This Lecture. Introduction to OpenGL. Outline. Why OpenGL? Programmer s View. Foundations of Computer Graphics
|
|
|
- Philomena Taylor
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Foundations of Computer Graphics Overview and Motivation This Lecture Introduction to OpenGL and simple demo code mytest1.cpp ; you compiled mytest3.cpp for HW 0 I am going to show (and write) actual code Code helps you understand HW 2 better Simple demo of mytest1 This lecture deals with very basic OpenGL setup. Next 2 lectures will likely be more interesting Initializing s Introduction to OpenGL OpenGL is a graphics API Portable software library (platform-independent) Layer between programmer and graphics hardware Uniform instruction set (hides different capabilities) OpenGL can fit in many places Between application and graphics system Between higher level API and graphics system Why OpenGL? Why do we need OpenGL or an API? Encapsulates many basic functions of 2D/3D graphics Think of it as high-level language (C++) for graphics History: Introduced SGI in 92, maintained by Khronos Precursor for DirectX, WebGL, Java3D etc. Programmer s View Application Application Graphics Package OpenGL Application Programming Interface Hardware and software (graphics card) Output Device Input Device Input Device Slide inspired by Greg Humphreys 1
2 Vertices Images OpenGL Rendering Pipeline Programmable in Modern GPUs (Vertex ) Geometry Primitive Operations Pixel Operations Scan Conversion (Rasterize) Texture Memory Programmable in Modern GPUs (Fragment ) Fragment Operations Framebuffer GPUs and Programmability Since 2003, can write vertex/pixel shaders Fixed function pipeline special type of shader Like writing C programs (see GLSL book) Performance >> CPU (even used for non-graphics) Operate in parallel on all vertices or fragments Traditional Approach: Fixed function pipeline (state machine) New Development (2003-): Programmable pipeline Initializing s Foundations of Computer Graphics Basic Setup and Buffers, Matrix Modes Initializing s Buffers and Window Interactions Buffers: Color (front, back, left, right), depth (z), accumulation, stencil. When you draw, you write to some buffer (most simply, front and depth) Buffers also used for vertices etc. Buffer data and buffer arrays (will see in creating objects) No window system interactions (for portability) But can use GLUT (or Motif, GLX, Tcl/Tk) Callbacks to implement mouse, keyboard interaction 2
3 Basic setup (can copy; slight OS diffs) int main(int argc, char** argv) glutinit(&argc, argv); // Requests the type of buffers (Single, RGB). // Think about what buffers you would need... glutinitdisplaymode (GLUT_SINGLE GLUT_RGB); // Need to add GLUT_3_2_CORE_PROFILE for Apple/Mac OS glutinitwindowsize (500, 500); glutinitwindowposition (100, 100); glutcreatewindow ("Simple Demo with s"); // glewinit(); // GLEW related stuff for non-apple systems init (); // Always initialize first // Now, we define callbacks and functions for various tasks.... Basic setup (can copy; slight OS diffs) int main(int argc, char** argv)... // Now, we define callbacks and functions for various tasks. glutdisplayfunc(display); glutreshapefunc(reshape) ; glutkeyboardfunc(keyboard); glutmousefunc(mouse) ; glutmotionfunc(mousedrag) ; glutmainloop(); // Start the main code deletebuffers(); //Termination. Delete buffers generated in init() return 0; /* ANSI C requires main to return int. */ Initializing s Viewing in OpenGL Inspired by old OpenGL. Now, only best practice, not requirement You could do your own thing, but this is still the best way to develop viewing Viewing consists of two parts Object positioning: model view transformation matrix View projection: projection transformation matrix Old OpenGL (no longer supported/taught in 167x), two matrix stacks GL_MODELVIEW_MATRIX, GL_PROJECTION_MATRIX Can push and pop matrices onto stacks New OpenGL: Use C++ STL templates to make stacks as needed e.g. stack <mat4> modelview ; modelview.push(mat4(1.0)) ; GLM libraries replace many deprecated commands. Include mat4 Viewing in OpenGL Convention: camera always at the origin, pointing in the z direction Transformations move objects relative to the camera In old OpenGL, Matrices are column-major and right-multiply top of stack. (Last transform in code is first actually applied). In new GLM, similarly (read the assignment notes and documentation). Basic initialization code for viewing #include <GL/glut.h> //also <GL/glew.h>; <GLUT/glut.h> for Mac OS #include <stdlib.h> //also stdio.h, assert.h, glm, others int mouseoldx, mouseoldy ; // For mouse motion GLfloat eyeloc = 2.0 ; // Where to look from; initially 0-2, 2 glm::mat4 projection, modelview; // The mvp matrices themselves void init (void) /* select clearing color */ glclearcolor (0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0); /* initialize viewing values */ projection = glm::mat4(1.0f); // The identity matrix // Think about this. Why is the up vector not normalized? modelview = glm::loakat(glm::vec3(0,-eyeloc,eyeloc), glm::vec3(0,0,0), glm::vec3(0,1,1)) ; // (To be cont d). Geometry and shader set up later... 3
4 Foundations of Computer Graphics Window System Interaction and Callbacks Initializing s Window System Interaction Not part of OpenGL Toolkits (GLUT) available (also freeglut) Callback functions for events (similar to X, Java,) Keyboard, Mouse, etc. Open, initialize, resize window Our main func included glutdisplayfunc(display); glutreshapefunc(reshape) ; glutkeyboardfunc(keyboard); glutmousefunc(mouse) ; glutmotionfunc(mousedrag) ; Basic window interaction code /* Defines what to do when various keys are pressed */ void keyboard (unsigned char key, int x, int y) switch (key) case 27: // Escape to quit exit(0) ; break ; default: break ; Basic window interaction code /* Reshapes the window appropriately */ void reshape(int w, int h) glviewport (0, 0, (GLsizei) w, (GLsizei) h); // Note that the field of view takes in a radian angle projection = glm::perspective(30.0f / 180.0f * glm::pi<float>(), (GLfloat)w / (GLfloat)h, 1.0f, 10.0f); gluniformmatrix4fv(projectionpos,1, GL_FALSE, &projection[0][0]); // To send the projection matrix to the shader Mouse motion (demo) void mouse(int button, int state, int x, int y) if (button == GLUT_LEFT_BUTTON) if (state == GLUT_UP) // Do Nothing ; else if (state == GLUT_DOWN) mouseoldx = x ; mouseoldy = y ; // so we can move wrt x, y else if (button == GLUT_RIGHT_BUTTON && state == GLUT_DOWN) // Reset glulookat eyeloc = 2.0 ; modelview = glm::lookat(glm::vec3(0, -eyeloc, eyeloc), glm::vec3(0, 0, 0), glm::vec3(0, 1, 1)); // Send the updated matrix to the shader gluniformmatrix4fv(modelviewpos,1,gl_false,&modelview[0][0]); glutpostredisplay() ; // Redraw scene 4
5 Mouse drag (demo) void mousedrag(int x, int y) int yloc = y - mouseoldy ; // We will use the y coord to zoom in/out eyeloc += 0.005*yloc ; // Where do we look from if (eyeloc < 0) eyeloc = 0.0 ; mouseoldy = y ; /* Set the eye location */ modelview = glm::lookat(glm::vec3(0, -eyeloc, eyeloc), glm::vec3(0, 0, 0), glm::vec3(0, 1, 1)); // Send the updated matrix over to the shader gluniformmatrix4fv(modelviewpos,1,gl_false,&modelview[0][0]); Foundations of Computer Graphics Drawing Basic OpenGL Primitives glutpostredisplay() ; Initializing s New OpenGL Primitives (fewer) Points Lines (also strips, loops) Polygon Triangle Quad Quad Strip Triangle Strip Triangle Fan Geometry Points (GL_POINTS) Stored in Homogeneous coordinates Line segments (GL_LINES) Also (GL_LINE_STRIP, GL_LINE_LOOP) Triangles (GL_TRIANGLES) Also strips, fans (GL_TRIANGLE_STRIP, GL_TRIANGLE_FAN) More complex primitives (GLUT): Sphere, teapot, cube, Must now be converted into triangles (which is what skeleton does) Old OpenGL: Drawing Enclose vertices between glbegin() glend() pair Can include normal C code and attributes like the colors Inside are commands like glvertex3f, glcolor3f Attributes must be set before the vertex Assembly line (pass vertices, transform, shade) These are vertex, fragment shaders on current GPUs Immediate Mode: Sent to server and drawn 5
6 Old OpenGL: Drawing (not used) void display(void) glclear (GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT); // draw polygon (square) of unit length centered at the origin // This code draws each vertex in a different color. glbegin(gl_polygon); glcolor3f (1.0, 0.0, 0.0); glvertex3f (0.5, 0.5, 0.0); glcolor3f (0.0, 1.0, 0.0); glvertex3f (-0.5, 0.5, 0.0); glcolor3f (0.0, 0.0, 1.0); glvertex3f (-0.5, -0.5, 0.0); glcolor3f (1.0, 1.0, 1.0); glvertex3f (0.5, -0.5, 0.0); glend(); glflush () ; (-.5,.5) GREEN (-.5, -.5) BLUE (.5,.5) RED (.5, -.5) WHITE Old OpenGL: Drawing Client-Server model (client generates vertices, server draws) even if on same machine glflush() forces client to send network packet glfinish() waits for ack, sparingly use synchronization New OpenGL: Vertex Array Objects (next) Modern OpenGL: Floor Specification const GLfloat floorverts[4][3] = 0.5, 0.5, 0.0,-0.5, 0.5, 0.0,-0.5, -0.5, 0.0, 0.5, -0.5, 0.0 ; const GLfloat floorcol[4][3] = 1.0, 0.0, 0.0,0.0, 1.0, 0.0,0.0, 0.0, 1.0,1.0, 1.0, 1.0 ; const GLubyte floorinds[1][6] = 0, 1, 2, 0, 2, 3 ; //triangles const GLfloat floorverts2[4][3] = 0.5, 0.5, 1.0,-0.5, 0.5, 1.0,-0.5, -0.5, 1.0,0.5, -0.5, 1.0 ; const GLfloat floorcol2[4][3] = 1.0, 0.0, 0.0,1.0, 0.0, 0.0,1.0, 0.0, 0.0,1.0, 0.0, 0.0 ; const GLubyte floorinds2[1][6] = 0, 1, 2, 0, 2, 3 ; //triangles Modern OpenGL: Vertex Array Objects const int numobjects = 2 ; // number of objects for buffer const int numperobj = 3 ; // Vertices, colors, indices GLuint VAOs[numobjects]; // A Vertex Array Object per object GLuint buffers[numperobj*numobjects]; // List of buffers geometric data GLuint objects[numobjects]; // For each object GLenum PrimType[numobjects];// Primitive Type (triangles, strips) GLsizei NumElems[numobjects] ; // Number of geometric elements // Floor Geometry is specified with a vertex array enum Vertices, Colors, Elements ; // For arrays for object enum FLOOR, FLOOR2 ; // For objects, for the floor //------In init below (creates buffer objects for later use) Modern OpenGL: Vertex Array Objects const int numobjects = 2 ; // number of objects for buffer const int numperobj = 3 ; // Vertices, colors, indices GLuint VAOs[numobjects]; // A Vertex Array Object per object GLuint buffers[numperobj*numobjects] ; // List of buffers geometric data //... //------In init below (creates buffer objects for later use) glgenvertexarrays(numobjects, VAOs); //create unique identifiers glgenbuffers(numperobj*numobjects, buffers); //and for buffers void deletebuffers() // Like a destructor gldeletevertexarrays(numobjects, VAOs); gldeletebuffers(numperobj*numobjects, buffers); Modern OpenGL: Initialize Buffers void initobject (GLuint object, GLfloat * vert, GLint sizevert, GLfloat * col, GLint sizecol, GLubyte * inds, GLint sizeind, GLenum type) int offset = object * numperobj; glbindvertexarray(vaos[object]); glbindbuffer(gl_array_buffer, buffers[vertices+offset]) ; glbufferdata(gl_array_buffer, sizevert, vert,gl_static_draw); // Use layout location 0 for the vertices glenablevertexattribarray(0); glvertexattribpointer(0, 3, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, 3 * sizeof(glfloat), 0); glbindbuffer(gl_array_buffer, buffers[colors+offset]) ; glbufferdata(gl_array_buffer, sizecol, col,gl_static_draw); // Use layout location 1 for the colors //... 6
7 Modern OpenGL: Initialize Buffers void initobject (GLuint object, GLfloat * vert, GLint sizevert, GLfloat * col, GLint sizecol, GLubyte * inds, GLint sizeind, GLenum type) //... // Use layout location 1 for the colors glenablevertexattribarray(1); glvertexattribpointer(1, 3, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, 3 * sizeof(glfloat), 0); glbindbuffer(gl_element_array_buffer, buffers[elements+offset]) ; glbufferdata(gl_element_array_buffer, sizeind, inds,gl_static_draw); PrimType[object] = type; NumElems[object] = sizeind; // Prevent further modification of this VAO by unbinding it glbindvertexarray(0); Modern OpenGL: Draw Vertex Object void drawobject(gluint object) glbindvertexarray(vaos[object]); gldrawelements(primtype[object], NumElems[object], GL_UNSIGNED_BYTE, 0); glbindvertexarray(0); //unbind void display(void) glclear (GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT); // clear all pixels drawobject(floor) ; drawobject(floor2) ; glflush (); // start processing buffered OpenGL commands Initialization for Drawing, Shading #include "shaders.h" GLuint vertexshader, fragmentshader, shaderprogram ; // shaders // Initialization in init() for Drawing glgenvertexarrays(numobjects, VAOs) ; glgenbuffers(numperobj*numobjects, buffers) ; initobject(floor, (GLfloat *) floorverts, sizeof(floorverts), (GLfloat *) floorcol, sizeof (floorcol), (GLubyte *) floorinds, sizeof (floorinds), GL_TRIANGLES) ; initobject(floor2, (GLfloat *) floorverts2, sizeof(floorverts2), (GLfloat *) floorcol2, sizeof (floorcol2), (GLubyte *) floorinds2, sizeof (floorinds2), GL_TRIANGLES) ; // In init() for s, discussed next vertexshader = initshaders(gl_vertex_shader, "shaders/nop.vert") ; fragmentshader = initshaders(gl_fragment_shader, "shaders/nop.frag") ; shaderprogram = initprogram(vertexshader, fragmentshader) ; Demo (change colors) Foundations of Computer Graphics Initializing s Initializing s 7
8 Full OpenGL Pipeline Vertex Tessellation Control Tessellation Evaluation Geometry Full OpenGL Pipeline Vertex Tessellation Control Tessellation Evaluation Geometry Primitive Setup Clipping Rasterization Primitive Setup Clipping Rasterization Texture/Image Data (Program) Fragment Final Pixel Color (Image) User/program generates original vertices, textures We cover programmable vertex and fragment shaders in course OpenGL primitive setup, clipping, rasterization not programmable Texture/Image Data (Program) Fragment Final Pixel Color (Image) Tessellation shaders take patches (splines) to output vertices Geometry shaders process primitives, can add/remove geometry Not covered in this course Simplified OpenGL Pipeline User specifies vertices (via vertex arrays) For each vertex in parallel OpenGL calls user-specified vertex shader: Transform vertex (ModelView, Projection), other ops For each primitive, OpenGL rasterizes Generates a fragment for each pixel the primitive covers For each fragment in parallel OpenGL calls user-specified fragment shader: Shading and lighting calculations OpenGL handles z-buffer depth test unless overwritten Setup Initializing (shader itself discussed later) 1. Create shader (Vertex and Fragment) 2. Compile shader 3. Attach shader to program 4. Link program 5. Use program Setup source is just sequence of strings Similar steps to compile a normal program Initialization Code GLuint initshaders (GLenum type, const char *filename) // Using GLSL shaders, OpenGL book, page 679 of 7 th edition GLuint shader = glcreate(type) ; GLint compiled ; string str = textfileread (filename) ; const GLchar * cstr = str.c_str() ; glsource (shader, 1, &cstr, NULL) ; glcompile (shader) ; glgetiv (shader, GL_COMPILE_STATUS, &compiled) ; if (!compiled) shadererrors (shader) ; throw 3 ; return shader ; 8
9 Linking Program GLuint initprogram (GLuint vertexshader, GLuint fragmentshader) GLuint program = glcreateprogram() ; GLint linked ; glattach(program, vertexshader) ; glattach(program, fragmentshader) ; gllinkprogram(program) ; glgetprogramiv(program, GL_LINK_STATUS, &linked) ; if (linked) gluseprogram(program) ; else programerrors(program) ; throw 4 ; cout<<" program successfully attached and linked." << endl; return program ; Basic (nop) vertex shader In shaders/ nop.vert.glsl nop.frag.glsl Written in GLSL (GL Shading Language) Vertex (out values interpolated to fragment) # version 330 core // Do not modify the above version directive to anything older. // inputs layout (location = 0) in vec3 position; layout (location = 1) in vec3 color; // outputs, if any out vec3 Color; // Uniform variables uniform mat4 modelview; uniform mat4 projection; void main() //... Basic (nop) vertex shader In shaders/ nop.vert.glsl nop.frag.glsl Written in GLSL (GL Shading Language) Vertex (out values interpolated to fragment) # version 330 core layout (location = 0) in vec3 position; layout (location = 1) in vec3 color; // outputs, if any out vec3 Color; // Uniform variables uniform mat4 modelview; uniform mat4 projection; void main() gl_position = projection * modelview * vec4(position, 1.0f); Color = color; // Just forward this color to the fragment shader Basic (nop) fragment shader # version 330 core // Do not modify the version directive to anything older than 330. // Fragment shader inputs are outputs of same name from vertex shader in vec3 Color; // Uniform variables (none) // Output out vec4 fragcolor; void main (void) fragcolor = vec4(color, 1.0f); 9
To Do. Demo: Surreal (now 15+ years ago) This Lecture. Outline. Computer Graphics. CSE 167 [Win 19], Lecture 6: OpenGL 1 Ravi Ramamoorthi
![To Do. Demo: Surreal (now 15+ years ago) This Lecture. Outline. Computer Graphics. CSE 167 [Win 19], Lecture 6: OpenGL 1 Ravi Ramamoorthi To Do. Demo: Surreal (now 15+ years ago) This Lecture. Outline. Computer Graphics. CSE 167 [Win 19], Lecture 6: OpenGL 1 Ravi Ramamoorthi](/thumbs/88/117691229.jpg) Computer Graphics CSE 167 [Win 19], Lecture 6: OpenGL 1 Ravi Ramamoorthi http://viscomp.ucsd.edu/classes/cse167/wi19 To Do HW 2 (much) more difficult than HW 1 Will cover all needed material mostly Tue
Computer Graphics CSE 167 [Win 19], Lecture 6: OpenGL 1 Ravi Ramamoorthi http://viscomp.ucsd.edu/classes/cse167/wi19 To Do HW 2 (much) more difficult than HW 1 Will cover all needed material mostly Tue
This Lecture. Why OpenGL? Introduction to OpenGL. Programmer s View
 Foundations of Computer Graphics Overview and Motivation This Lecture Introduction to OpenGL and simple demo code mytest1.cpp ; you compiled mytest3.cpp for HW 0 I am going to show (and write) actual code
Foundations of Computer Graphics Overview and Motivation This Lecture Introduction to OpenGL and simple demo code mytest1.cpp ; you compiled mytest3.cpp for HW 0 I am going to show (and write) actual code
To Do. Demo: Surreal (HW 3) This Lecture. Introduction to OpenGL. Outline. Foundations of Computer Graphics (Spring 2012)
 Foundations of Computer Graphics (Spring 2012) CS 184, Lecture 6: OpenGL 1 http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs184 To Do HW 1 due on Thu Must find partners for HW 2 (if problems, speak to TAs during section).
Foundations of Computer Graphics (Spring 2012) CS 184, Lecture 6: OpenGL 1 http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs184 To Do HW 1 due on Thu Must find partners for HW 2 (if problems, speak to TAs during section).
To Do. Computer Graphics (Fall 2008) Course Outline. Course Outline. Methodology for Lecture. Demo: Surreal (HW 3)
 Computer Graphics (Fall 2008) COMS 4160, Lecture 9: OpenGL 1 http://www.cs.columbia.edu/~cs4160 To Do Start thinking (now) about HW 3. Milestones are due soon. Course Course 3D Graphics Pipeline 3D Graphics
Computer Graphics (Fall 2008) COMS 4160, Lecture 9: OpenGL 1 http://www.cs.columbia.edu/~cs4160 To Do Start thinking (now) about HW 3. Milestones are due soon. Course Course 3D Graphics Pipeline 3D Graphics
Methodology for Lecture
 Basic Geometry Setup Methodology for Lecture Make mytest1 more ambitious Sequence of steps Demo Review of Last Demo Changed floor to all white, added global for teapot and teapotloc, moved geometry to
Basic Geometry Setup Methodology for Lecture Make mytest1 more ambitious Sequence of steps Demo Review of Last Demo Changed floor to all white, added global for teapot and teapotloc, moved geometry to
To Do. Review of Last Demo. Methodology for Lecture. Geometry Basic Setup. Outline. Foundations of Computer Graphics (Fall 2012)
 Foundations of Computer Graphics (Fall 2012) CS 184, Lecture 8: OpenGL 2 http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs184 To Do Continue working on HW 2. Can be difficult Class lectures, programs primary source Can
Foundations of Computer Graphics (Fall 2012) CS 184, Lecture 8: OpenGL 2 http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs184 To Do Continue working on HW 2. Can be difficult Class lectures, programs primary source Can
Basic Graphics Programming
 15-462 Computer Graphics I Lecture 2 Basic Graphics Programming Graphics Pipeline OpenGL API Primitives: Lines, Polygons Attributes: Color Example January 17, 2002 [Angel Ch. 2] Frank Pfenning Carnegie
15-462 Computer Graphics I Lecture 2 Basic Graphics Programming Graphics Pipeline OpenGL API Primitives: Lines, Polygons Attributes: Color Example January 17, 2002 [Angel Ch. 2] Frank Pfenning Carnegie
Information Coding / Computer Graphics, ISY, LiTH. OpenGL! ! where it fits!! what it contains!! how you work with it 11(40)
 11(40) Information Coding / Computer Graphics, ISY, LiTH OpenGL where it fits what it contains how you work with it 11(40) OpenGL The cross-platform graphics library Open = Open specification Runs everywhere
11(40) Information Coding / Computer Graphics, ISY, LiTH OpenGL where it fits what it contains how you work with it 11(40) OpenGL The cross-platform graphics library Open = Open specification Runs everywhere
Comp 410/510 Computer Graphics Spring Programming with OpenGL Part 2: First Program
 Comp 410/510 Computer Graphics Spring 2017 Programming with OpenGL Part 2: First Program Objectives Refine the first program Introduce a standard program structure - Initialization Program Structure Most
Comp 410/510 Computer Graphics Spring 2017 Programming with OpenGL Part 2: First Program Objectives Refine the first program Introduce a standard program structure - Initialization Program Structure Most
Announcement. Homework 1 has been posted in dropbox and course website. Due: 1:15 pm, Monday, September 12
 Announcement Homework 1 has been posted in dropbox and course website Due: 1:15 pm, Monday, September 12 Today s Agenda Primitives Programming with OpenGL OpenGL Primitives Polylines GL_POINTS GL_LINES
Announcement Homework 1 has been posted in dropbox and course website Due: 1:15 pm, Monday, September 12 Today s Agenda Primitives Programming with OpenGL OpenGL Primitives Polylines GL_POINTS GL_LINES
CS559: Computer Graphics. Lecture 12: OpenGL Li Zhang Spring 2008
 CS559: Computer Graphics Lecture 12: OpenGL Li Zhang Spring 2008 Reading Redbook Ch 1 & 2 So far: 3D Geometry Pipeline Model Space (Object Space) Rotation Translation Resizing World Space M Rotation Translation
CS559: Computer Graphics Lecture 12: OpenGL Li Zhang Spring 2008 Reading Redbook Ch 1 & 2 So far: 3D Geometry Pipeline Model Space (Object Space) Rotation Translation Resizing World Space M Rotation Translation
Today s Agenda. Basic design of a graphics system. Introduction to OpenGL
 Today s Agenda Basic design of a graphics system Introduction to OpenGL Image Compositing Compositing one image over another is most common choice can think of each image drawn on a transparent plastic
Today s Agenda Basic design of a graphics system Introduction to OpenGL Image Compositing Compositing one image over another is most common choice can think of each image drawn on a transparent plastic
ERKELEY DAVIS IRVINE LOS ANGELES RIVERSIDE SAN DIEGO SAN FRANCISCO EECS 104. Fundamentals of Computer Graphics. OpenGL
 ERKELEY DAVIS IRVINE LOS ANGELES RIVERSIDE SAN DIEGO SAN FRANCISCO SANTA BARBARA SANTA CRUZ EECS 104 Fundamentals of Computer Graphics OpenGL Slides courtesy of Dave Shreine, Ed Angel and Vicki Shreiner
ERKELEY DAVIS IRVINE LOS ANGELES RIVERSIDE SAN DIEGO SAN FRANCISCO SANTA BARBARA SANTA CRUZ EECS 104 Fundamentals of Computer Graphics OpenGL Slides courtesy of Dave Shreine, Ed Angel and Vicki Shreiner
CS Computer Graphics: OpenGL, Continued
 CS 543 - Computer Graphics: OpenGL, Continued by Robert W. Lindeman gogo@wpi.edu (with help from Emmanuel Agu ;-) Last time. OpenGL set up Basic structure OpenGL skeleton Callback functions, etc. R.W.
CS 543 - Computer Graphics: OpenGL, Continued by Robert W. Lindeman gogo@wpi.edu (with help from Emmanuel Agu ;-) Last time. OpenGL set up Basic structure OpenGL skeleton Callback functions, etc. R.W.
CS Computer Graphics: OpenGL, Continued
 CS 543 - Computer Graphics: OpenGL, Continued by Robert W. Lindeman gogo@wpi.edu (with help from Emmanuel Agu ;-) Last time. OpenGL set up Basic structure OpenGL skeleton Callback functions, etc. R.W.
CS 543 - Computer Graphics: OpenGL, Continued by Robert W. Lindeman gogo@wpi.edu (with help from Emmanuel Agu ;-) Last time. OpenGL set up Basic structure OpenGL skeleton Callback functions, etc. R.W.
Introduction to Computer Graphics with OpenGL/GLUT
 Introduction to Computer Graphics with OpenGL/GLUT What is OpenGL? A software interface to graphics hardware Graphics rendering API (Low Level) High-quality color images composed of geometric and image
Introduction to Computer Graphics with OpenGL/GLUT What is OpenGL? A software interface to graphics hardware Graphics rendering API (Low Level) High-quality color images composed of geometric and image
Precept 2 Aleksey Boyko February 18, 2011
 Precept 2 Aleksey Boyko February 18, 2011 Getting started Initialization Drawing Transformations Cameras Animation Input Keyboard Mouse Joystick? Textures Lights Programmable pipeline elements (shaders)
Precept 2 Aleksey Boyko February 18, 2011 Getting started Initialization Drawing Transformations Cameras Animation Input Keyboard Mouse Joystick? Textures Lights Programmable pipeline elements (shaders)
 OpenGL for dummies hello.c #include int main(int argc, char** argv) { glutinit(&argc, argv); glutinitdisplaymode (GLUT_SINGLE GLUT_RGB); glutinitwindowsize (250, 250); glutinitwindowposition
OpenGL for dummies hello.c #include int main(int argc, char** argv) { glutinit(&argc, argv); glutinitdisplaymode (GLUT_SINGLE GLUT_RGB); glutinitwindowsize (250, 250); glutinitwindowposition
Basic Graphics Programming
 CSCI 480 Computer Graphics Lecture 2 Basic Graphics Programming January 11, 2012 Jernej Barbic University of Southern California http://www-bcf.usc.edu/~jbarbic/cs480-s12/ Graphics Pipeline OpenGL API
CSCI 480 Computer Graphics Lecture 2 Basic Graphics Programming January 11, 2012 Jernej Barbic University of Southern California http://www-bcf.usc.edu/~jbarbic/cs480-s12/ Graphics Pipeline OpenGL API
Computer Graphics. OpenGL
 Computer Graphics OpenGL What is OpenGL? OpenGL (Open Graphics Library) is a library for computer graphics It consists of several procedures and functions that allow a programmer to specify the objects
Computer Graphics OpenGL What is OpenGL? OpenGL (Open Graphics Library) is a library for computer graphics It consists of several procedures and functions that allow a programmer to specify the objects
Lecture 4 of 41. Lab 1a: OpenGL Basics
 Lab 1a: OpenGL Basics William H. Hsu Department of Computing and Information Sciences, KSU KSOL course pages: http://snipurl.com/1y5gc Course web site: http://www.kddresearch.org/courses/cis636 Instructor
Lab 1a: OpenGL Basics William H. Hsu Department of Computing and Information Sciences, KSU KSOL course pages: http://snipurl.com/1y5gc Course web site: http://www.kddresearch.org/courses/cis636 Instructor
OpenGL refresher. Advanced Computer Graphics 2012
 Advanced Computer Graphics 2012 What you will see today Outline General OpenGL introduction Setting up: GLUT and GLEW Elementary rendering Transformations in OpenGL Texture mapping Programmable shading
Advanced Computer Graphics 2012 What you will see today Outline General OpenGL introduction Setting up: GLUT and GLEW Elementary rendering Transformations in OpenGL Texture mapping Programmable shading
C++ is Fun Part 13 at Turbine/Warner Bros.! Russell Hanson
 C++ is Fun Part 13 at Turbine/Warner Bros.! Russell Hanson Syllabus 1) First program and introduction to data types and control structures with applications for games learning how to use the programming
C++ is Fun Part 13 at Turbine/Warner Bros.! Russell Hanson Syllabus 1) First program and introduction to data types and control structures with applications for games learning how to use the programming
11/1/13. Basic Graphics Programming. Teaching Assistant. What is OpenGL. Course Producer. Where is OpenGL used. Graphics library (API)
 CSCI 420 Computer Graphics Lecture 2 Basic Graphics Programming Teaching Assistant Yijing Li Office hours TBA Jernej Barbic University of Southern California Graphics Pipeline OpenGL API Primitives: Lines,
CSCI 420 Computer Graphics Lecture 2 Basic Graphics Programming Teaching Assistant Yijing Li Office hours TBA Jernej Barbic University of Southern California Graphics Pipeline OpenGL API Primitives: Lines,
OpenGL/GLUT Intro. Week 1, Fri Jan 12
 University of British Columbia CPSC 314 Computer Graphics Jan-Apr 2007 Tamara Munzner OpenGL/GLUT Intro Week 1, Fri Jan 12 http://www.ugrad.cs.ubc.ca/~cs314/vjan2007 News Labs start next week Reminder:
University of British Columbia CPSC 314 Computer Graphics Jan-Apr 2007 Tamara Munzner OpenGL/GLUT Intro Week 1, Fri Jan 12 http://www.ugrad.cs.ubc.ca/~cs314/vjan2007 News Labs start next week Reminder:
Graphics Programming. Computer Graphics, VT 2016 Lecture 2, Chapter 2. Fredrik Nysjö Centre for Image analysis Uppsala University
 Graphics Programming Computer Graphics, VT 2016 Lecture 2, Chapter 2 Fredrik Nysjö Centre for Image analysis Uppsala University Graphics programming Typically deals with How to define a 3D scene with a
Graphics Programming Computer Graphics, VT 2016 Lecture 2, Chapter 2 Fredrik Nysjö Centre for Image analysis Uppsala University Graphics programming Typically deals with How to define a 3D scene with a
Computer Graphics (CS 4731) OpenGL/GLUT(Part 1)
 Computer Graphics (CS 4731) Lecture 2: Introduction to OpenGL/GLUT(Part 1) Prof Emmanuel Agu Computer Science Dept. Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI) Recall: OpenGL GLBasics OpenGL s function Rendering
Computer Graphics (CS 4731) Lecture 2: Introduction to OpenGL/GLUT(Part 1) Prof Emmanuel Agu Computer Science Dept. Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI) Recall: OpenGL GLBasics OpenGL s function Rendering
An Overview GLUT GLSL GLEW
 OpenGL, GLUT, GLEW, GLSL An Overview GLUT GLEW GLSL Objectives Give you an overview of the software that you will be using this semester OpenGL, GLUT, GLEW, GLSL What are they? How do you use them? What
OpenGL, GLUT, GLEW, GLSL An Overview GLUT GLEW GLSL Objectives Give you an overview of the software that you will be using this semester OpenGL, GLUT, GLEW, GLSL What are they? How do you use them? What
2/3/16. Interaction. Triangles (Clarification) Choice of Programming Language. Buffer Objects. The CPU-GPU bus. CSCI 420 Computer Graphics Lecture 3
 CSCI 420 Computer Graphics Lecture 3 Interaction Jernej Barbic University of Southern California [Angel Ch. 2] Triangles (Clarification) Can be any shape or size Well-shaped triangles have advantages for
CSCI 420 Computer Graphics Lecture 3 Interaction Jernej Barbic University of Southern California [Angel Ch. 2] Triangles (Clarification) Can be any shape or size Well-shaped triangles have advantages for
CS 4204 Computer Graphics
 CS 4204 Computer Graphics OpenGL Basics Yong Cao Virginia Tech References: 2001 Siggraph, An Interactive Introduction to OpenGL Programming, Dave Shreiner,Ed Angel, Vicki Shreiner Official Presentation
CS 4204 Computer Graphics OpenGL Basics Yong Cao Virginia Tech References: 2001 Siggraph, An Interactive Introduction to OpenGL Programming, Dave Shreiner,Ed Angel, Vicki Shreiner Official Presentation
Interaction. CSCI 420 Computer Graphics Lecture 3
 CSCI 420 Computer Graphics Lecture 3 Interaction Jernej Barbic University of Southern California Client/Server Model Callbacks Double Buffering Hidden Surface Removal Simple Transformations [Angel Ch.
CSCI 420 Computer Graphics Lecture 3 Interaction Jernej Barbic University of Southern California Client/Server Model Callbacks Double Buffering Hidden Surface Removal Simple Transformations [Angel Ch.
VR-programming tools (procedural) More VRML later in this course! (declarative)
 Realtime 3D Computer Graphics & Virtual Reality OpenGL Introduction VR-programming Input and display devices are the main hardware interface to users Immersion embeds users through the generation of live-like
Realtime 3D Computer Graphics & Virtual Reality OpenGL Introduction VR-programming Input and display devices are the main hardware interface to users Immersion embeds users through the generation of live-like
Exercise 1 Introduction to OpenGL
 Exercise 1 Introduction to OpenGL What we are going to do OpenGL Glut Small Example using OpenGl and Glut Alexandra Junghans 2 What is OpenGL? OpenGL Two Parts most widely used and supported graphics API
Exercise 1 Introduction to OpenGL What we are going to do OpenGL Glut Small Example using OpenGl and Glut Alexandra Junghans 2 What is OpenGL? OpenGL Two Parts most widely used and supported graphics API
Computer Graphics. Bing-Yu Chen National Taiwan University
 Computer Graphics Bing-Yu Chen National Taiwan University Introduction to OpenGL General OpenGL Introduction An Example OpenGL Program Drawing with OpenGL Transformations Animation and Depth Buffering
Computer Graphics Bing-Yu Chen National Taiwan University Introduction to OpenGL General OpenGL Introduction An Example OpenGL Program Drawing with OpenGL Transformations Animation and Depth Buffering
RECITATION - 1. Ceng477 Fall
 RECITATION - 1 Ceng477 Fall 2007-2008 2/ 53 Agenda General rules for the course General info on the libraries GLUT OpenGL GLUI Details about GLUT Functions Probably we will not cover this part 3/ 53 General
RECITATION - 1 Ceng477 Fall 2007-2008 2/ 53 Agenda General rules for the course General info on the libraries GLUT OpenGL GLUI Details about GLUT Functions Probably we will not cover this part 3/ 53 General
OpenGL pipeline Evolution and OpenGL Shading Language (GLSL) Part 2/3 Vertex and Fragment Shaders
 OpenGL pipeline Evolution and OpenGL Shading Language (GLSL) Part 2/3 Vertex and Fragment Shaders Prateek Shrivastava CS12S008 shrvstv@cse.iitm.ac.in 1 GLSL Data types Scalar types: float, int, bool Vector
OpenGL pipeline Evolution and OpenGL Shading Language (GLSL) Part 2/3 Vertex and Fragment Shaders Prateek Shrivastava CS12S008 shrvstv@cse.iitm.ac.in 1 GLSL Data types Scalar types: float, int, bool Vector
CS 4731 Lecture 3: Introduction to OpenGL and GLUT: Part II. Emmanuel Agu
 CS 4731 Lecture 3: Introduction to OpenGL and GLUT: Part II Emmanuel Agu Recall: OpenGL Skeleton void main(int argc, char** argv){ // First initialize toolkit, set display mode and create window glutinit(&argc,
CS 4731 Lecture 3: Introduction to OpenGL and GLUT: Part II Emmanuel Agu Recall: OpenGL Skeleton void main(int argc, char** argv){ // First initialize toolkit, set display mode and create window glutinit(&argc,
CS 432 Interactive Computer Graphics
 CS 432 Interactive Computer Graphics Lecture 1 Part 3 Anatomy of OpenGL Programs Matt Burlick - Drexel University - CS 432 1 Reading Angel Chapter 2 Red Book Chapter 4 Matt Burlick - Drexel University
CS 432 Interactive Computer Graphics Lecture 1 Part 3 Anatomy of OpenGL Programs Matt Burlick - Drexel University - CS 432 1 Reading Angel Chapter 2 Red Book Chapter 4 Matt Burlick - Drexel University
Computer graphics MN1
 Computer graphics MN1 http://www.opengl.org Todays lecture What is OpenGL? How do I use it? Rendering pipeline Points, vertices, lines,, polygons Matrices and transformations Lighting and shading Code
Computer graphics MN1 http://www.opengl.org Todays lecture What is OpenGL? How do I use it? Rendering pipeline Points, vertices, lines,, polygons Matrices and transformations Lighting and shading Code
Books, OpenGL, GLUT, GLUI, CUDA, OpenCL, OpenCV, PointClouds, and G3D
 Books, OpenGL, GLUT, GLUI, CUDA, OpenCL, OpenCV, PointClouds, and G3D CS334 Spring 2012 Daniel G. Aliaga Department of Computer Science Purdue University Computer Graphics Pipeline Geometric Primitives
Books, OpenGL, GLUT, GLUI, CUDA, OpenCL, OpenCV, PointClouds, and G3D CS334 Spring 2012 Daniel G. Aliaga Department of Computer Science Purdue University Computer Graphics Pipeline Geometric Primitives
CS 432 Interactive Computer Graphics
 CS 432 Interactive Computer Graphics Lecture 2 Part 1 Primitives and Buffers Matt Burlick - Drexel University - CS 432 1 Rendering in OpenGL Ok, so now we want to actually draw stuff! OpenGL (like most
CS 432 Interactive Computer Graphics Lecture 2 Part 1 Primitives and Buffers Matt Burlick - Drexel University - CS 432 1 Rendering in OpenGL Ok, so now we want to actually draw stuff! OpenGL (like most
OpenGL. Jimmy Johansson Norrköping Visualization and Interaction Studio Linköping University
 OpenGL Jimmy Johansson Norrköping Visualization and Interaction Studio Linköping University Background Software interface to graphics hardware 250+ commands Objects (models) are built from geometric primitives
OpenGL Jimmy Johansson Norrköping Visualization and Interaction Studio Linköping University Background Software interface to graphics hardware 250+ commands Objects (models) are built from geometric primitives
CS475/CS675 - Computer Graphics. OpenGL Drawing
 CS475/CS675 - Computer Graphics OpenGL Drawing What is OpenGL? Open Graphics Library API to specify geometric objects in 2D/3D and to control how they are rendered into the framebuffer. A software interface
CS475/CS675 - Computer Graphics OpenGL Drawing What is OpenGL? Open Graphics Library API to specify geometric objects in 2D/3D and to control how they are rendered into the framebuffer. A software interface
CS 548: COMPUTER GRAPHICS INTRODUCTION TO OPENGL AND GLUT SPRING 2015 DR. MICHAEL J. REALE
 CS 548: COMPUTER GRAPHICS INTRODUCTION TO OPENGL AND GLUT SPRING 2015 DR. MICHAEL J. REALE OVERVIEW OF LIBRARIES OPENGL CORE LIBRARY (OR BASIC LIBRARY) Hardware and platform independent Specification that
CS 548: COMPUTER GRAPHICS INTRODUCTION TO OPENGL AND GLUT SPRING 2015 DR. MICHAEL J. REALE OVERVIEW OF LIBRARIES OPENGL CORE LIBRARY (OR BASIC LIBRARY) Hardware and platform independent Specification that
CS 543 Lecture 1 (Part 3) Prof Emmanuel Agu. Computer Science Dept. Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI)
 Computer Graphics CS 543 Lecture 1 (Part 3) Prof Emmanuel Agu Computer Science Dept. Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI) Recall: OpenGL Skeleton void main(int argc, char** argv){ // First initialize
Computer Graphics CS 543 Lecture 1 (Part 3) Prof Emmanuel Agu Computer Science Dept. Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI) Recall: OpenGL Skeleton void main(int argc, char** argv){ // First initialize
Programming using OpenGL: A first Introduction
 Programming using OpenGL: A first Introduction CMPT 361 Introduction to Computer Graphics Torsten Möller Machiraju/Zhang/Möller 1 Today Overview GL, GLU, GLUT, and GLUI First example OpenGL functions and
Programming using OpenGL: A first Introduction CMPT 361 Introduction to Computer Graphics Torsten Möller Machiraju/Zhang/Möller 1 Today Overview GL, GLU, GLUT, and GLUI First example OpenGL functions and
Erik Anchondo cse 520 lab 4
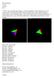 Erik Anchondo 2-6-19 cse 520 lab 4 1. Wrote a glsl program that displays a colored tetrahedron. The tetrahedron starts to rotate on the x axis when the mouse button is clicked once. If the mouse button
Erik Anchondo 2-6-19 cse 520 lab 4 1. Wrote a glsl program that displays a colored tetrahedron. The tetrahedron starts to rotate on the x axis when the mouse button is clicked once. If the mouse button
Rendering. Part 1 An introduction to OpenGL
 Rendering Part 1 An introduction to OpenGL Olivier Gourmel VORTEX Team IRIT University of Toulouse gourmel@irit.fr Image synthesis The Graphics Processing Unit (GPU): A highly parallel architecture specialized
Rendering Part 1 An introduction to OpenGL Olivier Gourmel VORTEX Team IRIT University of Toulouse gourmel@irit.fr Image synthesis The Graphics Processing Unit (GPU): A highly parallel architecture specialized
Lectures OpenGL Introduction
 Lectures OpenGL Introduction By Tom Duff Pixar Animation Studios Emeryville, California and George Ledin Jr Sonoma State University Rohnert Park, California 2004, Tom Duff and George Ledin Jr 1 What is
Lectures OpenGL Introduction By Tom Duff Pixar Animation Studios Emeryville, California and George Ledin Jr Sonoma State University Rohnert Park, California 2004, Tom Duff and George Ledin Jr 1 What is
Display Lists in OpenGL
 Display Lists in OpenGL Display lists are a mechanism for improving performance of interactive OpenGL applications. A display list is a group of OpenGL commands that have been stored for later execution.
Display Lists in OpenGL Display lists are a mechanism for improving performance of interactive OpenGL applications. A display list is a group of OpenGL commands that have been stored for later execution.
// double buffering and RGB glutinitdisplaymode(glut_double GLUT_RGBA); // your own initializations
 #include int main(int argc, char** argv) { glutinit(&argc, argv); Typical OpenGL/GLUT Main Program // GLUT, GLU, and OpenGL defs // program arguments // initialize glut and gl // double buffering
#include int main(int argc, char** argv) { glutinit(&argc, argv); Typical OpenGL/GLUT Main Program // GLUT, GLU, and OpenGL defs // program arguments // initialize glut and gl // double buffering
Computer Graphics 1 Computer Graphics 1
 Projects: an example Developed by Nate Robbins Shapes Tutorial What is OpenGL? Graphics rendering API high-quality color images composed of geometric and image primitives window system independent operating
Projects: an example Developed by Nate Robbins Shapes Tutorial What is OpenGL? Graphics rendering API high-quality color images composed of geometric and image primitives window system independent operating
GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT, GL_PROJECTION, GL_MODELVIEW
 OpenGL Syntax Functions have prefix gl and initial capital letters for each word glclearcolor(), glenable(), glpushmatrix() glu for GLU functions glulookat(), gluperspective() constants begin with GL_,
OpenGL Syntax Functions have prefix gl and initial capital letters for each word glclearcolor(), glenable(), glpushmatrix() glu for GLU functions glulookat(), gluperspective() constants begin with GL_,
Computer Graphics (CS 543) Lecture 1 (Part 2): Introduction to OpenGL/GLUT (Part 1)
 Computer Graphics (CS 543) Lecture 1 (Part 2): Introduction to OpenGL/GLUT (Part 1) Prof Emmanuel Agu Computer Science Dept. Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI) OpenGL/GLUT Installation OpenGL: Specific
Computer Graphics (CS 543) Lecture 1 (Part 2): Introduction to OpenGL/GLUT (Part 1) Prof Emmanuel Agu Computer Science Dept. Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI) OpenGL/GLUT Installation OpenGL: Specific
API for creating a display window and using keyboard/mouse interations. See RayWindow.cpp to see how these are used for Assignment3
 OpenGL Introduction Introduction OpenGL OpenGL is an API for computer graphics. Hardware-independent Windowing or getting input is not included in the API Low-level Only knows about triangles (kind of,
OpenGL Introduction Introduction OpenGL OpenGL is an API for computer graphics. Hardware-independent Windowing or getting input is not included in the API Low-level Only knows about triangles (kind of,
Philip Calderon CSE 520 Lab 3 Color Shader
 Philip Calderon CSE 520 Lab 3 Color Shader Summary: The purpose of lab 4 is to produce a pyramid tetrahedron that we are able to rotate it when clicked. Part 1: Color Tetrahedron Part 2: Rotation to show
Philip Calderon CSE 520 Lab 3 Color Shader Summary: The purpose of lab 4 is to produce a pyramid tetrahedron that we are able to rotate it when clicked. Part 1: Color Tetrahedron Part 2: Rotation to show
CS 432 Interactive Computer Graphics
 CS 432 Interactive Computer Graphics Lecture 2 Part 2 Introduction to Shaders Matt Burlick - Drexel University - CS 432 1 Shaders To understand shaders, let s look at the graphics pipeline again The job
CS 432 Interactive Computer Graphics Lecture 2 Part 2 Introduction to Shaders Matt Burlick - Drexel University - CS 432 1 Shaders To understand shaders, let s look at the graphics pipeline again The job
gvirtualxray Tutorial 01: Creating a Window and an OpenGL Context Using GLUT
 gvirtualxray Tutorial 01: Creating a Window and an OpenGL Context Using GLUT Dr Franck P. Vidal 4 th September 2014 1 Contents Table of contents 2 List of figures 3 List of listings 3 1 Introduction 4
gvirtualxray Tutorial 01: Creating a Window and an OpenGL Context Using GLUT Dr Franck P. Vidal 4 th September 2014 1 Contents Table of contents 2 List of figures 3 List of listings 3 1 Introduction 4
CSE 167. Discussion 03 ft. Glynn 10/16/2017
 CSE 167 Discussion 03 ft Glynn 10/16/2017 Announcements - Midterm next Tuesday(10/31) - Sample midterms are up - Project 1 late grading until this Friday - You will receive 75% of the points you ve earned
CSE 167 Discussion 03 ft Glynn 10/16/2017 Announcements - Midterm next Tuesday(10/31) - Sample midterms are up - Project 1 late grading until this Friday - You will receive 75% of the points you ve earned
Interaction Computer Graphics I Lecture 3
 15-462 Computer Graphics I Lecture 3 Interaction Client/Server Model Callbacks Double Buffering Hidden Surface Removal Simple Transformations January 21, 2003 [Angel Ch. 3] Frank Pfenning Carnegie Mellon
15-462 Computer Graphics I Lecture 3 Interaction Client/Server Model Callbacks Double Buffering Hidden Surface Removal Simple Transformations January 21, 2003 [Angel Ch. 3] Frank Pfenning Carnegie Mellon
Teacher Assistant : Tamir Grossinger Reception hours: by - Building 37 / office -102 Assignments: 4 programing using
 Teacher Assistant : Tamir Grossinger email: tamirgr@gmail.com Reception hours: by email - Building 37 / office -102 Assignments: 4 programing using C++ 1 theoretical You can find everything you need in
Teacher Assistant : Tamir Grossinger email: tamirgr@gmail.com Reception hours: by email - Building 37 / office -102 Assignments: 4 programing using C++ 1 theoretical You can find everything you need in
Programming with OpenGL Part 2: Complete Programs Computer Graphics I, Fall
 Programming with OpenGL Part 2: Complete Programs 91.427 Computer Graphics I, Fall 2008 1 1 Objectives Refine first program Alter default values Introduce standard program structure Simple viewing 2-D
Programming with OpenGL Part 2: Complete Programs 91.427 Computer Graphics I, Fall 2008 1 1 Objectives Refine first program Alter default values Introduce standard program structure Simple viewing 2-D
Books, OpenGL, GLUT, CUDA, OpenCL, OpenCV, PointClouds, G3D, and Qt
 Books, OpenGL, GLUT, CUDA, OpenCL, OpenCV, PointClouds, G3D, and Qt CS334 Fall 2015 Daniel G. Aliaga Department of Computer Science Purdue University Books (and by now means complete ) Interactive Computer
Books, OpenGL, GLUT, CUDA, OpenCL, OpenCV, PointClouds, G3D, and Qt CS334 Fall 2015 Daniel G. Aliaga Department of Computer Science Purdue University Books (and by now means complete ) Interactive Computer
LECTURE 02 OPENGL API
 COMPUTER GRAPHICS LECTURE 02 OPENGL API Still from Pixar s Inside Out, 2015 IMRAN IHSAN ASSISTANT PROFESSOR WWW.IMRANIHSAN.COM EARLY HISTORY OF APIS IFIPS (1973) formed two committees to come up with a
COMPUTER GRAPHICS LECTURE 02 OPENGL API Still from Pixar s Inside Out, 2015 IMRAN IHSAN ASSISTANT PROFESSOR WWW.IMRANIHSAN.COM EARLY HISTORY OF APIS IFIPS (1973) formed two committees to come up with a
Introduction to OpenGL
 Introduction to OpenGL Tutorial 1: Create a window and draw a 2D square Introduction: The aim of the first tutorial is to introduce you to the magic world of graphics based on the OpenGL and GLUT APIs.
Introduction to OpenGL Tutorial 1: Create a window and draw a 2D square Introduction: The aim of the first tutorial is to introduce you to the magic world of graphics based on the OpenGL and GLUT APIs.
CS 380 Introduction to Computer Graphics. LAB (1) : OpenGL Tutorial Reference : Foundations of 3D Computer Graphics, Steven J.
 CS 380 Introduction to Computer Graphics LAB (1) : OpenGL Tutorial 2018. 03. 05 Reference : Foundations of 3D Computer Graphics, Steven J. Gortler Goals Understand OpenGL pipeline Practice basic OpenGL
CS 380 Introduction to Computer Graphics LAB (1) : OpenGL Tutorial 2018. 03. 05 Reference : Foundations of 3D Computer Graphics, Steven J. Gortler Goals Understand OpenGL pipeline Practice basic OpenGL
Building Models. Prof. George Wolberg Dept. of Computer Science City College of New York
 Building Models Prof. George Wolberg Dept. of Computer Science City College of New York Objectives Introduce simple data structures for building polygonal models - Vertex lists - Edge lists Deprecated
Building Models Prof. George Wolberg Dept. of Computer Science City College of New York Objectives Introduce simple data structures for building polygonal models - Vertex lists - Edge lists Deprecated
CS559: Computer Graphics. Lecture 12: OpenGL Transformation Li Zhang Spring 2008
 CS559: Computer Graphics Lecture 2: OpenGL Transformation Li Zhang Spring 28 Today Transformation in OpenGL Reading Chapter 3 Last time Primitive Details glpolygonmode(glenum face, GLenum mode); face:
CS559: Computer Graphics Lecture 2: OpenGL Transformation Li Zhang Spring 28 Today Transformation in OpenGL Reading Chapter 3 Last time Primitive Details glpolygonmode(glenum face, GLenum mode); face:
Drawing Primitives. OpenGL basics
 CSC 706 Computer Graphics / Dr. N. Gueorguieva 1 OpenGL Libraries Drawing Primitives OpenGL basics OpenGL core library OpenGL32 on Windows GL on most unix/linux systems (libgl.a) OpenGL Utility Library
CSC 706 Computer Graphics / Dr. N. Gueorguieva 1 OpenGL Libraries Drawing Primitives OpenGL basics OpenGL core library OpenGL32 on Windows GL on most unix/linux systems (libgl.a) OpenGL Utility Library
2a. The triangles scale increases (expands) when the 'e' key is pressed and decreases (contracts) when the 'c' key is pressed.
 Erik Anchondo 1-29-19 cse 520 lab 3 1. Wrote a shader program to display three colored triangles, with one of each triangle being red, green, and blue. The colors change which triangle they are applied
Erik Anchondo 1-29-19 cse 520 lab 3 1. Wrote a shader program to display three colored triangles, with one of each triangle being red, green, and blue. The colors change which triangle they are applied
API Background. Prof. George Wolberg Dept. of Computer Science City College of New York
 API Background Prof. George Wolberg Dept. of Computer Science City College of New York Objectives Graphics API history OpenGL API OpenGL function format Immediate Mode vs Retained Mode Examples The Programmer
API Background Prof. George Wolberg Dept. of Computer Science City College of New York Objectives Graphics API history OpenGL API OpenGL function format Immediate Mode vs Retained Mode Examples The Programmer
COMPUTER GRAPHICS LAB # 3
 COMPUTER GRAPHICS LAB # 3 Chapter 2: COMPUTER GRAPHICS by F.S HILLs. Initial steps in drawing figures (polygon, rectangle etc) Objective: Basic understanding of simple code in OpenGL and initial steps
COMPUTER GRAPHICS LAB # 3 Chapter 2: COMPUTER GRAPHICS by F.S HILLs. Initial steps in drawing figures (polygon, rectangle etc) Objective: Basic understanding of simple code in OpenGL and initial steps
Comp 410/510 Computer Graphics Spring Programming with OpenGL Part 3: Shaders
 Comp 410/510 Computer Graphics Spring 2018 Programming with OpenGL Part 3: Shaders Objectives Basic shaders - Vertex shader - Fragment shader Programming shaders with GLSL Finish first program void init(void)
Comp 410/510 Computer Graphics Spring 2018 Programming with OpenGL Part 3: Shaders Objectives Basic shaders - Vertex shader - Fragment shader Programming shaders with GLSL Finish first program void init(void)
WebGL A quick introduction. J. Madeira V. 0.2 September 2017
 WebGL A quick introduction J. Madeira V. 0.2 September 2017 1 Interactive Computer Graphics Graphics library / package is intermediary between application and display hardware Application program maps
WebGL A quick introduction J. Madeira V. 0.2 September 2017 1 Interactive Computer Graphics Graphics library / package is intermediary between application and display hardware Application program maps
CS418 OpenGL & GLUT Programming Tutorial (I) Presented by : Wei-Wen Feng 1/30/2008
 CS418 OpenGL & GLUT Programming Tutorial (I) Presented by : Wei-Wen Feng 1/30/2008 2008/2/3 Slide 2 I Am Your TA Name : Wei-Wen Wen Feng 4th Year Graduate Student in Graphics I will be Holding discussion/tutorial
CS418 OpenGL & GLUT Programming Tutorial (I) Presented by : Wei-Wen Feng 1/30/2008 2008/2/3 Slide 2 I Am Your TA Name : Wei-Wen Wen Feng 4th Year Graduate Student in Graphics I will be Holding discussion/tutorial
Computação Gráfica. Computer Graphics Engenharia Informática (11569) 3º ano, 2º semestre. Chap. 4 Windows and Viewports
 Computação Gráfica Computer Graphics Engenharia Informática (11569) 3º ano, 2º semestre Chap. 4 Windows and Viewports Outline : Basic definitions in 2D: Global coordinates (scene domain): continuous domain
Computação Gráfica Computer Graphics Engenharia Informática (11569) 3º ano, 2º semestre Chap. 4 Windows and Viewports Outline : Basic definitions in 2D: Global coordinates (scene domain): continuous domain
Lecture 2 CISC440/640 Spring Department of Computer and Information Science
 Lecture 2 CISC440/640 Spring 2015 Department of Computer and Information Science Today s Topic The secrets of Glut-tony 2 So let s do some graphics! For the next week or so this is your world: -1 1-1 1
Lecture 2 CISC440/640 Spring 2015 Department of Computer and Information Science Today s Topic The secrets of Glut-tony 2 So let s do some graphics! For the next week or so this is your world: -1 1-1 1
CSE 167: Introduction to Computer Graphics Lecture #7: GLSL. Jürgen P. Schulze, Ph.D. University of California, San Diego Spring Quarter 2016
 CSE 167: Introduction to Computer Graphics Lecture #7: GLSL Jürgen P. Schulze, Ph.D. University of California, San Diego Spring Quarter 2016 Announcements Project 2 due Friday 4/22 at 2pm Midterm #1 on
CSE 167: Introduction to Computer Graphics Lecture #7: GLSL Jürgen P. Schulze, Ph.D. University of California, San Diego Spring Quarter 2016 Announcements Project 2 due Friday 4/22 at 2pm Midterm #1 on
Computer Graphics Course 2005
 Computer Graphics Course 2005 Introduction to GLUT, GLU and OpenGL Administrative Stuff Teaching Assistant: Rony Goldenthal Reception Hour: Wed. 18:00 19:00 Room 31 (Ross 1) Questions: E-mail: cg@cs Newsgroups:
Computer Graphics Course 2005 Introduction to GLUT, GLU and OpenGL Administrative Stuff Teaching Assistant: Rony Goldenthal Reception Hour: Wed. 18:00 19:00 Room 31 (Ross 1) Questions: E-mail: cg@cs Newsgroups:
Geometry Shaders. And how to use them
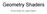 Geometry Shaders And how to use them OpenGL Pipeline (part of it) Vertex data Vertex shader Vertices Primitives Geometry shader Primitives Fragments Fragment shader Color Depth Stencil Vertex Data Attributes
Geometry Shaders And how to use them OpenGL Pipeline (part of it) Vertex data Vertex shader Vertices Primitives Geometry shader Primitives Fragments Fragment shader Color Depth Stencil Vertex Data Attributes
Announcements OpenGL. Computer Graphics. Spring CS4815
 Computer Graphics Spring 2017-2018 Outline 1 2 Tutes and Labs Tute02, vector review (see matrix) Week02 lab Lab Marking 10 labs in total each lab worth 3% of overall grade marked on attendance and completion
Computer Graphics Spring 2017-2018 Outline 1 2 Tutes and Labs Tute02, vector review (see matrix) Week02 lab Lab Marking 10 labs in total each lab worth 3% of overall grade marked on attendance and completion
Introduction to OpenGL: Part 2
 Introduction to OpenGL: Part 2 Introduction to OpenGL: Part 2 A more complex example recursive refinement Introduction to OpenGL: Part 2 A more complex example recursive refinement Can OpenGL draw continuous
Introduction to OpenGL: Part 2 Introduction to OpenGL: Part 2 A more complex example recursive refinement Introduction to OpenGL: Part 2 A more complex example recursive refinement Can OpenGL draw continuous
Lecture 3 Advanced Computer Graphics (CS & SE )
 Lecture 3 Advanced Computer Graphics (CS & SE 233.420) Programming with OpenGL Program Structure Primitives Attributes and States Programming in three dimensions Inputs and Interaction Working with Callbacks
Lecture 3 Advanced Computer Graphics (CS & SE 233.420) Programming with OpenGL Program Structure Primitives Attributes and States Programming in three dimensions Inputs and Interaction Working with Callbacks
Graphics Programming
 Graphics Programming 3 rd Week, 2011 OpenGL API (1) API (application programming interface) Interface between an application program and a graphics system Application Program OpenGL API Graphics Library
Graphics Programming 3 rd Week, 2011 OpenGL API (1) API (application programming interface) Interface between an application program and a graphics system Application Program OpenGL API Graphics Library
2. OpenGL -I. 2.1 What is OpenGL? Things OpenGL can do: -23-
 2.1 What is OpenGL? -23-2. OpenGL -I - Device-independent, application program interface (API) to graphics hardware - 3D-oriented - Event-driven Things OpenGL can do: - wireframe models - depth-cuing effect
2.1 What is OpenGL? -23-2. OpenGL -I - Device-independent, application program interface (API) to graphics hardware - 3D-oriented - Event-driven Things OpenGL can do: - wireframe models - depth-cuing effect
Image Processing. Geometry Processing. Reading: (Not really covered in our text. See Sects 18.1, 18.2.) Overview: Display
 CMSC 427: Chapter 2 Graphics Libraries and OpenGL Reading: (Not really covered in our text. See Sects 18.1, 18.2.) Overview: Graphics Libraries OpenGL and its Structure Drawing Primitives in OpenGL GLUT
CMSC 427: Chapter 2 Graphics Libraries and OpenGL Reading: (Not really covered in our text. See Sects 18.1, 18.2.) Overview: Graphics Libraries OpenGL and its Structure Drawing Primitives in OpenGL GLUT
From system point of view, a graphics application handles the user input, changes the internal state, called the virtual world by modeling or
 From system point of view, a graphics application handles the user input, changes the internal state, called the virtual world by modeling or animating it, and then immediately renders the updated model
From system point of view, a graphics application handles the user input, changes the internal state, called the virtual world by modeling or animating it, and then immediately renders the updated model
Interaction. CSCI 480 Computer Graphics Lecture 3
 CSCI 480 Computer Graphics Lecture 3 Interaction January 18, 2012 Jernej Barbic University of Southern California Client/Server Model Callbacks Double Buffering Hidden Surface Removal Simple Transformations
CSCI 480 Computer Graphics Lecture 3 Interaction January 18, 2012 Jernej Barbic University of Southern California Client/Server Model Callbacks Double Buffering Hidden Surface Removal Simple Transformations
Computer Graphics. Making Pictures. Computer Graphics CSC470 1
 Computer Graphics Making Pictures Computer Graphics CSC470 1 Getting Started Making Pictures Graphics display: Entire screen (a); windows system (b); [both have usual screen coordinates, with y-axis y
Computer Graphics Making Pictures Computer Graphics CSC470 1 Getting Started Making Pictures Graphics display: Entire screen (a); windows system (b); [both have usual screen coordinates, with y-axis y
Lecture 3. Understanding of OPenGL programming
 Lecture 3 Understanding of OPenGL programming What is OpenGL GL: stands for Graphic Library Software interface for rendering purposes for 2D or 3D geometric data objects. Various Pieces gl: The basic libraries.
Lecture 3 Understanding of OPenGL programming What is OpenGL GL: stands for Graphic Library Software interface for rendering purposes for 2D or 3D geometric data objects. Various Pieces gl: The basic libraries.
Computer Graphics Introduction to OpenGL
 Computer Graphics 2015 3. Introduction to OpenGL Hongxin Zhang State Key Lab of CAD&CG, Zhejiang University 2015-09-28 2. 2D Graphics Algorithms (cont.) Rasterization Computer Graphics @ ZJU Hongxin Zhang,
Computer Graphics 2015 3. Introduction to OpenGL Hongxin Zhang State Key Lab of CAD&CG, Zhejiang University 2015-09-28 2. 2D Graphics Algorithms (cont.) Rasterization Computer Graphics @ ZJU Hongxin Zhang,
Computer Graphics, Chapt 08
 Computer Graphics, Chapt 08 Creating an Image Components, parts of a scene to be displayed Trees, terrain Furniture, walls Store fronts and street scenes Atoms and molecules Stars and galaxies Describe
Computer Graphics, Chapt 08 Creating an Image Components, parts of a scene to be displayed Trees, terrain Furniture, walls Store fronts and street scenes Atoms and molecules Stars and galaxies Describe
Computer Graphics (Basic OpenGL)
 Computer Graphics (Basic OpenGL) Thilo Kielmann Fall 2008 Vrije Universiteit, Amsterdam kielmann@cs.vu.nl http://www.cs.vu.nl/ graphics/ Computer Graphics (Basic OpenGL, Input and Interaction), ((57))
Computer Graphics (Basic OpenGL) Thilo Kielmann Fall 2008 Vrije Universiteit, Amsterdam kielmann@cs.vu.nl http://www.cs.vu.nl/ graphics/ Computer Graphics (Basic OpenGL, Input and Interaction), ((57))
1.2 Basic Graphics Programming
 Fall 2018 CSCI 420: Computer Graphics 1.2 Basic Graphics Programming Hao Li http://cs420.hao-li.com 1 Last time Last Time Story Computer Graphics Image Last Time 3D Printing 3D Capture Animation Modeling
Fall 2018 CSCI 420: Computer Graphics 1.2 Basic Graphics Programming Hao Li http://cs420.hao-li.com 1 Last time Last Time Story Computer Graphics Image Last Time 3D Printing 3D Capture Animation Modeling
Computer Graphics (CS 543) Lecture 3b: Shader Setup & GLSL Introduction
 Computer Graphics (CS 543) Lecture 3b: Shader Setup & GLSL Introduction Prof Emmanuel Agu Computer Science Dept. Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI) OpenGL function format function name gluniform3f(x,y,z)
Computer Graphics (CS 543) Lecture 3b: Shader Setup & GLSL Introduction Prof Emmanuel Agu Computer Science Dept. Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI) OpenGL function format function name gluniform3f(x,y,z)
Graphics Pipeline & APIs
 Graphics Pipeline & APIs CPU Vertex Processing Rasterization Fragment Processing glclear (GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT GL_DEPTH_BUFFER_BIT); glpushmatrix (); gltranslatef (-0.15, -0.15, solidz); glmaterialfv(gl_front,
Graphics Pipeline & APIs CPU Vertex Processing Rasterization Fragment Processing glclear (GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT GL_DEPTH_BUFFER_BIT); glpushmatrix (); gltranslatef (-0.15, -0.15, solidz); glmaterialfv(gl_front,
Announcements OpenGL. Computer Graphics. Autumn 2009 CS4815
 Computer Graphics Autumn 2009 Outline 1 Labs 2 Labs Outline 1 Labs 2 Labs Labs Week02 lab Marking 8 10 labs in total each lab worth 2 3% of overall grade marked on attendance and completion of lab completed
Computer Graphics Autumn 2009 Outline 1 Labs 2 Labs Outline 1 Labs 2 Labs Labs Week02 lab Marking 8 10 labs in total each lab worth 2 3% of overall grade marked on attendance and completion of lab completed
Ulf Assarsson Department of Computer Engineering Chalmers University of Technology
 Ulf Assarsson Department of Computer Engineering Chalmers University of Technology Tracing Photons One way to form an image is to follow rays of light from a point source finding which rays enter the lens
Ulf Assarsson Department of Computer Engineering Chalmers University of Technology Tracing Photons One way to form an image is to follow rays of light from a point source finding which rays enter the lens
CSC Graphics Programming. Budditha Hettige Department of Statistics and Computer Science
 CSC 307 1.0 Graphics Programming Department of Statistics and Computer Science Graphics Programming 2 Common Uses for Computer Graphics Applications for real-time 3D graphics range from interactive games
CSC 307 1.0 Graphics Programming Department of Statistics and Computer Science Graphics Programming 2 Common Uses for Computer Graphics Applications for real-time 3D graphics range from interactive games
Models and Architectures. Angel and Shreiner: Interactive Computer Graphics 7E Addison-Wesley 2015
 Models and Architectures 1 Objectives Learn the basic design of a graphics system Introduce pipeline architecture Examine software components for an interactive graphics system 2 Image Formation Revisited
Models and Architectures 1 Objectives Learn the basic design of a graphics system Introduce pipeline architecture Examine software components for an interactive graphics system 2 Image Formation Revisited
