Data Structure Chapter 6
|
|
|
- Primrose Stewart
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ata Structure hapter Non-inary Trees r. Patrick han School of omputer Science and ngineering South hina University of Technology Outline Non-inary (eneral) Tree (h.) Parent Pointer mplementation (h.) ist of hildren mplementation (h..) eft-hild/ight-sibling mplementation (h..) ynamic eft-hild/ight-sibling mplementation (h..) ynamic Node mplementation (h..) K-ary Trees (h.) Sequential Tree mplementation (h.) ec : Non-inary Tree
2 eneral Tree (Non-binary Tree) tree T is a finite set of one or more nodes such that there is one designated node called the root of T The remaining nodes in (T {}) are partitioned into n disjoint subsets T, T,..., T k, each of which is a tree, and whose roots,,..., k, respectively, are children of ec : Non-inary Tree eneral Tree P P V V N M Q inary Tree eneral Tree - Two, one or zero child - ny number of child ec : Non-inary Tree
3 eneral Tree To maintain the structure of inary Tree, each node has eft child pointer ight child pointer ow about eneral Tree? P V N M Q ec : Non-inary Tree eneral Tree Node: T // eneral tree node T template <class lem> class TNode { public: TNode(const lem&); // onstructor ~TNode(); // estructor lem value(); // eturn value bool iseaf(); // TU if is a leaf TNode* parent(); // eturn parent TNode* leftmost_child(); // irst child TNode* right_sibling(); // ight sibling void setvalue(lem&); // Set value void insert_first(tnode<lem>* n); void insert_next(tnode<lem>* n); void remove_first(); // emove first child void remove_next(); // emove sibling }; P P P V V V ec : Non-inary Tree
4 eneral Tree: T // eneral Tree T template <class lem> class entree { private: void printhelp(tnode*); // Print helper function public: entree(); ~entree(); void clear(); TNode* root(); // onstructor // estructor // Send nodes to free store // eturn the root // ombine two subtrees void newroot(m, Tnode *, Tnode *); Void print(); // Print a tree }; ec : Non-inary Tree eneral Tree: Traversal template <class lem> void entree<lem>:: printhelp(tnode<lem>* subroot) { if (subroot->iseaf()) cout << "eaf: "; else cout << "nternal: "; cout << subroot->value() << "\n"; for (TNode<lem>* temp = subroot->leftmost_child(); temp!= NU; temp = temp->right_sibling()) printhelp(temp); } Print + temp = P ec : Non-inary Tree P Print + Print + temp = V V Print + Print + Print + P V nternal: nternal: P eaf: eaf: eaf: V eaf:
5 eneral Tree: mplementation Parent Pointer mplementation ist of hildren mplementation eft-hild/ight-sibling mplementation ynamic eft-hild/ight-sibling mplementation ynamic Node mplementation ec : Non-inary Tree Parent Pointer mplementation Only storing pointer may be the simplest general tree implementation Parent abel W Y Z W ood for answering the question re these two nodes in the same tree? ow to do that? Y Z ec : Non-inary Tree
6 Parent Pointer mplementation class entree { // entree for UNON/N private: int* array; // Node array int size; // Size of node array int N(int) const; // ind root public: entree(int); // onstructor ~entree() { delete [] array; } // estructor void UNON (int, int); // Merge equivalences void differ (int, int); // TU if not in same tree } ec : Non-inary Tree Parent Pointer mplementation int entree::n(int curr) const { while (array[curr]!=oot) curr = array[curr]; return curr; // t root } // eturn TU if nodes in different trees bool entree::differ(int a, int b) { int root = N(a); // ind root for a int root = N(b); // ind root for b return root!= root; // ompare roots } void entree::unon(int a, int b) { int root = N(a); // ind root for a int root = N(b); // ind root for b if (root!= root) array[root] = root; } array Parent ec : Non-inary Tree abel W Y W Y Z Z
7 Parent Pointer mplementation quivalence lass ssigning the members of a set to disjoint subsets called equivalence classes.g. Object and are equivalent Object and are equivalent Object and must be equivalence UNON/N implementation heck if two objects are equivalent: differ Set two objects are equivalent : UNON ec : Non-inary Tree Parent Pointer mplementation quivalence lass: xample (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ) ec : Non-inary Tree
8 Parent Pointer mplementation quivalence lass: xample (, ) s (, )? s (, )? s (, )? Yes Yes No ec : Non-inary Tree Parent Pointer mplementation quivalence lass: educe the cost The search cost can decrease by reducing the height of the tree Weighted Union ule ec : Non-inary Tree oin the tree with fewer nodes to the tree with more nodes ew > More More > ew (, )
9 Parent Pointer mplementation quivalence lass: educe the cost Path ompression int entree::n(int curr) const { if (array[curr] == OOT) return curr; ase ase return array[curr] = N(array[curr]); ecursive all } ec : Non-inary Tree atree.n(); Small xercise!!!! (, ) f (, )? (, ) f (, )? (, ) f (K, )? (, ) (, ) f (, )? (path compression) (, ) (, ) (, K) K ec : Non-inary Tree
10 Small xercise!!!! (, ) (, ) K (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ) K f (, )? f (, )? f (K, )? f (, )? (path compression) Yes No Yes Yes (, K) K ec : Non-inary Tree eneral Tree mplementation ist of hildren ndex Value Parent hildren can be found easily specially for the leftmost child ight sibling is more difficult ombining trees is difficult if the trees are stored in different array ec : Non-inary Tree
11 eneral Tree mplementation eft-hild/ight-sibling ndex eft-hild Value ec : Non-inary Tree Parent ight-sibling ndex mproved version of ist of hildren ight sibling pointer is added More space efficient as each node requires a fixed amount of space ombining trees is difficult if the trees are stored in different array eneral Tree mplementation ynamic eft-hild/ight-sibling NU NU NU NU ec : Non-inary Tree NU NU NU NU NU NU NU inked version of eft- hild/ight- Sibling onvert as a binary tree annot find the parent of a node
12 eneral Tree mplementation ynamic Node llocate variable space for each node Two implementation methods: rray-based ist inked ist ec : Non-inary Tree eneral Tree mplementation ynamic Node llocate an array of child pointers as part of the node ssume the number of children is known when the node is created ec : Non-inary Tree
13 eneral Tree mplementation ynamic Node Store a linked list of child pointers with each node More flexible (no assumption on number of child) but require more space ec : Non-inary Tree K-ary Trees K-ary Trees are trees with nodes have at most K children e.g. inary Tree, K = eneral Tree, K = inf K M ec : Non-inary Tree -ary Tree
14 K-ary Trees asy to implement relatively Many properties of binary trees can be extended When K becomes large, the potential number of NU pointers increase nternal and leaf nodes should be implemented differently K M ec : Non-inary Tree -ary Tree K-ary Trees K M ull -ary Tree (not complete) omplete -ary Tree (not ull) ull and complete -ary Tree ec : Non-inary Tree
15 Sequential Tree mplementations undamentally different approach to implementing trees Store a series of node values with the minimum information needed to reconstruct the tree structure Preorder traversal is used ec : Non-inary Tree Sequential Tree mplementations or inary Trees (preorder traversal), o not have enough information to reconstruct the tree / / / / / / / / / / NU pointer should also be added / / / dd to the internal node emove the / (NU pointer) of the leaf node ec : Non-inary Tree
16 Sequential Tree mplementations or eneral Tree, ) indicates when a node s child list has come to an end ) ) ) ) ) ) ) ec : Non-inary Tree Sequential Tree mplementations Space/Time Tradeoff Space saving No pointer is needed ost the benefit of tree Tree: fficient access O(log n) Sequential Tree: Sequential access O(n) ec : Non-inary Tree
Data Structure Lecture#14: Non-Binary Trees (Chapter 6) U Kang Seoul National University
 Data Structure Lecture#14: Non-Binary Trees (Chapter 6) U Kang Seoul National University U Kang 1 In This Lecture The concept of the general tree, its ADT, and its operation Motivation and the main idea
Data Structure Lecture#14: Non-Binary Trees (Chapter 6) U Kang Seoul National University U Kang 1 In This Lecture The concept of the general tree, its ADT, and its operation Motivation and the main idea
Chapter 20: Binary Trees
 Chapter 20: Binary Trees 20.1 Definition and Application of Binary Trees Definition and Application of Binary Trees Binary tree: a nonlinear linked list in which each node may point to 0, 1, or two other
Chapter 20: Binary Trees 20.1 Definition and Application of Binary Trees Definition and Application of Binary Trees Binary tree: a nonlinear linked list in which each node may point to 0, 1, or two other
Trees. Q: Why study trees? A: Many advance ADTs are implemented using tree-based data structures.
 Trees Q: Why study trees? : Many advance DTs are implemented using tree-based data structures. Recursive Definition of (Rooted) Tree: Let T be a set with n 0 elements. (i) If n = 0, T is an empty tree,
Trees Q: Why study trees? : Many advance DTs are implemented using tree-based data structures. Recursive Definition of (Rooted) Tree: Let T be a set with n 0 elements. (i) If n = 0, T is an empty tree,
Data Structure Lecture#15: Non-Binary Trees 2 (Chapter 6) U Kang Seoul National University
 Data Structure Lecture#15: Non-Binary Trees 2 (Chapter 6) U Kang Seoul National University U Kang (2016) 1 In This Lecture Main ideas in implementations of general trees Compare advantages and disadvantages
Data Structure Lecture#15: Non-Binary Trees 2 (Chapter 6) U Kang Seoul National University U Kang (2016) 1 In This Lecture Main ideas in implementations of general trees Compare advantages and disadvantages
Objectives. In this session, you will learn to:
 TRS Objectives n this session, you will learn to: Store data in a tree istinguish types of inary tree Traverse a inary Tree norder PreOrder PostOrder onstruct a inary Tree onstruct an expression inary
TRS Objectives n this session, you will learn to: Store data in a tree istinguish types of inary tree Traverse a inary Tree norder PreOrder PostOrder onstruct a inary Tree onstruct an expression inary
國立清華大學電機工程學系. Outline
 國立清華大學電機工程學系 2410 ata Structure hapter 5 Trees (Part I) Outline Introduction inary Trees inary Tree Traversal dditional inary Tree Operations Threaded inary Trees Heaps ch5.1-2 Genealogical harts no inbreeding
國立清華大學電機工程學系 2410 ata Structure hapter 5 Trees (Part I) Outline Introduction inary Trees inary Tree Traversal dditional inary Tree Operations Threaded inary Trees Heaps ch5.1-2 Genealogical harts no inbreeding
ITEC2620 Introduction to Data Structures
 T2620 ntroduction to ata Structures Lecture 4a inary Trees Review of Linked Lists Linked-Lists dynamic length arbitrary memory locations access by following links an only traverse link in forward direction
T2620 ntroduction to ata Structures Lecture 4a inary Trees Review of Linked Lists Linked-Lists dynamic length arbitrary memory locations access by following links an only traverse link in forward direction
CSE 326: Data Structures Binary Search Trees
 nnouncements (1/3/0) S 36: ata Structures inary Search Trees Steve Seitz Winter 0 HW # due now HW #3 out today, due at beginning of class next riday. Project due next Wed. night. Read hapter 4 1 Ts Seen
nnouncements (1/3/0) S 36: ata Structures inary Search Trees Steve Seitz Winter 0 HW # due now HW #3 out today, due at beginning of class next riday. Project due next Wed. night. Read hapter 4 1 Ts Seen
A Hierarchical Structure. Lecture11: Tree I. Tree Data Structures. Unix/Linux file systems. Bohyung Han CSE, POSTECH
 Unix/Linux file systems Hierarchical Structure (2015F) Lecture11: Tree I ohyung Han S, POSTH bhhan@postech.ac.kr 2 Tree ata Structures n abstract model of a hierarchical structure 2 dimensional structure
Unix/Linux file systems Hierarchical Structure (2015F) Lecture11: Tree I ohyung Han S, POSTH bhhan@postech.ac.kr 2 Tree ata Structures n abstract model of a hierarchical structure 2 dimensional structure
CS S-09 General Trees 1
 S245-2006S-09 eneral Trees 1 09-0: Trees with > 2 children How can we implement trees with nodes that have > 2 children? 09-1: Trees with > 2 children rray of hildren 09-2: Trees with > 2 children Linked
S245-2006S-09 eneral Trees 1 09-0: Trees with > 2 children How can we implement trees with nodes that have > 2 children? 09-1: Trees with > 2 children rray of hildren 09-2: Trees with > 2 children Linked
Binomial Queue deletemin ADTs Seen So Far
 Today s Outline Trees (inary Search Trees) hapter in Weiss S ata Structures Ruth nderson nnouncements Written HW # due next riday, 1/ Project due next Monday, /1 Today s Topics: Priority Queues inomial
Today s Outline Trees (inary Search Trees) hapter in Weiss S ata Structures Ruth nderson nnouncements Written HW # due next riday, 1/ Project due next Monday, /1 Today s Topics: Priority Queues inomial
Multi-way Search Trees. (Multi-way Search Trees) Data Structures and Programming Spring / 25
 Multi-way Search Trees (Multi-way Search Trees) Data Structures and Programming Spring 2017 1 / 25 Multi-way Search Trees Each internal node of a multi-way search tree T: has at least two children contains
Multi-way Search Trees (Multi-way Search Trees) Data Structures and Programming Spring 2017 1 / 25 Multi-way Search Trees Each internal node of a multi-way search tree T: has at least two children contains
CMSC 341 Lecture 15 Leftist Heaps
 Based on slides from previous iterations of this course CMSC 341 Lecture 15 Leftist Heaps Prof. John Park Review of Heaps Min Binary Heap A min binary heap is a Complete binary tree Neither child is smaller
Based on slides from previous iterations of this course CMSC 341 Lecture 15 Leftist Heaps Prof. John Park Review of Heaps Min Binary Heap A min binary heap is a Complete binary tree Neither child is smaller
Data Structure Chapter 5. Binary Trees
 http://5.6.4./css/ ata Structure hapter 5 Binary Trees r. Patrick han School of omputer Science and Engineering South hina University of Technology Outline Recursion (h.4) Binary Trees (h 5) Introduction
http://5.6.4./css/ ata Structure hapter 5 Binary Trees r. Patrick han School of omputer Science and Engineering South hina University of Technology Outline Recursion (h.4) Binary Trees (h 5) Introduction
A binary search tree or BST is a binary tree that is either empty or in which the data element of each node has a key and satisfies the conditions:
 1 The general binary tree shown is not terribly useful in practice. The chief use of binary trees is for providing rapid access to data (indexing, if you will) and the general binary tree does not have
1 The general binary tree shown is not terribly useful in practice. The chief use of binary trees is for providing rapid access to data (indexing, if you will) and the general binary tree does not have
A Hierarchical Structure. Lecture11: Trees I. Tree Data Structures. Unix/Linux file systems. Bohyung Han CSE, POSTECH
 Unix/Linux file systems Hierarchical Structure (2013F) Lecture11: Trees I ohyung Han S, POSTH bhhan@postech.ac.kr 2 Tree ata Structures n abstract model of a hierarchical structure 2 dimensional structure
Unix/Linux file systems Hierarchical Structure (2013F) Lecture11: Trees I ohyung Han S, POSTH bhhan@postech.ac.kr 2 Tree ata Structures n abstract model of a hierarchical structure 2 dimensional structure
Computational Geometry
 Orthogonal Range Searching omputational Geometry hapter 5 Range Searching Problem: Given a set of n points in R d, preprocess them such that reporting or counting the k points inside a d-dimensional axis-parallel
Orthogonal Range Searching omputational Geometry hapter 5 Range Searching Problem: Given a set of n points in R d, preprocess them such that reporting or counting the k points inside a d-dimensional axis-parallel
CMSC 341 Lecture 15 Leftist Heaps
 Based on slides from previous iterations of this course CMSC 341 Lecture 15 Leftist Heaps Prof. John Park Review of Heaps Min Binary Heap A min binary heap is a Complete binary tree Neither child is smaller
Based on slides from previous iterations of this course CMSC 341 Lecture 15 Leftist Heaps Prof. John Park Review of Heaps Min Binary Heap A min binary heap is a Complete binary tree Neither child is smaller
Binary Trees. Directed, Rooted Tree. Terminology. Trees. Binary Trees. Possible Implementation 4/18/2013
 Directed, Rooted Tree Binary Trees Chapter 5 CPTR 318 Every non-empty directed, rooted tree has A unique element called root One or more elements called leaves Every element except root has a unique parent
Directed, Rooted Tree Binary Trees Chapter 5 CPTR 318 Every non-empty directed, rooted tree has A unique element called root One or more elements called leaves Every element except root has a unique parent
Tree Structures. A hierarchical data structure whose point of entry is the root node
 Binary Trees 1 Tree Structures A tree is A hierarchical data structure whose point of entry is the root node This structure can be partitioned into disjoint subsets These subsets are themselves trees and
Binary Trees 1 Tree Structures A tree is A hierarchical data structure whose point of entry is the root node This structure can be partitioned into disjoint subsets These subsets are themselves trees and
Data Structures and Algorithms(6)
 Ming Zhang "ata Structures and Algorithms" ata Structures and Algorithms(6) Instructor: Ming Zhang Textbook Authors: Ming Zhang, Tengjiao Wang and Haiyan Zhao Higher ducation Press, 2008.6 (the "leventh
Ming Zhang "ata Structures and Algorithms" ata Structures and Algorithms(6) Instructor: Ming Zhang Textbook Authors: Ming Zhang, Tengjiao Wang and Haiyan Zhao Higher ducation Press, 2008.6 (the "leventh
Data Structures. Binary Trees. Root Level = 0. number of leaves:?? leaves Depth (Maximum level of the tree) leaves or nodes. Level=1.
 Data Structures inary Trees number of leaves:?? height leaves Depth (Maximum level of the tree) leaves or nodes Root Level = 0 Level=1 57 feet root 2 Level=2 Number of nodes: 2 (2+1) - 1 = 7 2 inary Trees
Data Structures inary Trees number of leaves:?? height leaves Depth (Maximum level of the tree) leaves or nodes Root Level = 0 Level=1 57 feet root 2 Level=2 Number of nodes: 2 (2+1) - 1 = 7 2 inary Trees
Trees and Tree Traversals. Binary Trees. COMP 210: Object-Oriented Programming Lecture Notes 8. Based on notes by Logan Mayfield
 OMP 210: Object-Oriented Programming Lecture Notes 8 Trees and Tree Traversals ased on notes by Logan Mayfield In these notes we look at inary Trees and how to traverse them. inary Trees Imagine a list.
OMP 210: Object-Oriented Programming Lecture Notes 8 Trees and Tree Traversals ased on notes by Logan Mayfield In these notes we look at inary Trees and how to traverse them. inary Trees Imagine a list.
Suppose that the following is from a correct C++ program:
 All multiple choice questions are equally weighted. You can generally assume that code shown in the questions is intended to be syntactically correct, unless something in the question or one of the answers
All multiple choice questions are equally weighted. You can generally assume that code shown in the questions is intended to be syntactically correct, unless something in the question or one of the answers
(2,4) Trees. 2/22/2006 (2,4) Trees 1
 (2,4) Trees 9 2 5 7 10 14 2/22/2006 (2,4) Trees 1 Outline and Reading Multi-way search tree ( 10.4.1) Definition Search (2,4) tree ( 10.4.2) Definition Search Insertion Deletion Comparison of dictionary
(2,4) Trees 9 2 5 7 10 14 2/22/2006 (2,4) Trees 1 Outline and Reading Multi-way search tree ( 10.4.1) Definition Search (2,4) tree ( 10.4.2) Definition Search Insertion Deletion Comparison of dictionary
Programming II (CS300)
 1 Programming II (CS300) Chapter 11: Binary Search Trees MOUNA KACEM mouna@cs.wisc.edu Fall 2018 General Overview of Data Structures 2 Introduction to trees 3 Tree: Important non-linear data structure
1 Programming II (CS300) Chapter 11: Binary Search Trees MOUNA KACEM mouna@cs.wisc.edu Fall 2018 General Overview of Data Structures 2 Introduction to trees 3 Tree: Important non-linear data structure
CSE 530A. B+ Trees. Washington University Fall 2013
 CSE 530A B+ Trees Washington University Fall 2013 B Trees A B tree is an ordered (non-binary) tree where the internal nodes can have a varying number of child nodes (within some range) B Trees When a key
CSE 530A B+ Trees Washington University Fall 2013 B Trees A B tree is an ordered (non-binary) tree where the internal nodes can have a varying number of child nodes (within some range) B Trees When a key
examines every node of a list until a matching node is found, or until all nodes have been examined and no match is found.
 A examines every node of a list until a matching node is found, or until all nodes have been examined and no match is found. For very long lists that are frequently searched, this can take a large amount
A examines every node of a list until a matching node is found, or until all nodes have been examined and no match is found. For very long lists that are frequently searched, this can take a large amount
Data Structures - Binary Trees and Operations on Binary Trees
 ata Structures - inary Trees and Operations on inary Trees MS 275 anko drovic (UI) MS 275 October 15, 2018 1 / 25 inary Trees binary tree is a finite set of elements. It can be empty partitioned into three
ata Structures - inary Trees and Operations on inary Trees MS 275 anko drovic (UI) MS 275 October 15, 2018 1 / 25 inary Trees binary tree is a finite set of elements. It can be empty partitioned into three
Module 4: Index Structures Lecture 13: Index structure. The Lecture Contains: Index structure. Binary search tree (BST) B-tree. B+-tree.
 The Lecture Contains: Index structure Binary search tree (BST) B-tree B+-tree Order file:///c /Documents%20and%20Settings/iitkrana1/My%20Documents/Google%20Talk%20Received%20Files/ist_data/lecture13/13_1.htm[6/14/2012
The Lecture Contains: Index structure Binary search tree (BST) B-tree B+-tree Order file:///c /Documents%20and%20Settings/iitkrana1/My%20Documents/Google%20Talk%20Received%20Files/ist_data/lecture13/13_1.htm[6/14/2012
Binary Trees. For example: Jargon: General Binary Trees. root node. level: internal node. edge. leaf node. Data Structures & File Management
 Binary Trees 1 A binary tree is either empty, or it consists of a node called the root together with two binary trees called the left subtree and the right subtree of the root, which are disjoint from
Binary Trees 1 A binary tree is either empty, or it consists of a node called the root together with two binary trees called the left subtree and the right subtree of the root, which are disjoint from
Binary Tree Node Relationships. Binary Trees. Quick Application: Expression Trees. Traversals
 Binary Trees 1 Binary Tree Node Relationships 2 A binary tree is either empty, or it consists of a node called the root together with two binary trees called the left subtree and the right subtree of the
Binary Trees 1 Binary Tree Node Relationships 2 A binary tree is either empty, or it consists of a node called the root together with two binary trees called the left subtree and the right subtree of the
CPSC 221: Data Structures Lecture #5. CPSC 221: Data Structures Lecture #5. Learning Goals. Today s Outline. Tree Terminology.
 PS 1: Data Structures ecture # ranching Out Steve Wolfman 0W1 PS 1: Data Structures ecture # ranching Out Steve Wolfman 0W1 earning Goals fter this unit, you should be able to... Determine if a given tree
PS 1: Data Structures ecture # ranching Out Steve Wolfman 0W1 PS 1: Data Structures ecture # ranching Out Steve Wolfman 0W1 earning Goals fter this unit, you should be able to... Determine if a given tree
Graphs V={A,B,C,D,E} E={ (A,D),(A,E),(B,D), (B,E),(C,D),(C,E)}
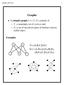 Graphs and Trees 1 Graphs (simple) graph G = (V, ) consists of V, a nonempty set of vertices and, a set of unordered pairs of distinct vertices called edges. xamples V={,,,,} ={ (,),(,),(,), (,),(,),(,)}
Graphs and Trees 1 Graphs (simple) graph G = (V, ) consists of V, a nonempty set of vertices and, a set of unordered pairs of distinct vertices called edges. xamples V={,,,,} ={ (,),(,),(,), (,),(,),(,)}
CPSC 223 Algorithms & Data Abstract Structures
 PS 223 lgorithms & ata bstract Structures Lecture 17: Self-alancing inary Search Trees * Material adapted from. arrano, K. Yerion, and K. ant Today Quiz alanced inary Search Trees (STs) Quick review of
PS 223 lgorithms & ata bstract Structures Lecture 17: Self-alancing inary Search Trees * Material adapted from. arrano, K. Yerion, and K. ant Today Quiz alanced inary Search Trees (STs) Quick review of
CMSC 341 Leftist Heaps
 CMSC 341 Leftist Heaps Based on slides from previous iterations of this course Today s Topics Review of Min Heaps Introduction of Left-ist Heaps Merge Operation Heap Operations Review of Heaps Min Binary
CMSC 341 Leftist Heaps Based on slides from previous iterations of this course Today s Topics Review of Min Heaps Introduction of Left-ist Heaps Merge Operation Heap Operations Review of Heaps Min Binary
Discussion 2C Notes (Week 8, February 25) TA: Brian Choi Section Webpage:
 Discussion 2C Notes (Week 8, February 25) TA: Brian Choi (schoi@cs.ucla.edu) Section Webpage: http://www.cs.ucla.edu/~schoi/cs32 Trees Definitions Yet another data structure -- trees. Just like a linked
Discussion 2C Notes (Week 8, February 25) TA: Brian Choi (schoi@cs.ucla.edu) Section Webpage: http://www.cs.ucla.edu/~schoi/cs32 Trees Definitions Yet another data structure -- trees. Just like a linked
Binary Trees
 Binary Trees 4-7-2005 Opening Discussion What did we talk about last class? Do you have any code to show? Do you have any questions about the assignment? What is a Tree? You are all familiar with what
Binary Trees 4-7-2005 Opening Discussion What did we talk about last class? Do you have any code to show? Do you have any questions about the assignment? What is a Tree? You are all familiar with what
B-Trees. nodes with many children a type node a class for B-trees. an elaborate example the insertion algorithm removing elements
 B-Trees 1 B-Trees nodes with many children a type node a class for B-trees 2 manipulating a B-tree an elaborate example the insertion algorithm removing elements MCS 360 Lecture 35 Introduction to Data
B-Trees 1 B-Trees nodes with many children a type node a class for B-trees 2 manipulating a B-tree an elaborate example the insertion algorithm removing elements MCS 360 Lecture 35 Introduction to Data
IX. Binary Trees (Chapter 10)
 IX. Binary Trees (Chapter 10) -1- A. Introduction: Searching a linked list. 1. Linear Search /* To linear search a list for a particular Item */ 1. Set Loc = 0; 2. Repeat the following: a. If Loc >= length
IX. Binary Trees (Chapter 10) -1- A. Introduction: Searching a linked list. 1. Linear Search /* To linear search a list for a particular Item */ 1. Set Loc = 0; 2. Repeat the following: a. If Loc >= length
 UNIT IV -NON-LINEAR DATA STRUCTURES 4.1 Trees TREE: A tree is a finite set of one or more nodes such that there is a specially designated node called the Root, and zero or more non empty sub trees T1,
UNIT IV -NON-LINEAR DATA STRUCTURES 4.1 Trees TREE: A tree is a finite set of one or more nodes such that there is a specially designated node called the Root, and zero or more non empty sub trees T1,
Week 9 Student Responsibilities. Mat Example: Minimal Spanning Tree. 3.3 Spanning Trees. Prim s Minimal Spanning Tree.
 Week 9 Student Responsibilities Reading: hapter 3.3 3. (Tucker),..5 (Rosen) Mat 3770 Spring 01 Homework Due date Tucker Rosen 3/1 3..3 3/1 DS & S Worksheets 3/6 3.3.,.5 3/8 Heapify worksheet ttendance
Week 9 Student Responsibilities Reading: hapter 3.3 3. (Tucker),..5 (Rosen) Mat 3770 Spring 01 Homework Due date Tucker Rosen 3/1 3..3 3/1 DS & S Worksheets 3/6 3.3.,.5 3/8 Heapify worksheet ttendance
Advanced Java Concepts Unit 5: Trees. Notes and Exercises
 Advanced Java Concepts Unit 5: Trees. Notes and Exercises A Tree is a data structure like the figure shown below. We don t usually care about unordered trees but that s where we ll start. Later we will
Advanced Java Concepts Unit 5: Trees. Notes and Exercises A Tree is a data structure like the figure shown below. We don t usually care about unordered trees but that s where we ll start. Later we will
Advanced Set Representation Methods
 Advanced Set Representation Methods AVL trees. 2-3(-4) Trees. Union-Find Set ADT DSA - lecture 4 - T.U.Cluj-Napoca - M. Joldos 1 Advanced Set Representation. AVL Trees Problem with BSTs: worst case operation
Advanced Set Representation Methods AVL trees. 2-3(-4) Trees. Union-Find Set ADT DSA - lecture 4 - T.U.Cluj-Napoca - M. Joldos 1 Advanced Set Representation. AVL Trees Problem with BSTs: worst case operation
Binary Trees, Binary Search Trees
 Binary Trees, Binary Search Trees Trees Linear access time of linked lists is prohibitive Does there exist any simple data structure for which the running time of most operations (search, insert, delete)
Binary Trees, Binary Search Trees Trees Linear access time of linked lists is prohibitive Does there exist any simple data structure for which the running time of most operations (search, insert, delete)
CS302 - Data Structures using C++
 CS302 - Data Structures using C++ Topic: Trees Kostas Alexis Trees List, stacks, and queues are linear in their organization of data. Items are one after another In this section, we organize data in a
CS302 - Data Structures using C++ Topic: Trees Kostas Alexis Trees List, stacks, and queues are linear in their organization of data. Items are one after another In this section, we organize data in a
Chapter 5. Binary Trees
 Chapter 5 Binary Trees Definitions and Properties A binary tree is made up of a finite set of elements called nodes It consists of a root and two subtrees There is an edge from the root to its children
Chapter 5 Binary Trees Definitions and Properties A binary tree is made up of a finite set of elements called nodes It consists of a root and two subtrees There is an edge from the root to its children
Data Structures and Algorithms
 Data Structures and Algorithms Spring 2017-2018 Outline 1 Priority Queues Outline Priority Queues 1 Priority Queues Jumping the Queue Priority Queues In normal queue, the mode of selection is first in,
Data Structures and Algorithms Spring 2017-2018 Outline 1 Priority Queues Outline Priority Queues 1 Priority Queues Jumping the Queue Priority Queues In normal queue, the mode of selection is first in,
COMP 103 RECAP/TODAY. Recap: General Tree Examples. Recap: Planning. General Trees. Taxonomies e.g. game genres. Tic Tac Toe search tree for moves
 P 103 2017-2 ecture 21 eneral rees arcus rean, indsay roves, Peter ndreae, and homas uehne, VUW indsay roves Sool of ngineering and omputer Science, Victoria University of Wellington 2 PRVIUSY RP/Y inary
P 103 2017-2 ecture 21 eneral rees arcus rean, indsay roves, Peter ndreae, and homas uehne, VUW indsay roves Sool of ngineering and omputer Science, Victoria University of Wellington 2 PRVIUSY RP/Y inary
Binary Trees. Examples:
 Binary Trees A tree is a data structure that is made of nodes and pointers, much like a linked list. The difference between them lies in how they are organized: In a linked list each node is connected
Binary Trees A tree is a data structure that is made of nodes and pointers, much like a linked list. The difference between them lies in how they are organized: In a linked list each node is connected
Data Structures and Algorithms
 Data Structures and Algorithms Trees Sidra Malik sidra.malik@ciitlahore.edu.pk Tree? In computer science, a tree is an abstract model of a hierarchical structure A tree is a finite set of one or more nodes
Data Structures and Algorithms Trees Sidra Malik sidra.malik@ciitlahore.edu.pk Tree? In computer science, a tree is an abstract model of a hierarchical structure A tree is a finite set of one or more nodes
Binary Trees. Height 1
 Binary Trees Definitions A tree is a finite set of one or more nodes that shows parent-child relationship such that There is a special node called root Remaining nodes are portioned into subsets T1,T2,T3.
Binary Trees Definitions A tree is a finite set of one or more nodes that shows parent-child relationship such that There is a special node called root Remaining nodes are portioned into subsets T1,T2,T3.
Introduction to Binary Trees
 Introduction to inary Trees 1 ackground ll data structures examined so far are linear data structures. Each element in a linear data structure has a clear predecessor and a clear successor. Precessors
Introduction to inary Trees 1 ackground ll data structures examined so far are linear data structures. Each element in a linear data structure has a clear predecessor and a clear successor. Precessors
Trees can be used to store entire records from a database, serving as an in-memory representation of the collection of records in a file.
 Large Trees 1 Trees can be used to store entire records from a database, serving as an in-memory representation of the collection of records in a file. Trees can also be used to store indices of the collection
Large Trees 1 Trees can be used to store entire records from a database, serving as an in-memory representation of the collection of records in a file. Trees can also be used to store indices of the collection
An AVL tree with N nodes is an excellent data. The Big-Oh analysis shows that most operations finish within O(log N) time
 B + -TREES MOTIVATION An AVL tree with N nodes is an excellent data structure for searching, indexing, etc. The Big-Oh analysis shows that most operations finish within O(log N) time The theoretical conclusion
B + -TREES MOTIVATION An AVL tree with N nodes is an excellent data structure for searching, indexing, etc. The Big-Oh analysis shows that most operations finish within O(log N) time The theoretical conclusion
Advanced Java Concepts Unit 5: Trees. Notes and Exercises
 dvanced Java Concepts Unit 5: Trees. Notes and Exercises Tree is a data structure like the figure shown below. We don t usually care about unordered trees but that s where we ll start. Later we will focus
dvanced Java Concepts Unit 5: Trees. Notes and Exercises Tree is a data structure like the figure shown below. We don t usually care about unordered trees but that s where we ll start. Later we will focus
2-3 Tree. Outline B-TREE. catch(...){ printf( "Assignment::SolveProblem() AAAA!"); } ADD SLIDES ON DISJOINT SETS
 Outline catch(...){ printf( "Assignment::SolveProblem() AAAA!"); } Balanced Search Trees 2-3 Trees 2-3-4 Trees Slide 4 Why care about advanced implementations? Same entries, different insertion sequence:
Outline catch(...){ printf( "Assignment::SolveProblem() AAAA!"); } Balanced Search Trees 2-3 Trees 2-3-4 Trees Slide 4 Why care about advanced implementations? Same entries, different insertion sequence:
Trees, Binary Trees, and Binary Search Trees
 COMP171 Trees, Binary Trees, and Binary Search Trees 2 Trees Linear access time of linked lists is prohibitive Does there exist any simple data structure for which the running time of most operations (search,
COMP171 Trees, Binary Trees, and Binary Search Trees 2 Trees Linear access time of linked lists is prohibitive Does there exist any simple data structure for which the running time of most operations (search,
6-TREE. Tree: Directed Tree: A directed tree is an acyclic digraph which has one node called the root node
 6-TREE Data Structure Management (330701) Tree: A tree is defined as a finite set of one or more nodes such that There is a special node called the root node R. The remaining nodes are divided into n 0
6-TREE Data Structure Management (330701) Tree: A tree is defined as a finite set of one or more nodes such that There is a special node called the root node R. The remaining nodes are divided into n 0
(2,4) Trees Goodrich, Tamassia (2,4) Trees 1
 (2,4) Trees 9 2 5 7 10 14 2004 Goodrich, Tamassia (2,4) Trees 1 Multi-Way Search Tree A multi-way search tree is an ordered tree such that Each internal node has at least two children and stores d -1 key-element
(2,4) Trees 9 2 5 7 10 14 2004 Goodrich, Tamassia (2,4) Trees 1 Multi-Way Search Tree A multi-way search tree is an ordered tree such that Each internal node has at least two children and stores d -1 key-element
Data Structure Instructor: Nabeel Alassaf Chapter 11 Binary Search Trees (Deletion by merging) Lecture 5
 Data Structure Instructor: Nabeel Alassaf Chapter 11 Binary Search Trees (Deletion by merging) Lecture ١ There are 3 cases in Deletion By Merging in your tree The Deletion depends on the Node situation
Data Structure Instructor: Nabeel Alassaf Chapter 11 Binary Search Trees (Deletion by merging) Lecture ١ There are 3 cases in Deletion By Merging in your tree The Deletion depends on the Node situation
國立清華大學電機工程學系. Outline
 國立清華大學電機工程學系 EE4 Data Structure Chapter 5 Trees (Part II) Outline Binary Search Trees Selection Trees Forests Set Representation Counting Binary Tree ch5.- Definition Binary Search Tree (BST) binary search
國立清華大學電機工程學系 EE4 Data Structure Chapter 5 Trees (Part II) Outline Binary Search Trees Selection Trees Forests Set Representation Counting Binary Tree ch5.- Definition Binary Search Tree (BST) binary search
Advanced Tree Structures
 Data Structure hapter 13 dvanced Tree Structures Dr. Patrick han School of omputer Science and Engineering South hina Universit of Technolog utline VL Tree (h 13..1) Interval Heap ST Recall, inar Search
Data Structure hapter 13 dvanced Tree Structures Dr. Patrick han School of omputer Science and Engineering South hina Universit of Technolog utline VL Tree (h 13..1) Interval Heap ST Recall, inar Search
TREES. Trees - Introduction
 TREES Chapter 6 Trees - Introduction All previous data organizations we've studied are linear each element can have only one predecessor and successor Accessing all elements in a linear sequence is O(n)
TREES Chapter 6 Trees - Introduction All previous data organizations we've studied are linear each element can have only one predecessor and successor Accessing all elements in a linear sequence is O(n)
Tree Data Structures CSC 221
 Tree Data Structures CSC 221 Specialized Trees Binary Tree: A restriction of trees such that the maximum degree of a node is 2. Order of nodes is now relevant May have zero nodes (emtpy tree) Formal Definition:
Tree Data Structures CSC 221 Specialized Trees Binary Tree: A restriction of trees such that the maximum degree of a node is 2. Order of nodes is now relevant May have zero nodes (emtpy tree) Formal Definition:
Trees: examples (Family trees)
 Ch 4: Trees it s a jungle out there... I think that I will never see a linked list useful as a tree; Linked lists are used by everybody, but it takes real smarts to do a tree Trees: examples (Family trees)
Ch 4: Trees it s a jungle out there... I think that I will never see a linked list useful as a tree; Linked lists are used by everybody, but it takes real smarts to do a tree Trees: examples (Family trees)
Trees can be used to store entire records from a database, serving as an in-memory representation of the collection of records in a file.
 Large Trees 1 Trees can be used to store entire records from a database, serving as an in-memory representation of the collection of records in a file. Trees can also be used to store indices of the collection
Large Trees 1 Trees can be used to store entire records from a database, serving as an in-memory representation of the collection of records in a file. Trees can also be used to store indices of the collection
Trees. Truong Tuan Anh CSE-HCMUT
 Trees Truong Tuan Anh CSE-HCMUT Outline Basic concepts Trees Trees A tree consists of a finite set of elements, called nodes, and a finite set of directed lines, called branches, that connect the nodes
Trees Truong Tuan Anh CSE-HCMUT Outline Basic concepts Trees Trees A tree consists of a finite set of elements, called nodes, and a finite set of directed lines, called branches, that connect the nodes
CSI33 Data Structures
 Outline Department of Mathematics and Computer Science Bronx Community College November 13, 2017 Outline Outline 1 C++ Supplement.1: Trees Outline C++ Supplement.1: Trees 1 C++ Supplement.1: Trees Uses
Outline Department of Mathematics and Computer Science Bronx Community College November 13, 2017 Outline Outline 1 C++ Supplement.1: Trees Outline C++ Supplement.1: Trees 1 C++ Supplement.1: Trees Uses
Lecture 37 Section 9.4. Wed, Apr 22, 2009
 Preorder Inorder Postorder Lecture 37 Section 9.4 Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Apr 22, 2009 Outline Preorder Inorder Postorder 1 2 3 Preorder Inorder Postorder 4 Preorder Inorder Postorder Definition (Traverse)
Preorder Inorder Postorder Lecture 37 Section 9.4 Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Apr 22, 2009 Outline Preorder Inorder Postorder 1 2 3 Preorder Inorder Postorder 4 Preorder Inorder Postorder Definition (Traverse)
Tree traversals and binary trees
 Tree traversals and binary trees Comp Sci 1575 Data Structures Valgrind Execute valgrind followed by any flags you might want, and then your typical way to launch at the command line in Linux. Assuming
Tree traversals and binary trees Comp Sci 1575 Data Structures Valgrind Execute valgrind followed by any flags you might want, and then your typical way to launch at the command line in Linux. Assuming
Heaps. 2/13/2006 Heaps 1
 Heaps /13/00 Heaps 1 Outline and Reading What is a heap ( 8.3.1) Height of a heap ( 8.3.) Insertion ( 8.3.3) Removal ( 8.3.3) Heap-sort ( 8.3.) Arraylist-based implementation ( 8.3.) Bottom-up construction
Heaps /13/00 Heaps 1 Outline and Reading What is a heap ( 8.3.1) Height of a heap ( 8.3.) Insertion ( 8.3.3) Removal ( 8.3.3) Heap-sort ( 8.3.) Arraylist-based implementation ( 8.3.) Bottom-up construction
INF2220: algorithms and data structures Series 1
 Universitetet i Oslo Institutt for Informatikk A. Maus, R.K. Runde, I. Yu INF2220: algorithms and data structures Series 1 Topic Trees & estimation of running time (Exercises with hints for solution) Issued:
Universitetet i Oslo Institutt for Informatikk A. Maus, R.K. Runde, I. Yu INF2220: algorithms and data structures Series 1 Topic Trees & estimation of running time (Exercises with hints for solution) Issued:
B-Trees. Version of October 2, B-Trees Version of October 2, / 22
 B-Trees Version of October 2, 2014 B-Trees Version of October 2, 2014 1 / 22 Motivation An AVL tree can be an excellent data structure for implementing dictionary search, insertion and deletion Each operation
B-Trees Version of October 2, 2014 B-Trees Version of October 2, 2014 1 / 22 Motivation An AVL tree can be an excellent data structure for implementing dictionary search, insertion and deletion Each operation
! Tree: set of nodes and directed edges. ! Parent: source node of directed edge. ! Child: terminal node of directed edge
 Trees (& Heaps) Week 12 Gaddis: 20 Weiss: 21.1-3 CS 5301 Spring 2015 Jill Seaman 1 Tree: non-recursive definition! Tree: set of nodes and directed edges - root: one node is distinguished as the root -
Trees (& Heaps) Week 12 Gaddis: 20 Weiss: 21.1-3 CS 5301 Spring 2015 Jill Seaman 1 Tree: non-recursive definition! Tree: set of nodes and directed edges - root: one node is distinguished as the root -
Trees. T.U. Cluj-Napoca -DSA Lecture 2 - M. Joldos 1
 Trees Terminology. Rooted Trees. Traversals. Labeled Trees and Expression Trees. Tree ADT. Tree Implementations. Binary Search Trees. Optimal Search Trees T.U. Cluj-Napoca -DSA Lecture 2 - M. Joldos 1
Trees Terminology. Rooted Trees. Traversals. Labeled Trees and Expression Trees. Tree ADT. Tree Implementations. Binary Search Trees. Optimal Search Trees T.U. Cluj-Napoca -DSA Lecture 2 - M. Joldos 1
Balanced Search Trees
 Balanced Search Trees Computer Science E-22 Harvard Extension School David G. Sullivan, Ph.D. Review: Balanced Trees A tree is balanced if, for each node, the node s subtrees have the same height or have
Balanced Search Trees Computer Science E-22 Harvard Extension School David G. Sullivan, Ph.D. Review: Balanced Trees A tree is balanced if, for each node, the node s subtrees have the same height or have
BST Implementation. Data Structures. Lecture 4 Binary search trees (BST) Dr. Mahmoud Attia Sakr University of Ain Shams
 Lecture 4 Binary search trees (BST) Dr. Mahmoud Attia Sakr mahmoud.sakr@cis.asu.edu.eg Cairo, Egypt, October 2012 Binary Search Trees (BST) 1. Hierarchical data structure with a single reference to root
Lecture 4 Binary search trees (BST) Dr. Mahmoud Attia Sakr mahmoud.sakr@cis.asu.edu.eg Cairo, Egypt, October 2012 Binary Search Trees (BST) 1. Hierarchical data structure with a single reference to root
Multidimensional Indexes [14]
![Multidimensional Indexes [14] Multidimensional Indexes [14]](/thumbs/88/117268268.jpg) CMSC 661, Principles of Database Systems Multidimensional Indexes [14] Dr. Kalpakis http://www.csee.umbc.edu/~kalpakis/courses/661 Motivation Examined indexes when search keys are in 1-D space Many interesting
CMSC 661, Principles of Database Systems Multidimensional Indexes [14] Dr. Kalpakis http://www.csee.umbc.edu/~kalpakis/courses/661 Motivation Examined indexes when search keys are in 1-D space Many interesting
Successor/Predecessor Rules in Binary Trees
 Successor/Predecessor Rules in inary Trees Thomas. nastasio July 7, 2003 Introduction inary tree traversals are commonly made in one of three patterns, inorder, preorder, and postorder. These traversals
Successor/Predecessor Rules in inary Trees Thomas. nastasio July 7, 2003 Introduction inary tree traversals are commonly made in one of three patterns, inorder, preorder, and postorder. These traversals
Data Structures in Java
 Data Strutures in Java Leture 8: Trees and Tree Traversals. 10/5/2015 Daniel Bauer 1 Trees in Computer Siene A lot of data omes in a hierarhial/nested struture. Mathematial expressions. Program struture.
Data Strutures in Java Leture 8: Trees and Tree Traversals. 10/5/2015 Daniel Bauer 1 Trees in Computer Siene A lot of data omes in a hierarhial/nested struture. Mathematial expressions. Program struture.
Tree: non-recursive definition. Trees, Binary Search Trees, and Heaps. Tree: recursive definition. Tree: example.
 Trees, Binary Search Trees, and Heaps CS 5301 Fall 2013 Jill Seaman Tree: non-recursive definition Tree: set of nodes and directed edges - root: one node is distinguished as the root - Every node (except
Trees, Binary Search Trees, and Heaps CS 5301 Fall 2013 Jill Seaman Tree: non-recursive definition Tree: set of nodes and directed edges - root: one node is distinguished as the root - Every node (except
COMP : Trees. COMP20012 Trees 219
 COMP20012 3: Trees COMP20012 Trees 219 Trees Seen lots of examples. Parse Trees Decision Trees Search Trees Family Trees Hierarchical Structures Management Directories COMP20012 Trees 220 Trees have natural
COMP20012 3: Trees COMP20012 Trees 219 Trees Seen lots of examples. Parse Trees Decision Trees Search Trees Family Trees Hierarchical Structures Management Directories COMP20012 Trees 220 Trees have natural
Chapter 10: Trees. A tree is a connected simple undirected graph with no simple circuits.
 Chapter 10: Trees A tree is a connected simple undirected graph with no simple circuits. Properties: o There is a unique simple path between any 2 of its vertices. o No loops. o No multiple edges. Example
Chapter 10: Trees A tree is a connected simple undirected graph with no simple circuits. Properties: o There is a unique simple path between any 2 of its vertices. o No loops. o No multiple edges. Example
Indexing. Outline. Introduction (Ch 10) Linear Index (Ch 10.1) Tree Index (Ch 10.3) 2-3 Tree (Ch 10.4) B-Tree (Ch 10.5) Data Structure Chapter 10
 http://125.216.243.100/csds/ Data Structure Chapter 10 Indexing Dr. Patrick Chan School of Computer Science and Engineering South China University of Technology Outline Introduction (Ch 10) Linear Index
http://125.216.243.100/csds/ Data Structure Chapter 10 Indexing Dr. Patrick Chan School of Computer Science and Engineering South China University of Technology Outline Introduction (Ch 10) Linear Index
CS350: Data Structures B-Trees
 B-Trees James Moscola Department of Engineering & Computer Science York College of Pennsylvania James Moscola Introduction All of the data structures that we ve looked at thus far have been memory-based
B-Trees James Moscola Department of Engineering & Computer Science York College of Pennsylvania James Moscola Introduction All of the data structures that we ve looked at thus far have been memory-based
8. Write an example for expression tree. [A/M 10] (A+B)*((C-D)/(E^F))
![8. Write an example for expression tree. [A/M 10] (A+B)*((C-D)/(E^F)) 8. Write an example for expression tree. [A/M 10] (A+B)*((C-D)/(E^F))](/thumbs/89/97773603.jpg) DHANALAKSHMI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING EC6301 OBJECT ORIENTED PROGRAMMING AND DATA STRUCTURES UNIT IV NONLINEAR DATA STRUCTURES Part A 1. Define Tree [N/D 08]
DHANALAKSHMI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING EC6301 OBJECT ORIENTED PROGRAMMING AND DATA STRUCTURES UNIT IV NONLINEAR DATA STRUCTURES Part A 1. Define Tree [N/D 08]
Extra: B+ Trees. Motivations. Differences between BST and B+ 10/27/2017. CS1: Java Programming Colorado State University
 Extra: B+ Trees CS1: Java Programming Colorado State University Slides by Wim Bohm and Russ Wakefield 1 Motivations Many times you want to minimize the disk accesses while doing a search. A binary search
Extra: B+ Trees CS1: Java Programming Colorado State University Slides by Wim Bohm and Russ Wakefield 1 Motivations Many times you want to minimize the disk accesses while doing a search. A binary search
Indexing. Introduction. Outline. Search Approach. Linear Index (Ch 10.1) Tree Index (Ch 10.3) 2-3 Tree (Ch 10.4) B-Tree (Ch 10.5) Introduction (Ch 10)
 http://125.216.243.100/csds/ Data Structure Chapter 10 Indexing Dr. Patrick Chan School of Computer Science and Engineering South China University of Technology Search Approach Sequential and List Method
http://125.216.243.100/csds/ Data Structure Chapter 10 Indexing Dr. Patrick Chan School of Computer Science and Engineering South China University of Technology Search Approach Sequential and List Method
M-ary Search Tree. B-Trees. B-Trees. Solution: B-Trees. B-Tree: Example. B-Tree Properties. Maximum branching factor of M Complete tree has height =
 M-ary Search Tree B-Trees Section 4.7 in Weiss Maximum branching factor of M Complete tree has height = # disk accesses for find: Runtime of find: 2 Solution: B-Trees specialized M-ary search trees Each
M-ary Search Tree B-Trees Section 4.7 in Weiss Maximum branching factor of M Complete tree has height = # disk accesses for find: Runtime of find: 2 Solution: B-Trees specialized M-ary search trees Each
Binary Trees. College of Computing & Information Technology King Abdulaziz University. CPCS-204 Data Structures I
 Binary Trees College of Computing & Information Technology King Abdulaziz University CPCS-204 Data Structures I Outline Tree Stuff Trees Binary Trees Implementation of a Binary Tree Tree Traversals Depth
Binary Trees College of Computing & Information Technology King Abdulaziz University CPCS-204 Data Structures I Outline Tree Stuff Trees Binary Trees Implementation of a Binary Tree Tree Traversals Depth
SCJ2013 Data Structure & Algorithms. Binary Search Tree. Nor Bahiah Hj Ahmad
 SCJ2013 Data Structure & Algorithms Binary Search Tree Nor Bahiah Hj Ahmad Binary Search Tree A binary search tree has the following properties: For every node n in the tree Value of n is greater than
SCJ2013 Data Structure & Algorithms Binary Search Tree Nor Bahiah Hj Ahmad Binary Search Tree A binary search tree has the following properties: For every node n in the tree Value of n is greater than
Trees. A tree is a directed graph with the property
 2: Trees Trees A tree is a directed graph with the property There is one node (the root) from which all other nodes can be reached by exactly one path. Seen lots of examples. Parse Trees Decision Trees
2: Trees Trees A tree is a directed graph with the property There is one node (the root) from which all other nodes can be reached by exactly one path. Seen lots of examples. Parse Trees Decision Trees
Data Structure Lecture#10: Binary Trees (Chapter 5) U Kang Seoul National University
 Data Structure Lecture#10: Binary Trees (Chapter 5) U Kang Seoul National University U Kang (2016) 1 In This Lecture The concept of binary tree, its terms, and its operations Full binary tree theorem Idea
Data Structure Lecture#10: Binary Trees (Chapter 5) U Kang Seoul National University U Kang (2016) 1 In This Lecture The concept of binary tree, its terms, and its operations Full binary tree theorem Idea
Algorithms. Deleting from Red-Black Trees B-Trees
 Algorithms Deleting from Red-Black Trees B-Trees Recall the rules for BST deletion 1. If vertex to be deleted is a leaf, just delete it. 2. If vertex to be deleted has just one child, replace it with that
Algorithms Deleting from Red-Black Trees B-Trees Recall the rules for BST deletion 1. If vertex to be deleted is a leaf, just delete it. 2. If vertex to be deleted has just one child, replace it with that
Multiway Search Trees. Multiway-Search Trees (cont d)
 Multiway Search Trees Each internal node v of a multi-way search tree T has at least two children contains d-1 items, where d is the number of children of v an item is of the form (k i,x i ) for 1 i d-1,
Multiway Search Trees Each internal node v of a multi-way search tree T has at least two children contains d-1 items, where d is the number of children of v an item is of the form (k i,x i ) for 1 i d-1,
Disjoint Sets. The obvious data structure for disjoint sets looks like this.
 CS61B Summer 2006 Instructor: Erin Korber Lecture 30: 15 Aug. Disjoint Sets Given a set of elements, it is often useful to break them up or partition them into a number of separate, nonoverlapping groups.
CS61B Summer 2006 Instructor: Erin Korber Lecture 30: 15 Aug. Disjoint Sets Given a set of elements, it is often useful to break them up or partition them into a number of separate, nonoverlapping groups.
C SCI 335 Software Analysis & Design III Lecture Notes Prof. Stewart Weiss Chapter 4: B Trees
 B-Trees AVL trees and other binary search trees are suitable for organizing data that is entirely contained within computer memory. When the amount of data is too large to fit entirely in memory, i.e.,
B-Trees AVL trees and other binary search trees are suitable for organizing data that is entirely contained within computer memory. When the amount of data is too large to fit entirely in memory, i.e.,
LECTURE 11 TREE TRAVERSALS
 DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS LECTURE 11 TREE TRAVERSALS IMRAN IHSAN ASSISTANT PROFESSOR AIR UNIVERSITY, ISLAMABAD BACKGROUND All the objects stored in an array or linked list can be accessed sequentially
DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS LECTURE 11 TREE TRAVERSALS IMRAN IHSAN ASSISTANT PROFESSOR AIR UNIVERSITY, ISLAMABAD BACKGROUND All the objects stored in an array or linked list can be accessed sequentially
Tree. A path is a connected sequence of edges. A tree topology is acyclic there is no loop.
 Tree A tree consists of a set of nodes and a set of edges connecting pairs of nodes. A tree has the property that there is exactly one path (no more, no less) between any pair of nodes. A path is a connected
Tree A tree consists of a set of nodes and a set of edges connecting pairs of nodes. A tree has the property that there is exactly one path (no more, no less) between any pair of nodes. A path is a connected
