Assignment 2 in Simulation of Telesystems Laboratory exercise: Introduction to Simulink and Communications Blockset
|
|
|
- Tracy Harris
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Mid Sweden University Revised: Magnus Eriksson Assignment 2 in Simulation of Telesystems Laboratory exercise: Introduction to Simulink and Communications Blockset You are expected to conclude exercise 1-7 within a week, and the rest within two weeks. Presentation: You do not have to send the lab report to the supervisor, but should demonstrate it during supervision seminars. Save or print out plots and code, and be prepared to demonstrate that the code works and explain the principles. Also write down all command-line Matlab commands and answers to the questions. Preparation Do the Matlab introduction exercise. The answers to these are partially presented during a lecture. 1. Help commands Start the Matlab program. Test the Matlab help commands: Help, helpwin, doc, lookfor, whatsnew. Shortly describe the difference between them. Get acquainted with the help text structure. Hint: Write helpwin help for help on the help command. 2. Toolboxes and Simulink libraries Inform yourself on what Matlab toolboxes and Simulink libraries that are installed, by means of the command ver and the help texts. Which of the toolboxes and libraries do you expect that you will meet during this course, or may gain your interest? (Nowadays Mathworks do not use the word blockset any more. For example Communications toolbox previously only consisted of.m-files, and Communications blockset of SImulink blocks and models. Nowadays both or part of the product Communication Systems Toolbox).
2 3. Simulink examples Run the Matlab command doc. Search for Communications systems toolbox examples. Browse through the example, and look especially under the headline Simulink examples. Run at least one of the Simulink models by clicking on Start simulation (the play icon). Note that some of the examples are matlab scripts and functions (i.e..m-files) rather than Simulink models. Several of the Simulink blocks in each model are subsystems that contain other blocks. Try to see the content of some subsystems. Some subsystems can be opened by double-clicking at the arrow. Others may be opened by clicking on the arrow icon on its symbol. You may also browse among the subsystems by choosing View -> Model browser options. Finally you may find the helptext for a subsystem from the background menu. Which model did you try? Which subsystem did you open? 4. Freeware Simulink models Download, install and try at least one user contributed Simulink model related to a communication systems standard from the Matlab Central File Exchange. See -> File exchange. Search for example for wireless, communication or network. Be prepared to demonstrate the model to the whole group of students. Note that some models require an old version of Matlab, for example version R2010. Presentation: Which model did you try? Did it work without errors? Demonstrate it to the supervisor. 5. Create a simple Matlab function Create a simple Matlab function (i.e. an.m file where the first line starts by the word function). The function should take an input argument, calculate something, and reply by an output argument. Save the function file, and call it from the command prompt by setting it in a function expression. Hint: Use the Matlab commands edit and function. Read their help texts. You may for example start our from some existing Matlab function by writing mkdir h:\matlab cd h:\matlab edit myfunction.m. A typical Matlab function starts with function y=function_name(x1, x2)
3 % This is a function with two input parameters % and one output parameter y = ; or: function [y1, y2]=function_name(x) % This is a function with one input parameter % and two output parameter Add a help text for your function after a % character on the second line, below the function declaration. Thus it would be possible to apply the help command on your function by writing help function_name. Save the file. Printout or write down your function. Make a function call, for example: myfunction(2)+myfunction(3) Presentation: Print out or write down your function, your function call and its result. 6. Create a simple Simulink model Create a simple Simulink model, by writing the Matlab command simulink in the command window, and choosing the menu alternative File -> New -> Model. Drag blocks from the Simulink Library Browser, and drop them into your model. Your model should at least include one source block, e.g. a signal generator, and one sink, for example a measurement instrument. Connect the source and sink blocks with wires by holding the mouse over a block connector, and dragging it to a connector on another block. Run the simulation. You may save your model by means of the menu File -> Save. If you create a large Simulink model, it may be practical to organize it into a hierarchy of several subsystems. Create a subsystem by marking several blocks (hold down the Shift button while clicking on each of the blocks), clicking with the right mouse button on the group of blocks, and choosing Create Subsystem on the background menu.
4 Open the preferences of your model by choosing the menu alternative Simulation -> Configuration parameters -> Solver. Here you may set the duration time of each simulation. Enter inf (infinite) in the end time field if you want the simulation to run until your click on the stop icon. You may set the Sampling time of the system, i.e. the clock frequency, in the box Fixed-step size. If you write auto in that field, the sampling time of the blocks in the model is automatically adopted to the sampling time of the source block. In digital communication applications it is normally necessary to choose sampling time type Fixed Step, and Discrete (no continuous states) solver. In signal processing applications, for example simulation of analogue and digital filters, it is often possible to reduce the simulation time by choosing other settings. In those cases, Simulink may automatically choose longer step-time, i.e. skip the simulation of some samples or clock-cycles, and interpolate the these values after the simulation has been carried out. Still sufficient accuracy will be achieved. Simulink is originally designed for efficient numerical solving of differential equations and difference equations describing analogue and digital filters, control systems, physical devices, etc. This facility can seldom be utilized in digital communication protocols and algorithms, since these involve highly non-linear functions and discrete events, and since the output signal of these blocks can be described as non-continuous functions and cannot be interpolated. However, Simulink is interesting for simulation of communication applications anyway, since it may be utilized as a tool for graphical data-flow oriented programming. 7. User defined functions The set of blocks in the Simulink library should not be considered as a generic programming language, supplying all conceivable demands. You often have to design your own blocks by means of conventional programming. One common approach is to utilize Matlab functions (.m functions). Develop and call a Matlab function of your own from Simulink. The Matlab function should somehow modify the signal. Hint: Use the Simulink block MATLAB fcn, which you can find in Simulink Library Browser -> Simulink -> User Defined Functions. Alternatively you may use the Simulink block Function, and write the name of your own.m file in it (except the.m file extension).
5 8. Automated Simulink calls A common problem is that you want to compile a plot that shows the relation between input parameters and simulation results, for example how the signal-tonoise ratio (SNR) affects the bit-error rate (BER). The SNR is the x-axis and the BER the y axis. Every point in the plot corresponds to one Simulink simulation run. Some ten points per curve may be required for a nice looking plot. To start Simulink manually for each point may be time consuming. The simulation series may be automated by means of a Matlab script that calls Simulink repeatedly. Hint: You may use the command sim. Write doc sim for further help, and see: a) Write a Matlab script that starts a Simulink simulation, for example an existing communication system model. A recommendation is that you do not use a Matlab function, i.e. the.m-file should not start with the keyword function. The reason is that Simulink, as well as Matlab scripts, easily can access variables in the so called Matlab base workspace, while Matlab functions use local (in its own workspace) and global variables. b) Send some calculation results from a Simulink model back to the Matlab script. It is recommended that you start out from an existing communication system, that you consider to study during your project. You may for example start out from a calculation of the Bit Error Ratio. Hint: Use the Simulink block Sinks -> To Workspace, or the command sim. The result is a so called Matlab struct. To see what fields that are included in the structr x, write x. To see the content of field y in the struct x, write x.y. The output signal often contains a vector with one value for each sample. Sometimes you want to know the last sample, for example the final bit error ratio, and in this case you may use the Matlab function end. Sometimes you want to know the average av the sample values, for example the average signal-to-noise ratio, and in that case you may use the Matlab function mean. Illustrate this. c) Use a Matlab script to control some parameter within a Simulink block, for example the gain of an amplifier, or the noise level of a channel model, and consequently the SNR. If you start out from an existing model of a communication system you may for example change the signal-to-noise ratio, the modulation method (M in MQAM), the error correction code, etc. Hint: To transfer parameters you may use the command set_param. d) Test several cases of the controlled parameter by means of a loop. Plot the controlled parameter on the x axis, and the simulation result (the estimated parameter) on the y axis. If the y axis shows the BER, a logarithmic scale is recommended, typically from 10-5 to If the x axis whos the SNR in db, a linear scale is recommended, while if it shows the SNR in times, a logarithmic scale is recommended. Hint: The sequence of input parameter values as well as simulation result values should be saved into two vectors of equal length. Use for or while, and end, to achieve a loop. Use the function num2str or int2str to convert the numerical inparameter values to strings that you may use in the set_param function call.
6 Use the commands plot or semilogy, title, xlabel and ylabel to create a nice looking plot. e) If the simulations take long time, it is practical to develop a separate Matlab script for simulation, and a second script (or function) that presents the simulation results in plots and tables. Develop a simulation script that saves the input parameters as well as the simulation results to the disk by means of the save command, successively during the simulation. Also develop a presentation script, or function, that retrieves the data, by means of the load command, and presents a plot. There are several advantages with this approach: You may modify the graphical presentation without running the time consuming simulations again. You may add some additional parameter values to the result, without simulating the previous results once again. If the simulations are interrupted, for example by a system crash or a power failure, the results may be partially saved to the disk, and you can easily modify the script to continue where it was interrupted. You may run simulations on several computers in parallel. Each computer runs a version of the simulation script, with different input parameters. The results are stored into several files. The presentation Matlab function compiles the result files into one file, and plots the results. f) Voluntary exercise: Demonstrate the parallelization mentioned above. g) Voluntary exercise: Investigate the effect of two input parameters. A curve is plotted in the same plot for every value of the second parameter. Alternatively, you may compare two Simulink models, for example two communication systems, and present the results in two curves in the same plot. Use the function legend to add information to the plot that states what each curve shows. 9. Control the simulation time and simulation accuracy If the simulation time is too short, the plot may show a jittery curve due random fluctuations originating from noise sources or randomized data sources. The BER may be estimated as 0 allthough there are noise and interference, since no bit errors occur during the short simulation. You may increase the simulation time in the Simulink model settings. a) Choose or develop a Simulink model that involves a random source. Experiment on what is a sufficient simulation time to avoid jittery curves (i.e. large differences for every new simulation), or to avoid that the BER becomes zero although there are noise. What model did you choose? Give a short example on sufficient simulation time, for example to achieve BER>0 for a couple of SNR values.
7 b) Voluntary exercise: Develop a Matlab script that runs the same simulation input parameter case several times (by means of an inner loop). It should store the result from each inner loop iteration in a vector, which we may call y, and calculate the average Y = mean(y). The script should automatically interrupt the inner loop (by means of the break command) when a certain condition is fulfilled, for example when the number of bit errors that have occurred is at least 3, or when the simulation time is above a certain number of seconds (by means of the tic and toc functions). c) Voluntary exercise: Further develop the above script to stop when the accuracy is sufficiently high. The script should estimate the standard deviation S of the above estimate Y, as S = std(y)/(sqrt(length(y)-1). The script should be interrupted when S is below a certain threshold value T. Those familiar with mathematical statistics may calculate the threshold value T for a certain confidence interval of Y. For example, you may want a 80% confidence interval of Y that is smaller than 5% of the y axis interval, i.e. the curve jitter amplitude should be less than 1/20 of the height of the y axis. You may assume that the y values have Gaussian distribution. Sometimes the mean result of each Simulation run is different for each simulation run, independently of the simulation time. Such a process is nonergodic, meaning that the time mean value (the average result from one infinitely long simulation run) differs from the ensemble mean value (the average result of all simulation runs for the same input parameter values). In this case it is necessary to add an extra loop that simulates each input parameter case several times, and calculate the average result, as above. The loop may be interrupted when the standard deviation of the results is sufficiently low. 11. Voluntary exercise: Use the bertool command to repeatedly call a Simulink model of a communication system, and plot the BER vs SNR. 10. Voluntary exercise: Discuss how the computational efficiency of your Matlab code and Simulink model can be improved Suggestions: - Find a way to divide the simulation sequence into several jobs that can run on several computers in parallel. - The profile command may generate statistics on what Matlab command lines, and what Simulink blocks, that consume most computational time. You may try to optimize those lines or blocks. - Analyze a time consuming sub-system, and replace it by a simplified model. This may for example be a look-up table, a saved signal vector or data sequence that is reused for every simulation run, or a channel model with a certain bit-error ratio. - Instead of simulating every combination of input parameters, a Monte Carlo simulation may be used, which analyzes random combinations of the input parameters. - If you compare for example two algorithms, the same random sequence may be used for each simulation. Thus, the relative performance will be more
8 accurate. One option is to reset the random generator to its initial state before each simulation run, a second option is to save sequence into a file or into a workspace array. - Use Real-Time Workshop and some compiler software to compile a Simulink model into executable code.
Computer Aided Design (CAD) Lecture 10. Introduction to Simulink (3) Dr.Eng. Basem ElHalawany
 Computer Aided Design (CAD) Lecture 10 Introduction to Simulink (3) Dr.Eng. Basem ElHalawany Schedule (Updated 28-10) Topics Estimated Duration (# Lectures) Introduction 1 Introduction to Matlab Environment
Computer Aided Design (CAD) Lecture 10 Introduction to Simulink (3) Dr.Eng. Basem ElHalawany Schedule (Updated 28-10) Topics Estimated Duration (# Lectures) Introduction 1 Introduction to Matlab Environment
Experiment 6 SIMULINK
 Experiment 6 SIMULINK Simulink Introduction to simulink SIMULINK is an interactive environment for modeling, analyzing, and simulating a wide variety of dynamic systems. SIMULINK provides a graphical user
Experiment 6 SIMULINK Simulink Introduction to simulink SIMULINK is an interactive environment for modeling, analyzing, and simulating a wide variety of dynamic systems. SIMULINK provides a graphical user
Experiment 3. Getting Start with Simulink
 Experiment 3 Getting Start with Simulink Objectives : By the end of this experiment, the student should be able to: 1. Build and simulate simple system model using Simulink 2. Use Simulink test and measurement
Experiment 3 Getting Start with Simulink Objectives : By the end of this experiment, the student should be able to: 1. Build and simulate simple system model using Simulink 2. Use Simulink test and measurement
Introduction to Simulink
 Introduction to Simulink Mikael Manngård Process Control Laboratory, Åbo Akademi University February 27, 2014 Simulink is an extension to MATLAB that is used for modeling and simulation of dynamic systems.
Introduction to Simulink Mikael Manngård Process Control Laboratory, Åbo Akademi University February 27, 2014 Simulink is an extension to MATLAB that is used for modeling and simulation of dynamic systems.
INTRODUCTION TO MATLAB, SIMULINK, AND THE COMMUNICATION TOOLBOX
 INTRODUCTION TO MATLAB, SIMULINK, AND THE COMMUNICATION TOOLBOX 1) Objective The objective of this lab is to review how to access Matlab, Simulink, and the Communications Toolbox, and to become familiar
INTRODUCTION TO MATLAB, SIMULINK, AND THE COMMUNICATION TOOLBOX 1) Objective The objective of this lab is to review how to access Matlab, Simulink, and the Communications Toolbox, and to become familiar
Experiment 8 SIMULINK
 Experiment 8 SIMULINK Simulink Introduction to simulink SIMULINK is an interactive environment for modeling, analyzing, and simulating a wide variety of dynamic systems. SIMULINK provides a graphical user
Experiment 8 SIMULINK Simulink Introduction to simulink SIMULINK is an interactive environment for modeling, analyzing, and simulating a wide variety of dynamic systems. SIMULINK provides a graphical user
Introduction to the MATLAB SIMULINK Program
 Introduction to the MATLAB SIMULINK Program Adapted from similar document by Dept. of Chemical Engineering, UC - Santa Barbara MATLAB, which stands for MATrix LABoratory, is a technical computing environment
Introduction to the MATLAB SIMULINK Program Adapted from similar document by Dept. of Chemical Engineering, UC - Santa Barbara MATLAB, which stands for MATrix LABoratory, is a technical computing environment
UNIVERSITI TEKNIKAL MALAYSIA MELAKA FAKULTI KEJURUTERAAN ELEKTRONIK DAN KEJURUTERAAN KOMPUTER
 UNIVERSITI TEKNIKAL MALAYSIA MELAKA FAKULTI KEJURUTERAAN ELEKTRONIK DAN KEJURUTERAAN KOMPUTER FAKULTI KEJURUTERAAN ELEKTRONIK DAN KEJURUTERAAN KOMPUTER BENC 2113 DENC ECADD 2532 ECADD LAB SESSION 6/7 LAB
UNIVERSITI TEKNIKAL MALAYSIA MELAKA FAKULTI KEJURUTERAAN ELEKTRONIK DAN KEJURUTERAAN KOMPUTER FAKULTI KEJURUTERAAN ELEKTRONIK DAN KEJURUTERAAN KOMPUTER BENC 2113 DENC ECADD 2532 ECADD LAB SESSION 6/7 LAB
Introduction to ARDUINO/SIMULINK
 Introduction to ARDUINO/SIMULINK Lab Objectives Install and verify Arduino software package for Simulink using a digital output to light a LED Communicate with the target board (Arduino) using external
Introduction to ARDUINO/SIMULINK Lab Objectives Install and verify Arduino software package for Simulink using a digital output to light a LED Communicate with the target board (Arduino) using external
Rotary Motion Servo Plant: SRV02. Rotary Experiment #00: QuaRC Integration. Using SRV02 with QuaRC. Student Manual
 Rotary Motion Servo Plant: SRV02 Rotary Experiment #00: QuaRC Integration Using SRV02 with QuaRC Student Manual SRV02 QuaRC Integration Instructor Manual Table of Contents 1. INTRODUCTION...1 2. PREREQUISITES...1
Rotary Motion Servo Plant: SRV02 Rotary Experiment #00: QuaRC Integration Using SRV02 with QuaRC Student Manual SRV02 QuaRC Integration Instructor Manual Table of Contents 1. INTRODUCTION...1 2. PREREQUISITES...1
UNIVERSITI TEKNIKAL MALAYSIA MELAKA FAKULTI KEJURUTERAAN ELEKTRONIK DAN KEJURUTERAAN KOMPUTER
 UNIVERSITI TEKNIKAL MALAYSIA MELAKA FAKULTI KEJURUTERAAN ELEKTRONIK DAN KEJURUTERAAN KOMPUTER FAKULTI KEJURUTERAAN ELEKTRONIK DAN KEJURUTERAAN KOMPUTER BENC 2113 DENC ECADD 2532 ECADD LAB SESSION 6/7 LAB
UNIVERSITI TEKNIKAL MALAYSIA MELAKA FAKULTI KEJURUTERAAN ELEKTRONIK DAN KEJURUTERAAN KOMPUTER FAKULTI KEJURUTERAAN ELEKTRONIK DAN KEJURUTERAAN KOMPUTER BENC 2113 DENC ECADD 2532 ECADD LAB SESSION 6/7 LAB
What is MATLAB? It is a high-level programming language. for numerical computations for symbolic computations for scientific visualizations
 What is MATLAB? It stands for MATrix LABoratory It is developed by The Mathworks, Inc (http://www.mathworks.com) It is an interactive, integrated, environment for numerical computations for symbolic computations
What is MATLAB? It stands for MATrix LABoratory It is developed by The Mathworks, Inc (http://www.mathworks.com) It is an interactive, integrated, environment for numerical computations for symbolic computations
Lab 6 : Introduction to Simulink, Link for CCS & Real-Time Workshop
 Lab 6 : Introduction to Simulink, Link for CCS & Real-Time Workshop September, 2006 1 Overview The purpose of this lab is to familiarize you with Simulink, Real Time Workshop, Link for CCS and how they
Lab 6 : Introduction to Simulink, Link for CCS & Real-Time Workshop September, 2006 1 Overview The purpose of this lab is to familiarize you with Simulink, Real Time Workshop, Link for CCS and how they
SIGNALS AND LINEAR SYSTEMS LABORATORY EELE
 The Islamic University of Gaza Faculty of Engineering Electrical Engineering Department SIGNALS AND LINEAR SYSTEMS LABORATORY EELE 3110 Experiment (5): Simulink Prepared by: Eng. Mohammed S. Abuwarda Eng.
The Islamic University of Gaza Faculty of Engineering Electrical Engineering Department SIGNALS AND LINEAR SYSTEMS LABORATORY EELE 3110 Experiment (5): Simulink Prepared by: Eng. Mohammed S. Abuwarda Eng.
MAT 275 Laboratory 1 Introduction to MATLAB
 MATLAB sessions: Laboratory 1 1 MAT 275 Laboratory 1 Introduction to MATLAB MATLAB is a computer software commonly used in both education and industry to solve a wide range of problems. This Laboratory
MATLAB sessions: Laboratory 1 1 MAT 275 Laboratory 1 Introduction to MATLAB MATLAB is a computer software commonly used in both education and industry to solve a wide range of problems. This Laboratory
Session 3 Introduction to SIMULINK
 Session 3 Introduction to SIMULINK Brian Daku Department of Electrical Engineering University of Saskatchewan email: daku@engr.usask.ca EE 290 Brian Daku Outline This section covers some basic concepts
Session 3 Introduction to SIMULINK Brian Daku Department of Electrical Engineering University of Saskatchewan email: daku@engr.usask.ca EE 290 Brian Daku Outline This section covers some basic concepts
Short Version of Matlab Manual
 Short Version of Matlab Manual This is an extract from the manual which was used in MA10126 in first year. Its purpose is to refamiliarise you with the matlab programming concepts. 1 Starting MATLAB 1.1.1.
Short Version of Matlab Manual This is an extract from the manual which was used in MA10126 in first year. Its purpose is to refamiliarise you with the matlab programming concepts. 1 Starting MATLAB 1.1.1.
FPGA Co-Simulation of Gaussian Filter Algorithm Application Note
 Michigan State University ECE 480 Tom Ganley November 19, 2010 FPGA Co-Simulation of Gaussian Filter Algorithm Application Note Abstract FPGA co-simulation of Gaussian Filter algorithms can be useful in
Michigan State University ECE 480 Tom Ganley November 19, 2010 FPGA Co-Simulation of Gaussian Filter Algorithm Application Note Abstract FPGA co-simulation of Gaussian Filter algorithms can be useful in
Introduction to Simulink. The Use of Mathematic Simulations in Electrical Engineering
 Introduction to Simulink The Use of Mathematic Simulations in Electrical Engineering Lecture Outline 1) Introduction to Simulink 2) Modelling of dynamics systems 2 Simulink Tool for modeling, simulating,
Introduction to Simulink The Use of Mathematic Simulations in Electrical Engineering Lecture Outline 1) Introduction to Simulink 2) Modelling of dynamics systems 2 Simulink Tool for modeling, simulating,
SIMULINK FOR BEGINNERS:
 1 SIMULINK FOR BEGINNERS: To begin your SIMULINK session open first MATLAB ICON by clicking mouse twice and then type»simulink You will now see the Simulink block library. 2 Browse through block libraries.
1 SIMULINK FOR BEGINNERS: To begin your SIMULINK session open first MATLAB ICON by clicking mouse twice and then type»simulink You will now see the Simulink block library. 2 Browse through block libraries.
Introduction to Simulink
 Introduction to Simulink There are several computer packages for finding solutions of differential equations, such as Maple, Mathematica, Maxima, MATLAB, etc. These systems provide both symbolic and numeric
Introduction to Simulink There are several computer packages for finding solutions of differential equations, such as Maple, Mathematica, Maxima, MATLAB, etc. These systems provide both symbolic and numeric
Data and Function Plotting with MATLAB (Linux-10)
 Data and Function Plotting with MATLAB (Linux-10) This tutorial describes the use of MATLAB for general plotting of experimental data and equations and for special plots like histograms. (Astronomers -
Data and Function Plotting with MATLAB (Linux-10) This tutorial describes the use of MATLAB for general plotting of experimental data and equations and for special plots like histograms. (Astronomers -
Introduction to Simulink
 University College of Southeast Norway Introduction to Simulink Hans-Petter Halvorsen, 2016.11.01 http://home.hit.no/~hansha Preface Simulink, developed by The MathWorks, is a commercial tool for modeling,
University College of Southeast Norway Introduction to Simulink Hans-Petter Halvorsen, 2016.11.01 http://home.hit.no/~hansha Preface Simulink, developed by The MathWorks, is a commercial tool for modeling,
Introduction to Simulink
 Introduction to Simulink by Vinay S. K. Guntu 4310 Feedback Control Systems 1 Simulink Basics Tutorial Simulink is a graphical extension to MATLAB for modeling and simulation of systems. Advantages 1)
Introduction to Simulink by Vinay S. K. Guntu 4310 Feedback Control Systems 1 Simulink Basics Tutorial Simulink is a graphical extension to MATLAB for modeling and simulation of systems. Advantages 1)
Experiment # 5. Introduction to Error Control Codes
 ECE 417 Winter 2003 Experiment # 5 Introduction to Error Control Codes 1 Purpose The purpose for this experiment is to provide you with an introduction to the field of error control coding. This will be
ECE 417 Winter 2003 Experiment # 5 Introduction to Error Control Codes 1 Purpose The purpose for this experiment is to provide you with an introduction to the field of error control coding. This will be
EE 301 Signals & Systems I MATLAB Tutorial with Questions
 EE 301 Signals & Systems I MATLAB Tutorial with Questions Under the content of the course EE-301, this semester, some MATLAB questions will be assigned in addition to the usual theoretical questions. This
EE 301 Signals & Systems I MATLAB Tutorial with Questions Under the content of the course EE-301, this semester, some MATLAB questions will be assigned in addition to the usual theoretical questions. This
MATLAB The first steps. Edited by Péter Vass
 MATLAB The first steps Edited by Péter Vass MATLAB The name MATLAB is derived from the expression MATrix LABoratory. It is used for the identification of a software and a programming language. As a software,
MATLAB The first steps Edited by Péter Vass MATLAB The name MATLAB is derived from the expression MATrix LABoratory. It is used for the identification of a software and a programming language. As a software,
Stokes Modelling Workshop
 Stokes Modelling Workshop 14/06/2016 Introduction to Matlab www.maths.nuigalway.ie/modellingworkshop16/files 14/06/2016 Stokes Modelling Workshop Introduction to Matlab 1 / 16 Matlab As part of this crash
Stokes Modelling Workshop 14/06/2016 Introduction to Matlab www.maths.nuigalway.ie/modellingworkshop16/files 14/06/2016 Stokes Modelling Workshop Introduction to Matlab 1 / 16 Matlab As part of this crash
Introduction to Matlab Simulink. Control Systems
 Introduction to Matlab Simulink & their application in Control Systems ENTC 462 - Spring 2007 Introduction Simulink (Simulation and Link) is an extension of MATLAB by Mathworks Inc. It works with MATLAB
Introduction to Matlab Simulink & their application in Control Systems ENTC 462 - Spring 2007 Introduction Simulink (Simulation and Link) is an extension of MATLAB by Mathworks Inc. It works with MATLAB
ECE 202 LAB 3 ADVANCED MATLAB
 Version 1.2 1 of 13 BEFORE YOU BEGIN PREREQUISITE LABS ECE 201 Labs EXPECTED KNOWLEDGE ECE 202 LAB 3 ADVANCED MATLAB Understanding of the Laplace transform and transfer functions EQUIPMENT Intel PC with
Version 1.2 1 of 13 BEFORE YOU BEGIN PREREQUISITE LABS ECE 201 Labs EXPECTED KNOWLEDGE ECE 202 LAB 3 ADVANCED MATLAB Understanding of the Laplace transform and transfer functions EQUIPMENT Intel PC with
Matlab Tutorial. Get familiar with MATLAB by using tutorials and demos found in MATLAB. You can click Start MATLAB Demos to start the help screen.
 University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering ECE 298JA Fall 2015 Matlab Tutorial 1 Overview The goal of this tutorial is to help you get familiar with MATLAB
University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering ECE 298JA Fall 2015 Matlab Tutorial 1 Overview The goal of this tutorial is to help you get familiar with MATLAB
Introduction to Matlab. Summer School CEA-EDF-INRIA 2011 of Numerical Analysis
 Introduction to Matlab 1 Outline What is Matlab? Matlab desktop & interface Scalar variables Vectors and matrices Exercise 1 Booleans Control structures File organization User defined functions Exercise
Introduction to Matlab 1 Outline What is Matlab? Matlab desktop & interface Scalar variables Vectors and matrices Exercise 1 Booleans Control structures File organization User defined functions Exercise
ECE-205 Lab 1. Introduction to Simulink and Matlab
 ECE-205 Lab 1 Introduction to Simulink and Matlab Throughout this lab we will focus on determining the behavior of a first order system written in the standard form dy( t) y( t) Kx( t) dt where xt () is
ECE-205 Lab 1 Introduction to Simulink and Matlab Throughout this lab we will focus on determining the behavior of a first order system written in the standard form dy( t) y( t) Kx( t) dt where xt () is
UNIT 5. Simulink. 1. Introduction
 UNIT 5 Simulink 1. Introduction... 1 2. Simulink... 2 2.1 Starting Simulink... 2 2.2 Model building... 3 2.3 Simulation parameters and Scope block... 5 2.4 Subsystems and masks... 11 2.5 S Functions...
UNIT 5 Simulink 1. Introduction... 1 2. Simulink... 2 2.1 Starting Simulink... 2 2.2 Model building... 3 2.3 Simulation parameters and Scope block... 5 2.4 Subsystems and masks... 11 2.5 S Functions...
MATLAB/Octave Tutorial
 University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering ECE 298JA Fall 2017 MATLAB/Octave Tutorial 1 Overview The goal of this tutorial is to help you get familiar
University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering ECE 298JA Fall 2017 MATLAB/Octave Tutorial 1 Overview The goal of this tutorial is to help you get familiar
SIMULINK A Tutorial by Tom Nguyen
 Introduction SIMULINK A Tutorial by Tom Nguyen Simulink (Simulation and Link) is an extension of MATLAB by Mathworks Inc. It works with MATLAB to offer modeling, simulating, and analyzing of dynamical
Introduction SIMULINK A Tutorial by Tom Nguyen Simulink (Simulation and Link) is an extension of MATLAB by Mathworks Inc. It works with MATLAB to offer modeling, simulating, and analyzing of dynamical
Computational Modelling 102 (Scientific Programming) Tutorials
 COMO 102 : Scientific Programming, Tutorials 2003 1 Computational Modelling 102 (Scientific Programming) Tutorials Dr J. D. Enlow Last modified August 18, 2003. Contents Tutorial 1 : Introduction 3 Tutorial
COMO 102 : Scientific Programming, Tutorials 2003 1 Computational Modelling 102 (Scientific Programming) Tutorials Dr J. D. Enlow Last modified August 18, 2003. Contents Tutorial 1 : Introduction 3 Tutorial
MATLAB Introductory Course Computer Exercise Session
 MATLAB Introductory Course Computer Exercise Session This course is a basic introduction for students that did not use MATLAB before. The solutions will not be collected. Work through the course within
MATLAB Introductory Course Computer Exercise Session This course is a basic introduction for students that did not use MATLAB before. The solutions will not be collected. Work through the course within
BME 5742 Bio-Systems Modeling and Control
 BME 5742 Bio-Systems Modeling and Control Lecture 4 Simulink Tutorial 1: Simulation of the Malthusian and Logistic Models Model Set Up, Scope Set Up Dr. Zvi Roth (FAU) 1 Getting started In the MATLAB command
BME 5742 Bio-Systems Modeling and Control Lecture 4 Simulink Tutorial 1: Simulation of the Malthusian and Logistic Models Model Set Up, Scope Set Up Dr. Zvi Roth (FAU) 1 Getting started In the MATLAB command
SIMULINK Tutorial. Select File-New-Model from the menu bar of this window. The following window should now appear.
 SIMULINK Tutorial Simulink is a block-orientated program that allows the simulation of dynamic systems in a block diagram format whether they are linear or nonlinear, in continuous or discrete forms. To
SIMULINK Tutorial Simulink is a block-orientated program that allows the simulation of dynamic systems in a block diagram format whether they are linear or nonlinear, in continuous or discrete forms. To
Lecturer: Keyvan Dehmamy
 MATLAB Tutorial Lecturer: Keyvan Dehmamy 1 Topics Introduction Running MATLAB and MATLAB Environment Getting help Variables Vectors, Matrices, and linear Algebra Mathematical Functions and Applications
MATLAB Tutorial Lecturer: Keyvan Dehmamy 1 Topics Introduction Running MATLAB and MATLAB Environment Getting help Variables Vectors, Matrices, and linear Algebra Mathematical Functions and Applications
ME 365 EXPERIMENT 3 INTRODUCTION TO LABVIEW
 ME 365 EXPERIMENT 3 INTRODUCTION TO LABVIEW Objectives: The goal of this exercise is to introduce the Laboratory Virtual Instrument Engineering Workbench, or LabVIEW software. LabVIEW is the primary software
ME 365 EXPERIMENT 3 INTRODUCTION TO LABVIEW Objectives: The goal of this exercise is to introduce the Laboratory Virtual Instrument Engineering Workbench, or LabVIEW software. LabVIEW is the primary software
CE890 / ENE801 Lecture 1 Introduction to MATLAB
 CE890 / ENE801 Lecture 1 Introduction to MATLAB CE890: Course Objectives Become familiar with a powerful tool for computations and visualization (MATLAB) Promote problem-solving skills using computers
CE890 / ENE801 Lecture 1 Introduction to MATLAB CE890: Course Objectives Become familiar with a powerful tool for computations and visualization (MATLAB) Promote problem-solving skills using computers
Introduction to MATLAB
 ELG 3125 - Lab 1 Introduction to MATLAB TA: Chao Wang (cwang103@site.uottawa.ca) 2008 Fall ELG 3125 Signal and System Analysis P. 1 Do You Speak MATLAB? MATLAB - The Language of Technical Computing ELG
ELG 3125 - Lab 1 Introduction to MATLAB TA: Chao Wang (cwang103@site.uottawa.ca) 2008 Fall ELG 3125 Signal and System Analysis P. 1 Do You Speak MATLAB? MATLAB - The Language of Technical Computing ELG
Mini-Project System Simulation over AWGN Using BPSK Modulation
 Mini-Project System Simulation over AWGN Using BPSK Modulation Part I: MATLAB Environment Due Date: June 5, 2006. This exercise will guide you to realize the basic operating environment. Some useful instructions
Mini-Project System Simulation over AWGN Using BPSK Modulation Part I: MATLAB Environment Due Date: June 5, 2006. This exercise will guide you to realize the basic operating environment. Some useful instructions
Introduction to MATLAB LAB 1
 Introduction to MATLAB LAB 1 1 Basics of MATLAB MATrix LABoratory A super-powerful graphing calculator Matrix based numeric computation Embedded Functions Also a programming language User defined functions
Introduction to MATLAB LAB 1 1 Basics of MATLAB MATrix LABoratory A super-powerful graphing calculator Matrix based numeric computation Embedded Functions Also a programming language User defined functions
Enterprise Architect basic usage
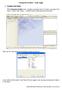 1. Creating a New Project Enterprise Architect basic usage When Enterprise Architect starts, it displays a greeting screen. To create a new project first choose Create a New Project... and then choose
1. Creating a New Project Enterprise Architect basic usage When Enterprise Architect starts, it displays a greeting screen. To create a new project first choose Create a New Project... and then choose
ME422 Mechanical Control Systems Matlab/Simulink Hints and Tips
 Cal Poly San Luis Obispo Mechanical Engineering ME Mechanical Control Systems Matlab/Simulink Hints and Tips Ridgely/Owen, last update Jan Building A Model The way in which we construct models for analyzing
Cal Poly San Luis Obispo Mechanical Engineering ME Mechanical Control Systems Matlab/Simulink Hints and Tips Ridgely/Owen, last update Jan Building A Model The way in which we construct models for analyzing
[ MATLAB ] [ Resources ] PART TWO: SIMULINK
![[ MATLAB ] [ Resources ] PART TWO: SIMULINK [ MATLAB ] [ Resources ] PART TWO: SIMULINK](/thumbs/82/85270175.jpg) Página 1 de 15 [ MATLAB ] [ Resources ] PART TWO: SIMULINK Contents Introduction Getting Started Handling of Blocks and Lines Annotations Some Examples NOTE: This tutorial is based on Simulink Version
Página 1 de 15 [ MATLAB ] [ Resources ] PART TWO: SIMULINK Contents Introduction Getting Started Handling of Blocks and Lines Annotations Some Examples NOTE: This tutorial is based on Simulink Version
MATLAB INTRODUCTION. Matlab can be used interactively as a super hand calculator, or, more powerfully, run using scripts (i.e., programs).
 L A B 6 M A T L A B MATLAB INTRODUCTION Matlab is a commercial product that is used widely by students and faculty and researchers at UTEP. It provides a "high-level" programming environment for computing
L A B 6 M A T L A B MATLAB INTRODUCTION Matlab is a commercial product that is used widely by students and faculty and researchers at UTEP. It provides a "high-level" programming environment for computing
Lab. Manual. Practical Special Topics (Matlab Programming) (EngE416) Prepared By Dr. Emad Saeid
 KINGDOM OF SAUDI ARABIA JAZAN UNIVERSTY College of Engineering Electrical Engineering Department المملكة العربية السعودية وزارة التعليم العالي جامعة جازان كلية الھندسة قسم الھندسة الكھربائية Lab. Manual
KINGDOM OF SAUDI ARABIA JAZAN UNIVERSTY College of Engineering Electrical Engineering Department المملكة العربية السعودية وزارة التعليم العالي جامعة جازان كلية الھندسة قسم الھندسة الكھربائية Lab. Manual
EL2310 Scientific Programming LAB1: MATLAB lab session. Patric Jensfelt
 EL2310 Scientific Programming LAB1: MATLAB lab session Patric Jensfelt Chapter 1 Introduction 1.1 Goals for this lab The goals for this lab is handle the computers in the computer rooms create and edit
EL2310 Scientific Programming LAB1: MATLAB lab session Patric Jensfelt Chapter 1 Introduction 1.1 Goals for this lab The goals for this lab is handle the computers in the computer rooms create and edit
Small rectangles (and sometimes squares like this
 Lab exercise 1: Introduction to LabView LabView is software for the real time acquisition, processing and visualization of measured data. A LabView program is called a Virtual Instrument (VI) because it,
Lab exercise 1: Introduction to LabView LabView is software for the real time acquisition, processing and visualization of measured data. A LabView program is called a Virtual Instrument (VI) because it,
Introduction to MATLAB. Simon O Keefe Non-Standard Computation Group
 Introduction to MATLAB Simon O Keefe Non-Standard Computation Group sok@cs.york.ac.uk Content n An introduction to MATLAB n The MATLAB interfaces n Variables, vectors and matrices n Using operators n Using
Introduction to MATLAB Simon O Keefe Non-Standard Computation Group sok@cs.york.ac.uk Content n An introduction to MATLAB n The MATLAB interfaces n Variables, vectors and matrices n Using operators n Using
ELEC ENG 4CL4 CONTROL SYSTEM DESIGN
 ELEC ENG 4CL4 CONTROL SYSTEM DESIGN Lab #1: MATLAB/Simulink simulation of continuous casting Objectives: To gain experience in simulating a control system (controller + plant) within MATLAB/Simulink. To
ELEC ENG 4CL4 CONTROL SYSTEM DESIGN Lab #1: MATLAB/Simulink simulation of continuous casting Objectives: To gain experience in simulating a control system (controller + plant) within MATLAB/Simulink. To
SystemVue 2011 Fundamentals (version ) LAB EXERCISE 1. SystemVue Basics
 SystemVue 2011 Fundamentals (version 1-2012) LAB EXERCISE 1 SystemVue Basics This lab exercise introduces the basic use model of SystemVue, including using the built-in templates, running analyses and
SystemVue 2011 Fundamentals (version 1-2012) LAB EXERCISE 1 SystemVue Basics This lab exercise introduces the basic use model of SystemVue, including using the built-in templates, running analyses and
CDA6530: Performance Models of Computers and Networks. Chapter 4: Using Matlab for Performance Analysis and Simulation
 CDA6530: Performance Models of Computers and Networks Chapter 4: Using Matlab for Performance Analysis and Simulation Objective Learn a useful tool for mathematical analysis and simulation Interpreted
CDA6530: Performance Models of Computers and Networks Chapter 4: Using Matlab for Performance Analysis and Simulation Objective Learn a useful tool for mathematical analysis and simulation Interpreted
2 SIMULATING A MODEL Simulink Tutorial
 2 SIMULATING A MODEL Simulink Tutorial 1 Introduction Simulation of dynamic systems has been proven to be immensely useful in system modeling and controller design. Simulink R is a add-on to MATLAB which
2 SIMULATING A MODEL Simulink Tutorial 1 Introduction Simulation of dynamic systems has been proven to be immensely useful in system modeling and controller design. Simulink R is a add-on to MATLAB which
MATLAB Tutorial EE351M DSP. Created: Thursday Jan 25, 2007 Rayyan Jaber. Modified by: Kitaek Bae. Outline
 MATLAB Tutorial EE351M DSP Created: Thursday Jan 25, 2007 Rayyan Jaber Modified by: Kitaek Bae Outline Part I: Introduction and Overview Part II: Matrix manipulations and common functions Part III: Plots
MATLAB Tutorial EE351M DSP Created: Thursday Jan 25, 2007 Rayyan Jaber Modified by: Kitaek Bae Outline Part I: Introduction and Overview Part II: Matrix manipulations and common functions Part III: Plots
Lecture 10: Simulink. What is Simulink?
 Lecture 10: Simulink Dr. Mohammed Hawa Electrical Engineering Department University of Jordan EE201: Computer Applications. See Textbook Chapter 10. What is Simulink? Simulink is a tool for modeling, simulating
Lecture 10: Simulink Dr. Mohammed Hawa Electrical Engineering Department University of Jordan EE201: Computer Applications. See Textbook Chapter 10. What is Simulink? Simulink is a tool for modeling, simulating
What is Simulink. >>simulink
 MATLAB Simulink What is Simulink Simulink is an input/output device GUI block diagram simulator. Simulink contains a Library Editor of tools from which we can build input/output devices and continuous
MATLAB Simulink What is Simulink Simulink is an input/output device GUI block diagram simulator. Simulink contains a Library Editor of tools from which we can build input/output devices and continuous
ELEC4042 Signal Processing 2 MATLAB Review (prepared by A/Prof Ambikairajah)
 Introduction ELEC4042 Signal Processing 2 MATLAB Review (prepared by A/Prof Ambikairajah) MATLAB is a powerful mathematical language that is used in most engineering companies today. Its strength lies
Introduction ELEC4042 Signal Processing 2 MATLAB Review (prepared by A/Prof Ambikairajah) MATLAB is a powerful mathematical language that is used in most engineering companies today. Its strength lies
2. Introduction to Matlab Control System Toolbox
 . Introduction to Matlab Control System Toolbox Consider a single-input, single-output (SISO), continuous-time, linear, time invariant (LTI) system defined by its transfer function: u(t) Y( S) num y(t)
. Introduction to Matlab Control System Toolbox Consider a single-input, single-output (SISO), continuous-time, linear, time invariant (LTI) system defined by its transfer function: u(t) Y( S) num y(t)
MATLAB Project: Getting Started with MATLAB
 Name Purpose: To learn to create matrices and use various MATLAB commands for reference later MATLAB functions used: [ ] : ; + - * ^, size, help, format, eye, zeros, ones, diag, rand, round, cos, sin,
Name Purpose: To learn to create matrices and use various MATLAB commands for reference later MATLAB functions used: [ ] : ; + - * ^, size, help, format, eye, zeros, ones, diag, rand, round, cos, sin,
Table of Contents. Introduction.*.. 7. Part /: Getting Started With MATLAB 5. Chapter 1: Introducing MATLAB and Its Many Uses 7
 MATLAB Table of Contents Introduction.*.. 7 About This Book 1 Foolish Assumptions 2 Icons Used in This Book 3 Beyond the Book 3 Where to Go from Here 4 Part /: Getting Started With MATLAB 5 Chapter 1:
MATLAB Table of Contents Introduction.*.. 7 About This Book 1 Foolish Assumptions 2 Icons Used in This Book 3 Beyond the Book 3 Where to Go from Here 4 Part /: Getting Started With MATLAB 5 Chapter 1:
Running 2D Ball Balancer Experiment
 Running 2D Ball Balancer Experiment Contents Purpose...1 Physical Setup...1 Procedures...3 Step 1: Calibration...3 Step 2: MATLAB and the Environment...4 Step 3: Setup File...5 Step 4: Compile and Run...5
Running 2D Ball Balancer Experiment Contents Purpose...1 Physical Setup...1 Procedures...3 Step 1: Calibration...3 Step 2: MATLAB and the Environment...4 Step 3: Setup File...5 Step 4: Compile and Run...5
Introduction to MATLAB
 Introduction to MATLAB 1 Introduction to MATLAB A Tutorial for the Course Computational Intelligence http://www.igi.tugraz.at/lehre/ci Stefan Häusler Institute for Theoretical Computer Science Inffeldgasse
Introduction to MATLAB 1 Introduction to MATLAB A Tutorial for the Course Computational Intelligence http://www.igi.tugraz.at/lehre/ci Stefan Häusler Institute for Theoretical Computer Science Inffeldgasse
CDA6530: Performance Models of Computers and Networks. Chapter 4: Using Matlab for Performance Analysis and Simulation
 CDA6530: Performance Models of Computers and Networks Chapter 4: Using Matlab for Performance Analysis and Simulation Objective Learn a useful tool for mathematical analysis and simulation Interpreted
CDA6530: Performance Models of Computers and Networks Chapter 4: Using Matlab for Performance Analysis and Simulation Objective Learn a useful tool for mathematical analysis and simulation Interpreted
Objectives. Simulink Basics
 Simulink Basics This material exempt per Department of Commerce license exception TSU Objectives After completing this module, you will be able to: Describe Simulink environment List some of the commonly
Simulink Basics This material exempt per Department of Commerce license exception TSU Objectives After completing this module, you will be able to: Describe Simulink environment List some of the commonly
MATLAB Tutorial. Digital Signal Processing. Course Details. Topics. MATLAB Environment. Introduction. Digital Signal Processing (DSP)
 Digital Signal Processing Prof. Nizamettin AYDIN naydin@yildiz.edu.tr naydin@ieee.org http://www.yildiz.edu.tr/~naydin Course Details Course Code : 0113620 Course Name: Digital Signal Processing (Sayısal
Digital Signal Processing Prof. Nizamettin AYDIN naydin@yildiz.edu.tr naydin@ieee.org http://www.yildiz.edu.tr/~naydin Course Details Course Code : 0113620 Course Name: Digital Signal Processing (Sayısal
Advanced Programming Features
 Advanced Programming Features Compute Tools 4 and 5 Program Area Level 5 The two advance programming templates for manipulating data are Compute Tools 4 and Compute Tools 5. Each of these templates provide
Advanced Programming Features Compute Tools 4 and 5 Program Area Level 5 The two advance programming templates for manipulating data are Compute Tools 4 and Compute Tools 5. Each of these templates provide
Lecture 1: What is MATLAB?
 Lecture 1: What is MATLAB? Dr. Mohammed Hawa Electrical Engineering Department University of Jordan EE201: Computer Applications. See Textbook Chapter 1. MATLAB MATLAB (MATrix LABoratory) is a numerical
Lecture 1: What is MATLAB? Dr. Mohammed Hawa Electrical Engineering Department University of Jordan EE201: Computer Applications. See Textbook Chapter 1. MATLAB MATLAB (MATrix LABoratory) is a numerical
EL2310 Scientific Programming
 (pronobis@kth.se) Overview Overview Wrap Up More on Scripts and Functions Basic Programming Lecture 2 Lecture 3 Lecture 4 Wrap Up Last time Loading data from file: load( filename ) Graphical input and
(pronobis@kth.se) Overview Overview Wrap Up More on Scripts and Functions Basic Programming Lecture 2 Lecture 3 Lecture 4 Wrap Up Last time Loading data from file: load( filename ) Graphical input and
Desktop Command window
 Chapter 1 Matlab Overview EGR1302 Desktop Command window Current Directory window Tb Tabs to toggle between Current Directory & Workspace Windows Command History window 1 Desktop Default appearance Command
Chapter 1 Matlab Overview EGR1302 Desktop Command window Current Directory window Tb Tabs to toggle between Current Directory & Workspace Windows Command History window 1 Desktop Default appearance Command
Getting Started with MATLAB
 Getting Started with MATLAB Math 315, Fall 2003 Matlab is an interactive system for numerical computations. It is widely used in universities and industry, and has many advantages over languages such as
Getting Started with MATLAB Math 315, Fall 2003 Matlab is an interactive system for numerical computations. It is widely used in universities and industry, and has many advantages over languages such as
MATLAB Tutorial. Primary Author: Shoumik Chatterjee Secondary Author: Dr. Chuan Li
 MATLAB Tutorial Primary Author: Shoumik Chatterjee Secondary Author: Dr. Chuan Li 1 Table of Contents Section 1: Accessing MATLAB using RamCloud server...3 Section 2: MATLAB GUI Basics. 6 Section 3: MATLAB
MATLAB Tutorial Primary Author: Shoumik Chatterjee Secondary Author: Dr. Chuan Li 1 Table of Contents Section 1: Accessing MATLAB using RamCloud server...3 Section 2: MATLAB GUI Basics. 6 Section 3: MATLAB
MATLAB Project: Getting Started with MATLAB
 Name Purpose: To learn to create matrices and use various MATLAB commands for reference later MATLAB built-in functions used: [ ] : ; + - * ^, size, help, format, eye, zeros, ones, diag, rand, round, cos,
Name Purpose: To learn to create matrices and use various MATLAB commands for reference later MATLAB built-in functions used: [ ] : ; + - * ^, size, help, format, eye, zeros, ones, diag, rand, round, cos,
CDA5530: Performance Models of Computers and Networks. Chapter 8: Using Matlab for Performance Analysis and Simulation
 CDA5530: Performance Models of Computers and Networks Chapter 8: Using Matlab for Performance Analysis and Simulation Objective Learn a useful tool for mathematical analysis and simulation Interpreted
CDA5530: Performance Models of Computers and Networks Chapter 8: Using Matlab for Performance Analysis and Simulation Objective Learn a useful tool for mathematical analysis and simulation Interpreted
W7 DATA ANALYSIS 2. Your graph should look something like that in Figure W7-2. It shows the expected bell shape of the Gaussian distribution.
 Drawing Simple Graphs W7 DATA ANALYSIS 2 In some experiments, large amounts of data may be recorded and manipulation is performed using computer software. Although sophisticated, specialist software exists
Drawing Simple Graphs W7 DATA ANALYSIS 2 In some experiments, large amounts of data may be recorded and manipulation is performed using computer software. Although sophisticated, specialist software exists
EE 216 Experiment 1. MATLAB Structure and Use
 EE216:Exp1-1 EE 216 Experiment 1 MATLAB Structure and Use This first laboratory experiment is an introduction to the use of MATLAB. The basic computer-user interfaces, data entry techniques, operations,
EE216:Exp1-1 EE 216 Experiment 1 MATLAB Structure and Use This first laboratory experiment is an introduction to the use of MATLAB. The basic computer-user interfaces, data entry techniques, operations,
STAT 391 Handout 1 Making Plots with Matlab Mar 26, 2006
 STAT 39 Handout Making Plots with Matlab Mar 26, 26 c Marina Meilă & Lei Xu mmp@cs.washington.edu This is intended to help you mainly with the graphics in the homework. Matlab is a matrix oriented mathematics
STAT 39 Handout Making Plots with Matlab Mar 26, 26 c Marina Meilă & Lei Xu mmp@cs.washington.edu This is intended to help you mainly with the graphics in the homework. Matlab is a matrix oriented mathematics
Introduction to Matlab
 What is Matlab? Introduction to Matlab Matlab is software written by a company called The Mathworks (mathworks.com), and was first created in 1984 to be a nice front end to the numerical routines created
What is Matlab? Introduction to Matlab Matlab is software written by a company called The Mathworks (mathworks.com), and was first created in 1984 to be a nice front end to the numerical routines created
Introduction to Matlab
 Introduction to Matlab Weichung Wang 2003 NCTS-NSF Workshop on Differential Equations, Surface Theory, and Mathematical Visualization NCTS, Hsinchu, February 13, 2003 DE, ST, MV Workshop Matlab 1 Main
Introduction to Matlab Weichung Wang 2003 NCTS-NSF Workshop on Differential Equations, Surface Theory, and Mathematical Visualization NCTS, Hsinchu, February 13, 2003 DE, ST, MV Workshop Matlab 1 Main
FLUENT Secondary flow in a teacup Author: John M. Cimbala, Penn State University Latest revision: 26 January 2016
 FLUENT Secondary flow in a teacup Author: John M. Cimbala, Penn State University Latest revision: 26 January 2016 Note: These instructions are based on an older version of FLUENT, and some of the instructions
FLUENT Secondary flow in a teacup Author: John M. Cimbala, Penn State University Latest revision: 26 January 2016 Note: These instructions are based on an older version of FLUENT, and some of the instructions
CITS2401 Computer Analysis & Visualisation
 FACULTY OF ENGINEERING, COMPUTING AND MATHEMATICS CITS2401 Computer Analysis & Visualisation SCHOOL OF COMPUTER SCIENCE AND SOFTWARE ENGINEERING Topic 13 Revision Notes CAV review Topics Covered Sample
FACULTY OF ENGINEERING, COMPUTING AND MATHEMATICS CITS2401 Computer Analysis & Visualisation SCHOOL OF COMPUTER SCIENCE AND SOFTWARE ENGINEERING Topic 13 Revision Notes CAV review Topics Covered Sample
A Guide to Using Some Basic MATLAB Functions
 A Guide to Using Some Basic MATLAB Functions UNC Charlotte Robert W. Cox This document provides a brief overview of some of the essential MATLAB functionality. More thorough descriptions are available
A Guide to Using Some Basic MATLAB Functions UNC Charlotte Robert W. Cox This document provides a brief overview of some of the essential MATLAB functionality. More thorough descriptions are available
Engineering Project-I. Module 1: Familiarization of LabVIEW and the Vernier Toolkit
 Engineering Project-I Module 1: Familiarization of LabVIEW and the Vernier Toolkit PREPARED BY Academic Services Unit January 2012 Applied Technology High Schools, 2012 Module 1: Familiarization of LabVIEW
Engineering Project-I Module 1: Familiarization of LabVIEW and the Vernier Toolkit PREPARED BY Academic Services Unit January 2012 Applied Technology High Schools, 2012 Module 1: Familiarization of LabVIEW
MATLAB Basics. Configure a MATLAB Package 6/7/2017. Stanley Liang, PhD York University. Get a MATLAB Student License on Matworks
 MATLAB Basics Stanley Liang, PhD York University Configure a MATLAB Package Get a MATLAB Student License on Matworks Visit MathWorks at https://www.mathworks.com/ It is recommended signing up with a student
MATLAB Basics Stanley Liang, PhD York University Configure a MATLAB Package Get a MATLAB Student License on Matworks Visit MathWorks at https://www.mathworks.com/ It is recommended signing up with a student
INTENDED LEARNING OUTCOMES
 COURSE CODE: GEE 216 COURSE TITLE: COMPUTER AND COMPUTING NUMBER OF UNITS: 3 Units COURSE DURATION: Three hours per week COURSE LECTURER: Engr. Obasi Chukwuemeka INTENDED LEARNING OUTCOMES At the completion
COURSE CODE: GEE 216 COURSE TITLE: COMPUTER AND COMPUTING NUMBER OF UNITS: 3 Units COURSE DURATION: Three hours per week COURSE LECTURER: Engr. Obasi Chukwuemeka INTENDED LEARNING OUTCOMES At the completion
Math Scientific Computing - Matlab Intro and Exercises: Spring 2003
 Math 64 - Scientific Computing - Matlab Intro and Exercises: Spring 2003 Professor: L.G. de Pillis Time: TTh :5pm 2:30pm Location: Olin B43 February 3, 2003 Matlab Introduction On the Linux workstations,
Math 64 - Scientific Computing - Matlab Intro and Exercises: Spring 2003 Professor: L.G. de Pillis Time: TTh :5pm 2:30pm Location: Olin B43 February 3, 2003 Matlab Introduction On the Linux workstations,
Root Locus Controller Design
 Islamic University of Gaza Faculty of Engineering Electrical Engineering department Control Systems Design Lab Eng. Mohammed S. Jouda Eng. Ola M. Skeik Experiment 4 Root Locus Controller Design Overview
Islamic University of Gaza Faculty of Engineering Electrical Engineering department Control Systems Design Lab Eng. Mohammed S. Jouda Eng. Ola M. Skeik Experiment 4 Root Locus Controller Design Overview
Systems & Control Lab.-Manual
 German University in Cairo - GUC Information Engineering and Technology Electronics, Communications, & Networks Systems & Control Lab.-Manual (3) A brief overview of: By: Eng. Moustafa Adly ON-OFF control
German University in Cairo - GUC Information Engineering and Technology Electronics, Communications, & Networks Systems & Control Lab.-Manual (3) A brief overview of: By: Eng. Moustafa Adly ON-OFF control
How do you roll? Fig. 1 - Capstone screen showing graph areas and menus
 How do you roll? Purpose: Observe and compare the motion of a cart rolling down hill versus a cart rolling up hill. Develop a mathematical model of the position versus time and velocity versus time for
How do you roll? Purpose: Observe and compare the motion of a cart rolling down hill versus a cart rolling up hill. Develop a mathematical model of the position versus time and velocity versus time for
MATLAB Premier. Middle East Technical University Department of Mechanical Engineering ME 304 1/50
 MATLAB Premier Middle East Technical University Department of Mechanical Engineering ME 304 1/50 Outline Introduction Basic Features of MATLAB Prompt Level and Basic Arithmetic Operations Scalars, Vectors,
MATLAB Premier Middle East Technical University Department of Mechanical Engineering ME 304 1/50 Outline Introduction Basic Features of MATLAB Prompt Level and Basic Arithmetic Operations Scalars, Vectors,
Modeling and Simulating Social Systems with MATLAB
 Modeling and Simulating Social Systems with MATLAB Lecture 2 Statistics and Plotting in MATLAB Olivia Woolley, Tobias Kuhn, Dario Biasini, Dirk Helbing Chair of Sociology, in particular of Modeling and
Modeling and Simulating Social Systems with MATLAB Lecture 2 Statistics and Plotting in MATLAB Olivia Woolley, Tobias Kuhn, Dario Biasini, Dirk Helbing Chair of Sociology, in particular of Modeling and
Getting Started with MATLAB
 Getting Started with MATLAB Math 4600 Lab: Gregory Handy http://www.math.utah.edu/ borisyuk/4600/ Logging in for the first time: This is what you do to start working on the computer. If your machine seems
Getting Started with MATLAB Math 4600 Lab: Gregory Handy http://www.math.utah.edu/ borisyuk/4600/ Logging in for the first time: This is what you do to start working on the computer. If your machine seems
Getting started with MATLAB
 Sapienza University of Rome Department of economics and law Advanced Monetary Theory and Policy EPOS 2013/14 Getting started with MATLAB Giovanni Di Bartolomeo giovanni.dibartolomeo@uniroma1.it Outline
Sapienza University of Rome Department of economics and law Advanced Monetary Theory and Policy EPOS 2013/14 Getting started with MATLAB Giovanni Di Bartolomeo giovanni.dibartolomeo@uniroma1.it Outline
Evolutionary Algorithms. Workgroup 1
 The workgroup sessions Evolutionary Algorithms Workgroup Workgroup 1 General The workgroups are given by: Hao Wang - h.wang@liacs.leideuniv.nl - Room 152 Furong Ye - f.ye@liacs.leidenuniv.nl Follow the
The workgroup sessions Evolutionary Algorithms Workgroup Workgroup 1 General The workgroups are given by: Hao Wang - h.wang@liacs.leideuniv.nl - Room 152 Furong Ye - f.ye@liacs.leidenuniv.nl Follow the
The iworx 214 and LabScribe V2.0 Tutorial. Overview
 The iworx 214 and LabScribe V2.0 Overview Figure T-1-1: The front and rear panels of IWX/214. The data acquisition unit used in the iworx teaching kits is the IWX/214 (Figure T-1-1 on page T-1-1). The
The iworx 214 and LabScribe V2.0 Overview Figure T-1-1: The front and rear panels of IWX/214. The data acquisition unit used in the iworx teaching kits is the IWX/214 (Figure T-1-1 on page T-1-1). The
Introduction to Microchip-SIMULINK Blocksets and MATLAB Plug-in for MPLAB IDE
 Introduction to Microchip-SIMULINK Blocksets and MATLAB Plug-in for MPLAB IDE Produced by Murali Manohara Chembarpu 2008 Microchip Technology Incorporated. All Rights Reserved. WebSeminar Title Slide 1
Introduction to Microchip-SIMULINK Blocksets and MATLAB Plug-in for MPLAB IDE Produced by Murali Manohara Chembarpu 2008 Microchip Technology Incorporated. All Rights Reserved. WebSeminar Title Slide 1
