CS 215 Lecture 17 Linked lists and time complexities
|
|
|
- Marianna Hampton
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CS 215 Lecture 17 Linked lists and time complexities Xiwei (Jeffrey) Wang 1 Department of Computer Science University of Kentucky Lexington, Kentucky July Most of the content is from the lecture slides of the book C++ for Everyone by Cay Horstmann.
2 Xiwei (Jeffrey) Wang (UK CS) CS 215 Lecture 17 Summer / 31 Recap of last time The permutations. Mutual recursion. The tower of Hanoi. Queues and Stacks.
3 Stacks and queues Xiwei (Jeffrey) Wang (UK CS) CS 215 Lecture 17 Summer / 31 Stack is a LIFO data structure. Queue is a FIFO data structure.
4 Using linked lists Xiwei (Jeffrey) Wang (UK CS) CS 215 Lecture 17 Summer / 31 Linked list is a data structure that supports efficient addition and removal of elements in the middle of a sequence. Consider the problem of storing employee records. Assume we use a vector to hold the data, what if we needed the data sorted by the employees' last names? Can we hope that the employees will be hired in order of their last names so that we will be putting them into the vector in the order we want? How else can the data be kept in the order we want it in the vector? Insert an employee; sort; insert an employee; sort; insert an employee; sort;
5 Xiwei (Jeffrey) Wang (UK CS) CS 215 Lecture 17 Summer / 31 Using linked lists For each new employee, we could find the position in the vector where their data should be inserted and insert it. But what about all the other records after this one? Won't they need to be MOVED inside the vector? Won't that take a lot of time shifting them toward the end of the vector? Use linked list which does not need any shifting. Rather than storing the data in a single block of memory, a linked list uses a different strategy. Each value is stored in its own memory block, together with the locations of the block "before" it and "after" it in the sequence. This memory block is traditionally called a node.
6 Xiwei (Jeffrey) Wang (UK CS) CS 215 Lecture 17 Summer / 31 Using linked lists Each node contains its data and a pointer to the previous node in the list and a pointer the next node in the list. David This is called a doubly-linked list. In a singly-linked list each node has a link only to the next node in the list, with no link to the predecessor elements. David
7 Using linked lists Xiwei (Jeffrey) Wang (UK CS) CS 215 Lecture 17 Summer / 31 Add a node to the doubly linked list: Only the links need to be changed. No shifting required! David
8 Using linked lists And what must happen when an employee leaves the company? With vector, we need to remove that record and then it takes a lot of time shifting those left toward the front of the vector. What about the linked list? To delete a node, only the links need to be changed. No shifting required! David Xiwei (Jeffrey) Wang (UK CS) CS 215 Lecture 17 Summer / 31
9 Using linked lists While insertion and deletion are that easy, where to do the insert or delete is the problem. Try to delete the 5th element in a linked list. You would have to first do a linear search just to find the 5th element! This is called Sequential Access. In a vector or an array, using the [ ], you can go directly to an element position. This is called Random Access. Random doesn't really mean "random", it means "arbitrary" go directly to any specific item without having to go through all of the items before it in the sequence to get there. The standard C++ library has an implementation of the linked list container structure. list<string> names; names.push_back("tom"); names.push_back("david"); names.push_back("harry"); Xiwei (Jeffrey) Wang (UK CS) CS 215 Lecture 17 Summer / 31
10 Iterator for linked lists To visit an element, you cannot use [], but a list iterator: list<string>::iterator pos; pos can "point" to an element in a list. It's not really a pointer, but it uses operator overloading to pretend to be one. list<string>::iterator pos; pos = names.begin(); pos++; // move pos to the next position in the list pos--; // move pos backward string value = *pos; // store the value from the list into value *pos = "Romeo"; // The list value at the position is changed Don t get confused with these two notations: *pos the value in the list at pos pos the iterator that indicates a position in the list Xiwei (Jeffrey) Wang (UK CS) CS 215 Lecture 17 Summer / 31
11 Iterator for vectors vectors also support iterator. The following two for loops do the same job. vector<person*>::iterator pos; for (pos = m_list.begin(); pos!= m_list.end(); pos++) { } (*pos)->print(cout); for (int i = 0; i < m_list.size(); i++) { m_list[i]->print(cout); } Xiwei (Jeffrey) Wang (UK CS) CS 215 Lecture 17 Summer / 31
12 Using linked lists To insert a new element, use the insert method: names.insert(pos, "Romeo"); If you want to insert an element to the head of the list, you have to reset the pos iterator: pos = names.begin(); names.insert(pos, "Romeo"); There is also an end method for lists which indicates the position AFTER the last one. That is exactly where a new last element should go: pos = names.end(); // Points past the end of the list names.insert(pos, "Juliet"); // Insert past the end of the list, A new last element is appended Xiwei (Jeffrey) Wang (UK CS) CS 215 Lecture 17 Summer / 31
13 Using linked lists Xiwei (Jeffrey) Wang (UK CS) CS 215 Lecture 17 Summer / 31 Because end indicates the position AFTER the last one, using that position is an error, just as it is an error to access an element in an array past the last element. string value = *names.end(); // ERROR!! The begin and end methods are used when looping through all the elements in a list. // while loop pos = names.begin(); while (pos!= names.end()) { cout << *pos << endl; not <= or < pos++; } // for loop for (pos = names.begin(); pos!= names.end(); pos++) { cout << *pos << endl; }
14 Xiwei (Jeffrey) Wang (UK CS) CS 215 Lecture 17 Summer / 31 Using linked lists The erase method removes an element at a position: pos = names.begin(); pos++; pos = names.erase(pos); This code removes the second element from the list. erase returns the position after the one removed so pos now points to what was the third element. This also works for vectors. In program 3, when you remove a person from the vector m_list, you should free the associated dynamic memory and erase the pointer from the vector as well.
15 Time complexity How does the performance change with the size of the input? Suppose it takes 2n 2 + 5n - 3 operations to sort a list of size n. What happens if we double the size of the input? 8n n - 3 : almost four times as long As n gets bigger and bigger, the 2n 2 term becomes more important, and the 5n term becomes less important. If we care mostly about big problems, we can ignore those lower-order terms. The order of complexity of an algorithm is a measure of how its performance changes as the problem instance gets bigger. Written in big O notation : O(n 2 ), O(n). Write the expression for number of operations: 2n 2 + 5n -3 Take the highest-order (fastest-growing) term: 2n 2 Drop the constant: n 2 So we say the algorithm has complexity O(n 2 ) "Order n squared" or "Big Oh of n squared" Xiwei (Jeffrey) Wang (UK CS) CS 215 Lecture 17 Summer / 31
16 worse Time complexity An expression like O(n 2 ) represents a complexity class: All the formulas with the highest-order term n 2 n 2 + 3n -1, n 2 /10 + n, 100n 2 50, Computer scientists have names for some of the most common complexity classes: O(1): constant. Doesn't depend on the size of the input. O(log n): logarithmic. Doubling the input adds an amount of time. O(n): linear. Doubling the input doubles the time. O(n 2 ): quadratic. Doubling the input quadruples the time. O(n k ): polynomial with order k. O(2 n ): exponential. Adding one to the input size doubles the time. Xiwei (Jeffrey) Wang (UK CS) CS 215 Lecture 17 Summer / 31
17 The efficiency of list, array, and vector operations How efficient are these operations on lists, arrays, and vectors? Getting the kth element. Adding or removing an element at a given position (an iterator or index). Adding or removing an element at the end. Xiwei (Jeffrey) Wang (UK CS) CS 215 Lecture 17 Summer / 31
18 The efficiency of list, array, and vector operations list getting the kth element Getting to the kth element requires starting at the beginning and advancing the iterator k times. If it takes time T to advance the iterator once, advancing the iterator to the kth element takes kt time so locating the kth element is an O(k) operation. array getting the kth element Getting to the kth element requires only a calculation for [] to go directly to the kth element. A simple calculation is O(1), so locating the kth element is an O(1) operation. vector getting the kth element Same as array, locating the kth element is an O(1) operation. Xiwei (Jeffrey) Wang (UK CS) CS 215 Lecture 17 Summer / 31
19 The efficiency of list, array, and vector operations list inserting and deleting These operations involve only changing two pointer values so it's O(1) operations. Note that we will have already done the searching for where to do the insert or delete so that time is not considered here. array and vector inserting and deleting Arrays are easy to visualize. Inserting and deleting for vector requires seeing how the vector class is implemented. Xiwei (Jeffrey) Wang (UK CS) CS 215 Lecture 17 Summer / 31
20 The efficiency of list, array, and vector operations Xiwei (Jeffrey) Wang (UK CS) CS 215 Lecture 17 Summer / 31 vector internal organization A vector keeps its data in a dynamic buffer (an array) and a pointer to that area; it keeps the value of the current capacity of the buffer; and it keeps the number of elements currently in the buffer.
21 The efficiency of list, array, and vector operations Xiwei (Jeffrey) Wang (UK CS) CS 215 Lecture 17 Summer / 31 array and vector inserting and deleting In both, to insert an element at position k, the elements with higher index values must be moved to make room for the new element. And size would be increased by one.
22 The efficiency of list, array, and vector operations Xiwei (Jeffrey) Wang (UK CS) CS 215 Lecture 17 Summer / 31 array and vector inserting and deleting To delete an element at position k, the elements with higher index values must be moved to take up the room that had been used for the deleted element value. And size would be reduced by one.
23 Xiwei (Jeffrey) Wang (UK CS) CS 215 Lecture 17 Summer / 31 The efficiency of list, array, and vector operations array and vector inserting and deleting For the analysis, we need to know how many elements are affected in a move. For simplicity, we will assume that insertions and deletions happen at random locations. Then, on average, where n is the size of the array or vector, each insertion or deletion moves n 2 elements. Insert and delete are O(n) operations.
24 The efficiency of list, array, and vector operations Xiwei (Jeffrey) Wang (UK CS) CS 215 Lecture 17 Summer / 31 list adding or removing an element at the end If we assume the list has a "maintenance pointer" which points to the last item in the list, then, same as always, just reset some pointer values: an O(1) operation. array adding or removing an element at the end The array must be large enough to insert at the end or we simply cannot insert. Inserting and deleting involve [], a simple calculation as before, plus arithmetic on the size. There is no moving of data so it s O(1). vector adding or removing an element at the end To insert at the end of a vector, the push_back method is used. When the capacity is sufficient, this is an O(1) process requiring only accessing and assigning to a position already there in the dynamic array (the buffer) and arithmetic on the size.
25 Xiwei (Jeffrey) Wang (UK CS) CS 215 Lecture 17 Summer / 31 The efficiency of list, array, and vector operations vector adding or removing an element at the end When the buffer is filled to its current capacity, the buffer will be increased in size to accommodate the call to the push_back method. v.push_back(9); 5 5
26 Xiwei (Jeffrey) Wang (UK CS) CS 215 Lecture 17 Summer / 31 The efficiency of list, array, and vector operations vector adding or removing an element at the end When the buffer is filled to its current capacity, the buffer will be increased in size to accommodate the call to the push_back method. v.push_back(9); 5 10
27 Xiwei (Jeffrey) Wang (UK CS) CS 215 Lecture 17 Summer / 31 The efficiency of list, array, and vector operations vector adding or removing an element at the end When the buffer is filled to its current capacity, the buffer will be increased in size to accommodate the call to the push_back method. v.push_back(9); 6 10
28 The efficiency of list, array, and vector operations Xiwei (Jeffrey) Wang (UK CS) CS 215 Lecture 17 Summer / 31 vector adding or removing an element at the end The reallocation does not happen very often. That helps with the efficiency. But makes the analysis a bit harder. The reallocation algorithm effects the analysis also. Suppose we choose to double the size with each reallocation. If we start a vector with capacity 10, we must reallocate when the buffer reaches sizes 10, 20, 40, 80, 160, 320, 640, 1280, and so on. Assume that one insertion without reallocation takes time T 1. Assume that reallocation of k elements takes time kt 2. What is the cost of 1,280 push_back operations? 1280 * T 1 for the 1280 insertions and the reallocation cost is:
29 The efficiency of list, array, and vector operations vector adding or removing an element at the end For 1280 push_backs, the total cost is a bit less than : The cost of n push_back operations is then less than: Because the second factor is a constant, we conclude that n push_back operations take O(n) time. But, we know that it isn't quite true that an individual push_back operation takes O(1) time because occasionally a push_back is unlucky and must reallocate the buffer. Xiwei (Jeffrey) Wang (UK CS) CS 215 Lecture 17 Summer / 31
30 Xiwei (Jeffrey) Wang (UK CS) CS 215 Lecture 17 Summer / 31 The efficiency of list, array, and vector operations vector adding or removing an element at the end However, if the cost of that reallocation is distributed over the preceding push_back operations, then the surcharge for each of them is still a constant amount. We say that push_back takes amortized O(1) time, which is written as O(1)+.
31 Xiwei (Jeffrey) Wang (UK CS) CS 215 Lecture 17 Summer / 31 Action items Read book chapter 13. PA 3 is due tomorrow midnight. Questions?
CPSC 260 Data Structures and Algorithms for Computer Engineers Linked Lists!
 CPSC 260 Data Structures and Algorithms for Computer Engineers Linked Lists! Winter 2013 Instructor: Hassan Khosravi Problems with Arrays and Vectors With arrays and vectors you are allocated a large space.
CPSC 260 Data Structures and Algorithms for Computer Engineers Linked Lists! Winter 2013 Instructor: Hassan Khosravi Problems with Arrays and Vectors With arrays and vectors you are allocated a large space.
Outline. runtime of programs algorithm efficiency Big-O notation List interface Array lists
 Outline runtime of programs algorithm efficiency Big-O notation List interface Array lists Runtime of Programs compare the following two program fragments: int result = 1; int result = 1; for (int i=2;
Outline runtime of programs algorithm efficiency Big-O notation List interface Array lists Runtime of Programs compare the following two program fragments: int result = 1; int result = 1; for (int i=2;
CS 231 Data Structures and Algorithms Fall Algorithm Analysis Lecture 16 October 10, Prof. Zadia Codabux
 CS 231 Data Structures and Algorithms Fall 2018 Algorithm Analysis Lecture 16 October 10, 2018 Prof. Zadia Codabux 1 Agenda Algorithm Analysis 2 Administrative No quiz this week 3 Algorithm Analysis 4
CS 231 Data Structures and Algorithms Fall 2018 Algorithm Analysis Lecture 16 October 10, 2018 Prof. Zadia Codabux 1 Agenda Algorithm Analysis 2 Administrative No quiz this week 3 Algorithm Analysis 4
CSE 143. Complexity Analysis. Program Efficiency. Constant Time Statements. Big Oh notation. Analyzing Loops. Constant Time Statements (2) CSE 143 1
 CSE 1 Complexity Analysis Program Efficiency [Sections 12.1-12., 12., 12.9] Count number of instructions executed by program on inputs of a given size Express run time as a function of the input size Assume
CSE 1 Complexity Analysis Program Efficiency [Sections 12.1-12., 12., 12.9] Count number of instructions executed by program on inputs of a given size Express run time as a function of the input size Assume
Recursion. COMS W1007 Introduction to Computer Science. Christopher Conway 26 June 2003
 Recursion COMS W1007 Introduction to Computer Science Christopher Conway 26 June 2003 The Fibonacci Sequence The Fibonacci numbers are: 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, 34,... We can calculate the nth Fibonacci
Recursion COMS W1007 Introduction to Computer Science Christopher Conway 26 June 2003 The Fibonacci Sequence The Fibonacci numbers are: 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, 34,... We can calculate the nth Fibonacci
Ch 8. Searching and Sorting Arrays Part 1. Definitions of Search and Sort
 Ch 8. Searching and Sorting Arrays Part 1 CS 2308 Fall 2011 Jill Seaman Lecture 1 1 Definitions of Search and Sort! Search: find an item in an array, return the index to the item, or -1 if not found.!
Ch 8. Searching and Sorting Arrays Part 1 CS 2308 Fall 2011 Jill Seaman Lecture 1 1 Definitions of Search and Sort! Search: find an item in an array, return the index to the item, or -1 if not found.!
CSCI-1200 Data Structures Spring 2018 Lecture 7 Order Notation & Basic Recursion
 CSCI-1200 Data Structures Spring 2018 Lecture 7 Order Notation & Basic Recursion Review from Lectures 5 & 6 Arrays and pointers, Pointer arithmetic and dereferencing, Types of memory ( automatic, static,
CSCI-1200 Data Structures Spring 2018 Lecture 7 Order Notation & Basic Recursion Review from Lectures 5 & 6 Arrays and pointers, Pointer arithmetic and dereferencing, Types of memory ( automatic, static,
Search Lesson Outline
 1. Searching Lesson Outline 2. How to Find a Value in an Array? 3. Linear Search 4. Linear Search Code 5. Linear Search Example #1 6. Linear Search Example #2 7. Linear Search Example #3 8. Linear Search
1. Searching Lesson Outline 2. How to Find a Value in an Array? 3. Linear Search 4. Linear Search Code 5. Linear Search Example #1 6. Linear Search Example #2 7. Linear Search Example #3 8. Linear Search
Binary Trees (and Big O notation)
 Binary Trees (and Big O notation) Professor Hugh C. Lauer CS-2303, System Programming Concepts (Slides include materials from The C Programming Language, 2 nd edition, by Kernighan and Ritchie, Absolute
Binary Trees (and Big O notation) Professor Hugh C. Lauer CS-2303, System Programming Concepts (Slides include materials from The C Programming Language, 2 nd edition, by Kernighan and Ritchie, Absolute
Today s Outline. CSE 326: Data Structures Asymptotic Analysis. Analyzing Algorithms. Analyzing Algorithms: Why Bother? Hannah Takes a Break
 Today s Outline CSE 326: Data Structures How s the project going? Finish up stacks, queues, lists, and bears, oh my! Math review and runtime analysis Pretty pictures Asymptotic analysis Hannah Tang and
Today s Outline CSE 326: Data Structures How s the project going? Finish up stacks, queues, lists, and bears, oh my! Math review and runtime analysis Pretty pictures Asymptotic analysis Hannah Tang and
Computer Programming
 Computer Programming Dr. Deepak B Phatak Dr. Supratik Chakraborty Department of Computer Science and Engineering Session : Template Class list Dr. Deepak B. Phatak & Dr. Supratik Chakraborty, 1 Quick Recap
Computer Programming Dr. Deepak B Phatak Dr. Supratik Chakraborty Department of Computer Science and Engineering Session : Template Class list Dr. Deepak B. Phatak & Dr. Supratik Chakraborty, 1 Quick Recap
Datatypes. List of data structures. Datatypes ISC
 Datatypes ISC-5315 1 Datatypes Effective use of algorithm in computer programs depends strongly on the representation of the data, so that retrieval and insertion of values are simple and fast. Using the
Datatypes ISC-5315 1 Datatypes Effective use of algorithm in computer programs depends strongly on the representation of the data, so that retrieval and insertion of values are simple and fast. Using the
PROGRAM EFFICIENCY & COMPLEXITY ANALYSIS
 Lecture 03-04 PROGRAM EFFICIENCY & COMPLEXITY ANALYSIS By: Dr. Zahoor Jan 1 ALGORITHM DEFINITION A finite set of statements that guarantees an optimal solution in finite interval of time 2 GOOD ALGORITHMS?
Lecture 03-04 PROGRAM EFFICIENCY & COMPLEXITY ANALYSIS By: Dr. Zahoor Jan 1 ALGORITHM DEFINITION A finite set of statements that guarantees an optimal solution in finite interval of time 2 GOOD ALGORITHMS?
Introduction to the Analysis of Algorithms. Algorithm
 Introduction to the Analysis of Algorithms Based on the notes from David Fernandez-Baca Bryn Mawr College CS206 Intro to Data Structures Algorithm An algorithm is a strategy (well-defined computational
Introduction to the Analysis of Algorithms Based on the notes from David Fernandez-Baca Bryn Mawr College CS206 Intro to Data Structures Algorithm An algorithm is a strategy (well-defined computational
l Determine if a number is odd or even l Determine if a number/character is in a range - 1 to 10 (inclusive) - between a and z (inclusive)
 Final Exam Exercises Chapters 1-7 + 11 Write C++ code to: l Determine if a number is odd or even CS 2308 Fall 2016 Jill Seaman l Determine if a number/character is in a range - 1 to 10 (inclusive) - between
Final Exam Exercises Chapters 1-7 + 11 Write C++ code to: l Determine if a number is odd or even CS 2308 Fall 2016 Jill Seaman l Determine if a number/character is in a range - 1 to 10 (inclusive) - between
List, Stack, and Queues
 List, Stack, and Queues R. J. Renka Department of Computer Science & Engineering University of North Texas 02/24/2010 3.1 Abstract Data Type An Abstract Data Type (ADT) is a set of objects with a set of
List, Stack, and Queues R. J. Renka Department of Computer Science & Engineering University of North Texas 02/24/2010 3.1 Abstract Data Type An Abstract Data Type (ADT) is a set of objects with a set of
! Determine if a number is odd or even. ! Determine if a number/character is in a range. - 1 to 10 (inclusive) - between a and z (inclusive)
 Final Exam Exercises Chapters 1-7 + 11 Write C++ code to:! Determine if a number is odd or even CS 2308 Fall 2018 Jill Seaman! Determine if a number/character is in a range - 1 to 10 (inclusive) - between
Final Exam Exercises Chapters 1-7 + 11 Write C++ code to:! Determine if a number is odd or even CS 2308 Fall 2018 Jill Seaman! Determine if a number/character is in a range - 1 to 10 (inclusive) - between
Measuring algorithm efficiency
 CMPT 225 Measuring algorithm efficiency Timing Counting Cost functions Cases Best case Average case Worst case Searching Sorting O Notation O notation's mathematical basis O notation classes and notations
CMPT 225 Measuring algorithm efficiency Timing Counting Cost functions Cases Best case Average case Worst case Searching Sorting O Notation O notation's mathematical basis O notation classes and notations
CSE373: Data Structures and Algorithms Lecture 4: Asymptotic Analysis. Aaron Bauer Winter 2014
 CSE373: Data Structures and Algorithms Lecture 4: Asymptotic Analysis Aaron Bauer Winter 2014 Previously, on CSE 373 We want to analyze algorithms for efficiency (in time and space) And do so generally
CSE373: Data Structures and Algorithms Lecture 4: Asymptotic Analysis Aaron Bauer Winter 2014 Previously, on CSE 373 We want to analyze algorithms for efficiency (in time and space) And do so generally
CSCI-1200 Data Structures Fall 2017 Lecture 7 Order Notation & Basic Recursion
 CSCI-1200 Data Structures Fall 2017 Lecture 7 Order Notation & Basic Recursion Announcements: Test 1 Information Test 1 will be held Monday, Sept 25th, 2017 from 6-7:50pm Students will be randomly assigned
CSCI-1200 Data Structures Fall 2017 Lecture 7 Order Notation & Basic Recursion Announcements: Test 1 Information Test 1 will be held Monday, Sept 25th, 2017 from 6-7:50pm Students will be randomly assigned
The Limits of Sorting Divide-and-Conquer Comparison Sorts II
 The Limits of Sorting Divide-and-Conquer Comparison Sorts II CS 311 Data Structures and Algorithms Lecture Slides Monday, October 12, 2009 Glenn G. Chappell Department of Computer Science University of
The Limits of Sorting Divide-and-Conquer Comparison Sorts II CS 311 Data Structures and Algorithms Lecture Slides Monday, October 12, 2009 Glenn G. Chappell Department of Computer Science University of
CS161 Handout 07 Summer 2013 July 17, 2013 Guide to Reductions. Thanks to Julie Tibshirani for helping with this handout!
 CS161 Handout 07 Summer 2013 July 17, 2013 Guide to Reductions Thanks to Julie Tibshirani for helping with this handout! We'll design many algorithms over the course of this class. Often, the algorithms
CS161 Handout 07 Summer 2013 July 17, 2013 Guide to Reductions Thanks to Julie Tibshirani for helping with this handout! We'll design many algorithms over the course of this class. Often, the algorithms
CS 106B Lecture 5: Stacks and Queues
 CS 106B Lecture 5: Stacks and Queues Monday, July 3, 2017 Programming Abstractions Summer 2017 Stanford University Computer Science Department Lecturer: Chris Gregg reading: Programming Abstractions in
CS 106B Lecture 5: Stacks and Queues Monday, July 3, 2017 Programming Abstractions Summer 2017 Stanford University Computer Science Department Lecturer: Chris Gregg reading: Programming Abstractions in
FINALTERM EXAMINATION Fall 2009 CS301- Data Structures Question No: 1 ( Marks: 1 ) - Please choose one The data of the problem is of 2GB and the hard
 FINALTERM EXAMINATION Fall 2009 CS301- Data Structures Question No: 1 The data of the problem is of 2GB and the hard disk is of 1GB capacity, to solve this problem we should Use better data structures
FINALTERM EXAMINATION Fall 2009 CS301- Data Structures Question No: 1 The data of the problem is of 2GB and the hard disk is of 1GB capacity, to solve this problem we should Use better data structures
EC8393FUNDAMENTALS OF DATA STRUCTURES IN C Unit 3
 UNIT 3 LINEAR DATA STRUCTURES 1. Define Data Structures Data Structures is defined as the way of organizing all data items that consider not only the elements stored but also stores the relationship between
UNIT 3 LINEAR DATA STRUCTURES 1. Define Data Structures Data Structures is defined as the way of organizing all data items that consider not only the elements stored but also stores the relationship between
Algorithm Analysis. Big Oh
 Algorithm Analysis with Big Oh Data Structures and Design with Java and JUnit Chapter 12 Rick Mercer Algorithm Analysis w Objectives Analyze the efficiency of algorithms Analyze a few classic algorithms
Algorithm Analysis with Big Oh Data Structures and Design with Java and JUnit Chapter 12 Rick Mercer Algorithm Analysis w Objectives Analyze the efficiency of algorithms Analyze a few classic algorithms
Chapter 2: Complexity Analysis
 Chapter 2: Complexity Analysis Objectives Looking ahead in this chapter, we ll consider: Computational and Asymptotic Complexity Big-O Notation Properties of the Big-O Notation Ω and Θ Notations Possible
Chapter 2: Complexity Analysis Objectives Looking ahead in this chapter, we ll consider: Computational and Asymptotic Complexity Big-O Notation Properties of the Big-O Notation Ω and Θ Notations Possible
Computer Science 210 Data Structures Siena College Fall Topic Notes: Linear Structures
 Computer Science 210 Data Structures Siena College Fall 2018 Topic Notes: Linear Structures The structures we ve seen so far, Vectors/ArrayLists and linked list variations, allow insertion and deletion
Computer Science 210 Data Structures Siena College Fall 2018 Topic Notes: Linear Structures The structures we ve seen so far, Vectors/ArrayLists and linked list variations, allow insertion and deletion
DEEPIKA KAMBOJ UNIT 2. What is Stack?
 What is Stack? UNIT 2 Stack is an important data structure which stores its elements in an ordered manner. You must have seen a pile of plates where one plate is placed on top of another. Now, when you
What is Stack? UNIT 2 Stack is an important data structure which stores its elements in an ordered manner. You must have seen a pile of plates where one plate is placed on top of another. Now, when you
CSCI 102L - Data Structures Midterm Exam #2 Spring 2011
 CSCI 102L - Data Structures Midterm Exam #2 Spring 2011 (12:30pm - 1:50pm, Thursday, March 24) Instructor: Bill Cheng ( This exam is closed book, closed notes, closed everything. No cheat sheet allowed.
CSCI 102L - Data Structures Midterm Exam #2 Spring 2011 (12:30pm - 1:50pm, Thursday, March 24) Instructor: Bill Cheng ( This exam is closed book, closed notes, closed everything. No cheat sheet allowed.
Sum this up for me. Let s write a method to calculate the sum from 1 to some n. Gauss also has a way of solving this. Which one is more efficient?
 Sum this up for me Let s write a method to calculate the sum from 1 to some n public static int sum1(int n) { int sum = 0; for (int i = 1; i
Sum this up for me Let s write a method to calculate the sum from 1 to some n public static int sum1(int n) { int sum = 0; for (int i = 1; i
The time and space are the two measure for efficiency of an algorithm.
 There are basically six operations: 5. Sorting: Arranging the elements of list in an order (either ascending or descending). 6. Merging: combining the two list into one list. Algorithm: The time and space
There are basically six operations: 5. Sorting: Arranging the elements of list in an order (either ascending or descending). 6. Merging: combining the two list into one list. Algorithm: The time and space
Chapter 4 Computation
 Chapter 4 Computation Hartmut Kaiser hkaiser@cct.lsu.edu http://www.cct.lsu.edu/~hkaiser/spring_2011/csc1253.html Slides adapted from: Bjarne Stroustrup, Programming Principles and Practice using C++ Abstract
Chapter 4 Computation Hartmut Kaiser hkaiser@cct.lsu.edu http://www.cct.lsu.edu/~hkaiser/spring_2011/csc1253.html Slides adapted from: Bjarne Stroustrup, Programming Principles and Practice using C++ Abstract
CMPSCI 187: Programming With Data Structures. Lecture 5: Analysis of Algorithms Overview 16 September 2011
 CMPSCI 187: Programming With Data Structures Lecture 5: Analysis of Algorithms Overview 16 September 2011 Analysis of Algorithms Overview What is Analysis of Algorithms? L&C s Dishwashing Example Being
CMPSCI 187: Programming With Data Structures Lecture 5: Analysis of Algorithms Overview 16 September 2011 Analysis of Algorithms Overview What is Analysis of Algorithms? L&C s Dishwashing Example Being
Java How to Program, 9/e. Copyright by Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
 Java How to Program, 9/e Copyright 1992-2012 by Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved. Searching data involves determining whether a value (referred to as the search key) is present in the data
Java How to Program, 9/e Copyright 1992-2012 by Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved. Searching data involves determining whether a value (referred to as the search key) is present in the data
CSCI-1200 Data Structures Spring 2016 Lecture 7 Iterators, STL Lists & Order Notation
 Today CSCI-1200 Data Structures Spring 2016 Lecture 7 Iterators, STL Lists & Order Notation Another vector operation: pop back Erasing items from vectors is inefficient! Iterators and iterator operations
Today CSCI-1200 Data Structures Spring 2016 Lecture 7 Iterators, STL Lists & Order Notation Another vector operation: pop back Erasing items from vectors is inefficient! Iterators and iterator operations
Basic Data Structures (Version 7) Name:
 Prerequisite Concepts for Analysis of Algorithms Basic Data Structures (Version 7) Name: Email: Concept: mathematics notation 1. log 2 n is: Code: 21481 (A) o(log 10 n) (B) ω(log 10 n) (C) Θ(log 10 n)
Prerequisite Concepts for Analysis of Algorithms Basic Data Structures (Version 7) Name: Email: Concept: mathematics notation 1. log 2 n is: Code: 21481 (A) o(log 10 n) (B) ω(log 10 n) (C) Θ(log 10 n)
CS11 Advanced C++ Fall Lecture 1
 CS11 Advanced C++ Fall 2006-2007 Lecture 1 Welcome! ~8 lectures Slides are posted on CS11 website http://www.cs.caltech.edu/courses/cs11 ~6 lab assignments More involved labs 2-3 week project at end CS
CS11 Advanced C++ Fall 2006-2007 Lecture 1 Welcome! ~8 lectures Slides are posted on CS11 website http://www.cs.caltech.edu/courses/cs11 ~6 lab assignments More involved labs 2-3 week project at end CS
Computer Science 210 Data Structures Siena College Fall Topic Notes: Complexity and Asymptotic Analysis
 Computer Science 210 Data Structures Siena College Fall 2017 Topic Notes: Complexity and Asymptotic Analysis Consider the abstract data type, the Vector or ArrayList. This structure affords us the opportunity
Computer Science 210 Data Structures Siena College Fall 2017 Topic Notes: Complexity and Asymptotic Analysis Consider the abstract data type, the Vector or ArrayList. This structure affords us the opportunity
CS/ENGRD 2110 Object-Oriented Programming and Data Structures Spring 2012 Thorsten Joachims. Lecture 10: Asymptotic Complexity and
 CS/ENGRD 2110 Object-Oriented Programming and Data Structures Spring 2012 Thorsten Joachims Lecture 10: Asymptotic Complexity and What Makes a Good Algorithm? Suppose you have two possible algorithms or
CS/ENGRD 2110 Object-Oriented Programming and Data Structures Spring 2012 Thorsten Joachims Lecture 10: Asymptotic Complexity and What Makes a Good Algorithm? Suppose you have two possible algorithms or
O(1) How long does a function take to run? CS61A Lecture 6
 How long does a function take to run? It depends on what computer it is run on! CS6A Lecture 6 20-06-28 Colleen Lewis Assumptions We want something independent of the speed of the computer We typically
How long does a function take to run? It depends on what computer it is run on! CS6A Lecture 6 20-06-28 Colleen Lewis Assumptions We want something independent of the speed of the computer We typically
Logistics. Half of the people will be in Wu & Chen The other half in DRLB A1 Will post past midterms tonight (expect similar types of questions)
 Data Structures Logistics Midterm next Monday Half of the people will be in Wu & Chen The other half in DRLB A1 Will post past midterms tonight (expect similar types of questions) Review on Wednesday Come
Data Structures Logistics Midterm next Monday Half of the people will be in Wu & Chen The other half in DRLB A1 Will post past midterms tonight (expect similar types of questions) Review on Wednesday Come
CS:3330 (22c:31) Algorithms
 What s an Algorithm? CS:3330 (22c:31) Algorithms Introduction Computer Science is about problem solving using computers. Software is a solution to some problems. Algorithm is a design inside a software.
What s an Algorithm? CS:3330 (22c:31) Algorithms Introduction Computer Science is about problem solving using computers. Software is a solution to some problems. Algorithm is a design inside a software.
Computer Programming. Basic Control Flow - Loops. Adapted from C++ for Everyone and Big C++ by Cay Horstmann, John Wiley & Sons
 Computer Programming Basic Control Flow - Loops Adapted from C++ for Everyone and Big C++ by Cay Horstmann, John Wiley & Sons Objectives To learn about the three types of loops: while for do To avoid infinite
Computer Programming Basic Control Flow - Loops Adapted from C++ for Everyone and Big C++ by Cay Horstmann, John Wiley & Sons Objectives To learn about the three types of loops: while for do To avoid infinite
MID TERM MEGA FILE SOLVED BY VU HELPER Which one of the following statement is NOT correct.
 MID TERM MEGA FILE SOLVED BY VU HELPER Which one of the following statement is NOT correct. In linked list the elements are necessarily to be contiguous In linked list the elements may locate at far positions
MID TERM MEGA FILE SOLVED BY VU HELPER Which one of the following statement is NOT correct. In linked list the elements are necessarily to be contiguous In linked list the elements may locate at far positions
! Determine if a number is odd or even. ! Determine if a number/character is in a range. - 1 to 10 (inclusive) - between a and z (inclusive)
 Final Exam Exercises CS 2308 Spring 2014 Jill Seaman Chapters 1-7 + 11 Write C++ code to: Determine if a number is odd or even Determine if a number/character is in a range - 1 to 10 (inclusive) - between
Final Exam Exercises CS 2308 Spring 2014 Jill Seaman Chapters 1-7 + 11 Write C++ code to: Determine if a number is odd or even Determine if a number/character is in a range - 1 to 10 (inclusive) - between
6.001 Notes: Section 4.1
 6.001 Notes: Section 4.1 Slide 4.1.1 In this lecture, we are going to take a careful look at the kinds of procedures we can build. We will first go back to look very carefully at the substitution model,
6.001 Notes: Section 4.1 Slide 4.1.1 In this lecture, we are going to take a careful look at the kinds of procedures we can build. We will first go back to look very carefully at the substitution model,
[ 11.2, 11.3, 11.4] Analysis of Algorithms. Complexity of Algorithms. 400 lecture note # Overview
![[ 11.2, 11.3, 11.4] Analysis of Algorithms. Complexity of Algorithms. 400 lecture note # Overview [ 11.2, 11.3, 11.4] Analysis of Algorithms. Complexity of Algorithms. 400 lecture note # Overview](/thumbs/93/113368535.jpg) 400 lecture note #0 [.2,.3,.4] Analysis of Algorithms Complexity of Algorithms 0. Overview The complexity of an algorithm refers to the amount of time and/or space it requires to execute. The analysis
400 lecture note #0 [.2,.3,.4] Analysis of Algorithms Complexity of Algorithms 0. Overview The complexity of an algorithm refers to the amount of time and/or space it requires to execute. The analysis
(Refer Slide Time: 1:27)
 Data Structures and Algorithms Dr. Naveen Garg Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi Lecture 1 Introduction to Data Structures and Algorithms Welcome to data
Data Structures and Algorithms Dr. Naveen Garg Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi Lecture 1 Introduction to Data Structures and Algorithms Welcome to data
Remember, to manage anything, we need to measure it. So, how do we compare two implementations? ArrayBag vs. LinkedBag Which is more efficient?
 CS706 Intro to Object Oriented Dev II - Spring 04 Announcements Week 4 Program due Two Weeks! Lab 3-4 required completion this week First web-cat submission Material Evaluation of efficiency Time Analysis
CS706 Intro to Object Oriented Dev II - Spring 04 Announcements Week 4 Program due Two Weeks! Lab 3-4 required completion this week First web-cat submission Material Evaluation of efficiency Time Analysis
Analysis of Algorithms. CS 1037a Topic 13
 Analysis of Algorithms CS 1037a Topic 13 Overview Time complexity - exact count of operations T(n) as a function of input size n - complexity analysis using O(...) bounds - constant time, linear, logarithmic,
Analysis of Algorithms CS 1037a Topic 13 Overview Time complexity - exact count of operations T(n) as a function of input size n - complexity analysis using O(...) bounds - constant time, linear, logarithmic,
Postfix (and prefix) notation
 Postfix (and prefix) notation Also called reverse Polish reversed form of notation devised by mathematician named Jan Łukasiewicz (so really lü-kä-sha-vech notation) Infix notation is: operand operator
Postfix (and prefix) notation Also called reverse Polish reversed form of notation devised by mathematician named Jan Łukasiewicz (so really lü-kä-sha-vech notation) Infix notation is: operand operator
Algorithm Analysis. CENG 707 Data Structures and Algorithms
 Algorithm Analysis CENG 707 Data Structures and Algorithms 1 Algorithm An algorithm is a set of instructions to be followed to solve a problem. There can be more than one solution (more than one algorithm)
Algorithm Analysis CENG 707 Data Structures and Algorithms 1 Algorithm An algorithm is a set of instructions to be followed to solve a problem. There can be more than one solution (more than one algorithm)
CS W3134: Data Structures in Java
 CS W3134: Data Structures in Java Lecture #10: Stacks, queues, linked lists 10/7/04 Janak J Parekh HW#2 questions? Administrivia Finish queues Stack/queue example Agenda 1 Circular queue: miscellany Having
CS W3134: Data Structures in Java Lecture #10: Stacks, queues, linked lists 10/7/04 Janak J Parekh HW#2 questions? Administrivia Finish queues Stack/queue example Agenda 1 Circular queue: miscellany Having
PIC 10A. Lecture 23: Intro to STL containers
 PIC 10A Lecture 23: Intro to STL containers STL STL stands for Standard Template Library There are many data structures that share similar features These data structures can be manipulated by a common
PIC 10A Lecture 23: Intro to STL containers STL STL stands for Standard Template Library There are many data structures that share similar features These data structures can be manipulated by a common
ECE 2400 Computer Systems Programming Fall 2018 Topic 8: Complexity Analysis
 ECE 2400 Computer Systems Programming Fall 2018 Topic 8: Complexity Analysis School of Electrical and Computer Engineering Cornell University revision: 2018-10-11-00-23 1 Analyzing Algorithms 2 1.1. Linear
ECE 2400 Computer Systems Programming Fall 2018 Topic 8: Complexity Analysis School of Electrical and Computer Engineering Cornell University revision: 2018-10-11-00-23 1 Analyzing Algorithms 2 1.1. Linear
10/5/2016. Comparing Algorithms. Analyzing Code ( worst case ) Example. Analyzing Code. Binary Search. Linear Search
 10/5/2016 CSE373: Data Structures and Algorithms Asymptotic Analysis (Big O,, and ) Steve Tanimoto Autumn 2016 This lecture material represents the work of multiple instructors at the University of Washington.
10/5/2016 CSE373: Data Structures and Algorithms Asymptotic Analysis (Big O,, and ) Steve Tanimoto Autumn 2016 This lecture material represents the work of multiple instructors at the University of Washington.
Introduction to Analysis of Algorithms
 Introduction to Analysis of Algorithms Analysis of Algorithms To determine how efficient an algorithm is we compute the amount of time that the algorithm needs to solve a problem. Given two algorithms
Introduction to Analysis of Algorithms Analysis of Algorithms To determine how efficient an algorithm is we compute the amount of time that the algorithm needs to solve a problem. Given two algorithms
Recap: Pointers. int* int& *p &i &*&* ** * * * * IFMP 18, M. Schwerhoff
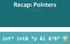 Recap: Pointers IFMP 18, M. Schwerhoff int* int& *p &i &*&* ** * * * * A 0 A 1 A 2 A 3 A 4 A 5 A 0 A 1 A 2 A 3 A 4 A 5 5 i int* p; A 0 A 1 A 2 A 3 A 4 A 5 5 i p int* p; p = &i; A 0 A 1 A 2 A 3 A 4 A 5
Recap: Pointers IFMP 18, M. Schwerhoff int* int& *p &i &*&* ** * * * * A 0 A 1 A 2 A 3 A 4 A 5 A 0 A 1 A 2 A 3 A 4 A 5 5 i int* p; A 0 A 1 A 2 A 3 A 4 A 5 5 i p int* p; p = &i; A 0 A 1 A 2 A 3 A 4 A 5
Summer Final Exam Review Session August 5, 2009
 15-111 Summer 2 2009 Final Exam Review Session August 5, 2009 Exam Notes The exam is from 10:30 to 1:30 PM in Wean Hall 5419A. The exam will be primarily conceptual. The major emphasis is on understanding
15-111 Summer 2 2009 Final Exam Review Session August 5, 2009 Exam Notes The exam is from 10:30 to 1:30 PM in Wean Hall 5419A. The exam will be primarily conceptual. The major emphasis is on understanding
Arrays. https://docs.oracle.com/javase/tutorial/java/nutsandbolts/arrays.html
 1 Arrays Arrays in Java an array is a container object that holds a fixed number of values of a single type the length of an array is established when the array is created 2 https://docs.oracle.com/javase/tutorial/java/nutsandbolts/arrays.html
1 Arrays Arrays in Java an array is a container object that holds a fixed number of values of a single type the length of an array is established when the array is created 2 https://docs.oracle.com/javase/tutorial/java/nutsandbolts/arrays.html
Week - 04 Lecture - 01 Merge Sort. (Refer Slide Time: 00:02)
 Programming, Data Structures and Algorithms in Python Prof. Madhavan Mukund Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Week - 04 Lecture - 01 Merge Sort (Refer
Programming, Data Structures and Algorithms in Python Prof. Madhavan Mukund Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Week - 04 Lecture - 01 Merge Sort (Refer
Data Structures Question Bank Multiple Choice
 Section 1. Fundamentals: Complexity, Algorthm Analysis 1. An algorithm solves A single problem or function Multiple problems or functions Has a single programming language implementation 2. A solution
Section 1. Fundamentals: Complexity, Algorthm Analysis 1. An algorithm solves A single problem or function Multiple problems or functions Has a single programming language implementation 2. A solution
Chapter 4. Computation. Bjarne Stroustrup.
 Chapter 4 Computation Bjarne Stroustrup www.stroustrup.com/programming Abstract Today, I ll present the basics of computation. In particular, we ll discuss expressions, how to iterate over a series of
Chapter 4 Computation Bjarne Stroustrup www.stroustrup.com/programming Abstract Today, I ll present the basics of computation. In particular, we ll discuss expressions, how to iterate over a series of
CH ALGORITHM ANALYSIS CH6. STACKS, QUEUES, AND DEQUES
 CH4.2-4.3. ALGORITHM ANALYSIS CH6. STACKS, QUEUES, AND DEQUES ACKNOWLEDGEMENT: THESE SLIDES ARE ADAPTED FROM SLIDES PROVIDED WITH DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS IN JAVA, GOODRICH, TAMASSIA AND GOLDWASSER
CH4.2-4.3. ALGORITHM ANALYSIS CH6. STACKS, QUEUES, AND DEQUES ACKNOWLEDGEMENT: THESE SLIDES ARE ADAPTED FROM SLIDES PROVIDED WITH DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS IN JAVA, GOODRICH, TAMASSIA AND GOLDWASSER
Data Structures Lecture 3 Order Notation and Recursion
 Data Structures Lecture 3 Order Notation and Recursion 1 Overview The median grade.cpp program from Lecture 2 and background on constructing and using vectors. Algorithm analysis; order notation Recursion
Data Structures Lecture 3 Order Notation and Recursion 1 Overview The median grade.cpp program from Lecture 2 and background on constructing and using vectors. Algorithm analysis; order notation Recursion
Sorting & Searching (and a Tower)
 Sorting & Searching (and a Tower) Sorting Sorting is the process of arranging a list of items into a particular order There must be some value on which the order is based There are many algorithms for
Sorting & Searching (and a Tower) Sorting Sorting is the process of arranging a list of items into a particular order There must be some value on which the order is based There are many algorithms for
Lecture 2: Implementing ADTs
 Lecture 2: Implementing ADTs Data Structures and Algorithms CSE 373 SP 18 - KASEY CHAMPION 1 Warm Up Discuss with your neighbors! From last lecture: - What is an ADT? - What is a data structure? From CSE
Lecture 2: Implementing ADTs Data Structures and Algorithms CSE 373 SP 18 - KASEY CHAMPION 1 Warm Up Discuss with your neighbors! From last lecture: - What is an ADT? - What is a data structure? From CSE
Choice of C++ as Language
 EECS 281: Data Structures and Algorithms Principles of Algorithm Analysis Choice of C++ as Language All algorithms implemented in this book are in C++, but principles are language independent That is,
EECS 281: Data Structures and Algorithms Principles of Algorithm Analysis Choice of C++ as Language All algorithms implemented in this book are in C++, but principles are language independent That is,
What is an algorithm?
 Reminders CS 142 Lecture 3 Analysis, ADTs & Objects Program 1 was assigned - Due on 1/27 by 11:55pm 2 Abstraction Measuring Algorithm Efficiency When you utilize the mylist.index(item) function you are
Reminders CS 142 Lecture 3 Analysis, ADTs & Objects Program 1 was assigned - Due on 1/27 by 11:55pm 2 Abstraction Measuring Algorithm Efficiency When you utilize the mylist.index(item) function you are
CS 311 Data Structures and Algorithms, Fall 2009 Midterm Exam Solutions. The Midterm Exam was give in class on Wednesday, October 21, 2009.
 CS 311 Data Structures and Algorithms, Fall 2009 Midterm Exam Solutions The Midterm Exam was give in class on Wednesday, October 21, 2009. 1. [4 pts] When we define a (non-template) class, we generally
CS 311 Data Structures and Algorithms, Fall 2009 Midterm Exam Solutions The Midterm Exam was give in class on Wednesday, October 21, 2009. 1. [4 pts] When we define a (non-template) class, we generally
Ashish Gupta, Data JUET, Guna
 Categories of data structures Data structures are categories in two classes 1. Linear data structure: - organized into sequential fashion - elements are attached one after another - easy to implement because
Categories of data structures Data structures are categories in two classes 1. Linear data structure: - organized into sequential fashion - elements are attached one after another - easy to implement because
DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS
 LECTURE 8 Babeş - Bolyai University Computer Science and Mathematics Faculty 2017-2018 In Lecture 7... ADT Queue ADT Matrix ADT List ADT Stack Today ADT Queue 1 ADT Queue 2 3 4 Note ADT Queue We will not
LECTURE 8 Babeş - Bolyai University Computer Science and Mathematics Faculty 2017-2018 In Lecture 7... ADT Queue ADT Matrix ADT List ADT Stack Today ADT Queue 1 ADT Queue 2 3 4 Note ADT Queue We will not
! Determine if a number is odd or even. ! Determine if a number/character is in a range. ! Assign a category based on ranges (wind speed)
 Final Exam Exercises Chapters 1-7 + 11 Write C++ code to:! Determine if a number is odd or even CS 2308 Spring 2013 Jill Seaman! Determine if a number/character is in a range - 1 to 10 (inclusive) - between
Final Exam Exercises Chapters 1-7 + 11 Write C++ code to:! Determine if a number is odd or even CS 2308 Spring 2013 Jill Seaman! Determine if a number/character is in a range - 1 to 10 (inclusive) - between
1) What is the primary purpose of template functions? 2) Suppose bag is a template class, what is the syntax for declaring a bag b of integers?
 Review for Final (Chapter 6 13, 15) 6. Template functions & classes 1) What is the primary purpose of template functions? A. To allow a single function to be used with varying types of arguments B. To
Review for Final (Chapter 6 13, 15) 6. Template functions & classes 1) What is the primary purpose of template functions? A. To allow a single function to be used with varying types of arguments B. To
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING
 INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad - 500 043 COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING TUTORIAL QUESTION BANK Course Name Course Code Class Branch DATA STRUCTURES ACS002 B. Tech
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad - 500 043 COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING TUTORIAL QUESTION BANK Course Name Course Code Class Branch DATA STRUCTURES ACS002 B. Tech
Basic memory model Using functions Writing functions. Basics Prototypes Parameters Return types Functions and memory Names and namespaces
 Basic memory model Using functions Writing functions Basics Prototypes Parameters Return types Functions and memory Names and namespaces When a program runs it requires main memory (RAM) space for Program
Basic memory model Using functions Writing functions Basics Prototypes Parameters Return types Functions and memory Names and namespaces When a program runs it requires main memory (RAM) space for Program
CPS311 Lecture: Procedures Last revised 9/9/13. Objectives:
 CPS311 Lecture: Procedures Last revised 9/9/13 Objectives: 1. To introduce general issues that any architecture must address in terms of calling/returning from procedures, passing parameters (including
CPS311 Lecture: Procedures Last revised 9/9/13 Objectives: 1. To introduce general issues that any architecture must address in terms of calling/returning from procedures, passing parameters (including
Binary Search Trees. Carlos Moreno uwaterloo.ca EIT https://ece.uwaterloo.ca/~cmoreno/ece250
 Carlos Moreno cmoreno @ uwaterloo.ca EIT-4103 https://ece.uwaterloo.ca/~cmoreno/ece250 Standard reminder to set phones to silent/vibrate mode, please! Previously, on ECE-250... We discussed trees (the
Carlos Moreno cmoreno @ uwaterloo.ca EIT-4103 https://ece.uwaterloo.ca/~cmoreno/ece250 Standard reminder to set phones to silent/vibrate mode, please! Previously, on ECE-250... We discussed trees (the
Algorithmic Complexity
 Algorithmic Complexity Algorithmic Complexity "Algorithmic Complexity", also called "Running Time" or "Order of Growth", refers to the number of steps a program takes as a function of the size of its inputs.
Algorithmic Complexity Algorithmic Complexity "Algorithmic Complexity", also called "Running Time" or "Order of Growth", refers to the number of steps a program takes as a function of the size of its inputs.
Intro to Algorithms. Professor Kevin Gold
 Intro to Algorithms Professor Kevin Gold What is an Algorithm? An algorithm is a procedure for producing outputs from inputs. A chocolate chip cookie recipe technically qualifies. An algorithm taught in
Intro to Algorithms Professor Kevin Gold What is an Algorithm? An algorithm is a procedure for producing outputs from inputs. A chocolate chip cookie recipe technically qualifies. An algorithm taught in
4.1 COMPUTATIONAL THINKING AND PROBLEM-SOLVING
 4.1 COMPUTATIONAL THINKING AND PROBLEM-SOLVING 4.1.2 ALGORITHMS ALGORITHM An Algorithm is a procedure or formula for solving a problem. It is a step-by-step set of operations to be performed. It is almost
4.1 COMPUTATIONAL THINKING AND PROBLEM-SOLVING 4.1.2 ALGORITHMS ALGORITHM An Algorithm is a procedure or formula for solving a problem. It is a step-by-step set of operations to be performed. It is almost
Recursion (Part 3) 1
 1 Recursion (Part 3) Computational complexity computational complexity is concerned with describing the amount of resources needed to run an algorithm for our purposes, the resource is time complexity
1 Recursion (Part 3) Computational complexity computational complexity is concerned with describing the amount of resources needed to run an algorithm for our purposes, the resource is time complexity
CS 103 Unit 15. Doubly-Linked Lists and Deques. Mark Redekopp
 1 CS 103 Unit 15 Doubly-Linked Lists and Deques Mark Redekopp 2 Singly-Linked List Review Used structures/classes and pointers to make linked data structures Singly-Linked Lists dynamically allocates each
1 CS 103 Unit 15 Doubly-Linked Lists and Deques Mark Redekopp 2 Singly-Linked List Review Used structures/classes and pointers to make linked data structures Singly-Linked Lists dynamically allocates each
CS 216 Exam 1 Fall SOLUTION
 CS 216 Exam 1 Fall 2004 - SOLUTION Name: Lab Section: Email Address: Student ID # This exam is closed note, closed book. You will have an hour and fifty minutes total to complete the exam. You may NOT
CS 216 Exam 1 Fall 2004 - SOLUTION Name: Lab Section: Email Address: Student ID # This exam is closed note, closed book. You will have an hour and fifty minutes total to complete the exam. You may NOT
CS 310: Order Notation (aka Big-O and friends)
 CS 310: Order Notation (aka Big-O and friends) Chris Kauffman Week 1-2 Logistics At Home Read Weiss Ch 1-4: Java Review Read Weiss Ch 5: Big-O Get your java environment set up Compile/Run code for Max
CS 310: Order Notation (aka Big-O and friends) Chris Kauffman Week 1-2 Logistics At Home Read Weiss Ch 1-4: Java Review Read Weiss Ch 5: Big-O Get your java environment set up Compile/Run code for Max
Formal Methods of Software Design, Eric Hehner, segment 24 page 1 out of 5
 Formal Methods of Software Design, Eric Hehner, segment 24 page 1 out of 5 [talking head] This lecture we study theory design and implementation. Programmers have two roles to play here. In one role, they
Formal Methods of Software Design, Eric Hehner, segment 24 page 1 out of 5 [talking head] This lecture we study theory design and implementation. Programmers have two roles to play here. In one role, they
Discussion 2C Notes (Week 3, January 21) TA: Brian Choi Section Webpage:
 Discussion 2C Notes (Week 3, January 21) TA: Brian Choi (schoi@cs.ucla.edu) Section Webpage: http://www.cs.ucla.edu/~schoi/cs32 Abstraction In Homework 1, you were asked to build a class called Bag. Let
Discussion 2C Notes (Week 3, January 21) TA: Brian Choi (schoi@cs.ucla.edu) Section Webpage: http://www.cs.ucla.edu/~schoi/cs32 Abstraction In Homework 1, you were asked to build a class called Bag. Let
Linked Lists
 Linked Lists 2-17-2005 Opening Discussion What did we talk about last class? Do you have any code to show? Do you have any questions about the assignment? Can you tell me what a linked list is and what
Linked Lists 2-17-2005 Opening Discussion What did we talk about last class? Do you have any code to show? Do you have any questions about the assignment? Can you tell me what a linked list is and what
Container Notes. Di erent Kinds of Containers. Types Defined by Containers. C++11 Container Notes C++11
 Di erent Kinds of Containers Container Notes A container is an object that stores other objects and has methods for accessing the elements. There are two fundamentally di erent kinds of containers: Sequences
Di erent Kinds of Containers Container Notes A container is an object that stores other objects and has methods for accessing the elements. There are two fundamentally di erent kinds of containers: Sequences
1. Write step by step code to delete element from existing Doubly Linked List. Suppose that all declarations are done
 1. Write step by step code to delete element from existing Doubly Linked List. Suppose that all declarations are done. first NULL 42 A A 13 A A 6 NULL Write code here first NULL 42 A A 13 A A 6 NULL p
1. Write step by step code to delete element from existing Doubly Linked List. Suppose that all declarations are done. first NULL 42 A A 13 A A 6 NULL Write code here first NULL 42 A A 13 A A 6 NULL p
CMSC 341 Lecture 10 Binary Search Trees
 CMSC 341 Lecture 10 Binary Search Trees John Park Based on slides from previous iterations of this course Review: Tree Traversals 2 Traversal Preorder, Inorder, Postorder H X M A K B E N Y L G W UMBC CMSC
CMSC 341 Lecture 10 Binary Search Trees John Park Based on slides from previous iterations of this course Review: Tree Traversals 2 Traversal Preorder, Inorder, Postorder H X M A K B E N Y L G W UMBC CMSC
Lecture 17: Hash Tables, Maps, Finish Linked Lists
 ....... \ \ \ / / / / \ \ \ \ / \ / \ \ \ V /,----' / ^ \ \.--..--. / ^ \ `--- ----` / ^ \. ` > < / /_\ \. ` / /_\ \ / /_\ \ `--' \ /. \ `----. / \ \ '--' '--' / \ / \ \ / \ / / \ \ (_ ) \ (_ ) / / \ \
....... \ \ \ / / / / \ \ \ \ / \ / \ \ \ V /,----' / ^ \ \.--..--. / ^ \ `--- ----` / ^ \. ` > < / /_\ \. ` / /_\ \ / /_\ \ `--' \ /. \ `----. / \ \ '--' '--' / \ / \ \ / \ / / \ \ (_ ) \ (_ ) / / \ \
Lecture No.04. Data Structures
 Lecture No.04 Data Structures Josephus Problem #include "CList.cpp" void main(int argc, char *argv[]) { CList list; int i, N=10, M=3; for(i=1; i
Lecture No.04 Data Structures Josephus Problem #include "CList.cpp" void main(int argc, char *argv[]) { CList list; int i, N=10, M=3; for(i=1; i
Total Score /15 /20 /30 /10 /5 /20 Grader
 NAME: NETID: CS2110 Fall 2009 Prelim 2 November 17, 2009 Write your name and Cornell netid. There are 6 questions on 8 numbered pages. Check now that you have all the pages. Write your answers in the boxes
NAME: NETID: CS2110 Fall 2009 Prelim 2 November 17, 2009 Write your name and Cornell netid. There are 6 questions on 8 numbered pages. Check now that you have all the pages. Write your answers in the boxes
CS197c: Programming in C++
 CS197c: Programming in C++ Lecture 2 Marc Cartright http://ciir.cs.umass.edu/~irmarc/cs197c/index.html Administration HW1 will be up this afternoon Written assignment Due in class next week See website
CS197c: Programming in C++ Lecture 2 Marc Cartright http://ciir.cs.umass.edu/~irmarc/cs197c/index.html Administration HW1 will be up this afternoon Written assignment Due in class next week See website
Purpose of Review. Review some basic C++ Familiarize us with Weiss s style Introduce specific constructs useful for implementing data structures
 C++ Review 1 Purpose of Review Review some basic C++ Familiarize us with Weiss s style Introduce specific constructs useful for implementing data structures 2 Class The Class defines the data structure
C++ Review 1 Purpose of Review Review some basic C++ Familiarize us with Weiss s style Introduce specific constructs useful for implementing data structures 2 Class The Class defines the data structure
CMPSCI 187: Programming With Data Structures. Lecture #26: Binary Search Trees David Mix Barrington 9 November 2012
 CMPSCI 187: Programming With Data Structures Lecture #26: Binary Search Trees David Mix Barrington 9 November 2012 Binary Search Trees Why Binary Search Trees? Trees, Binary Trees and Vocabulary The BST
CMPSCI 187: Programming With Data Structures Lecture #26: Binary Search Trees David Mix Barrington 9 November 2012 Binary Search Trees Why Binary Search Trees? Trees, Binary Trees and Vocabulary The BST
Course Review. Cpt S 223 Fall 2009
 Course Review Cpt S 223 Fall 2009 1 Final Exam When: Tuesday (12/15) 8-10am Where: in class Closed book, closed notes Comprehensive Material for preparation: Lecture slides & class notes Homeworks & program
Course Review Cpt S 223 Fall 2009 1 Final Exam When: Tuesday (12/15) 8-10am Where: in class Closed book, closed notes Comprehensive Material for preparation: Lecture slides & class notes Homeworks & program
CSC 273 Data Structures
 CSC 273 Data Structures Lecture 4- Recursion What Is Recursion? Consider hiring a contractor to build He hires a subcontractor for a portion of the job That subcontractor hires a sub-subcontractor to do
CSC 273 Data Structures Lecture 4- Recursion What Is Recursion? Consider hiring a contractor to build He hires a subcontractor for a portion of the job That subcontractor hires a sub-subcontractor to do
