Expression statements are formed by adding a semicolon to the end of certain types of expressions.
|
|
|
- Janis Francis
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Expression statements are formed by adding a semicolon to the end of certain types of expressions. Variable declaration statements declare variables. int width, height, area; String hello = "Hello, world!"; An assignment expression is an expression involving an assignment. area = width * height; A method call expression has no assignment. System.out.println(...); A block is a sequence of one or more statements enclosed by braces( ). x = 1; y = 2; System.out.println(y); System.out.println(x); A block with declarations int i = 5 + j; // i is declared in this // block j is from where // end of block, i disappears //can t access i here An empty statement or null statement is just a semicolon all by itself and results in no action. x = 1; y = 2;;;;; System.out.println(y); ;;;;; System.out.println(x);
2 A boolean expression is any expression that evaluates to either true or false. Java includes a primitive type boolean. Relational operators, <, <=, >, >= Equality operators, ==,!= int i = 3, j = 4; boolean flag; flag = 5 < 6; //flag is now true flag = (i == j); //flag is now false flag = (j + 2) <= 6; //flag is now true Operators that take boolean values as operands. x && y - true if x AND y are both true x y - true if either x OR y are true, or both!x - true if x is false - read NOT x boolean b = (ageofperson >= 18 && ageofperson < 65); System.out.println("full fare adult is " + b); b = (ageofperson < 18 ageofperson >= 65); System.out.println("reduced fare is " + b); if The if statement is a conditional statement. if ( BooleanExpr ) Statement If the expression BooleanExpr is true, then the statement, Statement, is executed. Otherwise, Statement is skipped. if statement with a single statement if (temperature < 32) System.out.println("Warning: Below freezing!"); System.out.println("It s " + temperature + " degrees"); if statement with a block if (temperature < 32) System.out.println("Warning: Below freezing!");
3 Problem A different number is initially placed in each of three boxes, labeled a, b, and c, respectively. The problem is to rearrange or sort the numbers so that the final number in box a is less than that in box b and that the number in box b is less than that in box c. 1. Place the first number in box a. 2. Place the second number in box b. 3. Place the third number in box c. 4. If the number in a is not larger than the number in b, go to step Interchange the number in a with that in b. 6. If the number in b is larger than the number in c, then go to step 7; otherwise, halt. 7. Interchange the numbers in b and c. 8. If the number in a is larger than that in b, then go to step 9; otherwise, halt. 9. Interchange the numbers in a and b. 10.Halt. // SortInput.java - sort three numbers import java.util.*; class SortInput public static void main (String[] args) int a, b, c, t; Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.println("type three integers:"); a = scan.nextint(); b = scan.nextint(); c = scan.nextint(); if (a > b) // swap a and b t = a; a = b; b = t; if (b > c) // swap b and c t = b; b = c; c = t; if (a > b) // swap a and b t = a; a = b; b = t; // This doesn t match the pseudo-code. Why not? System.out.print("The sorted order is : "); System.out.println(a + ", " + b + ", " + c);
4 if- An if- statement has the following form: if ( BooleanExpr ) Statement1 Statement2 If the expression BooleanExpr is true, then Statement1 is executed and Statement2 is skipped. If BooleanExpr is false, then Statement1 is skipped and Statement2 is executed. Finding the minimum if (x < y) min = x; min = y; System.out.println("min = " + min); A block in an if- statement if (temperature < 32) System.out.println(32 - temperature + " degrees below freezing!"); System.out.println("It s " + temperature + "degrees fahrenheit."); if- if (x < y); System.out.println("The smaller is " + x); if (y < x); System.out.println("The smaller is " + y); if (temperature < 32) System.out.print("It is now"); System.out.print(32 - temperature); System.out.println(" below freezing."); System.out.println("It's " + temperature + "degrees"); The if statement is a full-fledged statement and can be used anywhere a statement is expected. So, you can put another if statement in either branch of an if statement. if (ageofperson >= 18) if (ageofperson < 65) System.out.println("full fare adult"); if (ageofperson >= 18 && ageofperson < 65) System.out.println("full fare adult");
5 if (temperature < 32) if (temperature < 0) System.out.println((-temperature) + " degrees below Zero!" System.out.println(32 - temperature + "(F) below Freezing!"); System.out.println("It is " + temperature + " degrees fahrenheit."); if (18 <= age < 65). if (ageofperson < 18) System.out.println("child fare"); if (ageofperson < 65) System.out.println("adult fare"); System.out.println("senior fare"); Each statement is surrounded in the following figure. if (ageofperson < 18) System.out.println("child fare"); if (ageofperson < 65) System.out.println("adult fare"); System.out.println("senior fare"); Sometimes this chain of if--if--if- can get rather long, tedious, and inefficient.
6 while Misleading indentation if (Expression1) if (Expression2) Statement1 Statement2 The indenting suggests that Statement2 is executed whenever Expression1 is false. The proper indenting is if (Expression1) if (Expression2) Statement1 Statement2 Or, uses braces to force the grouping. if (Expression1) if (Expression2) Statement1 Statement2 The while statement allows us to write programs that run repeatedly. while ( BooleanExpr ) Statement Statement is executed repeatedly as long as the expression BooleanExpr is true. class Valentine public static void main(string[] args) int howmuch = 0; while (howmuch < 5) System.out.println("I love you."); howmuch++; Pseudocode using goto 1. Get a number. 2. If the number is 0 go to step Add the number to the running total. 4. Increment the count of numbers read in. 5. Go back to step Divide the running total by the count of number in order to get the average. 7. Print the average. Pseudocode using while Get a number. While the number is not 0 do the following: Add the number to the running total. Increment the count of numbers read in. Get a number. (when the loop exits) Divide the running total by the count of number in order to get the average. Print the average.
7 // Average.java - compute average of input values import java.util.*; public class Average public static void main(string[] args) double number; int count = 0; double runningtotal = 0; Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in); // initialization before first loop iteration System.out.println("Type some numbers, the last one being 0"); number = scan.nextdouble(); while (number!= 0) runningtotal = runningtotal + number; count = count + 1; // prepare for next iteration number = scan.nextdouble(); System.out.print("The average of the "); System.out.print(count); System.out.print(" numbers is "); System.out.println(runningTotal / count); int count = 13; System.out.println("The multiples of 13 between 1 and 100 are:"); while (count!= 100) System.out.println(count); count = count + 13; do-while A variant of the while statement. do Statement while ( BooleanExpr ); Statement is executed at least once. Execution stops when the expression BooleanExpr is false. Finding GCD (Greatest Common Divisor) for two integers. import java.util.*; class GreatestCommonDivisor public static void main(string[] args) Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.println("Enter 2 integers."); int num1 = scan.nextint(); int num2 = scan.nextint(); int m = num1, n = num2, remainder; do remainder = m % n; m = n; n = remainder; while( n!= 0); System.out.println("GCD (" + num1 + ", " + num2 + ") = " + m );
8 for The for statement is a looping statement that captures the initialization, termination test, and iteration preparation all in one place at the top of the loop. for ( ForInit; BooleanExpr; Updateexpr ) Statement // SquareRoots.java - print square roots of 1-10 import static java.lang.math.*; public class SquareRoots public static void main(string[] args) int i; double squareroot; for (i = 1; i <= 10; i++) squareroot = sqrt(i); System.out.println("the square root of " + i + " is " + squareroot); System.out.println("That's All!"); for The ForInit part of the for statement can be a local declaration. for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) squareroot = sqrt(i); System.out.println("the square root of " + i + " is " + squareroot); The int variable i is limited to the for statement. Outside the for statement, it disappears. break The break statement causes an exit from the innermost enclosing loop. while (true) //seemingly an infinite loop System("Enter a positive integer:") n = scan.nextint(); if (n < 0) // exit loop if n is negative System.out.print("squareroot of " + n); System.out.println(" = " + Math.sqrt(n)); // break jumps here
9 continue The continue statement causes the current iteration of a loop to stop and causes the next iteration of the loop to begin immediately. // BreakContinue.java - example of break and continue import java.util.*; class BreakContinue public static void main(string[] args) int n; Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in); while (true) //seemingly an infinite loop System.out.print("Enter a positive integer "); System.out.print("or 0 to exit:"); n = scan.nextint(); if (n == 0) // exit loop if n is 0 if (n < 0) continue; //wrong value System.out.print("squareroot of " + n); System.out.println(" = " + Math.sqrt(n)); //continue lands here at end of current iteration //break lands here System.out.println("a zero was entered"); switch The switch statement can be used in place of a long chain of if--if--if- statements when the condition tested evaluates to an integer numeric type. Day of week with if- if (dayofweek == 1) System.out.println("Sunday"); if (dayofweek == 2) System.out.println("Monday"); if (dayofweek == 3) System.out.println("Tuesday"); if (dayofweek == 4) System.out.println("Wednesday"); if (dayofweek == 5) System.out.println("Thursday"); if (dayofweek == 6) System.out.println("Friday"); if (dayofweek == 7) System.out.println("Saturday"); System.out.println("Not a day number " + dayofweek); Day of week with switch switch (dayofweek) case 1: System.out.println("Sunday"); case 2: System.out.println("Monday"); case 3: System.out.println("Tuesday"); case 4: System.out.println("Wednesday"); case 5: System.out.println("Thursday"); case 6: System.out.println("Friday"); case 7: System.out.println("Saturday"); default: System.out.println("Not a day number " + dayofweek);
10 Day of week grouping weekdays and weekends switch (dayofweek) case 1: case 7: System.out.println("Stay home today!"); case 2: case 3: case 4: case 5: case 6: System.out.println("Go to work."); default: println("not a day number " + dayofweek); Several rules of boolean algebra are useful for rewriting boolean expressions. Commutative law a or b == b or a a and b == b and a Distributive and law a and (b or c) == (a and b) or (a and c) Distributive or law a or (b and c) == (a or b) and (a or c) Double negation!!a == a DeMorgan s law!(a or b) ==!a and!b!(a and b) ==!a or!b In the expression x y, y will not be evaluated if x is true. In the expression x && y, y will not be evaluated if x is false. int x = 0; int y = 0; if (x == 0 y++ == 2) System.out.println ( true ); System.out.println ( y = + y); Same Result? int x = 0; int y = 0; if (x == 1 && y++ == 2) System.out.println ( true ); System.out.println ( y = + y); Same Result? int x = 0; int y = 0; if (y++ == 2 x == 0) System.out.println ( true ); System.out.println ( y = + y); int x = 0; int y = 0; if (y++ == 2 x == 1) System.out.println ( true ); System.out.println ( y = + y);
COSC 123 Computer Creativity. Java Decisions and Loops. Dr. Ramon Lawrence University of British Columbia Okanagan
 COSC 123 Computer Creativity Java Decisions and Loops Dr. Ramon Lawrence University of British Columbia Okanagan ramon.lawrence@ubc.ca Key Points 1) A decision is made by evaluating a condition in an if/else
COSC 123 Computer Creativity Java Decisions and Loops Dr. Ramon Lawrence University of British Columbia Okanagan ramon.lawrence@ubc.ca Key Points 1) A decision is made by evaluating a condition in an if/else
More Control Structures
 Chapter 8 More Control Structures 1 8.1 Exceptions When a Java program performs an illegal operation, an exception happens. If a program has no special provisions for dealing with exceptions, it will behave
Chapter 8 More Control Structures 1 8.1 Exceptions When a Java program performs an illegal operation, an exception happens. If a program has no special provisions for dealing with exceptions, it will behave
Oct Decision Structures cont d
 Oct. 29 - Decision Structures cont d Programming Style and the if Statement Even though an if statement usually spans more than one line, it is really one statement. For instance, the following if statements
Oct. 29 - Decision Structures cont d Programming Style and the if Statement Even though an if statement usually spans more than one line, it is really one statement. For instance, the following if statements
CSC 1051 Villanova University. CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I. Course website:
 Repetition CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University Course website: www.csc.villanova.edu/~map/1051/ Some slides in this
Repetition CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University Course website: www.csc.villanova.edu/~map/1051/ Some slides in this
Key Points. COSC 123 Computer Creativity. Java Decisions and Loops. Making Decisions Performing Comparisons. Making Decisions
 COSC 123 Computer Creativity Java Decisions and Loops Dr. Ramon Lawrence University of British Columbia Okanagan ramon.lawrence@ubc.ca Key Points 1) A decision is made by evaluating a condition in an if/
COSC 123 Computer Creativity Java Decisions and Loops Dr. Ramon Lawrence University of British Columbia Okanagan ramon.lawrence@ubc.ca Key Points 1) A decision is made by evaluating a condition in an if/
CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I
 Repetition CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University Course website: www.csc.villanova.edu/~map/1051/ Some slides in this
Repetition CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University Course website: www.csc.villanova.edu/~map/1051/ Some slides in this
Le L c e t c ur u e e 3 To T p o i p c i s c t o o b e b e co c v o e v r e ed e Control Statements
 Course Name: Advanced Java Lecture 3 Topics to be covered Control Statements Introduction The control statement are used to control the flow of execution of the program. This execution order depends on
Course Name: Advanced Java Lecture 3 Topics to be covered Control Statements Introduction The control statement are used to control the flow of execution of the program. This execution order depends on
COMP 202 Java in one week
 CONTENTS: Basics of Programming Variables and Assignment Data Types: int, float, (string) Example: Implementing a calculator COMP 202 Java in one week The Java Programming Language A programming language
CONTENTS: Basics of Programming Variables and Assignment Data Types: int, float, (string) Example: Implementing a calculator COMP 202 Java in one week The Java Programming Language A programming language
Java Programming: from the Beginning. Chapter 8 More Control Structures. CSc 2310: Principle of Programming g( (Java) Spring 2013
 CSc 2310: Principle of Programming g( (Java) Spring 2013 Java Programming: from the Beginning Chapter 8 More Control Structures 1 Copyright 2000 W. W. Norton & Company. All rights reserved. 81 8.1 Exceptions
CSc 2310: Principle of Programming g( (Java) Spring 2013 Java Programming: from the Beginning Chapter 8 More Control Structures 1 Copyright 2000 W. W. Norton & Company. All rights reserved. 81 8.1 Exceptions
Repetition, Looping. While Loop
 Repetition, Looping Last time we looked at how to use if-then statements to control the flow of a program. In this section we will look at different ways to repeat blocks of statements. Such repetitions
Repetition, Looping Last time we looked at how to use if-then statements to control the flow of a program. In this section we will look at different ways to repeat blocks of statements. Such repetitions
Loops. CSE 114, Computer Science 1 Stony Brook University
 Loops CSE 114, Computer Science 1 Stony Brook University http://www.cs.stonybrook.edu/~cse114 1 Motivation Suppose that you need to print a string (e.g., "Welcome to Java!") a user-defined times N: N?
Loops CSE 114, Computer Science 1 Stony Brook University http://www.cs.stonybrook.edu/~cse114 1 Motivation Suppose that you need to print a string (e.g., "Welcome to Java!") a user-defined times N: N?
COMP 202. Java in one week
 COMP 202 CONTENTS: Basics of Programming Variables and Assignment Data Types: int, float, (string) Example: Implementing a calculator Java in one week The Java Programming Language A programming language
COMP 202 CONTENTS: Basics of Programming Variables and Assignment Data Types: int, float, (string) Example: Implementing a calculator Java in one week The Java Programming Language A programming language
Please answer the following questions. Do not re-code the enclosed codes if you have already completed them.
 Dec. 9 Loops Please answer the following questions. Do not re-code the enclosed codes if you have already completed them. What is a loop? What are the three loops in Java? What do control structures do?
Dec. 9 Loops Please answer the following questions. Do not re-code the enclosed codes if you have already completed them. What is a loop? What are the three loops in Java? What do control structures do?
Sequence structure. The computer executes java statements one after the other in the order in which they are written. Total = total +grade;
 Control Statements Control Statements All programs could be written in terms of only one of three control structures: Sequence Structure Selection Structure Repetition Structure Sequence structure The
Control Statements Control Statements All programs could be written in terms of only one of three control structures: Sequence Structure Selection Structure Repetition Structure Sequence structure The
Java Programming: Guided Learning with Early Objects Chapter 5 Control Structures II: Repetition
 Java Programming: Guided Learning with Early Objects Chapter 5 Control Structures II: Repetition Learn about repetition (looping) control structures Explore how to construct and use: o Counter-controlled
Java Programming: Guided Learning with Early Objects Chapter 5 Control Structures II: Repetition Learn about repetition (looping) control structures Explore how to construct and use: o Counter-controlled
COMP-202 Unit 4: Programming With Iterations. CONTENTS: The while and for statements
 COMP-202 Unit 4: Programming With Iterations CONTENTS: The while and for statements Introduction (1) Suppose we want to write a program to be used in cash registers in stores to compute the amount of money
COMP-202 Unit 4: Programming With Iterations CONTENTS: The while and for statements Introduction (1) Suppose we want to write a program to be used in cash registers in stores to compute the amount of money
Values in 2 s Complement
 Values in 2 s Complement Java uses an encoding known as 2 s complement 1, which means that negative numbers are represented by inverting 2 all of the bits in a value, then adding 1 to the result. For example,
Values in 2 s Complement Java uses an encoding known as 2 s complement 1, which means that negative numbers are represented by inverting 2 all of the bits in a value, then adding 1 to the result. For example,
Example. Write a program which sums two random integers and lets the user repeatedly enter a new answer until it is correct.
 Example Write a program which sums two random integers and lets the user repeatedly enter a new answer until it is correct. 1... 2 Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); 3 int x = (int) (Math.random()
Example Write a program which sums two random integers and lets the user repeatedly enter a new answer until it is correct. 1... 2 Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); 3 int x = (int) (Math.random()
Chapter 3. Selections
 Chapter 3 Selections 1 Outline 1. Flow of Control 2. Conditional Statements 3. The if Statement 4. The if-else Statement 5. The Conditional operator 6. The Switch Statement 7. Useful Hints 2 1. Flow of
Chapter 3 Selections 1 Outline 1. Flow of Control 2. Conditional Statements 3. The if Statement 4. The if-else Statement 5. The Conditional operator 6. The Switch Statement 7. Useful Hints 2 1. Flow of
Java Programming: Guided Learning with Early Objects Chapter 5 Control Structures II: Repetition
 Java Programming: Guided Learning with Early Objects Chapter 5 Control Structures II: Repetition Learn about repetition (looping) control structures Explore how to construct and use: o Counter-controlled
Java Programming: Guided Learning with Early Objects Chapter 5 Control Structures II: Repetition Learn about repetition (looping) control structures Explore how to construct and use: o Counter-controlled
Java I/O and Control Structures
 Java I/O and Control Structures CSC 2014 Java Bootcamp Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University Some slides in this presentation are adapted from the slides accompanying
Java I/O and Control Structures CSC 2014 Java Bootcamp Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University Some slides in this presentation are adapted from the slides accompanying
In this chapter, you will:
 Java Programming: Guided Learning with Early Objects Chapter 4 Control Structures I: Selection In this chapter, you will: Make decisions with the if and if else structures Use compound statements in an
Java Programming: Guided Learning with Early Objects Chapter 4 Control Structures I: Selection In this chapter, you will: Make decisions with the if and if else structures Use compound statements in an
Basic computer skills such as using Windows, Internet Explorer, and Microsoft Word. Chapter 1 Introduction to Computers, Programs, and Java
 Basic computer skills such as using Windows, Internet Explorer, and Microsoft Word Chapter 1 Introduction to Computers, Programs, and Java Chapter 2 Primitive Data Types and Operations Chapter 3 Selection
Basic computer skills such as using Windows, Internet Explorer, and Microsoft Word Chapter 1 Introduction to Computers, Programs, and Java Chapter 2 Primitive Data Types and Operations Chapter 3 Selection
Introduction to Computer Science, Shimon Schocken, IDC Herzliya. Lectures Control Structures
 Introduction to Computer Science, Shimon Schocken, IDC Herzliya Lectures 3.1 3.2 Control Structures Control Structures, Shimon Schocken IDC Herzliya, www.intro2cs.com slide 1 Control structures A program
Introduction to Computer Science, Shimon Schocken, IDC Herzliya Lectures 3.1 3.2 Control Structures Control Structures, Shimon Schocken IDC Herzliya, www.intro2cs.com slide 1 Control structures A program
Java Basic Programming Constructs
 Java Basic Programming Constructs /* * This is your first java program. */ class HelloWorld{ public static void main(string[] args){ System.out.println( Hello World! ); A Closer Look at HelloWorld 2 This
Java Basic Programming Constructs /* * This is your first java program. */ class HelloWorld{ public static void main(string[] args){ System.out.println( Hello World! ); A Closer Look at HelloWorld 2 This
Computer Programming I - Unit 5 Lecture page 1 of 14
 page 1 of 14 I. The while Statement while, for, do Loops Note: Loop - a control structure that causes a sequence of statement(s) to be executed repeatedly. The while statement is one of three looping statements
page 1 of 14 I. The while Statement while, for, do Loops Note: Loop - a control structure that causes a sequence of statement(s) to be executed repeatedly. The while statement is one of three looping statements
1 class Lecture3 { 2 3 "Selections" // Keywords 8 if, else, else if, switch, case, default. Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 89 / 137
 1 class Lecture3 { 2 3 "Selections" 4 5 } 6 7 // Keywords 8 if, else, else if, switch, case, default Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 89 / 137 Flow Controls The basic algorithm (and program) is constituted
1 class Lecture3 { 2 3 "Selections" 4 5 } 6 7 // Keywords 8 if, else, else if, switch, case, default Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 89 / 137 Flow Controls The basic algorithm (and program) is constituted
Java I/O and Control Structures Algorithms in everyday life
 Introduction Java I/O and Control Structures Algorithms in everyday life CSC 2014 Java Bootcamp Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University Source: http://xkcd.com/627/
Introduction Java I/O and Control Structures Algorithms in everyday life CSC 2014 Java Bootcamp Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University Source: http://xkcd.com/627/
CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I
 Repetition CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University Course website: www.csc.villanova.edu/~map/1051/ Some slides in this
Repetition CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University Course website: www.csc.villanova.edu/~map/1051/ Some slides in this
CS111: PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE II
 CS111: PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE II Computer Science Department Lecture 1(c): Java Basics (II) Lecture Contents Java basics (part II) Conditions Loops Methods Conditions & Branching Conditional Statements A
CS111: PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE II Computer Science Department Lecture 1(c): Java Basics (II) Lecture Contents Java basics (part II) Conditions Loops Methods Conditions & Branching Conditional Statements A
1 class Lecture3 { 2 3 "Selections" // Keywords 8 if, else, else if, switch, case, default. Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 88 / 133
 1 class Lecture3 { 2 3 "Selections" 4 5 } 6 7 // Keywords 8 if, else, else if, switch, case, default Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 88 / 133 Flow Controls The basic algorithm (and program) is constituted
1 class Lecture3 { 2 3 "Selections" 4 5 } 6 7 // Keywords 8 if, else, else if, switch, case, default Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 88 / 133 Flow Controls The basic algorithm (and program) is constituted
Chapter 4: Control Structures I
 Chapter 4: Control Structures I Java Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program Design, Second Edition Chapter Objectives Learn about control structures. Examine relational and logical operators. Explore
Chapter 4: Control Structures I Java Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program Design, Second Edition Chapter Objectives Learn about control structures. Examine relational and logical operators. Explore
Exam 2, Version 2. For the following code, mark True or False for statements 1.8 to 1.10.
 1. True or False (clearly write True or False on each line). 1.1. It s possible for the body of a do-while loop to execute zero times F For the following code, mark True or False for statements 1.8 to
1. True or False (clearly write True or False on each line). 1.1. It s possible for the body of a do-while loop to execute zero times F For the following code, mark True or False for statements 1.8 to
CMPT 125: Lecture 4 Conditionals and Loops
 CMPT 125: Lecture 4 Conditionals and Loops Tamara Smyth, tamaras@cs.sfu.ca School of Computing Science, Simon Fraser University January 17, 2009 1 Flow of Control The order in which statements are executed
CMPT 125: Lecture 4 Conditionals and Loops Tamara Smyth, tamaras@cs.sfu.ca School of Computing Science, Simon Fraser University January 17, 2009 1 Flow of Control The order in which statements are executed
Tutorial # 4. Q1. Evaluate the logical (Boolean) expression in the following exercise
 Tutorial # 4 Q1. Evaluate the logical (Boolean) expression in the following exercise 1 int num1 = 3, num2 = 2; (num1 > num2) 2 double hours = 12.8; (hours > 40.2) 3 int funny = 7; (funny!= 1) 4 double
Tutorial # 4 Q1. Evaluate the logical (Boolean) expression in the following exercise 1 int num1 = 3, num2 = 2; (num1 > num2) 2 double hours = 12.8; (hours > 40.2) 3 int funny = 7; (funny!= 1) 4 double
Iteration statements - Loops
 Iteration statements - Loops : ) הוראות חזרה / לולאות ( statements Java has three kinds of iteration WHILE FOR DO... WHILE loop loop loop Iteration (repetition) statements causes Java to execute one or
Iteration statements - Loops : ) הוראות חזרה / לולאות ( statements Java has three kinds of iteration WHILE FOR DO... WHILE loop loop loop Iteration (repetition) statements causes Java to execute one or
Lectures 3-1, 3-2. Control Structures. Control Structures, Shimon Schocken IDC Herzliya, slide 1
 Introduction to Computer Science Shimon Schocken IDC Herzliya Lectures 3-1, 3-2 Control Structures Control Structures, Shimon Schocken IDC Herzliya, www.intro2cs.com slide 1 Shorthand operators (increment
Introduction to Computer Science Shimon Schocken IDC Herzliya Lectures 3-1, 3-2 Control Structures Control Structures, Shimon Schocken IDC Herzliya, www.intro2cs.com slide 1 Shorthand operators (increment
AP CS Unit 3: Control Structures Notes
 AP CS Unit 3: Control Structures Notes The if and if-else Statements. These statements are called control statements because they control whether a particular block of code is executed or not. Some texts
AP CS Unit 3: Control Structures Notes The if and if-else Statements. These statements are called control statements because they control whether a particular block of code is executed or not. Some texts
Java Coding 3. Over & over again!
 Java Coding 3 Over & over again! Repetition Java repetition statements while (condition) statement; do statement; while (condition); where for ( init; condition; update) statement; statement is any Java
Java Coding 3 Over & over again! Repetition Java repetition statements while (condition) statement; do statement; while (condition); where for ( init; condition; update) statement; statement is any Java
COMP-202: Foundations of Programming. Lecture 3: Boolean, Mathematical Expressions, and Flow Control Sandeep Manjanna, Summer 2015
 COMP-202: Foundations of Programming Lecture 3: Boolean, Mathematical Expressions, and Flow Control Sandeep Manjanna, Summer 2015 Announcements Slides will be posted before the class. There might be few
COMP-202: Foundations of Programming Lecture 3: Boolean, Mathematical Expressions, and Flow Control Sandeep Manjanna, Summer 2015 Announcements Slides will be posted before the class. There might be few
Java Foundations: Introduction to Program Design & Data Structures, 4e John Lewis, Peter DePasquale, Joseph Chase Test Bank: Chapter 2
 Java Foundations Introduction to Program Design and Data Structures 4th Edition Lewis TEST BANK Full download at : https://testbankreal.com/download/java-foundations-introduction-toprogram-design-and-data-structures-4th-edition-lewis-test-bank/
Java Foundations Introduction to Program Design and Data Structures 4th Edition Lewis TEST BANK Full download at : https://testbankreal.com/download/java-foundations-introduction-toprogram-design-and-data-structures-4th-edition-lewis-test-bank/
Arithmetic Compound Assignment Operators
 Arithmetic Compound Assignment Operators Note that these shorthand operators are not available in languages such as Matlab and R. Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 76 / 141 Example 1... 2 int x = 1; 3 System.out.println(x);
Arithmetic Compound Assignment Operators Note that these shorthand operators are not available in languages such as Matlab and R. Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 76 / 141 Example 1... 2 int x = 1; 3 System.out.println(x);
3chapter C ONTROL S TATEMENTS. Objectives
 3chapter C ONTROL S TATEMENTS Objectives To understand the flow of control in selection and loop statements ( 3.2 3.7). To use Boolean expressions to control selection statements and loop statements (
3chapter C ONTROL S TATEMENTS Objectives To understand the flow of control in selection and loop statements ( 3.2 3.7). To use Boolean expressions to control selection statements and loop statements (
CSC 1051 Algorithms and Data Structures I. Midterm Examination February 25, Name: KEY A
 CSC 1051 Algorithms and Data Structures I Midterm Examination February 25, 2016 Name: KEY A Question Value Score 1 10 2 10 3 10 4 10 5 10 6 10 7 10 8 10 9 10 10 10 TOTAL 100 Please answer questions in
CSC 1051 Algorithms and Data Structures I Midterm Examination February 25, 2016 Name: KEY A Question Value Score 1 10 2 10 3 10 4 10 5 10 6 10 7 10 8 10 9 10 10 10 TOTAL 100 Please answer questions in
Chapter 5 Control Statements: Part 2 Section 5.2 Essentials of Counter-Controlled Repetition
 Chapter 5 Control Statements: Part 2 Section 5.2 Essentials of Counter-Controlled Repetition 5.2 Q1: Counter-controlled repetition requires a. A control variable and initial value. b. A control variable
Chapter 5 Control Statements: Part 2 Section 5.2 Essentials of Counter-Controlled Repetition 5.2 Q1: Counter-controlled repetition requires a. A control variable and initial value. b. A control variable
Iteration: Intro. Two types of loops: 1. Pretest Condition precedes body Iterates 0+ times. 2. Posttest Condition follows body Iterates 1+ times
 Iteration: Intro Two types of loops: 1. Pretest Condition precedes body Iterates 0+ times 2. Posttest Condition follows body Iterates 1+ times 1 Iteration: While Loops Pretest loop Most general loop construct
Iteration: Intro Two types of loops: 1. Pretest Condition precedes body Iterates 0+ times 2. Posttest Condition follows body Iterates 1+ times 1 Iteration: While Loops Pretest loop Most general loop construct
Module 3 SELECTION STRUCTURES 2/15/19 CSE 1321 MODULE 3 1
 Module 3 SELECTION STRUCTURES 2/15/19 CSE 1321 MODULE 3 1 Motivation In the programs we have written thus far, statements are executed one after the other, in the order in which they appear. Programs often
Module 3 SELECTION STRUCTURES 2/15/19 CSE 1321 MODULE 3 1 Motivation In the programs we have written thus far, statements are executed one after the other, in the order in which they appear. Programs often
SOFTWARE DEVELOPMENT 1. Control Structures 2018W A. Ferscha (Institute of Pervasive Computing, JKU Linz)
 SOFTWARE DEVELOPMENT 1 Control Structures 2018W (Institute of Pervasive Computing, JKU Linz) WHAT IS CONTROL FLOW? The control flow determines the order in which instructions are executed. Default: from
SOFTWARE DEVELOPMENT 1 Control Structures 2018W (Institute of Pervasive Computing, JKU Linz) WHAT IS CONTROL FLOW? The control flow determines the order in which instructions are executed. Default: from
! definite loop: A loop that executes a known number of times. " The for loops we have seen so far are definite loops. ! We often use language like
 Indefinite loops while loop! indefinite loop: A loop where it is not obvious in advance how many times it will execute.! We often use language like " "Keep looping as long as or while this condition is
Indefinite loops while loop! indefinite loop: A loop where it is not obvious in advance how many times it will execute.! We often use language like " "Keep looping as long as or while this condition is
CONTENTS: Compilation Data and Expressions COMP 202. More on Chapter 2
 CONTENTS: Compilation Data and Expressions COMP 202 More on Chapter 2 Programming Language Levels There are many programming language levels: machine language assembly language high-level language Java,
CONTENTS: Compilation Data and Expressions COMP 202 More on Chapter 2 Programming Language Levels There are many programming language levels: machine language assembly language high-level language Java,
Scanner Objects. Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 82 / 133
 Scanner Objects It is not convenient to modify the source code and recompile it for a different radius. Reading from the console enables the program to receive an input from the user. A Scanner object
Scanner Objects It is not convenient to modify the source code and recompile it for a different radius. Reading from the console enables the program to receive an input from the user. A Scanner object
School of Computer Science CPS109 Course Notes 6 Alexander Ferworn Updated Fall 15. CPS109 Course Notes 6. Alexander Ferworn
 CPS109 Course Notes 6 Alexander Ferworn Unrelated Facts Worth Remembering Use metaphors to understand issues and explain them to others. Look up what metaphor means. Table of Contents Contents 1 ITERATION...
CPS109 Course Notes 6 Alexander Ferworn Unrelated Facts Worth Remembering Use metaphors to understand issues and explain them to others. Look up what metaphor means. Table of Contents Contents 1 ITERATION...
CS111: PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE II
 1 CS111: PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE II Computer Science Department Lecture 1: Introduction Lecture Contents 2 Course info Why programming?? Why Java?? Write once, run anywhere!! Java basics Input/output Variables
1 CS111: PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE II Computer Science Department Lecture 1: Introduction Lecture Contents 2 Course info Why programming?? Why Java?? Write once, run anywhere!! Java basics Input/output Variables
DM503 Programming B. Peter Schneider-Kamp.
 DM503 Programming B Peter Schneider-Kamp petersk@imada.sdu.dk! http://imada.sdu.dk/~petersk/dm503/! VARIABLES, EXPRESSIONS & STATEMENTS 2 Values and Types Values = basic data objects 42 23.0 "Hello!" Types
DM503 Programming B Peter Schneider-Kamp petersk@imada.sdu.dk! http://imada.sdu.dk/~petersk/dm503/! VARIABLES, EXPRESSIONS & STATEMENTS 2 Values and Types Values = basic data objects 42 23.0 "Hello!" Types
CONDITIONAL EXECUTION
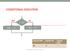 CONDITIONAL EXECUTION yes x > y? no max = x; max = y; logical AND logical OR logical NOT &&! Fundamentals of Computer Science I Outline Conditional Execution if then if then Nested if then statements Comparisons
CONDITIONAL EXECUTION yes x > y? no max = x; max = y; logical AND logical OR logical NOT &&! Fundamentals of Computer Science I Outline Conditional Execution if then if then Nested if then statements Comparisons
Chapter 4 Loops. Liang, Introduction to Java Programming, Eighth Edition, (c) 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 4 Loops 1 Motivations Suppose that you need to print a string (e.g., "Welcome to Java!") a hundred times. It would be tedious to have to write the following statement a hundred times: So, how do
Chapter 4 Loops 1 Motivations Suppose that you need to print a string (e.g., "Welcome to Java!") a hundred times. It would be tedious to have to write the following statement a hundred times: So, how do
Wentworth Institute of Technology. Engineering & Technology WIT COMP1000. Simple Control Flow: if-else statements
 WIT COMP1000 Simple Control Flow: if-else statements Control Flow Control flow is the order in which program statements are executed So far, all of our programs have been executed straight-through from
WIT COMP1000 Simple Control Flow: if-else statements Control Flow Control flow is the order in which program statements are executed So far, all of our programs have been executed straight-through from
Repe$$on CSC 121 Spring 2017 Howard Rosenthal
 Repe$$on CSC 121 Spring 2017 Howard Rosenthal Lesson Goals Learn the following three repetition structures in Java, their syntax, their similarities and differences, and how to avoid common errors when
Repe$$on CSC 121 Spring 2017 Howard Rosenthal Lesson Goals Learn the following three repetition structures in Java, their syntax, their similarities and differences, and how to avoid common errors when
Control Structures in Java if-else and switch
 Control Structures in Java if-else and switch Lecture 4 CGS 3416 Spring 2017 January 23, 2017 Lecture 4CGS 3416 Spring 2017 Selection January 23, 2017 1 / 26 Control Flow Control flow refers to the specification
Control Structures in Java if-else and switch Lecture 4 CGS 3416 Spring 2017 January 23, 2017 Lecture 4CGS 3416 Spring 2017 Selection January 23, 2017 1 / 26 Control Flow Control flow refers to the specification
Review. Primitive Data Types & Variables. String Mathematical operators: + - * / % Comparison: < > <= >= == int, long float, double boolean char
 Review Primitive Data Types & Variables int, long float, double boolean char String Mathematical operators: + - * / % Comparison: < > = == 1 1.3 Conditionals and Loops Introduction to Programming in
Review Primitive Data Types & Variables int, long float, double boolean char String Mathematical operators: + - * / % Comparison: < > = == 1 1.3 Conditionals and Loops Introduction to Programming in
Introduction to the Java Basics: Control Flow Statements
 Lesson 3: Introduction to the Java Basics: Control Flow Statements Repetition Structures THEORY Variable Assignment You can only assign a value to a variable that is consistent with the variable s declared
Lesson 3: Introduction to the Java Basics: Control Flow Statements Repetition Structures THEORY Variable Assignment You can only assign a value to a variable that is consistent with the variable s declared
Common Errors double area; 3 if (r > 0); 4 area = r r 3.14; 5 System.out.println(area); 6... Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 101 / 141
 Common Errors 2 double area; 3 if (r > 0); 4 area = r r 3.14; 5 System.out.println(area); 6... Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 101 / 141 Generating random numbers Example Write a program which generates
Common Errors 2 double area; 3 if (r > 0); 4 area = r r 3.14; 5 System.out.println(area); 6... Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 101 / 141 Generating random numbers Example Write a program which generates
Building Java Programs
 Building Java Programs Chapter 5 Lecture 5-1: while Loops, Fencepost Loops, and Sentinel Loops reading: 4.1, 5.1 self-check: Ch. 4 #2; Ch. 5 # 1-10 exercises: Ch. 4 #2, 4, 5, 8; Ch. 5 # 1-2 Copyright 2009
Building Java Programs Chapter 5 Lecture 5-1: while Loops, Fencepost Loops, and Sentinel Loops reading: 4.1, 5.1 self-check: Ch. 4 #2; Ch. 5 # 1-10 exercises: Ch. 4 #2, 4, 5, 8; Ch. 5 # 1-2 Copyright 2009
Example: Monte Carlo Simulation 1
 Example: Monte Carlo Simulation 1 Write a program which conducts a Monte Carlo simulation to estimate π. 1 See https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/monte_carlo_method. Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 133 / 149
Example: Monte Carlo Simulation 1 Write a program which conducts a Monte Carlo simulation to estimate π. 1 See https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/monte_carlo_method. Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 133 / 149
1 Short Answer (10 Points Each)
 1 Short Answer (10 Points Each) 1. Write a for loop that will calculate a factorial. Assume that the value n has been input by the user and have the loop create n! and store it in the variable fact. Recall
1 Short Answer (10 Points Each) 1. Write a for loop that will calculate a factorial. Assume that the value n has been input by the user and have the loop create n! and store it in the variable fact. Recall
Logic is the anatomy of thought. John Locke ( ) This sentence is false.
 Logic is the anatomy of thought. John Locke (1632 1704) This sentence is false. I know that I know nothing. anonymous Plato (In Apology, Plato relates that Socrates accounts for his seeming wiser than
Logic is the anatomy of thought. John Locke (1632 1704) This sentence is false. I know that I know nothing. anonymous Plato (In Apology, Plato relates that Socrates accounts for his seeming wiser than
Selec%on and Decision Structures in Java: If Statements and Switch Statements CSC 121 Spring 2016 Howard Rosenthal
 Selec%on and Decision Structures in Java: If Statements and Switch Statements CSC 121 Spring 2016 Howard Rosenthal Lesson Goals Understand Control Structures Understand how to control the flow of a program
Selec%on and Decision Structures in Java: If Statements and Switch Statements CSC 121 Spring 2016 Howard Rosenthal Lesson Goals Understand Control Structures Understand how to control the flow of a program
AP Programming - Chapter 6 Lecture
 page 1 of 21 The while Statement, Types of Loops, Looping Subtasks, Nested Loops I. The while Statement Note: Loop - a control structure that causes a sequence of statement(s) to be executed repeatedly.
page 1 of 21 The while Statement, Types of Loops, Looping Subtasks, Nested Loops I. The while Statement Note: Loop - a control structure that causes a sequence of statement(s) to be executed repeatedly.
CONTENTS: While loops Class (static) variables and constants Top Down Programming For loops Nested Loops
 COMP-202 Unit 4: Programming with Iterations Doing the same thing again and again and again and again and again and again and again and again and again... CONTENTS: While loops Class (static) variables
COMP-202 Unit 4: Programming with Iterations Doing the same thing again and again and again and again and again and again and again and again and again... CONTENTS: While loops Class (static) variables
Introduction to Computer Science Unit 2. Notes
 Introduction to Computer Science Unit 2. Notes Name: Objectives: By the completion of this packet, students should be able to describe the difference between.java and.class files and the JVM. create and
Introduction to Computer Science Unit 2. Notes Name: Objectives: By the completion of this packet, students should be able to describe the difference between.java and.class files and the JVM. create and
Term 1 Unit 1 Week 1 Worksheet: Output Solution
 4 Term 1 Unit 1 Week 1 Worksheet: Output Solution Consider the following what is output? 1. System.out.println("hot"); System.out.println("dog"); Output hot dog 2. System.out.print("hot\n\t\t"); System.out.println("dog");
4 Term 1 Unit 1 Week 1 Worksheet: Output Solution Consider the following what is output? 1. System.out.println("hot"); System.out.println("dog"); Output hot dog 2. System.out.print("hot\n\t\t"); System.out.println("dog");
switch-case Statements
 switch-case Statements A switch-case structure takes actions depending on the target variable. 2 switch (target) { 3 case v1: 4 // statements 5 break; 6 case v2: 7. 8. 9 case vk: 10 // statements 11 break;
switch-case Statements A switch-case structure takes actions depending on the target variable. 2 switch (target) { 3 case v1: 4 // statements 5 break; 6 case v2: 7. 8. 9 case vk: 10 // statements 11 break;
Some Sample AP Computer Science A Questions - Solutions
 Some Sample AP Computer Science A Questions - s Note: These aren't from actual AP tests. I've created these questions based on looking at actual AP tests. Also, in cases where it's not necessary to have
Some Sample AP Computer Science A Questions - s Note: These aren't from actual AP tests. I've created these questions based on looking at actual AP tests. Also, in cases where it's not necessary to have
Computer Programming, I. Laboratory Manual. Experiment #6. Loops
 Think Twice Code Once The Islamic University of Gaza Engineering Faculty Department of Computer Engineering Fall 2017 ECOM 2005 Khaleel I. Shaheen Computer Programming, I Laboratory Manual Experiment #6
Think Twice Code Once The Islamic University of Gaza Engineering Faculty Department of Computer Engineering Fall 2017 ECOM 2005 Khaleel I. Shaheen Computer Programming, I Laboratory Manual Experiment #6
Condensed Java. 12-Oct-15
 Condensed Java 12-Oct-15 Python and Java Python and Java are both object-oriented languages Conceptually, the languages are very similar The syntax, however, is quite different, and Java syntax is much
Condensed Java 12-Oct-15 Python and Java Python and Java are both object-oriented languages Conceptually, the languages are very similar The syntax, however, is quite different, and Java syntax is much
Motivating Examples (1.1) Selections. Motivating Examples (1.2) Learning Outcomes. EECS1022: Programming for Mobile Computing Winter 2018
 Motivating Examples (1.1) Selections EECS1022: Programming for Mobile Computing Winter 2018 CHEN-WEI WANG 1 import java.util.scanner; 2 public class ComputeArea { 3 public static void main(string[] args)
Motivating Examples (1.1) Selections EECS1022: Programming for Mobile Computing Winter 2018 CHEN-WEI WANG 1 import java.util.scanner; 2 public class ComputeArea { 3 public static void main(string[] args)
CSC 1051 Algorithms and Data Structures I. Midterm Examination February 24, Name: KEY 1
 CSC 1051 Algorithms and Data Structures I Midterm Examination February 24, 2014 Name: KEY 1 Question Value Score 1 10 2 10 3 10 4 10 5 10 6 10 7 10 8 10 9 10 10 10 TOTAL 100 Please answer questions in
CSC 1051 Algorithms and Data Structures I Midterm Examination February 24, 2014 Name: KEY 1 Question Value Score 1 10 2 10 3 10 4 10 5 10 6 10 7 10 8 10 9 10 10 10 TOTAL 100 Please answer questions in
Repe$$on CSC 121 Fall 2015 Howard Rosenthal
 Repe$$on CSC 121 Fall 2015 Howard Rosenthal Lesson Goals Learn the following three repetition methods, their similarities and differences, and how to avoid common errors when using them: while do-while
Repe$$on CSC 121 Fall 2015 Howard Rosenthal Lesson Goals Learn the following three repetition methods, their similarities and differences, and how to avoid common errors when using them: while do-while
Top-Down Program Development
 Top-Down Program Development Top-down development is a way of thinking when you try to solve a programming problem It involves starting with the entire problem, and breaking it down into more manageable
Top-Down Program Development Top-down development is a way of thinking when you try to solve a programming problem It involves starting with the entire problem, and breaking it down into more manageable
Selections. EECS1021: Object Oriented Programming: from Sensors to Actuators Winter 2019 CHEN-WEI WANG
 Selections EECS1021: Object Oriented Programming: from Sensors to Actuators Winter 2019 CHEN-WEI WANG Learning Outcomes The Boolean Data Type if Statement Compound vs. Primitive Statement Common Errors
Selections EECS1021: Object Oriented Programming: from Sensors to Actuators Winter 2019 CHEN-WEI WANG Learning Outcomes The Boolean Data Type if Statement Compound vs. Primitive Statement Common Errors
Important Java terminology
 1 Important Java terminology The information we manage in a Java program is either represented as primitive data or as objects. Primitive data פרימיטיביים) (נתונים include common, fundamental values as
1 Important Java terminology The information we manage in a Java program is either represented as primitive data or as objects. Primitive data פרימיטיביים) (נתונים include common, fundamental values as
Repetition, Looping CS101
 Repetition, Looping CS101 Last time we looked at how to use if-then statements to control the flow of a program. In this section we will look at different ways to repeat blocks of statements. Such repetitions
Repetition, Looping CS101 Last time we looked at how to use if-then statements to control the flow of a program. In this section we will look at different ways to repeat blocks of statements. Such repetitions
Algorithms and Java basics: pseudocode, variables, assignment, and interactive programs
 Algorithms and Java basics: pseudocode, variables, assignment, and interactive programs CSC 1051 Algorithms and Data Structures I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova
Algorithms and Java basics: pseudocode, variables, assignment, and interactive programs CSC 1051 Algorithms and Data Structures I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova
Introduction. C provides two styles of flow control:
 Introduction C provides two styles of flow control: Branching Looping Branching is deciding what actions to take and looping is deciding how many times to take a certain action. Branching constructs: if
Introduction C provides two styles of flow control: Branching Looping Branching is deciding what actions to take and looping is deciding how many times to take a certain action. Branching constructs: if
Chapter 5 Loops Liang, Introduction to Java Programming, Tenth Edition, Global Edition. Pearson Education Limited
 Chapter 5 Loops Liang, Introduction to Java Programming, Tenth Edition, Global Edition. Pearson Education Limited 2015 1 Motivations Suppose that you need to print a string (e.g., "Welcome to Java!") a
Chapter 5 Loops Liang, Introduction to Java Programming, Tenth Edition, Global Edition. Pearson Education Limited 2015 1 Motivations Suppose that you need to print a string (e.g., "Welcome to Java!") a
Object-oriented programming in...
 Programming Languages Week 12 Object-oriented programming in... College of Information Science and Engineering Ritsumeikan University plan this week intro to Java advantages and disadvantages language
Programming Languages Week 12 Object-oriented programming in... College of Information Science and Engineering Ritsumeikan University plan this week intro to Java advantages and disadvantages language
Algorithms and Java basics: pseudocode, variables, assignment, and interactive programs
 Algorithms and Java basics: pseudocode, variables, assignment, and interactive programs CSC 1051 Algorithms and Data Structures I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova
Algorithms and Java basics: pseudocode, variables, assignment, and interactive programs CSC 1051 Algorithms and Data Structures I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova
Computer Programming, I. Laboratory Manual. Experiment #2. Elementary Programming
 Think Twice Code Once The Islamic University of Gaza Engineering Faculty Department of Computer Engineering Fall 2017 ECOM 2005 Khaleel I. Shaheen Computer Programming, I Laboratory Manual Experiment #2
Think Twice Code Once The Islamic University of Gaza Engineering Faculty Department of Computer Engineering Fall 2017 ECOM 2005 Khaleel I. Shaheen Computer Programming, I Laboratory Manual Experiment #2
Control Structures: if and while A C S L E C T U R E 4
 Control Structures: if and while A C S - 1903 L E C T U R E 4 Control structures 3 constructs are essential building blocks for programs Sequences compound statement Decisions if, switch, conditional operator
Control Structures: if and while A C S - 1903 L E C T U R E 4 Control structures 3 constructs are essential building blocks for programs Sequences compound statement Decisions if, switch, conditional operator
CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I
 Repetition CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University Course website: www.csc.villanova.edu/~map/1051/ Some slides in this
Repetition CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University Course website: www.csc.villanova.edu/~map/1051/ Some slides in this
STUDENT LESSON A12 Iterations
 STUDENT LESSON A12 Iterations Java Curriculum for AP Computer Science, Student Lesson A12 1 STUDENT LESSON A12 Iterations INTRODUCTION: Solving problems on a computer very often requires a repetition of
STUDENT LESSON A12 Iterations Java Curriculum for AP Computer Science, Student Lesson A12 1 STUDENT LESSON A12 Iterations INTRODUCTION: Solving problems on a computer very often requires a repetition of
Fundamentals of Programming Data Types & Methods
 Fundamentals of Programming Data Types & Methods By Budditha Hettige Overview Summary (Previous Lesson) Java Data types Default values Variables Input data from keyboard Display results Methods Operators
Fundamentals of Programming Data Types & Methods By Budditha Hettige Overview Summary (Previous Lesson) Java Data types Default values Variables Input data from keyboard Display results Methods Operators
JAVA PROGRAMMING LAB. ABSTRACT In this Lab you will learn to define and invoke void and return java methods
 Islamic University of Gaza Faculty of Engineering Computer Engineering Dept. Computer Programming Lab (ECOM 2114) ABSTRACT In this Lab you will learn to define and invoke void and return java methods JAVA
Islamic University of Gaza Faculty of Engineering Computer Engineering Dept. Computer Programming Lab (ECOM 2114) ABSTRACT In this Lab you will learn to define and invoke void and return java methods JAVA
Conditionals and Loops Chapter 4. Instructor: Scott Kristjanson CMPT 125/125 SFU Burnaby, Fall 2013
 Conditionals and Loops Chapter 4 Instructor: Scott Kristjanson CMPT 125/125 SFU Burnaby, Fall 2013 2 Scope Flow of control Boolean expressions if and switch statements Comparing data while, do, and for
Conditionals and Loops Chapter 4 Instructor: Scott Kristjanson CMPT 125/125 SFU Burnaby, Fall 2013 2 Scope Flow of control Boolean expressions if and switch statements Comparing data while, do, and for
Example. Write a program which generates 2 random integers and asks the user to answer the math expression.
 Generating random numbers Example Write a program which generates 2 random integers and asks the user to answer the math expression. For example, the program shows 2 + 5 =? If the user answers 7, then
Generating random numbers Example Write a program which generates 2 random integers and asks the user to answer the math expression. For example, the program shows 2 + 5 =? If the user answers 7, then
Combo Lecture Lecture 14/15. Instructor: Craig Duckett
 Combo Lecture Lecture 14/15 Instructor: Craig Duckett Assignment Dates (By Due Date) Assignment 1 (LECTURE 5) GRADED! Section 1: Monday, January 22 nd Assignment 2 (LECTURE 8) GRADED! Section 1: Wednesday,
Combo Lecture Lecture 14/15 Instructor: Craig Duckett Assignment Dates (By Due Date) Assignment 1 (LECTURE 5) GRADED! Section 1: Monday, January 22 nd Assignment 2 (LECTURE 8) GRADED! Section 1: Wednesday,
Program Fundamentals
 Program Fundamentals /* HelloWorld.java * The classic Hello, world! program */ class HelloWorld { public static void main (String[ ] args) { System.out.println( Hello, world! ); } } /* HelloWorld.java
Program Fundamentals /* HelloWorld.java * The classic Hello, world! program */ class HelloWorld { public static void main (String[ ] args) { System.out.println( Hello, world! ); } } /* HelloWorld.java
Selec%on and Decision Structures in Java: If Statements and Switch Statements CSC 121 Fall 2016 Howard Rosenthal
 Selec%on and Decision Structures in Java: If Statements and Switch Statements CSC 121 Fall 2016 Howard Rosenthal Lesson Goals Understand Control Structures Understand how to control the flow of a program
Selec%on and Decision Structures in Java: If Statements and Switch Statements CSC 121 Fall 2016 Howard Rosenthal Lesson Goals Understand Control Structures Understand how to control the flow of a program
Example. Generating random numbers. Write a program which generates 2 random integers and asks the user to answer the math expression.
 Example Generating random numbers Write a program which generates 2 random integers and asks the user to answer the math expression. For example, the program shows 2 + 5 =? If the user answers 7, then
Example Generating random numbers Write a program which generates 2 random integers and asks the user to answer the math expression. For example, the program shows 2 + 5 =? If the user answers 7, then
Conditional Programming
 COMP-202 Conditional Programming Chapter Outline Control Flow of a Program The if statement The if - else statement Logical Operators The switch statement The conditional operator 2 Introduction So far,
COMP-202 Conditional Programming Chapter Outline Control Flow of a Program The if statement The if - else statement Logical Operators The switch statement The conditional operator 2 Introduction So far,
