Building Java Programs
|
|
|
- Christiana Page
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Building Java Programs Chapter 4 Lecture 4-2: Advanced if/else; Cumulative sum; reading: 4.2,
2 2
3 Advanced if/else reading:
4 Factoring if/else code factoring: Extracting common/redundant code. Can reduce or eliminate redundancy from if/else code. Example: if (a == 1) { System.out.println(a); x = 3; b = b + x; else if (a == 2) { System.out.println(a); x = 6; y = y + 10; b = b + x; else { // a == 3 System.out.println(a); x = 9; b = b + x; System.out.println(a); x = 3 * a; if (a == 2) { y = y + 10; b = b + x; 4
5 The "dangling if" problem What can be improved about the following code? if (x < 0) { System.out.println("x is negative"); else if (x >= 0) { System.out.println("x is non-negative"); The second if test is unnecessary and can be removed: if (x < 0) { System.out.println("x is negative"); else { System.out.println("x is non-negative"); This is also relevant in methods that use if with return... 5
6 if/else with return // Returns the larger of the two given integers. public static int max(int a, int b) { if (a > b) { return a; else { return b; Methods can return different values using if/else Whichever path the code enters, it will return that value. Returning a value causes a method to immediately exit. All paths through the code must reach a return statement. 6
7 All paths must return public static int max(int a, int b) { if (a > b) { return a; // Error: not all paths return a value The following also does not compile: public static int max(int a, int b) { if (a > b) { return a; else if (b >= a) { return b; The compiler thinks if/else/if code might skip all paths, even though mathematically it must choose one or the other. 7
8 Logical operators Tests can be combined using logical operators: Operator Description Example Result && and (2 == 3) && (-1 < 5) false or (2 == 3) (-1 < 5) true! not!(2 == 3) true "Truth tables" for each, used with logical values p and q: p q p && q p q true true true true true false false true false true false true false false false false p!p true fals e false true 8
9 Evaluating logical expressions Relational operators have lower precedence than math; logical operators have lower precedence than relational operators 5 * 7 >= * (7 1) && 7 <= 11 5 * 7 >= * 6 && 7 <= >= && 7 <= >= 33 && 7 <= 11 true && true true Relational operators cannot be "chained" as in algebra 2 <= x <= 10 true <= 10 (assume that x is 15) Error! Instead, combine multiple tests with && or 2 <= x && x <= 10 true && false false 9
10 Logical questions What is the result of each of the following expressions? int x = 42; int y = 17; int z = 25; y < x && y <= z x % 2 == y % 2 x % 2 == z % 2 x <= y + z && x >= y + z!(x < y && x < z) (x + y) % 2 == 0!((z - y) % 2 == 0) Answers: true, false, true, true, false 10
11 Cumulative algorithms reading: 4.2
12 Adding many numbers How would you find the sum of all integers from ? // This may require a lot of typing int sum = ; System.out.println("The sum is " + sum); What if we want the sum from 1-1,000,000? Or the sum up to any maximum? How can we generalize the above code? 12
13 Cumulative sum loop int sum = 0; for (int i = 1; i <= 1000; i++) { sum = sum + i; System.out.println("The sum is " + sum); cumulative sum: A variable that keeps a sum in progress and is updated repeatedly until summing is finished. The sum in the above code is an attempt at a cumulative sum. Cumulative sum variables must be declared outside the loops that update them, so that they will still exist after the loop. 13
14 Cumulative product This cumulative idea can be used with other operators: int product = 1; for (int i = 1; i <= 20; i++) { product = product * 2; System.out.println("2 ^ 20 = " + product); How would we make the base and exponent adjustable? 14
15 Scanner and cumulative sum We can do a cumulative sum of user input: Scanner console = new Scanner(System.in); int sum = 0; for (int i = 1; i <= 100; i++) { System.out.print("Type a number: "); sum = sum + console.nextint(); System.out.println("The sum is " + sum); 15
16 Cumulative sum question Modify the Receipt program from Ch. 2. Prompt for how many people, and each person's dinner cost. Use static methods to structure the solution. Example log of execution: How many people ate? 4 Person #1: How much did your dinner cost? Person #2: How much did your dinner cost? 15 Person #3: How much did your dinner cost? 30.0 Person #4: How much did your dinner cost? Subtotal: $75.0 Tax: $6.0 Tip: $11.25 Total: $
17 Cumulative sum answer // This program enhances our Receipt program using a cumulative sum. import java.util.*; public class Receipt2 { public static void main(string[] args) { Scanner console = new Scanner(System.in); double subtotal = meals(console); results(subtotal); // Prompts for number of people and returns total meal subtotal. public static double meals(scanner console) { System.out.print("How many people ate? "); int people = console.nextint(); double subtotal = 0.0; // cumulative sum... for (int i = 1; i <= people; i++) { System.out.print("Person #" + i + ": How much did your dinner cost? "); double personcost = console.nextdouble(); subtotal = subtotal + personcost; // add to sum return subtotal; 17
18 Cumulative answer, cont'd.... // Calculates total owed, assuming 8% tax and 15% tip public static void results(double subtotal) { double tax = subtotal *.08; double tip = subtotal *.15; double total = subtotal + tax + tip; System.out.println("Subtotal: $" + subtotal); System.out.println("Tax: $" + tax); System.out.println("Tip: $" + tip); System.out.println("Total: $" + total); 18
19 if/else, return question Write a method countfactors that returns the number of factors of an integer. countfactors(24) returns 8 because 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 8, 12, and 24 are factors of 24. Solution: // Returns how many factors the given number has. public static int countfactors(int number) { int count = 0; for (int i = 1; i <= number; i++) { if (number % i == 0) { count++; // i is a factor of number return count; 19
20 Nested if/else question Formula for body mass index (BMI): BMI below 18.5 Weight class underweight normal overweight 30.0 and up obese Write a program that produces output like the following: This program reads data for two people and computes their body mass index (BMI). Enter next person's information: height (in inches)? 70.0 weight (in pounds)? Enter next person's information: height (in inches)? 62.5 weight (in pounds)? Person 1 BMI = overweight Person 2 BMI = normal Difference =
21 Nested if/else answer // This program computes two people's body mass index (BMI) and // compares them. The code uses Scanner for input, and parameters/returns. import java.util.*; // so that I can use Scanner public class BMI { public static void main(string[] args) { introduction(); Scanner console = new Scanner(System.in); double bmi1 = person(console); double bmi2 = person(console); // report overall results report(1, bmi1); report(2, bmi2); System.out.println("Difference = " + Math.abs(bmi1 - bmi2));... // prints a welcome message explaining the program public static void introduction() { System.out.println("This program reads data for two people and"); System.out.println("computes their body mass index (BMI)."); System.out.println(); 21
22 Nested if/else, cont'd. // reads information for one person, computes their BMI, and returns it public static double person(scanner console) { System.out.println("Enter next person's information:"); System.out.print("height (in inches)? "); double height = console.nextdouble(); System.out.print("weight (in pounds)? "); double weight = console.nextdouble(); System.out.println(); double bodymass = bmi(height, weight); return bodymass; // Computes/returns a person's BMI based on their height and weight. public static double bmi(double height, double weight) { return (weight * 703 / height / height); // Outputs information about a person's BMI and weight status. public static void report(int number, double bmi) { System.out.println("Person " + number + " BMI = " + bmi); if (bmi < 18.5) { System.out.println("underweight"); else if (bmi < 25) { System.out.println("normal"); else if (bmi < 30) { System.out.println("overweight"); else { System.out.println("obese"); 22
COSC 236 Section 101 Computer Science 1 -- Prof. Michael A. Soderstrand
 COSC 236 Section 101 Computer Science 1 -- Prof. Michael A. Soderstrand COSC 236 Web Site You will always find the course material at: http://www.class-notes.us or http://www.class-notes.info or http://www.lecture-notes.tripod.com
COSC 236 Section 101 Computer Science 1 -- Prof. Michael A. Soderstrand COSC 236 Web Site You will always find the course material at: http://www.class-notes.us or http://www.class-notes.info or http://www.lecture-notes.tripod.com
Building Java Programs Chapter 4
 Building Java Programs Chapter 4 Conditional Execution Copyright (c) Pearson 2013. All rights reserved. The if statement Executes a block of statements only if a test is true if (test) { statement;...
Building Java Programs Chapter 4 Conditional Execution Copyright (c) Pearson 2013. All rights reserved. The if statement Executes a block of statements only if a test is true if (test) { statement;...
Building Java Programs
 Building Java Programs Chapter 4 Lecture 4-1: if and if/else Statements reading: 4.2 self-check: #4-5, 7, 10, 11 exercises: #7 videos: Ch. 4 #2-4 Loops with if/else if/else statements can be used with
Building Java Programs Chapter 4 Lecture 4-1: if and if/else Statements reading: 4.2 self-check: #4-5, 7, 10, 11 exercises: #7 videos: Ch. 4 #2-4 Loops with if/else if/else statements can be used with
Building Java Programs
 Building Java Programs Chapter 4 Lecture 4-1: Scanner; if/else reading: 3.3 3.4, 4.1, 4.5 2 Interactive Programs with Scanner reading: 3.3-3.4 Interactive programs We have written programs that print console
Building Java Programs Chapter 4 Lecture 4-1: Scanner; if/else reading: 3.3 3.4, 4.1, 4.5 2 Interactive Programs with Scanner reading: 3.3-3.4 Interactive programs We have written programs that print console
Returns & if/else. Parameters and Objects
 Returns & if/else Parameters and Objects Subset of the Supplement Lesson slides from: Building Java Programs, Chapter 3 & 4 by Stuart Reges and Marty Stepp (http://www.buildingjavaprograms.com/ ) & thanks
Returns & if/else Parameters and Objects Subset of the Supplement Lesson slides from: Building Java Programs, Chapter 3 & 4 by Stuart Reges and Marty Stepp (http://www.buildingjavaprograms.com/ ) & thanks
Topic 12 more if/else, cumulative algorithms, printf
 Topic 12 more if/else, cumulative algorithms, printf "We flew down weekly to meet with IBM, but they thought the way to measure software was the amount of code we wrote, when really the better the software,
Topic 12 more if/else, cumulative algorithms, printf "We flew down weekly to meet with IBM, but they thought the way to measure software was the amount of code we wrote, when really the better the software,
Advanced if/else & Cumulative Sum
 Advanced if/else & Cumulative Sum Subset of the Supplement Lesson slides from: Building Java Programs, Chapter 4 by Stuart Reges and Marty Stepp (http://www.buildingjavaprograms.com/ ) Questions to consider
Advanced if/else & Cumulative Sum Subset of the Supplement Lesson slides from: Building Java Programs, Chapter 4 by Stuart Reges and Marty Stepp (http://www.buildingjavaprograms.com/ ) Questions to consider
Topic 12 more if/else, cumulative algorithms, printf
 Topic 12 more if/else, cumulative algorithms, printf "We flew down weekly to meet with IBM, but they thought the way to measure software was the amount of code we wrote, when really the better the software,
Topic 12 more if/else, cumulative algorithms, printf "We flew down weekly to meet with IBM, but they thought the way to measure software was the amount of code we wrote, when really the better the software,
Topic 13 procedural design and Strings
 Topic 13 procedural design and Strings Ugly programs are like ugly suspension bridges: they're much more liable to collapse than pretty ones, because the way humans (especially engineerhumans) perceive
Topic 13 procedural design and Strings Ugly programs are like ugly suspension bridges: they're much more liable to collapse than pretty ones, because the way humans (especially engineerhumans) perceive
CSc 110, Autumn 2016 Lecture 10: Advanced if/else; Cumulative sum. Adapted from slides by Marty Stepp and Stuart Reges
 CSc 110, Autumn 2016 Lecture 10: Advanced if/else; Cumulative sum Adapted from slides by Marty Stepp and Stuart Reges Factoring if/else code factoring: Extracting common/redundant code. Can reduce or eliminate
CSc 110, Autumn 2016 Lecture 10: Advanced if/else; Cumulative sum Adapted from slides by Marty Stepp and Stuart Reges Factoring if/else code factoring: Extracting common/redundant code. Can reduce or eliminate
Building Java Programs
 Building Java Programs Chapter 4: Conditional Execution 1 loop techniques cumulative sum fencepost loops conditional execution Chapter outline the if statement and the if/else statement relational expressions
Building Java Programs Chapter 4: Conditional Execution 1 loop techniques cumulative sum fencepost loops conditional execution Chapter outline the if statement and the if/else statement relational expressions
Building Java Programs
 Building Java Programs Chapter 4 Lecture 4-1: if and if/else Statements reading: 4.2 self-check: #4-5, 7, 10, 11 exercises: #7 videos: Ch. 4 #2-4 The if/else statement Executes one block if a test is true,
Building Java Programs Chapter 4 Lecture 4-1: if and if/else Statements reading: 4.2 self-check: #4-5, 7, 10, 11 exercises: #7 videos: Ch. 4 #2-4 The if/else statement Executes one block if a test is true,
CSc 110, Autumn 2016 Lecture 12: Advanced if/else; Cumulative sum. Adapted from slides by Marty Stepp and Stuart Reges
 CSc 110, Autumn 2016 Lecture 12: Advanced if/else; Cumulative sum Adapted from slides by Marty Stepp and Stuart Reges Nested if/else question Write a program that produces output like the following: This
CSc 110, Autumn 2016 Lecture 12: Advanced if/else; Cumulative sum Adapted from slides by Marty Stepp and Stuart Reges Nested if/else question Write a program that produces output like the following: This
Building Java Programs
 Building Java Programs Chapter 4 Lecture 4-1: if and if/else Statements reading: 4.2 self-check: #4-5, 7, 10, 11 exercises: #7 videos: Ch. 4 #2-4 Loops with if/else if/else statements can be used with
Building Java Programs Chapter 4 Lecture 4-1: if and if/else Statements reading: 4.2 self-check: #4-5, 7, 10, 11 exercises: #7 videos: Ch. 4 #2-4 Loops with if/else if/else statements can be used with
Building Java Programs
 Building Java Programs Chapter 3: Parameters, Return, and Interactive Programs with Scanner 1 Lecture outline console input with Scanner objects input tokens Scanner as a parameter to a method cumulative
Building Java Programs Chapter 3: Parameters, Return, and Interactive Programs with Scanner 1 Lecture outline console input with Scanner objects input tokens Scanner as a parameter to a method cumulative
Building Java Programs
 Building Java Programs Chapter 4 Lecture 4-3: Strings; char; printf; procedural design reading: 3.3, 4.3, 4.5 1 Strings reading: 3.3 1 Strings string: An object storing a sequence of text characters. Unlike
Building Java Programs Chapter 4 Lecture 4-3: Strings; char; printf; procedural design reading: 3.3, 4.3, 4.5 1 Strings reading: 3.3 1 Strings string: An object storing a sequence of text characters. Unlike
Lecture 4: Conditionals
 Lecture 4: Conditionals Building Java Programs: A Back to Basics Approach by Stuart Reges and Marty Stepp Copyright (c) Pearson 2013. All rights reserved. Type boolean Type boolean boolean: A logical type
Lecture 4: Conditionals Building Java Programs: A Back to Basics Approach by Stuart Reges and Marty Stepp Copyright (c) Pearson 2013. All rights reserved. Type boolean Type boolean boolean: A logical type
Building Java Programs
 Building Java Programs Chapter 2 Lecture 2-1: Expressions and Variables reading: 2.1-2.2 1 Data and expressions reading: 2.1 self-check: 1-4 videos: Ch. 2 #1 2 Data types type: A category or set of data
Building Java Programs Chapter 2 Lecture 2-1: Expressions and Variables reading: 2.1-2.2 1 Data and expressions reading: 2.1 self-check: 1-4 videos: Ch. 2 #1 2 Data types type: A category or set of data
AP Computer Science. if/else, return values. Copyright 2010 by Pearson Education
 AP Computer Science if/else, return values The if statement Executes a block of statements only if a test is true statement;... statement; Example: double gpa = console.nextdouble(); if (gpa >= 2.0) {
AP Computer Science if/else, return values The if statement Executes a block of statements only if a test is true statement;... statement; Example: double gpa = console.nextdouble(); if (gpa >= 2.0) {
Building Java Programs
 Building Java Programs Chapter 2 Lecture 2-1: Expressions and Variables reading: 2.1-2.2 Copyright 2009 by Pearson Education Data and expressions reading: 2.1 self-check: 1-4 videos: Ch. 2 #1 Copyright
Building Java Programs Chapter 2 Lecture 2-1: Expressions and Variables reading: 2.1-2.2 Copyright 2009 by Pearson Education Data and expressions reading: 2.1 self-check: 1-4 videos: Ch. 2 #1 Copyright
CSc 110, Autumn Lecture 13: Cumulative Sum and Boolean Logic. Adapted from slides by Marty Stepp and Stuart Reges
 CSc 110, Autumn 2017 Lecture 13: Cumulative Sum and Boolean Logic Adapted from slides by Marty Stepp and Stuart Reges Adding many numbers How would you find the sum of all integers from 1-1000? # This
CSc 110, Autumn 2017 Lecture 13: Cumulative Sum and Boolean Logic Adapted from slides by Marty Stepp and Stuart Reges Adding many numbers How would you find the sum of all integers from 1-1000? # This
Building Java Programs
 Building Java Programs Chapter 2 Lecture 2-1: Expressions and Variables reading: 2.1-2.2 1 2 Data and expressions reading: 2.1 3 The computer s view Internally, computers store everything as 1 s and 0
Building Java Programs Chapter 2 Lecture 2-1: Expressions and Variables reading: 2.1-2.2 1 2 Data and expressions reading: 2.1 3 The computer s view Internally, computers store everything as 1 s and 0
Building Java Programs. Chapter 2: Primitive Data and Definite Loops
 Building Java Programs Chapter 2: Primitive Data and Definite Loops Copyright 2008 2006 by Pearson Education 1 Lecture outline data concepts Primitive types: int, double, char (for now) Expressions: operators,
Building Java Programs Chapter 2: Primitive Data and Definite Loops Copyright 2008 2006 by Pearson Education 1 Lecture outline data concepts Primitive types: int, double, char (for now) Expressions: operators,
Building Java Programs
 Building Java Programs Chapter 2 Lecture 2-1: Expressions and Variables reading: 2.1-2.2 1 Variables reading: 2.2 self-check: 1-15 exercises: 1-4 videos: Ch. 2 #2 2 Receipt example What's bad about the
Building Java Programs Chapter 2 Lecture 2-1: Expressions and Variables reading: 2.1-2.2 1 Variables reading: 2.2 self-check: 1-15 exercises: 1-4 videos: Ch. 2 #2 2 Receipt example What's bad about the
COSC 236 Section 101 Computer Science 1 -- Prof. Michael A. Soderstrand
 COSC 236 Section 101 Computer Science 1 -- Prof. Michael A. Soderstrand COSC 236 Web Site You will always find the course material at: http://www.class-notes.us or http://www.class-notes.info or http://www.lecture-notes.tripod.com
COSC 236 Section 101 Computer Science 1 -- Prof. Michael A. Soderstrand COSC 236 Web Site You will always find the course material at: http://www.class-notes.us or http://www.class-notes.info or http://www.lecture-notes.tripod.com
Topic 11 Scanner object, conditional execution
 Topic 11 Scanner object, conditional execution "There are only two kinds of programming languages: those people always [complain] about and those nobody uses." Bjarne Stroustroup, creator of C++ Copyright
Topic 11 Scanner object, conditional execution "There are only two kinds of programming languages: those people always [complain] about and those nobody uses." Bjarne Stroustroup, creator of C++ Copyright
Topic 4 Expressions and variables
 Topic 4 Expressions and variables "Once a person has understood the way variables are used in programming, he has understood the quintessence of programming." -Professor Edsger W. Dijkstra Based on slides
Topic 4 Expressions and variables "Once a person has understood the way variables are used in programming, he has understood the quintessence of programming." -Professor Edsger W. Dijkstra Based on slides
Building Java Programs
 Building Java Programs Chapter 5 Lecture 5-4: do/while loops, assertions reading: 5.1, 5.5 1 The do/while loop do/while loop: Performs its test at the end of each repetition. Guarantees that the loop's
Building Java Programs Chapter 5 Lecture 5-4: do/while loops, assertions reading: 5.1, 5.5 1 The do/while loop do/while loop: Performs its test at the end of each repetition. Guarantees that the loop's
Building Java Programs
 Building Java Programs Chapter 5 Lecture 5-1: while Loops, Fencepost Loops, and Sentinel Loops reading: 4.1, 5.1 self-check: Ch. 4 #2; Ch. 5 # 1-10 exercises: Ch. 4 #2, 4, 5, 8; Ch. 5 # 1-2 Copyright 2009
Building Java Programs Chapter 5 Lecture 5-1: while Loops, Fencepost Loops, and Sentinel Loops reading: 4.1, 5.1 self-check: Ch. 4 #2; Ch. 5 # 1-10 exercises: Ch. 4 #2, 4, 5, 8; Ch. 5 # 1-2 Copyright 2009
Building Java Programs
 Building Java Programs Chapter 5 Lecture 5-4: do/while loops, assertions reading: 5.1, 5.5 1 The do/while loop do/while loop: Performs its test at the end of each repetition. Guarantees that the loop's
Building Java Programs Chapter 5 Lecture 5-4: do/while loops, assertions reading: 5.1, 5.5 1 The do/while loop do/while loop: Performs its test at the end of each repetition. Guarantees that the loop's
! definite loop: A loop that executes a known number of times. " The for loops we have seen so far are definite loops. ! We often use language like
 Indefinite loops while loop! indefinite loop: A loop where it is not obvious in advance how many times it will execute.! We often use language like " "Keep looping as long as or while this condition is
Indefinite loops while loop! indefinite loop: A loop where it is not obvious in advance how many times it will execute.! We often use language like " "Keep looping as long as or while this condition is
Building Java Programs Chapter 2
 Building Java Programs Chapter 2 Primitive Data and Definite Loops Copyright (c) Pearson 2013. All rights reserved. Data types type: A category or set of data values. Constrains the operations that can
Building Java Programs Chapter 2 Primitive Data and Definite Loops Copyright (c) Pearson 2013. All rights reserved. Data types type: A category or set of data values. Constrains the operations that can
Chapter 3 Selections. 3.1 Introduction. 3.2 boolean Data Type
 3.1 Introduction Chapter 3 Selections Java provides selections that let you choose actions with two or more alternative courses. Selection statements use conditions. Conditions are Boolean expressions.
3.1 Introduction Chapter 3 Selections Java provides selections that let you choose actions with two or more alternative courses. Selection statements use conditions. Conditions are Boolean expressions.
Topic 11 Scanner object, conditional execution
 https://www.dignitymemorial.com/obituaries/brookline-ma/adele-koss-5237804 Topic 11 Scanner object, conditional execution Logical thinking and experience was as important as theory in using the computer
https://www.dignitymemorial.com/obituaries/brookline-ma/adele-koss-5237804 Topic 11 Scanner object, conditional execution Logical thinking and experience was as important as theory in using the computer
Chapter 3 Selections. Liang, Introduction to Java Programming, Eighth Edition, (c) 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 3 Selections Liang, Introduction to Java Programming, Eighth Edition, (c) 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved. 0132130807 1 Motivations If you assigned a negative value for radius
Chapter 3 Selections Liang, Introduction to Java Programming, Eighth Edition, (c) 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved. 0132130807 1 Motivations If you assigned a negative value for radius
Lecture 2: Operations and Data Types
 Lecture 2: Operations and Data Types Building Java Programs: A Back to Basics Approach by Stuart Reges and Marty Stepp Copyright (c) Pearson 2013. All rights reserved. Data types type: A category or set
Lecture 2: Operations and Data Types Building Java Programs: A Back to Basics Approach by Stuart Reges and Marty Stepp Copyright (c) Pearson 2013. All rights reserved. Data types type: A category or set
Building Java Programs Chapter 2. bug. Primitive Data and Definite Loops. Copyright (c) Pearson All rights reserved. Software Flaw.
 Building Java Programs Chapter 2 bug Primitive Data and Definite Loops Copyright (c) Pearson 2013. All rights reserved. 2 An Insect Software Flaw 3 4 Bug, Kentucky Bug Eyed 5 Cheesy Movie 6 Punch Buggy
Building Java Programs Chapter 2 bug Primitive Data and Definite Loops Copyright (c) Pearson 2013. All rights reserved. 2 An Insect Software Flaw 3 4 Bug, Kentucky Bug Eyed 5 Cheesy Movie 6 Punch Buggy
Building Java Programs Chapter 2
 Building Java Programs Chapter 2 Primitive Data and Definite Loops Copyright (c) Pearson 2013. All rights reserved. bug 2 An Insect 3 Software Flaw 4 Bug, Kentucky 5 Bug Eyed 6 Cheesy Movie 7 Punch Buggy
Building Java Programs Chapter 2 Primitive Data and Definite Loops Copyright (c) Pearson 2013. All rights reserved. bug 2 An Insect 3 Software Flaw 4 Bug, Kentucky 5 Bug Eyed 6 Cheesy Movie 7 Punch Buggy
Garfield AP CS. User Input, If/Else. Most slides from Building Java Programs. Thanks, Stuart Regesand Marty Stepp!
 Garfield AP CS User Input, If/Else Most slides from Building Java Programs. Thanks, Stuart Regesand Marty Stepp! Warmup Write a method add10 that takes one integer parameter. Your method should return
Garfield AP CS User Input, If/Else Most slides from Building Java Programs. Thanks, Stuart Regesand Marty Stepp! Warmup Write a method add10 that takes one integer parameter. Your method should return
Chapter 2: Basic Elements of Java
 Chapter 2: Basic Elements of Java TRUE/FALSE 1. The pair of characters // is used for single line comments. ANS: T PTS: 1 REF: 29 2. The == characters are a special symbol in Java. ANS: T PTS: 1 REF: 30
Chapter 2: Basic Elements of Java TRUE/FALSE 1. The pair of characters // is used for single line comments. ANS: T PTS: 1 REF: 29 2. The == characters are a special symbol in Java. ANS: T PTS: 1 REF: 30
Computer Programming, I. Laboratory Manual. Experiment #2. Elementary Programming
 Think Twice Code Once The Islamic University of Gaza Engineering Faculty Department of Computer Engineering Fall 2017 ECOM 2005 Khaleel I. Shaheen Computer Programming, I Laboratory Manual Experiment #2
Think Twice Code Once The Islamic University of Gaza Engineering Faculty Department of Computer Engineering Fall 2017 ECOM 2005 Khaleel I. Shaheen Computer Programming, I Laboratory Manual Experiment #2
CS 112 Introduction to Programming
 CS 112 Introduction to Programming (Spring 2012) Lecture #8: More on Conditional & Loop Zhong Shao Department of Computer Science Yale University Office: 314 Watson http://flint.cs.yale.edu/cs112 Acknowledgements:
CS 112 Introduction to Programming (Spring 2012) Lecture #8: More on Conditional & Loop Zhong Shao Department of Computer Science Yale University Office: 314 Watson http://flint.cs.yale.edu/cs112 Acknowledgements:
Flow of Control of Program Statements CS 112 Introduction to Programming. Basic if Conditional Statement Basic Test: Relational Operators
 Flow of Control of Program Statements CS 112 Introduction to Programming (Spring 2012) q Java provides two types of program flow of control statements: decision statements, or conditional statements: decide
Flow of Control of Program Statements CS 112 Introduction to Programming (Spring 2012) q Java provides two types of program flow of control statements: decision statements, or conditional statements: decide
CSS 161 Fundamentals of Compu3ng. Flow control (2) October 10, Instructor: Uma Murthy
 CSS 161 Fundamentals of Compu3ng Flow control (2) October 10, 2012 Instructor: Uma Murthy Outline Reminders: HW 2 due Monday Today: Errata Review condi3onals Boolean expressions (3.2) Loops (3.3) CSS 161:
CSS 161 Fundamentals of Compu3ng Flow control (2) October 10, 2012 Instructor: Uma Murthy Outline Reminders: HW 2 due Monday Today: Errata Review condi3onals Boolean expressions (3.2) Loops (3.3) CSS 161:
CS 1063 Introduction to Computer Programming Midterm Exam 2 Section 1 Sample Exam
 Seat Number Name CS 1063 Introduction to Computer Programming Midterm Exam 2 Section 1 Sample Exam This is a closed book exam. Answer all of the questions on the question paper in the space provided. If
Seat Number Name CS 1063 Introduction to Computer Programming Midterm Exam 2 Section 1 Sample Exam This is a closed book exam. Answer all of the questions on the question paper in the space provided. If
Some Sample AP Computer Science A Questions - Solutions
 Some Sample AP Computer Science A Questions - s Note: These aren't from actual AP tests. I've created these questions based on looking at actual AP tests. Also, in cases where it's not necessary to have
Some Sample AP Computer Science A Questions - s Note: These aren't from actual AP tests. I've created these questions based on looking at actual AP tests. Also, in cases where it's not necessary to have
Example: Monte Carlo Simulation 1
 Example: Monte Carlo Simulation 1 Write a program which conducts a Monte Carlo simulation to estimate π. 1 See https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/monte_carlo_method. Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 133 / 149
Example: Monte Carlo Simulation 1 Write a program which conducts a Monte Carlo simulation to estimate π. 1 See https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/monte_carlo_method. Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 133 / 149
AP Computer Science. Return values, Math, and double. Copyright 2010 by Pearson Education
 AP Computer Science Return values, Math, and double Distance between points Write a method that given x and y coordinates for two points prints the distance between them If you can t do all of it, pseudocode?
AP Computer Science Return values, Math, and double Distance between points Write a method that given x and y coordinates for two points prints the distance between them If you can t do all of it, pseudocode?
Building Java Programs
 Building Java Programs Chapter 5 Lecture 5-1: while Loops, Fencepost Loops, and Sentinel Loops reading: 5.1 5.2 1 2 A deceptive problem... Write a method printletters that prints each letter from a word
Building Java Programs Chapter 5 Lecture 5-1: while Loops, Fencepost Loops, and Sentinel Loops reading: 5.1 5.2 1 2 A deceptive problem... Write a method printletters that prints each letter from a word
Lecture 5: Methods CS2301
 Lecture 5: Methods NADA ALZAHRANI CS2301 1 Opening Problem Find the sum of integers from 1 to 10, from 20 to 30, and from 35 to 45, respectively. 2 Solution public static int sum(int i1, int i2) { int
Lecture 5: Methods NADA ALZAHRANI CS2301 1 Opening Problem Find the sum of integers from 1 to 10, from 20 to 30, and from 35 to 45, respectively. 2 Solution public static int sum(int i1, int i2) { int
COSC 236 Section 101 Computer Science 1 -- Prof. Michael A. Soderstrand
 COSC 236 Section 101 Computer Science 1 -- Prof. Michael A. Soderstrand COSC 236 Web Site I have decided to keep this site for the whole semester I still hope to have blackboard up and running, but you
COSC 236 Section 101 Computer Science 1 -- Prof. Michael A. Soderstrand COSC 236 Web Site I have decided to keep this site for the whole semester I still hope to have blackboard up and running, but you
Arrays. Weather Problem Array Declaration Accessing Elements Arrays and for Loops Array length field Quick Array Initialization Array Traversals
 Arrays Weather Problem Array Declaration Accessing Elements Arrays and for Loops Array length field Quick Array Initialization Array Traversals Can we solve this problem? Consider the following program
Arrays Weather Problem Array Declaration Accessing Elements Arrays and for Loops Array length field Quick Array Initialization Array Traversals Can we solve this problem? Consider the following program
Sequence structure. The computer executes java statements one after the other in the order in which they are written. Total = total +grade;
 Control Statements Control Statements All programs could be written in terms of only one of three control structures: Sequence Structure Selection Structure Repetition Structure Sequence structure The
Control Statements Control Statements All programs could be written in terms of only one of three control structures: Sequence Structure Selection Structure Repetition Structure Sequence structure The
In this chapter, you will:
 Java Programming: Guided Learning with Early Objects Chapter 4 Control Structures I: Selection In this chapter, you will: Make decisions with the if and if else structures Use compound statements in an
Java Programming: Guided Learning with Early Objects Chapter 4 Control Structures I: Selection In this chapter, you will: Make decisions with the if and if else structures Use compound statements in an
Chapter 4: Control Structures I
 Chapter 4: Control Structures I Java Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program Design, Second Edition Chapter Objectives Learn about control structures. Examine relational and logical operators. Explore
Chapter 4: Control Structures I Java Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program Design, Second Edition Chapter Objectives Learn about control structures. Examine relational and logical operators. Explore
1. An operation in which an overall value is computed incrementally, often using a loop.
 Practice Exam 2 Part I: Vocabulary (10 points) Write the terms defined by the statements below. 1. An operation in which an overall value is computed incrementally, often using a loop. 2. The < (less than)
Practice Exam 2 Part I: Vocabulary (10 points) Write the terms defined by the statements below. 1. An operation in which an overall value is computed incrementally, often using a loop. 2. The < (less than)
Tutorial # 4. Q1. Evaluate the logical (Boolean) expression in the following exercise
 Tutorial # 4 Q1. Evaluate the logical (Boolean) expression in the following exercise 1 int num1 = 3, num2 = 2; (num1 > num2) 2 double hours = 12.8; (hours > 40.2) 3 int funny = 7; (funny!= 1) 4 double
Tutorial # 4 Q1. Evaluate the logical (Boolean) expression in the following exercise 1 int num1 = 3, num2 = 2; (num1 > num2) 2 double hours = 12.8; (hours > 40.2) 3 int funny = 7; (funny!= 1) 4 double
CS 112 Introduction to Programming
 CS 112 Introduction to Programming Variables; Type Casting; Using Variables in for Loops Yang (Richard) Yang Computer Science Department Yale University 308A Watson, Phone: 432-6400 Email: yry@cs.yale.edu
CS 112 Introduction to Programming Variables; Type Casting; Using Variables in for Loops Yang (Richard) Yang Computer Science Department Yale University 308A Watson, Phone: 432-6400 Email: yry@cs.yale.edu
Building Java Programs
 Building Java Programs Chapter 5 Lecture 5-2: Random Numbers reading: 5.1, 5.6 1 http://xkcd.com/221/ 2 Randomness Lack of predictability: don't know what's coming next Random process: outcomes do not
Building Java Programs Chapter 5 Lecture 5-2: Random Numbers reading: 5.1, 5.6 1 http://xkcd.com/221/ 2 Randomness Lack of predictability: don't know what's coming next Random process: outcomes do not
Introduction to Computer Programming
 Introduction to Computer Programming Lecture 2- Primitive Data and Stepwise Refinement Data Types Type - A category or set of data values. Constrains the operations that can be performed on data Many languages
Introduction to Computer Programming Lecture 2- Primitive Data and Stepwise Refinement Data Types Type - A category or set of data values. Constrains the operations that can be performed on data Many languages
Midterm Examination (MTA)
 M105: Introduction to Programming with Java Midterm Examination (MTA) Spring 2013 / 2014 Question One: [6 marks] Choose the correct answer and write it on the external answer booklet. 1. Compilers and
M105: Introduction to Programming with Java Midterm Examination (MTA) Spring 2013 / 2014 Question One: [6 marks] Choose the correct answer and write it on the external answer booklet. 1. Compilers and
Midterm Review Session
 Midterm Review Session Programming Problems For more practice: http://webster.cs.washington.edu:8080/practiceit/ Copyright 2009 by Pearson Education Midterm Logistics Bring your UW Student ID card!! Will
Midterm Review Session Programming Problems For more practice: http://webster.cs.washington.edu:8080/practiceit/ Copyright 2009 by Pearson Education Midterm Logistics Bring your UW Student ID card!! Will
Selec%on and Decision Structures in Java: If Statements and Switch Statements CSC 121 Fall 2016 Howard Rosenthal
 Selec%on and Decision Structures in Java: If Statements and Switch Statements CSC 121 Fall 2016 Howard Rosenthal Lesson Goals Understand Control Structures Understand how to control the flow of a program
Selec%on and Decision Structures in Java: If Statements and Switch Statements CSC 121 Fall 2016 Howard Rosenthal Lesson Goals Understand Control Structures Understand how to control the flow of a program
CS 101 Spring 2007 Midterm 2 Name: ID:
 You only need to write your name and e-mail ID on the first page. This exam is CLOSED text book, closed-notes, closed-calculator, closed-neighbor, etc. Questions are worth different amounts, so be sure
You only need to write your name and e-mail ID on the first page. This exam is CLOSED text book, closed-notes, closed-calculator, closed-neighbor, etc. Questions are worth different amounts, so be sure
Java Programming: Guided Learning with Early Objects Chapter 5 Control Structures II: Repetition
 Java Programming: Guided Learning with Early Objects Chapter 5 Control Structures II: Repetition Learn about repetition (looping) control structures Explore how to construct and use: o Counter-controlled
Java Programming: Guided Learning with Early Objects Chapter 5 Control Structures II: Repetition Learn about repetition (looping) control structures Explore how to construct and use: o Counter-controlled
CS 112 Introduction to Programming
 CS 112 Introduction to Programming Conditional Statements Boolean Expressions and Methods Yang (Richard) Yang Computer Science Department Yale University 308A Watson, Phone: 432-6400 Email: yry@cs.yale.edu
CS 112 Introduction to Programming Conditional Statements Boolean Expressions and Methods Yang (Richard) Yang Computer Science Department Yale University 308A Watson, Phone: 432-6400 Email: yry@cs.yale.edu
CS 112 Introduction to Programming
 CS 112 Introduction to Programming Conditional Statements Boolean Expressions and Methods Yang (Richard) Yang Computer Science Department Yale University 308A Watson, Phone: 432-6400 Email: yry@cs.yale.edu
CS 112 Introduction to Programming Conditional Statements Boolean Expressions and Methods Yang (Richard) Yang Computer Science Department Yale University 308A Watson, Phone: 432-6400 Email: yry@cs.yale.edu
Building Java Programs
 Building Java Programs Chapter 7 Arrays reading: 7.1 2 Can we solve this problem? Consider the following program (input underlined): How many days' temperatures? 7 Day 1's high temp: 45 Day 2's high temp:
Building Java Programs Chapter 7 Arrays reading: 7.1 2 Can we solve this problem? Consider the following program (input underlined): How many days' temperatures? 7 Day 1's high temp: 45 Day 2's high temp:
b. Suppose you enter input from the console, when you run the program. What is the output?
 Part I. Show the printout of the following code: (write the printout next to each println statement if the println statement is executed in the program). a. Show the output of the following code: public
Part I. Show the printout of the following code: (write the printout next to each println statement if the println statement is executed in the program). a. Show the output of the following code: public
Selec%on and Decision Structures in Java: If Statements and Switch Statements CSC 121 Spring 2016 Howard Rosenthal
 Selec%on and Decision Structures in Java: If Statements and Switch Statements CSC 121 Spring 2016 Howard Rosenthal Lesson Goals Understand Control Structures Understand how to control the flow of a program
Selec%on and Decision Structures in Java: If Statements and Switch Statements CSC 121 Spring 2016 Howard Rosenthal Lesson Goals Understand Control Structures Understand how to control the flow of a program
CSIS 10A Assignment 3 Due: 2/21 at midnight
 CSIS 10A Assignment 3 Due: 2/21 at midnight Read: Chapter 3 Choose and complete any 10 points from the problems below by first downloading the assignment 3 folder from the website. Use BlueJ to complete
CSIS 10A Assignment 3 Due: 2/21 at midnight Read: Chapter 3 Choose and complete any 10 points from the problems below by first downloading the assignment 3 folder from the website. Use BlueJ to complete
Loops and Expression Types
 Software and Programming I Loops and Expression Types Roman Kontchakov / Carsten Fuhs Birkbeck, University of London Outline The while, for and do Loops Sections 4.1, 4.3 and 4.4 Variable Scope Section
Software and Programming I Loops and Expression Types Roman Kontchakov / Carsten Fuhs Birkbeck, University of London Outline The while, for and do Loops Sections 4.1, 4.3 and 4.4 Variable Scope Section
Java Programming: Guided Learning with Early Objects Chapter 5 Control Structures II: Repetition
 Java Programming: Guided Learning with Early Objects Chapter 5 Control Structures II: Repetition Learn about repetition (looping) control structures Explore how to construct and use: o Counter-controlled
Java Programming: Guided Learning with Early Objects Chapter 5 Control Structures II: Repetition Learn about repetition (looping) control structures Explore how to construct and use: o Counter-controlled
Over and Over Again GEEN163
 Over and Over Again GEEN163 There is no harm in repeating a good thing. Plato Homework A programming assignment has been posted on Blackboard You have to convert three flowcharts into programs Upload the
Over and Over Again GEEN163 There is no harm in repeating a good thing. Plato Homework A programming assignment has been posted on Blackboard You have to convert three flowcharts into programs Upload the
Example. Write a program which sums two random integers and lets the user repeatedly enter a new answer until it is correct.
 Example Write a program which sums two random integers and lets the user repeatedly enter a new answer until it is correct. 1... 2 Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); 3 int x = (int) (Math.random()
Example Write a program which sums two random integers and lets the user repeatedly enter a new answer until it is correct. 1... 2 Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); 3 int x = (int) (Math.random()
COSC 236 Section 101 Computer Science 1 -- Prof. Michael A. Soderstrand
 COSC 236 Section 101 Computer Science 1 -- Prof. Michael A. Soderstrand COSC 236 Web Site You will always find the course material at: http://www.class-notes.us or http://www.class-notes.info or http://www.lecture-notes.tripod.com
COSC 236 Section 101 Computer Science 1 -- Prof. Michael A. Soderstrand COSC 236 Web Site You will always find the course material at: http://www.class-notes.us or http://www.class-notes.info or http://www.lecture-notes.tripod.com
Controls Structure for Repetition
 Controls Structure for Repetition So far we have looked at the if statement, a control structure that allows us to execute different pieces of code based on certain conditions. However, the true power
Controls Structure for Repetition So far we have looked at the if statement, a control structure that allows us to execute different pieces of code based on certain conditions. However, the true power
Control Flow Practice Problems Mr. Fahrenbacher AP Computer Science A
 Control Flow Practice Problems Mr. Fahrenbacher AP Computer Science A This problem set has four sections. After each section is the answer key. This problem set is NOT exhaustive, but it is too long. Find
Control Flow Practice Problems Mr. Fahrenbacher AP Computer Science A This problem set has four sections. After each section is the answer key. This problem set is NOT exhaustive, but it is too long. Find
Motivating Examples (1.1) Selections. Motivating Examples (1.2) Learning Outcomes. EECS1022: Programming for Mobile Computing Winter 2018
 Motivating Examples (1.1) Selections EECS1022: Programming for Mobile Computing Winter 2018 CHEN-WEI WANG 1 import java.util.scanner; 2 public class ComputeArea { 3 public static void main(string[] args)
Motivating Examples (1.1) Selections EECS1022: Programming for Mobile Computing Winter 2018 CHEN-WEI WANG 1 import java.util.scanner; 2 public class ComputeArea { 3 public static void main(string[] args)
Jump Statements. The keyword break and continue are often used in repetition structures to provide additional controls.
 Jump Statements The keyword break and continue are often used in repetition structures to provide additional controls. break: the loop is terminated right after a break statement is executed. continue:
Jump Statements The keyword break and continue are often used in repetition structures to provide additional controls. break: the loop is terminated right after a break statement is executed. continue:
JAVA PROGRAMMING LAB. ABSTRACT In this Lab you will learn to define and invoke void and return java methods
 Islamic University of Gaza Faculty of Engineering Computer Engineering Dept. Computer Programming Lab (ECOM 2114) ABSTRACT In this Lab you will learn to define and invoke void and return java methods JAVA
Islamic University of Gaza Faculty of Engineering Computer Engineering Dept. Computer Programming Lab (ECOM 2114) ABSTRACT In this Lab you will learn to define and invoke void and return java methods JAVA
CONDITIONAL EXECUTION
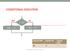 CONDITIONAL EXECUTION yes x > y? no max = x; max = y; logical AND logical OR logical NOT &&! Fundamentals of Computer Science I Outline Conditional Execution if then if then Nested if then statements Comparisons
CONDITIONAL EXECUTION yes x > y? no max = x; max = y; logical AND logical OR logical NOT &&! Fundamentals of Computer Science I Outline Conditional Execution if then if then Nested if then statements Comparisons
Motivations. Chapter 3: Selections and Conditionals. Relational Operators 8/31/18. Objectives. Problem: A Simple Math Learning Tool
 Chapter 3: Selections and Conditionals CS1: Java Programming Colorado State University Motivations If you assigned a negative value for radius in Listing 2.2, ComputeAreaWithConsoleInput.java, the program
Chapter 3: Selections and Conditionals CS1: Java Programming Colorado State University Motivations If you assigned a negative value for radius in Listing 2.2, ComputeAreaWithConsoleInput.java, the program
Final. Your Name CS Fall 2014 December 13, points total Your Instructor and Section
 Final Your Name CS 1063 - Fall 2014 December 13, 2014 100 points total Your Instructor and Section I. (10 points, 1 point each) Match each of the terms on the left by choosing the upper case letter of
Final Your Name CS 1063 - Fall 2014 December 13, 2014 100 points total Your Instructor and Section I. (10 points, 1 point each) Match each of the terms on the left by choosing the upper case letter of
NoSuchElementException 5. Name of the Exception that occurs when you try to read past the end of the input data in a file.
 CSC116 Practice Exam 2 - KEY Part I: Vocabulary (10 points) Write the terms defined by the statements below. Cumulative Algorithm 1. An operation in which an overall value is computed incrementally, often
CSC116 Practice Exam 2 - KEY Part I: Vocabulary (10 points) Write the terms defined by the statements below. Cumulative Algorithm 1. An operation in which an overall value is computed incrementally, often
CS 112 Introduction to Programming
 CS 112 Introduction to Programming Summary of Methods; User Input using Scanner Yang (Richard) Yang Computer Science Department Yale University 308A Watson, Phone: 432-6400 Email: yry@cs.yale.edu Admin
CS 112 Introduction to Programming Summary of Methods; User Input using Scanner Yang (Richard) Yang Computer Science Department Yale University 308A Watson, Phone: 432-6400 Email: yry@cs.yale.edu Admin
assertion: A statement that is either true or false.
 Logical assertions assertion: A statement that is either true or false. Examples: Java was created in 1995. The sky is purple. 23 is a prime number. 10 is greater than 20. x divided by 2 equals 7. (depends
Logical assertions assertion: A statement that is either true or false. Examples: Java was created in 1995. The sky is purple. 23 is a prime number. 10 is greater than 20. x divided by 2 equals 7. (depends
Building Java Programs
 Building Java Programs Chapter 5 Lecture 5-4: Assertions reading: 5.5 1 Punchline to a longer comic: http://www.smbc-comics.com/index.php?db=comics&id=2362#comic 2 Logical assertions assertion: A statement
Building Java Programs Chapter 5 Lecture 5-4: Assertions reading: 5.5 1 Punchline to a longer comic: http://www.smbc-comics.com/index.php?db=comics&id=2362#comic 2 Logical assertions assertion: A statement
Chapter 4: Conditionals and Recursion
 Chapter 4: Conditionals and Recursion Think Java: How to Think Like a Computer Scientist 5.1.2 by Allen B. Downey Agenda The modulus operator Random Number Generation Conditional Execution Alternative
Chapter 4: Conditionals and Recursion Think Java: How to Think Like a Computer Scientist 5.1.2 by Allen B. Downey Agenda The modulus operator Random Number Generation Conditional Execution Alternative
Data Structure and Programming Languages
 204700 Data Structure and Programming Languages Jakarin Chawachat From: http://ocw.mit.edu/courses/electrical-engineering-and-computerscience/6-092-introduction-to-programming-in-java-january-iap-2010/index.htm
204700 Data Structure and Programming Languages Jakarin Chawachat From: http://ocw.mit.edu/courses/electrical-engineering-and-computerscience/6-092-introduction-to-programming-in-java-january-iap-2010/index.htm
Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 45 / 79
 1 class Lecture2 { 2 3 "Elementray Programming" 4 5 } 6 7 / References 8 [1] Ch. 2 in YDL 9 [2] Ch. 2 and 3 in Sharan 10 [3] Ch. 2 in HS 11 / Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 45 / 79 Example Given a radius
1 class Lecture2 { 2 3 "Elementray Programming" 4 5 } 6 7 / References 8 [1] Ch. 2 in YDL 9 [2] Ch. 2 and 3 in Sharan 10 [3] Ch. 2 in HS 11 / Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 45 / 79 Example Given a radius
Loops. CSE 114, Computer Science 1 Stony Brook University
 Loops CSE 114, Computer Science 1 Stony Brook University http://www.cs.stonybrook.edu/~cse114 1 Motivation Suppose that you need to print a string (e.g., "Welcome to Java!") a user-defined times N: N?
Loops CSE 114, Computer Science 1 Stony Brook University http://www.cs.stonybrook.edu/~cse114 1 Motivation Suppose that you need to print a string (e.g., "Welcome to Java!") a user-defined times N: N?
arrays - part 1 My methods are really methods of working and thinking; this is why they have crept in everywhere anonymously. Emmy Noether, Ph.D.
 Topic 21 https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=66702 arrays - part 1 My methods are really methods of working and thinking; this is why they have crept in everywhere anonymously. Emmy Noether,
Topic 21 https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=66702 arrays - part 1 My methods are really methods of working and thinking; this is why they have crept in everywhere anonymously. Emmy Noether,
Check out how to use the random number generator (introduced in section 4.11 of the text) to get a number between 1 and 6 to create the simulation.
 Chapter 4 Lab Loops and Files Lab Objectives Be able to convert an algorithm using control structures into Java Be able to write a while loop Be able to write an do-while loop Be able to write a for loop
Chapter 4 Lab Loops and Files Lab Objectives Be able to convert an algorithm using control structures into Java Be able to write a while loop Be able to write an do-while loop Be able to write a for loop
CS1150 Principles of Computer Science Boolean, Selection Statements
 CS1150 Principles of Computer Science Boolean, Selection Statements Yanyan Zhuang Department of Computer Science http://www.cs.uccs.edu/~yzhuang CS1150 Math Center https://www.uccs.edu/mathcenter/schedules
CS1150 Principles of Computer Science Boolean, Selection Statements Yanyan Zhuang Department of Computer Science http://www.cs.uccs.edu/~yzhuang CS1150 Math Center https://www.uccs.edu/mathcenter/schedules
COSC 236 Section 101 Computer Science 1 -- Prof. Michael A. Soderstrand
 COSC 236 Section 101 Computer Science 1 -- Prof. Michael A. Soderstrand COSC 236 Web Site You will always find the course material at: http://www.class-notes.us or http://www.class-notes.info or http://www.lecture-notes.tripod.com
COSC 236 Section 101 Computer Science 1 -- Prof. Michael A. Soderstrand COSC 236 Web Site You will always find the course material at: http://www.class-notes.us or http://www.class-notes.info or http://www.lecture-notes.tripod.com
Programming: Java. Chapter Objectives. Chapter Objectives (continued) Program Design Including Data Structures. Chapter 7: User-Defined Methods
 Chapter 7: User-Defined Methods Java Programming: Program Design Including Data Structures Chapter Objectives Understand how methods are used in Java programming Learn about standard (predefined) methods
Chapter 7: User-Defined Methods Java Programming: Program Design Including Data Structures Chapter Objectives Understand how methods are used in Java programming Learn about standard (predefined) methods
CS 106A, Lecture 5 Booleans and Control Flow
 CS 106A, Lecture 5 Booleans and Control Flow suggested reading: Java Ch. 3.4-4.6 This document is copyright (C) Stanford Computer Science and Marty Stepp, licensed under Creative Commons Attribution 2.5
CS 106A, Lecture 5 Booleans and Control Flow suggested reading: Java Ch. 3.4-4.6 This document is copyright (C) Stanford Computer Science and Marty Stepp, licensed under Creative Commons Attribution 2.5
Jump Statements. The keyword break and continue are often used in repetition structures to provide additional controls.
 Jump Statements The keyword break and continue are often used in repetition structures to provide additional controls. break: the loop is terminated right after a break statement is executed. continue:
Jump Statements The keyword break and continue are often used in repetition structures to provide additional controls. break: the loop is terminated right after a break statement is executed. continue:
CS 112 Introduction to Programming
 CS 112 Introduction to Programming Program Analysis Yang (Richard) Yang Computer Science Department Yale University 308A Watson, Phone: 432-6400 Email: yry@cs.yale.edu Admin q PS5 Walkthrough Thursday
CS 112 Introduction to Programming Program Analysis Yang (Richard) Yang Computer Science Department Yale University 308A Watson, Phone: 432-6400 Email: yry@cs.yale.edu Admin q PS5 Walkthrough Thursday
