/$ IEEE
|
|
|
- Rodney Gardner
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON CIRCUITS AND SYSTEMS II: EXPRESS BRIEFS, VOL. 56, NO. 1, JANUARY Bit-Level Extrinsic Information Exchange Method for Double-Binary Turbo Codes Ji-Hoon Kim, Student Member, IEEE, and In-Cheol Park, Senior Member, IEEE Abstract Nonbinary turbo codes have many advantages over single-binary turbo codes, but their decoder implementations require much more memory, particularly for storing symbolic extrinsic information to be exchanged between two soft-input softoutput (SISO) decoders. To reduce the memory size required for double-binary turbo decoding, this paper presents a new method to convert symbolic extrinsic information to bit-level information and vice versa. By exchanging bit-level extrinsic information, the number of extrinsic information values to be exchanged in doublebinary turbo decoding is reduced to the same amount as that in single-binary turbo decoding. A double-binary turbo decoder is designed for the WiMAX standard to verify the proposed method, which reduces the total memory size by 20%. Index Terms Double-binary turbo codes, extrinsic information, maximum a posteriori algorithm, turbo decoding. I. INTRODUCTION T HE TURBO codes introduced in 1993 are among the most powerful forward error correction codes and provide nearoptimal performance approaching the Shannon limit [1]. Recently, nonbinary turbo codes have received a great deal of attention and are adopted in several mobile radio systems such as DVB-RCS and IEEE standard (WiMAX) [2], as they can offer many advantages over single-binary turbo codes [3]. Compared with classical single-binary turbo codes, the size of extrinsic information memory becomes large since the number of extrinsic information values to be exchanged between two soft-input soft-output (SISO) decoders increases significantly in nonbinary turbo decoding. Although nonuniform quantization adopted in single-binary turbo decoding can be applied to reduce the extrinsic memory size [4], the large memory size incurred by the increased number of extrinsic information values is still a major obstacle in implementing a nonbinary turbo decoder [5]. In order to reduce the memory size needed in double-binary turbo decoding, this paper presents a method to convert symbolic extrinsic information to bit-level information and vice versa. By converting symbol-level extrinsic information values into bit-level values, the number of extrinsic information values to be exchanged can be reduced. To verify the proposed Manuscript received October 07, 2007; revised January 12, 2008 and June 05, Current version published January 16, This work was supported by the IC Design Education Center (IDEC). This paper was recommended by Associate Editor G. M. Maggio. The authors are with the School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science, KAIST, Daejeon , Korea ( sckid@eeinfo.kaist.ac.kr; icpark@ee.kaist.ac.kr). Digital Object Identifier /TCSII method, a double-binary turbo decoder is implemented for the WiMAX standard. II. EXTRINSIC INFORMATION IN DOUBLE-BINARY TURBO CODES Focusing on nonbinary turbo decoding, we describe in this section the conventional symbol-level extrinsic information and implementation issues. A. Symbol-Level Extrinsic Information in Double-Binary Turbo Codes In an -ary turbo code where a symbol is represented in bits, the number of possible symbol-level extrinsic information values is [6]. Since the value of is two for double-binary turbo codes, three symbol-level extrinsic information values are defined (1) where belongs to, is the input symbol consisting of two bits, and means the probability. The extrinsic information is exchanged iteratively between two SISO decoders during the whole decoding process. As indicated in (1), the extrinsic information in double-binary turbo codes is defined as the ratio of two input symbols, each of which consists of two bits. To store the increased number of extrinsic information values, a large memory is needed in implementing a nonbinary turbo decoder. B. Memory Requirement in Double-Binary Turbo Decoder A typical turbo decoder is based on the time-multiplex architecture that contains only one SISO decoder, one interleaver, and one extrinsic memory [7]. For the SISO decoder, the slidingwindow technique, is widely used to reduce the memory needed to store metric values [5]. To avoid the complex dummy metric calculation required in the sliding-window technique, we can adopt the border memory in nonbinary turbo decoding [5]. However, the extrinsic information memory cannot be reduced even if the sliding-window technique is employed, and the size is determined by the largest frame size that is 2400 pairs in the WiMAX standard [2]. The experimental environment for the WiMAX turbo code is indicated in Table I, where denotes a quantization scheme that uses bits in total and bits to represent the fractional part. Taking into account the quantization scheme indicated in Table I, the memory size required for a double-binary SISO decoder is summarized in Table II, and that for storing extrinsic information values is tabulated in Table III. It is crucial to reduce the extrinsic information memory, as the extrinsic information /$ IEEE
2 82 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON CIRCUITS AND SYSTEMS II: EXPRESS BRIEFS, VOL. 56, NO. 1, JANUARY 2009 TABLE I SIMULATION ENVIRONMENT TABLE II MEMORY CONFIGURATION FOR ONE SISO DECODER Fig. 1. Block diagram of the proposed bit-level extrinsic information exchange. where the input symbol consists of a pair of two bits, and, i.e.,. The bit-level probabilities in (2) can be derived from the symbol-level probabilities in (1), as described in the following: TABLE III MEMORY CONFIGURATION FOR THE EXTRINSIC INFORMATION (3a) (3b) (3c) (3d) Considering the basic property of the probabilities memory is much bigger than the memory required in SISO decoding, as indicated in Tables II and III. In higher order nonbinary turbo decoders such as triple-binary and quaternary turbo decoders [6], [8], the extrinsic information memory becomes much bigger, since the number of extrinsic information values to be stored is proportional to. III. PROPOSED BIT-LEVEL EXTRINSIC INFORMATION EXCHANGE Here, we propose a new bit-level extrinsic information exchange method that can reduce the number of extrinsic values to be exchanged between two SISO decoders, as shown in Fig. 1. Specifically, we present two conversions symbol-to-bit conversion and bit-to-symbol conversion of extrinsic information. With simple conversions, the number of values to be exchanged can be reduced from the number of possible symbols,, to the number of bits in a symbol,, without inducing any modifications to conventional symbol-based double-binary SISO decoders. Therefore, the proposed method is effective in reducing the size of extrinsic information memory regardless of quantization. A. Bit-Level Extrinsic Information for Double-Binary Turbo Codes Like the symbol-level extrinsic information in (1), two bitlevel extrinsic information values are defined (4a) (4b) Similarly, for the symbol-level probabilities (5) From the aforementioned properties, can be expressed (6) Additionally, the following equation can be derived from (3): (7) Using (2), (4), and (7), we can derive (2) (8)
3 KIM AND PARK: BIT-LEVEL EXTRINSIC INFORMATION EXCHANGE METHOD FOR DOUBLE-BINARY TURBO CODES 83 By applying (6) to (8) (9) Since, we can obtain the following relations from (6): (10a) (10b) As expressed above, two bit-level extrinsic information values can be obtained from three symbol-level extrinsic information values. Therefore, the number of values to be stored in the memory can be reduced from three to two. C. Bit-to-Symbol Conversion of Extrinsic Information To keep the compatibility with the conventional symbolbased SISO decoder, we should retrieve the symbol-level extrinsic information values from the bit-level extrinsic information values, as shown in Fig. 1. Using the relations derived previously, the proposed bit-to-symbol conversion of extrinsic information can be classified into four cases by taking into account the sign values of the two bit-level extrinsic information values. 1) Case I: and : From (8) (11), we can relate with the two bit-level extrinsic information values as follows: By considering both (9) and (10), we can obtain the relations among the symbol-level extrinsic information values with the bit-level extrinsic information values (11) Based on the relations discussed earlier, we can derive the symbol-to-bit conversion and bit-to-symbol conversion of extrinsic information. B. Symbol-to-Bit Conversion of Extrinsic Information From (1) (3), we can derive two equations which relate the bit-level probabilities to the extrinsic information values, as shown in the following: (14) where is approximated to. From (14), can be determined (15) Additionally, we can use (11) to approximate (12) Similarly,. As a consequence, two bit-level extrinsic information values can be obtained from (12) (16) (13) Similarly,.
4 84 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON CIRCUITS AND SYSTEMS II: EXPRESS BRIEFS, VOL. 56, NO. 1, JANUARY ) Case II: and : Using the relations between and in (10a) and (10b), we can approximate and (17) Fig. 2. Comparison of BER performances of eight iterations for 1920-bit frame. We can approximate (11) by considering and (18) According to (9), can be expressed (23) (19) 3) Case III: and : In this case, symbollevel extrinsic information values can be retrieved similarly as discussed in Case II. Therefore (20) 4) Case IV: and : Since the two bit-level extrinsic information values are less than zero in this case, we can roughly approximate Therefore, and. As described previously, symbol-level extrinsic information values can be retrieved from bit-level extrinsic information values by using simple operations such as addition and maximum. Similarly, symbol-to-bit conversion can be derived for higher order nonbinary turbo codes by expressing the bit-level probabilities with the symbol-level probabilities. After the symbol-level extrinsic information is expressed with the bit-level extrinsic information, the bit-to-symbol conversion can be obtained by applying appropriate approximations according to the sign values of the bit-level extrinsic information. IV. EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS According to (8) and (21) (21) (22) The proposed conversion method is applied to decode the turbo code specified in the WiMAX standard. With the experimental environment denoted in Table I, Fig. 2 shows the BER performance of a turbo decoder employing the proposed conversion method and compares with that of the conventional turbo decoder [5] using the symbol-level extrinsic information directly. The BER performances are measured for a coding rate of 1/2. Although some approximations are applied in deriving the proposed conversions, they lead to only a slight degradation of the signal-to-noise ratio, about less than 0.1 db, since the extrinsic information does not need to be exact in decoding [4]. Consequently, we can reduce the number of extrinsic information values to be exchanged without inducing a considerable loss of error-correcting capability.
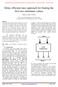
5 KIM AND PARK: BIT-LEVEL EXTRINSIC INFORMATION EXCHANGE METHOD FOR DOUBLE-BINARY TURBO CODES 85 Fig. 4. Block diagram and complexity of the proposed BSC. Fig. 3. Block diagram of the proposed double-binary turbo decoder. TABLE IV SINGLE-PORT SRAM SIZE REQUIRED FOR THE TURBO DECODER Fig. 4. As denoted in Fig. 4, the complexity of the proposed BSC is negligible compared to that of the total SISO decoder including the dedicated hardware interleaver and the hard-decision unit. Since the amount of values per symbol required for -ary extrinsic information is, the memory saving resulting from the proposed bit-level extrinsic information exchange increases as increases, although no results on performance loss have been reported yet for larger than two. A. Hardware Implementation With the quantization scheme indicated in Table I, a turbo decoder associated with the proposed conversion was designed in Verilog HDL and synthesized with a m CMOS standard-cell library and compiled SRAM memories. The turbo decoder is based on the time-multiplex architecture and employs a dedicated hardware interleaver [5], as shown in Fig. 3. The memory size required for the turbo decoder is summarized in Table IV. Since a separate border memory is needed for each SISO decoding, two border memories are integrated in the decoder implementation. By adopting the proposed bit-level extrinsic information exchange method, the memory size required for the extrinsic information is reduced to two-thirds of the conventional method, as denoted in Table IV. When several SISO decoders are adopted to achieve a higher throughput, the size of the state metric memory should be increased, but the proposed conversion is still effective in reducing the total memory size, as the extrinsic information memory is much larger than the state metric memory, as indicated in Table IV. The proposed symbol-to-bit conversion can be performed in the hard-decision unit that makes hard-decided values at the end of the decoding process [9], since the relations expressed in (13) are the same as those needed to calculate the log-likelihood ratio values. Therefore, the only hardware overhead caused by the proposed conversion method is the bit-to-symbol converter (BSC) shown in V. CONCLUSION We have presented a simple bit-level extrinsic information exchange method for double-binary turbo codes. The proposed method can reduce the number of extrinsic information values to be exchanged between two SISO decoders. Since the size of the extrinsic information memory is significant, the proposed method is effective in reducing the total memory size required in double-binary turbo decoders. To verify the proposed method, a double-binary turbo decoder is designed for the WiMAX turbo code. By applying the proposed conversion method, the total memory size is reduced by 20%. REFERENCES [1] C. Berrou, A. Glavieux, and P. Thitimajshima, Near Shannon limit error-correcting coding and decoding: Turbo-codes, in Proc. Int. Conf. Commun., May 1993, pp [2] Part 16: Air Interface for Fixed and Mobile Broadband Wireless Access Systems Amendment for Physical and Medium Access Control Layers for Combined Fixed and Mobile Operation in Licensed Bands, IEEE Std e/D5-2004, Nov [3] C. Douillard and C. Berrou, Turbo codes with rate- m=(m +1)constituent convolutional codes, IEEE Trans. Commun., vol. 53, no. 10, pp , Oct [4] J. Vogt, J. Ertel, and A. Finger, Reducing bit width of extrinsic memory in turbo decoder realizations, Electron. Lett., vol. 36, no. 20, pp , Sep [5] J. H. Kim and I. C. Park, Double-binary circular turbo decoding based on border metric encoding, IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II, Exp. Briefs, vol. 55, no. 1, pp , Jan [6] Y. Gao and M. R. Soleymani, Triple-binary circular recursive systematic convolutional turbo codes, in Proc. 5th Int. Symp. Wireless Pers. Multimedia Commun., 2002, vol. 3, pp [7] M. C. Shin and I. C. Park, SIMD processor-based turbo decoder supporting multiple third-generation wireless standards, IEEE Trans. Very Large Scale Integr. (VLSI) Syst., vol. 15, no. 7, pp , Jul [8] C. Berrou and M. Jezequel, Non-binary convolutional codes for turbo coding, Electron. Lett., vol. 35, no. 1, pp , Jan [9] S. J. Lee, N. R. Shanbhag, and A. C. Singer, Area-efficient highthroughput MAP decoder architectures, IEEE Trans. Very Large Scale Integr. (VLSI) Syst., vol. 13, no. 8, pp , Aug
ISSCC 2003 / SESSION 8 / COMMUNICATIONS SIGNAL PROCESSING / PAPER 8.7
 ISSCC 2003 / SESSION 8 / COMMUNICATIONS SIGNAL PROCESSING / PAPER 8.7 8.7 A Programmable Turbo Decoder for Multiple 3G Wireless Standards Myoung-Cheol Shin, In-Cheol Park KAIST, Daejeon, Republic of Korea
ISSCC 2003 / SESSION 8 / COMMUNICATIONS SIGNAL PROCESSING / PAPER 8.7 8.7 A Programmable Turbo Decoder for Multiple 3G Wireless Standards Myoung-Cheol Shin, In-Cheol Park KAIST, Daejeon, Republic of Korea
THE turbo code is one of the most attractive forward error
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON CIRCUITS AND SYSTEMS II: EXPRESS BRIEFS, VOL. 63, NO. 2, FEBRUARY 2016 211 Memory-Reduced Turbo Decoding Architecture Using NII Metric Compression Youngjoo Lee, Member, IEEE, Meng
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON CIRCUITS AND SYSTEMS II: EXPRESS BRIEFS, VOL. 63, NO. 2, FEBRUARY 2016 211 Memory-Reduced Turbo Decoding Architecture Using NII Metric Compression Youngjoo Lee, Member, IEEE, Meng
Memory-Reduced Turbo Decoding Architecture Using NII Metric Compression
 Memory-Reduced Turbo Decoding Architecture Using NII Metric Compression Syed kareem saheb, Research scholar, Dept. of ECE, ANU, GUNTUR,A.P, INDIA. E-mail:sd_kareem@yahoo.com A. Srihitha PG student dept.
Memory-Reduced Turbo Decoding Architecture Using NII Metric Compression Syed kareem saheb, Research scholar, Dept. of ECE, ANU, GUNTUR,A.P, INDIA. E-mail:sd_kareem@yahoo.com A. Srihitha PG student dept.
High Throughput Radix-4 SISO Decoding Architecture with Reduced Memory Requirement
 JOURNAL OF SEMICONDUCTOR TECHNOLOGY AND SCIENCE, VOL.14, NO.4, AUGUST, 2014 http://dx.doi.org/10.5573/jsts.2014.14.4.407 High Throughput Radix-4 SISO Decoding Architecture with Reduced Memory Requirement
JOURNAL OF SEMICONDUCTOR TECHNOLOGY AND SCIENCE, VOL.14, NO.4, AUGUST, 2014 http://dx.doi.org/10.5573/jsts.2014.14.4.407 High Throughput Radix-4 SISO Decoding Architecture with Reduced Memory Requirement
High Speed Downlink Packet Access efficient turbo decoder architecture: 3GPP Advanced Turbo Decoder
 I J C T A, 9(24), 2016, pp. 291-298 International Science Press High Speed Downlink Packet Access efficient turbo decoder architecture: 3GPP Advanced Turbo Decoder Parvathy M.*, Ganesan R.*,** and Tefera
I J C T A, 9(24), 2016, pp. 291-298 International Science Press High Speed Downlink Packet Access efficient turbo decoder architecture: 3GPP Advanced Turbo Decoder Parvathy M.*, Ganesan R.*,** and Tefera
Low Complexity Architecture for Max* Operator of Log-MAP Turbo Decoder
 International Journal of Current Engineering and Technology E-ISSN 2277 4106, P-ISSN 2347 5161 2015 INPRESSCO, All Rights Reserved Available at http://inpressco.com/category/ijcet Research Article Low
International Journal of Current Engineering and Technology E-ISSN 2277 4106, P-ISSN 2347 5161 2015 INPRESSCO, All Rights Reserved Available at http://inpressco.com/category/ijcet Research Article Low
VHDL Implementation of different Turbo Encoder using Log-MAP Decoder
 49 VHDL Implementation of different Turbo Encoder using Log-MAP Decoder Akash Kumar Gupta and Sanjeet Kumar Abstract Turbo code is a great achievement in the field of communication system. It can be created
49 VHDL Implementation of different Turbo Encoder using Log-MAP Decoder Akash Kumar Gupta and Sanjeet Kumar Abstract Turbo code is a great achievement in the field of communication system. It can be created
RECENTLY, researches on gigabit wireless personal area
 146 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON CIRCUITS AND SYSTEMS II: EXPRESS BRIEFS, VOL. 55, NO. 2, FEBRUARY 2008 An Indexed-Scaling Pipelined FFT Processor for OFDM-Based WPAN Applications Yuan Chen, Student Member, IEEE,
146 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON CIRCUITS AND SYSTEMS II: EXPRESS BRIEFS, VOL. 55, NO. 2, FEBRUARY 2008 An Indexed-Scaling Pipelined FFT Processor for OFDM-Based WPAN Applications Yuan Chen, Student Member, IEEE,
AS TURBO codes [1], or parallel concatenated convolutional
![AS TURBO codes [1], or parallel concatenated convolutional AS TURBO codes [1], or parallel concatenated convolutional](/thumbs/73/68229162.jpg) IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON VERY LARGE SCALE INTEGRATION (VLSI) SYSTEMS, VOL. 15, NO. 7, JULY 2007 801 SIMD Processor-Based Turbo Decoder Supporting Multiple Third-Generation Wireless Standards Myoung-Cheol Shin,
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON VERY LARGE SCALE INTEGRATION (VLSI) SYSTEMS, VOL. 15, NO. 7, JULY 2007 801 SIMD Processor-Based Turbo Decoder Supporting Multiple Third-Generation Wireless Standards Myoung-Cheol Shin,
EFFICIENT RECURSIVE IMPLEMENTATION OF A QUADRATIC PERMUTATION POLYNOMIAL INTERLEAVER FOR LONG TERM EVOLUTION SYSTEMS
 Rev. Roum. Sci. Techn. Électrotechn. et Énerg. Vol. 61, 1, pp. 53 57, Bucarest, 016 Électronique et transmission de l information EFFICIENT RECURSIVE IMPLEMENTATION OF A QUADRATIC PERMUTATION POLYNOMIAL
Rev. Roum. Sci. Techn. Électrotechn. et Énerg. Vol. 61, 1, pp. 53 57, Bucarest, 016 Électronique et transmission de l information EFFICIENT RECURSIVE IMPLEMENTATION OF A QUADRATIC PERMUTATION POLYNOMIAL
Interlaced Column-Row Message-Passing Schedule for Decoding LDPC Codes
 Interlaced Column-Row Message-Passing Schedule for Decoding LDPC Codes Saleh Usman, Mohammad M. Mansour, Ali Chehab Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering American University of Beirut Beirut
Interlaced Column-Row Message-Passing Schedule for Decoding LDPC Codes Saleh Usman, Mohammad M. Mansour, Ali Chehab Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering American University of Beirut Beirut
TURBO codes, [1], [2], have attracted much interest due
![TURBO codes, [1], [2], have attracted much interest due TURBO codes, [1], [2], have attracted much interest due](/thumbs/78/78049299.jpg) 800 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON INFORMATION THEORY, VOL. 47, NO. 2, FEBRUARY 2001 Zigzag Codes and Concatenated Zigzag Codes Li Ping, Member, IEEE, Xiaoling Huang, and Nam Phamdo, Senior Member, IEEE Abstract
800 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON INFORMATION THEORY, VOL. 47, NO. 2, FEBRUARY 2001 Zigzag Codes and Concatenated Zigzag Codes Li Ping, Member, IEEE, Xiaoling Huang, and Nam Phamdo, Senior Member, IEEE Abstract
Programmable Turbo Decoder Supporting Multiple Third-Generation Wireless Standards
 Programmable Turbo Decoder Supporting Multiple Third-eneration Wireless Standards Myoung-Cheol Shin and In-Cheol Park Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science, KAIST Yuseong-gu Daejeon,
Programmable Turbo Decoder Supporting Multiple Third-eneration Wireless Standards Myoung-Cheol Shin and In-Cheol Park Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science, KAIST Yuseong-gu Daejeon,
Comparison of Decoding Algorithms for Concatenated Turbo Codes
 Comparison of Decoding Algorithms for Concatenated Turbo Codes Drago Žagar, Nenad Falamić and Snježana Rimac-Drlje University of Osijek Faculty of Electrical Engineering Kneza Trpimira 2b, HR-31000 Osijek,
Comparison of Decoding Algorithms for Concatenated Turbo Codes Drago Žagar, Nenad Falamić and Snježana Rimac-Drlje University of Osijek Faculty of Electrical Engineering Kneza Trpimira 2b, HR-31000 Osijek,
DUE to the high computational complexity and real-time
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON CIRCUITS AND SYSTEMS FOR VIDEO TECHNOLOGY, VOL. 15, NO. 3, MARCH 2005 445 A Memory-Efficient Realization of Cyclic Convolution and Its Application to Discrete Cosine Transform Hun-Chen
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON CIRCUITS AND SYSTEMS FOR VIDEO TECHNOLOGY, VOL. 15, NO. 3, MARCH 2005 445 A Memory-Efficient Realization of Cyclic Convolution and Its Application to Discrete Cosine Transform Hun-Chen
Exploring Parallel Processing Levels for Convolutional Turbo Decoding
 Exploring Parallel Processing Levels for Convolutional Turbo Decoding Olivier Muller Electronics Department, GET/EST Bretagne Technopôle Brest Iroise, 29238 Brest, France olivier.muller@enst-bretagne.fr
Exploring Parallel Processing Levels for Convolutional Turbo Decoding Olivier Muller Electronics Department, GET/EST Bretagne Technopôle Brest Iroise, 29238 Brest, France olivier.muller@enst-bretagne.fr
THE orthogonal frequency-division multiplex (OFDM)
 26 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON CIRCUITS AND SYSTEMS II: EXPRESS BRIEFS, VOL. 57, NO. 1, JANUARY 2010 A Generalized Mixed-Radix Algorithm for Memory-Based FFT Processors Chen-Fong Hsiao, Yuan Chen, Member, IEEE,
26 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON CIRCUITS AND SYSTEMS II: EXPRESS BRIEFS, VOL. 57, NO. 1, JANUARY 2010 A Generalized Mixed-Radix Algorithm for Memory-Based FFT Processors Chen-Fong Hsiao, Yuan Chen, Member, IEEE,
Non-Binary Turbo Codes Interleavers
 Non-Binary Turbo Codes Interleavers Maria KOVACI, Horia BALTA University Polytechnic of Timişoara, Faculty of Electronics and Telecommunications, Postal Address, 30223 Timişoara, ROMANIA, E-Mail: mariakovaci@etcuttro,
Non-Binary Turbo Codes Interleavers Maria KOVACI, Horia BALTA University Polytechnic of Timişoara, Faculty of Electronics and Telecommunications, Postal Address, 30223 Timişoara, ROMANIA, E-Mail: mariakovaci@etcuttro,
Twiddle Factor Transformation for Pipelined FFT Processing
 Twiddle Factor Transformation for Pipelined FFT Processing In-Cheol Park, WonHee Son, and Ji-Hoon Kim School of EECS, Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology, Daejeon, Korea icpark@ee.kaist.ac.kr,
Twiddle Factor Transformation for Pipelined FFT Processing In-Cheol Park, WonHee Son, and Ji-Hoon Kim School of EECS, Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology, Daejeon, Korea icpark@ee.kaist.ac.kr,
A Modified Medium Access Control Algorithm for Systems with Iterative Decoding
 A Modified Medium Access Control Algorithm for Systems with Iterative Decoding Inkyu Lee Carl-Erik W. Sundberg Sunghyun Choi Dept. of Communications Eng. Korea University Seoul, Korea inkyu@korea.ac.kr
A Modified Medium Access Control Algorithm for Systems with Iterative Decoding Inkyu Lee Carl-Erik W. Sundberg Sunghyun Choi Dept. of Communications Eng. Korea University Seoul, Korea inkyu@korea.ac.kr
/$ IEEE
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON CIRCUITS AND SYSTEMS I: REGULAR PAPERS, VOL. 56, NO. 5, MAY 2009 1005 Low-Power Memory-Reduced Traceback MAP Decoding for Double-Binary Convolutional Turbo Decoder Cheng-Hung Lin,
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON CIRCUITS AND SYSTEMS I: REGULAR PAPERS, VOL. 56, NO. 5, MAY 2009 1005 Low-Power Memory-Reduced Traceback MAP Decoding for Double-Binary Convolutional Turbo Decoder Cheng-Hung Lin,
Overlapped Scheduling for Folded LDPC Decoding Based on Matrix Permutation
 Overlapped Scheduling for Folded LDPC Decoding Based on Matrix Permutation In-Cheol Park and Se-Hyeon Kang Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science, KAIST {icpark, shkang}@ics.kaist.ac.kr
Overlapped Scheduling for Folded LDPC Decoding Based on Matrix Permutation In-Cheol Park and Se-Hyeon Kang Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science, KAIST {icpark, shkang}@ics.kaist.ac.kr
A MULTIBANK MEMORY-BASED VLSI ARCHITECTURE OF DIGITAL VIDEO BROADCASTING SYMBOL DEINTERLEAVER
 A MULTIBANK MEMORY-BASED VLSI ARCHITECTURE OF DIGITAL VIDEO BROADCASTING SYMBOL DEINTERLEAVER D.HARI BABU 1, B.NEELIMA DEVI 2 1,2 Noble college of engineering and technology, Nadergul, Hyderabad, Abstract-
A MULTIBANK MEMORY-BASED VLSI ARCHITECTURE OF DIGITAL VIDEO BROADCASTING SYMBOL DEINTERLEAVER D.HARI BABU 1, B.NEELIMA DEVI 2 1,2 Noble college of engineering and technology, Nadergul, Hyderabad, Abstract-
ARITHMETIC operations based on residue number systems
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON CIRCUITS AND SYSTEMS II: EXPRESS BRIEFS, VOL. 53, NO. 2, FEBRUARY 2006 133 Improved Memoryless RNS Forward Converter Based on the Periodicity of Residues A. B. Premkumar, Senior Member,
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON CIRCUITS AND SYSTEMS II: EXPRESS BRIEFS, VOL. 53, NO. 2, FEBRUARY 2006 133 Improved Memoryless RNS Forward Converter Based on the Periodicity of Residues A. B. Premkumar, Senior Member,
A Novel Area Efficient Folded Modified Convolutional Interleaving Architecture for MAP Decoder
 A Novel Area Efficient Folded Modified Convolutional Interleaving Architecture for Decoder S.Shiyamala Department of ECE SSCET Palani, India. Dr.V.Rajamani Principal IGCET Trichy,India ABSTRACT This paper
A Novel Area Efficient Folded Modified Convolutional Interleaving Architecture for Decoder S.Shiyamala Department of ECE SSCET Palani, India. Dr.V.Rajamani Principal IGCET Trichy,India ABSTRACT This paper
An Area-Efficient BIRA With 1-D Spare Segments
 206 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON VERY LARGE SCALE INTEGRATION (VLSI) SYSTEMS, VOL. 26, NO. 1, JANUARY 2018 An Area-Efficient BIRA With 1-D Spare Segments Donghyun Kim, Hayoung Lee, and Sungho Kang Abstract The
206 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON VERY LARGE SCALE INTEGRATION (VLSI) SYSTEMS, VOL. 26, NO. 1, JANUARY 2018 An Area-Efficient BIRA With 1-D Spare Segments Donghyun Kim, Hayoung Lee, and Sungho Kang Abstract The
Capacity-approaching Codes for Solid State Storages
 Capacity-approaching Codes for Solid State Storages Jeongseok Ha, Department of Electrical Engineering Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) Contents Capacity-Approach Codes Turbo
Capacity-approaching Codes for Solid State Storages Jeongseok Ha, Department of Electrical Engineering Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) Contents Capacity-Approach Codes Turbo
Fast frame memory access method for H.264/AVC
 Fast frame memory access method for H.264/AVC Tian Song 1a), Tomoyuki Kishida 2, and Takashi Shimamoto 1 1 Computer Systems Engineering, Department of Institute of Technology and Science, Graduate School
Fast frame memory access method for H.264/AVC Tian Song 1a), Tomoyuki Kishida 2, and Takashi Shimamoto 1 1 Computer Systems Engineering, Department of Institute of Technology and Science, Graduate School
/$ IEEE
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON VERY LARGE SCALE INTEGRATION (VLSI) SYSTEMS, VOL. 14, NO. 10, OCTOBER 2006 1147 Transactions Briefs Highly-Parallel Decoding Architectures for Convolutional Turbo Codes Zhiyong He,
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON VERY LARGE SCALE INTEGRATION (VLSI) SYSTEMS, VOL. 14, NO. 10, OCTOBER 2006 1147 Transactions Briefs Highly-Parallel Decoding Architectures for Convolutional Turbo Codes Zhiyong He,
120 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON CIRCUITS AND SYSTEMS II: EXPRESS BRIEFS, VOL. 61, NO. 2, FEBRUARY 2014
 120 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON CIRCUITS AND SYSTEMS II: EXPRESS BRIEFS, VOL. 61, NO. 2, FEBRUARY 2014 VL-ECC: Variable Data-Length Error Correction Code for Embedded Memory in DSP Applications Jangwon Park,
120 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON CIRCUITS AND SYSTEMS II: EXPRESS BRIEFS, VOL. 61, NO. 2, FEBRUARY 2014 VL-ECC: Variable Data-Length Error Correction Code for Embedded Memory in DSP Applications Jangwon Park,
II. MOTIVATION AND IMPLEMENTATION
 An Efficient Design of Modified Booth Recoder for Fused Add-Multiply operator Dhanalakshmi.G Applied Electronics PSN College of Engineering and Technology Tirunelveli dhanamgovind20@gmail.com Prof.V.Gopi
An Efficient Design of Modified Booth Recoder for Fused Add-Multiply operator Dhanalakshmi.G Applied Electronics PSN College of Engineering and Technology Tirunelveli dhanamgovind20@gmail.com Prof.V.Gopi
Research Article Cooperative Signaling with Soft Information Combining
 Electrical and Computer Engineering Volume 2010, Article ID 530190, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2010/530190 Research Article Cooperative Signaling with Soft Information Combining Rui Lin, Philippa A. Martin, and
Electrical and Computer Engineering Volume 2010, Article ID 530190, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2010/530190 Research Article Cooperative Signaling with Soft Information Combining Rui Lin, Philippa A. Martin, and
Non-recursive complexity reduction encoding scheme for performance enhancement of polar codes
 Non-recursive complexity reduction encoding scheme for performance enhancement of polar codes 1 Prakash K M, 2 Dr. G S Sunitha 1 Assistant Professor, Dept. of E&C, Bapuji Institute of Engineering and Technology,
Non-recursive complexity reduction encoding scheme for performance enhancement of polar codes 1 Prakash K M, 2 Dr. G S Sunitha 1 Assistant Professor, Dept. of E&C, Bapuji Institute of Engineering and Technology,
Digital Filter Synthesis Considering Multiple Adder Graphs for a Coefficient
 Digital Filter Synthesis Considering Multiple Graphs for a Coefficient Jeong-Ho Han, and In-Cheol Park School of EECS, Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology, Daejeon, Korea jhhan.kr@gmail.com,
Digital Filter Synthesis Considering Multiple Graphs for a Coefficient Jeong-Ho Han, and In-Cheol Park School of EECS, Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology, Daejeon, Korea jhhan.kr@gmail.com,
The Lekha 3GPP LTE Turbo Decoder IP Core meets 3GPP LTE specification 3GPP TS V Release 10[1].
![The Lekha 3GPP LTE Turbo Decoder IP Core meets 3GPP LTE specification 3GPP TS V Release 10[1]. The Lekha 3GPP LTE Turbo Decoder IP Core meets 3GPP LTE specification 3GPP TS V Release 10[1].](/thumbs/77/75180706.jpg) Lekha IP Core: LW RI 1002 3GPP LTE Turbo Decoder IP Core V1.0 The Lekha 3GPP LTE Turbo Decoder IP Core meets 3GPP LTE specification 3GPP TS 36.212 V 10.5.0 Release 10[1]. Introduction The Lekha IP 3GPP
Lekha IP Core: LW RI 1002 3GPP LTE Turbo Decoder IP Core V1.0 The Lekha 3GPP LTE Turbo Decoder IP Core meets 3GPP LTE specification 3GPP TS 36.212 V 10.5.0 Release 10[1]. Introduction The Lekha IP 3GPP
Super Codes: A Flexible Multi Rate Coding System
 Super Codes: A Flexible Multi Rate Coding System Steven S. Pietrobon Small World Communications, 6 First Avenue, Payneham South SA 57, Australia. E mail: steven@sworld.com.au Abstract: We define super
Super Codes: A Flexible Multi Rate Coding System Steven S. Pietrobon Small World Communications, 6 First Avenue, Payneham South SA 57, Australia. E mail: steven@sworld.com.au Abstract: We define super
Discontinued IP. 3GPP2 Turbo Decoder v1.0. Features. Applications. General Description
 0 3GPP2 Turbo Decoder v1.0 DS275 April 28, 2005 0 0 Features Drop-in module for Spartan -3, Spartan-3E, Virtex -II and Virtex-II Pro FPGAs Implements the CDMA2000/3GPP2 specification[1] Core contains the
0 3GPP2 Turbo Decoder v1.0 DS275 April 28, 2005 0 0 Features Drop-in module for Spartan -3, Spartan-3E, Virtex -II and Virtex-II Pro FPGAs Implements the CDMA2000/3GPP2 specification[1] Core contains the
EFFICIENT PARALLEL MEMORY ORGANIZATION FOR TURBO DECODERS
 In Proceedings of the European Signal Processing Conference, pages 831-83, Poznan, Poland, September 27. EFFICIENT PARALLEL MEMORY ORGANIZATION FOR TURBO DECODERS Perttu Salmela, Ruirui Gu*, Shuvra S.
In Proceedings of the European Signal Processing Conference, pages 831-83, Poznan, Poland, September 27. EFFICIENT PARALLEL MEMORY ORGANIZATION FOR TURBO DECODERS Perttu Salmela, Ruirui Gu*, Shuvra S.
A Normal I/O Order Radix-2 FFT Architecture to Process Twin Data Streams for MIMO
 2402 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON VERY LARGE SCALE INTEGRATION (VLSI) SYSTEMS, VOL. 24, NO. 6, JUNE 2016 A Normal I/O Order Radix-2 FFT Architecture to Process Twin Data Streams for MIMO Antony Xavier Glittas,
2402 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON VERY LARGE SCALE INTEGRATION (VLSI) SYSTEMS, VOL. 24, NO. 6, JUNE 2016 A Normal I/O Order Radix-2 FFT Architecture to Process Twin Data Streams for MIMO Antony Xavier Glittas,
OPTIMIZED MAP TURBO DECODER
 OPTIMIZED MAP TURBO DECODER Curt Schurgers Francy Catthoor Marc Engels EE Department IMEC/KUL IMEC UCLA Kapeldreef 75 Kapeldreef 75 Los Angeles, CA 90024 3001 Heverlee 3001 Heverlee USA Belgium Belgium
OPTIMIZED MAP TURBO DECODER Curt Schurgers Francy Catthoor Marc Engels EE Department IMEC/KUL IMEC UCLA Kapeldreef 75 Kapeldreef 75 Los Angeles, CA 90024 3001 Heverlee 3001 Heverlee USA Belgium Belgium
A Novel Carry-look ahead approach to an Unified BCD and Binary Adder/Subtractor
 A Novel Carry-look ahead approach to an Unified BCD and Binary Adder/Subtractor Abstract Increasing prominence of commercial, financial and internet-based applications, which process decimal data, there
A Novel Carry-look ahead approach to an Unified BCD and Binary Adder/Subtractor Abstract Increasing prominence of commercial, financial and internet-based applications, which process decimal data, there
New Message-Passing Decoding Algorithm of LDPC Codes by Partitioning Check Nodes 1
 New Message-Passing Decoding Algorithm of LDPC Codes by Partitioning Check Nodes 1 Sunghwan Kim* O, Min-Ho Jang*, Jong-Seon No*, Song-Nam Hong, and Dong-Joon Shin *School of Electrical Engineering and
New Message-Passing Decoding Algorithm of LDPC Codes by Partitioning Check Nodes 1 Sunghwan Kim* O, Min-Ho Jang*, Jong-Seon No*, Song-Nam Hong, and Dong-Joon Shin *School of Electrical Engineering and
LLR-based Successive-Cancellation List Decoder for Polar Codes with Multi-bit Decision
 > REPLACE THIS LINE WITH YOUR PAPER IDENTIFICATION NUMBER (DOUBLE-CLIC HERE TO EDIT < LLR-based Successive-Cancellation List Decoder for Polar Codes with Multi-bit Decision Bo Yuan and eshab. Parhi, Fellow,
> REPLACE THIS LINE WITH YOUR PAPER IDENTIFICATION NUMBER (DOUBLE-CLIC HERE TO EDIT < LLR-based Successive-Cancellation List Decoder for Polar Codes with Multi-bit Decision Bo Yuan and eshab. Parhi, Fellow,
Area-Efficient High-Throughput MAP Decoder Architectures
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON VERY LARGE SCALE INTEGRATION (VLSI) SYSTEMS, VOL. 13, NO. 8, AUGUST 2005 921 Area-Efficient High-Throughput MAP Decoder Architectures Seok-Jun Lee, Member, IEEE, Naresh R. Shanbhag,
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON VERY LARGE SCALE INTEGRATION (VLSI) SYSTEMS, VOL. 13, NO. 8, AUGUST 2005 921 Area-Efficient High-Throughput MAP Decoder Architectures Seok-Jun Lee, Member, IEEE, Naresh R. Shanbhag,
VLSI Architectures for SISO-APP Decoders
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON VERY LARGE SCALE INTEGRATION (VLSI) SYSTEMS, VOL. 11, NO. 4, AUGUST 2003 627 VLSI Architectures for SISO-APP Decoders Mohammad M. Mansour, Student Member, IEEE, and Naresh R. Shanbhag,
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON VERY LARGE SCALE INTEGRATION (VLSI) SYSTEMS, VOL. 11, NO. 4, AUGUST 2003 627 VLSI Architectures for SISO-APP Decoders Mohammad M. Mansour, Student Member, IEEE, and Naresh R. Shanbhag,
Implementation of a Turbo Encoder and Turbo Decoder on DSP Processor-TMS320C6713
 International Journal of Engineering Research and Development e-issn : 2278-067X, p-issn : 2278-800X,.ijerd.com Volume 2, Issue 5 (July 2012), PP. 37-41 Implementation of a Turbo Encoder and Turbo Decoder
International Journal of Engineering Research and Development e-issn : 2278-067X, p-issn : 2278-800X,.ijerd.com Volume 2, Issue 5 (July 2012), PP. 37-41 Implementation of a Turbo Encoder and Turbo Decoder
AN EFFICIENT DESIGN OF VLSI ARCHITECTURE FOR FAULT DETECTION USING ORTHOGONAL LATIN SQUARES (OLS) CODES
 AN EFFICIENT DESIGN OF VLSI ARCHITECTURE FOR FAULT DETECTION USING ORTHOGONAL LATIN SQUARES (OLS) CODES S. SRINIVAS KUMAR *, R.BASAVARAJU ** * PG Scholar, Electronics and Communication Engineering, CRIT
AN EFFICIENT DESIGN OF VLSI ARCHITECTURE FOR FAULT DETECTION USING ORTHOGONAL LATIN SQUARES (OLS) CODES S. SRINIVAS KUMAR *, R.BASAVARAJU ** * PG Scholar, Electronics and Communication Engineering, CRIT
Hard Decision Based Low SNR Early Termination for LTE Turbo Decoding
 Hard Decision Based Low SNR Early Termination for LTE Turbo Decoding Jan Geldmacher, Klaus Hueske, and Jürgen Götze Information Processing Lab, TU Dortmund University Otto-Hahn-Strasse 4, 447 Dortmund,
Hard Decision Based Low SNR Early Termination for LTE Turbo Decoding Jan Geldmacher, Klaus Hueske, and Jürgen Götze Information Processing Lab, TU Dortmund University Otto-Hahn-Strasse 4, 447 Dortmund,
A Route Selection Scheme for Multi-Route Coding in Multihop Cellular Networks
 A Route Selection Scheme for Multi-Route Coding in Multihop Cellular Networks Hiraku Okada,HitoshiImai, Takaya Yamazato, Masaaki Katayama, Kenichi Mase Center for Transdisciplinary Research, Niigata University,
A Route Selection Scheme for Multi-Route Coding in Multihop Cellular Networks Hiraku Okada,HitoshiImai, Takaya Yamazato, Masaaki Katayama, Kenichi Mase Center for Transdisciplinary Research, Niigata University,
ISSN (Online), Volume 1, Special Issue 2(ICITET 15), March 2015 International Journal of Innovative Trends and Emerging Technologies
 VLSI IMPLEMENTATION OF HIGH PERFORMANCE DISTRIBUTED ARITHMETIC (DA) BASED ADAPTIVE FILTER WITH FAST CONVERGENCE FACTOR G. PARTHIBAN 1, P.SATHIYA 2 PG Student, VLSI Design, Department of ECE, Surya Group
VLSI IMPLEMENTATION OF HIGH PERFORMANCE DISTRIBUTED ARITHMETIC (DA) BASED ADAPTIVE FILTER WITH FAST CONVERGENCE FACTOR G. PARTHIBAN 1, P.SATHIYA 2 PG Student, VLSI Design, Department of ECE, Surya Group
Discontinued IP. Verification
 0 3GPP2 Turbo Decoder v2.1 DS275 February 15, 2007 0 0 Features Drop-in module for Spartan -3, Spartan-3E, Spartan-3A/3AN, Virtex -II, Virtex-II Pro, Virtex-4, and Virtex-5 FPGAs Implements the CDMA2000/3GPP2
0 3GPP2 Turbo Decoder v2.1 DS275 February 15, 2007 0 0 Features Drop-in module for Spartan -3, Spartan-3E, Spartan-3A/3AN, Virtex -II, Virtex-II Pro, Virtex-4, and Virtex-5 FPGAs Implements the CDMA2000/3GPP2
THERE has been great interest in recent years in coding
 186 IEEE JOURNAL ON SELECTED AREAS IN COMMUNICATIONS, VOL. 16, NO. 2, FEBRUARY 1998 Concatenated Decoding with a Reduced-Search BCJR Algorithm Volker Franz and John B. Anderson, Fellow, IEEE Abstract We
186 IEEE JOURNAL ON SELECTED AREAS IN COMMUNICATIONS, VOL. 16, NO. 2, FEBRUARY 1998 Concatenated Decoding with a Reduced-Search BCJR Algorithm Volker Franz and John B. Anderson, Fellow, IEEE Abstract We
An Efficient Carry Select Adder with Less Delay and Reduced Area Application
 An Efficient Carry Select Adder with Less Delay and Reduced Area Application Pandu Ranga Rao #1 Priyanka Halle #2 # Associate Professor Department of ECE Sreyas Institute of Engineering and Technology,
An Efficient Carry Select Adder with Less Delay and Reduced Area Application Pandu Ranga Rao #1 Priyanka Halle #2 # Associate Professor Department of ECE Sreyas Institute of Engineering and Technology,
BER Guaranteed Optimization and Implementation of Parallel Turbo Decoding on GPU
 2013 8th International Conference on Communications and Networking in China (CHINACOM) BER Guaranteed Optimization and Implementation of Parallel Turbo Decoding on GPU Xiang Chen 1,2, Ji Zhu, Ziyu Wen,
2013 8th International Conference on Communications and Networking in China (CHINACOM) BER Guaranteed Optimization and Implementation of Parallel Turbo Decoding on GPU Xiang Chen 1,2, Ji Zhu, Ziyu Wen,
Available online at ScienceDirect. Procedia Technology 25 (2016 )
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Technology 25 (2016 ) 544 551 Global Colloquium in Recent Advancement and Effectual Researches in Engineering, Science and Technology (RAEREST
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Technology 25 (2016 ) 544 551 Global Colloquium in Recent Advancement and Effectual Researches in Engineering, Science and Technology (RAEREST
PROPOSED DETERMINISTIC INTERLEAVERS FOR CCSDS TURBO CODE STANDARD
 PROPOSED DETERMINISTIC INTERLEAVERS FOR CCSDS TURBO CODE STANDARD 1 ALAA ELDIN.HASSAN, 2 MONA SHOKAIR, 2 ATEF ABOU ELAZM, 3 D.TRUHACHEV, 3 C.SCHLEGEL 1 Research Assistant: Dept. of Space Science, National
PROPOSED DETERMINISTIC INTERLEAVERS FOR CCSDS TURBO CODE STANDARD 1 ALAA ELDIN.HASSAN, 2 MONA SHOKAIR, 2 ATEF ABOU ELAZM, 3 D.TRUHACHEV, 3 C.SCHLEGEL 1 Research Assistant: Dept. of Space Science, National
Efficient Implementation of Single Error Correction and Double Error Detection Code with Check Bit Precomputation
 http://dx.doi.org/10.5573/jsts.2012.12.4.418 JOURNAL OF SEMICONDUCTOR TECHNOLOGY AND SCIENCE, VOL.12, NO.4, DECEMBER, 2012 Efficient Implementation of Single Error Correction and Double Error Detection
http://dx.doi.org/10.5573/jsts.2012.12.4.418 JOURNAL OF SEMICONDUCTOR TECHNOLOGY AND SCIENCE, VOL.12, NO.4, DECEMBER, 2012 Efficient Implementation of Single Error Correction and Double Error Detection
TURBO CODES with performance near the Shannon
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON VERY LARGE SCALE INTEGRATION (VLSI) SYSTEMS, VOL. 13, NO. 4, APRIL 2005 427 Parallel Interleaver Design and VLSI Architecture for Low-Latency MAP Turbo Decoders Rostislav (Reuven)
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON VERY LARGE SCALE INTEGRATION (VLSI) SYSTEMS, VOL. 13, NO. 4, APRIL 2005 427 Parallel Interleaver Design and VLSI Architecture for Low-Latency MAP Turbo Decoders Rostislav (Reuven)
Reduced Complexity of Decoding Algorithm for Irregular LDPC Codes Using a Split Row Method
 Journal of Wireless Networking and Communications 2012, 2(4): 29-34 DOI: 10.5923/j.jwnc.20120204.01 Reduced Complexity of Decoding Algorithm for Irregular Rachid El Alami *, Mostafa Mrabti, Cheikh Bamba
Journal of Wireless Networking and Communications 2012, 2(4): 29-34 DOI: 10.5923/j.jwnc.20120204.01 Reduced Complexity of Decoding Algorithm for Irregular Rachid El Alami *, Mostafa Mrabti, Cheikh Bamba
Efficient VLSI Huffman encoder implementation and its application in high rate serial data encoding
 LETTER IEICE Electronics Express, Vol.14, No.21, 1 11 Efficient VLSI Huffman encoder implementation and its application in high rate serial data encoding Rongshan Wei a) and Xingang Zhang College of Physics
LETTER IEICE Electronics Express, Vol.14, No.21, 1 11 Efficient VLSI Huffman encoder implementation and its application in high rate serial data encoding Rongshan Wei a) and Xingang Zhang College of Physics
The Lekha 3GPP LTE FEC IP Core meets 3GPP LTE specification 3GPP TS V Release 10[1].
![The Lekha 3GPP LTE FEC IP Core meets 3GPP LTE specification 3GPP TS V Release 10[1]. The Lekha 3GPP LTE FEC IP Core meets 3GPP LTE specification 3GPP TS V Release 10[1].](/thumbs/75/72771698.jpg) Lekha IP 3GPP LTE FEC Encoder IP Core V1.0 The Lekha 3GPP LTE FEC IP Core meets 3GPP LTE specification 3GPP TS 36.212 V 10.5.0 Release 10[1]. 1.0 Introduction The Lekha IP 3GPP LTE FEC Encoder IP Core
Lekha IP 3GPP LTE FEC Encoder IP Core V1.0 The Lekha 3GPP LTE FEC IP Core meets 3GPP LTE specification 3GPP TS 36.212 V 10.5.0 Release 10[1]. 1.0 Introduction The Lekha IP 3GPP LTE FEC Encoder IP Core
FIR Filter Synthesis Algorithms for Minimizing the Delay and the Number of Adders
 770 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON CIRCUITS AND SYSTEMS II: ANALOG AND DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSING, VOL. 48, NO. 8, AUGUST 2001 FIR Filter Synthesis Algorithms for Minimizing the Delay and the Number of Adders Hyeong-Ju
770 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON CIRCUITS AND SYSTEMS II: ANALOG AND DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSING, VOL. 48, NO. 8, AUGUST 2001 FIR Filter Synthesis Algorithms for Minimizing the Delay and the Number of Adders Hyeong-Ju
LOW-DENSITY parity-check (LDPC) codes, which are defined
 734 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON CIRCUITS AND SYSTEMS II: EXPRESS BRIEFS, VOL. 56, NO. 9, SEPTEMBER 2009 Design of a Multimode QC-LDPC Decoder Based on Shift-Routing Network Chih-Hao Liu, Chien-Ching Lin, Shau-Wei
734 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON CIRCUITS AND SYSTEMS II: EXPRESS BRIEFS, VOL. 56, NO. 9, SEPTEMBER 2009 Design of a Multimode QC-LDPC Decoder Based on Shift-Routing Network Chih-Hao Liu, Chien-Ching Lin, Shau-Wei
A New MIMO Detector Architecture Based on A Forward-Backward Trellis Algorithm
 A New MIMO etector Architecture Based on A Forward-Backward Trellis Algorithm Yang Sun and Joseph R Cavallaro epartment of Electrical and Computer Engineering Rice University, Houston, TX 775 Email: {ysun,
A New MIMO etector Architecture Based on A Forward-Backward Trellis Algorithm Yang Sun and Joseph R Cavallaro epartment of Electrical and Computer Engineering Rice University, Houston, TX 775 Email: {ysun,
P2FS: supporting atomic writes for reliable file system design in PCM storage
 LETTER IEICE Electronics Express, Vol.11, No.13, 1 6 P2FS: supporting atomic writes for reliable file system design in PCM storage Eunji Lee 1, Kern Koh 2, and Hyokyung Bahn 2a) 1 Department of Software,
LETTER IEICE Electronics Express, Vol.11, No.13, 1 6 P2FS: supporting atomic writes for reliable file system design in PCM storage Eunji Lee 1, Kern Koh 2, and Hyokyung Bahn 2a) 1 Department of Software,
Quasi-Cyclic Low-Density Parity-Check (QC-LDPC) Codes for Deep Space and High Data Rate Applications
 Quasi-Cyclic Low-Density Parity-Check (QC-LDPC) Codes for Deep Space and High Data Rate Applications Nikoleta Andreadou, Fotini-Niovi Pavlidou Dept. of Electrical & Computer Engineering Aristotle University
Quasi-Cyclic Low-Density Parity-Check (QC-LDPC) Codes for Deep Space and High Data Rate Applications Nikoleta Andreadou, Fotini-Niovi Pavlidou Dept. of Electrical & Computer Engineering Aristotle University
On the performance of turbo codes with convolutional interleavers
 University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Informatics - Papers (Archive) Faculty of Engineering and Information Sciences 5 On the performance of turbo codes with convolutional interleavers Sina
University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Informatics - Papers (Archive) Faculty of Engineering and Information Sciences 5 On the performance of turbo codes with convolutional interleavers Sina
Delay efficient mux approach for finding the first two minimum values
 Delay efficient mux approach for finding the first two minimum values Nakka Sivaraju¹ S Suman² ¹PG scholar, ECE Department, CEC, AP, India ²Assistant Professor, ECE Department, CEC, AP, India Abstract
Delay efficient mux approach for finding the first two minimum values Nakka Sivaraju¹ S Suman² ¹PG scholar, ECE Department, CEC, AP, India ²Assistant Professor, ECE Department, CEC, AP, India Abstract
DETECTION AND CORRECTION OF CELL UPSETS USING MODIFIED DECIMAL MATRIX
 DETECTION AND CORRECTION OF CELL UPSETS USING MODIFIED DECIMAL MATRIX ENDREDDY PRAVEENA 1 M.T.ech Scholar ( VLSID), Universal College Of Engineering & Technology, Guntur, A.P M. VENKATA SREERAJ 2 Associate
DETECTION AND CORRECTION OF CELL UPSETS USING MODIFIED DECIMAL MATRIX ENDREDDY PRAVEENA 1 M.T.ech Scholar ( VLSID), Universal College Of Engineering & Technology, Guntur, A.P M. VENKATA SREERAJ 2 Associate
< Irregular Repeat-Accumulate LDPC Code Proposal Technology Overview
 Project IEEE 802.20 Working Group on Mobile Broadband Wireless Access Title Irregular Repeat-Accumulate LDPC Code Proposal Technology Overview Date Submitted Source(s):
Project IEEE 802.20 Working Group on Mobile Broadband Wireless Access Title Irregular Repeat-Accumulate LDPC Code Proposal Technology Overview Date Submitted Source(s):
The design and implementation of TPC encoder and decoder
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS The design and implementation of TPC encoder and decoder To cite this article: L J Xiang et al 016 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 679 0103 Related content
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS The design and implementation of TPC encoder and decoder To cite this article: L J Xiang et al 016 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 679 0103 Related content
Test Resource Reused Debug Scheme to Reduce the Post-Silicon Debug Cost
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON COMPUTERS, VOL. 67, NO. 12, DECEMBER 2018 1835 Test Resource Reused Debug Scheme to Reduce the Post-Silicon Debug Cost Inhyuk Choi, Hyunggoy Oh, Young-Woo Lee, and Sungho Kang, Senior
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON COMPUTERS, VOL. 67, NO. 12, DECEMBER 2018 1835 Test Resource Reused Debug Scheme to Reduce the Post-Silicon Debug Cost Inhyuk Choi, Hyunggoy Oh, Young-Woo Lee, and Sungho Kang, Senior
Fixed Point LMS Adaptive Filter with Low Adaptation Delay
 Fixed Point LMS Adaptive Filter with Low Adaptation Delay INGUDAM CHITRASEN MEITEI Electronics and Communication Engineering Vel Tech Multitech Dr RR Dr SR Engg. College Chennai, India MR. P. BALAVENKATESHWARLU
Fixed Point LMS Adaptive Filter with Low Adaptation Delay INGUDAM CHITRASEN MEITEI Electronics and Communication Engineering Vel Tech Multitech Dr RR Dr SR Engg. College Chennai, India MR. P. BALAVENKATESHWARLU
Combined Copyright Protection and Error Detection Scheme for H.264/AVC
 Combined Copyright Protection and Error Detection Scheme for H.264/AVC XIAOMING CHEN, YUK YING CHUNG, FANGFEI XU, AHMED FAWZI OTOOM, *CHANGSEOK BAE School of Information Technologies, The University of
Combined Copyright Protection and Error Detection Scheme for H.264/AVC XIAOMING CHEN, YUK YING CHUNG, FANGFEI XU, AHMED FAWZI OTOOM, *CHANGSEOK BAE School of Information Technologies, The University of
Carry-Free Radix-2 Subtractive Division Algorithm and Implementation of the Divider
 Tamkang Journal of Science and Engineering, Vol. 3, No., pp. 29-255 (2000) 29 Carry-Free Radix-2 Subtractive Division Algorithm and Implementation of the Divider Jen-Shiun Chiang, Hung-Da Chung and Min-Show
Tamkang Journal of Science and Engineering, Vol. 3, No., pp. 29-255 (2000) 29 Carry-Free Radix-2 Subtractive Division Algorithm and Implementation of the Divider Jen-Shiun Chiang, Hung-Da Chung and Min-Show
IEEE Proof Web Version
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON VERY LARGE SCALE INTEGRATION (VLSI) SYSTEMS 1 From Parallelism Levels to a Multi-ASIP Architecture for Turbo Decoding Olivier Muller, Member, IEEE, Amer Baghdadi, and Michel Jézéquel,
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON VERY LARGE SCALE INTEGRATION (VLSI) SYSTEMS 1 From Parallelism Levels to a Multi-ASIP Architecture for Turbo Decoding Olivier Muller, Member, IEEE, Amer Baghdadi, and Michel Jézéquel,
PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS OF HIGH EFFICIENCY LOW DENSITY PARITY-CHECK CODE DECODER FOR LOW POWER APPLICATIONS
 American Journal of Applied Sciences 11 (4): 558-563, 2014 ISSN: 1546-9239 2014 Science Publication doi:10.3844/ajassp.2014.558.563 Published Online 11 (4) 2014 (http://www.thescipub.com/ajas.toc) PERFORMANCE
American Journal of Applied Sciences 11 (4): 558-563, 2014 ISSN: 1546-9239 2014 Science Publication doi:10.3844/ajassp.2014.558.563 Published Online 11 (4) 2014 (http://www.thescipub.com/ajas.toc) PERFORMANCE
INTERLEAVERS FOR PUNCTURED TURBO CODES. Institute for Telecommunications Research. University of South Australia. SPRI Building, Warrendi Road
 INTERLEAVERS FOR PUNCTURED TURBO CODES. Mark S. C. Ho 1, Steven S. Pietrobon 2 and Tim Giles 1 1 Mobile Communications Research Centre Institute for Telecommunications Research University of South Australia
INTERLEAVERS FOR PUNCTURED TURBO CODES. Mark S. C. Ho 1, Steven S. Pietrobon 2 and Tim Giles 1 1 Mobile Communications Research Centre Institute for Telecommunications Research University of South Australia
Improving Min-sum LDPC Decoding Throughput by Exploiting Intra-cell Bit Error Characteristic in MLC NAND Flash Memory
 Improving Min-sum LDPC Decoding Throughput by Exploiting Intra-cell Bit Error Characteristic in MLC NAND Flash Memory Wenzhe Zhao, Hongbin Sun, Minjie Lv, Guiqiang Dong, Nanning Zheng, and Tong Zhang Institute
Improving Min-sum LDPC Decoding Throughput by Exploiting Intra-cell Bit Error Characteristic in MLC NAND Flash Memory Wenzhe Zhao, Hongbin Sun, Minjie Lv, Guiqiang Dong, Nanning Zheng, and Tong Zhang Institute
High speed low complexity radix-16 Max-Log-MAP SISO decoder
 High speed low complexity radix-16 Max-Log-MAP SISO decoder Oscar David Sanchez Gonzalez, Christophe Jego, Michel Jezequel, Yannick Saouter To cite this version: Oscar David Sanchez Gonzalez, Christophe
High speed low complexity radix-16 Max-Log-MAP SISO decoder Oscar David Sanchez Gonzalez, Christophe Jego, Michel Jezequel, Yannick Saouter To cite this version: Oscar David Sanchez Gonzalez, Christophe
A Bandwidth Degradation Technique to Reduce Call Dropping Probability in Mobile Network Systems
 TELKOMNIKA Indonesian Journal of Electrical Engineering Vol. 16, No. 2, November 215, pp. 33 ~ 37 DOI: 1.11591/telkomnika.v16i2.8426 33 A Bandwidth Degradation Technique to Reduce Call Dropping Probability
TELKOMNIKA Indonesian Journal of Electrical Engineering Vol. 16, No. 2, November 215, pp. 33 ~ 37 DOI: 1.11591/telkomnika.v16i2.8426 33 A Bandwidth Degradation Technique to Reduce Call Dropping Probability
Chip Design for Turbo Encoder Module for In-Vehicle System
 Chip Design for Turbo Encoder Module for In-Vehicle System Majeed Nader Email: majeed@wayneedu Yunrui Li Email: yunruili@wayneedu John Liu Email: johnliu@wayneedu Abstract This paper studies design and
Chip Design for Turbo Encoder Module for In-Vehicle System Majeed Nader Email: majeed@wayneedu Yunrui Li Email: yunruili@wayneedu John Liu Email: johnliu@wayneedu Abstract This paper studies design and
Express Letters. A Simple and Efficient Search Algorithm for Block-Matching Motion Estimation. Jianhua Lu and Ming L. Liou
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON CIRCUITS AND SYSTEMS FOR VIDEO TECHNOLOGY, VOL. 7, NO. 2, APRIL 1997 429 Express Letters A Simple and Efficient Search Algorithm for Block-Matching Motion Estimation Jianhua Lu and
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON CIRCUITS AND SYSTEMS FOR VIDEO TECHNOLOGY, VOL. 7, NO. 2, APRIL 1997 429 Express Letters A Simple and Efficient Search Algorithm for Block-Matching Motion Estimation Jianhua Lu and
Quantized Iterative Message Passing Decoders with Low Error Floor for LDPC Codes
 Quantized Iterative Message Passing Decoders with Low Error Floor for LDPC Codes Xiaojie Zhang and Paul H. Siegel University of California, San Diego 1. Introduction Low-density parity-check (LDPC) codes
Quantized Iterative Message Passing Decoders with Low Error Floor for LDPC Codes Xiaojie Zhang and Paul H. Siegel University of California, San Diego 1. Introduction Low-density parity-check (LDPC) codes
A Low-Power ECC Check Bit Generator Implementation in DRAMs
 252 SANG-UHN CHA et al : A LOW-POWER ECC CHECK BIT GENERATOR IMPLEMENTATION IN DRAMS A Low-Power ECC Check Bit Generator Implementation in DRAMs Sang-Uhn Cha *, Yun-Sang Lee **, and Hongil Yoon * Abstract
252 SANG-UHN CHA et al : A LOW-POWER ECC CHECK BIT GENERATOR IMPLEMENTATION IN DRAMS A Low-Power ECC Check Bit Generator Implementation in DRAMs Sang-Uhn Cha *, Yun-Sang Lee **, and Hongil Yoon * Abstract
A LOSSLESS INDEX CODING ALGORITHM AND VLSI DESIGN FOR VECTOR QUANTIZATION
 A LOSSLESS INDEX CODING ALGORITHM AND VLSI DESIGN FOR VECTOR QUANTIZATION Ming-Hwa Sheu, Sh-Chi Tsai and Ming-Der Shieh Dept. of Electronic Eng., National Yunlin Univ. of Science and Technology, Yunlin,
A LOSSLESS INDEX CODING ALGORITHM AND VLSI DESIGN FOR VECTOR QUANTIZATION Ming-Hwa Sheu, Sh-Chi Tsai and Ming-Der Shieh Dept. of Electronic Eng., National Yunlin Univ. of Science and Technology, Yunlin,
A Self-Organized Femtocell for IEEE e System
 A Self-Organized Femtocell for IEEE 80.16e System Young Jin Sang, Hae Gwang Hwang and Kwang Soon Kim School of Electrical and Electronic Engineering, Yonsei University 134, Shinchong-dong, Seodaemun-gu,
A Self-Organized Femtocell for IEEE 80.16e System Young Jin Sang, Hae Gwang Hwang and Kwang Soon Kim School of Electrical and Electronic Engineering, Yonsei University 134, Shinchong-dong, Seodaemun-gu,
Implementation of Efficient Modified Booth Recoder for Fused Sum-Product Operator
 Implementation of Efficient Modified Booth Recoder for Fused Sum-Product Operator A.Sindhu 1, K.PriyaMeenakshi 2 PG Student [VLSI], Dept. of ECE, Muthayammal Engineering College, Rasipuram, Tamil Nadu,
Implementation of Efficient Modified Booth Recoder for Fused Sum-Product Operator A.Sindhu 1, K.PriyaMeenakshi 2 PG Student [VLSI], Dept. of ECE, Muthayammal Engineering College, Rasipuram, Tamil Nadu,
A New List Decoding Algorithm for Short-Length TBCCs With CRC
 Received May 15, 2018, accepted June 11, 2018, date of publication June 14, 2018, date of current version July 12, 2018. Digital Object Identifier 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2847348 A New List Decoding Algorithm
Received May 15, 2018, accepted June 11, 2018, date of publication June 14, 2018, date of current version July 12, 2018. Digital Object Identifier 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2847348 A New List Decoding Algorithm
Reduced complexity Log-MAP algorithm with Jensen inequality based non-recursive max operator for turbo TCM decoding
 Sybis and Tyczka EURASIP Journal on Wireless Communications and Networking 2013, 2013:238 RESEARCH Open Access Reduced complexity Log-MAP algorithm with Jensen inequality based non-recursive max operator
Sybis and Tyczka EURASIP Journal on Wireless Communications and Networking 2013, 2013:238 RESEARCH Open Access Reduced complexity Log-MAP algorithm with Jensen inequality based non-recursive max operator
Reduced-State Soft-Input/Soft-Output Algorithms for Complexity Reduction in Iterative and Non-Iterative Data Detection
 Reduced-State Soft-Input/Soft-Output Algorithms for Complexity Reduction in Iterative and Non-Iterative Data Detection Xiaopeng Chen and Keith M. Chugg Abstract Soft-input/soft-output (SISO) algorithms
Reduced-State Soft-Input/Soft-Output Algorithms for Complexity Reduction in Iterative and Non-Iterative Data Detection Xiaopeng Chen and Keith M. Chugg Abstract Soft-input/soft-output (SISO) algorithms
Near Optimal Repair Rate Built-in Redundancy Analysis with Very Small Hardware Overhead
 Near Optimal Repair Rate Built-in Redundancy Analysis with Very Small Hardware Overhead Woosung Lee, Keewon Cho, Jooyoung Kim, and Sungho Kang Department of Electrical & Electronic Engineering, Yonsei
Near Optimal Repair Rate Built-in Redundancy Analysis with Very Small Hardware Overhead Woosung Lee, Keewon Cho, Jooyoung Kim, and Sungho Kang Department of Electrical & Electronic Engineering, Yonsei
Design and Implementation of Signed, Rounded and Truncated Multipliers using Modified Booth Algorithm for Dsp Systems.
 Design and Implementation of Signed, Rounded and Truncated Multipliers using Modified Booth Algorithm for Dsp Systems. K. Ram Prakash 1, A.V.Sanju 2 1 Professor, 2 PG scholar, Department of Electronics
Design and Implementation of Signed, Rounded and Truncated Multipliers using Modified Booth Algorithm for Dsp Systems. K. Ram Prakash 1, A.V.Sanju 2 1 Professor, 2 PG scholar, Department of Electronics
SINCE its introduction in 1993 [1], turbo codes have found
![SINCE its introduction in 1993 [1], turbo codes have found SINCE its introduction in 1993 [1], turbo codes have found](/thumbs/89/98781237.jpg) 1718 IEEE JOURNAL OF SOLID-STATE CIRCUITS, VOL. 40, NO. 8, AUGUST 2005 A 285-MHz Pipelined MAP Decoder in 0.18-m CMOS Seok-Jun Lee, Member, IEEE, Naresh R. Shanbhag, Senior Member, IEEE, and Andrew C.
1718 IEEE JOURNAL OF SOLID-STATE CIRCUITS, VOL. 40, NO. 8, AUGUST 2005 A 285-MHz Pipelined MAP Decoder in 0.18-m CMOS Seok-Jun Lee, Member, IEEE, Naresh R. Shanbhag, Senior Member, IEEE, and Andrew C.
NOWADAYS, multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO)
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON CIRCUITS AND SYSTEMS I: REGULAR PAPERS, VOL. 56, NO. 3, MARCH 2009 685 Probabilistic Spherical Detection and VLSI Implementation for Multiple-Antenna Systems Chester Sungchung Park,
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON CIRCUITS AND SYSTEMS I: REGULAR PAPERS, VOL. 56, NO. 3, MARCH 2009 685 Probabilistic Spherical Detection and VLSI Implementation for Multiple-Antenna Systems Chester Sungchung Park,
Efficient Majority Logic Fault Detector/Corrector Using Euclidean Geometry Low Density Parity Check (EG-LDPC) Codes
 Efficient Majority Logic Fault Detector/Corrector Using Euclidean Geometry Low Density Parity Check (EG-LDPC) Codes 1 U.Rahila Begum, 2 V. Padmajothi 1 PG Student, 2 Assistant Professor 1 Department Of
Efficient Majority Logic Fault Detector/Corrector Using Euclidean Geometry Low Density Parity Check (EG-LDPC) Codes 1 U.Rahila Begum, 2 V. Padmajothi 1 PG Student, 2 Assistant Professor 1 Department Of
FAST Fourier transform (FFT) is an important signal processing
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON CIRCUITS AND SYSTEMS I: REGULAR PAPERS, VOL. 54, NO. 4, APRIL 2007 889 Balanced Binary-Tree Decomposition for Area-Efficient Pipelined FFT Processing Hyun-Yong Lee, Student Member,
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON CIRCUITS AND SYSTEMS I: REGULAR PAPERS, VOL. 54, NO. 4, APRIL 2007 889 Balanced Binary-Tree Decomposition for Area-Efficient Pipelined FFT Processing Hyun-Yong Lee, Student Member,
SINGLE PASS DEPENDENT BIT ALLOCATION FOR SPATIAL SCALABILITY CODING OF H.264/SVC
 SINGLE PASS DEPENDENT BIT ALLOCATION FOR SPATIAL SCALABILITY CODING OF H.264/SVC Randa Atta, Rehab F. Abdel-Kader, and Amera Abd-AlRahem Electrical Engineering Department, Faculty of Engineering, Port
SINGLE PASS DEPENDENT BIT ALLOCATION FOR SPATIAL SCALABILITY CODING OF H.264/SVC Randa Atta, Rehab F. Abdel-Kader, and Amera Abd-AlRahem Electrical Engineering Department, Faculty of Engineering, Port
A Review on Analysis on Codes using Different Algorithms
 A Review on Analysis on Codes using Different Algorithms Devansh Vats Gaurav Kochar Rakesh Joon (ECE/GITAM/MDU) (ECE/GITAM/MDU) (HOD-ECE/GITAM/MDU) Abstract-Turbo codes are a new class of forward error
A Review on Analysis on Codes using Different Algorithms Devansh Vats Gaurav Kochar Rakesh Joon (ECE/GITAM/MDU) (ECE/GITAM/MDU) (HOD-ECE/GITAM/MDU) Abstract-Turbo codes are a new class of forward error
LOW-DENSITY PARITY-CHECK (LDPC) codes [1] can
![LOW-DENSITY PARITY-CHECK (LDPC) codes [1] can LOW-DENSITY PARITY-CHECK (LDPC) codes [1] can](/thumbs/96/128999908.jpg) 208 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON MAGNETICS, VOL 42, NO 2, FEBRUARY 2006 Structured LDPC Codes for High-Density Recording: Large Girth and Low Error Floor J Lu and J M F Moura Department of Electrical and Computer
208 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON MAGNETICS, VOL 42, NO 2, FEBRUARY 2006 Structured LDPC Codes for High-Density Recording: Large Girth and Low Error Floor J Lu and J M F Moura Department of Electrical and Computer
