Associative Containers and Iterators. Ali Malik
|
|
|
- Kelley McGee
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Associative Containers and Iterators Ali Malik
2 Game Plan Recap Associative Containers Iterators Map Iterators The auto keyword (maybe) Range-Based for Loops (maybe)
3 Recap
4 Structs You can define your own mini-types that bundle multiple variables together: struct point { int x; int y; }; Useful for Assignment 1
5 Overview of STL Algorithms Iterators Allocators Containers Functors/Lambdas Adapters
6 Overview of STL Algorithms Iterators Allocators Containers Functors/Lambdas Adapters
7 Sequence Containers Provides access to sequences of elements. Examples: std::vector<t> std::list<t> std::deque<t>
8 std::vector<t> Some new stuff there: const int knumints = 5; using vecsz_t = std::vector<int>::size_type; std::sort(vec.begin(), vec.end()); This let s us use vecsz_t as an alias/synonym for the type std::vector<int>::size_type;
9 std::deque<t> A deque (pronounced deck ) is a double ended queue. Can do everything a vector can do and also Unlike a vector, it is possible (and fast) to push_front and pop_front.
10 Container Adapters How can we implement stack and queue using the containers we have? Stack: Just limit the functionality of a vector/deque to only allow push_back and pop_back. Queue: Just limit the functionality of a deque to only allow push_back and pop_front. Plus only allow access to top element
11 Associative Containers
12 Associative Container Scenario: You want to count the frequency of words in a file. What do you use? vector<string>, vector<int>
13 Associative Container Scenario: You want to count the frequency of words in a file. What do you use? vector<string>, vector<int> We would need to keep two vectors with indexes denoting pairs
14 Associative Container Scenario: You want to count the frequency of words in a file. What do you use? vector<string>, vector<int>
15 Associative Container Scenario: You want to count the frequency of words in a file. What do you use? vector<string>, vector<int> vector<std::pair<string,int>>
16 Associative Container Scenario: You want to count the frequency of words in a file. What do you use? vector<string>, vector<int> vector<std::pair<string,int>> No quick way to lookup based on word
17 Associative Container Scenario: You want to count the frequency of words in a file. What do you use? vector<string>, vector<int> vector<std::pair<string,int>>
18 Associative Container Scenario: You want to count the frequency of words in a file. What do you use? vector<string>, vector<int> vector<std::pair<string,int>> std::map<string, int>
19 Associative Container Scenario: You want to count the frequency of words in a file. What do you use? vector<string>, vector<int> vector<std::pair<string,int>> std::map<string, int>
20 Associative Container It is useful to have a data structure that can associate values. Associative containers do exactly that!
21 Associative Container Have no idea of a sequence. Data is accessed using the key instead of indexes. std::map<t1, T2> std::set<t> std::unordered_map<t1, T2> std::unordered_set<t>
22 Associative Container Have no idea of a sequence. Data is accessed using the key instead of indexes. std::map<t1, T2> std::set<t> std::unordered_map<t1, T2> std::unordered_set<t>
23 Associative Container Have no idea of a sequence. Data is accessed using the key instead of indexes. std::map<t1, T2> std::set<t> std::unordered_map<t1, T2> std::unordered_set<t> Based on ordering property of keys. Keys need to be comparable using < (less than) operator.
24 Associative Container Have no idea of a sequence. Data is accessed using the key instead of indexes. std::map<t1, T2> std::set<t> std::unordered_map<t1, T2> std::unordered_set<t>
25 Associative Container Have no idea of a sequence. Data is accessed using the key instead of indexes. std::map<t1, T2> std::set<t> std::unordered_map<t1, T2> std::unordered_set<t>
26 Associative Container Have no idea of a sequence. Data is accessed using the key instead of indexes. std::map<t1, T2> std::set<t> std::unordered_map<t1, T2> std::unordered_set<t> Based on hash function. You need to define how the key can be hashed.
27 Associative Container Have no idea of a sequence. Data is accessed using the key instead of indexes. std::map<t1, T2> std::set<t> std::unordered_map<t1, T2> std::unordered_set<t>
28 Associative Container Have no idea of a sequence. Data is accessed using the key instead of indexes. std::map<t1, T2> std::set<t> std::unordered_map<t1, T2> std::unordered_set<t> You can define < and hash function operators for your own classes!
29 std::map<t1, T2> Methods mostly same as Stanford map. Check documentation for full list of methods. We can do a small example, counting frequency of words in a file: Map Example (MapExample.pro)
30 std::set<t> Methods mostly same as Stanford map. Check documentation for full list of methods. Key point: A set is just a specific case of a map that doesn t have a value. We can do a small example of adding and removing stuff: Set Example (SetExample.pro)
31 Announcements
32 Game Plan Recap Associative Containers Iterators Map Iterator The auto keyword Range-Based for Loops
33 Iterators How do we iterate over associative containers? Remember: Assoc. containers have no notion of a sequence/indexing for(int i = umm?; i < uhh?; i++ maybe?) {
34 Iterators How do we iterate over associative containers? Remember: Assoc. containers have no notion of a sequence/indexing for(int i = umm?; i < uhh?; i++ maybe?) {
35 Iterators How do we iterate over associative containers? Remember: Assoc. containers have no notion of a sequence/indexing for(int i = umm?; i < uhh?; i++ maybe?) { C++ has a solution!
36 Iterators
37 First: A note
38 A note We are going on a journey.
39 A note
40 A note We could in theory fly to the end destination.
41 A note
42 A note But then we would miss the experience
43 A note We are going on a journey.
44 A note We are going on a journey. At the end lies simplicity, but if we jump to it we miss out on understanding.
45 A note We are going on a journey. At the end lies simplicity, but if we jump to it we miss out on understanding. So we will walk to it.
46 Iterators
47 Iterators Iterators allow iteration over any container, whether it is ordered or not.
48 Iterators Let s try and get a mental model of iterators: Say we have a std::set<int> myset
49 Iterators Let s try and get a mental model of iterators: Say we have a std::set<int> myset 2 1 3
50 Iterators Let s try and get a mental model of iterators: Say we have a std::set<int> myset
51 Iterators Let s try and get a mental model of iterators: Say we have a std::set<int> myset Iterators let us view a non-linear collection in a linear manner
52 Iterators How do they work? We don t care right now. We will just use them like any other thing - assume they just work somehow.
53 Iterators - Usage Let s try and get a mental model of iterators:
54 Iterators - Usage Let s try and get a mental model of iterators: We can get an iterator pointing to the start of the sequence by calling myset.begin() myset.begin();
55 Iterators - Usage Let s try and get a mental model of iterators: myset.begin();
56 Iterators - Usage Let s try and get a mental model of iterators: How do we store it in a variable? myset.begin();
57 Iterators - Usage Let s try and get a mental model of iterators: ??? iter = myset.begin();
58 Iterators - Usage Let s try and get a mental model of iterators: What is the type of the iterator???? iter = myset.begin();
59 Iterators - Usage Let s try and get a mental model of iterators: What is the type of the iterator???? iter = myset.begin();
60 Iterators - Usage Let s try and get a mental model of iterators: ??? iter = myset.begin();
61 Iterators - Usage Let s try and get a mental model of iterators: set<int>::iterator iter = myset.begin();
62 Iterators - Usage Let s try and get a mental model of iterators: It is the iterator type defined in the set<int> class! set<int>::iterator iter = myset.begin();
63 Iterators - Usage Let s try and get a mental model of iterators: set<int>::iterator iter = myset.begin();
64 Iterators - Usage Let s try and get a mental model of iterators: 12 1 iter 2 3
65 Iterators - Usage Let s try and get a mental model of iterators: We can get the value of an iterator by using the dereference * operator iter 2 3
66 Iterators - Usage Let s try and get a mental model of iterators: We can get the value of an iterator by using the dereference * operator iter cout << *iter << endl; // prints 1
67 Iterators - Usage Let s try and get a mental model of iterators: 12 1 iter 2 3
68 Iterators - Usage Let s try and get a mental model of iterators: We can advance the iterator one by using the ++ operator (prefix) 12 1 iter 2 3
69 Iterators - Usage Let s try and get a mental model of iterators: We can advance the iterator one by using the ++ operator (prefix) iter ++iter; // advances iterator
70 Iterators - Usage Let s try and get a mental model of iterators: And so on iter 3
71 Iterators - Usage Let s try and get a mental model of iterators: And so on iter cout << *iter << endl; // prints 2
72 Iterators - Usage Let s try and get a mental model of iterators: And so on iter 3
73 Iterators - Usage Let s try and get a mental model of iterators: And so on iter ++iter; // advances iterator
74 Iterators - Usage Let s try and get a mental model of iterators: And so on iter
75 Iterators - Usage Let s try and get a mental model of iterators: And so on iter cout << *iter << endl; // prints 3
76 Iterators - Usage Let s try and get a mental model of iterators: And so on iter
77 Iterators - Usage Let s try and get a mental model of iterators: And so on iter ++iter; // advances iterator
78 Iterators - Usage Let s try and get a mental model of iterators: And so on iter
79 Iterators - Usage Let s try and get a mental model of iterators: And so on iter cout << *iter << endl; // prints
80 Iterators - Usage Let s try and get a mental model of iterators: And so on iter
81 Iterators - Usage Let s try and get a mental model of iterators: And so on iter ++iter; // advances iterator
82 Iterators - Usage Let s try and get a mental model of iterators: iter
83 Iterators - Usage Let s try and get a mental model of iterators: We can check if we have hit the end by comparing to myset.end() iter
84 Iterators - Usage Let s try and get a mental model of iterators: We can check if we have hit the end by comparing to myset.end() iter if(iter == myset.end()) return;
85 Iterators - Usage A summary of the essential iterator operations: Create iterator Dereference iterator to read value currently pointed to Advance iterator Compare against another iterator (especially.end() iterator)
86 Iterators - Usage Let s do some examples: Basic Iterator (BasicIter.pro)
87 Iterators Our examples have used sets, but (almost) all C++ containers have iterators. Why is this powerful? Many scenarios require looking at elements, regardless of what type of container is storing those elements. Iterators let us go through sequences of elements in a standardised way.
88 Iterators Example (find number occurrences): int numoccurences(vector<int>& cont, int elemtocount) { int counter = 0; vector<int>::iterator iter; for(iter = cont.begin(); iter!= cont.end(); ++iter) { if(*iter == elemtocount) ++counter; } return counter; }
89 Iterators Example (find number occurrences): Can I make this work for std::list<int>? int numoccurences(vector<int>& cont, int elemtocount) { int counter = 0; vector<int>::iterator iter; for(iter = cont.begin(); iter!= cont.end(); ++iter) { if(*iter == elemtocount) ++counter; } return counter; }
90 Iterators Example (find number occurrences): Can I make this work for std::list<int>? int numoccurences(vector<int>& cont, int elemtocount) { int counter = 0; vector<int>::iterator iter; for(iter = cont.begin(); iter!= cont.end(); ++iter) { if(*iter == elemtocount) ++counter; } return counter; }
91 Iterators Example (find number occurrences): int numoccurences(list<int>& cont, int elemtocount) { int counter = 0; list<int>::iterator iter; for(iter = cont.begin(); iter!= cont.end(); ++iter) { if(*iter == elemtocount) ++counter; } return counter; }
92 Iterators This standard interface for looping through things is going to be really powerful. We will cover it sometime this week or next week!
93 Map Iterators
94 Map Iterators Map iterators are slightly different because we have both keys and values. The iterator of a map<string, int> points to a std::pair<string, int>.
95 The std::pair Class A pair is simply two objects bundled together. Syntax: std::pair<string, int> p; p.first = "Phone number"; p.second = ;
96 Map Iterators Example: map<int, int> m; map<int, int>::iterator i = m.begin(); map<int, int>::iterator end = m.end(); while(i!= end) { cout << (*i).first << (*i).second << endl; ++i; }
97 Next Time Templates and Iterators
98
Advanced Associative Containers. Ali Malik
 Advanced Associative Containers Ali Malik malikali@stanford.edu Game Plan Recap Map Iterators Further Usage Multimap auto and Range Based for Recap Associative Containers Useful abstraction for associating
Advanced Associative Containers Ali Malik malikali@stanford.edu Game Plan Recap Map Iterators Further Usage Multimap auto and Range Based for Recap Associative Containers Useful abstraction for associating
Sequential Containers. Ali Malik
 Sequential Containers Ali Malik malikali@stanford.edu Game Plan Recap Overview of STL Sequence Containers std::vector std::deque Container Adapters Announcements Recap getline vs >> Bug favnum = fullname
Sequential Containers Ali Malik malikali@stanford.edu Game Plan Recap Overview of STL Sequence Containers std::vector std::deque Container Adapters Announcements Recap getline vs >> Bug favnum = fullname
Sequential Containers. Ali Malik
 Sequential Containers Ali Malik malikali@stanford.edu Game Plan Recap Stream wrapup Overview of STL Sequence Containers std::vector std::deque Container Adapters Announcements Recap stringstream Sometimes
Sequential Containers Ali Malik malikali@stanford.edu Game Plan Recap Stream wrapup Overview of STL Sequence Containers std::vector std::deque Container Adapters Announcements Recap stringstream Sometimes
Associative Containers & Iterators. Cristian Cibils
 Associative Containers & Iterators Cristian Cibils (ccibils@stanford.edu) Recap of Sequence Containers Sequence containers store data stored in order STL and Stanford sequence containers are similar but
Associative Containers & Iterators Cristian Cibils (ccibils@stanford.edu) Recap of Sequence Containers Sequence containers store data stored in order STL and Stanford sequence containers are similar but
Template based set of collection classes STL collection types (container types)
 STL Collection Types Template based set of collection classes STL collection types (container types) Sequences vector - collection of elements of type T list - doubly linked list, only sequential access
STL Collection Types Template based set of collection classes STL collection types (container types) Sequences vector - collection of elements of type T list - doubly linked list, only sequential access
SSE2034: System Software Experiment 3
 SSE2034: System Software Experiment 3 Spring 2016 Jinkyu Jeong (jinkyu@skku.edu) Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University http://csl.skku.edu STL Collection Types Template based set of collection
SSE2034: System Software Experiment 3 Spring 2016 Jinkyu Jeong (jinkyu@skku.edu) Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University http://csl.skku.edu STL Collection Types Template based set of collection
CSCI 104 C++ STL; Iterators, Maps, Sets. Mark Redekopp David Kempe
 CSCI 104 C++ STL; Iterators, Maps, Sets Mark Redekopp David Kempe Container Classes ArrayLists, LinkedList, Deques, etc. are classes used simply for storing (or contain) other items C++ Standard Template
CSCI 104 C++ STL; Iterators, Maps, Sets Mark Redekopp David Kempe Container Classes ArrayLists, LinkedList, Deques, etc. are classes used simply for storing (or contain) other items C++ Standard Template
CS197c: Programming in C++
 CS197c: Programming in C++ Lecture 2 Marc Cartright http://ciir.cs.umass.edu/~irmarc/cs197c/index.html Administration HW1 will be up this afternoon Written assignment Due in class next week See website
CS197c: Programming in C++ Lecture 2 Marc Cartright http://ciir.cs.umass.edu/~irmarc/cs197c/index.html Administration HW1 will be up this afternoon Written assignment Due in class next week See website
auto map<deque<string>, vector<string>> mymap; for(auto iter = mymap.begin(); iter!= mymap.end(); ++iter) {
 auto auto auto How can we clean this up better? The auto keyword! map mymap; for(auto iter = mymap.begin(); iter!= mymap.end(); ++iter) { } dosomething(*(iter).first, *(iter).second);
auto auto auto How can we clean this up better? The auto keyword! map mymap; for(auto iter = mymap.begin(); iter!= mymap.end(); ++iter) { } dosomething(*(iter).first, *(iter).second);
THE STANDARD TEMPLATE LIBRARY (STL) Week 6 BITE 1513 Computer Game Programming
 THE STANDARD TEMPLATE LIBRARY (STL) Week 6 BITE 1513 Computer Game Programming What the heck is STL???? Another hard to understand and lazy to implement stuff? Standard Template Library The standard template
THE STANDARD TEMPLATE LIBRARY (STL) Week 6 BITE 1513 Computer Game Programming What the heck is STL???? Another hard to understand and lazy to implement stuff? Standard Template Library The standard template
STL Quick Reference for CS 241
 STL Quick Reference for CS 241 Spring 2018 The purpose of this document is to provide basic information on those elements of the C++14 standard library we think are most likely to be needed in CS 241.
STL Quick Reference for CS 241 Spring 2018 The purpose of this document is to provide basic information on those elements of the C++14 standard library we think are most likely to be needed in CS 241.
EE 355 Unit 10. C++ STL - Vectors and Deques. Mark Redekopp
 1 EE 355 Unit 10 C++ STL - Vectors and Deques Mark Redekopp 2 Templates We ve built a list to store integers But what if we want a list of double s or char s or other objects We would have to define the
1 EE 355 Unit 10 C++ STL - Vectors and Deques Mark Redekopp 2 Templates We ve built a list to store integers But what if we want a list of double s or char s or other objects We would have to define the
Purpose of Review. Review some basic C++ Familiarize us with Weiss s style Introduce specific constructs useful for implementing data structures
 C++ Review 1 Purpose of Review Review some basic C++ Familiarize us with Weiss s style Introduce specific constructs useful for implementing data structures 2 Class The Class defines the data structure
C++ Review 1 Purpose of Review Review some basic C++ Familiarize us with Weiss s style Introduce specific constructs useful for implementing data structures 2 Class The Class defines the data structure
Functions. Ali Malik
 Functions Ali Malik malikali@stanford.edu Game Plan Recap Operator Overloading Functions Lambdas Announcements Recap Classes - Issues C++ doesn t know how to use operators on types defined by us An algorithm
Functions Ali Malik malikali@stanford.edu Game Plan Recap Operator Overloading Functions Lambdas Announcements Recap Classes - Issues C++ doesn t know how to use operators on types defined by us An algorithm
STL Containers, Part II
 CS106L Handout #08 Fall 2007 October 17, 2007 STL Containers, Part II Introduction Last week we talked about vector and deque, the STL's two managed array classes. However, the STL offers many other containers,
CS106L Handout #08 Fall 2007 October 17, 2007 STL Containers, Part II Introduction Last week we talked about vector and deque, the STL's two managed array classes. However, the STL offers many other containers,
Container Notes. Di erent Kinds of Containers. Types Defined by Containers. C++11 Container Notes C++11
 Di erent Kinds of Containers Container Notes A container is an object that stores other objects and has methods for accessing the elements. There are two fundamentally di erent kinds of containers: Sequences
Di erent Kinds of Containers Container Notes A container is an object that stores other objects and has methods for accessing the elements. There are two fundamentally di erent kinds of containers: Sequences
Sequence Containers. Cristian Cibils
 Sequence Containers Cristian Cibils (ccibils@stanford.edu) The Design of C++ Classes & Inheritance Algorithms Iterators Templates Containers Streams Atomic Types Structs A struct is an easy way to bundle
Sequence Containers Cristian Cibils (ccibils@stanford.edu) The Design of C++ Classes & Inheritance Algorithms Iterators Templates Containers Streams Atomic Types Structs A struct is an easy way to bundle
C++ Standard Template Library. Contents. Pierre Fierz. 1 Introduction. 2 Organization of STL Header Files. Organization of STL Header Files
 Contents Chapter 3 1 Lecture Advanced C++ 05.03.2012 2 3 4 Associative 5 Associative 6 Bernese University of Applied Sciences School of Engineering and Information Technology Division of Computer Science
Contents Chapter 3 1 Lecture Advanced C++ 05.03.2012 2 3 4 Associative 5 Associative 6 Bernese University of Applied Sciences School of Engineering and Information Technology Division of Computer Science
TDDD38 - Advanced programming in C++
 TDDD38 - Advanced programming in C++ STL II Christoffer Holm Department of Computer and information science 1 Iterators 2 Associative Containers 3 Container Adaptors 4 Lambda Functions 1 Iterators 2 Associative
TDDD38 - Advanced programming in C++ STL II Christoffer Holm Department of Computer and information science 1 Iterators 2 Associative Containers 3 Container Adaptors 4 Lambda Functions 1 Iterators 2 Associative
CS 103 Unit 12 Slides
 1 CS 103 Unit 12 Slides Standard Template Library Vectors & Deques Mark Redekopp 2 Templates We ve built a list to store integers But what if we want a list of double s or char s or other objects We would
1 CS 103 Unit 12 Slides Standard Template Library Vectors & Deques Mark Redekopp 2 Templates We ve built a list to store integers But what if we want a list of double s or char s or other objects We would
Standard Template Library
 Standard Template Library Wednesday, October 10, 2007 10:09 AM 9.3 "Quick Peek" STL history 1990s Alex Stepanov & Meng Lee of HP Labs 1994 ANSI/IS0 standard Components Container class templates Iterators
Standard Template Library Wednesday, October 10, 2007 10:09 AM 9.3 "Quick Peek" STL history 1990s Alex Stepanov & Meng Lee of HP Labs 1994 ANSI/IS0 standard Components Container class templates Iterators
CSCI 104 C++ STL; Iterators, Maps, Sets. Mark Redekopp David Kempe
 1 CSCI 104 C++ STL; Iterators, Maps, Sets Mark Redekopp David Kempe 2 Container Classes ArrayLists, LinkedList, Deques, etc. are classes used simply for storing (or contain) other items C++ Standard Template
1 CSCI 104 C++ STL; Iterators, Maps, Sets Mark Redekopp David Kempe 2 Container Classes ArrayLists, LinkedList, Deques, etc. are classes used simply for storing (or contain) other items C++ Standard Template
Functions. Ali Malik
 Functions Ali Malik malikali@stanford.edu Game Plan Recap Operator Overloading Functions Lambdas Announcements Recap Classes - Issues C++ doesn t know how to use operators on types defined by us: We can
Functions Ali Malik malikali@stanford.edu Game Plan Recap Operator Overloading Functions Lambdas Announcements Recap Classes - Issues C++ doesn t know how to use operators on types defined by us: We can
Dynamic Data Structures
 Dynamic Data Structures We have seen that the STL containers vector, deque, list, set and map can grow and shrink dynamically. We now examine how some of these containers can be implemented in C++. To
Dynamic Data Structures We have seen that the STL containers vector, deque, list, set and map can grow and shrink dynamically. We now examine how some of these containers can be implemented in C++. To
Lectures 11,12. Online documentation & links
 Lectures 11,12 1. Quicksort algorithm 2. Mergesort algorithm 3. Big O notation 4. Estimating computational efficiency of binary search, quicksort and mergesort algorithms 5. Basic Data Structures: Arrays
Lectures 11,12 1. Quicksort algorithm 2. Mergesort algorithm 3. Big O notation 4. Estimating computational efficiency of binary search, quicksort and mergesort algorithms 5. Basic Data Structures: Arrays
CS 103 Unit 15. Doubly-Linked Lists and Deques. Mark Redekopp
 1 CS 103 Unit 15 Doubly-Linked Lists and Deques Mark Redekopp 2 Singly-Linked List Review Used structures/classes and pointers to make linked data structures Singly-Linked Lists dynamically allocates each
1 CS 103 Unit 15 Doubly-Linked Lists and Deques Mark Redekopp 2 Singly-Linked List Review Used structures/classes and pointers to make linked data structures Singly-Linked Lists dynamically allocates each
CSCI-1200 Data Structures Spring 2018 Lecture 14 Associative Containers (Maps), Part 1 (and Problem Solving Too)
 CSCI-1200 Data Structures Spring 2018 Lecture 14 Associative Containers (Maps), Part 1 (and Problem Solving Too) HW6 NOTE: Do not use the STL map or STL pair for HW6. (It s okay to use them for the contest.)
CSCI-1200 Data Structures Spring 2018 Lecture 14 Associative Containers (Maps), Part 1 (and Problem Solving Too) HW6 NOTE: Do not use the STL map or STL pair for HW6. (It s okay to use them for the contest.)
Chapter 5. The Standard Template Library.
 Object-oriented programming B, Lecture 11e. 1 Chapter 5. The Standard Template Library. 5.1. Overview of main STL components. The Standard Template Library (STL) has been developed by Alexander Stepanov,
Object-oriented programming B, Lecture 11e. 1 Chapter 5. The Standard Template Library. 5.1. Overview of main STL components. The Standard Template Library (STL) has been developed by Alexander Stepanov,
6.096 Introduction to C++
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 6.096 Introduction to C++ January (IAP) 2009 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. Massachusetts Institute
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 6.096 Introduction to C++ January (IAP) 2009 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. Massachusetts Institute
CS 103 Unit 11. Linked Lists. Mark Redekopp
 1 CS 103 Unit 11 Linked Lists Mark Redekopp 2 NULL Pointer Just like there was a null character in ASCII = '\0' whose ue was 0 There is a NULL pointer whose ue is 0 NULL is "keyword" you can use in C/C++
1 CS 103 Unit 11 Linked Lists Mark Redekopp 2 NULL Pointer Just like there was a null character in ASCII = '\0' whose ue was 0 There is a NULL pointer whose ue is 0 NULL is "keyword" you can use in C/C++
STL: C++ Standard Library
 STL: C++ Standard Library Encapsulates complex data structures and algorithms CSC 330 OO Software Design 1 We ve emphasized the importance of software reuse. Recognizing that many data structures and algorithms
STL: C++ Standard Library Encapsulates complex data structures and algorithms CSC 330 OO Software Design 1 We ve emphasized the importance of software reuse. Recognizing that many data structures and algorithms
Ali Malik Handout 12 CS106L Winter 2018 Jan 30th, C++ Reference
 Ali Malik Handout 12 CS106L Winter 2018 Jan 30th, 2018 C++ Reference The purpose of this handout is to provide a summary and reference of the concepts covered in lecture as well as common constructs used
Ali Malik Handout 12 CS106L Winter 2018 Jan 30th, 2018 C++ Reference The purpose of this handout is to provide a summary and reference of the concepts covered in lecture as well as common constructs used
EE 355 Unit 11b. Doubly-Linked Lists and Deques. Mark Redekopp
 1 EE 355 Unit 11b Doubly-Linked Lists and Deques Mark Redekopp 2 Singly-Linked List Review Used structures/classes and pointers to make linked data structures Singly-Linked Lists dynamically allocates
1 EE 355 Unit 11b Doubly-Linked Lists and Deques Mark Redekopp 2 Singly-Linked List Review Used structures/classes and pointers to make linked data structures Singly-Linked Lists dynamically allocates
CSE 100: C++ TEMPLATES AND ITERATORS
 CSE 100: C++ TEMPLATES AND ITERATORS Announcements Gradesource and clickers: We ll be making one more pass for unregistered clickers tonight, but after that you ll be on your own How is Assignment 1 going?
CSE 100: C++ TEMPLATES AND ITERATORS Announcements Gradesource and clickers: We ll be making one more pass for unregistered clickers tonight, but after that you ll be on your own How is Assignment 1 going?
Arrays. Returning arrays Pointers Dynamic arrays Smart pointers Vectors
 Arrays Returning arrays Pointers Dynamic arrays Smart pointers Vectors To declare an array specify the type, its name, and its size in []s int arr1[10]; //or int arr2[] = {1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8}; arr2 has 8
Arrays Returning arrays Pointers Dynamic arrays Smart pointers Vectors To declare an array specify the type, its name, and its size in []s int arr1[10]; //or int arr2[] = {1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8}; arr2 has 8
Lectures 19, 20, 21. two valid iterators in [first, last) such that i precedes j, then *j is not less than *i.
 Lectures 19, 20, 21 1. STL library examples of applications Explanations: The member function pop_back removes the last element of the controlled sequence. The member function pop_front removes the first
Lectures 19, 20, 21 1. STL library examples of applications Explanations: The member function pop_back removes the last element of the controlled sequence. The member function pop_front removes the first
Modern and Lucid C++ for Professional Programmers. Part 7 Standard Containers & Iterators. Department I - C Plus Plus
 Department I - C Plus Plus Modern and Lucid C++ for Professional Programmers Part 7 Standard Containers & Iterators Prof. Peter Sommerlad / Thomas Corbat Rapperswil, 8.11.2017 HS2017 STL Containers: General
Department I - C Plus Plus Modern and Lucid C++ for Professional Programmers Part 7 Standard Containers & Iterators Prof. Peter Sommerlad / Thomas Corbat Rapperswil, 8.11.2017 HS2017 STL Containers: General
Today. andyoucanalsoconsultchapters6amd7inthetextbook. cis15-fall2007-parsons-lectvii.1 2
 TEMPLATES Today This lecture looks at techniques for generic programming: Generic pointers Templates The standard template library Thebestreferenceis: http://www.cppreference.com/index.html andyoucanalsoconsultchapters6amd7inthetextbook.
TEMPLATES Today This lecture looks at techniques for generic programming: Generic pointers Templates The standard template library Thebestreferenceis: http://www.cppreference.com/index.html andyoucanalsoconsultchapters6amd7inthetextbook.
CS11 Advanced C++ Fall Lecture 1
 CS11 Advanced C++ Fall 2006-2007 Lecture 1 Welcome! ~8 lectures Slides are posted on CS11 website http://www.cs.caltech.edu/courses/cs11 ~6 lab assignments More involved labs 2-3 week project at end CS
CS11 Advanced C++ Fall 2006-2007 Lecture 1 Welcome! ~8 lectures Slides are posted on CS11 website http://www.cs.caltech.edu/courses/cs11 ~6 lab assignments More involved labs 2-3 week project at end CS
Exceptions, Templates, and the STL
 Exceptions, Templates, and the STL CSE100 Principles of Programming with C++, Fall 2018 (based off Chapter 16 slides by Pearson) Ryan Dougherty Arizona State University http://www.public.asu.edu/~redoughe/
Exceptions, Templates, and the STL CSE100 Principles of Programming with C++, Fall 2018 (based off Chapter 16 slides by Pearson) Ryan Dougherty Arizona State University http://www.public.asu.edu/~redoughe/
Lecture 4a Using The Standard Template Library. Jack Applin, Guest Lecturer
 Lecture 4a Using The Standard Template Library Jack Applin, Guest Lecturer November 28 th, 2017 2017-12-04 CS253 Fall 2017 Bruce Draper 1 PA9 is online Announcements Efficiency assignment Same as PA8 But
Lecture 4a Using The Standard Template Library Jack Applin, Guest Lecturer November 28 th, 2017 2017-12-04 CS253 Fall 2017 Bruce Draper 1 PA9 is online Announcements Efficiency assignment Same as PA8 But
CSS 342 Data Structures, Algorithms, and Discrete Mathematics I. Standard Template Library
 CSS 342 Data Structures, Algorithms, and Discrete Mathematics I Standard Template Library 1 Standard Template Library Need to understand basic data types, so we build them ourselves Once understood, we
CSS 342 Data Structures, Algorithms, and Discrete Mathematics I Standard Template Library 1 Standard Template Library Need to understand basic data types, so we build them ourselves Once understood, we
CS 103 Unit 11. Linked Lists. Mark Redekopp
 1 CS 103 Unit 11 Linked Lists Mark Redekopp 2 NULL Pointer Just like there was a null character in ASCII = '\0' whose ue was 0 There is a NULL pointer whose ue is 0 NULL is "keyword" you can use in C/C++
1 CS 103 Unit 11 Linked Lists Mark Redekopp 2 NULL Pointer Just like there was a null character in ASCII = '\0' whose ue was 0 There is a NULL pointer whose ue is 0 NULL is "keyword" you can use in C/C++
The Standard Template Library Classes
 The Standard Template Library Classes Lecture 33 Sections 9.7, 9.8 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Apr 23, 2014 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) The Standard Template Library Classes
The Standard Template Library Classes Lecture 33 Sections 9.7, 9.8 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Apr 23, 2014 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) The Standard Template Library Classes
CSE 100: C++ TEMPLATES AND ITERATORS
 1 CSE 100: C++ TEMPLATES AND ITERATORS 2 Announcements Look out for the extra weekend section More on git and C++ (iterators) Live demo by your friendly tutors Not mandatory but it will be fun Bring your
1 CSE 100: C++ TEMPLATES AND ITERATORS 2 Announcements Look out for the extra weekend section More on git and C++ (iterators) Live demo by your friendly tutors Not mandatory but it will be fun Bring your
Sets and MultiSets. Contents. Steven J. Zeil. July 19, Overview of Sets and Maps 4
 Steven J. Zeil July 19, 2013 Contents 1 Overview of Sets and Maps 4 1 2 The Set ADT 6 2.1 The template header................................. 14 2.2 Internal type names.................................
Steven J. Zeil July 19, 2013 Contents 1 Overview of Sets and Maps 4 1 2 The Set ADT 6 2.1 The template header................................. 14 2.2 Internal type names.................................
Chapter 17: Linked Lists
 Chapter 17: Linked Lists 17.1 Introduction to the Linked List ADT Introduction to the Linked List ADT Linked list: set of data structures (nodes) that contain references to other data structures list head
Chapter 17: Linked Lists 17.1 Introduction to the Linked List ADT Introduction to the Linked List ADT Linked list: set of data structures (nodes) that contain references to other data structures list head
EL2310 Scientific Programming
 Lecture 16: STL, C++1y (ramviyas@kth.se) Overview Overview Lecture 16: STL and C++1y Reminders Wrap up C++11 Reminders The help sessions and deadline C++ help session: Fri 24.10.2015, 15:00-17:00, Room
Lecture 16: STL, C++1y (ramviyas@kth.se) Overview Overview Lecture 16: STL and C++1y Reminders Wrap up C++11 Reminders The help sessions and deadline C++ help session: Fri 24.10.2015, 15:00-17:00, Room
Prefix Trees Tables in Practice
 Prefix Trees CS 311 Data Structures and Algorithms Lecture Slides Friday, December 7, 2007 Glenn G. Chappell Department of Computer Science University of Alaska Fairbanks CHAPPELLG@member.ams.org 2005
Prefix Trees CS 311 Data Structures and Algorithms Lecture Slides Friday, December 7, 2007 Glenn G. Chappell Department of Computer Science University of Alaska Fairbanks CHAPPELLG@member.ams.org 2005
Lesson 13 - Vectors Dynamic Data Storage
 Lesson 13 - Vectors Dynamic Data Storage Summary In this lesson we introduce the Standard Template Library by demonstrating the use of Vectors to provide dynamic storage of data elements. New Concepts
Lesson 13 - Vectors Dynamic Data Storage Summary In this lesson we introduce the Standard Template Library by demonstrating the use of Vectors to provide dynamic storage of data elements. New Concepts
CPSC 427a: Object-Oriented Programming
 CPSC 427a: Object-Oriented Programming Michael J. Fischer Lecture 17 November 1, 2011 CPSC 427a, Lecture 17 1/21 CPSC 427a, Lecture 17 2/21 CPSC 427a, Lecture 17 3/21 A bit of history C++ standardization.
CPSC 427a: Object-Oriented Programming Michael J. Fischer Lecture 17 November 1, 2011 CPSC 427a, Lecture 17 1/21 CPSC 427a, Lecture 17 2/21 CPSC 427a, Lecture 17 3/21 A bit of history C++ standardization.
Const Correctness. Ali Malik
 Const Correctness Ali Malik malikali@stanford.edu Game Plan Recap Const Everything Prep for Next Time Announcements Recap Recap: References Another name for an already existing object. int x = 15; int
Const Correctness Ali Malik malikali@stanford.edu Game Plan Recap Const Everything Prep for Next Time Announcements Recap Recap: References Another name for an already existing object. int x = 15; int
STL Containers, Part I
 CS106L Handout #06 Fall 2007 October 10, 2007 STL Containers, Part I Introduction Arguably the most powerful library in the C++ language, the Standard Template Library (STL) is a programmer's dream. It
CS106L Handout #06 Fall 2007 October 10, 2007 STL Containers, Part I Introduction Arguably the most powerful library in the C++ language, the Standard Template Library (STL) is a programmer's dream. It
PIC 10A. Lecture 23: Intro to STL containers
 PIC 10A Lecture 23: Intro to STL containers STL STL stands for Standard Template Library There are many data structures that share similar features These data structures can be manipulated by a common
PIC 10A Lecture 23: Intro to STL containers STL STL stands for Standard Template Library There are many data structures that share similar features These data structures can be manipulated by a common
CSCI-1200 Data Structures Fall 2017 Lecture 9 Iterators & STL Lists
 Review from Lecture 8 CSCI-1200 Data Structures Fall 2017 Lecture 9 Iterators & STL Lists Designing our own container classes Dynamically allocated memory in classes Copy constructors, assignment operators,
Review from Lecture 8 CSCI-1200 Data Structures Fall 2017 Lecture 9 Iterators & STL Lists Designing our own container classes Dynamically allocated memory in classes Copy constructors, assignment operators,
Polymorphism. Programming in C++ A problem of reuse. Swapping arguments. Session 4 - Genericity, Containers. Code that works for many types.
 Session 4 - Genericity, Containers Polymorphism Code that works for many types. Dr Christos Kloukinas City, UoL http://staff.city.ac.uk/c.kloukinas/cpp (slides originally produced by Dr Ross Paterson)
Session 4 - Genericity, Containers Polymorphism Code that works for many types. Dr Christos Kloukinas City, UoL http://staff.city.ac.uk/c.kloukinas/cpp (slides originally produced by Dr Ross Paterson)
CSCI-1200 Data Structures Spring 2018 Lecture 10 Vector Iterators & Linked Lists
 CSCI-1200 Data Structures Spring 2018 Lecture 10 Vector Iterators & Linked Lists Review from Lecture 9 Explored a program to maintain a class enrollment list and an associated waiting list. Unfortunately,
CSCI-1200 Data Structures Spring 2018 Lecture 10 Vector Iterators & Linked Lists Review from Lecture 9 Explored a program to maintain a class enrollment list and an associated waiting list. Unfortunately,
CSCI-1200 Data Structures Spring 2016 Lecture 7 Iterators, STL Lists & Order Notation
 Today CSCI-1200 Data Structures Spring 2016 Lecture 7 Iterators, STL Lists & Order Notation Another vector operation: pop back Erasing items from vectors is inefficient! Iterators and iterator operations
Today CSCI-1200 Data Structures Spring 2016 Lecture 7 Iterators, STL Lists & Order Notation Another vector operation: pop back Erasing items from vectors is inefficient! Iterators and iterator operations
Sixth lecture; classes, objects, reference operator.
 Sixth lecture; classes, objects, reference operator. 1 Some notes on the administration of the class: From here on out, homework assignments should be a bit shorter, and labs a bit longer. My office hours
Sixth lecture; classes, objects, reference operator. 1 Some notes on the administration of the class: From here on out, homework assignments should be a bit shorter, and labs a bit longer. My office hours
C++ 프로그래밍실습. Visual Studio Smart Computing Laboratory
 C++ 프로그래밍실습 Visual Studio 2015 Contents STL Exercise Practice1 STL Practice 1-1 : Sets The insert method of set class ensures that the set does not contain duplicate keys Without specified position s.insert(123);
C++ 프로그래밍실습 Visual Studio 2015 Contents STL Exercise Practice1 STL Practice 1-1 : Sets The insert method of set class ensures that the set does not contain duplicate keys Without specified position s.insert(123);
Containers in C++ and Java
 Containers in C++ and Java 1 1. Which of the following statements is true? a) Equality on the basis of reference implies equality on the basis of content. b) Equality on the basis of content implies equality
Containers in C++ and Java 1 1. Which of the following statements is true? a) Equality on the basis of reference implies equality on the basis of content. b) Equality on the basis of content implies equality
1. The term STL stands for?
 1. The term STL stands for? a) Simple Template Library b) Static Template Library c) Single Type Based Library d) Standard Template Library Answer : d 2. Which of the following statements regarding the
1. The term STL stands for? a) Simple Template Library b) Static Template Library c) Single Type Based Library d) Standard Template Library Answer : d 2. Which of the following statements regarding the
The Standard Template Library. EECS 211 Winter 2018
 The Standard Template Library EECS 211 Winter 2018 2 Problem: finding the maximum element of a vector A simple fixed-size vector struct: struct Int_vec int* data; size_t size; ; 3 Solution: max_int_vec
The Standard Template Library EECS 211 Winter 2018 2 Problem: finding the maximum element of a vector A simple fixed-size vector struct: struct Int_vec int* data; size_t size; ; 3 Solution: max_int_vec
EL2310 Scientific Programming
 Lecture 14: Object Oriented Programming in C++ (fpokorny@kth.se) Overview Overview Lecture 14: Object Oriented Programming in C++ Wrap Up Introduction to Object Oriented Paradigm Classes More on Classes
Lecture 14: Object Oriented Programming in C++ (fpokorny@kth.se) Overview Overview Lecture 14: Object Oriented Programming in C++ Wrap Up Introduction to Object Oriented Paradigm Classes More on Classes
Recap: Pointers. int* int& *p &i &*&* ** * * * * IFMP 18, M. Schwerhoff
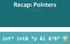 Recap: Pointers IFMP 18, M. Schwerhoff int* int& *p &i &*&* ** * * * * A 0 A 1 A 2 A 3 A 4 A 5 A 0 A 1 A 2 A 3 A 4 A 5 5 i int* p; A 0 A 1 A 2 A 3 A 4 A 5 5 i p int* p; p = &i; A 0 A 1 A 2 A 3 A 4 A 5
Recap: Pointers IFMP 18, M. Schwerhoff int* int& *p &i &*&* ** * * * * A 0 A 1 A 2 A 3 A 4 A 5 A 0 A 1 A 2 A 3 A 4 A 5 5 i int* p; A 0 A 1 A 2 A 3 A 4 A 5 5 i p int* p; p = &i; A 0 A 1 A 2 A 3 A 4 A 5
! Search: find a given target item in an array, ! Linear Search: Very simple search method: ! Operators such as =, +, <, and others can be
 Operator Overloading and Templates Week 6 Gaddis: 8.1, 14.5, 16.2-16.4 CS 5301 Spring 2015 Jill Seaman Linear Search! Search: find a given target item in an array, return the index of the item, or -1 if
Operator Overloading and Templates Week 6 Gaddis: 8.1, 14.5, 16.2-16.4 CS 5301 Spring 2015 Jill Seaman Linear Search! Search: find a given target item in an array, return the index of the item, or -1 if
CSCI-1200 Data Structures Fall 2013 Lecture 9 Iterators & Lists
 Review from Lecture 8 CSCI-1200 Data Structures Fall 2013 Lecture 9 Iterators & Lists Explored a program to maintain a class enrollment list and an associated waiting list. Unfortunately, erasing items
Review from Lecture 8 CSCI-1200 Data Structures Fall 2013 Lecture 9 Iterators & Lists Explored a program to maintain a class enrollment list and an associated waiting list. Unfortunately, erasing items
Type Aliases. Examples: using newtype = existingtype; // C++11 typedef existingtype newtype; // equivalent, still works
 Type Aliases A name may be defined as a synonym for an existing type name. Traditionally, typedef is used for this purpose. In the new standard, an alias declaration can also be used C++11.Thetwoformsareequivalent.
Type Aliases A name may be defined as a synonym for an existing type name. Traditionally, typedef is used for this purpose. In the new standard, an alias declaration can also be used C++11.Thetwoformsareequivalent.
Programming Abstractions
 Programming Abstractions C S 1 0 6 X Cynthia Lee Today s Topics ADTs Stack Example: Reverse-Polish Notation calculator Queue Example: Mouse Events Stacks New ADT: Stack stack.h template
Programming Abstractions C S 1 0 6 X Cynthia Lee Today s Topics ADTs Stack Example: Reverse-Polish Notation calculator Queue Example: Mouse Events Stacks New ADT: Stack stack.h template
2014 Spring CS140 Final Exam - James Plank
 2014 Spring CS140 Final Exam - James Plank Question 1 - Big O Part A: Suppose my friend Fred wants to prove the following statement: 5n 3 + 500 log 2 (n) = O(n 3 ) To do that, Fred is going to have to
2014 Spring CS140 Final Exam - James Plank Question 1 - Big O Part A: Suppose my friend Fred wants to prove the following statement: 5n 3 + 500 log 2 (n) = O(n 3 ) To do that, Fred is going to have to
CSCI-1200 Data Structures Fall 2010 Lecture 8 Iterators
 CSCI-1200 Data Structures Fall 2010 Lecture 8 Iterators Review from Lecture 7 Designing our own container classes Dynamically allocated memory in classes Copy constructors, assignment operators, and destructors
CSCI-1200 Data Structures Fall 2010 Lecture 8 Iterators Review from Lecture 7 Designing our own container classes Dynamically allocated memory in classes Copy constructors, assignment operators, and destructors
CS183 Software Design. Textbooks. Grading Criteria. CS183-Su02-Lecture 1 20 May by Eric A. Durant, Ph.D. 1
 CS183 Software Design Dr. Eric A. Durant Email: durant@msoe.edu Web: http://people.msoe.edu/~durant/ courses/cs183 (coming soon) Office: CC43 (enter through CC27) Phone: 277-7439 1 Textbooks Required (same
CS183 Software Design Dr. Eric A. Durant Email: durant@msoe.edu Web: http://people.msoe.edu/~durant/ courses/cs183 (coming soon) Office: CC43 (enter through CC27) Phone: 277-7439 1 Textbooks Required (same
To know the relationships among containers, iterators, and algorithms ( 22.2).
 CHAPTER 22 STL Containers Objectives To know the relationships among containers, iterators, and algorithms ( 22.2). To distinguish sequence containers, associative containers, and container adapters (
CHAPTER 22 STL Containers Objectives To know the relationships among containers, iterators, and algorithms ( 22.2). To distinguish sequence containers, associative containers, and container adapters (
EE 355 Unit 13 C++ STL; Iterators, Maps, Sets. Mark Redekopp
 1 EE 355 Unit 13 C++ STL; Iterators, Maps, Sets Mark Redekopp 2 No more 'for(i=0; i < max; i++)' ITERATORS 3 Arrays Review Arrays are contiguous pieces of memory To find a single value, computer only needs
1 EE 355 Unit 13 C++ STL; Iterators, Maps, Sets Mark Redekopp 2 No more 'for(i=0; i < max; i++)' ITERATORS 3 Arrays Review Arrays are contiguous pieces of memory To find a single value, computer only needs
C++ Programming Lecture 2 Software Engineering Group
 C++ Programming Lecture 2 Software Engineering Group Philipp D. Schubert Contents 1. Compiler errors 2. Functions 3. std::string 4. std::vector 5. Containers 6. Pointer and reference types Compiler errors
C++ Programming Lecture 2 Software Engineering Group Philipp D. Schubert Contents 1. Compiler errors 2. Functions 3. std::string 4. std::vector 5. Containers 6. Pointer and reference types Compiler errors
CSE100. Advanced Data Structures. Lecture 4. (Based on Paul Kube course materials)
 CSE100 Advanced Data Structures Lecture 4 (Based on Paul Kube course materials) Lecture 4 Binary search trees Toward a binary search tree implementation using C++ templates Reading: Weiss Ch 4, sections
CSE100 Advanced Data Structures Lecture 4 (Based on Paul Kube course materials) Lecture 4 Binary search trees Toward a binary search tree implementation using C++ templates Reading: Weiss Ch 4, sections
Programming Abstractions
 Programming Abstractions C S 1 0 6 B Cynthia Lee Compound Containers I t s t u r t l e s a l l t h e w a y down Comparing two similar codes: Vector numbers; numbers.add(1); numbers.add(2); numbers.add(3);
Programming Abstractions C S 1 0 6 B Cynthia Lee Compound Containers I t s t u r t l e s a l l t h e w a y down Comparing two similar codes: Vector numbers; numbers.add(1); numbers.add(2); numbers.add(3);
Using Associative Containers
 Using Associative Containers Lecture 18 Hartmut Kaiser hkaiser@cct.lsu.edu http://www.cct.lsu.edu/ hkaiser/spring_2015/csc1254.html Programming Principle of the Day Single Responsibility Principle - A
Using Associative Containers Lecture 18 Hartmut Kaiser hkaiser@cct.lsu.edu http://www.cct.lsu.edu/ hkaiser/spring_2015/csc1254.html Programming Principle of the Day Single Responsibility Principle - A
STL components. STL: C++ Standard Library Standard Template Library (STL) Main Ideas. Components. Encapsulates complex data structures and algorithms
 STL: C++ Standard Library Standard Template Library (STL) Encapsulates complex data structures and algorithms is a library of generic container classes which are both efficient and functional C++ STL developed
STL: C++ Standard Library Standard Template Library (STL) Encapsulates complex data structures and algorithms is a library of generic container classes which are both efficient and functional C++ STL developed
CSCI-1200 Data Structures Fall 2014 Lecture 8 Iterators
 Review from Lecture 7 CSCI-1200 Data Structures Fall 2014 Lecture 8 Iterators Designing our own container classes Dynamically allocated memory in classes Copy constructors, assignment operators, and destructors
Review from Lecture 7 CSCI-1200 Data Structures Fall 2014 Lecture 8 Iterators Designing our own container classes Dynamically allocated memory in classes Copy constructors, assignment operators, and destructors
Outline. Variables Automatic type inference. Generic programming. Generic programming. Templates Template compilation
 Outline EDAF30 Programming in C++ 4. The standard library. Algorithms and containers. Sven Gestegård Robertz Computer Science, LTH 2018 1 Type inference 2 3 The standard library Algorithms Containers Sequences
Outline EDAF30 Programming in C++ 4. The standard library. Algorithms and containers. Sven Gestegård Robertz Computer Science, LTH 2018 1 Type inference 2 3 The standard library Algorithms Containers Sequences
CSC 427: Data Structures and Algorithm Analysis. Fall 2004
 CSC 47: Data Structures and Algorithm Analysis Fall 4 Associative containers STL data structures and algorithms sets: insert, find, erase, empty, size, begin/end maps: operator[], find, erase, empty, size,
CSC 47: Data Structures and Algorithm Analysis Fall 4 Associative containers STL data structures and algorithms sets: insert, find, erase, empty, size, begin/end maps: operator[], find, erase, empty, size,
Programming Abstractions
 Programming Abstractions C S 1 0 6 B Cynthia Lee Today s Topics ADTs Containers within containers Example: anagram finder Recursion First steps in this fun/crazy new concept Factorial! Compound Containers
Programming Abstractions C S 1 0 6 B Cynthia Lee Today s Topics ADTs Containers within containers Example: anagram finder Recursion First steps in this fun/crazy new concept Factorial! Compound Containers
STL. Prof Tejada Week 14
 STL Prof Tejada Week 14 Standard Template Library (STL) What is the STL? A generic collection of commonly used data structures and algorithms In 1994, STL was adopted as a standard part of C++ Why used
STL Prof Tejada Week 14 Standard Template Library (STL) What is the STL? A generic collection of commonly used data structures and algorithms In 1994, STL was adopted as a standard part of C++ Why used
Queue Implementations
 Queue Implementations 1 Circular Queues buffer of fixed capacity improvements and cost estimates 2 Deques the double ended queue queue as double linked circular list MCS 360 Lecture 17 Introduction to
Queue Implementations 1 Circular Queues buffer of fixed capacity improvements and cost estimates 2 Deques the double ended queue queue as double linked circular list MCS 360 Lecture 17 Introduction to
C++: Overview and Features
 C++: Overview and Features Richard Newman r.newman@rdg.ac.uk Room CS127 2003-12-11 Programming & Design, 2003 1 Introduction You have: used streams seen how classes are used seen some C++ code Today: good
C++: Overview and Features Richard Newman r.newman@rdg.ac.uk Room CS127 2003-12-11 Programming & Design, 2003 1 Introduction You have: used streams seen how classes are used seen some C++ code Today: good
CSE 250: Data Structures Fall 2015 Sample Final Exam
 Preferred Name: UBIT: CSE 250: Data Structures Fall 2015 Sample Final Exam DIRECTIONS: Closed Notes. Closed Book. No electronics. Time Limit: 3 hours Make sure you write your NAME and UBIT above. Note
Preferred Name: UBIT: CSE 250: Data Structures Fall 2015 Sample Final Exam DIRECTIONS: Closed Notes. Closed Book. No electronics. Time Limit: 3 hours Make sure you write your NAME and UBIT above. Note
Lecture on pointers, references, and arrays and vectors
 Lecture on pointers, references, and arrays and vectors pointers for example, check out: http://www.programiz.com/cpp-programming/pointers [the following text is an excerpt of this website] #include
Lecture on pointers, references, and arrays and vectors pointers for example, check out: http://www.programiz.com/cpp-programming/pointers [the following text is an excerpt of this website] #include
Chapter 17: Linked Lists
 Chapter 17: Linked Lists Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Copyright Publishing as Pearson 2009 Pearson Addison-Wesley Education, Inc. Publishing as Pearson Addison-Wesley 17.1 Introduction to the
Chapter 17: Linked Lists Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Copyright Publishing as Pearson 2009 Pearson Addison-Wesley Education, Inc. Publishing as Pearson Addison-Wesley 17.1 Introduction to the
Patterns: Working with Arrays
 Steven Zeil October 14, 2013 Outline 1 Static & Dynamic Allocation Static Allocation Dynamic Allocation 2 Partially Filled Arrays Adding Elements Searching for Elements Removing Elements 3 Arrays and Templates
Steven Zeil October 14, 2013 Outline 1 Static & Dynamic Allocation Static Allocation Dynamic Allocation 2 Partially Filled Arrays Adding Elements Searching for Elements Removing Elements 3 Arrays and Templates
Pointers, Dynamic Data, and Reference Types
 Pointers, Dynamic Data, and Reference Types Review on Pointers Reference Variables Dynamic Memory Allocation The new operator The delete operator Dynamic Memory Allocation for Arrays 1 C++ Data Types simple
Pointers, Dynamic Data, and Reference Types Review on Pointers Reference Variables Dynamic Memory Allocation The new operator The delete operator Dynamic Memory Allocation for Arrays 1 C++ Data Types simple
Exam 3 Chapters 7 & 9
 Exam 3 Chapters 7 & 9 CSC 2100-002/003 29 Mar 2017 Read through the entire test first BEFORE starting Put your name at the TOP of every page The test has 4 sections worth a total of 100 points o True/False
Exam 3 Chapters 7 & 9 CSC 2100-002/003 29 Mar 2017 Read through the entire test first BEFORE starting Put your name at the TOP of every page The test has 4 sections worth a total of 100 points o True/False
Exercise 6.2 A generic container class
 Exercise 6.2 A generic container class The goal of this exercise is to write a class Array that mimics the behavior of a C++ array, but provides more intelligent memory management a) Start with the input
Exercise 6.2 A generic container class The goal of this exercise is to write a class Array that mimics the behavior of a C++ array, but provides more intelligent memory management a) Start with the input
COMP6771 Advanced C++ Programming
 1. COMP6771 Advanced C++ Programming Week 7 Part One: Member Templates and 2016 www.cse.unsw.edu.au/ cs6771 2. Member Templates Consider this STL code: 1 #include 2 #include 3 #include
1. COMP6771 Advanced C++ Programming Week 7 Part One: Member Templates and 2016 www.cse.unsw.edu.au/ cs6771 2. Member Templates Consider this STL code: 1 #include 2 #include 3 #include
Lecture 12. Monday, February 7 CS 215 Fundamentals of Programming II - Lecture 12 1
 Lecture 12 Log into Linux. Copy files on csserver in /home/hwang/cs215/lecture12/*.* Reminder: Practical Exam 1 is Wednesday 3pm-5pm in KC-267. Questions about Project 2 or Homework 6? Submission system
Lecture 12 Log into Linux. Copy files on csserver in /home/hwang/cs215/lecture12/*.* Reminder: Practical Exam 1 is Wednesday 3pm-5pm in KC-267. Questions about Project 2 or Homework 6? Submission system
EL2310 Scientific Programming
 Lecture 15: Inheritance and Polymorphism, STL (pronobis@kth.se) Overview Overview Lecture 15: Inheritance and Polymorphism, STL Wrap Up Additional Bits about Classes Overloading Inheritance Polymorphism
Lecture 15: Inheritance and Polymorphism, STL (pronobis@kth.se) Overview Overview Lecture 15: Inheritance and Polymorphism, STL Wrap Up Additional Bits about Classes Overloading Inheritance Polymorphism
CSE 374 Programming Concepts & Tools. Hal Perkins Spring 2010
 CSE 374 Programming Concepts & Tools Hal Perkins Spring 2010 Lecture 19 Introduction ti to C++ C++ C++ is an enormous language: g All of C Classes and objects (kind of like Java, some crucial differences)
CSE 374 Programming Concepts & Tools Hal Perkins Spring 2010 Lecture 19 Introduction ti to C++ C++ C++ is an enormous language: g All of C Classes and objects (kind of like Java, some crucial differences)
Templates and Vectors
 Templates and Vectors 1 Generic Programming function templates class templates 2 the STL vector class a vector of strings enumerating elements with an iterator inserting and erasing 3 Writing our own vector
Templates and Vectors 1 Generic Programming function templates class templates 2 the STL vector class a vector of strings enumerating elements with an iterator inserting and erasing 3 Writing our own vector
CSE 100: C++ TEMPLATES AND ITERATORS
 CSE 100: C++ TEMPLATES AND ITERATORS Announcements iclickers: Please register at ted.ucsd.edu. Start ASAP!! For PA1 (Due next week). 10/6 grading and 10/8 regrading How is Assignment 1 going? A. I haven
CSE 100: C++ TEMPLATES AND ITERATORS Announcements iclickers: Please register at ted.ucsd.edu. Start ASAP!! For PA1 (Due next week). 10/6 grading and 10/8 regrading How is Assignment 1 going? A. I haven
CSI33 Data Structures
 Outline Department of Mathematics and Computer Science Bronx Community College November 22, 2017 Outline Outline 1 Chapter 12: C++ Templates Outline Chapter 12: C++ Templates 1 Chapter 12: C++ Templates
Outline Department of Mathematics and Computer Science Bronx Community College November 22, 2017 Outline Outline 1 Chapter 12: C++ Templates Outline Chapter 12: C++ Templates 1 Chapter 12: C++ Templates
