CS 312 Exam 1 Fall KG Kris Megan Roman Sonika
|
|
|
- Kristina McDaniel
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CS 312 Exam 1 Fall 2015 Name: SOLUTION SOLUTION SOLUTION UTEID: SOLUTION SOLUTION SOLUTION _ Circle your TA's Name: Aila CK Jialin Katherine B KG Kris Megan Roman Sonika Problem Number Topic Points Possible 1 Expressions 18 2 Code Tracing 16 3 Method Trace 14 4 Programming 10 5 Programming 10 6 Programming 15 7 Graphics 15 TOTAL POINTS OFF: SCORE OUT OF 98: Points Off Instructions: 1. Please turn off your cell phones 2. There are 7 questions on this test. 3. You have 2 hours to complete the test. 4. Place your answers on this test, not scratch paper. 5. You may not use a calculator. 6. When code is required, write Java code. You may use only features that we discussed up to topics 1-12, including those covered in the textbook for that material (Chapters 1-4). 7. Style is not evaluated when grading. 8. The proctors will not answer questions. If you believe a question has an error or is ambiguous, state your assumption and answer based on your assumption. 9. If you finish early bring your exam and scratch paper to the proctor and show them your UTID. CS 312 Exam 1 Fall
2 1. Expressions - 1 point each, 18 points total. For each Java expression in the left hand column, indicate the result of the expression in the right hand column. You must show a value of the appropriate type. For example, 7.0 rather than 7 for a double and "7" instead of 7 for a String. Answers that do not indicate the data type correctly are wrong. A. 3 * * 5-13 B * 6 / (4 + 2) * 5 17 C. 20 / / / 2 6 D. 1.0 / / / E. 2.5 * / F. 375 % 100 / 7 * 2 20 G. 4 * 6 % % 4 24 H. "UT" + "horns" + 3 "UThorns3" I "C!" "5C!115" J. 2 + "RE" + 2 * 10 "2RE20" K. (double) (25 / 10 * 3) 6.0 L. (int) (25 / 10.0 * ) 7 M. (int) (-7.0 / 2 * 3.1) -10 The Math methods ceil, floor, pow, and abs all return doubles. N. Math.pow(2.0, 3.0) 8.0 O. Math.max(20 / 10, 10 % 20) // returns an int 10 P. Math.floor(3.99 * 4) 15.0 Q. Math.ceil(-3.011) -3.0 R. Math.abs( Math.ceil(-3.5) * Math.floor(6.8 / 2 * 3)) 30.0 CS 312 Exam 1 Fall
3 2. Code tracing - 2 points each, 14 points total. Place you answer in the box to the right of the code. If the code results in a syntax or runtime error, state the kind of error that occurs. A. What is output by the following code when it is run? int xa = 5; 13 5 int ya = xa; xa = xa ya; System.out.print(xa + " " + ya); B. What is output by the following code when it is run? int xb = 2; int yb = 5; int zb = xb * yb + 1; yb -= zb; xb++; System.out.print(xb + " " + yb + " " + zb); C. What is output by the following code when it is run? int xc = 4; int yc = 3; yc *= 2 + xc; xc -= xc * 2; System.out.print(xc + " " + yc); D. What is output by the following code when it is run? double ad = 1.5; int xd = 4; int yd = 5; double bd = yd / xd + ad - 3; System.out.print(ad + " " + bd); E. What is output by the following code when it is run? int xe = -4; 6 30 int ye = 5; for(int i = 0; i <= 4; i++) { xe += 2; ye = 5 * xe; System.out.print(xe + " " + ye); CS 312 Exam 1 Fall
4 F. How many asterisks does the following code print out? Don't show the output. Simply state the number of asterisks that are printed out when the code runs. for(int i = 10; i <= 35; i++) { 26 System.out.print("*"); G. How many asterisks does the following code print out? Don't show the output. Simply state the number of asterisks that are printed out when the code runs. 400 for(int ig = 0; ig < 8; ig++) { for(int jg = 0; jg < 5; jg++) { for(int kg = 0; kg < 10; kg++) { System.out.print("*"); H. How many asterisks does the following code print out? Don't show the output. Simply state the number of asterisks that are printed out when the code runs. for(int ih = 2; ih < 6; ih++) { for(int jh = 0; jh < ih; jh++) { System.out.print("*"); 62 System.out.print("*"); for(int jh = 10; jh >= 0 ; jh--) { System.out.print("*"); CS 312 Exam 1 Fall
5 3. Method Tracing and Parameters Simulation. 2 points each, 14 points total. For each part write what the output to the screen will be when the code is run. Consider the following methods that are all part of the same program: public static void a(int x, int y) { x = x * 3; x--; y = y - 3; System.out.print(x + " " + y + " "); public static int b(int x, int y) { x++; y *= 3; return x + y; public static void c(int x) { if (x < 5) { x *= 3; else { x = x / 3; if(x % 2 == 1) { x += 2; System.out.print(x); public static int d(int i) { i++; i++; i = b(i + 1, i - 2); System.out.print(i); return i; A. Given the methods above, what is output by the following code? int xa = 3; int ya = 2; 8-1 a(xa, ya); B. Given the methods above, what is output by the following code? int xb = 4; int yb = -2; a(xb, yb); System.out.print(xb + " " + yb); CS 312 Exam 1 Fall
6 C. Given the methods above, what is output by the following code? int xc = -3; int yc = 4; yc = b(xc, yc); System.out.print(xc + " " + yc); D. Given the methods on the previous page, what is output by the following code? int xd = 45; 17 c(xd); E. Given the methods on the previous page, what is output by the following code? int xe = -3; 3 int ye = 7; c(ye + xe + 1); F. Given the methods on the previous page, what is output by the following code? int xf = 4; 20 d(xf); G. Given the methods on the previous page, what is output by the following code? int xg = 3; 16x is 16! System.out.print("x is " + d(xg) + "!"); CS 312 Exam 1 Fall
7 4. Programming - Write a Java method name printfigure that prints out a figure based on a single integer parameter, size. When the parameter size is 1 the output is: * When the parameter size is 2 the output is:...*..**.*** **** When the parameter size is 3 the output is:...*...**...***...****...*****...******..*******.******** ********* When the parameter size is 4 the output is:...*...**...***...****...*****...******...*******...********...*********...**********...***********...************...*************..**************.*************** **************** Complete your printfigure method on the next page, including the method header. You cannot use any String variables or String methods on this question. Of course you can use String literals such as "." and "*". CS 312 Exam 1 Fall
8 public static void printfigure(int size) { final int NUM_LINES = size * size; for(int line = 1; line <= NUM_LINES; line++) { final int DOTS = NUM_LINES - line; for(int i = 0; i < DOTS; i++) { System.out.print("."); for(int i = 0; i < line; i++) { System.out.print("*"); System.out.println(); Criteria: header, 1 point number of lines correct, 1 point outer loop correct: 2 points prints correct number of dots: 3 points prints correct number of stars: 2 points println: 1 point CS 312 Exam 1 Fall
9 5. Programming - Write a static method named printmultiples that accepts an integer value and an integer num as parameters. The method prints a complete line of output reporting the first num multiples of values. Consider the following examples: printmultiples(8, 2); prints: The first 2 multiples of 8 are 8, 16 printmultiples(4, 6); prints: The first 6 multiples of 4 are 4, 8, 12, 16, 20, 24 Assume the parameter num is >= 2. value can be any integer value. public static void printmultiples(int value, int num) { System.out.print("The first " + num + " multiples of " + value + " are "); for(int i = 1; i < num; i++) { System.out.print(value * i + ", "); System.out.println(value * num); // or print header with parameters: 1 point print first part, "The first... ": 1 point for loop: 3 points print out multiples in correct order: 3 points multiples of value calculated correctly: 1 point no comma after last value handled correctly: 1 point return statement in loop: -4 CS 312 Exam 1 Fall
10 6. Programming - Write a method, timesallsame that accepts a single parameter, an integer that specifies the number of times to flip a set of 3 coins. The method returns the number of times the 3 coins were flipped and were all the same, either all heads or all tails. Assume the integer parameter is greater than or equal to 0. To simulate flipping a coin, use the Math.random() method: public static double random() Returns a double value with a, greater than or equal to 0.0 and less than 1.0. Returned values are chosen with (approximately) uniform distribution from that range. Assume values < 0.5 are heads, and values >= 0.5 are tails. Complete the timesallsame below including the method header. int total = 0; for(int i = 0; i < numflips; i++) { double c1 = Math.random(); double c2 = Math.random(); double c3 = Math.random(); if(c1 < 0.5 && c2 < 0.5 && c3 < 0.5) { total++; else if(c1 >= 0.5 && c2 >= 0.5 && c3 >= 0.5) { total++; return total; header: 1 point total variable: 1 point loop correct: 3 points call Math.random correctly 3 times: 3 points correctly determine if all flips the same for a given set: 5 points increment total correctly if appropriate: 1 point return correct value: 1 point CS 312 Exam 1 Fall
11 7. Graphics Programming. Complete a method to produce the following output of concentric circles. The parameters for the method are The Graphics object for the DrawingPanel. Color has already been set to BLACK The width and height of the drawing panel given as integers. The drawing panel has already been created. The number of circles to draw. Here is the output of the method call drawcircles(g, 700, 400, 3); Here is the output of the method call drawcircles(g, 400, 600, 8); Complete the method on the next page. CS 312 Exam 1 Fall
12 public static void drawcircles(graphics g, int width, int height, int numovals) { int x = 0; int y = 0; int ovalwidth = width; int ovalheight = height; int widthfraction = width / (numovals * 2); int heightfraction = height / (numovals * 2); for(int i = 0; i < numovals; i++) { g.drawoval(x, y, ovalwidth, ovalheight); x += widthfraction; y += heightfraction; ovalwidth -= widthfraction * 2; ovalheight -= heightfraction * 2; loop correct, correct number of ovals: 3 points draw first oval correctly: 2 points calculate x and y coordinates of each oval correctly: 4 points calculate width and height of each oval correctly: 4 points calls to draw oval correct, with correct parameters: 2 points CS 312 Exam 1 Fall
13 CS 312 Exam 1 Fall
CS 312 Midterm 1 Spring 2013
 CS 312 Midterm 1 Spring 2013 Your Name Your UTEID Circle your TAs Name: VICKY LUIS Problem Number Topic Points Possible 1 Expressions 11 2 Loop Evaluation 6 3 Method Tracing 10 4 Method Tracing 3 5 Writing
CS 312 Midterm 1 Spring 2013 Your Name Your UTEID Circle your TAs Name: VICKY LUIS Problem Number Topic Points Possible 1 Expressions 11 2 Loop Evaluation 6 3 Method Tracing 10 4 Method Tracing 3 5 Writing
CS 312 Exam 2 Fall KG Kris Megan Roman Sonika
 CS 312 Exam 2 Fall 2015 Your Name Your UTEID Circle your TA's Name: Aila CK Jialin Katherine B KG Kris Megan Roman Sonika Problem Number Topic Points Possible 1 code trace 32 2 scanners 15 3 program logic
CS 312 Exam 2 Fall 2015 Your Name Your UTEID Circle your TA's Name: Aila CK Jialin Katherine B KG Kris Megan Roman Sonika Problem Number Topic Points Possible 1 code trace 32 2 scanners 15 3 program logic
CS 312 Midterm 1 Spring 2013
 CS 312 Midterm 1 Spring 2013 Your Name KEY AND CRITERIA Problem Number Topic Points Possible 1 Expressions 11 2 Loop Evaluation 6 3 Method Tracing 10 4 Method Tracing 3 5 Writing Methods 5 6 Tracing Graphics
CS 312 Midterm 1 Spring 2013 Your Name KEY AND CRITERIA Problem Number Topic Points Possible 1 Expressions 11 2 Loop Evaluation 6 3 Method Tracing 10 4 Method Tracing 3 5 Writing Methods 5 6 Tracing Graphics
CS 312 Midterm 2 Fall 2013
 CS 312 Midterm 2 Fall 2013 Your Name Your UTEID Circle your TAs Name: EDAENA LEIF MUBASHIR Problem Number Topic Points Possible 1 code trace 28 2 arrays 14 3 strings 16 4 program logic 16 5 scanner 23
CS 312 Midterm 2 Fall 2013 Your Name Your UTEID Circle your TAs Name: EDAENA LEIF MUBASHIR Problem Number Topic Points Possible 1 code trace 28 2 arrays 14 3 strings 16 4 program logic 16 5 scanner 23
CS 305j Midterm 1 Fall 2007
 Points off 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Total off Net Score CS 305j Midterm 1 Fall 2007 Your Name Your UTEID Circle you TA's name: Priyanka Jacob Instructions: 1. Please turn off your cell phones 2. There are 7 questions
Points off 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Total off Net Score CS 305j Midterm 1 Fall 2007 Your Name Your UTEID Circle you TA's name: Priyanka Jacob Instructions: 1. Please turn off your cell phones 2. There are 7 questions
CS 305j Midterm 1 Fall 2008
 Points off 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Total off Net Score CS 305j Midterm 1 Fall 2008 Your Name Your UTEID Circle you TA's name: Ann Alex Instructions: 1. Please turn off your cell phones 2. There are 7 questions on
Points off 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Total off Net Score CS 305j Midterm 1 Fall 2008 Your Name Your UTEID Circle you TA's name: Ann Alex Instructions: 1. Please turn off your cell phones 2. There are 7 questions on
CS 305j Midterm 1 Fall 2006
 Points off 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Total off Net Score CS 305j Midterm 1 Fall 2006 Your Name Your UTEID Circle you TA's name: Brad Jacob Instructions: 1. Please turn off your cell phones 2. There are 7 questions
Points off 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Total off Net Score CS 305j Midterm 1 Fall 2006 Your Name Your UTEID Circle you TA's name: Brad Jacob Instructions: 1. Please turn off your cell phones 2. There are 7 questions
CS 312 Exam 2 Fall Circle your TA's Name: Aish Anthony Bri Carla Chris
 CS 312 Exam 2 Fall 2017 Your Name Your UTEID Circle your TA's Name: Aish Anthony Bri Carla Chris CK Dayanny Fatima Hailey Omer Problem Number Topic Points Possible 1 code trace 28 2 program logic 8 3 strings
CS 312 Exam 2 Fall 2017 Your Name Your UTEID Circle your TA's Name: Aish Anthony Bri Carla Chris CK Dayanny Fatima Hailey Omer Problem Number Topic Points Possible 1 code trace 28 2 program logic 8 3 strings
CS 314 Exam 2 Fall 2017
 Points off 1 2 3 4 5 Total off CS 314 Exam 2 Fall 2017 Your Name Your UTEID Circle your TAs Name: Gilbert Jacob Jorge Joseph Lucas Rebecca Shelby Instructions: 1. There are 5 questions on this test. 100
Points off 1 2 3 4 5 Total off CS 314 Exam 2 Fall 2017 Your Name Your UTEID Circle your TAs Name: Gilbert Jacob Jorge Joseph Lucas Rebecca Shelby Instructions: 1. There are 5 questions on this test. 100
CS 312 Final Fall 2015
 CS 312 Final Fall 2015 Your Name: SOLUTION SOLUTION SOLUTION SOLUTION Your UTEID Problem Number Topic Points Possible 1 expressions 10 2 program logic 15 3 code tracing 15 4 Strings 15 5 arrays 1 15 6
CS 312 Final Fall 2015 Your Name: SOLUTION SOLUTION SOLUTION SOLUTION Your UTEID Problem Number Topic Points Possible 1 expressions 10 2 program logic 15 3 code tracing 15 4 Strings 15 5 arrays 1 15 6
Points off Total off Net Score. CS 314 Final Exam Fall 2016
 Points off 1 2 3 4 5 6 Total off Net Score CS 314 Final Exam Fall 2016 Your Name Your UTEID Instructions: 1. There are 6 questions on this test. 100 points available. Scores will be scaled to 300 points.
Points off 1 2 3 4 5 6 Total off Net Score CS 314 Final Exam Fall 2016 Your Name Your UTEID Instructions: 1. There are 6 questions on this test. 100 points available. Scores will be scaled to 300 points.
Lecture 6: While Loops and the Math Class
 Lecture 6: While Loops and the Math Class Building Java Programs: A Back to Basic Approach by Stuart Reges and Marty Stepp Copyright (c) Pearson 2013. All rights reserved. while loops 2 Categories of loops
Lecture 6: While Loops and the Math Class Building Java Programs: A Back to Basic Approach by Stuart Reges and Marty Stepp Copyright (c) Pearson 2013. All rights reserved. while loops 2 Categories of loops
CS 312 Final Fall 2013
 CS 312 Final Fall 2013 Your Name Your UTEID Problem Number Topic Points Possible 1 short answer 1 12 2 program logic 16 3 short answer 2 14 4 return methods 10 5 arrays 1 20 6 critters 20 7 arrays 2 20
CS 312 Final Fall 2013 Your Name Your UTEID Problem Number Topic Points Possible 1 short answer 1 12 2 program logic 16 3 short answer 2 14 4 return methods 10 5 arrays 1 20 6 critters 20 7 arrays 2 20
CS 307 Midterm 2 Spring 2008
 Points off 1 2 3 4 Total off Net Score Exam Number: CS 307 Midterm 2 Spring 2008 Name UTEID login name TA's Name: Mario Ruchica Vishvas (Circle One) Instructions: 1. Please turn off your cell phones and
Points off 1 2 3 4 Total off Net Score Exam Number: CS 307 Midterm 2 Spring 2008 Name UTEID login name TA's Name: Mario Ruchica Vishvas (Circle One) Instructions: 1. Please turn off your cell phones and
CS 314 Exam 2 Spring
 Points off 1 2 3 4 5 Total off CS 314 Exam 2 Spring 2017 Your Name Your UTEID Instructions: 1. There are 5 questions on this test. 100 points available. Scores will be scaled to 200 points. 2. You have
Points off 1 2 3 4 5 Total off CS 314 Exam 2 Spring 2017 Your Name Your UTEID Instructions: 1. There are 5 questions on this test. 100 points available. Scores will be scaled to 200 points. 2. You have
CS 305j Midterm 2 Fall 2006
 Exam Number: Points off 1 2 3 4 5 6 Total off Net Score CS 305j Midterm 2 Fall 2006 Your Name Your UTEID Circle you TA's name: Brad Jacob Instructions: 1. Please turn off your cell phones 2. There are
Exam Number: Points off 1 2 3 4 5 6 Total off Net Score CS 305j Midterm 2 Fall 2006 Your Name Your UTEID Circle you TA's name: Brad Jacob Instructions: 1. Please turn off your cell phones 2. There are
Practice Midterm 1 Answer Key
 CS 120 Software Design I Fall 2018 Practice Midterm 1 Answer Key University of Wisconsin - La Crosse Due Date: October 5 NAME: Do not turn the page until instructed to do so. This booklet contains 10 pages
CS 120 Software Design I Fall 2018 Practice Midterm 1 Answer Key University of Wisconsin - La Crosse Due Date: October 5 NAME: Do not turn the page until instructed to do so. This booklet contains 10 pages
CS 307 Midterm 1 Fall 2007
 Points off 1 2 3 4 Total off Net Score CS 307 Midterm 1 Fall 2007 Your Name Your UTEID Circle yours TA s name: David Joseph Ola Instructions: 1. Please turn off your cell phones 2. There are 4 questions
Points off 1 2 3 4 Total off Net Score CS 307 Midterm 1 Fall 2007 Your Name Your UTEID Circle yours TA s name: David Joseph Ola Instructions: 1. Please turn off your cell phones 2. There are 4 questions
CS 307 Midterm 2 Spring 2011
 Points off 1 2 3 4 5 Total off Net Score Exam Number: CS 307 Midterm 2 Spring 2011 Name UTEID login name TA's Name: Dan Muhibur Oliver (Circle One) Instructions: 1. Please turn off your cell phones and
Points off 1 2 3 4 5 Total off Net Score Exam Number: CS 307 Midterm 2 Spring 2011 Name UTEID login name TA's Name: Dan Muhibur Oliver (Circle One) Instructions: 1. Please turn off your cell phones and
Points off Total off Net Score. CS 314 Final Exam Spring 2016
 Points off 1 2 3 4 5 6 Total off Net Score CS 314 Final Exam Spring 2016 Your Name Your UTEID Instructions: 1. There are 6 questions on this test. 100 points available. Scores will be scaled to 300 points.
Points off 1 2 3 4 5 6 Total off Net Score CS 314 Final Exam Spring 2016 Your Name Your UTEID Instructions: 1. There are 6 questions on this test. 100 points available. Scores will be scaled to 300 points.
CS111: PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE II
 CS111: PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE II Computer Science Department Lecture 1(c): Java Basics (II) Lecture Contents Java basics (part II) Conditions Loops Methods Conditions & Branching Conditional Statements A
CS111: PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE II Computer Science Department Lecture 1(c): Java Basics (II) Lecture Contents Java basics (part II) Conditions Loops Methods Conditions & Branching Conditional Statements A
CS 312 Midterm 2 Fall Jose Stas Aaron
 CS 312 Midterm 2 Fall 2014 SOLUTION SOLUTION SOLUTION Circle your TA's Name: Dory Tamara Eric Jose Stas Aaron Problem Number Topic Points Possible 1 code trace 30 2 scanners 15 3 program logic 16 4 strings
CS 312 Midterm 2 Fall 2014 SOLUTION SOLUTION SOLUTION Circle your TA's Name: Dory Tamara Eric Jose Stas Aaron Problem Number Topic Points Possible 1 code trace 30 2 scanners 15 3 program logic 16 4 strings
AP CS Unit 3: Control Structures Notes
 AP CS Unit 3: Control Structures Notes The if and if-else Statements. These statements are called control statements because they control whether a particular block of code is executed or not. Some texts
AP CS Unit 3: Control Structures Notes The if and if-else Statements. These statements are called control statements because they control whether a particular block of code is executed or not. Some texts
CS110: PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE I
 CS110: PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE I Computer Science Department Lecture 8: Methods Lecture Contents: 2 Introduction Program modules in java Defining Methods Calling Methods Scope of local variables Passing Parameters
CS110: PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE I Computer Science Department Lecture 8: Methods Lecture Contents: 2 Introduction Program modules in java Defining Methods Calling Methods Scope of local variables Passing Parameters
CS 307 Midterm 2 Fall 2008
 Points off 1 2 3 4 5 Total off Net Score Exam Number: CS 307 Midterm 2 Fall 2008 Name UTEID login name TA's Name: Mikie Ron Sarah (Circle One) Instructions: 1. Please turn off your cell phones and other
Points off 1 2 3 4 5 Total off Net Score Exam Number: CS 307 Midterm 2 Fall 2008 Name UTEID login name TA's Name: Mikie Ron Sarah (Circle One) Instructions: 1. Please turn off your cell phones and other
CS 312 Midterm 2 Fall 2013
 CS 312 Midterm 2 Fall 2013 SOLUTION SOLUTION SOLUTION SOLUTION SOLUTION Problem Number Topic Points Possible 1 code trace 28 2 arrays 14 3 strings 16 4 program logic 16 5 scanner 23 6 arrays and strings
CS 312 Midterm 2 Fall 2013 SOLUTION SOLUTION SOLUTION SOLUTION SOLUTION Problem Number Topic Points Possible 1 code trace 28 2 arrays 14 3 strings 16 4 program logic 16 5 scanner 23 6 arrays and strings
The Math Class. Using various math class methods. Formatting the values.
 The Math Class Using various math class methods. Formatting the values. The Math class is used for mathematical operations; in our case some of its functions will be used. In order to use the Math class,
The Math Class Using various math class methods. Formatting the values. The Math class is used for mathematical operations; in our case some of its functions will be used. In order to use the Math class,
CS 312 Final Fall 2016
 CS 312 Final Fall 2016 Your Name Your UTEID Problem Number Topic Points Possible 1 expressions 10 2 program logic 20 3 code tracing 15 4 critters 15 5 arrays 15 6 strings 15 7 2d arrays 15 8 ArrayList
CS 312 Final Fall 2016 Your Name Your UTEID Problem Number Topic Points Possible 1 expressions 10 2 program logic 20 3 code tracing 15 4 critters 15 5 arrays 15 6 strings 15 7 2d arrays 15 8 ArrayList
Chapter 6 Methods. Dr. Hikmat Jaber
 Chapter 6 Methods Dr. Hikmat Jaber 1 Opening Problem Find the sum of integers from 1 to 10, from 20 to 30, and from 35 to 45, respectively. 2 Problem int sum = 0; for (int i = 1; i
Chapter 6 Methods Dr. Hikmat Jaber 1 Opening Problem Find the sum of integers from 1 to 10, from 20 to 30, and from 35 to 45, respectively. 2 Problem int sum = 0; for (int i = 1; i
CS 314 Final Spring 2013 SOLUTION - SOLUTION - SOLUTION - SOLUTION - SOLUTION - SOLUTION - SOLUTION
 Points off 1 2 3 4 5 6 Total off Net Score CS 314 Final Spring 2013 SOLUTION - SOLUTION - SOLUTION - SOLUTION - SOLUTION - SOLUTION - SOLUTION Your UTEID Instructions: 1. There are 6 questions on this
Points off 1 2 3 4 5 6 Total off Net Score CS 314 Final Spring 2013 SOLUTION - SOLUTION - SOLUTION - SOLUTION - SOLUTION - SOLUTION - SOLUTION Your UTEID Instructions: 1. There are 6 questions on this
Building Java Programs
 Building Java Programs Chapter 3 Lecture 3-2: Return values, Math, and double reading: 3.2, 2.1-2.2 Copyright 2011 by Pearson Education 2 Method name Math.abs(value) Math.ceil(value) Math.floor(value)
Building Java Programs Chapter 3 Lecture 3-2: Return values, Math, and double reading: 3.2, 2.1-2.2 Copyright 2011 by Pearson Education 2 Method name Math.abs(value) Math.ceil(value) Math.floor(value)
Building Java Programs
 Building Java Programs Chapter 3 Return values, Math, and double reading: 3.2, 2.1-2.2 Copyright 2011 by Pearson Education 2 Java's Math class Method name Math.abs(value) Math.ceil(value) Math.floor(value)
Building Java Programs Chapter 3 Return values, Math, and double reading: 3.2, 2.1-2.2 Copyright 2011 by Pearson Education 2 Java's Math class Method name Math.abs(value) Math.ceil(value) Math.floor(value)
Chapter 5 Methods. Liang, Introduction to Java Programming, Eighth Edition, (c) 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 5 Methods 1 Opening Problem Find the sum of integers from 1 to 10, from 20 to 30, and from 35 to 45, respectively. 2 Problem int sum = 0; for (int i = 1; i
Chapter 5 Methods 1 Opening Problem Find the sum of integers from 1 to 10, from 20 to 30, and from 35 to 45, respectively. 2 Problem int sum = 0; for (int i = 1; i
C212 Early Evaluation Exam Mon Feb Name: Please provide brief (common sense) justifications with your answers below.
 C212 Early Evaluation Exam Mon Feb 10 2014 Name: Please provide brief (common sense) justifications with your answers below. 1. What is the type (and value) of this expression: 5 * (7 + 4 / 2) 2. What
C212 Early Evaluation Exam Mon Feb 10 2014 Name: Please provide brief (common sense) justifications with your answers below. 1. What is the type (and value) of this expression: 5 * (7 + 4 / 2) 2. What
1 Short Answer (10 Points Each)
 1 Short Answer (10 Points Each) 1. Write a for loop that will calculate a factorial. Assume that the value n has been input by the user and have the loop create n! and store it in the variable fact. Recall
1 Short Answer (10 Points Each) 1. Write a for loop that will calculate a factorial. Assume that the value n has been input by the user and have the loop create n! and store it in the variable fact. Recall
CS 307 Midterm 2 Fall 2010
 Points off 1 2 3 4 Total off Net Score Exam Number: CS 307 Midterm 2 Fall 2010 Name UTEID login name TA's Name: Harsh Yi-Chao (Circle One) Instructions: 1. Please turn off your cell phones and other electronic
Points off 1 2 3 4 Total off Net Score Exam Number: CS 307 Midterm 2 Fall 2010 Name UTEID login name TA's Name: Harsh Yi-Chao (Circle One) Instructions: 1. Please turn off your cell phones and other electronic
Points off A 4B 5 Total off Net Score. CS 314 Final Exam Spring 2015
 Points off 1 2 3 4A 4B 5 Total off Net Score CS 314 Final Exam Spring 2015 Your Name Your UTEID Instructions: 1. There are 5 questions on this test. 100 points available. 2. You have 3 hours to complete
Points off 1 2 3 4A 4B 5 Total off Net Score CS 314 Final Exam Spring 2015 Your Name Your UTEID Instructions: 1. There are 5 questions on this test. 100 points available. 2. You have 3 hours to complete
Java provides a rich set of operators to manipulate variables. We can divide all the Java operators into the following groups:
 JAVA OPERATORS GENERAL Java provides a rich set of operators to manipulate variables. We can divide all the Java operators into the following groups: Arithmetic Operators Relational Operators Bitwise Operators
JAVA OPERATORS GENERAL Java provides a rich set of operators to manipulate variables. We can divide all the Java operators into the following groups: Arithmetic Operators Relational Operators Bitwise Operators
CS 314 Exam 2 Spring 2018
 Points off 1 2 3 4 5 Total off CS 314 Exam 2 Spring 2018 Your Name Your UTEID Circle your TA's Name: Aish Anthony Chris Dayanny Hailey Ivan Jacob Joseph Lucas Shelby Instructions: 1. There are 5 questions
Points off 1 2 3 4 5 Total off CS 314 Exam 2 Spring 2018 Your Name Your UTEID Circle your TA's Name: Aish Anthony Chris Dayanny Hailey Ivan Jacob Joseph Lucas Shelby Instructions: 1. There are 5 questions
Definite Loops. Computer Science S-111 Harvard University David G. Sullivan, Ph.D. Using a Variable for Counting
 Unit 2, Part 2 Definite Loops Computer Science S-111 Harvard University David G. Sullivan, Ph.D. Using a Variable for Counting Let's say that we're using a variable i to count the number of times that
Unit 2, Part 2 Definite Loops Computer Science S-111 Harvard University David G. Sullivan, Ph.D. Using a Variable for Counting Let's say that we're using a variable i to count the number of times that
Practice Midterm 1. Problem Points Score TOTAL 50
 CS 120 Software Design I Spring 2019 Practice Midterm 1 University of Wisconsin - La Crosse February 25 NAME: Do not turn the page until instructed to do so. This booklet contains 10 pages including the
CS 120 Software Design I Spring 2019 Practice Midterm 1 University of Wisconsin - La Crosse February 25 NAME: Do not turn the page until instructed to do so. This booklet contains 10 pages including the
Points off Total off Net Score. CS 314 Final Exam Spring 2017
 Points off 1 2 3 4 5 6 Total off Net Score CS 314 Final Exam Spring 2017 Your Name Your UTEID Instructions: 1. There are 6 questions on this test. 100 points available. Scores will be scaled to 300 points.
Points off 1 2 3 4 5 6 Total off Net Score CS 314 Final Exam Spring 2017 Your Name Your UTEID Instructions: 1. There are 6 questions on this test. 100 points available. Scores will be scaled to 300 points.
CS 314 Exam 1 Fall 2017
 Points off 1 2 3 4 5A 5B Total off Net Score CS 314 Exam 1 Fall 2017 Your Name Your UTEID Circle your TAs Name: Gilbert Jacob Jorge Joseph Lucas Rebecca Shelby Instructions: 1. There are 5 questions on
Points off 1 2 3 4 5A 5B Total off Net Score CS 314 Exam 1 Fall 2017 Your Name Your UTEID Circle your TAs Name: Gilbert Jacob Jorge Joseph Lucas Rebecca Shelby Instructions: 1. There are 5 questions on
CONDITIONAL EXECUTION
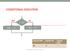 CONDITIONAL EXECUTION yes x > y? no max = x; max = y; logical AND logical OR logical NOT &&! Fundamentals of Computer Science I Outline Conditional Execution if then if then Nested if then statements Comparisons
CONDITIONAL EXECUTION yes x > y? no max = x; max = y; logical AND logical OR logical NOT &&! Fundamentals of Computer Science I Outline Conditional Execution if then if then Nested if then statements Comparisons
Lecture 5: Methods CS2301
 Lecture 5: Methods NADA ALZAHRANI CS2301 1 Opening Problem Find the sum of integers from 1 to 10, from 20 to 30, and from 35 to 45, respectively. 2 Solution public static int sum(int i1, int i2) { int
Lecture 5: Methods NADA ALZAHRANI CS2301 1 Opening Problem Find the sum of integers from 1 to 10, from 20 to 30, and from 35 to 45, respectively. 2 Solution public static int sum(int i1, int i2) { int
1. Which of the following is the correct expression of character 4? a. 4 b. "4" c. '\0004' d. '4'
 Practice questions: 1. Which of the following is the correct expression of character 4? a. 4 b. "4" c. '\0004' d. '4' 2. Will System.out.println((char)4) display 4? a. Yes b. No 3. The expression "Java
Practice questions: 1. Which of the following is the correct expression of character 4? a. 4 b. "4" c. '\0004' d. '4' 2. Will System.out.println((char)4) display 4? a. Yes b. No 3. The expression "Java
1. An operation in which an overall value is computed incrementally, often using a loop.
 Practice Exam 2 Part I: Vocabulary (10 points) Write the terms defined by the statements below. 1. An operation in which an overall value is computed incrementally, often using a loop. 2. The < (less than)
Practice Exam 2 Part I: Vocabulary (10 points) Write the terms defined by the statements below. 1. An operation in which an overall value is computed incrementally, often using a loop. 2. The < (less than)
Computer Science 1 Honors
 Computer Science 1 Honors Will be Most methods are too complex simply to call them and let them do their job. Methods almost always need more information. For example, a method that finds a square root,
Computer Science 1 Honors Will be Most methods are too complex simply to call them and let them do their job. Methods almost always need more information. For example, a method that finds a square root,
Topic 14 while loops and loop patterns
 Topic 14 while loops and loop patterns "Given enough eyeballs, all bugs are shallow (e.g., given a large enough beta-tester and co-developer base, almost every problem will be characterized quickly and
Topic 14 while loops and loop patterns "Given enough eyeballs, all bugs are shallow (e.g., given a large enough beta-tester and co-developer base, almost every problem will be characterized quickly and
CSE 142, Autumn 2011 Midterm Exam: Friday, November 4, 2011
 CSE 142, Autumn 2011 Midterm Exam: Friday, November 4, 2011 Name: Section: Student ID #: TA: You have 50 minutes to complete this exam. You may receive a deduction if you keep working after the instructor
CSE 142, Autumn 2011 Midterm Exam: Friday, November 4, 2011 Name: Section: Student ID #: TA: You have 50 minutes to complete this exam. You may receive a deduction if you keep working after the instructor
Introduction to Computer Science Unit 2. Notes
 Introduction to Computer Science Unit 2. Notes Name: Objectives: By the completion of this packet, students should be able to describe the difference between.java and.class files and the JVM. create and
Introduction to Computer Science Unit 2. Notes Name: Objectives: By the completion of this packet, students should be able to describe the difference between.java and.class files and the JVM. create and
CS 314 Final Fall 2012
 Points off 1 2A 2B 2C 3 4A 4B 5 Total off Net Score CS 314 Final Fall 2012 Your Name_ Your UTEID Instructions: 1. There are 5 questions on this exam. The raw point total on the exam is 110. 2. You have
Points off 1 2A 2B 2C 3 4A 4B 5 Total off Net Score CS 314 Final Fall 2012 Your Name_ Your UTEID Instructions: 1. There are 5 questions on this exam. The raw point total on the exam is 110. 2. You have
CIS 110 Introduction To Computer Programming. October 5th, 2011 Exam 1. Answer key for review problems
 CIS 110 Introduction To Computer Programming October 5th, 2011 Exam 1 Answer key for review problems Scores: 1 2 3 4 5 6 Total (100 max) CIS 110 Exam 1 Instructions You have 50 minutes to finish this exam.
CIS 110 Introduction To Computer Programming October 5th, 2011 Exam 1 Answer key for review problems Scores: 1 2 3 4 5 6 Total (100 max) CIS 110 Exam 1 Instructions You have 50 minutes to finish this exam.
CS 314 Midterm 2 Spring 2013
 Points off 1 2 3 4 5 Total off Net Score CS 314 Midterm 2 Spring 2013 Your Name Your UTEID Circle yours TA s name: Donghyuk Lixun Padmini Zihao Instructions: 1. There are 5 questions on this test. The
Points off 1 2 3 4 5 Total off Net Score CS 314 Midterm 2 Spring 2013 Your Name Your UTEID Circle yours TA s name: Donghyuk Lixun Padmini Zihao Instructions: 1. There are 5 questions on this test. The
CS 314 Midterm 1 Fall 2011
 Points off 1 2 3 4 5 Total off Net Score CS 314 Midterm 1 Fall 2011 Your Name_ Your UTEID Circle yours TA s name: Swati Yuanzhong Instructions: 1. There are 5 questions on this test. 2. You have 2 hours
Points off 1 2 3 4 5 Total off Net Score CS 314 Midterm 1 Fall 2011 Your Name_ Your UTEID Circle yours TA s name: Swati Yuanzhong Instructions: 1. There are 5 questions on this test. 2. You have 2 hours
Midterm Review Session
 Midterm Review Session Programming Problems For more practice: http://webster.cs.washington.edu:8080/practiceit/ Copyright 2009 by Pearson Education Midterm Logistics Bring your UW Student ID card!! Will
Midterm Review Session Programming Problems For more practice: http://webster.cs.washington.edu:8080/practiceit/ Copyright 2009 by Pearson Education Midterm Logistics Bring your UW Student ID card!! Will
CS 314 Final Fall 2011
 Points off 1 2A 2B 2C 3 4 5 Total off Net Score CS 314 Final Fall 2011 Your Name_ Your UTEID Instructions: 1. There are 5 questions on this test. 2. You have 3 hours to complete the test. 3. You may not
Points off 1 2A 2B 2C 3 4 5 Total off Net Score CS 314 Final Fall 2011 Your Name_ Your UTEID Instructions: 1. There are 5 questions on this test. 2. You have 3 hours to complete the test. 3. You may not
CSEN202: Introduction to Computer Science Spring Semester 2017 Midterm Exam
 Page 0 German University in Cairo April 6, 2017 Media Engineering and Technology Faculty Prof. Dr. Slim Abdennadher CSEN202: Introduction to Computer Science Spring Semester 2017 Midterm Exam Bar Code
Page 0 German University in Cairo April 6, 2017 Media Engineering and Technology Faculty Prof. Dr. Slim Abdennadher CSEN202: Introduction to Computer Science Spring Semester 2017 Midterm Exam Bar Code
Points off Total off Net Score. CS 314 Final Exam Spring Your Name Your UTEID
 Points off 1 2 3 4 5 6 Total off Net Score CS 314 Final Exam Spring 2018 Your Name Your UTEID Instructions: 1. There are 6 questions on this test. 100 points available. Scores will be scaled to 300 points.
Points off 1 2 3 4 5 6 Total off Net Score CS 314 Final Exam Spring 2018 Your Name Your UTEID Instructions: 1. There are 6 questions on this test. 100 points available. Scores will be scaled to 300 points.
CS 314 Midterm 1 Fall 2012
 Points off 1 2 3 4 5 Total off Net Score CS 314 Midterm 1 Fall 2012 Your Name_ Your UTEID Circle yours TA s name: John Zihao Instructions: 1. There are 5 questions on this test. 2. You have 2 hours to
Points off 1 2 3 4 5 Total off Net Score CS 314 Midterm 1 Fall 2012 Your Name_ Your UTEID Circle yours TA s name: John Zihao Instructions: 1. There are 5 questions on this test. 2. You have 2 hours to
Chapter 5 Methods / Functions
 Chapter 5 Methods / Functions 1 Motivations A method is a construct for grouping statements together to perform a function. Using a method, you can write the code once for performing the function in a
Chapter 5 Methods / Functions 1 Motivations A method is a construct for grouping statements together to perform a function. Using a method, you can write the code once for performing the function in a
CS 1063 Introduction to Computer Programming Midterm Exam 2 Section 1 Sample Exam
 Seat Number Name CS 1063 Introduction to Computer Programming Midterm Exam 2 Section 1 Sample Exam This is a closed book exam. Answer all of the questions on the question paper in the space provided. If
Seat Number Name CS 1063 Introduction to Computer Programming Midterm Exam 2 Section 1 Sample Exam This is a closed book exam. Answer all of the questions on the question paper in the space provided. If
Introduction to Computer Science Unit 2. Notes
 Introduction to Computer Science Unit 2. Notes Name: Objectives: By the completion of this packet, students should be able to describe the difference between.java and.class files and the JVM. create and
Introduction to Computer Science Unit 2. Notes Name: Objectives: By the completion of this packet, students should be able to describe the difference between.java and.class files and the JVM. create and
Building Java Programs
 Building Java Programs Chapter 3 Lecture 7: Return values, Math, and casting reading: 3.2, 2.1-2.2 (Slides adapted from Stuart Reges, Hélène Martin, and Marty Stepp) Copyright 2011 by Pearson Education
Building Java Programs Chapter 3 Lecture 7: Return values, Math, and casting reading: 3.2, 2.1-2.2 (Slides adapted from Stuart Reges, Hélène Martin, and Marty Stepp) Copyright 2011 by Pearson Education
CSE 142, Summer 2013 Midterm Exam, Friday, July 26, 2013
 CSE 142, Summer 2013 Midterm Exam, Friday, July 26, 2013 Name: Section: TA: Student ID #: You have 60 minutes to complete this exam. You may receive a deduction if you keep working after the instructor
CSE 142, Summer 2013 Midterm Exam, Friday, July 26, 2013 Name: Section: TA: Student ID #: You have 60 minutes to complete this exam. You may receive a deduction if you keep working after the instructor
Topic 6 Nested for Loops
 Topic 6 Nested for Loops "Complexity has and will maintain a strong fascination for many people. It is true that we live in a complex world and strive to solve inherently complex problems, which often
Topic 6 Nested for Loops "Complexity has and will maintain a strong fascination for many people. It is true that we live in a complex world and strive to solve inherently complex problems, which often
CS 312 Final Fall Your Name SOLUTION SOLUTION SOLUTION SOLUTION SOLUTION. Your UTEID SOLUTION SOLUTION SOLUTION SOLUTION SOLUTION _
 CS 312 Final Fall 2013 Your Name SOLUTION SOLUTION SOLUTION SOLUTION SOLUTION Your UTEID SOLUTION SOLUTION SOLUTION SOLUTION SOLUTION _ Problem Number Topic Points Possible 1 short answer 1 12 2 program
CS 312 Final Fall 2013 Your Name SOLUTION SOLUTION SOLUTION SOLUTION SOLUTION Your UTEID SOLUTION SOLUTION SOLUTION SOLUTION SOLUTION _ Problem Number Topic Points Possible 1 short answer 1 12 2 program
Exam Percentage: / 55 = %
 1/6 CS 1316 - Exam 1 - Spring 2010 Name: CS 1316 - Exam 1 - Spring 2010 Your Grading TA: Your Section : INTEGRITY: By taking this exam, you pledge that this is your work and you have neither given nor
1/6 CS 1316 - Exam 1 - Spring 2010 Name: CS 1316 - Exam 1 - Spring 2010 Your Grading TA: Your Section : INTEGRITY: By taking this exam, you pledge that this is your work and you have neither given nor
Problem Grade Total
 CS 101, Prof. Loftin: Final Exam, May 11, 2009 Name: All your work should be done on the pages provided. Scratch paper is available, but you should present everything which is to be graded on the pages
CS 101, Prof. Loftin: Final Exam, May 11, 2009 Name: All your work should be done on the pages provided. Scratch paper is available, but you should present everything which is to be graded on the pages
Programming Language. Functions. Eng. Anis Nazer First Semester
 Programming Language Functions Eng. Anis Nazer First Semester 2016-2017 Definitions Function : a set of statements that are written once, and can be executed upon request Functions are separate entities
Programming Language Functions Eng. Anis Nazer First Semester 2016-2017 Definitions Function : a set of statements that are written once, and can be executed upon request Functions are separate entities
To define methods, invoke methods, and pass arguments to a method ( ). To develop reusable code that is modular, easy-toread, easy-to-debug,
 1 To define methods, invoke methods, and pass arguments to a method ( 5.2-5.5). To develop reusable code that is modular, easy-toread, easy-to-debug, and easy-to-maintain. ( 5.6). To use method overloading
1 To define methods, invoke methods, and pass arguments to a method ( 5.2-5.5). To develop reusable code that is modular, easy-toread, easy-to-debug, and easy-to-maintain. ( 5.6). To use method overloading
CS 314 Exam 2 Spring 2016
 Points off 1 2 3 4 5 6 Total off Raw Score CS 314 Exam 2 Spring 2016 Your Name Your UTEID Instructions: 1. There are 6 questions on this test. 100 points available. Scores will be scaled to 200 points.
Points off 1 2 3 4 5 6 Total off Raw Score CS 314 Exam 2 Spring 2016 Your Name Your UTEID Instructions: 1. There are 6 questions on this test. 100 points available. Scores will be scaled to 200 points.
Topic 5 for loops and nested loops
 Topic 5 for loops and nested loops Always to see the general in the particular is the very foundation of genius. -Arthur Schopenhauer Based on slides by Marty Stepp and Stuart Reges from http://www.buildingjavaprograms.com/
Topic 5 for loops and nested loops Always to see the general in the particular is the very foundation of genius. -Arthur Schopenhauer Based on slides by Marty Stepp and Stuart Reges from http://www.buildingjavaprograms.com/
McGill University School of Computer Science COMP-202A Introduction to Computing 1
 McGill University School of Computer Science COMP-202A Introduction to Computing 1 Midterm Exam Thursday, October 26, 2006, 18:00-20:00 (6:00 8:00 PM) Instructors: Mathieu Petitpas, Shah Asaduzzaman, Sherif
McGill University School of Computer Science COMP-202A Introduction to Computing 1 Midterm Exam Thursday, October 26, 2006, 18:00-20:00 (6:00 8:00 PM) Instructors: Mathieu Petitpas, Shah Asaduzzaman, Sherif
COE 212 Engineering Programming. Welcome to Exam II Thursday April 21, Instructors: Dr. Salim Haddad Dr. Joe Tekli Dr. Wissam F.
 1 COE 212 Engineering Programming Welcome to Exam II Thursday April 21, 2016 Instructors: Dr. Salim Haddad Dr. Joe Tekli Dr. Wissam F. Fawaz Name: Student ID: Instructions: 1. This exam is Closed Book.
1 COE 212 Engineering Programming Welcome to Exam II Thursday April 21, 2016 Instructors: Dr. Salim Haddad Dr. Joe Tekli Dr. Wissam F. Fawaz Name: Student ID: Instructions: 1. This exam is Closed Book.
CS Introduction to Programming Midterm Exam #1 - Prof. Reed Fall 2009
 CS 102 - Introduction to Programming Midterm Exam #1 - Prof. Reed Fall 2009 What is your name?: There are two sections: I. True/False..................... 60 points; ( 30 questions, 2 points each) II.
CS 102 - Introduction to Programming Midterm Exam #1 - Prof. Reed Fall 2009 What is your name?: There are two sections: I. True/False..................... 60 points; ( 30 questions, 2 points each) II.
Activity 4: Methods. Content Learning Objectives. Process Skill Goals
 Activity 4: Methods Java programs are organized into classes, each of which has one or more methods, each of which has one or more statements. Writing methods allows you to break down a complex program
Activity 4: Methods Java programs are organized into classes, each of which has one or more methods, each of which has one or more statements. Writing methods allows you to break down a complex program
CS 111X - Fall Test 1
 CS 111X - Fall 2016 - Test 1 1/9 Computing ID: CS 111X - Fall 2016 - Test 1 Name: Computing ID: On my honor as a student, I have neither given nor received unauthorized assistance on this exam. Signature:
CS 111X - Fall 2016 - Test 1 1/9 Computing ID: CS 111X - Fall 2016 - Test 1 Name: Computing ID: On my honor as a student, I have neither given nor received unauthorized assistance on this exam. Signature:
Building Java Programs
 Building Java Programs Chapter 3 Lecture 3-2: Return values, Math, and double reading: 3.2, 2.1-2.2 Java's Math class Method name Math.abs(value) Math.ceil(value) Math.floor(value) Description absolute
Building Java Programs Chapter 3 Lecture 3-2: Return values, Math, and double reading: 3.2, 2.1-2.2 Java's Math class Method name Math.abs(value) Math.ceil(value) Math.floor(value) Description absolute
Sample Midterm Exam #2
 Sample Midterm Exam #2 1. Expressions For each expression in the left-hand column, indicate its value in the right-hand column. Be sure to list a constant of appropriate type (e.g., 7.0 rather than 7 for
Sample Midterm Exam #2 1. Expressions For each expression in the left-hand column, indicate its value in the right-hand column. Be sure to list a constant of appropriate type (e.g., 7.0 rather than 7 for
Constants. Why Use Constants? main Method Arguments. CS256 Computer Science I Kevin Sahr, PhD. Lecture 25: Miscellaneous
 CS256 Computer Science I Kevin Sahr, PhD Lecture 25: Miscellaneous 1 main Method Arguments recall the method header of the main method note the argument list public static void main (String [] args) we
CS256 Computer Science I Kevin Sahr, PhD Lecture 25: Miscellaneous 1 main Method Arguments recall the method header of the main method note the argument list public static void main (String [] args) we
Building Java Programs
 Building Java Programs Chapter 3 Lecture 3-2: Return; doubles and casting reading: 3.2, 4.1 videos: Ch. 3 #2 Copyright 2009 by Pearson Education Finish Car example Lecture outline Returns Java Math library
Building Java Programs Chapter 3 Lecture 3-2: Return; doubles and casting reading: 3.2, 4.1 videos: Ch. 3 #2 Copyright 2009 by Pearson Education Finish Car example Lecture outline Returns Java Math library
Table of Contents Date(s) Title/Topic Page #s. Chapter 4: Writing Classes 4.1 Objects Revisited
 Table of Contents Date(s) Title/Topic Page #s 11/6 Chapter 3 Reflection/Corrections 56 Chapter 4: Writing Classes 4.1 Objects Revisited 57 58-59 look over your Ch 3 Tests and write down comments/ reflections/corrections
Table of Contents Date(s) Title/Topic Page #s 11/6 Chapter 3 Reflection/Corrections 56 Chapter 4: Writing Classes 4.1 Objects Revisited 57 58-59 look over your Ch 3 Tests and write down comments/ reflections/corrections
CIS 110 Introduction To Computer Programming. October 5th, 2011 Exam 1. Answer key
 CIS 110 Introduction To Computer Programming October 5th, 2011 Exam 1 Answer key Scores: 1 2 3 4 5 6 Total (100 max) CIS 110 Exam 1 Instructions You have 50 minutes to finish this exam. Time will begin
CIS 110 Introduction To Computer Programming October 5th, 2011 Exam 1 Answer key Scores: 1 2 3 4 5 6 Total (100 max) CIS 110 Exam 1 Instructions You have 50 minutes to finish this exam. Time will begin
Computer Science is...
 Computer Science is... Automated Software Verification Using mathematical logic, computer scientists try to design tools to automatically detect runtime and logical errors in huge, complex programs. Right:
Computer Science is... Automated Software Verification Using mathematical logic, computer scientists try to design tools to automatically detect runtime and logical errors in huge, complex programs. Right:
CS 307 Midterm 2 Fall 2009
 Points off 1 2 3 4 5 Total off Net Score Exam Number: CS 307 Midterm 2 Fall 2009 Name UTEID login name TA's Name: Oswaldo Rashid Swati (Circle One) Instructions: 1. Please turn off your cell phones and
Points off 1 2 3 4 5 Total off Net Score Exam Number: CS 307 Midterm 2 Fall 2009 Name UTEID login name TA's Name: Oswaldo Rashid Swati (Circle One) Instructions: 1. Please turn off your cell phones and
CS 307 Midterm 1[corrected] Spring 2008
![CS 307 Midterm 1[corrected] Spring 2008 CS 307 Midterm 1[corrected] Spring 2008](/thumbs/71/65843664.jpg) Points off 1 2 3 4 5 Total off Net Score CS 307 Midterm 1[corrected] Spring 2008 Your Name Your UTEID Circle yours TA s name: Ruchica Mario Vishvas Instructions: 1. Please turn off or silence your cell
Points off 1 2 3 4 5 Total off Net Score CS 307 Midterm 1[corrected] Spring 2008 Your Name Your UTEID Circle yours TA s name: Ruchica Mario Vishvas Instructions: 1. Please turn off or silence your cell
Following is the general form of a typical decision making structure found in most of the programming languages:
 Decision Making Decision making structures have one or more conditions to be evaluated or tested by the program, along with a statement or statements that are to be executed if the condition is determined
Decision Making Decision making structures have one or more conditions to be evaluated or tested by the program, along with a statement or statements that are to be executed if the condition is determined
Term 1 Unit 1 Week 1 Worksheet: Output Solution
 4 Term 1 Unit 1 Week 1 Worksheet: Output Solution Consider the following what is output? 1. System.out.println("hot"); System.out.println("dog"); Output hot dog 2. System.out.print("hot\n\t\t"); System.out.println("dog");
4 Term 1 Unit 1 Week 1 Worksheet: Output Solution Consider the following what is output? 1. System.out.println("hot"); System.out.println("dog"); Output hot dog 2. System.out.print("hot\n\t\t"); System.out.println("dog");
Building Java Programs
 Building Java Programs Chapter 3 Lecture 3-2: Return values, Math, and double reading: 3.2, 2.1-2.2 Method name Math.abs(value) Math.ceil(value) Math.floor(value) Java's Math class Description absolute
Building Java Programs Chapter 3 Lecture 3-2: Return values, Math, and double reading: 3.2, 2.1-2.2 Method name Math.abs(value) Math.ceil(value) Math.floor(value) Java's Math class Description absolute
(c) ((!(a && b)) == (!a!b)) TRUE / FALSE. (f) ((!(a b)) == (!a &&!b)) TRUE / FALSE. (g) (!(!a) && (c-d > 0) && (b!b))
 ComS 207: Programming I Midterm 2, Tue. Mar 21, 2006 Student Name: Student ID Number: Recitation Section: 1. True/False Questions (10 x 1p each = 10p) Determine the value of each boolean expression given
ComS 207: Programming I Midterm 2, Tue. Mar 21, 2006 Student Name: Student ID Number: Recitation Section: 1. True/False Questions (10 x 1p each = 10p) Determine the value of each boolean expression given
Final Exam. COMP Summer I June 26, points
 Final Exam COMP 14-090 Summer I 2000 June 26, 2000 200 points 1. Closed book and closed notes. No outside material allowed. 2. Write all answers on the test itself. Do not write any answers in a blue book
Final Exam COMP 14-090 Summer I 2000 June 26, 2000 200 points 1. Closed book and closed notes. No outside material allowed. 2. Write all answers on the test itself. Do not write any answers in a blue book
CS 314 Exam 1 Spring 2018
 Points off 1 2 3 4 5 6 Total off Net Score CS 314 Exam 1 Spring 2018 Your Name Your UTEID Circle your TAs Name: Aish Anthony Chris Dayanny Hailey Ivan Jacob Joseph Lucas Shelby Instructions: 1. There are
Points off 1 2 3 4 5 6 Total off Net Score CS 314 Exam 1 Spring 2018 Your Name Your UTEID Circle your TAs Name: Aish Anthony Chris Dayanny Hailey Ivan Jacob Joseph Lucas Shelby Instructions: 1. There are
CS 111X - Fall Test 1 - KEY KEY KEY KEY KEY KEY KEY
 CS 111X - Fall 2016 - Test 1 1/9 Computing ID: CS 111X - Fall 2016 - Test 1 - KEY KEY KEY KEY KEY KEY KEY Name: Computing ID: On my honor as a student, I have neither given nor received unauthorized assistance
CS 111X - Fall 2016 - Test 1 1/9 Computing ID: CS 111X - Fall 2016 - Test 1 - KEY KEY KEY KEY KEY KEY KEY Name: Computing ID: On my honor as a student, I have neither given nor received unauthorized assistance
CS111: PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE II
 1 CS111: PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE II Computer Science Department Lecture 1: Introduction Lecture Contents 2 Course info Why programming?? Why Java?? Write once, run anywhere!! Java basics Input/output Variables
1 CS111: PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE II Computer Science Department Lecture 1: Introduction Lecture Contents 2 Course info Why programming?? Why Java?? Write once, run anywhere!! Java basics Input/output Variables
Welcome to the Primitives and Expressions Lab!
 Welcome to the Primitives and Expressions Lab! Learning Outcomes By the end of this lab: 1. Be able to define chapter 2 terms. 2. Describe declarations, variables, literals and constants for primitive
Welcome to the Primitives and Expressions Lab! Learning Outcomes By the end of this lab: 1. Be able to define chapter 2 terms. 2. Describe declarations, variables, literals and constants for primitive
Programming Exercise 7: Static Methods
 Programming Exercise 7: Static Methods Due date for section 001: Monday, February 29 by 10 am Due date for section 002: Wednesday, March 2 by 10 am Purpose: Introduction to writing methods and code re-use.
Programming Exercise 7: Static Methods Due date for section 001: Monday, February 29 by 10 am Due date for section 002: Wednesday, March 2 by 10 am Purpose: Introduction to writing methods and code re-use.
Chapter 5 Methods. Liang, Introduction to Java Programming, Ninth Edition, (c) 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 5 Methods 1 Opening Problem Find the sum of integers from 1 to 10, from 20 to 30, and from 35 to 45, respectively. 2 Problem int sum = 0; for (int i = 1; i
Chapter 5 Methods 1 Opening Problem Find the sum of integers from 1 to 10, from 20 to 30, and from 35 to 45, respectively. 2 Problem int sum = 0; for (int i = 1; i
Question: Total Points: Score:
 CS 170 Exam 1 Section 003 Fall 2013 Name (print): Instructions: Keep your eyes on your own paper and do your best to prevent anyone else from seeing your work. Do NOT communicate with anyone other than
CS 170 Exam 1 Section 003 Fall 2013 Name (print): Instructions: Keep your eyes on your own paper and do your best to prevent anyone else from seeing your work. Do NOT communicate with anyone other than
1. Expressions - 1 point each. -1 for missing or extra " OR.0. differences in capitalization of true and false okay. No limit on points off.
 CS312 Fall 2017 Final Solution and Grading Criteria. Grading acronyms: AIOBE - Array Index out of Bounds Exception may occur BOD - Benefit of the Doubt. Not certain code works, but, can't prove otherwise
CS312 Fall 2017 Final Solution and Grading Criteria. Grading acronyms: AIOBE - Array Index out of Bounds Exception may occur BOD - Benefit of the Doubt. Not certain code works, but, can't prove otherwise
