CS 112 Introduction to Programming
|
|
|
- Garey Terry
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CS 112 Introduction to Programming Conditional Statements Boolean Expressions and Methods Yang (Richard) Yang Computer Science Department Yale University 308A Watson, Phone:
2 Admin. q Walkthrough of PS4 8 pm at DL 220 on Monday 6 pm at DL 220 on Tuesday q Office hour scheduling 2
3 Recap: Scanner q Some Scanner methods: Method nextint() Description Returns an int from source nextdouble() Returns a double from source next() nextline() Returns a one-word String from source Returns a one-line String from source q Java uses objects to remember the source of a scanner Scanner console = new Scanner(System.in); console.nextint();
4 Recap: Scanning Details q nextint(), nextdouble(), next() are token based scanning methods q nextline() collects any input character into a string until the first new line and discards the new line q When nextint(), nextdouble()parses a token, but cannot parse it correctly, the method throws an exception q A robust program will check condition before invoking nextint() or nextdouble()
5 Java Conditional Statements q Conditional statements, also called decision statements, decide whether or not to execute a particular sequence of statements
6 The if Statement q Example: int na = 0; for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) { double grade = console.nextdouble(); if (grade >= 90) { System.out.println("Welcome to Yale!"); na ++; // This is called accumulative sum
7 Recall: Basic Boolean Expression q A basic Boolean expression is to compare two values using a relational operator : Operator Meaning Example Value == equals == 2 true!= does not equal 3.2!= 2.5 true < less than 10 < 5 false > greater than 10 > 5 true <= less than or equal to 126 <= 100 false >= greater than or equal to 5.0 >= 5.0 true q Note the difference between the equality operator (==) and the assignment operator (=) 7
8 Example: Basic Boolean Expression Flip.java 8
9 Outline: Conditional Program Flow Control q Our journey of introducing conditionals simple if (a <comp> b) nested if/else
10 Motivation: Chaos Game q Play on equilateral triangle, with vertices R (node 0), G (node 1), B (node 2) B Start at R Repeat N times Pick a random vertex Move halfway between current point and vertex Draw a point in color of chosen vertex Chaos.java 10
11 Motivation: Chaos Game 11
12 Motivation: Chaos Game public static void main (String[] args) { for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) { int rand = getrand(0, 2); if (rand == 0) { // if (rand == 1) { // if (rand == 2) { // Q: How many comparisons in each round (iteration)? 12
13 Solution II: Nested Comparison public static void main (String[] args) { for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) { int rand = getrand(0, 2); if (rand == 0) { // else if (rand == 1) { // else if (rand == 2) { // Q: Average # of comparisons per iteration? Benefit of nested comparison: reduce # comparisons 13
14 Grading Curve FIX: Using nested comparison to achieve mutual exclusion. q How is this code for grading based on percentiles? Scanner console = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.print("What percentile? "); int percent = console.nextint(); if (percent >= 90) { System.out.println("You got an A!"); else if (percent >= 80) { System.out.println("You got a B!"); else if (percent >= 70) { System.out.println("You got a C!"); else if (percent >= 60) { System.out.println("You got a D!"); else if (percent < 60) { System.out.println("You got an F!");... 14
15 Summary: Why nested if/else q Mutually exclusive test conditions => Reduces # of comparisons q Non-mutual exclusive test conditions => Achieves mutual exclusion if (percent >= 90) { // assigns A else if (percent >= 80) { // assigns B else if (percent >= 70) { // assigns C else if (percent >= 60) { // D else { // F a > b a < b a == b P >= 60 P >= 70 P >= 80 P >=90 15
16 Exercise: Barnsley Game q Play Chaos game with different rules Barnsley.java 16
17 Exercise: Barnsley Game public static void main(string[] args) { StdDraw.setPenRadius(0.002); StdDraw.setPenColor(Color.GREEN); int T = 40000; double x = 0.0, y = 0.0; for (int t = 0; t < T; t++) { double rand = Math.random(); // if (rand <= 0.7) { // 0-0.7: 70% x =.78 * x +.03 * y +.11; y = -.03 * x +.74 * y +.27; else if (rand <= ) { // : 15% // 15% x = -.14 * x +.26 * y +.57; y =.25 * x +.22 * y -.04; else if (rand < ) { // : %13 x =.17 * x -.21 * y +.41; y =.22 * x +.18 * y +.09; else { // 2% x = 0.5; y =.27 * y; StdDraw.point(x, y); // end of for // end of main 17
18 Exercise: Barnsley Game q Questions to think about What does computation tell us about nature? What does nature tell us about computation? 18
19 Outline: Conditional Program Flow Control q Our journey of introducing conditionals simple if (a <comp> b) nested if/else Complexity of nested if/else: all path must return; mismatched else
20 Matching Nested if Statements q Nested if statements may have a matching problem if (temperature < 50) if (temperature < 100) System.out.println( Cool! ); else System.out.println( Hot! ); 20
21 Nested if w/ Ambiguity if (temperature < 50) if (temperature < 100) System.out.println( Cool! ); else System.out.println( Hot! ); if (temperature < 50) if (temperature < 100) System.out.println( Cool! ); else System.out.println( Hot! ); t < 50 Yes No t < 50 Yes No t < 100 Yes Hot! t < 100 Yes Hot! Cool! Cool! Give a value of temperature to produce differentt results 21
22 Nested if Statements if (temperature < 50) if (temperature < 100) System.out.println( Cool! ); else System.out.println( Hot! ); if (temperature < 50) if (temperature < 100) System.out.println( Cool! ); else System.out.println( Hot! ); - Rule: an else clause is matched to the last unmatched if (no matter what the indentation implies) - If you find such statements confusing, avoid writing such structures and always use block statements ({) to make the structure clear. 22
23 if/else with return q A method with a return requires that all paths through the code must reach a return statement. q The compiler analyzes this by considering the syntax only!
24 if/else with return static int mymethod() { if (test1) { statement(s); return x; else if (test2) { statement(s); return y; else { statement(s); return z; // end of method else return else if if return return
25 if/else with return static int mymethod() { if (test1) { statement(s); return x; else if (test2) { statement(s); return y; else { statement(s); return z; return // end of method // ERROR: missing return in a path else if if return return
26 if/else with return public static int max(int a, int b) { if (a > b) { return a; // Error: not all paths return a value public static int max(int a, int b) { if (a > b) { return a; else if (a <= b) { return b; // Error: syntax analysis missing a path public static int max(int a, int b) { if (a > b) { return a; else if (a <= b) { return b; // OK public static int max(int a, int b) { int mymax = a; // default if (b > a) { mymax = b; return mymax; // OK public static int max(int a, int b) { if (b > a) { return b; return a; // OK
27 Outline: Conditional Program Flow Control q Our journey of introducing conditionals simple if (a <comp> b) nested if/else Complexity of nested if/else: all path must return; mismatched else <condition> combining multiple <comp>;
28 Motivation: Testing Containment q We may need to check multiple conditions (x,y) (0,0) H W Test if point (x, y) is in the rectangle? (0 <= x <= W) and (0 <= y <= H) SYNTAX ERROR (0 <= x) && ( x <= W) && (0 <= y) && (y <= H) 28
29 Logical Operators q Tests can be combined using logical operators: Operator Description Example Result && and (2 == 3) && (-1 < 5) false or (2 == 3) (-1 < 5) true! not!(2 == 3) true q "Truth tables" for each, used with logical values p and q: p q p && q p q true true true true true false false true false true false true false false false false p!p true false false true
30 Extension: Testing Containment q We may need to check multiple conditions (0,0) (x,y) h H w W Test if dark rectangle is in the bigger rectangle? 30
31 Exercise q Write a method to compute the number of days in a month public static int daysinmonth( int year, int month ) 31
32 Applying Boolean Exp. in daysinmonth q Use a logical OR to combine the cases if (m == 1 m == 3 m == 5 m == 7 m == 8 m == 10 m == 12) numdays = 31; 32
33 Applying Boolean Exp. in daysinmonth q Implement leap year condition: most years that are evenly divisible by 4 are leap years; However, there are some exceptions to this rule: Years that are evenly divisible by 100 are not leap years, unless they are also evenly divisible by 400 leap year or 4 year % 400 == 0 and year % 4 == 0 year % 100!= 0 33
34 Testing Leap Year leap year or year % 400 == 0 and year % 4 == 0 year % 100!= 0 y % 400 == 0 (y % 100!= 0 && y % 4 == 0) 34
35 Outline: Conditional Program Flow Control q Our journey of introducing conditionals simple if (a <comp> b) nested if/else Complexity of nested if/else: all path must return; mismatched else <condition> combining multiple <comp>; Boolean variables/expressions/methods
36 Reuse Testing for Leap Year q How do we define a method to reuse the ability to test if a year is a leap year?? isleapyear(int year); 36
37 Recall: boolean Type q boolean: A primitive type whose values are true and false. Like other types, it is legal to: create a boolean variable and assign it values pass a boolean value as a parameter return boolean value as a method call a method that returns a boolean and use it as a test
38 boolean Expressions q Similar to arithmetic expressions, except that the operands are Boolean values, Boolean variables, or a test using a relational operator (e.g., <, >). the operators are &&! Example boolean lovescs = true; boolean student = age < 21; // allow only CS-loving students over 21 if (student && lovescs) System.out.println( Pass"); // an alternative if (age < 21 && lovescs) System.out.println( Pass");
39 boolean Expressions: Example Boolean goodage = age >= 18 && age < 29; boolean goodheight = height >= 78 && height < 84; boolean rich = salary >= ; if ((goodage && goodheight) rich) { System.out.println("Okay, let's go out!"); else { System.out.println("It's not you, it's me...");
40 Mixed Arithmetic, Relation, Logical, and Assignment Expression q Example: boolean mystery = 5 * 7 >= * (7 1) && 7 <= 11; q Precedence ordering of boolean expression Arithmetic operators Relations operators (==,!=, <, >, <=, >=) Note that equality and relational operators cannot be chained (e.g., 1 < x < 3 is invalid) NOT (!) AND (&&) OR ( ) Assignment operators (=)
41 Example boolean mystery = 5 * 7 >= * (7 1) && 7 <= 11; 5 * 7 >= * 6 && 7 <= >= && 7 <= >= 33 && 7 <= 11 true && true true
42 English vs boolean q OR vs Exclusive OR I ll either watch TV or go to gym: Exclusive OR watchtv gotogym can be both true q x is between 1 and 10 1 <= x <= 10 1 <= x && x <= 10 q x is either 1 or 2 or 3 x == x ==1 x == 2 x == 3
43 Logical AND/OR Evaluation q Java uses shortcircuit when evaluating && and a && b shortcircuit: if a is false, b is not evaluated if ((count!= 0) && (total / count > AVG_THRESHOLD)){ // a b shortcircuit: if a is true, b is not evaluated 43
CS 112 Introduction to Programming
 CS 112 Introduction to Programming Conditional Statements Boolean Expressions and Methods Yang (Richard) Yang Computer Science Department Yale University 308A Watson, Phone: 432-6400 Email: yry@cs.yale.edu
CS 112 Introduction to Programming Conditional Statements Boolean Expressions and Methods Yang (Richard) Yang Computer Science Department Yale University 308A Watson, Phone: 432-6400 Email: yry@cs.yale.edu
Lecture 4: Conditionals
 Lecture 4: Conditionals Building Java Programs: A Back to Basics Approach by Stuart Reges and Marty Stepp Copyright (c) Pearson 2013. All rights reserved. Type boolean Type boolean boolean: A logical type
Lecture 4: Conditionals Building Java Programs: A Back to Basics Approach by Stuart Reges and Marty Stepp Copyright (c) Pearson 2013. All rights reserved. Type boolean Type boolean boolean: A logical type
CS 112 Introduction to Programming
 CS 112 Introduction to Programming Summary of Methods; User Input using Scanner Yang (Richard) Yang Computer Science Department Yale University 308A Watson, Phone: 432-6400 Email: yry@cs.yale.edu Admin
CS 112 Introduction to Programming Summary of Methods; User Input using Scanner Yang (Richard) Yang Computer Science Department Yale University 308A Watson, Phone: 432-6400 Email: yry@cs.yale.edu Admin
CS 112 Introduction to Programming
 CS 112 Introduction to Programming (Spring 2012) Lecture #8: More on Conditional & Loop Zhong Shao Department of Computer Science Yale University Office: 314 Watson http://flint.cs.yale.edu/cs112 Acknowledgements:
CS 112 Introduction to Programming (Spring 2012) Lecture #8: More on Conditional & Loop Zhong Shao Department of Computer Science Yale University Office: 314 Watson http://flint.cs.yale.edu/cs112 Acknowledgements:
Flow of Control of Program Statements CS 112 Introduction to Programming. Basic if Conditional Statement Basic Test: Relational Operators
 Flow of Control of Program Statements CS 112 Introduction to Programming (Spring 2012) q Java provides two types of program flow of control statements: decision statements, or conditional statements: decide
Flow of Control of Program Statements CS 112 Introduction to Programming (Spring 2012) q Java provides two types of program flow of control statements: decision statements, or conditional statements: decide
Garfield AP CS. User Input, If/Else. Most slides from Building Java Programs. Thanks, Stuart Regesand Marty Stepp!
 Garfield AP CS User Input, If/Else Most slides from Building Java Programs. Thanks, Stuart Regesand Marty Stepp! Warmup Write a method add10 that takes one integer parameter. Your method should return
Garfield AP CS User Input, If/Else Most slides from Building Java Programs. Thanks, Stuart Regesand Marty Stepp! Warmup Write a method add10 that takes one integer parameter. Your method should return
CS 112 Introduction to Programming
 CS 112 Introduction to Programming Program Analysis Yang (Richard) Yang Computer Science Department Yale University 308A Watson, Phone: 432-6400 Email: yry@cs.yale.edu Admin q PS5 Walkthrough Thursday
CS 112 Introduction to Programming Program Analysis Yang (Richard) Yang Computer Science Department Yale University 308A Watson, Phone: 432-6400 Email: yry@cs.yale.edu Admin q PS5 Walkthrough Thursday
Topic 11 Scanner object, conditional execution
 Topic 11 Scanner object, conditional execution "There are only two kinds of programming languages: those people always [complain] about and those nobody uses." Bjarne Stroustroup, creator of C++ Copyright
Topic 11 Scanner object, conditional execution "There are only two kinds of programming languages: those people always [complain] about and those nobody uses." Bjarne Stroustroup, creator of C++ Copyright
Topic 11 Scanner object, conditional execution
 https://www.dignitymemorial.com/obituaries/brookline-ma/adele-koss-5237804 Topic 11 Scanner object, conditional execution Logical thinking and experience was as important as theory in using the computer
https://www.dignitymemorial.com/obituaries/brookline-ma/adele-koss-5237804 Topic 11 Scanner object, conditional execution Logical thinking and experience was as important as theory in using the computer
AP Computer Science. if/else, return values. Copyright 2010 by Pearson Education
 AP Computer Science if/else, return values The if statement Executes a block of statements only if a test is true statement;... statement; Example: double gpa = console.nextdouble(); if (gpa >= 2.0) {
AP Computer Science if/else, return values The if statement Executes a block of statements only if a test is true statement;... statement; Example: double gpa = console.nextdouble(); if (gpa >= 2.0) {
Building Java Programs
 Building Java Programs Chapter 4 Lecture 4-1: if and if/else Statements reading: 4.2 self-check: #4-5, 7, 10, 11 exercises: #7 videos: Ch. 4 #2-4 The if/else statement Executes one block if a test is true,
Building Java Programs Chapter 4 Lecture 4-1: if and if/else Statements reading: 4.2 self-check: #4-5, 7, 10, 11 exercises: #7 videos: Ch. 4 #2-4 The if/else statement Executes one block if a test is true,
Advanced if/else & Cumulative Sum
 Advanced if/else & Cumulative Sum Subset of the Supplement Lesson slides from: Building Java Programs, Chapter 4 by Stuart Reges and Marty Stepp (http://www.buildingjavaprograms.com/ ) Questions to consider
Advanced if/else & Cumulative Sum Subset of the Supplement Lesson slides from: Building Java Programs, Chapter 4 by Stuart Reges and Marty Stepp (http://www.buildingjavaprograms.com/ ) Questions to consider
COMP-202: Foundations of Programming. Lecture 3: Boolean, Mathematical Expressions, and Flow Control Sandeep Manjanna, Summer 2015
 COMP-202: Foundations of Programming Lecture 3: Boolean, Mathematical Expressions, and Flow Control Sandeep Manjanna, Summer 2015 Announcements Slides will be posted before the class. There might be few
COMP-202: Foundations of Programming Lecture 3: Boolean, Mathematical Expressions, and Flow Control Sandeep Manjanna, Summer 2015 Announcements Slides will be posted before the class. There might be few
Building Java Programs
 Building Java Programs Chapter 4 Lecture 4-1: Scanner; if/else reading: 3.3 3.4, 4.1, 4.5 2 Interactive Programs with Scanner reading: 3.3-3.4 Interactive programs We have written programs that print console
Building Java Programs Chapter 4 Lecture 4-1: Scanner; if/else reading: 3.3 3.4, 4.1, 4.5 2 Interactive Programs with Scanner reading: 3.3-3.4 Interactive programs We have written programs that print console
CS 112 Introduction to Programming
 CS 112 Introduction to Programming Java Primitive Data Types; Arithmetic Expressions Yang (Richard) Yang Computer Science Department Yale University 308A Watson, Phone: 432-6400 Email: yry@cs.yale.edu
CS 112 Introduction to Programming Java Primitive Data Types; Arithmetic Expressions Yang (Richard) Yang Computer Science Department Yale University 308A Watson, Phone: 432-6400 Email: yry@cs.yale.edu
Admin. CS 112 Introduction to Programming. Recap: Java Static Methods. Recap: Decomposition Example. Recap: Static Method Example
 Admin CS 112 Introduction to Programming q Programming assignment 2 to be posted tonight Java Primitive Data Types; Arithmetic Expressions Yang (Richard) Yang Computer Science Department Yale University
Admin CS 112 Introduction to Programming q Programming assignment 2 to be posted tonight Java Primitive Data Types; Arithmetic Expressions Yang (Richard) Yang Computer Science Department Yale University
COSC 236 Section 101 Computer Science 1 -- Prof. Michael A. Soderstrand
 COSC 236 Section 101 Computer Science 1 -- Prof. Michael A. Soderstrand COSC 236 Web Site You will always find the course material at: http://www.class-notes.us or http://www.class-notes.info or http://www.lecture-notes.tripod.com
COSC 236 Section 101 Computer Science 1 -- Prof. Michael A. Soderstrand COSC 236 Web Site You will always find the course material at: http://www.class-notes.us or http://www.class-notes.info or http://www.lecture-notes.tripod.com
Returns & if/else. Parameters and Objects
 Returns & if/else Parameters and Objects Subset of the Supplement Lesson slides from: Building Java Programs, Chapter 3 & 4 by Stuart Reges and Marty Stepp (http://www.buildingjavaprograms.com/ ) & thanks
Returns & if/else Parameters and Objects Subset of the Supplement Lesson slides from: Building Java Programs, Chapter 3 & 4 by Stuart Reges and Marty Stepp (http://www.buildingjavaprograms.com/ ) & thanks
CS 112 Introduction to Programming
 CS 112 Introduction to Programming Graphics; Animation Yang (Richard) Yang Computer Science Department Yale University 308A Watson, Phone: 432-6400 Email: yry@cs.yale.edu Admin q Issues on PS3 NumberCoolness:
CS 112 Introduction to Programming Graphics; Animation Yang (Richard) Yang Computer Science Department Yale University 308A Watson, Phone: 432-6400 Email: yry@cs.yale.edu Admin q Issues on PS3 NumberCoolness:
CS 112 Introduction to Programming
 CS 112 Introduction to Programming Graphics; Animation Yang (Richard) Yang Computer Science Department Yale University 308A Watson, Phone: 432-6400 Email: yry@cs.yale.edu Admin q Issues on PS3 NumberCoolness:
CS 112 Introduction to Programming Graphics; Animation Yang (Richard) Yang Computer Science Department Yale University 308A Watson, Phone: 432-6400 Email: yry@cs.yale.edu Admin q Issues on PS3 NumberCoolness:
Building Java Programs
 Building Java Programs Chapter 4 Lecture 4-1: if and if/else Statements reading: 4.2 self-check: #4-5, 7, 10, 11 exercises: #7 videos: Ch. 4 #2-4 Loops with if/else if/else statements can be used with
Building Java Programs Chapter 4 Lecture 4-1: if and if/else Statements reading: 4.2 self-check: #4-5, 7, 10, 11 exercises: #7 videos: Ch. 4 #2-4 Loops with if/else if/else statements can be used with
H212 Introduction to Software Systems Honors
 Introduction to Software Systems Honors Lecture #04: Fall 2015 1/20 Office hours Monday, Wednesday: 10:15 am to 12:00 noon Tuesday, Thursday: 2:00 to 3:45 pm Office: Lindley Hall, Room 401C 2/20 Printing
Introduction to Software Systems Honors Lecture #04: Fall 2015 1/20 Office hours Monday, Wednesday: 10:15 am to 12:00 noon Tuesday, Thursday: 2:00 to 3:45 pm Office: Lindley Hall, Room 401C 2/20 Printing
Fundamentals of Programming Data Types & Methods
 Fundamentals of Programming Data Types & Methods By Budditha Hettige Overview Summary (Previous Lesson) Java Data types Default values Variables Input data from keyboard Display results Methods Operators
Fundamentals of Programming Data Types & Methods By Budditha Hettige Overview Summary (Previous Lesson) Java Data types Default values Variables Input data from keyboard Display results Methods Operators
Building Java Programs
 Building Java Programs Chapter 4: Conditional Execution 1 loop techniques cumulative sum fencepost loops conditional execution Chapter outline the if statement and the if/else statement relational expressions
Building Java Programs Chapter 4: Conditional Execution 1 loop techniques cumulative sum fencepost loops conditional execution Chapter outline the if statement and the if/else statement relational expressions
Chapter 3. Selections
 Chapter 3 Selections 1 Outline 1. Flow of Control 2. Conditional Statements 3. The if Statement 4. The if-else Statement 5. The Conditional operator 6. The Switch Statement 7. Useful Hints 2 1. Flow of
Chapter 3 Selections 1 Outline 1. Flow of Control 2. Conditional Statements 3. The if Statement 4. The if-else Statement 5. The Conditional operator 6. The Switch Statement 7. Useful Hints 2 1. Flow of
Introduction to Java Unit 1. Using BlueJ to Write Programs
 Introduction to Java Unit 1. Using BlueJ to Write Programs 1. Open up BlueJ. Click on the Project menu and select New Project. You should see the window on the right. Navigate to wherever you plan to save
Introduction to Java Unit 1. Using BlueJ to Write Programs 1. Open up BlueJ. Click on the Project menu and select New Project. You should see the window on the right. Navigate to wherever you plan to save
CS 112 Introduction to Programming
 CS 112 Introduction to Programming Variables; Type Casting; Using Variables in for Loops Yang (Richard) Yang Computer Science Department Yale University 308A Watson, Phone: 432-6400 Email: yry@cs.yale.edu
CS 112 Introduction to Programming Variables; Type Casting; Using Variables in for Loops Yang (Richard) Yang Computer Science Department Yale University 308A Watson, Phone: 432-6400 Email: yry@cs.yale.edu
More Things We Can Do With It! Overview. Circle Calculations. πr 2. π = More operators and expression types More statements
 More Things We Can Do With It! More operators and expression types More s 11 October 2007 Ariel Shamir 1 Overview Variables and declaration More operators and expressions String type and getting input
More Things We Can Do With It! More operators and expression types More s 11 October 2007 Ariel Shamir 1 Overview Variables and declaration More operators and expressions String type and getting input
Building Java Programs. Chapter 2: Primitive Data and Definite Loops
 Building Java Programs Chapter 2: Primitive Data and Definite Loops Copyright 2008 2006 by Pearson Education 1 Lecture outline data concepts Primitive types: int, double, char (for now) Expressions: operators,
Building Java Programs Chapter 2: Primitive Data and Definite Loops Copyright 2008 2006 by Pearson Education 1 Lecture outline data concepts Primitive types: int, double, char (for now) Expressions: operators,
Flow of Control Branching 2. Cheng, Wei COMP May 19, Title
 Flow of Control Branching 2 Cheng, Wei COMP110-001 May 19, 2014 Title Review of Previous Lecture If else Q1: Write a small program that Reads an integer from user Prints Even if the integer is even Otherwise,
Flow of Control Branching 2 Cheng, Wei COMP110-001 May 19, 2014 Title Review of Previous Lecture If else Q1: Write a small program that Reads an integer from user Prints Even if the integer is even Otherwise,
Admin. CS 112 Introduction to Programming. Recap: Exceptions. Summary: for loop. Recap: CaesarFile using Loop. Summary: Flow Control Statements
 Admin. CS 112 Introduction to Programming q Puzzle Day from Friday to Monday Arrays; Loop Patterns (break) Yang (Richard) Yang Computer Science Department Yale University 308A Watson, Phone: 432-6400 Email:
Admin. CS 112 Introduction to Programming q Puzzle Day from Friday to Monday Arrays; Loop Patterns (break) Yang (Richard) Yang Computer Science Department Yale University 308A Watson, Phone: 432-6400 Email:
CSS 161 Fundamentals of Compu3ng. Flow control (2) October 10, Instructor: Uma Murthy
 CSS 161 Fundamentals of Compu3ng Flow control (2) October 10, 2012 Instructor: Uma Murthy Outline Reminders: HW 2 due Monday Today: Errata Review condi3onals Boolean expressions (3.2) Loops (3.3) CSS 161:
CSS 161 Fundamentals of Compu3ng Flow control (2) October 10, 2012 Instructor: Uma Murthy Outline Reminders: HW 2 due Monday Today: Errata Review condi3onals Boolean expressions (3.2) Loops (3.3) CSS 161:
CS 112 Introduction to Programming
 CS 112 Introduction to Programming Arrays; Loop Patterns (break) Yang (Richard) Yang Computer Science Department Yale University 308A Watson, Phone: 432-6400 Email: yry@cs.yale.edu Admin. q Puzzle Day
CS 112 Introduction to Programming Arrays; Loop Patterns (break) Yang (Richard) Yang Computer Science Department Yale University 308A Watson, Phone: 432-6400 Email: yry@cs.yale.edu Admin. q Puzzle Day
Computational Expression
 Computational Expression Variables, Primitive Data Types, Expressions Janyl Jumadinova 28-30 January, 2019 Janyl Jumadinova Computational Expression 28-30 January, 2019 1 / 17 Variables Variable is a name
Computational Expression Variables, Primitive Data Types, Expressions Janyl Jumadinova 28-30 January, 2019 Janyl Jumadinova Computational Expression 28-30 January, 2019 1 / 17 Variables Variable is a name
Building Java Programs
 Building Java Programs Chapter 2 Lecture 2-1: Expressions and Variables reading: 2.1-2.2 1 2 Data and expressions reading: 2.1 3 The computer s view Internally, computers store everything as 1 s and 0
Building Java Programs Chapter 2 Lecture 2-1: Expressions and Variables reading: 2.1-2.2 1 2 Data and expressions reading: 2.1 3 The computer s view Internally, computers store everything as 1 s and 0
CS 106 Introduction to Computer Science I
 CS 106 Introduction to Computer Science I 06 / 02 / 2015 Instructor: Michael Eckmann Today s Topics Operators continue if/else statements User input Operators + when used with numeric types (e.g. int,
CS 106 Introduction to Computer Science I 06 / 02 / 2015 Instructor: Michael Eckmann Today s Topics Operators continue if/else statements User input Operators + when used with numeric types (e.g. int,
Topic 4 Expressions and variables
 Topic 4 Expressions and variables "Once a person has understood the way variables are used in programming, he has understood the quintessence of programming." -Professor Edsger W. Dijkstra Based on slides
Topic 4 Expressions and variables "Once a person has understood the way variables are used in programming, he has understood the quintessence of programming." -Professor Edsger W. Dijkstra Based on slides
AP Computer Science Unit 1. Writing Programs Using BlueJ
 AP Computer Science Unit 1. Writing Programs Using BlueJ 1. Open up BlueJ. Click on the Project menu and select New Project. You should see the window on the right. Navigate to wherever you plan to save
AP Computer Science Unit 1. Writing Programs Using BlueJ 1. Open up BlueJ. Click on the Project menu and select New Project. You should see the window on the right. Navigate to wherever you plan to save
Chapter 4: Control Structures I
 Chapter 4: Control Structures I Java Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program Design, Second Edition Chapter Objectives Learn about control structures. Examine relational and logical operators. Explore
Chapter 4: Control Structures I Java Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program Design, Second Edition Chapter Objectives Learn about control structures. Examine relational and logical operators. Explore
Administration. Conditional Statements. Agenda. Syntax. Flow of control. Lab 2 due now on floppy Lab 3 due tomorrow via FTP
 Administration Conditional Statements CS 99 Summer 2000 Michael Clarkson Lecture 4 Lab 2 due now on floppy Lab 3 due tomorrow via FTP need Instruct account password Lab 4 posted this afternoon Prelim 1
Administration Conditional Statements CS 99 Summer 2000 Michael Clarkson Lecture 4 Lab 2 due now on floppy Lab 3 due tomorrow via FTP need Instruct account password Lab 4 posted this afternoon Prelim 1
Programming with Java
 Programming with Java Data Types & Input Statement Lecture 04 First stage Software Engineering Dep. Saman M. Omer 2017-2018 Objectives q By the end of this lecture you should be able to : ü Know rules
Programming with Java Data Types & Input Statement Lecture 04 First stage Software Engineering Dep. Saman M. Omer 2017-2018 Objectives q By the end of this lecture you should be able to : ü Know rules
AP Computer Science. Return values, Math, and double. Copyright 2010 by Pearson Education
 AP Computer Science Return values, Math, and double Distance between points Write a method that given x and y coordinates for two points prints the distance between them If you can t do all of it, pseudocode?
AP Computer Science Return values, Math, and double Distance between points Write a method that given x and y coordinates for two points prints the distance between them If you can t do all of it, pseudocode?
Admin. CS 112 Introduction to Programming. Recap. Example: Nested Loop. Example: Rewrite
 Admin CS 112 Introduction to Programming Graphics; Animation Yang (Richard) Yang Computer Science Department Yale University 308A Watson, Phone: 432-6400 Email: yry@cs.yale.edu q Issues on PS3 NumberCoolness:
Admin CS 112 Introduction to Programming Graphics; Animation Yang (Richard) Yang Computer Science Department Yale University 308A Watson, Phone: 432-6400 Email: yry@cs.yale.edu q Issues on PS3 NumberCoolness:
Topic 12 more if/else, cumulative algorithms, printf
 Topic 12 more if/else, cumulative algorithms, printf "We flew down weekly to meet with IBM, but they thought the way to measure software was the amount of code we wrote, when really the better the software,
Topic 12 more if/else, cumulative algorithms, printf "We flew down weekly to meet with IBM, but they thought the way to measure software was the amount of code we wrote, when really the better the software,
2.2 - Making Decisions
 2.2 - Making Decisions So far we have only made programs that execute the statements in order, starting with the statements at the top of the screen and moving down. However, you can write programs that
2.2 - Making Decisions So far we have only made programs that execute the statements in order, starting with the statements at the top of the screen and moving down. However, you can write programs that
ECE 122 Engineering Problem Solving with Java
 ECE 122 Engineering Problem Solving with Java Lecture 3 Expression Evaluation and Program Interaction Outline Problem: How do I input data and use it in complicated expressions Creating complicated expressions
ECE 122 Engineering Problem Solving with Java Lecture 3 Expression Evaluation and Program Interaction Outline Problem: How do I input data and use it in complicated expressions Creating complicated expressions
4. Java Project Design, Input Methods
 4-1 4. Java Project Design, Input Methods Review and Preview You should now be fairly comfortable with creating, compiling and running simple Java projects. In this class, we continue learning new Java
4-1 4. Java Project Design, Input Methods Review and Preview You should now be fairly comfortable with creating, compiling and running simple Java projects. In this class, we continue learning new Java
Chapter 4: Conditionals and Recursion
 Chapter 4: Conditionals and Recursion Think Java: How to Think Like a Computer Scientist 5.1.2 by Allen B. Downey Agenda The modulus operator Random Number Generation Conditional Execution Alternative
Chapter 4: Conditionals and Recursion Think Java: How to Think Like a Computer Scientist 5.1.2 by Allen B. Downey Agenda The modulus operator Random Number Generation Conditional Execution Alternative
COMP 250: Java Programming I. Carlos G. Oliver, Jérôme Waldispühl January 17-18, 2018 Slides adapted from M. Blanchette
 COMP 250: Java Programming I Carlos G. Oliver, Jérôme Waldispühl January 17-18, 2018 Slides adapted from M. Blanchette Variables and types [Downey Ch 2] Variable: temporary storage location in memory.
COMP 250: Java Programming I Carlos G. Oliver, Jérôme Waldispühl January 17-18, 2018 Slides adapted from M. Blanchette Variables and types [Downey Ch 2] Variable: temporary storage location in memory.
Selec%on and Decision Structures in Java: If Statements and Switch Statements CSC 121 Fall 2016 Howard Rosenthal
 Selec%on and Decision Structures in Java: If Statements and Switch Statements CSC 121 Fall 2016 Howard Rosenthal Lesson Goals Understand Control Structures Understand how to control the flow of a program
Selec%on and Decision Structures in Java: If Statements and Switch Statements CSC 121 Fall 2016 Howard Rosenthal Lesson Goals Understand Control Structures Understand how to control the flow of a program
Building Java Programs Chapter 4
 Building Java Programs Chapter 4 Conditional Execution Copyright (c) Pearson 2013. All rights reserved. The if statement Executes a block of statements only if a test is true if (test) { statement;...
Building Java Programs Chapter 4 Conditional Execution Copyright (c) Pearson 2013. All rights reserved. The if statement Executes a block of statements only if a test is true if (test) { statement;...
Building Java Programs
 Building Java Programs Chapter 5 Random Numbers reading: 5.1, 5.6 1 http://xkcd.com/221/ 2 The while loop while loop: Repeatedly executes its body as long as a logical test is true. while (test) { statement(s);
Building Java Programs Chapter 5 Random Numbers reading: 5.1, 5.6 1 http://xkcd.com/221/ 2 The while loop while loop: Repeatedly executes its body as long as a logical test is true. while (test) { statement(s);
Chapter 3 Selections. Liang, Introduction to Java Programming, Eighth Edition, (c) 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 3 Selections Liang, Introduction to Java Programming, Eighth Edition, (c) 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved. 0132130807 1 Motivations If you assigned a negative value for radius
Chapter 3 Selections Liang, Introduction to Java Programming, Eighth Edition, (c) 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved. 0132130807 1 Motivations If you assigned a negative value for radius
Using Java Classes Fall 2018 Margaret Reid-Miller
 Using Java Classes 15-121 Fall 2018 Margaret Reid-Miller Today Strings I/O (using Scanner) Loops, Conditionals, Scope Math Class (random) Fall 2018 15-121 (Reid-Miller) 2 The Math Class The Math class
Using Java Classes 15-121 Fall 2018 Margaret Reid-Miller Today Strings I/O (using Scanner) Loops, Conditionals, Scope Math Class (random) Fall 2018 15-121 (Reid-Miller) 2 The Math Class The Math class
Lesson 7 Part 2 Flags
 Lesson 7 Part 2 Flags A Flag is a boolean variable that signals when some condition exists in a program. When a flag is set to true, it means some condition exists When a flag is set to false, it means
Lesson 7 Part 2 Flags A Flag is a boolean variable that signals when some condition exists in a program. When a flag is set to true, it means some condition exists When a flag is set to false, it means
AP Computer Science Unit 1. Writing Programs Using BlueJ
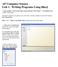 AP Computer Science Unit 1. Writing Programs Using BlueJ 1. Open up BlueJ. Click on the Project menu and select New Project. You should see the window on the right. Navigate to wherever you plan to save
AP Computer Science Unit 1. Writing Programs Using BlueJ 1. Open up BlueJ. Click on the Project menu and select New Project. You should see the window on the right. Navigate to wherever you plan to save
Full file at
 Java Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program Design, 3 rd Edition 2-1 Chapter 2 Basic Elements of Java At a Glance Instructor s Manual Table of Contents Overview Objectives s Quick Quizzes Class
Java Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program Design, 3 rd Edition 2-1 Chapter 2 Basic Elements of Java At a Glance Instructor s Manual Table of Contents Overview Objectives s Quick Quizzes Class
CS 302: INTRODUCTION TO PROGRAMMING. Lectures 7&8
 CS 302: INTRODUCTION TO PROGRAMMING Lectures 7&8 Hopefully the Programming Assignment #1 released by tomorrow REVIEW The switch statement is an alternative way of writing what? How do you end a case in
CS 302: INTRODUCTION TO PROGRAMMING Lectures 7&8 Hopefully the Programming Assignment #1 released by tomorrow REVIEW The switch statement is an alternative way of writing what? How do you end a case in
COMP-202 Unit 4: Programming With Iterations. CONTENTS: The while and for statements
 COMP-202 Unit 4: Programming With Iterations CONTENTS: The while and for statements Introduction (1) Suppose we want to write a program to be used in cash registers in stores to compute the amount of money
COMP-202 Unit 4: Programming With Iterations CONTENTS: The while and for statements Introduction (1) Suppose we want to write a program to be used in cash registers in stores to compute the amount of money
School of Computer Science CPS109 Course Notes 5 Alexander Ferworn Updated Fall 15
 Table of Contents 1 INTRODUCTION... 1 2 IF... 1 2.1 BOOLEAN EXPRESSIONS... 3 2.2 BLOCKS... 3 2.3 IF-ELSE... 4 2.4 NESTING... 5 3 SWITCH (SOMETIMES KNOWN AS CASE )... 6 3.1 A BIT ABOUT BREAK... 7 4 CONDITIONAL
Table of Contents 1 INTRODUCTION... 1 2 IF... 1 2.1 BOOLEAN EXPRESSIONS... 3 2.2 BLOCKS... 3 2.3 IF-ELSE... 4 2.4 NESTING... 5 3 SWITCH (SOMETIMES KNOWN AS CASE )... 6 3.1 A BIT ABOUT BREAK... 7 4 CONDITIONAL
CS 112 Introduction to Programming. Exercise: MatchDB. match1. Removing break. Solution I: Using break. Loop Patterns: break; Fencepost.
 CS 112 Introduction to Programming CS112@Yale Loop Patterns: Fencepost Yang (Richard) Yang Computer Science Department Yale University 308A Watson, Phone: 432-6400 Email: yry@cs.yale.edu http://www.ultimateecards.com/image/772-jan-29-national-puzzle-day-card
CS 112 Introduction to Programming CS112@Yale Loop Patterns: Fencepost Yang (Richard) Yang Computer Science Department Yale University 308A Watson, Phone: 432-6400 Email: yry@cs.yale.edu http://www.ultimateecards.com/image/772-jan-29-national-puzzle-day-card
Following is the general form of a typical decision making structure found in most of the programming languages:
 Decision Making Decision making structures have one or more conditions to be evaluated or tested by the program, along with a statement or statements that are to be executed if the condition is determined
Decision Making Decision making structures have one or more conditions to be evaluated or tested by the program, along with a statement or statements that are to be executed if the condition is determined
Sequence structure. The computer executes java statements one after the other in the order in which they are written. Total = total +grade;
 Control Statements Control Statements All programs could be written in terms of only one of three control structures: Sequence Structure Selection Structure Repetition Structure Sequence structure The
Control Statements Control Statements All programs could be written in terms of only one of three control structures: Sequence Structure Selection Structure Repetition Structure Sequence structure The
BASIC COMPUTATION. public static void main(string [] args) Fundamentals of Computer Science I
![BASIC COMPUTATION. public static void main(string [] args) Fundamentals of Computer Science I BASIC COMPUTATION. public static void main(string [] args) Fundamentals of Computer Science I](/thumbs/81/83968367.jpg) BASIC COMPUTATION x public static void main(string [] args) Fundamentals of Computer Science I Outline Using Eclipse Data Types Variables Primitive and Class Data Types Expressions Declaration Assignment
BASIC COMPUTATION x public static void main(string [] args) Fundamentals of Computer Science I Outline Using Eclipse Data Types Variables Primitive and Class Data Types Expressions Declaration Assignment
Selec%on and Decision Structures in Java: If Statements and Switch Statements CSC 121 Spring 2016 Howard Rosenthal
 Selec%on and Decision Structures in Java: If Statements and Switch Statements CSC 121 Spring 2016 Howard Rosenthal Lesson Goals Understand Control Structures Understand how to control the flow of a program
Selec%on and Decision Structures in Java: If Statements and Switch Statements CSC 121 Spring 2016 Howard Rosenthal Lesson Goals Understand Control Structures Understand how to control the flow of a program
Flow Control. Key Notion. Statement Categories. 28-Oct-10
 Boaz Kantor Introduction to Computer Science, Fall semester 2010-2011 IDC Herzliya Flow Control Raistlin: This alters time. Astinus: This alters nothing...time flows on, undisturbed. Raistlin: And carries
Boaz Kantor Introduction to Computer Science, Fall semester 2010-2011 IDC Herzliya Flow Control Raistlin: This alters time. Astinus: This alters nothing...time flows on, undisturbed. Raistlin: And carries
McGill University School of Computer Science COMP-202A Introduction to Computing 1
 McGill University School of Computer Science COMP-202A Introduction to Computing 1 Midterm Exam Thursday, October 26, 2006, 18:00-20:00 (6:00 8:00 PM) Instructors: Mathieu Petitpas, Shah Asaduzzaman, Sherif
McGill University School of Computer Science COMP-202A Introduction to Computing 1 Midterm Exam Thursday, October 26, 2006, 18:00-20:00 (6:00 8:00 PM) Instructors: Mathieu Petitpas, Shah Asaduzzaman, Sherif
Boolean Expressions. So, for example, here are the results of several simple Boolean expressions:
 Boolean Expressions Now we have the ability to read in some information, calculate some formulas and display the information to the user in a nice format. However, the real power of computer programs lies
Boolean Expressions Now we have the ability to read in some information, calculate some formulas and display the information to the user in a nice format. However, the real power of computer programs lies
Chapter 2: Basic Elements of Java
 Chapter 2: Basic Elements of Java TRUE/FALSE 1. The pair of characters // is used for single line comments. ANS: T PTS: 1 REF: 29 2. The == characters are a special symbol in Java. ANS: T PTS: 1 REF: 30
Chapter 2: Basic Elements of Java TRUE/FALSE 1. The pair of characters // is used for single line comments. ANS: T PTS: 1 REF: 29 2. The == characters are a special symbol in Java. ANS: T PTS: 1 REF: 30
CS 112 Introduction to Programming
 CS 112 Introduction to Programming Animation (sleep and double buffering); Methods with Return; Yang (Richard) Yang Computer Science Department Yale University 308A Watson, Phone: 432-6400 Email: yry@cs.yale.edu
CS 112 Introduction to Programming Animation (sleep and double buffering); Methods with Return; Yang (Richard) Yang Computer Science Department Yale University 308A Watson, Phone: 432-6400 Email: yry@cs.yale.edu
CS 112 Introduction to Programming
 CS 112 Introduction to Programming Animation (sleep and double buffering); Methods with Return; Yang (Richard) Yang Computer Science Department Yale University 308A Watson, Phone: 432-6400 Email: yry@cs.yale.edu
CS 112 Introduction to Programming Animation (sleep and double buffering); Methods with Return; Yang (Richard) Yang Computer Science Department Yale University 308A Watson, Phone: 432-6400 Email: yry@cs.yale.edu
Module 3 SELECTION STRUCTURES 2/15/19 CSE 1321 MODULE 3 1
 Module 3 SELECTION STRUCTURES 2/15/19 CSE 1321 MODULE 3 1 Motivation In the programs we have written thus far, statements are executed one after the other, in the order in which they appear. Programs often
Module 3 SELECTION STRUCTURES 2/15/19 CSE 1321 MODULE 3 1 Motivation In the programs we have written thus far, statements are executed one after the other, in the order in which they appear. Programs often
Data Conversion & Scanner Class
 Data Conversion & Scanner Class Quick review of last lecture August 29, 2007 ComS 207: Programming I (in Java) Iowa State University, FALL 2007 Instructor: Alexander Stoytchev Numeric Primitive Data Storing
Data Conversion & Scanner Class Quick review of last lecture August 29, 2007 ComS 207: Programming I (in Java) Iowa State University, FALL 2007 Instructor: Alexander Stoytchev Numeric Primitive Data Storing
CS 177 Recitation. Week 8 Methods
 CS 177 Recitation Week 8 Methods Questions? Announcements Project 3 milestone due next Thursday 10/22 9pm Turn in with: turnin c cs177=xxxx p project3m Project3.java Make sure you turn in to project3m
CS 177 Recitation Week 8 Methods Questions? Announcements Project 3 milestone due next Thursday 10/22 9pm Turn in with: turnin c cs177=xxxx p project3m Project3.java Make sure you turn in to project3m
Building Java Programs
 Building Java Programs Chapter 1 Lecture 2: Static Methods reading: 1.4-1.5 (Slides adapted from Stuart Reges, Hélène Martin, and Marty Stepp) 2 Recall: structure, syntax class: a program public class
Building Java Programs Chapter 1 Lecture 2: Static Methods reading: 1.4-1.5 (Slides adapted from Stuart Reges, Hélène Martin, and Marty Stepp) 2 Recall: structure, syntax class: a program public class
Flow Control. Boaz Kantor Introduction to Computer Science, Fall semester IDC Herzliya
 Boaz Kantor Introduction to Computer Science, Fall semester 2010-2011 IDC Herzliya Flow Control Raistlin: This alters time. Astinus: This alters nothing...time flows on, undisturbed. Raistlin: And carries
Boaz Kantor Introduction to Computer Science, Fall semester 2010-2011 IDC Herzliya Flow Control Raistlin: This alters time. Astinus: This alters nothing...time flows on, undisturbed. Raistlin: And carries
CSE115 / CSE503 Introduction to Computer Science I Dr. Carl Alphonce 343 Davis Hall Office hours:
 CSE115 / CSE503 Introduction to Computer Science I Dr. Carl Alphonce 343 Davis Hall alphonce@buffalo.edu Office hours: Tuesday 10:00 AM 12:00 PM * Wednesday 4:00 PM 5:00 PM Friday 11:00 AM 12:00 PM OR
CSE115 / CSE503 Introduction to Computer Science I Dr. Carl Alphonce 343 Davis Hall alphonce@buffalo.edu Office hours: Tuesday 10:00 AM 12:00 PM * Wednesday 4:00 PM 5:00 PM Friday 11:00 AM 12:00 PM OR
Primitive data, expressions, and variables
 How the computer sees the world Primitive data, expressions, and variables Readings:.. Internally, the computer stores everything in terms of s and 0 s Example: h 0000 "hi" 0000000 0 0000 How can the computer
How the computer sees the world Primitive data, expressions, and variables Readings:.. Internally, the computer stores everything in terms of s and 0 s Example: h 0000 "hi" 0000000 0 0000 How can the computer
CMPT 125: Lecture 4 Conditionals and Loops
 CMPT 125: Lecture 4 Conditionals and Loops Tamara Smyth, tamaras@cs.sfu.ca School of Computing Science, Simon Fraser University January 17, 2009 1 Flow of Control The order in which statements are executed
CMPT 125: Lecture 4 Conditionals and Loops Tamara Smyth, tamaras@cs.sfu.ca School of Computing Science, Simon Fraser University January 17, 2009 1 Flow of Control The order in which statements are executed
CS/IT 114 Introduction to Java, Part 1 FALL 2016 CLASS 19: NOV. 15TH INSTRUCTOR: JIAYIN WANG
 CS/IT 114 Introduction to Java, Part 1 FALL 2016 CLASS 19: NOV. 15TH INSTRUCTOR: JIAYIN WANG 1 Notice Assignment Class Exercise 19 is assigned Homework 8 is assigned Both Homework 8 and Exercise 19 are
CS/IT 114 Introduction to Java, Part 1 FALL 2016 CLASS 19: NOV. 15TH INSTRUCTOR: JIAYIN WANG 1 Notice Assignment Class Exercise 19 is assigned Homework 8 is assigned Both Homework 8 and Exercise 19 are
Building Java Programs
 Building Java Programs Chapter 4 Lecture 4-2: Advanced if/else; Cumulative sum; reading: 4.2, 4.4-4.5 2 Advanced if/else reading: 4.4-4.5 Factoring if/else code factoring: Extracting common/redundant code.
Building Java Programs Chapter 4 Lecture 4-2: Advanced if/else; Cumulative sum; reading: 4.2, 4.4-4.5 2 Advanced if/else reading: 4.4-4.5 Factoring if/else code factoring: Extracting common/redundant code.
CS-201 Introduction to Programming with Java
 CS-201 Introduction to Programming with Java California State University, Los Angeles Computer Science Department Lecture IX: Methods Introduction method: construct for grouping statements together to
CS-201 Introduction to Programming with Java California State University, Los Angeles Computer Science Department Lecture IX: Methods Introduction method: construct for grouping statements together to
Object Oriented Programming. Java-Lecture 1
 Object Oriented Programming Java-Lecture 1 Standard output System.out is known as the standard output object Methods to display text onto the standard output System.out.print prints text onto the screen
Object Oriented Programming Java-Lecture 1 Standard output System.out is known as the standard output object Methods to display text onto the standard output System.out.print prints text onto the screen
Chapter 2: Data and Expressions
 Chapter 2: Data and Expressions CS 121 Department of Computer Science College of Engineering Boise State University January 15, 2015 Chapter 2: Data and Expressions CS 121 1 / 1 Chapter 2 Part 1: Data
Chapter 2: Data and Expressions CS 121 Department of Computer Science College of Engineering Boise State University January 15, 2015 Chapter 2: Data and Expressions CS 121 1 / 1 Chapter 2 Part 1: Data
COMP 202 Java in one week
 CONTENTS: Basics of Programming Variables and Assignment Data Types: int, float, (string) Example: Implementing a calculator COMP 202 Java in one week The Java Programming Language A programming language
CONTENTS: Basics of Programming Variables and Assignment Data Types: int, float, (string) Example: Implementing a calculator COMP 202 Java in one week The Java Programming Language A programming language
Using APIs. Chapter 3. Outline Fields Overall Layout. Java By Abstraction Chapter 3. Field Summary static double PI
 Outline Chapter 3 Using APIs 3.1 Anatomy of an API 3.1.1 Overall Layout 3.1.2 Fields 3.1.3 Methods 3.2 A Development Walkthrough 3.2.1 3.2.2 The Mortgage Application 3.2.3 Output Formatting 3.2.4 Relational
Outline Chapter 3 Using APIs 3.1 Anatomy of an API 3.1.1 Overall Layout 3.1.2 Fields 3.1.3 Methods 3.2 A Development Walkthrough 3.2.1 3.2.2 The Mortgage Application 3.2.3 Output Formatting 3.2.4 Relational
JAVA PROGRAMMING LAB. ABSTRACT In this Lab you will learn to define and invoke void and return java methods
 Islamic University of Gaza Faculty of Engineering Computer Engineering Dept. Computer Programming Lab (ECOM 2114) ABSTRACT In this Lab you will learn to define and invoke void and return java methods JAVA
Islamic University of Gaza Faculty of Engineering Computer Engineering Dept. Computer Programming Lab (ECOM 2114) ABSTRACT In this Lab you will learn to define and invoke void and return java methods JAVA
Constants. Why Use Constants? main Method Arguments. CS256 Computer Science I Kevin Sahr, PhD. Lecture 25: Miscellaneous
 CS256 Computer Science I Kevin Sahr, PhD Lecture 25: Miscellaneous 1 main Method Arguments recall the method header of the main method note the argument list public static void main (String [] args) we
CS256 Computer Science I Kevin Sahr, PhD Lecture 25: Miscellaneous 1 main Method Arguments recall the method header of the main method note the argument list public static void main (String [] args) we
CIS 1068 Design and Abstraction Spring 2017 Midterm 1a
 Spring 2017 Name: TUID: Page Points Score 1 28 2 18 3 12 4 12 5 15 6 15 Total: 100 Instructions The exam is closed book, closed notes. You may not use a calculator, cell phone, etc. i Some API Reminders
Spring 2017 Name: TUID: Page Points Score 1 28 2 18 3 12 4 12 5 15 6 15 Total: 100 Instructions The exam is closed book, closed notes. You may not use a calculator, cell phone, etc. i Some API Reminders
Java Coding 3. Over & over again!
 Java Coding 3 Over & over again! Repetition Java repetition statements while (condition) statement; do statement; while (condition); where for ( init; condition; update) statement; statement is any Java
Java Coding 3 Over & over again! Repetition Java repetition statements while (condition) statement; do statement; while (condition); where for ( init; condition; update) statement; statement is any Java
Lecture Set 2: Starting Java
 Lecture Set 2: Starting Java 1. Java Concepts 2. Java Programming Basics 3. User output 4. Variables and types 5. Expressions 6. User input 7. Uninitialized Variables 0 This Course: Intro to Procedural
Lecture Set 2: Starting Java 1. Java Concepts 2. Java Programming Basics 3. User output 4. Variables and types 5. Expressions 6. User input 7. Uninitialized Variables 0 This Course: Intro to Procedural
St. Edmund Preparatory High School Brooklyn, NY
 AP Computer Science Mr. A. Pinnavaia Summer Assignment St. Edmund Preparatory High School Name: I know it has been about 7 months since you last thought about programming. It s ok. I wouldn t want to think
AP Computer Science Mr. A. Pinnavaia Summer Assignment St. Edmund Preparatory High School Name: I know it has been about 7 months since you last thought about programming. It s ok. I wouldn t want to think
FLOW CONTROL. Author: Boaz Kantor The Interdisciplinary Center, Herzliya Introduction to Computer Science Winter Semester
 Author: Boaz Kantor The Interdisciplinary Center, Herzliya Introduction to Computer Science Winter 2008-9 Semester FLOW CONTROL Flow Control Hold 2 balls in left hand, 1 ball in right Throw ball from left
Author: Boaz Kantor The Interdisciplinary Center, Herzliya Introduction to Computer Science Winter 2008-9 Semester FLOW CONTROL Flow Control Hold 2 balls in left hand, 1 ball in right Throw ball from left
AP Computer Science A
 AP Computer Science A 1st Quarter Notes Table of Contents - section links Click on the date or topic below to jump to that section Date : 9/8/2017 Aim : Java Basics Objects and Classes Data types: Primitive
AP Computer Science A 1st Quarter Notes Table of Contents - section links Click on the date or topic below to jump to that section Date : 9/8/2017 Aim : Java Basics Objects and Classes Data types: Primitive
Lecture Set 2: Starting Java
 Lecture Set 2: Starting Java 1. Java Concepts 2. Java Programming Basics 3. User output 4. Variables and types 5. Expressions 6. User input 7. Uninitialized Variables 0 This Course: Intro to Procedural
Lecture Set 2: Starting Java 1. Java Concepts 2. Java Programming Basics 3. User output 4. Variables and types 5. Expressions 6. User input 7. Uninitialized Variables 0 This Course: Intro to Procedural
CS 112 Introduction to Programming
 Sierpinski Valentine http://xkcd.com/543/ 1 CS 112 Introduction to Programming Switch; Text Processing Yang (Richard) Yang Computer Science Department Yale University 308A Watson, Phone: 432-6400 Email:
Sierpinski Valentine http://xkcd.com/543/ 1 CS 112 Introduction to Programming Switch; Text Processing Yang (Richard) Yang Computer Science Department Yale University 308A Watson, Phone: 432-6400 Email:
Sierpinski Valentine.
 Sierpinski Valentine http://xkcd.com/543/ 1 CS 112 Introduction to Programming Switch; Text Processing Yang (Richard) Yang Computer Science Department Yale University 308A Watson, Phone: 432-6400 Email:
Sierpinski Valentine http://xkcd.com/543/ 1 CS 112 Introduction to Programming Switch; Text Processing Yang (Richard) Yang Computer Science Department Yale University 308A Watson, Phone: 432-6400 Email:
Chapter 3 Selection Statements
 Chapter 3 Selection Statements 3.1 Introduction Java provides selection statements that let you choose actions with two or more alternative courses. Selection statements use conditions. Conditions are
Chapter 3 Selection Statements 3.1 Introduction Java provides selection statements that let you choose actions with two or more alternative courses. Selection statements use conditions. Conditions are
Course Outline. Introduction to java
 Course Outline 1. Introduction to OO programming 2. Language Basics Syntax and Semantics 3. Algorithms, stepwise refinements. 4. Quiz/Assignment ( 5. Repetitions (for loops) 6. Writing simple classes 7.
Course Outline 1. Introduction to OO programming 2. Language Basics Syntax and Semantics 3. Algorithms, stepwise refinements. 4. Quiz/Assignment ( 5. Repetitions (for loops) 6. Writing simple classes 7.
A Quick and Dirty Overview of Java and. Java Programming
 Department of Computer Science New Mexico State University. CS 272 A Quick and Dirty Overview of Java and.......... Java Programming . Introduction Objectives In this document we will provide a very brief
Department of Computer Science New Mexico State University. CS 272 A Quick and Dirty Overview of Java and.......... Java Programming . Introduction Objectives In this document we will provide a very brief
