Simple C++ Program. #include <iostream> using namespace std; int main() { //Note cout << Hello World << endl; return 0;
|
|
|
- Marylou Cameron
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Programming Review
2 Simple C++ Program cout << Hello World << endl;
3 Variables gpa = 4.0;
4 Formatting gpa = 4.0;
5 Conditionals gpa = 4.0; cout << Letter Grade is cout << an A ; cout << not A ;
6 Control Structures times = 3; gpa = 4.0; cout << Letter Grade is ; cout << an A ; cout << not A ; cout <<! ;
7 Functions double calculategpa() return 4.0; times = 3; gpa = calculategpa(); cout << Letter Grade is ; cout << an A ; cout << not A ; cout <<! ;
8 times = 3; gpa = calculategpa(); Function Overloading cout << Letter Grade is ; cout << an A ; cout << not A ; cout <<! ; double calculategpa() return 4.0; double calculategpa(double g1) return g1; double calculategpa(double g1, double g2) return (g1 + g2) / 2.0;
9 Default Function Parameters times = 3; gpa = calculategpa(); double calculategpa(double g1 = 4.0) return g1; double calculategpa(double g1, double g2) return (g1 + g2) / 2.0; cout << Letter Grade is ; cout << an A ; cout << not A ; cout <<! ;
10 Pass By Reference gpa = calculategpa(×); double calculategpa(int& times, double g1 = 4.0) times = 1; return g1; double calculategpa(int times, double g1, double g2) times = 2; return (g1 + g2) / 2; cout << Letter Grade is ; cout << an A ; cout << not A ; cout <<! ;
11 Random Number Generation #include <cstdlib> #include <ctime> srand(time(0)); gpa = calculategpa(×); double calculategpa(int& times, double g1 = 4.0) times = rand() % 10; return g1; double calculategpa(int times, double g1, double g2) times = (rand() % 10) + 1; return (g1 + g2) / 2; cout << Letter Grade is ; cout << an A ; cout << not A ; cout <<! ;
12 #include <cstdlib> #include <ctime> #include <fstream> ofstream output; srand(time(0)); gpa = calculategpa(×); output.open( gpa.txt ); File I/O double calculategpa(int& times, double g1 = 4.0) times = rand() % 10; return g1; double calculategpa(int times, double g1, double g2) times = (rand() % 10) + 1; return (g1 + g2) / 2; output << fixed << showpoint << setprecision(2); output << GPA: << gpa << \n ; output << Letter Grade is ; output << an A ; output << not A ; output <<! ; output.close();
13 #include <cstdlib> #include <ctime> #include <fstream> ofstream output; srand(time(0)); gpa = calculategpa(×); output.open( gpa.txt ); Arrays double calculategpa(int& times, double g1 = 4.0) times = rand() % 10; return g1; double calculategpa(int times, double g1, double g2) times = (rand() % 10) + 1; return (g1 + g2) / 2; output << fixed << showpoint << setprecision(2); output << GPA: << gpa << \n ; output << Letter Grade is ; output << an A ; output << not A ; output <<! ; double calculategpa(double grades[], int number) double ret = 0.0; for (int i = 0; i < number; i++) ret += grades[i]; ret /= number; return ret; output.close();
14 #include <cstdlib> #include <ctime> #include <fstream> int *times; ofstream output; srand(time(0)); times = new int; gpa = calculategpa(times); output.open( gpa.txt ); Pointers and Memory Allocation double calculategpa(int* times, double g1 = 4.0) *times = rand() % 10; return g1; double calculategpa(int times, double g1, double g2) times = (rand() % 10) + 1; return (g1 + g2) / 2; output << fixed << showpoint << setprecision(2); output << GPA: << gpa << \n ; output << Letter Grade is ; output << an A ; output << not A ; for (int i = 0; i < *times; i++) output <<! ; output.close(); delete times; double calculategpa(double grades[], int number) double ret = 0.0; for (int i = 0; i < number; i++) ret += grades[i]; ret /= number; return ret;
15 Need More? Professor Myers' COP3014 lecture notes: +/notes/index3014.html
Software Design & Programming I
 Software Design & Programming I Starting Out with C++ (From Control Structures through Objects) 7th Edition Written by: Tony Gaddis Pearson - Addison Wesley ISBN: 13-978-0-132-57625-3 Chapter 3 Introduction
Software Design & Programming I Starting Out with C++ (From Control Structures through Objects) 7th Edition Written by: Tony Gaddis Pearson - Addison Wesley ISBN: 13-978-0-132-57625-3 Chapter 3 Introduction
Come and join us at WebLyceum
 Come and join us at WebLyceum For Past Papers, Quiz, Assignments, GDBs, Video Lectures etc Go to http://www.weblyceum.com and click Register In Case of any Problem Contact Administrators Rana Muhammad
Come and join us at WebLyceum For Past Papers, Quiz, Assignments, GDBs, Video Lectures etc Go to http://www.weblyceum.com and click Register In Case of any Problem Contact Administrators Rana Muhammad
Strings and Streams. Professor Hugh C. Lauer CS-2303, System Programming Concepts
 Strings and Streams Professor Hugh C. Lauer CS-2303, System Programming Concepts (Slides include materials from The C Programming Language, 2 nd edition, by Kernighan and Ritchie, Absolute C++, by Walter
Strings and Streams Professor Hugh C. Lauer CS-2303, System Programming Concepts (Slides include materials from The C Programming Language, 2 nd edition, by Kernighan and Ritchie, Absolute C++, by Walter
for (int i = 1; i <= 3; i++) { do { cout << "Enter a positive integer: "; cin >> n;
 // Workshop 1 #include using namespace std; int main () int n, k; int sumdigits; for (int i = 1; i n; cin.clear (); cin.ignore (100,
// Workshop 1 #include using namespace std; int main () int n, k; int sumdigits; for (int i = 1; i n; cin.clear (); cin.ignore (100,
[CSE10200] Programming Basis ( 프로그래밍기초 ) Chapter 7. Seungkyu Lee. Assistant Professor, Dept. of Computer Engineering Kyung Hee University
![[CSE10200] Programming Basis ( 프로그래밍기초 ) Chapter 7. Seungkyu Lee. Assistant Professor, Dept. of Computer Engineering Kyung Hee University [CSE10200] Programming Basis ( 프로그래밍기초 ) Chapter 7. Seungkyu Lee. Assistant Professor, Dept. of Computer Engineering Kyung Hee University](/thumbs/76/73745429.jpg) [CSE10200] Programming Basis ( 프로그래밍기초 ) Chapter 7 Seungkyu Lee Assistant Professor, Dept. of Computer Engineering Kyung Hee University Input entities Keyboard, files Output entities Monitor, files Standard
[CSE10200] Programming Basis ( 프로그래밍기초 ) Chapter 7 Seungkyu Lee Assistant Professor, Dept. of Computer Engineering Kyung Hee University Input entities Keyboard, files Output entities Monitor, files Standard
File Operations. Lecture 16 COP 3014 Spring April 18, 2018
 File Operations Lecture 16 COP 3014 Spring 2018 April 18, 2018 Input/Ouput to and from files File input and file output is an essential in programming. Most software involves more than keyboard input and
File Operations Lecture 16 COP 3014 Spring 2018 April 18, 2018 Input/Ouput to and from files File input and file output is an essential in programming. Most software involves more than keyboard input and
PROGRAMMING EXAMPLE: Checking Account Balance
 Programming Example: Checking Account Balance 1 PROGRAMMING EXAMPLE: Checking Account Balance A local bank in your town is looking for someone to write a program that calculates a customer s checking account
Programming Example: Checking Account Balance 1 PROGRAMMING EXAMPLE: Checking Account Balance A local bank in your town is looking for someone to write a program that calculates a customer s checking account
Files Total: // Files Example 1. #include <iostream> #include <fstream>
 Files // Files Example 1 datafile.open("datafile01.txt"); 61.7 86.36 78.12 Total: 261.43 // Prime the reading of the file. while(datafile) cout
Files // Files Example 1 datafile.open("datafile01.txt"); 61.7 86.36 78.12 Total: 261.43 // Prime the reading of the file. while(datafile) cout
Fundamentals of Programming Session 25
 Fundamentals of Programming Session 25 Instructor: Reza Entezari-Maleki Email: entezari@ce.sharif.edu 1 Fall 2013 These slides have been created using Deitel s slides Sharif University of Technology Outlines
Fundamentals of Programming Session 25 Instructor: Reza Entezari-Maleki Email: entezari@ce.sharif.edu 1 Fall 2013 These slides have been created using Deitel s slides Sharif University of Technology Outlines
The C++ Language. Output. Input and Output. Another type supplied by C++ Very complex, made up of several simple types.
 The C++ Language Input and Output Output! Output is information generated by a program.! Frequently sent the screen or a file.! An output stream is used to send information. Another type supplied by C++
The C++ Language Input and Output Output! Output is information generated by a program.! Frequently sent the screen or a file.! An output stream is used to send information. Another type supplied by C++
Reading from and Writing to Files. Files (3.12) Steps to Using Files. Section 3.12 & 13.1 & Data stored in variables is temporary
 Reading from and Writing to Files Section 3.12 & 13.1 & 13.5 11/3/08 CS150 Introduction to Computer Science 1 1 Files (3.12) Data stored in variables is temporary We will learn how to write programs that
Reading from and Writing to Files Section 3.12 & 13.1 & 13.5 11/3/08 CS150 Introduction to Computer Science 1 1 Files (3.12) Data stored in variables is temporary We will learn how to write programs that
IS 0020 Program Design and Software Tools
 1 IS 0020 Program Design and Software Tools Stack/Queue - File Processing Lecture 10 March 29, 2005 Introduction 2 Storage of data Arrays, variables are temporary Files are permanent Magnetic disk, optical
1 IS 0020 Program Design and Software Tools Stack/Queue - File Processing Lecture 10 March 29, 2005 Introduction 2 Storage of data Arrays, variables are temporary Files are permanent Magnetic disk, optical
Arrays in C++ Instructor: Andy Abreu
 Arrays in C++ Instructor: Andy Abreu Reason behind the idea When we are programming, often we have to process a large amount of information. We can do so by creating a lot of variables to keep track of
Arrays in C++ Instructor: Andy Abreu Reason behind the idea When we are programming, often we have to process a large amount of information. We can do so by creating a lot of variables to keep track of
Review for COSC 120 8/31/2017. Review for COSC 120 Computer Systems. Review for COSC 120 Computer Structure
 Computer Systems Computer System Computer Structure C++ Environment Imperative vs. object-oriented programming in C++ Input / Output Primitive data types Software Banking System Compiler Music Player Text
Computer Systems Computer System Computer Structure C++ Environment Imperative vs. object-oriented programming in C++ Input / Output Primitive data types Software Banking System Compiler Music Player Text
Week 3: File I/O and Formatting 3.7 Formatting Output
 Week 3: File I/O and Formatting 3.7 Formatting Output Formatting: the way a value is printed: Gaddis: 3.7, 3.8, 5.11 CS 1428 Fall 2014 Jill Seaman spacing decimal points, fractional values, number of digits
Week 3: File I/O and Formatting 3.7 Formatting Output Formatting: the way a value is printed: Gaddis: 3.7, 3.8, 5.11 CS 1428 Fall 2014 Jill Seaman spacing decimal points, fractional values, number of digits
C++ Programming Lecture 10 File Processing
 C++ Programming Lecture 10 File Processing By Ghada Al-Mashaqbeh The Hashemite University Computer Engineering Department Outline Introduction. The Data Hierarchy. Files and Streams. Creating a Sequential
C++ Programming Lecture 10 File Processing By Ghada Al-Mashaqbeh The Hashemite University Computer Engineering Department Outline Introduction. The Data Hierarchy. Files and Streams. Creating a Sequential
File I/O Christian Schumacher, Info1 D-MAVT 2013
 File I/O Christian Schumacher, chschuma@inf.ethz.ch Info1 D-MAVT 2013 Input and Output in C++ Stream objects Formatted output Writing and reading files References General Remarks I/O operations are essential
File I/O Christian Schumacher, chschuma@inf.ethz.ch Info1 D-MAVT 2013 Input and Output in C++ Stream objects Formatted output Writing and reading files References General Remarks I/O operations are essential
Fundamentals of Programming Session 27
 Fundamentals of Programming Session 27 Instructor: Reza Entezari-Maleki Email: entezari@ce.sharif.edu 1 Fall 2013 These slides have been created using Deitel s slides Sharif University of Technology Outlines
Fundamentals of Programming Session 27 Instructor: Reza Entezari-Maleki Email: entezari@ce.sharif.edu 1 Fall 2013 These slides have been created using Deitel s slides Sharif University of Technology Outlines
Introduction to C ++
 Introduction to C ++ Thomas Branch tcb06@ic.ac.uk Imperial College Software Society November 15, 2012 1 / 63 Buy Software Soc. s Free Membership at https://www.imperialcollegeunion.org/shop/ club-society-project-products/software-products/436/
Introduction to C ++ Thomas Branch tcb06@ic.ac.uk Imperial College Software Society November 15, 2012 1 / 63 Buy Software Soc. s Free Membership at https://www.imperialcollegeunion.org/shop/ club-society-project-products/software-products/436/
I/O Streams and Standard I/O Devices (cont d.)
 Chapter 3: Input/Output Objectives In this chapter, you will: Learn what a stream is and examine input and output streams Explore how to read data from the standard input device Learn how to use predefined
Chapter 3: Input/Output Objectives In this chapter, you will: Learn what a stream is and examine input and output streams Explore how to read data from the standard input device Learn how to use predefined
Example 3. #include <iostream> using namespace std; int main()
 1 Repetition Structure Examples Example 1 #include float number, sum=0; // number to be read cin >> number; // read first number cout
1 Repetition Structure Examples Example 1 #include float number, sum=0; // number to be read cin >> number; // read first number cout
1- Write a single C++ statement that: A. Calculates the sum of the two integrates 11 and 12 and outputs the sum to the consol.
 1- Write a single C++ statement that: A. Calculates the sum of the two integrates 11 and 12 and outputs the sum to the consol. B. Outputs to the console a floating point number f1 in scientific format
1- Write a single C++ statement that: A. Calculates the sum of the two integrates 11 and 12 and outputs the sum to the consol. B. Outputs to the console a floating point number f1 in scientific format
LAB 4.1 Relational Operators and the if Statement
 LAB 4.1 Relational Operators and the if Statement // This program tests whether or not an initialized value of num2 // is equal to a value of num1 input by the user. int main( ) int num1, // num1 is not
LAB 4.1 Relational Operators and the if Statement // This program tests whether or not an initialized value of num2 // is equal to a value of num1 input by the user. int main( ) int num1, // num1 is not
Superior University. Department of Electrical Engineering CS-115. Computing Fundamentals. Experiment No.7. User Defined Functions II
 Superior University Department of Electrical Engineering CS-115 Computing Fundamentals Experiment No.7 User Defined Functions II Prepared for By: Name: ID: Section: Semester: Total Marks: Obtained Marks:
Superior University Department of Electrical Engineering CS-115 Computing Fundamentals Experiment No.7 User Defined Functions II Prepared for By: Name: ID: Section: Semester: Total Marks: Obtained Marks:
CSc Introduc/on to Compu/ng. Lecture 19 Edgardo Molina Fall 2011 City College of New York
 CSc 10200 Introduc/on to Compu/ng Lecture 19 Edgardo Molina Fall 2011 City College of New York 18 Standard Device Files Logical file object: Stream that connects a file of logically related data to a program
CSc 10200 Introduc/on to Compu/ng Lecture 19 Edgardo Molina Fall 2011 City College of New York 18 Standard Device Files Logical file object: Stream that connects a file of logically related data to a program
Simulations. buffer of fixed capacity using the STL deque. modeling arrival times generating and processing jobs
 Simulations 1 Circular Queues buffer of fixed capacity using the STL deque 2 Simulating Waiting Lines using Queues modeling arrival times generating and processing jobs MCS 360 Lecture 18 Introduction
Simulations 1 Circular Queues buffer of fixed capacity using the STL deque 2 Simulating Waiting Lines using Queues modeling arrival times generating and processing jobs MCS 360 Lecture 18 Introduction
Course "Data Processing" Name: Master-1: Nuclear Energy Session /2018 Examen - Part A Page 1
 Examen - Part A Page 1 1. mydir directory contains three files: filea.txt fileb.txt filec.txt. How many files will be in the directory after performing the following operations: $ ls filea.txt fileb.txt
Examen - Part A Page 1 1. mydir directory contains three files: filea.txt fileb.txt filec.txt. How many files will be in the directory after performing the following operations: $ ls filea.txt fileb.txt
Declaring a 2D Array
 Lecture 13 Declaring a 2D Array Model: type name[row_size ][ column_size] Example: int grades[10][20]; string students[10][20]; 2D Array data structure Say we have the following array: int grades[4][8];
Lecture 13 Declaring a 2D Array Model: type name[row_size ][ column_size] Example: int grades[10][20]; string students[10][20]; 2D Array data structure Say we have the following array: int grades[4][8];
Honors Computer Science C++ Mr. Clausen Program 3A, 3B, 3C
 Honors Computer Science C++ Mr. Clausen Program 3A, 3B, 3C Program 3A Cone Heads (25 points) Write a program to calculate the volume and surface area of a right circular cone. Allow the user to enter values
Honors Computer Science C++ Mr. Clausen Program 3A, 3B, 3C Program 3A Cone Heads (25 points) Write a program to calculate the volume and surface area of a right circular cone. Allow the user to enter values
Sol. Sol. a. void remove_items_less_than(int arr[], int size, int value) #include <iostream> #include <ctime> using namespace std;
![Sol. Sol. a. void remove_items_less_than(int arr[], int size, int value) #include <iostream> #include <ctime> using namespace std; Sol. Sol. a. void remove_items_less_than(int arr[], int size, int value) #include <iostream> #include <ctime> using namespace std;](/thumbs/80/81955324.jpg) r6.14 For the operations on partially filled arrays below, provide the header of a func tion. d. Remove all elements that are less than a given value. Sol a. void remove_items_less_than(int arr[], int
r6.14 For the operations on partially filled arrays below, provide the header of a func tion. d. Remove all elements that are less than a given value. Sol a. void remove_items_less_than(int arr[], int
Elements of C in C++ data types if else statement for loops. random numbers rolling a die
 Elements of C in C++ 1 Types and Control Statements data types if else statement for loops 2 Simulations random numbers rolling a die 3 Functions and Pointers defining a function call by value and call
Elements of C in C++ 1 Types and Control Statements data types if else statement for loops 2 Simulations random numbers rolling a die 3 Functions and Pointers defining a function call by value and call
Scientific Computing
 Scientific Computing Martin Lotz School of Mathematics The University of Manchester Lecture 1, September 22, 2014 Outline Course Overview Programming Basics The C++ Programming Language Outline Course
Scientific Computing Martin Lotz School of Mathematics The University of Manchester Lecture 1, September 22, 2014 Outline Course Overview Programming Basics The C++ Programming Language Outline Course
CS2141 Software Development using C/C++ Stream I/O
 CS2141 Software Development using C/C++ Stream I/O iostream Two libraries can be used for input and output: stdio and iostream The iostream library is newer and better: It is object oriented It can make
CS2141 Software Development using C/C++ Stream I/O iostream Two libraries can be used for input and output: stdio and iostream The iostream library is newer and better: It is object oriented It can make
Loops! Loops! Loops! Lecture 5 COP 3014 Fall September 25, 2017
 Loops! Loops! Loops! Lecture 5 COP 3014 Fall 2017 September 25, 2017 Repetition Statements Repetition statements are called loops, and are used to repeat the same code mulitple times in succession. The
Loops! Loops! Loops! Lecture 5 COP 3014 Fall 2017 September 25, 2017 Repetition Statements Repetition statements are called loops, and are used to repeat the same code mulitple times in succession. The
C++ Input/Output: Streams
 C++ Input/Output: Streams Basic I/O 1 The basic data type for I/O in C++ is the stream. C++ incorporates a complex hierarchy of stream types. The most basic stream types are the standard input/output streams:
C++ Input/Output: Streams Basic I/O 1 The basic data type for I/O in C++ is the stream. C++ incorporates a complex hierarchy of stream types. The most basic stream types are the standard input/output streams:
Wentworth Institute of Technology COMP201 Computer Science II Spring 2015 Derbinsky. C++ Kitchen Sink. Lecture 14.
 Lecture 14 1 Exceptions Iterators Random numbers Casting Enumerations Pairs The Big Three Outline 2 Error Handling It is often easier to write a program by first assuming that nothing incorrect will happen
Lecture 14 1 Exceptions Iterators Random numbers Casting Enumerations Pairs The Big Three Outline 2 Error Handling It is often easier to write a program by first assuming that nothing incorrect will happen
Lab 8 The Stack (LIFO) Structure
 Lab 8 The Stack (LIFO) Structure Objective: The stack segment in memory is where the 80x86 maintains the stack. The stack stores important information about program including local variables, subroutine
Lab 8 The Stack (LIFO) Structure Objective: The stack segment in memory is where the 80x86 maintains the stack. The stack stores important information about program including local variables, subroutine
File Input / Output Streams in C++ CS 16: Solving Problems with Computers I Lecture #9
 File Input / Output Streams in C++ CS 16: Solving Problems with Computers I Lecture #9 Ziad Matni Dept. of Computer Science, UCSB Midterm Exam grades out! Announcements If you want to see your exams, visit
File Input / Output Streams in C++ CS 16: Solving Problems with Computers I Lecture #9 Ziad Matni Dept. of Computer Science, UCSB Midterm Exam grades out! Announcements If you want to see your exams, visit
Piyush Kumar. input data. both cout and cin are data objects and are defined as classes ( type istream ) class
 C++ IO C++ IO All I/O is in essence, done one character at a time For : COP 3330. Object oriented Programming (Using C++) http://www.compgeom.com/~piyush/teach/3330 Concept: I/O operations act on streams
C++ IO C++ IO All I/O is in essence, done one character at a time For : COP 3330. Object oriented Programming (Using C++) http://www.compgeom.com/~piyush/teach/3330 Concept: I/O operations act on streams
Tutorial 12 Craps Game Application: Introducing Random Number Generation and Enumerations
 Tutorial 12 Craps Game Application: Introducing Random Number Generation and Enumerations Outline 12.1 Test-Driving the Craps Game Application 12.2 Random Number Generation 12.3 Using an enum in the Craps
Tutorial 12 Craps Game Application: Introducing Random Number Generation and Enumerations Outline 12.1 Test-Driving the Craps Game Application 12.2 Random Number Generation 12.3 Using an enum in the Craps
C++ Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program Design, Fourth Edition. Chapter 5: Control Structures II (Repetition)
 C++ Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program Design, Fourth Edition Chapter 5: Control Structures II (Repetition) Objectives In this chapter, you will: Learn about repetition (looping) control structures
C++ Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program Design, Fourth Edition Chapter 5: Control Structures II (Repetition) Objectives In this chapter, you will: Learn about repetition (looping) control structures
 Consider the following statements. string str1 = "ABCDEFGHIJKLM"; string str2; After the statement str2 = str1.substr(1,4); executes, the value of str2 is " ". Given the function prototype: float test(int,
Consider the following statements. string str1 = "ABCDEFGHIJKLM"; string str2; After the statement str2 = str1.substr(1,4); executes, the value of str2 is " ". Given the function prototype: float test(int,
CS 117 Programming II, Spring 2018 Dr. Ghriga. Midterm Exam Estimated Time: 2 hours. March 21, DUE DATE: March 28, 2018 at 12:00 PM
 CS 117 Programming II, Spring 2018 Dr. Ghriga Midterm Exam Estimated Time: 2 hours March 21, 2018 DUE DATE: March 28, 2018 at 12:00 PM INSTRUCTIONS: Do all exercises for a total of 100 points. You are
CS 117 Programming II, Spring 2018 Dr. Ghriga Midterm Exam Estimated Time: 2 hours March 21, 2018 DUE DATE: March 28, 2018 at 12:00 PM INSTRUCTIONS: Do all exercises for a total of 100 points. You are
CS201- Introduction to Programming Current Quizzes
 CS201- Introduction to Programming Current Quizzes Q.1 char name [] = Hello World ; In the above statement, a memory of characters will be allocated 13 11 12 (Ans) Q.2 A function is a block of statements
CS201- Introduction to Programming Current Quizzes Q.1 char name [] = Hello World ; In the above statement, a memory of characters will be allocated 13 11 12 (Ans) Q.2 A function is a block of statements
Chapter 15 - C++ As A "Better C"
 Chapter 15 - C++ As A "Better C" Outline 15.1 Introduction 15.2 C++ 15.3 A Simple Program: Adding Two Integers 15.4 C++ Standard Library 15.5 Header Files 15.6 Inline Functions 15.7 References and Reference
Chapter 15 - C++ As A "Better C" Outline 15.1 Introduction 15.2 C++ 15.3 A Simple Program: Adding Two Integers 15.4 C++ Standard Library 15.5 Header Files 15.6 Inline Functions 15.7 References and Reference
Lab 7 (50 pts) Due Sunday, May 20)
 Lab 7 (50 pts) Due Sunday, May 20) For this lab, you will be comparing sorting algorithms, specifically the speed of selection, insertion, quick, and merge sort on random, in-order, and reverse-order lists
Lab 7 (50 pts) Due Sunday, May 20) For this lab, you will be comparing sorting algorithms, specifically the speed of selection, insertion, quick, and merge sort on random, in-order, and reverse-order lists
Objects and streams and files CS427: Elements of Software Engineering
 Objects and streams and files CS427: Elements of Software Engineering Lecture 6.2 (C++) 10am, 13 Feb 2012 CS427 Objects and streams and files 1/18 Today s topics 1 Recall...... Dynamic Memory Allocation...
Objects and streams and files CS427: Elements of Software Engineering Lecture 6.2 (C++) 10am, 13 Feb 2012 CS427 Objects and streams and files 1/18 Today s topics 1 Recall...... Dynamic Memory Allocation...
Lab 15 Review of Arrays, Array of Objects and Vector Dr. John Abraham, Professor
 Lab 15 Review of Arrays, Array of Objects and Vector Dr. John Abraham, Professor I have noticed over the years that students have great deal of difficulty dealing with composite and abstract data types.
Lab 15 Review of Arrays, Array of Objects and Vector Dr. John Abraham, Professor I have noticed over the years that students have great deal of difficulty dealing with composite and abstract data types.
C++ Basics. Lecture 2 COP 3014 Spring January 8, 2018
 C++ Basics Lecture 2 COP 3014 Spring 2018 January 8, 2018 Structure of a C++ Program Sequence of statements, typically grouped into functions. function: a subprogram. a section of a program performing
C++ Basics Lecture 2 COP 3014 Spring 2018 January 8, 2018 Structure of a C++ Program Sequence of statements, typically grouped into functions. function: a subprogram. a section of a program performing
c++ keywords: ( all lowercase ) Note: cin and cout are NOT keywords.
 Chapter 1 File Extensions: Source code (cpp), Object code (obj), and Executable code (exe). Preprocessor processes directives and produces modified source Compiler takes modified source and produces object
Chapter 1 File Extensions: Source code (cpp), Object code (obj), and Executable code (exe). Preprocessor processes directives and produces modified source Compiler takes modified source and produces object
More File Operations. Lecture 17 COP 3014 Spring april 18, 2018
 More File Operations Lecture 17 COP 3014 Spring 2018 april 18, 2018 eof() member function A useful member function of the input stream classes is eof() Stands for end of file Returns a bool value, answering
More File Operations Lecture 17 COP 3014 Spring 2018 april 18, 2018 eof() member function A useful member function of the input stream classes is eof() Stands for end of file Returns a bool value, answering
CS 1704 Homework 2 C++ Pointer Basics Fall 2002
 Instructions: Opscan forms will be passed out in class on Tuesday, Sept 24. Write your name and code your ID number on the opscan form. Turn in your completed opscan at class on Thursday Sept 26, or at
Instructions: Opscan forms will be passed out in class on Tuesday, Sept 24. Write your name and code your ID number on the opscan form. Turn in your completed opscan at class on Thursday Sept 26, or at
1. (18 pts) Short Answer. Provide brief (1-3 sentence) answers to the following:
 CSCE A211 Midterm Exam #1 Name: Please write neatly and show as much of your work as possible for partial credit. The exam is open book and open notes. You can also use a computer for accessing an e- book,
CSCE A211 Midterm Exam #1 Name: Please write neatly and show as much of your work as possible for partial credit. The exam is open book and open notes. You can also use a computer for accessing an e- book,
BEng (Hons) Electronic Engineering. Resit Examinations for / Semester 1
 BEng (Hons) Electronic Engineering Cohort: BEE/10B/FT Resit Examinations for 2016-2017 / Semester 1 MODULE: Programming for Engineers MODULE CODE: PROG1114 Duration: 3 Hours Instructions to Candidates:
BEng (Hons) Electronic Engineering Cohort: BEE/10B/FT Resit Examinations for 2016-2017 / Semester 1 MODULE: Programming for Engineers MODULE CODE: PROG1114 Duration: 3 Hours Instructions to Candidates:
Dynamic Allocation of Memory
 Dynamic Allocation of Memory Lecture 4 Sections 10.9-10.10 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Fri, Jan 25, 2013 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Dynamic Allocation of Memory Fri, Jan 25, 2013
Dynamic Allocation of Memory Lecture 4 Sections 10.9-10.10 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Fri, Jan 25, 2013 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Dynamic Allocation of Memory Fri, Jan 25, 2013
Pre- Defined Func-ons in C++ Review for Midterm #1
 Pre- Defined Func-ons in C++ Review for Midterm #1 CS 16: Solving Problems with Computers I Lecture #6 Ziad Matni Dept. of Computer Science, UCSB Announcements Homework #5 due today Homework #6 issued
Pre- Defined Func-ons in C++ Review for Midterm #1 CS 16: Solving Problems with Computers I Lecture #6 Ziad Matni Dept. of Computer Science, UCSB Announcements Homework #5 due today Homework #6 issued
Lecture 9. Introduction
 Lecture 9 File Processing Streams Stream I/O template hierarchy Create, update, process files Sequential and random access Formatted and raw processing Namespaces Lec 9 Programming in C++ 1 Storage of
Lecture 9 File Processing Streams Stream I/O template hierarchy Create, update, process files Sequential and random access Formatted and raw processing Namespaces Lec 9 Programming in C++ 1 Storage of
Islamic University of Gaza Computer Engineering Dept. C++ Programming. For Industrial And Electrical Engineering By Instructor: Ruba A.
 Islamic University of Gaza Computer Engineering Dept. C++ Programming For Industrial And Electrical Engineering By Instructor: Ruba A. Salamh Chapter Four: Loops 2 Chapter Goals To implement while, for
Islamic University of Gaza Computer Engineering Dept. C++ Programming For Industrial And Electrical Engineering By Instructor: Ruba A. Salamh Chapter Four: Loops 2 Chapter Goals To implement while, for
Chapter 5: Control Structures II (Repetition) Objectives (cont d.) Objectives. while Looping (Repetition) Structure. Why Is Repetition Needed?
 Chapter 5: Control Structures II (Repetition) Objectives In this chapter, you will: Learn about repetition (looping) control structures Explore how to construct and use countercontrolled, sentinel-controlled,
Chapter 5: Control Structures II (Repetition) Objectives In this chapter, you will: Learn about repetition (looping) control structures Explore how to construct and use countercontrolled, sentinel-controlled,
Given the C++ declaration statement below, which of the following represents the value of exforsys? e) None of the above. 1K
 Instruction: When specified, you may choose more than one answer; otherwise, choose ONE answer for each question. Choose the answer(s) by circling it/them on the Answer Sheet provided. Questions 1-12 are
Instruction: When specified, you may choose more than one answer; otherwise, choose ONE answer for each question. Choose the answer(s) by circling it/them on the Answer Sheet provided. Questions 1-12 are
Chapter Four: Loops. Slides by Evan Gallagher. C++ for Everyone by Cay Horstmann Copyright 2012 by John Wiley & Sons. All rights reserved
 Chapter Four: Loops Slides by Evan Gallagher The Three Loops in C++ C++ has these three looping statements: while for do The while Loop while (condition) { statements } The condition is some kind of test
Chapter Four: Loops Slides by Evan Gallagher The Three Loops in C++ C++ has these three looping statements: while for do The while Loop while (condition) { statements } The condition is some kind of test
Pointers II. Class 31
 Pointers II Class 31 Compile Time all of the variables we have seen so far have been declared at compile time they are written into the program code you can see by looking at the program how many variables
Pointers II Class 31 Compile Time all of the variables we have seen so far have been declared at compile time they are written into the program code you can see by looking at the program how many variables
CSCE 206: Structured Programming in C++
 CSCE 206: Structured Programming in C++ 2017 Spring Exam 2 Monday, March 20, 2017 Total - 100 Points B Instructions: Total of 13 pages, including this cover and the last page. Before starting the exam,
CSCE 206: Structured Programming in C++ 2017 Spring Exam 2 Monday, March 20, 2017 Total - 100 Points B Instructions: Total of 13 pages, including this cover and the last page. Before starting the exam,
PIC 10A. Final Review
 PIC 10A Final Review Final exam Thursday, December 18, 2014 8:00 AM - 11:00 AM MS 5200. In our usual class room. (Verify on my.ucla.edu!!) The final exam is worth 30% of your grade, same weight as 2 midterms.
PIC 10A Final Review Final exam Thursday, December 18, 2014 8:00 AM - 11:00 AM MS 5200. In our usual class room. (Verify on my.ucla.edu!!) The final exam is worth 30% of your grade, same weight as 2 midterms.
Designing Loops and General Debug Pre-Defined Functions in C++ CS 16: Solving Problems with Computers I Lecture #6
 Designing Loops and General Debug Pre-Defined Functions in C++ CS 16: Solving Problems with Computers I Lecture #6 Ziad Matni Dept. of Computer Science, UCSB Announcements Homework #5 due today Lab #3
Designing Loops and General Debug Pre-Defined Functions in C++ CS 16: Solving Problems with Computers I Lecture #6 Ziad Matni Dept. of Computer Science, UCSB Announcements Homework #5 due today Lab #3
LAB 7.1 Working with One-Dimensional Arrays
 LAB 7.1 Working with One-Dimensional Arrays Copy and paste the following program into Visual Studio IDE. This program will read in a group of test scores (positive integers from 1 to 100) from the keyboard
LAB 7.1 Working with One-Dimensional Arrays Copy and paste the following program into Visual Studio IDE. This program will read in a group of test scores (positive integers from 1 to 100) from the keyboard
C Legacy Code Topics. Objectives. In this appendix you ll:
 cppfp2_appf_legacycode.fm Page 1 Monday, March 25, 2013 3:44 PM F C Legacy Code Topics Objectives In this appendix you ll: Redirect keyboard input to come from a file and redirect screen output to a file.
cppfp2_appf_legacycode.fm Page 1 Monday, March 25, 2013 3:44 PM F C Legacy Code Topics Objectives In this appendix you ll: Redirect keyboard input to come from a file and redirect screen output to a file.
The American University in Cairo Department of Computer Science & Engineering CSCI &09 Dr. KHALIL Exam-I Fall 2011
 The American University in Cairo Department of Computer Science & Engineering CSCI 106-07&09 Dr. KHALIL Exam-I Fall 2011 Last Name :... ID:... First Name:... Form I Section No.: EXAMINATION INSTRUCTIONS
The American University in Cairo Department of Computer Science & Engineering CSCI 106-07&09 Dr. KHALIL Exam-I Fall 2011 Last Name :... ID:... First Name:... Form I Section No.: EXAMINATION INSTRUCTIONS
Input and Output. Data Processing Course, I. Hrivnacova, IPN Orsay
 Input and Output Data Processing Course, I. Hrivnacova, IPN Orsay Output to the Screen Input from the Keyboard IO Headers Output to a File Input from a File Formatting I. Hrivnacova @ Data Processing Course
Input and Output Data Processing Course, I. Hrivnacova, IPN Orsay Output to the Screen Input from the Keyboard IO Headers Output to a File Input from a File Formatting I. Hrivnacova @ Data Processing Course
Strings and Stream I/O
 Strings and Stream I/O C Strings In addition to the string class, C++ also supports old-style C strings In C, strings are stored as null-terminated character arrays str1 char * str1 = "What is your name?
Strings and Stream I/O C Strings In addition to the string class, C++ also supports old-style C strings In C, strings are stored as null-terminated character arrays str1 char * str1 = "What is your name?
This chapter introduces the notion of namespace. We also describe how to manage input and output with C++ commands via the terminal or files.
 C++ PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE: NAMESPACE AND MANGEMENT OF INPUT/OUTPUT WITH C++. CAAM 519, CHAPTER 15 This chapter introduces the notion of namespace. We also describe how to manage input and output with C++
C++ PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE: NAMESPACE AND MANGEMENT OF INPUT/OUTPUT WITH C++. CAAM 519, CHAPTER 15 This chapter introduces the notion of namespace. We also describe how to manage input and output with C++
Why Is Repetition Needed?
 Why Is Repetition Needed? Repetition allows efficient use of variables. It lets you process many values using a small number of variables. For example, to add five numbers: Inefficient way: Declare a variable
Why Is Repetition Needed? Repetition allows efficient use of variables. It lets you process many values using a small number of variables. For example, to add five numbers: Inefficient way: Declare a variable
Preview 8/28/2018. Review for COSC 120 (File Processing: Reading Data From a File)
 Preview Relational operator If, if--if, nested if statement Logical operators Validating Inputs Compare two c-string Switch Statement Increment decrement operator While, Do-While, For Loop Break, Continue
Preview Relational operator If, if--if, nested if statement Logical operators Validating Inputs Compare two c-string Switch Statement Increment decrement operator While, Do-While, For Loop Break, Continue
File I/O. File Names and Types. I/O Streams. Stream Extraction and Insertion. A file name should reflect its contents
 File I/O 1 File Names and Types A file name should reflect its contents Payroll.dat Students.txt Grades.txt A file s extension indicates the kind of data the file holds.dat,.txt general program input or
File I/O 1 File Names and Types A file name should reflect its contents Payroll.dat Students.txt Grades.txt A file s extension indicates the kind of data the file holds.dat,.txt general program input or
Lectures 19, 20, 21. two valid iterators in [first, last) such that i precedes j, then *j is not less than *i.
 Lectures 19, 20, 21 1. STL library examples of applications Explanations: The member function pop_back removes the last element of the controlled sequence. The member function pop_front removes the first
Lectures 19, 20, 21 1. STL library examples of applications Explanations: The member function pop_back removes the last element of the controlled sequence. The member function pop_front removes the first
More Flow Control Functions in C++ CS 16: Solving Problems with Computers I Lecture #4
 More Flow Control Functions in C++ CS 16: Solving Problems with Computers I Lecture #4 Ziad Matni Dept. of Computer Science, UCSB Administrative CHANGED T.A. OFFICE/OPEN LAB HOURS! Thursday, 10 AM 12 PM
More Flow Control Functions in C++ CS 16: Solving Problems with Computers I Lecture #4 Ziad Matni Dept. of Computer Science, UCSB Administrative CHANGED T.A. OFFICE/OPEN LAB HOURS! Thursday, 10 AM 12 PM
Recap: Pointers. int* int& *p &i &*&* ** * * * * IFMP 18, M. Schwerhoff
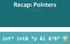 Recap: Pointers IFMP 18, M. Schwerhoff int* int& *p &i &*&* ** * * * * A 0 A 1 A 2 A 3 A 4 A 5 A 0 A 1 A 2 A 3 A 4 A 5 5 i int* p; A 0 A 1 A 2 A 3 A 4 A 5 5 i p int* p; p = &i; A 0 A 1 A 2 A 3 A 4 A 5
Recap: Pointers IFMP 18, M. Schwerhoff int* int& *p &i &*&* ** * * * * A 0 A 1 A 2 A 3 A 4 A 5 A 0 A 1 A 2 A 3 A 4 A 5 5 i int* p; A 0 A 1 A 2 A 3 A 4 A 5 5 i p int* p; p = &i; A 0 A 1 A 2 A 3 A 4 A 5
Programming II with C++ (CSNB244) Lab 10. Topics: Files and Stream
 Topics: Files and Stream In this lab session, you will learn very basic and most common I/O operations required for C++ programming. The second part of this tutorial will teach you how to read and write
Topics: Files and Stream In this lab session, you will learn very basic and most common I/O operations required for C++ programming. The second part of this tutorial will teach you how to read and write
Exercise: Inventing Language
 Memory Computers get their powerful flexibility from the ability to store and retrieve data Data is stored in main memory, also known as Random Access Memory (RAM) Exercise: Inventing Language Get a separate
Memory Computers get their powerful flexibility from the ability to store and retrieve data Data is stored in main memory, also known as Random Access Memory (RAM) Exercise: Inventing Language Get a separate
Introduction to C++ Professor Hugh C. Lauer CS-2303, System Programming Concepts
 Introduction to C++ Professor Hugh C. Lauer CS-2303, System Programming Concepts (Slides include materials from The C Programming Language, 2 nd edition, by Kernighan and Ritchie, Absolute C++, by Walter
Introduction to C++ Professor Hugh C. Lauer CS-2303, System Programming Concepts (Slides include materials from The C Programming Language, 2 nd edition, by Kernighan and Ritchie, Absolute C++, by Walter
The cin Object. cout << "Enter the length and the width of the rectangle? "; cin >> length >> width;
 The cin Object Short for console input. It is used to read data typed at the keyboard. Must include the iostream library. When this instruction is executed, it waits for the user to type, it reads the
The cin Object Short for console input. It is used to read data typed at the keyboard. Must include the iostream library. When this instruction is executed, it waits for the user to type, it reads the
C/C++ Programming Lecture 7 Name:
 1. The increment (++) and decrement (--) operators increase or decrease a variable s value by one, respectively. They are great if all you want to do is increment (or decrement) a variable: i++;. HOWEVER,
1. The increment (++) and decrement (--) operators increase or decrease a variable s value by one, respectively. They are great if all you want to do is increment (or decrement) a variable: i++;. HOWEVER,
Chapter 3 - Notes Input/Output
 Chapter 3 - Notes Input/Output I. I/O Streams and Standard I/O Devices A. I/O Background 1. Stream of Bytes: A sequence of bytes from the source to the destination. 2. 2 Types of Streams: i. Input Stream:
Chapter 3 - Notes Input/Output I. I/O Streams and Standard I/O Devices A. I/O Background 1. Stream of Bytes: A sequence of bytes from the source to the destination. 2. 2 Types of Streams: i. Input Stream:
a data type is Types
 Pointers Class 2 a data type is Types Types a data type is a set of values a set of operations defined on those values in C++ (and most languages) there are two flavors of types primitive or fundamental
Pointers Class 2 a data type is Types Types a data type is a set of values a set of operations defined on those values in C++ (and most languages) there are two flavors of types primitive or fundamental
Engineering Problem Solving with C++, 3e Chapter 2 Test Bank
 1. Match each of the following data types with literal constants of that data type. A data type can be used more than once. A. integer B 1.427E3 B. double D "Oct" C. character B -63.29 D. string F #Hashtag
1. Match each of the following data types with literal constants of that data type. A data type can be used more than once. A. integer B 1.427E3 B. double D "Oct" C. character B -63.29 D. string F #Hashtag
What we will learn about this week:
 What we will learn about this week: Streams Basic file I/O Tools for Stream I/O Manipulators Character I/O Get and Put EOF function Pre-defined character functions Objects 1 I/O Streams as an Introduction
What we will learn about this week: Streams Basic file I/O Tools for Stream I/O Manipulators Character I/O Get and Put EOF function Pre-defined character functions Objects 1 I/O Streams as an Introduction
Computational Physics
 Computational Physics numerical methods with C++ (and UNIX) 2018-19 Fernando Barao Instituto Superior Tecnico, Dep. Fisica email: fernando.barao@tecnico.ulisboa.pt Computational Physics 2018-19 (Phys Dep
Computational Physics numerical methods with C++ (and UNIX) 2018-19 Fernando Barao Instituto Superior Tecnico, Dep. Fisica email: fernando.barao@tecnico.ulisboa.pt Computational Physics 2018-19 (Phys Dep
Introduction to C++ (Extensions to C)
 Introduction to C++ (Extensions to C) C is purely procedural, with no objects, classes or inheritance. C++ is a hybrid of C with OOP! The most significant extensions to C are: much stronger type checking.
Introduction to C++ (Extensions to C) C is purely procedural, with no objects, classes or inheritance. C++ is a hybrid of C with OOP! The most significant extensions to C are: much stronger type checking.
CSci 1113 Midterm 2. Name: Student ID:
 CSci 1113 Midterm 2 Name: Student ID: Instructions: Please pick and answer any 6 of the 8 problems for a total of 90 points. If you answer more than 6 problems, only the first 6 will be graded. The time
CSci 1113 Midterm 2 Name: Student ID: Instructions: Please pick and answer any 6 of the 8 problems for a total of 90 points. If you answer more than 6 problems, only the first 6 will be graded. The time
Streams. Rupesh Nasre.
 Streams Rupesh Nasre. OOAIA January 2018 I/O Input stream istream cin Defaults to keyboard / stdin Output stream ostream cout std::string name; std::cout > name; std::cout
Streams Rupesh Nasre. OOAIA January 2018 I/O Input stream istream cin Defaults to keyboard / stdin Output stream ostream cout std::string name; std::cout > name; std::cout
Object Oriented Programming COP3330 / CGS5409
 Object Oriented Programming COP3330 / CGS5409 Multiple Inheritance Template Classes and Functions Inheritance is supported by most object oriented languages C++ allows a special kind of inheritance known
Object Oriented Programming COP3330 / CGS5409 Multiple Inheritance Template Classes and Functions Inheritance is supported by most object oriented languages C++ allows a special kind of inheritance known
Standard Library. Lecture 27. Containers. STL Containers. Standard Library
 Standard Library Lecture 27 Containers (templates) Streams (I/O facilities) Standard Library Portable, type-safe, efficient Try to use as much as possible Heavy use of templates Streams: #include
Standard Library Lecture 27 Containers (templates) Streams (I/O facilities) Standard Library Portable, type-safe, efficient Try to use as much as possible Heavy use of templates Streams: #include
Arrays. Lecture 9 COP 3014 Fall October 16, 2017
 Arrays Lecture 9 COP 3014 Fall 2017 October 16, 2017 Array Definition An array is an indexed collection of data elements of the same type. Indexed means that the array elements are numbered (starting at
Arrays Lecture 9 COP 3014 Fall 2017 October 16, 2017 Array Definition An array is an indexed collection of data elements of the same type. Indexed means that the array elements are numbered (starting at
Pointers and Strings Prentice Hall, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Pointers and Strings 1 sizeof operator Pointer Expressions and Pointer Arithmetic Relationship Between Pointers and Arrays Arrays of Pointers Case Study: Card Shuffling and Dealing Simulation sizeof operator
Pointers and Strings 1 sizeof operator Pointer Expressions and Pointer Arithmetic Relationship Between Pointers and Arrays Arrays of Pointers Case Study: Card Shuffling and Dealing Simulation sizeof operator
Loops and Files. of do-while loop
 L E S S O N S E T 5 Loops and Files PURPOSE PROCEDURE 1. To introduce counter and event controlled loops 2. To work with the while loop 3. To introduce the do-while loop 4. To work with the for loop 5.
L E S S O N S E T 5 Loops and Files PURPOSE PROCEDURE 1. To introduce counter and event controlled loops 2. To work with the while loop 3. To introduce the do-while loop 4. To work with the for loop 5.
C++_ MARKS 40 MIN
 C++_16.9.2018 40 MARKS 40 MIN https://tinyurl.com/ya62ayzs 1) Declaration of a pointer more than once may cause A. Error B. Abort C. Trap D. Null 2Whice is not a correct variable type in C++? A. float
C++_16.9.2018 40 MARKS 40 MIN https://tinyurl.com/ya62ayzs 1) Declaration of a pointer more than once may cause A. Error B. Abort C. Trap D. Null 2Whice is not a correct variable type in C++? A. float
CS 1428 Review. CS 2308 :: Spring 2016 Molly O Neil
 CS 1428 Review CS 2308 :: Spring 2016 Molly O Neil Structure of a C++ Program Hello world // This program prints a greeting to the screen #include using namespace std; int main() { cout
CS 1428 Review CS 2308 :: Spring 2016 Molly O Neil Structure of a C++ Program Hello world // This program prints a greeting to the screen #include using namespace std; int main() { cout
Chapter Four: Loops II
 Chapter Four: Loops II Slides by Evan Gallagher & Nikolay Kirov Chapter Goals To understand nested loops To implement programs that read and process data sets To use a computer for simulations Processing
Chapter Four: Loops II Slides by Evan Gallagher & Nikolay Kirov Chapter Goals To understand nested loops To implement programs that read and process data sets To use a computer for simulations Processing
Page 1 Name: CUNYfirstID: CS111 Summer Term 1- Final 6/27/18
 Page 1 PART I Basic Questions A,B,C are required to be correctly answered to obtain a grade higher than C-. Part 1 Questions are worth 10 points each. A) // NumbersGreaterThan - loop through an array and
Page 1 PART I Basic Questions A,B,C are required to be correctly answered to obtain a grade higher than C-. Part 1 Questions are worth 10 points each. A) // NumbersGreaterThan - loop through an array and
1. a) What #include statement do you put at the top of a program that does uses cin, cout or endl?
 Exercises with solutions. 1. a) What #include statement do you put at the top of a program that does uses cin, cout or endl? #include b) What using statement do you always put at the top of
Exercises with solutions. 1. a) What #include statement do you put at the top of a program that does uses cin, cout or endl? #include b) What using statement do you always put at the top of
