Garrett Hall CSC 173 C Programming Weeks 3-4
|
|
|
- Muriel Abigail Woods
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Garrett Hall CSC 173 C Programming Weeks Overview The program parses code from an input file and evaluates it. The evaluator can handle basic mathematical operations (+, -, *, /, ^) and trigonometric functions (Sin, Cos, Tan, Asin, Acos, Atan). In addition, the evaluator can handle variables and even solve simple algebraic equalities using a system of substitution rules (described next). 2. Evaluation The evaluation system is described first because it provides examples for the capabilities and syntax of the program as a whole. To run these examples, run the program and type the filename at the prompt. 2.1 Substitution Rules All algebra in the evaluation is based upon substitution rules which are indicated by the -> token. If the left side of a rule is matched then the expression is replaced by the right side. For instance, the rule a-a -> will replace any two identical expressions that are subtracted with a. example1.1 a-a -> ; x-x; x - x Note that substitution rule variables such as a can match any complex expression such as x*3. example1.2 a-a -> ; x*3-x*3; (x * 3) - (x * 3) Note: Substitution rule variables must be single character a-z and are unrelated to variables appearing outside of the build rule. For instance x-x -> would have produced the same output as above. 2.2 Normal Variables Unlike variables that appear in a substitution rule, normal variables can bind to numbers. The assignment operator = indicates a binding when the variable is on the left and the number is on the right. example2.1 x = 3; x - 2; x = 3
2 x It is important to note that variables cannot be reassigned and there is no symbol table. Instead, the expression x=3 is similar to the rule x ->3 where x is a text match. For instance: example2.2 x = 3; x = 5; x = 3 x = 5 3 = 5 False The program can also handle multi-variable equations. example2.3 z = y / 2; y = 4; z = (y / 2) y = 4 z = (y / 2) z = (4 / 2) z = Simple Algebra Rules Rules and variables are combined to make basic algebra systems. The substitution rule algorithm is designed to simplify expressions as much as possible given a set of rules. A simple problem would be x2 4. The evaluator doesn t know anything about dealing with variable expressions until we add some rules. By adding the rule a*b=c -> a=c/b evaluator can now deal with a larger subset of problems example3.1 a*b=c -> a=c/b; x * 2 = 4; (x * 2) = 4 x = 2 To deal with multiplicands in reverse order ( 2 x ) we can add a reflexive rule example3.2 a*b -> b*a; 2 * y = 4; (2 * y) = 4 (y * 2) = 4 y = 2 The example can be extended with identities example3.3
3 a/a -> 1; z * w = z; (z * w) = z (w * z) = z w = 1 Or transitive rules a*(b*c) -> (a*b)*c; 2 * u * v = y; (2 * (u * v)) = u (2 * (v * u)) = u ((v * u) * 2) = u ((2 * v) * u) = u (v * 2) = 1 v =.5 example3.4 Note: The steps in red are omitted from output, but I ve added them for clarity. This is because the evaluation algorithm is essentially looking two steps ahead. 2.4 Advanced Algebra Here are some more advanced examples using a larger algebra base found in the rules file. 2 2x 9y y 1 2z z example4.1 2 * x^2 = 9 * y; y / 2 * z = 1 / z; (2 * (x ^ 2)) = (9 * y) (y / (2 * z)) = (1 / z) (2 * (x ^ 2)) = (9 * y) ((x ^ 2) * 2) = (9 * y) ((x ^ 2) * 2) = (y * 9) ((4.5 * y) ^.5) = x (y / (2 * z)) = (1 / z) (y / (z * 2)) = (1 / z) (y / (2 * z)) = (1 / z) ((2 * z) / z) = y ((4.5 * y) ^.5) = x ((y * 4.5) ^.5) = x ((4.5 * y) ^.5) = x ((x ^ 2) / y) = 4.5 ((2 * z) / z) = y ((z * 2) / z) = y 2 = y y = 2 ((x ^ 2) / y) = 4.5 ((x ^ 2) / 2) = 4.5 ((x ^ 2) *.5) = 4.5 x = 3 The output is a rather verbose series of manipulations, but the correct values are finally arrived at.
4 Note: The evaluator cannot handle systems of inequalities or equations, although it would be possible to extend it to do so. Multivariable equations are only solvable if assignments can be found for all variables except one. Here we solve for the double angle identities. Note these identities are not rules themselves, but are found by expansion example4.2 Cos(x)^2+Sin(x)^2; ((Cosx) ^ 2) + ((Sinx) ^ 2) ((Cosx) * (Cosx)) + ((Sinx) * (Sinx)) Cos(x - x) Cos() 1 The gcc math library for acos returns a single number example4.3 = Cos(x)^2-Sin(x)^2; = (((Cosx) ^ 2) - ((Sinx) ^ 2)) = (((Cosx) ^ 2) - ((Sinx) ^ 2)) = (Cos(2 * x)) (x * 2) = (Acos) (x * 2) = (Acos) (x * 2) = x = Evaluation Algorithm Because evaluation is not the main focus of this assignment I won t discuss it in much detail although it is the most complex aspect of the program. The evaluator transverses the AST built by the parser (detailed later). At each node, the evaluator checks if the node matches any substitution rule. When multiple substitutions are possible the algorithm performs a breadth-first search of fixed depth on the substitution rules. The resulting node with the best heuristic value is chosen. This heuristic favors eliminating variables, simplifying expressions, and moving variables to the left side of an expression (i.e. x=2 is better than 2=x). If numbers are found on either side of an operator node, the operator is replaced by the numeric result of the operation. 3. Implementation The program does the following: 1. Reads input from file specified in main.c 2. Tokenizes it in scanner.c using a DFA 3. Parses it in parser.c using a recursive-descent LL(1) parser 4. Builds abstract symbol trees (binary tree data structures described in AST.c) 5. Evaluates the code in evaluate.c 3.1. Language Below the language is described in terms of the regular expressions accepted by the scanner and the context free grammar (CFG) accepted by the parser Character Classes digit
5 lower a b... z upper A B... Z Accepted Tokens token number variable function -> white ) * + / - ^ ( ; eof number digit digit (. digit ) variable lowercase ( lowercase uppercase digit) function uppercase lowercase lowercase (Function keywords are: Cos, Sin, Tan, Acos, Asin, and Atan) white tab newline space comparison < <= = >= > Context-free Grammar statement rule ; statement rule expression -> expression expression The -> token indicates a special substitution rule. expression field comparison field field Comparisons will evaluate to true or false although = will act as an assignment to an unbound variable. For example x=2 will act as an assignment statement if x was previously unassigned. Otherwise it will be a comparison. field field + field field field 1 field 1 ( field ) The field i are non-terminals which represent the order of operations. Specifically i is the priority of the operation. The non-terminals are right-recursive which allows LL(1) parsing (no infinite loops) and creates parse trees. field field - field field ( field ) field field / field field ( field ) field field * field field ( field ) field field ^ field field ( field ) field atom atom atom number variable function( field ) The -atom is a signed atom and uses a flag so that it can only occur in the first atom. Otherwise the negative sign could be infinitely nested. Function keywords are Cos, Sin, Tan, Acos, Asin, and Atan.
6 3.2 Scanner DFA S 1 lower lower F F 2 F C lower C Alphabet Sets lower = {a, b,...,z} upper = {A, B,...,Z} symbol = {+ - * / ^ ; ) ( < = > eof } digit = {, 1,...,9} F = white U { ( } V = number U upper U lower upper F 1 lower C Function Token V C lower V 1 V Variable Token digit digit C N 3 digit digit digit N 1 {. } C {. } N 2 digit C Number Token { < = > } C { = } E 1 { < = > } { < > } C { < } E 2 { < > } { < > } C { > } E 3 { < > } Equality Token { # } { # } { > } C C 1 { # } C Comment Token { - } R 1 { > } Rule Token symbol U white Other Tokens
7 3.3. Abstract Symbol Tree (AST) The parser which implements the CFG generates a binary tree. This is not the concrete parse tree because redundant non-terminals are not added to the tree, so it is an AST. For example, the production arrived at through field3 field4 field5 atom number is reduced to simply number. Each node in the AST has an associated class: AST_BINARY: a binary operation on two nodes + AST_UNARY: a unary operation on one node Cos AST_COMPARE: comparison between two nodes <= AST_NUMBER: single node that is a number 9.32 AST_VARIABLE: single node that is a variable myvar AST_BOUND: single node that is an assigned variable myvar = 9.32 This is the parse tree for the statement 9*3+5; Notice the order of operations inherent in the tree structure: statement rule expression field field1 field2 field3 field field1 field2 field3 field3 field4 field4 field4 field5 field5 field5 atom atom atom number * number + number ; 9 * ;
8 The AST is simply: 9 + * Generating the AST To view the tree-structure of input the flag in main.c must be changed by changing the line tree_flag(); to tree_flag(1); codefile 1*2+3^4/(5+6); + * 1 2 / ^ The output is in prefix notation. If the flag is turned off tree_flag(); the code will simply evaluate. In this case the result is in fully parenthesized infix notation: (1 * 2) + ((3 ^ 4) / (5 + 6)) 2 + ((3 ^ 4) / (5 + 6)) 2 + (81 / (5 + 6)) 2 + (81 / 11) Error Handling Below are a few examples of possible errors. Comments must always begin and close with the pound sign. # Good # # Bad Error end of file in comment at line 2, col
9 Because testing for equality and assignments are interchangeable only the token = should be used. x == 4; Comparison '==' should be '=' at line 1, col 2 Operators should not occur next to each other. Parentheses avoid this problem. - 2 / + 3; Atom expected '+' found at line 1, col 6-2 / (+ 3); (-2) / (+3) -2 / (+3) -2 / The format of functions must include parentheses and the first letter must be capitalized. Cos; '' cannot be in function name at line 1, col cos(); ';' expected '(' found at line 1, col 3 Cos ; '' cannot be in function name at line 1, col Cos(); Cos 1
MATVEC: MATRIX-VECTOR COMPUTATION LANGUAGE REFERENCE MANUAL. John C. Murphy jcm2105 Programming Languages and Translators Professor Stephen Edwards
 MATVEC: MATRIX-VECTOR COMPUTATION LANGUAGE REFERENCE MANUAL John C. Murphy jcm2105 Programming Languages and Translators Professor Stephen Edwards Language Reference Manual Introduction The purpose of
MATVEC: MATRIX-VECTOR COMPUTATION LANGUAGE REFERENCE MANUAL John C. Murphy jcm2105 Programming Languages and Translators Professor Stephen Edwards Language Reference Manual Introduction The purpose of
CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages
 CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages Context Free Grammars and Parsing 1 Recall: Architecture of Compilers, Interpreters Source Parser Static Analyzer Intermediate Representation Front End Back
CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages Context Free Grammars and Parsing 1 Recall: Architecture of Compilers, Interpreters Source Parser Static Analyzer Intermediate Representation Front End Back
CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages. Context Free Grammars
 CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages Context Free Grammars 1 Architecture of Compilers, Interpreters Source Analyzer Optimizer Code Generator Abstract Syntax Tree Front End Back End Compiler
CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages Context Free Grammars 1 Architecture of Compilers, Interpreters Source Analyzer Optimizer Code Generator Abstract Syntax Tree Front End Back End Compiler
Introduction to MATLAB
 Outlines January 30, 2008 Outlines Part I: Part II: Writing MATLAB Functions Starting MATLAB Exiting MATLAB Getting Help Command Window Workspace Command History Current Directory Selector Real Values
Outlines January 30, 2008 Outlines Part I: Part II: Writing MATLAB Functions Starting MATLAB Exiting MATLAB Getting Help Command Window Workspace Command History Current Directory Selector Real Values
CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages. Architecture of Compilers, Interpreters
 : Organization of Programming Languages Context Free Grammars 1 Architecture of Compilers, Interpreters Source Scanner Parser Static Analyzer Intermediate Representation Front End Back End Compiler / Interpreter
: Organization of Programming Languages Context Free Grammars 1 Architecture of Compilers, Interpreters Source Scanner Parser Static Analyzer Intermediate Representation Front End Back End Compiler / Interpreter
CS-201 Introduction to Programming with Java
 CS-201 Introduction to Programming with Java California State University, Los Angeles Computer Science Department Lecture V: Mathematical Functions, Characters, and Strings Introduction How would you estimate
CS-201 Introduction to Programming with Java California State University, Los Angeles Computer Science Department Lecture V: Mathematical Functions, Characters, and Strings Introduction How would you estimate
Introduction to MATLAB
 Outlines September 9, 2004 Outlines Part I: Review of Previous Lecture Part II: Part III: Writing MATLAB Functions Review of Previous Lecture Outlines Part I: Review of Previous Lecture Part II: Part III:
Outlines September 9, 2004 Outlines Part I: Review of Previous Lecture Part II: Part III: Writing MATLAB Functions Review of Previous Lecture Outlines Part I: Review of Previous Lecture Part II: Part III:
MIT Specifying Languages with Regular Expressions and Context-Free Grammars. Martin Rinard Massachusetts Institute of Technology
 MIT 6.035 Specifying Languages with Regular essions and Context-Free Grammars Martin Rinard Massachusetts Institute of Technology Language Definition Problem How to precisely define language Layered structure
MIT 6.035 Specifying Languages with Regular essions and Context-Free Grammars Martin Rinard Massachusetts Institute of Technology Language Definition Problem How to precisely define language Layered structure
MIT Specifying Languages with Regular Expressions and Context-Free Grammars
 MIT 6.035 Specifying Languages with Regular essions and Context-Free Grammars Martin Rinard Laboratory for Computer Science Massachusetts Institute of Technology Language Definition Problem How to precisely
MIT 6.035 Specifying Languages with Regular essions and Context-Free Grammars Martin Rinard Laboratory for Computer Science Massachusetts Institute of Technology Language Definition Problem How to precisely
Compiler Construction
 Compiled on 5/05/207 at 3:2pm Abbreviations NFA. Non-deterministic finite automaton DFA. Deterministic finite automaton Compiler Construction Collection of exercises Version May 5, 207 General Remarks
Compiled on 5/05/207 at 3:2pm Abbreviations NFA. Non-deterministic finite automaton DFA. Deterministic finite automaton Compiler Construction Collection of exercises Version May 5, 207 General Remarks
Ordinary Differential Equation Solver Language (ODESL) Reference Manual
 Ordinary Differential Equation Solver Language (ODESL) Reference Manual Rui Chen 11/03/2010 1. Introduction ODESL is a computer language specifically designed to solve ordinary differential equations (ODE
Ordinary Differential Equation Solver Language (ODESL) Reference Manual Rui Chen 11/03/2010 1. Introduction ODESL is a computer language specifically designed to solve ordinary differential equations (ODE
flex is not a bad tool to use for doing modest text transformations and for programs that collect statistics on input.
 flex is not a bad tool to use for doing modest text transformations and for programs that collect statistics on input. More often than not, though, you ll want to use flex to generate a scanner that divides
flex is not a bad tool to use for doing modest text transformations and for programs that collect statistics on input. More often than not, though, you ll want to use flex to generate a scanner that divides
CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages
 CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages Context Free Grammars 1 Architecture of Compilers, Interpreters Source Analyzer Optimizer Code Generator Abstract Syntax Tree Front End Back End Compiler
CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages Context Free Grammars 1 Architecture of Compilers, Interpreters Source Analyzer Optimizer Code Generator Abstract Syntax Tree Front End Back End Compiler
Project 1: Scheme Pretty-Printer
 Project 1: Scheme Pretty-Printer CSC 4101, Fall 2017 Due: 7 October 2017 For this programming assignment, you will implement a pretty-printer for a subset of Scheme in either C++ or Java. The code should
Project 1: Scheme Pretty-Printer CSC 4101, Fall 2017 Due: 7 October 2017 For this programming assignment, you will implement a pretty-printer for a subset of Scheme in either C++ or Java. The code should
Compiler Construction
 Compiler Construction Collection of exercises Version February 7, 26 Abbreviations NFA. Non-deterministic finite automaton DFA. Deterministic finite automaton Lexical analysis. Construct deterministic
Compiler Construction Collection of exercises Version February 7, 26 Abbreviations NFA. Non-deterministic finite automaton DFA. Deterministic finite automaton Lexical analysis. Construct deterministic
Fundamental Data Types. CSE 130: Introduction to Programming in C Stony Brook University
 Fundamental Data Types CSE 130: Introduction to Programming in C Stony Brook University Program Organization in C The C System C consists of several parts: The C language The preprocessor The compiler
Fundamental Data Types CSE 130: Introduction to Programming in C Stony Brook University Program Organization in C The C System C consists of several parts: The C language The preprocessor The compiler
A programming language requires two major definitions A simple one pass compiler
 A programming language requires two major definitions A simple one pass compiler [Syntax: what the language looks like A context-free grammar written in BNF (Backus-Naur Form) usually suffices. [Semantics:
A programming language requires two major definitions A simple one pass compiler [Syntax: what the language looks like A context-free grammar written in BNF (Backus-Naur Form) usually suffices. [Semantics:
CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages
 CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages Context Free Grammars 1 Architecture of Compilers, Interpreters Source Analyzer Optimizer Code Generator Abstract Syntax Tree Front End Back End Compiler
CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages Context Free Grammars 1 Architecture of Compilers, Interpreters Source Analyzer Optimizer Code Generator Abstract Syntax Tree Front End Back End Compiler
Week 2: Syntax Specification, Grammars
 CS320 Principles of Programming Languages Week 2: Syntax Specification, Grammars Jingke Li Portland State University Fall 2017 PSU CS320 Fall 17 Week 2: Syntax Specification, Grammars 1/ 62 Words and Sentences
CS320 Principles of Programming Languages Week 2: Syntax Specification, Grammars Jingke Li Portland State University Fall 2017 PSU CS320 Fall 17 Week 2: Syntax Specification, Grammars 1/ 62 Words and Sentences
Parsing. Note by Baris Aktemur: Our slides are adapted from Cooper and Torczon s slides that they prepared for COMP 412 at Rice.
 Parsing Note by Baris Aktemur: Our slides are adapted from Cooper and Torczon s slides that they prepared for COMP 412 at Rice. Copyright 2010, Keith D. Cooper & Linda Torczon, all rights reserved. Students
Parsing Note by Baris Aktemur: Our slides are adapted from Cooper and Torczon s slides that they prepared for COMP 412 at Rice. Copyright 2010, Keith D. Cooper & Linda Torczon, all rights reserved. Students
Introduction to Engineering gii
 25.108 Introduction to Engineering gii Dr. Jay Weitzen Lecture Notes I: Introduction to Matlab from Gilat Book MATLAB - Lecture # 1 Starting with MATLAB / Chapter 1 Topics Covered: 1. Introduction. 2.
25.108 Introduction to Engineering gii Dr. Jay Weitzen Lecture Notes I: Introduction to Matlab from Gilat Book MATLAB - Lecture # 1 Starting with MATLAB / Chapter 1 Topics Covered: 1. Introduction. 2.
Comp 411 Principles of Programming Languages Lecture 3 Parsing. Corky Cartwright January 11, 2019
 Comp 411 Principles of Programming Languages Lecture 3 Parsing Corky Cartwright January 11, 2019 Top Down Parsing What is a context-free grammar (CFG)? A recursive definition of a set of strings; it is
Comp 411 Principles of Programming Languages Lecture 3 Parsing Corky Cartwright January 11, 2019 Top Down Parsing What is a context-free grammar (CFG)? A recursive definition of a set of strings; it is
CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages. Context Free Grammars
 CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages Context Free Grammars 1 Architecture of Compilers, Interpreters Source Analyzer Optimizer Code Generator Abstract Syntax Tree Front End Back End Compiler
CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages Context Free Grammars 1 Architecture of Compilers, Interpreters Source Analyzer Optimizer Code Generator Abstract Syntax Tree Front End Back End Compiler
Syntax Analysis, III Comp 412
 COMP 412 FALL 2017 Syntax Analysis, III Comp 412 source code IR Front End Optimizer Back End IR target code Copyright 2017, Keith D. Cooper & Linda Torczon, all rights reserved. Students enrolled in Comp
COMP 412 FALL 2017 Syntax Analysis, III Comp 412 source code IR Front End Optimizer Back End IR target code Copyright 2017, Keith D. Cooper & Linda Torczon, all rights reserved. Students enrolled in Comp
Principles of Programming Languages COMP251: Syntax and Grammars
 Principles of Programming Languages COMP251: Syntax and Grammars Prof. Dekai Wu Department of Computer Science and Engineering The Hong Kong University of Science and Technology Hong Kong, China Fall 2007
Principles of Programming Languages COMP251: Syntax and Grammars Prof. Dekai Wu Department of Computer Science and Engineering The Hong Kong University of Science and Technology Hong Kong, China Fall 2007
Architecture of Compilers, Interpreters. CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages. Front End Scanner and Parser. Implementing the Front End
 Architecture of Compilers, Interpreters : Organization of Programming Languages ource Analyzer Optimizer Code Generator Context Free Grammars Intermediate Representation Front End Back End Compiler / Interpreter
Architecture of Compilers, Interpreters : Organization of Programming Languages ource Analyzer Optimizer Code Generator Context Free Grammars Intermediate Representation Front End Back End Compiler / Interpreter
CSE 401 Midterm Exam Sample Solution 2/11/15
 Question 1. (10 points) Regular expression warmup. For regular expression questions, you must restrict yourself to the basic regular expression operations covered in class and on homework assignments:
Question 1. (10 points) Regular expression warmup. For regular expression questions, you must restrict yourself to the basic regular expression operations covered in class and on homework assignments:
Context-Free Grammar (CFG)
 Context-Free Grammar (CFG) context-free grammar looks like this bunch of rules: ain idea: + 1 (),, are non-terminal symbols aka variables. When you see them, you apply rules to expand. One of them is designated
Context-Free Grammar (CFG) context-free grammar looks like this bunch of rules: ain idea: + 1 (),, are non-terminal symbols aka variables. When you see them, you apply rules to expand. One of them is designated
Syntax Analysis, III Comp 412
 Updated algorithm for removal of indirect left recursion to match EaC3e (3/2018) COMP 412 FALL 2018 Midterm Exam: Thursday October 18, 7PM Herzstein Amphitheater Syntax Analysis, III Comp 412 source code
Updated algorithm for removal of indirect left recursion to match EaC3e (3/2018) COMP 412 FALL 2018 Midterm Exam: Thursday October 18, 7PM Herzstein Amphitheater Syntax Analysis, III Comp 412 source code
SCHEME 8. 1 Introduction. 2 Primitives COMPUTER SCIENCE 61A. March 23, 2017
 SCHEME 8 COMPUTER SCIENCE 61A March 2, 2017 1 Introduction In the next part of the course, we will be working with the Scheme programming language. In addition to learning how to write Scheme programs,
SCHEME 8 COMPUTER SCIENCE 61A March 2, 2017 1 Introduction In the next part of the course, we will be working with the Scheme programming language. In addition to learning how to write Scheme programs,
Announcements. Written Assignment 1 out, due Friday, July 6th at 5PM.
 Syntax Analysis Announcements Written Assignment 1 out, due Friday, July 6th at 5PM. xplore the theoretical aspects of scanning. See the limits of maximal-munch scanning. Class mailing list: There is an
Syntax Analysis Announcements Written Assignment 1 out, due Friday, July 6th at 5PM. xplore the theoretical aspects of scanning. See the limits of maximal-munch scanning. Class mailing list: There is an
1. true / false By a compiler we mean a program that translates to code that will run natively on some machine.
 1. true / false By a compiler we mean a program that translates to code that will run natively on some machine. 2. true / false ML can be compiled. 3. true / false FORTRAN can reasonably be considered
1. true / false By a compiler we mean a program that translates to code that will run natively on some machine. 2. true / false ML can be compiled. 3. true / false FORTRAN can reasonably be considered
SYED AMMAL ENGINEERING COLLEGE (An ISO 9001:2008 Certified Institution) Dr. E.M. Abdullah Campus, Ramanathapuram
 CS6660 COMPILER DESIGN Question Bank UNIT I-INTRODUCTION TO COMPILERS 1. Define compiler. 2. Differentiate compiler and interpreter. 3. What is a language processing system? 4. List four software tools
CS6660 COMPILER DESIGN Question Bank UNIT I-INTRODUCTION TO COMPILERS 1. Define compiler. 2. Differentiate compiler and interpreter. 3. What is a language processing system? 4. List four software tools
Full file at
 Java Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program Design, 3 rd Edition 2-1 Chapter 2 Basic Elements of Java At a Glance Instructor s Manual Table of Contents Overview Objectives s Quick Quizzes Class
Java Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program Design, 3 rd Edition 2-1 Chapter 2 Basic Elements of Java At a Glance Instructor s Manual Table of Contents Overview Objectives s Quick Quizzes Class
10/4/18. Lexical and Syntactic Analysis. Lexical and Syntax Analysis. Tokenizing Source. Scanner. Reasons to Separate Lexical and Syntactic Analysis
 Lexical and Syntactic Analysis Lexical and Syntax Analysis In Text: Chapter 4 Two steps to discover the syntactic structure of a program Lexical analysis (Scanner): to read the input characters and output
Lexical and Syntactic Analysis Lexical and Syntax Analysis In Text: Chapter 4 Two steps to discover the syntactic structure of a program Lexical analysis (Scanner): to read the input characters and output
Where We Are. CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages. This Lecture. Programming Languages. Motivation for Grammars
 CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages Context Free Grammars Where We Are Programming languages Ruby OCaml Implementing programming languages Scanner Uses regular expressions Finite automata Parser
CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages Context Free Grammars Where We Are Programming languages Ruby OCaml Implementing programming languages Scanner Uses regular expressions Finite automata Parser
Stacks, Queues and Hierarchical Collections
 Programming III Stacks, Queues and Hierarchical Collections 2501ICT Nathan Contents Linked Data Structures Revisited Stacks Queues Trees Binary Trees Generic Trees Implementations 2 Copyright 2002- by
Programming III Stacks, Queues and Hierarchical Collections 2501ICT Nathan Contents Linked Data Structures Revisited Stacks Queues Trees Binary Trees Generic Trees Implementations 2 Copyright 2002- by
Section 7.6 Graphs of the Sine and Cosine Functions
 Section 7.6 Graphs of the Sine and Cosine Functions We are going to learn how to graph the sine and cosine functions on the xy-plane. Just like with any other function, it is easy to do by plotting points.
Section 7.6 Graphs of the Sine and Cosine Functions We are going to learn how to graph the sine and cosine functions on the xy-plane. Just like with any other function, it is easy to do by plotting points.
CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages. Context Free Grammars
 CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages Context Free Grammars 1 Architecture of Compilers, Interpreters Source Analyzer Optimizer Code Generator Abstract Syntax Tree Front End Back End Compiler
CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages Context Free Grammars 1 Architecture of Compilers, Interpreters Source Analyzer Optimizer Code Generator Abstract Syntax Tree Front End Back End Compiler
Syntax Analysis. Prof. James L. Frankel Harvard University. Version of 6:43 PM 6-Feb-2018 Copyright 2018, 2015 James L. Frankel. All rights reserved.
 Syntax Analysis Prof. James L. Frankel Harvard University Version of 6:43 PM 6-Feb-2018 Copyright 2018, 2015 James L. Frankel. All rights reserved. Context-Free Grammar (CFG) terminals non-terminals start
Syntax Analysis Prof. James L. Frankel Harvard University Version of 6:43 PM 6-Feb-2018 Copyright 2018, 2015 James L. Frankel. All rights reserved. Context-Free Grammar (CFG) terminals non-terminals start
CS606- compiler instruction Solved MCQS From Midterm Papers
 CS606- compiler instruction Solved MCQS From Midterm Papers March 06,2014 MC100401285 Moaaz.pk@gmail.com Mc100401285@gmail.com PSMD01 Final Term MCQ s and Quizzes CS606- compiler instruction If X is a
CS606- compiler instruction Solved MCQS From Midterm Papers March 06,2014 MC100401285 Moaaz.pk@gmail.com Mc100401285@gmail.com PSMD01 Final Term MCQ s and Quizzes CS606- compiler instruction If X is a
CSE 401 Midterm Exam 11/5/10
 Name There are 5 questions worth a total of 100 points. Please budget your time so you get to all of the questions. Keep your answers brief and to the point. The exam is closed books, closed notes, closed
Name There are 5 questions worth a total of 100 points. Please budget your time so you get to all of the questions. Keep your answers brief and to the point. The exam is closed books, closed notes, closed
download instant at
 chaptersolutions (USA) 2010/9/1 13:17 page 2 #3 2 Chapter 3 3.1 from page 106 The token sequence for the first four lines (by line) is: ID(main),LPAREN,RPAREN,LBRACE CONST,ID(float),ID(payment),ASSIGN,FLOATNUM(384.00),SEMICOLON
chaptersolutions (USA) 2010/9/1 13:17 page 2 #3 2 Chapter 3 3.1 from page 106 The token sequence for the first four lines (by line) is: ID(main),LPAREN,RPAREN,LBRACE CONST,ID(float),ID(payment),ASSIGN,FLOATNUM(384.00),SEMICOLON
Lexical Analysis (ASU Ch 3, Fig 3.1)
 Lexical Analysis (ASU Ch 3, Fig 3.1) Implementation by hand automatically ((F)Lex) Lex generates a finite automaton recogniser uses regular expressions Tasks remove white space (ws) display source program
Lexical Analysis (ASU Ch 3, Fig 3.1) Implementation by hand automatically ((F)Lex) Lex generates a finite automaton recogniser uses regular expressions Tasks remove white space (ws) display source program
Character Set. The character set of C represents alphabet, digit or any symbol used to represent information. Digits 0, 1, 2, 3, 9
 Character Set The character set of C represents alphabet, digit or any symbol used to represent information. Types Uppercase Alphabets Lowercase Alphabets Character Set A, B, C, Y, Z a, b, c, y, z Digits
Character Set The character set of C represents alphabet, digit or any symbol used to represent information. Types Uppercase Alphabets Lowercase Alphabets Character Set A, B, C, Y, Z a, b, c, y, z Digits
A Simple Syntax-Directed Translator
 Chapter 2 A Simple Syntax-Directed Translator 1-1 Introduction The analysis phase of a compiler breaks up a source program into constituent pieces and produces an internal representation for it, called
Chapter 2 A Simple Syntax-Directed Translator 1-1 Introduction The analysis phase of a compiler breaks up a source program into constituent pieces and produces an internal representation for it, called
Syntax-Directed Translation. Lecture 14
 Syntax-Directed Translation Lecture 14 (adapted from slides by R. Bodik) 9/27/2006 Prof. Hilfinger, Lecture 14 1 Motivation: parser as a translator syntax-directed translation stream of tokens parser ASTs,
Syntax-Directed Translation Lecture 14 (adapted from slides by R. Bodik) 9/27/2006 Prof. Hilfinger, Lecture 14 1 Motivation: parser as a translator syntax-directed translation stream of tokens parser ASTs,
CS 314 Principles of Programming Languages
 CS 314 Principles of Programming Languages Lecture 2: Syntax Analysis Zheng (Eddy) Zhang Rutgers University January 22, 2018 Announcement First recitation starts this Wednesday Homework 1 will be release
CS 314 Principles of Programming Languages Lecture 2: Syntax Analysis Zheng (Eddy) Zhang Rutgers University January 22, 2018 Announcement First recitation starts this Wednesday Homework 1 will be release
This book is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 License
 6. Syntax Learning objectives: syntax and semantics syntax diagrams and EBNF describe context-free grammars terminal and nonterminal symbols productions definition of EBNF by itself parse tree grammars
6. Syntax Learning objectives: syntax and semantics syntax diagrams and EBNF describe context-free grammars terminal and nonterminal symbols productions definition of EBNF by itself parse tree grammars
Lecture 4: Syntax Specification
 The University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill Spring 2002 Lecture 4: Syntax Specification Jan 16 1 Phases of Compilation 2 1 Syntax Analysis Syntax: Webster s definition: 1 a : the way in which linguistic
The University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill Spring 2002 Lecture 4: Syntax Specification Jan 16 1 Phases of Compilation 2 1 Syntax Analysis Syntax: Webster s definition: 1 a : the way in which linguistic
Parsing. CS321 Programming Languages Ozyegin University
 Parsing Barış Aktemur CS321 Programming Languages Ozyegin University Parser is the part of the interpreter/compiler that takes the tokenized input from the lexer (aka scanner and builds an abstract syntax
Parsing Barış Aktemur CS321 Programming Languages Ozyegin University Parser is the part of the interpreter/compiler that takes the tokenized input from the lexer (aka scanner and builds an abstract syntax
Compiler Construction
 Compiler Construction Exercises 1 Review of some Topics in Formal Languages 1. (a) Prove that two words x, y commute (i.e., satisfy xy = yx) if and only if there exists a word w such that x = w m, y =
Compiler Construction Exercises 1 Review of some Topics in Formal Languages 1. (a) Prove that two words x, y commute (i.e., satisfy xy = yx) if and only if there exists a word w such that x = w m, y =
CSCE 314 Programming Languages
 CSCE 314 Programming Languages Syntactic Analysis Dr. Hyunyoung Lee 1 What Is a Programming Language? Language = syntax + semantics The syntax of a language is concerned with the form of a program: how
CSCE 314 Programming Languages Syntactic Analysis Dr. Hyunyoung Lee 1 What Is a Programming Language? Language = syntax + semantics The syntax of a language is concerned with the form of a program: how
CS 314 Principles of Programming Languages. Lecture 3
 CS 314 Principles of Programming Languages Lecture 3 Zheng Zhang Department of Computer Science Rutgers University Wednesday 14 th September, 2016 Zheng Zhang 1 CS@Rutgers University Class Information
CS 314 Principles of Programming Languages Lecture 3 Zheng Zhang Department of Computer Science Rutgers University Wednesday 14 th September, 2016 Zheng Zhang 1 CS@Rutgers University Class Information
SMPL - A Simplified Modeling Language for Mathematical Programming
 SMPL - A Simplified Modeling Language for Mathematical Programming Mihály Csaba Markót November 3, 2008 1 Purpose and Scope This working paper describes SMPL, an initiative of a Simplified Modeling Language
SMPL - A Simplified Modeling Language for Mathematical Programming Mihály Csaba Markót November 3, 2008 1 Purpose and Scope This working paper describes SMPL, an initiative of a Simplified Modeling Language
CSCE 120: Learning To Code
 CSCE 120: Learning To Code Manipulating Data I Introduction This module is designed to get you started working with data by understanding and using variables and data types in JavaScript. It will also
CSCE 120: Learning To Code Manipulating Data I Introduction This module is designed to get you started working with data by understanding and using variables and data types in JavaScript. It will also
CSE 3302 Programming Languages Lecture 2: Syntax
 CSE 3302 Programming Languages Lecture 2: Syntax (based on slides by Chengkai Li) Leonidas Fegaras University of Texas at Arlington CSE 3302 L2 Spring 2011 1 How do we define a PL? Specifying a PL: Syntax:
CSE 3302 Programming Languages Lecture 2: Syntax (based on slides by Chengkai Li) Leonidas Fegaras University of Texas at Arlington CSE 3302 L2 Spring 2011 1 How do we define a PL? Specifying a PL: Syntax:
Language Basics. /* The NUMBER GAME - User tries to guess a number between 1 and 10 */ /* Generate a random number between 1 and 10 */
 Overview Language Basics This chapter describes the basic elements of Rexx. It discusses the simple components that make up the language. These include script structure, elements of the language, operators,
Overview Language Basics This chapter describes the basic elements of Rexx. It discusses the simple components that make up the language. These include script structure, elements of the language, operators,
Theoretical Part. Chapter one:- - What are the Phases of compiler? Answer:
 Theoretical Part Chapter one:- - What are the Phases of compiler? Six phases Scanner Parser Semantic Analyzer Source code optimizer Code generator Target Code Optimizer Three auxiliary components Literal
Theoretical Part Chapter one:- - What are the Phases of compiler? Six phases Scanner Parser Semantic Analyzer Source code optimizer Code generator Target Code Optimizer Three auxiliary components Literal
Optimizing Finite Automata
 Optimizing Finite Automata We can improve the DFA created by MakeDeterministic. Sometimes a DFA will have more states than necessary. For every DFA there is a unique smallest equivalent DFA (fewest states
Optimizing Finite Automata We can improve the DFA created by MakeDeterministic. Sometimes a DFA will have more states than necessary. For every DFA there is a unique smallest equivalent DFA (fewest states
Definition: A context-free grammar (CFG) is a 4- tuple. variables = nonterminals, terminals, rules = productions,,
 CMPSCI 601: Recall From Last Time Lecture 5 Definition: A context-free grammar (CFG) is a 4- tuple, variables = nonterminals, terminals, rules = productions,,, are all finite. 1 ( ) $ Pumping Lemma for
CMPSCI 601: Recall From Last Time Lecture 5 Definition: A context-free grammar (CFG) is a 4- tuple, variables = nonterminals, terminals, rules = productions,,, are all finite. 1 ( ) $ Pumping Lemma for
Supplemental Materials: Grammars, Parsing, and Expressions. Topics. Grammars 10/11/2017. CS2: Data Structures and Algorithms Colorado State University
 Supplemental Materials: Grammars, Parsing, and Expressions CS2: Data Structures and Algorithms Colorado State University Original slides by Chris Wilcox, Updated by Russ Wakefield and Wim Bohm Topics Grammars
Supplemental Materials: Grammars, Parsing, and Expressions CS2: Data Structures and Algorithms Colorado State University Original slides by Chris Wilcox, Updated by Russ Wakefield and Wim Bohm Topics Grammars
A simple syntax-directed
 Syntax-directed is a grammaroriented compiling technique Programming languages: Syntax: what its programs look like? Semantic: what its programs mean? 1 A simple syntax-directed Lexical Syntax Character
Syntax-directed is a grammaroriented compiling technique Programming languages: Syntax: what its programs look like? Semantic: what its programs mean? 1 A simple syntax-directed Lexical Syntax Character
COMP-421 Compiler Design. Presented by Dr Ioanna Dionysiou
 COMP-421 Compiler Design Presented by Dr Ioanna Dionysiou Administrative! [ALSU03] Chapter 3 - Lexical Analysis Sections 3.1-3.4, 3.6-3.7! Reading for next time [ALSU03] Chapter 3 Copyright (c) 2010 Ioanna
COMP-421 Compiler Design Presented by Dr Ioanna Dionysiou Administrative! [ALSU03] Chapter 3 - Lexical Analysis Sections 3.1-3.4, 3.6-3.7! Reading for next time [ALSU03] Chapter 3 Copyright (c) 2010 Ioanna
Stating the obvious, people and computers do not speak the same language.
 3.4 SYSTEM SOFTWARE 3.4.3 TRANSLATION SOFTWARE INTRODUCTION Stating the obvious, people and computers do not speak the same language. People have to write programs in order to instruct a computer what
3.4 SYSTEM SOFTWARE 3.4.3 TRANSLATION SOFTWARE INTRODUCTION Stating the obvious, people and computers do not speak the same language. People have to write programs in order to instruct a computer what
PROGRAMMING IN C AND C++:
 PROGRAMMING IN C AND C++: Week 1 1. Introductions 2. Using Dos commands, make a directory: C:\users\YearOfJoining\Sectionx\USERNAME\CS101 3. Getting started with Visual C++. 4. Write a program to print
PROGRAMMING IN C AND C++: Week 1 1. Introductions 2. Using Dos commands, make a directory: C:\users\YearOfJoining\Sectionx\USERNAME\CS101 3. Getting started with Visual C++. 4. Write a program to print
Compilation 2012 Context-Free Languages Parsers and Scanners. Jan Midtgaard Michael I. Schwartzbach Aarhus University
 Compilation 2012 Parsers and Scanners Jan Midtgaard Michael I. Schwartzbach Aarhus University Context-Free Grammars Example: sentence subject verb object subject person person John Joe Zacharias verb asked
Compilation 2012 Parsers and Scanners Jan Midtgaard Michael I. Schwartzbach Aarhus University Context-Free Grammars Example: sentence subject verb object subject person person John Joe Zacharias verb asked
First Midterm Exam CS164, Fall 2007 Oct 2, 2007
 P a g e 1 First Midterm Exam CS164, Fall 2007 Oct 2, 2007 Please read all instructions (including these) carefully. Write your name, login, and SID. No electronic devices are allowed, including cell phones
P a g e 1 First Midterm Exam CS164, Fall 2007 Oct 2, 2007 Please read all instructions (including these) carefully. Write your name, login, and SID. No electronic devices are allowed, including cell phones
CS164: Midterm I. Fall 2003
 CS164: Midterm I Fall 2003 Please read all instructions (including these) carefully. Write your name, login, and circle the time of your section. Read each question carefully and think about what s being
CS164: Midterm I Fall 2003 Please read all instructions (including these) carefully. Write your name, login, and circle the time of your section. Read each question carefully and think about what s being
SC/MATH Boolean Formulae. Ref: G. Tourlakis, Mathematical Logic, John Wiley & Sons, York University
 SC/MATH 1090 1- Boolean Formulae Ref: G. Tourlakis, Mathematical Logic, John Wiley & Sons, 2008. York University Department of Computer Science and Engineering York University- MATH 1090 01-Boolean 1 Overview
SC/MATH 1090 1- Boolean Formulae Ref: G. Tourlakis, Mathematical Logic, John Wiley & Sons, 2008. York University Department of Computer Science and Engineering York University- MATH 1090 01-Boolean 1 Overview
Syntax Analysis. Martin Sulzmann. Martin Sulzmann Syntax Analysis 1 / 38
 Syntax Analysis Martin Sulzmann Martin Sulzmann Syntax Analysis 1 / 38 Syntax Analysis Objective Recognize individual tokens as sentences of a language (beyond regular languages). Example 1 (OK) Program
Syntax Analysis Martin Sulzmann Martin Sulzmann Syntax Analysis 1 / 38 Syntax Analysis Objective Recognize individual tokens as sentences of a language (beyond regular languages). Example 1 (OK) Program
ML 4 A Lexer for OCaml s Type System
 ML 4 A Lexer for OCaml s Type System CS 421 Fall 2017 Revision 1.0 Assigned October 26, 2017 Due November 2, 2017 Extension November 4, 2017 1 Change Log 1.0 Initial Release. 2 Overview To complete this
ML 4 A Lexer for OCaml s Type System CS 421 Fall 2017 Revision 1.0 Assigned October 26, 2017 Due November 2, 2017 Extension November 4, 2017 1 Change Log 1.0 Initial Release. 2 Overview To complete this
ANSI C Programming Simple Programs
 ANSI C Programming Simple Programs /* This program computes the distance between two points */ #include #include #include main() { /* Declare and initialize variables */ double
ANSI C Programming Simple Programs /* This program computes the distance between two points */ #include #include #include main() { /* Declare and initialize variables */ double
Lexical Analysis. Lexical analysis is the first phase of compilation: The file is converted from ASCII to tokens. It must be fast!
 Lexical Analysis Lexical analysis is the first phase of compilation: The file is converted from ASCII to tokens. It must be fast! Compiler Passes Analysis of input program (front-end) character stream
Lexical Analysis Lexical analysis is the first phase of compilation: The file is converted from ASCII to tokens. It must be fast! Compiler Passes Analysis of input program (front-end) character stream
10/5/17. Lexical and Syntactic Analysis. Lexical and Syntax Analysis. Tokenizing Source. Scanner. Reasons to Separate Lexical and Syntax Analysis
 Lexical and Syntactic Analysis Lexical and Syntax Analysis In Text: Chapter 4 Two steps to discover the syntactic structure of a program Lexical analysis (Scanner): to read the input characters and output
Lexical and Syntactic Analysis Lexical and Syntax Analysis In Text: Chapter 4 Two steps to discover the syntactic structure of a program Lexical analysis (Scanner): to read the input characters and output
Interpreter. Scanner. Parser. Tree Walker. read. request token. send token. send AST I/O. Console
 Scanning 1 read Interpreter Scanner request token Parser send token Console I/O send AST Tree Walker 2 Scanner This process is known as: Scanning, lexing (lexical analysis), and tokenizing This is the
Scanning 1 read Interpreter Scanner request token Parser send token Console I/O send AST Tree Walker 2 Scanner This process is known as: Scanning, lexing (lexical analysis), and tokenizing This is the
Will introduce various operators supported by C language Identify supported operations Present some of terms characterizing operators
 Operators Overview Will introduce various operators supported by C language Identify supported operations Present some of terms characterizing operators Operands and Operators Mathematical or logical relationships
Operators Overview Will introduce various operators supported by C language Identify supported operations Present some of terms characterizing operators Operands and Operators Mathematical or logical relationships
FRAC: Language Reference Manual
 FRAC: Language Reference Manual Justin Chiang jc4127 Kunal Kamath kak2211 Calvin Li ctl2124 Anne Zhang az2350 1. Introduction FRAC is a domain-specific programming language that enables the programmer
FRAC: Language Reference Manual Justin Chiang jc4127 Kunal Kamath kak2211 Calvin Li ctl2124 Anne Zhang az2350 1. Introduction FRAC is a domain-specific programming language that enables the programmer
Solving for the Unknown: Basic Operations & Trigonometry ID1050 Quantitative & Qualitative Reasoning
 Solving for the Unknown: Basic Operations & Trigonometry ID1050 Quantitative & Qualitative Reasoning What is Algebra? An expression is a combination of numbers and operations that leads to a numerical
Solving for the Unknown: Basic Operations & Trigonometry ID1050 Quantitative & Qualitative Reasoning What is Algebra? An expression is a combination of numbers and operations that leads to a numerical
Syntax and Parsing COMS W4115. Prof. Stephen A. Edwards Fall 2003 Columbia University Department of Computer Science
 Syntax and Parsing COMS W4115 Prof. Stephen A. Edwards Fall 2003 Columbia University Department of Computer Science Lexical Analysis (Scanning) Lexical Analysis (Scanning) Goal is to translate a stream
Syntax and Parsing COMS W4115 Prof. Stephen A. Edwards Fall 2003 Columbia University Department of Computer Science Lexical Analysis (Scanning) Lexical Analysis (Scanning) Goal is to translate a stream
Our Strategy for Learning Fortran 90
 Our Strategy for Learning Fortran 90 We want to consider some computational problems which build in complexity. evaluating an integral solving nonlinear equations vector/matrix operations fitting data
Our Strategy for Learning Fortran 90 We want to consider some computational problems which build in complexity. evaluating an integral solving nonlinear equations vector/matrix operations fitting data
Examples of attributes: values of evaluated subtrees, type information, source file coordinates,
 1 2 3 Attributes can be added to the grammar symbols, and program fragments can be added as semantic actions to the grammar, to form a syntax-directed translation scheme. Some attributes may be set by
1 2 3 Attributes can be added to the grammar symbols, and program fragments can be added as semantic actions to the grammar, to form a syntax-directed translation scheme. Some attributes may be set by
Defining Functions. CSc 372. Comparative Programming Languages. 5 : Haskell Function Definitions. Department of Computer Science University of Arizona
 Defining Functions CSc 372 Comparative Programming Languages 5 : Haskell Function Definitions Department of Computer Science University of Arizona collberg@gmail.com When programming in a functional language
Defining Functions CSc 372 Comparative Programming Languages 5 : Haskell Function Definitions Department of Computer Science University of Arizona collberg@gmail.com When programming in a functional language
Chapter 3. Parsing #1
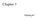 Chapter 3 Parsing #1 Parser source file get next character scanner get token parser AST token A parser recognizes sequences of tokens according to some grammar and generates Abstract Syntax Trees (ASTs)
Chapter 3 Parsing #1 Parser source file get next character scanner get token parser AST token A parser recognizes sequences of tokens according to some grammar and generates Abstract Syntax Trees (ASTs)
Introduction. Problem Solving on Computer. Data Structures (collection of data and relationships) Algorithms
 Introduction Problem Solving on Computer Data Structures (collection of data and relationships) Algorithms 1 Objective of Data Structures Two Goals: 1) Identify and develop useful high-level data types
Introduction Problem Solving on Computer Data Structures (collection of data and relationships) Algorithms 1 Objective of Data Structures Two Goals: 1) Identify and develop useful high-level data types
CS 314 Principles of Programming Languages
 CS 314 Principles of Programming Languages Lecture 5: Syntax Analysis (Parsing) Zheng (Eddy) Zhang Rutgers University January 31, 2018 Class Information Homework 1 is being graded now. The sample solution
CS 314 Principles of Programming Languages Lecture 5: Syntax Analysis (Parsing) Zheng (Eddy) Zhang Rutgers University January 31, 2018 Class Information Homework 1 is being graded now. The sample solution
Tail Calls. CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages. Tail Recursion. Tail Recursion (cont d) Names and Binding. Tail Recursion (cont d)
 CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages Tail Calls A tail call is a function call that is the last thing a function does before it returns let add x y = x + y let f z = add z z (* tail call *)
CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages Tail Calls A tail call is a function call that is the last thing a function does before it returns let add x y = x + y let f z = add z z (* tail call *)
Stacks, Queues and Hierarchical Collections. 2501ICT Logan
 Stacks, Queues and Hierarchical Collections 2501ICT Logan Contents Linked Data Structures Revisited Stacks Queues Trees Binary Trees Generic Trees Implementations 2 Queues and Stacks Queues and Stacks
Stacks, Queues and Hierarchical Collections 2501ICT Logan Contents Linked Data Structures Revisited Stacks Queues Trees Binary Trees Generic Trees Implementations 2 Queues and Stacks Queues and Stacks
BSCS Fall Mid Term Examination December 2012
 PUNJAB UNIVERSITY COLLEGE OF INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY University of the Punjab Sheet No.: Invigilator Sign: BSCS Fall 2009 Date: 14-12-2012 Mid Term Examination December 2012 Student ID: Section: Morning
PUNJAB UNIVERSITY COLLEGE OF INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY University of the Punjab Sheet No.: Invigilator Sign: BSCS Fall 2009 Date: 14-12-2012 Mid Term Examination December 2012 Student ID: Section: Morning
ITEC2620 Introduction to Data Structures
 ITEC2620 Introduction to Data Structures Lecture 9b Grammars I Overview How can a computer do Natural Language Processing? Grammar checking? Artificial Intelligence Represent knowledge so that brute force
ITEC2620 Introduction to Data Structures Lecture 9b Grammars I Overview How can a computer do Natural Language Processing? Grammar checking? Artificial Intelligence Represent knowledge so that brute force
Lexical and Syntax Analysis
 Lexical and Syntax Analysis In Text: Chapter 4 N. Meng, F. Poursardar Lexical and Syntactic Analysis Two steps to discover the syntactic structure of a program Lexical analysis (Scanner): to read the input
Lexical and Syntax Analysis In Text: Chapter 4 N. Meng, F. Poursardar Lexical and Syntactic Analysis Two steps to discover the syntactic structure of a program Lexical analysis (Scanner): to read the input
CS412/413. Introduction to Compilers Tim Teitelbaum. Lecture 2: Lexical Analysis 23 Jan 08
 CS412/413 Introduction to Compilers Tim Teitelbaum Lecture 2: Lexical Analysis 23 Jan 08 Outline Review compiler structure What is lexical analysis? Writing a lexer Specifying tokens: regular expressions
CS412/413 Introduction to Compilers Tim Teitelbaum Lecture 2: Lexical Analysis 23 Jan 08 Outline Review compiler structure What is lexical analysis? Writing a lexer Specifying tokens: regular expressions
ECON 502 INTRODUCTION TO MATLAB Nov 9, 2007 TA: Murat Koyuncu
 ECON 502 INTRODUCTION TO MATLAB Nov 9, 2007 TA: Murat Koyuncu 0. What is MATLAB? 1 MATLAB stands for matrix laboratory and is one of the most popular software for numerical computation. MATLAB s basic
ECON 502 INTRODUCTION TO MATLAB Nov 9, 2007 TA: Murat Koyuncu 0. What is MATLAB? 1 MATLAB stands for matrix laboratory and is one of the most popular software for numerical computation. MATLAB s basic
Compiler Construction
 Compiler Construction Lecture 2: Lexical Analysis I (Introduction) Thomas Noll Lehrstuhl für Informatik 2 (Software Modeling and Verification) noll@cs.rwth-aachen.de http://moves.rwth-aachen.de/teaching/ss-14/cc14/
Compiler Construction Lecture 2: Lexical Analysis I (Introduction) Thomas Noll Lehrstuhl für Informatik 2 (Software Modeling and Verification) noll@cs.rwth-aachen.de http://moves.rwth-aachen.de/teaching/ss-14/cc14/
UNIT -2 LEXICAL ANALYSIS
 OVER VIEW OF LEXICAL ANALYSIS UNIT -2 LEXICAL ANALYSIS o To identify the tokens we need some method of describing the possible tokens that can appear in the input stream. For this purpose we introduce
OVER VIEW OF LEXICAL ANALYSIS UNIT -2 LEXICAL ANALYSIS o To identify the tokens we need some method of describing the possible tokens that can appear in the input stream. For this purpose we introduce
Non-deterministic Finite Automata (NFA)
 Non-deterministic Finite Automata (NFA) CAN have transitions on the same input to different states Can include a ε or λ transition (i.e. move to new state without reading input) Often easier to design
Non-deterministic Finite Automata (NFA) CAN have transitions on the same input to different states Can include a ε or λ transition (i.e. move to new state without reading input) Often easier to design
CSE 401 Midterm Exam Sample Solution 11/4/11
 Question 1. (12 points, 2 each) The front end of a compiler consists of three parts: scanner, parser, and (static) semantics. Collectively these need to analyze the input program and decide if it is correctly
Question 1. (12 points, 2 each) The front end of a compiler consists of three parts: scanner, parser, and (static) semantics. Collectively these need to analyze the input program and decide if it is correctly
Parser Tools: lex and yacc-style Parsing
 Parser Tools: lex and yacc-style Parsing Version 6.11.0.6 Scott Owens January 6, 2018 This documentation assumes familiarity with lex and yacc style lexer and parser generators. 1 Contents 1 Lexers 3 1.1
Parser Tools: lex and yacc-style Parsing Version 6.11.0.6 Scott Owens January 6, 2018 This documentation assumes familiarity with lex and yacc style lexer and parser generators. 1 Contents 1 Lexers 3 1.1
CS 4240: Compilers and Interpreters Project Phase 1: Scanner and Parser Due Date: October 4 th 2015 (11:59 pm) (via T-square)
 CS 4240: Compilers and Interpreters Project Phase 1: Scanner and Parser Due Date: October 4 th 2015 (11:59 pm) (via T-square) Introduction This semester, through a project split into 3 phases, we are going
CS 4240: Compilers and Interpreters Project Phase 1: Scanner and Parser Due Date: October 4 th 2015 (11:59 pm) (via T-square) Introduction This semester, through a project split into 3 phases, we are going
1. [5 points each] True or False. If the question is currently open, write O or Open.
![1. [5 points each] True or False. If the question is currently open, write O or Open. 1. [5 points each] True or False. If the question is currently open, write O or Open.](/thumbs/89/98345819.jpg) University of Nevada, Las Vegas Computer Science 456/656 Spring 2018 Practice for the Final on May 9, 2018 The entire examination is 775 points. The real final will be much shorter. Name: No books, notes,
University of Nevada, Las Vegas Computer Science 456/656 Spring 2018 Practice for the Final on May 9, 2018 The entire examination is 775 points. The real final will be much shorter. Name: No books, notes,
