NonLinear Analysis of a Cantilever Beam
|
|
|
- Andrea Fitzgerald
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 NonLinear Analysis of a Cantilever Beam Introduction This tutorial was created using ANSYS 7.0 The purpose of this tutorial is to outline the steps required to do a simple nonlinear analysis of the beam shown below. There are several causes for nonlinear behaviour such as Changing Status (ex. contact elements), Material Nonlinearities and Geometric Nonlinearities (change in response due to large deformations). This tutorial will deal specifically with Geometric Nonlinearities. To solve this problem, the load will added incrementally. After each increment, the stiffness matrix will be adjusted before increasing the load. The solution will be compared to the equivalent solution using a linear response. Preprocessing: Defining the Problem 1. Give example a Title Utility Menu > File > Change Title Create Keypoints Preprocessor > Modeling > Create > Keypoints > In Active CS We are going to define 2 keypoints (the beam vertices) for this structure to create a beam with a length of 5 inches: Keypoint Coordinates (x,y) 1 (0,0) 2 (5,0)
2 3. Define Lines Preprocessor > Modeling > Create > Lines > Lines > Straight Line Create a line between Keypoint 1 and Keypoint Define Element Types Preprocessor > Element Type > Add/Edit/Delete... For this problem we will use the BEAM3 (Beam 2D elastic) element. This element has 3 degrees of freedom (translation along the X and Y axis's, and rotation about the Z axis). With only 3 degrees of freedom, the BEAM3 element can only be used in 2D analysis. 5. Define Real Constants Preprocessor > Real Constants... > Add... In the 'Real Constants for BEAM3' window, enter the following geometric properties: i. Cross-sectional area AREA: ii. Area Moment of Inertia IZZ: 4.069e-5 iii. Total beam height HEIGHT: This defines an element with a solid rectangular cross section 0.25 x inches. 6. Define Element Material Properties Preprocessor > Material Props > Material Models > Structural > Linear > Elastic > Isotropic In the window that appears, enter the following geometric properties for steel: i. Young's modulus EX: 30e6 ii. Poisson's Ratio PRXY: 0.3 If you are wondering why a 'Linear' model was chosen when this is a non-linear example, it is because this example is for non-linear geometry, not non-linear material properties. If we were considering a block of wood, for example, we would have to consider non-linear material properties. 7. Define Mesh Size Preprocessor > Meshing > Size Cntrls > ManualSize > Lines > All Lines... For this example we will specify an element edge length of 0.1 " (50 element divisions along the line). 8. Mesh the frame Preprocessor > Meshing > Mesh > Lines > click 'Pick All' LMESH,ALL Solution: Assigning Loads and Solving 1. Define Analysis Type
3 Solution > New Analysis > Static ANTYPE,0 2. Set Solution Controls Select Solution > Analysis Type > Sol'n Control... The following image will appear: Ensure the following selections are made (as shown above) A. Ensure Large Static Displacements are permitted (this will include the effects of large deflection in the results) B. Ensure Automatic time stepping is on. Automatic time stepping allows ANSYS to determine appropriate sizes to break the load steps into. Decreasing the step size usually ensures better accuracy, however, this takes time. The Automatic Time Step feature will determine an appropriate balance. This feature also activates the ANSYS bisection feature which will allow recovery if convergence fails. C. Enter 5 as the number of substeps. This will set the initial substep to 1/5 th of the total load. The following example explains this: Assume that the applied load is 100 lb*in. If the Automatic Time Stepping was off, there would be 5 load steps (each increasing by 1/5 th of the total load): 20 lb*in 40 lb*in 60 lb*in 80 lb*in
4 100 lb*in Now, with the Automatic Time Stepping is on, the first step size will still be 20 lb*in. However, the remaining substeps will be determined based on the response of the material due to the previous load increment. D. Enter a maximum number of substeps of This stops the program if the solution does not converge after 1000 steps. E. Enter a minimum number of substeps of 1. F. Ensure all solution items are writen to a results file. NOTE There are several options which have not been changed from their default values. For more information about these commands, type help followed by the command into the command line. Function 3. Apply Constraints Solution > Define Loads > Apply > Structural > Displacement > On Keypoints 4. Apply Loads Command Comments Load Step KBC Loads are either linearly interpolated (ramped) from the one substep to another (ie - the load will increase from 10 lbs to 20 lbs in a linear fashion) or they are step functions (ie. the load steps directly from 10 lbs to 20 lbs). By default, the load is ramped. You may wish to use the stepped loading for rate-dependent behaviour or transient load steps. Output OUTRES This command controls the solution data written to the database. By default, all of the solution items are written at the end of each load step. You may select only a specific iten (ie Nodal DOF solution) to decrease processing time. Stress Stiffness Newton Raphson Convergence Values SSTIF NROPT Fix Keypoint 1 (ie all DOFs constrained). This command activates stress stiffness effects in nonlinear analyses. When large static deformations are permitted (as they are in this case), stress stiffening is automatically included. For some special nonlinear cases, this can cause divergence because some elements do not provide a complete consistent tangent. By default, the program will automatically choose the Newton- Raphson options. Options include the full Newton-Raphson, the modified Newton-Raphson, the previously computed matrix, and the full Newton-Raphson with unsymmetric matrices of elements. CNVTOL By default, the program checks the out-of-balance load for any active DOF.
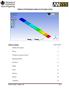
5 Solution > Define Loads > Apply > Structural > Force/Moment > On Keypoints Place a -100 lb*in moment in the MZ direction at the right end of the beam (Keypoint 2) 5. Solve the System Solution > Solve > Current LS SOLVE The following will appear on your screan for NonLinear Analyses This shows the convergence of the solution. General Postprocessing: Viewing the Results 1. View the deformed shape General Postproc > Plot Results > Deformed Shape... > Def + undeformed PLDISP,1
6 2. View the deflection contour plot General Postproc > Plot Results > Contour Plot > Nodal Solu... > DOF solution, UY PLNSOL,U,Y,0,1 3. List Horizontal Displacement If this example is performed as a linear model there will be no nodal deflection in the horizontal direction due to the small deflections assumptions. However, this is not realistic for large deflections. Modeling the system non-linearly, these horizontal deflections are calculated by ANSYS. General Postproc > List Results > Nodal Solution...> DOF solution, UX
7 Other results can be obtained as shown in previous linear static analyses. Command File Mode of Solution The above example was solved using a mixture of the Graphical User Interface (or GUI) and the command language interface of ANSYS. This problem has also been solved using the ANSYS command language interface that you may want to browse. Open the file and save it to your computer. Now go to 'File > Read input from...' and select the file.
NonLinear Materials AH-ALBERTA Web:
 NonLinear Materials Introduction This tutorial was completed using ANSYS 7.0 The purpose of the tutorial is to describe how to include material nonlinearities in an ANSYS model. For instance, the case
NonLinear Materials Introduction This tutorial was completed using ANSYS 7.0 The purpose of the tutorial is to describe how to include material nonlinearities in an ANSYS model. For instance, the case
Structural static analysis - Analyzing 2D frame
 Structural static analysis - Analyzing 2D frame In this tutorial we will analyze 2D frame (see Fig.1) consisting of 2D beams with respect to resistance to two different kinds of loads: (a) the downward
Structural static analysis - Analyzing 2D frame In this tutorial we will analyze 2D frame (see Fig.1) consisting of 2D beams with respect to resistance to two different kinds of loads: (a) the downward
Structural modal analysis - 2D frame
 Structural modal analysis - 2D frame Determine the first six vibration characteristics, namely natural frequencies and mode shapes, of a structure depicted in Fig. 1, when Young s modulus= 27e9Pa, Poisson
Structural modal analysis - 2D frame Determine the first six vibration characteristics, namely natural frequencies and mode shapes, of a structure depicted in Fig. 1, when Young s modulus= 27e9Pa, Poisson
Structural static analysis - Analyzing 2D frame
 Structural static analysis - Analyzing 2D frame In this tutorial we will analyze 2D frame (see Fig.1) consisting of 2D beams with respect to resistance to two different kinds of loads: (a) the downward
Structural static analysis - Analyzing 2D frame In this tutorial we will analyze 2D frame (see Fig.1) consisting of 2D beams with respect to resistance to two different kinds of loads: (a) the downward
Two Dimensional Truss
 Two Dimensional Truss Introduction This tutorial was created using ANSYS 7.0 to solve a simple 2D Truss problem. This is the first of four introductory ANSYS tutorials. Problem Description Determine the
Two Dimensional Truss Introduction This tutorial was created using ANSYS 7.0 to solve a simple 2D Truss problem. This is the first of four introductory ANSYS tutorials. Problem Description Determine the
Exercise 1. 3-Point Bending Using the GUI and the Bottom-up-Method
 Exercise 1 3-Point Bending Using the GUI and the Bottom-up-Method Contents Learn how to... 1 Given... 2 Questions... 2 Taking advantage of symmetries... 2 A. Preprocessor (Setting up the Model)... 3 A.1
Exercise 1 3-Point Bending Using the GUI and the Bottom-up-Method Contents Learn how to... 1 Given... 2 Questions... 2 Taking advantage of symmetries... 2 A. Preprocessor (Setting up the Model)... 3 A.1
Structural modal analysis - 2D frame
 Structural modal analysis - 2D frame Determine the first six vibration characteristics, namely natural frequencies and mode shapes, of a structure depicted in Fig. 1, when Young s modulus= 27e9Pa, Poisson
Structural modal analysis - 2D frame Determine the first six vibration characteristics, namely natural frequencies and mode shapes, of a structure depicted in Fig. 1, when Young s modulus= 27e9Pa, Poisson
Example Cantilever beam
 Course in ANSYS Example0300 Example Cantilever beam Objective: Compute the maximum deflection and locate point of maximum deflection Tasks: How should this be modelled? Compare results with results obtained
Course in ANSYS Example0300 Example Cantilever beam Objective: Compute the maximum deflection and locate point of maximum deflection Tasks: How should this be modelled? Compare results with results obtained
Module 3: Buckling of 1D Simply Supported Beam
 Module : Buckling of 1D Simply Supported Beam Table of Contents Page Number Problem Description Theory Geometry 4 Preprocessor 7 Element Type 7 Real Constants and Material Properties 8 Meshing 9 Solution
Module : Buckling of 1D Simply Supported Beam Table of Contents Page Number Problem Description Theory Geometry 4 Preprocessor 7 Element Type 7 Real Constants and Material Properties 8 Meshing 9 Solution
Module 1.2: Moment of a 1D Cantilever Beam
 Module 1.: Moment of a 1D Cantilever Beam Table of Contents Page Number Problem Description Theory Geometry Preprocessor 6 Element Type 6 Real Constants and Material Properties 7 Meshing 9 Loads 10 Solution
Module 1.: Moment of a 1D Cantilever Beam Table of Contents Page Number Problem Description Theory Geometry Preprocessor 6 Element Type 6 Real Constants and Material Properties 7 Meshing 9 Loads 10 Solution
Course in ANSYS. Example0153. ANSYS Computational Mechanics, AAU, Esbjerg
 Course in Example0153 Example Offshore structure F Objective: Display the deflection figure and von Mises stress distribution Tasks: Import geometry from IGES. Display the deflection figure? Display the
Course in Example0153 Example Offshore structure F Objective: Display the deflection figure and von Mises stress distribution Tasks: Import geometry from IGES. Display the deflection figure? Display the
Ansys Lab Frame Analysis
 Ansys Lab Frame Analysis Analyze the highway overpass frame shown in Figure. The main horizontal beam is W24x162 (area = 47.7 in 2, moment of inertia = 5170 in 4, height = 25 in). The inclined members
Ansys Lab Frame Analysis Analyze the highway overpass frame shown in Figure. The main horizontal beam is W24x162 (area = 47.7 in 2, moment of inertia = 5170 in 4, height = 25 in). The inclined members
Coupled Structural/Thermal Analysis
 Coupled Structural/Thermal Analysis Introduction This tutorial was completed using ANSYS 7.0 The purpose of this tutorial is to outline a simple coupled thermal/structural analysis. A steel link, with
Coupled Structural/Thermal Analysis Introduction This tutorial was completed using ANSYS 7.0 The purpose of this tutorial is to outline a simple coupled thermal/structural analysis. A steel link, with
Melting Using Element Death
 Melting Using Element Death Introduction This tutorial was completed using ANSYS 7.0 The purpose of the tutorial is to outline the steps required to use element death to model melting of a material. Element
Melting Using Element Death Introduction This tutorial was completed using ANSYS 7.0 The purpose of the tutorial is to outline the steps required to use element death to model melting of a material. Element
Statically Indeterminate Beam
 Problem: Using Castigliano's Theorem, determine the deflection at point A. Neglect the weight of the beam. W 1 N/m B 5 cm H 1 cm 1.35 m Overview Anticipated time to complete this tutorial: 45 minutes Tutorial
Problem: Using Castigliano's Theorem, determine the deflection at point A. Neglect the weight of the beam. W 1 N/m B 5 cm H 1 cm 1.35 m Overview Anticipated time to complete this tutorial: 45 minutes Tutorial
Module 1.5: Moment Loading of a 2D Cantilever Beam
 Module 1.5: Moment Loading of a D Cantilever Beam Table of Contents Page Number Problem Description Theory Geometry 4 Preprocessor 7 Element Type 7 Real Constants and Material Properties 8 Meshing 9 Loads
Module 1.5: Moment Loading of a D Cantilever Beam Table of Contents Page Number Problem Description Theory Geometry 4 Preprocessor 7 Element Type 7 Real Constants and Material Properties 8 Meshing 9 Loads
Example Plate with a hole
 Course in ANSYS Example Plate with a hole A Objective: Determine the maximum stress in the x-direction for point A and display the deformation figure Tasks: Create a submodel to increase the accuracy of
Course in ANSYS Example Plate with a hole A Objective: Determine the maximum stress in the x-direction for point A and display the deformation figure Tasks: Create a submodel to increase the accuracy of
Course in ANSYS. Example Truss 2D. Example0150
 Course in ANSYS Example0150 Example Truss 2D Objective: Compute the maximum deflection Tasks: Display the deflection figure? Topics: Topics: Start of analysis, Element type, Real constants, Material, modeling,
Course in ANSYS Example0150 Example Truss 2D Objective: Compute the maximum deflection Tasks: Display the deflection figure? Topics: Topics: Start of analysis, Element type, Real constants, Material, modeling,
Course in ANSYS. Example0154. ANSYS Computational Mechanics, AAU, Esbjerg
 Course in Example0154 Example Frame 2D E = 210000N/mm 2 n = 0.3 L= 1000mm H = 1000mm a = 20mm b = 50mm c = 400mm F = 10000N I = 208333N/mm 4 Example0154 2 Example Frame 2D Objective: Compute the maximum
Course in Example0154 Example Frame 2D E = 210000N/mm 2 n = 0.3 L= 1000mm H = 1000mm a = 20mm b = 50mm c = 400mm F = 10000N I = 208333N/mm 4 Example0154 2 Example Frame 2D Objective: Compute the maximum
6. Results Combination in Hexagonal Shell
 6. Results Combination in Hexagonal Shell Applicable CivilFEM Product: All CivilFEM Products Level of Difficulty: Moderate Interactive Time Required: 0 minutes Discipline: Load combinations results Analysis
6. Results Combination in Hexagonal Shell Applicable CivilFEM Product: All CivilFEM Products Level of Difficulty: Moderate Interactive Time Required: 0 minutes Discipline: Load combinations results Analysis
Course in ANSYS. Example0410. ANSYS Computational Mechanics, AAU, Esbjerg
 Course in Example0410 Example Frame 2D Objective: Compute the harmonic response Tasks: Perform a modal analysis Display the mode shapes Perform a harmonic analysis Topics: Topics: Start of analysis, Element
Course in Example0410 Example Frame 2D Objective: Compute the harmonic response Tasks: Perform a modal analysis Display the mode shapes Perform a harmonic analysis Topics: Topics: Start of analysis, Element
Latch Spring. Problem:
 Problem: Shown in the figure is a 12-gauge (0.1094 in) by 3/4 in latching spring which supports a load of F = 3 lb. The inside radius of the bend is 1/8 in. Estimate the stresses at the inner and outer
Problem: Shown in the figure is a 12-gauge (0.1094 in) by 3/4 in latching spring which supports a load of F = 3 lb. The inside radius of the bend is 1/8 in. Estimate the stresses at the inner and outer
Transient Thermal Conduction Example
 Transient Thermal Conduction Example Introduction This tutorial was created using ANSYS 7.0 to solve a simple transient conduction problem. Special thanks to Jesse Arnold for the analytical solution shown
Transient Thermal Conduction Example Introduction This tutorial was created using ANSYS 7.0 to solve a simple transient conduction problem. Special thanks to Jesse Arnold for the analytical solution shown
ANSYS Tutorials. Table of Contents. Grady Lemoine
 ANSYS Tutorials Grady Lemoine Table of Contents Example 1: 2-D Static Stress Analysis in ANSYS...2 Example 2: 3-D Static Stress Analysis...5 Example 3: 2-D Frame With Multiple Materials and Element Types...10
ANSYS Tutorials Grady Lemoine Table of Contents Example 1: 2-D Static Stress Analysis in ANSYS...2 Example 2: 3-D Static Stress Analysis...5 Example 3: 2-D Frame With Multiple Materials and Element Types...10
Chapter 2. Structural Tutorial
 Chapter 2. Structural Tutorial Tutorials> Chapter 2. Structural Tutorial Static Analysis of a Corner Bracket Problem Specification Problem Description Build Geometry Define Materials Generate Mesh Apply
Chapter 2. Structural Tutorial Tutorials> Chapter 2. Structural Tutorial Static Analysis of a Corner Bracket Problem Specification Problem Description Build Geometry Define Materials Generate Mesh Apply
file://c:\documents and Settings\sala\Configuración local\temp\~hha54f.htm
 Página 1 de 26 Tutorials Chapter 2. Structural Tutorial 2.1. Static Analysis of a Corner Bracket 2.1.1. Problem Specification Applicable ANSYS Products: Level of Difficulty: Interactive Time Required:
Página 1 de 26 Tutorials Chapter 2. Structural Tutorial 2.1. Static Analysis of a Corner Bracket 2.1.1. Problem Specification Applicable ANSYS Products: Level of Difficulty: Interactive Time Required:
Course in ANSYS. Example0505. ANSYS Computational Mechanics, AAU, Esbjerg
 Course in Example0505 Example Plate Objective: Compute the buckling load Tasks: How should this be modelled? Compare results with results obtained from norm calculations? Topics: Element type, Real constants,
Course in Example0505 Example Plate Objective: Compute the buckling load Tasks: How should this be modelled? Compare results with results obtained from norm calculations? Topics: Element type, Real constants,
Course in ANSYS. Example0152. ANSYS Computational Mechanics, AAU, Esbjerg
 Course in Example0152 Example Truss 2D E = 210e09N/m 2 n = 0.3 L1 = L2 = L3 = 3.6m H = 3.118m a = b = 0.050mm F1 = 280kN F2 = 210kN F3 = 280kN F4 = 360kN Example0152 2 Example Truss 2D Objective: Compute
Course in Example0152 Example Truss 2D E = 210e09N/m 2 n = 0.3 L1 = L2 = L3 = 3.6m H = 3.118m a = b = 0.050mm F1 = 280kN F2 = 210kN F3 = 280kN F4 = 360kN Example0152 2 Example Truss 2D Objective: Compute
Bell Crank. Problem: Joseph Shigley and Charles Mischke. Mechanical Engineering Design 5th ed (New York: McGraw Hill, May 2002) page 87.
 Problem: A cast-iron bell-crank lever, depicted in the figure below is acted upon by forces F 1 of 250 lb and F 2 of 333 lb. The section A-A at the central pivot has a curved inner surface with a radius
Problem: A cast-iron bell-crank lever, depicted in the figure below is acted upon by forces F 1 of 250 lb and F 2 of 333 lb. The section A-A at the central pivot has a curved inner surface with a radius
Course in ANSYS. Example0500. ANSYS Computational Mechanics, AAU, Esbjerg
 Course in Example0500 Example Column beam Objective: Compute the critical buckling load and display the mode shape Tasks: Create a table and compare results with results obtained from buckling theory?
Course in Example0500 Example Column beam Objective: Compute the critical buckling load and display the mode shape Tasks: Create a table and compare results with results obtained from buckling theory?
Module 1.6: Distributed Loading of a 2D Cantilever Beam
 Module 1.6: Distributed Loading of a 2D Cantilever Beam Table of Contents Page Number Problem Description 2 Theory 2 Geometry 4 Preprocessor 7 Element Type 7 Real Constants and Material Properties 8 Meshing
Module 1.6: Distributed Loading of a 2D Cantilever Beam Table of Contents Page Number Problem Description 2 Theory 2 Geometry 4 Preprocessor 7 Element Type 7 Real Constants and Material Properties 8 Meshing
ANSYS 5.6 Tutorials Lecture # 2 - Static Structural Analysis
 R50 ANSYS 5.6 Tutorials Lecture # 2 - Static Structural Analysis Example 1 Static Analysis of a Bracket 1. Problem Description: The objective of the problem is to demonstrate the basic ANSYS procedures
R50 ANSYS 5.6 Tutorials Lecture # 2 - Static Structural Analysis Example 1 Static Analysis of a Bracket 1. Problem Description: The objective of the problem is to demonstrate the basic ANSYS procedures
Course in ANSYS. Example0504. ANSYS Computational Mechanics, AAU, Esbjerg
 Course in Example0504 Example Cantilever beam Objective: Compute the buckling load Tasks: Display the deflection figure? Topics: Topics: Start of analysis, Element type, Real constants, Material, modeling,
Course in Example0504 Example Cantilever beam Objective: Compute the buckling load Tasks: Display the deflection figure? Topics: Topics: Start of analysis, Element type, Real constants, Material, modeling,
Buckling of Euler Column
 Problem: An Euler column with one end fixed and one end free is to be made of an aluminum alloy (E = 71 GPa). The cross sectional area of the column is 600 mm and the column is.5 m long. Determine the
Problem: An Euler column with one end fixed and one end free is to be made of an aluminum alloy (E = 71 GPa). The cross sectional area of the column is 600 mm and the column is.5 m long. Determine the
Course in ANSYS. Example0601. ANSYS Computational Mechanics, AAU, Esbjerg
 Course in Example0601 Example Turbine Blade Example0601 2 Example Turbine Blade Objective: Solve for the temperature distribution within the 6mm thick turbine blade, with 2mm x 6mm rectangular cooling
Course in Example0601 Example Turbine Blade Example0601 2 Example Turbine Blade Objective: Solve for the temperature distribution within the 6mm thick turbine blade, with 2mm x 6mm rectangular cooling
Course in ANSYS. Example0303. ANSYS Computational Mechanics, AAU, Esbjerg
 Course in Example0303 Example Gear axle 3D Objective: Compute the maximum stress von Mise Tasks: How should this be modeled? Topics: Element type, Real constants, modeling, Plot results, output graphics,
Course in Example0303 Example Gear axle 3D Objective: Compute the maximum stress von Mise Tasks: How should this be modeled? Topics: Element type, Real constants, modeling, Plot results, output graphics,
Module 1.7: Point Loading of a 3D Cantilever Beam
 Module 1.7: Point Loading of a D Cantilever Beam Table of Contents Page Number Problem Description Theory Geometry 4 Preprocessor 6 Element Type 6 Material Properties 7 Meshing 8 Loads 9 Solution 15 General
Module 1.7: Point Loading of a D Cantilever Beam Table of Contents Page Number Problem Description Theory Geometry 4 Preprocessor 6 Element Type 6 Material Properties 7 Meshing 8 Loads 9 Solution 15 General
ECE421: Electronics for Instrumentation
 ECE421: Electronics for Instrumentation Lecture #8: Introduction to FEA & ANSYS Mostafa Soliman, Ph.D. March 23 rd 2015 Mostafa Soliman, Ph.D. 1 Outline Introduction to Finite Element Analysis Introduction
ECE421: Electronics for Instrumentation Lecture #8: Introduction to FEA & ANSYS Mostafa Soliman, Ph.D. March 23 rd 2015 Mostafa Soliman, Ph.D. 1 Outline Introduction to Finite Element Analysis Introduction
Institute of Mechatronics and Information Systems
 EXERCISE 2 Free vibrations of a beam arget Getting familiar with the fundamental issues of free vibrations analysis of elastic medium, with the use of a finite element computation system ANSYS. Program
EXERCISE 2 Free vibrations of a beam arget Getting familiar with the fundamental issues of free vibrations analysis of elastic medium, with the use of a finite element computation system ANSYS. Program
Exercise 1. 3-Point Bending Using the Static Structural Module of. Ansys Workbench 14.0
 Exercise 1 3-Point Bending Using the Static Structural Module of Contents Ansys Workbench 14.0 Learn how to...1 Given...2 Questions...2 Taking advantage of symmetries...2 A. Getting started...3 A.1 Choose
Exercise 1 3-Point Bending Using the Static Structural Module of Contents Ansys Workbench 14.0 Learn how to...1 Given...2 Questions...2 Taking advantage of symmetries...2 A. Getting started...3 A.1 Choose
Lecture # 5 Modal or Dynamic Analysis of an Airplane Wing
 Lecture # 5 Modal or Dynamic Analysis of an Airplane Wing Problem Description This is a simple modal analysis of a wing of a model airplane. The wing is of uniform configuration along its length and its
Lecture # 5 Modal or Dynamic Analysis of an Airplane Wing Problem Description This is a simple modal analysis of a wing of a model airplane. The wing is of uniform configuration along its length and its
Dhanalakshmi College Of Engineering
 Dhanalakshmi College Of Engineering Manimangalam, Tambaram, Chennai 601 301 DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING ME 6711 SIMULATION AND ANALYSIS LABORATORY VII SEMESTER - R 2013 LABORATORY MANUAL Name
Dhanalakshmi College Of Engineering Manimangalam, Tambaram, Chennai 601 301 DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING ME 6711 SIMULATION AND ANALYSIS LABORATORY VII SEMESTER - R 2013 LABORATORY MANUAL Name
3. Check by Eurocode 3 a Steel Truss
 TF 3. Check by Eurocode 3 a Steel Truss Applicable CivilFEM Product: All CivilFEM Products Level of Difficulty: Moderate Interactive Time Required: 40 minutes Discipline: Structural Steel Analysis Type:
TF 3. Check by Eurocode 3 a Steel Truss Applicable CivilFEM Product: All CivilFEM Products Level of Difficulty: Moderate Interactive Time Required: 40 minutes Discipline: Structural Steel Analysis Type:
Institute of Mechatronics and Information Systems
 EXERCISE 4 Free vibrations of an electrical machine model Target Getting familiar with the fundamental issues of free vibrations analysis of a simplified model of an electrical machine, with the use of
EXERCISE 4 Free vibrations of an electrical machine model Target Getting familiar with the fundamental issues of free vibrations analysis of a simplified model of an electrical machine, with the use of
Essay 5 Tutorial for a Three-Dimensional Heat Conduction Problem Using ANSYS
 Essay 5 Tutorial for a Three-Dimensional Heat Conduction Problem Using ANSYS 5.1 Introduction The problem selected to illustrate the use of ANSYS software for a three-dimensional steadystate heat conduction
Essay 5 Tutorial for a Three-Dimensional Heat Conduction Problem Using ANSYS 5.1 Introduction The problem selected to illustrate the use of ANSYS software for a three-dimensional steadystate heat conduction
ANSYS. Geometry. Material Properties. E=2.8E7 psi v=0.3. ansys.fem.ir Written By:Mehdi Heydarzadeh Page 1
 Attention: This tutorial is outdated, you will be redirected automatically to the new site. If you are not redirected, click this link to the confluence site. Problem Specification Geometry Material Properties
Attention: This tutorial is outdated, you will be redirected automatically to the new site. If you are not redirected, click this link to the confluence site. Problem Specification Geometry Material Properties
Finite Element Course ANSYS Mechanical Tutorial Tutorial 3 Cantilever Beam
 Problem Specification Finite Element Course ANSYS Mechanical Tutorial Tutorial 3 Cantilever Beam Consider the beam in the figure below. It is clamped on the left side and has a point force of 8kN acting
Problem Specification Finite Element Course ANSYS Mechanical Tutorial Tutorial 3 Cantilever Beam Consider the beam in the figure below. It is clamped on the left side and has a point force of 8kN acting
Modelling and Analysis Lab (FEA)
 Channabasaveshwara Institute of Technology (Affiliated to VTU, Belagavi & Approved by AICTE, New Delhi) (NAAC Accredited & ISO 9001:2015 Certified Institution) NH 206 (B.H. Road), Gubbi, Tumakuru 572 216.
Channabasaveshwara Institute of Technology (Affiliated to VTU, Belagavi & Approved by AICTE, New Delhi) (NAAC Accredited & ISO 9001:2015 Certified Institution) NH 206 (B.H. Road), Gubbi, Tumakuru 572 216.
Multi-Step Analysis of a Cantilever Beam
 LESSON 4 Multi-Step Analysis of a Cantilever Beam LEGEND 75000. 50000. 25000. 0. -25000. -50000. -75000. 0. 3.50 7.00 10.5 14.0 17.5 21.0 Objectives: Demonstrate multi-step analysis set up in MSC/Advanced_FEA.
LESSON 4 Multi-Step Analysis of a Cantilever Beam LEGEND 75000. 50000. 25000. 0. -25000. -50000. -75000. 0. 3.50 7.00 10.5 14.0 17.5 21.0 Objectives: Demonstrate multi-step analysis set up in MSC/Advanced_FEA.
Release 10. Kent L. Lawrence. Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering University of Texas at Arlington SDC PUBLICATIONS
 ANSYS Release 10 Tutorial Kent L. Lawrence Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering University of Texas at Arlington SDC PUBLICATIONS Schroff Development Corporation www.schroff.com www.schroff-europe.com
ANSYS Release 10 Tutorial Kent L. Lawrence Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering University of Texas at Arlington SDC PUBLICATIONS Schroff Development Corporation www.schroff.com www.schroff-europe.com
ANSYS Tutorial Release 11.0
 ANSYS Tutorial Release 11.0 Structural & Thermal Analysis Using the ANSYS Release 11.0 Environment Kent L. Lawrence Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering University of Texas at Arlington SDC PUBLICATIONS
ANSYS Tutorial Release 11.0 Structural & Thermal Analysis Using the ANSYS Release 11.0 Environment Kent L. Lawrence Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering University of Texas at Arlington SDC PUBLICATIONS
5. Shell Reinforcement According To Eurocode 2
 5. Shell Reinforcement According To Eurocode Applicable CivilFEM Product: All CivilFEM Products Level of Difficulty: Moderate Interactive Time Required: 5 minutes Discipline: Concrete Shell Reinforcement
5. Shell Reinforcement According To Eurocode Applicable CivilFEM Product: All CivilFEM Products Level of Difficulty: Moderate Interactive Time Required: 5 minutes Discipline: Concrete Shell Reinforcement
Statically Indeterminate Beam
 Problem: A rectangular aluminum bar.5 inches thick and 2 inches wide is welded to fixed supports at the ends, and the bar supports a load W=800 lb, acting through the pin as shown. Find the reactions at
Problem: A rectangular aluminum bar.5 inches thick and 2 inches wide is welded to fixed supports at the ends, and the bar supports a load W=800 lb, acting through the pin as shown. Find the reactions at
Module 1.3W Distributed Loading of a 1D Cantilever Beam
 Module 1.3W Distributed Loading of a 1D Cantilever Beam Table of Contents Page Number Problem Description 2 Theory 2 Workbench Analysis System 4 Engineering Data 5 Geometry 6 Model 11 Setup 13 Solution
Module 1.3W Distributed Loading of a 1D Cantilever Beam Table of Contents Page Number Problem Description 2 Theory 2 Workbench Analysis System 4 Engineering Data 5 Geometry 6 Model 11 Setup 13 Solution
Linear and Nonlinear Analysis of a Cantilever Beam
 LESSON 1 Linear and Nonlinear Analysis of a Cantilever Beam P L Objectives: Create a beam database to be used for the specified subsequent exercises. Compare small vs. large displacement analysis. Linear
LESSON 1 Linear and Nonlinear Analysis of a Cantilever Beam P L Objectives: Create a beam database to be used for the specified subsequent exercises. Compare small vs. large displacement analysis. Linear
Course in. FEM ANSYS Classic
 Course in Geometric modeling Modeling Programme for Lesson: Modeling considerations Element Type Real Constants Material Properties Sections Geometry/Modeling WorkPlane & Coordinate systems Keypoints Lines
Course in Geometric modeling Modeling Programme for Lesson: Modeling considerations Element Type Real Constants Material Properties Sections Geometry/Modeling WorkPlane & Coordinate systems Keypoints Lines
Chapter 5 Modeling and Simulation of Mechanism
 Chapter 5 Modeling and Simulation of Mechanism In the present study, KED analysis of four bar planar mechanism using MATLAB program and ANSYS software has been carried out. The analysis has also been carried
Chapter 5 Modeling and Simulation of Mechanism In the present study, KED analysis of four bar planar mechanism using MATLAB program and ANSYS software has been carried out. The analysis has also been carried
ME 442. Marc/Mentat-2011 Tutorial-1
 ME 442 Overview Marc/Mentat-2011 Tutorial-1 The purpose of this tutorial is to introduce the new user to the MSC/MARC/MENTAT finite element program. It should take about one hour to complete. The MARC/MENTAT
ME 442 Overview Marc/Mentat-2011 Tutorial-1 The purpose of this tutorial is to introduce the new user to the MSC/MARC/MENTAT finite element program. It should take about one hour to complete. The MARC/MENTAT
Structural static analysis dome
 Structural static analysis dome Calculate the maximum displacements of the dome depicted in Fig.1 and consisting of two types of beams with the crosssectional area: 0.08m*0.21m ( zig-zags ) and 0.07m*0.16m
Structural static analysis dome Calculate the maximum displacements of the dome depicted in Fig.1 and consisting of two types of beams with the crosssectional area: 0.08m*0.21m ( zig-zags ) and 0.07m*0.16m
LAB MANUAL. Dharmapuri ME6711-SIMULATION AND ANALYSIS. Regulation : Branch : B.E. Mechanical Engineering
 Dharmapuri 636 703 LAB MANUAL Regulation : Branch : 2013 B.E. Mechanical Engineering Year & Semester : IV Year / VII Semester ME6711-SIMULATION AND ANALYSIS Varuvan Vadivelan Institute of Technology, Dharmapuri
Dharmapuri 636 703 LAB MANUAL Regulation : Branch : 2013 B.E. Mechanical Engineering Year & Semester : IV Year / VII Semester ME6711-SIMULATION AND ANALYSIS Varuvan Vadivelan Institute of Technology, Dharmapuri
Chapter 3 Analysis of Original Steel Post
 Chapter 3. Analysis of original steel post 35 Chapter 3 Analysis of Original Steel Post This type of post is a real functioning structure. It is in service throughout the rail network of Spain as part
Chapter 3. Analysis of original steel post 35 Chapter 3 Analysis of Original Steel Post This type of post is a real functioning structure. It is in service throughout the rail network of Spain as part
ANSYS Tutorial Version 6
 ANSYS Tutorial Version 6 Fracture Analysis Consultants, Inc www.fracanalysis.com Revised: November 2011 Table of Contents: 1.0 Introduction... 4 2.0 Tutorial 1: Crack Insertion and Growth in a Cube...
ANSYS Tutorial Version 6 Fracture Analysis Consultants, Inc www.fracanalysis.com Revised: November 2011 Table of Contents: 1.0 Introduction... 4 2.0 Tutorial 1: Crack Insertion and Growth in a Cube...
Tutorial 1: Welded Frame - Problem Description
 Tutorial 1: Welded Frame - Problem Description Introduction In this first tutorial, we will analyse a simple frame: firstly as a welded frame, and secondly as a pin jointed truss. In each case, we will
Tutorial 1: Welded Frame - Problem Description Introduction In this first tutorial, we will analyse a simple frame: firstly as a welded frame, and secondly as a pin jointed truss. In each case, we will
Figure E3-1 A plane struss structure under applied loading. Start MARC Designer. From the main menu, select STATIC STRESS ANALYSIS.
 Example 3 Static Stress Analysis on a Plane Truss Structure Problem Statement: In this exercise, you will use MARC Designer software to carry out a static stress analysis on a simple plane truss structure,
Example 3 Static Stress Analysis on a Plane Truss Structure Problem Statement: In this exercise, you will use MARC Designer software to carry out a static stress analysis on a simple plane truss structure,
Exercise 2: Mesh Resolution, Element Shapes, Basis Functions & Convergence Analyses
 Exercise 2: Mesh Resolution, Element Shapes, Basis Functions & Convergence Analyses Goals In this exercise, we will explore the strengths and weaknesses of different element types (tetrahedrons vs. hexahedrons,
Exercise 2: Mesh Resolution, Element Shapes, Basis Functions & Convergence Analyses Goals In this exercise, we will explore the strengths and weaknesses of different element types (tetrahedrons vs. hexahedrons,
FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS LABORATORY MANUAL ANSYS. Course Instructor: Dr. R.Ganesan
 FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS MECH 460 LABORATORY MANUAL ANSYS Course Instructor: Dr. R.Ganesan Prepared by A. Zabihollah Approved by Dr. R. Ganesan Winter 2007 Table of Contents 1. INTRODUCTION.3 1.1 Starting
FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS MECH 460 LABORATORY MANUAL ANSYS Course Instructor: Dr. R.Ganesan Prepared by A. Zabihollah Approved by Dr. R. Ganesan Winter 2007 Table of Contents 1. INTRODUCTION.3 1.1 Starting
Analysis of Pile Behaviour due to Damped Vibration by Finite Element Method (FEM)
 ISSN 2395-1621 Analysis of Pile Behaviour due to Damped Vibration by Finite Element Method (FEM) #1 L.M.Sardesai, #2 G.A.Kadam 1 sardesaileena@rediffmail.com.com 2 ganeshkadam07@gmail.com #1 Mechanical
ISSN 2395-1621 Analysis of Pile Behaviour due to Damped Vibration by Finite Element Method (FEM) #1 L.M.Sardesai, #2 G.A.Kadam 1 sardesaileena@rediffmail.com.com 2 ganeshkadam07@gmail.com #1 Mechanical
AUTO CAD LAB MANUAL. B. Tech IV Year - I Semester DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING. Aurora s Technological And Research Institute
 AUTO CAD LAB MANUAL B. Tech IV Year - I Semester : NAME ROLL NO : BRANCH : DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Aurora s Technological And Research Institute Parvathapur, Uppal, Hyderabad-98. 1 LIST OF
AUTO CAD LAB MANUAL B. Tech IV Year - I Semester : NAME ROLL NO : BRANCH : DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Aurora s Technological And Research Institute Parvathapur, Uppal, Hyderabad-98. 1 LIST OF
IJMH - International Journal of Management and Humanities ISSN:
 EXPERIMENTAL STRESS ANALYSIS SPUR GEAR USING ANSYS SOFTWARE T.VADIVELU 1 (Department of Mechanical Engineering, JNTU KAKINADA, Kodad, India, vadimay28@gmail.com) Abstract Spur Gear is one of the most important
EXPERIMENTAL STRESS ANALYSIS SPUR GEAR USING ANSYS SOFTWARE T.VADIVELU 1 (Department of Mechanical Engineering, JNTU KAKINADA, Kodad, India, vadimay28@gmail.com) Abstract Spur Gear is one of the most important
Chapter 3. Thermal Tutorial
 Chapter 3. Thermal Tutorial Tutorials> Chapter 3. Thermal Tutorial Solidification of a Casting Problem Specification Problem Description Prepare for a Thermal Analysis Input Geometry Define Materials Generate
Chapter 3. Thermal Tutorial Tutorials> Chapter 3. Thermal Tutorial Solidification of a Casting Problem Specification Problem Description Prepare for a Thermal Analysis Input Geometry Define Materials Generate
ANSYS EXERCISE ANSYS 5.6 Temperature Distribution in a Turbine Blade with Cooling Channels
 I. ANSYS EXERCISE ANSYS 5.6 Temperature Distribution in a Turbine Blade with Cooling Channels Copyright 2001-2005, John R. Baker John R. Baker; phone: 270-534-3114; email: jbaker@engr.uky.edu This exercise
I. ANSYS EXERCISE ANSYS 5.6 Temperature Distribution in a Turbine Blade with Cooling Channels Copyright 2001-2005, John R. Baker John R. Baker; phone: 270-534-3114; email: jbaker@engr.uky.edu This exercise
Geometric Linear Analysis of a Cantilever Beam
 WORKSHOP PROBLEM 2a Geometric Linear Analysis of a Cantilever Beam Objectives: Demonstrate the use of geometric linear analysis. Observe the behavior of the cantilever beam under four increasing load magnitudes.
WORKSHOP PROBLEM 2a Geometric Linear Analysis of a Cantilever Beam Objectives: Demonstrate the use of geometric linear analysis. Observe the behavior of the cantilever beam under four increasing load magnitudes.
Torsional-lateral buckling large displacement analysis with a simple beam using Abaqus 6.10
 Torsional-lateral buckling large displacement analysis with a simple beam using Abaqus 6.10 This document contains an Abaqus tutorial for performing a buckling analysis using the finite element program
Torsional-lateral buckling large displacement analysis with a simple beam using Abaqus 6.10 This document contains an Abaqus tutorial for performing a buckling analysis using the finite element program
Prescribed Deformations
 u Prescribed Deformations Outline 1 Description 2 Finite Element Model 2.1 Geometry Definition 2.2 Properties 2.3 Boundary Conditions 2.3.1 Constraints 2.3.2 Prescribed Deformation 2.4 Loads 2.4.1 Dead
u Prescribed Deformations Outline 1 Description 2 Finite Element Model 2.1 Geometry Definition 2.2 Properties 2.3 Boundary Conditions 2.3.1 Constraints 2.3.2 Prescribed Deformation 2.4 Loads 2.4.1 Dead
Analysis Steps 1. Start Abaqus and choose to create a new model database
 Source: Online tutorials for ABAQUS Problem Description The two dimensional bridge structure, which consists of steel T sections (b=0.25, h=0.25, I=0.125, t f =t w =0.05), is simply supported at its lower
Source: Online tutorials for ABAQUS Problem Description The two dimensional bridge structure, which consists of steel T sections (b=0.25, h=0.25, I=0.125, t f =t w =0.05), is simply supported at its lower
Appendix B: Creating and Analyzing a Simple Model in Abaqus/CAE
 Getting Started with Abaqus: Interactive Edition Appendix B: Creating and Analyzing a Simple Model in Abaqus/CAE The following section is a basic tutorial for the experienced Abaqus user. It leads you
Getting Started with Abaqus: Interactive Edition Appendix B: Creating and Analyzing a Simple Model in Abaqus/CAE The following section is a basic tutorial for the experienced Abaqus user. It leads you
MECH 3130: Mechanics of Materials. Fall Laboratory Manual. Volume II
 MECH 3130: Mechanics of Materials Fall 2015 Laboratory Manual Volume II Instructor Dr. Peter Schwartz Dr. Nels Madsen Lab Teaching Assistants Quang Nguyen: qzn0003@auburn.edu Abhiram Pasumarthy rzp0025@auburn.edu
MECH 3130: Mechanics of Materials Fall 2015 Laboratory Manual Volume II Instructor Dr. Peter Schwartz Dr. Nels Madsen Lab Teaching Assistants Quang Nguyen: qzn0003@auburn.edu Abhiram Pasumarthy rzp0025@auburn.edu
INTRODUCTION TO THE SYSTEM
 INTRODUCTION TO THE SYSTEM 1 INTRODUCTION TO THE SYSTEM 1. Introduction The ANSYS computer program is a large-scale multi-purpose finite element program, which may be used for solving several classes of
INTRODUCTION TO THE SYSTEM 1 INTRODUCTION TO THE SYSTEM 1. Introduction The ANSYS computer program is a large-scale multi-purpose finite element program, which may be used for solving several classes of
CE366/ME380 Finite Elements in Applied Mechanics I Fall 2007
 CE366/ME380 Finite Elements in Applied Mechanics I Fall 2007 FE Project 1: 2D Plane Stress Analysis of acantilever Beam (Due date =TBD) Figure 1 shows a cantilever beam that is subjected to a concentrated
CE366/ME380 Finite Elements in Applied Mechanics I Fall 2007 FE Project 1: 2D Plane Stress Analysis of acantilever Beam (Due date =TBD) Figure 1 shows a cantilever beam that is subjected to a concentrated
Introduction. Co-rotational Concept
 1 2D Co-rotational Truss Formulation by Louie L. Yaw Walla Walla University April 23, 29 key words: geometrically nonlinear analysis, 2d co-rotational truss, corotational truss, variationally consistent,
1 2D Co-rotational Truss Formulation by Louie L. Yaw Walla Walla University April 23, 29 key words: geometrically nonlinear analysis, 2d co-rotational truss, corotational truss, variationally consistent,
Linear Static Analysis of a Spring Element (CELAS)
 Linear Static Analysis of a Spring Element (CELAS) Objectives: Modify nodal analysis and nodal definition coordinate systems to reference a local coordinate system. Define bar elements connected with a
Linear Static Analysis of a Spring Element (CELAS) Objectives: Modify nodal analysis and nodal definition coordinate systems to reference a local coordinate system. Define bar elements connected with a
FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF A PROPPED CANTILEVER BEAM
 FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF A PROPPED CANTILEVER BEAM Problem Description: Instructor: Professor James Sherwood Revised: Venkat Putcha, Dimitri Soteropoulos Programs Utilized: HyperMesh Desktop 12.0, OptiStruct,
FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF A PROPPED CANTILEVER BEAM Problem Description: Instructor: Professor James Sherwood Revised: Venkat Putcha, Dimitri Soteropoulos Programs Utilized: HyperMesh Desktop 12.0, OptiStruct,
Linear Static Analysis for a 3-D Slideline Contact
 WORKSHOP PROBLEM 10a Linear Static Analysis for a 3-D Slideline Contact Objectives: Demonstrate the use of slideline contact. Run an MSC/NASTRAN linear static analysis. Create an accurate deformation plot
WORKSHOP PROBLEM 10a Linear Static Analysis for a 3-D Slideline Contact Objectives: Demonstrate the use of slideline contact. Run an MSC/NASTRAN linear static analysis. Create an accurate deformation plot
COMPUTER AIDED ENGINEERING. Part-1
 COMPUTER AIDED ENGINEERING Course no. 7962 Finite Element Modelling and Simulation Finite Element Modelling and Simulation Part-1 Modeling & Simulation System A system exists and operates in time and space.
COMPUTER AIDED ENGINEERING Course no. 7962 Finite Element Modelling and Simulation Finite Element Modelling and Simulation Part-1 Modeling & Simulation System A system exists and operates in time and space.
ANSYS Workbench Guide
 ANSYS Workbench Guide Introduction This document serves as a step-by-step guide for conducting a Finite Element Analysis (FEA) using ANSYS Workbench. It will cover the use of the simulation package through
ANSYS Workbench Guide Introduction This document serves as a step-by-step guide for conducting a Finite Element Analysis (FEA) using ANSYS Workbench. It will cover the use of the simulation package through
CHAPTER 8 FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS
 If you have any questions about this tutorial, feel free to contact Wenjin Tao (w.tao@mst.edu). CHAPTER 8 FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS Finite Element Analysis (FEA) is a practical application of the Finite
If you have any questions about this tutorial, feel free to contact Wenjin Tao (w.tao@mst.edu). CHAPTER 8 FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS Finite Element Analysis (FEA) is a practical application of the Finite
TWO-DIMENSIONAL PROBLEM OF THE THEORY OF ELASTICITY. INVESTIGATION OF STRESS CONCENTRATION FACTORS.
 Ex_1_2D Plate.doc 1 TWO-DIMENSIONAL PROBLEM OF THE THEORY OF ELASTICITY. INVESTIGATION OF STRESS CONCENTRATION FACTORS. 1. INTRODUCTION Two-dimensional problem of the theory of elasticity is a particular
Ex_1_2D Plate.doc 1 TWO-DIMENSIONAL PROBLEM OF THE THEORY OF ELASTICITY. INVESTIGATION OF STRESS CONCENTRATION FACTORS. 1. INTRODUCTION Two-dimensional problem of the theory of elasticity is a particular
CHAPTER 4. Numerical Models. descriptions of the boundary conditions, element types, validation, and the force
 CHAPTER 4 Numerical Models This chapter presents the development of numerical models for sandwich beams/plates subjected to four-point bending and the hydromat test system. Detailed descriptions of the
CHAPTER 4 Numerical Models This chapter presents the development of numerical models for sandwich beams/plates subjected to four-point bending and the hydromat test system. Detailed descriptions of the
University of Utah ME EN 6510/5510 Introduction to Finite Elements Fall 2005
 University of Utah ME EN 6510/5510 Introduction to Finite Elements Fall 2005 Running ANSYS on the CADE lab workstations CADE Lab Accounts You need to get account information in EMCB 224 from the operators
University of Utah ME EN 6510/5510 Introduction to Finite Elements Fall 2005 Running ANSYS on the CADE lab workstations CADE Lab Accounts You need to get account information in EMCB 224 from the operators
Aufgabe 1: Dreipunktbiegung mit ANSYS Workbench
 Aufgabe 1: Dreipunktbiegung mit ANSYS Workbench Contents Beam under 3-Pt Bending [Balken unter 3-Pkt-Biegung]... 2 Taking advantage of symmetries... 3 Starting and Configuring ANSYS Workbench... 4 A. Pre-Processing:
Aufgabe 1: Dreipunktbiegung mit ANSYS Workbench Contents Beam under 3-Pt Bending [Balken unter 3-Pkt-Biegung]... 2 Taking advantage of symmetries... 3 Starting and Configuring ANSYS Workbench... 4 A. Pre-Processing:
FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF A PROPPED CANTILEVER BEAM
 FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF A PROPPED CANTILEVER BEAM Problem Description: Instructor: Professor James Sherwood Revised: Venkat Putcha, Dimitri Soteropoulos, Sanjay Nainani Programs Utilized: HyperMesh
FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF A PROPPED CANTILEVER BEAM Problem Description: Instructor: Professor James Sherwood Revised: Venkat Putcha, Dimitri Soteropoulos, Sanjay Nainani Programs Utilized: HyperMesh
CAD/CAM LABORATORY MANUAL
 BALAJI INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY AND SCIENCE LAKNEPALLY (V), NARSAMPET (M), WARANGAL-506331 CAD/CAM LABORATORY MANUAL DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING N. KISHORE KUMAR, Assistant professor LIST OF EXPERIMENTS
BALAJI INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY AND SCIENCE LAKNEPALLY (V), NARSAMPET (M), WARANGAL-506331 CAD/CAM LABORATORY MANUAL DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING N. KISHORE KUMAR, Assistant professor LIST OF EXPERIMENTS
CE Advanced Structural Analysis. Lab 4 SAP2000 Plane Elasticity
 Department of Civil & Geological Engineering COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING CE 463.3 Advanced Structural Analysis Lab 4 SAP2000 Plane Elasticity February 27 th, 2013 T.A: Ouafi Saha Professor: M. Boulfiza 1. Rectangular
Department of Civil & Geological Engineering COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING CE 463.3 Advanced Structural Analysis Lab 4 SAP2000 Plane Elasticity February 27 th, 2013 T.A: Ouafi Saha Professor: M. Boulfiza 1. Rectangular
Numerically Generated Tangent Sti ness Matrices for Geometrically Non-Linear Structures
 Numerically Generated Tangent Sti ness Matrices for Geometrically Non-Linear Structures Sonia Lebofsky Athesis submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Master of Science in
Numerically Generated Tangent Sti ness Matrices for Geometrically Non-Linear Structures Sonia Lebofsky Athesis submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Master of Science in
Creating and Analyzing a Simple Model in Abaqus/CAE
 Appendix B: Creating and Analyzing a Simple Model in Abaqus/CAE The following section is a basic tutorial for the experienced Abaqus user. It leads you through the Abaqus/CAE modeling process by visiting
Appendix B: Creating and Analyzing a Simple Model in Abaqus/CAE The following section is a basic tutorial for the experienced Abaqus user. It leads you through the Abaqus/CAE modeling process by visiting
Interface with FE programs
 Page 1 of 47 Interdisciplinary > RFlex > Flexible body Interface Interface with FE programs RecurDyn/RFlex can import FE model from ANSYS, NX/NASTRAN, MSC/NASTRAN and I-DEAS. Figure 1 RecurDyn/RFlex Interface
Page 1 of 47 Interdisciplinary > RFlex > Flexible body Interface Interface with FE programs RecurDyn/RFlex can import FE model from ANSYS, NX/NASTRAN, MSC/NASTRAN and I-DEAS. Figure 1 RecurDyn/RFlex Interface
Truss Bracket. Problem:
 Problem: The truss structure shown above is mounted on the sides of buildings during construction for use as scaffolding for workers. A design team has created a new bracket design (shown below) to use
Problem: The truss structure shown above is mounted on the sides of buildings during construction for use as scaffolding for workers. A design team has created a new bracket design (shown below) to use
Linear Static Analysis of a Plate with Hole
 Fergyanto E. Gunawan (f.e.gunawan@gmail.com) Department of Mechanical Engineering Toyohashi University of Technology Objectives: Modeling a symmetric structure Bottom-up and top-down approaches in modeling
Fergyanto E. Gunawan (f.e.gunawan@gmail.com) Department of Mechanical Engineering Toyohashi University of Technology Objectives: Modeling a symmetric structure Bottom-up and top-down approaches in modeling
General modeling guidelines
 General modeling guidelines Some quotes from industry FEA experts: Finite element analysis is a very powerful tool with which to design products of superior quality. Like all tools, it can be used properly,
General modeling guidelines Some quotes from industry FEA experts: Finite element analysis is a very powerful tool with which to design products of superior quality. Like all tools, it can be used properly,
Tutorial. Spring Foundation
 Page i Preface This tutorial provides an example on how to model a spring foundation using BRIGADE/Plus. Page ii Contents 1 OVERVIEW... 1 2 GEOMETRY... 1 3 MATERIAL AND SECTION PROPERTIES... 2 4 STEP DEFINITION...
Page i Preface This tutorial provides an example on how to model a spring foundation using BRIGADE/Plus. Page ii Contents 1 OVERVIEW... 1 2 GEOMETRY... 1 3 MATERIAL AND SECTION PROPERTIES... 2 4 STEP DEFINITION...
