COMP 110/L Lecture 5. Kyle Dewey
|
|
|
- Lesley Parrish
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 COMP 110/L Lecture 5 Kyle Dewey
2 Outlines Methods Defining methods Calling methods
3 Methods
4 Motivation
5 Motivation Input Program Output -Start off with some high-level motivation -You write your program, and it s one giant block -This is difficult to reason about
6 Motivation -Simpler approach: write a bunch of smaller programs, and stitch them together -Each program is a lot easier to reason about than the one big program -If we re careful about how these different pieces interact with each other, then we only ever have to think about the small programs Input Subprogram 1 Subprogram 2 Subprogram 3 Subprogram 4 Output
7 Code Reuse
8 Code Reuse System.out.println(...) -You re already familiar with these
9 Code Reuse System.out.println(...) nextint() -You re already familiar with these
10 Code Reuse System.out.println(...) nextint() nextlong() -You re already familiar with these
11 Code Reuse System.out.println(...) nextint() nextlong() nextdouble() -You re already familiar with these
12 Code Reuse System.out.println(...) nextint() nextlong() nextdouble() You have used all of these multiple times. -You re already familiar with these, and you ve used them a bunch of times
13 Code Reuse System.out.println(...) nextint() nextlong() nextdouble() You have used all of these multiple times. These are all methods. -You re already familiar with these, and you ve used them a bunch of times
14 Methods Distinct subprograms.
15 Methods Distinct subprograms. Input Subprogram 1 Subprogram 2 Subprogram 3 Subprogram 4 Output -Taking that illustration from before...
16 Methods Distinct subprograms. Input Method 1 Method 2 Method 3 Method 4 Output -...each one of those subprograms is a method
17 Method Terminology We can define a method Make it available to the rest of the program We can call a method Execute the subprogram
18 Method Anatomy Methods take some number of inputs (can be 0). Methods may produce an output.
19 Method Anatomy Methods take some number of inputs (can be 0). Methods may produce an output. Input? Method Output?
20 Method Anatomy Methods take some number of inputs (can be 0). Methods may produce an output. Input? Method Output? System.out.println( Hello );
21 Method Anatomy Methods take some number of inputs (can be 0). Methods may produce an output. Input? Method Output? System.out.println( Hello ); One input, no outputs (cannot assign to a variable).
22 Method Anatomy Methods take some number of inputs (can be 0). Methods may produce an output. Input? Method Output? System.out.println( Hello ); One input, no outputs (cannot assign to a variable). Math.pow(2, 3);
23 Method Anatomy Methods take some number of inputs (can be 0). Methods may produce an output. Input? Method Output? System.out.println( Hello ); One input, no outputs (cannot assign to a variable). Math.pow(2, 3); Two inputs, one output.
24 inputscanner.nextint();
25 inputscanner.nextint(); No inputs, one output.
26 inputscanner.nextint(); No inputs, one output. System.out.print( Goodbye );
27 inputscanner.nextint(); No inputs, one output. System.out.print( Goodbye ); One input, no outputs (cannot assign to a variable)
28 inputscanner.nextint(); No inputs, one output. System.out.print( Goodbye ); One input, no outputs (cannot assign to a variable) inputscanner.nextlong();
29 inputscanner.nextint(); No inputs, one output. System.out.print( Goodbye ); One input, no outputs (cannot assign to a variable) inputscanner.nextlong(); No inputs, one output.
30 inputscanner.nextint(); No inputs, one output. System.out.print( Goodbye ); One input, no outputs (cannot assign to a variable) inputscanner.nextlong(); No inputs, one output. inputscanner.nextdouble();
31 inputscanner.nextint(); No inputs, one output. System.out.print( Goodbye ); One input, no outputs (cannot assign to a variable) inputscanner.nextlong(); No inputs, one output. inputscanner.nextdouble(); No inputs, one output.
32 Defining a Method Easiest to see with real code. Example: Return42.java -The `return` reserved word says that the method should end and return with a given value at this point
33 Example: ReturnParameter.java
34 Example: MultParameters1.java
35 Example: MultParameters2.java
36 Example: MultParameters3.java
37 Method Definition General Form public static returntype methodname(parameter_list) {... return expression; }
38 Method Definition General Form public static Magic returntype methodname(parameter_list) {... return expression; }
39 Method Definition General Form public static returntype Magic Type of value produced methodname(parameter_list) {... return expression; }
40 Method Definition General Form public static returntype Magic Type of value produced methodname(parameter_list) {... return expression; } Name given to method; same naming rules as variables
41 Method Definition General Form public static returntype Magic Type of value produced methodname(parameter_list) {... return expression; Inputs to } method (int x) Name given to method; same naming rules as variables
42 Method Definition General Form public static returntype Magic Type of value produced methodname(parameter_list) {... return expression; Inputs to } method Method ends (int x) Name given to method; same naming rules as variables here, evaluates expression, and produces its result
43 Methods which Produce no Values Methods which produce no values have a void return type Example: ReturnNothing.java
44 main Method main is just another method. main serves as the entry point to your program.
45 -main s return type is void - it produces no value (doesn t return anything) -String[] is actually a type, so args is a parameter -Later on we ll get into what the type `String[]` is (not the same as just String), along with what this parameter to main holds main Method main is just another method. main serves as the entry point to your program. public static void main(string[] args) {... }
46 Calling Methods Execution enters the method calls The method is executed The method returns to wherever it was called from
47 Calling Methods Execution enters the method calls The method is executed The method returns to wherever it was called from Method 1 Method 2
48 Calling Methods Execution enters the method calls The method is executed The method returns to wherever it was called from Execution Method 1 Method 2 -Initially, execution is in method 1
49 Calling Methods Execution enters the method calls The method is executed The method returns to wherever it was called from Execution Calls Method 1 Method 2 -Method 1 then calls method 2
50 Calling Methods Execution enters the method calls The method is executed The method returns to wherever it was called from Calls Execution Method 1 Method 2 -Execution transfers to method 2 as a result of the call
51 Calling Methods Execution enters the method calls The method is executed The method returns to wherever it was called from Execution Calls Method 1 Method 2 Returns -Method 2 eventually completes, returning back to method 1
52 Calling Methods Execution enters the method calls The method is executed The method returns to wherever it was called from Execution Calls Method 1 Method 2 Returns -Once the return is complete, execution resumes back in method 1 wherever it left off
COMP 110/L Lecture 4. Kyle Dewey
 COMP 110/L Lecture 4 Kyle Dewey Outline New types: long and double Reading in with Scanner Performing operations on them How they interact with each other and other types Exponentiation with Math.pow()
COMP 110/L Lecture 4 Kyle Dewey Outline New types: long and double Reading in with Scanner Performing operations on them How they interact with each other and other types Exponentiation with Math.pow()
AP Computer Science Unit 1. Writing Programs Using BlueJ
 AP Computer Science Unit 1. Writing Programs Using BlueJ 1. Open up BlueJ. Click on the Project menu and select New Project. You should see the window on the right. Navigate to wherever you plan to save
AP Computer Science Unit 1. Writing Programs Using BlueJ 1. Open up BlueJ. Click on the Project menu and select New Project. You should see the window on the right. Navigate to wherever you plan to save
AP Computer Science Unit 1. Writing Programs Using BlueJ
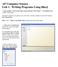 AP Computer Science Unit 1. Writing Programs Using BlueJ 1. Open up BlueJ. Click on the Project menu and select New Project. You should see the window on the right. Navigate to wherever you plan to save
AP Computer Science Unit 1. Writing Programs Using BlueJ 1. Open up BlueJ. Click on the Project menu and select New Project. You should see the window on the right. Navigate to wherever you plan to save
Introduction to Java Unit 1. Using BlueJ to Write Programs
 Introduction to Java Unit 1. Using BlueJ to Write Programs 1. Open up BlueJ. Click on the Project menu and select New Project. You should see the window on the right. Navigate to wherever you plan to save
Introduction to Java Unit 1. Using BlueJ to Write Programs 1. Open up BlueJ. Click on the Project menu and select New Project. You should see the window on the right. Navigate to wherever you plan to save
COMP 110/L Lecture 6. Kyle Dewey
 COMP 110/L Lecture 6 Kyle Dewey Outline Methods Variable scope Call-by-value Testing with JUnit Variable Scope Question Does this compile? public class Test { public static void main(string[] args) { int
COMP 110/L Lecture 6 Kyle Dewey Outline Methods Variable scope Call-by-value Testing with JUnit Variable Scope Question Does this compile? public class Test { public static void main(string[] args) { int
COMP 110/L Lecture 7. Kyle Dewey
 COMP 110/L Lecture 7 Kyle Dewey Outline Introduction to objects Constructors and new Instance variables Instance methods static vs. non-static Object-Oriented Programming Basic Idea The world is composed
COMP 110/L Lecture 7 Kyle Dewey Outline Introduction to objects Constructors and new Instance variables Instance methods static vs. non-static Object-Oriented Programming Basic Idea The world is composed
Notes - Recursion. A geeky definition of recursion is as follows: Recursion see Recursion.
 Notes - Recursion So far we have only learned how to solve problems iteratively using loops. We will now learn how to solve problems recursively by having a method call itself. A geeky definition of recursion
Notes - Recursion So far we have only learned how to solve problems iteratively using loops. We will now learn how to solve problems recursively by having a method call itself. A geeky definition of recursion
AP Computer Science Unit 1. Programs
 AP Computer Science Unit 1. Programs Open DrJava. Under the File menu click on New Java Class and the window to the right should appear. Fill in the information as shown and click OK. This code is generated
AP Computer Science Unit 1. Programs Open DrJava. Under the File menu click on New Java Class and the window to the right should appear. Fill in the information as shown and click OK. This code is generated
COMP-202: Foundations of Programming. Lecture 2: Java basics and our first Java program! Jackie Cheung, Winter 2016
 COMP-202: Foundations of Programming Lecture 2: Java basics and our first Java program! Jackie Cheung, Winter 2016 Learn about cutting-edge research over lunch with cool profs January 18-22, 2015 11:30
COMP-202: Foundations of Programming Lecture 2: Java basics and our first Java program! Jackie Cheung, Winter 2016 Learn about cutting-edge research over lunch with cool profs January 18-22, 2015 11:30
COMP-202 More Complex OOP
 COMP-202 More Complex OOP Defining your own types: Remember that we can define our own types/classes. These classes are objects and have attributes and behaviors You create an object or an instance of
COMP-202 More Complex OOP Defining your own types: Remember that we can define our own types/classes. These classes are objects and have attributes and behaviors You create an object or an instance of
1001ICT Introduction To Programming Lecture Notes
 1001ICT Introduction To Programming Lecture Notes School of Information and Communication Technology Griffith University Semester 2, 2015 1 2 Elements of Java Java is a popular, modern, third generation
1001ICT Introduction To Programming Lecture Notes School of Information and Communication Technology Griffith University Semester 2, 2015 1 2 Elements of Java Java is a popular, modern, third generation
4. Java Project Design, Input Methods
 4-1 4. Java Project Design, Input Methods Review and Preview You should now be fairly comfortable with creating, compiling and running simple Java projects. In this class, we continue learning new Java
4-1 4. Java Project Design, Input Methods Review and Preview You should now be fairly comfortable with creating, compiling and running simple Java projects. In this class, we continue learning new Java
Pull Lecture Materials and Open PollEv. Poll Everywhere: pollev.com/comp110. Lecture 12. else-if and while loops. Once in a while
 Pull Lecture Materials and Open PollEv Poll Everywhere: pollev.com/comp110 Lecture 12 else-if and while loops Once in a while Fall 2016 if-then-else Statements General form of an if-then-else statement:
Pull Lecture Materials and Open PollEv Poll Everywhere: pollev.com/comp110 Lecture 12 else-if and while loops Once in a while Fall 2016 if-then-else Statements General form of an if-then-else statement:
CS 177 Recitation. Week 1 Intro to Java
 CS 177 Recitation Week 1 Intro to Java Questions? Computers Computers can do really complex stuff. How? By manipulating data according to lists of instructions. Fundamentally, this is all that a computer
CS 177 Recitation Week 1 Intro to Java Questions? Computers Computers can do really complex stuff. How? By manipulating data according to lists of instructions. Fundamentally, this is all that a computer
Unit 4: Classes and Objects Notes
 Unit 4: Classes and Objects Notes AP CS A Another Data Type. So far, we have used two types of primitive variables: ints and doubles. Another data type is the boolean data type. Variables of type boolean
Unit 4: Classes and Objects Notes AP CS A Another Data Type. So far, we have used two types of primitive variables: ints and doubles. Another data type is the boolean data type. Variables of type boolean
CS125 : Introduction to Computer Science. Lecture Notes #11 Procedural Composition and Abstraction. c 2005, 2004 Jason Zych
 CS125 : Introduction to Computer Science Lecture Notes #11 Procedural Composition and Abstraction c 2005, 2004 Jason Zych 1 Lecture 11 : Procedural Composition and Abstraction Solving a problem...with
CS125 : Introduction to Computer Science Lecture Notes #11 Procedural Composition and Abstraction c 2005, 2004 Jason Zych 1 Lecture 11 : Procedural Composition and Abstraction Solving a problem...with
CSE 1223: Introduction to Computer Programming in Java Chapter 7 File I/O
 CSE 1223: Introduction to Computer Programming in Java Chapter 7 File I/O 1 Sending Output to a (Text) File import java.util.scanner; import java.io.*; public class TextFileOutputDemo1 public static void
CSE 1223: Introduction to Computer Programming in Java Chapter 7 File I/O 1 Sending Output to a (Text) File import java.util.scanner; import java.io.*; public class TextFileOutputDemo1 public static void
COMP 122/L Lecture 1. Kyle Dewey
 COMP 122/L Lecture 1 Kyle Dewey About Me I research automated testing techniques and their intersection with CS education This is my first semester at CSUN Third time teaching this content About this Class
COMP 122/L Lecture 1 Kyle Dewey About Me I research automated testing techniques and their intersection with CS education This is my first semester at CSUN Third time teaching this content About this Class
COMP-202 Unit 4: Programming With Iterations. CONTENTS: The while and for statements
 COMP-202 Unit 4: Programming With Iterations CONTENTS: The while and for statements Introduction (1) Suppose we want to write a program to be used in cash registers in stores to compute the amount of money
COMP-202 Unit 4: Programming With Iterations CONTENTS: The while and for statements Introduction (1) Suppose we want to write a program to be used in cash registers in stores to compute the amount of money
CONTENTS: What Is Programming? How a Computer Works Programming Languages Java Basics. COMP-202 Unit 1: Introduction
 CONTENTS: What Is Programming? How a Computer Works Programming Languages Java Basics COMP-202 Unit 1: Introduction Announcements Did you miss the first lecture? Come talk to me after class. If you want
CONTENTS: What Is Programming? How a Computer Works Programming Languages Java Basics COMP-202 Unit 1: Introduction Announcements Did you miss the first lecture? Come talk to me after class. If you want
COMP 110/L Lecture 13. Kyle Dewey
 COMP 110/L Lecture 13 Kyle Dewey Outline char, charat() Command-line arguments and arrays Array access Array length Array update Integer.parseInt char, charat() char Represents a single character char
COMP 110/L Lecture 13 Kyle Dewey Outline char, charat() Command-line arguments and arrays Array access Array length Array update Integer.parseInt char, charat() char Represents a single character char
Chapter 5 Methods. public class FirstMethod { public static void main(string[] args) { double x= -2.0, y; for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++ ) { y = f( x );
![Chapter 5 Methods. public class FirstMethod { public static void main(string[] args) { double x= -2.0, y; for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++ ) { y = f( x ); Chapter 5 Methods. public class FirstMethod { public static void main(string[] args) { double x= -2.0, y; for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++ ) { y = f( x );](/thumbs/82/85488895.jpg) Chapter 5 Methods Sections Pages Review Questions Programming Exercises 5.1 5.11 142 166 1 18 2 22 (evens), 30 Method Example 1. This is of a main() method using a another method, f. public class FirstMethod
Chapter 5 Methods Sections Pages Review Questions Programming Exercises 5.1 5.11 142 166 1 18 2 22 (evens), 30 Method Example 1. This is of a main() method using a another method, f. public class FirstMethod
Object Oriented Programming. Java-Lecture 1
 Object Oriented Programming Java-Lecture 1 Standard output System.out is known as the standard output object Methods to display text onto the standard output System.out.print prints text onto the screen
Object Oriented Programming Java-Lecture 1 Standard output System.out is known as the standard output object Methods to display text onto the standard output System.out.print prints text onto the screen
Visual Programming. Lecture 2: More types, Methods, Conditionals
 Visual Programming Lecture 2: More types, Methods, Conditionals Mahmoud El-Gayyar elgayyar@ci.suez.edu.eg Outline Lecture 1 Review More types Methods Conditionals 2 Outline Lecture 1 Review More types
Visual Programming Lecture 2: More types, Methods, Conditionals Mahmoud El-Gayyar elgayyar@ci.suez.edu.eg Outline Lecture 1 Review More types Methods Conditionals 2 Outline Lecture 1 Review More types
CONTENTS: While loops Class (static) variables and constants Top Down Programming For loops Nested Loops
 COMP-202 Unit 4: Programming with Iterations Doing the same thing again and again and again and again and again and again and again and again and again... CONTENTS: While loops Class (static) variables
COMP-202 Unit 4: Programming with Iterations Doing the same thing again and again and again and again and again and again and again and again and again... CONTENTS: While loops Class (static) variables
Overview. Lab 5 Methods and Parameters
 Lab 5 Methods and Parameters Overview At this point in the course, you should have a set of skills which allow you to create functionality at the level of using control structures like if statements and
Lab 5 Methods and Parameters Overview At this point in the course, you should have a set of skills which allow you to create functionality at the level of using control structures like if statements and
Data Structure and Programming Languages
 204700 Data Structure and Programming Languages Jakarin Chawachat From: http://ocw.mit.edu/courses/electrical-engineering-and-computerscience/6-092-introduction-to-programming-in-java-january-iap-2010/index.htm
204700 Data Structure and Programming Languages Jakarin Chawachat From: http://ocw.mit.edu/courses/electrical-engineering-and-computerscience/6-092-introduction-to-programming-in-java-january-iap-2010/index.htm
ing execution. That way, new results can be computed each time the Class The Scanner
 ing execution. That way, new results can be computed each time the run, depending on the data that is entered. The Scanner Class The Scanner class, which is part of the standard Java class provides convenient
ing execution. That way, new results can be computed each time the run, depending on the data that is entered. The Scanner Class The Scanner class, which is part of the standard Java class provides convenient
Chapter 12 Supplement: Recursion with Java 1.5. Mr. Dave Clausen La Cañada High School
 Chapter 12 Supplement: Recursion with Java 1.5 La Cañada High School Recursion: Definitions Recursion The process of a subprogram (method) calling itself. A clearly defined stopping state must exist. The
Chapter 12 Supplement: Recursion with Java 1.5 La Cañada High School Recursion: Definitions Recursion The process of a subprogram (method) calling itself. A clearly defined stopping state must exist. The
Building Java Programs. Chapter 2: Primitive Data and Definite Loops
 Building Java Programs Chapter 2: Primitive Data and Definite Loops Copyright 2008 2006 by Pearson Education 1 Lecture outline data concepts Primitive types: int, double, char (for now) Expressions: operators,
Building Java Programs Chapter 2: Primitive Data and Definite Loops Copyright 2008 2006 by Pearson Education 1 Lecture outline data concepts Primitive types: int, double, char (for now) Expressions: operators,
Static Methods. Why use methods?
 Static Methods A method is just a collection of code. They are also called functions or procedures. It provides a way to break a larger program up into smaller, reusable chunks. This also has the benefit
Static Methods A method is just a collection of code. They are also called functions or procedures. It provides a way to break a larger program up into smaller, reusable chunks. This also has the benefit
Lecture 1 - Introduction (Class Notes)
 Lecture 1 - Introduction (Class Notes) Outline: How does a computer work? Very brief! What is programming? The evolution of programming languages Generations of programming languages Compiled vs. Interpreted
Lecture 1 - Introduction (Class Notes) Outline: How does a computer work? Very brief! What is programming? The evolution of programming languages Generations of programming languages Compiled vs. Interpreted
COMP-202: Foundations of Programming. Lecture 4: Methods Jackie Cheung, Winter 2016
 COMP-202: Foundations of Programming Lecture 4: Methods Jackie Cheung, Winter 2016 Announcements Quiz 1 postponed: Due Jan 26 at 11:59pm Assignment 1 postponed: Due on Feb 1 at 11:59pm 2 Review What is
COMP-202: Foundations of Programming Lecture 4: Methods Jackie Cheung, Winter 2016 Announcements Quiz 1 postponed: Due Jan 26 at 11:59pm Assignment 1 postponed: Due on Feb 1 at 11:59pm 2 Review What is
The NetBeans IDE is a big file --- a minimum of around 30 MB. After you have downloaded the file, simply execute the file to install the software.
 Introduction to Netbeans This document is a brief introduction to writing and compiling a program using the NetBeans Integrated Development Environment (IDE). An IDE is a program that automates and makes
Introduction to Netbeans This document is a brief introduction to writing and compiling a program using the NetBeans Integrated Development Environment (IDE). An IDE is a program that automates and makes
More types, Methods, Conditionals. ARCS Lab.
 More types, Methods, Conditionals ARCS Lab. Division Division ( / ) operates differently on integers and on doubles! Example double a = 5.0/2.0; 0; // a = 2.5 int b = 4/2; // b = 2 int c = 5/2; // c =
More types, Methods, Conditionals ARCS Lab. Division Division ( / ) operates differently on integers and on doubles! Example double a = 5.0/2.0; 0; // a = 2.5 int b = 4/2; // b = 2 int c = 5/2; // c =
COMP-202: Foundations of Programming. Lecture 2: Java basics and our first Java program! Jackie Cheung, Winter 2015
 COMP-202: Foundations of Programming Lecture 2: Java basics and our first Java program! Jackie Cheung, Winter 2015 Assignment Due Date Assignment 1 is now due on Tuesday, Jan 20 th, 11:59pm. Quiz 1 is
COMP-202: Foundations of Programming Lecture 2: Java basics and our first Java program! Jackie Cheung, Winter 2015 Assignment Due Date Assignment 1 is now due on Tuesday, Jan 20 th, 11:59pm. Quiz 1 is
Mobile App:IT. Methods & Classes
 Mobile App:IT Methods & Classes WHAT IS A METHOD? - A method is a set of code which is referred to by name and can be called (invoked) at any point in a program simply by utilizing the method's name. -
Mobile App:IT Methods & Classes WHAT IS A METHOD? - A method is a set of code which is referred to by name and can be called (invoked) at any point in a program simply by utilizing the method's name. -
Programming with Java
 Programming with Java Variables and Output Statement Lecture 03 First stage Software Engineering Dep. Saman M. Omer 2017-2018 Objectives ü Declare and assign values to variable ü How to use eclipse ü What
Programming with Java Variables and Output Statement Lecture 03 First stage Software Engineering Dep. Saman M. Omer 2017-2018 Objectives ü Declare and assign values to variable ü How to use eclipse ü What
CS 112 Introduction to Programming
 CS 112 Introduction to Programming Conditional Statements Boolean Expressions and Methods Yang (Richard) Yang Computer Science Department Yale University 308A Watson, Phone: 432-6400 Email: yry@cs.yale.edu
CS 112 Introduction to Programming Conditional Statements Boolean Expressions and Methods Yang (Richard) Yang Computer Science Department Yale University 308A Watson, Phone: 432-6400 Email: yry@cs.yale.edu
CS 112 Introduction to Programming
 CS 112 Introduction to Programming Conditional Statements Boolean Expressions and Methods Yang (Richard) Yang Computer Science Department Yale University 308A Watson, Phone: 432-6400 Email: yry@cs.yale.edu
CS 112 Introduction to Programming Conditional Statements Boolean Expressions and Methods Yang (Richard) Yang Computer Science Department Yale University 308A Watson, Phone: 432-6400 Email: yry@cs.yale.edu
Midterms Save the Dates!
 University of British Columbia CPSC 111, Intro to Computation Alan J. Hu (Using the Scanner and String Classes) Anatomy of a Java Program Readings This Week s Reading: Ch 3.1-3.8 (Major conceptual jump
University of British Columbia CPSC 111, Intro to Computation Alan J. Hu (Using the Scanner and String Classes) Anatomy of a Java Program Readings This Week s Reading: Ch 3.1-3.8 (Major conceptual jump
A token is a sequence of characters not including any whitespace.
 Scanner A Scanner object reads from an input source (keyboard, file, String, etc) next() returns the next token as a String nextint() returns the next token as an int nextdouble() returns the next token
Scanner A Scanner object reads from an input source (keyboard, file, String, etc) next() returns the next token as a String nextint() returns the next token as an int nextdouble() returns the next token
Controls Structure for Repetition
 Controls Structure for Repetition So far we have looked at the if statement, a control structure that allows us to execute different pieces of code based on certain conditions. However, the true power
Controls Structure for Repetition So far we have looked at the if statement, a control structure that allows us to execute different pieces of code based on certain conditions. However, the true power
Data Structure and Programming Languages
 204700 Data Structure and Programming Languages Jakarin Chawachat From: http://ocw.mit.edu/courses/electrical-engineering-and-computerscience/6-092-introduction-to-programming-in-java-january-iap-2010/index.htm
204700 Data Structure and Programming Languages Jakarin Chawachat From: http://ocw.mit.edu/courses/electrical-engineering-and-computerscience/6-092-introduction-to-programming-in-java-january-iap-2010/index.htm
Research Group. 2: More types, Methods, Conditionals
 Research Group 2: More types, Methods, Conditionals Outline Lecture 1 Review More types Methods Conditionals 2 Types Kinds of values that can be stored and manipulated. boolean: Truth value (true or false).
Research Group 2: More types, Methods, Conditionals Outline Lecture 1 Review More types Methods Conditionals 2 Types Kinds of values that can be stored and manipulated. boolean: Truth value (true or false).
CS125 : Introduction to Computer Science. Lecture Notes #4 Type Checking, Input/Output, and Programming Style
 CS125 : Introduction to Computer Science Lecture Notes #4 Type Checking, Input/Output, and Programming Style c 2005, 2004, 2002, 2001, 2000 Jason Zych 1 Lecture 4 : Type Checking, Input/Output, and Programming
CS125 : Introduction to Computer Science Lecture Notes #4 Type Checking, Input/Output, and Programming Style c 2005, 2004, 2002, 2001, 2000 Jason Zych 1 Lecture 4 : Type Checking, Input/Output, and Programming
CS 177 Week 5 Recitation Slides. Loops
 CS 177 Week 5 Recitation Slides Loops 1 Announcements Project 1 due tonight at 9PM because of evac. Project 2 is posted and is due on Oct. 8th 9pm Exam 1 Wednesday Sept 30 6:30 7:20 PM Please see class
CS 177 Week 5 Recitation Slides Loops 1 Announcements Project 1 due tonight at 9PM because of evac. Project 2 is posted and is due on Oct. 8th 9pm Exam 1 Wednesday Sept 30 6:30 7:20 PM Please see class
Chapter 5: Methods. by Tony Gaddis. Starting Out with Java: From Control Structures through Objects. Fourth Edition
 Chapter 5: Methods Starting Out with Java: From Control Structures through Objects Fourth Edition by Tony Gaddis Addison Wesley is an imprint of 2010 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved. Reading
Chapter 5: Methods Starting Out with Java: From Control Structures through Objects Fourth Edition by Tony Gaddis Addison Wesley is an imprint of 2010 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved. Reading
Warm up question. 2)Which of the following operators are defined on a half integer? Which of the following would it be useful to write as behaviors?
 Warm up question Suppose we have defined a class called half-integer The point of the class is to be able to store regular integers and also half integers (i.e. 3.5) 1)What would be a good way to represent
Warm up question Suppose we have defined a class called half-integer The point of the class is to be able to store regular integers and also half integers (i.e. 3.5) 1)What would be a good way to represent
ALICE: An introduction to progamming
 ALICE: An introduction to progamming What is Computer Science? Computer Science Do you know the difference between ICT and Computer Science? Any suggestions as to what jobs you could do if you were a Computer
ALICE: An introduction to progamming What is Computer Science? Computer Science Do you know the difference between ICT and Computer Science? Any suggestions as to what jobs you could do if you were a Computer
CS 106 Introduction to Computer Science I
 CS 106 Introduction to Computer Science I 06 / 10 / 2015 Instructor: Michael Eckmann Today s Topics Questions / comments? Method terminology and Programmer defined methods Michael Eckmann - Skidmore College
CS 106 Introduction to Computer Science I 06 / 10 / 2015 Instructor: Michael Eckmann Today s Topics Questions / comments? Method terminology and Programmer defined methods Michael Eckmann - Skidmore College
COMP-202 Unit 4: Programming with Iterations
 COMP-202 Unit 4: Programming with Iterations Doing the same thing again and again and again and again and again and again and again and again and again... CONTENTS: While loops Class (static) variables
COMP-202 Unit 4: Programming with Iterations Doing the same thing again and again and again and again and again and again and again and again and again... CONTENTS: While loops Class (static) variables
Important Java terminology
 1 Important Java terminology The information we manage in a Java program is either represented as primitive data or as objects. Primitive data פרימיטיביים) (נתונים include common, fundamental values as
1 Important Java terminology The information we manage in a Java program is either represented as primitive data or as objects. Primitive data פרימיטיביים) (נתונים include common, fundamental values as
Static methods. Not actually a valid Java static method. Fundamentals of Computer Science Keith Vertanen
 Static methods http://xkcd.com/221/ Not actually a valid Java static method Fundamentals of Computer Science Keith Vertanen One big main(): Programs thus far public class DiceRolling public static void
Static methods http://xkcd.com/221/ Not actually a valid Java static method Fundamentals of Computer Science Keith Vertanen One big main(): Programs thus far public class DiceRolling public static void
Wentworth Institute of Technology. Engineering & Technology WIT COMP1000. Java Basics
 WIT COMP1000 Java Basics Java Origins Java was developed by James Gosling at Sun Microsystems in the early 1990s It was derived largely from the C++ programming language with several enhancements Java
WIT COMP1000 Java Basics Java Origins Java was developed by James Gosling at Sun Microsystems in the early 1990s It was derived largely from the C++ programming language with several enhancements Java
CSE 143 Lecture 10. Recursion
 CSE 143 Lecture 10 Recursion slides created by Marty Stepp and Alyssa Harding http://www.cs.washington.edu/143/ Recursion Iteration: a programming technique in which you describe actions to be repeated
CSE 143 Lecture 10 Recursion slides created by Marty Stepp and Alyssa Harding http://www.cs.washington.edu/143/ Recursion Iteration: a programming technique in which you describe actions to be repeated
Repe$$on CSC 121 Fall 2015 Howard Rosenthal
 Repe$$on CSC 121 Fall 2015 Howard Rosenthal Lesson Goals Learn the following three repetition methods, their similarities and differences, and how to avoid common errors when using them: while do-while
Repe$$on CSC 121 Fall 2015 Howard Rosenthal Lesson Goals Learn the following three repetition methods, their similarities and differences, and how to avoid common errors when using them: while do-while
Module - 3 Classes, Inheritance, Exceptions, Packages and Interfaces. OOC 4 th Sem, B Div Prof. Mouna M. Naravani
 Module - 3 Classes, Inheritance, Exceptions, Packages and Interfaces OOC 4 th Sem, B Div 2016-17 Prof. Mouna M. Naravani Introducing Classes A class defines a new data type (User defined data type). This
Module - 3 Classes, Inheritance, Exceptions, Packages and Interfaces OOC 4 th Sem, B Div 2016-17 Prof. Mouna M. Naravani Introducing Classes A class defines a new data type (User defined data type). This
Using APIs. Chapter 3. Outline Fields Overall Layout. Java By Abstraction Chapter 3. Field Summary static double PI
 Outline Chapter 3 Using APIs 3.1 Anatomy of an API 3.1.1 Overall Layout 3.1.2 Fields 3.1.3 Methods 3.2 A Development Walkthrough 3.2.1 3.2.2 The Mortgage Application 3.2.3 Output Formatting 3.2.4 Relational
Outline Chapter 3 Using APIs 3.1 Anatomy of an API 3.1.1 Overall Layout 3.1.2 Fields 3.1.3 Methods 3.2 A Development Walkthrough 3.2.1 3.2.2 The Mortgage Application 3.2.3 Output Formatting 3.2.4 Relational
CIS 110: Introduction to Computer Programming
 CIS 110: Introduction to Computer Programming Lecture 6 Flexible Methods ( 3.1-3.2) 9/27/2011 CIS 110 (11fa) - University of Pennsylvania 1 Announcements Homework 2 due at 23:59:59 tonight! Watch Piazza
CIS 110: Introduction to Computer Programming Lecture 6 Flexible Methods ( 3.1-3.2) 9/27/2011 CIS 110 (11fa) - University of Pennsylvania 1 Announcements Homework 2 due at 23:59:59 tonight! Watch Piazza
cis20.1 design and implementation of software applications I fall 2007 lecture # I.2 topics: introduction to java, part 1
 topics: introduction to java, part 1 cis20.1 design and implementation of software applications I fall 2007 lecture # I.2 cis20.1-fall2007-sklar-leci.2 1 Java. Java is an object-oriented language: it is
topics: introduction to java, part 1 cis20.1 design and implementation of software applications I fall 2007 lecture # I.2 cis20.1-fall2007-sklar-leci.2 1 Java. Java is an object-oriented language: it is
Lecture 1: Introduction to Java
 Accelerating Information Technology Innovation http://aiti.mit.edu Lecture 1: Introduction to Java AITI Nigeria Summer 2012 University of Lagos. Agenda First Lab.. Class is Hands on remember? Recap Previously
Accelerating Information Technology Innovation http://aiti.mit.edu Lecture 1: Introduction to Java AITI Nigeria Summer 2012 University of Lagos. Agenda First Lab.. Class is Hands on remember? Recap Previously
Getting started with Java
 Getting started with Java Magic Lines public class MagicLines { public static void main(string[] args) { } } Comments Comments are lines in your code that get ignored during execution. Good for leaving
Getting started with Java Magic Lines public class MagicLines { public static void main(string[] args) { } } Comments Comments are lines in your code that get ignored during execution. Good for leaving
CSE 1223: Introduction to Computer Programming in Java Chapter 1 Computer Basics
 CSE 1223: Introduction to Computer Programming in Java Chapter 1 Computer Basics 1 Computer Basics Computer system: hardware + software Hardware: the physical components Software: the instructions that
CSE 1223: Introduction to Computer Programming in Java Chapter 1 Computer Basics 1 Computer Basics Computer system: hardware + software Hardware: the physical components Software: the instructions that
First Java Program - Output to the Screen
 First Java Program - Output to the Screen These notes are written assuming that the reader has never programmed in Java, but has programmed in another language in the past. In any language, one of the
First Java Program - Output to the Screen These notes are written assuming that the reader has never programmed in Java, but has programmed in another language in the past. In any language, one of the
1. Find the output of following java program. class MainClass { public static void main (String arg[])
![1. Find the output of following java program. class MainClass { public static void main (String arg[]) 1. Find the output of following java program. class MainClass { public static void main (String arg[])](/thumbs/75/72215142.jpg) 1. Find the output of following java program. public static void main(string arg[]) int arr[][]=4,3,2,1; int i,j; for(i=1;i>-1;i--) for(j=1;j>-1;j--) System.out.print(arr[i][j]); 1234 The above java program
1. Find the output of following java program. public static void main(string arg[]) int arr[][]=4,3,2,1; int i,j; for(i=1;i>-1;i--) for(j=1;j>-1;j--) System.out.print(arr[i][j]); 1234 The above java program
AP CS Unit 3: Control Structures Notes
 AP CS Unit 3: Control Structures Notes The if and if-else Statements. These statements are called control statements because they control whether a particular block of code is executed or not. Some texts
AP CS Unit 3: Control Structures Notes The if and if-else Statements. These statements are called control statements because they control whether a particular block of code is executed or not. Some texts
COMP-202. Recursion. COMP Recursion, 2011 Jörg Kienzle and others
 COMP-202 Recursion Recursion Recursive Definitions Run-time Stacks Recursive Programming Recursion vs. Iteration Indirect Recursion Lecture Outline 2 Recursive Definitions (1) A recursive definition is
COMP-202 Recursion Recursion Recursive Definitions Run-time Stacks Recursive Programming Recursion vs. Iteration Indirect Recursion Lecture Outline 2 Recursive Definitions (1) A recursive definition is
CIS 110: Introduction to Computer Programming
 CIS 110: Introduction to Computer Programming Lecture 5 The Loop-the-Loop ( 2.3-2.4) 9/21/2011 CIS 110 (11fa) - University of Pennsylvania 1 Outline 1. For-loops! 2. Algorithm Design and Pseudocode 9/21/2011
CIS 110: Introduction to Computer Programming Lecture 5 The Loop-the-Loop ( 2.3-2.4) 9/21/2011 CIS 110 (11fa) - University of Pennsylvania 1 Outline 1. For-loops! 2. Algorithm Design and Pseudocode 9/21/2011
Programming Constructs Overview. Method Call System.out.print( hello ); Method Parameters
 Programming Constructs Overview Method calls More selection statements More assignment operators Conditional operator Unary increment and decrement operators Iteration statements Defining methods 27 October
Programming Constructs Overview Method calls More selection statements More assignment operators Conditional operator Unary increment and decrement operators Iteration statements Defining methods 27 October
COMP 110/L Lecture 10. Kyle Dewey
 COMP 110/L Lecture 10 Kyle Dewey switch Outline switch Problem if is verbose when checking many conditions. Problem if is verbose when checking many conditions. if (x == 5) { return foo ; else if (x ==
COMP 110/L Lecture 10 Kyle Dewey switch Outline switch Problem if is verbose when checking many conditions. Problem if is verbose when checking many conditions. if (x == 5) { return foo ; else if (x ==
Consistency. CS 475, Spring 2018 Concurrent & Distributed Systems
 Consistency CS 475, Spring 2018 Concurrent & Distributed Systems Review: 2PC, Timeouts when Coordinator crashes What if the bank doesn t hear back from coordinator? If bank voted no, it s OK to abort If
Consistency CS 475, Spring 2018 Concurrent & Distributed Systems Review: 2PC, Timeouts when Coordinator crashes What if the bank doesn t hear back from coordinator? If bank voted no, it s OK to abort If
COMP 215: INTRO TO PROGRAM DESIGN. Prof. Chris Jermaine Chris Prof. Chris Dr. Chris
 COMP 215: INTRO TO PROGRAM DESIGN Prof. Chris Jermaine cmj4@cs.rice.edu Chris Prof. Chris Dr. Chris 1 This Class 50% of content: modern programming and program design The Java programming language will
COMP 215: INTRO TO PROGRAM DESIGN Prof. Chris Jermaine cmj4@cs.rice.edu Chris Prof. Chris Dr. Chris 1 This Class 50% of content: modern programming and program design The Java programming language will
COMP-202: Foundations of Programming. Lecture 2: Variables, and Data Types Sandeep Manjanna, Summer 2015
 COMP-202: Foundations of Programming Lecture 2: Variables, and Data Types Sandeep Manjanna, Summer 2015 Announcements Midterm Exams on 4 th of June (12:35 14:35) Room allocation will be announced soon
COMP-202: Foundations of Programming Lecture 2: Variables, and Data Types Sandeep Manjanna, Summer 2015 Announcements Midterm Exams on 4 th of June (12:35 14:35) Room allocation will be announced soon
AP Programming - Chapter 17 Lecture page 1 of 5
 page 1 of 5 Recursion I. Thinking Recursively In this chapter we look at another method of repetition, recursion. A recursive computation solves a problem by calling itself to solve a smaller piece of
page 1 of 5 Recursion I. Thinking Recursively In this chapter we look at another method of repetition, recursion. A recursive computation solves a problem by calling itself to solve a smaller piece of
Real World. static methods and Console & JavaFX App Intros. Lecture 16. Go ahead and PULL Lecture Materials & Sign-in on PollEv
 Go ahead and PULL Lecture Materials & Sign-in on PollEv Poll Everywhere: pollev.com/comp110 Lecture 16 static methods and Console & JavaFX App Intros Real World Spring 2016 Today Our first apps without
Go ahead and PULL Lecture Materials & Sign-in on PollEv Poll Everywhere: pollev.com/comp110 Lecture 16 static methods and Console & JavaFX App Intros Real World Spring 2016 Today Our first apps without
COMP 110 Programming Exercise: Simulation of the Game of Craps
 COMP 110 Programming Exercise: Simulation of the Game of Craps Craps is a game of chance played by rolling two dice for a series of rolls and placing bets on the outcomes. The background on probability,
COMP 110 Programming Exercise: Simulation of the Game of Craps Craps is a game of chance played by rolling two dice for a series of rolls and placing bets on the outcomes. The background on probability,
Programming with Java
 Programming with Java Data Types & Input Statement Lecture 04 First stage Software Engineering Dep. Saman M. Omer 2017-2018 Objectives q By the end of this lecture you should be able to : ü Know rules
Programming with Java Data Types & Input Statement Lecture 04 First stage Software Engineering Dep. Saman M. Omer 2017-2018 Objectives q By the end of this lecture you should be able to : ü Know rules
Lecture Set 4: More About Methods and More About Operators
 Lecture Set 4: More About Methods and More About Operators Methods Definitions Invocations More arithmetic operators Operator Side effects Operator Precedence Short-circuiting main method public static
Lecture Set 4: More About Methods and More About Operators Methods Definitions Invocations More arithmetic operators Operator Side effects Operator Precedence Short-circuiting main method public static
Administration. Classes. Objects Part II. Agenda. Review: Object References. Object Aliases. CS 99 Summer 2000 Michael Clarkson Lecture 7
 Administration Classes CS 99 Summer 2000 Michael Clarkson Lecture 7 Lab 7 due tomorrow Question: Lab 6.equals( SquareRoot )? Lab 8 posted today Prelim 2 in six days! Covers two weeks of material: lectures
Administration Classes CS 99 Summer 2000 Michael Clarkson Lecture 7 Lab 7 due tomorrow Question: Lab 6.equals( SquareRoot )? Lab 8 posted today Prelim 2 in six days! Covers two weeks of material: lectures
CS/IT 114 Introduction to Java, Part 1 FALL 2016 CLASS 3: SEP. 13TH INSTRUCTOR: JIAYIN WANG
 CS/IT 114 Introduction to Java, Part 1 FALL 2016 CLASS 3: SEP. 13TH INSTRUCTOR: JIAYIN WANG 1 Notice Reading Assignment Chapter 1: Introduction to Java Programming Homework 1 It is due this coming Sunday
CS/IT 114 Introduction to Java, Part 1 FALL 2016 CLASS 3: SEP. 13TH INSTRUCTOR: JIAYIN WANG 1 Notice Reading Assignment Chapter 1: Introduction to Java Programming Homework 1 It is due this coming Sunday
Question: Total Points: Score:
 CS 170 Exam 1 Section 000 Spring 2014 Name (print):. Instructions Keep your eyes on your own paper and do your best to prevent anyone else from seeing your work. Do NOT communicate with anyone other than
CS 170 Exam 1 Section 000 Spring 2014 Name (print):. Instructions Keep your eyes on your own paper and do your best to prevent anyone else from seeing your work. Do NOT communicate with anyone other than
Last Time. University of British Columbia CPSC 111, Intro to Computation Alan J. Hu. Readings
 University of British Columbia CPSC 111, Intro to Computation Alan J. Hu Writing a Simple Java Program Intro to Variables Readings Your textbook is Big Java (3rd Ed). This Week s Reading: Ch 2.1-2.5, Ch
University of British Columbia CPSC 111, Intro to Computation Alan J. Hu Writing a Simple Java Program Intro to Variables Readings Your textbook is Big Java (3rd Ed). This Week s Reading: Ch 2.1-2.5, Ch
Midterms Save the Dates!
 University of British Columbia CPSC 111, Intro to Computation Alan J. Hu Errors (Using the Scanner and String Classes) Anatomy of a Java Program Readings This Week s Reading: Ch 3.1-3.8 (Major conceptual
University of British Columbia CPSC 111, Intro to Computation Alan J. Hu Errors (Using the Scanner and String Classes) Anatomy of a Java Program Readings This Week s Reading: Ch 3.1-3.8 (Major conceptual
Introduction to the Java Basics: Control Flow Statements
 Lesson 3: Introduction to the Java Basics: Control Flow Statements Repetition Structures THEORY Variable Assignment You can only assign a value to a variable that is consistent with the variable s declared
Lesson 3: Introduction to the Java Basics: Control Flow Statements Repetition Structures THEORY Variable Assignment You can only assign a value to a variable that is consistent with the variable s declared
CISC-124. Passing Parameters. A Java method cannot change the value of any of the arguments passed to its parameters.
 CISC-124 20180215 These notes are intended to summarize and clarify some of the topics that have been covered recently in class. The posted code samples also have extensive explanations of the material.
CISC-124 20180215 These notes are intended to summarize and clarify some of the topics that have been covered recently in class. The posted code samples also have extensive explanations of the material.
Lecture 05: Methods. AITI Nigeria Summer 2012 University of Lagos.
 Lecture 05: Methods AITI Nigeria Summer 2012 University of Lagos. Agenda What a method is Why we use methods How to declare a method The four parts of a method How to use (invoke) a method The purpose
Lecture 05: Methods AITI Nigeria Summer 2012 University of Lagos. Agenda What a method is Why we use methods How to declare a method The four parts of a method How to use (invoke) a method The purpose
CIS 110: Introduction to Computer Programming. Lecture 2 Decomposition and Static Methods ( 1.4)
 CIS 110: Introduction to Computer Programming Lecture 2 Decomposition and Static Methods ( 1.4) Outline Structure and redundancy in algorithms Static methods Procedural decomposition 9/16/2011 CIS 110
CIS 110: Introduction to Computer Programming Lecture 2 Decomposition and Static Methods ( 1.4) Outline Structure and redundancy in algorithms Static methods Procedural decomposition 9/16/2011 CIS 110
CPE 101, reusing/mod slides from a UW course (used by permission) Lecture 5: Input and Output (I/O)
 CPE 101, reusing/mod slides from a UW course (used by permission) Lecture 5: Input and Output (I/O) Overview (5) Topics Output: printf Input: scanf Basic format codes More on initializing variables 2000
CPE 101, reusing/mod slides from a UW course (used by permission) Lecture 5: Input and Output (I/O) Overview (5) Topics Output: printf Input: scanf Basic format codes More on initializing variables 2000
Administration. Conditional Statements. Agenda. Syntax. Flow of control. Lab 2 due now on floppy Lab 3 due tomorrow via FTP
 Administration Conditional Statements CS 99 Summer 2000 Michael Clarkson Lecture 4 Lab 2 due now on floppy Lab 3 due tomorrow via FTP need Instruct account password Lab 4 posted this afternoon Prelim 1
Administration Conditional Statements CS 99 Summer 2000 Michael Clarkson Lecture 4 Lab 2 due now on floppy Lab 3 due tomorrow via FTP need Instruct account password Lab 4 posted this afternoon Prelim 1
Lecture 5: Methods CS2301
 Lecture 5: Methods NADA ALZAHRANI CS2301 1 Opening Problem Find the sum of integers from 1 to 10, from 20 to 30, and from 35 to 45, respectively. 2 Solution public static int sum(int i1, int i2) { int
Lecture 5: Methods NADA ALZAHRANI CS2301 1 Opening Problem Find the sum of integers from 1 to 10, from 20 to 30, and from 35 to 45, respectively. 2 Solution public static int sum(int i1, int i2) { int
HOW TO WRITE RECURSIVE FUNCTIONS ON YOUR OWN
 HOW TO WRITE RECURSIVE FUNCTIONS ON YOUR OWN In this tutorial, you ll learn - well, you ve already read the title - how to write recursive functions on your own. If you re the person to whom recursive
HOW TO WRITE RECURSIVE FUNCTIONS ON YOUR OWN In this tutorial, you ll learn - well, you ve already read the title - how to write recursive functions on your own. If you re the person to whom recursive
COSC 236 Section 101 Computer Science 1 -- Prof. Michael A. Soderstrand
 COSC 236 Section 101 Computer Science 1 -- Prof. Michael A. Soderstrand COSC 236 Web Site You will always find the course material at: http://www.class-notes.us or http://www.class-notes.info or http://www.lecture-notes.tripod.com
COSC 236 Section 101 Computer Science 1 -- Prof. Michael A. Soderstrand COSC 236 Web Site You will always find the course material at: http://www.class-notes.us or http://www.class-notes.info or http://www.lecture-notes.tripod.com
1.00 Lecture 2. What s an IDE?
 1.00 Lecture 2 Interactive Development Environment: Eclipse Reading for next time: Big Java: sections 3.1-3.9 (Pretend the method is main() in each example) What s an IDE? An integrated development environment
1.00 Lecture 2 Interactive Development Environment: Eclipse Reading for next time: Big Java: sections 3.1-3.9 (Pretend the method is main() in each example) What s an IDE? An integrated development environment
Java using LEGO Mindstorms and LeJOS. University of Idaho
 Java using LEGO Mindstorms and LeJOS University of Idaho 2 Contents 1 Introduction 1 1.1 Setting up Java and Eclipse................................ 1 1.2 Setting up the Lego Brick to work with LeJOS.....................
Java using LEGO Mindstorms and LeJOS University of Idaho 2 Contents 1 Introduction 1 1.1 Setting up Java and Eclipse................................ 1 1.2 Setting up the Lego Brick to work with LeJOS.....................
Warmup : Name that tune!
 Warmup : Name that tune! Write, using a loop, Java code to print the lyrics to the song 99 Bottles of Beer on the Wall 99 bottles of beer on the wall. 99 bottles of beer. Take one down, pass it around,
Warmup : Name that tune! Write, using a loop, Java code to print the lyrics to the song 99 Bottles of Beer on the Wall 99 bottles of beer on the wall. 99 bottles of beer. Take one down, pass it around,
Java Loop Control. Programming languages provide various control structures that allow for more complicated execution paths.
 Loop Control There may be a situation when you need to execute a block of code several number of times. In general, statements are executed sequentially: The first statement in a function is executed first,
Loop Control There may be a situation when you need to execute a block of code several number of times. In general, statements are executed sequentially: The first statement in a function is executed first,
Recursion. Recursion [Bono] 1
![Recursion. Recursion [Bono] 1 Recursion. Recursion [Bono] 1](/thumbs/78/77868425.jpg) Recursion Idea A few examples wishful thinking method Recursion in classes Ex: palindromes Helper functions Computational complexity of recursive functions Recursive functions with multiple calls Recursion
Recursion Idea A few examples wishful thinking method Recursion in classes Ex: palindromes Helper functions Computational complexity of recursive functions Recursive functions with multiple calls Recursion
COMP15111: Introduction to Architecture
 COMP15111 Lecture 9 1/33 COMP15111: Introduction to Architecture Lecture 9: Methods Pete Jinks School of Computer Science, University of Manchester Autumn 2011 COMP15111 Lecture 9 A Java Program 2/33 Lecture
COMP15111 Lecture 9 1/33 COMP15111: Introduction to Architecture Lecture 9: Methods Pete Jinks School of Computer Science, University of Manchester Autumn 2011 COMP15111 Lecture 9 A Java Program 2/33 Lecture
CSC 1051 Algorithms and Data Structures I. Midterm Examination February 25, Name: KEY A
 CSC 1051 Algorithms and Data Structures I Midterm Examination February 25, 2016 Name: KEY A Question Value Score 1 10 2 10 3 10 4 10 5 10 6 10 7 10 8 10 9 10 10 10 TOTAL 100 Please answer questions in
CSC 1051 Algorithms and Data Structures I Midterm Examination February 25, 2016 Name: KEY A Question Value Score 1 10 2 10 3 10 4 10 5 10 6 10 7 10 8 10 9 10 10 10 TOTAL 100 Please answer questions in
