Bugs in Deployed Software
|
|
|
- Juliana Bond
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Bell: Bit-Encoding Online Memory Leak Detection Michael D. Bond Kathryn S. McKinley University of Texas at Austin Bugs in Deployed Software Humans rely on software for critical tasks Bugs are costly & risky Software more complex More bugs & harder to fix 1
2 Bugs in Deployed Software Humans rely on software for critical tasks Bugs are costly & risky Software more complex More bugs & harder to fix Bugs are a problem in deployed software In-house testing incomplete Performance is critical Focus on space overhead Why do bug tools want so much space? Store lots of info about the program Correlate program locations (sites) & data Ex: DirectedGraph.java:309 Tag each object with one or more sites Alloc site Last-use site Header Field 1 Field 2 Field 3 2
3 Why do bug tools want so much space? Store lots of info about the program Correlate program locations (sites) & data Ex: DirectedGraph.java:309 Tag each object with one or more sites Alloc site Last-use site Header Field 1 Field 2 Field 3 Bug detection applications AVIO tracks last-use site of each object Leak detection reports leaking objects sites [JRockit,.NET Memory Profiler, Purify, SWAT, Valgrind] High space overhead if many small objects Why do bug tools want so much space? Store lots of info about the program Correlate program locations (sites) & data Ex: DirectedGraph.java:309 Tag each object with one or more sites Alloc site Last-use site Header Field 1 Field 2 Field 3 Bug detection applications AVIO tracks last-use site of each object Leak detection reports leaking objects sites SWAT: 75% space [JRockit,.NET Memory Profiler, Purify, SWAT, Valgrind] overhead on twolf High space overhead if many small objects 3
4 How many bits do we need? Site Header Field 1 Field 2 Field 3 How many bits do we need? Site Header Field 1 Field 2 Field 3 32 bits 4
5 How many bits do we need? Site Header Field 1 Field 2 Field 3 32 bits 20 bits if # sites < 1,000, bits for common case (hot sites) How many bits do we need? Site Header Field 1 Field 2 Field 3 32 bits 20 bits if # sites < 1,000, bits for common case (hot sites) 1 bit? 5
6 How many bits do we need? Site Header Field 1 Field 2 Field 3 32 bits 20 bits if # sites < 1,000, bits for common case (hot sites) 1 bit? One bit loses info about site How many bits do we need? ? bit? One bit loses info about site But with many objects 6
7 Bell: Bit-Encoding Leak Location site Stores per-object sites in single bit Reconstructs sites by looking at multiple objects bits Outline Introduction Memory leaks Bell encoding and decoding Leak detection using Bell Related work 7
8 Memory Leaks Memory bugs Memory corruption: dangling refs, buffer overflows Memory leaks Lost objects: unreachable but t freed Useless objects: reachable but t used again Memory Leaks Memory bugs Memory corruption: dangling refs, buffer overflows Memory leaks Lost objects: unreachable but t freed Useless objects: reachable but t used again Managed Languages 80% of new software in Java or C# by 2010 [Gartner] Type safety & GC eliminate many bugs 8
9 Memory Leaks Memory bugs Memory corruption: dangling refs, buffer overflows Memory leaks Lost objects: unreachable but t freed Useless objects: reachable but t used again Managed Languages 80% of new software in Java or C# by 2010 [Gartner] Type safety & GC eliminate many bugs Memory Leaks Leaks Memory occur bugs in practice in managed languages [Cork, Memory JRockit, corruption: JProbe, LeakBot, dangling.net refs, Memory buffer Profiler] overflows Memory leaks Lost objects: unreachable but t freed Useless objects: reachable but t used again Managed Languages 80% of new software in Java or C# by 2010 [Gartner] Type safety & GC eliminate many bugs 9
10 Outline Introduction Memory leaks Bell encoding and decoding Leak detection using Bell Related work Bell s Encoding Function f ( site, object ) = 0 or 1 10
11 Bell s Encoding Function f ( site, object ) = 0 or 1 Color indicates site (ex: allocation site) Bell s Encoding Function f ( site, object ) = 0 or 1 may match f ( site, object ) = 0 or 1 11
12 Bell s Encoding Function f ( site, object ) = 0 or 1 may match f ( site, object ) = 0 or 1 Probability of match is ½ unbiased function How do we find leaking sites? Problem: leaking objects with unkwn allocation sites 12
13 How do we find leaking sites? f ( site, object ) Solution: for each site, see how many objects it matches How do we find leaking sites? f ( site, object ) Site matches all objects it allocated 13
14 How do we find leaking sites? f ( site, object ) Site matches all objects it allocated Site matches ~50% objects it didn t allocate How do we find leaking sites? f ( site, object ) Site matches all objects it allocated matches allocobjs + ½ (leakingobjs - allocobjs) Site matches ~50% objects it didn t allocate 14
15 How do we find leaking sites? f ( site, object ) matches allocobjs + ½ (leakingobjs - allocobjs) allocobjs 2 x matches - leakingobjs How do we find leaking sites? f ( site, object ) matches allocobjs + ½ (leakingobjs - allocobjs) allocobjs 2 x matches 6 - leakingobjs 15
16 How do we find leaking sites? f ( site, object ) matches allocobjs + ½ (leakingobjs - allocobjs) allocobjs 2 x matches 6 - leakingobjs 9 How do we find leaking sites? f ( site, object ) matches allocobjs + ½ (leakingobjs - allocobjs) allocobjs 2 x matches 6-3 leakingobjs 9 16
17 Bell Decoding foreach possible site matches 0 foreach potentially leaking object if f ( site, object ) = object s site bit matches matches + 1 allocobjs = 2 x matches leakingobjs if allocobjs > threshold(leakingobjs) print site is the site for allocobjs objects Bell Decoding foreach possible site matches 0 foreach potentially leaking object if f ( site, object ) = object s site bit matches matches + 1 allocobjs = 2 x matches leakingobjs if allocobjs > threshold(leakingobjs) print site is the site for allocobjs objects 17
18 Bell Decoding foreach possible site matches 0 foreach potentially leaking object if f ( site, object ) = object s site bit matches matches + 1 allocobjs = 2 x matches leakingobjs if allocobjs > threshold(leakingobjs) print site is the site for allocobjs objects Bell Decoding foreach possible site matches 0 foreach potentially leaking object if f ( site, object ) = object s site bit matches matches + 1 allocobjs = 2 x matches leakingobjs if allocobjs > threshold(leakingobjs) print site is the site for allocobjs objects Threshold avoids reporting sites that allocated objects (false positives) 18
19 Bell Decoding foreach possible site matches 0 foreach potentially leaking object if f ( site, object ) = object s site bit matches matches + 1 (false positives) allocobjs = 2 x matches leakingobjs if allocobjs > threshold(leakingobjs) print site is the site for allocobjs objects Threshold avoids reporting sites that allocated objects Decoding misses sites that allocated few objects (false negatives) Bell Decoding foreach possible site matches 0 foreach potentially leaking where site is possible object if f ( site, object ) = object s site bit matches matches + 1 allocobjs = 2 x matches leakingobjs if allocobjs > threshold(leakingobjs) print site is the site for allocobjs objects Dynamic type check narrows possible objects 19
20 Outline Introduction Memory leaks Bell encoding and decoding Leak detection using Bell Related work Leak Detection using Bell Sleigh Bell encodes allocation and last-use sites Stale objects potential leaks [SWAT] Periodic decoding of highly stale objects 20
21 Leak Detection using Bell Sleigh Bell encodes allocation and last-use sites Stale objects potential leaks [SWAT] Periodic decoding of highly stale objects Implementation in Jikes RVM Find leaks in Eclipse and SPEC JBB2000 Leak Detection using Bell o.allocsite o.staleness o.lastusesite 21
22 Leak Detection using Bell o.allocsite o.staleness o.lastusesite No space overhead since four free bits in object header Maintaining Sleigh s Bits // Object allocation: s 1 : o = new MyObject(); o.allocsite o.staleness o.lastusesite 22
23 Maintaining Sleigh s Bits // Object allocation: s 1 : o = new MyObject(); // Instrumentation: o.allocsite = f(s 1, o); o.allocsite o.staleness o.lastusesite Maintaining Sleigh s Bits // Object allocation: s 1 : o = new MyObject(); // Instrumentation: o.allocsite = f(s 1, o); // Object use: s 2 : tmp = o.f; o.allocsite o.staleness o.lastusesite 23
24 Maintaining Sleigh s Bits // Object allocation: s 1 : o = new MyObject(); // Instrumentation: o.allocsite = f(s 1, o); // Object use: s 2 : tmp = o.f; // Instrumentation: o.lastusesite = f(s 2, o); o.staleness = 0; o.allocsite o.staleness o.lastusesite The Encoding Function // Object allocation: s 1 : o = new MyObject(); // Instrumentation: o.allocsite = f(s 1, o); // Object use: s 2 : tmp = o.f; // Instrumentation: o.lastusesite = f(s 2, o); o.staleness = 0; f ( site, object ) := bit 31 ( site х object ) 24
25 The Encoding Function // Object allocation: s 1 : o = new MyObject(); // Instrumentation: o.allocsite = f(s 1, o); // Object use: s 2 : tmp = o.f; // Instrumentation: o.lastusesite = f(s 2, o); o.staleness = 0; f ( site, object ) := bit 31 ( site х object х object ) Object Movement Restrictions // Object allocation: s 1 : o = new MyObject(); // Instrumentation: o.allocsite = f(s 1, o); // Object use: s 2 : tmp = o.f; // Instrumentation: o.lastusesite = f(s 2, o); o.staleness = 0; f ( site, object ) := bit 31 ( site х object х object ) Objects may t move (Mostly) n-moving collector Mark-sweep Generational mark-sweep C and C++ do t move objects 25
26 Sleigh s Time Overhead // Object allocation: s 1 : o = new MyObject(); // Instrumentation: o.allocsite = f(s 1, o); // Object use: s 2 : tmp = o.f; // Instrumentation: o.lastusesite = f(s 2, o); o.staleness = 0; f ( site, object ) := bit 31 ( site х object х object ) DaCapo [Blackburn et al. 06] SPEC JBB2000 SPEC JVM98 Sleigh s Time Overhead // Object allocation: s 1 : o = new MyObject(); // Instrumentation: o.allocsite = f(s 1, o); // Object use: s 2 : tmp = o.f; // Instrumentation: o.lastusesite = f(s 2, o); o.staleness = 0; f ( site, object ) := bit 31 ( site х object х object ) DaCapo [Blackburn et al. 06] SPEC JBB2000 SPEC JVM98 29% time overhead (11% with adaptive profiling) 26
27 Finding and Fixing Leaks Leaks in Eclipse and SPEC JBB2000 Finding and Fixing Leaks Leaks in Eclipse and SPEC JBB2000 Data structures leak 27
28 Finding and Fixing Leaks Leaks in Eclipse and SPEC JBB2000 Data structures leak Finding and Fixing Leaks Leaks in Eclipse and SPEC JBB2000 Data structures leak Most interesting: stale roots 28
29 Finding and Fixing Leaks Leaks in Eclipse and SPEC JBB2000 Data structures leak Most interesting: stale roots many Finding and Fixing Leaks Leaks in Eclipse and SPEC JBB2000 Data structures leak Most interesting: stale roots many few 29
30 Finding and Fixing Leaks Leaks in Eclipse and SPEC JBB2000 Data structures leak Most interesting: stale roots Need significant number of stale data structures Finding and Fixing Leaks Leaks in Eclipse and SPEC JBB2000 Data structures leak Most interesting: stale roots Sleigh s output directly useful for fixing leaks 30
31 Bell Decoding Again foreach possible site matches 0 foreach potentially leaking object where site is possible and object is root of stale data structure if f ( site, object ) = object s site bit matches matches + 1 allocobjs = 2 x matches leakingobjs if allocobjs > threshold(leakingobjs) print site is the site for allocobjs objects Consider roots of stale data structures only Related Work Leak detectors store per-object sites [JRockit,.NET Memory Profiler, Purify, SWAT, Valgrind] Sampling [Jump et al. 04] Trades accuracy for lower overhead (like Bell) Adds some overhead; requires conditional instrumentation No encoding or decoding Communication complexity & information theory 31
32 Summary site Bell encodes sites in a single bit and decodes sites using multiple objects bits Leak detection with low overhead Thank You Questions? 32
Probabilistic Calling Context
 Probabilistic Calling Context Michael D. Bond Kathryn S. McKinley University of Texas at Austin Why Context Sensitivity? Static program location not enough at com.mckoi.db.jdbcserver.jdbcinterface.execquery():213
Probabilistic Calling Context Michael D. Bond Kathryn S. McKinley University of Texas at Austin Why Context Sensitivity? Static program location not enough at com.mckoi.db.jdbcserver.jdbcinterface.execquery():213
Acknowledgements These slides are based on Kathryn McKinley s slides on garbage collection as well as E Christopher Lewis s slides
 Garbage Collection Last time Compiling Object-Oriented Languages Today Motivation behind garbage collection Garbage collection basics Garbage collection performance Specific example of using GC in C++
Garbage Collection Last time Compiling Object-Oriented Languages Today Motivation behind garbage collection Garbage collection basics Garbage collection performance Specific example of using GC in C++
Exploiting the Behavior of Generational Garbage Collector
 Exploiting the Behavior of Generational Garbage Collector I. Introduction Zhe Xu, Jia Zhao Garbage collection is a form of automatic memory management. The garbage collector, attempts to reclaim garbage,
Exploiting the Behavior of Generational Garbage Collector I. Introduction Zhe Xu, Jia Zhao Garbage collection is a form of automatic memory management. The garbage collector, attempts to reclaim garbage,
Garbage Collection (1)
 Garbage Collection (1) Advanced Operating Systems Lecture 7 This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nd/4.0/
Garbage Collection (1) Advanced Operating Systems Lecture 7 This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nd/4.0/
I J C S I E International Science Press
 Vol. 5, No. 2, December 2014, pp. 53-56 I J C S I E International Science Press Tolerating Memory Leaks at Runtime JITENDER SINGH YADAV, MOHIT YADAV, KIRTI AZAD AND JANPREET SINGH JOLLY CSE B-tech 4th
Vol. 5, No. 2, December 2014, pp. 53-56 I J C S I E International Science Press Tolerating Memory Leaks at Runtime JITENDER SINGH YADAV, MOHIT YADAV, KIRTI AZAD AND JANPREET SINGH JOLLY CSE B-tech 4th
Complex, concurrent software. Precision (no false positives) Find real bugs in real executions
 Harry Xu May 2012 Complex, concurrent software Precision (no false positives) Find real bugs in real executions Need to modify JVM (e.g., object layout, GC, or ISA-level code) Need to demonstrate realism
Harry Xu May 2012 Complex, concurrent software Precision (no false positives) Find real bugs in real executions Need to modify JVM (e.g., object layout, GC, or ISA-level code) Need to demonstrate realism
Run-time Environments -Part 3
 Run-time Environments -Part 3 Y.N. Srikant Computer Science and Automation Indian Institute of Science Bangalore 560 012 NPTEL Course on Compiler Design Outline of the Lecture Part 3 What is run-time support?
Run-time Environments -Part 3 Y.N. Srikant Computer Science and Automation Indian Institute of Science Bangalore 560 012 NPTEL Course on Compiler Design Outline of the Lecture Part 3 What is run-time support?
Towards Parallel, Scalable VM Services
 Towards Parallel, Scalable VM Services Kathryn S McKinley The University of Texas at Austin Kathryn McKinley Towards Parallel, Scalable VM Services 1 20 th Century Simplistic Hardware View Faster Processors
Towards Parallel, Scalable VM Services Kathryn S McKinley The University of Texas at Austin Kathryn McKinley Towards Parallel, Scalable VM Services 1 20 th Century Simplistic Hardware View Faster Processors
Tolerating Memory Leaks
 Tolerating Memory Leaks UT Austin Technical Report TR-07-64 December 7, 2007 Michael D. Bond Kathryn S. McKinley Department of Computer Sciences The University of Texas at Austin {mikebond,mckinley}@cs.utexas.edu
Tolerating Memory Leaks UT Austin Technical Report TR-07-64 December 7, 2007 Michael D. Bond Kathryn S. McKinley Department of Computer Sciences The University of Texas at Austin {mikebond,mckinley}@cs.utexas.edu
Efficient Runtime Tracking of Allocation Sites in Java
 Efficient Runtime Tracking of Allocation Sites in Java Rei Odaira, Kazunori Ogata, Kiyokuni Kawachiya, Tamiya Onodera, Toshio Nakatani IBM Research - Tokyo Why Do You Need Allocation Site Information?
Efficient Runtime Tracking of Allocation Sites in Java Rei Odaira, Kazunori Ogata, Kiyokuni Kawachiya, Tamiya Onodera, Toshio Nakatani IBM Research - Tokyo Why Do You Need Allocation Site Information?
GC Assertions: Using the Garbage Collector to Check Heap Properties
 GC Assertions: Using the Garbage Collector to Check Heap Properties Edward E. Aftandilian Samuel Z. Guyer Department of Computer Science Tufts University {eaftan,sguyer}@cs.tufts.edu Abstract This paper
GC Assertions: Using the Garbage Collector to Check Heap Properties Edward E. Aftandilian Samuel Z. Guyer Department of Computer Science Tufts University {eaftan,sguyer}@cs.tufts.edu Abstract This paper
Managed runtimes & garbage collection. CSE 6341 Some slides by Kathryn McKinley
 Managed runtimes & garbage collection CSE 6341 Some slides by Kathryn McKinley 1 Managed runtimes Advantages? Disadvantages? 2 Managed runtimes Advantages? Reliability Security Portability Performance?
Managed runtimes & garbage collection CSE 6341 Some slides by Kathryn McKinley 1 Managed runtimes Advantages? Disadvantages? 2 Managed runtimes Advantages? Reliability Security Portability Performance?
Runtime. The optimized program is ready to run What sorts of facilities are available at runtime
 Runtime The optimized program is ready to run What sorts of facilities are available at runtime Compiler Passes Analysis of input program (front-end) character stream Lexical Analysis token stream Syntactic
Runtime The optimized program is ready to run What sorts of facilities are available at runtime Compiler Passes Analysis of input program (front-end) character stream Lexical Analysis token stream Syntactic
Managed runtimes & garbage collection
 Managed runtimes Advantages? Managed runtimes & garbage collection CSE 631 Some slides by Kathryn McKinley Disadvantages? 1 2 Managed runtimes Portability (& performance) Advantages? Reliability Security
Managed runtimes Advantages? Managed runtimes & garbage collection CSE 631 Some slides by Kathryn McKinley Disadvantages? 1 2 Managed runtimes Portability (& performance) Advantages? Reliability Security
Garbage Collection. Weiyuan Li
 Garbage Collection Weiyuan Li Why GC exactly? - Laziness - Performance - free is not free - combats memory fragmentation - More flame wars Basic concepts - Type Safety - Safe: ML, Java (not really) - Unsafe:
Garbage Collection Weiyuan Li Why GC exactly? - Laziness - Performance - free is not free - combats memory fragmentation - More flame wars Basic concepts - Type Safety - Safe: ML, Java (not really) - Unsafe:
Older-First Garbage Collection in Practice: Evaluation in a Java Virtual Machine
 Older-First Garbage Collection in Practice: Evaluation in a Java Virtual Machine Darko Stefanovic (Univ. of New Mexico) Matthew Hertz (Univ. of Massachusetts) Stephen M. Blackburn (Australian National
Older-First Garbage Collection in Practice: Evaluation in a Java Virtual Machine Darko Stefanovic (Univ. of New Mexico) Matthew Hertz (Univ. of Massachusetts) Stephen M. Blackburn (Australian National
Dynamic Storage Allocation
 6.172 Performance Engineering of Software Systems LECTURE 10 Dynamic Storage Allocation Charles E. Leiserson October 12, 2010 2010 Charles E. Leiserson 1 Stack Allocation Array and pointer A un Allocate
6.172 Performance Engineering of Software Systems LECTURE 10 Dynamic Storage Allocation Charles E. Leiserson October 12, 2010 2010 Charles E. Leiserson 1 Stack Allocation Array and pointer A un Allocate
Cycle Tracing. Presented by: Siddharth Tiwary
 Cycle Tracing Chapter 4, pages 41--56, 2010. From: "Garbage Collection and the Case for High-level Low-level Programming," Daniel Frampton, Doctoral Dissertation, Australian National University. Presented
Cycle Tracing Chapter 4, pages 41--56, 2010. From: "Garbage Collection and the Case for High-level Low-level Programming," Daniel Frampton, Doctoral Dissertation, Australian National University. Presented
Automatic Memory Management
 Automatic Memory Management Why Automatic Memory Management? Storage management is still a hard problem in modern programming Why Automatic Memory Management? Storage management is still a hard problem
Automatic Memory Management Why Automatic Memory Management? Storage management is still a hard problem in modern programming Why Automatic Memory Management? Storage management is still a hard problem
Garbage Collection Algorithms. Ganesh Bikshandi
 Garbage Collection Algorithms Ganesh Bikshandi Announcement MP4 posted Term paper posted Introduction Garbage : discarded or useless material Collection : the act or process of collecting Garbage collection
Garbage Collection Algorithms Ganesh Bikshandi Announcement MP4 posted Term paper posted Introduction Garbage : discarded or useless material Collection : the act or process of collecting Garbage collection
Pause-Less GC for Improving Java Responsiveness. Charlie Gracie IBM Senior Software charliegracie
 Pause-Less GC for Improving Java Responsiveness Charlie Gracie IBM Senior Software Developer charlie_gracie@ca.ibm.com @crgracie charliegracie 1 Important Disclaimers THE INFORMATION CONTAINED IN THIS
Pause-Less GC for Improving Java Responsiveness Charlie Gracie IBM Senior Software Developer charlie_gracie@ca.ibm.com @crgracie charliegracie 1 Important Disclaimers THE INFORMATION CONTAINED IN THIS
Efficient Context Sensitivity for Dynamic Analyses via Calling Context Uptrees and Customized Memory Management
 to Reuse * * Evaluated * OOPSLA * Artifact * AEC Efficient Context Sensitivity for Dynamic Analyses via Calling Context Uptrees and Customized Memory Management Jipeng Huang Michael D. Bond Ohio State
to Reuse * * Evaluated * OOPSLA * Artifact * AEC Efficient Context Sensitivity for Dynamic Analyses via Calling Context Uptrees and Customized Memory Management Jipeng Huang Michael D. Bond Ohio State
Book keeping. Will post HW5 tonight. OK to work in pairs. Midterm review next Wednesday
 Garbage Collection Book keeping Will post HW5 tonight Will test file reading and writing Also parsing the stuff you reads and looking for some patterns On the long side But you ll have two weeks to do
Garbage Collection Book keeping Will post HW5 tonight Will test file reading and writing Also parsing the stuff you reads and looking for some patterns On the long side But you ll have two weeks to do
Dynamic Memory Allocation: Advanced Concepts
 Dynamic Memory Allocation: Advanced Concepts Keeping Track of Free Blocks Method 1: Implicit list using length links all blocks 5 4 6 Method : Explicit list among the free blocks using pointers 5 4 6 Kai
Dynamic Memory Allocation: Advanced Concepts Keeping Track of Free Blocks Method 1: Implicit list using length links all blocks 5 4 6 Method : Explicit list among the free blocks using pointers 5 4 6 Kai
Free-Me: A Static Analysis for Automatic Individual Object Reclamation
 Free-Me: A Static Analysis for Automatic Individual Object Reclamation Samuel Z. Guyer, Kathryn McKinley, Daniel Frampton Presented by: Jason VanFickell Thanks to Dimitris Prountzos for slides adapted
Free-Me: A Static Analysis for Automatic Individual Object Reclamation Samuel Z. Guyer, Kathryn McKinley, Daniel Frampton Presented by: Jason VanFickell Thanks to Dimitris Prountzos for slides adapted
Dynamic Memory Allocation
 Dynamic Memory Allocation CS61, Lecture 11 Prof. Stephen Chong October 6, 2011 Announcements 1/2 Reminder: No section on Monday Monday sections have been rescheduled See website for details Please attend
Dynamic Memory Allocation CS61, Lecture 11 Prof. Stephen Chong October 6, 2011 Announcements 1/2 Reminder: No section on Monday Monday sections have been rescheduled See website for details Please attend
Advanced Programming & C++ Language
 Advanced Programming & C++ Language ~6~ Introduction to Memory Management Ariel University 2018 Dr. Miri (Kopel) Ben-Nissan Stack & Heap 2 The memory a program uses is typically divided into four different
Advanced Programming & C++ Language ~6~ Introduction to Memory Management Ariel University 2018 Dr. Miri (Kopel) Ben-Nissan Stack & Heap 2 The memory a program uses is typically divided into four different
Compiler Construction
 Compiler Construction Lecture 18: Code Generation V (Implementation of Dynamic Data Structures) Thomas Noll Lehrstuhl für Informatik 2 (Software Modeling and Verification) noll@cs.rwth-aachen.de http://moves.rwth-aachen.de/teaching/ss-14/cc14/
Compiler Construction Lecture 18: Code Generation V (Implementation of Dynamic Data Structures) Thomas Noll Lehrstuhl für Informatik 2 (Software Modeling and Verification) noll@cs.rwth-aachen.de http://moves.rwth-aachen.de/teaching/ss-14/cc14/
Lecture 15 Garbage Collection
 Lecture 15 Garbage Collection I. Introduction to GC -- Reference Counting -- Basic Trace-Based GC II. Copying Collectors III. Break Up GC in Time (Incremental) IV. Break Up GC in Space (Partial) Readings:
Lecture 15 Garbage Collection I. Introduction to GC -- Reference Counting -- Basic Trace-Based GC II. Copying Collectors III. Break Up GC in Time (Incremental) IV. Break Up GC in Space (Partial) Readings:
Program Calling Context. Motivation
 Program alling ontext Motivation alling context enhances program understanding and dynamic analyses by providing a rich representation of program location ollecting calling context can be expensive The
Program alling ontext Motivation alling context enhances program understanding and dynamic analyses by providing a rich representation of program location ollecting calling context can be expensive The
Hard Real-Time Garbage Collection in Java Virtual Machines
 Hard Real-Time Garbage Collection in Java Virtual Machines... towards unrestricted real-time programming in Java Fridtjof Siebert, IPD, University of Karlsruhe 1 Jamaica Systems Structure Exisiting GC
Hard Real-Time Garbage Collection in Java Virtual Machines... towards unrestricted real-time programming in Java Fridtjof Siebert, IPD, University of Karlsruhe 1 Jamaica Systems Structure Exisiting GC
Garbage Collection. Steven R. Bagley
 Garbage Collection Steven R. Bagley Reference Counting Counts number of pointers to an Object deleted when the count hits zero Eager deleted as soon as it is finished with Problem: Circular references
Garbage Collection Steven R. Bagley Reference Counting Counts number of pointers to an Object deleted when the count hits zero Eager deleted as soon as it is finished with Problem: Circular references
How s the Parallel Computing Revolution Going? Towards Parallel, Scalable VM Services
 How s the Parallel Computing Revolution Going? Towards Parallel, Scalable VM Services Kathryn S McKinley The University of Texas at Austin Kathryn McKinley Towards Parallel, Scalable VM Services 1 20 th
How s the Parallel Computing Revolution Going? Towards Parallel, Scalable VM Services Kathryn S McKinley The University of Texas at Austin Kathryn McKinley Towards Parallel, Scalable VM Services 1 20 th
Leak Pruning. 1. Introduction. Abstract. Department of Computer Sciences The University of Texas at Austin
 Leak Pruning Michael D. Bond Kathryn S. McKinley Department of Computer Sciences The University of Texas at Austin {mikebond,mckinley}@cs.utexas.edu Abstract Managed languages improve programmer productivity
Leak Pruning Michael D. Bond Kathryn S. McKinley Department of Computer Sciences The University of Texas at Austin {mikebond,mckinley}@cs.utexas.edu Abstract Managed languages improve programmer productivity
PERFBLOWER: Quickly Detecting Memory-Related Performance Problems via Amplification
 PERFBLOWER: Quickly Detecting Memory-Related Performance Problems via Amplification Lu Fang 1, Liang Dou 2, and Guoqing Xu 1 1 University of California, Irvine, USA {lfang3, guoqingx}@ics.uci.edu 2 East
PERFBLOWER: Quickly Detecting Memory-Related Performance Problems via Amplification Lu Fang 1, Liang Dou 2, and Guoqing Xu 1 1 University of California, Irvine, USA {lfang3, guoqingx}@ics.uci.edu 2 East
A program execution is memory safe so long as memory access errors never occur:
 A program execution is memory safe so long as memory access errors never occur: Buffer overflows, null pointer dereference, use after free, use of uninitialized memory, illegal free Memory safety categories
A program execution is memory safe so long as memory access errors never occur: Buffer overflows, null pointer dereference, use after free, use of uninitialized memory, illegal free Memory safety categories
Automatic Garbage Collection
 Automatic Garbage Collection Announcements: PS6 due Monday 12/6 at 11:59PM Final exam on Thursday 12/16 o PS6 tournament and review session that week Garbage In OCaml programs (and in most other programming
Automatic Garbage Collection Announcements: PS6 due Monday 12/6 at 11:59PM Final exam on Thursday 12/16 o PS6 tournament and review session that week Garbage In OCaml programs (and in most other programming
Hybrid Static-Dynamic Analysis for Statically Bounded Region Serializability
 Hybrid Static-Dynamic Analysis for Statically Bounded Region Serializability Aritra Sengupta, Swarnendu Biswas, Minjia Zhang, Michael D. Bond and Milind Kulkarni ASPLOS 2015, ISTANBUL, TURKEY Programming
Hybrid Static-Dynamic Analysis for Statically Bounded Region Serializability Aritra Sengupta, Swarnendu Biswas, Minjia Zhang, Michael D. Bond and Milind Kulkarni ASPLOS 2015, ISTANBUL, TURKEY Programming
Systems software design. Software build configurations; Debugging, profiling & Quality Assurance tools
 Systems software design Software build configurations; Debugging, profiling & Quality Assurance tools Who are we? Krzysztof Kąkol Software Developer Jarosław Świniarski Software Developer Presentation
Systems software design Software build configurations; Debugging, profiling & Quality Assurance tools Who are we? Krzysztof Kąkol Software Developer Jarosław Świniarski Software Developer Presentation
One-Slide Summary. Lecture Outine. Automatic Memory Management #1. Why Automatic Memory Management? Garbage Collection.
 Automatic Memory Management #1 One-Slide Summary An automatic memory management system deallocates objects when they are no longer used and reclaims their storage space. We must be conservative and only
Automatic Memory Management #1 One-Slide Summary An automatic memory management system deallocates objects when they are no longer used and reclaims their storage space. We must be conservative and only
Compiler Construction
 Compiler Construction Thomas Noll Software Modeling and Verification Group RWTH Aachen University https://moves.rwth-aachen.de/teaching/ss-16/cc/ Recap: Static Data Structures Outline of Lecture 18 Recap:
Compiler Construction Thomas Noll Software Modeling and Verification Group RWTH Aachen University https://moves.rwth-aachen.de/teaching/ss-16/cc/ Recap: Static Data Structures Outline of Lecture 18 Recap:
FastTrack: Efficient and Precise Dynamic Race Detection (+ identifying destructive races)
 FastTrack: Efficient and Precise Dynamic Race Detection (+ identifying destructive races) Cormac Flanagan UC Santa Cruz Stephen Freund Williams College Multithreading and Multicore! Multithreaded programming
FastTrack: Efficient and Precise Dynamic Race Detection (+ identifying destructive races) Cormac Flanagan UC Santa Cruz Stephen Freund Williams College Multithreading and Multicore! Multithreaded programming
Agenda. CSE P 501 Compilers. Java Implementation Overview. JVM Architecture. JVM Runtime Data Areas (1) JVM Data Types. CSE P 501 Su04 T-1
 Agenda CSE P 501 Compilers Java Implementation JVMs, JITs &c Hal Perkins Summer 2004 Java virtual machine architecture.class files Class loading Execution engines Interpreters & JITs various strategies
Agenda CSE P 501 Compilers Java Implementation JVMs, JITs &c Hal Perkins Summer 2004 Java virtual machine architecture.class files Class loading Execution engines Interpreters & JITs various strategies
Garbage Collection (2) Advanced Operating Systems Lecture 9
 Garbage Collection (2) Advanced Operating Systems Lecture 9 Lecture Outline Garbage collection Generational algorithms Incremental algorithms Real-time garbage collection Practical factors 2 Object Lifetimes
Garbage Collection (2) Advanced Operating Systems Lecture 9 Lecture Outline Garbage collection Generational algorithms Incremental algorithms Real-time garbage collection Practical factors 2 Object Lifetimes
18-642: Code Style for Compilers
 18-642: Code Style for Compilers 9/25/2017 1 Anti-Patterns: Coding Style: Language Use Code compiles with warnings Warnings are turned off or over-ridden Insufficient warning level set Language safety
18-642: Code Style for Compilers 9/25/2017 1 Anti-Patterns: Coding Style: Language Use Code compiles with warnings Warnings are turned off or over-ridden Insufficient warning level set Language safety
MEMORY MANAGEMENT HEAP, STACK AND GARBAGE COLLECTION
 MEMORY MANAGEMENT HEAP, STACK AND GARBAGE COLLECTION 2 1. What is the Heap Size: 2 2. What is Garbage Collection: 3 3. How are Java objects stored in memory? 3 4. What is the difference between stack and
MEMORY MANAGEMENT HEAP, STACK AND GARBAGE COLLECTION 2 1. What is the Heap Size: 2 2. What is Garbage Collection: 3 3. How are Java objects stored in memory? 3 4. What is the difference between stack and
Ulterior Reference Counting: Fast Garbage Collection without a Long Wait
 Ulterior Reference Counting: Fast Garbage Collection without a Long Wait ABSTRACT Stephen M Blackburn Department of Computer Science Australian National University Canberra, ACT, 000, Australia Steve.Blackburn@anu.edu.au
Ulterior Reference Counting: Fast Garbage Collection without a Long Wait ABSTRACT Stephen M Blackburn Department of Computer Science Australian National University Canberra, ACT, 000, Australia Steve.Blackburn@anu.edu.au
Oracle Developer Studio Code Analyzer
 Oracle Developer Studio Code Analyzer The Oracle Developer Studio Code Analyzer ensures application reliability and security by detecting application vulnerabilities, including memory leaks and memory
Oracle Developer Studio Code Analyzer The Oracle Developer Studio Code Analyzer ensures application reliability and security by detecting application vulnerabilities, including memory leaks and memory
Legato: Bounded Region Serializability Using Commodity Hardware Transactional Memory. Aritra Sengupta Man Cao Michael D. Bond and Milind Kulkarni
 Legato: Bounded Region Serializability Using Commodity Hardware al Memory Aritra Sengupta Man Cao Michael D. Bond and Milind Kulkarni 1 Programming Language Semantics? Data Races C++ no guarantee of semantics
Legato: Bounded Region Serializability Using Commodity Hardware al Memory Aritra Sengupta Man Cao Michael D. Bond and Milind Kulkarni 1 Programming Language Semantics? Data Races C++ no guarantee of semantics
Garbage Collection Techniques
 Garbage Collection Techniques Michael Jantz COSC 340: Software Engineering 1 Memory Management Memory Management Recognizing when allocated objects are no longer needed Deallocating (freeing) the memory
Garbage Collection Techniques Michael Jantz COSC 340: Software Engineering 1 Memory Management Memory Management Recognizing when allocated objects are no longer needed Deallocating (freeing) the memory
Simple Overflow. #include <stdio.h> int main(void){ unsigned int num = 0xffffffff;
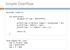 Simple Overflow 1 #include int main(void){ unsigned int num = 0xffffffff; printf("num is %d bits long\n", sizeof(num) * 8); printf("num = 0x%x\n", num); printf("num + 1 = 0x%x\n", num + 1); }
Simple Overflow 1 #include int main(void){ unsigned int num = 0xffffffff; printf("num is %d bits long\n", sizeof(num) * 8); printf("num = 0x%x\n", num); printf("num + 1 = 0x%x\n", num + 1); }
ACM Trivia Bowl. Thursday April 3 rd (two days from now) 7pm OLS 001 Snacks and drinks provided All are welcome! I will be there.
 #1 ACM Trivia Bowl Thursday April 3 rd (two days from now) 7pm OLS 001 Snacks and drinks provided All are welcome! I will be there. If you are in one of the top three teams, I will give you one point of
#1 ACM Trivia Bowl Thursday April 3 rd (two days from now) 7pm OLS 001 Snacks and drinks provided All are welcome! I will be there. If you are in one of the top three teams, I will give you one point of
Myths and Realities: The Performance Impact of Garbage Collection
 Myths and Realities: The Performance Impact of Garbage Collection Tapasya Patki February 17, 2011 1 Motivation Automatic memory management has numerous software engineering benefits from the developer
Myths and Realities: The Performance Impact of Garbage Collection Tapasya Patki February 17, 2011 1 Motivation Automatic memory management has numerous software engineering benefits from the developer
Verifying a Concurrent Garbage Collector using a Rely-Guarantee Methodology
 Verifying a Concurrent Garbage Collector using a Rely-Guarantee Methodology Yannick Zakowski David Cachera Delphine Demange Gustavo Petri David Pichardie Suresh Jagannathan Jan Vitek Automatic memory management
Verifying a Concurrent Garbage Collector using a Rely-Guarantee Methodology Yannick Zakowski David Cachera Delphine Demange Gustavo Petri David Pichardie Suresh Jagannathan Jan Vitek Automatic memory management
HeapMD: Identifying Heap-based Bugs using Anomaly Detection
 HeapMD: Identifying Heap-based Bugs using Anomaly Detection Trishul M. Chilimbi Microsoft Research Redmond, WA trishulc@microsoft.com Vinod Ganapathy University of Wisconsin Madison, WI vg@cs.wisc.edu
HeapMD: Identifying Heap-based Bugs using Anomaly Detection Trishul M. Chilimbi Microsoft Research Redmond, WA trishulc@microsoft.com Vinod Ganapathy University of Wisconsin Madison, WI vg@cs.wisc.edu
Programming Language Implementation
 A Practical Introduction to Programming Language Implementation 2014: Week 10 Garbage Collection College of Information Science and Engineering Ritsumeikan University 1 review of last week s topics dynamic
A Practical Introduction to Programming Language Implementation 2014: Week 10 Garbage Collection College of Information Science and Engineering Ritsumeikan University 1 review of last week s topics dynamic
Adaptive Optimization using Hardware Performance Monitors. Master Thesis by Mathias Payer
 Adaptive Optimization using Hardware Performance Monitors Master Thesis by Mathias Payer Supervising Professor: Thomas Gross Supervising Assistant: Florian Schneider Adaptive Optimization using HPM 1/21
Adaptive Optimization using Hardware Performance Monitors Master Thesis by Mathias Payer Supervising Professor: Thomas Gross Supervising Assistant: Florian Schneider Adaptive Optimization using HPM 1/21
Garbage Collection. Akim D le, Etienne Renault, Roland Levillain. May 15, CCMP2 Garbage Collection May 15, / 35
 Garbage Collection Akim Demaille, Etienne Renault, Roland Levillain May 15, 2017 CCMP2 Garbage Collection May 15, 2017 1 / 35 Table of contents 1 Motivations and Definitions 2 Reference Counting Garbage
Garbage Collection Akim Demaille, Etienne Renault, Roland Levillain May 15, 2017 CCMP2 Garbage Collection May 15, 2017 1 / 35 Table of contents 1 Motivations and Definitions 2 Reference Counting Garbage
Opera&ng Systems CMPSCI 377 Garbage Collec&on. Emery Berger and Mark Corner University of Massachuse9s Amherst
 Opera&ng Systems CMPSCI 377 Garbage Collec&on Emery Berger and Mark Corner University of Massachuse9s Amherst Ques
Opera&ng Systems CMPSCI 377 Garbage Collec&on Emery Berger and Mark Corner University of Massachuse9s Amherst Ques
Causes of Software Failures
 Causes of Software Failures Hardware Faults Permanent faults, e.g., wear-and-tear component Transient faults, e.g., bit flips due to radiation Software Faults (Bugs) (40% failures) Nondeterministic bugs,
Causes of Software Failures Hardware Faults Permanent faults, e.g., wear-and-tear component Transient faults, e.g., bit flips due to radiation Software Faults (Bugs) (40% failures) Nondeterministic bugs,
Dynamic Memory Allocation II October 22, 2008
 15-213 Dynamic Memory Allocation II October 22, 2008 Topics Explicit doubly-linked free lists Segregated free lists Garbage collection Review of pointers Memory-related perils and pitfalls class18.ppt
15-213 Dynamic Memory Allocation II October 22, 2008 Topics Explicit doubly-linked free lists Segregated free lists Garbage collection Review of pointers Memory-related perils and pitfalls class18.ppt
Dynamic Memory Alloca/on: Advanced Concepts
 Dynamic Memory Alloca/on: Advanced Concepts CS 485 Systems Programming Fall 2015 Instructor: James Griffioen Adapted from slides by R. Bryant and D. O Hallaron (hip://csapp.cs.cmu.edu/public/instructors.html)
Dynamic Memory Alloca/on: Advanced Concepts CS 485 Systems Programming Fall 2015 Instructor: James Griffioen Adapted from slides by R. Bryant and D. O Hallaron (hip://csapp.cs.cmu.edu/public/instructors.html)
Method-Level Phase Behavior in Java Workloads
 Method-Level Phase Behavior in Java Workloads Andy Georges, Dries Buytaert, Lieven Eeckhout and Koen De Bosschere Ghent University Presented by Bruno Dufour dufour@cs.rutgers.edu Rutgers University DCS
Method-Level Phase Behavior in Java Workloads Andy Georges, Dries Buytaert, Lieven Eeckhout and Koen De Bosschere Ghent University Presented by Bruno Dufour dufour@cs.rutgers.edu Rutgers University DCS
SoK: Eternal War in Memory
 SoK: Eternal War in Memory László Szekeres, Mathias Payer, Tao Wei, Dawn Song Presenter: Wajih 11/7/2017 Some slides are taken from original S&P presentation 1 What is SoK paper? Systematization of Knowledge
SoK: Eternal War in Memory László Szekeres, Mathias Payer, Tao Wei, Dawn Song Presenter: Wajih 11/7/2017 Some slides are taken from original S&P presentation 1 What is SoK paper? Systematization of Knowledge
Program Analysis. Uday Khedker. ( uday) Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay
 Program Analysis (www.cse.iitb.ac.in/ uday) Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay January 2008 Part 1 About These Slides CS 618 Program Analysis: About
Program Analysis (www.cse.iitb.ac.in/ uday) Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay January 2008 Part 1 About These Slides CS 618 Program Analysis: About
Vertical Profiling: Understanding the Behavior of Object-Oriented Applications
 Vertical Profiling: Understanding the Behavior of Object-Oriented Applications Matthias Hauswirth, Amer Diwan University of Colorado at Boulder Peter F. Sweeney, Michael Hind IBM Thomas J. Watson Research
Vertical Profiling: Understanding the Behavior of Object-Oriented Applications Matthias Hauswirth, Amer Diwan University of Colorado at Boulder Peter F. Sweeney, Michael Hind IBM Thomas J. Watson Research
Run-time Environments - 3
 Run-time Environments - 3 Y.N. Srikant Computer Science and Automation Indian Institute of Science Bangalore 560 012 NPTEL Course on Principles of Compiler Design Outline of the Lecture n What is run-time
Run-time Environments - 3 Y.N. Srikant Computer Science and Automation Indian Institute of Science Bangalore 560 012 NPTEL Course on Principles of Compiler Design Outline of the Lecture n What is run-time
Name, Scope, and Binding. Outline [1]
![Name, Scope, and Binding. Outline [1] Name, Scope, and Binding. Outline [1]](/thumbs/87/96221326.jpg) Name, Scope, and Binding In Text: Chapter 3 Outline [1] Variable Binding Storage bindings and lifetime Type bindings Type Checking Scope Lifetime vs. Scope Referencing Environments N. Meng, S. Arthur 2
Name, Scope, and Binding In Text: Chapter 3 Outline [1] Variable Binding Storage bindings and lifetime Type bindings Type Checking Scope Lifetime vs. Scope Referencing Environments N. Meng, S. Arthur 2
Quantifying the Performance of Garbage Collection vs. Explicit Memory Management
 Quantifying the Performance of Garbage Collection vs. Explicit Memory Management Matthew Hertz Canisius College Emery Berger University of Massachusetts Amherst Explicit Memory Management malloc / new
Quantifying the Performance of Garbage Collection vs. Explicit Memory Management Matthew Hertz Canisius College Emery Berger University of Massachusetts Amherst Explicit Memory Management malloc / new
Greater complexity & reliance
 Tolerating Memory Leaks Michael. ond Kathryn S. McKinley ugs in eployed Software eployed software fails ifferent environment and inputs different behaviors Greater complexity & reliance 1 ugs in eployed
Tolerating Memory Leaks Michael. ond Kathryn S. McKinley ugs in eployed Software eployed software fails ifferent environment and inputs different behaviors Greater complexity & reliance 1 ugs in eployed
Rethinking the Memory Hierarchy for Modern Languages. Po-An Tsai, Yee Ling Gan, and Daniel Sanchez
 Rethinking the Memory Hierarchy for Modern Languages Po-An Tsai, Yee Ling Gan, and Daniel Sanchez Memory systems expose an inexpressive interface 2 Memory systems expose an inexpressive interface Flat
Rethinking the Memory Hierarchy for Modern Languages Po-An Tsai, Yee Ling Gan, and Daniel Sanchez Memory systems expose an inexpressive interface 2 Memory systems expose an inexpressive interface Flat
Motivation for Dynamic Memory. Dynamic Memory Allocation. Stack Organization. Stack Discussion. Questions answered in this lecture:
 CS 537 Introduction to Operating Systems UNIVERSITY of WISCONSIN-MADISON Computer Sciences Department Dynamic Memory Allocation Questions answered in this lecture: When is a stack appropriate? When is
CS 537 Introduction to Operating Systems UNIVERSITY of WISCONSIN-MADISON Computer Sciences Department Dynamic Memory Allocation Questions answered in this lecture: When is a stack appropriate? When is
Performance of Non-Moving Garbage Collectors. Hans-J. Boehm HP Labs
 Performance of Non-Moving Garbage Collectors Hans-J. Boehm HP Labs Why Use (Tracing) Garbage Collection to Reclaim Program Memory? Increasingly common Java, C#, Scheme, Python, ML,... gcc, w3m, emacs,
Performance of Non-Moving Garbage Collectors Hans-J. Boehm HP Labs Why Use (Tracing) Garbage Collection to Reclaim Program Memory? Increasingly common Java, C#, Scheme, Python, ML,... gcc, w3m, emacs,
TI2725-C, C programming lab, course
 Valgrind tutorial Valgrind is a tool which can find memory leaks in your programs, such as buffer overflows and bad memory management. This document will show per example how Valgrind responds to buggy
Valgrind tutorial Valgrind is a tool which can find memory leaks in your programs, such as buffer overflows and bad memory management. This document will show per example how Valgrind responds to buggy
CS527 Software Security
 Security Policies Purdue University, Spring 2018 Security Policies A policy is a deliberate system of principles to guide decisions and achieve rational outcomes. A policy is a statement of intent, and
Security Policies Purdue University, Spring 2018 Security Policies A policy is a deliberate system of principles to guide decisions and achieve rational outcomes. A policy is a statement of intent, and
Software Security II: Memory Errors - Attacks & Defenses
 1 Software Security II: Memory Errors - Attacks & Defenses Chengyu Song Slides modified from Dawn Song 2 Administrivia Lab1 Writeup 3 Buffer overflow Out-of-bound memory writes (mostly sequential) Allow
1 Software Security II: Memory Errors - Attacks & Defenses Chengyu Song Slides modified from Dawn Song 2 Administrivia Lab1 Writeup 3 Buffer overflow Out-of-bound memory writes (mostly sequential) Allow
Implementation Garbage Collection
 CITS 3242 Programming Paradigms Part IV: Advanced Topics Topic 19: Implementation Garbage Collection Most languages in the functional, logic, and object-oriented paradigms include some form of automatic
CITS 3242 Programming Paradigms Part IV: Advanced Topics Topic 19: Implementation Garbage Collection Most languages in the functional, logic, and object-oriented paradigms include some form of automatic
Honours/Master/PhD Thesis Projects Supervised by Dr. Yulei Sui
 Honours/Master/PhD Thesis Projects Supervised by Dr. Yulei Sui Projects 1 Information flow analysis for mobile applications 2 2 Machine-learning-guide typestate analysis for UAF vulnerabilities 3 3 Preventing
Honours/Master/PhD Thesis Projects Supervised by Dr. Yulei Sui Projects 1 Information flow analysis for mobile applications 2 2 Machine-learning-guide typestate analysis for UAF vulnerabilities 3 3 Preventing
Static Analysis and Bugfinding
 Static Analysis and Bugfinding Alex Kantchelian 09/12/2011 Last week we talked about runtime checking methods: tools for detecting vulnerabilities being exploited in deployment. So far, these tools have
Static Analysis and Bugfinding Alex Kantchelian 09/12/2011 Last week we talked about runtime checking methods: tools for detecting vulnerabilities being exploited in deployment. So far, these tools have
Towards Garbage Collection Modeling
 Towards Garbage Collection Modeling Peter Libič Petr Tůma Department of Distributed and Dependable Systems Faculty of Mathematics and Physics, Charles University Malostranské nám. 25, 118 00 Prague, Czech
Towards Garbage Collection Modeling Peter Libič Petr Tůma Department of Distributed and Dependable Systems Faculty of Mathematics and Physics, Charles University Malostranské nám. 25, 118 00 Prague, Czech
CS61C : Machine Structures
 inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c/su06 CS61C : Machine Structures Lecture #6: Memory Management CS 61C L06 Memory Management (1) 2006-07-05 Andy Carle Memory Management (1/2) Variable declaration allocates
inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c/su06 CS61C : Machine Structures Lecture #6: Memory Management CS 61C L06 Memory Management (1) 2006-07-05 Andy Carle Memory Management (1/2) Variable declaration allocates
CS-527 Software Security
 CS-527 Software Security Memory Safety Asst. Prof. Mathias Payer Department of Computer Science Purdue University TA: Kyriakos Ispoglou https://nebelwelt.net/teaching/17-527-softsec/ Spring 2017 Eternal
CS-527 Software Security Memory Safety Asst. Prof. Mathias Payer Department of Computer Science Purdue University TA: Kyriakos Ispoglou https://nebelwelt.net/teaching/17-527-softsec/ Spring 2017 Eternal
Write Barrier Removal by Static Analysis
 Write Barrier Removal by Static Analysis Karen Zee Martin Rinard MIT Laboratory for Computer Science Research Goal Use static program analysis to identify and remove unnecessary write barriers in programs
Write Barrier Removal by Static Analysis Karen Zee Martin Rinard MIT Laboratory for Computer Science Research Goal Use static program analysis to identify and remove unnecessary write barriers in programs
Memory Leak Detection with Context Awareness
 Memory Leak Detection with Context Awareness Woosup Lim Quality Assurance Division Altibase Ltd. Seoul 152-790, Korea woosup.lim@gmail.com Seongsoo Park Department of Computer Engineering Sungkyunkwan
Memory Leak Detection with Context Awareness Woosup Lim Quality Assurance Division Altibase Ltd. Seoul 152-790, Korea woosup.lim@gmail.com Seongsoo Park Department of Computer Engineering Sungkyunkwan
6.172 Performance Engineering of Software Systems Spring Lecture 9. P after. Figure 1: A diagram of the stack (Image by MIT OpenCourseWare.
 6.172 Performance Engineering of Software Systems Spring 2009 Lecture 9 MIT OpenCourseWare Dynamic Storage Allocation Stack allocation: LIFO (last-in-first-out) Array and pointer A used unused P before
6.172 Performance Engineering of Software Systems Spring 2009 Lecture 9 MIT OpenCourseWare Dynamic Storage Allocation Stack allocation: LIFO (last-in-first-out) Array and pointer A used unused P before
CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages
 CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages Memory Management and Garbage Collection CMSC 330 Spring 2017 1 Memory Attributes Memory to store data in programming languages has the following lifecycle
CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages Memory Management and Garbage Collection CMSC 330 Spring 2017 1 Memory Attributes Memory to store data in programming languages has the following lifecycle
Lightweight Data Race Detection for Production Runs
 Lightweight Data Race Detection for Production Runs Swarnendu Biswas, UT Austin Man Cao, Ohio State University Minjia Zhang, Microsoft Research Michael D. Bond, Ohio State University Benjamin P. Wood,
Lightweight Data Race Detection for Production Runs Swarnendu Biswas, UT Austin Man Cao, Ohio State University Minjia Zhang, Microsoft Research Michael D. Bond, Ohio State University Benjamin P. Wood,
<Insert Picture Here>
 1 2010-0237 The Maxine Inspector: A Specialized Tool for VM Development, Santa Clara, CA Michael L. Van De Vanter Researcher, Oracle Sun Labs The Maxine Project at Oracle Sun Labs:
1 2010-0237 The Maxine Inspector: A Specialized Tool for VM Development, Santa Clara, CA Michael L. Van De Vanter Researcher, Oracle Sun Labs The Maxine Project at Oracle Sun Labs:
Glacier: A Garbage Collection Simulation System
 Glacier: A Garbage Collection Simulation System Bruno Dufour Sable Research Group McGill University Glacier: A Garbage Collection Simulation System p.1/19 Outline Introduction Objectives & motivation Requirements
Glacier: A Garbage Collection Simulation System Bruno Dufour Sable Research Group McGill University Glacier: A Garbage Collection Simulation System p.1/19 Outline Introduction Objectives & motivation Requirements
Plug: Automatically Tolerating Memory Leaks in C and C++ Applications
 Plug: Automatically Tolerating Memory Leaks in C and C++ Applications Gene Novark Emery D. Berger Dept. of Computer Science University of Massachusetts Amherst Amherst, MA 01003 gnovark@cs.umass.edu, emery@cs.umass.edu
Plug: Automatically Tolerating Memory Leaks in C and C++ Applications Gene Novark Emery D. Berger Dept. of Computer Science University of Massachusetts Amherst Amherst, MA 01003 gnovark@cs.umass.edu, emery@cs.umass.edu
CS 345. Garbage Collection. Vitaly Shmatikov. slide 1
 CS 345 Garbage Collection Vitaly Shmatikov slide 1 Major Areas of Memory Static area Fixed size, fixed content, allocated at compile time Run-time stack Variable size, variable content (activation records)
CS 345 Garbage Collection Vitaly Shmatikov slide 1 Major Areas of Memory Static area Fixed size, fixed content, allocated at compile time Run-time stack Variable size, variable content (activation records)
A new Mono GC. Paolo Molaro October 25, 2006
 A new Mono GC Paolo Molaro lupus@novell.com October 25, 2006 Current GC: why Boehm Ported to the major architectures and systems Featurefull Very easy to integrate Handles managed pointers in unmanaged
A new Mono GC Paolo Molaro lupus@novell.com October 25, 2006 Current GC: why Boehm Ported to the major architectures and systems Featurefull Very easy to integrate Handles managed pointers in unmanaged
CSE P 501 Compilers. Memory Management and Garbage Collec<on Hal Perkins Winter UW CSE P 501 Winter 2016 W-1
 CSE P 501 Compilers Memory Management and Garbage Collec
CSE P 501 Compilers Memory Management and Garbage Collec
The Z Garbage Collector Low Latency GC for OpenJDK
 The Z Garbage Collector Low Latency GC for OpenJDK Per Lidén & Stefan Karlsson HotSpot Garbage Collection Team Jfokus VM Tech Summit 2018 Safe Harbor Statement The following is intended to outline our
The Z Garbage Collector Low Latency GC for OpenJDK Per Lidén & Stefan Karlsson HotSpot Garbage Collection Team Jfokus VM Tech Summit 2018 Safe Harbor Statement The following is intended to outline our
Phase-based Adaptive Recompilation in a JVM
 Phase-based Adaptive Recompilation in a JVM Dayong Gu Clark Verbrugge Sable Research Group, School of Computer Science McGill University, Montréal, Canada {dgu1, clump}@cs.mcgill.ca April 7, 2008 Sable
Phase-based Adaptive Recompilation in a JVM Dayong Gu Clark Verbrugge Sable Research Group, School of Computer Science McGill University, Montréal, Canada {dgu1, clump}@cs.mcgill.ca April 7, 2008 Sable
Robust Memory Management Schemes
 Robust Memory Management Schemes Prepared by : Fadi Sbahi & Ali Bsoul Supervised By: Dr. Lo ai Tawalbeh Jordan University of Science and Technology Robust Memory Management Schemes Introduction. Memory
Robust Memory Management Schemes Prepared by : Fadi Sbahi & Ali Bsoul Supervised By: Dr. Lo ai Tawalbeh Jordan University of Science and Technology Robust Memory Management Schemes Introduction. Memory
A Novel Approach to Explain the Detection of Memory Errors and Execution on Different Application Using Dr Memory.
 A Novel Approach to Explain the Detection of Memory Errors and Execution on Different Application Using Dr Memory. Yashaswini J 1, Tripathi Ashish Ashok 2 1, 2 School of computer science and engineering,
A Novel Approach to Explain the Detection of Memory Errors and Execution on Different Application Using Dr Memory. Yashaswini J 1, Tripathi Ashish Ashok 2 1, 2 School of computer science and engineering,
CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages
 CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages Memory Management and Garbage Collection CMSC 330 - Spring 2013 1 Memory Attributes! Memory to store data in programming languages has the following lifecycle
CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages Memory Management and Garbage Collection CMSC 330 - Spring 2013 1 Memory Attributes! Memory to store data in programming languages has the following lifecycle
Short-term Memory for Self-collecting Mutators. Martin Aigner, Andreas Haas, Christoph Kirsch, Ana Sokolova Universität Salzburg
 Short-term Memory for Self-collecting Mutators Martin Aigner, Andreas Haas, Christoph Kirsch, Ana Sokolova Universität Salzburg CHESS Seminar, UC Berkeley, September 2010 Heap Management explicit heap
Short-term Memory for Self-collecting Mutators Martin Aigner, Andreas Haas, Christoph Kirsch, Ana Sokolova Universität Salzburg CHESS Seminar, UC Berkeley, September 2010 Heap Management explicit heap
Memory Allocation III
 Memory Allocation III CSE 351 Spring 2017 Instructor: Ruth Anderson Teaching Assistants: Dylan Johnson Kevin Bi Linxing Preston Jiang Cody Ohlsen Yufang Sun Joshua Curtis Administrivia Homework 5 Due Wed
Memory Allocation III CSE 351 Spring 2017 Instructor: Ruth Anderson Teaching Assistants: Dylan Johnson Kevin Bi Linxing Preston Jiang Cody Ohlsen Yufang Sun Joshua Curtis Administrivia Homework 5 Due Wed
