Recursion. Java recursive programming: Writing methods that call themselves to solve problems recursively.
|
|
|
- Sharlene Winifred Walsh
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Recursion recursion: The definition of an operation in terms of itself. Solving a problem using recursion depends on solving smaller occurrences of the same problem. Java recursive programming: Writing methods that call themselves to solve problems recursively. An equally powerful substitute for iteration (loops) Particularly well-suited to solving certain types of problems 1
2 Why learn recursion? "cultural experience" - A different way of thinking on problems Can solve some kinds of problems better than iteration Leads to elegant, simplistic, short code (when used well) Many programming languages ("functional" languages such as Scheme, ML, and Haskell) use recursion exclusively (no loops) A key component of the our assignments number 2 2
3 Exercise 1 (To a student in the front row) How many students total are directly behind you in your "column" of the classroom? You have poor vision, so you can see only the people right next to you. So you can't just look back and count. But you are allowed to ask questions of the person next to you. How can we solve this problem? (recursively ) 3
4 Each person can solve a small part of the problem. What is a small version of the problem that would be easy to answer? What information from a neighbor might help me? The idea Recursion is all about breaking a big problem into smaller occurrences of that same problem. 4
5 Recursive algorithm Number of people behind me: If there is someone behind me, ask him/her how many people are behind him/her. - When they respond with a value N, then I will answer N + 1. If there is nobody behind me, I will answer 0. 5
6 Exercise 2 - Recursive algorithm How do you look up a name in the phone book? Search : middle page = (first page + last page)/2 Go to middle page If (name is on middle page) done; this is the base case if (name is alphabetically before middle page) last page = middle page redefine search area to front half Search same process on reduced number of pages name must be after middle page first page = middle page redefine search area to back half Search same process on reduced number of pages 6
7 Recursive algorithm - Overview Natural approach to some (not all) problems. A definition in terms of itself. A recursive algorithm uses itself to solve one or more smaller identical problems. Each successive call to itself must be a smaller version of itself. A recursive algorithm must eventually terminate. A recursive algorithm must have at least one base, or stopping, case. A base case does not execute a recursive call. 7
8 Recursive Algorithm Design Three key Components of a Recursive Algorithm Design: 1. What is a smaller identical problem(s)? ) פירוק ( Decomposition 2. How are the answers to smaller problems combined to form the answer for a larger problem? ) הרכבה ( Composition 3. What is the smallest problem which can be solved easily (without further decomposition)? ) מקרה בסיסי ( case Base/stopping 8
9 Factorial (N!) N! = (N-1)! * N // for N > 1 1! = 1 3! = = 2! * 3 = = ( 1! * 2 ) * 3 = 1 * 2 * 3 Recursive design: Decomposition: (N-1)! Composition: * N Base case: 1! public static int factorial(int n) int fact; if (n > 1) // recursive case (decomposition) fact = factorial(n 1) * n; // composition fact = 1; // base case return fact; 9
10 public static int factorial(int 3) int fact; if (n > 1) fact = factorial(2) * 3; fact = 1; return fact; Each recursive call to itself must be a smaller version of itself. public static int factorial(int 2) int fact; if (n > 1) fact = factorial(1) * 2; fact = 1; return fact; A base case does not execute a recursive call and stops the recursion. public static int factorial(int 1) int fact; if (n > 1) fact = factorial(n - 1) * n; fact = 1; return fact; 10
11 public static int factorial(int 3) int fact; if (n > 1) fact = factorial(2) * 3; fact = 1; return fact; return 6 return 2 public static int factorial(int 2) int fact; if (n > 1) fact = factorial(1) * 2; fact = 1; return fact; return 1 public static int factorial(int 1) int fact; if (n > 1) fact = factorial(n - 1) * n; fact = 1; return fact; 11
12 Improved factorial Method public static int factorial(int n) if (n ==1) return1; return factorial(n 1) * n; 12
13 How recursion works Factorial( 1 ) n = 1 fact = 1 Top of the stack Factorial( 2 ) n = 2 Factorial( 2 ) n = 2 fact = 2 Factorial( 3 ) n = 3 Factorial( 3 ) n = 3 Factorial( 3 ) n = 3 fact = 6 res= factorial(3) res= factorial(3) res= factorial(3) res =factorial(3) Stack memory (LIFO) In java, when a method encounters another method, it gets pushed to the top of the stack and temporarily stops the original method until the new method is completed. Once the method being called finished, the program picks up from where it left off. 13
14 Calculation power X y = x*x* *x y times Recursive definitions (assume non-negative y): X y = X*(X y-1 ) Base case: x 0 =1 public static int power(int x, int y) if (y == 0) return 1; return x*power(x, y 1); 14
15 Calculation product Calculation product of two non - negative integers without multiplication operator * ( only + and - operators) The product a*b is actually a+a+ +a (b times). x * y = x + x + x + x + + x y times Recursive definitions : x * y = x + ( x 1) * y Base case: 0 * Y = 0 public static int recmult( int x, int y ) if( x == 0) return 0; return x + recmult( x-1,y); 15
16 Recursive addition public static int add(int a, int b) if(b == 0) return a; if(b < 0) Base case return add(a-1,b+1); return add(a+1,b-1); a b a b public static void main(string[] args) int x=reader.nextint(); // 5 int y=reader.nextint(); // 2 System.out.println(add(x,y));
17 Recursive subtraction public static int sub(int a, int b) if(b == 0) return a; if(b < 0) Base case return sub(a+1,b+1); return sub(a-1,b-1); a b a b public static void main(string[] args) int x=reader.nextint(); // 5 int y=reader.nextint(); // 2 System.out.println(sub(x,y));
18 Recursive integer division public static int divide(int a, int b) if(b == 0) return 0; Base cases if(a < b) return 0; if(b == 1) return a; return add(1, divide(sub(a,b),b)); public static void main(string[ ] args) int a=reader.nextint(); //5 int b=reader.nextint(); //2 System.out.println(divide(a,b)); a b 5 2?? 18
19 Fibonacci series Fibonacci was born on 1170 in Pisa, Italy and died on His real name is Leonardo Pisano. The N - th Fibonacci number is the sum of the previous two Fibonacci numbers : Number element in series 0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, Recursive Design: Decomposition & Composition fibonacci(n) = fibonacci(n-1) + fibonacci(n-2) Base case: fibonacci(1) = 0 fibonacci(2) = 1 Binary Recursion is a process where function is called twice at a time instead of once at a time public static fibonacci(int n) if (n<=1) return 1; return fibonacci(n-1) + fibonacci(n-2); 19
20 Fibonacci series n= ) רקורסיה כפולה recursion( Binary 20
21 Recursion and loops public static int recloop(int num) if(num == 1) return 1; int sum = num; for(int i=1; i<num; i++) sum = sum + recloop(i); return sum; // recloop public static void main(string[ ] args) System.out.println("enter an integer -> "); int x=reader.nextint(); System.out.println("what= + recloop(x)); input output
22 Printing stars public static void stars1(int n) if (n<1) return; System.out.print(" * "); stars1(n-1); public static void stars2(int n) if (n>1) stars2(n-1); System.out.print(" * "); If the method stars1 is called with the value 3, is it equivalent to the method stars2? Explain. 22
23 Invoke stars1 static void stars1( 3 ) if (n<1) FALSE return; System.out.print(" * "); stars1(2); static void stars1( 2 ) if (n<1) FALSE return; System.out.print(" * "); stars1(1); First output : * Second output : ** static void stars1( 1 ) if (n<1) FALSE return; System.out.print(" * "); stars1(0); Third output : *** static void stars1( 0 ) if (n<1) TRUE return; System.out.print(" * "); stars1(n-1); 23
24 Invoke stars2 static void stars2( 3 ) if (n>1) TRUE stars2(2); System.out.print(" * "); Third output : *** static void stars2( 2 ) if (n>1) TRUE stars2(1); System.out.print(" * "); Second output : ** static void stars2( 1 ) if (n>1) FALSE stars1(i-1); System.out.print(" * "); First output : * 24
25 Mutual recursion Mutual Recursion ( רקורסיה הדדית ) is the kind of recursion where recursive methods calling each other. For example: YES method calling NO method and NO method calling YES method recursively. public static void YES (int num) System.out.println( yes ); if (num>1) NO(num-1); invoke YES(5) would produce next output: public static void NO (int num) System.out.println( no ); if (num>1) YES(num-1); yes no yes no yes 25
26 Reverse an array The method gets an array and it's length as parameters and returns the array after reversing it's values. public static int[ ] reversearr(int[ ] arr, int length) if(length <= arr.length / 2 ) return arr; //swapping the values int tempval = arr[length - 1]; arr[length - 1] = arr[arr.length - length]; arr[arr.length - length] = tempval; return reversearr(arr, length - 1); int[ ] a = 1,2,3,4,5 ; a = reversearr( a,a.length); Method returns the array after reversing it's values:
27 Reverse a string public static String reversestring(string s) if (s.length() <= 1) return s; return reversestring (s.substring(1)) + s.charat(0)); a b c d b c d c d d + a + b + c + d System.out.print("Enter the string:"); String str = reader.next(); System.out.print("The reverse string is" + reversestring(str)); would produce next output: dcba 27
28 Sum numbers in an array This method calls itself with an index argument that is higher than the current index. The result of the method call is added to the array element at the index. Base case: If the index is equal to the length of the array, we know that all of the array elements have been processed. public static int recsum(int[ ] array, int index) if (index == array.length) return 0; return array[index] + recsum(array, index + 1); 28
29 Sum numbers in array - example Invoke recsum recsum(a,0) recsum(a,1) recsum(a,2) recsum(a,3) recsum(a,4) 0 Base case 0 recsum(a,5) 29
30 Find max value in an array The method gets an array of int value and it's length. It will return the max value in the array. public static int findmax(int array[ ], int length) if (length == 1) return array[0]; // base case int result = findmax(array, length - 1); if (array[length - 1] > result) return array[length - 1]; return result; 30
31 Recursive binary search This method returns the index of the entry if the target value is found or -1 if it is not found. public static int binsearch( int a[ ],int target, int first,int last ) int location = -1; //target not found; if(first <= last) int mid=(first + last)/2; if(target == a[mid]) location = mid; if(target < a[mid]) //first half location = binsearch( a, target, first, mid - 1) //second half location = biansearch(a, target, mid + 1, last ) return location; 31
32 Binary Search Example target is 33 The array a looks like this: Indexes Contents mid = (0 + 9) / 2 (which is 4) 33 > a[mid] (that is, 33 > a[4]) So, if 33 is in the array, then 33 is one of: Eliminated half of the remaining elements from consideration because array elements are sorted. 32
33 target is 33 The array a looks like this: Indexes Contents Binary Search Example, cont mid = (5 + 9) / 2 (which is 7) 33 < a[mid] (that is, 33 < a[7]) So, if 33 is in the array, then 33 is one of: Eliminate half of the remaining elements mid = (5 + 6) / 2 (which is 5) 33 == a[mid] So we found 33 at index 5:
34 Bubble Sort - example 34
35 Bubble Sort - recursive solution Algorithm : 1.Compare each pair of adjacent elements from the beginning of an array and, if they are in reversed order, swap them. 2.If at least one swap has been done, repeat step 1. public static void swap(int a[ ],int i) int t=a[ i ]; a[ i ]=a[ i+1 ]; a[ i+1 ]=t; public static int[ ] recbubsort(int arr[ ], int n) if(n < 2) return arr; for(int i = 0; i < n-1; i++) if(arr[ i] > arr[i+1]) swap( arr, i); // help method return recbubsort(arr,n-1); Help method will swap the elements at i and i+1 indexes of array a. 35
36 Towers of Hanoi The Towers of Hanoi is a mathematical game or puzzle. It was invented by the French mathematician, Eduard Lucas, in
37 Towers of Hanoi rules: The objective of the puzzle is to move the entire stack to another rod, obeying the following rules: Only one disk may be moved at a time. Each move consists of taking the upper disk from one of the rods and sliding it onto another rod, on top of the other disks that may already be present on that rod. No disk may be placed on top of a smaller disk. 37
38 Recursive Algorithm To move n disks from peg a to peg c: move n 1 disks from a to b. This leaves disk #n alone on peg a move disk #n from a to c move n 1 disks from b to c so they sit on disk #n 38
39 Recursive Algorithm pseudo code חנוי)מספר_דיסקיות,מוט_מקור,מוט_יעד,מוט_עזר(.1 אם מספר_דיסקיות = 1 העבר את הדיסקית ממוט_מקור למוט_יעד 2. אחרת 2.1 חנוי(מספר_דיסקיות - 1,מוט_מקור,מוט_עזר,מוט_יעד) 2.2 חנוי( 1,מוט_מקור,מוט_יעד,מוט_יעזר) 2.3 חנוי(מספר_דיסקיות -1,מוט_עזר,מוט_יעד,מוט_מקור) 39
40 Towers of Hanoi Java solution public static void hanoi (int x, char from, char to, char aux ) if (x==1) System.out.println( "Move disk from + from + " to + to); hanoi(x-1, from, aux, to); System.out.println( "Move disk from + from+ " to + to); hanoi(x-1,aux,to,from); 40
41 Towers of Hanoi num=3 System.out.print( Enter an integer ); int num = reader.nextint(); hanoi(num, 'a', 'c ', 'b' ); 41
Recursion in Java. Recursion: Recursion is the process of defining something in terms of itself. La Giaconda ( Mona Lisa ) Louvre, Paris.
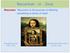 Recursion in Java Recursion: Recursion is the process of defining something in terms of itself. Leonardo da Vinci 1452 1519 La Giaconda ( Mona Lisa ) Louvre, Paris. 1 Why learn recursion? "cultural experience
Recursion in Java Recursion: Recursion is the process of defining something in terms of itself. Leonardo da Vinci 1452 1519 La Giaconda ( Mona Lisa ) Louvre, Paris. 1 Why learn recursion? "cultural experience
Recursion. EECS2030: Advanced Object Oriented Programming Fall 2017 CHEN-WEI WANG
 Recursion EECS2030: Advanced Object Oriented Programming Fall 2017 CHEN-WEI WANG Recursion: Principle Recursion is useful in expressing solutions to problems that can be recursively defined: Base Cases:
Recursion EECS2030: Advanced Object Oriented Programming Fall 2017 CHEN-WEI WANG Recursion: Principle Recursion is useful in expressing solutions to problems that can be recursively defined: Base Cases:
COSC 236 Section 101 Computer Science 1 -- Prof. Michael A. Soderstrand
 COSC 236 Section 101 Computer Science 1 -- Prof. Michael A. Soderstrand COSC 236 Web Site You will always find the course material at: http://www.class-notes.us or http://www.class-notes.info or http://www.lecture-notes.tripod.com
COSC 236 Section 101 Computer Science 1 -- Prof. Michael A. Soderstrand COSC 236 Web Site You will always find the course material at: http://www.class-notes.us or http://www.class-notes.info or http://www.lecture-notes.tripod.com
Recursion: Factorial (1) Recursion. Recursion: Principle. Recursion: Factorial (2) Recall the formal definition of calculating the n factorial:
 Recursion EECS2030: Advanced Object Oriented Programming Fall 2017 CHEN-WEI WANG Recursion: Factorial (1) Recall the formal definition of calculating the n factorial: 1 if n = 0 n! = n (n 1) (n 2) 3 2
Recursion EECS2030: Advanced Object Oriented Programming Fall 2017 CHEN-WEI WANG Recursion: Factorial (1) Recall the formal definition of calculating the n factorial: 1 if n = 0 n! = n (n 1) (n 2) 3 2
Recursion. Chapter 7. Copyright 2012 by Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved
 Recursion Chapter 7 Contents What Is Recursion? Tracing a Recursive Method Recursive Methods That Return a Value Recursively Processing an Array Recursively Processing a Linked Chain The Time Efficiency
Recursion Chapter 7 Contents What Is Recursion? Tracing a Recursive Method Recursive Methods That Return a Value Recursively Processing an Array Recursively Processing a Linked Chain The Time Efficiency
Recursion. Tracing Method Calls via a Stack. Beyond this lecture...
 Recursion EECS2030 B: Advanced Object Oriented Programming Fall 2018 CHEN-WEI WANG Recursion: Principle Recursion is useful in expressing solutions to problems that can be recursively defined: Base Cases:
Recursion EECS2030 B: Advanced Object Oriented Programming Fall 2018 CHEN-WEI WANG Recursion: Principle Recursion is useful in expressing solutions to problems that can be recursively defined: Base Cases:
Chapter 10: Recursive Problem Solving
 2400 COMPUTER PROGRAMMING FOR INTERNATIONAL ENGINEERS Chapter 0: Recursive Problem Solving Objectives Students should Be able to explain the concept of recursive definition Be able to use recursion in
2400 COMPUTER PROGRAMMING FOR INTERNATIONAL ENGINEERS Chapter 0: Recursive Problem Solving Objectives Students should Be able to explain the concept of recursive definition Be able to use recursion in
Recursion. Let s start by looking at some problems that are nicely solved using recursion. First, let s look at generating The Fibonacci series.
 Recursion The programs we have discussed so far have been primarily iterative and procedural. Code calls other methods in a hierarchical manner. For some problems, it is very useful to have the methods
Recursion The programs we have discussed so far have been primarily iterative and procedural. Code calls other methods in a hierarchical manner. For some problems, it is very useful to have the methods
CSE 143 Lecture 10. Recursion
 CSE 143 Lecture 10 Recursion slides created by Marty Stepp and Alyssa Harding http://www.cs.washington.edu/143/ Recursion Iteration: a programming technique in which you describe actions to be repeated
CSE 143 Lecture 10 Recursion slides created by Marty Stepp and Alyssa Harding http://www.cs.washington.edu/143/ Recursion Iteration: a programming technique in which you describe actions to be repeated
Recursion. Chapter 17 CMPE13. Cyrus Bazeghi
 Recursion Chapter 17 CMPE13 Cyrus Bazeghi What is Recursion? A recursive function is one that solves its task by calling itself on smaller pieces of data. Similar to recurrence function in mathematics.
Recursion Chapter 17 CMPE13 Cyrus Bazeghi What is Recursion? A recursive function is one that solves its task by calling itself on smaller pieces of data. Similar to recurrence function in mathematics.
Recursive Definitions
 Recursion Objectives Explain the underlying concepts of recursion Examine recursive methods and unravel their processing steps Explain when recursion should and should not be used Demonstrate the use of
Recursion Objectives Explain the underlying concepts of recursion Examine recursive methods and unravel their processing steps Explain when recursion should and should not be used Demonstrate the use of
What is Recursion? Chapter 17 Recursion. Executing RunningSum. High-Level Example: Binary Search
 Chapter 17 Recursion Original slides from Gregory Byrd, North Carolina State University Modified slides by Chris Wilcox, Colorado State University! A recursive function is one that solves its task by calling
Chapter 17 Recursion Original slides from Gregory Byrd, North Carolina State University Modified slides by Chris Wilcox, Colorado State University! A recursive function is one that solves its task by calling
Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Persion required for reproduction or display. What is Recursion?
 Chapter 17 Recursion Original slides from Gregory Byrd, North Carolina State University Modified slides by Chris Wilcox, Colorado State University! A recursive function is one that solves its task by calling
Chapter 17 Recursion Original slides from Gregory Byrd, North Carolina State University Modified slides by Chris Wilcox, Colorado State University! A recursive function is one that solves its task by calling
Recursion. Chapter 5
 Recursion Chapter 5 Chapter Objectives To understand how to think recursively To learn how to trace a recursive method To learn how to write recursive algorithms and methods for searching arrays To learn
Recursion Chapter 5 Chapter Objectives To understand how to think recursively To learn how to trace a recursive method To learn how to write recursive algorithms and methods for searching arrays To learn
Recursive Problem Solving
 Recursive Problem Solving Objectives Students should: Be able to explain the concept of recursive definition. Be able to use recursion in Java to solve problems. 2 Recursive Problem Solving How to solve
Recursive Problem Solving Objectives Students should: Be able to explain the concept of recursive definition. Be able to use recursion in Java to solve problems. 2 Recursive Problem Solving How to solve
CSE11 Lecture 20 Fall 2013 Recursion
 CSE11 Lecture 20 Fall 2013 Recursion Recursion recursion: The definition of an operation in terms of itself. Solving a problem using recursion depends on solving smaller or simpler occurrences of the same
CSE11 Lecture 20 Fall 2013 Recursion Recursion recursion: The definition of an operation in terms of itself. Solving a problem using recursion depends on solving smaller or simpler occurrences of the same
Objectives. Recursion. One Possible Way. How do you look up a name in the phone book? Recursive Methods Must Eventually Terminate.
 Objectives Recursion Chapter 11 become familiar with the idea of recursion learn to use recursion as a programming tool become familiar with the binary search algorithm as an example of recursion become
Objectives Recursion Chapter 11 become familiar with the idea of recursion learn to use recursion as a programming tool become familiar with the binary search algorithm as an example of recursion become
C22a: Problem Solving using Recursion
 CISC 3115 TY3 C22a: Problem Solving using Recursion Hui Chen Department of Computer & Information Science CUNY Brooklyn College 11/6/2018 CUNY Brooklyn College 1 Outline Characteristics of recursion Recursion
CISC 3115 TY3 C22a: Problem Solving using Recursion Hui Chen Department of Computer & Information Science CUNY Brooklyn College 11/6/2018 CUNY Brooklyn College 1 Outline Characteristics of recursion Recursion
Reduction & Recursion Overview
 Reduction & Recursion Overview Reduction definition Reduction techniques Recursion definition Recursive thinking (Many) recursion examples Indirect recursion Runtime stack Factorial isnumericstring add
Reduction & Recursion Overview Reduction definition Reduction techniques Recursion definition Recursive thinking (Many) recursion examples Indirect recursion Runtime stack Factorial isnumericstring add
Announcements. Recursion and why study it. Recursive programming. Recursion basic idea
 Announcements Recursion and why study it Tutoring schedule updated Do you find the sessions helpful? Midterm exam 1: Tuesday, April 11, in class Scope: will cover up to recursion Closed book but one sheet,
Announcements Recursion and why study it Tutoring schedule updated Do you find the sessions helpful? Midterm exam 1: Tuesday, April 11, in class Scope: will cover up to recursion Closed book but one sheet,
Chapter 17 Recursion
 Chapter 17 Recursion What is Recursion? A recursive function is one that solves its task by calling itself on smaller pieces of data. Similar to recurrence relation in mathematics. Sometimes recursion
Chapter 17 Recursion What is Recursion? A recursive function is one that solves its task by calling itself on smaller pieces of data. Similar to recurrence relation in mathematics. Sometimes recursion
Lecture 19: Recursion
 Lecture 19: Recursion Building Java Programs: A Back to Basics Approach by Stuart Reges and Marty Stepp Copyright (c) Pearson 2013. All rights reserved. Recursion recursion: The definition of an operation
Lecture 19: Recursion Building Java Programs: A Back to Basics Approach by Stuart Reges and Marty Stepp Copyright (c) Pearson 2013. All rights reserved. Recursion recursion: The definition of an operation
APCS-AB: Java. Recursion in Java December 12, week14 1
 APCS-AB: Java Recursion in Java December 12, 2005 week14 1 Check point Double Linked List - extra project grade Must turn in today MBCS - Chapter 1 Installation Exercises Analysis Questions week14 2 Scheme
APCS-AB: Java Recursion in Java December 12, 2005 week14 1 Check point Double Linked List - extra project grade Must turn in today MBCS - Chapter 1 Installation Exercises Analysis Questions week14 2 Scheme
Chapter 6 Recursion. The Concept of Recursion
 Data Structures for Java William H. Ford William R. Topp Chapter 6 Recursion Bret Ford 2005, Prentice Hall The Concept of Recursion An algorithm is recursive if it can be broken into smaller problems of
Data Structures for Java William H. Ford William R. Topp Chapter 6 Recursion Bret Ford 2005, Prentice Hall The Concept of Recursion An algorithm is recursive if it can be broken into smaller problems of
Lecture 24 Tao Wang 1
 Lecture 24 Tao Wang 1 Objectives Introduction of recursion How recursion works How recursion ends Infinite recursion Recursion vs. Iteration Recursion that Returns a Value Edition 2 Introduction If we
Lecture 24 Tao Wang 1 Objectives Introduction of recursion How recursion works How recursion ends Infinite recursion Recursion vs. Iteration Recursion that Returns a Value Edition 2 Introduction If we
9/16/14. Overview references to sections in text RECURSION. What does generic mean? A little about generics used in A3
 Overview references to sections in text 2 Note: We ve covered everything in JavaSummary.pptx! What is recursion 7.1-7.39 slide 1-7 Base case 7.1-7.10 slide 13 How Java stack frames work 7.8-7.10 slide
Overview references to sections in text 2 Note: We ve covered everything in JavaSummary.pptx! What is recursion 7.1-7.39 slide 1-7 Base case 7.1-7.10 slide 13 How Java stack frames work 7.8-7.10 slide
BBM 201 DATA STRUCTURES
 BBM 201 DATA STRUCTURES Lecture 2: Recursion & Performance analysis 2018-2019 Fall System Life Cycle Programs pass through a period called system life cycle, which is defined by the following steps: 1.
BBM 201 DATA STRUCTURES Lecture 2: Recursion & Performance analysis 2018-2019 Fall System Life Cycle Programs pass through a period called system life cycle, which is defined by the following steps: 1.
Programming with Recursion. What Is Recursion?
 Chapter 7 Programming with Recursion Fall 2017 Yanjun Li CS2200 1 What Is Recursion? How is recursion like a set of Russian dolls? Fall 2017 Yanjun Li CS2200 2 What Is Recursion? Recursive call A method
Chapter 7 Programming with Recursion Fall 2017 Yanjun Li CS2200 1 What Is Recursion? How is recursion like a set of Russian dolls? Fall 2017 Yanjun Li CS2200 2 What Is Recursion? Recursive call A method
Lecture 7 CS2110 Fall 2014 RECURSION
 Lecture 7 CS2110 Fall 2014 RECURSION Overview references to sections in text 2 Note: We ve covered everything in JavaSummary.pptx! What is recursion? 7.1-7.39 slide 1-7 Base case 7.1-7.10 slide 13 How
Lecture 7 CS2110 Fall 2014 RECURSION Overview references to sections in text 2 Note: We ve covered everything in JavaSummary.pptx! What is recursion? 7.1-7.39 slide 1-7 Base case 7.1-7.10 slide 13 How
Problems with simple variables
 Problems with simple variables Hard to give up values high number of variables. Complex to sort a high number of variables by value. Impossible to use loops. Example problem: Read one hundred numbers,
Problems with simple variables Hard to give up values high number of variables. Complex to sort a high number of variables by value. Impossible to use loops. Example problem: Read one hundred numbers,
Recursion. Readings: RS Chapter 12. Recursion. Recursion: The definition of an operation in terms of itself.
 Recursion Readings: RS Chapter 12 CSC216: Programming Concepts Java NC State CSC216 Faculty Slides are modified from those provided by Marty Stepp www.buildingjavaprograms.com Some materials from Joseph
Recursion Readings: RS Chapter 12 CSC216: Programming Concepts Java NC State CSC216 Faculty Slides are modified from those provided by Marty Stepp www.buildingjavaprograms.com Some materials from Joseph
Solving problems by recursion
 Solving problems by recursion How can you solve a complex problem? Devise a complex solution Break the complex problem into simpler problems Sometimes, the simpler problem is similar to (but smaller than)
Solving problems by recursion How can you solve a complex problem? Devise a complex solution Break the complex problem into simpler problems Sometimes, the simpler problem is similar to (but smaller than)
Complexity of Algorithms
 Complexity of Algorithms Time complexity is abstracted to the number of steps or basic operations performed in the worst case during a computation. Now consider the following: 1. How much time does it
Complexity of Algorithms Time complexity is abstracted to the number of steps or basic operations performed in the worst case during a computation. Now consider the following: 1. How much time does it
1 Recursion. 2 Recursive Algorithms. 2.1 Example: The Dictionary Search Problem. CSci 235 Software Design and Analysis II Introduction to Recursion
 1 Recursion Recursion is a powerful tool for solving certain kinds of problems. Recursion breaks a problem into smaller problems that are identical to the original, in such a way that solving the smaller
1 Recursion Recursion is a powerful tool for solving certain kinds of problems. Recursion breaks a problem into smaller problems that are identical to the original, in such a way that solving the smaller
Identify recursive algorithms Write simple recursive algorithms Understand recursive function calling
 Recursion Identify recursive algorithms Write simple recursive algorithms Understand recursive function calling With reference to the call stack Compute the result of simple recursive algorithms Understand
Recursion Identify recursive algorithms Write simple recursive algorithms Understand recursive function calling With reference to the call stack Compute the result of simple recursive algorithms Understand
RECURSION. Data Structures & SWU Rachel Cardell- Oliver
 RECURSION Data Structures & Algorithms @ SWU Rachel Cardell- Oliver Hello. This is Rachel Cardell-Oliver from the University of Western Australia. In this lecture I will give a brief introduction to the
RECURSION Data Structures & Algorithms @ SWU Rachel Cardell- Oliver Hello. This is Rachel Cardell-Oliver from the University of Western Australia. In this lecture I will give a brief introduction to the
Recursion. Garfield AP Computer Science. As usual, significant borrowings from Stuart Reges and Marty Stepp at UW -- thanks!!
 Recursion Garfield AP Computer Science As usual, significant borrowings from Stuart Reges and Marty Stepp at UW -- thanks!! Definitions recursion: The definition of an operation in terms of itself. Solving
Recursion Garfield AP Computer Science As usual, significant borrowings from Stuart Reges and Marty Stepp at UW -- thanks!! Definitions recursion: The definition of an operation in terms of itself. Solving
8/5/10 TODAY'S OUTLINE. Recursion COMP 10 EXPLORING COMPUTER SCIENCE. Revisit search and sorting using recursion. Recursion WHAT DOES THIS CODE DO?
 8/5/10 TODAY'S OUTLINE Recursion COMP 10 EXPLORING COMPUTER SCIENCE Revisit search and sorting using recursion Binary search Merge sort Lecture 8 Recursion WHAT DOES THIS CODE DO? A function is recursive
8/5/10 TODAY'S OUTLINE Recursion COMP 10 EXPLORING COMPUTER SCIENCE Revisit search and sorting using recursion Binary search Merge sort Lecture 8 Recursion WHAT DOES THIS CODE DO? A function is recursive
Recursion. notes Chapter 8
 Recursion notes Chapter 8 1 Tower of Hanoi A B C move the stack of n disks from A to C can move one disk at a time from the top of one stack onto another stack cannot move a larger disk onto a smaller
Recursion notes Chapter 8 1 Tower of Hanoi A B C move the stack of n disks from A to C can move one disk at a time from the top of one stack onto another stack cannot move a larger disk onto a smaller
Decision-Making and Repetition
 2.2 Recursion Introduction A recursive method is a method that call itself. You may already be familiar with the factorial function (N!) in mathematics. For any positive integer N, N! is defined to be
2.2 Recursion Introduction A recursive method is a method that call itself. You may already be familiar with the factorial function (N!) in mathematics. For any positive integer N, N! is defined to be
11/2/2017 RECURSION. Chapter 5. Recursive Thinking. Section 5.1
 RECURSION Chapter 5 Recursive Thinking Section 5.1 1 Recursive Thinking Recursion is a problem-solving approach that can be used to generate simple solutions to certain kinds of problems that are difficult
RECURSION Chapter 5 Recursive Thinking Section 5.1 1 Recursive Thinking Recursion is a problem-solving approach that can be used to generate simple solutions to certain kinds of problems that are difficult
Divide & Conquer. 2. Conquer the sub-problems by solving them recursively. 1. Divide the problem into number of sub-problems
 Divide & Conquer Divide & Conquer The Divide & Conquer approach breaks down the problem into multiple smaller sub-problems, solves the sub-problems recursively, then combines the solutions of the sub-problems
Divide & Conquer Divide & Conquer The Divide & Conquer approach breaks down the problem into multiple smaller sub-problems, solves the sub-problems recursively, then combines the solutions of the sub-problems
Chapter 15: Recursion
 Chapter 15: Recursion Starting Out with Java: From Control Structures through Objects Fifth Edition by Tony Gaddis Chapter Topics Chapter 15 discusses the following main topics: Introduction to Recursion
Chapter 15: Recursion Starting Out with Java: From Control Structures through Objects Fifth Edition by Tony Gaddis Chapter Topics Chapter 15 discusses the following main topics: Introduction to Recursion
Chapter 17 Recursion
 Chapter 17 Recursion What is Recursion? A recursive function is one that solves its task by calling itself on smaller pieces of data. Similar to recurrence function in mathematics. Like iteration -- can
Chapter 17 Recursion What is Recursion? A recursive function is one that solves its task by calling itself on smaller pieces of data. Similar to recurrence function in mathematics. Like iteration -- can
Programming II (CS300)
 1 Programming II (CS300) Chapter 10 Recursion and Search MOUNA KACEM mouna@cs.wisc.edu Spring 2019 Recursion: General Overview 2 Recursion in Algorithms Recursion is the use of recursive algorithms to
1 Programming II (CS300) Chapter 10 Recursion and Search MOUNA KACEM mouna@cs.wisc.edu Spring 2019 Recursion: General Overview 2 Recursion in Algorithms Recursion is the use of recursive algorithms to
Recursion Chapter 17. Instructor: Scott Kristjanson CMPT 125/125 SFU Burnaby, Fall 2013
 Recursion Chapter 17 Instructor: Scott Kristjanson CMPT 125/125 SFU Burnaby, Fall 2013 2 Scope Introduction to Recursion: The concept of recursion Recursive methods Infinite recursion When to use (and
Recursion Chapter 17 Instructor: Scott Kristjanson CMPT 125/125 SFU Burnaby, Fall 2013 2 Scope Introduction to Recursion: The concept of recursion Recursive methods Infinite recursion When to use (and
CMSC 132: Object-Oriented Programming II. Recursive Algorithms. Department of Computer Science University of Maryland, College Park
 CMSC 132: Object-Oriented Programming II Recursive Algorithms Department of Computer Science University of Maryland, College Park Recursion Recursion is a strategy for solving problems A procedure that
CMSC 132: Object-Oriented Programming II Recursive Algorithms Department of Computer Science University of Maryland, College Park Recursion Recursion is a strategy for solving problems A procedure that
Jalil Boudjadar, Tommy Färnqvist. IDA, Linköping University
 Lecture 15 Recursion TDDD86: DALP Print version of the lecture Data structures, algorithms and programming paradigms 1 november 2016 Jalil Boudjadar, Tommy Färnqvist. IDA, Linköping University 15.1 Content
Lecture 15 Recursion TDDD86: DALP Print version of the lecture Data structures, algorithms and programming paradigms 1 november 2016 Jalil Boudjadar, Tommy Färnqvist. IDA, Linköping University 15.1 Content
Recursion Chapter 3.5
 Recursion Chapter 3.5-1 - Outline Induction Linear recursion Example 1: Factorials Example 2: Powers Example 3: Reversing an array Binary recursion Example 1: The Fibonacci sequence Example 2: The Tower
Recursion Chapter 3.5-1 - Outline Induction Linear recursion Example 1: Factorials Example 2: Powers Example 3: Reversing an array Binary recursion Example 1: The Fibonacci sequence Example 2: The Tower
Chapter 12 Supplement: Recursion with Java 1.5. Mr. Dave Clausen La Cañada High School
 Chapter 12 Supplement: Recursion with Java 1.5 La Cañada High School Recursion: Definitions Recursion The process of a subprogram (method) calling itself. A clearly defined stopping state must exist. The
Chapter 12 Supplement: Recursion with Java 1.5 La Cañada High School Recursion: Definitions Recursion The process of a subprogram (method) calling itself. A clearly defined stopping state must exist. The
Recursion. Jordi Cortadella Department of Computer Science
 Recursion Jordi Cortadella Department of Computer Science Recursion Introduction to Programming Dept. CS, UPC 2 Principle: Reduce a complex problem into a simpler instance of the same problem Recursion
Recursion Jordi Cortadella Department of Computer Science Recursion Introduction to Programming Dept. CS, UPC 2 Principle: Reduce a complex problem into a simpler instance of the same problem Recursion
1.7 Recursion. Department of CSE
 1.7 Recursion 1 Department of CSE Objectives To learn the concept and usage of Recursion in C Examples of Recursion in C 2 Department of CSE What is recursion? Sometimes, the best way to solve a problem
1.7 Recursion 1 Department of CSE Objectives To learn the concept and usage of Recursion in C Examples of Recursion in C 2 Department of CSE What is recursion? Sometimes, the best way to solve a problem
recursive algorithms 1
 COMP 250 Lecture 11 recursive algorithms 1 Oct. 2, 2017 1 Example 1: Factorial (iterative)! = 1 2 3 1 factorial( n ){ // assume n >= 1 result = 1 for (k = 2; k
COMP 250 Lecture 11 recursive algorithms 1 Oct. 2, 2017 1 Example 1: Factorial (iterative)! = 1 2 3 1 factorial( n ){ // assume n >= 1 result = 1 for (k = 2; k
CSE 2123 Recursion. Jeremy Morris
 CSE 2123 Recursion Jeremy Morris 1 Past Few Weeks For the past few weeks we have been focusing on data structures Classes & Object-oriented programming Collections Lists, Sets, Maps, etc. Now we turn our
CSE 2123 Recursion Jeremy Morris 1 Past Few Weeks For the past few weeks we have been focusing on data structures Classes & Object-oriented programming Collections Lists, Sets, Maps, etc. Now we turn our
Recursion. Example R1
 Recursion Certain computer problems are solved by repeating the execution of one or more statements a certain number of times. So far, we have implemented the repetition of one or more statements by using
Recursion Certain computer problems are solved by repeating the execution of one or more statements a certain number of times. So far, we have implemented the repetition of one or more statements by using
Chapter 18 Recursion. Motivations
 Chapter 18 Recursion CS1: Java Programming Colorado State University Original slides by Daniel Liang Modified slides by Chris Wilcox 1 Motivations Suppose you want to find all the files under a directory
Chapter 18 Recursion CS1: Java Programming Colorado State University Original slides by Daniel Liang Modified slides by Chris Wilcox 1 Motivations Suppose you want to find all the files under a directory
מבוא לתכנות ב- JAVA תרגול 7
 מבוא לתכנות ב- JAVA תרגול 7 רקורסיה - הקדמה הגדרה רקורסיבית: חדר הוא מסודר אם צד שמאל שלו מסודר שלו מסודר. וצד ימין שיטת פתרון רקורסיבית: פתרון מופעים פשוטים יותר של בעיה בכדי לפתור את הבעיה המקורית רקורסיה
מבוא לתכנות ב- JAVA תרגול 7 רקורסיה - הקדמה הגדרה רקורסיבית: חדר הוא מסודר אם צד שמאל שלו מסודר שלו מסודר. וצד ימין שיטת פתרון רקורסיבית: פתרון מופעים פשוטים יותר של בעיה בכדי לפתור את הבעיה המקורית רקורסיה
Programming II (CS300)
 1 Programming II (CS300) Chapter 10 Recursion and Search MOUNA KACEM Recursion: General Overview 2 Recursion in Algorithms Recursion is the use of recursive algorithms to solve a problem A recursive algorithm
1 Programming II (CS300) Chapter 10 Recursion and Search MOUNA KACEM Recursion: General Overview 2 Recursion in Algorithms Recursion is the use of recursive algorithms to solve a problem A recursive algorithm
Sorting & Searching (and a Tower)
 Sorting & Searching (and a Tower) Sorting Sorting is the process of arranging a list of items into a particular order There must be some value on which the order is based There are many algorithms for
Sorting & Searching (and a Tower) Sorting Sorting is the process of arranging a list of items into a particular order There must be some value on which the order is based There are many algorithms for
EE 368. Weeks 4 (Notes)
 EE 368 Weeks 4 (Notes) 1 Read Chapter 3 Recursion and Backtracking Recursion - Recursive Definition - Some Examples - Pros and Cons A Class of Recursive Algorithms (steps or mechanics about performing
EE 368 Weeks 4 (Notes) 1 Read Chapter 3 Recursion and Backtracking Recursion - Recursive Definition - Some Examples - Pros and Cons A Class of Recursive Algorithms (steps or mechanics about performing
CMPS 12A Winter 2006 Prof. Scott A. Brandt Final Exam, March 21, Name:
 CMPS 12A Winter 2006 Prof. Scott A. Brandt Final Exam, March 21, 2006 Name: Email: This is a closed note, closed book exam. There are II sections worth a total of 200 points. Plan your time accordingly.
CMPS 12A Winter 2006 Prof. Scott A. Brandt Final Exam, March 21, 2006 Name: Email: This is a closed note, closed book exam. There are II sections worth a total of 200 points. Plan your time accordingly.
Wednesday January 31, 2:30-4pm ENGMC 103
 Academic Forum Wednesday January 31, 2:30-4pm ENGMC 103 The academic forum is an opportunity for students to provide feedback to the department on all aspects of the undergraduate academic experience,
Academic Forum Wednesday January 31, 2:30-4pm ENGMC 103 The academic forum is an opportunity for students to provide feedback to the department on all aspects of the undergraduate academic experience,
Recursive Thinking. Chapter 8: Recursion. Recursive Definitions. Recursion. Java Software Solutions for AP* Computer Science A 2nd Edition
 Chapter 8: Recursion Presentation slides for Recursive Thinking Recursion is a programming technique in which a method can call itself to solve a problem Java Software Solutions for AP* Computer Science
Chapter 8: Recursion Presentation slides for Recursive Thinking Recursion is a programming technique in which a method can call itself to solve a problem Java Software Solutions for AP* Computer Science
q To develop recursive methods for recursive mathematical functions ( ).
 Chapter 8 Recursion CS: Java Programming Colorado State University Motivations Suppose you want to find all the files under a directory that contains a particular word. How do you solve this problem? There
Chapter 8 Recursion CS: Java Programming Colorado State University Motivations Suppose you want to find all the files under a directory that contains a particular word. How do you solve this problem? There
q To develop recursive methods for recursive mathematical functions ( ).
 /2/8 Chapter 8 Recursion CS: Java Programming Colorado State University Motivations Suppose you want to find all the files under a directory that contains a particular word. How do you solve this problem?
/2/8 Chapter 8 Recursion CS: Java Programming Colorado State University Motivations Suppose you want to find all the files under a directory that contains a particular word. How do you solve this problem?
Programming II (CS300)
 1 Programming II (CS300) Chapter 9 (Part II) Recursion MOUNA KACEM Recursion: General Overview 2 Recursion in Algorithms Recursion is the use of recursive algorithms to solve a problem A recursive algorithm
1 Programming II (CS300) Chapter 9 (Part II) Recursion MOUNA KACEM Recursion: General Overview 2 Recursion in Algorithms Recursion is the use of recursive algorithms to solve a problem A recursive algorithm
CSE 230 Intermediate Programming in C and C++ Recursion
 CSE 230 Intermediate Programming in C and C++ Recursion Fall 2017 Stony Brook University Instructor: Shebuti Rayana What is recursion? Sometimes, the best way to solve a problem is by solving a smaller
CSE 230 Intermediate Programming in C and C++ Recursion Fall 2017 Stony Brook University Instructor: Shebuti Rayana What is recursion? Sometimes, the best way to solve a problem is by solving a smaller
Recursion. Thinking Recursively. Tracing the Recursive Definition of List. CMPT 126: Lecture 10. Recursion
 Recursion CMPT 126: Lecture 10 Recursion Tamara Smyth, tamaras@cs.sfu.ca School of Computing Science, Simon Fraser University October 25, 2007 Recursion is the process of defining something in terms of
Recursion CMPT 126: Lecture 10 Recursion Tamara Smyth, tamaras@cs.sfu.ca School of Computing Science, Simon Fraser University October 25, 2007 Recursion is the process of defining something in terms of
Iteration statements - Loops
 Iteration statements - Loops : ) הוראות חזרה / לולאות ( statements Java has three kinds of iteration WHILE FOR DO... WHILE loop loop loop Iteration (repetition) statements causes Java to execute one or
Iteration statements - Loops : ) הוראות חזרה / לולאות ( statements Java has three kinds of iteration WHILE FOR DO... WHILE loop loop loop Iteration (repetition) statements causes Java to execute one or
1.00 Introduction to Computers and Engineering Problem Solving. Quiz 1 March 7, 2003
 1.00 Introduction to Computers and Engineering Problem Solving Quiz 1 March 7, 2003 Name: Email Address: TA: Section: You have 90 minutes to complete this exam. For coding questions, you do not need to
1.00 Introduction to Computers and Engineering Problem Solving Quiz 1 March 7, 2003 Name: Email Address: TA: Section: You have 90 minutes to complete this exam. For coding questions, you do not need to
CmpSci 187: Programming with Data Structures Spring 2015
 CmpSci 187: Programming with Data Structures Spring 2015 Lecture #9 John Ridgway February 26, 2015 1 Recursive Definitions, Algorithms, and Programs Recursion in General In mathematics and computer science
CmpSci 187: Programming with Data Structures Spring 2015 Lecture #9 John Ridgway February 26, 2015 1 Recursive Definitions, Algorithms, and Programs Recursion in General In mathematics and computer science
What is an algorithm?
 /0/ What is an algorithm? Searching and Sorting (Savitch, Chapter 7.) TOPICS Algorithms Complexity Binary Search Bubble Sort Insertion Sort Selection Sort A finite set of precise instrucons for performing
/0/ What is an algorithm? Searching and Sorting (Savitch, Chapter 7.) TOPICS Algorithms Complexity Binary Search Bubble Sort Insertion Sort Selection Sort A finite set of precise instrucons for performing
CS103L SPRING 2017 UNIT 8: RECURSION
 CS103L SPRING 2017 UNIT 8: RECURSION RECURSION A recursion function is defined in terms of itself Applies to math, e.g. recursion relations, sequences Fibonacci: F 0 = 1, F 1 = 1, F n = F n-1 + F n-2 Applies
CS103L SPRING 2017 UNIT 8: RECURSION RECURSION A recursion function is defined in terms of itself Applies to math, e.g. recursion relations, sequences Fibonacci: F 0 = 1, F 1 = 1, F n = F n-1 + F n-2 Applies
CSE 214 Computer Science II Recursion
 CSE 214 Computer Science II Recursion Fall 2017 Stony Brook University Instructor: Shebuti Rayana shebuti.rayana@stonybrook.edu http://www3.cs.stonybrook.edu/~cse214/sec02/ Introduction Basic design technique
CSE 214 Computer Science II Recursion Fall 2017 Stony Brook University Instructor: Shebuti Rayana shebuti.rayana@stonybrook.edu http://www3.cs.stonybrook.edu/~cse214/sec02/ Introduction Basic design technique
Notes - Recursion. A geeky definition of recursion is as follows: Recursion see Recursion.
 Notes - Recursion So far we have only learned how to solve problems iteratively using loops. We will now learn how to solve problems recursively by having a method call itself. A geeky definition of recursion
Notes - Recursion So far we have only learned how to solve problems iteratively using loops. We will now learn how to solve problems recursively by having a method call itself. A geeky definition of recursion
CMSC 150 LECTURE 7 RECURSION
 CMSC 150 INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTING ACKNOWLEDGEMENT: THESE SLIDES ARE ADAPTED FROM SLIDES PROVIDED WITH INTRODUCTION TO PROGRAMMING IN JAVA: AN INTERDISCIPLINARY APPROACH, SEDGEWICK AND WAYNE (PEARSON ADDISON-WESLEY
CMSC 150 INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTING ACKNOWLEDGEMENT: THESE SLIDES ARE ADAPTED FROM SLIDES PROVIDED WITH INTRODUCTION TO PROGRAMMING IN JAVA: AN INTERDISCIPLINARY APPROACH, SEDGEWICK AND WAYNE (PEARSON ADDISON-WESLEY
Recursive Methods and Problem Solving. Chris Kiekintveld CS 2401 (Fall 2010) Elementary Data Structures and Algorithms
 Recursive Methods and Problem Solving Chris Kiekintveld CS 2401 (Fall 2010) Elementary Data Structures and Algorithms Review: Calling Methods int x(int n) { int m = 0; n = n + m + 1; return n; int y(int
Recursive Methods and Problem Solving Chris Kiekintveld CS 2401 (Fall 2010) Elementary Data Structures and Algorithms Review: Calling Methods int x(int n) { int m = 0; n = n + m + 1; return n; int y(int
Recursion (Rosen, 6 th edition, Section 4.3, 4.4)
 Recursion (Rosen, 6 th edition, Section 4.3, 4.4) Carol Zander For recursion, the focus is mostly on recursive algorithms. While recursive definitions will sometimes be used in definitions (you already
Recursion (Rosen, 6 th edition, Section 4.3, 4.4) Carol Zander For recursion, the focus is mostly on recursive algorithms. While recursive definitions will sometimes be used in definitions (you already
Recursion. Dr. Jürgen Eckerle FS Recursive Functions
 Recursion Dr. Jürgen Eckerle FS 2008 Recursive Functions Recursion, in mathematics and computer science, is a method of defining functions in which the function being defined is applied within its own
Recursion Dr. Jürgen Eckerle FS 2008 Recursive Functions Recursion, in mathematics and computer science, is a method of defining functions in which the function being defined is applied within its own
CSE 143 Lecture 11. Decimal Numbers
 CSE 143 Lecture 11 Recursive Programming slides created by Marty Stepp http://www.cs.washington.edu/143/ Decimal Numbers A visual review of decimal numbers: We get 348 by adding powers of 10 348 = 300
CSE 143 Lecture 11 Recursive Programming slides created by Marty Stepp http://www.cs.washington.edu/143/ Decimal Numbers A visual review of decimal numbers: We get 348 by adding powers of 10 348 = 300
 www.thestudycampus.com Recursion Recursion is a process for solving problems by subdividing a larger problem into smaller cases of the problem itself and then solving the smaller, more trivial parts. Recursion
www.thestudycampus.com Recursion Recursion is a process for solving problems by subdividing a larger problem into smaller cases of the problem itself and then solving the smaller, more trivial parts. Recursion
CSC 273 Data Structures
 CSC 273 Data Structures Lecture 4- Recursion What Is Recursion? Consider hiring a contractor to build He hires a subcontractor for a portion of the job That subcontractor hires a sub-subcontractor to do
CSC 273 Data Structures Lecture 4- Recursion What Is Recursion? Consider hiring a contractor to build He hires a subcontractor for a portion of the job That subcontractor hires a sub-subcontractor to do
Top-down programming design
 1 Top-down programming design Top-down design is a programming style, the mainstay of traditional procedural languages, in which design begins by specifying complex pieces and then dividing them into successively
1 Top-down programming design Top-down design is a programming style, the mainstay of traditional procedural languages, in which design begins by specifying complex pieces and then dividing them into successively
COMP-202. Recursion. COMP Recursion, 2013 Jörg Kienzle and others
 COMP-202 Recursion Recursion Recursive Definitions Run-time Stacks Recursive Programming Recursion vs. Iteration Indirect Recursion Lecture Outline 2 Recursive Definitions (1) A recursive definition is
COMP-202 Recursion Recursion Recursive Definitions Run-time Stacks Recursive Programming Recursion vs. Iteration Indirect Recursion Lecture Outline 2 Recursive Definitions (1) A recursive definition is
NCS 301 DATA STRUCTURE USING C
 NCS 301 DATA STRUCTURE USING C Unit-1 Part-2 Recursion Hammad Mashkoor Lari Assistant Professor Allenhouse Institute of Technology www.ncs301ds.wordpress.com Introduction Recursion is defined as defining
NCS 301 DATA STRUCTURE USING C Unit-1 Part-2 Recursion Hammad Mashkoor Lari Assistant Professor Allenhouse Institute of Technology www.ncs301ds.wordpress.com Introduction Recursion is defined as defining
Search,Sort,Recursion
 Search,Sort,Recursion Searching, Sorting and Recursion Searching Linear Search Inserting into an Array Deleting from an Array Selection Sort Bubble Sort Binary Search Recursive Binary Search Searching
Search,Sort,Recursion Searching, Sorting and Recursion Searching Linear Search Inserting into an Array Deleting from an Array Selection Sort Bubble Sort Binary Search Recursive Binary Search Searching
STUDENT LESSON A12 Iterations
 STUDENT LESSON A12 Iterations Java Curriculum for AP Computer Science, Student Lesson A12 1 STUDENT LESSON A12 Iterations INTRODUCTION: Solving problems on a computer very often requires a repetition of
STUDENT LESSON A12 Iterations Java Curriculum for AP Computer Science, Student Lesson A12 1 STUDENT LESSON A12 Iterations INTRODUCTION: Solving problems on a computer very often requires a repetition of
CIS Introduction to Computer Programming Spring Exam 1
 CIS 110 - Introduction to Computer Programming Spring 2017 - Exam 1 Name: Recitation (e.g. 201): PennKey (e.g. eeaton): My signature below certifies that I have complied with the University of Pennsylvania
CIS 110 - Introduction to Computer Programming Spring 2017 - Exam 1 Name: Recitation (e.g. 201): PennKey (e.g. eeaton): My signature below certifies that I have complied with the University of Pennsylvania
COMP 250 Fall Recursive algorithms 1 Oct. 2, 2017
 Recursion Recursion is a technique for solving problems in which the solution to the problem of size n is based on solutions to versions of the problem of size smaller than n. Many problems can be solved
Recursion Recursion is a technique for solving problems in which the solution to the problem of size n is based on solutions to versions of the problem of size smaller than n. Many problems can be solved
SOFTWARE DEVELOPMENT 1. Recursion 2018W A. Ferscha (Institute of Pervasive Computing, JKU Linz)
 SOFTWARE DEVELOPMENT 1 Recursion 2018W (Institute of Pervasive Computing, JKU Linz) PRINCIPLE OF SELF-REFERENCE Recursion: Describing something in a self-similar way. An elegant, powerful and simple way
SOFTWARE DEVELOPMENT 1 Recursion 2018W (Institute of Pervasive Computing, JKU Linz) PRINCIPLE OF SELF-REFERENCE Recursion: Describing something in a self-similar way. An elegant, powerful and simple way
CS/CE 2336 Computer Science II
 S/E 2336 omputer Science II UT D Session 10 Recursion dapted from D Liang s Introduction to Java Programming, 8 th Ed 2 factorial(0) = 1; omputing Factorial factorial(n) = n*factorial(n-1); n! = n * (n-1)!
S/E 2336 omputer Science II UT D Session 10 Recursion dapted from D Liang s Introduction to Java Programming, 8 th Ed 2 factorial(0) = 1; omputing Factorial factorial(n) = n*factorial(n-1); n! = n * (n-1)!
Searching and Sorting (Savitch, Chapter 7.4)
 Searching and Sorting (Savitch, Chapter 7.4) TOPICS Algorithms Complexity Binary Search Bubble Sort Insertion Sort Selection Sort What is an algorithm? A finite set of precise instruc6ons for performing
Searching and Sorting (Savitch, Chapter 7.4) TOPICS Algorithms Complexity Binary Search Bubble Sort Insertion Sort Selection Sort What is an algorithm? A finite set of precise instruc6ons for performing
Two Approaches to Algorithms An Example (1) Iteration (2) Recursion
 2. Recursion Algorithm Two Approaches to Algorithms (1) Iteration It exploits while-loop, for-loop, repeat-until etc. Classical, conventional, and general approach (2) Recursion Self-function call It exploits
2. Recursion Algorithm Two Approaches to Algorithms (1) Iteration It exploits while-loop, for-loop, repeat-until etc. Classical, conventional, and general approach (2) Recursion Self-function call It exploits
1 P a g e A r y a n C o l l e g e \ B S c _ I T \ C \
 BSc IT C Programming (2013-2017) Unit I Q1. What do you understand by type conversion? (2013) Q2. Why we need different data types? (2013) Q3 What is the output of the following (2013) main() Printf( %d,
BSc IT C Programming (2013-2017) Unit I Q1. What do you understand by type conversion? (2013) Q2. Why we need different data types? (2013) Q3 What is the output of the following (2013) main() Printf( %d,
KF5008 Algorithm Efficiency; Sorting and Searching Algorithms;
 KF5008 Algorithm Efficiency; Sorting and Searching Algorithms; Efficiency: Principles An algorithm is a step-by-step procedure for solving a stated problem. The algorithm will be performed by a processor
KF5008 Algorithm Efficiency; Sorting and Searching Algorithms; Efficiency: Principles An algorithm is a step-by-step procedure for solving a stated problem. The algorithm will be performed by a processor
Recursive Algorithms. CS 180 Sunil Prabhakar Department of Computer Science Purdue University
 Recursive Algorithms CS 180 Sunil Prabhakar Department of Computer Science Purdue University Recursive Algorithms Within a given method, we are allowed to call other accessible methods. It is also possible
Recursive Algorithms CS 180 Sunil Prabhakar Department of Computer Science Purdue University Recursive Algorithms Within a given method, we are allowed to call other accessible methods. It is also possible
We cover recursion in 150. Why do it again in 151?
 Recursion We cover recursion in 150. Why do it again in 151? First, good solutions to problems are often recursive. Here is a quick way to sort a list of objects: split the list in half, recursively sort
Recursion We cover recursion in 150. Why do it again in 151? First, good solutions to problems are often recursive. Here is a quick way to sort a list of objects: split the list in half, recursively sort
Chapter 13. Recursion. Copyright 2016 Pearson, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 13 Recursion Copyright 2016 Pearson, Inc. All rights reserved. Learning Objectives Recursive void Functions Tracing recursive calls Infinite recursion, overflows Recursive Functions that Return
Chapter 13 Recursion Copyright 2016 Pearson, Inc. All rights reserved. Learning Objectives Recursive void Functions Tracing recursive calls Infinite recursion, overflows Recursive Functions that Return
Outline. Simple Recursive Examples Analyzing Recursion Sorting The Tower of Hanoi Divide-and-conquer Approach In-Class Work. 1 Chapter 6: Recursion
 Outline 1 A Function Can Call Itself A recursive definition of a function is one which makes a function call to the function being defined. The function call is then a recursive function call. A definition
Outline 1 A Function Can Call Itself A recursive definition of a function is one which makes a function call to the function being defined. The function call is then a recursive function call. A definition
12/30/2013 S. NALINI,AP/CSE
 12/30/2013 S. NALINI,AP/CSE 1 UNIT I ITERATIVE AND RECURSIVE ALGORITHMS Iterative Algorithms: Measures of Progress and Loop Invariants-Paradigm Shift: Sequence of Actions versus Sequence of Assertions-
12/30/2013 S. NALINI,AP/CSE 1 UNIT I ITERATIVE AND RECURSIVE ALGORITHMS Iterative Algorithms: Measures of Progress and Loop Invariants-Paradigm Shift: Sequence of Actions versus Sequence of Assertions-
