Advanced Placement Computer Science. Inheritance and Polymorphism
|
|
|
- Scarlett Caldwell
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Advanced Placement Computer Science Inheritance and Polymorphism What s past is prologue. Don t write it twice write it once and reuse it. Mike Scott The University of Texas at Austin Inheritance, Polymorphism, and Interfaces 1
2 Main Tenants of OO Programming 8Encapsulation abstraction, information hiding, responsibility driven programming 8Inheritance code reuse, specialization "New code using old code." 8Polymorphism do X for a collection of various types of objects, where X is different depending on the type of object "Old code using new code." Inheritance, Polymorphism, and Interfaces 2
3 Explanation of Inheritance 81 of the fundamental principles of OOP allows code reuse 8Models the IS-A relationship a student is-a person an undergraduate is-a student a rectangle is-a shape a rook is-a piece 8Contrast with the Has-A relationship (or uses a) a student has-a name a rook has-a position a Stack uses a List 8Is-a relationships indicate inheritance, has-a relationships indicate composition (fields) Inheritance, Polymorphism, and Interfaces 3
4 Nomenclature of Inheritance 8The extends keyword is used to specify which preexisting class a new class is inheriting from public class Student extends Person 8Person is said to be the parent class of Student the super class of Student the base class of Student an ancestor of Student 8Student is said to be a child class of Person a sub class of Person a derived class of Person a descendant of Person Inheritance, Polymorphism, and Interfaces 4
5 The Mechanics of Inheritance 8 Java is a pure object oriented language 8 all code is part of some class 8 all classes, except one, must inherit from exactly one other class 8 The Object class is the cosmic super class The Object class does not inherit from any other class The Object class has several important methods: tostring, equals, hashcode, clone, getclass 8 implications: all classes are descendants of Object all classes, and thus all objects, have a tostring, equals, hashcode, clone, and getclass method tostring, equals, hashcode, clone normally overridden Inheritance, Polymorphism, and Interfaces 5
6 Inheriting from a Class 8If a class header does not include the extends clause the class extends the Object class by default public class Card Object is an ancestor to all classes it is the only class that does not extend some other class 8A class extends exactly one other class extending two or more classes is multiple inheritance. Java does not support this directly, rather it uses Interfaces. Inheritance, Polymorphism, and Interfaces 6
7 Implications of Inheritance 8The sub class gains all of the behavior (methods) and data regarding state (instance variables) of the super class and all ancestor classes 8Sub classes can: add new fields add new methods override existing methods (change behavior) 8Sub classes may not remove fields remove methods 8Note, even though an object may have instance variables from its parent they may not be accessible by the code of the child class if the fields are private Inheritance, Polymorphism, and Interfaces 7
8 The Real Picture Fields from Object class Instance variables declared in Object A String object Fields from String class Instance Variables declared in String Behaviors (methods) from String class and Object class. Inheritance, Polymorphism, and Interfaces 8
9 Access Modifiers and Inheritance 8public accessible to all classes 8private accessible only within that class. Hidden from all sub classes. 8protected accessible by classes within the same package and all descendant classes 8Instance variables should be private 8protected methods are used to allow descendant classes to modify instance variables in ways other classes can't Inheritance, Polymorphism, and Interfaces 9
10 Instance Variables - Private or Protected 8Why is it good design to make the instance variables of an object private instead of protected? 8protected also allows classes in the same package to access the data a class in a package does not necessarily inherit from other classes in the same package 8What if when the data changes something else must be done? How would the descendant classes know to do the required changes? Excellent example in the MBCS Inheritance, Polymorphism, and Interfaces 10
11 MBCS Example public class Fish { private Location myloc; // Why private? // What if subclasses override move() and need to change // the Location? Don't subclasses need access to it? private Environment theenv; // If a Fish changes its location theenv must be updated protected void changelocation(location newloc) { // Change location and notify Environment Location oldloc = location(); myloc = newloc; environment().recordmove(this, oldloc); // object is again at location myloc in environment Making myloc private and forcing sub classes to call changelocation to alter the location of a fish guarantees the environment is correctly updated with the now location. Inheritance, Polymorphism, and Interfaces 11
12 Shape Classes 8Declare a class called ClosedShape assume all shapes have x and y coordinates override Object's version of tostring 8Possible sub classes of ClosedShape Rectangle Circle Ellipse Square 8Possible hierarchy ClosedShape -> Rectangle -> Square Inheritance, Polymorphism, and Interfaces 12
13 A ClosedShape class public class ClosedShape { private int imyx; private int tmyy; public ClosedShape() { this(0,0); public ClosedShape (int x, int y) { imyx = x; imyy = y; public String tostring() { return "x: " + imyx + " y: " + imyy; public int getx(){ return imyx; public int gety(){ return imyy; // Other methods not shown Inheritance, Polymorphism, and Interfaces 13
14 Constructors 8Constructors handle initialization of objects 8When creating an object with one or more ancestors (every type except Object) a chain of constructor calls takes place 8The reserved word super may be used in a constructor to specify which of the parent's constructors to call must be first line of constructor 8if no parent constructor is explicitly called the default, 0 parameter constructor of the parent is called if no default constructor exists a syntax error results 8If a parent constructor is called another constructor in the same class may no be called no super();this(); allowed. One or the other, not both good place for an initialization method Inheritance, Polymorphism, and Interfaces 14
15 A Rectangle Constructor public class Rectangle extends ClosedShape { private int imywidth; private int imyheight; public Rectangle(int width, int height, int x, int y) { super(x,y); // calls the 2 int constructor in // ClosedShape imywidth = width; imyheight = height; // other methods not shown Inheritance, Polymorphism, and Interfaces 15
16 A Rectangle Class public class Rectangle extends ClosedShape { private int imywidth; private int imyheight; public Rectangle() { this(0, 0); public Rectangle(int width, int height) { this(width, height, 0, 0); public Rectangle(int width, int height, int x, int y) { super(x, y); imywidth = width; imyheight = height; public String tostring() { return super.tostring() + " width: " + imywidth + " height: " + imyheight; Inheritance, Polymorphism, and Interfaces 16
17 Initialization method public class Rectangle extends ClosedShape { private int imywidth; private int imyheight; public Rectangle() { init(0, 0); public Rectangle(int width, int height) { init(width, height); public Rectangle(int width, int height, int x, int y) { super(x, y); init(width, height); private void init(int width, int height) { imywidth = width; imyheight = height; Inheritance, Polymorphism, and Interfaces 17
18 Overriding methods 8any method that is not final may be overridden by a descendant class overriding is a replacement of a behavior overloading is the addition of a behavior 8same signature as method in ancestor 8may not reduce visibility 8may use the original method if simply want to add more behavior to existing also called partial overriding 8The Rectangle class adds data, partially overrides tostring Inheritance, Polymorphism, and Interfaces 18
19 The Keyword super 8super is used to access something (any protected or public field or method) from the super class that has been overridden 8Rectangle's tostring makes use of the tostring in ClosedShape my calling super.tostring() 8without the super calling tostring would result in infinite recursive calls 8Java does not allow nested supers super.super.tostring() results in a syntax error even though technically this refers to a valid method, Object's tostring 8Rectangle partially overrides ClosedShape's tostring Inheritance, Polymorphism, and Interfaces 19
20 What Can Rectangles Do? Rectangle r1 = new Rectangle(); Rectangle r2 = new Rectangle(10, 15); Rectangle r3 = new Rectangle(10, 15, 2, 3); System.out.println( r1 ); System.out.println( r2 ); System.out.println( r3 ); int a = r1.getx() + r1.gety(); ClosedShape s = new Rectangle(5, 10, 3, 4); System.out.println( s.tostring() ); a += s.getx(); ClosedShape[] slist = new ClosedShape[3]; slist[0] = new ClosedShape(5, 10); slist[1] = new Rectangle(10, 25, 10, 7); slist[2] = r2; for(int i = 0; i < slist.length; i++) System.out.println( slist[i].tostring() ); Inheritance, Polymorphism, and Interfaces 20
21 The role of final in Inheritance 8A class may be declared as final that class may not be extended 8A method in a class may be declared as final that method may not be overridden guarantees behavior in all descendants can speed up a program by allowing static binding (binding or determination at compile time what code will actually be executed) Inheritance, Polymorphism, and Interfaces 21
22 Abstract Classes and Methods 8An abstract class is used to define a class to gather together behaviors but: an object of that type never exists and can never be created or instantiated. a Shape or a Mammal 8a method may be declared abstract in its header, after visibility modifier no body to the method all derived classes must eventually implement this method (or they must be abstract as well) any class with 1 or more abstract methods must be an abstract class Inheritance, Polymorphism, and Interfaces 22
23 An Abstract ClosedShape Class public abstract class ClosedShape { private int imyx; private int imyy; public ClosedShape() { this(0,0); public ClosedShape (int x, int y) { imyx = x; imyy = y; public String tostring() { return "x: " + imyx + " y: " + imyy; public abstract int getarea(); public int getx(){ return imyx; public int gety(){ return imyy; Inheritance, Polymorphism, and Interfaces 23
24 Classes that Inherit from ClosedShape 8Rectangle inherits from ClosedShape 8What if Rectangle is unchanged 8Problem: If I have a Rectangle object what happens when I call: Rectangle r = new Rectangle(10, 5, 0, 0); System.out.println( r.getarea(); ) 8Undefined behavior = BAD 8As is the Rectangle class would not compile 8If a class inherits from an abstract class that has abstract methods those methods must be defined in the child or the child must be abstract as well Inheritance, Polymorphism, and Interfaces 24
25 Implementing getarea() public class Rectangle extends ClosedShape { private int imywidth; private int imyheight; public int getarea() { return imywidth * imyheight; // other methods not shown public class Square extends Rectangle { public Square() { public Square(int side) { super(side, side); public Square(int side, int x, int y) { super(side, side, x, y); Inheritance, Polymorphism, and Interfaces 25
26 A Circle Class public class Circle extends ClosedShape { int imyradius; public Circle() { this(1); public Circle(int radius) { imyradius = radius; public Circle(int radius, int x, int y) { super(x,y); imyradius = radius; public int getarea() { return Math.PI * imyradius * imyradius; public String tostring() { return super.tostring() + " radius: " + imyradius; Inheritance, Polymorphism, and Interfaces 26
27 Polymorphism in Action public class UsesShapes { public static void go() { ClosedShape[] slist = new ClosedShape[10]; int a, b, c, d; int x; for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { a = (int)(math.random() * 100); b = (int)(math.random() * 100); c = (int)(math.random() * 100); d = (int)(math.random() * 100); x = (int)(math.random() * 3 ); if( x == 0 ) slist[i] = new Rectangle(a,b,c,d); else if(x == 1) slist[i] = new Square(a,c,d); else slist[i] = new Circle(a,c,d); int total =0; for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { total += slist[i].getarea(); System.out.println( slist[i] ); Inheritance, Polymorphism, and Interfaces 27
28 The Kicker 8We want to expand our pallet of shapes 8Triangle could also be a sub class of ClosedShape. it would inherit from ClosedShape public int getarea() { return 0.5 * imywidth * imyheight; 8What changes do we have to make to the code on the previous slide for totaling area so it will now handle Triangles as well? 8Power. Inheritance, Polymorphism, and Interfaces 28
29 Genericity 8One of the goals of OOP is the support of code reuse to allow more efficient program development 8If a algorithm is essentially the same, but the code would vary based on the data type genericity allows only a single version of that code to exist some languages support genericity via templates in Java, Polymorphism and the inheritance requirement along with interfaces are used the remove duplicates example Inheritance, Polymorphism, and Interfaces 29
30 /* pre: list!= null, for all n such that 0 <= n < list.length, list[n]!= null post: return an array of Objects with all duplicates in list removed, i.e. each element in returned array is unique */ public static Object[] removedups(object[] list) { int numunique = 0; Object[] temp = new Object[list.length]; boolean unique; int index; for(int i = 0; i < list.length; i++) { unique = true; index = 0; while(unique && index < numunique) { unique = list[i].equals( temp[index] ); index++; if(unique) { temp[numunique] = list[i]; numunique++; Object[] result = new Object[numUnique]; System.arraycopy(temp, 0, result, 0, numunique); Inheritance, Polymorphism, and Interfaces 30
31 Object Variables Rectangle r = new Rectangle(10, 20); ClosedShape s = r; System.out.println("Area is " + s.getarea()); 8The above code works if Rectangle extends ClosedShape 8An object variable may point to an object of its base type or a descendant in the inheritance chain The is-a relationship is met. A Rectangle object is-a shape so s may point to it 8This is a form of polymorphism and is used extensively in the Java Collection classes Vector, ArrayList are lists of Objects Inheritance, Polymorphism, and Interfaces 31
32 Type Compatibility Rectangle r = new Rectangle(5, 10); ClosedShape s = r; s.changewidth(20); // syntax error 8polymorphism allows s to point at a Rect object but there are limitations 8The above code will not compile 8Statically, s is declared to be a shape no changewidth method in Shape class must cast s to a Rectangle Rectangle r = new Rectangle(5, 10); Shape s = r; ((Rectangle)s).changeWidth(20); //Okay Inheritance, Polymorphism, and Interfaces 32
33 Problems with Casting 8The following code compiles but a Class Cast Exception is thrown at runtime Rectangle r = new Rectangle(5, 10); Circle c = new Circle(5); Shape s = c; ((Rectangle)s).changeWidth(4); 8Casting must be done carefully and correctly 8If unsure of what type object will be the use the instanceof operator or the getclass() method expression instanceof ClassName Inheritance, Polymorphism, and Interfaces 33
34 Multiple Inheritance 8Inheritance models the "is-a" relationship between real world things 8one of the benefits is code reuse, completing programs faster, with less effort 8in the real world a thing can have "is-a" relationships with several other things a Graduate Teaching Assistant is-a Graduate Student. Graduate Teaching Assistant is-a Faculty Member a Student is-a Person. a Student is a SortableObject Inheritance, Polymorphism, and Interfaces 34
35 The Power of Polymorphism 8Polymorphism allows collections, such as ArrayList, to hold anything genericity, C++ achieves via templates 8Polymorphism also allows a method to work on multiple types create a sorting method that accepts arrays of SortableObjects it can sort anything again, C++ has templated functions 8Java uses a limited form of multiple inheritance Inheritance, Polymorphism, and Interfaces 35
36 Interfaces 8A Java interface is a "pure abstract class". Design only, no implementation. 8Interfaces are declared in a way similar to classes but consist only of public abstract methods public final static fields 8A Java class extends exactly one other class, but can implement as many interfaces as desired Inheritance, Polymorphism, and Interfaces 36
37 Common Interfaces in Java 8One of the most interesting interfaces is: Comparable package java.lang public interface Comparable { public int compareto( Object other ); 8compareTo should return an int <0 if the calling object is less than the parameter, 0 if they are equal, and an int >0 if the calling object is greater than the parameter Inheritance, Polymorphism, and Interfaces 37
38 Implementing an Interface public class Card implements Comparable { public int compareto(object otherobject) { Card other = (Card)otherObject; int result = imysuit - other.imysuit; if(result == 0) result = imyvalue - other.imyvalue; // other methods not shown 8unlike the equals method no steps to prevent a miscast 8If a class declares that it will implement an interface, but does not provide an implementation of all the methods in that interface, that class must be abstract Inheritance, Polymorphism, and Interfaces 38
39 Polymorphism Again public static SelectionSort(Comparable[] list) { Comparable temp; int small; for(int i = 0; i < list.length - 1; i++) { small = i; for(int j = i + 1; j < list.length; j++) { if( list[j].compareto(list[small]) < 0) small = j; // end of j loop temp = list[i]; list[i] = list[small]; list[small] = temp; // end of i loop Inheritance, Polymorphism, and Interfaces 39
Outline. Inheritance. Abstract Classes Interfaces. Class Extension Overriding Methods Inheritance and Constructors Polymorphism.
 Outline Inheritance Class Extension Overriding Methods Inheritance and Constructors Polymorphism Abstract Classes Interfaces 1 OOP Principles Encapsulation Methods and data are combined in classes Not
Outline Inheritance Class Extension Overriding Methods Inheritance and Constructors Polymorphism Abstract Classes Interfaces 1 OOP Principles Encapsulation Methods and data are combined in classes Not
ITI Introduction to Computing II
 ITI 1121. Introduction to Computing II Marcel Turcotte School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Inheritance Introduction Generalization/specialization Version of January 20, 2014 Abstract
ITI 1121. Introduction to Computing II Marcel Turcotte School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Inheritance Introduction Generalization/specialization Version of January 20, 2014 Abstract
ITI Introduction to Computing II
 ITI 1121. Introduction to Computing II Marcel Turcotte School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Inheritance Introduction Generalization/specialization Version of January 21, 2013 Abstract
ITI 1121. Introduction to Computing II Marcel Turcotte School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Inheritance Introduction Generalization/specialization Version of January 21, 2013 Abstract
Topic 5 Polymorphism. " Inheritance is new code that reuses old code. Polymorphism is old code that reuses new code.
 Topic 5 Polymorphism " Inheritance is new code that reuses old code. Polymorphism is old code that reuses new code. 1 Polymorphism Another feature of OOP literally having many forms object variables in
Topic 5 Polymorphism " Inheritance is new code that reuses old code. Polymorphism is old code that reuses new code. 1 Polymorphism Another feature of OOP literally having many forms object variables in
Java Object Oriented Design. CSC207 Fall 2014
 Java Object Oriented Design CSC207 Fall 2014 Design Problem Design an application where the user can draw different shapes Lines Circles Rectangles Just high level design, don t write any detailed code
Java Object Oriented Design CSC207 Fall 2014 Design Problem Design an application where the user can draw different shapes Lines Circles Rectangles Just high level design, don t write any detailed code
CS-202 Introduction to Object Oriented Programming
 CS-202 Introduction to Object Oriented Programming California State University, Los Angeles Computer Science Department Lecture III Inheritance and Polymorphism Introduction to Inheritance Introduction
CS-202 Introduction to Object Oriented Programming California State University, Los Angeles Computer Science Department Lecture III Inheritance and Polymorphism Introduction to Inheritance Introduction
CREATED BY: Muhammad Bilal Arslan Ahmad Shaad. JAVA Chapter No 5. Instructor: Muhammad Naveed
 CREATED BY: Muhammad Bilal Arslan Ahmad Shaad JAVA Chapter No 5 Instructor: Muhammad Naveed Muhammad Bilal Arslan Ahmad Shaad Chapter No 5 Object Oriented Programming Q: Explain subclass and inheritance?
CREATED BY: Muhammad Bilal Arslan Ahmad Shaad JAVA Chapter No 5 Instructor: Muhammad Naveed Muhammad Bilal Arslan Ahmad Shaad Chapter No 5 Object Oriented Programming Q: Explain subclass and inheritance?
COMP200 INHERITANCE. OOP using Java, from slides by Shayan Javed
 1 1 COMP200 INHERITANCE OOP using Java, from slides by Shayan Javed 2 Inheritance Derive new classes (subclass) from existing ones (superclass). Only the Object class (java.lang) has no superclass Every
1 1 COMP200 INHERITANCE OOP using Java, from slides by Shayan Javed 2 Inheritance Derive new classes (subclass) from existing ones (superclass). Only the Object class (java.lang) has no superclass Every
Java Class Design. Eugeny Berkunsky, Computer Science dept., National University of Shipbuilding
 Java Class Design Eugeny Berkunsky, Computer Science dept., National University of Shipbuilding eugeny.berkunsky@gmail.com http://www.berkut.mk.ua Objectives Implement encapsulation Implement inheritance
Java Class Design Eugeny Berkunsky, Computer Science dept., National University of Shipbuilding eugeny.berkunsky@gmail.com http://www.berkut.mk.ua Objectives Implement encapsulation Implement inheritance
CMSC131. Inheritance. Object. When we talked about Object, I mentioned that all Java classes are "built" on top of that.
 CMSC131 Inheritance Object When we talked about Object, I mentioned that all Java classes are "built" on top of that. This came up when talking about the Java standard equals operator: boolean equals(object
CMSC131 Inheritance Object When we talked about Object, I mentioned that all Java classes are "built" on top of that. This came up when talking about the Java standard equals operator: boolean equals(object
Object Oriented Programming in Java. Jaanus Pöial, PhD Tallinn, Estonia
 Object Oriented Programming in Java Jaanus Pöial, PhD Tallinn, Estonia Motivation for Object Oriented Programming Decrease complexity (use layers of abstraction, interfaces, modularity,...) Reuse existing
Object Oriented Programming in Java Jaanus Pöial, PhD Tallinn, Estonia Motivation for Object Oriented Programming Decrease complexity (use layers of abstraction, interfaces, modularity,...) Reuse existing
CH. 2 OBJECT-ORIENTED PROGRAMMING
 CH. 2 OBJECT-ORIENTED PROGRAMMING ACKNOWLEDGEMENT: THESE SLIDES ARE ADAPTED FROM SLIDES PROVIDED WITH DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS IN JAVA, GOODRICH, TAMASSIA AND GOLDWASSER (WILEY 2016) OBJECT-ORIENTED
CH. 2 OBJECT-ORIENTED PROGRAMMING ACKNOWLEDGEMENT: THESE SLIDES ARE ADAPTED FROM SLIDES PROVIDED WITH DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS IN JAVA, GOODRICH, TAMASSIA AND GOLDWASSER (WILEY 2016) OBJECT-ORIENTED
Inheritance. Transitivity
 Inheritance Classes can be organized in a hierarchical structure based on the concept of inheritance Inheritance The property that instances of a sub-class can access both data and behavior associated
Inheritance Classes can be organized in a hierarchical structure based on the concept of inheritance Inheritance The property that instances of a sub-class can access both data and behavior associated
What is Inheritance?
 Inheritance 1 Agenda What is and Why Inheritance? How to derive a sub-class? Object class Constructor calling chain super keyword Overriding methods (most important) Hiding methods Hiding fields Type casting
Inheritance 1 Agenda What is and Why Inheritance? How to derive a sub-class? Object class Constructor calling chain super keyword Overriding methods (most important) Hiding methods Hiding fields Type casting
OBJECT ORİENTATİON ENCAPSULATİON
 OBJECT ORİENTATİON Software development can be seen as a modeling activity. The first step in the software development is the modeling of the problem we are trying to solve and building the conceptual
OBJECT ORİENTATİON Software development can be seen as a modeling activity. The first step in the software development is the modeling of the problem we are trying to solve and building the conceptual
Inheritance, Polymorphism, and Interfaces
 Inheritance, Polymorphism, and Interfaces Chapter 8 Inheritance Basics (ch.8 idea) Inheritance allows programmer to define a general superclass with certain properties (methods, fields/member variables)
Inheritance, Polymorphism, and Interfaces Chapter 8 Inheritance Basics (ch.8 idea) Inheritance allows programmer to define a general superclass with certain properties (methods, fields/member variables)
Contents. I. Classes, Superclasses, and Subclasses. Topic 04 - Inheritance
 Contents Topic 04 - Inheritance I. Classes, Superclasses, and Subclasses - Inheritance Hierarchies Controlling Access to Members (public, no modifier, private, protected) Calling constructors of superclass
Contents Topic 04 - Inheritance I. Classes, Superclasses, and Subclasses - Inheritance Hierarchies Controlling Access to Members (public, no modifier, private, protected) Calling constructors of superclass
Inheritance Motivation
 Inheritance Inheritance Motivation Inheritance in Java is achieved through extending classes Inheritance enables: Code re-use Grouping similar code Flexibility to customize Inheritance Concepts Many real-life
Inheritance Inheritance Motivation Inheritance in Java is achieved through extending classes Inheritance enables: Code re-use Grouping similar code Flexibility to customize Inheritance Concepts Many real-life
INHERITANCE & POLYMORPHISM. INTRODUCTION IB DP Computer science Standard Level ICS3U. INTRODUCTION IB DP Computer science Standard Level ICS3U
 C A N A D I A N I N T E R N A T I O N A L S C H O O L O F H O N G K O N G INHERITANCE & POLYMORPHISM P2 LESSON 12 P2 LESSON 12.1 INTRODUCTION inheritance: OOP allows a programmer to define new classes
C A N A D I A N I N T E R N A T I O N A L S C H O O L O F H O N G K O N G INHERITANCE & POLYMORPHISM P2 LESSON 12 P2 LESSON 12.1 INTRODUCTION inheritance: OOP allows a programmer to define new classes
COS226 - Spring 2018 Class Meeting # 13 March 26, 2018 Inheritance & Polymorphism
 COS226 - Spring 2018 Class Meeting # 13 March 26, 2018 Inheritance & Polymorphism Ibrahim Albluwi Composition A GuitarString has a RingBuffer. A MarkovModel has a Symbol Table. A Symbol Table has a Binary
COS226 - Spring 2018 Class Meeting # 13 March 26, 2018 Inheritance & Polymorphism Ibrahim Albluwi Composition A GuitarString has a RingBuffer. A MarkovModel has a Symbol Table. A Symbol Table has a Binary
Day 4. COMP1006/1406 Summer M. Jason Hinek Carleton University
 Day 4 COMP1006/1406 Summer 2016 M. Jason Hinek Carleton University today s agenda assignments questions about assignment 2 a quick look back constructors signatures and overloading encapsulation / information
Day 4 COMP1006/1406 Summer 2016 M. Jason Hinek Carleton University today s agenda assignments questions about assignment 2 a quick look back constructors signatures and overloading encapsulation / information
Reusing Classes. Hendrik Speleers
 Hendrik Speleers Overview Composition Inheritance Polymorphism Method overloading vs. overriding Visibility of variables and methods Specification of a contract Abstract classes, interfaces Software development
Hendrik Speleers Overview Composition Inheritance Polymorphism Method overloading vs. overriding Visibility of variables and methods Specification of a contract Abstract classes, interfaces Software development
Lecture 36: Cloning. Last time: Today: 1. Object 2. Polymorphism and abstract methods 3. Upcasting / downcasting
 Lecture 36: Cloning Last time: 1. Object 2. Polymorphism and abstract methods 3. Upcasting / downcasting Today: 1. Project #7 assigned 2. equals reconsidered 3. Copying and cloning 4. Composition 11/27/2006
Lecture 36: Cloning Last time: 1. Object 2. Polymorphism and abstract methods 3. Upcasting / downcasting Today: 1. Project #7 assigned 2. equals reconsidered 3. Copying and cloning 4. Composition 11/27/2006
Inheritance and Encapsulation. Amit Gupta
 Inheritance and Encapsulation Amit Gupta Project 1 How did it go? What did you like about it? What did you not like? What can we do to help? Suggestions Ask questions if you don t understand a concept
Inheritance and Encapsulation Amit Gupta Project 1 How did it go? What did you like about it? What did you not like? What can we do to help? Suggestions Ask questions if you don t understand a concept
CS5000: Foundations of Programming. Mingon Kang, PhD Computer Science, Kennesaw State University
 CS5000: Foundations of Programming Mingon Kang, PhD Computer Science, Kennesaw State University Inheritance Three main programming mechanisms that constitute object-oriented programming (OOP) Encapsulation
CS5000: Foundations of Programming Mingon Kang, PhD Computer Science, Kennesaw State University Inheritance Three main programming mechanisms that constitute object-oriented programming (OOP) Encapsulation
Super-Classes and sub-classes
 Super-Classes and sub-classes Subclasses. Overriding Methods Subclass Constructors Inheritance Hierarchies Polymorphism Casting 1 Subclasses: Often you want to write a class that is a special case of an
Super-Classes and sub-classes Subclasses. Overriding Methods Subclass Constructors Inheritance Hierarchies Polymorphism Casting 1 Subclasses: Often you want to write a class that is a special case of an
Chapter 11 Inheritance and Polymorphism. Motivations. Suppose you will define classes to model circles,
 Chapter 11 Inheritance and Polymorphism 1 Motivations Suppose you will define classes to model circles, rectangles, and triangles. These classes have many common features. What is the best way to design
Chapter 11 Inheritance and Polymorphism 1 Motivations Suppose you will define classes to model circles, rectangles, and triangles. These classes have many common features. What is the best way to design
Inheritance and Polymorphism
 Object Oriented Programming Designed and Presented by Dr. Ayman Elshenawy Elsefy Dept. of Systems & Computer Eng.. Al-Azhar University Website: eaymanelshenawy.wordpress.com Email : eaymanelshenawy@azhar.edu.eg
Object Oriented Programming Designed and Presented by Dr. Ayman Elshenawy Elsefy Dept. of Systems & Computer Eng.. Al-Azhar University Website: eaymanelshenawy.wordpress.com Email : eaymanelshenawy@azhar.edu.eg
Object-oriented programming. and data-structures CS/ENGRD 2110 SUMMER 2018
 Object-oriented programming 1 and data-structures CS/ENGRD 2110 SUMMER 2018 Lecture 4: OO Principles - Polymorphism http://courses.cs.cornell.edu/cs2110/2018su Lecture 3 Recap 2 Good design principles.
Object-oriented programming 1 and data-structures CS/ENGRD 2110 SUMMER 2018 Lecture 4: OO Principles - Polymorphism http://courses.cs.cornell.edu/cs2110/2018su Lecture 3 Recap 2 Good design principles.
Inheritance, and Polymorphism.
 Inheritance and Polymorphism by Yukong Zhang Object-oriented programming languages are the most widely used modern programming languages. They model programming based on objects which are very close to
Inheritance and Polymorphism by Yukong Zhang Object-oriented programming languages are the most widely used modern programming languages. They model programming based on objects which are very close to
Introduction to Inheritance
 Introduction to Inheritance James Brucker These slides cover only the basics of inheritance. What is Inheritance? One class incorporates all the attributes and behavior from another class -- it inherits
Introduction to Inheritance James Brucker These slides cover only the basics of inheritance. What is Inheritance? One class incorporates all the attributes and behavior from another class -- it inherits
Java and OOP. Part 3 Extending classes. OOP in Java : W. Milner 2005 : Slide 1
 Java and OOP Part 3 Extending classes OOP in Java : W. Milner 2005 : Slide 1 Inheritance Suppose we want a version of an existing class, which is slightly different from it. We want to avoid starting again
Java and OOP Part 3 Extending classes OOP in Java : W. Milner 2005 : Slide 1 Inheritance Suppose we want a version of an existing class, which is slightly different from it. We want to avoid starting again
Inheritance and Polymorphism
 Inheritance and Polymorphism Dr. M. G. Abbas Malik Assistant Professor Faculty of Computing and IT (North Jeddah Branch) King Abdulaziz University, Jeddah, KSA mgmalik@kau.edu.sa www.sanlp.org/malik/cpit305/ap.html
Inheritance and Polymorphism Dr. M. G. Abbas Malik Assistant Professor Faculty of Computing and IT (North Jeddah Branch) King Abdulaziz University, Jeddah, KSA mgmalik@kau.edu.sa www.sanlp.org/malik/cpit305/ap.html
Inheritance (continued) Inheritance
 Objectives Chapter 11 Inheritance and Polymorphism Learn about inheritance Learn about subclasses and superclasses Explore how to override the methods of a superclass Examine how constructors of superclasses
Objectives Chapter 11 Inheritance and Polymorphism Learn about inheritance Learn about subclasses and superclasses Explore how to override the methods of a superclass Examine how constructors of superclasses
Chapter 10 Inheritance and Polymorphism. Dr. Hikmat Jaber
 Chapter 10 Inheritance and Polymorphism Dr. Hikmat Jaber 1 Motivations Suppose you will define classes to model circles, rectangles, and triangles. These classes have many common features. What is the
Chapter 10 Inheritance and Polymorphism Dr. Hikmat Jaber 1 Motivations Suppose you will define classes to model circles, rectangles, and triangles. These classes have many common features. What is the
Inheritance. Inheritance allows the following two changes in derived class: 1. add new members; 2. override existing (in base class) methods.
 Inheritance Inheritance is the act of deriving a new class from an existing one. Inheritance allows us to extend the functionality of the object. The new class automatically contains some or all methods
Inheritance Inheritance is the act of deriving a new class from an existing one. Inheritance allows us to extend the functionality of the object. The new class automatically contains some or all methods
CS/ENGRD 2110 SPRING Lecture 7: Interfaces and Abstract Classes
 CS/ENGRD 2110 SPRING 2019 Lecture 7: Interfaces and Abstract Classes http://courses.cs.cornell.edu/cs2110 1 Announcements 2 A2 is due Thursday night (14 February) Go back to Lecture 6 & discuss method
CS/ENGRD 2110 SPRING 2019 Lecture 7: Interfaces and Abstract Classes http://courses.cs.cornell.edu/cs2110 1 Announcements 2 A2 is due Thursday night (14 February) Go back to Lecture 6 & discuss method
Graphical Interface and Application (I3305) Semester: 1 Academic Year: 2017/2018 Dr Antoun Yaacoub
 Lebanese University Faculty of Science Computer Science BS Degree Graphical Interface and Application (I3305) Semester: 1 Academic Year: 2017/2018 Dr Antoun Yaacoub 2 Crash Course in JAVA Classes A Java
Lebanese University Faculty of Science Computer Science BS Degree Graphical Interface and Application (I3305) Semester: 1 Academic Year: 2017/2018 Dr Antoun Yaacoub 2 Crash Course in JAVA Classes A Java
CS1150 Principles of Computer Science Objects and Classes
 CS1150 Principles of Computer Science Objects and Classes Yanyan Zhuang Department of Computer Science http://www.cs.uccs.edu/~yzhuang CS1150 UC. Colorado Springs Object-Oriented Thinking Chapters 1-8
CS1150 Principles of Computer Science Objects and Classes Yanyan Zhuang Department of Computer Science http://www.cs.uccs.edu/~yzhuang CS1150 UC. Colorado Springs Object-Oriented Thinking Chapters 1-8
Today. Book-keeping. Inheritance. Subscribe to sipb-iap-java-students. Slides and code at Interfaces.
 Today Book-keeping Inheritance Subscribe to sipb-iap-java-students Interfaces Slides and code at http://sipb.mit.edu/iap/java/ The Object class Problem set 1 released 1 2 So far... Inheritance Basic objects,
Today Book-keeping Inheritance Subscribe to sipb-iap-java-students Interfaces Slides and code at http://sipb.mit.edu/iap/java/ The Object class Problem set 1 released 1 2 So far... Inheritance Basic objects,
ITI Introduction to Computing II
 ITI 1121. Introduction to Computing II Marcel Turcotte School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Inheritance (part II) Polymorphism Version of January 21, 2013 Abstract These lecture notes
ITI 1121. Introduction to Computing II Marcel Turcotte School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Inheritance (part II) Polymorphism Version of January 21, 2013 Abstract These lecture notes
Lecture Notes Chapter #9_b Inheritance & Polymorphism
 Lecture Notes Chapter #9_b Inheritance & Polymorphism Inheritance results from deriving new classes from existing classes Root Class all java classes are derived from the java.lang.object class GeometricObject1
Lecture Notes Chapter #9_b Inheritance & Polymorphism Inheritance results from deriving new classes from existing classes Root Class all java classes are derived from the java.lang.object class GeometricObject1
Agenda. Objects and classes Encapsulation and information hiding Documentation Packages
 Preliminaries II 1 Agenda Objects and classes Encapsulation and information hiding Documentation Packages Inheritance Polymorphism Implementation of inheritance in Java Abstract classes Interfaces Generics
Preliminaries II 1 Agenda Objects and classes Encapsulation and information hiding Documentation Packages Inheritance Polymorphism Implementation of inheritance in Java Abstract classes Interfaces Generics
Programming Exercise 14: Inheritance and Polymorphism
 Programming Exercise 14: Inheritance and Polymorphism Purpose: Gain experience in extending a base class and overriding some of its methods. Background readings from textbook: Liang, Sections 11.1-11.5.
Programming Exercise 14: Inheritance and Polymorphism Purpose: Gain experience in extending a base class and overriding some of its methods. Background readings from textbook: Liang, Sections 11.1-11.5.
Practice for Chapter 11
 Practice for Chapter 11 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Object-oriented programming allows you to derive new classes from existing
Practice for Chapter 11 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Object-oriented programming allows you to derive new classes from existing
Computer Science 210: Data Structures
 Computer Science 210: Data Structures Summary Today writing a Java program guidelines on clear code object-oriented design inheritance polymorphism this exceptions interfaces READING: GT chapter 2 Object-Oriented
Computer Science 210: Data Structures Summary Today writing a Java program guidelines on clear code object-oriented design inheritance polymorphism this exceptions interfaces READING: GT chapter 2 Object-Oriented
ITI Introduction to Computing II
 ITI 1121. Introduction to Computing II Marcel Turcotte School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Inheritance (part II) Polymorphism Version of January 21, 2013 Abstract These lecture notes
ITI 1121. Introduction to Computing II Marcel Turcotte School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Inheritance (part II) Polymorphism Version of January 21, 2013 Abstract These lecture notes
Object Oriented Programming. Java-Lecture 11 Polymorphism
 Object Oriented Programming Java-Lecture 11 Polymorphism Abstract Classes and Methods There will be a situation where you want to develop a design of a class which is common to many classes. Abstract class
Object Oriented Programming Java-Lecture 11 Polymorphism Abstract Classes and Methods There will be a situation where you want to develop a design of a class which is common to many classes. Abstract class
Programming in C# Inheritance and Polymorphism
 Programming in C# Inheritance and Polymorphism C# Classes Classes are used to accomplish: Modularity: Scope for global (static) methods Blueprints for generating objects or instances: Per instance data
Programming in C# Inheritance and Polymorphism C# Classes Classes are used to accomplish: Modularity: Scope for global (static) methods Blueprints for generating objects or instances: Per instance data
Software Paradigms (Lesson 3) Object-Oriented Paradigm (2)
 Software Paradigms (Lesson 3) Object-Oriented Paradigm (2) Table of Contents 1 Reusing Classes... 2 1.1 Composition... 2 1.2 Inheritance... 4 1.2.1 Extending Classes... 5 1.2.2 Method Overriding... 7 1.2.3
Software Paradigms (Lesson 3) Object-Oriented Paradigm (2) Table of Contents 1 Reusing Classes... 2 1.1 Composition... 2 1.2 Inheritance... 4 1.2.1 Extending Classes... 5 1.2.2 Method Overriding... 7 1.2.3
1B1b Inheritance. Inheritance. Agenda. Subclass and Superclass. Superclass. Generalisation & Specialisation. Shapes and Squares. 1B1b Lecture Slides
 1B1b Inheritance Agenda Introduction to inheritance. How Java supports inheritance. Inheritance is a key feature of object-oriented oriented programming. 1 2 Inheritance Models the kind-of or specialisation-of
1B1b Inheritance Agenda Introduction to inheritance. How Java supports inheritance. Inheritance is a key feature of object-oriented oriented programming. 1 2 Inheritance Models the kind-of or specialisation-of
Chapter 6: Inheritance
 Chapter 6: Inheritance EECS 1030 moodle.yorku.ca State of an object final int WIDTH = 3; final int HEIGTH = 4; final int WEIGHT = 80; GoldenRectangle rectangle = new GoldenRectangle(WIDTH, HEIGHT, WEIGHT);
Chapter 6: Inheritance EECS 1030 moodle.yorku.ca State of an object final int WIDTH = 3; final int HEIGTH = 4; final int WEIGHT = 80; GoldenRectangle rectangle = new GoldenRectangle(WIDTH, HEIGHT, WEIGHT);
Programming II (CS300)
 1 Programming II (CS300) Chapter 05: Inheritance and Interfaces MOUNA KACEM mouna@cs.wisc.edu Fall 2018 Inheritance and Interfaces 2 Introduction Inheritance and Class Hierarchy Polymorphism Abstract Classes
1 Programming II (CS300) Chapter 05: Inheritance and Interfaces MOUNA KACEM mouna@cs.wisc.edu Fall 2018 Inheritance and Interfaces 2 Introduction Inheritance and Class Hierarchy Polymorphism Abstract Classes
index.pdf January 21,
 index.pdf January 21, 2013 1 ITI 1121. Introduction to Computing II Circle Let s complete the implementation of the class Circle. Marcel Turcotte School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Version
index.pdf January 21, 2013 1 ITI 1121. Introduction to Computing II Circle Let s complete the implementation of the class Circle. Marcel Turcotte School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Version
IST311. Advanced Issues in OOP: Inheritance and Polymorphism
 IST311 Advanced Issues in OOP: Inheritance and Polymorphism IST311/602 Cleveland State University Prof. Victor Matos Adapted from: Introduction to Java Programming: Comprehensive Version, Eighth Edition
IST311 Advanced Issues in OOP: Inheritance and Polymorphism IST311/602 Cleveland State University Prof. Victor Matos Adapted from: Introduction to Java Programming: Comprehensive Version, Eighth Edition
Java Inheritance. Written by John Bell for CS 342, Spring Based on chapter 6 of Learning Java by Niemeyer & Leuck, and other sources.
 Java Inheritance Written by John Bell for CS 342, Spring 2018 Based on chapter 6 of Learning Java by Niemeyer & Leuck, and other sources. Review Which of the following is true? A. Java classes may either
Java Inheritance Written by John Bell for CS 342, Spring 2018 Based on chapter 6 of Learning Java by Niemeyer & Leuck, and other sources. Review Which of the following is true? A. Java classes may either
CMSC 132: Object-Oriented Programming II
 CMSC 132: Object-Oriented Programming II Java Support for OOP Department of Computer Science University of Maryland, College Park Object Oriented Programming (OOP) OO Principles Abstraction Encapsulation
CMSC 132: Object-Oriented Programming II Java Support for OOP Department of Computer Science University of Maryland, College Park Object Oriented Programming (OOP) OO Principles Abstraction Encapsulation
Last class. -More on polymorphism -super -Introduction to interfaces
 Last class -More on polymorphism -super -Introduction to interfaces Interfaces Sometimes in Java, we will have 2 classes that both share a similar structure, but neither of them is clearly the parent or
Last class -More on polymorphism -super -Introduction to interfaces Interfaces Sometimes in Java, we will have 2 classes that both share a similar structure, but neither of them is clearly the parent or
Inheritance -- Introduction
 Inheritance -- Introduction Another fundamental object-oriented technique is called inheritance, which, when used correctly, supports reuse and enhances software designs Chapter 8 focuses on: the concept
Inheritance -- Introduction Another fundamental object-oriented technique is called inheritance, which, when used correctly, supports reuse and enhances software designs Chapter 8 focuses on: the concept
The Essence of OOP using Java, Nested Top-Level Classes. Preface
 The Essence of OOP using Java, Nested Top-Level Classes Baldwin explains nested top-level classes, and illustrates a very useful polymorphic structure where nested classes extend the enclosing class and
The Essence of OOP using Java, Nested Top-Level Classes Baldwin explains nested top-level classes, and illustrates a very useful polymorphic structure where nested classes extend the enclosing class and
More On inheritance. What you can do in subclass regarding methods:
 More On inheritance What you can do in subclass regarding methods: The inherited methods can be used directly as they are. You can write a new static method in the subclass that has the same signature
More On inheritance What you can do in subclass regarding methods: The inherited methods can be used directly as they are. You can write a new static method in the subclass that has the same signature
Making New instances of Classes
 Making New instances of Classes NOTE: revised from previous version of Lecture04 New Operator Classes are user defined datatypes in OOP languages How do we make instances of these new datatypes? Using
Making New instances of Classes NOTE: revised from previous version of Lecture04 New Operator Classes are user defined datatypes in OOP languages How do we make instances of these new datatypes? Using
Advanced Programming - JAVA Lecture 4 OOP Concepts in JAVA PART II
 Advanced Programming - JAVA Lecture 4 OOP Concepts in JAVA PART II Mahmoud El-Gayyar elgayyar@ci.suez.edu.eg Ad hoc-polymorphism Outline Method overloading Sub-type Polymorphism Method overriding Dynamic
Advanced Programming - JAVA Lecture 4 OOP Concepts in JAVA PART II Mahmoud El-Gayyar elgayyar@ci.suez.edu.eg Ad hoc-polymorphism Outline Method overloading Sub-type Polymorphism Method overriding Dynamic
Polymorphism and Interfaces. CGS 3416 Spring 2018
 Polymorphism and Interfaces CGS 3416 Spring 2018 Polymorphism and Dynamic Binding If a piece of code is designed to work with an object of type X, it will also work with an object of a class type that
Polymorphism and Interfaces CGS 3416 Spring 2018 Polymorphism and Dynamic Binding If a piece of code is designed to work with an object of type X, it will also work with an object of a class type that
Chapter 10 Classes Continued. Fundamentals of Java
 Chapter 10 Classes Continued Objectives Know when it is appropriate to include class (static) variables and methods in a class. Understand the role of Java interfaces in a software system and define an
Chapter 10 Classes Continued Objectives Know when it is appropriate to include class (static) variables and methods in a class. Understand the role of Java interfaces in a software system and define an
More About Classes CS 1025 Computer Science Fundamentals I Stephen M. Watt University of Western Ontario
 More About Classes CS 1025 Computer Science Fundamentals I Stephen M. Watt University of Western Ontario The Story So Far... Classes as collections of fields and methods. Methods can access fields, and
More About Classes CS 1025 Computer Science Fundamentals I Stephen M. Watt University of Western Ontario The Story So Far... Classes as collections of fields and methods. Methods can access fields, and
Inheritance. Inheritance Reserved word protected Reserved word super Overriding methods Class Hierarchies Reading for this lecture: L&L
 Inheritance Inheritance Reserved word protected Reserved word super Overriding methods Class Hierarchies Reading for this lecture: L&L 9.1 9.4 1 Inheritance Inheritance allows a software developer to derive
Inheritance Inheritance Reserved word protected Reserved word super Overriding methods Class Hierarchies Reading for this lecture: L&L 9.1 9.4 1 Inheritance Inheritance allows a software developer to derive
8. Polymorphism and Inheritance
 8. Polymorphism and Inheritance Harald Gall, Prof. Dr. Institut für Informatik Universität Zürich http://seal.ifi.uzh.ch/info1 Objectives Describe polymorphism and inheritance in general Define interfaces
8. Polymorphism and Inheritance Harald Gall, Prof. Dr. Institut für Informatik Universität Zürich http://seal.ifi.uzh.ch/info1 Objectives Describe polymorphism and inheritance in general Define interfaces
Argument Passing All primitive data types (int etc.) are passed by value and all reference types (arrays, strings, objects) are used through refs.
 Local Variable Initialization Unlike instance vars, local vars must be initialized before they can be used. Eg. void mymethod() { int foo = 42; int bar; bar = bar + 1; //compile error bar = 99; bar = bar
Local Variable Initialization Unlike instance vars, local vars must be initialized before they can be used. Eg. void mymethod() { int foo = 42; int bar; bar = bar + 1; //compile error bar = 99; bar = bar
Methods Common to all Classes
 Methods Common to all Classes 9-2-2013 OOP concepts Overloading vs. Overriding Use of this. and this(); use of super. and super() Methods common to all classes: tostring(), equals(), hashcode() HW#1 posted;
Methods Common to all Classes 9-2-2013 OOP concepts Overloading vs. Overriding Use of this. and this(); use of super. and super() Methods common to all classes: tostring(), equals(), hashcode() HW#1 posted;
CS 251 Intermediate Programming Inheritance
 CS 251 Intermediate Programming Inheritance Brooke Chenoweth University of New Mexico Spring 2018 Inheritance We don t inherit the earth from our parents, We only borrow it from our children. What is inheritance?
CS 251 Intermediate Programming Inheritance Brooke Chenoweth University of New Mexico Spring 2018 Inheritance We don t inherit the earth from our parents, We only borrow it from our children. What is inheritance?
CS/ENGRD 2110 FALL Lecture 7: Interfaces and Abstract Classes
 CS/ENGRD 2110 FALL 2017 Lecture 7: Interfaces and Abstract Classes http://courses.cs.cornell.edu/cs2110 1 Announcements 2 A2 is due tomorrow night (17 February) Get started on A3 a method every other day.
CS/ENGRD 2110 FALL 2017 Lecture 7: Interfaces and Abstract Classes http://courses.cs.cornell.edu/cs2110 1 Announcements 2 A2 is due tomorrow night (17 February) Get started on A3 a method every other day.
Inheritance & Polymorphism Recap. Inheritance & Polymorphism 1
 Inheritance & Polymorphism Recap Inheritance & Polymorphism 1 Introduction! Besides composition, another form of reuse is inheritance.! With inheritance, an object can inherit behavior from another object,
Inheritance & Polymorphism Recap Inheritance & Polymorphism 1 Introduction! Besides composition, another form of reuse is inheritance.! With inheritance, an object can inherit behavior from another object,
Chapter 14 Abstract Classes and Interfaces
 Chapter 14 Abstract Classes and Interfaces 1 What is abstract class? Abstract class is just like other class, but it marks with abstract keyword. In abstract class, methods that we want to be overridden
Chapter 14 Abstract Classes and Interfaces 1 What is abstract class? Abstract class is just like other class, but it marks with abstract keyword. In abstract class, methods that we want to be overridden
OVERRIDING. 7/11/2015 Budditha Hettige 82
 OVERRIDING 7/11/2015 (budditha@yahoo.com) 82 What is Overriding Is a language feature Allows a subclass or child class to provide a specific implementation of a method that is already provided by one of
OVERRIDING 7/11/2015 (budditha@yahoo.com) 82 What is Overriding Is a language feature Allows a subclass or child class to provide a specific implementation of a method that is already provided by one of
Inheritance (Extends) Overriding methods IS-A Vs. HAS-A Polymorphism. superclass. is-a. subclass
 Inheritance and Polymorphism Inheritance (Extends) Overriding methods IS-A Vs. HAS-A Polymorphism Inheritance (semantics) We now have two classes that do essentially the same thing The fields are exactly
Inheritance and Polymorphism Inheritance (Extends) Overriding methods IS-A Vs. HAS-A Polymorphism Inheritance (semantics) We now have two classes that do essentially the same thing The fields are exactly
What are the characteristics of Object Oriented programming language?
 What are the various elements of OOP? Following are the various elements of OOP:- Class:- A class is a collection of data and the various operations that can be performed on that data. Object- This is
What are the various elements of OOP? Following are the various elements of OOP:- Class:- A class is a collection of data and the various operations that can be performed on that data. Object- This is
COP 3330 Final Exam Review
 COP 3330 Final Exam Review I. The Basics (Chapters 2, 5, 6) a. comments b. identifiers, reserved words c. white space d. compilers vs. interpreters e. syntax, semantics f. errors i. syntax ii. run-time
COP 3330 Final Exam Review I. The Basics (Chapters 2, 5, 6) a. comments b. identifiers, reserved words c. white space d. compilers vs. interpreters e. syntax, semantics f. errors i. syntax ii. run-time
Inheritance. Notes Chapter 6 and AJ Chapters 7 and 8
 Inheritance Notes Chapter 6 and AJ Chapters 7 and 8 1 Inheritance you know a lot about an object by knowing its class for example what is a Komondor? http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/file:komondor_delvin.jpg
Inheritance Notes Chapter 6 and AJ Chapters 7 and 8 1 Inheritance you know a lot about an object by knowing its class for example what is a Komondor? http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/file:komondor_delvin.jpg
STUDENT LESSON A20 Inheritance, Polymorphism, and Abstract Classes
 STUDENT LESSON A20 Inheritance, Polymorphism, and Abstract Classes Java Curriculum for AP Computer Science, Student Lesson A20 1 STUDENT LESSON A20 Inheritance, Polymorphism, and Abstract Classes INTRODUCTION:
STUDENT LESSON A20 Inheritance, Polymorphism, and Abstract Classes Java Curriculum for AP Computer Science, Student Lesson A20 1 STUDENT LESSON A20 Inheritance, Polymorphism, and Abstract Classes INTRODUCTION:
Java Primer. CITS2200 Data Structures and Algorithms. Topic 2
 CITS2200 Data Structures and Algorithms Topic 2 Java Primer Review of Java basics Primitive vs Reference Types Classes and Objects Class Hierarchies Interfaces Exceptions Reading: Lambert and Osborne,
CITS2200 Data Structures and Algorithms Topic 2 Java Primer Review of Java basics Primitive vs Reference Types Classes and Objects Class Hierarchies Interfaces Exceptions Reading: Lambert and Osborne,
OOPs Concepts. 1. Data Hiding 2. Encapsulation 3. Abstraction 4. Is-A Relationship 5. Method Signature 6. Polymorphism 7. Constructors 8.
 OOPs Concepts 1. Data Hiding 2. Encapsulation 3. Abstraction 4. Is-A Relationship 5. Method Signature 6. Polymorphism 7. Constructors 8. Type Casting Let us discuss them in detail: 1. Data Hiding: Every
OOPs Concepts 1. Data Hiding 2. Encapsulation 3. Abstraction 4. Is-A Relationship 5. Method Signature 6. Polymorphism 7. Constructors 8. Type Casting Let us discuss them in detail: 1. Data Hiding: Every
Abstract Classes. Abstract Classes a and Interfaces. Class Shape Hierarchy. Problem AND Requirements. Abstract Classes.
 a and Interfaces Class Shape Hierarchy Consider the following class hierarchy Shape Circle Square Problem AND Requirements Suppose that in order to exploit polymorphism, we specify that 2-D objects must
a and Interfaces Class Shape Hierarchy Consider the following class hierarchy Shape Circle Square Problem AND Requirements Suppose that in order to exploit polymorphism, we specify that 2-D objects must
Computer Science II (20073) Week 1: Review and Inheritance
 Computer Science II 4003-232-01 (20073) Week 1: Review and Inheritance Richard Zanibbi Rochester Institute of Technology Review of CS-I Hardware and Software Hardware Physical devices in a computer system
Computer Science II 4003-232-01 (20073) Week 1: Review and Inheritance Richard Zanibbi Rochester Institute of Technology Review of CS-I Hardware and Software Hardware Physical devices in a computer system
Implements vs. Extends When Defining a Class
 Implements vs. Extends When Defining a Class implements: Keyword followed by the name of an INTERFACE Interfaces only have method PROTOTYPES You CANNOT create on object of an interface type extends: Keyword
Implements vs. Extends When Defining a Class implements: Keyword followed by the name of an INTERFACE Interfaces only have method PROTOTYPES You CANNOT create on object of an interface type extends: Keyword
Introduction to Programming Using Java (98-388)
 Introduction to Programming Using Java (98-388) Understand Java fundamentals Describe the use of main in a Java application Signature of main, why it is static; how to consume an instance of your own class;
Introduction to Programming Using Java (98-388) Understand Java fundamentals Describe the use of main in a Java application Signature of main, why it is static; how to consume an instance of your own class;
Basic Principles of OO. Example: Ice/Water Dispenser. Systems Thinking. Interfaces: Describing Behavior. People's Roles wrt Systems
 Basics of OO Programming with Java/C# Basic Principles of OO Abstraction Encapsulation Modularity Breaking up something into smaller, more manageable pieces Hierarchy Refining through levels of abstraction
Basics of OO Programming with Java/C# Basic Principles of OO Abstraction Encapsulation Modularity Breaking up something into smaller, more manageable pieces Hierarchy Refining through levels of abstraction
Inheritance Systems. Merchandise. Television Camcorder Shirt Shoe Dress 9.1.1
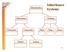 Merchandise Inheritance Systems Electronics Clothing Television Camcorder Shirt Shoe Dress Digital Analog 9.1.1 Another AcademicDisciplines Hierarchy Mathematics Engineering Algebra Probability Geometry
Merchandise Inheritance Systems Electronics Clothing Television Camcorder Shirt Shoe Dress Digital Analog 9.1.1 Another AcademicDisciplines Hierarchy Mathematics Engineering Algebra Probability Geometry
CS-140 Fall 2017 Test 1 Version Practice Practice for Nov. 20, Name:
 CS-140 Fall 2017 Test 1 Version Practice Practice for Nov. 20, 2017 Name: 1. (10 points) For the following, Check T if the statement is true, the F if the statement is false. (a) T F : If a child overrides
CS-140 Fall 2017 Test 1 Version Practice Practice for Nov. 20, 2017 Name: 1. (10 points) For the following, Check T if the statement is true, the F if the statement is false. (a) T F : If a child overrides
Lesson 10A OOP Fundamentals. By John B. Owen All rights reserved 2011, revised 2014
 Lesson 10A OOP Fundamentals By John B. Owen All rights reserved 2011, revised 2014 Table of Contents Objectives Definition Pointers vs containers Object vs primitives Constructors Methods Object class
Lesson 10A OOP Fundamentals By John B. Owen All rights reserved 2011, revised 2014 Table of Contents Objectives Definition Pointers vs containers Object vs primitives Constructors Methods Object class
Questions Answer Key Questions Answer Key Questions Answer Key
 Benha University Term: 2 nd (2013/2014) Class: 2 nd Year Students Subject: Object Oriented Programming Faculty of Computers & Informatics Date: 26/4/2014 Time: 1 hours Exam: Mid-Term (A) Name:. Status:
Benha University Term: 2 nd (2013/2014) Class: 2 nd Year Students Subject: Object Oriented Programming Faculty of Computers & Informatics Date: 26/4/2014 Time: 1 hours Exam: Mid-Term (A) Name:. Status:
INHERITANCE. Spring 2019
 INHERITANCE Spring 2019 INHERITANCE BASICS Inheritance is a technique that allows one class to be derived from another A derived class inherits all of the data and methods from the original class Suppose
INHERITANCE Spring 2019 INHERITANCE BASICS Inheritance is a technique that allows one class to be derived from another A derived class inherits all of the data and methods from the original class Suppose
The Sun s Java Certification and its Possible Role in the Joint Teaching Material
 The Sun s Java Certification and its Possible Role in the Joint Teaching Material Nataša Ibrajter Faculty of Science Department of Mathematics and Informatics Novi Sad 1 Contents Kinds of Sun Certified
The Sun s Java Certification and its Possible Role in the Joint Teaching Material Nataša Ibrajter Faculty of Science Department of Mathematics and Informatics Novi Sad 1 Contents Kinds of Sun Certified
CO Java SE 8: Fundamentals
 CO-83527 Java SE 8: Fundamentals Summary Duration 5 Days Audience Application Developer, Developer, Project Manager, Systems Administrator, Technical Administrator, Technical Consultant and Web Administrator
CO-83527 Java SE 8: Fundamentals Summary Duration 5 Days Audience Application Developer, Developer, Project Manager, Systems Administrator, Technical Administrator, Technical Consultant and Web Administrator
Introduction to OOP with Java. Instructor: AbuKhleif, Mohammad Noor Sep 2017
 Introduction to OOP with Java Instructor: AbuKhleif, Mohammad Noor Sep 2017 Lecture 11: Inheritance and Polymorphism Part 1 Instructor: AbuKhleif, Mohammad Noor Sep 2017 Instructor AbuKhleif, Mohammad
Introduction to OOP with Java Instructor: AbuKhleif, Mohammad Noor Sep 2017 Lecture 11: Inheritance and Polymorphism Part 1 Instructor: AbuKhleif, Mohammad Noor Sep 2017 Instructor AbuKhleif, Mohammad
C++ Important Questions with Answers
 1. Name the operators that cannot be overloaded. sizeof,.,.*,.->, ::,? 2. What is inheritance? Inheritance is property such that a parent (or super) class passes the characteristics of itself to children
1. Name the operators that cannot be overloaded. sizeof,.,.*,.->, ::,? 2. What is inheritance? Inheritance is property such that a parent (or super) class passes the characteristics of itself to children
Inheritance (Deitel chapter 9)
 Inheritance (Deitel chapter 9) 1 2 Plan Introduction Superclasses and Subclasses protected Members Constructors and Finalizers in Subclasses Software Engineering with Inheritance 3 Introduction Inheritance
Inheritance (Deitel chapter 9) 1 2 Plan Introduction Superclasses and Subclasses protected Members Constructors and Finalizers in Subclasses Software Engineering with Inheritance 3 Introduction Inheritance
Programming II (CS300)
 1 Programming II (CS300) Chapter 05: Inheritance and Interfaces MOUNA KACEM mouna@cs.wisc.edu Spring 2018 Inheritance and Interfaces 2 Introduction Inheritance and Class Hierarchy Polymorphism Abstract
1 Programming II (CS300) Chapter 05: Inheritance and Interfaces MOUNA KACEM mouna@cs.wisc.edu Spring 2018 Inheritance and Interfaces 2 Introduction Inheritance and Class Hierarchy Polymorphism Abstract
Abstract Classes and Interfaces
 Abstract Classes and Interfaces Reading: Reges and Stepp: 9.5 9.6 CSC216: Programming Concepts Sarah Heckman 1 Abstract Classes A Java class that cannot be instantiated, but instead serves as a superclass
Abstract Classes and Interfaces Reading: Reges and Stepp: 9.5 9.6 CSC216: Programming Concepts Sarah Heckman 1 Abstract Classes A Java class that cannot be instantiated, but instead serves as a superclass
Subclass Gist Example: Chess Super Keyword Shadowing Overriding Why? L10 - Polymorphism and Abstract Classes The Four Principles of Object Oriented
 Table of Contents L01 - Introduction L02 - Strings Some Examples Reserved Characters Operations Immutability Equality Wrappers and Primitives Boxing/Unboxing Boxing Unboxing Formatting L03 - Input and
Table of Contents L01 - Introduction L02 - Strings Some Examples Reserved Characters Operations Immutability Equality Wrappers and Primitives Boxing/Unboxing Boxing Unboxing Formatting L03 - Input and
