CSE 142 Sample Final Exam #1 (based on Spring 2005's final; thanks to Stuart Reges)
|
|
|
- Randolf Banks
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CSE 142 Sample Final Exam #1 (based on Spring 2005's final; thanks to Stuart Reges) 1. Expressions For each expression at left, indicate its value in the right column. List a value of appropriate type and capitalization. e.g., 7 for an int, 7.0 for a double, "hello" for a String, true or false for a boolean. Expression 8.0 / 4 / / * 3 88 % 10 % 5/2 + 7 % 8 2 * " = " + 5 * > 20 && 16 % 4 > 2 2 * ( )/5 * 10-7/4 Value 2. Array Mystery Consider the following method: public static void arraymystery(int[] a) { for (int i = 1; i < a.length; i++) { a[i] = i + a[i - 1] - a[i]; Indicate in the right-hand column what values would be stored in the array after the method arraymystery executes if the integer array in the left-hand column is passed as a parameter to it. Original Contents of Array int[] a1 = {7; arraymystery(a1); int[] a2 = {4, 3, 6; arraymystery(a2); int[] a3 = {7, 4, 8, 6, 2; arraymystery(a3); int[] a4 = {10, 2, 5, 10; arraymystery(a4); int[] a5 = {2, 4, -1, 6, -2, 8; arraymystery(a5); Final Contents of Array 1 of 11
2 3. Reference Semantics Mystery The following program produces 4 lines of output. Write the output below, as it would appear on the console. public class BasicPoint { int x; int y; public BasicPoint() { x = 2; y = 2; public class ReferenceMystery { public static void main(string[] args) { int a = 7; int b = 9; BasicPoint p1 = new BasicPoint(); BasicPoint p2 = new BasicPoint(); addtoxtwice(a, p1); System.out.println(a + " " + b + " " + p1.x + " " + p2.x); addtoxtwice(b, p2); System.out.println(a + " " + b + " " + p1.x + " " + p2.x); public static void addtoxtwice(int a, BasicPoint p1) { a = a + a; p1.x = a; System.out.println(a + " " + p1.x); 2 of 11
3 4. Inheritance Mystery Assume that the following classes have been defined: public class A extends B { public void method2() { System.out.print("a 2 "); method1(); public class B extends C { public String tostring() { return "b"; public void method2() { System.out.print("b 2 "); super.method2(); public class C { public String tostring() { return "c"; public void method1() { System.out.print("c 1 "); public void method2() { System.out.print("c 2 "); public class D extends B { public void method1() { System.out.print("d 1 "); method2(); Given the classes above, what output is produced by the following code? C[] elements = {new A(), new B(), new C(), new D(); for (int i = 0; i < elements.length; i++) { System.out.println(elements[i]); elements[i].method1(); System.out.println(); elements[i].method2(); System.out.println(); System.out.println(); 3 of 11
4 5. File Processing Write a static method named printstrings that takes as a parameter a Scanner holding a sequence of integer/string pairs and that prints to System.out one line of output for each pair with the given String repeated the given number of times. For example if the Scanner contains the following data: 6 fun. 3 hello 10 <> wow! your method should produce the following output: fun.fun.fun.fun.fun.fun. hellohellohello <><><><><><><><><><> 2525 wow!wow!wow!wow! Notice that there is one line of output for each integer/string pair. The first line has 6 occurrences of "fun.", the second line has 3 occurrences of "hello", the third line has 10 occurrences of "<>", the fourth line has 2 occurrences of "25" the fifth line has 4 occurrences of "wow!". Notice that there are no extra spaces included in the output. You are to exactly reproduce the format of this sample output. You may assume that the input values always come in pairs with an integer followed by a String (which itself could be numeric, such as "25" above). If the Scanner is empty (no integer/string pairs), your method should produce no output. 4 of 11
5 6. File Processing Write a static method named reverselines that accepts a Scanner containing an input file as a parameter and that echoes the input file to System.out with each line of text reversed. For example, given the following input file: If this method works properly, the lines of text in this file will be reversed. Remember that some lines might be blank. Your method should print the following output:,ylreporp skrow dohtem siht fi elif siht ni txet fo senil eht.desrever eb lliw.knalb eb thgim senil emos taht rebmemer Notice that some of the input lines can be blank lines. 5 of 11
6 7. Array Programming Write a static method isalleven that takes an array of integers as a parameter and that returns a boolean value indicating whether or not all of the values are even numbers (true for yes, false for no). For example, if a variable called list stores the following values: int[] list = {18, 0, 4, 204, 8, 4, 2, 18, 206, 1492, 42; Then the call of isalleven(list) should return true because each of these integers is an even number. If instead the list had stored these values: int[] list = {2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 208, 16, 7, 92, 14; Then the call should return false because, although most of these values are even, the value 7 is an odd number. 6 of 11
7 8. Array Programming Write a static method named isunique that takes an array of integers as a parameter and that returns a boolean value indicating whether or not the values in the array are unique (true for yes, false for no). The values in the list are considered unique if there is no pair of values that are equal. For example, if a variable called list stores the following values: int[] list = {3, 8, 12, 2, 9, 17, 43, -8, 46, 203, 14, 97, 10, 4; Then the call of isunique(list) should return true because there are no duplicated values in this list. If instead the list stored these values: int[] list = {4, 7, 2, 3, 9, 12, -47, -19, 308, 3, 74; Then the call should return false because the value 3 appears twice in this list. Notice that given this definition, a list of 0 or 1 elements would be considered unique. 7 of 11
8 9. Critters Write a class Ostrich that extends the Critter class from the Critters assignment, including its getmove and getcolor methods. An Ostrich object first stays in the same place for 10 moves, then moves 10 steps to either the WEST or the EAST, then repeats. In other words, after sitting still for 10 moves, the ostrich randomly picks to go west or east, then walks 10 steps in that same direction. Then it stops and sits still for 10 moves and repeats. Whenever an Ostrich is moving (that is, whenever its last call to getmove returned a direction other than Direction.CENTER), its color should be white (Color.WHITE). As soon as it stops moving, and initially when it first appears in the critter world, its color should be cyan (Color.CYAN). When randomly choosing west vs. east, the two directions should be equally likely. You may add anything needed (fields, other methods) to implement the above behavior appropriately. All other critter behavior not discussed here uses the default values. 8 of 11
9 Solutions "10 = 307" false Call int[] a1 = {7; arraymystery(a1); int[] a2 = {4, 3, 6; arraymystery(a2); int[] a3 = {7, 4, 8, 6, 2; arraymystery(a3); int[] a4 = {10, 2, 5, 10; arraymystery(a4); int[] a5 = {2, 4, -1, 6, -2, 8; arraymystery(a5); Final Contents of Array {7 {4, 2, -2 {7, 4, -2, -5, -3 {10, 9, 6, -1 {2, -1, 2, -1, 5, b c 1 a 2 c 1 b c 1 b 2 c 2 c c 1 c 2 b d 1 b 2 c 2 b 2 c 2 5. public static void printstrings(scanner input) { while (input.hasnextint()) { int times = input.nextint(); String word = input.next(); for (int i = 0; i < times; i++) { System.out.print(word); System.out.println(); 9 of 11
10 6. public static void reverselines(scanner input) { while (input.hasnextline()) { String text = input.nextline(); for (int i = text.length() - 1; i >= 0; i--) { System.out.print(text.charAt(i)); System.out.println(); 7. public static boolean isalleven(int[] list) { for (int i = 0; i < list.length; i++) { if (list[i] % 2!= 0) { return false; return true; 8. public static boolean isunique(int[] list) { for (int i = 0; i < list.length; i++) { for (int j = i + 1; j < list.length; j++) { if (list[i] == list[j]) { return false; return true; 10 of 11
11 9. import java.awt.*; import java.util.*; // for Color // for Random public class Ostrich extends Critter { private Random rand; private int steps; private boolean west; // true if going west; false if east private boolean hiding; public Ostrich() { rand = new Random(); hiding = true; steps = 0; west = rand.nextboolean(); // or call nextint(2) and map 0=false, 1=true public Color getcolor() { if (hiding) { return Color.CYAN; else { return Color.WHITE; public Direction getmove() { if (steps == 10) { steps = 0; // Pick a new direction and re-set the steps counter hiding =!hiding; west = rand.nextboolean(); steps++; if (hiding) { return Direction.CENTER; else if (west) { return Direction.WEST; else { return Direction.EAST; 11 of 11
CSE 142 Sample Final Exam #1
 CSE 142 Sample Final Exam #1 1. Expressions (5 points) For each expression in the left-hand column, indicate its value in the right-hand column. Be sure to list a constant of appropriate type (e.g., 7.0
CSE 142 Sample Final Exam #1 1. Expressions (5 points) For each expression in the left-hand column, indicate its value in the right-hand column. Be sure to list a constant of appropriate type (e.g., 7.0
CSE 142, Spring 2009, Sample Final Exam #2. Good luck!
 CSE 142, Spring 2009, Sample Final Exam #2 Name: Section: Student ID #: TA: Rules: You have 110 minutes to complete this exam. You will receive a deduction if you keep working after the instructor calls
CSE 142, Spring 2009, Sample Final Exam #2 Name: Section: Student ID #: TA: Rules: You have 110 minutes to complete this exam. You will receive a deduction if you keep working after the instructor calls
CSc 110 Sample Final Exam #1
 CSc 110 Sample Final Exam #1 1. While Loop Simulation For each call of the function below, write the output that is printed: def mystery(i, j): while (i!= 0 and j!= 0): i = i // j j = (j - 1) // 2 print(str(i)
CSc 110 Sample Final Exam #1 1. While Loop Simulation For each call of the function below, write the output that is printed: def mystery(i, j): while (i!= 0 and j!= 0): i = i // j j = (j - 1) // 2 print(str(i)
CSE 142 Sample Final Exam #4
 1. Expressions CSE 142 Sample Final Exam #4 For each expression in the left-hand column, indicate its value in the right-hand column. Be sure to list a constant of appropriate type and capitalization.
1. Expressions CSE 142 Sample Final Exam #4 For each expression in the left-hand column, indicate its value in the right-hand column. Be sure to list a constant of appropriate type and capitalization.
CSE 142 Sample Final Exam #2
 CSE 142 Sample Final Exam #2 1. Expressions (5 points) For each expression in the left-hand column, indicate its value in the right-hand column. Be sure to list a constant of appropriate type (e.g., 7.0
CSE 142 Sample Final Exam #2 1. Expressions (5 points) For each expression in the left-hand column, indicate its value in the right-hand column. Be sure to list a constant of appropriate type (e.g., 7.0
CSE 142 Sample Final Exam #2
 CSE 142 Sample Final Exam #2 1. Array Mystery Consider the following method: public static int arraymystery(int[] array) { int x = 0; for (int i = 0; i < array.length - 1; i++) { if (array[i] > array[i
CSE 142 Sample Final Exam #2 1. Array Mystery Consider the following method: public static int arraymystery(int[] array) { int x = 0; for (int i = 0; i < array.length - 1; i++) { if (array[i] > array[i
CSE 142, Spring 2010 Final Exam Wednesday, June 9, Name: Student ID #: Rules:
 CSE 142, Spring 2010 Final Exam Wednesday, June 9, 2010 Name: Section: Student ID #: TA: Rules: You have 110 minutes to complete this exam. You may receive a deduction if you keep working after the instructor
CSE 142, Spring 2010 Final Exam Wednesday, June 9, 2010 Name: Section: Student ID #: TA: Rules: You have 110 minutes to complete this exam. You may receive a deduction if you keep working after the instructor
CSE 142 SPRING 2008 FINAL EXAM
 CSE 142 SPRING 2008 FINAL EXAM 1. Expressions (10 points) For each expression in the left-hand column, indicate its value in the right-hand column. Be sure to list a constant of appropriate type (e.g.,
CSE 142 SPRING 2008 FINAL EXAM 1. Expressions (10 points) For each expression in the left-hand column, indicate its value in the right-hand column. Be sure to list a constant of appropriate type (e.g.,
1. Reference Mystery, 5 points. What output is produced by this program? import java.util.*;
 CSE142 Sample Final Exam, Winter 2018 1. Reference Mystery, 5 points. What output is produced by this program? import java.util.*; public class Rectangle { int w; int h; public Rectangle(int width, int
CSE142 Sample Final Exam, Winter 2018 1. Reference Mystery, 5 points. What output is produced by this program? import java.util.*; public class Rectangle { int w; int h; public Rectangle(int width, int
Sample Midterm Exam #2
 Sample Midterm Exam #2 1. Expressions For each expression in the left-hand column, indicate its value in the right-hand column. Be sure to list a constant of appropriate type (e.g., 7.0 rather than 7 for
Sample Midterm Exam #2 1. Expressions For each expression in the left-hand column, indicate its value in the right-hand column. Be sure to list a constant of appropriate type (e.g., 7.0 rather than 7 for
CSE 142 Sample Final Exam #2 (based on Autumn 2007's final)
 1. Array Mystery Consider the following method: CSE 142 Sample Final Exam #2 (based on Autumn 2007's final) public static void arraymystery(int[] a) { for (int i = a.length - 2; i > 0; i--) { if (a[i +
1. Array Mystery Consider the following method: CSE 142 Sample Final Exam #2 (based on Autumn 2007's final) public static void arraymystery(int[] a) { for (int i = a.length - 2; i > 0; i--) { if (a[i +
CSE 142, Autumn 2010 Final Exam Wednesday, December 15, Name:
 CSE 142, Autumn 2010 Final Exam Wednesday, December 15, 2010 Name: Section: Student ID #: TA: Rules: You have 110 minutes to complete this exam. You may receive a deduction if you keep working after the
CSE 142, Autumn 2010 Final Exam Wednesday, December 15, 2010 Name: Section: Student ID #: TA: Rules: You have 110 minutes to complete this exam. You may receive a deduction if you keep working after the
Building Java Programs Sample Final Exam #1. Name of Student. Section (e.g., AA)
 Building Java Programs Sample Final Exam #1 Name of Student Section (e.g., AA) TA This is an open-book/open-note exam. Space is provided for your answers. Use the backs of pages if necessary. The exam
Building Java Programs Sample Final Exam #1 Name of Student Section (e.g., AA) TA This is an open-book/open-note exam. Space is provided for your answers. Use the backs of pages if necessary. The exam
CSE 142, Spring 2009, Final Exam
 CSE 142, Spring 2009, Final Exam Name: Section: Student ID #: TA: Rules: You have 110 minutes to complete this exam. You will receive a deduction if you keep working after the instructor calls for papers.
CSE 142, Spring 2009, Final Exam Name: Section: Student ID #: TA: Rules: You have 110 minutes to complete this exam. You will receive a deduction if you keep working after the instructor calls for papers.
Building Java Programs
 Building Java Programs Chapter 8 Lecture 8-4: Static Methods and Data Critter exercise: Snake Method constructor public Snake() eat Never eats fight always forfeits getcolor black Behavior getmove 1 E,
Building Java Programs Chapter 8 Lecture 8-4: Static Methods and Data Critter exercise: Snake Method constructor public Snake() eat Never eats fight always forfeits getcolor black Behavior getmove 1 E,
CSE 142, Autumn 2008 Final Exam Key
 1. Expressions Expression -(1 + 2 * 3 + (1 + 2) * 3) 1 + 2 + "(3 + 4)" + 5 * 6 + 7 30 % 9 + 5 % 8-11 % 4 % 2 4 < 10!= (5 == 6 9 >= 9) (double) 45 / 10.0 / 2 + 7 / 4.0 * 10 CSE 142, Autumn 2008 Final Exam
1. Expressions Expression -(1 + 2 * 3 + (1 + 2) * 3) 1 + 2 + "(3 + 4)" + 5 * 6 + 7 30 % 9 + 5 % 8-11 % 4 % 2 4 < 10!= (5 == 6 9 >= 9) (double) 45 / 10.0 / 2 + 7 / 4.0 * 10 CSE 142, Autumn 2008 Final Exam
CSE 142 Sample Final Exam #4 (based on Autumn 2008's final)
 1. Array Mystery Consider the following method: CSE 142 Sample Final Exam #4 (based on Autumn 2008's final) public static void arraymystery(int[] a) { for (int i = a.length - 2; i > 0; i--) { if (a[i -
1. Array Mystery Consider the following method: CSE 142 Sample Final Exam #4 (based on Autumn 2008's final) public static void arraymystery(int[] a) { for (int i = a.length - 2; i > 0; i--) { if (a[i -
CSE 143. Lecture 9: introduction to recursion reading: 12.1
 CSE 143 Lecture 9: introduction to recursion reading: 12.1 Recursion recursion: The definition of an operation in terms of itself. Solving a problem using recursion depends on solving smaller occurrences
CSE 143 Lecture 9: introduction to recursion reading: 12.1 Recursion recursion: The definition of an operation in terms of itself. Solving a problem using recursion depends on solving smaller occurrences
CSE 142, Winter 2007 Final Exam. Name:
 1 of 10 CSE 142, Winter 2007 Final Exam Name: Section: Student ID #: TA: You have 110 minutes to complete this exam. You may receive a deduction if you keep working after the instructor calls for papers.
1 of 10 CSE 142, Winter 2007 Final Exam Name: Section: Student ID #: TA: You have 110 minutes to complete this exam. You may receive a deduction if you keep working after the instructor calls for papers.
Recursion. Garfield AP Computer Science. As usual, significant borrowings from Stuart Reges and Marty Stepp at UW -- thanks!!
 Recursion Garfield AP Computer Science As usual, significant borrowings from Stuart Reges and Marty Stepp at UW -- thanks!! Definitions recursion: The definition of an operation in terms of itself. Solving
Recursion Garfield AP Computer Science As usual, significant borrowings from Stuart Reges and Marty Stepp at UW -- thanks!! Definitions recursion: The definition of an operation in terms of itself. Solving
CS 112 Introduction to Programming. (Spring 2012)
 CS 112 Introduction to Programming (Spring 2012) Lecture #32: Inheritance and Class Hierarchy Zhong Shao Department of Computer Science Yale University Office: 314 Watson http://flint.cs.yale.edu/cs112
CS 112 Introduction to Programming (Spring 2012) Lecture #32: Inheritance and Class Hierarchy Zhong Shao Department of Computer Science Yale University Office: 314 Watson http://flint.cs.yale.edu/cs112
CIS 110 Introduction To Computer Programming. December 19th, 2011 Final. Answer key
 CIS 110 Introduction To Computer Programming December 19th, 2011 Final Answer key CIS 110 final instructions You have 120 minutes to finish this exam. Time will begin when called by a proctor and end precisely
CIS 110 Introduction To Computer Programming December 19th, 2011 Final Answer key CIS 110 final instructions You have 120 minutes to finish this exam. Time will begin when called by a proctor and end precisely
CSE 142, Autumn 2008 Midterm Exam, Friday, October 31, 2008
 CSE 142, Autumn 2008 Midterm Exam, Friday, October 31, 2008 Name: Section: Student ID #: TA: You have 50 minutes to complete this exam. You may receive a deduction if you keep working after the instructor
CSE 142, Autumn 2008 Midterm Exam, Friday, October 31, 2008 Name: Section: Student ID #: TA: You have 50 minutes to complete this exam. You may receive a deduction if you keep working after the instructor
Building Java Programs
 Building Java Programs Chapter 8 Lecture 8-3: Encapsulation; Homework 8 (Critters) reading: 8.3-8.4 Encapsulation reading: 8.4 2 Encapsulation encapsulation: Hiding implementation details from clients.
Building Java Programs Chapter 8 Lecture 8-3: Encapsulation; Homework 8 (Critters) reading: 8.3-8.4 Encapsulation reading: 8.4 2 Encapsulation encapsulation: Hiding implementation details from clients.
Assignment 11: Critters
 Assignment 11: Critters HW11 Assignment Specification 1 Critters A simulation world with animal objects with behavior: fight animal fighting getcolor color to display getmove movement tostring letter to
Assignment 11: Critters HW11 Assignment Specification 1 Critters A simulation world with animal objects with behavior: fight animal fighting getcolor color to display getmove movement tostring letter to
CSc 110, Spring 2017 Lecture 38: Critters. Adapted from slides by Marty Stepp and Stuart Reges
 CSc 110, Spring 2017 Lecture 38: Critters Adapted from slides by Marty Stepp and Stuart Reges 1 Calling overridden methods Subclasses can call overridden methods with super super(classname, self).method(parameters)
CSc 110, Spring 2017 Lecture 38: Critters Adapted from slides by Marty Stepp and Stuart Reges 1 Calling overridden methods Subclasses can call overridden methods with super super(classname, self).method(parameters)
CS 112 Introduction to Programming
 CS 112 Introduction to Programming (Spring 2012) Lecture #31: Software Reuse through Inheritance Zhong Shao Department of Computer Science Yale University Office: 314 Watson http://flint.cs.yale.edu/cs112
CS 112 Introduction to Programming (Spring 2012) Lecture #31: Software Reuse through Inheritance Zhong Shao Department of Computer Science Yale University Office: 314 Watson http://flint.cs.yale.edu/cs112
Array basics. Readings: 7.1
 Array basics Readings: 7.1 1 How would you solve this? Consider the following program: How many days' temperatures? 7 Day 1's high temp: 45 Day 2's high temp: 44 Day 3's high temp: 39 Day 4's high temp:
Array basics Readings: 7.1 1 How would you solve this? Consider the following program: How many days' temperatures? 7 Day 1's high temp: 45 Day 2's high temp: 44 Day 3's high temp: 39 Day 4's high temp:
CIS 110 Introduction To Computer Programming. December 19th, 2011 Final. Answer key for review problems
 CIS 110 Introduction To Computer Programming December 19th, 2011 Final Answer key for review problems CIS 110 final instructions You have 120 minutes to finish this exam. Time will begin when called by
CIS 110 Introduction To Computer Programming December 19th, 2011 Final Answer key for review problems CIS 110 final instructions You have 120 minutes to finish this exam. Time will begin when called by
int x = 42, y = 33; //1 int z = x + y; //2 System.out.println(x + "+" + y + "=" + z); //3
 In requested outputs below, show all output in the order of execution, with correct line breaks, without mixing in comments or intermediate steps. You increase your chances of partial credit if you also
In requested outputs below, show all output in the order of execution, with correct line breaks, without mixing in comments or intermediate steps. You increase your chances of partial credit if you also
CS Week 5. Jim Williams, PhD
 CS 200 - Week 5 Jim Williams, PhD The Study Cycle Check Am I using study methods that are effective? Do I understand the material enough to teach it to others? http://students.lsu.edu/academicsuccess/studying/strategies/tests/studying
CS 200 - Week 5 Jim Williams, PhD The Study Cycle Check Am I using study methods that are effective? Do I understand the material enough to teach it to others? http://students.lsu.edu/academicsuccess/studying/strategies/tests/studying
1. An operation in which an overall value is computed incrementally, often using a loop.
 Practice Exam 2 Part I: Vocabulary (10 points) Write the terms defined by the statements below. 1. An operation in which an overall value is computed incrementally, often using a loop. 2. The < (less than)
Practice Exam 2 Part I: Vocabulary (10 points) Write the terms defined by the statements below. 1. An operation in which an overall value is computed incrementally, often using a loop. 2. The < (less than)
d. If a is false and b is false then the output is "ELSE" Answer?
 Intermediate Level 1) Predict the output for the below code: public void foo( boolean a, boolean b) if( a ) System.out.println("A"); if(a && b) System.out.println( "A && B"); if (!b ) System.out.println(
Intermediate Level 1) Predict the output for the below code: public void foo( boolean a, boolean b) if( a ) System.out.println("A"); if(a && b) System.out.println( "A && B"); if (!b ) System.out.println(
Homework 9: Critters (cont.)
 Homework 9: Critters (cont.) Critter exercise: Snake Method Behavior constructor public Snake() eat Never eats fight always forfeits getcolor black getmove 1 E, 1 S; 2 W, 1 S; 3 E, 1 S; 4 W, 1 S; 5 E,
Homework 9: Critters (cont.) Critter exercise: Snake Method Behavior constructor public Snake() eat Never eats fight always forfeits getcolor black getmove 1 E, 1 S; 2 W, 1 S; 3 E, 1 S; 4 W, 1 S; 5 E,
Introduction to Computer Science Unit 2. Exercises
 Introduction to Computer Science Unit 2. Exercises Note: Curly brackets { are optional if there is only one statement associated with the if (or ) statement. 1. If the user enters 82, what is 2. If the
Introduction to Computer Science Unit 2. Exercises Note: Curly brackets { are optional if there is only one statement associated with the if (or ) statement. 1. If the user enters 82, what is 2. If the
CSE 143 Lecture 10. Recursion
 CSE 143 Lecture 10 Recursion slides created by Marty Stepp and Alyssa Harding http://www.cs.washington.edu/143/ Recursion Iteration: a programming technique in which you describe actions to be repeated
CSE 143 Lecture 10 Recursion slides created by Marty Stepp and Alyssa Harding http://www.cs.washington.edu/143/ Recursion Iteration: a programming technique in which you describe actions to be repeated
CS 101 Exam 2 Spring Id Name
 CS 101 Exam 2 Spring 2005 Email Id Name This exam is open text book and closed notes. Different questions have different points associated with them. Because your goal is to maximize your number of points,
CS 101 Exam 2 Spring 2005 Email Id Name This exam is open text book and closed notes. Different questions have different points associated with them. Because your goal is to maximize your number of points,
CSE142 Sample Final Exam Key Autumn 2018
 CSE142 Sample Final Exam Key Autumn 2018 1. The program produces the following output: 1 7 [2, 4, 6] 0 8 1 7-1 [2, 4, 6] 5 7 [2, 4, 6] 2. Original Array Final Array -------------- ----------------------------
CSE142 Sample Final Exam Key Autumn 2018 1. The program produces the following output: 1 7 [2, 4, 6] 0 8 1 7-1 [2, 4, 6] 5 7 [2, 4, 6] 2. Original Array Final Array -------------- ----------------------------
Array basics. How would you solve this? Arrays. What makes the problem hard? Array auto-initialization. Array declaration. Readings: 7.
 How would you solve this? Array basics Readings:. Consider the following program: How many days' temperatures? Day 's high temp: Day 's high temp: Day 's high temp: Day 's high temp: Day 's high temp:
How would you solve this? Array basics Readings:. Consider the following program: How many days' temperatures? Day 's high temp: Day 's high temp: Day 's high temp: Day 's high temp: Day 's high temp:
CSc 110, Spring 2017 Lecture 37: Critters. Adapted from slides by Marty Stepp and Stuart Reges
 CSc 110, Spring 2017 Lecture 37: Critters Adapted from slides by Marty Stepp and Stuart Reges 1 Calling overridden methods Subclasses can call overridden methods with super super(classname, self).method(parameters)
CSc 110, Spring 2017 Lecture 37: Critters Adapted from slides by Marty Stepp and Stuart Reges 1 Calling overridden methods Subclasses can call overridden methods with super super(classname, self).method(parameters)
CSE 142, Summer 2013 Midterm Exam, Friday, July 26, 2013
 CSE 142, Summer 2013 Midterm Exam, Friday, July 26, 2013 Name: Section: TA: Student ID #: You have 60 minutes to complete this exam. You may receive a deduction if you keep working after the instructor
CSE 142, Summer 2013 Midterm Exam, Friday, July 26, 2013 Name: Section: TA: Student ID #: You have 60 minutes to complete this exam. You may receive a deduction if you keep working after the instructor
COSC 236 Section 101 Computer Science 1 -- Prof. Michael A. Soderstrand
 COSC 236 Section 101 Computer Science 1 -- Prof. Michael A. Soderstrand COSC 236 Web Site You will always find the course material at: http://www.class-notes.us or http://www.class-notes.info or http://www.lecture-notes.tripod.com
COSC 236 Section 101 Computer Science 1 -- Prof. Michael A. Soderstrand COSC 236 Web Site You will always find the course material at: http://www.class-notes.us or http://www.class-notes.info or http://www.lecture-notes.tripod.com
CSE142 Final Exam Key Summer 2018
 CSE142 Final Exam Key Summer 2018 1. Original Array Final Array -------------- ---------------------------- [10, 10, 10] [11, 11, 10] [2, 3, 4, 5] [3, 5, 5, 5] [3, 4, 5, 7, 9] [3, 5, 7, 9, 10] [2, 3, 5,
CSE142 Final Exam Key Summer 2018 1. Original Array Final Array -------------- ---------------------------- [10, 10, 10] [11, 11, 10] [2, 3, 4, 5] [3, 5, 5, 5] [3, 4, 5, 7, 9] [3, 5, 7, 9, 10] [2, 3, 5,
CSE 142 Sample Midterm Exam #3
 CSE 142 Sample Midterm Exam #3 1. Expressions (10 points) For each expression in the left-hand column, indicate its value in the right-hand column. Be sure to list a constant of appropriate type (e.g.,
CSE 142 Sample Midterm Exam #3 1. Expressions (10 points) For each expression in the left-hand column, indicate its value in the right-hand column. Be sure to list a constant of appropriate type (e.g.,
Menu Driven Systems. While loops, menus and the switch statement. Mairead Meagher Dr. Siobhán Drohan. Produced by:
 Menu Driven Systems While loops, menus and the switch statement Produced by: Mairead Meagher Dr. Siobhán Drohan Department of Computing and Mathematics http://www.wit.ie/ Topics list while loops recap
Menu Driven Systems While loops, menus and the switch statement Produced by: Mairead Meagher Dr. Siobhán Drohan Department of Computing and Mathematics http://www.wit.ie/ Topics list while loops recap
Solution to Test of Computer Science 203x Level Score: / 100 Time: 100 Minutes
 Solution to Test of Computer Science 203x Level Score: / 100 Time: 100 Minutes PART I: Multiple Choice (3 points each) Note: The correct answer can be any combination of A, B, C, D. Example, Sample Question:
Solution to Test of Computer Science 203x Level Score: / 100 Time: 100 Minutes PART I: Multiple Choice (3 points each) Note: The correct answer can be any combination of A, B, C, D. Example, Sample Question:
NoSuchElementException 5. Name of the Exception that occurs when you try to read past the end of the input data in a file.
 CSC116 Practice Exam 2 - KEY Part I: Vocabulary (10 points) Write the terms defined by the statements below. Cumulative Algorithm 1. An operation in which an overall value is computed incrementally, often
CSC116 Practice Exam 2 - KEY Part I: Vocabulary (10 points) Write the terms defined by the statements below. Cumulative Algorithm 1. An operation in which an overall value is computed incrementally, often
Midterm Examination (MTA)
 M105: Introduction to Programming with Java Midterm Examination (MTA) Spring 2013 / 2014 Question One: [6 marks] Choose the correct answer and write it on the external answer booklet. 1. Compilers and
M105: Introduction to Programming with Java Midterm Examination (MTA) Spring 2013 / 2014 Question One: [6 marks] Choose the correct answer and write it on the external answer booklet. 1. Compilers and
Section 003 Fall CS 170 Exam 2. Name (print): Instructions:
 CS 170 Exam 2 Section 003 Fall 2012 Name (print): Instructions: Keep your eyes on your own paper and do your best to prevent anyone else from seeing your work. Do NOT communicate with anyone other than
CS 170 Exam 2 Section 003 Fall 2012 Name (print): Instructions: Keep your eyes on your own paper and do your best to prevent anyone else from seeing your work. Do NOT communicate with anyone other than
CSE 142 Sample Midterm Exam #3
 CSE 142 Sample Midterm Exam #3 1. Expressions For each expression in the left-hand column, indicate its value in the right-hand column. Be sure to list a constant of appropriate type (e.g., 7.0 rather
CSE 142 Sample Midterm Exam #3 1. Expressions For each expression in the left-hand column, indicate its value in the right-hand column. Be sure to list a constant of appropriate type (e.g., 7.0 rather
Page 1 / 3. Page 2 / 18. Page 3 / 8. Page 4 / 21. Page 5 / 15. Page 6 / 20. Page 7 / 15. Total / 100. Pledge:
 This pledged exam is open text book and closed notes. Different questions have different points associated with them. Because your goal is to maximize your number of points, we recommend that you do not
This pledged exam is open text book and closed notes. Different questions have different points associated with them. Because your goal is to maximize your number of points, we recommend that you do not
Building Java Programs
 Building Java Programs Chapter 8: Classes Lecture 8-3: More Critters, static Testing Critters Focus on one specific Critter of one specific type Only spawn 1 of each Critter type Make sure your fields
Building Java Programs Chapter 8: Classes Lecture 8-3: More Critters, static Testing Critters Focus on one specific Critter of one specific type Only spawn 1 of each Critter type Make sure your fields
CSE 142, Autumn 2011 Midterm Exam: Friday, November 4, 2011
 CSE 142, Autumn 2011 Midterm Exam: Friday, November 4, 2011 Name: Section: Student ID #: TA: You have 50 minutes to complete this exam. You may receive a deduction if you keep working after the instructor
CSE 142, Autumn 2011 Midterm Exam: Friday, November 4, 2011 Name: Section: Student ID #: TA: You have 50 minutes to complete this exam. You may receive a deduction if you keep working after the instructor
(A) 99 ** (B) 100 (C) 101 (D) 100 initial integers plus any additional integers required during program execution
 Ch 5 Arrays Multiple Choice Test 01. An array is a ** (A) data structure with one, or more, elements of the same type. (B) data structure with LIFO access. (C) data structure, which allows transfer between
Ch 5 Arrays Multiple Choice Test 01. An array is a ** (A) data structure with one, or more, elements of the same type. (B) data structure with LIFO access. (C) data structure, which allows transfer between
CS 120 Fall 2008 Practice Final Exam v1.0m. Name: Model Solution. True/False Section, 20 points: 10 true/false, 2 points each
 CS 120 Fall 2008 Practice Final Exam v1.0m Name: Model Solution True/False Section, 20 points: 10 true/false, 2 points each Multiple Choice Section, 32 points: 8 multiple choice, 4 points each Code Tracing
CS 120 Fall 2008 Practice Final Exam v1.0m Name: Model Solution True/False Section, 20 points: 10 true/false, 2 points each Multiple Choice Section, 32 points: 8 multiple choice, 4 points each Code Tracing
CSE 142, Autumn 2010 Midterm Exam, Friday, November 5, 2010
 CSE 142, Autumn 2010 Midterm Exam, Friday, November 5, 2010 Name: Section: TA: Student ID #: You have 50 minutes to complete this exam. You may receive a deduction if you keep working after the instructor
CSE 142, Autumn 2010 Midterm Exam, Friday, November 5, 2010 Name: Section: TA: Student ID #: You have 50 minutes to complete this exam. You may receive a deduction if you keep working after the instructor
CSC 1051 Algorithms and Data Structures I. Final Examination May 12, Name
 CSC 1051 Algorithms and Data Structures I Final Examination May 12, 2017 Name Question Value Score 1 10 2 10 3 10 4 10 5 10 6 10 7 10 8 10 9 10 10 10 TOTAL 100 Please answer questions in the spaces provided.
CSC 1051 Algorithms and Data Structures I Final Examination May 12, 2017 Name Question Value Score 1 10 2 10 3 10 4 10 5 10 6 10 7 10 8 10 9 10 10 10 TOTAL 100 Please answer questions in the spaces provided.
CSE 142, Autumn 2018 Programming Assignment #9: Critters (20 points) Due Tuesday, December 4th, 9:00 PM
 CSE 142, Autumn 2018 Programming Assignment #9: Critters (20 points) Due Tuesday, December 4th, 9:00 PM This assignment focuses on classes and objects. Turn in Ant.java, Bird.java, Hippo.java, Vulture.java,
CSE 142, Autumn 2018 Programming Assignment #9: Critters (20 points) Due Tuesday, December 4th, 9:00 PM This assignment focuses on classes and objects. Turn in Ant.java, Bird.java, Hippo.java, Vulture.java,
CSC 1051 Algorithms and Data Structures I. Midterm Examination February 24, Name: KEY 1
 CSC 1051 Algorithms and Data Structures I Midterm Examination February 24, 2014 Name: KEY 1 Question Value Score 1 10 2 10 3 10 4 10 5 10 6 10 7 10 8 10 9 10 10 10 TOTAL 100 Please answer questions in
CSC 1051 Algorithms and Data Structures I Midterm Examination February 24, 2014 Name: KEY 1 Question Value Score 1 10 2 10 3 10 4 10 5 10 6 10 7 10 8 10 9 10 10 10 TOTAL 100 Please answer questions in
CSE142 Sample Midterm, Winter 2018
 CSE142 Sample Midterm, Winter 2018 1. Expressions, 10 points. For each expression in the left-hand column, indicate its value in the right-hand column. Be sure to list a constant of appropriate type (e.g.,
CSE142 Sample Midterm, Winter 2018 1. Expressions, 10 points. For each expression in the left-hand column, indicate its value in the right-hand column. Be sure to list a constant of appropriate type (e.g.,
CSCI 355 LAB #2 Spring 2004
 CSCI 355 LAB #2 Spring 2004 More Java Objectives: 1. To explore several Unix commands for displaying information about processes. 2. To explore some differences between Java and C++. 3. To write Java applications
CSCI 355 LAB #2 Spring 2004 More Java Objectives: 1. To explore several Unix commands for displaying information about processes. 2. To explore some differences between Java and C++. 3. To write Java applications
Critters. Critter #2 Attack.ROAR Attack.POUNCE Attack.SCRATCH. Critter #1
 Critters This assignment was co-created by Stuart Reges and Marty Stepp. This program focuses on classes, objects, and inheritance. You will write the following files: Ant.java, Bird.java, Crab.java, FireAnt.java,
Critters This assignment was co-created by Stuart Reges and Marty Stepp. This program focuses on classes, objects, and inheritance. You will write the following files: Ant.java, Bird.java, Crab.java, FireAnt.java,
CSE143 Notes for Monday, 4/25/11
 CSE143 Notes for Monday, 4/25/11 I began a new topic: recursion. We have seen how to write code using loops, which a technique called iteration. Recursion an alternative to iteration that equally powerful.
CSE143 Notes for Monday, 4/25/11 I began a new topic: recursion. We have seen how to write code using loops, which a technique called iteration. Recursion an alternative to iteration that equally powerful.
CS 307 Midterm 2 Spring 2011
 Points off 1 2 3 4 5 Total off Net Score Exam Number: CS 307 Midterm 2 Spring 2011 Name UTEID login name TA's Name: Dan Muhibur Oliver (Circle One) Instructions: 1. Please turn off your cell phones and
Points off 1 2 3 4 5 Total off Net Score Exam Number: CS 307 Midterm 2 Spring 2011 Name UTEID login name TA's Name: Dan Muhibur Oliver (Circle One) Instructions: 1. Please turn off your cell phones and
CSE 373 Section Handout #1 Numeric Data
 Numeric Data 1. binaryzeros Write a method named binaryzeros that accepts an integer n as a parameter and returns the number of zeros that occur in the binary representation of n. For example, the call
Numeric Data 1. binaryzeros Write a method named binaryzeros that accepts an integer n as a parameter and returns the number of zeros that occur in the binary representation of n. For example, the call
Topic 23 arrays - part 3 (tallying, text processing)
 Topic 23 arrays - part 3 (tallying, text processing) "42 million of anything is a lot." -Doug Burger (commenting on the number of transistors in the Pentium IV processor) Copyright Pearson Education, 2010
Topic 23 arrays - part 3 (tallying, text processing) "42 million of anything is a lot." -Doug Burger (commenting on the number of transistors in the Pentium IV processor) Copyright Pearson Education, 2010
CS 112 Introduction to Programming
 CS 112 Introduction to Programming Critters/Event-Driven Programming Yang (Richard) Yang Computer Science Department Yale University 308A Watson, Phone: 432-6400 Email: yry@cs.yale.edu Admin q Class project
CS 112 Introduction to Programming Critters/Event-Driven Programming Yang (Richard) Yang Computer Science Department Yale University 308A Watson, Phone: 432-6400 Email: yry@cs.yale.edu Admin q Class project
Name CIS 201 Midterm II: Chapters 1-8
 Name CIS 201 Midterm II: Chapters 1-8 December 15, 2010 Directions: This is a closed book, closed notes midterm. Place your answers in the space provided. The point value for each question is indicated.
Name CIS 201 Midterm II: Chapters 1-8 December 15, 2010 Directions: This is a closed book, closed notes midterm. Place your answers in the space provided. The point value for each question is indicated.
AP Computer Science Unit 1. Writing Programs Using BlueJ
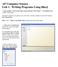 AP Computer Science Unit 1. Writing Programs Using BlueJ 1. Open up BlueJ. Click on the Project menu and select New Project. You should see the window on the right. Navigate to wherever you plan to save
AP Computer Science Unit 1. Writing Programs Using BlueJ 1. Open up BlueJ. Click on the Project menu and select New Project. You should see the window on the right. Navigate to wherever you plan to save
Building Java Programs
 Building Java Programs Chapter 9 Inheritance, Polymorphism; reading: 9.2 2 The software crisis software engineering: The practice of developing, designing, documenting, testing large computer programs.
Building Java Programs Chapter 9 Inheritance, Polymorphism; reading: 9.2 2 The software crisis software engineering: The practice of developing, designing, documenting, testing large computer programs.
CS 112 Introduction to Programming
 CS 112 Introduction to Programming Reference Semantics; 2D Arrays; Array as State Yang (Richard) Yang Computer Science Department Yale University 308A Watson, Phone: 432-6400 Email: yry@cs.yale.edu Admin
CS 112 Introduction to Programming Reference Semantics; 2D Arrays; Array as State Yang (Richard) Yang Computer Science Department Yale University 308A Watson, Phone: 432-6400 Email: yry@cs.yale.edu Admin
CS 112 Introduction to Programming
 CS 112 Introduction to Programming Reference Semantics; 2D Arrays; Array as State Yang (Richard) Yang Computer Science Department Yale University 308A Watson, Phone: 432-6400 Email: yry@cs.yale.edu Admin
CS 112 Introduction to Programming Reference Semantics; 2D Arrays; Array as State Yang (Richard) Yang Computer Science Department Yale University 308A Watson, Phone: 432-6400 Email: yry@cs.yale.edu Admin
CS 101 Spring 2007 Midterm 2 Name: ID:
 You only need to write your name and e-mail ID on the first page. This exam is CLOSED text book, closed-notes, closed-calculator, closed-neighbor, etc. Questions are worth different amounts, so be sure
You only need to write your name and e-mail ID on the first page. This exam is CLOSED text book, closed-notes, closed-calculator, closed-neighbor, etc. Questions are worth different amounts, so be sure
Admin. CS 112 Introduction to Programming. Recap: Arrays. Arrays class. Array Return (call) Array Return (declare) q Exam 1 Max: 50 Avg/median: 32
 Admin 100# 95# 90# 85# 80# CS 112 Introduction to Programming q Exam 1 Max: 50 Avg/median: 32 75# 70# 65# 60# 55# 50# 45# 40# 35# 30# 25# Reference Semantics; 2D Arrays; Array as State Yang (Richard) Yang
Admin 100# 95# 90# 85# 80# CS 112 Introduction to Programming q Exam 1 Max: 50 Avg/median: 32 75# 70# 65# 60# 55# 50# 45# 40# 35# 30# 25# Reference Semantics; 2D Arrays; Array as State Yang (Richard) Yang
CSE 143 Lecture 10. Recursive Programming. reading: slides adapted from Marty Stepp and Hélène Martin
 CSE 143 Lecture 10 Recursive Programming reading: 12.2-12.3 slides adapted from Marty Stepp and Hélène Martin http://www.cs.washington.edu/143/ Exercise Write a recursive method pow accepts an integer
CSE 143 Lecture 10 Recursive Programming reading: 12.2-12.3 slides adapted from Marty Stepp and Hélène Martin http://www.cs.washington.edu/143/ Exercise Write a recursive method pow accepts an integer
COMP 202 Java in one week
 CONTENTS: Basics of Programming Variables and Assignment Data Types: int, float, (string) Example: Implementing a calculator COMP 202 Java in one week The Java Programming Language A programming language
CONTENTS: Basics of Programming Variables and Assignment Data Types: int, float, (string) Example: Implementing a calculator COMP 202 Java in one week The Java Programming Language A programming language
CSE 142, Summer 2010 Midterm Exam, Friday, July 30, 2010
 CSE 142, Summer 2010 Midterm Exam, Friday, July 30, 2010 Name: Section: TA: Student ID #: You have 60 minutes to complete this exam. You may receive a deduction if you keep working after the instructor
CSE 142, Summer 2010 Midterm Exam, Friday, July 30, 2010 Name: Section: TA: Student ID #: You have 60 minutes to complete this exam. You may receive a deduction if you keep working after the instructor
CIS October 16, 2018
 CIS 1068 October 16, 2018 administrative stuff @@@ ADD ME @@@ Midterm Remember, the material is cumulative You ll see this stuff again Legal Identifiers c00lg33k is a legal identifier Legal Identifiers
CIS 1068 October 16, 2018 administrative stuff @@@ ADD ME @@@ Midterm Remember, the material is cumulative You ll see this stuff again Legal Identifiers c00lg33k is a legal identifier Legal Identifiers
CSC 1051 Algorithms and Data Structures I. Final Examination May 12, Name: KEY. Question Value Score
 CSC 1051 Algorithms and Data Structures I Final Examination May 12, 2017 Name: KEY Question Value Score 1 10 2 10 3 10 4 10 5 10 6 10 7 10 8 10 9 10 10 10 TOTAL 100 Please answer questions in the spaces
CSC 1051 Algorithms and Data Structures I Final Examination May 12, 2017 Name: KEY Question Value Score 1 10 2 10 3 10 4 10 5 10 6 10 7 10 8 10 9 10 10 10 TOTAL 100 Please answer questions in the spaces
(A) 99 (B) 100 (C) 101 (D) 100 initial integers plus any additional integers required during program execution
 Ch 5 Arrays Multiple Choice 01. An array is a (A) (B) (C) (D) data structure with one, or more, elements of the same type. data structure with LIFO access. data structure, which allows transfer between
Ch 5 Arrays Multiple Choice 01. An array is a (A) (B) (C) (D) data structure with one, or more, elements of the same type. data structure with LIFO access. data structure, which allows transfer between
Chapter 3. Selections
 Chapter 3 Selections 1 Outline 1. Flow of Control 2. Conditional Statements 3. The if Statement 4. The if-else Statement 5. The Conditional operator 6. The Switch Statement 7. Useful Hints 2 1. Flow of
Chapter 3 Selections 1 Outline 1. Flow of Control 2. Conditional Statements 3. The if Statement 4. The if-else Statement 5. The Conditional operator 6. The Switch Statement 7. Useful Hints 2 1. Flow of
Building Java Programs Chapter 7
 Building Java Programs Chapter 7 Arrays Copyright (c) Pearson 2013. All rights reserved. Can we solve this problem? Consider the following program (input underlined): How many days' temperatures? 7 Day
Building Java Programs Chapter 7 Arrays Copyright (c) Pearson 2013. All rights reserved. Can we solve this problem? Consider the following program (input underlined): How many days' temperatures? 7 Day
COSC 236 Section 101 Computer Science 1 -- Prof. Michael A. Soderstrand
 COSC 236 Section 101 Computer Science 1 -- Prof. Michael A. Soderstrand COSC 236 Web Site You will always find the course material at: http://www.class-notes.us or http://www.class-notes.info or http://www.lecture-notes.tripod.com
COSC 236 Section 101 Computer Science 1 -- Prof. Michael A. Soderstrand COSC 236 Web Site You will always find the course material at: http://www.class-notes.us or http://www.class-notes.info or http://www.lecture-notes.tripod.com
CSE 143X: Accelerated Computer Programming I/II HW5: Critters (due Friday, October 30, :30pm)
 CSE 143X: Accelerated Computer Programming I/II HW5: Critters (due Friday, October 30, 2015 11:30pm) This assignment focuses on Objects and Classes. Turn in the following files using the link on the course
CSE 143X: Accelerated Computer Programming I/II HW5: Critters (due Friday, October 30, 2015 11:30pm) This assignment focuses on Objects and Classes. Turn in the following files using the link on the course
Object Oriented Programming. Java-Lecture 1
 Object Oriented Programming Java-Lecture 1 Standard output System.out is known as the standard output object Methods to display text onto the standard output System.out.print prints text onto the screen
Object Oriented Programming Java-Lecture 1 Standard output System.out is known as the standard output object Methods to display text onto the standard output System.out.print prints text onto the screen
CSEN202: Introduction to Computer Science Spring Semester 2017 Midterm Exam
 Page 0 German University in Cairo April 6, 2017 Media Engineering and Technology Faculty Prof. Dr. Slim Abdennadher CSEN202: Introduction to Computer Science Spring Semester 2017 Midterm Exam Bar Code
Page 0 German University in Cairo April 6, 2017 Media Engineering and Technology Faculty Prof. Dr. Slim Abdennadher CSEN202: Introduction to Computer Science Spring Semester 2017 Midterm Exam Bar Code
CIS 1068 Design and Abstraction Spring 2017 Midterm 1a
 Spring 2017 Name: TUID: Page Points Score 1 28 2 18 3 12 4 12 5 15 6 15 Total: 100 Instructions The exam is closed book, closed notes. You may not use a calculator, cell phone, etc. i Some API Reminders
Spring 2017 Name: TUID: Page Points Score 1 28 2 18 3 12 4 12 5 15 6 15 Total: 100 Instructions The exam is closed book, closed notes. You may not use a calculator, cell phone, etc. i Some API Reminders
Admin. CS 112 Introduction to Programming. Admin. Admin. Recap. Recap: Polymorphism and Arrays. the Google doc to record the teaming
 Admin CS 112 Introduction to Programming Critters/Event-Driven Programming Yang (Richard) Yang Computer Science Department Yale University 308A Watson, Phone: 432-6400 Email: yry@cs.yale.edu q Class project
Admin CS 112 Introduction to Programming Critters/Event-Driven Programming Yang (Richard) Yang Computer Science Department Yale University 308A Watson, Phone: 432-6400 Email: yry@cs.yale.edu q Class project
Spring 2018 June 20 th, 2018 Extra Practice Problems. Short Problems
 CS106A Chris Piech Spring 2018 June 20 th, 2018 Extra Practice Problems Some of these problems are courtesy of Julia Daniel! Short Problems 1. Read integers in the console from a user until the user enters
CS106A Chris Piech Spring 2018 June 20 th, 2018 Extra Practice Problems Some of these problems are courtesy of Julia Daniel! Short Problems 1. Read integers in the console from a user until the user enters
Topic 21 arrays - part 1
 Topic 21 arrays - part 1 "Should array indices start at 0 or 1? My compromise of 0.5 was rejected without, I thought, proper consideration. " - Stan Kelly-Bootle Copyright Pearson Education, 2010 Based
Topic 21 arrays - part 1 "Should array indices start at 0 or 1? My compromise of 0.5 was rejected without, I thought, proper consideration. " - Stan Kelly-Bootle Copyright Pearson Education, 2010 Based
Introduction to Java Unit 1. Using BlueJ to Write Programs
 Introduction to Java Unit 1. Using BlueJ to Write Programs 1. Open up BlueJ. Click on the Project menu and select New Project. You should see the window on the right. Navigate to wherever you plan to save
Introduction to Java Unit 1. Using BlueJ to Write Programs 1. Open up BlueJ. Click on the Project menu and select New Project. You should see the window on the right. Navigate to wherever you plan to save
AP Computer Science Unit 1. Writing Programs Using BlueJ
 AP Computer Science Unit 1. Writing Programs Using BlueJ 1. Open up BlueJ. Click on the Project menu and select New Project. You should see the window on the right. Navigate to wherever you plan to save
AP Computer Science Unit 1. Writing Programs Using BlueJ 1. Open up BlueJ. Click on the Project menu and select New Project. You should see the window on the right. Navigate to wherever you plan to save
Building Java Programs
 Building Java Programs Chapter 7 Arrays reading: 7.1 2 Can we solve this problem? Consider the following program (input underlined): How many days' temperatures? 7 Day 1's high temp: 45 Day 2's high temp:
Building Java Programs Chapter 7 Arrays reading: 7.1 2 Can we solve this problem? Consider the following program (input underlined): How many days' temperatures? 7 Day 1's high temp: 45 Day 2's high temp:
1 Short Answer (5 Points Each)
 1 Short Answer (5 Points Each) 1. Write a declaration of an array of 300 strings. String strarray[] = new String[300];. Write a method that takes in an integer n as a parameter and returns one half of
1 Short Answer (5 Points Each) 1. Write a declaration of an array of 300 strings. String strarray[] = new String[300];. Write a method that takes in an integer n as a parameter and returns one half of
CS 101 Fall 2006 Midterm 3 Name: ID:
 You only need to write your name and e-mail ID on the first page. This exam is CLOSED text book, closed-notes, closed-calculator, closed-neighbor, etc. Questions are worth different amounts, so be sure
You only need to write your name and e-mail ID on the first page. This exam is CLOSED text book, closed-notes, closed-calculator, closed-neighbor, etc. Questions are worth different amounts, so be sure
Course Outline. Introduction to java
 Course Outline 1. Introduction to OO programming 2. Language Basics Syntax and Semantics 3. Algorithms, stepwise refinements. 4. Quiz/Assignment ( 5. Repetitions (for loops) 6. Writing simple classes 7.
Course Outline 1. Introduction to OO programming 2. Language Basics Syntax and Semantics 3. Algorithms, stepwise refinements. 4. Quiz/Assignment ( 5. Repetitions (for loops) 6. Writing simple classes 7.
CSE142 Sample Midterm Spring Name UW NetId (e.g. whitab) Section (e.g., AA) TA
 CSE142 Sample Midterm Spring 2018 Name UW NetId (e.g. whitab) Section (e.g., AA) TA This exam is divided into nine questions with the following points: # Problem Area Points Score ---------------------------------------------
CSE142 Sample Midterm Spring 2018 Name UW NetId (e.g. whitab) Section (e.g., AA) TA This exam is divided into nine questions with the following points: # Problem Area Points Score ---------------------------------------------
Lab Assignment Three
 Lab Assignment Three C212/A592 Fall Semester 2010 Due in OnCourse by Friday, September 17, 11:55pm (Dropbox will stay open until Saturday, September 18, 11:55pm) Abstract Read and solve the problems below.
Lab Assignment Three C212/A592 Fall Semester 2010 Due in OnCourse by Friday, September 17, 11:55pm (Dropbox will stay open until Saturday, September 18, 11:55pm) Abstract Read and solve the problems below.
AP CS Unit 6: Inheritance Exercises
 AP CS Unit 6: Inheritance Exercises 1. Suppose your program contains two classes: a Student class and a Female class. Which of the following is true? a) Making the Student class a subclass of the Female
AP CS Unit 6: Inheritance Exercises 1. Suppose your program contains two classes: a Student class and a Female class. Which of the following is true? a) Making the Student class a subclass of the Female
arrays - part 1 My methods are really methods of working and thinking; this is why they have crept in everywhere anonymously. Emmy Noether, Ph.D.
 Topic 21 https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=66702 arrays - part 1 My methods are really methods of working and thinking; this is why they have crept in everywhere anonymously. Emmy Noether,
Topic 21 https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=66702 arrays - part 1 My methods are really methods of working and thinking; this is why they have crept in everywhere anonymously. Emmy Noether,
