu byu@cse.cuhk.edu.hk CENG342 L6. Spring 27 The Processor: Datapath & Control q We're ready to look at an implementation of the MIPS q Simplified to contain only: memory-reference
CENG 342 Lecture 6: Datapath Bei Yu byu@cse.cuhk.edu.hk CENG342 L6. Spring 27 The Processor: Datapath & Control q We're ready to look at an implementation of the MIPS q Simplified to contain only: memory-reference
ECE232: Hardware Organization and Design
 ECE232: Hardware Organization and Design Lecture 14: One Cycle MIPs Datapath Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, UCB R-Format Instructions Read two register operands Perform
ECE232: Hardware Organization and Design Lecture 14: One Cycle MIPs Datapath Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, UCB R-Format Instructions Read two register operands Perform
The Processor: Datapath & Control
 Orange Coast College Business Division Computer Science Department CS 116- Computer Architecture The Processor: Datapath & Control Processor Design Step 3 Assemble Datapath Meeting Requirements Build the
Orange Coast College Business Division Computer Science Department CS 116- Computer Architecture The Processor: Datapath & Control Processor Design Step 3 Assemble Datapath Meeting Requirements Build the
The Processor: Datapath and Control. Jin-Soo Kim Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University
 The Processor: Datapath and Control Jin-Soo Kim (jinsookim@skku.edu) Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University http://csl.skku.edu Introduction CPU performance factors Instruction count Determined
The Processor: Datapath and Control Jin-Soo Kim (jinsookim@skku.edu) Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University http://csl.skku.edu Introduction CPU performance factors Instruction count Determined
CENG 3420 Computer Organization and Design. Lecture 06: MIPS Processor - I. Bei Yu
 CENG 342 Computer Organization and Design Lecture 6: MIPS Processor - I Bei Yu CEG342 L6. Spring 26 The Processor: Datapath & Control q We're ready to look at an implementation of the MIPS q Simplified
CENG 342 Computer Organization and Design Lecture 6: MIPS Processor - I Bei Yu CEG342 L6. Spring 26 The Processor: Datapath & Control q We're ready to look at an implementation of the MIPS q Simplified
Chapter 4. The Processor
 Chapter 4 The Processor Introduction CPU performance factors Instruction count Determined by ISA and compiler CPI and Cycle time Determined by CPU hardware We will examine two MIPS implementations A simplified
Chapter 4 The Processor Introduction CPU performance factors Instruction count Determined by ISA and compiler CPI and Cycle time Determined by CPU hardware We will examine two MIPS implementations A simplified
Single Cycle CPU Design. Mehran Rezaei
 Single Cycle CPU Design Mehran Rezaei What does it mean? Instruction Fetch Instruction Memory clk pc 32 32 address add $t,$t,$t2 instruction Next Logic to generate the address of next instruction The Branch
Single Cycle CPU Design Mehran Rezaei What does it mean? Instruction Fetch Instruction Memory clk pc 32 32 address add $t,$t,$t2 instruction Next Logic to generate the address of next instruction The Branch
Review: Abstract Implementation View
 Review: Abstract Implementation View Split memory (Harvard) model - single cycle operation Simplified to contain only the instructions: memory-reference instructions: lw, sw arithmetic-logical instructions:
Review: Abstract Implementation View Split memory (Harvard) model - single cycle operation Simplified to contain only the instructions: memory-reference instructions: lw, sw arithmetic-logical instructions:
CS3350B Computer Architecture Quiz 3 March 15, 2018
 CS3350B Computer Architecture Quiz 3 March 15, 2018 Student ID number: Student Last Name: Question 1.1 1.2 1.3 2.1 2.2 2.3 Total Marks The quiz consists of two exercises. The expected duration is 30 minutes.
CS3350B Computer Architecture Quiz 3 March 15, 2018 Student ID number: Student Last Name: Question 1.1 1.2 1.3 2.1 2.2 2.3 Total Marks The quiz consists of two exercises. The expected duration is 30 minutes.
ELEC 5200/6200 Computer Architecture and Design Spring 2017 Lecture 4: Datapath and Control
 ELEC 52/62 Computer Architecture and Design Spring 217 Lecture 4: Datapath and Control Ujjwal Guin, Assistant Professor Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Auburn University, Auburn, AL 36849
ELEC 52/62 Computer Architecture and Design Spring 217 Lecture 4: Datapath and Control Ujjwal Guin, Assistant Professor Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Auburn University, Auburn, AL 36849
Chapter 4. The Processor
 Chapter 4 The Processor Introduction CPU performance factors Instruction count Determined by ISA and compiler CPI and Cycle time Determined by CPU hardware 4.1 Introduction We will examine two MIPS implementations
Chapter 4 The Processor Introduction CPU performance factors Instruction count Determined by ISA and compiler CPI and Cycle time Determined by CPU hardware 4.1 Introduction We will examine two MIPS implementations
LECTURE 5. Single-Cycle Datapath and Control
 LECTURE 5 Single-Cycle Datapath and Control PROCESSORS In lecture 1, we reminded ourselves that the datapath and control are the two components that come together to be collectively known as the processor.
LECTURE 5 Single-Cycle Datapath and Control PROCESSORS In lecture 1, we reminded ourselves that the datapath and control are the two components that come together to be collectively known as the processor.
The Processor (1) Jinkyu Jeong Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University
 The Processor (1) Jinkyu Jeong (jinkyu@skku.edu) Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University http://csl.skku.edu EEE3050: Theory on Computer Architectures, Spring 2017, Jinkyu Jeong (jinkyu@skku.edu)
The Processor (1) Jinkyu Jeong (jinkyu@skku.edu) Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University http://csl.skku.edu EEE3050: Theory on Computer Architectures, Spring 2017, Jinkyu Jeong (jinkyu@skku.edu)
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 10- CPU Microarchitecture. Processor Microarchitecture Introduction
 EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 10- CPU Microarchitecture Feb 18, 2010 John Wawrzynek Spring 2010 EECS150 - Lec10-cpu Page 1 Processor Microarchitecture Introduction Microarchitecture: how to implement
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 10- CPU Microarchitecture Feb 18, 2010 John Wawrzynek Spring 2010 EECS150 - Lec10-cpu Page 1 Processor Microarchitecture Introduction Microarchitecture: how to implement
Systems Architecture
 Systems Architecture Lecture 15: A Simple Implementation of MIPS Jeremy R. Johnson Anatole D. Ruslanov William M. Mongan Some or all figures from Computer Organization and Design: The Hardware/Software
Systems Architecture Lecture 15: A Simple Implementation of MIPS Jeremy R. Johnson Anatole D. Ruslanov William M. Mongan Some or all figures from Computer Organization and Design: The Hardware/Software
CpE242 Computer Architecture and Engineering Designing a Single Cycle Datapath
 CpE242 Computer Architecture and Engineering Designing a Single Cycle Datapath CPE 442 single-cycle datapath.1 Outline of Today s Lecture Recap and Introduction Where are we with respect to the BIG picture?
CpE242 Computer Architecture and Engineering Designing a Single Cycle Datapath CPE 442 single-cycle datapath.1 Outline of Today s Lecture Recap and Introduction Where are we with respect to the BIG picture?
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture. MIPS CPU Datapath, Control Introduction
 CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture MIPS CPU Datapath, Control Introduction Instructor: Alan Christopher 7/28/214 Summer 214 -- Lecture #2 1 Review of Last Lecture Critical path constrains clock
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture MIPS CPU Datapath, Control Introduction Instructor: Alan Christopher 7/28/214 Summer 214 -- Lecture #2 1 Review of Last Lecture Critical path constrains clock
CS/COE0447: Computer Organization
 CS/COE0447: Computer Organization and Assembly Language Datapath and Control Sangyeun Cho Dept. of Computer Science A simple MIPS We will design a simple MIPS processor that supports a small instruction
CS/COE0447: Computer Organization and Assembly Language Datapath and Control Sangyeun Cho Dept. of Computer Science A simple MIPS We will design a simple MIPS processor that supports a small instruction
CS/COE0447: Computer Organization
 A simple MIPS CS/COE447: Computer Organization and Assembly Language Datapath and Control Sangyeun Cho Dept. of Computer Science We will design a simple MIPS processor that supports a small instruction
A simple MIPS CS/COE447: Computer Organization and Assembly Language Datapath and Control Sangyeun Cho Dept. of Computer Science We will design a simple MIPS processor that supports a small instruction
Mark Redekopp and Gandhi Puvvada, All rights reserved. EE 357 Unit 15. Single-Cycle CPU Datapath and Control
 EE 37 Unit Single-Cycle CPU path and Control CPU Organization Scope We will build a CPU to implement our subset of the MIPS ISA Memory Reference Instructions: Load Word (LW) Store Word (SW) Arithmetic
EE 37 Unit Single-Cycle CPU path and Control CPU Organization Scope We will build a CPU to implement our subset of the MIPS ISA Memory Reference Instructions: Load Word (LW) Store Word (SW) Arithmetic
The Processor. Z. Jerry Shi Department of Computer Science and Engineering University of Connecticut. CSE3666: Introduction to Computer Architecture
 The Processor Z. Jerry Shi Department of Computer Science and Engineering University of Connecticut CSE3666: Introduction to Computer Architecture Introduction CPU performance factors Instruction count
The Processor Z. Jerry Shi Department of Computer Science and Engineering University of Connecticut CSE3666: Introduction to Computer Architecture Introduction CPU performance factors Instruction count
Inf2C - Computer Systems Lecture Processor Design Single Cycle
 Inf2C - Computer Systems Lecture 10-11 Processor Design Single Cycle Boris Grot School of Informatics University of Edinburgh Previous lectures Combinational circuits Combinations of gates (INV, AND, OR,
Inf2C - Computer Systems Lecture 10-11 Processor Design Single Cycle Boris Grot School of Informatics University of Edinburgh Previous lectures Combinational circuits Combinations of gates (INV, AND, OR,
CS3350B Computer Architecture Winter Lecture 5.7: Single-Cycle CPU: Datapath Control (Part 2)
 CS335B Computer Architecture Winter 25 Lecture 5.7: Single-Cycle CPU: Datapath Control (Part 2) Marc Moreno Maza www.csd.uwo.ca/courses/cs335b [Adapted from lectures on Computer Organization and Design,
CS335B Computer Architecture Winter 25 Lecture 5.7: Single-Cycle CPU: Datapath Control (Part 2) Marc Moreno Maza www.csd.uwo.ca/courses/cs335b [Adapted from lectures on Computer Organization and Design,
COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND DESIGN. 5 th Edition. The Hardware/Software Interface. Chapter 4. The Processor
 COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND DESIGN The Hardware/Software Interface 5 th Edition Chapter 4 The Processor Introduction CPU performance factors Instruction count Determined by ISA and compiler CPI and Cycle
COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND DESIGN The Hardware/Software Interface 5 th Edition Chapter 4 The Processor Introduction CPU performance factors Instruction count Determined by ISA and compiler CPI and Cycle
Chapter 4. The Processor Designing the datapath
 Chapter 4 The Processor Designing the datapath Introduction CPU performance determined by Instruction Count Clock Cycles per Instruction (CPI) and Cycle time Determined by Instruction Set Architecure (ISA)
Chapter 4 The Processor Designing the datapath Introduction CPU performance determined by Instruction Count Clock Cycles per Instruction (CPI) and Cycle time Determined by Instruction Set Architecure (ISA)
COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND DESIGN. 5 th Edition. The Hardware/Software Interface. Chapter 4. The Processor
 COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND DESIGN The Hardware/Software Interface 5 th Edition Chapter 4 The Processor COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND DESIGN The Hardware/Software Interface 5 th Edition The Processor - Introduction
COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND DESIGN The Hardware/Software Interface 5 th Edition Chapter 4 The Processor COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND DESIGN The Hardware/Software Interface 5 th Edition The Processor - Introduction
Design of the MIPS Processor
 Design of the MIPS Processor We will study the design of a simple version of MIPS that can support the following instructions: I-type instructions LW, SW R-type instructions, like ADD, SUB Conditional
Design of the MIPS Processor We will study the design of a simple version of MIPS that can support the following instructions: I-type instructions LW, SW R-type instructions, like ADD, SUB Conditional
Chapter 4. Instruction Execution. Introduction. CPU Overview. Multiplexers. Chapter 4 The Processor 1. The Processor.
 COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND DESIGN The Hardware/Software Interface 5 th Edition COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND DESIGN The Hardware/Software Interface 5 th Edition Chapter 4 The Processor The Processor - Introduction
COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND DESIGN The Hardware/Software Interface 5 th Edition COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND DESIGN The Hardware/Software Interface 5 th Edition Chapter 4 The Processor The Processor - Introduction
CPE 335 Computer Organization. Basic MIPS Architecture Part I
 CPE 335 Computer Organization Basic MIPS Architecture Part I Dr. Iyad Jafar Adapted from Dr. Gheith Abandah slides http://www.abandah.com/gheith/courses/cpe335_s8/index.html CPE232 Basic MIPS Architecture
CPE 335 Computer Organization Basic MIPS Architecture Part I Dr. Iyad Jafar Adapted from Dr. Gheith Abandah slides http://www.abandah.com/gheith/courses/cpe335_s8/index.html CPE232 Basic MIPS Architecture
CPE 335. Basic MIPS Architecture Part II
 CPE 335 Computer Organization Basic MIPS Architecture Part II Dr. Iyad Jafar Adapted from Dr. Gheith Abandah slides http://www.abandah.com/gheith/courses/cpe335_s08/index.html CPE232 Basic MIPS Architecture
CPE 335 Computer Organization Basic MIPS Architecture Part II Dr. Iyad Jafar Adapted from Dr. Gheith Abandah slides http://www.abandah.com/gheith/courses/cpe335_s08/index.html CPE232 Basic MIPS Architecture
COMP303 Computer Architecture Lecture 9. Single Cycle Control
 COMP33 Computer Architecture Lecture 9 Single Cycle Control A Single Cycle Datapath We have everything except control signals (underlined) RegDst busw Today s lecture will look at how to generate the control
COMP33 Computer Architecture Lecture 9 Single Cycle Control A Single Cycle Datapath We have everything except control signals (underlined) RegDst busw Today s lecture will look at how to generate the control
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture Datapath. Instructors: John Wawrzynek & Vladimir Stojanovic
 CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture Datapath Instructors: John Wawrzynek & Vladimir Stojanovic http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c/fa15 1 Components of a Computer Processor Control Enable? Read/Write
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture Datapath Instructors: John Wawrzynek & Vladimir Stojanovic http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c/fa15 1 Components of a Computer Processor Control Enable? Read/Write
Lecture Topics. Announcements. Today: Single-Cycle Processors (P&H ) Next: continued. Milestone #3 (due 2/9) Milestone #4 (due 2/23)
 Lecture Topics Today: Single-Cycle Processors (P&H 4.1-4.4) Next: continued 1 Announcements Milestone #3 (due 2/9) Milestone #4 (due 2/23) Exam #1 (Wednesday, 2/15) 2 1 Exam #1 Wednesday, 2/15 (3:00-4:20
Lecture Topics Today: Single-Cycle Processors (P&H 4.1-4.4) Next: continued 1 Announcements Milestone #3 (due 2/9) Milestone #4 (due 2/23) Exam #1 (Wednesday, 2/15) 2 1 Exam #1 Wednesday, 2/15 (3:00-4:20
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 9- CPU Microarchitecture. Watson: Jeopardy-playing Computer
 EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 9- CPU Microarchitecture Feb 15, 2011 John Wawrzynek Spring 2011 EECS150 - Lec09-cpu Page 1 Watson: Jeopardy-playing Computer Watson is made up of a cluster of ninety IBM
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 9- CPU Microarchitecture Feb 15, 2011 John Wawrzynek Spring 2011 EECS150 - Lec09-cpu Page 1 Watson: Jeopardy-playing Computer Watson is made up of a cluster of ninety IBM
The overall datapath for RT, lw,sw beq instrucution
 Designing The Main Control Unit: Remember the three instruction classes {R-type, Memory, Branch}: a) R-type : Op rs rt rd shamt funct 1.src 2.src dest. 31-26 25-21 20-16 15-11 10-6 5-0 a) Memory : Op rs
Designing The Main Control Unit: Remember the three instruction classes {R-type, Memory, Branch}: a) R-type : Op rs rt rd shamt funct 1.src 2.src dest. 31-26 25-21 20-16 15-11 10-6 5-0 a) Memory : Op rs
361 datapath.1. Computer Architecture EECS 361 Lecture 8: Designing a Single Cycle Datapath
 361 datapath.1 Computer Architecture EECS 361 Lecture 8: Designing a Single Cycle Datapath Outline of Today s Lecture Introduction Where are we with respect to the BIG picture? Questions and Administrative
361 datapath.1 Computer Architecture EECS 361 Lecture 8: Designing a Single Cycle Datapath Outline of Today s Lecture Introduction Where are we with respect to the BIG picture? Questions and Administrative
Pipeline design. Mehran Rezaei
 Pipeline design Mehran Rezaei How Can We Improve the Performance? Exec Time = IC * CPI * CCT Optimization IC CPI CCT Source Level * Compiler * * ISA * * Organization * * Technology * With Pipelining We
Pipeline design Mehran Rezaei How Can We Improve the Performance? Exec Time = IC * CPI * CCT Optimization IC CPI CCT Source Level * Compiler * * ISA * * Organization * * Technology * With Pipelining We
CS61C : Machine Structures
 inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c CS61C : Machine Structures Lecture #19 Designing a Single-Cycle CPU 27-7-26 Scott Beamer Instructor AI Focuses on Poker CS61C L19 CPU Design : Designing a Single-Cycle CPU
inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c CS61C : Machine Structures Lecture #19 Designing a Single-Cycle CPU 27-7-26 Scott Beamer Instructor AI Focuses on Poker CS61C L19 CPU Design : Designing a Single-Cycle CPU
Processor: Multi- Cycle Datapath & Control
 Processor: Multi- Cycle Datapath & Control (Based on text: David A. Patterson & John L. Hennessy, Computer Organization and Design: The Hardware/Software Interface, 3 rd Ed., Morgan Kaufmann, 27) COURSE
Processor: Multi- Cycle Datapath & Control (Based on text: David A. Patterson & John L. Hennessy, Computer Organization and Design: The Hardware/Software Interface, 3 rd Ed., Morgan Kaufmann, 27) COURSE
Chapter 4. The Processor. Instruction count Determined by ISA and compiler. We will examine two MIPS implementations
 Chapter 4 The Processor Part I Introduction CPU performance factors Instruction count Determined by ISA and compiler CPI and Cycle time Determined by CPU hardware We will examine two MIPS implementations
Chapter 4 The Processor Part I Introduction CPU performance factors Instruction count Determined by ISA and compiler CPI and Cycle time Determined by CPU hardware We will examine two MIPS implementations
CSE 378 Midterm 2/12/10 Sample Solution
 Question 1. (6 points) (a) Rewrite the instruction sub $v0,$t8,$a2 using absolute register numbers instead of symbolic names (i.e., if the instruction contained $at, you would rewrite that as $1.) sub
Question 1. (6 points) (a) Rewrite the instruction sub $v0,$t8,$a2 using absolute register numbers instead of symbolic names (i.e., if the instruction contained $at, you would rewrite that as $1.) sub
CSEN 601: Computer System Architecture Summer 2014
 CSEN 601: Computer System Architecture Summer 2014 Practice Assignment 5 Solutions Exercise 5-1: (Midterm Spring 2013) a. What are the values of the control signals (except ALUOp) for each of the following
CSEN 601: Computer System Architecture Summer 2014 Practice Assignment 5 Solutions Exercise 5-1: (Midterm Spring 2013) a. What are the values of the control signals (except ALUOp) for each of the following
ECE260: Fundamentals of Computer Engineering
 Datapath for a Simplified Processor James Moscola Dept. of Engineering & Computer Science York College of Pennsylvania Based on Computer Organization and Design, 5th Edition by Patterson & Hennessy Introduction
Datapath for a Simplified Processor James Moscola Dept. of Engineering & Computer Science York College of Pennsylvania Based on Computer Organization and Design, 5th Edition by Patterson & Hennessy Introduction
CPU Design Steps. EECC550 - Shaaban
 CPU Design Steps 1. Analyze instruction set operations using independent RTN => datapath requirements. 2. Select set of datapath components & establish clock methodology. 3. Assemble datapath meeting the
CPU Design Steps 1. Analyze instruction set operations using independent RTN => datapath requirements. 2. Select set of datapath components & establish clock methodology. 3. Assemble datapath meeting the
The Big Picture: Where are We Now? EEM 486: Computer Architecture. Lecture 3. Designing a Single Cycle Datapath
 The Big Picture: Where are We Now? EEM 486: Computer Architecture Lecture 3 The Five Classic Components of a Computer Processor Input Control Memory Designing a Single Cycle path path Output Today s Topic:
The Big Picture: Where are We Now? EEM 486: Computer Architecture Lecture 3 The Five Classic Components of a Computer Processor Input Control Memory Designing a Single Cycle path path Output Today s Topic:
Introduction. Datapath Basics
 Introduction CPU performance factors - Instruction count; determined by ISA and compiler - CPI and Cycle time; determined by CPU hardware 1 We will examine a simplified MIPS implementation in this course
Introduction CPU performance factors - Instruction count; determined by ISA and compiler - CPI and Cycle time; determined by CPU hardware 1 We will examine a simplified MIPS implementation in this course
MIPS-Lite Single-Cycle Control
 MIPS-Lite Single-Cycle Control COE68: Computer Organization and Architecture Dr. Gul N. Khan http://www.ee.ryerson.ca/~gnkhan Electrical and Computer Engineering Ryerson University Overview Single cycle
MIPS-Lite Single-Cycle Control COE68: Computer Organization and Architecture Dr. Gul N. Khan http://www.ee.ryerson.ca/~gnkhan Electrical and Computer Engineering Ryerson University Overview Single cycle
CS 110 Computer Architecture Single-Cycle CPU Datapath & Control
 CS Computer Architecture Single-Cycle CPU Datapath & Control Instructor: Sören Schwertfeger http://shtech.org/courses/ca/ School of Information Science and Technology SIST ShanghaiTech University Slides
CS Computer Architecture Single-Cycle CPU Datapath & Control Instructor: Sören Schwertfeger http://shtech.org/courses/ca/ School of Information Science and Technology SIST ShanghaiTech University Slides
Design of Digital Circuits 2017 Srdjan Capkun Onur Mutlu (Guest starring: Frank K. Gürkaynak and Aanjhan Ranganathan)
 Microarchitecture Design of Digital Circuits 27 Srdjan Capkun Onur Mutlu (Guest starring: Frank K. Gürkaynak and Aanjhan Ranganathan) http://www.syssec.ethz.ch/education/digitaltechnik_7 Adapted from Digital
Microarchitecture Design of Digital Circuits 27 Srdjan Capkun Onur Mutlu (Guest starring: Frank K. Gürkaynak and Aanjhan Ranganathan) http://www.syssec.ethz.ch/education/digitaltechnik_7 Adapted from Digital
Adding Support for jal to Single Cycle Datapath (For More Practice Exercise 5.20)
 Adding Support for jal to Single Cycle Datapath (For More Practice Exercise 5.20) The MIPS jump and link instruction, jal is used to support procedure calls by jumping to jump address (similar to j ) and
Adding Support for jal to Single Cycle Datapath (For More Practice Exercise 5.20) The MIPS jump and link instruction, jal is used to support procedure calls by jumping to jump address (similar to j ) and
Full Datapath. CSCI 402: Computer Architectures. The Processor (2) 3/21/19. Fengguang Song Department of Computer & Information Science IUPUI
 CSCI 42: Computer Architectures The Processor (2) Fengguang Song Department of Computer & Information Science IUPUI Full Datapath Branch Target Instruction Fetch Immediate 4 Today s Contents We have looked
CSCI 42: Computer Architectures The Processor (2) Fengguang Song Department of Computer & Information Science IUPUI Full Datapath Branch Target Instruction Fetch Immediate 4 Today s Contents We have looked
CC 311- Computer Architecture. The Processor - Control
 CC 311- Computer Architecture The Processor - Control Control Unit Functions: Instruction code Control Unit Control Signals Select operations to be performed (ALU, read/write, etc.) Control data flow (multiplexor
CC 311- Computer Architecture The Processor - Control Control Unit Functions: Instruction code Control Unit Control Signals Select operations to be performed (ALU, read/write, etc.) Control data flow (multiplexor
Designing a Multicycle Processor
 Designing a Multicycle Processor Arquitectura de Computadoras Arturo Díaz D PérezP Centro de Investigación n y de Estudios Avanzados del IPN adiaz@cinvestav.mx Arquitectura de Computadoras Multicycle-
Designing a Multicycle Processor Arquitectura de Computadoras Arturo Díaz D PérezP Centro de Investigación n y de Estudios Avanzados del IPN adiaz@cinvestav.mx Arquitectura de Computadoras Multicycle-
Outline. EEL-4713 Computer Architecture Designing a Single Cycle Datapath
 Outline EEL-473 Computer Architecture Designing a Single Cycle path Introduction The steps of designing a processor path and timing for register-register operations path for logical operations with immediates
Outline EEL-473 Computer Architecture Designing a Single Cycle path Introduction The steps of designing a processor path and timing for register-register operations path for logical operations with immediates
Guerrilla Session 3: MIPS CPU
 CS61C Summer 2015 Guerrilla Session 3: MIPS CPU Problem 1: swai (Sp04 Final): We want to implement a new I- type instruction swai (store word then auto- increment). The operation performs the regular sw
CS61C Summer 2015 Guerrilla Session 3: MIPS CPU Problem 1: swai (Sp04 Final): We want to implement a new I- type instruction swai (store word then auto- increment). The operation performs the regular sw
CPU Organization (Design)
 ISA Requirements CPU Organization (Design) Datapath Design: Capabilities & performance characteristics of principal Functional Units (FUs) needed by ISA instructions (e.g., Registers, ALU, Shifters, Logic
ISA Requirements CPU Organization (Design) Datapath Design: Capabilities & performance characteristics of principal Functional Units (FUs) needed by ISA instructions (e.g., Registers, ALU, Shifters, Logic
CO Computer Architecture and Programming Languages CAPL. Lecture 18 & 19
 CO2-3224 Computer Architecture and Programming Languages CAPL Lecture 8 & 9 Dr. Kinga Lipskoch Fall 27 Single Cycle Disadvantages & Advantages Uses the clock cycle inefficiently the clock cycle must be
CO2-3224 Computer Architecture and Programming Languages CAPL Lecture 8 & 9 Dr. Kinga Lipskoch Fall 27 Single Cycle Disadvantages & Advantages Uses the clock cycle inefficiently the clock cycle must be
361 control.1. EECS 361 Computer Architecture Lecture 9: Designing Single Cycle Control
 36 control. EECS 36 Computer Architecture Lecture 9: Designing Single Cycle Control Recap: The MIPS Subset ADD and subtract add rd, rs, rt sub rd, rs, rt OR Imm: ori rt, rs, imm6 3 3 26 2 6 op rs rt rd
36 control. EECS 36 Computer Architecture Lecture 9: Designing Single Cycle Control Recap: The MIPS Subset ADD and subtract add rd, rs, rt sub rd, rs, rt OR Imm: ori rt, rs, imm6 3 3 26 2 6 op rs rt rd
Single Cycle Datapath
 Single Cycle atapath Lecture notes from MKP, H. H. Lee and S. Yalamanchili Section 4.1-4.4 Appendices B.3, B.7, B.8, B.11,.2 ing Note: Appendices A-E in the hardcopy text correspond to chapters 7-11 in
Single Cycle atapath Lecture notes from MKP, H. H. Lee and S. Yalamanchili Section 4.1-4.4 Appendices B.3, B.7, B.8, B.11,.2 ing Note: Appendices A-E in the hardcopy text correspond to chapters 7-11 in
Lecture 12: Single-Cycle Control Unit. Spring 2018 Jason Tang
 Lecture 12: Single-Cycle Control Unit Spring 2018 Jason Tang 1 Topics Control unit design Single cycle processor Control unit circuit implementation 2 Computer Organization Computer Processor Memory Devices
Lecture 12: Single-Cycle Control Unit Spring 2018 Jason Tang 1 Topics Control unit design Single cycle processor Control unit circuit implementation 2 Computer Organization Computer Processor Memory Devices
CSE 2021 COMPUTER ORGANIZATION
 CSE 22 COMPUTER ORGANIZATION HUGH CHESSER CHESSER HUGH CSEB 2U 2U CSEB Agenda Topics:. Sample Exam/Quiz Q - Review 2. Multiple cycle implementation Patterson: Section 4.5 Reminder: Quiz #2 Next Wednesday
CSE 22 COMPUTER ORGANIZATION HUGH CHESSER CHESSER HUGH CSEB 2U 2U CSEB Agenda Topics:. Sample Exam/Quiz Q - Review 2. Multiple cycle implementation Patterson: Section 4.5 Reminder: Quiz #2 Next Wednesday
ECE468 Computer Organization and Architecture. Designing a Single Cycle Datapath
 ECE468 Computer Organization and Architecture Designing a Single Cycle Datapath ECE468 datapath1 The Big Picture: Where are We Now? The Five Classic Components of a Computer Processor Control Input Datapath
ECE468 Computer Organization and Architecture Designing a Single Cycle Datapath ECE468 datapath1 The Big Picture: Where are We Now? The Five Classic Components of a Computer Processor Control Input Datapath
ECE170 Computer Architecture. Single Cycle Control. Review: 3b: Add & Subtract. Review: 3e: Store Operations. Review: 3d: Load Operations
 ECE7 Computer Architecture Single Cycle Control Review: 3a: Overview of the Fetch Unit The common operations Fetch the : mem[] Update the program counter: Sequential Code: < + Branch and Jump: < something
ECE7 Computer Architecture Single Cycle Control Review: 3a: Overview of the Fetch Unit The common operations Fetch the : mem[] Update the program counter: Sequential Code: < + Branch and Jump: < something
Fundamentals of Computer Systems
 Fundamentals of Computer Systems Single Cycle MIPS Processor Stephen. Edwards Columbia University Summer 26 Illustrations Copyright 27 Elsevier The path The lw The sw R-Type s The beq The Controller Encoding
Fundamentals of Computer Systems Single Cycle MIPS Processor Stephen. Edwards Columbia University Summer 26 Illustrations Copyright 27 Elsevier The path The lw The sw R-Type s The beq The Controller Encoding
CS Computer Architecture Spring Week 10: Chapter
 CS 35101 Computer Architecture Spring 2008 Week 10: Chapter 5.1-5.3 Materials adapated from Mary Jane Irwin (www.cse.psu.edu/~mji) and Kevin Schaffer [adapted from D. Patterson slides] CS 35101 Ch 5.1
CS 35101 Computer Architecture Spring 2008 Week 10: Chapter 5.1-5.3 Materials adapated from Mary Jane Irwin (www.cse.psu.edu/~mji) and Kevin Schaffer [adapted from D. Patterson slides] CS 35101 Ch 5.1
RISC Processor Design
 RISC Processor Design Single Cycle Implementation - MIPS Virendra Singh Indian Institute of Science Bangalore virendra@computer.org Lecture 13 SE-273: Processor Design Feb 07, 2011 SE-273@SERC 1 Courtesy:
RISC Processor Design Single Cycle Implementation - MIPS Virendra Singh Indian Institute of Science Bangalore virendra@computer.org Lecture 13 SE-273: Processor Design Feb 07, 2011 SE-273@SERC 1 Courtesy:
CSCI 402: Computer Architectures. Fengguang Song Department of Computer & Information Science IUPUI. Today s Content
 3/6/8 CSCI 42: Computer Architectures The Processor (2) Fengguang Song Department of Computer & Information Science IUPUI Today s Content We have looked at how to design a Data Path. 4.4, 4.5 We will design
3/6/8 CSCI 42: Computer Architectures The Processor (2) Fengguang Song Department of Computer & Information Science IUPUI Today s Content We have looked at how to design a Data Path. 4.4, 4.5 We will design
CS222: Processor Design
 CS222: Processor Design Dr. A. Sahu Dept of Comp. Sc. & Engg. Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati Processor Design building blocks Outline A simple implementation: Single Cycle Data pathandcontrol
CS222: Processor Design Dr. A. Sahu Dept of Comp. Sc. & Engg. Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati Processor Design building blocks Outline A simple implementation: Single Cycle Data pathandcontrol
Working on the Pipeline
 Computer Science 6C Spring 27 Working on the Pipeline Datapath Control Signals Computer Science 6C Spring 27 MemWr: write memory MemtoReg: ALU; Mem RegDst: rt ; rd RegWr: write register 4 PC Ext Imm6 Adder
Computer Science 6C Spring 27 Working on the Pipeline Datapath Control Signals Computer Science 6C Spring 27 MemWr: write memory MemtoReg: ALU; Mem RegDst: rt ; rd RegWr: write register 4 PC Ext Imm6 Adder
Lecture #17: CPU Design II Control
 Lecture #7: CPU Design II Control 25-7-9 Anatomy: 5 components of any Computer Personal Computer Computer Processor Control ( brain ) This week ( ) path ( brawn ) (where programs, data live when running)
Lecture #7: CPU Design II Control 25-7-9 Anatomy: 5 components of any Computer Personal Computer Computer Processor Control ( brain ) This week ( ) path ( brawn ) (where programs, data live when running)
Lecture 8: Control COS / ELE 375. Computer Architecture and Organization. Princeton University Fall Prof. David August
 Lecture 8: Control COS / ELE 375 Computer Architecture and Organization Princeton University Fall 2015 Prof. David August 1 Datapath and Control Datapath The collection of state elements, computation elements,
Lecture 8: Control COS / ELE 375 Computer Architecture and Organization Princeton University Fall 2015 Prof. David August 1 Datapath and Control Datapath The collection of state elements, computation elements,
UC Berkeley CS61C : Machine Structures
 inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs6c UC Berkeley CS6C : Machine Structures The Internet is broken?! The Clean Slate team at Stanford wants to revamp the Internet, making it safer (from viruses), more reliable
inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs6c UC Berkeley CS6C : Machine Structures The Internet is broken?! The Clean Slate team at Stanford wants to revamp the Internet, making it safer (from viruses), more reliable
Single Cycle Datapath
 Single Cycle atapath Lecture notes from MKP, H. H. Lee and S. Yalamanchili Section 4.-4.4 Appendices B.7, B.8, B.,.2 Practice Problems:, 4, 6, 9 ing (2) Introduction We will examine two MIPS implementations
Single Cycle atapath Lecture notes from MKP, H. H. Lee and S. Yalamanchili Section 4.-4.4 Appendices B.7, B.8, B.,.2 Practice Problems:, 4, 6, 9 ing (2) Introduction We will examine two MIPS implementations
Computer Architecture, IFE CS and T&CS, 4 th sem. Single-Cycle Architecture
 Single-Cycle Architecture Data flow Data flow is synchronized with clock (edge) in sequential systems Architecture Elements - assumptions Program (Instruction) memory: All instructions & buses are 32-bit
Single-Cycle Architecture Data flow Data flow is synchronized with clock (edge) in sequential systems Architecture Elements - assumptions Program (Instruction) memory: All instructions & buses are 32-bit
Multiple Cycle Data Path
 Multiple Cycle Data Path CS 365 Lecture 7 Prof. Yih Huang CS365 1 Multicycle Approach Break up the instructions into steps, each step takes a cycle balance the amount of work to be done restrict each cycle
Multiple Cycle Data Path CS 365 Lecture 7 Prof. Yih Huang CS365 1 Multicycle Approach Break up the instructions into steps, each step takes a cycle balance the amount of work to be done restrict each cycle
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Single- Cycle CPU Datapath & Control Part 2
 CS 6C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Single- Cycle CPU Datapath & Control Part 2 Instructors: Krste Asanovic & Vladimir Stojanovic hfp://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs6c/ Review:
CS 6C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Single- Cycle CPU Datapath & Control Part 2 Instructors: Krste Asanovic & Vladimir Stojanovic hfp://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs6c/ Review:
Design of the MIPS Processor (contd)
 Design of the MIPS Processor (contd) First, revisit the datapath for add, sub, lw, sw. We will augment it to accommodate the beq and j instructions. Execution of branch instructions beq $at, $zero, L add
Design of the MIPS Processor (contd) First, revisit the datapath for add, sub, lw, sw. We will augment it to accommodate the beq and j instructions. Execution of branch instructions beq $at, $zero, L add
Chapter 5 Solutions: For More Practice
 Chapter 5 Solutions: For More Practice 1 Chapter 5 Solutions: For More Practice 5.4 Fetching, reading registers, and writing the destination register takes a total of 300ps for both floating point add/subtract
Chapter 5 Solutions: For More Practice 1 Chapter 5 Solutions: For More Practice 5.4 Fetching, reading registers, and writing the destination register takes a total of 300ps for both floating point add/subtract
CS359: Computer Architecture. The Processor (A) Yanyan Shen Department of Computer Science and Engineering
 CS359: Computer Architecture The Processor (A) Yanyan Shen Department of Computer Science and Engineering Eecuting R-type Instructions 7 Instructions ADD and subtract add rd, rs, rt sub rd, rs, rt OR Immediate:
CS359: Computer Architecture The Processor (A) Yanyan Shen Department of Computer Science and Engineering Eecuting R-type Instructions 7 Instructions ADD and subtract add rd, rs, rt sub rd, rs, rt OR Immediate:
are Softw Instruction Set Architecture Microarchitecture are rdw
 Program, Application Software Programming Language Compiler/Interpreter Operating System Instruction Set Architecture Hardware Microarchitecture Digital Logic Devices (transistors, etc.) Solid-State Physics
Program, Application Software Programming Language Compiler/Interpreter Operating System Instruction Set Architecture Hardware Microarchitecture Digital Logic Devices (transistors, etc.) Solid-State Physics
Chapter 4. The Processor
 Chapter 4 The Processor Introduction CPU performance factors Instruction count Determined by ISA and compiler CPI and Cycle time Determined by CPU hardware We will examine two MIPS implementations A simplified
Chapter 4 The Processor Introduction CPU performance factors Instruction count Determined by ISA and compiler CPI and Cycle time Determined by CPU hardware We will examine two MIPS implementations A simplified
Multi-cycle Approach. Single cycle CPU. Multi-cycle CPU. Requires state elements to hold intermediate values. one clock cycle or instruction
 Multi-cycle Approach Single cycle CPU State element Combinational logic State element clock one clock cycle or instruction Multi-cycle CPU Requires state elements to hold intermediate values State Element
Multi-cycle Approach Single cycle CPU State element Combinational logic State element clock one clock cycle or instruction Multi-cycle CPU Requires state elements to hold intermediate values State Element
Processor (multi-cycle)
 CS359: Computer Architecture Processor (multi-cycle) Yanyan Shen Department of Computer Science and Engineering Five Instruction Steps ) Instruction Fetch ) Instruction Decode and Register Fetch 3) R-type
CS359: Computer Architecture Processor (multi-cycle) Yanyan Shen Department of Computer Science and Engineering Five Instruction Steps ) Instruction Fetch ) Instruction Decode and Register Fetch 3) R-type
Major CPU Design Steps
 Datapath Major CPU Design Steps. Analyze instruction set operations using independent RTN ISA => RTN => datapath requirements. This provides the the required datapath components and how they are connected
Datapath Major CPU Design Steps. Analyze instruction set operations using independent RTN ISA => RTN => datapath requirements. This provides the the required datapath components and how they are connected
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture Control and Pipelining
 CS 6C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture Control and Pipelining Instructors: Vladimir Stojanovic and Nicholas Weaver http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs6c/sp6 Datapath Control Signals ExtOp: zero, sign
CS 6C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture Control and Pipelining Instructors: Vladimir Stojanovic and Nicholas Weaver http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs6c/sp6 Datapath Control Signals ExtOp: zero, sign
UC Berkeley CS61C : Machine Structures
 inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs6c UC Berkeley CS6C : Machine Structures Lecture 26 Single-cycle CPU Control 27-3-2 Exhausted TA Ben Sussman www.icanhascheezburger.com Qutrits Bring Quantum Computers Closer:
inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs6c UC Berkeley CS6C : Machine Structures Lecture 26 Single-cycle CPU Control 27-3-2 Exhausted TA Ben Sussman www.icanhascheezburger.com Qutrits Bring Quantum Computers Closer:
Project Description EEC 483 Computer Organization, Spring 2019
 Project Description EEC 483 Computer Organization, Spring 2019 Title: Implement a (single-cycle) MIPS processor on Altera DE10-Lite using Quartus and VHDL Goal: This project is designed to help understand
Project Description EEC 483 Computer Organization, Spring 2019 Title: Implement a (single-cycle) MIPS processor on Altera DE10-Lite using Quartus and VHDL Goal: This project is designed to help understand
EECS 151/251A Fall 2017 Digital Design and Integrated Circuits. Instructor: John Wawrzynek and Nicholas Weaver. Lecture 13 EE141
 EECS 151/251A Fall 2017 Digital Design and Integrated Circuits Instructor: John Wawrzynek and Nicholas Weaver Lecture 13 Project Introduction You will design and optimize a RISC-V processor Phase 1: Design
EECS 151/251A Fall 2017 Digital Design and Integrated Circuits Instructor: John Wawrzynek and Nicholas Weaver Lecture 13 Project Introduction You will design and optimize a RISC-V processor Phase 1: Design
ECE 30, Lab #8 Spring 2014
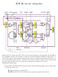 ECE 30, Lab #8 Spring 20 Shown above is a multi-cycle CPU. There are six special registers in this datapath: PC, IR, MDR, A, B, and ALUOut. Of these, PC and IR are enabled to change when PCWr and IRWr
ECE 30, Lab #8 Spring 20 Shown above is a multi-cycle CPU. There are six special registers in this datapath: PC, IR, MDR, A, B, and ALUOut. Of these, PC and IR are enabled to change when PCWr and IRWr
CS 61C Summer 2016 Guerrilla Section 4: MIPS CPU (Datapath & Control)
 CS 61C Summer 2016 Guerrilla Section 4: MIPS CPU (Datapath & Control) 1) If this exam were a CPU, you d be halfway through the pipeline (Sp15 Final) We found that the instruction fetch and memory stages
CS 61C Summer 2016 Guerrilla Section 4: MIPS CPU (Datapath & Control) 1) If this exam were a CPU, you d be halfway through the pipeline (Sp15 Final) We found that the instruction fetch and memory stages
COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND DESIGN
 COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND DESIGN The Hardware/Software Interface 5 th Edition Chapter 4 The Processor Introduction CPU performance factors Instruction count Determined by ISA and compiler CPI and Cycle
COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND DESIGN The Hardware/Software Interface 5 th Edition Chapter 4 The Processor Introduction CPU performance factors Instruction count Determined by ISA and compiler CPI and Cycle
Ch 5: Designing a Single Cycle Datapath
 Ch 5: esigning a Single Cycle path Computer Systems Architecture CS 365 The Big Picture: Where are We Now? The Five Classic Components of a Computer Processor Control Memory path Input Output Today s Topic:
Ch 5: esigning a Single Cycle path Computer Systems Architecture CS 365 The Big Picture: Where are We Now? The Five Classic Components of a Computer Processor Control Memory path Input Output Today s Topic:
Single Cycle Data Path
 Single ycle ata Path S 365 Lecture 6 Prof. Yih Huang S365 1 MIPS Lite We're ready to look at an implementation of the MIPS Simplified to support only: memory-reference instructions: lw, sw arithmetic-logical
Single ycle ata Path S 365 Lecture 6 Prof. Yih Huang S365 1 MIPS Lite We're ready to look at an implementation of the MIPS Simplified to support only: memory-reference instructions: lw, sw arithmetic-logical
Lecture 4: Review of MIPS. Instruction formats, impl. of control and datapath, pipelined impl.
 Lecture 4: Review of MIPS Instruction formats, impl. of control and datapath, pipelined impl. 1 MIPS Instruction Types Data transfer: Load and store Integer arithmetic/logic Floating point arithmetic Control
Lecture 4: Review of MIPS Instruction formats, impl. of control and datapath, pipelined impl. 1 MIPS Instruction Types Data transfer: Load and store Integer arithmetic/logic Floating point arithmetic Control
Final Exam Spring 2017
 COE 3 / ICS 233 Computer Organization Final Exam Spring 27 Friday, May 9, 27 7:3 AM Computer Engineering Department College of Computer Sciences & Engineering King Fahd University of Petroleum & Minerals
COE 3 / ICS 233 Computer Organization Final Exam Spring 27 Friday, May 9, 27 7:3 AM Computer Engineering Department College of Computer Sciences & Engineering King Fahd University of Petroleum & Minerals
