ALGOL 48 AND ALGOL 50 ALGOLIC LANGUAGES IN MATHE- MATICS
|
|
|
- Charity Washington
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ALGOL 48 AND ALGOL 50 ALGOLIC LANGUAGES IN MATHE- MATICS Abstract This article describes how to express programs with assignment statements and conditional go tos in mathematical logic without any programming constructs used in Fortran and Algol. The names come from imagining mathematicians devising a programming language in 1948 and elaborating it in There are just two innovations regarding the values of variables as functions, of a natural number valued time, e.g. x(t) instead of a program variable x, and regarding a program counter pc(t) as just another variable. This way of writing programs has a number of advantages. One is that statements and proofs of correctness are just ordinary proofs in the domain of variables supplemented by Peano arithmetic. We introduce the programming languages Algol 48 and Algol 50 to illustrate in a simpler setting some ideas to be used in Elephant These are the explicit use of time in a programming language and the representation of the program by logical sentences. The former permits a direct expression of the operational semantics of the language, and the latter permits proofs of properties of programs without any special theory of programming. The properties are deduced from the program itself together with axioms for the domain. We use these names, because the languages cover some of the ground of Algol 60 but use only a mathematical formalism old fashioned recursion equations that precedes the development of programming languages. They are programming languages I imagine mathematicians might have created in 1950 had they seen the need for something other than machine language. Algol 48 is a preliminary version of Algol 50 just as Algol 58 was a preliminary version of Algol 60. Consider the Algol 60 fragment. 1
2 0 start : p := 0; 1 i := n; 2 loop : if i = 0 then go to done; 3 p := p + m; 4 i := i 1; 5 go to loop; 6 done : The program computes the product mn by initializing a partial product p to 0 and then adding m to it n times. The correctness of the Algol 60 program is represented by the statement that if the program is entered at start it will reach the label done, and when it does, the variable p will have the value mn. Different program verification formalisms represent this assertion in various ways, often not entirely formal. Its partial correctness is conventionally proved by attaching the invariant assertion p = m(n i) to the label loop. Its termination is proved by noting that the variable i starts out with the value n and counts down to 0. This proof is expressed in various ways in the different formalisms for verifying programs. 0.1 Algol 48 In Algol 48 we write this algorithm as a set of old fashioned recursion equations for three functions of time, namely p(t), i(t) and pc(t), where the first two correspond to the variables in the program, and pc(t) tells how the program counter changes. The only ideas that would have been unconventional in 1948 are the explicit use of a program counter and the conditional expressions. We have p(t + 1) = if pc(t) = 0 then 0 else if pc(t) = 3 then p(t) + m else p(t),. and i(t + 1) = if pc(t) = 1 then n else if pc(t) = 4 then i(t) 1 else i(t), 2
3 pc(t + 1) = if pc(t) = 2 i(t) = 0 then 6 else if pc(t) = 5 then 2 else pc(t) + 1. The correctness of the Algol 48 program is represented by the sentence m n(n 0 t(pc(t) = 0 t (t > t pc(t ) = 6 p(t ) = mn))) This sentence may be proved from the sentences representing the program supplemented by the axioms of arithmetic and the axiom schema of mathematical induction. No special theory of programming is required. The easiest proof uses mathematical induction on n applied to a formula involving p(t) = m(n i(t)). Algol 48 programs are organized quite differently from Algol 60 programs. Namely, the changes to variables are sorted by variable rather than sequentially by time. 0.2 Algol 50 However, by reifying variables, Algol 50 permits writing programs in a way that permits regarding programs in this fragment of Algol 60 as just sugared versions of Algol 50 programs. Instead of writing var(t) for some variable var, we write value(var, ξ(t)), where ξ is a state vector giving the values of all the variables. In the above program, we ll have value(p, ξ(t)), value(i, ξ(t)) and value(pc, ξ(t)). The variables of the Algol 60 program correspond to functions of time in the above first Algol 50 version and become distinct constant symbols in the version of Algol 50 with reified variables. Their distinctness is made explicit by the unique names axiom i p i pc p pc. In expressing the program we use the assignment and contents functions, a(var, value, ξ) and c(var, ξ), of (McCarthy 1963) and (McCarthy and Painter 1967). a(var, value, ξ) is the new state ξ that results when the variable var is assigned the value value in state ξ. c(var, ξ) is the value of var in state ξ. 3
4 As described in those papers the functions a and c satisfy the axioms. c(var, a(var, val, ξ)) = val, and var1 var2 c(var2, a(var1, val, ξ)) = c(var2, ξ), a(var, val2, a(var, val1, ξ)) = a(var, val2, ξ), var1 var2 a(var2, val2, a(var1, val1, ξ)) = a(var1, val1, a(var2, val2, ξ)). The following function definitions shorten the expression of programs. Note that they are just function definitions and not special constructs. step(ξ) = a(pc, value(pc, ξ) + 1, ξ), goto(label, ξ) = a(pc, label, ξ). We make the further abbreviation loop = start + 2 specially for this program, and with this notation our program becomes t (ξ(t + 1) = if c(pc, ξ(t)) = start then step a(p, 0, ξ(t)) else if c(pc, ξ(t)) = start + 1 then step a(i, n, ξ(t)) else if c(pc, ξ(t)) = loop then (if c(i, ξ(t)) = 0 then goto(done, ξ(t)) else step ξ(t)) else if c(pc, ξ(t)) = loop + 1 then step a(p, c(p, ξ(t)) + m, ξ(t)) else if c(pc, ξ(t)) = loop + 2 then step a(i, c(i, ξ(t)) 1, ξ(t)) else if c(pc, ξ(t)) = loop + 3 then goto(loop, ξ(t)) else ξ(t + 1)) In Algol 50, the consequents of the clauses of the conditional expression are in 1-1 correspondence with the statements of the corresponding Algol 60 4
5 program. Therefore, the Algol 60 program can be regarded as an abbreviation of the corresponding Algol 50 program. The (operational) semantics of the Algol 60 program is then given by the sentence expressing the corresponding Algol 50 program together with the axioms describing the data domain, which in this case would be the Peano axioms for natural numbers. The transformation to go from Algol 60 to Algol 50 would be entirely local, i.e. statement by statement, were it not for the need to use statement numbers explicitly in Algol 50. Program fragments can be combined into larger fragments by taking the conjunction of the sentences representing them, identifying labels where this is wanted to achieve a go to from one fragment to another and adding sentences to make sure that the program counter ranges don t overlap. The correctness of the Algol 50 program for multiplication by addition is expressed by tξ 0 (c(pc, ξ(t)) = start ξ(t) = ξ 0 t (t > t c(p, ξ(t )) = mn c(pc, ξ(t )) = done var( (var {p, i, pc}) c(var, ξ(t )) = c(var, ξ 0 )))) Note that we quantify over all initial state vectors. The last part of the correctness formula states that the program fragment doesn t alter the state vector other than by altering p, i and pc. We have not carried the Algol 50 idea far enough to verify that all of Algol 60 is conveniently representable in the same style, but no fundamental difficulties are apparent. In treating recursive procedures, a stack can be introduced, but it would be more elegant to do without it by explicitly saying that the return is to the statement after the corresponding procedure call and variables are restored to their values at the time of the call. This requires the ability to parse the past, needed also for Elephant We advocate an extended Algol 50 for expressing the operational semantics of Algol-like programming languages, i.e. for describing the sequence of events that occurs when the program is executed. However, our present application is just to illustrate in a simpler setting some features that Elephant will require. In particular, proper treatment of calling a function procedure with side-effects will require a state that can have a value during the evaluation of an expression. Nissim Francez and Amir Pnueli (see references) used an explicit time for similar purposes. Unfortunately, they abandoned it for temporal logic. 5
6 While some kinds of temporal logic are decidable, temporal logic is too weak to express many important properties of programs. 6
SOME LISP HISTORY AND SOME PROGRAM LANGUAGE IDEAS John McCarthy, Stanford University Berlin, 2002 June 19
 SOME LISP HISTORY AND SOME PROGRAM LANGUAGE IDEAS John McCarthy, Stanford University Berlin, 2002 June 19 I suppose I m here because of Lisp, although I hav involved in the Lisp community for a very long
SOME LISP HISTORY AND SOME PROGRAM LANGUAGE IDEAS John McCarthy, Stanford University Berlin, 2002 June 19 I suppose I m here because of Lisp, although I hav involved in the Lisp community for a very long
Programming Languages Third Edition
 Programming Languages Third Edition Chapter 12 Formal Semantics Objectives Become familiar with a sample small language for the purpose of semantic specification Understand operational semantics Understand
Programming Languages Third Edition Chapter 12 Formal Semantics Objectives Become familiar with a sample small language for the purpose of semantic specification Understand operational semantics Understand
Introduction to Axiomatic Semantics
 Introduction to Axiomatic Semantics Meeting 10, CSCI 5535, Spring 2009 Announcements Homework 3 due tonight Homework 2 is graded 13 (mean), 14 (median), out of 21 total, but Graduate class: final project
Introduction to Axiomatic Semantics Meeting 10, CSCI 5535, Spring 2009 Announcements Homework 3 due tonight Homework 2 is graded 13 (mean), 14 (median), out of 21 total, but Graduate class: final project
AXIOMS OF AN IMPERATIVE LANGUAGE PARTIAL CORRECTNESS WEAK AND STRONG CONDITIONS. THE AXIOM FOR nop
 AXIOMS OF AN IMPERATIVE LANGUAGE We will use the same language, with the same abstract syntax that we used for operational semantics. However, we will only be concerned with the commands, since the language
AXIOMS OF AN IMPERATIVE LANGUAGE We will use the same language, with the same abstract syntax that we used for operational semantics. However, we will only be concerned with the commands, since the language
3.7 Denotational Semantics
 3.7 Denotational Semantics Denotational semantics, also known as fixed-point semantics, associates to each programming language construct a well-defined and rigorously understood mathematical object. These
3.7 Denotational Semantics Denotational semantics, also known as fixed-point semantics, associates to each programming language construct a well-defined and rigorously understood mathematical object. These
Theorem proving. PVS theorem prover. Hoare style verification PVS. More on embeddings. What if. Abhik Roychoudhury CS 6214
 Theorem proving PVS theorem prover Abhik Roychoudhury National University of Singapore Both specification and implementation can be formalized in a suitable logic. Proof rules for proving statements in
Theorem proving PVS theorem prover Abhik Roychoudhury National University of Singapore Both specification and implementation can be formalized in a suitable logic. Proof rules for proving statements in
Chapter 2 & 3: Representations & Reasoning Systems (2.2)
 Chapter 2 & 3: A Representation & Reasoning System & Using Definite Knowledge Representations & Reasoning Systems (RRS) (2.2) Simplifying Assumptions of the Initial RRS (2.3) Datalog (2.4) Semantics (2.5)
Chapter 2 & 3: A Representation & Reasoning System & Using Definite Knowledge Representations & Reasoning Systems (RRS) (2.2) Simplifying Assumptions of the Initial RRS (2.3) Datalog (2.4) Semantics (2.5)
UNIT 3
 UNIT 3 Presentation Outline Sequence control with expressions Conditional Statements, Loops Exception Handling Subprogram definition and activation Simple and Recursive Subprogram Subprogram Environment
UNIT 3 Presentation Outline Sequence control with expressions Conditional Statements, Loops Exception Handling Subprogram definition and activation Simple and Recursive Subprogram Subprogram Environment
AXIOMS FOR THE INTEGERS
 AXIOMS FOR THE INTEGERS BRIAN OSSERMAN We describe the set of axioms for the integers which we will use in the class. The axioms are almost the same as what is presented in Appendix A of the textbook,
AXIOMS FOR THE INTEGERS BRIAN OSSERMAN We describe the set of axioms for the integers which we will use in the class. The axioms are almost the same as what is presented in Appendix A of the textbook,
An Evolution of Mathematical Tools
 An Evolution of Mathematical Tools From Conceptualization to Formalization Here's what we do when we build a formal model (or do a computation): 0. Identify a collection of objects/events in the real world.
An Evolution of Mathematical Tools From Conceptualization to Formalization Here's what we do when we build a formal model (or do a computation): 0. Identify a collection of objects/events in the real world.
The Rule of Constancy(Derived Frame Rule)
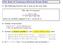 The Rule of Constancy(Derived Frame Rule) The following derived rule is used on the next slide The rule of constancy {P } C {Q} {P R} C {Q R} where no variable assigned to in C occurs in R Outline of derivation
The Rule of Constancy(Derived Frame Rule) The following derived rule is used on the next slide The rule of constancy {P } C {Q} {P R} C {Q R} where no variable assigned to in C occurs in R Outline of derivation
Chapter 3 (part 3) Describing Syntax and Semantics
 Chapter 3 (part 3) Describing Syntax and Semantics Chapter 3 Topics Introduction The General Problem of Describing Syntax Formal Methods of Describing Syntax Attribute Grammars Describing the Meanings
Chapter 3 (part 3) Describing Syntax and Semantics Chapter 3 Topics Introduction The General Problem of Describing Syntax Formal Methods of Describing Syntax Attribute Grammars Describing the Meanings
This is already grossly inconvenient in present formalisms. Why do we want to make this convenient? GENERAL GOALS
 1 THE FORMALIZATION OF MATHEMATICS by Harvey M. Friedman Ohio State University Department of Mathematics friedman@math.ohio-state.edu www.math.ohio-state.edu/~friedman/ May 21, 1997 Can mathematics be
1 THE FORMALIZATION OF MATHEMATICS by Harvey M. Friedman Ohio State University Department of Mathematics friedman@math.ohio-state.edu www.math.ohio-state.edu/~friedman/ May 21, 1997 Can mathematics be
Lectures 20, 21: Axiomatic Semantics
 Lectures 20, 21: Axiomatic Semantics Polyvios Pratikakis Computer Science Department, University of Crete Type Systems and Static Analysis Based on slides by George Necula Pratikakis (CSD) Axiomatic Semantics
Lectures 20, 21: Axiomatic Semantics Polyvios Pratikakis Computer Science Department, University of Crete Type Systems and Static Analysis Based on slides by George Necula Pratikakis (CSD) Axiomatic Semantics
The semantics of a programming language is concerned with the meaning of programs, that is, how programs behave when executed on computers.
 Semantics The semantics of a programming language is concerned with the meaning of programs, that is, how programs behave when executed on computers. The semantics of a programming language assigns a precise
Semantics The semantics of a programming language is concerned with the meaning of programs, that is, how programs behave when executed on computers. The semantics of a programming language assigns a precise
Semantics. There is no single widely acceptable notation or formalism for describing semantics Operational Semantics
 There is no single widely acceptable notation or formalism for describing semantics Operational Describe the meaning of a program by executing its statements on a machine, either simulated or actual. The
There is no single widely acceptable notation or formalism for describing semantics Operational Describe the meaning of a program by executing its statements on a machine, either simulated or actual. The
Lecture 5 - Axiomatic semantics
 Program Verification March 2014 Lecture 5 - Axiomatic semantics Lecturer: Noam Rinetzky Scribes by: Nir Hemed 1.1 Axiomatic semantics The development of the theory is contributed to Robert Floyd, C.A.R
Program Verification March 2014 Lecture 5 - Axiomatic semantics Lecturer: Noam Rinetzky Scribes by: Nir Hemed 1.1 Axiomatic semantics The development of the theory is contributed to Robert Floyd, C.A.R
Proving the Correctness of Distributed Algorithms using TLA
 Proving the Correctness of Distributed Algorithms using TLA Khushboo Kanjani, khush@cs.tamu.edu, Texas A & M University 11 May 2007 Abstract This work is a summary of the Temporal Logic of Actions(TLA)
Proving the Correctness of Distributed Algorithms using TLA Khushboo Kanjani, khush@cs.tamu.edu, Texas A & M University 11 May 2007 Abstract This work is a summary of the Temporal Logic of Actions(TLA)
Typed Lambda Calculus for Syntacticians
 Department of Linguistics Ohio State University January 12, 2012 The Two Sides of Typed Lambda Calculus A typed lambda calculus (TLC) can be viewed in two complementary ways: model-theoretically, as a
Department of Linguistics Ohio State University January 12, 2012 The Two Sides of Typed Lambda Calculus A typed lambda calculus (TLC) can be viewed in two complementary ways: model-theoretically, as a
Consider a description of arithmetic. It includes two equations that define the structural types of digit and operator:
 Syntax A programming language consists of syntax, semantics, and pragmatics. We formalize syntax first, because only syntactically correct programs have semantics. A syntax definition of a language lists
Syntax A programming language consists of syntax, semantics, and pragmatics. We formalize syntax first, because only syntactically correct programs have semantics. A syntax definition of a language lists
Typed Lambda Calculus
 Department of Linguistics Ohio State University Sept. 8, 2016 The Two Sides of A typed lambda calculus (TLC) can be viewed in two complementary ways: model-theoretically, as a system of notation for functions
Department of Linguistics Ohio State University Sept. 8, 2016 The Two Sides of A typed lambda calculus (TLC) can be viewed in two complementary ways: model-theoretically, as a system of notation for functions
Part II. Hoare Logic and Program Verification. Why specify programs? Specification and Verification. Code Verification. Why verify programs?
 Part II. Hoare Logic and Program Verification Part II. Hoare Logic and Program Verification Dilian Gurov Props: Models: Specs: Method: Tool: safety of data manipulation source code logic assertions Hoare
Part II. Hoare Logic and Program Verification Part II. Hoare Logic and Program Verification Dilian Gurov Props: Models: Specs: Method: Tool: safety of data manipulation source code logic assertions Hoare
Introduction to Automata Theory. BİL405 - Automata Theory and Formal Languages 1
 Introduction to Automata Theory BİL405 - Automata Theory and Formal Languages 1 Automata, Computability and Complexity Automata, Computability and Complexity are linked by the question: What are the fundamental
Introduction to Automata Theory BİL405 - Automata Theory and Formal Languages 1 Automata, Computability and Complexity Automata, Computability and Complexity are linked by the question: What are the fundamental
! Use of formal notations. ! in software system descriptions. ! for a broad range of effects. ! and varying levels of use. !
 What Are Formal Methods? David S. Rosenblum ICS 221 Winter 2001! Use of formal notations! first-order logic, state machines, etc.! in software system descriptions! system models, constraints, specifications,
What Are Formal Methods? David S. Rosenblum ICS 221 Winter 2001! Use of formal notations! first-order logic, state machines, etc.! in software system descriptions! system models, constraints, specifications,
Handout 9: Imperative Programs and State
 06-02552 Princ. of Progr. Languages (and Extended ) The University of Birmingham Spring Semester 2016-17 School of Computer Science c Uday Reddy2016-17 Handout 9: Imperative Programs and State Imperative
06-02552 Princ. of Progr. Languages (and Extended ) The University of Birmingham Spring Semester 2016-17 School of Computer Science c Uday Reddy2016-17 Handout 9: Imperative Programs and State Imperative
A short manual for the tool Accumulator
 A short manual for the tool Accumulator ZHAO Jianhua State Key Laboratory of Novel Software Technology Dept. of Computer Sci. and Tech. Nanjing University Nanjing, Jiangsu, P.R.China 210093 zhaojh@nju.edu.cn
A short manual for the tool Accumulator ZHAO Jianhua State Key Laboratory of Novel Software Technology Dept. of Computer Sci. and Tech. Nanjing University Nanjing, Jiangsu, P.R.China 210093 zhaojh@nju.edu.cn
3.4 Deduction and Evaluation: Tools Conditional-Equational Logic
 3.4 Deduction and Evaluation: Tools 3.4.1 Conditional-Equational Logic The general definition of a formal specification from above was based on the existence of a precisely defined semantics for the syntax
3.4 Deduction and Evaluation: Tools 3.4.1 Conditional-Equational Logic The general definition of a formal specification from above was based on the existence of a precisely defined semantics for the syntax
6. Hoare Logic and Weakest Preconditions
 6. Hoare Logic and Weakest Preconditions Program Verification ETH Zurich, Spring Semester 07 Alexander J. Summers 30 Program Correctness There are many notions of correctness properties for a given program
6. Hoare Logic and Weakest Preconditions Program Verification ETH Zurich, Spring Semester 07 Alexander J. Summers 30 Program Correctness There are many notions of correctness properties for a given program
Formal Systems II: Applications
 Formal Systems II: Applications Functional Verification of Java Programs: Java Dynamic Logic Bernhard Beckert Mattias Ulbrich SS 2017 KIT INSTITUT FÜR THEORETISCHE INFORMATIK KIT University of the State
Formal Systems II: Applications Functional Verification of Java Programs: Java Dynamic Logic Bernhard Beckert Mattias Ulbrich SS 2017 KIT INSTITUT FÜR THEORETISCHE INFORMATIK KIT University of the State
Axiomatic Specification. Al-Said, Apcar, Jerejian
 Axiomatic Specification Al-Said, Apcar, Jerejian 1 Axioms: Wffs that can be written down without any reference to any other Wffs. Wffs that are stipulated as unproved premises for the proof of other wffs
Axiomatic Specification Al-Said, Apcar, Jerejian 1 Axioms: Wffs that can be written down without any reference to any other Wffs. Wffs that are stipulated as unproved premises for the proof of other wffs
Chapter 6 Control Flow. June 9, 2015
 Chapter 6 Control Flow June 9, 2015 Expression evaluation It s common in programming languages to use the idea of an expression, which might be a simple object function invocation over some number of arguments
Chapter 6 Control Flow June 9, 2015 Expression evaluation It s common in programming languages to use the idea of an expression, which might be a simple object function invocation over some number of arguments
1 Introduction CHAPTER ONE: SETS
 1 Introduction CHAPTER ONE: SETS Scientific theories usually do not directly describe the natural phenomena under investigation, but rather a mathematical idealization of them that abstracts away from
1 Introduction CHAPTER ONE: SETS Scientific theories usually do not directly describe the natural phenomena under investigation, but rather a mathematical idealization of them that abstracts away from
CS 161 Computer Security
 Wagner Spring 2014 CS 161 Computer Security 1/27 Reasoning About Code Often functions make certain assumptions about their arguments, and it is the caller s responsibility to make sure those assumptions
Wagner Spring 2014 CS 161 Computer Security 1/27 Reasoning About Code Often functions make certain assumptions about their arguments, and it is the caller s responsibility to make sure those assumptions
Lecture 4 Searching Arrays
 Lecture 4 Searching Arrays 15-122: Principles of Imperative Computation (Spring 2018) Frank Pfenning One of the fundamental and recurring problems in computer science is to find elements in collections,
Lecture 4 Searching Arrays 15-122: Principles of Imperative Computation (Spring 2018) Frank Pfenning One of the fundamental and recurring problems in computer science is to find elements in collections,
Lecture Notes on Linear Search
 Lecture Notes on Linear Search 15-122: Principles of Imperative Computation Frank Pfenning Lecture 5 January 28, 2014 1 Introduction One of the fundamental and recurring problems in computer science is
Lecture Notes on Linear Search 15-122: Principles of Imperative Computation Frank Pfenning Lecture 5 January 28, 2014 1 Introduction One of the fundamental and recurring problems in computer science is
Chapter 3. Describing Syntax and Semantics ISBN
 Chapter 3 Describing Syntax and Semantics ISBN 0-321-49362-1 Chapter 3 Topics Describing the Meanings of Programs: Dynamic Semantics Copyright 2015 Pearson. All rights reserved. 2 Semantics There is no
Chapter 3 Describing Syntax and Semantics ISBN 0-321-49362-1 Chapter 3 Topics Describing the Meanings of Programs: Dynamic Semantics Copyright 2015 Pearson. All rights reserved. 2 Semantics There is no
Hoare Logic. COMP2600 Formal Methods for Software Engineering. Rajeev Goré
 Hoare Logic COMP2600 Formal Methods for Software Engineering Rajeev Goré Australian National University Semester 2, 2016 (Slides courtesy of Ranald Clouston) COMP 2600 Hoare Logic 1 Australian Capital
Hoare Logic COMP2600 Formal Methods for Software Engineering Rajeev Goré Australian National University Semester 2, 2016 (Slides courtesy of Ranald Clouston) COMP 2600 Hoare Logic 1 Australian Capital
Harvard School of Engineering and Applied Sciences CS 152: Programming Languages
 Harvard School of Engineering and Applied Sciences CS 152: Programming Languages Lecture 19 Tuesday, April 3, 2018 1 Introduction to axiomatic semantics The idea in axiomatic semantics is to give specifications
Harvard School of Engineering and Applied Sciences CS 152: Programming Languages Lecture 19 Tuesday, April 3, 2018 1 Introduction to axiomatic semantics The idea in axiomatic semantics is to give specifications
Chapter 3. Describing Syntax and Semantics ISBN
 Chapter 3 Describing Syntax and Semantics ISBN 0-321-49362-1 Chapter 3 Topics Introduction The General Problem of Describing Syntax Formal Methods of Describing Syntax Attribute Grammars Describing the
Chapter 3 Describing Syntax and Semantics ISBN 0-321-49362-1 Chapter 3 Topics Introduction The General Problem of Describing Syntax Formal Methods of Describing Syntax Attribute Grammars Describing the
Chapter 3. Describing Syntax and Semantics
 Chapter 3 Describing Syntax and Semantics Chapter 3 Topics Introduction The General Problem of Describing Syntax Formal Methods of Describing Syntax Attribute Grammars Describing the Meanings of Programs:
Chapter 3 Describing Syntax and Semantics Chapter 3 Topics Introduction The General Problem of Describing Syntax Formal Methods of Describing Syntax Attribute Grammars Describing the Meanings of Programs:
CSCI.6962/4962 Software Verification Fundamental Proof Methods in Computer Science (Arkoudas and Musser) Sections p.
 CSCI.6962/4962 Software Verification Fundamental Proof Methods in Computer Science (Arkoudas and Musser) Sections 10.1-10.3 p. 1/106 CSCI.6962/4962 Software Verification Fundamental Proof Methods in Computer
CSCI.6962/4962 Software Verification Fundamental Proof Methods in Computer Science (Arkoudas and Musser) Sections 10.1-10.3 p. 1/106 CSCI.6962/4962 Software Verification Fundamental Proof Methods in Computer
Chapter 3. Describing Syntax and Semantics
 Chapter 3 Describing Syntax and Semantics Chapter 3 Topics Introduction The General Problem of Describing Syntax Formal Methods of Describing Syntax Attribute Grammars Describing the Meanings of Programs:
Chapter 3 Describing Syntax and Semantics Chapter 3 Topics Introduction The General Problem of Describing Syntax Formal Methods of Describing Syntax Attribute Grammars Describing the Meanings of Programs:
Com S 541. Programming Languages I
 Programming Languages I Lecturer: TA: Markus Lumpe Department of Computer Science 113 Atanasoff Hall http://www.cs.iastate.edu/~lumpe/coms541.html TR 12:40-2, W 5 Pramod Bhanu Rama Rao Office hours: TR
Programming Languages I Lecturer: TA: Markus Lumpe Department of Computer Science 113 Atanasoff Hall http://www.cs.iastate.edu/~lumpe/coms541.html TR 12:40-2, W 5 Pramod Bhanu Rama Rao Office hours: TR
CS 6110 S14 Lecture 1 Introduction 24 January 2014
 CS 6110 S14 Lecture 1 Introduction 24 January 2014 1 Introduction What is a program? Is it just something that tells the computer what to do? Yes, but there is much more to it than that. The basic expressions
CS 6110 S14 Lecture 1 Introduction 24 January 2014 1 Introduction What is a program? Is it just something that tells the computer what to do? Yes, but there is much more to it than that. The basic expressions
Type Systems COMP 311 Rice University Houston, Texas
 Rice University Houston, Texas 1 Type Systems for Programming Language were invented by mathematicians before electronic computers were invented. What is a type? A meaningful subset of the set of the domain
Rice University Houston, Texas 1 Type Systems for Programming Language were invented by mathematicians before electronic computers were invented. What is a type? A meaningful subset of the set of the domain
VS 3 : SMT Solvers for Program Verification
 VS 3 : SMT Solvers for Program Verification Saurabh Srivastava 1,, Sumit Gulwani 2, and Jeffrey S. Foster 1 1 University of Maryland, College Park, {saurabhs,jfoster}@cs.umd.edu 2 Microsoft Research, Redmond,
VS 3 : SMT Solvers for Program Verification Saurabh Srivastava 1,, Sumit Gulwani 2, and Jeffrey S. Foster 1 1 University of Maryland, College Park, {saurabhs,jfoster}@cs.umd.edu 2 Microsoft Research, Redmond,
CSCI.6962/4962 Software Verification Fundamental Proof Methods in Computer Science (Arkoudas and Musser) Section 17.1
 CSCI.6962/4962 Software Verification Fundamental Proof Methods in Computer Science (Arkoudas and Musser) Section 17.1 Instructor: Carlos Varela Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute Spring 2018 CSCI.6962/4962
CSCI.6962/4962 Software Verification Fundamental Proof Methods in Computer Science (Arkoudas and Musser) Section 17.1 Instructor: Carlos Varela Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute Spring 2018 CSCI.6962/4962
SEQUENCES, MATHEMATICAL INDUCTION, AND RECURSION
 CHAPTER 5 SEQUENCES, MATHEMATICAL INDUCTION, AND RECURSION Alessandro Artale UniBZ - http://www.inf.unibz.it/ artale/ SECTION 5.5 Application: Correctness of Algorithms Copyright Cengage Learning. All
CHAPTER 5 SEQUENCES, MATHEMATICAL INDUCTION, AND RECURSION Alessandro Artale UniBZ - http://www.inf.unibz.it/ artale/ SECTION 5.5 Application: Correctness of Algorithms Copyright Cengage Learning. All
Introduction to Axiomatic Semantics (1/2)
 #1 Introduction to Axiomatic Semantics (1/2) How s The Homework Going? Remember that you can t just define a meaning function in terms of itself you must use some fixed point machinery. #2 #3 Observations
#1 Introduction to Axiomatic Semantics (1/2) How s The Homework Going? Remember that you can t just define a meaning function in terms of itself you must use some fixed point machinery. #2 #3 Observations
Static semantics. Lecture 3-6: Semantics. Attribute grammars (2) Attribute grammars. Attribute grammars example. Dynamic semantics
 Lecture 3-6: Semantics Static semantics Attribute grammars Dynamic semantics Denotational semantics: semantic equations Axiomatic semantics: inference rules and correctness proofs Static semantics Semantics
Lecture 3-6: Semantics Static semantics Attribute grammars Dynamic semantics Denotational semantics: semantic equations Axiomatic semantics: inference rules and correctness proofs Static semantics Semantics
(a) (4 pts) Prove that if a and b are rational, then ab is rational. Since a and b are rational they can be written as the ratio of integers a 1
 CS 70 Discrete Mathematics for CS Fall 2000 Wagner MT1 Sol Solutions to Midterm 1 1. (16 pts.) Theorems and proofs (a) (4 pts) Prove that if a and b are rational, then ab is rational. Since a and b are
CS 70 Discrete Mathematics for CS Fall 2000 Wagner MT1 Sol Solutions to Midterm 1 1. (16 pts.) Theorems and proofs (a) (4 pts) Prove that if a and b are rational, then ab is rational. Since a and b are
1.3. Conditional expressions To express case distinctions like
 Introduction Much of the theory developed in the underlying course Logic II can be implemented in a proof assistant. In the present setting this is interesting, since we can then machine extract from a
Introduction Much of the theory developed in the underlying course Logic II can be implemented in a proof assistant. In the present setting this is interesting, since we can then machine extract from a
#23: Sequences March 28, 2009
 #23: Sequences March 28, 2009 a mysterious rule easy peasy Suppose n is an integer, and consider this simple rule: if n is even, divide it by two; otherwise, multiply n by 3, and add one. Pretty simple,
#23: Sequences March 28, 2009 a mysterious rule easy peasy Suppose n is an integer, and consider this simple rule: if n is even, divide it by two; otherwise, multiply n by 3, and add one. Pretty simple,
Contents. Chapter 1 SPECIFYING SYNTAX 1
 Contents Chapter 1 SPECIFYING SYNTAX 1 1.1 GRAMMARS AND BNF 2 Context-Free Grammars 4 Context-Sensitive Grammars 8 Exercises 8 1.2 THE PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE WREN 10 Ambiguity 12 Context Constraints in Wren
Contents Chapter 1 SPECIFYING SYNTAX 1 1.1 GRAMMARS AND BNF 2 Context-Free Grammars 4 Context-Sensitive Grammars 8 Exercises 8 1.2 THE PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE WREN 10 Ambiguity 12 Context Constraints in Wren
Status: Informal Type: Technical. This document gives an example of the Compliance Notation.
 Project: Title: Status: Informal Type: Technical Author: Name Location Signature Date R.D. Arthan Abstract: WIN01 This document gives an example of the. Distribution: Library Copyright c : Lemma 1 Ltd
Project: Title: Status: Informal Type: Technical Author: Name Location Signature Date R.D. Arthan Abstract: WIN01 This document gives an example of the. Distribution: Library Copyright c : Lemma 1 Ltd
Typing Control. Chapter Conditionals
 Chapter 26 Typing Control 26.1 Conditionals Let s expand our language with a conditional construct. We can use if0 like before, but for generality it s going to be more convenient to have a proper conditional
Chapter 26 Typing Control 26.1 Conditionals Let s expand our language with a conditional construct. We can use if0 like before, but for generality it s going to be more convenient to have a proper conditional
A Small Interpreted Language
 A Small Interpreted Language What would you need to build a small computing language based on mathematical principles? The language should be simple, Turing equivalent (i.e.: it can compute anything that
A Small Interpreted Language What would you need to build a small computing language based on mathematical principles? The language should be simple, Turing equivalent (i.e.: it can compute anything that
Incremental Proof Development in Dafny
 15-414 Lecture 17 1 Instructor: Matt Fredrikson Incremental Proof Development in Dafny TA: Ryan Wagner In this discussion, we ll see in more detail how to go about proving the total correctness of imperative
15-414 Lecture 17 1 Instructor: Matt Fredrikson Incremental Proof Development in Dafny TA: Ryan Wagner In this discussion, we ll see in more detail how to go about proving the total correctness of imperative
SOFTWARE ENGINEERING DESIGN I
 2 SOFTWARE ENGINEERING DESIGN I 3. Schemas and Theories The aim of this course is to learn how to write formal specifications of computer systems, using classical logic. The key descriptional technique
2 SOFTWARE ENGINEERING DESIGN I 3. Schemas and Theories The aim of this course is to learn how to write formal specifications of computer systems, using classical logic. The key descriptional technique
APCS-AB: Java. Recursion in Java December 12, week14 1
 APCS-AB: Java Recursion in Java December 12, 2005 week14 1 Check point Double Linked List - extra project grade Must turn in today MBCS - Chapter 1 Installation Exercises Analysis Questions week14 2 Scheme
APCS-AB: Java Recursion in Java December 12, 2005 week14 1 Check point Double Linked List - extra project grade Must turn in today MBCS - Chapter 1 Installation Exercises Analysis Questions week14 2 Scheme
Induction and Semantics in Dafny
 15-414 Lecture 11 1 Instructor: Matt Fredrikson Induction and Semantics in Dafny TA: Ryan Wagner Encoding the syntax of Imp Recall the abstract syntax of Imp: a AExp ::= n Z x Var a 1 + a 2 b BExp ::=
15-414 Lecture 11 1 Instructor: Matt Fredrikson Induction and Semantics in Dafny TA: Ryan Wagner Encoding the syntax of Imp Recall the abstract syntax of Imp: a AExp ::= n Z x Var a 1 + a 2 b BExp ::=
Introduction to Axiomatic Semantics (1/2)
 #1 Introduction to Axiomatic Semantics (1/2) How s The Homework Going? Remember: just do the counterexample guided abstraction refinement part of DPLL(T). If you notice any other errors, those are good
#1 Introduction to Axiomatic Semantics (1/2) How s The Homework Going? Remember: just do the counterexample guided abstraction refinement part of DPLL(T). If you notice any other errors, those are good
Specifying Concurrent Systems with TLA +
 Specifying Concurrent Systems with TLA + Leslie Lamport 9 Feb 2000 c 1999 by Leslie Lamport Preliminary Draft Be sure to read the description of this document on page 3 of the Introduction. Contents Introduction.................................
Specifying Concurrent Systems with TLA + Leslie Lamport 9 Feb 2000 c 1999 by Leslie Lamport Preliminary Draft Be sure to read the description of this document on page 3 of the Introduction. Contents Introduction.................................
Verification Condition Generation via Theorem Proving
 Verification Condition Generation via Theorem Proving John Matthews Galois Connections Inc. J Strother Moore University of Texas at Austin Sandip Ray University of Texas at Austin Daron Vroon Georgia Institute
Verification Condition Generation via Theorem Proving John Matthews Galois Connections Inc. J Strother Moore University of Texas at Austin Sandip Ray University of Texas at Austin Daron Vroon Georgia Institute
CSCC24 Functional Programming Scheme Part 2
 CSCC24 Functional Programming Scheme Part 2 Carolyn MacLeod 1 winter 2012 1 Based on slides from Anya Tafliovich, and with many thanks to Gerald Penn and Prabhakar Ragde. 1 The Spirit of Lisp-like Languages
CSCC24 Functional Programming Scheme Part 2 Carolyn MacLeod 1 winter 2012 1 Based on slides from Anya Tafliovich, and with many thanks to Gerald Penn and Prabhakar Ragde. 1 The Spirit of Lisp-like Languages
MIDTERM EXAMINATION. CSE 130: Principles of Programming Languages. Professor Goguen. February 16, points total
 CSE 130, Winter 2006 MIDTERM EXAMINATION CSE 130: Principles of Programming Languages Professor Goguen February 16, 2006 100 points total Don t start the exam until you are told to. Turn off any cell phone
CSE 130, Winter 2006 MIDTERM EXAMINATION CSE 130: Principles of Programming Languages Professor Goguen February 16, 2006 100 points total Don t start the exam until you are told to. Turn off any cell phone
Specifying Concurrent Systems with TLA +
 Specifying Concurrent Systems with TLA + Leslie Lamport 18 Oct 1999 c 1999 by Leslie Lamport Incomplete Preliminary Draft Be sure to read the description of this document on page 3 of the Introduction.
Specifying Concurrent Systems with TLA + Leslie Lamport 18 Oct 1999 c 1999 by Leslie Lamport Incomplete Preliminary Draft Be sure to read the description of this document on page 3 of the Introduction.
MITOCW watch?v=kz7jjltq9r4
 MITOCW watch?v=kz7jjltq9r4 PROFESSOR: We're going to look at the most fundamental of all mathematical data types, namely sets, and let's begin with the definitions. So informally, a set is a collection
MITOCW watch?v=kz7jjltq9r4 PROFESSOR: We're going to look at the most fundamental of all mathematical data types, namely sets, and let's begin with the definitions. So informally, a set is a collection
Dynamic Programming Algorithms
 CSC 364S Notes University of Toronto, Fall 2003 Dynamic Programming Algorithms The setting is as follows. We wish to find a solution to a given problem which optimizes some quantity Q of interest; for
CSC 364S Notes University of Toronto, Fall 2003 Dynamic Programming Algorithms The setting is as follows. We wish to find a solution to a given problem which optimizes some quantity Q of interest; for
Defining Languages GMU
 Defining Languages CS463 @ GMU How do we discuss languages? We might focus on these qualities: readability: how well does a language explicitly and clearly describe its purpose? writability: how expressive
Defining Languages CS463 @ GMU How do we discuss languages? We might focus on these qualities: readability: how well does a language explicitly and clearly describe its purpose? writability: how expressive
Static verification of program running time
 Static verification of program running time CIS 673 course project report Caleb Stanford December 2016 Contents 1 Introduction 2 1.1 Total Correctness is Not Enough.................................. 2
Static verification of program running time CIS 673 course project report Caleb Stanford December 2016 Contents 1 Introduction 2 1.1 Total Correctness is Not Enough.................................. 2
Programming Languages Fall 2013
 Programming Languages Fall 2013 Lecture 3: Induction Prof. Liang Huang huang@qc.cs.cuny.edu Recursive Data Types (trees) data Ast = ANum Integer APlus Ast Ast ATimes Ast Ast eval (ANum x) = x eval (ATimes
Programming Languages Fall 2013 Lecture 3: Induction Prof. Liang Huang huang@qc.cs.cuny.edu Recursive Data Types (trees) data Ast = ANum Integer APlus Ast Ast ATimes Ast Ast eval (ANum x) = x eval (ATimes
Critical Analysis of Computer Science Methodology: Theory
 Critical Analysis of Computer Science Methodology: Theory Björn Lisper Dept. of Computer Science and Engineering Mälardalen University bjorn.lisper@mdh.se http://www.idt.mdh.se/ blr/ March 3, 2004 Critical
Critical Analysis of Computer Science Methodology: Theory Björn Lisper Dept. of Computer Science and Engineering Mälardalen University bjorn.lisper@mdh.se http://www.idt.mdh.se/ blr/ March 3, 2004 Critical
Computing Fundamentals 2 Introduction to CafeOBJ
 Computing Fundamentals 2 Introduction to CafeOBJ Lecturer: Patrick Browne Lecture Room: K408 Lab Room: A308 Based on work by: Nakamura Masaki, João Pascoal Faria, Prof. Heinrich Hußmann. See notes on slides
Computing Fundamentals 2 Introduction to CafeOBJ Lecturer: Patrick Browne Lecture Room: K408 Lab Room: A308 Based on work by: Nakamura Masaki, João Pascoal Faria, Prof. Heinrich Hußmann. See notes on slides
What is Iteration? CMPT-101. Recursion. Understanding Recursion. The Function Header and Documentation. Recursively Adding Numbers
 What is Iteration? CMPT-101 Week 6 Iteration, Iteration, Iteration, Iteration, Iteration, Iteration,... To iterate means to do the same thing again and again and again and again... There are two primary
What is Iteration? CMPT-101 Week 6 Iteration, Iteration, Iteration, Iteration, Iteration, Iteration,... To iterate means to do the same thing again and again and again and again... There are two primary
P1 Engineering Computation
 1EC 2001 1 / 1 P1 Engineering Computation David Murray david.murray@eng.ox.ac.uk www.robots.ox.ac.uk/ dwm/courses/1ec Hilary 2001 1EC 2001 2 / 1 Algorithms: Design, Constructs and Correctness 1EC 2001
1EC 2001 1 / 1 P1 Engineering Computation David Murray david.murray@eng.ox.ac.uk www.robots.ox.ac.uk/ dwm/courses/1ec Hilary 2001 1EC 2001 2 / 1 Algorithms: Design, Constructs and Correctness 1EC 2001
Lecture 6: Arithmetic and Threshold Circuits
 IAS/PCMI Summer Session 2000 Clay Mathematics Undergraduate Program Advanced Course on Computational Complexity Lecture 6: Arithmetic and Threshold Circuits David Mix Barrington and Alexis Maciel July
IAS/PCMI Summer Session 2000 Clay Mathematics Undergraduate Program Advanced Course on Computational Complexity Lecture 6: Arithmetic and Threshold Circuits David Mix Barrington and Alexis Maciel July
Example. program sort; var a : array[0..10] of integer; procedure readarray; : function partition (y, z :integer) :integer; var i, j,x, v :integer; :
![Example. program sort; var a : array[0..10] of integer; procedure readarray; : function partition (y, z :integer) :integer; var i, j,x, v :integer; : Example. program sort; var a : array[0..10] of integer; procedure readarray; : function partition (y, z :integer) :integer; var i, j,x, v :integer; :](/thumbs/74/69682489.jpg) Runtime Environment Relationship between names and data objects (of target machine) Allocation & de-allocation is managed by run time support package Each execution of a procedure is an activation of the
Runtime Environment Relationship between names and data objects (of target machine) Allocation & de-allocation is managed by run time support package Each execution of a procedure is an activation of the
1 The Axiom of Extensionality
 1 The Axiom of Extensionality Primitive notion: Set A set is a group, a collection, or an aggregate of things. In fact, the words set, group, collection, and aggregate are all synonyms denoting the same
1 The Axiom of Extensionality Primitive notion: Set A set is a group, a collection, or an aggregate of things. In fact, the words set, group, collection, and aggregate are all synonyms denoting the same
Program Analysis: Lecture 02 Page 1 of 32
 Program Analysis: Lecture 02 Page 1 of 32 Program Analysis/ Mooly Sagiv Lecture 1, 31/10/2012 Operational Semantics Notes by: Kalev Alpernas As background to the subject of Program Analysis, we will first
Program Analysis: Lecture 02 Page 1 of 32 Program Analysis/ Mooly Sagiv Lecture 1, 31/10/2012 Operational Semantics Notes by: Kalev Alpernas As background to the subject of Program Analysis, we will first
G Programming Languages - Fall 2012
 G22.2110-003 Programming Languages - Fall 2012 Lecture 4 Thomas Wies New York University Review Last week Control Structures Selection Loops Adding Invariants Outline Subprograms Calling Sequences Parameter
G22.2110-003 Programming Languages - Fall 2012 Lecture 4 Thomas Wies New York University Review Last week Control Structures Selection Loops Adding Invariants Outline Subprograms Calling Sequences Parameter
LOGIC AND DISCRETE MATHEMATICS
 LOGIC AND DISCRETE MATHEMATICS A Computer Science Perspective WINFRIED KARL GRASSMANN Department of Computer Science University of Saskatchewan JEAN-PAUL TREMBLAY Department of Computer Science University
LOGIC AND DISCRETE MATHEMATICS A Computer Science Perspective WINFRIED KARL GRASSMANN Department of Computer Science University of Saskatchewan JEAN-PAUL TREMBLAY Department of Computer Science University
Goals: Define the syntax of a simple imperative language Define a semantics using natural deduction 1
 Natural Semantics Goals: Define the syntax of a simple imperative language Define a semantics using natural deduction 1 1 Natural deduction is an instance of first-order logic; that is, it is the formal
Natural Semantics Goals: Define the syntax of a simple imperative language Define a semantics using natural deduction 1 1 Natural deduction is an instance of first-order logic; that is, it is the formal
Recursive Functions. 6.1 Primitive Recursive Functions
 6 Recursive Functions The intuitive notion of an effectively computable function is the notion of a function for which there are definite, explicit rules, following which one could in principle compute
6 Recursive Functions The intuitive notion of an effectively computable function is the notion of a function for which there are definite, explicit rules, following which one could in principle compute
Chapter 3. Syntax - the form or structure of the expressions, statements, and program units
 Syntax - the form or structure of the expressions, statements, and program units Semantics - the meaning of the expressions, statements, and program units Who must use language definitions? 1. Other language
Syntax - the form or structure of the expressions, statements, and program units Semantics - the meaning of the expressions, statements, and program units Who must use language definitions? 1. Other language
Lecture 2: SML Basics
 15-150 Lecture 2: SML Basics Lecture by Dan Licata January 19, 2012 I d like to start off by talking about someone named Alfred North Whitehead. With someone named Bertrand Russell, Whitehead wrote Principia
15-150 Lecture 2: SML Basics Lecture by Dan Licata January 19, 2012 I d like to start off by talking about someone named Alfred North Whitehead. With someone named Bertrand Russell, Whitehead wrote Principia
Ensuring a Rigorous Curriculum: Practices and Goals
 Ensuring a Rigorous Curriculum: Practices and Goals Allen B. Tucker Bowdoin College www.bowdoin.edu/~allen April 12, 2002 1 of 30 Goals of an Undergraduate Program To prepare graduates for the computing
Ensuring a Rigorous Curriculum: Practices and Goals Allen B. Tucker Bowdoin College www.bowdoin.edu/~allen April 12, 2002 1 of 30 Goals of an Undergraduate Program To prepare graduates for the computing
The Diagonal Lemma: An Informal Exposition
 The Diagonal Lemma: An Informal Exposition Richard G Heck, Jr At the heart of Gödel s incompleteness theorem is the so-called diagonal lemma whose purpose is to allow us to construct self-referential sentences,
The Diagonal Lemma: An Informal Exposition Richard G Heck, Jr At the heart of Gödel s incompleteness theorem is the so-called diagonal lemma whose purpose is to allow us to construct self-referential sentences,
Formal Methods in Software Engineering. Lecture 07
 Formal Methods in Software Engineering Lecture 07 What is Temporal Logic? Objective: We describe temporal aspects of formal methods to model and specify concurrent systems and verify their correctness
Formal Methods in Software Engineering Lecture 07 What is Temporal Logic? Objective: We describe temporal aspects of formal methods to model and specify concurrent systems and verify their correctness
Proofwriting Checklist
 CS103 Winter 2019 Proofwriting Checklist Cynthia Lee Keith Schwarz Over the years, we ve found many common proofwriting errors that can easily be spotted once you know how to look for them. In this handout,
CS103 Winter 2019 Proofwriting Checklist Cynthia Lee Keith Schwarz Over the years, we ve found many common proofwriting errors that can easily be spotted once you know how to look for them. In this handout,
A Theory of Parallel Computation The π-calculus
 A Theory of Parallel Computation The π-calculus Background DFAs, NFAs, pushdown automata, Turing machines... All are mathematical entities that model computation. These abstract systems have concrete,
A Theory of Parallel Computation The π-calculus Background DFAs, NFAs, pushdown automata, Turing machines... All are mathematical entities that model computation. These abstract systems have concrete,
Hardware versus software
 Logic 1 Hardware versus software 2 In hardware such as chip design or architecture, designs are usually proven to be correct using proof tools In software, a program is very rarely proved correct Why?
Logic 1 Hardware versus software 2 In hardware such as chip design or architecture, designs are usually proven to be correct using proof tools In software, a program is very rarely proved correct Why?
Recursion and Induction
 Recursion and Induction Paul S. Miner NASA Langley Formal Methods Group p.s.miner@nasa.gov 28 November 2007 Outline Recursive definitions in PVS Simple inductive proofs Automated proofs by induction More
Recursion and Induction Paul S. Miner NASA Langley Formal Methods Group p.s.miner@nasa.gov 28 November 2007 Outline Recursive definitions in PVS Simple inductive proofs Automated proofs by induction More
Midterm I Exam Principles of Imperative Computation André Platzer Ananda Gunawardena. February 23, 2012
 Midterm I Exam 15-122 Principles of Imperative Computation André Platzer Ananda Gunawardena February 23, 2012 Name: Sample Solution Andrew ID: aplatzer Section: Instructions This exam is closed-book with
Midterm I Exam 15-122 Principles of Imperative Computation André Platzer Ananda Gunawardena February 23, 2012 Name: Sample Solution Andrew ID: aplatzer Section: Instructions This exam is closed-book with
This book is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 License
 6. Syntax Learning objectives: syntax and semantics syntax diagrams and EBNF describe context-free grammars terminal and nonterminal symbols productions definition of EBNF by itself parse tree grammars
6. Syntax Learning objectives: syntax and semantics syntax diagrams and EBNF describe context-free grammars terminal and nonterminal symbols productions definition of EBNF by itself parse tree grammars
Definition: A context-free grammar (CFG) is a 4- tuple. variables = nonterminals, terminals, rules = productions,,
 CMPSCI 601: Recall From Last Time Lecture 5 Definition: A context-free grammar (CFG) is a 4- tuple, variables = nonterminals, terminals, rules = productions,,, are all finite. 1 ( ) $ Pumping Lemma for
CMPSCI 601: Recall From Last Time Lecture 5 Definition: A context-free grammar (CFG) is a 4- tuple, variables = nonterminals, terminals, rules = productions,,, are all finite. 1 ( ) $ Pumping Lemma for
Dynamic Programming Algorithms
 Based on the notes for the U of Toronto course CSC 364 Dynamic Programming Algorithms The setting is as follows. We wish to find a solution to a given problem which optimizes some quantity Q of interest;
Based on the notes for the U of Toronto course CSC 364 Dynamic Programming Algorithms The setting is as follows. We wish to find a solution to a given problem which optimizes some quantity Q of interest;
A Partial Correctness Proof for Programs with Decided Specifications
 Applied Mathematics & Information Sciences 1(2)(2007), 195-202 An International Journal c 2007 Dixie W Publishing Corporation, U. S. A. A Partial Correctness Proof for Programs with Decided Specifications
Applied Mathematics & Information Sciences 1(2)(2007), 195-202 An International Journal c 2007 Dixie W Publishing Corporation, U. S. A. A Partial Correctness Proof for Programs with Decided Specifications
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/22891 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation Author: Gouw, Stijn de Title: Combining monitoring with run-time assertion checking Issue
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/22891 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation Author: Gouw, Stijn de Title: Combining monitoring with run-time assertion checking Issue
An Annotated Language
 Hoare Logic An Annotated Language State and Semantics Expressions are interpreted as functions from states to the corresponding domain of interpretation Operators have the obvious interpretation Free of
Hoare Logic An Annotated Language State and Semantics Expressions are interpreted as functions from states to the corresponding domain of interpretation Operators have the obvious interpretation Free of
