Programming Languages
|
|
|
- Theresa Maxwell
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CSE 130 : Fall 2008 Programmg Languages Lecture 4: Variables, Environments, Scope News PA 1 due Frida 5pm PA 2 out esterda (due net Fi) Fri) Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego Variables and Bdgs Q: How to use variables L? Q: How to assign to a variable? # = 2+2 val : t = 4 = e Bd the value of epression e to the variable Variables and Bdgs # = 2+2 val : t = 4 # = * * val : t = 64 # z = [;;+] val z : t list = [4;64;68] Later declared epressions can use ost recent bound value used for evaluation Sounds like C/Java? NO!
2 Environments ( Phone Book ) How L deals with variables Variables = names Values = phone number Environments and Evaluation L begs a top-level environment Some names bound = e z 4 : t 64 : t [4;64;68] : t list 8 : t L program = Sequence of variable bdgs Program evaluated b evaluatg bdgs order 1. Evaluate epr e current env to get value v : t 2. Etend env to bd to v : t (Repeat with net bdg) Environments Phone book Variables = names Values = phone number 1. Evaluate: Fd and use most recent value of variable 2. Etend: Add new bdg at end of phone book Eample # = 2+2 val : t = 4 # = * * val : t = 64 4 : t 4 : t 64 : t # z = [;;+] val z : t list = [4;64;68] 4 : t # = + val : t = 8 New bdg! z z 64 : t [4;64;68] : t list 4 : t 64 : t [4;64;68] : t list 8 : t
3 Environments 1. Evaluate: Use most recent bound value of var 2. Etend: Add new bdg at end How is this different from C/Java s store? Environments 1. Evaluate: Use most recent bound value of var 2. Etend: Add new bdg at end How is this different from C/Java s store? # = 2+2 val : t = 4 4 : t # f = fun -> + ; val f : t -> t = fn 4 : t f fn <code, >: t->t # = + ; val : t = 8 # f 0; val it : t = 4 New bdg: No change or mutation Old bdg frozen f # = 2+2; val : t = 4 4 : t # f = fun -> + ; val f : t -> t = fn 4 : t f fn <code, >: t->t # = + ; val : t = 8; 4 : t # f 0; f fn <code, >: t->t val it : t = 4 8 : t Environments 1. Evaluate: Use most recent bound value of var 2. Etend: Add new bdg at end How is this different from C/Java s store? # = 2+2; val : t = 4 # f = fun -> + val f : t -> t = fn Bdg used to eval (f ) # = + ; val : t = 8 4 : t f fn <code, >: t->t # f 0; 8 : t val it : t = 4 Bdg for subsequent Cannot change the world Cannot assign to variables Can etend the env b addg a fresh bdg Does not affect previous uses of variable Environment at fun declaration frozen side fun value Frozen env used to evaluate application (f ) Q: Wh is this a good thg? # = 2+2 Bdg used to eval (f ) val : t = 4 # f = fun -> + val f : t -> t = fn # = + val : t = 8; # f 0 val it : t = 4 4 : t f fn <code,, >: t->t 8 : t Bdg for subsequent
4 Cannot change the world Q: Wh is this a good thg? A: Function behavior frozen at declaration Nothg entered afterwards changes function Same puts alwas produce same outputs So? Localizes debuggg Localizes testg/reasong g about program No sharg means no evil aliasg effects Eamples of no sharg Remember: No addresses, no sharg. Each variable is bound to a fresh stance of a value Tuples, Lists Efficient implementation without sharg? There is sharg and poters but hidden from ou Compiler s job is to optimize code to efficientl implement these no-sharg sharg semantics Your job is to use the simplified no-sharg semantics to write correct, cleaner, readable, etendable sstems Function bdgs Functions are values, can bd usg fname = fun -> e Problem: Can t defe recursive functions! fname is bound after computg rhs value no (or old ) bdg for occurences of fname side id e rec fname = e Occurences of fname side e bound to this defition rec fac = if <=1 then 1 else *fac (-1) Local bdgs: - So far: bdgs that rema until a re-bdg ( global ) Local, temporar variables are useful side functions Avoid repeatg computations ake functions more readable = e1 e2 Let- is an epression! Evaluatg - env E: 1. Evaluate epr e1 env E to get value v : t 2. Use etended E [ a v : t] (onl) to evaluate e2
5 Local bdgs Evaluatg - env E: 1. Evaluate epr e1 env E to get value v : t 2. Use etended E [ a v : t] to evaluate e2 Let- is an epression! Evaluatg - env E: 1. Evaluate epr e1 env E to get value v : t 2. Use etended E [ a v : t] to evaluate e2 = 10 * 10 : t = = 10 * 10 : t 100 : t Nested bdgs Evaluatg - env E: 1. Evaluate epr e1 env E to get value v : t 2. Use etended E [ a v : t] to evaluate e2 = : t ( = 20 * ) 10 : t + 20 : t 10 : t Nested bdgs = 10 = 20 * = 10 = 20 * Correct Formattg
6 Eample Nested function bdgs rec filter f s = if s = [] then [] else h = hd s t = filter f (tl s) if (f h) then h::t else t a = 20 f = = 10 g z = + z a + (g ) Env frozen with function Used to evaluate fun appl. Vl Values appl. are frozen env at defition f 0; Recap Recap Variables are names for values Environment: dictionar/phonebook ost recent bdg used Entries never changed, new entries added Build comple epressions with local bdgs - epression The -bdg is visible ( scope) side -epression Elsewhere the bdg is not visible Environment frozen at fun defition Re-bdg variables cannot change a function Same I/O behavior at ever call
7 Static/Leical Scopg Net: Functions For each occurrence of a variable, there is a unique place program tet where the variable was defed ost recent bdg environment Static/Leical: Determed from the program tet Without eecutg the program Epressions Tpes Values Ver useful for readabilit, debuggg: Don t have to figure out where a variable got assigned Unique, staticall known defition for each occurrence Q: What s the value of a function?
Variables and Bindings
 Net: Variables Variables and Bindings Q: How to use variables in ML? Q: How to assign to a variable? # let = 2+2;; val : int = 4 let = e;; Bind the value of epression e to the variable Variables and Bindings
Net: Variables Variables and Bindings Q: How to use variables in ML? Q: How to assign to a variable? # let = 2+2;; val : int = 4 let = e;; Bind the value of epression e to the variable Variables and Bindings
Programming Languages
 CSE 130 : Fall 2008 Programming Languages Lecture 3: Epressions and Types Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego News PA 1 due (net) Fri 10/10 5pm PA 2 out today or tomorrow Office hours posted on Webpage: Held in
CSE 130 : Fall 2008 Programming Languages Lecture 3: Epressions and Types Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego News PA 1 due (net) Fri 10/10 5pm PA 2 out today or tomorrow Office hours posted on Webpage: Held in
Programming Languages
 CSE 130: Spring 2010 Programming Languages Lecture 3: Epressions and Types Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego A Problem fun -> +1 Can functions only have a single parameter? A Solution: Simultaneous Binding Parameter
CSE 130: Spring 2010 Programming Languages Lecture 3: Epressions and Types Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego A Problem fun -> +1 Can functions only have a single parameter? A Solution: Simultaneous Binding Parameter
News. CSE 130: Programming Languages. Environments & Closures. Functions are first-class values. Recap: Functions as first-class values
 CSE 130: Programming Languages Environments & Closures News PA 3 due THIS Friday (5/1) Midterm NEXT Friday (5/8) Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego Recap: Functions as first-class values Arguments, return values,
CSE 130: Programming Languages Environments & Closures News PA 3 due THIS Friday (5/1) Midterm NEXT Friday (5/8) Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego Recap: Functions as first-class values Arguments, return values,
Programming Languages
 CSE 130 : Spring 2011 Programming Languages Lecture 3: Crash Course Ctd, Expressions and Types Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego A shorthand for function binding # let neg = fun f -> fun x -> not (f x); # let
CSE 130 : Spring 2011 Programming Languages Lecture 3: Crash Course Ctd, Expressions and Types Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego A shorthand for function binding # let neg = fun f -> fun x -> not (f x); # let
Side note: Tail Recursion. Begin at the beginning. Side note: Tail Recursion. Base Types. Base Type: int. Base Type: int
 Begin at the beginning Epressions (Synta) Compile-time Static Eec-time Dynamic Types Values (Semantics) 1. Programmer enters epression 2. ML checks if epression is well-typed Using a precise set of rules,
Begin at the beginning Epressions (Synta) Compile-time Static Eec-time Dynamic Types Values (Semantics) 1. Programmer enters epression 2. ML checks if epression is well-typed Using a precise set of rules,
Tail Recursion: Factorial. Begin at the beginning. How does it execute? Tail recursion. Tail recursive factorial. Tail recursive factorial
 Begin at the beginning Epressions (Synta) Compile-time Static Eec-time Dynamic Types Values (Semantics) 1. Programmer enters epression 2. ML checks if epression is well-typed Using a precise set of rules,
Begin at the beginning Epressions (Synta) Compile-time Static Eec-time Dynamic Types Values (Semantics) 1. Programmer enters epression 2. ML checks if epression is well-typed Using a precise set of rules,
Recap. Recap. If-then-else expressions. If-then-else expressions. If-then-else expressions. If-then-else expressions
 Recap Epressions (Synta) Compile-time Static Eec-time Dynamic Types (Semantics) Recap Integers: +,-,* floats: +,-,* Booleans: =,
Recap Epressions (Synta) Compile-time Static Eec-time Dynamic Types (Semantics) Recap Integers: +,-,* floats: +,-,* Booleans: =,
Recap: Functions as first-class values
 Recap: Functions as first-class values Arguments, return values, bindings What are the benefits? Parameterized, similar functions (e.g. Testers) Creating, (Returning) Functions Iterator, Accumul, Reuse
Recap: Functions as first-class values Arguments, return values, bindings What are the benefits? Parameterized, similar functions (e.g. Testers) Creating, (Returning) Functions Iterator, Accumul, Reuse
Begin at the beginning
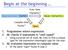 Begin at the beginning Expressions (Syntax) Exec-time Dynamic Values (Semantics) Compile-time Static Types 1. Programmer enters expression 2. ML checks if expression is well-typed Using a precise set of
Begin at the beginning Expressions (Syntax) Exec-time Dynamic Values (Semantics) Compile-time Static Types 1. Programmer enters expression 2. ML checks if expression is well-typed Using a precise set of
News. Programming Languages. Recap. Recap: Environments. Functions. of functions: Closures. CSE 130 : Fall Lecture 5: Functions and Datatypes
 CSE 130 : Fall 2007 Programming Languages News PA deadlines shifted PA #2 now due 10/24 (next Wed) Lecture 5: Functions and Datatypes Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego Recap: Environments Phone book Variables
CSE 130 : Fall 2007 Programming Languages News PA deadlines shifted PA #2 now due 10/24 (next Wed) Lecture 5: Functions and Datatypes Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego Recap: Environments Phone book Variables
Programming Languages
 CSE 130 : Winter 2009 Programming Languages News PA 2 out, and due Mon 1/26 5pm Lecture 5: Functions and Datatypes t UC San Diego Recap: Environments Phone book Variables = names Values = phone number
CSE 130 : Winter 2009 Programming Languages News PA 2 out, and due Mon 1/26 5pm Lecture 5: Functions and Datatypes t UC San Diego Recap: Environments Phone book Variables = names Values = phone number
Programming Languages
 CSE 130 : Fall 2008 Programming Languages Lecture 2: A Crash Course in ML Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego News On webpage: Suggested HW #1, sample for Quiz #1 on Thu PA #1 (due next Fri 10/10) No make-up quizzes
CSE 130 : Fall 2008 Programming Languages Lecture 2: A Crash Course in ML Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego News On webpage: Suggested HW #1, sample for Quiz #1 on Thu PA #1 (due next Fri 10/10) No make-up quizzes
Programming Languages
 CSE 130: Fall 2009 Programming Languages Lecture 2: A Crash Course in ML News On webpage: Suggested HW #1 PA #1 (due next Fri 10/9) Technical issues installing Ocaml - should be resolved soon! Ranjit Jhala
CSE 130: Fall 2009 Programming Languages Lecture 2: A Crash Course in ML News On webpage: Suggested HW #1 PA #1 (due next Fri 10/9) Technical issues installing Ocaml - should be resolved soon! Ranjit Jhala
Programming Languages
 CSE 130: Spring 2010 Programming Languages Lecture 2: A Crash Course in ML Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego News On webpage: Suggested HW #1 PA #1 (due next Wed 4/9) Please post questions to WebCT Today: A crash
CSE 130: Spring 2010 Programming Languages Lecture 2: A Crash Course in ML Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego News On webpage: Suggested HW #1 PA #1 (due next Wed 4/9) Please post questions to WebCT Today: A crash
News. Programming Languages. Complex types: Lists. Recap: ML s Holy Trinity. CSE 130: Spring 2012
 News CSE 130: Spring 2012 Programming Languages On webpage: Suggested HW #1 PA #1 (due next Fri 4/13) Lecture 2: A Crash Course in ML Please post questions to Piazza Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego Today: A
News CSE 130: Spring 2012 Programming Languages On webpage: Suggested HW #1 PA #1 (due next Fri 4/13) Lecture 2: A Crash Course in ML Please post questions to Piazza Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego Today: A
Recap from last time. Programming Languages. CSE 130 : Fall Lecture 3: Data Types. Put it together: a filter function
 CSE 130 : Fall 2011 Recap from last time Programming Languages Lecture 3: Data Types Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego 1 2 A shorthand for function binding Put it together: a filter function # let neg = fun f
CSE 130 : Fall 2011 Recap from last time Programming Languages Lecture 3: Data Types Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego 1 2 A shorthand for function binding Put it together: a filter function # let neg = fun f
Preparing for Class: Watch le Videos! What is an ML program?
 Why are we here? CSE 341 : Programmg Languages Lecture 3 Local Bdgs, Options, Purity Zach Tatlock Sprg 2014 To work together to free our mds from the shackles of imperative programmg. 2 Preparg for Class:
Why are we here? CSE 341 : Programmg Languages Lecture 3 Local Bdgs, Options, Purity Zach Tatlock Sprg 2014 To work together to free our mds from the shackles of imperative programmg. 2 Preparg for Class:
Building up a language SICP Variations on a Scheme. Meval. The Core Evaluator. Eval. Apply. 2. syntax procedures. 1.
 6.001 SICP Variations on a Scheme Scheme Evaluator A Grand Tour Techniques for language design: Interpretation: eval/appl Semantics vs. snta Sntactic transformations Building up a language... 3. 1. eval/appl
6.001 SICP Variations on a Scheme Scheme Evaluator A Grand Tour Techniques for language design: Interpretation: eval/appl Semantics vs. snta Sntactic transformations Building up a language... 3. 1. eval/appl
Programming Languages
 CSE 130 : Fall 2008 Programming Languages Lecture 6: Datatypes t and Recursion Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego News PA 2 Due Fri (and PA3 up) PA3 is a bit difficult, but do it yourself, or repent in the final
CSE 130 : Fall 2008 Programming Languages Lecture 6: Datatypes t and Recursion Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego News PA 2 Due Fri (and PA3 up) PA3 is a bit difficult, but do it yourself, or repent in the final
CSE 130 Programming Languages. Lecture 3: Datatypes. Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego
 CSE 130 Programming Languages Lecture 3: Datatypes Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego News? PA #2 (coming tonight) Ocaml-top issues? Pleas post questions to Piazza Recap: ML s Holy Trinity Expressions (Syntax)
CSE 130 Programming Languages Lecture 3: Datatypes Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego News? PA #2 (coming tonight) Ocaml-top issues? Pleas post questions to Piazza Recap: ML s Holy Trinity Expressions (Syntax)
Programming Languages
 CSE 130 : Fall 2009 Programming Languages Lecture 13: Whats in a name? Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego f = open( foo.txt, read ) f.readlines() for l in f.readlines(): f.close ou now know enough to do PA5
CSE 130 : Fall 2009 Programming Languages Lecture 13: Whats in a name? Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego f = open( foo.txt, read ) f.readlines() for l in f.readlines(): f.close ou now know enough to do PA5
Next: What s in a name? Programming Languages. Data model in functional PL. What s in a name? CSE 130 : Fall Lecture 13: What s in a Name?
 Next: What s in a name? CSE 13 : Fall 211 Programming Languages Lecture 13: What s in a Name? More precisely: How should programmer think of data What does a variable x really mean? Ranjit Jhala UC San
Next: What s in a name? CSE 13 : Fall 211 Programming Languages Lecture 13: What s in a Name? More precisely: How should programmer think of data What does a variable x really mean? Ranjit Jhala UC San
OCaml. ML Flow. Complex types: Lists. Complex types: Lists. The PL for the discerning hacker. All elements must have same type.
 OCaml The PL for the discerning hacker. ML Flow Expressions (Syntax) Compile-time Static 1. Enter expression 2. ML infers a type Exec-time Dynamic Types 3. ML crunches expression down to a value 4. Value
OCaml The PL for the discerning hacker. ML Flow Expressions (Syntax) Compile-time Static 1. Enter expression 2. ML infers a type Exec-time Dynamic Types 3. ML crunches expression down to a value 4. Value
7.3.3 A Language With Nested Procedure Declarations
 7.3. ACCESS TO NONLOCAL DATA ON THE STACK 443 7.3.3 A Language With Nested Procedure Declarations The C family of languages, and many other familiar languages do not support nested procedures, so we troduce
7.3. ACCESS TO NONLOCAL DATA ON THE STACK 443 7.3.3 A Language With Nested Procedure Declarations The C family of languages, and many other familiar languages do not support nested procedures, so we troduce
Programming Languages
 CSE 130 : Spring 2011 Programming Languages Lecture 13: What s in a Name? Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego Next: What s in a name? More precisely: How should programmer think of data What does a variable x really
CSE 130 : Spring 2011 Programming Languages Lecture 13: What s in a Name? Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego Next: What s in a name? More precisely: How should programmer think of data What does a variable x really
Recap: ML s Holy Trinity. Story So Far... CSE 130 Programming Languages. Datatypes. A function is a value! Next: functions, but remember.
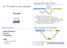 CSE 130 Programming Languages Recap: ML s Holy Trinity Expressions (Syntax) Exec-time Dynamic Values (Semantics) Datatypes Compile-time Static Types Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego 1. Programmer enters expression
CSE 130 Programming Languages Recap: ML s Holy Trinity Expressions (Syntax) Exec-time Dynamic Values (Semantics) Datatypes Compile-time Static Types Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego 1. Programmer enters expression
CSE 130 Programming Languages. Datatypes. Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego
 CSE 130 Programming Languages Datatypes Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego Recap: ML s Holy Trinity Expressions (Syntax) Exec-time Dynamic Values (Semantics) Compile-time Static Types 1. Programmer enters expression
CSE 130 Programming Languages Datatypes Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego Recap: ML s Holy Trinity Expressions (Syntax) Exec-time Dynamic Values (Semantics) Compile-time Static Types 1. Programmer enters expression
Programming Languages
 CSE 130 : Winter 2013 Programming Languages Lecture 3: Crash Course, Datatypes Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego 1 Story So Far... Simple Expressions Branches Let-Bindings... Today: Finish Crash Course Datatypes
CSE 130 : Winter 2013 Programming Languages Lecture 3: Crash Course, Datatypes Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego 1 Story So Far... Simple Expressions Branches Let-Bindings... Today: Finish Crash Course Datatypes
CSE 130: Programming Languages. Polymorphism. Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego
 CSE 130: Programming Languages Polymorphism Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego Q: What is the value of res? let f g = let x = 0 in g 2 let x = 100 let h y = x + y let res = f h (a) 0 (b) 2 (c) 100 (d) 102 (e) 12
CSE 130: Programming Languages Polymorphism Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego Q: What is the value of res? let f g = let x = 0 in g 2 let x = 100 let h y = x + y let res = f h (a) 0 (b) 2 (c) 100 (d) 102 (e) 12
COP-5555 PROGRAMMING LANGUAGEPRINCIPLES NOTES ON RPAL
 COP-5555 PROGRAMMING LANGUAGEPRINCIPLES NOTES ON 1. Introduction is a subset of PAL, the Pedagogic Algorithmic Language. There are three versions of PAL:, LPAL, and JPAL. The only one of terest here is.
COP-5555 PROGRAMMING LANGUAGEPRINCIPLES NOTES ON 1. Introduction is a subset of PAL, the Pedagogic Algorithmic Language. There are three versions of PAL:, LPAL, and JPAL. The only one of terest here is.
An example DFA: reaching definitions
 Dataflow analysis: what is it? Dataflow analysis A common framework for expressg algorithms that compute formation ab a program Why is such a framework useful? Dataflow analysis: what is it? A common framework
Dataflow analysis: what is it? Dataflow analysis A common framework for expressg algorithms that compute formation ab a program Why is such a framework useful? Dataflow analysis: what is it? A common framework
Programming Languages
 What about more complex data? CSE 130 : Fall 2012 Programming Languages Expressions Values Lecture 3: Datatypes Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego Types Many kinds of expressions: 1. Simple 2. Variables 3. Functions
What about more complex data? CSE 130 : Fall 2012 Programming Languages Expressions Values Lecture 3: Datatypes Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego Types Many kinds of expressions: 1. Simple 2. Variables 3. Functions
Plan (next 4 weeks) 1. Fast forward. 2. Rewind. 3. Slow motion. Rapid introduction to what s in OCaml. Go over the pieces individually
 Plan (next 4 weeks) 1. Fast forward Rapid introduction to what s in OCaml 2. Rewind 3. Slow motion Go over the pieces individually History, Variants Meta Language Designed by Robin Milner @ Edinburgh Language
Plan (next 4 weeks) 1. Fast forward Rapid introduction to what s in OCaml 2. Rewind 3. Slow motion Go over the pieces individually History, Variants Meta Language Designed by Robin Milner @ Edinburgh Language
The code generator must statically assign a location in the AR for each temporary add $a0 $t1 $a0 ; $a0 = e 1 + e 2 addiu $sp $sp 4 ; adjust $sp (!
 Lecture Outline Code Generation (II) Adapted from Lectures b Profs. Ale Aiken and George Necula (UCB) Allocating temporaries in the Activation Record Let s optimie cgen a little Code generation for OO
Lecture Outline Code Generation (II) Adapted from Lectures b Profs. Ale Aiken and George Necula (UCB) Allocating temporaries in the Activation Record Let s optimie cgen a little Code generation for OO
Lines and Their Slopes
 8.2 Lines and Their Slopes Linear Equations in Two Variables In the previous chapter we studied linear equations in a single variable. The solution of such an equation is a real number. A linear equation
8.2 Lines and Their Slopes Linear Equations in Two Variables In the previous chapter we studied linear equations in a single variable. The solution of such an equation is a real number. A linear equation
Today s Plan. Programming Languages. Example : Factorial. Recursion. CSE 130 : Spring Lecture 6: Higher-Order Functions
 CSE 130 : Spring 2011 Programming Languages Lecture 6: Higher-Order Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego Today s Plan A little more practice with recursion Base Pattern -> Base Expression Induction Pattern -> Induction
CSE 130 : Spring 2011 Programming Languages Lecture 6: Higher-Order Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego Today s Plan A little more practice with recursion Base Pattern -> Base Expression Induction Pattern -> Induction
CVO103: Programming Languages. Lecture 5 Design and Implementation of PLs (1) Expressions
 CVO103: Programming Languages Lecture 5 Design and Implementation of PLs (1) Expressions Hakjoo Oh 2018 Spring Hakjoo Oh CVO103 2018 Spring, Lecture 5 April 3, 2018 1 / 23 Plan Part 1 (Preliminaries):
CVO103: Programming Languages Lecture 5 Design and Implementation of PLs (1) Expressions Hakjoo Oh 2018 Spring Hakjoo Oh CVO103 2018 Spring, Lecture 5 April 3, 2018 1 / 23 Plan Part 1 (Preliminaries):
Programming Languages
 CSE 130 : Fall 2008 Programming Languages Lecture 12: What s in a Name? Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego A crash course in Python Interpreted, imperative, OO Language g Everything is an object Dynamic Typing
CSE 130 : Fall 2008 Programming Languages Lecture 12: What s in a Name? Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego A crash course in Python Interpreted, imperative, OO Language g Everything is an object Dynamic Typing
Any questions. Say hello to OCaml. Say hello to OCaml. Why readability matters. History, Variants. Plan (next 4 weeks)
 Any questions Say hello to OCaml? void sort(int arr[], int beg, int end){ if (end > beg + 1){ int piv = arr[beg]; int l = beg + 1; int r = end; while (l!= r-1){ if(arr[l]
Any questions Say hello to OCaml? void sort(int arr[], int beg, int end){ if (end > beg + 1){ int piv = arr[beg]; int l = beg + 1; int r = end; while (l!= r-1){ if(arr[l]
Programming Languages. Example 5. Example 4. CSE 130 : Fall type, can reuse code for all types! let rec cat l = match l with
 CSE 130 : Fall 2008 Programming Languages Lecture 9: s and Signatures Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego Previously: Polymorphism enables Reuse Can reuse generic functions: map : a * b b * a filter: ( a bool *
CSE 130 : Fall 2008 Programming Languages Lecture 9: s and Signatures Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego Previously: Polymorphism enables Reuse Can reuse generic functions: map : a * b b * a filter: ( a bool *
So what does studying PL buy me?
 So what does studying PL buy me? Enables you to better choose the right language but isn t that decided by libraries, standards, and my boss? Yes. Chicken-and-egg. My goal: educate tomorrow s tech leaders
So what does studying PL buy me? Enables you to better choose the right language but isn t that decided by libraries, standards, and my boss? Yes. Chicken-and-egg. My goal: educate tomorrow s tech leaders
A Crash Course on Standard ML
 A Crash Course on Standard ML Hongwei Xi Version of November 23, 2004 1 Start Type sml-cm at a Unix wdow to get an teractive terpreter for Standard ML (SML). You can later quit the terpreter by typg ctrl-d.
A Crash Course on Standard ML Hongwei Xi Version of November 23, 2004 1 Start Type sml-cm at a Unix wdow to get an teractive terpreter for Standard ML (SML). You can later quit the terpreter by typg ctrl-d.
OCaml. History, Variants. ML s holy trinity. Interacting with ML. Base type: Integers. Base type: Strings. *Notes from Sorin Lerner at UCSD*
 OCaml 1. Introduction Rapid introduction to what s in OCaml 2. Focus on Features Individually as Needed as Semester Progresses *Notes from Sorin Lerner at UCSD* History, Variants Meta Language Designed
OCaml 1. Introduction Rapid introduction to what s in OCaml 2. Focus on Features Individually as Needed as Semester Progresses *Notes from Sorin Lerner at UCSD* History, Variants Meta Language Designed
Programming Languages Lecture 14: Sum, Product, Recursive Types
 CSE 230: Winter 200 Principles of Programming Languages Lecture 4: Sum, Product, Recursive Types The end is nigh HW 3 No HW 4 (= Final) Project (Meeting + Talk) Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego Recap Goal: Relate
CSE 230: Winter 200 Principles of Programming Languages Lecture 4: Sum, Product, Recursive Types The end is nigh HW 3 No HW 4 (= Final) Project (Meeting + Talk) Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego Recap Goal: Relate
Typical workflow. CSE341: Programming Languages. Lecture 17 Implementing Languages Including Closures. Reality more complicated
 Typical workflow concrete synta (string) "(fn => + ) 4" Parsing CSE341: Programming Languages abstract synta (tree) Lecture 17 Implementing Languages Including Closures Function Constant + 4 Var Var Type
Typical workflow concrete synta (string) "(fn => + ) 4" Parsing CSE341: Programming Languages abstract synta (tree) Lecture 17 Implementing Languages Including Closures Function Constant + 4 Var Var Type
About coding style Spring February 9, 2004
 About codg style 15-212 Sprg 2004 February 9, 2004 Contents 1 Correctness 2 2 Specification 2 3 Style 2 3.1 if-then- Expressions... 3 3.1.1 Boolean if-then- Expressions... 3 3.1.2 if-then- stead of Pattern
About codg style 15-212 Sprg 2004 February 9, 2004 Contents 1 Correctness 2 2 Specification 2 3 Style 2 3.1 if-then- Expressions... 3 3.1.1 Boolean if-then- Expressions... 3 3.1.2 if-then- stead of Pattern
Programming Languages
 CSE 130 : Spring 2010 Programming Languages News PA 4 is up (Due Fri, 5pm) Lecture 12: Crash course in Python Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego MidtermGeneral Statistics Total of 80 points < 20 9 people Mean:
CSE 130 : Spring 2010 Programming Languages News PA 4 is up (Due Fri, 5pm) Lecture 12: Crash course in Python Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego MidtermGeneral Statistics Total of 80 points < 20 9 people Mean:
CS 403 Compiler Construction Lecture 8 Syntax Tree and Intermediate Code Generation [Based on Chapter 6 of Aho2] This Lecture
![CS 403 Compiler Construction Lecture 8 Syntax Tree and Intermediate Code Generation [Based on Chapter 6 of Aho2] This Lecture CS 403 Compiler Construction Lecture 8 Syntax Tree and Intermediate Code Generation [Based on Chapter 6 of Aho2] This Lecture](/thumbs/83/87638068.jpg) CS 403 Compiler Construction Lecture 8 Snta Tree and Intermediate Code Generation [Based on Chapter 6 of Aho2] 1 This Lecture 2 1 Remember: Phases of a Compiler This lecture: Intermediate Code This lecture:
CS 403 Compiler Construction Lecture 8 Snta Tree and Intermediate Code Generation [Based on Chapter 6 of Aho2] 1 This Lecture 2 1 Remember: Phases of a Compiler This lecture: Intermediate Code This lecture:
CSE 341, Autumn 2005, Assignment 3 ML - MiniML Interpreter
 Due: Thurs October 27, 10:00pm CSE 341, Autumn 2005, Assignment 3 ML - MiniML Interpreter Note: This is a much longer assignment than anything we ve seen up until now. You are given two weeks to complete
Due: Thurs October 27, 10:00pm CSE 341, Autumn 2005, Assignment 3 ML - MiniML Interpreter Note: This is a much longer assignment than anything we ve seen up until now. You are given two weeks to complete
Lecture 12 Date:
 Information Technolog Delhi Lecture 2 Date: 3.09.204 The Signal Flow Graph Information Technolog Delhi Signal Flow Graph Q: Using individual device scattering parameters to analze a comple microwave network
Information Technolog Delhi Lecture 2 Date: 3.09.204 The Signal Flow Graph Information Technolog Delhi Signal Flow Graph Q: Using individual device scattering parameters to analze a comple microwave network
The Phases of a Compiler. Course Overview. In Chapter 4. Syntax Analysis. Syntax Analysis. Multi Pass Compiler. PART I: overview material
 Course Overview The Phases of a Compiler PART I: overview material Introduction 2 Language processors (tombstone diagrams, bootstrappg) 3 Architecture of a compiler PART II: side a compiler 4 Sntax analsis
Course Overview The Phases of a Compiler PART I: overview material Introduction 2 Language processors (tombstone diagrams, bootstrappg) 3 Architecture of a compiler PART II: side a compiler 4 Sntax analsis
A Programming Language. A different language g is a different vision of life. CSE 130 : Fall Two variables. L1: x++; y--; (y=0)?
 CSE 130 : Fall 2008 Programming Languages Lecture 1: Hello, world. Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego A Programming Language Two variables x,y Three operations x++ x-- (x=0)? L1:L2; L1: x++; y--; (y=0)?l2:l1 L2:
CSE 130 : Fall 2008 Programming Languages Lecture 1: Hello, world. Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego A Programming Language Two variables x,y Three operations x++ x-- (x=0)? L1:L2; L1: x++; y--; (y=0)?l2:l1 L2:
Implementing Recursion
 Implementing Recursion Shriram Krishnamurthi 2003-09-19 We ve seen that there are (at least two, fairly distinct ways of representing environments To implement recursive environments, we need to provide
Implementing Recursion Shriram Krishnamurthi 2003-09-19 We ve seen that there are (at least two, fairly distinct ways of representing environments To implement recursive environments, we need to provide
Recursion. Q: What does this evaluate to? Q: What does this evaluate to? CSE 130 : Programming Languages. Higher-Order Functions
 CSE 130 : Programming Languages Higher-Order Functions Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego Recursion A way of life A different way to view computation Solutions for bigger problems From solutions for sub-problems
CSE 130 : Programming Languages Higher-Order Functions Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego Recursion A way of life A different way to view computation Solutions for bigger problems From solutions for sub-problems
12.4 The Ellipse. Standard Form of an Ellipse Centered at (0, 0) (0, b) (0, -b) center
 . The Ellipse The net one of our conic sections we would like to discuss is the ellipse. We will start b looking at the ellipse centered at the origin and then move it awa from the origin. Standard Form
. The Ellipse The net one of our conic sections we would like to discuss is the ellipse. We will start b looking at the ellipse centered at the origin and then move it awa from the origin. Standard Form
Using Characteristics of a Quadratic Function to Describe Its Graph. The graphs of quadratic functions can be described using key characteristics:
 Chapter Summar Ke Terms standard form of a quadratic function (.1) factored form of a quadratic function (.1) verte form of a quadratic function (.1) concavit of a parabola (.1) reference points (.) transformation
Chapter Summar Ke Terms standard form of a quadratic function (.1) factored form of a quadratic function (.1) verte form of a quadratic function (.1) concavit of a parabola (.1) reference points (.) transformation
Programming Languages
 CSE 230: Winter 2008 Principles of Programming Languages Ocaml/HW #3 Q-A Session Push deadline = Mar 10 Session Mon 3pm? Lecture 15: Type Systems Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego Why Typed Languages? Development
CSE 230: Winter 2008 Principles of Programming Languages Ocaml/HW #3 Q-A Session Push deadline = Mar 10 Session Mon 3pm? Lecture 15: Type Systems Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego Why Typed Languages? Development
CS 312 Problem Set 1: An Introduction to SML
 CS 312 Problem Set 1: An Introduction to SML Assigned: September 1, 2003 Revised: September 4, 2003 Due: 11:59PM, September 10th, 2003 1 Introduction The goal of this problem set is to expose you to as
CS 312 Problem Set 1: An Introduction to SML Assigned: September 1, 2003 Revised: September 4, 2003 Due: 11:59PM, September 10th, 2003 1 Introduction The goal of this problem set is to expose you to as
Week 27 Algebra 1 Assignment:
 Week 7 Algebra Assignment: Da : p. 494 #- odd, -, 8- Da : pp. 496-497 #-9 odd, -6 Da : pp. 0-0 #-9 odd, -, -9 Da 4: p. 09 #-4, 7- Da : pp. - #-9 odd Notes on Assignment: Page 494: General notes for this
Week 7 Algebra Assignment: Da : p. 494 #- odd, -, 8- Da : pp. 496-497 #-9 odd, -6 Da : pp. 0-0 #-9 odd, -, -9 Da 4: p. 09 #-4, 7- Da : pp. - #-9 odd Notes on Assignment: Page 494: General notes for this
CS 312, Fall Exam 1
 Name: ID number: CS 312, Fall 2003 Exam 1 October 16, 2003 Problem 1 2 3 4 Total Grader Grade 18 24 28 30 There are 4 problems on this exam. Please check now that you have a complete exam booklet with
Name: ID number: CS 312, Fall 2003 Exam 1 October 16, 2003 Problem 1 2 3 4 Total Grader Grade 18 24 28 30 There are 4 problems on this exam. Please check now that you have a complete exam booklet with
CPSC W1 University of British Columbia
 Definition of Programming Languages CPSC 311 2016W1 University of British Columbia Practice Midterm Eamination 26 October 2016, 19:00 21:00 Joshua Dunfield Student Name: Signature: Student Number: CS userid:
Definition of Programming Languages CPSC 311 2016W1 University of British Columbia Practice Midterm Eamination 26 October 2016, 19:00 21:00 Joshua Dunfield Student Name: Signature: Student Number: CS userid:
Programming Languages. Tail Recursion. CSE 130: Winter Lecture 8: NOT TR. last thing function does is a recursive call
 CSE 130: Winter 2010 News Programming Languages Lecture 8: Higher-Order Od Functions Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego Today s Plan Finish Static Scoping Tail Recursion last thing function does is a recursive
CSE 130: Winter 2010 News Programming Languages Lecture 8: Higher-Order Od Functions Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego Today s Plan Finish Static Scoping Tail Recursion last thing function does is a recursive
Today. Recap from last Week. Factorial. Factorial. How does it execute? How does it execute? More on recursion. Higher-order functions
 Recap from last Week Three key ways to build complex types/values 1. Each-of types Value of T contas value of T1 and a value of T2 2. One-of types Value of T contas value of T1 or a value of T2 Today More
Recap from last Week Three key ways to build complex types/values 1. Each-of types Value of T contas value of T1 and a value of T2 2. One-of types Value of T contas value of T1 or a value of T2 Today More
Winter Compiler Construction T9 IR part 2 + Runtime organization. Announcements. Today. Know thy group s code
 Winter 26-27 Compiler Construction T9 IR part 2 + Runtime organization Mool Sagiv and Roman Manevich School of Computer Science Tel-Aviv Universit Announcements What is epected in PA3 documentation (5
Winter 26-27 Compiler Construction T9 IR part 2 + Runtime organization Mool Sagiv and Roman Manevich School of Computer Science Tel-Aviv Universit Announcements What is epected in PA3 documentation (5
Systems of Linear Equations
 Sstems of Linear Equations Gaussian Elimination Tpes of Solutions A linear equation is an equation that can be written in the form: a a a n n b The coefficients a i and the constant b can be real or comple
Sstems of Linear Equations Gaussian Elimination Tpes of Solutions A linear equation is an equation that can be written in the form: a a a n n b The coefficients a i and the constant b can be real or comple
COMP 181. Prelude. Intermediate representations. Today. High-level IR. Types of IRs. Intermediate representations and code generation
 Prelude COMP 181 Lecture 14 Intermediate representations and code generation October 19, 2006 Who is Seth Lloyd? Professor of mechanical engineering at MIT, pioneer in quantum computing Article in Nature:
Prelude COMP 181 Lecture 14 Intermediate representations and code generation October 19, 2006 Who is Seth Lloyd? Professor of mechanical engineering at MIT, pioneer in quantum computing Article in Nature:
CSci 4223 Principles of Programming Languages
 Review CSci 4223 Prciples of Programmg Languages Lecture 8 Features learned: functions, tuples, lists, let expressions, options, records, datatypes, case expressions, type synonyms, pattern matchg, exceptions
Review CSci 4223 Prciples of Programmg Languages Lecture 8 Features learned: functions, tuples, lists, let expressions, options, records, datatypes, case expressions, type synonyms, pattern matchg, exceptions
Recap: ML s Holy Trinity
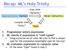 Recap: ML s Holy Trinity Expressions (Syntax) Exec-time Dynamic Values (Semantics) Compile-time Static Types 1. Programmer enters expression 2. ML checks if expression is well-typed Using a precise set
Recap: ML s Holy Trinity Expressions (Syntax) Exec-time Dynamic Values (Semantics) Compile-time Static Types 1. Programmer enters expression 2. ML checks if expression is well-typed Using a precise set
Factorial. Next. Factorial. How does it execute? Tail recursion. How does it execute? More on recursion. Higher-order functions
 Next More on recursion Higher-order functions takg and returng functions Factorial let rec fact n = Along the way, will see map and fold 1 2 Factorial let rec fact n = if n
Next More on recursion Higher-order functions takg and returng functions Factorial let rec fact n = Along the way, will see map and fold 1 2 Factorial let rec fact n = if n
A Programming Language. A different language g is a different vision of life. CSE 130 : Spring Two variables. L1: x++; y--; (y=0)?
 CSE 130 : Spring 2010 Programming Languages Lecture 1: Hello, world. Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego A Programming Language Two variables x,y Three operations x++ x-- (x=0)? L1:L2; L1: x++; y--; (y=0)?l2:l1
CSE 130 : Spring 2010 Programming Languages Lecture 1: Hello, world. Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego A Programming Language Two variables x,y Three operations x++ x-- (x=0)? L1:L2; L1: x++; y--; (y=0)?l2:l1
Next. Tail Recursion: Factorial. How does it execute? Tail recursion. Tail recursive factorial. Tail recursive factorial.
 Next Tail Recursion: Factorial More on recursion Higher-order functions takg and returng functions Along the way, will see map and fold let rec fact n = if n
Next Tail Recursion: Factorial More on recursion Higher-order functions takg and returng functions Along the way, will see map and fold let rec fact n = if n
Simple example. Analysis of programs with pointers. Program model. Points-to relation
 Simple eample Analsis of programs with pointers := 5 ptr := & *ptr := 9 := program S1 S2 S3 S4 What are the defs and uses of in this program? Problem: just looking at variable names will not give ou the
Simple eample Analsis of programs with pointers := 5 ptr := & *ptr := 9 := program S1 S2 S3 S4 What are the defs and uses of in this program? Problem: just looking at variable names will not give ou the
type environment updated subtype sound
 #1 Type Checkg #2 One-Slide Summary A type environment gives types for free variables. You typecheck a let-body with an environment that has been updated to conta the new let-variable. If an object of
#1 Type Checkg #2 One-Slide Summary A type environment gives types for free variables. You typecheck a let-body with an environment that has been updated to conta the new let-variable. If an object of
Lambda Calculus.
 Lambda Calculus Oded Padon & Mooly Sagiv (original slides by Kathleen Fisher, John Mitchell, Shachar Itzhaky, S. Tanimoto, Stephen A. Edwards) Benjamin Pierce Types and Programming Languages http://www.cs.cornell.edu/courses/cs3110/2008fa/recitations/rec26.html
Lambda Calculus Oded Padon & Mooly Sagiv (original slides by Kathleen Fisher, John Mitchell, Shachar Itzhaky, S. Tanimoto, Stephen A. Edwards) Benjamin Pierce Types and Programming Languages http://www.cs.cornell.edu/courses/cs3110/2008fa/recitations/rec26.html
Fall Lecture 3 September 4. Stephen Brookes
 15-150 Fall 2018 Lecture 3 September 4 Stephen Brookes Today A brief remark about equality types Using patterns Specifying what a function does equality in ML e1 = e2 Only for expressions whose type is
15-150 Fall 2018 Lecture 3 September 4 Stephen Brookes Today A brief remark about equality types Using patterns Specifying what a function does equality in ML e1 = e2 Only for expressions whose type is
Announcements. CSCI 334: Principles of Programming Languages. Lecture 19: C++
 Announcements CSCI 4: Principles of Programming Languages Lecture 19: C++ HW8 pro tip: the HW7 solutions have a complete, correct implementation of the CPS version of bubble sort in SML. All ou need to
Announcements CSCI 4: Principles of Programming Languages Lecture 19: C++ HW8 pro tip: the HW7 solutions have a complete, correct implementation of the CPS version of bubble sort in SML. All ou need to
CSE341: Programming Languages Lecture 11 Type Inference. Dan Grossman Spring 2016
 CSE341: Programming Languages Lecture 11 Type Inference Dan Grossman Spring 2016 Type-checking (Static) type-checking can reject a program before it runs to prevent the possibility of some errors A feature
CSE341: Programming Languages Lecture 11 Type Inference Dan Grossman Spring 2016 Type-checking (Static) type-checking can reject a program before it runs to prevent the possibility of some errors A feature
CSE 130 [Winter 2014] Programming Languages
![CSE 130 [Winter 2014] Programming Languages CSE 130 [Winter 2014] Programming Languages](/thumbs/85/92581372.jpg) CSE 130 [Winter 2014] Programming Languages Introduction to OCaml (Continued) Ravi Chugh! Jan 14 Announcements HW #1 due Mon Jan 20 Post questions/discussion to Piazza Check Piazza for TA/Tutor lab hours
CSE 130 [Winter 2014] Programming Languages Introduction to OCaml (Continued) Ravi Chugh! Jan 14 Announcements HW #1 due Mon Jan 20 Post questions/discussion to Piazza Check Piazza for TA/Tutor lab hours
Unit I - Chapter 3 Polynomial Functions 3.1 Characteristics of Polynomial Functions
 Math 3200 Unit I Ch 3 - Polnomial Functions 1 Unit I - Chapter 3 Polnomial Functions 3.1 Characteristics of Polnomial Functions Goal: To Understand some Basic Features of Polnomial functions: Continuous
Math 3200 Unit I Ch 3 - Polnomial Functions 1 Unit I - Chapter 3 Polnomial Functions 3.1 Characteristics of Polnomial Functions Goal: To Understand some Basic Features of Polnomial functions: Continuous
Programming Languages. Programming with λ-calculus. Lecture 11: Type Systems. Special Hour to discuss HW? if-then-else int
 CSE 230: Winter 2010 Principles of Programming Languages Lecture 11: Type Systems News New HW up soon Special Hour to discuss HW? Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego Programming with λ-calculus Encode: bool if-then-else
CSE 230: Winter 2010 Principles of Programming Languages Lecture 11: Type Systems News New HW up soon Special Hour to discuss HW? Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego Programming with λ-calculus Encode: bool if-then-else
CSE 341 Section 5. Winter 2018
 CSE 341 Section 5 Winter 2018 Midterm Review! Variable Bindings, Shadowing, Let Expressions Boolean, Comparison and Arithmetic Operations Equality Types Types, Datatypes, Type synonyms Tuples, Records
CSE 341 Section 5 Winter 2018 Midterm Review! Variable Bindings, Shadowing, Let Expressions Boolean, Comparison and Arithmetic Operations Equality Types Types, Datatypes, Type synonyms Tuples, Records
Programming Languages Lecture 15: Recursive Types & Subtyping
 CSE 230: Winter 2008 Principles of Programming Languages Lecture 15: Recursive Types & Subtyping Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego News? Formalize first-order type systems Simple types (integers and booleans)
CSE 230: Winter 2008 Principles of Programming Languages Lecture 15: Recursive Types & Subtyping Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego News? Formalize first-order type systems Simple types (integers and booleans)
Module Mechanisms CS412/413. Modules + abstract types. Abstract types. Multiple Implementations. How to type-check?
 CS412/413 Introduction to Compilers and Translators Andrew Mers Cornell Universit Lecture 19: ADT mechanisms 10 March 00 Module Mechanisms Last time: modules, was to implement ADTs Module collection of
CS412/413 Introduction to Compilers and Translators Andrew Mers Cornell Universit Lecture 19: ADT mechanisms 10 March 00 Module Mechanisms Last time: modules, was to implement ADTs Module collection of
EECS1022 Winter 2018 Additional Notes Tracing Point, PointCollector, and PointCollectorTester
 EECS1022 Winter 2018 Additional Notes Tracing, Collector, and CollectorTester Chen-Wei Wang Contents 1 Class 1 2 Class Collector 2 Class CollectorTester 7 1 Class 1 class { 2 double ; double ; 4 (double
EECS1022 Winter 2018 Additional Notes Tracing, Collector, and CollectorTester Chen-Wei Wang Contents 1 Class 1 2 Class Collector 2 Class CollectorTester 7 1 Class 1 class { 2 double ; double ; 4 (double
Computer Science CSC324 Wednesday February 13, Homework Assignment #3 Due: Thursday February 28, 2013, by 10 p.m.
 Computer Science CSC324 Wednesday February 13, 2013 St. George Campus University of Toronto Homework Assignment #3 Due: Thursday February 28, 2013, by 10 p.m. Silent Policy A silent policy takes effect
Computer Science CSC324 Wednesday February 13, 2013 St. George Campus University of Toronto Homework Assignment #3 Due: Thursday February 28, 2013, by 10 p.m. Silent Policy A silent policy takes effect
Semantics. Names. Binding Time
 /24/ CSE 3302 Programming Languages Semantics Chengkai Li, Weimin He Spring Names Names: identif language entities variables, procedures, functions, constants, data tpes, Attributes: properties of names
/24/ CSE 3302 Programming Languages Semantics Chengkai Li, Weimin He Spring Names Names: identif language entities variables, procedures, functions, constants, data tpes, Attributes: properties of names
To figure this out we need a more precise understanding of how ML works
 Announcements: What are the following numbers: 74/2/70/17 (2:30,2:30,3:35,7:30) PS2 due Thursday 9/20 11:59PM Guest lecture on Tuesday 9/25 o No RDZ office hours next Friday, I am on travel A brief comment
Announcements: What are the following numbers: 74/2/70/17 (2:30,2:30,3:35,7:30) PS2 due Thursday 9/20 11:59PM Guest lecture on Tuesday 9/25 o No RDZ office hours next Friday, I am on travel A brief comment
Scope, Functions, and Storage Management
 Scope, Functions, and Storage Management Implementing Functions and Blocks cs3723 1 Simplified Machine Model (Compare To List Abstract Machine) Registers Code Data Program Counter (current instruction)
Scope, Functions, and Storage Management Implementing Functions and Blocks cs3723 1 Simplified Machine Model (Compare To List Abstract Machine) Registers Code Data Program Counter (current instruction)
Programming in C. main. Level 2. Level 2 Level 2. Level 3 Level 3
 Programming in C main Level 2 Level 2 Level 2 Level 3 Level 3 1 Programmer-Defined Functions Modularize with building blocks of programs Divide and Conquer Construct a program from smaller pieces or components
Programming in C main Level 2 Level 2 Level 2 Level 3 Level 3 1 Programmer-Defined Functions Modularize with building blocks of programs Divide and Conquer Construct a program from smaller pieces or components
Chapter 9: Rational Equations and Functions
 Chapter 9: Rational Equations and Functions Chapter 9: Rational Equations and Functions Assignment Sheet Date Topic Assignment Completed 9.: Inverse and Joint Variation pg. 57 # - 4 odd, 54 9..: Graphing
Chapter 9: Rational Equations and Functions Chapter 9: Rational Equations and Functions Assignment Sheet Date Topic Assignment Completed 9.: Inverse and Joint Variation pg. 57 # - 4 odd, 54 9..: Graphing
1.5 LIMITS. The Limit of a Function
 60040_005.qd /5/05 :0 PM Page 49 SECTION.5 Limits 49.5 LIMITS Find its of functions graphicall and numericall. Use the properties of its to evaluate its of functions. Use different analtic techniques to
60040_005.qd /5/05 :0 PM Page 49 SECTION.5 Limits 49.5 LIMITS Find its of functions graphicall and numericall. Use the properties of its to evaluate its of functions. Use different analtic techniques to
Programming Languages. So why study PL? A Programming Language. A different language is a different vision of life. CSE 130 : Fall 2015
 CSE 130 : Fall 2015 Programming Languages Lecture 1: Hello, World! Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego A Programming Language So why study PL? Two variables x, y Three operations x++ x-- (x=0)? L1:L2; L1: x++; y--;
CSE 130 : Fall 2015 Programming Languages Lecture 1: Hello, World! Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego A Programming Language So why study PL? Two variables x, y Three operations x++ x-- (x=0)? L1:L2; L1: x++; y--;
Programming Languages. So why study PL? A Programming Language. A different language is a different vision of life. CSE 130 : Spring 2015
 CSE 130 : Spring 2015 Programming Languages Lecture 1: Hello, World Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego A Programming Language So why study PL? Two variables x, y Three operations x++ x-- (x=0)? L1:L2; L1: x++;
CSE 130 : Spring 2015 Programming Languages Lecture 1: Hello, World Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego A Programming Language So why study PL? Two variables x, y Three operations x++ x-- (x=0)? L1:L2; L1: x++;
Determine Whether Two Functions Are Equivalent. Determine whether the functions in each pair are equivalent by. and g (x) 5 x 2
 .1 Functions and Equivalent Algebraic Epressions On September, 1999, the Mars Climate Orbiter crashed on its first da of orbit. Two scientific groups used different measurement sstems (Imperial and metric)
.1 Functions and Equivalent Algebraic Epressions On September, 1999, the Mars Climate Orbiter crashed on its first da of orbit. Two scientific groups used different measurement sstems (Imperial and metric)
B + -trees. Kerttu Pollari-Malmi
 B + -trees Kerttu Pollari-Malmi This tet is based partl on the course tet book b Cormen and partl on the old lecture slides written b Matti Luukkainen and Matti Nkänen. 1 Introduction At first, read the
B + -trees Kerttu Pollari-Malmi This tet is based partl on the course tet book b Cormen and partl on the old lecture slides written b Matti Luukkainen and Matti Nkänen. 1 Introduction At first, read the
CHECK Your Understanding
 CHECK Your Understanding. State the domain and range of each relation. Then determine whether the relation is a function, and justif our answer.. a) e) 5(, ), (, 9), (, 7), (, 5), (, ) 5 5 f) 55. State
CHECK Your Understanding. State the domain and range of each relation. Then determine whether the relation is a function, and justif our answer.. a) e) 5(, ), (, 9), (, 7), (, 5), (, ) 5 5 f) 55. State
Scope and Introduction to Functional Languages. Review and Finish Scoping. Announcements. Assignment 3 due Thu at 11:55pm. Website has SML resources
 Scope and Introduction to Functional Languages Prof. Evan Chang Meeting 7, CSCI 3155, Fall 2009 Announcements Assignment 3 due Thu at 11:55pm Submit in pairs Website has SML resources Text: Harper, Programming
Scope and Introduction to Functional Languages Prof. Evan Chang Meeting 7, CSCI 3155, Fall 2009 Announcements Assignment 3 due Thu at 11:55pm Submit in pairs Website has SML resources Text: Harper, Programming
Section 1.4 Limits involving infinity
 Section. Limits involving infinit (/3/08) Overview: In later chapters we will need notation and terminolog to describe the behavior of functions in cases where the variable or the value of the function
Section. Limits involving infinit (/3/08) Overview: In later chapters we will need notation and terminolog to describe the behavior of functions in cases where the variable or the value of the function
Dialects of ML. CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages. Dialects of ML (cont.) Features of ML. Functional Languages. Features of ML (cont.
 CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages OCaml 1 Functional Programming Dialects of ML ML (Meta Language) Univ. of Edinburgh,1973 Part of a theorem proving system LCF The Logic of Computable Functions
CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages OCaml 1 Functional Programming Dialects of ML ML (Meta Language) Univ. of Edinburgh,1973 Part of a theorem proving system LCF The Logic of Computable Functions
