LAB #8. Last Survey, I promise!!! Please fill out this really quick survey about paired programming and information about your declared major and CS.
|
|
|
- Gwendoline Poole
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 LAB #8 Each lab will begin with a brief demonstration by the TAs for the core concepts examined in this lab. As such, this document will not serve to tell you everything the TAs will in the demo. It is highly encouraged that you ask questions and take notes. In order to get credit for the lab, you need to be checked off by the end of lab. For nonzero lab 6 or 7, you can earn full points for completion of the lab outside of lab time, but you must finish the labs before leaving today!!!! For extenuating circumstance, contact your lab TAs and Jennifer Parham-Mocello. Pair Programming From this lab forward, you can choose a partner for pair programming. You must be checked off together. You only need one computer for pair programming. One person will be the driver, who controls the computer and codes, while the other is the navigator, who observes and advises. After 20 minutes, your TA will switch driver and navigator, continuing this pattern until the task is complete. Please read more about pair programming and the benefits: Pair Programming Student Handout Lab 8 Details: In this lab, you will not implement anything new. Instead, you will debug programs written for you. Due to not getting to 2-d arrays last week, along with the number of students who did not finish Lab 6 and 7, I wanted to give you a little bit of a break!!! For non-zero lab 6 or 7, you can earn full points for completion of the lab outside of lab time, but you must finish these labs before leaving today!!!! If you don t finish lab 8, you can get all the points back at the beginning of Lab 9 next week, since lab 8 is just debugging and can be done on your own. (1 pt) Paired Programming/Major Survey Last Survey, I promise!!! Please fill out this really quick survey about paired programming and information about your declared major and CS. (3 pts) Debugging using a debugger The purpose of a debugger such as GDB is to allow you to see what is going on "inside" another program while it executes -- or what another program was doing at the moment it crashed. GDB can do four main kinds of things (plus other things in support of these) to help you catch bugs in the act:
2 Start your program, specifying anything that might affect its behavior. Make your program stop on specified conditions. Examine what has happened, when your program has stopped. Change things in your program, so you can experiment with correcting the effects of one bug and go on to learn about another. GDB Manpage is a good source of information, i.e. man gdb. The first thing you need to do to start debugging your program is to compile it with debugging symbols, this is accomplished with the -g flag: g++ filename.cpp -g -o filename Lets start with a simple program that gets a line of text from the user, and prints it out backwards to the screen: #include <iostream> #include <string.h> using namespace std; int main(int argc, char *argv[]){ char input[50]; int i = 0; cin >> input; for(i = strlen(input); i >= 0; i--){ cout << input[i]; cout << endl; return 0; compile and start the debugger with: g++ debug.cpp -g -o debug gdb./debug (start another session which will run gdb)
3 Here is a mini tutorial for the 8 main commands that you will mostly be using in your debugging session 1. break 2. run 3. print 4. next & step 5. continue 6. display & watch 7. where (or bt) 1. The break Command: gdb will remember the line numbers of your source file. This will let us easily set up break points in the program. A break point, is a line in the code where you want execution to pause. Once you pause execution you will be able to examine variables, and walk through the program, and other things of that nature. Continuing with our example lets set up a break point at line 6, just before we declare int i = 0; break 9 Breakpoint 1 at 0x400923: file debug.cpp, line The run Command: run will begin initial execution of your program. This will run your program as you normally would outside of the debugger, until it reaches a break point line. This means if you need to pass
4 any command line arguments, you list them after run just as they would be listed after the program name on the command line. At this moment, you will have been returned to the gdb command prompt. (Using run again after your program has been started, will ask to terminate the current execution and start over) From our example: Starting program: /nfs/farm/classes/eecs/fall2013/eecs /private/a.out Breakpoint 1, main (argc=1, argv=0x7fffffffd008) at debug.cpp:9 9 int i = 0; 3. The print Command: print will let you see the values of data in your program. It takes an argument of the variable name. In our example, we are paused right before we declare and initialize i. Let s look what the value of i is now: print i $1 = i contains garbage, we haven t put anything into it yet. 4. The next and step Commands: next and step do basically the same thing, step line by line through the program. The difference is that next steps over a function call, and step will step into it. Now in our example, we will step to the beginning of the next instruction step 11 cin >> input; before we execute the cin, let s check the value of i again: print i $2 = 0 i is now equal to 0, like it should be. Now, let s use next to move into the cin statement:
5 next What happened here? We weren't returned to the gdb prompt. Well the program is inside cin, waiting for us to input something. Input string here, and press enter. 5. The continue Command continue will pick up execution of the program after it has reached a break point. Let s continue to the end of the program now: continue Continuing. olleh Program exited normally. Here we've reached the end of our program, you can see that it printed in reverse "input", which is what was fed to cin. 6. The display and watch Commands: display will show a variable s contents at each step of the way in your program. Let s start over in our example. Delete the breakpoint at line 6 del break 1 This deletes our first breakpoint at line 9. You can also clear all breakpoints w/ clear. Now, let s set a new breakpoint at line 14, the cout statement inside the for loop break 14 Breakpoint 2 at 0x40094c: file debug.cpp, line 14. Run the program again, and enter the input. When it returns to the gdb command prompt, we will display input[i] and watch it through the for loop with each next or breakpoint. Breakpoint 2, main (argc=1, argv=0x7fffffffd008) at debug.cpp:14 14 cout << input[i]; display input[i] 1: input[i] = 0 '\0' next 13 for(i=strlen(input);i>=0;i--) { 1: input[i] = 0 '\0'
6 next Breakpoint 2, main (argc=1, argv=0x7fffffffd008) at debug.cpp:14 14 cout << input[i]; 1: input[i] = 111 'o' next 13 for(i=strlen(input);i>=0;i--) { 1: input[i] = 111 'o' next Here we stepped through the loop, always looking at what input[i] was equal to. We can also watch a variable, which allows us to see the contents at any point when the memory changes. watch input Watchpoint 2: input continue Continuing. hello Watchpoint 2: input Old value = "\030\320\377\377\377\177\000\000\065\n@\000\000\000\000\000\210\373\240\031\ 065\000\000\000\360\t@", '\000' <repeats 13 times>, "0\b@\000\000\000\000\000\000", <incomplete sequence \320> New value = "h\320\377\377\377\177\000\000\065\n@\000\000\000\000\000\210\373\240\031\065 \000\000\000\360\t@", '\000' <repeats 13 times>, "0\b@\000\000\000\000\000\000", <incomplete sequence \320> 0x b82a in std::basic_istream<char, std::char_traits<char> >& std::operator>><char, std::char_traits<char> >(std::basic_istream<char, std::char_traits<char> >&, char*) () from /usr/lib64/libstdc++.so.6 continue Continuing. Watchpoint 2: input Old value = "h\320\377\377\377\177\000\000\065\n@\000\000\000\000\000\210\373\240\031\065 \000\000\000\360\t@", '\000' <repeats 13 times>, "0\b@\000\000\000\000\000\000", <incomplete sequence \320> New value = "he\377\377\377\177\000\000\065\n@\000\000\000\000\000\210\373\240\031\065\00 0\000\000\360\t@", '\000' <repeats 13 times>, "0\b@\000\000\000\000\000\000", <incomplete sequence \320> 0x b82a in std::basic_istream<char, std::char_traits<char> >& std::operator>><char, std::char_traits<char> >(std::basic_istream<char, std::char_traits<char> >&, char*) () from /usr/lib64/libstdc++.so.6 7. The where (or bt) Command
7 The where (or bt) command prints a backtrace of all stack frames. This may not make much sense but it is useful in seeing where our program crashes. Let s modify our program just a little so that it will crash: #include <iostream> #include <string.h> using namespace std; int main(int argc, char *argv[]){ char *input = NULL; int i = 0; cin >> input; for(i = strlen(input); i >= 0; i--){ cout << input[i]; cout << endl; return 0; Here we've changed input to be a pointer to a char and set it to NULL to make sure it doesn t point anywhere until we set it. Recompile and run gdb on it again to see what happens when it crashes. r Starting program: /nfs/farm/classes/eecs/fall2013/eecs /private/a.out hello Program received signal SIGSEGV, Segmentation fault. 0x b826 in std::basic_istream<char, std::char_traits<char> >& std::operator>><char, std::char_traits<char> >(std::basic_istream<char, std::char_traits<char> >&, char*) () from /usr/lib64/libstdc++.so.6 where #0 0x b826 in std::basic_istream<char, std::char_traits<char> >& std::operator>><char, std::char_traits<char> >(std::basic_istream<char, std::char_traits<char> >&, char*) () from /usr/lib64/libstdc++.so.6 #1 0x in main (argc=1, argv=0x7fffffffd008) at debug.cpp:11 We see at the bottom, two frames. #1 is the top most frame and shows where we crashed. Use the up command to move up the stack. up
8 #1 0x in main (argc=1, argv=0x7fffffffd008) at debug.cpp:11 11 cin >> input; Here we see line #11 11 cin >> input; The line where we crashed. Here are some more tutorials for the gdb: (3 pts) Understanding Errors Here is a functional program that compares two strings supplied as command line arguments to see if they are equal. If they are equal, it returns true, and if they are not equal, then it returns false. Copy and paste this program into a new source file. #include <iostream> using namespace std; bool is_equal(char *str1, char *str2) { int i; for(i=0; str1[i]!='\0' && str2[i]!='\0'; i++) if(str1[i]!=str2[i]) return false; if(str1[i]!='\0' str2[i]!='\0') return false; return true; int main() { char *str1=null, *str2=null; str1=new char[256]; str2=new char[256]; cout << enter string 1: ; cin >> str1; cout << enter string 2: ; cin >> str2; cout << is_equal(str1, str2) << endl;
9 return 0; Now, you are going to deliberately create errors, and record on a piece of paper what you notice about these errors. For example, when you remove a semicolon from a line 12 in the program, then the compiler gives you an error on a few lines below, at the next statement, alarming you that you have a missing semicolon before the statement on line 14. Perform each of these errors, and record your understanding of the error and why it is the error it is After you make the error, restore the program back to functional before making another error!!! Syntax errors (What does the compiler say!!!) Remove a semicolon from line 14. Remove the curly brace from line 5. Add an & to the str1 and str2 arguments in the call to is_equal() on line 27. Remove the asterisk/splat from the char pointers str1 and str2 on line 18. Remove the return type, bool, from the is_equal() function on line 5. Remove one of the parameters in the is_equal() function on line 5. Comment out line 6, and declare i in the for loop on line 7. Logic errors (What is the output!!!) Put two asterisks/splats on the parameters of line 5, and put ampersand, &, in front of the arguments on line 27. Let s use the gdb debugger If we were to have this type of error and didn t know what is going on, where would be the first place you would look? You should think to yourself, what are the values of str1 and str2 when the function is_equal() is called, i.e. not before the call, but after the call! Use the gdb debugger to set the appropriate breakpoint in the program (after the call to the is_equal() function but at the declaration of the local variables) and display the values of str1 and str2. Are these what you expect? Make your changes back and look at what you are passing when the program is correct, rather than when you added the extra splat and ampersand. Comment out line 11 and 12, and run with hell and hello as input. How would you use gdb to discover this error? Comment out line 19 and 20, and run with any strings as input. How would you use gdb to discover this error? The above program allocates memory, but it does not free the memory. We will learn about a utility in Linux that allows us to view how much memory we have allocated and deallocated (freed) during a run of your program. You can run your program through this utility called valgrind. For example, type valgrind prog_name at the prompt.
10 % valgrind str_equal Make sure this program doesn t have any memory leaks using valgrind. What statements do you need to add? (3 pts) Debugging Logic Errors (by printing and tracing): Below is code that has logic errors. Logic errors are usually caught by using print statements to make sure the contents of variables are what you think they are, printing indicator messages, and commenting out code to localize the error. In the following code, go through the code and systematically fixing the logic errors by inserting print statements to check the contents of the variables. You might want to use comments to narrow the scope of your code to help find the errors. You can copy and paste the code below or download from here: prime_debug.cpp #include <iostream> #define PROMPT "Please enter a whole number:" #define NOT_PRIME "The number is not a prime number./n" #define PRIME "The number is a prime number./n" using std::cout; using std::cin; void is_prime(int); int main(){ char number; /* number provided by user */ cout << PROMPT; /* promt user */ cin >> number; /* wait for user input */ is_prime(number); /*determine if number prime or not*/ return 0; /* exit program */ /* Prime numbers are defined as any number greater * than one that is only divisible by one and itself. * Dividing the number by two shortens the time it * takes to complete. */ void is_prime(int number){ for(int i = 3; i < number/2; ++i) if( number/i == 0 ){ /* if divisible */ cout << NOT_PRIME << number; /* not prime */ return; /* exit program */ /* if number is not divisible by anything * than it must be prime */ cout << PRIME << number;
11 Extended Learning (Lab 9) Implement Towers of Hanoi First, you can implement this is using a static 2-D array with 3 columns for the 3 posts, and you can initialize the array with the numbers 1, 2, and 3 in the first column to represent the initial state of the game. The goal is to print out the board after each move in the game, seeing the following output. Example with two disks: Begin by designing these two functions, towers() and print_array(). To help you out, your towers() function will be recursive with the following prototype: void towers(int disks, int b[][cols], int from_col, int to_col, int spare); Here is an outline of the recursive towers function: If(number of disks is >= 1) Call Towers with (disks-1, b, from_col, spare, to_col) Move the disk Print the board Call Towers with (disks-1, b, spare, to_col, from_col)
LAB #8. GDB can do four main kinds of things (plus other things in support of these) to help you catch bugs in the act:
 LAB #8 Each lab will begin with a brief demonstration by the TAs for the core concepts examined in this lab. As such, this document will not serve to tell you everything the TAs will in the demo. It is
LAB #8 Each lab will begin with a brief demonstration by the TAs for the core concepts examined in this lab. As such, this document will not serve to tell you everything the TAs will in the demo. It is
Lab 8. Follow along with your TA as they demo GDB. Make sure you understand all of the commands, how and when to use them.
 Lab 8 Each lab will begin with a recap of last lab and a brief demonstration by the TAs for the core concepts examined in this lab. As such, this document will not serve to tell you everything the TAs
Lab 8 Each lab will begin with a recap of last lab and a brief demonstration by the TAs for the core concepts examined in this lab. As such, this document will not serve to tell you everything the TAs
CSCI0330 Intro Computer Systems Doeppner. Lab 02 - Tools Lab. Due: Sunday, September 23, 2018 at 6:00 PM. 1 Introduction 0.
 CSCI0330 Intro Computer Systems Doeppner Lab 02 - Tools Lab Due: Sunday, September 23, 2018 at 6:00 PM 1 Introduction 0 2 Assignment 0 3 gdb 1 3.1 Setting a Breakpoint 2 3.2 Setting a Watchpoint on Local
CSCI0330 Intro Computer Systems Doeppner Lab 02 - Tools Lab Due: Sunday, September 23, 2018 at 6:00 PM 1 Introduction 0 2 Assignment 0 3 gdb 1 3.1 Setting a Breakpoint 2 3.2 Setting a Watchpoint on Local
C++ for Everyone, 2e, Cay Horstmann, Copyright 2012 John Wiley and Sons, Inc. All rights reserved. Using a Debugger WE5.
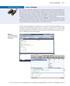 Using a Debugger WE5 W o r k E D E x a m p l e 5.2 Using a Debugger As you have undoubtedly realized by now, computer programs rarely run perfectly the first time. At times, it can be quite frustrating
Using a Debugger WE5 W o r k E D E x a m p l e 5.2 Using a Debugger As you have undoubtedly realized by now, computer programs rarely run perfectly the first time. At times, it can be quite frustrating
CS354 gdb Tutorial Written by Chris Feilbach
 CS354 gdb Tutorial Written by Chris Feilbach Purpose This tutorial aims to show you the basics of using gdb to debug C programs. gdb is the GNU debugger, and is provided on systems that
CS354 gdb Tutorial Written by Chris Feilbach Purpose This tutorial aims to show you the basics of using gdb to debug C programs. gdb is the GNU debugger, and is provided on systems that
IDE: Integrated Development Environment
 Name: Student ID: Lab Instructor: Borja Sotomayor Do not write in this area 1 2 3 TOTAL Maximum possible points: 30 One of the goals of this lab is to introduce the Eclipse IDE, a software environment
Name: Student ID: Lab Instructor: Borja Sotomayor Do not write in this area 1 2 3 TOTAL Maximum possible points: 30 One of the goals of this lab is to introduce the Eclipse IDE, a software environment
CS 103 Lab - Party Like A Char Star
 1 Introduction In this lab you will implement a "hangman" game where the user is shown blanks representing letter of a word and then tries to guess and fill in the letters with a limited number of guesses.
1 Introduction In this lab you will implement a "hangman" game where the user is shown blanks representing letter of a word and then tries to guess and fill in the letters with a limited number of guesses.
Outline. Computer programming. Debugging. What is it. Debugging. Hints. Debugging
 Outline Computer programming Debugging Hints Gathering evidence Common C errors "Education is a progressive discovery of our own ignorance." Will Durant T.U. Cluj-Napoca - Computer Programming - lecture
Outline Computer programming Debugging Hints Gathering evidence Common C errors "Education is a progressive discovery of our own ignorance." Will Durant T.U. Cluj-Napoca - Computer Programming - lecture
GDB Tutorial. A Walkthrough with Examples. CMSC Spring Last modified March 22, GDB Tutorial
 A Walkthrough with Examples CMSC 212 - Spring 2009 Last modified March 22, 2009 What is gdb? GNU Debugger A debugger for several languages, including C and C++ It allows you to inspect what the program
A Walkthrough with Examples CMSC 212 - Spring 2009 Last modified March 22, 2009 What is gdb? GNU Debugger A debugger for several languages, including C and C++ It allows you to inspect what the program
Scientific Computing
 Scientific Computing Martin Lotz School of Mathematics The University of Manchester Lecture 1, September 22, 2014 Outline Course Overview Programming Basics The C++ Programming Language Outline Course
Scientific Computing Martin Lotz School of Mathematics The University of Manchester Lecture 1, September 22, 2014 Outline Course Overview Programming Basics The C++ Programming Language Outline Course
#include <iostream> #include <algorithm> #include <cmath> using namespace std; int f1(int x, int y) { return (double)(x/y); }
 1. (9 pts) Show what will be output by the cout s in this program. As in normal program execution, any update to a variable should affect the next statement. (Note: boolalpha simply causes Booleans to
1. (9 pts) Show what will be output by the cout s in this program. As in normal program execution, any update to a variable should affect the next statement. (Note: boolalpha simply causes Booleans to
Lab # 02. Basic Elements of C++ _ Part1
 Lab # 02 Basic Elements of C++ _ Part1 Lab Objectives: After performing this lab, the students should be able to: Become familiar with the basic components of a C++ program, including functions, special
Lab # 02 Basic Elements of C++ _ Part1 Lab Objectives: After performing this lab, the students should be able to: Become familiar with the basic components of a C++ program, including functions, special
1. Allowed you to see the value of one or more variables, or 2. Indicated where you were in the execution of a program
 CS0449 GDB Lab What is a debugger? A debugger is a program that helps you find logical mistakes in your programs by running them in a controlled way. Undoubtedly by this point in your programming life,
CS0449 GDB Lab What is a debugger? A debugger is a program that helps you find logical mistakes in your programs by running them in a controlled way. Undoubtedly by this point in your programming life,
377 Student Guide to C++
 377 Student Guide to C++ c Mark Corner January 21, 2004 1 Introduction In this course you will be using the C++ language to complete several programming assignments. Up to this point we have only provided
377 Student Guide to C++ c Mark Corner January 21, 2004 1 Introduction In this course you will be using the C++ language to complete several programming assignments. Up to this point we have only provided
CSE 374 Programming Concepts & Tools
 CSE 374 Programming Concepts & Tools Hal Perkins Fall 2017 Lecture 11 gdb and Debugging 1 Administrivia HW4 out now, due next Thursday, Oct. 26, 11 pm: C code and libraries. Some tools: gdb (debugger)
CSE 374 Programming Concepts & Tools Hal Perkins Fall 2017 Lecture 11 gdb and Debugging 1 Administrivia HW4 out now, due next Thursday, Oct. 26, 11 pm: C code and libraries. Some tools: gdb (debugger)
CSE 374 Programming Concepts & Tools. Brandon Myers Winter 2015 Lecture 11 gdb and Debugging (Thanks to Hal Perkins)
 CSE 374 Programming Concepts & Tools Brandon Myers Winter 2015 Lecture 11 gdb and Debugging (Thanks to Hal Perkins) Hacker tool of the week (tags) Problem: I want to find the definition of a function or
CSE 374 Programming Concepts & Tools Brandon Myers Winter 2015 Lecture 11 gdb and Debugging (Thanks to Hal Perkins) Hacker tool of the week (tags) Problem: I want to find the definition of a function or
Multiple Choice (Questions 1 14) 28 Points Select all correct answers (multiple correct answers are possible)
 Name Closed notes, book and neighbor. If you have any questions ask them. Notes: Segment of code necessary C++ statements to perform the action described not a complete program Program a complete C++ program
Name Closed notes, book and neighbor. If you have any questions ask them. Notes: Segment of code necessary C++ statements to perform the action described not a complete program Program a complete C++ program
Problem Set 1: Unix Commands 1
 Problem Set 1: Unix Commands 1 WARNING: IF YOU DO NOT FIND THIS PROBLEM SET TRIVIAL, I WOULD NOT RECOMMEND YOU TAKE THIS OFFERING OF 300 AS YOU DO NOT POSSESS THE REQUISITE BACKGROUND TO PASS THE COURSE.
Problem Set 1: Unix Commands 1 WARNING: IF YOU DO NOT FIND THIS PROBLEM SET TRIVIAL, I WOULD NOT RECOMMEND YOU TAKE THIS OFFERING OF 300 AS YOU DO NOT POSSESS THE REQUISITE BACKGROUND TO PASS THE COURSE.
Lab Instructor : Jean Lai
 Lab Instructor : Jean Lai Group related statements to perform a specific task. Structure the program (No duplicate codes!) Must be declared before used. Can be invoked (called) as any number of times.
Lab Instructor : Jean Lai Group related statements to perform a specific task. Structure the program (No duplicate codes!) Must be declared before used. Can be invoked (called) as any number of times.
CS 11 C track: lecture 6
 CS 11 C track: lecture 6 Last week: pointer arithmetic This week: The gdb program struct typedef linked lists gdb for debugging (1) gdb: the Gnu DeBugger http://courses.cms.caltech.edu/cs11/material /c/mike/misc/gdb.html
CS 11 C track: lecture 6 Last week: pointer arithmetic This week: The gdb program struct typedef linked lists gdb for debugging (1) gdb: the Gnu DeBugger http://courses.cms.caltech.edu/cs11/material /c/mike/misc/gdb.html
Binomial pricer (1.1)
 1 Binomial pricer 1.1 Program shell 1.2 Entering data 1.3 Functions 1.4 Separate compilation 1.5 CRR pricer 1.6 Pointers 1.7 Function pointers 1.8 Taking stock In the binomial model the prices of assets
1 Binomial pricer 1.1 Program shell 1.2 Entering data 1.3 Functions 1.4 Separate compilation 1.5 CRR pricer 1.6 Pointers 1.7 Function pointers 1.8 Taking stock In the binomial model the prices of assets
EE 355 Lab 4 - Party Like A Char Star
 1 Introduction In this lab you will implement a "hangman" game where the user is shown blanks representing letter of a word and then tries to guess and fill in the letters with a limited number of guesses
1 Introduction In this lab you will implement a "hangman" game where the user is shown blanks representing letter of a word and then tries to guess and fill in the letters with a limited number of guesses
Programming Tips for CS758/858
 Programming Tips for CS758/858 January 28, 2016 1 Introduction The programming assignments for CS758/858 will all be done in C. If you are not very familiar with the C programming language we recommend
Programming Tips for CS758/858 January 28, 2016 1 Introduction The programming assignments for CS758/858 will all be done in C. If you are not very familiar with the C programming language we recommend
GE U111 Engineering Problem Solving & Computation Lecture 6 February 2, 2004
 GE U111 Engineering Problem Solving & Computation Lecture 6 February 2, 2004 Functions and Program Structure Today we will be learning about functions. You should already have an idea of their uses. Cout
GE U111 Engineering Problem Solving & Computation Lecture 6 February 2, 2004 Functions and Program Structure Today we will be learning about functions. You should already have an idea of their uses. Cout
CS/COE 0449 term 2174 Lab 5: gdb
 CS/COE 0449 term 2174 Lab 5: gdb What is a debugger? A debugger is a program that helps you find logical mistakes in your programs by running them in a controlled way. Undoubtedly by this point in your
CS/COE 0449 term 2174 Lab 5: gdb What is a debugger? A debugger is a program that helps you find logical mistakes in your programs by running them in a controlled way. Undoubtedly by this point in your
Laboratory 1 Semester 1 11/12
 CS2106 National University of Singapore School of Computing Laboratory 1 Semester 1 11/12 MATRICULATION NUMBER: In this lab exercise, you will get familiarize with some basic UNIX commands, editing and
CS2106 National University of Singapore School of Computing Laboratory 1 Semester 1 11/12 MATRICULATION NUMBER: In this lab exercise, you will get familiarize with some basic UNIX commands, editing and
AN OVERVIEW OF C++ 1
 AN OVERVIEW OF C++ 1 OBJECTIVES Introduction What is object-oriented programming? Two versions of C++ C++ console I/O C++ comments Classes: A first look Some differences between C and C++ Introducing function
AN OVERVIEW OF C++ 1 OBJECTIVES Introduction What is object-oriented programming? Two versions of C++ C++ console I/O C++ comments Classes: A first look Some differences between C and C++ Introducing function
CS 103 Lab 6 - Party Like A Char Star
 1 Introduction In this lab you will implement a "hangman" game where the user is shown blanks representing letter of a word and then tries to guess and fill in the letters with a limited number of guesses.
1 Introduction In this lab you will implement a "hangman" game where the user is shown blanks representing letter of a word and then tries to guess and fill in the letters with a limited number of guesses.
Chapter 2. Procedural Programming
 Chapter 2 Procedural Programming 2: Preview Basic concepts that are similar in both Java and C++, including: standard data types control structures I/O functions Dynamic memory management, and some basic
Chapter 2 Procedural Programming 2: Preview Basic concepts that are similar in both Java and C++, including: standard data types control structures I/O functions Dynamic memory management, and some basic
CSE 410: Systems Programming
 CSE 410: Systems Programming Recitation 4: Introduction to gdb Introduction The GNU Debugger, or gdb, is a powerful symbolic debugger. Symbolic debuggers are available for many languages and platforms,
CSE 410: Systems Programming Recitation 4: Introduction to gdb Introduction The GNU Debugger, or gdb, is a powerful symbolic debugger. Symbolic debuggers are available for many languages and platforms,
Program Organization and Comments
 C / C++ PROGRAMMING Program Organization and Comments Copyright 2013 Dan McElroy Programming Organization The layout of a program should be fairly straight forward and simple. Although it may just look
C / C++ PROGRAMMING Program Organization and Comments Copyright 2013 Dan McElroy Programming Organization The layout of a program should be fairly straight forward and simple. Although it may just look
1 Unit 8 'for' Loops
 1 Unit 8 'for' Loops 2 Control Structures We need ways of making decisions in our program To repeat code until we want it to stop To only execute certain code if a condition is true To execute one segment
1 Unit 8 'for' Loops 2 Control Structures We need ways of making decisions in our program To repeat code until we want it to stop To only execute certain code if a condition is true To execute one segment
EE 355 Lab 3 - Algorithms & Control Structures
 1 Introduction In this lab you will gain experience writing C/C++ programs that utilize loops and conditional structures. This assignment should be performed INDIVIDUALLY. This is a peer evaluated lab
1 Introduction In this lab you will gain experience writing C/C++ programs that utilize loops and conditional structures. This assignment should be performed INDIVIDUALLY. This is a peer evaluated lab
Lecture 07 Debugging Programs with GDB
 Lecture 07 Debugging Programs with GDB In this lecture What is debugging Most Common Type of errors Process of debugging Examples Further readings Exercises What is Debugging Debugging is the process of
Lecture 07 Debugging Programs with GDB In this lecture What is debugging Most Common Type of errors Process of debugging Examples Further readings Exercises What is Debugging Debugging is the process of
CSE au Midterm Exam Nov. 2, 2018 Sample Solution
 Question 1. (16 points) Build tools and make. We re building a C++ software back-end prototype for a new food web site. So far, we ve got the following source files with the code for two main programs
Question 1. (16 points) Build tools and make. We re building a C++ software back-end prototype for a new food web site. So far, we ve got the following source files with the code for two main programs
C++ for Java Programmers
 Basics all Finished! Everything we have covered so far: Lecture 5 Operators Variables Arrays Null Terminated Strings Structs Functions 1 2 45 mins of pure fun Introduction Today: Pointers Pointers Even
Basics all Finished! Everything we have covered so far: Lecture 5 Operators Variables Arrays Null Terminated Strings Structs Functions 1 2 45 mins of pure fun Introduction Today: Pointers Pointers Even
Exercise Session 6 Computer Architecture and Systems Programming
 Systems Group Department of Computer Science ETH Zürich Exercise Session 6 Computer Architecture and Systems Programming Herbstsemester 2016 Agenda GDB Outlook on assignment 6 GDB The GNU Debugger 3 Debugging..
Systems Group Department of Computer Science ETH Zürich Exercise Session 6 Computer Architecture and Systems Programming Herbstsemester 2016 Agenda GDB Outlook on assignment 6 GDB The GNU Debugger 3 Debugging..
Introduction to C ++
 Introduction to C ++ Thomas Branch tcb06@ic.ac.uk Imperial College Software Society October 18, 2012 1 / 48 Buy Software Soc. s Free Membership at https://www.imperialcollegeunion.org/shop/ club-society-project-products/software-products/436/
Introduction to C ++ Thomas Branch tcb06@ic.ac.uk Imperial College Software Society October 18, 2012 1 / 48 Buy Software Soc. s Free Membership at https://www.imperialcollegeunion.org/shop/ club-society-project-products/software-products/436/
Laboratory 0 Week 0 Advanced Structured Programming An Introduction to Visual Studio and C++
 Laboratory 0 Week 0 Advanced Structured Programming An Introduction to Visual Studio and C++ 0.1 Introduction This is a session to familiarize working with the Visual Studio development environment. It
Laboratory 0 Week 0 Advanced Structured Programming An Introduction to Visual Studio and C++ 0.1 Introduction This is a session to familiarize working with the Visual Studio development environment. It
Lab#5 Due Wednesday, February 25, at the start of class. Purpose: To develop familiarity with C++ pointer variables
 Lab#5 Due Wednesday, February 25, at the start of class Purpose: To develop familiarity with C++ pointer variables Introduction: In this lab, you will learn by experimentation the answers to some questions
Lab#5 Due Wednesday, February 25, at the start of class Purpose: To develop familiarity with C++ pointer variables Introduction: In this lab, you will learn by experimentation the answers to some questions
CS2141 Software Development using C/C++ C++ Basics
 CS2141 Software Development using C/C++ C++ Basics Integers Basic Types Can be short, long, or just plain int C++ does not define the size of them other than short
CS2141 Software Development using C/C++ C++ Basics Integers Basic Types Can be short, long, or just plain int C++ does not define the size of them other than short
CMSC 202 Midterm Exam 1 Fall 2015
 1. (15 points) There are six logic or syntax errors in the following program; find five of them. Circle each of the five errors you find and write the line number and correction in the space provided below.
1. (15 points) There are six logic or syntax errors in the following program; find five of them. Circle each of the five errors you find and write the line number and correction in the space provided below.
18-600: Recitation #3
 18-600: Recitation #3 Bomb Lab & GDB Overview September 12th, 2017 1 Today X86-64 Overview Bomb Lab Introduction GDB Tutorial 2 3 x86-64: Register Conventions Arguments passed in registers: %rdi, %rsi,
18-600: Recitation #3 Bomb Lab & GDB Overview September 12th, 2017 1 Today X86-64 Overview Bomb Lab Introduction GDB Tutorial 2 3 x86-64: Register Conventions Arguments passed in registers: %rdi, %rsi,
Lecture 2, September 4
 Lecture 2, September 4 Intro to C/C++ Instructor: Prashant Shenoy, TA: Shashi Singh 1 Introduction C++ is an object-oriented language and is one of the most frequently used languages for development due
Lecture 2, September 4 Intro to C/C++ Instructor: Prashant Shenoy, TA: Shashi Singh 1 Introduction C++ is an object-oriented language and is one of the most frequently used languages for development due
Computer Science II Lecture 1 Introduction and Background
 Computer Science II Lecture 1 Introduction and Background Discussion of Syllabus Instructor, TAs, office hours Course web site, http://www.cs.rpi.edu/courses/fall04/cs2, will be up soon Course emphasis,
Computer Science II Lecture 1 Introduction and Background Discussion of Syllabus Instructor, TAs, office hours Course web site, http://www.cs.rpi.edu/courses/fall04/cs2, will be up soon Course emphasis,
int n = 10; int sum = 10; while (n > 1) { sum = sum + n; n--; } cout << "The sum of the integers 1 to 10 is " << sum << endl;
 Debugging Some have said that any monkey can write a program the hard part is debugging it. While this is somewhat oversimplifying the difficult process of writing a program, it is sometimes more time
Debugging Some have said that any monkey can write a program the hard part is debugging it. While this is somewhat oversimplifying the difficult process of writing a program, it is sometimes more time
Once you have installed MobaXterm, open MobaXterm. Go to Sessions -> New Session, and click on the SSH icon.
 Lab 1 In order to get credit for the lab, you need to be checked off by the end of lab. For nonzero labs, you can earn a maximum of 3 points for lab work completed outside of lab time, but you must finish
Lab 1 In order to get credit for the lab, you need to be checked off by the end of lab. For nonzero labs, you can earn a maximum of 3 points for lab work completed outside of lab time, but you must finish
CMSC 341 Lecture 2 Dynamic Memory and Pointers
 CMSC 341 Lecture 2 Dynamic Memory and Pointers Park Sects. 01 & 02 Based on earlier course slides at UMBC Today s Topics Stack vs Heap Allocating and freeing memory new and delete Memory Leaks Valgrind
CMSC 341 Lecture 2 Dynamic Memory and Pointers Park Sects. 01 & 02 Based on earlier course slides at UMBC Today s Topics Stack vs Heap Allocating and freeing memory new and delete Memory Leaks Valgrind
EE355 Lab 5 - The Files Are *In* the Computer
 1 Introduction In this lab you will modify a working word scramble game that selects a word from a predefined word bank to support a user-defined word bank that is read in from a file. This is a peer evaluated
1 Introduction In this lab you will modify a working word scramble game that selects a word from a predefined word bank to support a user-defined word bank that is read in from a file. This is a peer evaluated
Multiple Choice (Questions 1 13) 26 Points Select all correct answers (multiple correct answers are possible)
 Name Closed notes, book and neighbor. If you have any questions ask them. Notes: Segment of code necessary C++ statements to perform the action described not a complete program Program a complete C++ program
Name Closed notes, book and neighbor. If you have any questions ask them. Notes: Segment of code necessary C++ statements to perform the action described not a complete program Program a complete C++ program
COMP322 - Introduction to C++ Lecture 01 - Introduction
 COMP322 - Introduction to C++ Lecture 01 - Introduction Robert D. Vincent School of Computer Science 6 January 2010 What this course is Crash course in C++ Only 14 lectures Single-credit course What this
COMP322 - Introduction to C++ Lecture 01 - Introduction Robert D. Vincent School of Computer Science 6 January 2010 What this course is Crash course in C++ Only 14 lectures Single-credit course What this
Multiple Choice (Questions 1 13) 26 Points Select all correct answers (multiple correct answers are possible)
 Name Closed notes, book and neighbor. If you have any questions ask them. Notes: Segment of code necessary C++ statements to perform the action described not a complete program Program a complete C++ program
Name Closed notes, book and neighbor. If you have any questions ask them. Notes: Segment of code necessary C++ statements to perform the action described not a complete program Program a complete C++ program
Discussion 1E. Jie(Jay) Wang Week 10 Dec.2
 Discussion 1E Jie(Jay) Wang Week 10 Dec.2 Outline Dynamic memory allocation Class Final Review Dynamic Allocation of Memory Recall int len = 100; double arr[len]; // error! What if I need to compute the
Discussion 1E Jie(Jay) Wang Week 10 Dec.2 Outline Dynamic memory allocation Class Final Review Dynamic Allocation of Memory Recall int len = 100; double arr[len]; // error! What if I need to compute the
PIC 10A Pointers, Arrays, and Dynamic Memory Allocation. Ernest Ryu UCLA Mathematics
 PIC 10A Pointers, Arrays, and Dynamic Memory Allocation Ernest Ryu UCLA Mathematics Pointers A variable is stored somewhere in memory. The address-of operator & returns the memory address of the variable.
PIC 10A Pointers, Arrays, and Dynamic Memory Allocation Ernest Ryu UCLA Mathematics Pointers A variable is stored somewhere in memory. The address-of operator & returns the memory address of the variable.
Laboratory Assignment #4 Debugging in Eclipse CDT 1
 Lab 4 (10 points) November 20, 2013 CS-2301, System Programming for Non-majors, B-term 2013 Objective Laboratory Assignment #4 Debugging in Eclipse CDT 1 Due: at 11:59 pm on the day of your lab session
Lab 4 (10 points) November 20, 2013 CS-2301, System Programming for Non-majors, B-term 2013 Objective Laboratory Assignment #4 Debugging in Eclipse CDT 1 Due: at 11:59 pm on the day of your lab session
Discussion 1H Notes (Week 3, April 14) TA: Brian Choi Section Webpage:
 Discussion 1H Notes (Week 3, April 14) TA: Brian Choi (schoi@cs.ucla.edu) Section Webpage: http://www.cs.ucla.edu/~schoi/cs31 More on Arithmetic Expressions The following two are equivalent:! x = x + 5;
Discussion 1H Notes (Week 3, April 14) TA: Brian Choi (schoi@cs.ucla.edu) Section Webpage: http://www.cs.ucla.edu/~schoi/cs31 More on Arithmetic Expressions The following two are equivalent:! x = x + 5;
Using a debugger. Segmentation fault? GDB to the rescue!
 Using a debugger Segmentation fault? GDB to the rescue! But first... Let's talk about the quiz Let's talk about the previous homework assignment Let's talk about the current homework assignment K findkey(v
Using a debugger Segmentation fault? GDB to the rescue! But first... Let's talk about the quiz Let's talk about the previous homework assignment Let's talk about the current homework assignment K findkey(v
Multiple Choice (Questions 1 14) 28 Points Select all correct answers (multiple correct answers are possible)
 Name Closed notes, book and neighbor. If you have any questions ask them. Notes: Segment of code necessary C++ statements to perform the action described not a complete program Program a complete C++ program
Name Closed notes, book and neighbor. If you have any questions ask them. Notes: Segment of code necessary C++ statements to perform the action described not a complete program Program a complete C++ program
Welcome Back. CSCI 262 Data Structures. Hello, Let s Review. Hello, Let s Review. How to Review 1/9/ Review. Here s a simple C++ program:
 Welcome Back CSCI 262 Data Structures 2 - Review What you learned in CSCI 261 (or equivalent): Variables Types Arrays Expressions Conditionals Branches & Loops Functions Recursion Classes & Objects Streams
Welcome Back CSCI 262 Data Structures 2 - Review What you learned in CSCI 261 (or equivalent): Variables Types Arrays Expressions Conditionals Branches & Loops Functions Recursion Classes & Objects Streams
Reviewing gcc, make, gdb, and Linux Editors 1
 Reviewing gcc, make, gdb, and Linux Editors 1 Colin Gordon csgordon@cs.washington.edu University of Washington CSE333 Section 1, 3/31/11 1 Lots of material borrowed from 351/303 slides Colin Gordon (University
Reviewing gcc, make, gdb, and Linux Editors 1 Colin Gordon csgordon@cs.washington.edu University of Washington CSE333 Section 1, 3/31/11 1 Lots of material borrowed from 351/303 slides Colin Gordon (University
Your First C++ Program. September 1, 2010
 Your First C++ Program September 1, 2010 Your First C++ Program //*********************************************************** // File name: hello.cpp // Author: Bob Smith // Date: 09/01/2010 // Purpose:
Your First C++ Program September 1, 2010 Your First C++ Program //*********************************************************** // File name: hello.cpp // Author: Bob Smith // Date: 09/01/2010 // Purpose:
CSE 351. GDB Introduction
 CSE 351 GDB Introduction Lab 2 Out either tonight or tomorrow Due April 27 th (you have ~12 days) Reading and understanding x86_64 assembly Debugging and disassembling programs Today: General debugging
CSE 351 GDB Introduction Lab 2 Out either tonight or tomorrow Due April 27 th (you have ~12 days) Reading and understanding x86_64 assembly Debugging and disassembling programs Today: General debugging
FORM 2 (Please put your name and form # on the scantron!!!!) CS 161 Exam II:
 FORM 2 (Please put your name and form # on the scantron!!!!) CS 161 Exam II: True (A)/False(B) (2 pts each): 1. The declaration below declares three pointer variables of type pointer to double that is
FORM 2 (Please put your name and form # on the scantron!!!!) CS 161 Exam II: True (A)/False(B) (2 pts each): 1. The declaration below declares three pointer variables of type pointer to double that is
CS102 Software Engineering Principles
 CS102 Software Engineering Principles Bill Cheng http://merlot.usc.edu/cs102-s12 1 Software Engineering Principles You need to develop a plan before you start writing your code Choose the proper data structures
CS102 Software Engineering Principles Bill Cheng http://merlot.usc.edu/cs102-s12 1 Software Engineering Principles You need to develop a plan before you start writing your code Choose the proper data structures
Portland State University Maseeh College of Engineering and Computer Science. Proficiency Examination Process
 Portland State University Maseeh College of Engineering and Computer Science Proficiency Examination Process 2016-2017 PSU Expectations of Student Competencies Students that apply to PSU s Computer Science
Portland State University Maseeh College of Engineering and Computer Science Proficiency Examination Process 2016-2017 PSU Expectations of Student Competencies Students that apply to PSU s Computer Science
Lecture Notes CPSC 224 (Spring 2012) Today... Java basics. S. Bowers 1 of 8
 Today... Java basics S. Bowers 1 of 8 Java main method (cont.) In Java, main looks like this: public class HelloWorld { public static void main(string[] args) { System.out.println("Hello World!"); Q: How
Today... Java basics S. Bowers 1 of 8 Java main method (cont.) In Java, main looks like this: public class HelloWorld { public static void main(string[] args) { System.out.println("Hello World!"); Q: How
Pointers, Dynamic Data, and Reference Types
 Pointers, Dynamic Data, and Reference Types Review on Pointers Reference Variables Dynamic Memory Allocation The new operator The delete operator Dynamic Memory Allocation for Arrays 1 C++ Data Types simple
Pointers, Dynamic Data, and Reference Types Review on Pointers Reference Variables Dynamic Memory Allocation The new operator The delete operator Dynamic Memory Allocation for Arrays 1 C++ Data Types simple
Your first C++ program
 Your first C++ program #include using namespace std; int main () cout
Your first C++ program #include using namespace std; int main () cout
Lecture 14. No in-class files today. Homework 7 (due on Wednesday) and Project 3 (due in 10 days) posted. Questions?
 Lecture 14 No in-class files today. Homework 7 (due on Wednesday) and Project 3 (due in 10 days) posted. Questions? Friday, February 11 CS 215 Fundamentals of Programming II - Lecture 14 1 Outline Static
Lecture 14 No in-class files today. Homework 7 (due on Wednesday) and Project 3 (due in 10 days) posted. Questions? Friday, February 11 CS 215 Fundamentals of Programming II - Lecture 14 1 Outline Static
CS11 Intro C++ Spring 2018 Lecture 1
 CS11 Intro C++ Spring 2018 Lecture 1 Welcome to CS11 Intro C++! An introduction to the C++ programming language and tools Prerequisites: CS11 C track, or equivalent experience with a curly-brace language,
CS11 Intro C++ Spring 2018 Lecture 1 Welcome to CS11 Intro C++! An introduction to the C++ programming language and tools Prerequisites: CS11 C track, or equivalent experience with a curly-brace language,
BOOLEAN EXPRESSIONS CONTROL FLOW (IF-ELSE) INPUT/OUTPUT. Problem Solving with Computers-I
 BOOLEAN EXPRESSIONS CONTROL FLOW (IF-ELSE) INPUT/OUTPUT Problem Solving with Computers-I Announcements HW02: Complete (individually)using dark pencil or pen, turn in during lab section next Wednesday Please
BOOLEAN EXPRESSIONS CONTROL FLOW (IF-ELSE) INPUT/OUTPUT Problem Solving with Computers-I Announcements HW02: Complete (individually)using dark pencil or pen, turn in during lab section next Wednesday Please
CSCI-1200 Data Structures Spring 2016 Lecture 6 Pointers & Dynamic Memory
 Announcements CSCI-1200 Data Structures Spring 2016 Lecture 6 Pointers & Dynamic Memory There will be no lecture on Tuesday, Feb. 16. Prof. Thompson s office hours are canceled for Monday, Feb. 15. Prof.
Announcements CSCI-1200 Data Structures Spring 2016 Lecture 6 Pointers & Dynamic Memory There will be no lecture on Tuesday, Feb. 16. Prof. Thompson s office hours are canceled for Monday, Feb. 15. Prof.
Linux Tutorial #1. Introduction. Login to a remote Linux machine. Using vim to create and edit C++ programs
 Linux Tutorial #1 Introduction The Linux operating system is now over 20 years old, and is widely used in industry and universities because it is fast, flexible and free. Because Linux is open source,
Linux Tutorial #1 Introduction The Linux operating system is now over 20 years old, and is widely used in industry and universities because it is fast, flexible and free. Because Linux is open source,
GDB Linux GNU Linux Distribution. gdb gcc g++ -g gdb EB_01.cpp
 B Linux GDB GDB Linux GNU GPL Linux Distribution Linux E-B.1 gcc g++ -g EB_01.cpp EB_01.cpp E/EB/EB_01.cpp 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 /**** :EB_01.cpp : *****/ #include
B Linux GDB GDB Linux GNU GPL Linux Distribution Linux E-B.1 gcc g++ -g EB_01.cpp EB_01.cpp E/EB/EB_01.cpp 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 /**** :EB_01.cpp : *****/ #include
12. Debugging. Overview. COMP1917: Computing 1. Developing Programs. The Programming Cycle. Programming cycle. Do-it-yourself debugging
 COMP1917 12s2 Debugging 1 COMP1917: Computing 1 12. Debugging Overview Programming cycle Do-it-yourself debugging Debugging withgdb Nastier bugs Memory leaks COMP1917 12s2 Debugging 2 Developing Programs
COMP1917 12s2 Debugging 1 COMP1917: Computing 1 12. Debugging Overview Programming cycle Do-it-yourself debugging Debugging withgdb Nastier bugs Memory leaks COMP1917 12s2 Debugging 2 Developing Programs
Week 5, continued. This is CS50. Harvard University. Fall Cheng Gong
 This is CS50. Harvard University. Fall 2014. Cheng Gong Table of Contents News... 1 Buffer Overflow... 1 Malloc... 6 Linked Lists... 7 Searching... 13 Inserting... 16 Removing... 19 News Good news everyone!
This is CS50. Harvard University. Fall 2014. Cheng Gong Table of Contents News... 1 Buffer Overflow... 1 Malloc... 6 Linked Lists... 7 Searching... 13 Inserting... 16 Removing... 19 News Good news everyone!
Chapter 3. More Flow of Control. Copyright 2007 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Pearson Addison-Wesley
 Chapter 3 More Flow of Control Overview 3.1 Using Boolean Expressions 3.2 Multiway Branches 3.3 More about C++ Loop Statements 3.4 Designing Loops Slide 3-3 Flow Of Control Flow of control refers to the
Chapter 3 More Flow of Control Overview 3.1 Using Boolean Expressions 3.2 Multiway Branches 3.3 More about C++ Loop Statements 3.4 Designing Loops Slide 3-3 Flow Of Control Flow of control refers to the
Basic program The following is a basic program in C++; Basic C++ Source Code Compiler Object Code Linker (with libraries) Executable
 Basic C++ Overview C++ is a version of the older C programming language. This is a language that is used for a wide variety of applications and which has a mature base of compilers and libraries. C++ is
Basic C++ Overview C++ is a version of the older C programming language. This is a language that is used for a wide variety of applications and which has a mature base of compilers and libraries. C++ is
Lecture 15a Persistent Memory & Shared Pointers
 Lecture 15a Persistent Memory & Shared Pointers Dec. 5 th, 2017 Jack Applin, Guest Lecturer 2017-12-04 CS253 Fall 2017 Jack Applin & Bruce Draper 1 Announcements PA9 is due today Recitation : extra help
Lecture 15a Persistent Memory & Shared Pointers Dec. 5 th, 2017 Jack Applin, Guest Lecturer 2017-12-04 CS253 Fall 2017 Jack Applin & Bruce Draper 1 Announcements PA9 is due today Recitation : extra help
Computer Science II Lab 3 Testing and Debugging
 Computer Science II Lab 3 Testing and Debugging Introduction Testing and debugging are important steps in programming. Loosely, you can think of testing as verifying that your program works and debugging
Computer Science II Lab 3 Testing and Debugging Introduction Testing and debugging are important steps in programming. Loosely, you can think of testing as verifying that your program works and debugging
CS2255 HOMEWORK #1 Fall 2012
 CS55 HOMEWORK #1 Fall 01 1.What is assigned to the variable a given the statement below with the following assumptions: x = 10, y = 7, and z, a, and b are all int variables. a = x >= y; a. 10 b. 7 c. The
CS55 HOMEWORK #1 Fall 01 1.What is assigned to the variable a given the statement below with the following assumptions: x = 10, y = 7, and z, a, and b are all int variables. a = x >= y; a. 10 b. 7 c. The
CS103L SPRING 2018 UNIT 7: FILE I/O
 CS103L SPRING 2018 UNIT 7: FILE I/O I/O STREAMS IN C++ I/O: short for input/ouput Older term from mainframe days for getting data into and out of your program C++ offers object oriented abstractions to
CS103L SPRING 2018 UNIT 7: FILE I/O I/O STREAMS IN C++ I/O: short for input/ouput Older term from mainframe days for getting data into and out of your program C++ offers object oriented abstractions to
Welcome Back. CSCI 262 Data Structures. Hello, Let s Review. Hello, Let s Review. How to Review 8/19/ Review. Here s a simple C++ program:
 Welcome Back CSCI 262 Data Structures 2 - Review What you learned in CSCI 261 (or equivalent): Variables Types Arrays Expressions Conditionals Branches & Loops Functions Recursion Classes & Objects Streams
Welcome Back CSCI 262 Data Structures 2 - Review What you learned in CSCI 261 (or equivalent): Variables Types Arrays Expressions Conditionals Branches & Loops Functions Recursion Classes & Objects Streams
Class Information ANNOUCEMENTS
 Class Information ANNOUCEMENTS Third homework due TODAY at 11:59pm. Extension? First project has been posted, due Monday October 23, 11:59pm. Midterm exam: Friday, October 27, in class. Don t forget to
Class Information ANNOUCEMENTS Third homework due TODAY at 11:59pm. Extension? First project has been posted, due Monday October 23, 11:59pm. Midterm exam: Friday, October 27, in class. Don t forget to
Chapter 4 - Notes Control Structures I (Selection)
 Chapter 4 - Notes Control Structures I (Selection) I. Control Structures A. Three Ways to Process a Program 1. In Sequence: Starts at the beginning and follows the statements in order 2. Selectively (by
Chapter 4 - Notes Control Structures I (Selection) I. Control Structures A. Three Ways to Process a Program 1. In Sequence: Starts at the beginning and follows the statements in order 2. Selectively (by
A SHORT COURSE ON C++
 Introduction to A SHORT COURSE ON School of Mathematics Semester 1 2008 Introduction to OUTLINE 1 INTRODUCTION TO 2 FLOW CONTROL AND FUNCTIONS If Else Looping Functions Cmath Library Prototyping Introduction
Introduction to A SHORT COURSE ON School of Mathematics Semester 1 2008 Introduction to OUTLINE 1 INTRODUCTION TO 2 FLOW CONTROL AND FUNCTIONS If Else Looping Functions Cmath Library Prototyping Introduction
Overloading Functions & Command Line Use in C++ CS 16: Solving Problems with Computers I Lecture #6
 Overloading Functions & Command Line Use in C++ CS 16: Solving Problems with Computers I Lecture #6 Ziad Matni Dept. of Computer Science, UCSB A reminder about Labs Announcements Please make sure you READ
Overloading Functions & Command Line Use in C++ CS 16: Solving Problems with Computers I Lecture #6 Ziad Matni Dept. of Computer Science, UCSB A reminder about Labs Announcements Please make sure you READ
TDDB68. Lesson 1. Simon Ståhlberg
 TDDB68 Lesson 1 Simon Ståhlberg Contents General information about the labs Overview of the labs Memory layout of C programs ("Lab 00") General information about Pintos System calls Lab 1 Debugging Administration
TDDB68 Lesson 1 Simon Ståhlberg Contents General information about the labs Overview of the labs Memory layout of C programs ("Lab 00") General information about Pintos System calls Lab 1 Debugging Administration
CS 103 Lab The Files are *In* the Computer
 CS 103 Lab The Files are *In* the Computer 1 Introduction In this lab you will modify a word scramble game so that instead of using a hardcoded word list, it selects a word from a file. You will learn
CS 103 Lab The Files are *In* the Computer 1 Introduction In this lab you will modify a word scramble game so that instead of using a hardcoded word list, it selects a word from a file. You will learn
CA31-1K DIS. Pointers. TA: You Lu
 CA31-1K DIS Pointers TA: You Lu Pointers Recall that while we think of variables by their names like: int numbers; Computer likes to think of variables by their memory address: 0012FED4 A pointer is a
CA31-1K DIS Pointers TA: You Lu Pointers Recall that while we think of variables by their names like: int numbers; Computer likes to think of variables by their memory address: 0012FED4 A pointer is a
Lab: Supplying Inputs to Programs
 Steven Zeil May 25, 2013 Contents 1 Running the Program 2 2 Supplying Standard Input 4 3 Command Line Parameters 4 1 In this lab, we will look at some of the different ways that basic I/O information can
Steven Zeil May 25, 2013 Contents 1 Running the Program 2 2 Supplying Standard Input 4 3 Command Line Parameters 4 1 In this lab, we will look at some of the different ways that basic I/O information can
Using the Xcode Debugger
 g Using the Xcode Debugger J Objectives In this appendix you ll: Set breakpoints and run a program in the debugger. Use the Continue program execution command to continue execution. Use the Auto window
g Using the Xcode Debugger J Objectives In this appendix you ll: Set breakpoints and run a program in the debugger. Use the Continue program execution command to continue execution. Use the Auto window
Homework #3 CS2255 Fall 2012
 Homework #3 CS2255 Fall 2012 MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The, also known as the address operator, returns the memory address of a variable. a. asterisk ( * ) b. ampersand ( & ) c. percent sign (%) d. exclamation
Homework #3 CS2255 Fall 2012 MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The, also known as the address operator, returns the memory address of a variable. a. asterisk ( * ) b. ampersand ( & ) c. percent sign (%) d. exclamation
Consider the above code. This code compiles and runs, but has an error. Can you tell what the error is?
 Discussion 1H Notes (Week 8, May 20) TA: Brian Choi (schoi@cs.ucla.edu) Section Webpage: http://www.cs.ucla.edu/~schoi/cs31 Dynamic Allocation of Memory Recall that when you create an array, you must know
Discussion 1H Notes (Week 8, May 20) TA: Brian Choi (schoi@cs.ucla.edu) Section Webpage: http://www.cs.ucla.edu/~schoi/cs31 Dynamic Allocation of Memory Recall that when you create an array, you must know
CS 103 Unit 11. Linked Lists. Mark Redekopp
 1 CS 103 Unit 11 Linked Lists Mark Redekopp 2 NULL Pointer Just like there was a null character in ASCII = '\0' whose ue was 0 There is a NULL pointer whose ue is 0 NULL is "keyword" you can use in C/C++
1 CS 103 Unit 11 Linked Lists Mark Redekopp 2 NULL Pointer Just like there was a null character in ASCII = '\0' whose ue was 0 There is a NULL pointer whose ue is 0 NULL is "keyword" you can use in C/C++
Compiling with Multiple Files The Importance of Debugging CS 16: Solving Problems with Computers I Lecture #7
 Compiling with Multiple Files The Importance of Debugging CS 16: Solving Problems with Computers I Lecture #7 Ziad Matni Dept. of Computer Science, UCSB Programming in Multiple Files The Magic of Makefiles!
Compiling with Multiple Files The Importance of Debugging CS 16: Solving Problems with Computers I Lecture #7 Ziad Matni Dept. of Computer Science, UCSB Programming in Multiple Files The Magic of Makefiles!
Tutorial 13 Salary Survey Application: Introducing One- Dimensional Arrays
 Tutorial 13 Salary Survey Application: Introducing One- Dimensional Arrays Outline 13.1 Test-Driving the Salary Survey Application 13.2 Introducing Arrays 13.3 Declaring and Initializing Arrays 13.4 Constructing
Tutorial 13 Salary Survey Application: Introducing One- Dimensional Arrays Outline 13.1 Test-Driving the Salary Survey Application 13.2 Introducing Arrays 13.3 Declaring and Initializing Arrays 13.4 Constructing
Introduction to Programming
 Introduction to Programming session 6 Instructor: Reza Entezari-Maleki Email: entezari@ce.sharif.edu 1 Spring 2011 These slides are created using Deitel s slides Sharif University of Technology Outlines
Introduction to Programming session 6 Instructor: Reza Entezari-Maleki Email: entezari@ce.sharif.edu 1 Spring 2011 These slides are created using Deitel s slides Sharif University of Technology Outlines
United States Naval Academy Electrical and Computer Engineering Department EC310-6 Week Midterm Spring AY2017
 United States Naval Academy Electrical and Computer Engineering Department EC310-6 Week Midterm Spring AY2017 1. Do a page check: you should have 8 pages including this cover sheet. 2. You have 50 minutes
United States Naval Academy Electrical and Computer Engineering Department EC310-6 Week Midterm Spring AY2017 1. Do a page check: you should have 8 pages including this cover sheet. 2. You have 50 minutes
Lab 1: First Steps in C++ - Eclipse
 Lab 1: First Steps in C++ - Eclipse Step Zero: Select workspace 1. Upon launching eclipse, we are ask to chose a workspace: 2. We select a new workspace directory (e.g., C:\Courses ): 3. We accept the
Lab 1: First Steps in C++ - Eclipse Step Zero: Select workspace 1. Upon launching eclipse, we are ask to chose a workspace: 2. We select a new workspace directory (e.g., C:\Courses ): 3. We accept the
