UNIT 5 OPERATIONS WITH FRACTIONS
|
|
|
- Anne Fleming
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Unit Media Lesson UNIT OPERATIONS WITH FRACTIONS INTRODUCTION In this Unit, we will use the multiple meanings and representations of fractions that we studied in the previous unit to develop understanding and processes for performing operations with fractions. You are likely familiar with algorithms for computing fraction operations. Please accept the challenge of really thinking through the meaning of operations and the different contexts of fractions so you understand why we perform operations as we do. If you accept this challenge, this unit will help you see the meaning of these processes not just the steps. The table below shows the learning objectives that are the achievement goal for this unit. Read through them carefully now to gain initial exposure to the terms and concept names for the lesson. Refer back to the list at the end of the lesson to see if you can perform each objective. Learning Objective Media Examples You Try Add fractions with like denominators 4 Add fractions with unlike denominators 4 Add improper fractions and mixed numbers 4 Subtract fractions with like denominators 8 Subtract fractions with unlike denominators 6 8 Subtract improper fractions and mixed numbers 7 8 Multiply a unit fraction times a whole number 9 Multiply a composite fraction times a whole number 0 Multiply a whole number times a fraction Multiply two fractions Multiply mixed numbers 4 Divide a whole number by a fraction 6 9 Divide fraction with common denominators 7 9 Divide fraction with uncommon denominators 8 9 Divide mixed numbers 0 Perform +,,, on signed fraction 4 Use the order of operations with signed fractions 4
2 Unit Media Lesson UNIT MEDIA LESSON SECTION.: ADDING FRACTIONS In this section, we will learn to visualize the addition of fractions using an area model and number lines. Recall that the operation of addition is combining two amounts or adding one amount on to another. We will achieve this with fractions by ensuring we have a common unit fraction (common denominator) for the numbers we are combining. We can then add the number of copies of each fraction while retaining the common denominator. Problem MEDIA EXAMPLE Adding Fractions with Like Denominators Use the diagrams given to represent the values in the addition problem and find the sum. Then perform the operation and represent the sum using the symbolic representation of the algorithm.. Jon had have? of a pepperoni pizza and of a mushroom pizza. How much of one whole pizza did Jon is copies of is copies of Combined, we have a total of copies of or the fraction.. Christianne sprinted 8 of a mile and then jogged another 7 8 of a mile. How far did she run in total? 8 is copies of 7 8 is copies of Combined, we have a total of copies of or the fraction. Simplified result as an improper fraction: Simplified result as a mixed number:
3 Problem MEDIA EXAMPLE Adding Fractions with Unlike Denominators Unit Media Lesson Use the diagrams given to represent the values in the addition problem and find the sum. Then perform the operation and represent the sum using the symbolic representation of the algorithm. a) Step : Rewrite the given fractions with a common denominator. is equivalent to is equivalent to Step : Rewrite the equivalent fractions with the common denominator using copies of language using a common unit fraction. : is copies of : is copies of Step : Combine (add). Combined, we have a total of copies of or the fraction. Step 4: Simplify if necessary. b) 4 8
4 c) Unit Media Lesson Problem MEDIA EXAMPLE Adding Improper Fractions and Mixed Numbers Use the diagrams given to represent the values in the addition problem and find the sum. Then perform the operation and represent the sum using the symbolic representation of the algorithm. a)
5 b) 4 Unit Media Lesson Step : Rewrite the fractional parts of the mixed numbers with a common denominator Step : Rewrite the equivalent fractions with the common denominator using copies of language using a common unit fraction. : is copies of : is copies of Step : Combine the fractional parts and the whole number parts. Fractional Parts: Combined, we have a total of copies of or the fraction. Whole Numbers plus fractional parts: Combined we have a total of Step 4: Simplify if necessary. c) 9
6 Problem 4 YOU TRY - Adding Numbers with Fractions Unit Media Lesson Use the diagrams given to represent the values in the addition problem and find the sum. Then perform the operation and represent the sum using the symbolic representation of the algorithm. a) 4 Step : Rewrite the given fractions with a common denominator. is equivalent to 4 is equivalent to Step : Rewrite the equivalent fractions with the common denominator using copies of language using a common unit fraction. : is copies of 4 : is copies of Step : Combine (add). Combined, we have a total of copies of or the fraction. Step 4: Simplify if necessary. b) 4 8 6
7 Unit Media Lesson SECTION.: SUBTRACTING FRACTIONS In this section, we will learn to visualize subtracting fractions using an area model and number lines. We will investigate this idea using our two models of subtraction; subtraction as taking away a part of a whole, and subtraction as comparing two quantities. Problem MEDIA EXAMPLE Subtracting Fractions with Like Denominators Use the diagrams given to represent the values in the subtraction problem and find the difference. Then perform the operation and represent the difference using the symbolic representation of the algorithm. a) The day after Thanksgiving, there was breakfast. How much pie is leftover now? of a pumpkin pie remaining. Lara ate of a pie for b) Billy ran 8 of a mile. Roberta ran 8 of a mile. How much further did Roberta run? 7
8 Problem 6 MEDIA EXAMPLE Subtracting Fractions with Unlike Denominators Unit Media Lesson Use the diagrams given to represent the values in the subtraction problem and find the difference. Then perform the operation and represent the difference using the symbolic representation of the algorithm. a) b) 6 c) Perform the operation and represent the difference using the symbolic representation of the algorithm
9 Unit Media Lesson Problem 7 MEDIA EXAMPLE Subtracting Improper Fractions and Mixed Numbers Use the diagrams given to represent the values in the subtraction problem and find the difference. Then perform the operation and represent the difference using the symbolic representation of the algorithm. a) 8 6 b) 4 c) 0 9
10 Unit Media Lesson Problem 8 YOU TRY - Subtracting Numbers with Fractions Use the diagrams given to represent the values in the subtraction problem and find the difference. Then perform the operation and represent the difference using the symbolic representation of the algorithm. a) Michael lives 8 school does Rachel live? of a mile from school. Rachel lives 7 8 of a mile from school. How much closer to b) c) Barney had 7 8 of his weekly salary left after paying his bills. He then spent a weekend trip. What fraction of his weekly salary remains? 4 of his weekly salary on 0
11 Unit Media Lesson SECTION.: MULTIPLYING FRACTIONS In this section, we will examine multiplying fractions using the idea that a b or a b is equivalent to a copies of b. Problem 9 MEDIA EXAMPLE Multiplying a Unit Fraction and a Whole Number Use the diagrams given to represent the multiplication problem and find the product. Then perform the operation and represent the product using the symbolic representation of the algorithm. a) Ebony ate of a pizza. The pizza had slices. How many slices did she eat? b) Kimber was 0 miles from home. She travelled How many miles did she travel while listening to her favorite song? of this distance while listening to her favorite song. c) Logan has a gallon bucket. He fills it 4 of the way to the top. How much water is in the bucket?
12 Problem 0 Unit Media Lesson MEDIA EXAMPLE Multiplying a Composite Fraction and a Whole Number Use the diagrams given to represent the multiplication problem and find the product. Then perform the operation and represent the product using the symbolic representation of the algorithm. a) Ebony ate of a pizza. The pizza had slices. How many slices did she eat? b) Kimber was 0 miles from home. She travelled How many miles did she travel while listening to her favorite song? of this distance while listening to her favorite song. c) Logan has a gallon bucket. He fills it 4 of the way to the top. How much water is in the bucket?
13 Problem YOU TRY Multiplying Unit or Composite Fractions with Whole Numbers Unit Media Lesson Use the diagrams given to represent the multiplication problem and find the product. Then perform the operation and represent the product using the symbolic representation of the algorithm. a) Carese was running a 0 kilometer race. She ran did she run in minutes? of the race in minutes. How many kilometers b) Casey s gas tank holds gallons. The gas gage says it is tank? full. How many gallons of gas are in her
14 Problem MEDIA EXAMPLE Multiplying Whole Numbers and Fractions Unit Media Lesson Use the diagrams given to represent the multiplication problem and find the product. Then perform the operation and represent the product using the symbolic representation of the algorithm. a) Ashley has packs of cupcakes. There are 4 cupcakes per pack. How many cupcakes does Ashley have? b) Anderson jogged around a lake times this week. The distance around the lake is did Anderson jog in total over the week? of a mile. How far c) Knia is having a dinner party with a total of 7 people. She bought of a pound of cold cuts per person. How many pounds of cold cuts did she buy in total? 4
15 Problem MEDIA EXAMPLE Multiplying Two Fractions Unit Media Lesson Use the diagrams given to represent the multiplication problem and find the product. Then perform the operation and represent the product using the symbolic representation of the algorithm. a) Yesterday, Cameron walked had walked of a mile to school. Today, Cameron s friend picked him up after he of the way to school. How far to Cameron walk today? b) Jassey bought a rectangular piece of land to grow vegetables. The land is mile wide. How many square miles of land did Jassey buy? of a mile long and 4 of a c) Ray made a tray of brownies. He ate of the tray after they had cooled. The next day, he ate 4 of what was left over in the tray. How much of the whole tray did Ray eat the next day?
16 Unit Media Lesson Problem 4 MEDIA EXAMPLE Multiplying Mixed Numbers Create a diagram to represent the multiplication problem and find the product. Then perform the operation and represent the product using the symbolic representation of the algorithm. a) According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, the buying power of the dollar is 4 times larger in 06 when compared to 99. Determine the comparable buying power in 06 of $0 in 99. b) J Von bought a rectangular piece of land in Alaska. The land was How many square miles of land did he buy? 4 miles wide and 8 miles long. 6
17 Unit Media Lesson Problem YOU TRY Multiplying Mixed Numbers, Fractions, and Whole Numbers Create a diagram to represent the multiplication problem and find the product. Then perform the operation and represent the product using the symbolic representation of the algorithm. a) Rick walked around a track 6 times this month. The distance around the track is did Rick walk in total over the month? 4 of a mile. How far b) Kate has a rectangular piece a land to raise horses. The land is wide. How many square miles of land does Kate own? of a mile long and 8 of a mile c) Javier makes times as much an hour as when he first started his job. If he made $9 an hour when he first started, how much does Javier make now? 7
18 Unit Media Lesson SECTION.4: DIVIDING FRACTIONS In this section, we will learn to visualize dividing fractions using an area model and number lines. We will investigate this idea using two models of division; dividing as partitioning the dividend into a known number of copies, and dividing as determining how many copies of a given size are in the dividend. In general, we do not usually find a common denominator to divide fractions. However, we will begin with examples by finding common denominators to illustrate a general process for dividing fractions. Problem 6 MEDIA EXAMPLE Dividing Whole Numbers by Fractions Use the diagrams given to represent the division problem and find the quotient. a) Tia made cakes for her guests. If each guest receives of a cake, how many guests can Tia serve? Symbolic Representation: b) Elaine ran 6 miles this month. If she ran of a mile every day she ran, how many days did Elaine run? Symbolic Representation: 8
19 Unit Media Lesson Problem 7 MEDIA EXAMPLE Dividing Fractions Using Common Denominators Use the diagrams given to represent the division problem and find the quotient. a) 9 Symbolic Representation: b) 8 Symbolic Representation: c) 8 4 Symbolic Representation: d) What patterns do you observe in problems a through c? 9
20 Unit Media Lesson Results: Based on the previous examples, we can divide two fractions by dividing their numerators (left to right) and their denominators (left to right) just like we multiply the numerators and denominators of fractions to multiply them. The last two problems illustrate this fact below or 4 4 Problem: The previous two problems worked out nicely because dividing the numerators and denominators resulted in an integer in both the resulting numerator and denominator. Consider this problem that doesn t work out as nicely Using the division method actually made the problem worse! We want the result as a fraction of one integer over another integer, not a fraction with fractions as numerators and denominators. Solution: We will find a common denominator for the two fractions we are dividing and perform the division like we did for the first problems. Then we will check for patterns to simplify the process. 7. Original Problem. Rewrite the two fractions with a common denominator of.. Divide the numerators and the denominators Rewrite the division in the numerator as a fraction. 0 0 Pattern: Let s look at the original problem and the final answer. Final Solution: 7 Comparable Method: Rule: To divide two fractions, multiply the first fraction by the reciprocal of the second fraction. (Note: The reciprocal of a fraction a b is b a. In this example, the reciprocal of is. 0
21 Unit Media Lesson Problem 8 MEDIA EXAMPLE Dividing Fractions with Unlike Denominators Divide the fractions by multiplying the first fraction by the reciprocal of the second fraction. Simplify your result if necessary. Write any answers greater than as both an improper fraction and a mixed number. a) b) 8 0 c) Problem 9 YOU TRY Dividing Fractions a) A snail crawled meters this week. If he crawled did he crawl? of a meter every day he crawled, how many days Symbolic Representation: b) Divide the fractions by dividing the numerators and the denominators. Simplify your result if necessary. i. 8 9 ii. iii c) Divide the fractions by multiplying the first fraction by the reciprocal of the second fraction. Simplify your result if necessary. i. 9 ii. 6 4 iii
22 Problem 0 MEDIA EXAMPLE Dividing Mixed Numbers Unit Media Lesson Rewrite any mixed numbers as improper fractions. Then perform the division by multiplying the first fraction by the reciprocal of the second fraction. Simplify your result if necessary and rewrite your result as a mixed number when possible. a) b) 4 8 c) Problem YOU TRY Dividing Mixed Numbers Rewrite any mixed numbers as improper fractions. Then perform the division by multiplying the first fraction by the reciprocal of the second fraction. Simplify your result if necessary and rewrite your result as a mixed number when possible. a) b) 6 c) 6 4
23 Unit Media Lesson SECTION.: SIGNED FRACTIONS AND THE ORDER OF OPERATIONS In this section, we will use our knowledge of operations on integers and the order of operations to perform operations with signed fractions and the order of operations with fractions. Problem MEDIA EXAMPLE Operations on Signed Fractions Perform the indicated operations on the fractions and/or mixed numbers using your knowledge of signed numbers. a) 7 b) 7 c) 4 4 d) e) f) Problem MEDIA EXAMPLE The Order of Operations and Signed Fractions Perform the indicated operations on the fractions and/or mixed numbers using your knowledge of signed numbers and the order of operations. a) b) 9 7 c) 4
24 Problem 4 YOU TRY The Order of Operations and Signed Fractions Unit Media Lesson Perform the indicated operations on the fractions and/or mixed numbers using your knowledge of signed numbers and the order of operations. a) 4 4 b) 9 4 c) 4 4
Fractions Part 1 Chapter Problems
 Fractions Part Chapter Problems Meaning of Fractions Identify the numerator in each of the following fractions:...... Identify the denominator in each of the following fractions:... 0... State whether
Fractions Part Chapter Problems Meaning of Fractions Identify the numerator in each of the following fractions:...... Identify the denominator in each of the following fractions:... 0... State whether
UNIT 4 INTRODUCTION TO FRACTIONS AND DECIMALS
 UNIT 4 INTRODUCTION TO FRACTIONS AND DECIMALS INTRODUCTION In this Unit, we will investigate fractions and decimals. We have seen fractions before in the context of division. For example, we can think
UNIT 4 INTRODUCTION TO FRACTIONS AND DECIMALS INTRODUCTION In this Unit, we will investigate fractions and decimals. We have seen fractions before in the context of division. For example, we can think
UNIT 1 PLACE VALUE AND WHOLE NUMBERS
 UNIT 1 PLACE VALUE AND WHOLE NUMBERS INTRODUCTION We will begin our study of Arithmetic by learning about the number system we use today. The Base-10 Number System or Hindu-Arabic Numeral System began
UNIT 1 PLACE VALUE AND WHOLE NUMBERS INTRODUCTION We will begin our study of Arithmetic by learning about the number system we use today. The Base-10 Number System or Hindu-Arabic Numeral System began
Math KCAS Flashbacks
 Set 1 1. Cameron bought a package of bean seeds to plant at least two rows of beans. He wants each row to have the same number of seeds but found that this was not possible. Which of the following could
Set 1 1. Cameron bought a package of bean seeds to plant at least two rows of beans. He wants each row to have the same number of seeds but found that this was not possible. Which of the following could
Part 1: Dividing Fractions Using Visual Representations
 Part : Dividing Fractions Using Visual Representations To divide fractions, remember that division can be represented by repeated subtraction, just like multiplication can be represented by repeated addition.
Part : Dividing Fractions Using Visual Representations To divide fractions, remember that division can be represented by repeated subtraction, just like multiplication can be represented by repeated addition.
Part 1: Dividing Fractions Using Visual Representations
 Part 1: Dividing Fractions Using Visual Representations To divide fractions, remember that division can be represented by repeated subtraction, just like multiplication can be represented by repeated addition.
Part 1: Dividing Fractions Using Visual Representations To divide fractions, remember that division can be represented by repeated subtraction, just like multiplication can be represented by repeated addition.
Study Guide For use with pages
 . GOAL For use with pages Write fractions as decimals and vice versa. VOCABULARY A rational number is a number that can be written as a quotient of two integers. In a terminating decimal, the division
. GOAL For use with pages Write fractions as decimals and vice versa. VOCABULARY A rational number is a number that can be written as a quotient of two integers. In a terminating decimal, the division
Parent Guide to 5 th Grade
 Parent Guide to 5 th Grade 2017 Assembled by Bain 5 th grade Teachers: M.Gregory, K.Brock, K.DeSeve, J.Hayes, L.McElrath, and A.Treadwell Table of Contents Adding and Subtracting Fractions - Area Models
Parent Guide to 5 th Grade 2017 Assembled by Bain 5 th grade Teachers: M.Gregory, K.Brock, K.DeSeve, J.Hayes, L.McElrath, and A.Treadwell Table of Contents Adding and Subtracting Fractions - Area Models
April 25, Lesson 8.2B
 Lesson 8.2B Content Objective: I can substitute a number in for a variable and solve for the expression I can turn word problems into expressions, equations, and inequalities and solve for the variable.
Lesson 8.2B Content Objective: I can substitute a number in for a variable and solve for the expression I can turn word problems into expressions, equations, and inequalities and solve for the variable.
CHAPTER 5: ADDING AND SUBTRACTING FRACTIONS AND DECIMALS
 CHAPTER : ADDING AND SUBTRACTING FRACTIONS AND DECIMALS. ADDING LIKE FRACTIONS P -. ADDING UNLIKE FRACTIONS P -. ADDING MIXED NUMBERS P 6-7. SUBTRACTING FRACTIONS FROM WHOLE NUMBERS P -9. SUBTRACTING FRACTIONS
CHAPTER : ADDING AND SUBTRACTING FRACTIONS AND DECIMALS. ADDING LIKE FRACTIONS P -. ADDING UNLIKE FRACTIONS P -. ADDING MIXED NUMBERS P 6-7. SUBTRACTING FRACTIONS FROM WHOLE NUMBERS P -9. SUBTRACTING FRACTIONS
Name Date Class F 63 H 0.63 B 2.5 D G 6.3 I A 18 C F 60 H 0.6 B 1.8 D 0.018
 Name Date Class 3-4 Practice A Multiplying Decimals Multiply. Choose the letter for the best answer. 1. 5 0.05 A 25 C 0.25 2. 9 0.7 F 63 H 0.63 B 2.5 D 0.025 G 6.3 I 0.063 3. 6 0.003 A 18 C 0.18 4. 5 1.2
Name Date Class 3-4 Practice A Multiplying Decimals Multiply. Choose the letter for the best answer. 1. 5 0.05 A 25 C 0.25 2. 9 0.7 F 63 H 0.63 B 2.5 D 0.025 G 6.3 I 0.063 3. 6 0.003 A 18 C 0.18 4. 5 1.2
Multiply the dividend by the reciprocal of the divisor.
 Domain Lesson 6 Complex Fractions Common Core Standards: 7.RP., 7.RP. Getting the Idea To divide fractions, first find the reciprocal of the divisor. Then multiply the dividend by the reciprocal of the
Domain Lesson 6 Complex Fractions Common Core Standards: 7.RP., 7.RP. Getting the Idea To divide fractions, first find the reciprocal of the divisor. Then multiply the dividend by the reciprocal of the
Name Student ID Number. Group Name. Group Members. Fractions
 Name Student ID Number Group Name Group Members Fractions Many people struggle with and even fear working with fractions. Part of the reason people struggle is because they do not know what a fraction
Name Student ID Number Group Name Group Members Fractions Many people struggle with and even fear working with fractions. Part of the reason people struggle is because they do not know what a fraction
FRACTIONS. Printable Review Problems. Kristine Nannini
 FRACTIONS Printable Review Problems Standards Included: 4.NF.1- Explain why a fraction a/b is equivalent to a fraction (n a)/(n b) by using visual fraction models, with attention to how the number and
FRACTIONS Printable Review Problems Standards Included: 4.NF.1- Explain why a fraction a/b is equivalent to a fraction (n a)/(n b) by using visual fraction models, with attention to how the number and
Math 6 Unit 03 Part B-NOTES Fraction Operations
 Math Unit 0 Part B-NOTES Fraction Operations Review/Prep for.ns Adding and Subtracting Fractions With Unlike Denominators Note: You can use any common denominator to add and subtract unlike fractions;
Math Unit 0 Part B-NOTES Fraction Operations Review/Prep for.ns Adding and Subtracting Fractions With Unlike Denominators Note: You can use any common denominator to add and subtract unlike fractions;
Adding and Subtracting All Sorts of Numbers
 Knowing WHEN to add or subtract Adding and Subtracting All Sorts of Numbers We use addition when we know the parts and want to find the total. We use subtraction when we know the total and want to take
Knowing WHEN to add or subtract Adding and Subtracting All Sorts of Numbers We use addition when we know the parts and want to find the total. We use subtraction when we know the total and want to take
Represent and evaluate addition and subtraction applications symbolically that contain more than one operation
 UNIT 3 ORDER OF OPERATIONS AND PROPERTIES INTRODUCTION Thus far, we have only performed one mathematical operation at a time. Many mathematical situations require us to perform multiple operations. The
UNIT 3 ORDER OF OPERATIONS AND PROPERTIES INTRODUCTION Thus far, we have only performed one mathematical operation at a time. Many mathematical situations require us to perform multiple operations. The
Grade 4 Fractions. Answer the questions. For more such worksheets visit (1) Convert into a mixed fraction. (2) Convert
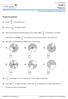 ID : aefractions [1] Grade Fractions For more such worksheets visit www.edugain.com Answer the questions (1) Convert 63 13 (2) Convert 6 7 12 into a mixed fraction. to improper fraction. (3) Aleser had
ID : aefractions [1] Grade Fractions For more such worksheets visit www.edugain.com Answer the questions (1) Convert 63 13 (2) Convert 6 7 12 into a mixed fraction. to improper fraction. (3) Aleser had
Fractions and Mixed Numbers
 6 CHAPTER Fractions and Mixed Numbers Worksheet Adding Fractions Find the equivalent fraction. Shade the models. _? 6. _?.? Reteach A Find the equivalent fractions. To get the equivalent fraction, multiply
6 CHAPTER Fractions and Mixed Numbers Worksheet Adding Fractions Find the equivalent fraction. Shade the models. _? 6. _?.? Reteach A Find the equivalent fractions. To get the equivalent fraction, multiply
Coached Instruction Supplement
 Practice Coach PLUS Coached Instruction Supplement Mathematics 5 Practice Coach PLUS, Coached Instruction Supplement, Mathematics, Grade 5 676NASP Triumph Learning Triumph Learning, LLC. All rights reserved.
Practice Coach PLUS Coached Instruction Supplement Mathematics 5 Practice Coach PLUS, Coached Instruction Supplement, Mathematics, Grade 5 676NASP Triumph Learning Triumph Learning, LLC. All rights reserved.
Name: Class: Date: ID: A
 Name: Class: Date: 5 Short Answer Estimate by rounding to the nearest whole number. 1. 114.3406 19.2647 Subtract. 2. 7.42 1.9 Evaluate each expression for the given value of the variable. 3. 5w if w =
Name: Class: Date: 5 Short Answer Estimate by rounding to the nearest whole number. 1. 114.3406 19.2647 Subtract. 2. 7.42 1.9 Evaluate each expression for the given value of the variable. 3. 5w if w =
Math 7 Notes Unit Three: Applying Rational Numbers
 Math 7 Notes Unit Three: Applying Rational Numbers Strategy note to teachers: Typically students need more practice doing computations with fractions. You may want to consider teaching the sections on
Math 7 Notes Unit Three: Applying Rational Numbers Strategy note to teachers: Typically students need more practice doing computations with fractions. You may want to consider teaching the sections on
_ _ _ _ _ _. Add and Subtract Parts of a Whole R54. Name. Justin has 3_. How much cheese does he have in all?
 Lesson 7.1 Add and Subtract Parts of a Whole Justin has 8pound of cheddar cheese and 2_ 8pound of brick cheese. How much cheese does he have in all? Step 1 Use fraction strips to model the problem. Use
Lesson 7.1 Add and Subtract Parts of a Whole Justin has 8pound of cheddar cheese and 2_ 8pound of brick cheese. How much cheese does he have in all? Step 1 Use fraction strips to model the problem. Use
Introduction to Fractions
 Introduction to Fractions Fractions represent parts of a whole. The top part of a fraction is called the numerator, while the bottom part of a fraction is called the denominator. The denominator states
Introduction to Fractions Fractions represent parts of a whole. The top part of a fraction is called the numerator, while the bottom part of a fraction is called the denominator. The denominator states
Using Equivalent Fractions to Solve Problems
 Using Equivalent Fractions to Solve Problems Home Link -1 1 Fill in the equivalent fractions in the table below. Multi ply Both the Numerator and Denominator by: Fraction 6 1 _ 6_ 6_ 9 1 16 10_ 1 6_ 1
Using Equivalent Fractions to Solve Problems Home Link -1 1 Fill in the equivalent fractions in the table below. Multi ply Both the Numerator and Denominator by: Fraction 6 1 _ 6_ 6_ 9 1 16 10_ 1 6_ 1
Add and Subtract Parts of a Whole
 Lesson 7. Add and Subtract Parts of a Whole Justin has _ pound of cheddar cheese and 2_ pound of brick cheese. How much cheese does he have in all? Step Use fraction strips to model the problem. Use three
Lesson 7. Add and Subtract Parts of a Whole Justin has _ pound of cheddar cheese and 2_ pound of brick cheese. How much cheese does he have in all? Step Use fraction strips to model the problem. Use three
Fractions / 8 / / 10 1 ½ / 12
 Fractions / 8 / 60 / ½ / 0 / What is a fraction? Loosely speaking, a fraction is a quantity that cannot be represented by a whole number. Why do we need fractions? Consider the following scenario. Can
Fractions / 8 / 60 / ½ / 0 / What is a fraction? Loosely speaking, a fraction is a quantity that cannot be represented by a whole number. Why do we need fractions? Consider the following scenario. Can
Fractions and their Equivalent Forms
 Fractions Fractions and their Equivalent Forms Little kids use the concept of a fraction long before we ever formalize their knowledge in school. Watching little kids share a candy bar or a bottle of soda
Fractions Fractions and their Equivalent Forms Little kids use the concept of a fraction long before we ever formalize their knowledge in school. Watching little kids share a candy bar or a bottle of soda
Answer Key. ANSWER: a. 2; b.
 1 a. What can you multiply by to get? b. What can you multiply by to get 7? c. What can you multiply by to get? ANSWER: a. ; b. 7 ; c. or COMMENTS & EXTENSIONS: In general, fractions derive their meaning
1 a. What can you multiply by to get? b. What can you multiply by to get 7? c. What can you multiply by to get? ANSWER: a. ; b. 7 ; c. or COMMENTS & EXTENSIONS: In general, fractions derive their meaning
Review: Number Systems
 Review: Number Systems Divisibility Prime/Composite Properties Factors/Multiples Prime Factorization GCF/LCM Decimals Coordinate Graphing Fractions Integers A number is divisible by If the last digit is
Review: Number Systems Divisibility Prime/Composite Properties Factors/Multiples Prime Factorization GCF/LCM Decimals Coordinate Graphing Fractions Integers A number is divisible by If the last digit is
MATH STUDENT BOOK. 6th Grade Unit 5
 MATH STUDENT BOOK th Grade Unit 5 Unit 5 Fraction Operations MATH 05 Fraction Operations 1. ADDING AND SUBTRACTING FRACTIONS 5 ADDING FRACTIONS WITH LIKE DENOMINATORS FRACTIONS WITH UNLIKE DENOMINATORS
MATH STUDENT BOOK th Grade Unit 5 Unit 5 Fraction Operations MATH 05 Fraction Operations 1. ADDING AND SUBTRACTING FRACTIONS 5 ADDING FRACTIONS WITH LIKE DENOMINATORS FRACTIONS WITH UNLIKE DENOMINATORS
UNIT 4 PRACTICE PROBLEMS
 UNIT 4 PRACTICE PROBLEMS 1 Determine the fraction represented by the area shaded pink using the given unit Unit Fraction 2 Determine the fraction represented by the shaded area using the given unit Unit
UNIT 4 PRACTICE PROBLEMS 1 Determine the fraction represented by the area shaded pink using the given unit Unit Fraction 2 Determine the fraction represented by the shaded area using the given unit Unit
Coached Instruction Supplement
 Practice Coach PLUS Coached Instruction Supplement Mathematics 7 Practice Coach PLUS, Coached Instruction Supplement, Mathematics, Grade 7 678NASP Triumph Learning Triumph Learning, LLC. All rights reserved.
Practice Coach PLUS Coached Instruction Supplement Mathematics 7 Practice Coach PLUS, Coached Instruction Supplement, Mathematics, Grade 7 678NASP Triumph Learning Triumph Learning, LLC. All rights reserved.
Multiplying and Dividing Rational Expressions
 COMMON CORE Locker LESSON 9. Multiplying and Dividing Rational Expressions Name Class Date 9. Multiplying and Dividing Rational Expressions Essential Question: How can you multiply and divide rational
COMMON CORE Locker LESSON 9. Multiplying and Dividing Rational Expressions Name Class Date 9. Multiplying and Dividing Rational Expressions Essential Question: How can you multiply and divide rational
Addition with Unlike Denominators
 Lesson. Addition with Unlike Denominators Karen is stringing a necklace with beads. She puts green beads on _ of the string and purple beads on 0of the string. How much of the string does Karen cover with
Lesson. Addition with Unlike Denominators Karen is stringing a necklace with beads. She puts green beads on _ of the string and purple beads on 0of the string. How much of the string does Karen cover with
9.1 Adding and Subtracting Rational Expressions
 Name Class Date 9.1 Adding and Subtracting Rational Expressions Essential Question: How can you add and subtract rational expressions? Resource Locker Explore Identifying Excluded Values Given a rational
Name Class Date 9.1 Adding and Subtracting Rational Expressions Essential Question: How can you add and subtract rational expressions? Resource Locker Explore Identifying Excluded Values Given a rational
SUMMER REVIEW PACKET 2 FOR STUDENTS ENTERING ALGEBRA 1
 SUMMER REVIEW PACKET FOR STUDENTS ENTERING ALGEBRA Dear Students, Welcome to Ma ayanot. We are very happy that you will be with us in the Fall. The Math department is looking forward to working with you
SUMMER REVIEW PACKET FOR STUDENTS ENTERING ALGEBRA Dear Students, Welcome to Ma ayanot. We are very happy that you will be with us in the Fall. The Math department is looking forward to working with you
Vocabulary: Bits and Pieces III
 Vocabulary: Bits and Pieces III Concept Example Meaning of decimal There are two ways to think of a decimal: As a number whose value is signaled by place value, or as a representation of a fraction.. 43
Vocabulary: Bits and Pieces III Concept Example Meaning of decimal There are two ways to think of a decimal: As a number whose value is signaled by place value, or as a representation of a fraction.. 43
Reteach. Chapter 9. Grade 5
 Reteach Chapter 9 Grade Lesson 1 Reteach Round Fractions Round Up If the numerator is almost as large as the denominator, round the number up to the next whole number Example: 1 9 rounds to 1 9 is almost
Reteach Chapter 9 Grade Lesson 1 Reteach Round Fractions Round Up If the numerator is almost as large as the denominator, round the number up to the next whole number Example: 1 9 rounds to 1 9 is almost
Equivalent fractions are
 MATHEMATICS 8 CHAPTER FRACTION OPERATIONS REVIEW: EQUIVALENT FRACTIONS AND IMPROPER FRACTIONS AND MIXED NUMBERS Date The numerator is The denominator is A proper fraction is An improper fraction is A mixed
MATHEMATICS 8 CHAPTER FRACTION OPERATIONS REVIEW: EQUIVALENT FRACTIONS AND IMPROPER FRACTIONS AND MIXED NUMBERS Date The numerator is The denominator is A proper fraction is An improper fraction is A mixed
Adding Integers with the Same Sign
 Name Date Class - Adding Integers with the Same Sign How do you add integers with the same sign? Add 4 5. Add 4. Step Check the signs. Are the integers both positive or negative? 4 and 5 are both positive.
Name Date Class - Adding Integers with the Same Sign How do you add integers with the same sign? Add 4 5. Add 4. Step Check the signs. Are the integers both positive or negative? 4 and 5 are both positive.
How can you write a fraction as a sum of unit fractions with the same denominator?
 ? Name.5 Essential Question Write Fractions How can you write a fraction as a sum of unit fractions with the same denominator? Number and Operations.. lso..,..,..e MTHEMTIL PROESSES..,..F Unlock the Problem
? Name.5 Essential Question Write Fractions How can you write a fraction as a sum of unit fractions with the same denominator? Number and Operations.. lso..,..,..e MTHEMTIL PROESSES..,..F Unlock the Problem
Rational number operations can often be simplified by converting mixed numbers to improper fractions Add EXAMPLE:
 Rational number operations can often be simplified by converting mixed numbers to improper fractions Add ( 2) EXAMPLE: 2 Multiply 1 Negative fractions can be written with the negative number in the numerator
Rational number operations can often be simplified by converting mixed numbers to improper fractions Add ( 2) EXAMPLE: 2 Multiply 1 Negative fractions can be written with the negative number in the numerator
LESSON 5 - DECIMALS INTRODUCTION
 LESSON 5 - DECIMALS INTRODUCTION Now that we know something about whole numbers and fractions, we will begin working with types of numbers that are extensions of whole numbers and related to fractions.
LESSON 5 - DECIMALS INTRODUCTION Now that we know something about whole numbers and fractions, we will begin working with types of numbers that are extensions of whole numbers and related to fractions.
Fractions and their Equivalent Forms
 Fractions Fractions and their Equivalent Forms Little kids use the concept of a fraction long before we ever formalize their knowledge in school. Watching little kids share a candy bar or a bottle of soda
Fractions Fractions and their Equivalent Forms Little kids use the concept of a fraction long before we ever formalize their knowledge in school. Watching little kids share a candy bar or a bottle of soda
KNOWLEDGE OF NUMBER SENSE, CONCEPTS, AND OPERATIONS
 DOMAIN I. COMPETENCY 1.0 MATHEMATICS KNOWLEDGE OF NUMBER SENSE, CONCEPTS, AND OPERATIONS Skill 1.1 Compare the relative value of real numbers (e.g., integers, fractions, decimals, percents, irrational
DOMAIN I. COMPETENCY 1.0 MATHEMATICS KNOWLEDGE OF NUMBER SENSE, CONCEPTS, AND OPERATIONS Skill 1.1 Compare the relative value of real numbers (e.g., integers, fractions, decimals, percents, irrational
Scheme of work Elementary 1, the maths pathway
 Objective Code Objective Exemplification Links to prior objectives Resources, enrichment, notes E1.1 Multiply and divide numbers by 10, 100 and 1000 including decimals. 6 x 10, 6.5 x 10, 0.65 10 3 x 100,
Objective Code Objective Exemplification Links to prior objectives Resources, enrichment, notes E1.1 Multiply and divide numbers by 10, 100 and 1000 including decimals. 6 x 10, 6.5 x 10, 0.65 10 3 x 100,
MONDAY FEBRUARY 23rd. 2. Work on the next five slides - complete at least 3 out of the 5 problems
 1. Download lesson MONDAY FEBRUARY 23rd - Number Sense Part Two 2. Work on the next five slides - complete at least 3 out of the 5 problems Bellwork #1 What is the absolute value of the temperature shown
1. Download lesson MONDAY FEBRUARY 23rd - Number Sense Part Two 2. Work on the next five slides - complete at least 3 out of the 5 problems Bellwork #1 What is the absolute value of the temperature shown
CHAPTER 3 ADDING AND SUBTRACTING FRACTIONS
 3.1 Adding and Subtracting Like Fractions 83 CHAPTER 3 ADDING AND SUBTRACTING FRACTIONS 3.1 Adding and Subtracting Like Fractions 3.1 Margin Exercises 1. (a && The denominators are the same, so & and &
3.1 Adding and Subtracting Like Fractions 83 CHAPTER 3 ADDING AND SUBTRACTING FRACTIONS 3.1 Adding and Subtracting Like Fractions 3.1 Margin Exercises 1. (a && The denominators are the same, so & and &
Math 7 Notes Unit Three: Applying Rational Numbers
 Math 7 Notes Unit Three: Applying Rational Numbers Strategy note to teachers: Typically students need more practice doing computations with fractions. You may want to consider teaching the sections on
Math 7 Notes Unit Three: Applying Rational Numbers Strategy note to teachers: Typically students need more practice doing computations with fractions. You may want to consider teaching the sections on
Fractions and their Equivalent Forms
 Fractions Fractions and their Equivalent Forms Little kids use the concept of a fraction long before we ever formalize their knowledge in school. Watching little kids share a candy bar or a bottle of soda
Fractions Fractions and their Equivalent Forms Little kids use the concept of a fraction long before we ever formalize their knowledge in school. Watching little kids share a candy bar or a bottle of soda
Section 2.3 Rational Numbers. A rational number is a number that may be written in the form a b. for any integer a and any nonzero integer b.
 Section 2.3 Rational Numbers A rational number is a number that may be written in the form a b for any integer a and any nonzero integer b. Why is division by zero undefined? For example, we know that
Section 2.3 Rational Numbers A rational number is a number that may be written in the form a b for any integer a and any nonzero integer b. Why is division by zero undefined? For example, we know that
5 th Grade Math CRCT Common Core GPS Study Guide
 5 th Grade Math CRCT Common Core GPS Study Guide Dutchtown Elementary School We are a family of learners Dear 5 th Grade Parents, Please download this study guide to help prepare your child for the upcoming
5 th Grade Math CRCT Common Core GPS Study Guide Dutchtown Elementary School We are a family of learners Dear 5 th Grade Parents, Please download this study guide to help prepare your child for the upcoming
UNIT 6 OPERATIONS WITH DECIMALS
 UNIT 6 OPERATIONS WITH DECIMALS INTRODUCTION In this Unit, we will use our understanding of operations, decimals, and place value to perform operations with decimals. The table below shows the learning
UNIT 6 OPERATIONS WITH DECIMALS INTRODUCTION In this Unit, we will use our understanding of operations, decimals, and place value to perform operations with decimals. The table below shows the learning
1-3 Multiplying and Dividing Real Numbers
 Multiplying and Dividing 1-3 Multiplying and Dividing Real Numbers Real Numbers Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz 1 2 pts Bell Quiz 1-3 Add or Subtract 1. 3 8 2 pts 2. - 8 + 12 2 pts 3. 4 (-4) 2
Multiplying and Dividing 1-3 Multiplying and Dividing Real Numbers Real Numbers Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz 1 2 pts Bell Quiz 1-3 Add or Subtract 1. 3 8 2 pts 2. - 8 + 12 2 pts 3. 4 (-4) 2
Preparing For Algebra and Statistics (1 st Edition)
 Preparing For Algebra and Statistics ( st Edition) By Matt Teachout (College of the Canyons) (with help and support from the COC Math Department) Book Introduction: This book was written to combine arithmetic
Preparing For Algebra and Statistics ( st Edition) By Matt Teachout (College of the Canyons) (with help and support from the COC Math Department) Book Introduction: This book was written to combine arithmetic
Name Jack needs to finish _ 5 of a school. 1. Celia has listened to 5 of the
 1. Celia has listened to 5 of the songs on her new CD. Which equation could Celia use to find s, the fraction of the songs she has left to listen to? A B C 5 5 9 D s 9 s s s 5 2. The table below shows
1. Celia has listened to 5 of the songs on her new CD. Which equation could Celia use to find s, the fraction of the songs she has left to listen to? A B C 5 5 9 D s 9 s s s 5 2. The table below shows
Name. List the 5 smallest whole numbers that are a. multiples of 4 and not multiples of 2. b. multiples of 43 and odd. c. even and not multiples of 4.
 1 List the 5 smallest whole numbers that are a. multiples of and not multiples of. b. multiples of and odd. c. even and not multiples of. ETA handmind Add and Subtract Fractions Lesson 1 1 Add Unlike Fractions
1 List the 5 smallest whole numbers that are a. multiples of and not multiples of. b. multiples of and odd. c. even and not multiples of. ETA handmind Add and Subtract Fractions Lesson 1 1 Add Unlike Fractions
Lesson Plan -- Multiplying and Dividing Integers
 Lesson Plan -- Multiplying and Dividing Integers Chapter Resources - Lesson 3-9 Multiply Integers - Lesson 3-9 Multiply Integers Answers - Lesson 3-10 Divide Integers - Lesson 3-10 Divide Integers Answers
Lesson Plan -- Multiplying and Dividing Integers Chapter Resources - Lesson 3-9 Multiply Integers - Lesson 3-9 Multiply Integers Answers - Lesson 3-10 Divide Integers - Lesson 3-10 Divide Integers Answers
Rational Numbers pp
 LESSON 3-1 Rational Numbers pp. 112 114 Vocabulary rational number (p. 112) relatively prime (p. 112) Additional Examples Example 1 Simplify. 5 1 0 5 1 5 is a common factor. 10 2 5 5 1 5 Divide the numerator
LESSON 3-1 Rational Numbers pp. 112 114 Vocabulary rational number (p. 112) relatively prime (p. 112) Additional Examples Example 1 Simplify. 5 1 0 5 1 5 is a common factor. 10 2 5 5 1 5 Divide the numerator
Lesson 6.1. Addition with Unlike Denominators Essential Question How can you use models to add fractions that have different denominators?
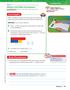 Name Addition with Unlike Denominators Essential Question How can you use models to add fractions that have different denominators? Investigate Hands On Lesson 6.1 Number and Operations Fractions 5.NF.A.1,
Name Addition with Unlike Denominators Essential Question How can you use models to add fractions that have different denominators? Investigate Hands On Lesson 6.1 Number and Operations Fractions 5.NF.A.1,
CIV Module Unit Session Learning Objectives
 CIV Module Unit Session Learning Objectives C IV Module: Essentials of Recognizing a Fraction 1. Learning that a fraction is a part of a whole through the use of area models C IV Module: Essentials of
CIV Module Unit Session Learning Objectives C IV Module: Essentials of Recognizing a Fraction 1. Learning that a fraction is a part of a whole through the use of area models C IV Module: Essentials of
GENERAL MATH FOR PASSING
 GENERAL MATH FOR PASSING Your math and problem solving skills will be a key element in achieving a passing score on your exam. It will be necessary to brush up on your math and problem solving skills.
GENERAL MATH FOR PASSING Your math and problem solving skills will be a key element in achieving a passing score on your exam. It will be necessary to brush up on your math and problem solving skills.
Two Plus You. Unit. National PASS Center 2013
 Two Plus You Unit National PASS Center 0 National PASS Center Geneseo Migrant Center Mt. Morris-Leicester Road Leicester, NY 44 () 6-7960 () 6-7969 (fax) www.migrant.net/pass Authors: Editor: Proofer:
Two Plus You Unit National PASS Center 0 National PASS Center Geneseo Migrant Center Mt. Morris-Leicester Road Leicester, NY 44 () 6-7960 () 6-7969 (fax) www.migrant.net/pass Authors: Editor: Proofer:
SAMPLE LESSON DO NOT COPY. i TELL ME MORE COMPARING FRACTIONS EXAMPLES
 .H i TELL ME MORE The student is expected to compare two fractions having the same numerator or denominator in problems by reasoning about their sizes and justifying the conclusion using symbols, words,
.H i TELL ME MORE The student is expected to compare two fractions having the same numerator or denominator in problems by reasoning about their sizes and justifying the conclusion using symbols, words,
(-,+) (+,+) Plotting Points
 Algebra Basics +y (-,+) (+,+) -x +x (-,-) (+,-) Plotting Points -y Commutative Property of Addition/Multiplication * You can commute or move the terms * This only applies to addition and multiplication
Algebra Basics +y (-,+) (+,+) -x +x (-,-) (+,-) Plotting Points -y Commutative Property of Addition/Multiplication * You can commute or move the terms * This only applies to addition and multiplication
Fractions and their Equivalent Forms
 Fractions Fractions and their Equivalent Forms Little kids use the concept of a fraction long before we ever formalize their knowledge in school. Watching little kids share a candy bar or a bottle of soda
Fractions Fractions and their Equivalent Forms Little kids use the concept of a fraction long before we ever formalize their knowledge in school. Watching little kids share a candy bar or a bottle of soda
Rational and Irrational Numbers can be written as 1_ 2.
 ? L E S S O N 1.1 Rational and Irrational Numbers ESSENTIAL QUESTION 8.NS.1 Know that numbers that are not rational are called irrational. Understand informally that every number has a decimal expansion;
? L E S S O N 1.1 Rational and Irrational Numbers ESSENTIAL QUESTION 8.NS.1 Know that numbers that are not rational are called irrational. Understand informally that every number has a decimal expansion;
Chapter 3 (Operations with Rational Numbers) Bringing It All Together #1
 Chapter 3 (Operations with Rational Numbers) Bringing It All Together #1 Vocabulary Check State whether the statement is true or false. If false, replace the underlined word or number to make a true sentence.
Chapter 3 (Operations with Rational Numbers) Bringing It All Together #1 Vocabulary Check State whether the statement is true or false. If false, replace the underlined word or number to make a true sentence.
1 Addition and Subtraction
 Worsheet for 5.: Operations with Fractions Addition and Subtraction Adding/subtracting when there is a common denominator Draw a picture to work out each problem. Write your answer in lowest terms; if
Worsheet for 5.: Operations with Fractions Addition and Subtraction Adding/subtracting when there is a common denominator Draw a picture to work out each problem. Write your answer in lowest terms; if
Vocabulary: Bits and Pieces II
 Vocabulary: Bits and Pieces II Concept Estimation: Students have developed benchmark fractions. They can use these to substitute for all the fractions in a computation. Or they may use a combination of
Vocabulary: Bits and Pieces II Concept Estimation: Students have developed benchmark fractions. They can use these to substitute for all the fractions in a computation. Or they may use a combination of
BASIC MATH CONTENTS. Section 1... Whole Number Review. Section 2... Decimal Review. Section 3... Fraction Review. Section 4...
 BASIC MATH The purpose of this booklet is to refresh the reader s skills in basic mathematics. There are basic mathematical processes, which must be followed throughout all areas of math applications.
BASIC MATH The purpose of this booklet is to refresh the reader s skills in basic mathematics. There are basic mathematical processes, which must be followed throughout all areas of math applications.
360 right angle, 90. Types of Angles
 Angle Measures Lesson 8 8 Angles Type Measure Right angle 90 Obtuse angle Acute angle more than 90, less than 80 less than 90 0 9 2 2 3 0 9 2 2 3 Straight angle 80 8 7 6 5 4 8 7 6 5 4 Full circle 360 right
Angle Measures Lesson 8 8 Angles Type Measure Right angle 90 Obtuse angle Acute angle more than 90, less than 80 less than 90 0 9 2 2 3 0 9 2 2 3 Straight angle 80 8 7 6 5 4 8 7 6 5 4 Full circle 360 right
Fraction and Mixed-Number Addition and Subtraction
 Fraction and Mixed-Number Addition and Subtraction Objective To guide students in the use of pattern blocks to add and subtract fractions and mixed numbers. www.everydaymathonline.com epresentations etoolkit
Fraction and Mixed-Number Addition and Subtraction Objective To guide students in the use of pattern blocks to add and subtract fractions and mixed numbers. www.everydaymathonline.com epresentations etoolkit
Reteach. Teacher Edition. Chapter 9. Grade 4
 Reteach Teacher Edition Chapter 9 Grade Lesson Reteach Add Like Fractions Remember that to add like fractions, you find the sum of the numerators, but keep the denominator the same. Find _ 1 + _ 1. Use
Reteach Teacher Edition Chapter 9 Grade Lesson Reteach Add Like Fractions Remember that to add like fractions, you find the sum of the numerators, but keep the denominator the same. Find _ 1 + _ 1. Use
Lesson 1: Arithmetic Review
 Lesson 1: Arithmetic Review Topics and Objectives: Order of Operations Fractions o Improper fractions and mixed numbers o Equivalent fractions o Fractions in simplest form o One and zero Operations on
Lesson 1: Arithmetic Review Topics and Objectives: Order of Operations Fractions o Improper fractions and mixed numbers o Equivalent fractions o Fractions in simplest form o One and zero Operations on
Lesson 6: Collecting Rational Number Like Terms
 Lesson 6: Collecting Rational Number Like Terms Classwork Opening Exercise Do the computations, leaving your answers in simplest/standard form. Show your steps. 1. Terry weighs kg. Janice weighs kg less
Lesson 6: Collecting Rational Number Like Terms Classwork Opening Exercise Do the computations, leaving your answers in simplest/standard form. Show your steps. 1. Terry weighs kg. Janice weighs kg less
Lesson 2: Generating Equivalent Expressions
 Lesson 2: Generating Equivalent Expressions Classwork Opening Exercise Additive inverses have a sum of zero. Multiplicative inverses have a product of 1. Fill in the center column of the table with the
Lesson 2: Generating Equivalent Expressions Classwork Opening Exercise Additive inverses have a sum of zero. Multiplicative inverses have a product of 1. Fill in the center column of the table with the
Possible answer: Add 4.5 to the product of 6 and 0.1. Divide 3.6 by 0.4 and then subtract 0.5. Multiply the sum of 6 and 7 by
 -1 1. Consider the expression 1 - ( + ). a. Which operation is done first, subtraction or addition? addition b. Write the computation in words. Possible answer: Subtract the sum of and from 1.. Consider
-1 1. Consider the expression 1 - ( + ). a. Which operation is done first, subtraction or addition? addition b. Write the computation in words. Possible answer: Subtract the sum of and from 1.. Consider
Name Class Date. Associative Property: When you add, you can group any of the numbers. When you multiply, you can group any of the numbers.
 Name Class Date Properties of Numbers Extension: Equivalent Expressions Essential question: How do you write equivalent expressions using properties? Properties of Numbers Commutative Property: You can
Name Class Date Properties of Numbers Extension: Equivalent Expressions Essential question: How do you write equivalent expressions using properties? Properties of Numbers Commutative Property: You can
Introductory Algebra
 Introductory Algebra Student Media Workbook Manuscript An open source (CC-BY) media work book Adapted by Jesse Frausto and Elaine Pham Santiago Canyon College Continuing Education Division This is an adaptation
Introductory Algebra Student Media Workbook Manuscript An open source (CC-BY) media work book Adapted by Jesse Frausto and Elaine Pham Santiago Canyon College Continuing Education Division This is an adaptation
Multiplying and Dividing Fractions and Mixed Numbers
 Multiplying and Dividing Fractions and Mixed Numbers When two fractions are multiplied, the result is another fraction with a denominator that is equal to the product of the denominators of the two fractions.
Multiplying and Dividing Fractions and Mixed Numbers When two fractions are multiplied, the result is another fraction with a denominator that is equal to the product of the denominators of the two fractions.
A. Incorrect! To simplify this expression you need to find the product of 7 and 4, not the sum.
 Problem Solving Drill 05: Exponents and Radicals Question No. 1 of 10 Question 1. Simplify: 7u v 4u 3 v 6 Question #01 (A) 11u 5 v 7 (B) 8u 6 v 6 (C) 8u 5 v 7 (D) 8u 3 v 9 To simplify this expression you
Problem Solving Drill 05: Exponents and Radicals Question No. 1 of 10 Question 1. Simplify: 7u v 4u 3 v 6 Question #01 (A) 11u 5 v 7 (B) 8u 6 v 6 (C) 8u 5 v 7 (D) 8u 3 v 9 To simplify this expression you
Lesson #17 Function Introduction
 Lesson #17 Function Introduction A.A.37 A.A.40 A.A.41 Define a relation and function Write functions in functional notation Use functional notation to evaluate functions for given values in the domain
Lesson #17 Function Introduction A.A.37 A.A.40 A.A.41 Define a relation and function Write functions in functional notation Use functional notation to evaluate functions for given values in the domain
Lesson 2.1. Ahn and four friends decided to make macaroni & cheese. They were very hungry so Ahn decided to make two boxes instead of one.
 Write and Solve Proportions Lesson 2.1 EXPLORE! Ahn and four friends decided to make macaroni & cheese. They were very hungry so Ahn decided to make two boxes instead of one. The directions for one box
Write and Solve Proportions Lesson 2.1 EXPLORE! Ahn and four friends decided to make macaroni & cheese. They were very hungry so Ahn decided to make two boxes instead of one. The directions for one box
Warm Up Simplify each expression. Assume all variables are nonzero.
 Warm Up Simplify each expression. Assume all variables are nonzero. 1. x 5 x 2 3. x 6 x 2 x 7 x 4 Factor each expression. 2. y 3 y 3 y 6 4. y 2 1 y 5 y 3 5. x 2 2x 8 (x 4)(x + 2) 6. x 2 5x x(x 5) 7. x
Warm Up Simplify each expression. Assume all variables are nonzero. 1. x 5 x 2 3. x 6 x 2 x 7 x 4 Factor each expression. 2. y 3 y 3 y 6 4. y 2 1 y 5 y 3 5. x 2 2x 8 (x 4)(x + 2) 6. x 2 5x x(x 5) 7. x
5 th Grade Common Core. Math Review. 40 Pages. All Standards. Jennifer Findley
 5 th Grade Common Core Math Review 40 Pages All Standards Jennifer Findley The first 30 pages contain standards in all 5 domains, grouped this way: The last ten pages contain only Number and Operation
5 th Grade Common Core Math Review 40 Pages All Standards Jennifer Findley The first 30 pages contain standards in all 5 domains, grouped this way: The last ten pages contain only Number and Operation
Grade 6 Math Circles November 10, 2010 Algebra
 1 University of Waterloo Faculty of Mathematics Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing Grade 6 Math Circles November 10, 2010 Algebra Solving Equations (Addition & Subtraction) When we are given
1 University of Waterloo Faculty of Mathematics Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing Grade 6 Math Circles November 10, 2010 Algebra Solving Equations (Addition & Subtraction) When we are given
Fractions and Decimals
 FRACTIONS AND DECIMALS 9 Fractions and Decimals Chapter. INTRODUCTION You have learnt fractions and decimals in earlier classes. The study of fractions included proper, improper and mixed fractions as
FRACTIONS AND DECIMALS 9 Fractions and Decimals Chapter. INTRODUCTION You have learnt fractions and decimals in earlier classes. The study of fractions included proper, improper and mixed fractions as
I Can Grade 4 Math. Example. AACPS Division of Curriculum & Instruction Model Content Frameworks, PARCC December I need help from my teacher.
 I Can Grade 4 Math Major Content Supporting Content Additional Content I Can Example I don t yet know it. I need help from my teacher. I sometimes need help. I can do this all by myself. I can teach this.
I Can Grade 4 Math Major Content Supporting Content Additional Content I Can Example I don t yet know it. I need help from my teacher. I sometimes need help. I can do this all by myself. I can teach this.
Section 1.2 Fractions
 Objectives Section 1.2 Fractions Factor and prime factor natural numbers Recognize special fraction forms Multiply and divide fractions Build equivalent fractions Simplify fractions Add and subtract fractions
Objectives Section 1.2 Fractions Factor and prime factor natural numbers Recognize special fraction forms Multiply and divide fractions Build equivalent fractions Simplify fractions Add and subtract fractions
Fractions and Decimals
 Chapter Fractions and Decimals FRACTION: A fraction is a number representing a part of a whole. The whole may be a single object or a group of objects. 5 is a fraction with numerator and denominator 5.
Chapter Fractions and Decimals FRACTION: A fraction is a number representing a part of a whole. The whole may be a single object or a group of objects. 5 is a fraction with numerator and denominator 5.
2.1 Introduction to Fractions and Mixed Numbers. A Introduction to Fractions SAMPLE. 3 7 Figure 1. The whole candy bar can be represented as 7 7.
 Chapter Fractions and Mixed Numbers Objectives A. Understand the basic concepts of fractions. B. Graph fractions on a number line. C. Understand the basic concepts of mixed numbers. D. Graph mixed numbers
Chapter Fractions and Mixed Numbers Objectives A. Understand the basic concepts of fractions. B. Graph fractions on a number line. C. Understand the basic concepts of mixed numbers. D. Graph mixed numbers
Blackwater Community School Curriculum Map
 Blackwater Community School Curriculum Map 205-206 Fifth Grade Quarter 3 Module 4: Multiplication and Division of Fractions and Decimal Fractions - Part 2, Topics E-H Approximately 2 Days - Begin around
Blackwater Community School Curriculum Map 205-206 Fifth Grade Quarter 3 Module 4: Multiplication and Division of Fractions and Decimal Fractions - Part 2, Topics E-H Approximately 2 Days - Begin around
5 8 ). a. Which operation is done first, subtraction or addition? a. Which operation is done first, addition or multiplication?
 7-1 Homework 1 Consider the expression - ( 3 4 + 5 ). a. Which operation is done first, subtraction or addition? b. Write the computation in words. Consider the expression 4.5 + 6 0.1. a. Which operation
7-1 Homework 1 Consider the expression - ( 3 4 + 5 ). a. Which operation is done first, subtraction or addition? b. Write the computation in words. Consider the expression 4.5 + 6 0.1. a. Which operation
Released December Year. Small Steps Guidance and Examples. Block 2 - Fractions
 Released December 07 Year 5 Small Steps Guidance and Examples Block - Fractions Year 5 Spring Term Teaching Guidance Overview Small Steps Equivalent fractions Improper fractions to mixed numbers Mixed
Released December 07 Year 5 Small Steps Guidance and Examples Block - Fractions Year 5 Spring Term Teaching Guidance Overview Small Steps Equivalent fractions Improper fractions to mixed numbers Mixed
Topic 3: Fractions. Topic 1 Integers. Topic 2 Decimals. Topic 3 Fractions. Topic 4 Ratios. Topic 5 Percentages. Topic 6 Algebra
 Topic : Fractions Topic Integers Topic Decimals Topic Fractions Topic Ratios Topic Percentages Duration / weeks Content Outline PART (/ week) Introduction Converting Fractions to Decimals Converting Decimals
Topic : Fractions Topic Integers Topic Decimals Topic Fractions Topic Ratios Topic Percentages Duration / weeks Content Outline PART (/ week) Introduction Converting Fractions to Decimals Converting Decimals
Name Period Date. UNIT 3: EXPRESSIONS AND EQUATIONS WEEK 12: Student Packet
 Name Period Date UNIT : EXPRESSIONS AND EQUATIONS WEEK 2: Student Packet 2. Inputs and Outputs Use tables, graphs, equations, and words to solve problems. Informally introduce the slope-intercept form
Name Period Date UNIT : EXPRESSIONS AND EQUATIONS WEEK 2: Student Packet 2. Inputs and Outputs Use tables, graphs, equations, and words to solve problems. Informally introduce the slope-intercept form
Decimals Quiz-Study Guide. Name: Hour: Date:
 Decimals Quiz-Study Guide Name: Hour: Date: Section 1 N1A: I can apply and understand whole numbers to millions, fractions and decimals to the thousandths (including location on a number line) A. Select
Decimals Quiz-Study Guide Name: Hour: Date: Section 1 N1A: I can apply and understand whole numbers to millions, fractions and decimals to the thousandths (including location on a number line) A. Select
multiply a fraction or whole number by a fraction.
 Content Standard MAFS.5.NF Number and Operations Fractions MAFS.5.NF.2 Apply and extend previous understanding of multiplication and division to multiply and divide fractions. MAFS.5.NF.2.4 Apply and extend
Content Standard MAFS.5.NF Number and Operations Fractions MAFS.5.NF.2 Apply and extend previous understanding of multiplication and division to multiply and divide fractions. MAFS.5.NF.2.4 Apply and extend
