Fractions and Decimals
|
|
|
- Emerald Hoover
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 FRACTIONS AND DECIMALS 9 Fractions and Decimals Chapter. INTRODUCTION You have learnt fractions and decimals in earlier classes. The study of fractions included proper, improper and mixed fractions as well as their addition and subtraction. We also studied comparison of fractions, equivalent fractions, representation of fractions on the number line and ordering of fractions. Our study of decimals included, their comparison, their representation on the number line and their addition and subtraction. We shall now learn multiplication and division of fractions as well as of decimals.. HOW WELL HAVE YOU LEARNT ABOUT FRACTIONS? A proper fraction is a fraction that represents a part of a whole. Is 7 a proper fraction? Which is bigger, the numerator or the denominator? An improper fraction is a combination of whole and a proper fraction. Is 7 an improper fraction? Which is bigger here, the numerator or the denominator? The improper fraction 7 can be written as. This is a mixed fraction. Can you write five examples each of proper, improper and mixed fractions? EXAMPLE Write five equivalent fractions of. SOLUTION One of the equivalent fractions of is 6 = =. Find the other four. 0
2 0 MATHEMATICS EXAMPLE Ramesh solved 7 part of an exercise while Seema solved solved lesser part? of it. Who SOLUTION EXAMPLE In order to find who solved lesser part of the exercise, let us compare 7 and. Converting them to like fractions we have, = 0, = 8. 7 Since0 < 8, so 0 8 <. Thus, < 7. Ramesh solved lesser part than Seema. Sameera purchased kg apples and kg oranges. What is the total weight of fruits purchased by her? SOLUTION The total weight of the fruits = + kg = kg = + kg = kg = 8 kg EXAMPLE Suman studies for hours daily. She devotes hours of her time for Science and Mathematics. How much time does she devote for other subjects? SOLUTION Total time of Suman s study = Time devoted by her for Science and Mathematics = h = 7 h = h
3 FRACTIONS AND DECIMALS 7 Thus, time devoted by her for other subjects = h 7 = h = h = h EXERCISE. = 8 h. Solve: (ii) 7 + (iii) 8 7 (v) + + (vi) + (vii) 0. Arrange the following in descending order: + (iv) ,, (ii),, In a magic square, the sum of the numbers in each row, in each column and along the diagonals is the same. Is this a magic square? (Along the first row = ).. A rectangular sheet of paper is cm long and 0 cm wide. Find its perimeter.. Find the perimeters of Δ ABE (ii) the rectangle BCDE in this figure. Whose perimeter is greater? 6. Salil wants to put a picture in a frame. The picture is 7 cm wide. cm cm cm 7 cm 6 To fit in the frame the picture cannot be more than 7 0 the picture be trimmed? cm wide. How much should
4 MATHEMATICS 7. Ritu ate part of an apple and the remaining apple was eaten by her brother Somu. How much part of the apple did Somu eat? Who had the larger share? By how much? 8. Michael finished colouring a picture in 7 hour. Vaibhav finished colouring the same picture in hour. Who worked longer? By what fraction was it longer?. MULTIPLICATION OF FRACTIONS You know how to find the area of a rectangle. It is equal to length breadth. If the length and breadth of a rectangle are 7 cm and cm respectively, then what will be its area? Its area would be 7 = 8 cm. What will be the area of the rectangle if its length and breadth are 7 cm and cm respectively? You will say it will be 7 = 7 cm. The numbers and 7 are fractions. To calculate the area of the given rectangle, we need to know how to multiply fractions. We shall learn that now... Multiplication of a Fraction by a Whole Number Fig. Observe the pictures at the left (Fig.). Each shaded part is part of a circle. How much will the two shaded parts represent together? They will represent + =. Combining the two shaded parts, we get Fig.. What part of a circle does the shaded part in Fig. represent? It represents part of a circle. or Fig.
5 FRACTIONS AND DECIMALS The shaded portions in Fig. taken together are the same as the shaded portion in Fig., i.e., we get Fig.. = Fig. or =. Can you now tell what this picture will represent? (Fig.) = And this? (Fig.) Fig. = Fig. Let us now find We have We also have So Similarly Can you tell. = + + = = = = = = = 7 =? =?? = The fractions that we considered till now, i.e.,,, 7 and were proper fractions.
6 MATHEMATICS For improper fractions also we have, Try, = 8 7 =? = 0 7 =? Thus, to multiply a whole number with a proper or an improper fraction, we multiply the whole number with the numerator of the fraction, keeping the denominator same.. Find: (a) 7 (b) (c) 8 (d) 6 If the product is an improper fraction express it as a mixed fraction.. Represent pictorially : = Find: (ii) To multiply a mixed fraction to a whole number, first convert the mixed fraction to an improper fraction and then multiply. Therefore, Similarly, = 7 = 9 = = 8. 7 =? Fraction as an operator of Observe these figures (Fig.6) The two squares are exactly similar. Each shaded portion represents of. So, both the shaded portions together will represent of. Combine the shaded parts. It represents. So, we say of is. We can also get it as =. Thus, of = = Fig.6
7 FRACTIONS AND DECIMALS Also, look at these similar squares (Fig.7). Each shaded portion represents of. So, the three shaded portions represent of. Combine the shaded parts. It represents i.e.,. So, of is. Also, =. Fig.7 Thus, of = =. So we see that of represents multiplication. Farida has 0 marbles. Reshma has th of the number of marbles what Farida has. How many marbles Reshma has? As, of indicates multiplication, so, Reshma has 0 = marbles. Similarly, we have of 6 is 6 = 6 = 8. Can you tell, what is of 0?, (ii) of 6?, (iii) of? EXAMPLE In a class of 0 students of the total number of studetns like to study English, of the total number like to study Mathematics and the remaining students like to study Science. How many students like to study English? (ii) How many students like to study Mathematics? (iii) What fraction of the total number of students like to study Science? SOLUTION Total number of students in the class = 0. Of these of the total number of students like to study English.
8 6 MATHEMATICS Thus, the number of students who like to study English = of 0 = 0 = 8. (ii) Try yourself. (iii) The number of students who like English and Mathematics = =. Thus, the number of students who like Science = 0 = 6. Thus, the required fraction is 6 0. EXERCISE.. Which of the drawings (a) to (d) show : (ii) (iii) (iv) (a) (b) (c) (d). Some pictures (a) to (c) are given below. Tell which of them show: = (ii) = (iii) = = (a) (b) =. Multiply and reduce to lowest form and convert into a mixed fraction: 7 (ii) (iii) (c) 6 (iv) 7 (v) 9 (vi) 6 (vii) (viii) 7 0 (ix) (x)
9 FRACTIONS AND DECIMALS 7. Shade: (iii) of the circles in box (a) (ii) of the squares in box (c). of the triangles in box (b). Find: (a) (a) (b) (c) of (ii) 6 (b) of 8 (ii) 7 (c) of 6 (ii) 6 (d) of 0 (ii) 6. Multiply and express as a mixed fraction : (a) (b) 6 (c) 7 (d) 6 (e) 6 (f) 8 7. Find: (a) of (ii) (b) 9 8 of (ii) Vidya and Pratap went for a picnic. Their mother gave them a water bottle that contained litres of water. Vidya consumed of the water. Pratap consumed the remaining water. How much water did Vidya drink? (ii) What fraction of the total quantity of water did Pratap drink?.. Multiplication of a Fraction by a Fraction Farida had a 9 cm long strip of ribbon. She cut this strip into four equal parts. How did she do it? She folded the strip twice. What fraction of the total length will each part represent? Each part will be 9 of the strip. She took one part and divided it in two equal parts by
10 8 MATHEMATICS folding the part once. What will one of the pieces represent? It will represent of 9 or 9. Let us now see how to find the product of two fractions like 9. To do this we first learn to find the products like. (a) How do we find of a whole? We divide the whole in three equal parts. Each of Fig.8 A the three parts represents of the whole. Take one part of these three parts, and shade it as shown in Fig.8. (b) How will you find of this shaded part? Divide this one-third ( ) shaded part into two equal parts. Each of these two parts represents of i.e., (Fig.9). Fig.9 Take out part of these two and name it A. A represents. (c) What fraction is A of the whole? For this, divide each of the remaining parts also in two equal parts. How many such equal parts do you have now? There are six such equal parts. A is one of these parts. So, A is 6 of the whole. Thus, = 6. How did we decide that A was 6 of the whole? The whole was divided in 6 = parts and = part was taken out of it. Thus, or = 6 = =
11 FRACTIONS AND DECIMALS 9 The value of can be found in a similar way. Divide the whole into two equal parts and then divide one of these parts in three equal parts. Take one of these parts. This will represent i.e., 6. Therefore Hence = 6 = = = 6 as discussed earlier. Find and ; and and check whether you get = ; = Fill in these boxes: 7 = 7 = (ii) 7 = = (iii) 7 = = (iv) 7 = = EXAMPLE 6 Sushant reads part of a book in hour. How much part of the book will he read in hours? SOLUTION The part of the book read by Sushant in hour =. So, the part of the book read by him in hours = = = = Let us now find. We know that =. So, = = 6 = 6
12 0 MATHEMATICS Also, 6 =. Thus, = = 6. This is also shown by the figures drawn below. Each of these five equal shapes (Fig.0) are parts of five similar circles. Take one such shape. To obtain this shape we first divide a circle in three equal parts. Further divide each of these three parts in two equal parts. One part out of it is the shape we considered. What will it represent? It will represent = 6. The total of such parts would be 6 = 6. Fig.0 Similarly 7 = 7 =. Find: ; Find: 8 7 ;. So, we find that we multiply two fractions as 8 = 7 Value of the Products We can thus find 7 as 7 = 7 =. Product of Numerators Product of Denominators. You have seen that the product of two whole numbers is bigger than each of the two whole numbers. For example, = and >, >. What happens to the value of the product when we multiply two fractions? Let us first consider the product of two proper fractions. We have, 8 <, 8 < Product is less than each of the fractions = , = , = ,
13 FRACTIONS AND DECIMALS You will find that when two proper fractions are multiplied, the product is less than each of the fractions. Or, we say the value of the product of two proper fractions is smaller than each of the two fractions. Check this by constructing five more examples. Let us now multiply two improper fractions. 7 = 6 6 = 6 7 >, > Product is greater than each of the fractions , , = , = 8 We find that the product of two improper fractions is greater than each of the two fractions. Or, the value of the product of two improper fractions is more than each of the two fractions. Construct five more examples for yourself and verify the above statement. Let us now multiply a proper and an improper fraction, say and 7. We have 7 =. Here, < 7 and > The product obtained is less than the improper fraction and greater than the proper fraction involved in the multiplication. Check it for 6 7, 8.. Find: EXERCISE. of (a) (b) (c) (ii) 7 of (a) 9 (b) 6 (c) 0
14 MATHEMATICS. Multiply and reduce to lowest form (if possible) : (v) (ii) (vi) 8. Multiply the following fractions: (ii) 7 (iii) 7 9 (vii) (iii) (iv) (iv) (v) (vi) 7. Which is greater: 7 of or of 8 (vii) (ii) of or of 7. Saili plants saplings, in a row, in her garden. The distance between two adjacent saplings is m. Find the distance between the first and the last sapling. 6. Lipika reads a book for hours everyday. She reads the entire book in 6 days. How many hours in all were required by her to read the book? 7. A car runs 6 km using litre of petrol. How much distance will it cover using litres of petrol. 8. (a) Provide the number in the box, such that = 0. 0 (ii) The simplest form of the number obtained in is. (b) Provide the number in the box, such that =. 7 (ii) The simplest form of the number obtained in is.. DIVISION OF FRACTIONS John has a paper strip of length 6 cm. He cuts this strip in smaller strips of length cm each. You know that he would get 6 = strips.
15 FRACTIONS AND DECIMALS John cuts another strip of length 6 cm into smaller strips of length cm each. How many strips will he get now? He will get 6 strips. A paper strip of length cm can be cut into smaller strips of length cm each to give pieces. So, we are required to divide a whole number by a fraction or a fraction by another fraction. Let us see how to do that... Division of Whole Number by a Fraction Let us find. We divide a whole into a number of equal parts such that each part is half of the whole. The number of such half ( ) parts would be. Observe the figure (Fig.). How many half parts do you see? There are two half parts. So, =. Also, = =. Thus, = Similarly, = number of parts obtained when each of the whole, are divided Fig. into equal parts = (From Fig.) Fig. Observe also that, = =. Thus, = =. Find in a similar way, and.
16 MATHEMATICS Reciprocal of a fraction The number can be obtained by interchanging the numerator and denominator of or by inverting. Similarly, is obtained by inverting. Let us first see about the inverting of such numbers. Observe these products and fill in the blanks : 7 = = = = = = 6 6 = = 9 Multiply five more such pairs. The non-zero numbers whose product with each other is, are called the reciprocals of each other. So reciprocal of 9 is 9 and the reciprocal of 9 is 9. What is the receiprocal of 9? 7? You will see that the reciprocal of is obtained by inverting it. You get. THINK, DISCUSS AND WRITE Will the reciprocal of a proper fraction be again a proper fraction? (ii) Will the reciprocal of an improper fraction be again an improper fraction? Therefore, we can say that = = reciprocal of. = = reciprocal of. = = So, = reciprocal of =. 9 = =
17 FRACTIONS AND DECIMALS Thus, to divide a whole number by any fraction, multiply that whole number by the reciprocal of that fraction. Find : 7 (ii) 6 7 (iii) 8 9 While dividing a whole number by a mixed fraction, first convert the mixed fraction into improper fraction and then solve it. Thus, = =? Also, = 0 =?.. Division of a Fraction by a Whole Number What will be? Based on our earlier observations we have: = = = = So, 7 = 7 =? What is 7 6, 7 8? While dividing mixed fractions by whole numbers, convert the mixed fractions into improper fractions. That is, = 8 = ; = = ;.. Division of a Fraction by Another Fraction We can now find 6. 6 = reciprocal of 6 = 6 =. = = Similarly, 8 = 8 reciprocal of =? and, =? Find: 6 (ii) 7 7 Find: (ii) (iii) (iv) 9 6
18 6 MATHEMATICS. Find: (ii) (v) (vi) EXERCISE. (iii) (iv) 8 7. Find the reciprocal of each of the following fractions. Classify the reciprocals as proper fractions, improper fractions and whole numbers. 9 (ii) (iii) (v) (vi) (vii) 7 8. Find: 7 (ii) 9 6 (iii) (v) (vi). Find: (ii) (vi) (vii) 7 7 (iii) 9 (viii) 8 (iv) 7 7 (iv) 6 7 (iv) (v) 8. HOW WELL HAVE YOU LEARNT ABOUT DECIMAL NUMBERS You have learnt about decimal numbers in the earlier classes. Let us briefly recall them here. Look at the following table and fill up the blank spaces. Hundreds Tens Ones Tenths Hundredths Thousandths Number (00) (0) ()
19 FRACTIONS AND DECIMALS 7 In the table, you wrote the decimal number, given its place-value expansion. You can do the reverse, too. That is, given the number you can write its expanded form. For example,.7 = John has `.0 and Salma has `.7. Who has more money? To find this we need to compare the decimal numbers.0 and.7. To do this, we first compare the digits on the left of the decimal point, starting from the leftmost digit. Here both the digits and, to the left of the decimal point, are same. So we compare the digits on the right of the decimal point starting from the tenths place. We find that < 7, so we say.0 <.7. Thus, Salma has more money than John. If the digits at the tenths place are also same then compare the digits at the hundredths place and so on. Now compare quickly,.6 and.67; 0. and 0.0; 9.6 and 9.6. While converting lower units of money, length and weight, to their higher units, we are required to use decimals. For example, paise = ` 00 = ` 0.0, g = 000 kg = 0.00 kg, 7 cm = 0.07 m. Write 7 paise = `, 0 g = kg, 8 cm = m. We also know how to add and subtract decimals. Thus, is What is the value of ? The difference 9..6 is 9. Tell the value of Which is greater? EXERCISE. 0. or 0.0 (ii) 0.7 or 0. (iii) 7 or 0.7 (iv).7 or.9 (v).0 or.0 (vi) 0.8 or Express as rupees using decimals : 7 paise (ii) 7 rupees 7 paise (iii) 77 rupees 77 paise (iv) 0 paise (v) paise.. Express cm in metre and kilometre (ii) Express mm in cm, m and km
20 8 MATHEMATICS. Express in kg: 00 g (ii) 70 g (iii) kg 8 g. Write the following decimal numbers in the expanded form: 0.0 (ii).0 (iii) 00.0 (iv).0 6. Write the place value of in the following decimal numbers:.6 (ii).7 (iii) 0. (iv) 9. (v) Dinesh went from place A to place B and from there to place C. A is 7. km from B and B is.7 km from C. Ayub went from place A to place D and from there to place C. D is 9. km from A and C is.8 km from D. Who travelled more and by how much? 8. Shyama bought kg 00 g apples and kg 0 g mangoes. Sarala bought kg 800 g oranges and kg 0 g bananas. Who bought more fruits? 9. How much less is 8 km than.6 km?.6 MULTIPLICATION OF DECIMAL NUMBERS Reshma purchased.kg vegetable at the rate of ` 8.0 per kg. How much money should she pay? Certainly it would be ` (8.0.0). Both 8. and. are decimal numbers. So, we have come across a situation where we need to know how to multiply two decimals. Let us now learn the multiplication of two decimal numbers. First we find Now, 0. = 0. So, = 0 0 = 0 0 = 00 = 0.0. Let us see it s pictorial representation (Fig.) The fraction 0 represents part out of 0 equal parts. The shaded part in the picture represents 0. We know that, 0 0 means 0 of. So, divide this 0 0 th part into 0 equal parts and take one part out of it. Fig.
21 FRACTIONS AND DECIMALS 9 Thus, we have, (Fig.). 0 0 Fig. The dotted square is one part out of 0 of the 0 th part. That is, it represents or Can the dotted square be represented in some other way? How many small squares do you find in Fig.? There are 00 small squares. So the dotted square represents one out of 00 or 0.0. Hence, = 0.0. Note that 0. occurs two times in the product. In 0. there is one digit to the right of the decimal point. In 0.0 there are two digits (i.e., + ) to the right of the decimal point. Let us now find We have, = 0 0 As we did for, let us divide the square into equal parts and take three parts out of it, to get 0. Again divide each of these three equal parts into 0 equal parts and take two from each. We get 0 0. The dotted squares represent or (Fig.) 0 0 Since there are 6 dotted squares out of 00, so they also reprsent Fig.
22 0 MATHEMATICS Thus, = Observe that = 6 and the number of digits to the right of the decimal point in 0.06 is (= + ). Check whether this applies to also. Find by applying these observations. While finding and 0. 0., you might have noticed that first we multiplied them as whole numbers ignoring the decimal point. In 0. 0., we found 0 0 or. Similarly in we found 0 0 or. Then, we counted the number of digits starting from the rightmost digit and moved towards left. We then put the decimal point there. The number of digits to be counted is obtained by adding the number of digits to the right of the decimal point in the decimal numbers that are being multiplied. Let us now find... Multiply and. We get 00. Both, in. and., there is digit to the right of the decimal point. So, count + = digits from the rightmost digit (i.e., 0) in 00 and move towards left. We get.00 or. Find in a similar way..6,... While multiplying. and., you will first multiply and. For placing the decimal in the product obtained, you will count + = (Why?) digits starting from the rightmost digit. Thus,.. =. Find.7... Find:.7 (ii).8. (iii)... Arrange the products obtained in () in descending order. EXAMPLE 7 The side of an equilateral triangle is. cm. Find its perimeter. SOLUTION All the sides of an equilateral triangle are equal. So, length of each side =. cm Thus, perimeter =. cm = 0. cm EXAMPLE 8 The length of a rectangle is 7. cm and its breadth is. cm. What is the area of the rectangle? SOLUTION Length of the rectangle = 7. cm Breadth of the rectangle =. cm Therefore, area of the rectangle = 7.. cm = 7.7 cm
23 FRACTIONS AND DECIMALS.6. Multiplication of Decimal Numbers by 0, 00 and 000 Reshma observed that. = whereas. =. Thus, she found that depending 0 00 on the position of the decimal point the decimal number can be converted to a fraction with denominator 0 or 00. She wondered what would happen if a decimal number is multiplied by 0 or 00 or 000. Let us see if we can find a pattern of multiplying numbers by 0 or 00 or 000. Have a look at the table given below and fill in the blanks:.76 0 = 76 0 = =.6 0 = = = 76 or =.6 00 = = = = 760 or. 000 = = = ; = ; = Observe the shift of the decimal point of the products in the table. Here the numbers are multiplied by 0,00 and 000. In.76 0 = 7.6, the digits are same i.e.,, 7 and 6. Do you observe this in other products also? Observe.76 and 7.6. To which side has the decimal point shifted, right or left? The decimal point has shifted to the right by one place. Note that 0 has one zero over. In = 76.0, observe.76 and To which side and by how many digits has the decimal point shifted? The decimal point has shifted to the right by two places. Note that 00 has two zeros over one. Do you observe similar shifting of decimal point in other products also? So we say, when a decimal number is multiplied by 0, 00 or 000, the digits in the product are same as in the decimal number but the decimal point in the product is shifted to the right by as, many of places as there are zeros over one. Find: 0. 0 Based on these observations we can now say (ii) = 0.7, = 7 and = 70. (iii) Can you now tell.97 0 =? =? =? Can you now help Reshma to find the total amount i.e., ` 8.0 0, that she has to pay?
24 MATHEMATICS EXERCISE.6. Find: 0. 6 (ii) 8.6 (iii).7 (iv) 0. (v) (vi).0 (vii) Find the area of rectangle whose length is.7cm and breadth is cm.. Find:. 0 (ii) (iii).7 0 (iv) (v). 00 (vi) (vii).6 00 (viii) (ix) 0. 0 (x) (xi) (xii) A two-wheeler covers a distance of. km in one litre of petrol. How much distance will it cover in 0 litres of petrol?. Find:. 0. (ii) 0..7 (iii) (iv).. (v) (vi). 0. (vii) (viii) (ix) (x) DIVISION OF DECIMAL NUMBERS Savita was preparing a design to decorate her classroom. She needed a few coloured strips of paper of length.9 cm each. She had a strip of coloured paper of length 9. cm. How many pieces of the required length will she get out of this strip? She thought it would be 9. cm. Is she correct?.9 Both 9. and.9 are decimal numbers. So we need to know the division of decimal numbers too!.7. Division by 0, 00 and 000 Let us find the division of a decimal number by 0, 00 and 000. Consider = 0 0 = 00 =. Similarly,. 00 = = = Let us see if we can find a pattern for dividing numbers by 0, 00 or 000. This may help us in dividing numbers by 0, 00 or 000 in a shorter way.. 0 =.. 0 =. 0 = =. 00 = =. 00 = =. 000 = =. 000 = =
25 FRACTIONS AND DECIMALS Take. 0 =.. In. and., the digits are same i.e.,,, and but the decimal point has shifted in the quotient. To which side and by how many digits? The decimal point has shifted to the left by one place. Note that 0 has one zero over. Consider now. 00 = 0.. In. and 0. the digits are same, but what about the decimal point in the quotient? It has shifted to the left by two places. Note that 00 has two zeros over. So we can say that, while dividing a number by 0, 00 or 000, the digits of the number and the quotient are same but the decimal point in the quotient shifts to the left by as many places as there are zeros over. Using this observation let us now quickly find:.8 0 = 0.8,.8 00 = 0.08, = Division of a Decimal Number by a Whole Number Let us find 6.. Remember we also write it as 6.. So, 6. = 6 0 = 6 as learnt in fractions.. 0 = = 0 = =. 0 Or, let us first divide 6 by. We get. There is one digit to the right of the decimal point in 6.. Place the decimal in such that there would be one digit to its right. We get. again. To find 9., first find 9. We get 9. There is one digit to the right of the decimal point in 9.. Place the decimal point in 9 such that there would be one digit to its right. You will get.9. (ii). =?; 8. 6 =? Now,.96 = = = = =. 00 Or, divide 96 by. You get. There are two digits to the right of the decimal in.96. Making similar placement of the decimal in, you will get.. Note that here and in the next section, we have considered only those divisions in which, ignoring the decimal, the number would be completely divisible by another number to give remainder zero. Like, in 9., the number 9 when divided by, leaves remainder zero. However, there are situations in which the number may not be completely divisible by another number, i.e., we may not get remainder zero. For example, 9 7. We deal with such situations in later classes. Thus, = 6.8 Find:. 0 (ii). 00 (iii) =?; (ii). =? Find:. (ii) 6. 7
26 MATHEMATICS EXAMPLE 9 Find the average of.,.8 and 7.6. SOLUTION The average of.,.8 and 7.6 is = =...7. Division of a Decimal Number by another Decimal Number Let us find. 0. i.e.,. 0.. We have. 0. = = =. Thus,. 0. = What do you observe? For., we find that there is one digit to the right of the 0. decimal in 0.. This could be converted to whole number by dividing by 0. Accordingly. was also converted to a fraction by dividing by 0. Or, we say the decimal point was shifted by one place to the right in 0. to make it. So, there was a shift of one decimal point to the right in. also to make it. Thus,.. =.. = = 0. Find and. in a similar way Let us now find 0... We can write it is as 0., as discussed above. We get.7. Find.96 0.,. 0.. Consider now,.7 0. as.9. How will you find So, = = =? We can write it as 7. (How?) and we get the quotient 7? We know that 7 can be written as EXAMPLE 0 Each side of a regular polygon is. cm in length. The perimeter of the polygon is.cm. How many sides does the polygon have? SOLUTION Find: (ii) The perimeter of a regular polygon is the sum of the lengths of all its equal sides =. cm. Length of each side =. cm. Thus, the number of sides =.. = = The polygon has sides. (iii).6.
27 FRACTIONS AND DECIMALS EXAMPLE A car covers a distance of 89. km in. hours. What is the average distance covered by it in hour? SOLUTION Distance covered by the car = 89. km. Time required to cover this distance =. hours. So distance covered by it in hour = 89.. = 89 = 0. km. EXERCISE.7. Find: 0. (ii) 0. (iii).8 (iv) 6. 6 (v) 6. (vi).9 7 (vii).96 (viii) Find:.8 0 (ii). 0 (iii) (iv). 0 (v) 7. 0 (vi) (vii) Find:.7 00 (ii) (iii) (iv).6 00 (v).6 00 (vi) Find: (ii) (iii) (iv) (v) Find: 7. (ii) 6 0. (iii). 0. (iv) (v) (vi) (vii) (viii) 7.8. (ix) A vehicle covers a distance of. km in. litres of petrol. How much distance will it cover in one litre of petrol? WHAT HAVE WE DISCUSSED?. We have learnt about fractions and decimals alongwith the operations of addition and subtraction on them, in the earlier class.. We now study the operations of multiplication and division on fractions as well as on decimals.. We have learnt how to multiply fractions. Two fractions are multiplied by multiplying their numerators and denominators seperately and writing the product as product of numerators product of denominators. For example, = = A fraction acts as an operator of. For example, of is =.
28 6 MATHEMATICS. (a) The product of two proper fractions is less than each of the fractions that are multiplied. (b) The product of a proper and an improper fraction is less than the improper fraction and greater than the proper fraction. (c) The product of two imporper fractions is greater than the two fractions. 6. A reciprocal of a fraction is obtained by inverting it upside down. 7. We have seen how to divide two fractions. (a) While dividing a whole number by a fraction, we multiply the whole number with the reciprocal of that fraction. (b) (c) 0 For example, = = While dividing a fraction by a whole number we multiply the fraction by the reciprocal of the whole number. For example, 7 = = 7 While dividing one fraction by another fraction, we multuiply the first fraction by the reciprocal of the other. So, = 7 = We also learnt how to multiply two decimal numbers. While multiplying two decimal numbers, first multiply them as whole numbers. Count the number of digits to the right of the decimal point in both the decimal numbers. Add the number of digits counted. Put the decimal point in the product by counting the digits from its rightmost place. The count should be the sum obtained earlier. For example, = To multiply a decimal number by 0, 00 or 000, we move the decimal point in the number to the right by as many places as there are zeros over. Thus 0. 0 =., =, = 0 0. We have seen how to divide decimal numbers. (a) To divide a decimal number by a whole number, we first divide them as whole numbers. Then place the decimal point in the quotient as in the decimal number. For example, 8. =. Note that here we consider only those divisions in which the remainder is zero. (b) To divide a decimal number by 0, 00 or 000, shift the digits in the decimal number to the left by as many places as there are zeros over, to get the quotient. So,.9 0 =.9,.9 00 = 0.9, = 0.09 (c) While dividing two decimal numbers, first shift the decimal point to the right by equal number of places in both, to convert the divisor to a whole number. Then divide. Thus,. 0. = =.
Fractions and Decimals
 Chapter Fractions and Decimals FRACTION: A fraction is a number representing a part of a whole. The whole may be a single object or a group of objects. 5 is a fraction with numerator and denominator 5.
Chapter Fractions and Decimals FRACTION: A fraction is a number representing a part of a whole. The whole may be a single object or a group of objects. 5 is a fraction with numerator and denominator 5.
WHOLE NUMBERS AND DECIMALS
 WHOLE NUMBERS AND DECIMALS 2 IN THIS CHAPTER YOU WILL: WHAT S IN CHAPTER 2? 2 01 Mental addition 2 02 Mental subtraction 2 03 Rounding decimals and money 2 04 Adding and subtracting decimals 2 05 Mental
WHOLE NUMBERS AND DECIMALS 2 IN THIS CHAPTER YOU WILL: WHAT S IN CHAPTER 2? 2 01 Mental addition 2 02 Mental subtraction 2 03 Rounding decimals and money 2 04 Adding and subtracting decimals 2 05 Mental
Know how to use fractions to describe part of something Write an improper fraction as a mixed number Write a mixed number as an improper fraction
 . Fractions Know how to use fractions to describe part of something Write an improper fraction as a mixed number Write a mixed number as an improper fraction Key words fraction denominator numerator proper
. Fractions Know how to use fractions to describe part of something Write an improper fraction as a mixed number Write a mixed number as an improper fraction Key words fraction denominator numerator proper
50 MATHCOUNTS LECTURES (6) OPERATIONS WITH DECIMALS
 BASIC KNOWLEDGE 1. Decimal representation: A decimal is used to represent a portion of whole. It contains three parts: an integer (which indicates the number of wholes), a decimal point (which separates
BASIC KNOWLEDGE 1. Decimal representation: A decimal is used to represent a portion of whole. It contains three parts: an integer (which indicates the number of wholes), a decimal point (which separates
Maths Curriculum Maps Progress in Understanding Mathematics Assessment. Termly content for Pathway 5
 Maths Curriculum Maps Progress in Understanding Mathematics Assessment Termly content for Pathway 5 Pathway 5 Step 1 Step 2 Step 3 NUMBER Number and place value Read, write, order and compare numbers to
Maths Curriculum Maps Progress in Understanding Mathematics Assessment Termly content for Pathway 5 Pathway 5 Step 1 Step 2 Step 3 NUMBER Number and place value Read, write, order and compare numbers to
Grade 4 Fractions. Answer the questions. For more such worksheets visit (1) Convert into a mixed fraction. (2) Convert
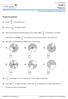 ID : aefractions [1] Grade Fractions For more such worksheets visit www.edugain.com Answer the questions (1) Convert 63 13 (2) Convert 6 7 12 into a mixed fraction. to improper fraction. (3) Aleser had
ID : aefractions [1] Grade Fractions For more such worksheets visit www.edugain.com Answer the questions (1) Convert 63 13 (2) Convert 6 7 12 into a mixed fraction. to improper fraction. (3) Aleser had
Lesson 1: THE DECIMAL SYSTEM
 Lesson 1: THE DECIMAL SYSTEM The word DECIMAL comes from a Latin word, which means "ten. The Decimal system uses the following ten digits to write a number: 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, and 9. Each time
Lesson 1: THE DECIMAL SYSTEM The word DECIMAL comes from a Latin word, which means "ten. The Decimal system uses the following ten digits to write a number: 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, and 9. Each time
Mathematics in Y3 Year Group Expectations
 Mathematics in Y3 Year Group Expectations What the National Curriculum requires in mathematics in Y3 NUMBER PLACE VALUE: count from 0 in multiples of 4, 8, 50 and 100; find 10 or 100 more or less than
Mathematics in Y3 Year Group Expectations What the National Curriculum requires in mathematics in Y3 NUMBER PLACE VALUE: count from 0 in multiples of 4, 8, 50 and 100; find 10 or 100 more or less than
I can use number bonds and matching subtraction facts up to 20.
 Year 1, Maths end of year expectations I can count to and past 100. Forwards and backwards starting from any number. I can count, read and write numbers to 100 in numerals and count in jumps of 2, 5 and
Year 1, Maths end of year expectations I can count to and past 100. Forwards and backwards starting from any number. I can count, read and write numbers to 100 in numerals and count in jumps of 2, 5 and
Topic 3: Fractions. Topic 1 Integers. Topic 2 Decimals. Topic 3 Fractions. Topic 4 Ratios. Topic 5 Percentages. Topic 6 Algebra
 Topic : Fractions Topic Integers Topic Decimals Topic Fractions Topic Ratios Topic Percentages Duration / weeks Content Outline PART (/ week) Introduction Converting Fractions to Decimals Converting Decimals
Topic : Fractions Topic Integers Topic Decimals Topic Fractions Topic Ratios Topic Percentages Duration / weeks Content Outline PART (/ week) Introduction Converting Fractions to Decimals Converting Decimals
Unit 1: Numeration I Can Statements
 Unit 1: Numeration I can write a number using proper spacing without commas. e.g., 934 567. I can write a number to 1 000 000 in words. I can show my understanding of place value in a given number. I can
Unit 1: Numeration I can write a number using proper spacing without commas. e.g., 934 567. I can write a number to 1 000 000 in words. I can show my understanding of place value in a given number. I can
Burnley Brow Year 5 Mathematics Overview
 Burnley Brow Year 5 Mathematics Overview 2016-2017 Inspire Maths 5 Long-term Plan Unit title Key concepts 1 Whole Numbers (1) Numbers to 10 million Place and value Comparing numbers within 10 million Rounding
Burnley Brow Year 5 Mathematics Overview 2016-2017 Inspire Maths 5 Long-term Plan Unit title Key concepts 1 Whole Numbers (1) Numbers to 10 million Place and value Comparing numbers within 10 million Rounding
Unit Maps: Grade 4 Math
 Place Value of Whole Numbers and Decimals 4.3 Number and operations. The student represents, compares, and orders whole numbers and decimals and understands relationships related to place value. Place
Place Value of Whole Numbers and Decimals 4.3 Number and operations. The student represents, compares, and orders whole numbers and decimals and understands relationships related to place value. Place
Rational Number is a number that can be written as a quotient of two integers. DECIMALS are special fractions whose denominators are powers of 10.
 PA Ch 5 Rational Expressions Rational Number is a number that can be written as a quotient of two integers. DECIMALS are special fractions whose denominators are powers of 0. Since decimals are special
PA Ch 5 Rational Expressions Rational Number is a number that can be written as a quotient of two integers. DECIMALS are special fractions whose denominators are powers of 0. Since decimals are special
Grade 4. Number Strand. Achievement Indicators. 1. Represent and describe whole numbers to , pictorially and symbolically.
 Number Strand Outcomes 1. Represent and describe whole numbers to 10 000, pictorially and symbolically. Grade 4 Achievement Indicators Read a four-digit numeral without using the word and (e.g., 5321 is
Number Strand Outcomes 1. Represent and describe whole numbers to 10 000, pictorially and symbolically. Grade 4 Achievement Indicators Read a four-digit numeral without using the word and (e.g., 5321 is
Dawood Public School Course Outline Class IV Math
 Dawood Public School Course Outline 2016-2017 Class IV Math Books: Lu jitan, New Syllabus Primary Mathematics 4 along with practice books 4a and 4b, Singapore; Oxford University Monthly Syllabus for the
Dawood Public School Course Outline 2016-2017 Class IV Math Books: Lu jitan, New Syllabus Primary Mathematics 4 along with practice books 4a and 4b, Singapore; Oxford University Monthly Syllabus for the
MATH LEVEL 2 LESSON PLAN 5 DECIMAL FRACTIONS Copyright Vinay Agarwala, Checked: 1/22/18
 Section 1: The Decimal Number MATH LEVEL 2 LESSON PLAN 5 DECIMAL FRACTIONS 2018 Copyright Vinay Agarwala, Checked: 1/22/18 1. The word DECIMAL comes from a Latin word, which means "ten. The Decimal system
Section 1: The Decimal Number MATH LEVEL 2 LESSON PLAN 5 DECIMAL FRACTIONS 2018 Copyright Vinay Agarwala, Checked: 1/22/18 1. The word DECIMAL comes from a Latin word, which means "ten. The Decimal system
Christ Church, Church of England (VC) Primary School. Aspire, celebrate and learn in an inclusive community. A parent s guide to Year 5 Maths
 Christ Church, Church of England (VC) Primary School Aspire, celebrate and learn in an inclusive community A parent s guide to Year 5 Maths 1 By the end of Year 5 children should be able to Learning objectives
Christ Church, Church of England (VC) Primary School Aspire, celebrate and learn in an inclusive community A parent s guide to Year 5 Maths 1 By the end of Year 5 children should be able to Learning objectives
Year Five Maths Curriculum NUMBER Addition and Subtraction Pupils should be taught to:
 Number and Place Value Addition and Subtraction read, write, order and compare numbers to at least 1 000 000 and determine the value of each digit count forwards or backwards in steps of powers of 10 for
Number and Place Value Addition and Subtraction read, write, order and compare numbers to at least 1 000 000 and determine the value of each digit count forwards or backwards in steps of powers of 10 for
Gateway Regional School District VERTICAL ALIGNMENT OF MATHEMATICS STANDARDS Grades 3-6
 NUMBER SENSE & OPERATIONS 3.N.1 Exhibit an understanding of the values of the digits in the base ten number system by reading, modeling, writing, comparing, and ordering whole numbers through 9,999. Our
NUMBER SENSE & OPERATIONS 3.N.1 Exhibit an understanding of the values of the digits in the base ten number system by reading, modeling, writing, comparing, and ordering whole numbers through 9,999. Our
TIMSS 2011 Fourth Grade Mathematics Item Descriptions developed during the TIMSS 2011 Benchmarking
 TIMSS 2011 Fourth Grade Mathematics Item Descriptions developed during the TIMSS 2011 Benchmarking Items at Low International Benchmark (400) M01_05 M05_01 M07_04 M08_01 M09_01 M13_01 Solves a word problem
TIMSS 2011 Fourth Grade Mathematics Item Descriptions developed during the TIMSS 2011 Benchmarking Items at Low International Benchmark (400) M01_05 M05_01 M07_04 M08_01 M09_01 M13_01 Solves a word problem
Information for Parents/Carers. Mathematics Targets - A Year 1 Mathematician
 Mathematics Targets - A Year 1 Mathematician Number I can count reliably to 100. I can count on and back in 1s, 2s, 5s and 10s from any given number up to 100. I can write all numbers in words to 20. I
Mathematics Targets - A Year 1 Mathematician Number I can count reliably to 100. I can count on and back in 1s, 2s, 5s and 10s from any given number up to 100. I can write all numbers in words to 20. I
Stage 4 Help Sheet. S4/2 Round to nearest 10, 100, 1000, S4/1 Count in multiples Now you must learn these multiples. S4/3 Negative numbers
 thousands hundreds tens thousands hundreds tens thousands hundreds tens Stage Help Sheet S/ Count in multiples Now you must learn these multiples Multiples of 6 Multiples of 7 Multiples of 9 Multiples
thousands hundreds tens thousands hundreds tens thousands hundreds tens Stage Help Sheet S/ Count in multiples Now you must learn these multiples Multiples of 6 Multiples of 7 Multiples of 9 Multiples
Fractions, Decimals, Ratio and Percentages (FDRP) Measures (MEA)
 Termly assessment Number and Place Value (NPV) Addition and Subtraction (AS) Multiplication and Division (MD) Fractions, Decimals, Ratio and Percentages (FDRP) Measures (MEA) Geometry (GEO) Statistics
Termly assessment Number and Place Value (NPV) Addition and Subtraction (AS) Multiplication and Division (MD) Fractions, Decimals, Ratio and Percentages (FDRP) Measures (MEA) Geometry (GEO) Statistics
FRACTIONS AND DECIMALS
 Mathematics Revision Guides Fractions and Decimals Page of MK HOME TUITION Mathematics Revision Guides Level: GCSE Foundation Tier FRACTIONS AND DECIMALS Version: Date: -0-0 Mathematics Revision Guides
Mathematics Revision Guides Fractions and Decimals Page of MK HOME TUITION Mathematics Revision Guides Level: GCSE Foundation Tier FRACTIONS AND DECIMALS Version: Date: -0-0 Mathematics Revision Guides
TOPIC 2 DECIMALS (and INTRODUCTION TO FRACTIONS) WEEK 3
 TOPIC DECIMALS (and INTRODUCTION TO FRACTIONS) WEEK 3 Association between Fractions and Decimals is a fraction. It means divided by. If we divide by the result is not a whole number. It is a half of whole
TOPIC DECIMALS (and INTRODUCTION TO FRACTIONS) WEEK 3 Association between Fractions and Decimals is a fraction. It means divided by. If we divide by the result is not a whole number. It is a half of whole
Mathematics Scope & Sequence Grade 4
 Mathematics Scope & Sequence Grade 4 Revised: May 24, 2016 First Nine Weeks (39 days) Whole Numbers Place Value 4.2B represent the value of the digit in whole numbers through 1,000,000,000 and decimals
Mathematics Scope & Sequence Grade 4 Revised: May 24, 2016 First Nine Weeks (39 days) Whole Numbers Place Value 4.2B represent the value of the digit in whole numbers through 1,000,000,000 and decimals
Number Sense Workbook 7, Part 1: Unit 3
 Number Sense Workbook, Part : Unit Worksheet NS- page. a),, : 0,,,,, 0, : 0,, 0,, 0,, 0. a) Yes No Yes; Yes; Yes. a) 0 All whole numbers, since any whole number times zero is zero.. is a factor of. is
Number Sense Workbook, Part : Unit Worksheet NS- page. a),, : 0,,,,, 0, : 0,, 0,, 0,, 0. a) Yes No Yes; Yes; Yes. a) 0 All whole numbers, since any whole number times zero is zero.. is a factor of. is
Position. By the end of the year, it is expected that children will be able to sequence events in chronological order. My Numeracy Targets Year 1
 My Numeracy Targets Year 1 Number and place value Multiplication and Division Addition and subtraction I can count up and down from 0 to 100 and more. I can count, read and write numbers up to 100. I can
My Numeracy Targets Year 1 Number and place value Multiplication and Division Addition and subtraction I can count up and down from 0 to 100 and more. I can count, read and write numbers up to 100. I can
Wincham CP School Scheme of Work for Maths Year Group 5 Year A & B. Active Learn Year 5 Text books
 Wincham CP School Scheme of Work for Maths Year Group 5 Year A & B Key to Strands (KS1) NPV: Number and Place Value NAS: Number, Addition and Subtraction NMD: Number, Multiplication and Division F: Fractions
Wincham CP School Scheme of Work for Maths Year Group 5 Year A & B Key to Strands (KS1) NPV: Number and Place Value NAS: Number, Addition and Subtraction NMD: Number, Multiplication and Division F: Fractions
Linby Primary School Targets Ladder. Linby Primary School Targets Ladder
 Target Sheet 1a I can read numbers to 10 (1, 2, 3 etc) written as digits 1,2,3,.Make sure you can do this out of order (5, 9, 2) I can count up to 10 objects accurately and consistently. (Both things that
Target Sheet 1a I can read numbers to 10 (1, 2, 3 etc) written as digits 1,2,3,.Make sure you can do this out of order (5, 9, 2) I can count up to 10 objects accurately and consistently. (Both things that
Mathematics Year 5. Key Stage Strand Objective Child Speak Target Greater Depth Target. Number Place Value
 Key Stage Strand Objective Child Speak Target Greater Depth Target [KEY] Read, write, order and compare numbers to at least 1 000 000 and determine the value of each digit. GD objective: Independently
Key Stage Strand Objective Child Speak Target Greater Depth Target [KEY] Read, write, order and compare numbers to at least 1 000 000 and determine the value of each digit. GD objective: Independently
Place Value and Operations with Whole Numbers
 M a t h e m a t i c s Place Value and Operations with Whole Numbers Project: Food in Space.........................2 Developing understanding and fluency with multi-digit multiplication, and developing
M a t h e m a t i c s Place Value and Operations with Whole Numbers Project: Food in Space.........................2 Developing understanding and fluency with multi-digit multiplication, and developing
Math 9 Final Exam Review and Outline
 Math 9 Final Exam Review and Outline Your Final Examination in Mathematics 9 is a comprehensive final of all material covered in the course. It is broken down into the three sections: Number Sense, Patterns
Math 9 Final Exam Review and Outline Your Final Examination in Mathematics 9 is a comprehensive final of all material covered in the course. It is broken down into the three sections: Number Sense, Patterns
Maths - Knowledge Key Performance Indicator Milestones Milestones Year 5 Year 6
 Addition and Subtraction Number and Place Value Maths - Knowledge Key Performance Indicator Milestones Milestones Year 5 Year 6 I can read numbers to at least 1 000 000 I can write numbers to at least
Addition and Subtraction Number and Place Value Maths - Knowledge Key Performance Indicator Milestones Milestones Year 5 Year 6 I can read numbers to at least 1 000 000 I can write numbers to at least
The Common Curriculum Framework. for K 9 MATHEMATICS. Western and Northern Canadian Protocol. May 2006
 The Common Curriculum Framework for K 9 MATHEMATICS Western and Northern Canadian Protocol May 2006 Grade 5 Strand: Number 1. Represent and describe whole numbers to 1 000 000. [C, CN, V, T] 2. Use estimation
The Common Curriculum Framework for K 9 MATHEMATICS Western and Northern Canadian Protocol May 2006 Grade 5 Strand: Number 1. Represent and describe whole numbers to 1 000 000. [C, CN, V, T] 2. Use estimation
Use grouping symbols including parentheses, brackets, or braces in numerical expressions, and evaluate expressions with these symbols
 Operations and Algebraic Thinking AR.Math.Content.5.OA.A.1 AR.Math.Content.5.OA.A.2 Write and interpret numerical expressions Use grouping symbols including parentheses, brackets, or braces in numerical
Operations and Algebraic Thinking AR.Math.Content.5.OA.A.1 AR.Math.Content.5.OA.A.2 Write and interpret numerical expressions Use grouping symbols including parentheses, brackets, or braces in numerical
Stage 4 PROMPT sheet. 4/2 Round to nearest 10, 100, 1000, 4/1 Count in multiples Now you must learn these multiples. 4/3 Negative numbers
 Stage PROMPT sheet / Count in multiples Now you must learn these multiples Multiples of 6 Multiples of 7 Multiples of 9 Multiples of 6 7 9 0 7 7 6 00 0 6 0 9 6 7 6 7 00 6 60 70 90 0 / Round to nearest
Stage PROMPT sheet / Count in multiples Now you must learn these multiples Multiples of 6 Multiples of 7 Multiples of 9 Multiples of 6 7 9 0 7 7 6 00 0 6 0 9 6 7 6 7 00 6 60 70 90 0 / Round to nearest
Fractions and Mixed Numbers
 6 CHAPTER Fractions and Mixed Numbers Worksheet Adding Fractions Find the equivalent fraction. Shade the models. _? 6. _?.? Reteach A Find the equivalent fractions. To get the equivalent fraction, multiply
6 CHAPTER Fractions and Mixed Numbers Worksheet Adding Fractions Find the equivalent fraction. Shade the models. _? 6. _?.? Reteach A Find the equivalent fractions. To get the equivalent fraction, multiply
Expected Standards for Year 6: Mathematics Curriculum (taken from ncetm progression maps)
 Expected Standards for Year 6: Mathematics Curriculum (taken from ncetm progression maps) Place Value Addition and Subtraction Multiplication and Division Fractions Ratio and Proportion Measurement Geometry
Expected Standards for Year 6: Mathematics Curriculum (taken from ncetm progression maps) Place Value Addition and Subtraction Multiplication and Division Fractions Ratio and Proportion Measurement Geometry
PROGRESSION IS HIGHLIGHTED IN THE FOLLOWING DOCUMENT VIA BOLDED TEXT. MATHEMATICAL PROCESSES
 Alberta's Program of Studies (Curriculum) - Mathematics - Number (Strand with Achievement Outcomes) Note: These strands are not intended to be discrete units of instruction. The integration of outcomes
Alberta's Program of Studies (Curriculum) - Mathematics - Number (Strand with Achievement Outcomes) Note: These strands are not intended to be discrete units of instruction. The integration of outcomes
Maths Target Wall Year 1
 Maths Target Wall Year 1 I can count up and down from 0 to 100 and more. I can count, read and write numbers up to 100. I can count in 2 or 5 or 10 When you show me a number, I can tell you what is one
Maths Target Wall Year 1 I can count up and down from 0 to 100 and more. I can count, read and write numbers up to 100. I can count in 2 or 5 or 10 When you show me a number, I can tell you what is one
Summer 2013 Modules 9-13
 Summer 201 Modules 9-1 Mastering the Fundamentals Chris Millett Copyright 201 All rights reserved. Written permission must be secured from the author to use or reproduce any part of this book. Academic
Summer 201 Modules 9-1 Mastering the Fundamentals Chris Millett Copyright 201 All rights reserved. Written permission must be secured from the author to use or reproduce any part of this book. Academic
NF5-21 Multiplying Unit Fractions Pages 13 14
 NF- Multiplying Unit Fractions Pages STANDARDS.NF.B. Goals Students will develop and apply the formula for multiplying unit fractions by unit fractions. Vocabulary denominator numerator of (to mean multiply
NF- Multiplying Unit Fractions Pages STANDARDS.NF.B. Goals Students will develop and apply the formula for multiplying unit fractions by unit fractions. Vocabulary denominator numerator of (to mean multiply
To be able to count up and down in tenths
 Progression Grid: Year Year 2 Year 3 Year Year Year 6 Counting in Fractional steps To be able to count in fractions up to 0, starting from any number and using the/2 and 2/ equivalence on the number line
Progression Grid: Year Year 2 Year 3 Year Year Year 6 Counting in Fractional steps To be able to count in fractions up to 0, starting from any number and using the/2 and 2/ equivalence on the number line
Developing Year 5 expectations Mastering Y5 expectations Going to greater depth with Y5 expectations
 Year 5 Understanding and investigating within number Place value, ordering and rounding Counting reading, writing, comparing, ordering and rounding whole numbers using place value Properties of numbers
Year 5 Understanding and investigating within number Place value, ordering and rounding Counting reading, writing, comparing, ordering and rounding whole numbers using place value Properties of numbers
Maths Curriculum Overview Year 1
 Year 1 Count to and across 100, forwards and backwards beginning with 0 or one from any given number Count, read and write numbers to 100 in numerals, count in multiples of twos fives and tens Given a
Year 1 Count to and across 100, forwards and backwards beginning with 0 or one from any given number Count, read and write numbers to 100 in numerals, count in multiples of twos fives and tens Given a
2014 National Curriculum - Maths Band 1
 2014 National Curriculum - Maths Band 1 count to and across 100, forwards and backwards, beginning with 0 or 1, or from any given number read, write and interpret mathematical statements involving addition
2014 National Curriculum - Maths Band 1 count to and across 100, forwards and backwards, beginning with 0 or 1, or from any given number read, write and interpret mathematical statements involving addition
Scott Foresman Investigations in Number, Data, and Space Content Scope & Sequence Correlated to Academic Language Notebooks The Language of Math
 Scott Foresman Investigations in Number, Data, and Space Content Scope & Sequence Correlated to Academic Language Notebooks The Language of Math Grade 5 Content Scope & Sequence Unit 1: Number Puzzles
Scott Foresman Investigations in Number, Data, and Space Content Scope & Sequence Correlated to Academic Language Notebooks The Language of Math Grade 5 Content Scope & Sequence Unit 1: Number Puzzles
Rational Numbers CHAPTER Introduction
 RATIONAL NUMBERS Rational Numbers CHAPTER. Introduction In Mathematics, we frequently come across simple equations to be solved. For example, the equation x + () is solved when x, because this value of
RATIONAL NUMBERS Rational Numbers CHAPTER. Introduction In Mathematics, we frequently come across simple equations to be solved. For example, the equation x + () is solved when x, because this value of
NS6-50 Dividing Whole Numbers by Unit Fractions Pages 16 17
 NS6-0 Dividing Whole Numbers by Unit Fractions Pages 6 STANDARDS 6.NS.A. Goals Students will divide whole numbers by unit fractions. Vocabulary division fraction unit fraction whole number PRIOR KNOWLEDGE
NS6-0 Dividing Whole Numbers by Unit Fractions Pages 6 STANDARDS 6.NS.A. Goals Students will divide whole numbers by unit fractions. Vocabulary division fraction unit fraction whole number PRIOR KNOWLEDGE
BASIC MATH CONTENTS. Section 1... Whole Number Review. Section 2... Decimal Review. Section 3... Fraction Review. Section 4...
 BASIC MATH The purpose of this booklet is to refresh the reader s skills in basic mathematics. There are basic mathematical processes, which must be followed throughout all areas of math applications.
BASIC MATH The purpose of this booklet is to refresh the reader s skills in basic mathematics. There are basic mathematical processes, which must be followed throughout all areas of math applications.
WHOLE NUMBER AND DECIMAL OPERATIONS
 WHOLE NUMBER AND DECIMAL OPERATIONS Whole Number Place Value : 5,854,902 = Ten thousands thousands millions Hundred thousands Ten thousands Adding & Subtracting Decimals : Line up the decimals vertically.
WHOLE NUMBER AND DECIMAL OPERATIONS Whole Number Place Value : 5,854,902 = Ten thousands thousands millions Hundred thousands Ten thousands Adding & Subtracting Decimals : Line up the decimals vertically.
Fractions with a denominator of 10, 100 or can be written as decimals. A decimal is any number which has a decimal comma.
 101 Unit 8 Decimals Fractions with a denominator of 10, or 1 000 can be written as decimals. A decimal is any number which has a decimal comma. A decimal comma separates whole numbers from tenths, hundredths
101 Unit 8 Decimals Fractions with a denominator of 10, or 1 000 can be written as decimals. A decimal is any number which has a decimal comma. A decimal comma separates whole numbers from tenths, hundredths
4 th Grade MCA3 Standards, Benchmarks, Test Specifications & Sampler Questions
 4 th Grade MCA3 Standards, Benchmarks, Test Specifications & Sampler Questions Standard No. Benchmark (4 th Grade) Sampler Item Demonstrate fluency with multiplication and division facts. 4.1.1.1 Factors
4 th Grade MCA3 Standards, Benchmarks, Test Specifications & Sampler Questions Standard No. Benchmark (4 th Grade) Sampler Item Demonstrate fluency with multiplication and division facts. 4.1.1.1 Factors
HOW TO DIVIDE: MCC6.NS.2 Fluently divide multi-digit numbers using the standard algorithm. WORD DEFINITION IN YOUR WORDS EXAMPLE
 MCC6.NS. Fluently divide multi-digit numbers using the standard algorithm. WORD DEFINITION IN YOUR WORDS EXAMPLE Dividend A number that is divided by another number. Divisor A number by which another number
MCC6.NS. Fluently divide multi-digit numbers using the standard algorithm. WORD DEFINITION IN YOUR WORDS EXAMPLE Dividend A number that is divided by another number. Divisor A number by which another number
use all four operations to solve problems involving measure [for example, length, mass, volume, money] using decimal notation including scaling
![use all four operations to solve problems involving measure [for example, length, mass, volume, money] using decimal notation including scaling use all four operations to solve problems involving measure [for example, length, mass, volume, money] using decimal notation including scaling](/thumbs/77/75343910.jpg) Year 5 overview The POS may be moved round and the amount of time is just a guidance,you are free to alter the amount of time as there are a few free weeks in the year. POS Autumn term place value read,
Year 5 overview The POS may be moved round and the amount of time is just a guidance,you are free to alter the amount of time as there are a few free weeks in the year. POS Autumn term place value read,
1. Alicia tosses 3 fair coins. What is the probability that she gets at 1. least 1 head? Express your answer as a common fraction.
 Blitz, Page 1 1. Alicia tosses 3 fair coins. What is the probability that she gets at 1. least 1 head? Express your answer as a common fraction. 2. It took Anita 2.25 hours to walk 12.5 km. At this rate,
Blitz, Page 1 1. Alicia tosses 3 fair coins. What is the probability that she gets at 1. least 1 head? Express your answer as a common fraction. 2. It took Anita 2.25 hours to walk 12.5 km. At this rate,
Pre-Algebra Notes Unit Five: Rational Numbers and Equations
 Pre-Algebra Notes Unit Five: Rational Numbers and Equations Rational Numbers Rational numbers are numbers that can be written as a quotient of two integers. Since decimals are special fractions, all the
Pre-Algebra Notes Unit Five: Rational Numbers and Equations Rational Numbers Rational numbers are numbers that can be written as a quotient of two integers. Since decimals are special fractions, all the
Math 7 Notes Unit Three: Applying Rational Numbers
 Math 7 Notes Unit Three: Applying Rational Numbers Strategy note to teachers: Typically students need more practice doing computations with fractions. You may want to consider teaching the sections on
Math 7 Notes Unit Three: Applying Rational Numbers Strategy note to teachers: Typically students need more practice doing computations with fractions. You may want to consider teaching the sections on
Year 1 Year 2 Year 3 Year 4 Year 5 Year 6 count to and across 100, forwards and backwards, beginning with 0 or 1, or from any given number
 Mathematics Programme of Study: Key stages 1 and 2 Number and place value count to and across 100, forwards and backwards, beginning with 0 or 1, or from any given number count, read and write to 100 in
Mathematics Programme of Study: Key stages 1 and 2 Number and place value count to and across 100, forwards and backwards, beginning with 0 or 1, or from any given number count, read and write to 100 in
Using Equivalent Fractions to Solve Problems
 Using Equivalent Fractions to Solve Problems Home Link -1 1 Fill in the equivalent fractions in the table below. Multi ply Both the Numerator and Denominator by: Fraction 6 1 _ 6_ 6_ 9 1 16 10_ 1 6_ 1
Using Equivalent Fractions to Solve Problems Home Link -1 1 Fill in the equivalent fractions in the table below. Multi ply Both the Numerator and Denominator by: Fraction 6 1 _ 6_ 6_ 9 1 16 10_ 1 6_ 1
Coached Instruction Supplement
 Practice Coach PLUS Coached Instruction Supplement Mathematics 5 Practice Coach PLUS, Coached Instruction Supplement, Mathematics, Grade 5 676NASP Triumph Learning Triumph Learning, LLC. All rights reserved.
Practice Coach PLUS Coached Instruction Supplement Mathematics 5 Practice Coach PLUS, Coached Instruction Supplement, Mathematics, Grade 5 676NASP Triumph Learning Triumph Learning, LLC. All rights reserved.
Read, write, order and compare numbers up to and determine the value of each digit. Round any whole number to a required degree of accuracy
 Autumn Term Area Year 6 Year 5 Number and place value Addition Multiplication and division up to 10 000 000 and determine the value of each digit Round any whole number to a required degree of accuracy
Autumn Term Area Year 6 Year 5 Number and place value Addition Multiplication and division up to 10 000 000 and determine the value of each digit Round any whole number to a required degree of accuracy
Mathematics LV 3 (with QuickTables)
 Mathematics LV 3 (with QuickTables) This course covers the topics shown below. Students navigate learning paths based on their level of readiness. Institutional users may customize the scope and sequence
Mathematics LV 3 (with QuickTables) This course covers the topics shown below. Students navigate learning paths based on their level of readiness. Institutional users may customize the scope and sequence
School District of Marshfield Mathematics Standards
 MATHEMATICS Counting and Cardinality, Operations and Algebraic Thinking, Number and Operations in Base Ten, Measurement and Data, and Geometry Operations and Algebraic Thinking Use the Four Operations
MATHEMATICS Counting and Cardinality, Operations and Algebraic Thinking, Number and Operations in Base Ten, Measurement and Data, and Geometry Operations and Algebraic Thinking Use the Four Operations
Minnesota 4 th Grade 2007 Math Strands & Standards
 Minnesota 4 th Grade 2007 Math Strands & Standards Number & Operation Algebra Geometry & Measurement Demonstrate mastery of multiplication and division basic facts; multiply multi-digit numbers; solve
Minnesota 4 th Grade 2007 Math Strands & Standards Number & Operation Algebra Geometry & Measurement Demonstrate mastery of multiplication and division basic facts; multiply multi-digit numbers; solve
OA: Operations and Algebraic Thinking
 OA: Operations and Algebraic Thinking I can write and explain the meaning of a multiplication equation. 4.OA.1 I can create and solve multiplication equations that compare two sets. 4.OA.1 I can represent
OA: Operations and Algebraic Thinking I can write and explain the meaning of a multiplication equation. 4.OA.1 I can create and solve multiplication equations that compare two sets. 4.OA.1 I can represent
Grade 5 Mathematics MCA-III Item Sampler Teacher Guide
 Grade 5 Mathematics MCA-III Item Sampler Teacher Guide Grade 5 Mathematics MCA Item Sampler Parent/Teacher Guide The purpose of the Item Samplers is to familiarize students with the online MCA test format.
Grade 5 Mathematics MCA-III Item Sampler Teacher Guide Grade 5 Mathematics MCA Item Sampler Parent/Teacher Guide The purpose of the Item Samplers is to familiarize students with the online MCA test format.
Maths Programme of Study 3.3
 1 4/9/17 2 11/9/17 3 18/9/17 4 25/9/17 5 2/10/17 Recognise place value of each digit in 4-digit numbers. Identify, estimate and represent numbers using different representations including measures. Compare
1 4/9/17 2 11/9/17 3 18/9/17 4 25/9/17 5 2/10/17 Recognise place value of each digit in 4-digit numbers. Identify, estimate and represent numbers using different representations including measures. Compare
Donnington Primary School Mathematics Statements
 Year 1 / Band 1 Count to and across 100, forwards and backwards, beginning with 0 or 1, or from any given number Count, read and write numbers to 100 in numerals; count in multiples of twos, fives and
Year 1 / Band 1 Count to and across 100, forwards and backwards, beginning with 0 or 1, or from any given number Count, read and write numbers to 100 in numerals; count in multiples of twos, fives and
Aston Hall s A-Z of mathematical terms
 Aston Hall s A-Z of mathematical terms The following guide is a glossary of mathematical terms, covering the concepts children are taught in FS2, KS1 and KS2. This may be useful to clear up any homework
Aston Hall s A-Z of mathematical terms The following guide is a glossary of mathematical terms, covering the concepts children are taught in FS2, KS1 and KS2. This may be useful to clear up any homework
What is a Fraction? Fractions. One Way To Remember Numerator = North / 16. Example. What Fraction is Shaded? 9/16/16. Fraction = Part of a Whole
 // Fractions Pages What is a Fraction? Fraction Part of a Whole Top Number? Bottom Number? Page Numerator tells how many parts you have Denominator tells how many parts are in the whole Note: the fraction
// Fractions Pages What is a Fraction? Fraction Part of a Whole Top Number? Bottom Number? Page Numerator tells how many parts you have Denominator tells how many parts are in the whole Note: the fraction
Mathematics LV 4 (with QuickTables)
 Mathematics LV 4 (with QuickTables) This course covers the topics shown below. Students navigate learning paths based on their level of readiness. Institutional users may customize the scope and sequence
Mathematics LV 4 (with QuickTables) This course covers the topics shown below. Students navigate learning paths based on their level of readiness. Institutional users may customize the scope and sequence
National Curriculum 2014: Progression in Mathematics
 Number and Place Value Year 1 Year 2 Year 3 count to and across 100, forwards and backwards, beginning with 0 or 1, or from any given number count, read and write numbers to 100 in numerals, count in different
Number and Place Value Year 1 Year 2 Year 3 count to and across 100, forwards and backwards, beginning with 0 or 1, or from any given number count, read and write numbers to 100 in numerals, count in different
Maths Key Performance Indicators
 Band 1 Count to and across 100, forwards and backwards, beginning with 0 or 1, or from any given number Count and read numbers to 100 in numerals Count and write numbers to 100 in numerals Count in steps
Band 1 Count to and across 100, forwards and backwards, beginning with 0 or 1, or from any given number Count and read numbers to 100 in numerals Count and write numbers to 100 in numerals Count in steps
Mississippi College and Career Readiness Standards for Mathematics Scaffolding Document. Grade 4
 Mississippi College and Career Readiness Standards for Mathematics Scaffolding Document Grade 4 Operations and Algebraic Thinking (OA) Use the four operations with whole numbers to solve problems 4.OA.1
Mississippi College and Career Readiness Standards for Mathematics Scaffolding Document Grade 4 Operations and Algebraic Thinking (OA) Use the four operations with whole numbers to solve problems 4.OA.1
Medium Term Plans for Mathematics (revised version) - Year Five (Summer Term)
 Oral mental starters (ongoing, throughout the term): Identify multiples and count from (and back to) 0 in multiples of, 4, 6, 7, 8, 9, 11,1,, 0, 100 and 1000 Recall and use multiplication and division
Oral mental starters (ongoing, throughout the term): Identify multiples and count from (and back to) 0 in multiples of, 4, 6, 7, 8, 9, 11,1,, 0, 100 and 1000 Recall and use multiplication and division
Released December Year. Small Steps Guidance and Examples. Block 2 - Fractions
 Released December 07 Year 5 Small Steps Guidance and Examples Block - Fractions Year 5 Spring Term Teaching Guidance Overview Small Steps Equivalent fractions Improper fractions to mixed numbers Mixed
Released December 07 Year 5 Small Steps Guidance and Examples Block - Fractions Year 5 Spring Term Teaching Guidance Overview Small Steps Equivalent fractions Improper fractions to mixed numbers Mixed
Year 5 Maths Objectives
 Counting Year 5 Maths Objectives Number - number and place value Count forwards or backwards in steps of powers of 10 for any given number up to 1 000 000 Count forwards and backwards in decimal steps
Counting Year 5 Maths Objectives Number - number and place value Count forwards or backwards in steps of powers of 10 for any given number up to 1 000 000 Count forwards and backwards in decimal steps
360 right angle, 90. Types of Angles
 Angle Measures Lesson 8 8 Angles Type Measure Right angle 90 Obtuse angle Acute angle more than 90, less than 80 less than 90 0 9 2 2 3 0 9 2 2 3 Straight angle 80 8 7 6 5 4 8 7 6 5 4 Full circle 360 right
Angle Measures Lesson 8 8 Angles Type Measure Right angle 90 Obtuse angle Acute angle more than 90, less than 80 less than 90 0 9 2 2 3 0 9 2 2 3 Straight angle 80 8 7 6 5 4 8 7 6 5 4 Full circle 360 right
Mathematics Curriculum Objectives Year Six. Trinity Primary
 Mathematics Curriculum Objectives Year Six Trinity Primary Counting Year 6 Number I can count backwards I can count backwards I can find the difference through zero to include through zero to include between
Mathematics Curriculum Objectives Year Six Trinity Primary Counting Year 6 Number I can count backwards I can count backwards I can find the difference through zero to include through zero to include between
Converting between Percents, Decimals, and Fractions
 Section. PRE-ACTIVITY PREPARATION Converting between Percents, Decimals, and Fractions Think about how often you have heard, read, or used the term percent (%) in its many everyday applications: The sales
Section. PRE-ACTIVITY PREPARATION Converting between Percents, Decimals, and Fractions Think about how often you have heard, read, or used the term percent (%) in its many everyday applications: The sales
NUMBER AND PLACE VALUE ADDITION AND SUBTRACTION MULTIPLICATION AND DIVISION FRACTIONS Count to and across 100, forwards
 2014 STATUTORY REQUIREMENTS OVERVIEW - YEAR 1 NUMBER AND PLACE VALUE ADDITION AND SUBTRACTION MULTIPLICATION AND DIVISION FRACTIONS Count to and across 100, forwards Read, write and interpret Solve one-step
2014 STATUTORY REQUIREMENTS OVERVIEW - YEAR 1 NUMBER AND PLACE VALUE ADDITION AND SUBTRACTION MULTIPLICATION AND DIVISION FRACTIONS Count to and across 100, forwards Read, write and interpret Solve one-step
Hart Plain Junior School Hart Plain Junior School Maths overview
 Hart Plain Junior School Hart Plain Junior School Maths overview Year 3 Maths Overview Number Addition + sub Multiplication/division Fractions Measurement Geometry Stats read, write, order and compare
Hart Plain Junior School Hart Plain Junior School Maths overview Year 3 Maths Overview Number Addition + sub Multiplication/division Fractions Measurement Geometry Stats read, write, order and compare
Contents. Heinemann Maths Zone Copyright Pearson Australia (a divsion of Pearson Australia Group Pty Ltd)
 Contents Chapter 1 Whole numbers R1.1 Mathematics in sentences R1.2 Rounding to the first digit R1.3 Operations on whole numbers R1.4 Addition of whole numbers R1.5 Consecutive numbers R1.6 Ordering R1.7
Contents Chapter 1 Whole numbers R1.1 Mathematics in sentences R1.2 Rounding to the first digit R1.3 Operations on whole numbers R1.4 Addition of whole numbers R1.5 Consecutive numbers R1.6 Ordering R1.7
Number and Place Value
 Number and Place Value Reading and writing numbers Ordering and comparing numbers Place value Representing and estimating numbers Rounding numbers Round to nearest 100 000 up to 1 000 000, extend to rounding
Number and Place Value Reading and writing numbers Ordering and comparing numbers Place value Representing and estimating numbers Rounding numbers Round to nearest 100 000 up to 1 000 000, extend to rounding
Table of Contents. Student Practice Pages. Number Lines and Operations Numbers. Inverse Operations and Checking Answers... 40
 Table of Contents Introduction... Division by Tens... 38 Common Core State Standards Correlation... Division of -Digit Numbers... 39 Student Practice Pages Number Lines and Operations Numbers Inverse Operations
Table of Contents Introduction... Division by Tens... 38 Common Core State Standards Correlation... Division of -Digit Numbers... 39 Student Practice Pages Number Lines and Operations Numbers Inverse Operations
 - 0.8.00-0.8. 7 ANSWERS: ) : ) : ) : ) : 8 RATIO WORD PROBLEM EXAMPLES: Ratio Compares two amounts or values; they can be written in ways. As a fraction With a colon : With words to A classroom has girls
- 0.8.00-0.8. 7 ANSWERS: ) : ) : ) : ) : 8 RATIO WORD PROBLEM EXAMPLES: Ratio Compares two amounts or values; they can be written in ways. As a fraction With a colon : With words to A classroom has girls
For more information, see the Math Notes box in Lesson of the Core Connections, Course 1 text.
 Number TYPES OF NUMBERS When two or more integers are multiplied together, each number is a factor of the product. Nonnegative integers that have eactly two factors, namely, one and itself, are called
Number TYPES OF NUMBERS When two or more integers are multiplied together, each number is a factor of the product. Nonnegative integers that have eactly two factors, namely, one and itself, are called
Mathematics Curriculum Medium Term Planning Year Five
 Curriculum Medium Term Planning Year Five Year Five Programme of Study Number Number and Place Value Statutory Requirements Pupils should be taught to: read, write, order and compare numbers to at least
Curriculum Medium Term Planning Year Five Year Five Programme of Study Number Number and Place Value Statutory Requirements Pupils should be taught to: read, write, order and compare numbers to at least
Inmans Primary School Mathematics Long Term Plan
 Year 1 Inmans Primary School Mathematics Long Term Plan Number Number and place value Count to and across 100, forwards and backwards, beginning with 0 or 1, or from any given number Count, read and write
Year 1 Inmans Primary School Mathematics Long Term Plan Number Number and place value Count to and across 100, forwards and backwards, beginning with 0 or 1, or from any given number Count, read and write
Number and Place Value. Calculations
 Maths Targets Number and Place Value I can count to and across 100, forwards and backwards, beginning from 0 or 1, or from any given number I can count in multiples of twos, five and tens I can count,
Maths Targets Number and Place Value I can count to and across 100, forwards and backwards, beginning from 0 or 1, or from any given number I can count in multiples of twos, five and tens I can count,
Accuplacer Arithmetic Study Guide
 Accuplacer Arithmetic Study Guide I. Terms Numerator: which tells how many parts you have (the number on top) Denominator: which tells how many parts in the whole (the number on the bottom) Example: parts
Accuplacer Arithmetic Study Guide I. Terms Numerator: which tells how many parts you have (the number on top) Denominator: which tells how many parts in the whole (the number on the bottom) Example: parts
Use decimal notation for tenths, hundredths and thousandths
 Maths Long Term Plan Year AUTUMN Number and place value () Read, write, order and compare numbers up to 0 000 000 and determine the value of each digit Use decimal notation for tenths, hundredths and thousandths
Maths Long Term Plan Year AUTUMN Number and place value () Read, write, order and compare numbers up to 0 000 000 and determine the value of each digit Use decimal notation for tenths, hundredths and thousandths
Pre-Algebra Notes Unit Five: Rational Numbers and Equations
 Pre-Algebra Notes Unit Five: Rational Numbers and Equations Rational Numbers Rational numbers are numbers that can be written as a quotient of two integers. Since decimals are special fractions, all the
Pre-Algebra Notes Unit Five: Rational Numbers and Equations Rational Numbers Rational numbers are numbers that can be written as a quotient of two integers. Since decimals are special fractions, all the
Year 1 Yearly Overview
 Year 1 Yearly Overview Counting Identifying, representing and estimating Reading and writing Comparing Count to and across 100, forwards & backwards, beginning with 0 or 1, or from any given number Count,
Year 1 Yearly Overview Counting Identifying, representing and estimating Reading and writing Comparing Count to and across 100, forwards & backwards, beginning with 0 or 1, or from any given number Count,
Exploring Adding and Subtracting Decimals. :i + Ml = HH. d) = e) f) = d) = e}
 3.1 Exploring Adding and Subtracting Decimals Add and subtract decimals using mental math. 1. Rewrite these number sentences using near numbers, to make them easier to estimate. Then calculate. The first
3.1 Exploring Adding and Subtracting Decimals Add and subtract decimals using mental math. 1. Rewrite these number sentences using near numbers, to make them easier to estimate. Then calculate. The first
read, write and interpret mathematical statements involving addition (+), subtraction (-) and equals (=) signs
 Year 1 NUMBER Number and place value count to and across 100, forwards and backwards, beginning with 0 or 1, or from any given number count, read and write numbers to 100 in numerals; count in multiples
Year 1 NUMBER Number and place value count to and across 100, forwards and backwards, beginning with 0 or 1, or from any given number count, read and write numbers to 100 in numerals; count in multiples
Number and Place Value KS1 Y1 Count to and across 100, forwards and backwards, beginning with 0 or 1, or from any given number.
 South Hylton Primary School Maths Curriculum 2014 Number and Place Value KS1 Y1 Count to and across 100, forwards and backwards, beginning with 0 or 1, or from any given number. Count, read and write numbers
South Hylton Primary School Maths Curriculum 2014 Number and Place Value KS1 Y1 Count to and across 100, forwards and backwards, beginning with 0 or 1, or from any given number. Count, read and write numbers
