Arithmetic Circuits. Design of Digital Circuits 2014 Srdjan Capkun Frank K. Gürkaynak.
|
|
|
- Paul Little
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Arithmetic Circuits Design of Digital Circuits 2014 Srdjan Capkun Frank K. Gürkaynak Adapted from Digital Design and Computer Architecture, David Money Harris & Sarah L. Harris 2007 Elsevier 1
2 In This Lecture Why are arithmetic circuits so important Adders Adding two binary numbers Adding more than two binary numbers Circuits Based on Adders Multipliers Functions that do not use adders Arithmetic Logic Units 2
3 Motivation: Arithmetic Circuits Core of every digital circuit Everything else is side-dish, arithmetic circuits are the heart of the digital system Determines the performance of the system Dictates clock rate, speed, area If arithmetic circuits are optimized performance will improve Opportunities for improvement ovel algorithms require novel combinations of arithmetic circuits, there is always room for improvement 3
4 Example: ARM Microcontroller Most popular embedded micro controller. Contains: Multiplier Accumulator ALU/Adder Shifter Incrementer 4
5 Example: ARM Instructions 5
6 Arithmetic Based Instructions of ARM 6
7 Types of Arithmetic Circuits In order of complexity: Shift / Rotate Compare Increment / Decrement egation Addition / Subtraction Multiplication Division Square Root Exponentation Logarithmic / Trigonometric Functions 7
8 Relation Between Arithmetic Operators 8
9 Addition Addition is the most important operation in computer arithmetic. Our topics will be: Adding 1-bit numbers : Counting bits Adding two numbers : Basics of addition Circuits based on adders : Subtractors, Comparators Adding multiple numbers : Chains of Adders Later we will also talk about fast adder architectures 9
10 Half-Adder (2,2) Counter The Half Adder (HA) is the simplest arithmetic block It can add two 1-bit numbers, result is a 2-bit number Can be realized easily 10
11 Full-Adder (3,2) Counter The Full Adder (FA) is the essential arithmetic block It can add three 1-bit numbers, result is a 2-bit number There are many realizations both at gate and transistor level. Since it is used in building many arithmetic operations, the performance of one FA influences the overall performance greatly. 11
12 Adding Multiple 1-bit umbers 12
13 Adding Multiple Digits Similar to decimal addition Starting from the right, each digit is added The carry from one digit is added to the digit to the left 13
14 Adding Multiple Digits Similar to decimal addition Starting from the right, each digit is added The carry from one digit is added to the digit to the left 14
15 Ripple Carry Adder (RCA) 15
16 Curse of the Carry The most significant outputs of the adder depends on the least significant inputs 16
17 Adding Multiple umbers Multiple fast adders not a good idea If more than 2 numbers are to be added, multiple fast adders are not really efficient Use an array of ripple carry adders Popular and efficient solution Use carry save adder trees Instead of using carry propagate adders (the adders we have seen so far), carry save adders are used to reduce multiple inputs to two, and then a single carry propagate adder is used to sum up. 17
18 Array of Ripple Carry Adders 18
19 Carry Save Principle Reduces three numbers to two with a single gate delay C + S = E + F + G 19
20 Carry Save Principle Z = D + E + F + G + H An array of carry save adders reduce the inputs to two A final (fast) carry propagate adder (CPA) merges the two numbers Performance mostly dictated by CPA 20
21 Multipliers Largest common arithmetic block Requires a lot of calculation Has three parts Partial Product Generation Carry Save Tree to reduce partial products Carry Propagate Adder to finalize the addition Adder performance (once again) is important Many optimization alternatives 21
22 Decimal Multiplication 22
23 Binary Multiplication 23
24 For n-bit Multiplier m-bit Multiplicand Generate Partial Products For each bit of the multiplier the partial product is either when 0 : all zeroes when 1 : the multiplicand achieved easily by AD gates Reduce Partial Products This is the job of a carry save adder Generate the Result (n + m bits) This is a large, fast Carry Propagate Adder 24
25 Parallel Multiplier 25
26 Parallel Multiplier 26
27 Operations Based on Adders Several well-known arithmetic operation are based on adders: egator Incrementer Subtracter Adder Subtracter Comparator 27
28 egating Two s Complement umbers To negate a two s complement number -A = A + 1 All bits are inverted One is added to the result Can be realized easily by an adder. B input is optimized away 28
29 Incrementer B input is zero Carry In (C in ) of the adder can be used as the Increment (Inc) input Decrementer similar in principle 29
30 Subtracter B input is inverted C in of the adder is used to complement B 30
31 Subtracter B input is inverted C in of the adder is used to complement B It can be made programmable so that both additions and subtractions can be performed at the same time 31
32 Comparator Based on a Subtractor (A = B) = EQ (A!= B) = EQ (A > B) = GE EQ (A >= B) = GE (A < B) = GE (A <= B) = GE + EQ 32
33 Functions Realized Without Adders ot all arithmetic functions are realized by using adders Shift / Rotate Units Binary Logic functions are also used by processors AD OR XOR OT These are implemented very easily 33
34 Shifters Logical shifter: shifts value to left or right and fills empty spaces with 0 s Ex: >> 2 =?? Ex: << 2 =?? Arithmetic shifter: same as logical shifter, but on right shift, fills empty spaces with the old most significant bit (msb). Ex: >>> 2 =?? Ex: <<< 2 =?? Rotator: rotates bits in a circle, such that bits shifted off one end are shifted into the other end Ex: ROR 2 =?? Ex: ROL 2 =?? 34
35 Shifters Logical shifter: shifts value to left or right and fills empty spaces with 0 s Ex: >> 2 = Ex: << 2 = Arithmetic shifter: same as logical shifter, but on right shift, fills empty spaces with the old most significant bit (msb). Ex: >>> 2 = Ex: <<< 2 = Rotator: rotates bits in a circle, such that bits shifted off one end are shifted into the other end Ex: ROR 2 = Ex: ROL 2 =
36 Shifter Design A 3 A 2 A 1 A 0 shamt 1: S 1: Y 3 11 shamt 1:0 A 3:0 >> Y 3: S 1:0 S 1:0 Y 2 10 Y S 1:0 10 Y
37 Shifters as Multipliers and Dividers A left shift by bits multiplies a number by 2 Ex: << 2 = (1 2 2 = 4) Ex: << 2 = ( = -12) The arithmetic right shift by divides a number by 2 Ex: >>> 2 = (8 2 2 = 2) Ex: >>> 2 = ( = -4) 37
38 Other Functions We have covered 90% of the arithmetic functions commonly used in a CPU Division Dedicated architectures not very common Mostly implemented by existing hardware (multipliers, subtractors comparators) iteratively Exponential, Logarithmic, Trigonometric Functions Dedicated hardware (less common) umerical approximations: exp(x) = 1 + x 2 /2! + x 3 /3! + Look-up tables (more common) 38
39 Arithmetic Logic Unit The reason why we study digital circuits: the part of the CPU that does something (other than copying data) Defines the basic operations that the CPU can perform directly Other functions can be realized using the existing ones iteratively. (i.e. multiplication can be realized by shifting and adding) Mostly, a collection of resources that work in parallel. Depending on the operation one of the outputs is selected 39
40 Example: Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU), pg243 F 2:0 Function A ALU B 3 F 000 A & B 001 A B 010 A + B 011 not used 100 A & ~B Y 101 A ~B 110 A - B 111 SLT 40
41 3 Zero Extend Carnegie Mellon Example: ALU Design F 2:0 Function A B 000 A & B 001 A B 010 A + B F not used C out + [-1] S 100 A & ~B 2 F 1:0 101 A ~B Y 110 A - B 111 SLT 41
42 3 Zero Extend Carnegie Mellon Set Less Than (SLT) Example A B F 2 Configure a 32-bit ALU for the set if less than (SLT) operation. Suppose A = 25 and B = 32. A is less than B, so we expect Y to be the 32-bit representation of 1 (0x ). C out + [-1] S 2 F 1:0 Y 42
43 3 Zero Extend Carnegie Mellon Set Less Than (SLT) Example C out A + Y B [-1] S 2 F 2 F 1:0 Configure a 32-bit ALU for the set if less than (SLT) operation. Suppose A = 25 and B = 32. A is less than B, so we expect Y to be the 32-bit representation of 1 (0x ). For SLT, F 2:0 = 111. F2 = 1 configures the adder unit as a subtracter. So = -7. The two s complement representation of -7 has a 1 in the most significant bit, so S 31 = 1. With F 1:0 = 11, the final multiplexer selects Y = S 31 (zero extended) = 0x
44 What Did We Learn? How can we add, subtract, multiply binary numbers What other circuits depend on adders Subtracter Incrementer Comparator Important part of Multiplier Other functions (shifting) How is an Arithmetic Logic Unit constructed 44
Arithmetic Logic Unit. Digital Computer Design
 Arithmetic Logic Unit Digital Computer Design Arithmetic Circuits Arithmetic circuits are the central building blocks of computers. Computers and digital logic perform many arithmetic functions: addition,
Arithmetic Logic Unit Digital Computer Design Arithmetic Circuits Arithmetic circuits are the central building blocks of computers. Computers and digital logic perform many arithmetic functions: addition,
Chapter 5. Digital Design and Computer Architecture, 2 nd Edition. David Money Harris and Sarah L. Harris. Chapter 5 <1>
 Chapter 5 Digital Design and Computer Architecture, 2 nd Edition David Money Harris and Sarah L. Harris Chapter 5 Chapter 5 :: Topics Introduction Arithmetic Circuits umber Systems Sequential Building
Chapter 5 Digital Design and Computer Architecture, 2 nd Edition David Money Harris and Sarah L. Harris Chapter 5 Chapter 5 :: Topics Introduction Arithmetic Circuits umber Systems Sequential Building
Digital Logic & Computer Design CS Professor Dan Moldovan Spring 2010
 Digital Logic & Computer Design CS 434 Professor Dan Moldovan Spring 2 Copyright 27 Elsevier 5- Chapter 5 :: Digital Building Blocks Digital Design and Computer Architecture David Money Harris and Sarah
Digital Logic & Computer Design CS 434 Professor Dan Moldovan Spring 2 Copyright 27 Elsevier 5- Chapter 5 :: Digital Building Blocks Digital Design and Computer Architecture David Money Harris and Sarah
Lecture Topics. Announcements. Today: Integer Arithmetic (P&H ) Next: continued. Consulting hours. Introduction to Sim. Milestone #1 (due 1/26)
 Lecture Topics Today: Integer Arithmetic (P&H 3.1-3.4) Next: continued 1 Announcements Consulting hours Introduction to Sim Milestone #1 (due 1/26) 2 1 Overview: Integer Operations Internal representation
Lecture Topics Today: Integer Arithmetic (P&H 3.1-3.4) Next: continued 1 Announcements Consulting hours Introduction to Sim Milestone #1 (due 1/26) 2 1 Overview: Integer Operations Internal representation
Computer Architecture and Organization: L04: Micro-operations
 Computer Architecture and Organization: L4: Micro-operations By: A. H. Abdul Hafez Abdul.hafez@hku.edu.tr, ah.abdulhafez@gmail.com, hafez@research.iiit.ac.in 1 Outlines 1. Arithmetic microoperation 2.
Computer Architecture and Organization: L4: Micro-operations By: A. H. Abdul Hafez Abdul.hafez@hku.edu.tr, ah.abdulhafez@gmail.com, hafez@research.iiit.ac.in 1 Outlines 1. Arithmetic microoperation 2.
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 13 - Combinational Logic & Arithmetic Circuits Part 3
 EECS15 - Digital Design Lecture 13 - Combinational Logic & Arithmetic Circuits Part 3 October 8, 22 John Wawrzynek Fall 22 EECS15 - Lec13-cla3 Page 1 Multiplication a 3 a 2 a 1 a Multiplicand b 3 b 2 b
EECS15 - Digital Design Lecture 13 - Combinational Logic & Arithmetic Circuits Part 3 October 8, 22 John Wawrzynek Fall 22 EECS15 - Lec13-cla3 Page 1 Multiplication a 3 a 2 a 1 a Multiplicand b 3 b 2 b
Digital Circuit Design and Language. Datapath Design. Chang, Ik Joon Kyunghee University
 Digital Circuit Design and Language Datapath Design Chang, Ik Joon Kyunghee University Typical Synchronous Design + Control Section : Finite State Machine + Data Section: Adder, Multiplier, Shift Register
Digital Circuit Design and Language Datapath Design Chang, Ik Joon Kyunghee University Typical Synchronous Design + Control Section : Finite State Machine + Data Section: Adder, Multiplier, Shift Register
Design of Digital Circuits 2017 Srdjan Capkun Onur Mutlu (Guest starring: Frank K. Gürkaynak and Aanjhan Ranganathan)
 Microarchitecture Design of Digital Circuits 27 Srdjan Capkun Onur Mutlu (Guest starring: Frank K. Gürkaynak and Aanjhan Ranganathan) http://www.syssec.ethz.ch/education/digitaltechnik_7 Adapted from Digital
Microarchitecture Design of Digital Circuits 27 Srdjan Capkun Onur Mutlu (Guest starring: Frank K. Gürkaynak and Aanjhan Ranganathan) http://www.syssec.ethz.ch/education/digitaltechnik_7 Adapted from Digital
ENGR 303 Introduction to Logic Design Lecture 7. Dr. Chuck Brown Engineering and Computer Information Science Folsom Lake College
 Introduction to Logic Design Lecture 7 Dr. Chuck Brown Engineering and Computer Information Science Folsom Lake College Outline for Todays Lecture Shifter Multiplier / Divider Memory Shifters Logical
Introduction to Logic Design Lecture 7 Dr. Chuck Brown Engineering and Computer Information Science Folsom Lake College Outline for Todays Lecture Shifter Multiplier / Divider Memory Shifters Logical
REGISTER TRANSFER LANGUAGE
 REGISTER TRANSFER LANGUAGE The operations executed on the data stored in the registers are called micro operations. Classifications of micro operations Register transfer micro operations Arithmetic micro
REGISTER TRANSFER LANGUAGE The operations executed on the data stored in the registers are called micro operations. Classifications of micro operations Register transfer micro operations Arithmetic micro
Chapter 3: part 3 Binary Subtraction
 Chapter 3: part 3 Binary Subtraction Iterative combinational circuits Binary adders Half and full adders Ripple carry and carry lookahead adders Binary subtraction Binary adder-subtractors Signed binary
Chapter 3: part 3 Binary Subtraction Iterative combinational circuits Binary adders Half and full adders Ripple carry and carry lookahead adders Binary subtraction Binary adder-subtractors Signed binary
Tailoring the 32-Bit ALU to MIPS
 Tailoring the 32-Bit ALU to MIPS MIPS ALU extensions Overflow detection: Carry into MSB XOR Carry out of MSB Branch instructions Shift instructions Slt instruction Immediate instructions ALU performance
Tailoring the 32-Bit ALU to MIPS MIPS ALU extensions Overflow detection: Carry into MSB XOR Carry out of MSB Branch instructions Shift instructions Slt instruction Immediate instructions ALU performance
Let s put together a Manual Processor
 Lecture 14 Let s put together a Manual Processor Hardware Lecture 14 Slide 1 The processor Inside every computer there is at least one processor which can take an instruction, some operands and produce
Lecture 14 Let s put together a Manual Processor Hardware Lecture 14 Slide 1 The processor Inside every computer there is at least one processor which can take an instruction, some operands and produce
Week 6: Processor Components
 Week 6: Processor Components Microprocessors So far, we ve been about making devices, such such as adders, counters and registers. The ultimate goal is to make a microprocessor, which is a digital device
Week 6: Processor Components Microprocessors So far, we ve been about making devices, such such as adders, counters and registers. The ultimate goal is to make a microprocessor, which is a digital device
COMP 303 Computer Architecture Lecture 6
 COMP 303 Computer Architecture Lecture 6 MULTIPLY (unsigned) Paper and pencil example (unsigned): Multiplicand 1000 = 8 Multiplier x 1001 = 9 1000 0000 0000 1000 Product 01001000 = 72 n bits x n bits =
COMP 303 Computer Architecture Lecture 6 MULTIPLY (unsigned) Paper and pencil example (unsigned): Multiplicand 1000 = 8 Multiplier x 1001 = 9 1000 0000 0000 1000 Product 01001000 = 72 n bits x n bits =
Timing for Ripple Carry Adder
 Timing for Ripple Carry Adder 1 2 3 Look Ahead Method 5 6 7 8 9 Look-Ahead, bits wide 10 11 Multiplication Simple Gradeschool Algorithm for 32 Bits (6 Bit Result) Multiplier Multiplicand AND gates 32
Timing for Ripple Carry Adder 1 2 3 Look Ahead Method 5 6 7 8 9 Look-Ahead, bits wide 10 11 Multiplication Simple Gradeschool Algorithm for 32 Bits (6 Bit Result) Multiplier Multiplicand AND gates 32
Review: MIPS Organization
 1 MIPS Arithmetic Review: MIPS Organization Processor Memory src1 addr 5 src2 addr 5 dst addr 5 write data Register File registers ($zero - $ra) bits src1 data src2 data read/write addr 1 1100 2 30 words
1 MIPS Arithmetic Review: MIPS Organization Processor Memory src1 addr 5 src2 addr 5 dst addr 5 write data Register File registers ($zero - $ra) bits src1 data src2 data read/write addr 1 1100 2 30 words
Arithmetic-logic units
 Arithmetic-logic units An arithmetic-logic unit, or ALU, performs many different arithmetic and logic operations. The ALU is the heart of a processor you could say that everything else in the CPU is there
Arithmetic-logic units An arithmetic-logic unit, or ALU, performs many different arithmetic and logic operations. The ALU is the heart of a processor you could say that everything else in the CPU is there
Number Systems and Computer Arithmetic
 Number Systems and Computer Arithmetic Counting to four billion two fingers at a time What do all those bits mean now? bits (011011011100010...01) instruction R-format I-format... integer data number text
Number Systems and Computer Arithmetic Counting to four billion two fingers at a time What do all those bits mean now? bits (011011011100010...01) instruction R-format I-format... integer data number text
Lecture 8: Addition, Multiplication & Division
 Lecture 8: Addition, Multiplication & Division Today s topics: Signed/Unsigned Addition Multiplication Division 1 Signed / Unsigned The hardware recognizes two formats: unsigned (corresponding to the C
Lecture 8: Addition, Multiplication & Division Today s topics: Signed/Unsigned Addition Multiplication Division 1 Signed / Unsigned The hardware recognizes two formats: unsigned (corresponding to the C
UNIT-III REGISTER TRANSFER LANGUAGE AND DESIGN OF CONTROL UNIT
 UNIT-III 1 KNREDDY UNIT-III REGISTER TRANSFER LANGUAGE AND DESIGN OF CONTROL UNIT Register Transfer: Register Transfer Language Register Transfer Bus and Memory Transfers Arithmetic Micro operations Logic
UNIT-III 1 KNREDDY UNIT-III REGISTER TRANSFER LANGUAGE AND DESIGN OF CONTROL UNIT Register Transfer: Register Transfer Language Register Transfer Bus and Memory Transfers Arithmetic Micro operations Logic
EXPERIMENT #8: BINARY ARITHMETIC OPERATIONS
 EE 2 Lab Manual, EE Department, KFUPM EXPERIMENT #8: BINARY ARITHMETIC OPERATIONS OBJECTIVES: Design and implement a circuit that performs basic binary arithmetic operations such as addition, subtraction,
EE 2 Lab Manual, EE Department, KFUPM EXPERIMENT #8: BINARY ARITHMETIC OPERATIONS OBJECTIVES: Design and implement a circuit that performs basic binary arithmetic operations such as addition, subtraction,
Two-Level CLA for 4-bit Adder. Two-Level CLA for 4-bit Adder. Two-Level CLA for 16-bit Adder. A Closer Look at CLA Delay
 Two-Level CLA for 4-bit Adder Individual carry equations C 1 = g 0 +p 0, C 2 = g 1 +p 1 C 1,C 3 = g 2 +p 2 C 2, = g 3 +p 3 C 3 Fully expanded (infinite hardware) CLA equations C 1 = g 0 +p 0 C 2 = g 1
Two-Level CLA for 4-bit Adder Individual carry equations C 1 = g 0 +p 0, C 2 = g 1 +p 1 C 1,C 3 = g 2 +p 2 C 2, = g 3 +p 3 C 3 Fully expanded (infinite hardware) CLA equations C 1 = g 0 +p 0 C 2 = g 1
CPE300: Digital System Architecture and Design
 CPE300: Digital System Architecture and Design Fall 2011 MW 17:30-18:45 CBC C316 Arithmetic Unit 10122011 http://www.egr.unlv.edu/~b1morris/cpe300/ 2 Outline Recap Fixed Point Arithmetic Addition/Subtraction
CPE300: Digital System Architecture and Design Fall 2011 MW 17:30-18:45 CBC C316 Arithmetic Unit 10122011 http://www.egr.unlv.edu/~b1morris/cpe300/ 2 Outline Recap Fixed Point Arithmetic Addition/Subtraction
CS/COE0447: Computer Organization
 CS/COE0447: Computer Organization and Assembly Language Chapter 3 Sangyeun Cho Dept. of Computer Science Five classic components I am like a control tower I am like a pack of file folders I am like a conveyor
CS/COE0447: Computer Organization and Assembly Language Chapter 3 Sangyeun Cho Dept. of Computer Science Five classic components I am like a control tower I am like a pack of file folders I am like a conveyor
EE260: Logic Design, Spring n Integer multiplication. n Booth s algorithm. n Integer division. n Restoring, non-restoring
 EE 260: Introduction to Digital Design Arithmetic II Yao Zheng Department of Electrical Engineering University of Hawaiʻi at Mānoa Overview n Integer multiplication n Booth s algorithm n Integer division
EE 260: Introduction to Digital Design Arithmetic II Yao Zheng Department of Electrical Engineering University of Hawaiʻi at Mānoa Overview n Integer multiplication n Booth s algorithm n Integer division
CS/COE0447: Computer Organization
 Five classic components CS/COE0447: Computer Organization and Assembly Language I am like a control tower I am like a pack of file folders Chapter 3 I am like a conveyor belt + service stations I exchange
Five classic components CS/COE0447: Computer Organization and Assembly Language I am like a control tower I am like a pack of file folders Chapter 3 I am like a conveyor belt + service stations I exchange
CSC 220: Computer Organization Unit 10 Arithmetic-logic units
 College of Computer and Information Sciences Department of Computer Science CSC 220: Computer Organization Unit 10 Arithmetic-logic units 1 Remember: 2 Arithmetic-logic units An arithmetic-logic unit,
College of Computer and Information Sciences Department of Computer Science CSC 220: Computer Organization Unit 10 Arithmetic-logic units 1 Remember: 2 Arithmetic-logic units An arithmetic-logic unit,
Register Transfer and Micro-operations
 Register Transfer Language Register Transfer Bus Memory Transfer Micro-operations Some Application of Logic Micro Operations Register Transfer and Micro-operations Learning Objectives After reading this
Register Transfer Language Register Transfer Bus Memory Transfer Micro-operations Some Application of Logic Micro Operations Register Transfer and Micro-operations Learning Objectives After reading this
Jan Rabaey Homework # 7 Solutions EECS141
 UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences Last modified on March 30, 2004 by Gang Zhou (zgang@eecs.berkeley.edu) Jan Rabaey Homework # 7
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences Last modified on March 30, 2004 by Gang Zhou (zgang@eecs.berkeley.edu) Jan Rabaey Homework # 7
Week 7: Assignment Solutions
 Week 7: Assignment Solutions 1. In 6-bit 2 s complement representation, when we subtract the decimal number +6 from +3, the result (in binary) will be: a. 111101 b. 000011 c. 100011 d. 111110 Correct answer
Week 7: Assignment Solutions 1. In 6-bit 2 s complement representation, when we subtract the decimal number +6 from +3, the result (in binary) will be: a. 111101 b. 000011 c. 100011 d. 111110 Correct answer
ECE 341 Midterm Exam
 ECE 341 Midterm Exam Time allowed: 75 minutes Total Points: 75 Points Scored: Name: Problem No. 1 (8 points) For each of the following statements, indicate whether the statement is TRUE or FALSE: (a) A
ECE 341 Midterm Exam Time allowed: 75 minutes Total Points: 75 Points Scored: Name: Problem No. 1 (8 points) For each of the following statements, indicate whether the statement is TRUE or FALSE: (a) A
Introduction to Digital Logic Missouri S&T University CPE 2210 Multipliers/Dividers
 Introduction to Digital Logic Missouri S&T University CPE 2210 Multipliers/Dividers Egemen K. Çetinkaya Egemen K. Çetinkaya Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering Missouri University of Science
Introduction to Digital Logic Missouri S&T University CPE 2210 Multipliers/Dividers Egemen K. Çetinkaya Egemen K. Çetinkaya Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering Missouri University of Science
Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU)
 Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) Introduction to Computer Yung-Yu Chuang with slides by Sedgewick & Wayne (introcs.cs.princeton.edu), Nisan & Schocken (www.nand2tetris.org) and Harris & Harris (DDCA) Let's
Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) Introduction to Computer Yung-Yu Chuang with slides by Sedgewick & Wayne (introcs.cs.princeton.edu), Nisan & Schocken (www.nand2tetris.org) and Harris & Harris (DDCA) Let's
Binary Adders: Half Adders and Full Adders
 Binary Adders: Half Adders and Full Adders In this set of slides, we present the two basic types of adders: 1. Half adders, and 2. Full adders. Each type of adder functions to add two binary bits. In order
Binary Adders: Half Adders and Full Adders In this set of slides, we present the two basic types of adders: 1. Half adders, and 2. Full adders. Each type of adder functions to add two binary bits. In order
MIPS Integer ALU Requirements
 MIPS Integer ALU Requirements Add, AddU, Sub, SubU, AddI, AddIU: 2 s complement adder/sub with overflow detection. And, Or, Andi, Ori, Xor, Xori, Nor: Logical AND, logical OR, XOR, nor. SLTI, SLTIU (set
MIPS Integer ALU Requirements Add, AddU, Sub, SubU, AddI, AddIU: 2 s complement adder/sub with overflow detection. And, Or, Andi, Ori, Xor, Xori, Nor: Logical AND, logical OR, XOR, nor. SLTI, SLTIU (set
Lecture Topics. Announcements. Today: Integer Arithmetic (P&H ) Next: The MIPS ISA (P&H ) Consulting hours. Milestone #1 (due 1/26)
 Lecture Topics Today: Integer Arithmetic (P&H 3.1-3.4) Next: The MIPS ISA (P&H 2.1-2.14) 1 Announcements Consulting hours Milestone #1 (due 1/26) Milestone #2 (due 2/2) 2 1 Review: Integer Operations Internal
Lecture Topics Today: Integer Arithmetic (P&H 3.1-3.4) Next: The MIPS ISA (P&H 2.1-2.14) 1 Announcements Consulting hours Milestone #1 (due 1/26) Milestone #2 (due 2/2) 2 1 Review: Integer Operations Internal
Chapter 3 Arithmetic for Computers
 Chapter 3 Arithmetic for Computers 1 Arithmetic Where we've been: Abstractions: Instruction Set Architecture Assembly Language and Machine Language What's up ahead: Implementing the Architecture operation
Chapter 3 Arithmetic for Computers 1 Arithmetic Where we've been: Abstractions: Instruction Set Architecture Assembly Language and Machine Language What's up ahead: Implementing the Architecture operation
COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE AND ORGANIZATION Register Transfer and Micro-operations 1. Introduction A digital system is an interconnection of digital
 Register Transfer and Micro-operations 1. Introduction A digital system is an interconnection of digital hardware modules that accomplish a specific information-processing task. Digital systems vary in
Register Transfer and Micro-operations 1. Introduction A digital system is an interconnection of digital hardware modules that accomplish a specific information-processing task. Digital systems vary in
Addition and multiplication
 Addition and multiplication Arithmetic is the most basic thing you can do with a computer, but it s not as easy as you might expect! These next few lectures focus on addition, subtraction, multiplication
Addition and multiplication Arithmetic is the most basic thing you can do with a computer, but it s not as easy as you might expect! These next few lectures focus on addition, subtraction, multiplication
NUMBER OPERATIONS. Mahdi Nazm Bojnordi. CS/ECE 3810: Computer Organization. Assistant Professor School of Computing University of Utah
 NUMBER OPERATIONS Mahdi Nazm Bojnordi Assistant Professor School of Computing University of Utah CS/ECE 3810: Computer Organization Overview Homework 4 is due tonight Verify your uploaded file before the
NUMBER OPERATIONS Mahdi Nazm Bojnordi Assistant Professor School of Computing University of Utah CS/ECE 3810: Computer Organization Overview Homework 4 is due tonight Verify your uploaded file before the
Arithmetic Circuits. Nurul Hazlina Adder 2. Multiplier 3. Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) 4. HDL for Arithmetic Circuit
 Nurul Hazlina 1 1. Adder 2. Multiplier 3. Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) 4. HDL for Arithmetic Circuit Nurul Hazlina 2 Introduction 1. Digital circuits are frequently used for arithmetic operations 2. Fundamental
Nurul Hazlina 1 1. Adder 2. Multiplier 3. Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) 4. HDL for Arithmetic Circuit Nurul Hazlina 2 Introduction 1. Digital circuits are frequently used for arithmetic operations 2. Fundamental
carry in carry 1101 carry carry
 Chapter Binary arithmetic Arithmetic is the process of applying a mathematical operator (such as negation or addition) to one or more operands (the values being operated upon). Binary arithmetic works
Chapter Binary arithmetic Arithmetic is the process of applying a mathematical operator (such as negation or addition) to one or more operands (the values being operated upon). Binary arithmetic works
Chapter 4 Design of Function Specific Arithmetic Circuits
 Chapter 4 Design of Function Specific Arithmetic Circuits Contents Chapter 4... 55 4.1 Introduction:... 55 4.1.1 Incrementer/Decrementer Circuit...56 4.1.2 2 s Complement Circuit...56 4.1.3 Priority Encoder
Chapter 4 Design of Function Specific Arithmetic Circuits Contents Chapter 4... 55 4.1 Introduction:... 55 4.1.1 Incrementer/Decrementer Circuit...56 4.1.2 2 s Complement Circuit...56 4.1.3 Priority Encoder
361 div.1. Computer Architecture EECS 361 Lecture 7: ALU Design : Division
 361 div.1 Computer Architecture EECS 361 Lecture 7: ALU Design : Division Outline of Today s Lecture Introduction to Today s Lecture Divide Questions and Administrative Matters Introduction to Single cycle
361 div.1 Computer Architecture EECS 361 Lecture 7: ALU Design : Division Outline of Today s Lecture Introduction to Today s Lecture Divide Questions and Administrative Matters Introduction to Single cycle
Real Digital Problem Set #6
 Real igital Problem et #6. (2 points) ketch a block diagram for a magnitude comparator bit-slice circuit. Create K-maps to define the bit-slice circuit, and use them to find optimal logic equations. ketch
Real igital Problem et #6. (2 points) ketch a block diagram for a magnitude comparator bit-slice circuit. Create K-maps to define the bit-slice circuit, and use them to find optimal logic equations. ketch
e-pg Pathshala Subject : Computer Science Paper: Embedded System Module: Introduction to Computing Module No: CS/ES/1 Quadrant 1 e-text
 e-pg Pathshala Subject : Computer Science Paper: Embedded System Module: Introduction to Computing Module No: CS/ES/1 Quadrant 1 e-text About the course : In this digital world, embedded systems are more
e-pg Pathshala Subject : Computer Science Paper: Embedded System Module: Introduction to Computing Module No: CS/ES/1 Quadrant 1 e-text About the course : In this digital world, embedded systems are more
For Example: P: LOAD 5 R0. The command given here is used to load a data 5 to the register R0.
 Register Transfer Language Computers are the electronic devices which have several sets of digital hardware which are inter connected to exchange data. Digital hardware comprises of VLSI Chips which are
Register Transfer Language Computers are the electronic devices which have several sets of digital hardware which are inter connected to exchange data. Digital hardware comprises of VLSI Chips which are
Introduction to Boole algebra. Binary algebra
 Introduction to Boole algebra Binary algebra Boole algebra George Boole s book released in 1847 We have only two digits: true and false We have NOT, AND, OR, XOR etc operations We have axioms and theorems
Introduction to Boole algebra Binary algebra Boole algebra George Boole s book released in 1847 We have only two digits: true and false We have NOT, AND, OR, XOR etc operations We have axioms and theorems
Register Transfer Language and Microoperations (Part 2)
 Register Transfer Language and Microoperations (Part 2) Adapted by Dr. Adel Ammar Computer Organization 1 MICROOPERATIONS Computer system microoperations are of four types: Register transfer microoperations
Register Transfer Language and Microoperations (Part 2) Adapted by Dr. Adel Ammar Computer Organization 1 MICROOPERATIONS Computer system microoperations are of four types: Register transfer microoperations
Chapter 4. Combinational Logic
 Chapter 4. Combinational Logic Tong In Oh 1 4.1 Introduction Combinational logic: Logic gates Output determined from only the present combination of inputs Specified by a set of Boolean functions Sequential
Chapter 4. Combinational Logic Tong In Oh 1 4.1 Introduction Combinational logic: Logic gates Output determined from only the present combination of inputs Specified by a set of Boolean functions Sequential
BINARY SYSTEM. Binary system is used in digital systems because it is:
 CHAPTER 2 CHAPTER CONTENTS 2.1 Binary System 2.2 Binary Arithmetic Operation 2.3 Signed & Unsigned Numbers 2.4 Arithmetic Operations of Signed Numbers 2.5 Hexadecimal Number System 2.6 Octal Number System
CHAPTER 2 CHAPTER CONTENTS 2.1 Binary System 2.2 Binary Arithmetic Operation 2.3 Signed & Unsigned Numbers 2.4 Arithmetic Operations of Signed Numbers 2.5 Hexadecimal Number System 2.6 Octal Number System
Microcomputers. Outline. Number Systems and Digital Logic Review
 Microcomputers Number Systems and Digital Logic Review Lecture 1-1 Outline Number systems and formats Common number systems Base Conversion Integer representation Signed integer representation Binary coded
Microcomputers Number Systems and Digital Logic Review Lecture 1-1 Outline Number systems and formats Common number systems Base Conversion Integer representation Signed integer representation Binary coded
DIGITAL TECHNICS. Dr. Bálint Pődör. Óbuda University, Microelectronics and Technology Institute
 DIGITAL TECHNIC Dr. Bálint Pődör Óbuda University, Microelectronics and Technology Institute 4. LECTURE: COMBINATIONAL LOGIC DEIGN: ARITHMETIC (THROUGH EXAMPLE) 2nd (Autumn) term 28/29 COMBINATIONAL LOGIC
DIGITAL TECHNIC Dr. Bálint Pődör Óbuda University, Microelectronics and Technology Institute 4. LECTURE: COMBINATIONAL LOGIC DEIGN: ARITHMETIC (THROUGH EXAMPLE) 2nd (Autumn) term 28/29 COMBINATIONAL LOGIC
CO Computer Architecture and Programming Languages CAPL. Lecture 9
 CO20-320241 Computer Architecture and Programming Languages CAPL Lecture 9 Dr. Kinga Lipskoch Fall 2017 A Four-bit Number Circle CAPL Fall 2017 2 / 38 Functional Parts of an ALU CAPL Fall 2017 3 / 38 Addition
CO20-320241 Computer Architecture and Programming Languages CAPL Lecture 9 Dr. Kinga Lipskoch Fall 2017 A Four-bit Number Circle CAPL Fall 2017 2 / 38 Functional Parts of an ALU CAPL Fall 2017 3 / 38 Addition
CS/COE 0447 Example Problems for Exam 2 Spring 2011
 CS/COE 0447 Example Problems for Exam 2 Spring 2011 1) Show the steps to multiply the 4-bit numbers 3 and 5 with the fast shift-add multipler. Use the table below. List the multiplicand (M) and product
CS/COE 0447 Example Problems for Exam 2 Spring 2011 1) Show the steps to multiply the 4-bit numbers 3 and 5 with the fast shift-add multipler. Use the table below. List the multiplicand (M) and product
CS101 Lecture 25: The Machinery of Computation: Computer Architecture. John Magee 29 July 2013 Some material copyright Jones and Bartlett
 CS101 Lecture 25: The Machinery of Computation: Computer Architecture John Magee 29 July 2013 Some material copyright Jones and Bartlett 1 Overview/Questions What did we do last time? Can we relate this
CS101 Lecture 25: The Machinery of Computation: Computer Architecture John Magee 29 July 2013 Some material copyright Jones and Bartlett 1 Overview/Questions What did we do last time? Can we relate this
Arithmetic Logic Unit
 Arithmetic Logic Unit A.R. Hurson Department of Computer Science Missouri University of Science & Technology A.R. Hurson 1 Arithmetic Logic Unit It is a functional bo designed to perform "basic" arithmetic,
Arithmetic Logic Unit A.R. Hurson Department of Computer Science Missouri University of Science & Technology A.R. Hurson 1 Arithmetic Logic Unit It is a functional bo designed to perform "basic" arithmetic,
Chapter 4 Arithmetic
 Computer Eng 1 (ECE290) Chapter 4 Arithmetic Functions and Circuits HOANG Trang Reference: 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. Lecture note of Prof.Donna J.Brown Overview Binary adders Half and full adders Ripple
Computer Eng 1 (ECE290) Chapter 4 Arithmetic Functions and Circuits HOANG Trang Reference: 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. Lecture note of Prof.Donna J.Brown Overview Binary adders Half and full adders Ripple
Chapter 4 Arithmetic Functions
 Logic and Computer Design Fundamentals Chapter 4 Arithmetic Functions Charles Kime & Thomas Kaminski 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. (Hyperlinks are active in View Show mode) Overview Iterative combinational
Logic and Computer Design Fundamentals Chapter 4 Arithmetic Functions Charles Kime & Thomas Kaminski 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. (Hyperlinks are active in View Show mode) Overview Iterative combinational
Experiment 7 Arithmetic Circuits Design and Implementation
 Experiment 7 Arithmetic Circuits Design and Implementation Introduction: Addition is just what you would expect in computers. Digits are added bit by bit from right to left, with carries passed to the
Experiment 7 Arithmetic Circuits Design and Implementation Introduction: Addition is just what you would expect in computers. Digits are added bit by bit from right to left, with carries passed to the
Combinational Circuits
 Combinational Circuits Q. What is a combinational circuit? A. Digital: signals are or. A. No feedback: no loops. analog circuits: signals vary continuously sequential circuits: loops allowed (stay tuned)
Combinational Circuits Q. What is a combinational circuit? A. Digital: signals are or. A. No feedback: no loops. analog circuits: signals vary continuously sequential circuits: loops allowed (stay tuned)
Binary Adders. Ripple-Carry Adder
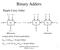 Ripple-Carry Adder Binary Adders x n y n x y x y c n FA c n - c 2 FA c FA c s n MSB position Longest delay (Critical-path delay): d c(n) = n d carry = 2n gate delays d s(n-) = (n-) d carry +d sum = 2n
Ripple-Carry Adder Binary Adders x n y n x y x y c n FA c n - c 2 FA c FA c s n MSB position Longest delay (Critical-path delay): d c(n) = n d carry = 2n gate delays d s(n-) = (n-) d carry +d sum = 2n
6. Combinational Circuits. Building Blocks. Digital Circuits. Wires. Q. What is a digital system? A. Digital: signals are 0 or 1.
 Digital Circuits 6 Combinational Circuits Q What is a digital system? A Digital: signals are or analog: signals vary continuously Q Why digital systems? A Accurate, reliable, fast, cheap Basic abstractions
Digital Circuits 6 Combinational Circuits Q What is a digital system? A Digital: signals are or analog: signals vary continuously Q Why digital systems? A Accurate, reliable, fast, cheap Basic abstractions
ECE 2030B 1:00pm Computer Engineering Spring problems, 5 pages Exam Two 10 March 2010
 Instructions: This is a closed book, closed note exam. Calculators are not permitted. If you have a question, raise your hand and I will come to you. Please work the exam in pencil and do not separate
Instructions: This is a closed book, closed note exam. Calculators are not permitted. If you have a question, raise your hand and I will come to you. Please work the exam in pencil and do not separate
Digital Design with FPGAs. By Neeraj Kulkarni
 Digital Design with FPGAs By Neeraj Kulkarni Some Basic Electronics Basic Elements: Gates: And, Or, Nor, Nand, Xor.. Memory elements: Flip Flops, Registers.. Techniques to design a circuit using basic
Digital Design with FPGAs By Neeraj Kulkarni Some Basic Electronics Basic Elements: Gates: And, Or, Nor, Nand, Xor.. Memory elements: Flip Flops, Registers.. Techniques to design a circuit using basic
Chapter 4. The Processor
 Chapter 4 The Processor Introduction CPU performance factors Instruction count Determined by ISA and compiler CPI and Cycle time Determined by CPU hardware We will examine two MIPS implementations A simplified
Chapter 4 The Processor Introduction CPU performance factors Instruction count Determined by ISA and compiler CPI and Cycle time Determined by CPU hardware We will examine two MIPS implementations A simplified
Advanced Computer Architecture-CS501
 Advanced Computer Architecture Lecture No. 34 Reading Material Vincent P. Heuring & Harry F. Jordan Chapter 6 Computer Systems Design and Architecture 6.1, 6.2 Summary Introduction to ALSU Radix Conversion
Advanced Computer Architecture Lecture No. 34 Reading Material Vincent P. Heuring & Harry F. Jordan Chapter 6 Computer Systems Design and Architecture 6.1, 6.2 Summary Introduction to ALSU Radix Conversion
Combinational Logic Circuits
 Combinational Logic Circuits By Dr. M. Hebaishy Digital Logic Design Ch- Rem.!) Types of Logic Circuits Combinational Logic Memoryless Outputs determined by current values of inputs Sequential Logic Has
Combinational Logic Circuits By Dr. M. Hebaishy Digital Logic Design Ch- Rem.!) Types of Logic Circuits Combinational Logic Memoryless Outputs determined by current values of inputs Sequential Logic Has
ELCT 501: Digital System Design
 ELCT 501: Digital System Lecture 4: CAD tools (Continued) Dr. Mohamed Abd El Ghany, Basic VHDL Concept Via an Example Problem: write VHDL code for 1-bit adder 4-bit adder 2 1-bit adder Inputs: A (1 bit)
ELCT 501: Digital System Lecture 4: CAD tools (Continued) Dr. Mohamed Abd El Ghany, Basic VHDL Concept Via an Example Problem: write VHDL code for 1-bit adder 4-bit adder 2 1-bit adder Inputs: A (1 bit)
Binary Arithmetic. Daniel Sanchez Computer Science & Artificial Intelligence Lab M.I.T.
 Binary Arithmetic Daniel Sanchez Computer Science & Artificial Intelligence Lab M.I.T. MIT 6.004 Fall 2018 Reminder: Encoding Positive Integers Bit i in a binary representation (in right-to-left order)
Binary Arithmetic Daniel Sanchez Computer Science & Artificial Intelligence Lab M.I.T. MIT 6.004 Fall 2018 Reminder: Encoding Positive Integers Bit i in a binary representation (in right-to-left order)
EE878 Special Topics in VLSI. Computer Arithmetic for Digital Signal Processing
 EE878 Special Topics in VLSI Computer Arithmetic for Digital Signal Processing Part 6c High-Speed Multiplication - III Spring 2017 Koren Part.6c.1 Array Multipliers The two basic operations - generation
EE878 Special Topics in VLSI Computer Arithmetic for Digital Signal Processing Part 6c High-Speed Multiplication - III Spring 2017 Koren Part.6c.1 Array Multipliers The two basic operations - generation
COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND DESIGN. 5 th Edition. The Hardware/Software Interface. Chapter 3. Arithmetic for Computers Implementation
 COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND DESIGN The Hardware/Software Interface 5 th Edition Chapter 3 Arithmetic for Computers Implementation Today Review representations (252/352 recap) Floating point Addition: Ripple
COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND DESIGN The Hardware/Software Interface 5 th Edition Chapter 3 Arithmetic for Computers Implementation Today Review representations (252/352 recap) Floating point Addition: Ripple
VTU NOTES QUESTION PAPERS NEWS RESULTS FORUMS Arithmetic (a) The four possible cases Carry (b) Truth table x y
 Arithmetic A basic operation in all digital computers is the addition and subtraction of two numbers They are implemented, along with the basic logic functions such as AND,OR, NOT,EX- OR in the ALU subsystem
Arithmetic A basic operation in all digital computers is the addition and subtraction of two numbers They are implemented, along with the basic logic functions such as AND,OR, NOT,EX- OR in the ALU subsystem
Ripple Counters. Lecture 30 1
 Ripple Counters A register that goes through a prescribed sequence of states upon the application of input pulses is called a counter. The input pulses may be clock pulses, or they may originate from some
Ripple Counters A register that goes through a prescribed sequence of states upon the application of input pulses is called a counter. The input pulses may be clock pulses, or they may originate from some
Systems Architecture
 Systems Architecture Lecture 15: A Simple Implementation of MIPS Jeremy R. Johnson Anatole D. Ruslanov William M. Mongan Some or all figures from Computer Organization and Design: The Hardware/Software
Systems Architecture Lecture 15: A Simple Implementation of MIPS Jeremy R. Johnson Anatole D. Ruslanov William M. Mongan Some or all figures from Computer Organization and Design: The Hardware/Software
FPGA Design Challenge :Techkriti 14 Digital Design using Verilog Part 1
 FPGA Design Challenge :Techkriti 14 Digital Design using Verilog Part 1 Anurag Dwivedi Digital Design : Bottom Up Approach Basic Block - Gates Digital Design : Bottom Up Approach Gates -> Flip Flops Digital
FPGA Design Challenge :Techkriti 14 Digital Design using Verilog Part 1 Anurag Dwivedi Digital Design : Bottom Up Approach Basic Block - Gates Digital Design : Bottom Up Approach Gates -> Flip Flops Digital
Chapter 3 Arithmetic for Computers. ELEC 5200/ From P-H slides
 Chapter 3 Arithmetic for Computers 1 Arithmetic for Computers Operations on integers Addition and subtraction Multiplication and division Dealing with overflow Floating-point real numbers Representation
Chapter 3 Arithmetic for Computers 1 Arithmetic for Computers Operations on integers Addition and subtraction Multiplication and division Dealing with overflow Floating-point real numbers Representation
ECE 30 Introduction to Computer Engineering
 ECE 30 Introduction to Computer Engineering Study Problems, Set #6 Spring 2015 1. With x = 1111 1111 1111 1111 1011 0011 0101 0011 2 and y = 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0010 1101 0111 2 representing two s
ECE 30 Introduction to Computer Engineering Study Problems, Set #6 Spring 2015 1. With x = 1111 1111 1111 1111 1011 0011 0101 0011 2 and y = 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0010 1101 0111 2 representing two s
Arithmetic and Logical Operations
 Arithmetic and Logical Operations 2 CMPE2c x +y + sum Or in tabular form Binary Addition Carry Out Sum B A Carry In Binary Addition And as a full adder a b co ci sum 4-bit Ripple-Carry adder: Carry values
Arithmetic and Logical Operations 2 CMPE2c x +y + sum Or in tabular form Binary Addition Carry Out Sum B A Carry In Binary Addition And as a full adder a b co ci sum 4-bit Ripple-Carry adder: Carry values
DC57 COMPUTER ORGANIZATION JUNE 2013
 Q2 (a) How do various factors like Hardware design, Instruction set, Compiler related to the performance of a computer? The most important measure of a computer is how quickly it can execute programs.
Q2 (a) How do various factors like Hardware design, Instruction set, Compiler related to the performance of a computer? The most important measure of a computer is how quickly it can execute programs.
Module 2: Computer Arithmetic
 Module 2: Computer Arithmetic 1 B O O K : C O M P U T E R O R G A N I Z A T I O N A N D D E S I G N, 3 E D, D A V I D L. P A T T E R S O N A N D J O H N L. H A N N E S S Y, M O R G A N K A U F M A N N
Module 2: Computer Arithmetic 1 B O O K : C O M P U T E R O R G A N I Z A T I O N A N D D E S I G N, 3 E D, D A V I D L. P A T T E R S O N A N D J O H N L. H A N N E S S Y, M O R G A N K A U F M A N N
CS140 Lecture 03: The Machinery of Computation: Combinational Logic
 CS140 Lecture 03: The Machinery of Computation: Combinational Logic John Magee 25 January 2017 Some material copyright Jones and Bartlett Some slides credit Aaron Stevens 1 Overview/Questions What did
CS140 Lecture 03: The Machinery of Computation: Combinational Logic John Magee 25 January 2017 Some material copyright Jones and Bartlett Some slides credit Aaron Stevens 1 Overview/Questions What did
An instruction set processor consist of two important units: Data Processing Unit (DataPath) Program Control Unit
 DataPath Design An instruction set processor consist of two important units: Data Processing Unit (DataPath) Program Control Unit Add & subtract instructions for fixed binary numbers are found in the
DataPath Design An instruction set processor consist of two important units: Data Processing Unit (DataPath) Program Control Unit Add & subtract instructions for fixed binary numbers are found in the
Parallel logic circuits
 Computer Mathematics Week 9 Parallel logic circuits College of Information cience and Engineering Ritsumeikan University last week the mathematics of logic circuits the foundation of all digital design
Computer Mathematics Week 9 Parallel logic circuits College of Information cience and Engineering Ritsumeikan University last week the mathematics of logic circuits the foundation of all digital design
Software and Hardware
 Software and Hardware Numbers At the most fundamental level, a computer manipulates electricity according to specific rules To make those rules produce something useful, we need to associate the electrical
Software and Hardware Numbers At the most fundamental level, a computer manipulates electricity according to specific rules To make those rules produce something useful, we need to associate the electrical
Learning Outcomes. Spiral 2-2. Digital System Design DATAPATH COMPONENTS
 2-2. 2-2.2 Learning Outcomes piral 2-2 Arithmetic Components and Their Efficient Implementations I understand the control inputs to counters I can design logic to control the inputs of counters to create
2-2. 2-2.2 Learning Outcomes piral 2-2 Arithmetic Components and Their Efficient Implementations I understand the control inputs to counters I can design logic to control the inputs of counters to create
END-TERM EXAMINATION
 (Please Write your Exam Roll No. immediately) END-TERM EXAMINATION DECEMBER 2006 Exam. Roll No... Exam Series code: 100919DEC06200963 Paper Code: MCA-103 Subject: Digital Electronics Time: 3 Hours Maximum
(Please Write your Exam Roll No. immediately) END-TERM EXAMINATION DECEMBER 2006 Exam. Roll No... Exam Series code: 100919DEC06200963 Paper Code: MCA-103 Subject: Digital Electronics Time: 3 Hours Maximum
Computer Organisation CS303
 Computer Organisation CS303 Module Period Assignments 1 Day 1 to Day 6 1. Write a program to evaluate the arithmetic statement: X=(A-B + C * (D * E-F))/G + H*K a. Using a general register computer with
Computer Organisation CS303 Module Period Assignments 1 Day 1 to Day 6 1. Write a program to evaluate the arithmetic statement: X=(A-B + C * (D * E-F))/G + H*K a. Using a general register computer with
Computer Arithmetic Multiplication & Shift Chapter 3.4 EEC170 FQ 2005
 Computer Arithmetic Multiplication & Shift Chapter 3.4 EEC170 FQ 200 Multiply We will start with unsigned multiply and contrast how humans and computers multiply Layout 8-bit 8 Pipelined Multiplier 1 2
Computer Arithmetic Multiplication & Shift Chapter 3.4 EEC170 FQ 200 Multiply We will start with unsigned multiply and contrast how humans and computers multiply Layout 8-bit 8 Pipelined Multiplier 1 2
Computer Architecture Set Four. Arithmetic
 Computer Architecture Set Four Arithmetic Arithmetic Where we ve been: Performance (seconds, cycles, instructions) Abstractions: Instruction Set Architecture Assembly Language and Machine Language What
Computer Architecture Set Four Arithmetic Arithmetic Where we ve been: Performance (seconds, cycles, instructions) Abstractions: Instruction Set Architecture Assembly Language and Machine Language What
CHAPTER 6 ARITHMETIC, LOGIC INSTRUCTIONS, AND PROGRAMS
 CHAPTER 6 ARITHMETIC, LOGIC INSTRUCTIONS, AND PROGRAMS Addition of Unsigned Numbers The instruction ADD is used to add two operands Destination operand is always in register A Source operand can be a register,
CHAPTER 6 ARITHMETIC, LOGIC INSTRUCTIONS, AND PROGRAMS Addition of Unsigned Numbers The instruction ADD is used to add two operands Destination operand is always in register A Source operand can be a register,
CS 5803 Introduction to High Performance Computer Architecture: Arithmetic Logic Unit. A.R. Hurson 323 CS Building, Missouri S&T
 CS 5803 Introduction to High Performance Computer Architecture: Arithmetic Logic Unit A.R. Hurson 323 CS Building, Missouri S&T hurson@mst.edu 1 Outline Motivation Design of a simple ALU How to design
CS 5803 Introduction to High Performance Computer Architecture: Arithmetic Logic Unit A.R. Hurson 323 CS Building, Missouri S&T hurson@mst.edu 1 Outline Motivation Design of a simple ALU How to design
Chapter 4. The Processor
 Chapter 4 The Processor Introduction CPU performance factors Instruction count Determined by ISA and compiler CPI and Cycle time Determined by CPU hardware 4.1 Introduction We will examine two MIPS implementations
Chapter 4 The Processor Introduction CPU performance factors Instruction count Determined by ISA and compiler CPI and Cycle time Determined by CPU hardware 4.1 Introduction We will examine two MIPS implementations
CS222: Processor Design
 CS222: Processor Design Dr. A. Sahu Dept of Comp. Sc. & Engg. Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati Processor Design building blocks Outline A simple implementation: Single Cycle Data pathandcontrol
CS222: Processor Design Dr. A. Sahu Dept of Comp. Sc. & Engg. Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati Processor Design building blocks Outline A simple implementation: Single Cycle Data pathandcontrol
The ALU consists of combinational logic. Processes all data in the CPU. ALL von Neuman machines have an ALU loop.
 CS 320 Ch 10 Computer Arithmetic The ALU consists of combinational logic. Processes all data in the CPU. ALL von Neuman machines have an ALU loop. Signed integers are typically represented in sign-magnitude
CS 320 Ch 10 Computer Arithmetic The ALU consists of combinational logic. Processes all data in the CPU. ALL von Neuman machines have an ALU loop. Signed integers are typically represented in sign-magnitude
Arithmetic Operations
 Arithmetic Operations Arithmetic Operations addition subtraction multiplication division Each of these operations on the integer representations: unsigned two's complement 1 Addition One bit of binary
Arithmetic Operations Arithmetic Operations addition subtraction multiplication division Each of these operations on the integer representations: unsigned two's complement 1 Addition One bit of binary
Basic Arithmetic and the ALU. Basic Arithmetic and the ALU. Background. Background. Integer multiplication, division
 Basic Arithmetic and the ALU Forecast Representing numbs, 2 s Complement, unsigned ition and subtraction /Sub ALU full add, ripple carry, subtraction, togeth Carry-Lookahead addition, etc. Logical opations
Basic Arithmetic and the ALU Forecast Representing numbs, 2 s Complement, unsigned ition and subtraction /Sub ALU full add, ripple carry, subtraction, togeth Carry-Lookahead addition, etc. Logical opations
ECE331: Hardware Organization and Design
 ECE331: Hardware Organization and Design Lecture 9: Binary Addition & Multiplication Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, UCB Pop Quiz! Using 4 bits signed integer notation:
ECE331: Hardware Organization and Design Lecture 9: Binary Addition & Multiplication Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, UCB Pop Quiz! Using 4 bits signed integer notation:
Outline. EEL-4713 Computer Architecture Multipliers and shifters. Deriving requirements of ALU. MIPS arithmetic instructions
 Outline EEL-4713 Computer Architecture Multipliers and shifters Multiplication and shift registers Chapter 3, section 3.4 Next lecture Division, floating-point 3.5 3.6 EEL-4713 Ann Gordon-Ross.1 EEL-4713
Outline EEL-4713 Computer Architecture Multipliers and shifters Multiplication and shift registers Chapter 3, section 3.4 Next lecture Division, floating-point 3.5 3.6 EEL-4713 Ann Gordon-Ross.1 EEL-4713
