Virtual Memory Outline
|
|
|
- Mavis Lawson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Virtual Memory Outline Background Demand Paging Copy-on-Write Page Replacement Allocation of Frames Thrashing Memory-Mapped Files Allocating Kernel Memory Other Considerations Operating-System Examples 1
2 Background Virtual memory separation of user logical memory from physical memory only part of the program needs to be in memory for execution logical address space can therefore be much larger than physical address space allows address spaces to be shared by several processes allows for more efficient process creation Benefits of not requiring the entire program in memory before execution programs can be larger than the physical address space more programs can be resident in memory at the same time faster program startup 2
3 Virtual-address Space Space between heap and stack is not used, unless the heap or stack grows virtual memory does not require physical pages for such holes Shared memory pages can be easily shared by virtual memory shared libraries can be mapped read-only into address space of each process shared memory IPC can be implemented easily parent pages can be shared with child during fork() 3
4 Shared Library Using Virtual Memory 4
5 Demand Paging Bring a page into memory only when it is needed less I/O needed less memory needed faster response more applications simultaneously resident in memory Page is needed reference to it invalid reference abort not-in-memory bring to memory Lazy swapper never swaps a page into memory unless page will be needed Swapper that deals with pages is a pager 5
6 Demand Paging System 6
7 Valid-Invalid Bit Each page table entry associated with a valid invalid bit (v in-memory, i not-in-memory) initially set to invalid for all page table entries Example of a page table snapshot: Frame # valid-invalid bit v v v v i. i i page table Valid invalid bit in page table set to i during address translation causes a page fault 7
8 Page Table When Some Pages Are Not in Main Memory 8
9 Steps in Handling a Page Fault 9
10 Steps in Handling a Page Fault (2) 1. First reference to data or instructions on a page occurs 2. Memory access traps to the OS with a page fault operating system looks at another table to decide: invalid reference abort, or just not in memory 3. Find a free frame in physical memory 4. Read page from disk into free frame 5. Update page table valid-invalid bit to 'v' 6. Restart the instruction that caused the page fault 10
11 Performance of Demand Paging Page Fault Rate 0 p 1.0 if p = 0 no page faults if p = 1, every reference is a fault Effective Access Time (EAT) EAT = (1 p) x memory access + p (page fault overhead + swap page out + swap page in + restart overhead ) 11
12 Demand Paging Example Memory access time = 200 nanoseconds Average page-fault service time = 8 milliseconds EAT = (1 p) x p (8 milliseconds) = (1 p x p x 8,000,000 = p x 7,999,800 If one access out of 1,000 causes a page fault, then EAT = 8.2 microseconds. This is a slowdown by a factor of 40!! 12
13 Process Creation Copy-on-Write Original process creation fork() system called duplicates parent address space for child demand paging with copy-on-write allow sharing address spaces Copy-on-Write (COW) allows both parent and child processes to initially share the same pages in memory shared pages marked as copy-on-write pages if either process modifies a shared page, then the page is copied only the modified pages are copied COW allows more efficient process creation as only modified pages are copied Free pages are allocated from a pool of zeroed-out pages 13
14 Process 1 Modifies Page C Before After 14
15 Need For Page Replacement Review of demand paging separates logical memory from physical memory allows logical address space > physical address space enables a greater degree of multiprogramming higher CPU utilization and throughput allows fast process startup Drawbacks of demand paging may increase later individual memory access times potential for over-allocation of physical memory Over-allocation of memory currently active processes may reference more pages than room in physical memory pages from active processes may need to be replaced 15
16 Page Replacement Page replacement is needed when a page fault occurs, and there are no free frames to allocate terminate user process? swap out an entire process? find some page in memory, hopefully not really in use, and swap it out? Same page may be brought into memory several times 16
17 Basic Page Replacement 1. Find the location of the desired page on disk 2. Find a free frame: - If there is a free frame, use it - If there is no free frame, use a page replacement algorithm to select a victim frame 3. Bring the desired page into the (newly) free frame; update the page and frame tables 4. Restart the process Reducing page fault overhead use modify bit to with each frame only copy the replacement page to memory, if modified 17
18 Basic Page Replacement (2) 18
19 Page Replacement Algorithms Criteria get the lowest page fault rate Page replacement schemes first in first out (FIFO) optimal page replacement least recently used (LRU) LRU approximation algorithms counting based replacement Evaluation of replacement algorithm simulate it on a particular string of memory page references compute the number of page faults on the reference string In all our examples, the reference string is: 7, 0, 1, 2, 0, 3, 0, 4, 2, 3, 0, 3, 2, 1, 2, 0, 1, 7, 0, 1 19
20 Expected Graph of Page Faults Versus The Number of Frames 20
21 First-In-First-Out (FIFO) Algorithm Simplest page replacement algorithm each page associated a time when it was brought in memory replace the oldest page, during page replacement implemented using a FIFO queue of all pages replacement page found from the head of the queue new page added to the tail of the queue 21
22 Belady's Anomaly For some page replacement algorithm, the page fault rate may increase as the number of frames increases! can happen with FIFO replacement scheme Example reference string: 1, 2, 3, 4, 1, 2, 5, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 FIFO replacement algorithm 22
23 Optimal Page Replacement Algorithm with the lowest page fault rate replace the page that will not be used for the longest period provably optimal does not suffer from Belady's anomaly needs future information! 23
24 Least Recently Used (LRU) Algorithm Approximate the optimal page replacement algorithm detect and store when each page is used replace page that has not been used for the longest period a very good replacement policy requires hardware support to be accurate and fast does not suffer from Belady's anomaly 24
25 LRU Implementation Counter implementation every page table entry has a time-of-use field copy the clock into the time-of-use field on every page access for replacement, find the page with the smallest time-of-use field replacement algorithm requires search of the full page table each memory access needs additional write to time-of-use field counter overflow? 25
26 LRU Implementation (2) Stack implementation keep a stack of page numbers in a linked list move page to top of stack when referenced find replacement page from bottom of stack each update is more expensive due to stack operations no search for replacement 26
27 LRU Approximation Algorithms Reference bit algorithm associate reference bit with each page set bit when page is references; clear all bits occasionally replace page that has reference bit = 0 (if one exists) cannot store the order of accesses in one bit! Record reference bit algorithm each page associated with a 8-bit field for recording reference bit at regular intervals right shift 8-bit field move reference bit into highest order bit page with lowest value in 8-bit field is the LRU page Example: (reference bit, 8-bit field) (1, ) (0, ) (0, ) (0, ) 27
28 LRU Approximation Algorithms (2) Second-chance algorithm single reference (RF) bit basic FIFO replacement algo find replacement page proceed, if RF=0 give page 2nd chance, if RF=1 and move onto next page, clear reference bit circular queue of pages pointer indicates next replacement page what is all bits are set? 28
29 Counting-Based Algorithms Keep a counter of the number of references that have been made to each page. Least frequently used replace page with the smallest count (most active page should have largest count) Most frequently used replace page with the largest count (page with smallest count was brought in last and will be accessed next) Not very popular algorithms 29
30 Page Buffering Algorithms Optimizations by maintaining a list of victim frames Scheme 1 bring new page into one of victim frame slots then, copy-out the replacement page to memory memory access to new page does not wait for copy-out Scheme 2 copy-out modified pages to disk when paging device is idle replacement is now faster Scheme 3 remember which page is in each victim frame if new page is in one of victim frame, then use directly works well if replacement algorithm replaces a page that is needed after afterwards 30
31 Allocation of Frames How many frames in physical memory should the OS allocate to each process? Minimum number of frames is there a minimum number of frames a process needs? depends of the maximum number of pages any instruction in the ISA can reference at a time direct addressing load/store need 2 frames what can happen if we do not provide this minimum? one for instruction, and one for memory reference one-level indirect addressing needs 3 frames one for instruction, one for address, and one for memory reference PDP-11 needs 6 frames, IBM 370 needs 8 frames should there be a maximum number? 31
32 Frame Allocation Algorithms Equal allocation divide m frames equally among n processes each process gets about m/n frames may give some process more frames than it needs! Proportional allocation each process may need different amounts of memory allocate memory proportional to process size Example: si = size of process pi m = 64 si = 10 S = si s2 = 127 m = total number of frames s ai = allocation for pi = i m S a2 = a1 = 32
33 Other Frame Allocation Issues Global Vs. local allocation global replacement process selects a replacement frame from the set of all frames one process can take a frame from another process cannot control its own page-fault rate local replacement each process selects from only its own set of allocated frames may hinder progress by not allowing high-priority process access to frames of low-priority process Non-uniform memory access memory may be distributed on multi-processor systems how to assign frames in such situations? assign memory which is close to where a process is running 33
34 Thrashing A process is thrashing if it spends more time paging than executing process keeps swapping active pages in and out leads to a very high page fault rate Causes of thrashing behavior process does not have enough pages Vicious cycle of thrashing not having enough frames cause more page faults lowers CPU utilization OS thinks that it needs to increase the degree of multiprogramming another process added to the system even less frames per process leads to more page faults cycle continues 34
35 Thrashing (2) Thrashing becomes more likely with increasing degree of multiprogramming Can we prevent thrashing by using a local replacement algorithm? 35
36 Preventing Thrashing Behavior Give a process as many frames as it needs how to know how many frames a process needs?! Working-Set model based on the locality model of process execution each process phase uses a small set of memory references / frames execution moves from one program phase to another the number of frames required for each phase is called the working set Implementation assume a particular working-set window, WSSi (working set of Process Pi) = total number of pages referenced in the most recent D = Σ WSSi total demand frames If D > m Thrashing, then suspend one of the processes 36
37 Working Sets and Page Fault Rates Page faults spike at the start of every new program working set (also called a phase) page fault rate falls until the next program phase behavior repeats 37
38 Preventing Thrashing Behavior (2) Page-Fault frequency scheme working set model is needs several assumptions and is complicated measure the page fault rate routinely establish acceptable page-fault rate If actual rate too low, process loses frame or increase processes If actual rate too high, process gains frame, or suspend processes 38
39 Memory-Mapped Files Memory-mapped file I/O allows file I/O to be treated as routine memory access by mapping a disk block to a page in memory removes the need to read(), write() system calls converts disk access to memory access simplifies disk access for the user Mechanism details a file is initially read using demand paging a page-sized portion of the file is read from the file system into a physical frame subsequent reads/writes to/from the file are treated as ordinary memory accesses 39
40 Memory Mapped Files (2) Allows several processes to map the same file allowing the pages in memory to be shared 40
41 Memory-Mapped Files (3) Examples of OS using memory-mapped files Solaris, Unix, and Linux provide the mmap() system call to create a memory-mapped file files accessed using open(), read(), write() are mapped to kernel address space in Solaris Windows NT and XP use memory mapped files to accomplish shared memory 41
42 Memory-Mapped I/O Special I/O instructions may be available to transfer data and control messages to the I/O controller Memory-mapped I/O I/O device registers mapped to logical memory address spaces convenient and fast There may be a control bit to indicate if data is available in the data register if CPU polls the control bit, then method of operation is called programmed I/O if device sends interrupt to CPU to indicate data availability, then mode of operation is interrupt driven I/O 42
43 Allocating Kernel Memory Kernel memory often allocated from a free memory pool not using demand paging Reasons for treating kernel memory allocation differently some kernel memory needs to be contiguous attempt to minimize memory waste due to internal fragmentation kernel requests memory for structures of varying size do not use paging system Strategies for managing free memory buddy system slab allocator 43
44 Buddy System Power-of-2 allocator satisfies requests in units sized as power of 2 request rounded up to next highest power of 2 when smaller allocation needed than is available, current chunk split into two buddies of next-lower power of 2 continue until appropriate sized chunk available Example: 21kb requested from 256kb 44
45 Slab Allocator Slab contains several physically contiguous pages. Cache consists of one or more slabs Single cache for each unique kernel data structure cache filled with instantiations of the data structure (objects) Slab allocation algorithm create cache of objects in contiguous space, mark as free store objects in free slots, mark as used if current slab is full of used objects, allocate next object from empty slab if no empty slabs, go to free slots in the next slab Benefits no fragmentation fast memory request satisfaction 45
46 Slab Allocation (2) 46
47 Other Virtual Memory Issues Prepaging reduce page faults at process startup prepage all or some process pages before they are referenced I/O and memory wasted if prepaged pages are unused Issues in deciding a page size internal fragmentation page table size large page size preferred to reduce size of page table I/O overhead small page size preferred to reduce memory lost on the final page large page size preferred to reduce disk latency and seek time Page faults large page size reduces number of generated page faults 47
48 Other Virtual Memory Issues (2) TLB Reach amount of memory accessible from the TLB TLB Reach = (TLB Size) X (Page Size) ideally, the working set of each process is stored in the TLB improving TLB reach increase the page size provide multiple page sizes I/O interlock pages must sometimes be locked into memory consider I/O - Pages that are used for copying a file from a device must be locked from being selected for eviction by a page replacement algorithm provide a lock bit with every page frame 48
49 Other Virtual Memory Issues (3) Program structure being aware of the paging structure can help performance example: Int[128,128] data; Each row is stored in one page program 1: 128 * 128 = 16, 384 page faults for (j = 0; j <128; j++) for (i = 0; i < 128; i++) data[i,j] = 0; Program 2: 128 page faults for (i = 0; i < 128; i++) for (j = 0; j < 128; j++) data[i,j] = 0; 49
Chapter 9: Virtual Memory
 Chapter 9: Virtual Memory Background Demand Paging Chapter 9: Virtual Memory Copy-on-Write Page Replacement Allocation of Frames Thrashing Memory-Mapped Files Allocating Kernel Memory Other Considerations
Chapter 9: Virtual Memory Background Demand Paging Chapter 9: Virtual Memory Copy-on-Write Page Replacement Allocation of Frames Thrashing Memory-Mapped Files Allocating Kernel Memory Other Considerations
Chapter 9: Virtual Memory. Chapter 9: Virtual Memory. Objectives. Background. Virtual-address address Space
 Chapter 9: Virtual Memory Chapter 9: Virtual Memory Background Demand Paging Copy-on-Write Page Replacement Allocation of Frames Thrashing Memory-Mapped Files Allocating Kernel Memory Other Considerations
Chapter 9: Virtual Memory Chapter 9: Virtual Memory Background Demand Paging Copy-on-Write Page Replacement Allocation of Frames Thrashing Memory-Mapped Files Allocating Kernel Memory Other Considerations
Chapter 9: Virtual Memory
 Chapter 9: Virtual Memory Chapter 9: Virtual Memory Background Demand Paging Copy-on-Write Page Replacement Allocation of Frames Thrashing Memory-Mapped Files Allocating Kernel Memory Other Considerations
Chapter 9: Virtual Memory Chapter 9: Virtual Memory Background Demand Paging Copy-on-Write Page Replacement Allocation of Frames Thrashing Memory-Mapped Files Allocating Kernel Memory Other Considerations
Chapter 8: Virtual Memory. Operating System Concepts
 Chapter 8: Virtual Memory Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne 2009 Chapter 8: Virtual Memory Background Demand Paging Copy-on-Write Page Replacement Allocation of Frames Thrashing Memory-Mapped Files Allocating
Chapter 8: Virtual Memory Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne 2009 Chapter 8: Virtual Memory Background Demand Paging Copy-on-Write Page Replacement Allocation of Frames Thrashing Memory-Mapped Files Allocating
Chapter 9: Virtual Memory
 Chapter 9: Virtual Memory Chapter 9: Virtual Memory 9.1 Background 9.2 Demand Paging 9.3 Copy-on-Write 9.4 Page Replacement 9.5 Allocation of Frames 9.6 Thrashing 9.7 Memory-Mapped Files 9.8 Allocating
Chapter 9: Virtual Memory Chapter 9: Virtual Memory 9.1 Background 9.2 Demand Paging 9.3 Copy-on-Write 9.4 Page Replacement 9.5 Allocation of Frames 9.6 Thrashing 9.7 Memory-Mapped Files 9.8 Allocating
Chapter 9: Virtual-Memory Management. Operating System Concepts 8 th Edition,
 Chapter 9: Virtual-Memory Management, Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne 2009 Chapter 9: Virtual-Memory Management Background Demand Paging Copy-on-Write Page Replacement Allocation of Frames Thrashing Memory-Mapped
Chapter 9: Virtual-Memory Management, Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne 2009 Chapter 9: Virtual-Memory Management Background Demand Paging Copy-on-Write Page Replacement Allocation of Frames Thrashing Memory-Mapped
Chapter 3: Virtual Memory ว ตถ ประสงค. Background สามารถอธ บายข อด ในการท ระบบใช ว ธ การจ ดการหน วยความจ าแบบเสม อนได
 Chapter 9: Virtual Memory Chapter 3: Virtual Memory Background Demand Paging Copy-on-Write Page Replacement Allocation of Frames Thrashing Memory-Mapped Files Allocating Kernel Memory Other Considerations
Chapter 9: Virtual Memory Chapter 3: Virtual Memory Background Demand Paging Copy-on-Write Page Replacement Allocation of Frames Thrashing Memory-Mapped Files Allocating Kernel Memory Other Considerations
Operating System Concepts
 Chapter 9: Virtual-Memory Management 9.1 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne 2005 Chapter 9: Virtual Memory Background Demand Paging Copy-on-Write Page Replacement Allocation of Frames Thrashing Memory-Mapped
Chapter 9: Virtual-Memory Management 9.1 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne 2005 Chapter 9: Virtual Memory Background Demand Paging Copy-on-Write Page Replacement Allocation of Frames Thrashing Memory-Mapped
CS307: Operating Systems
 CS307: Operating Systems Chentao Wu 吴晨涛 Associate Professor Dept. of Computer Science and Engineering Shanghai Jiao Tong University SEIEE Building 3-513 wuct@cs.sjtu.edu.cn Download Lectures ftp://public.sjtu.edu.cn
CS307: Operating Systems Chentao Wu 吴晨涛 Associate Professor Dept. of Computer Science and Engineering Shanghai Jiao Tong University SEIEE Building 3-513 wuct@cs.sjtu.edu.cn Download Lectures ftp://public.sjtu.edu.cn
Chapter 10: Virtual Memory. Background
 Chapter 10: Virtual Memory Background Demand Paging Process Creation Page Replacement Allocation of Frames Thrashing Operating System Examples 10.1 Background Virtual memory separation of user logical
Chapter 10: Virtual Memory Background Demand Paging Process Creation Page Replacement Allocation of Frames Thrashing Operating System Examples 10.1 Background Virtual memory separation of user logical
Chapter 9: Virtual-Memory
 Chapter 9: Virtual-Memory Management Chapter 9: Virtual-Memory Management Background Demand Paging Page Replacement Allocation of Frames Thrashing Other Considerations Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne 2013
Chapter 9: Virtual-Memory Management Chapter 9: Virtual-Memory Management Background Demand Paging Page Replacement Allocation of Frames Thrashing Other Considerations Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne 2013
First-In-First-Out (FIFO) Algorithm
 First-In-First-Out (FIFO) Algorithm Reference string: 7,0,1,2,0,3,0,4,2,3,0,3,0,3,2,1,2,0,1,7,0,1 3 frames (3 pages can be in memory at a time per process) 15 page faults Can vary by reference string:
First-In-First-Out (FIFO) Algorithm Reference string: 7,0,1,2,0,3,0,4,2,3,0,3,0,3,2,1,2,0,1,7,0,1 3 frames (3 pages can be in memory at a time per process) 15 page faults Can vary by reference string:
OPERATING SYSTEM. Chapter 9: Virtual Memory
 OPERATING SYSTEM Chapter 9: Virtual Memory Chapter 9: Virtual Memory Background Demand Paging Copy-on-Write Page Replacement Allocation of Frames Thrashing Memory-Mapped Files Allocating Kernel Memory
OPERATING SYSTEM Chapter 9: Virtual Memory Chapter 9: Virtual Memory Background Demand Paging Copy-on-Write Page Replacement Allocation of Frames Thrashing Memory-Mapped Files Allocating Kernel Memory
Chapter 10: Virtual Memory. Background. Demand Paging. Valid-Invalid Bit. Virtual Memory That is Larger Than Physical Memory
 Chapter 0: Virtual Memory Background Background Demand Paging Process Creation Page Replacement Allocation of Frames Thrashing Operating System Examples Virtual memory separation of user logical memory
Chapter 0: Virtual Memory Background Background Demand Paging Process Creation Page Replacement Allocation of Frames Thrashing Operating System Examples Virtual memory separation of user logical memory
Chapter 9: Virtual Memory. Operating System Concepts 9th Edition
 Chapter 9: Virtual Memory Chapter 9: Virtual Memory Background Demand Paging Copy-on-Write Page Replacement Allocation of Frames Thrashing Memory-Mapped Files Allocating Kernel Memory Other Considerations
Chapter 9: Virtual Memory Chapter 9: Virtual Memory Background Demand Paging Copy-on-Write Page Replacement Allocation of Frames Thrashing Memory-Mapped Files Allocating Kernel Memory Other Considerations
Chapter 9: Virtual Memory. Operating System Concepts 9 th Edition
 Chapter 9: Virtual Memory Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne 2013 Chapter 9: Virtual Memory Background Demand Paging Copy-on-Write Page Replacement Allocation of Frames Thrashing Memory-Mapped Files Allocating
Chapter 9: Virtual Memory Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne 2013 Chapter 9: Virtual Memory Background Demand Paging Copy-on-Write Page Replacement Allocation of Frames Thrashing Memory-Mapped Files Allocating
Where are we in the course?
 Previous Lectures Memory Management Approaches Allocate contiguous memory for the whole process Use paging (map fixed size logical pages to physical frames) Use segmentation (user s view of address space
Previous Lectures Memory Management Approaches Allocate contiguous memory for the whole process Use paging (map fixed size logical pages to physical frames) Use segmentation (user s view of address space
Chapter 10: Virtual Memory
 Chapter 10: Virtual Memory Chapter 10: Virtual Memory Background Demand Paging Copy-on-Write Page Replacement Allocation of Frames Thrashing Memory-Mapped Files Allocating Kernel Memory Other Considerations
Chapter 10: Virtual Memory Chapter 10: Virtual Memory Background Demand Paging Copy-on-Write Page Replacement Allocation of Frames Thrashing Memory-Mapped Files Allocating Kernel Memory Other Considerations
Chapter 9: Virtual Memory
 Chapter 9: Virtual Memory Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne 2013 Chapter 9: Virtual Memory Background Demand Paging Copy-on-Write Page Replacement Allocation of Frames Thrashing Memory-Mapped Files Allocating
Chapter 9: Virtual Memory Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne 2013 Chapter 9: Virtual Memory Background Demand Paging Copy-on-Write Page Replacement Allocation of Frames Thrashing Memory-Mapped Files Allocating
Chapter 9: Virtual Memory
 Chapter 9: Virtual Memory Chapter 9: Virtual Memory Background Demand Paging Process Creation Page Replacement Allocation of Frames Thrashing Demand Segmentation Operating System Examples 9.2 Background
Chapter 9: Virtual Memory Chapter 9: Virtual Memory Background Demand Paging Process Creation Page Replacement Allocation of Frames Thrashing Demand Segmentation Operating System Examples 9.2 Background
Operating System Concepts 9 th Edition
 Chapter 9: Virtual Memory Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne 2013 Chapter 9: Virtual Memory Background Demand Paging Copy-on-Write Page Replacement Allocation of Frames Thrashing Memory-Mapped Files Allocating
Chapter 9: Virtual Memory Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne 2013 Chapter 9: Virtual Memory Background Demand Paging Copy-on-Write Page Replacement Allocation of Frames Thrashing Memory-Mapped Files Allocating
Chapter 9: Virtual Memory. Operating System Concepts 9 th Edition
 Chapter 9: Virtual Memory Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne 2013 Chapter 9: Virtual Memory Background Demand Paging Copy-on-Write Page Replacement Allocation of Frames Thrashing Memory-Mapped Files Allocating
Chapter 9: Virtual Memory Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne 2013 Chapter 9: Virtual Memory Background Demand Paging Copy-on-Write Page Replacement Allocation of Frames Thrashing Memory-Mapped Files Allocating
Virtual Memory. Overview: Virtual Memory. Virtual address space of a process. Virtual Memory. Demand Paging
 TDDB68 Concurrent programming and operating systems Overview: Virtual Memory Virtual Memory [SGG7/8] Chapter 9 Background Demand Paging Page Replacement Allocation of Frames Thrashing and Data Access Locality
TDDB68 Concurrent programming and operating systems Overview: Virtual Memory Virtual Memory [SGG7/8] Chapter 9 Background Demand Paging Page Replacement Allocation of Frames Thrashing and Data Access Locality
Chapter 8: Virtual Memory. Operating System Concepts Essentials 2 nd Edition
 Chapter 8: Virtual Memory Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne 2013 Chapter 8: Virtual Memory Background Demand Paging Copy-on-Write Page Replacement Allocation of Frames Thrashing Memory-Mapped Files Allocating
Chapter 8: Virtual Memory Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne 2013 Chapter 8: Virtual Memory Background Demand Paging Copy-on-Write Page Replacement Allocation of Frames Thrashing Memory-Mapped Files Allocating
Virtual Memory COMPSCI 386
 Virtual Memory COMPSCI 386 Motivation An instruction to be executed must be in physical memory, but there may not be enough space for all ready processes. Typically the entire program is not needed. Exception
Virtual Memory COMPSCI 386 Motivation An instruction to be executed must be in physical memory, but there may not be enough space for all ready processes. Typically the entire program is not needed. Exception
Demand Paging. Valid-Invalid Bit. Steps in Handling a Page Fault. Page Fault. Transfer of a Paged Memory to Contiguous Disk Space
 Demand Paging Transfer of a Paged Memory to Contiguous Disk Space Bring a page into memory only when it is needed. Less I/O needed Less memory needed Faster response More users Page is needed reference
Demand Paging Transfer of a Paged Memory to Contiguous Disk Space Bring a page into memory only when it is needed. Less I/O needed Less memory needed Faster response More users Page is needed reference
Background. Demand Paging. valid-invalid bit. Tevfik Koşar. CSC Operating Systems Spring 2007
 CSC 0 - Operating Systems Spring 007 Lecture - XIII Virtual Memory Tevfik Koşar Background Virtual memory separation of user logical memory from physical memory. Only part of the program needs to be in
CSC 0 - Operating Systems Spring 007 Lecture - XIII Virtual Memory Tevfik Koşar Background Virtual memory separation of user logical memory from physical memory. Only part of the program needs to be in
CS370 Operating Systems
 CS370 Operating Systems Colorado State University Yashwant K Malaiya Fall 2017 Lecture 23 Virtual memory Slides based on Text by Silberschatz, Galvin, Gagne Various sources 1 1 FAQ Is a page replaces when
CS370 Operating Systems Colorado State University Yashwant K Malaiya Fall 2017 Lecture 23 Virtual memory Slides based on Text by Silberschatz, Galvin, Gagne Various sources 1 1 FAQ Is a page replaces when
Module 9: Virtual Memory
 Module 9: Virtual Memory Background Demand Paging Performance of Demand Paging Page Replacement Page-Replacement Algorithms Allocation of Frames Thrashing Other Considerations Demand Segmentation Operating
Module 9: Virtual Memory Background Demand Paging Performance of Demand Paging Page Replacement Page-Replacement Algorithms Allocation of Frames Thrashing Other Considerations Demand Segmentation Operating
Virtual Memory. Overview: Virtual Memory. Virtual address space of a process. Virtual Memory
 TDIU Operating systems Overview: Virtual Memory Virtual Memory Background Demand Paging Page Replacement Allocation of Frames Thrashing and Data Access Locality [SGG7/8/9] Chapter 9 Copyright Notice: The
TDIU Operating systems Overview: Virtual Memory Virtual Memory Background Demand Paging Page Replacement Allocation of Frames Thrashing and Data Access Locality [SGG7/8/9] Chapter 9 Copyright Notice: The
Virtual Memory. CSCI 315 Operating Systems Design Department of Computer Science
 Virtual Memory CSCI 315 Operating Systems Design Department of Computer Science Notice: The slides for this lecture were based on those Operating Systems Concepts, 9th ed., by Silberschatz, Galvin, and
Virtual Memory CSCI 315 Operating Systems Design Department of Computer Science Notice: The slides for this lecture were based on those Operating Systems Concepts, 9th ed., by Silberschatz, Galvin, and
Virtual Memory. Virtual Memory. Demand Paging. valid-invalid bit. Virtual Memory Larger than Physical Memory
 Virtual Memory Virtual Memory CSCI Operating Systems Design Department of Computer Science Virtual memory separation of user logical memory from physical memory. Only part of the program needs to be in
Virtual Memory Virtual Memory CSCI Operating Systems Design Department of Computer Science Virtual memory separation of user logical memory from physical memory. Only part of the program needs to be in
Module 9: Virtual Memory
 Module 9: Virtual Memory Background Demand Paging Performance of Demand Paging Page Replacement Page-Replacement Algorithms Allocation of Frames Thrashing Other Considerations Demand Segmenation 9.1 Background
Module 9: Virtual Memory Background Demand Paging Performance of Demand Paging Page Replacement Page-Replacement Algorithms Allocation of Frames Thrashing Other Considerations Demand Segmenation 9.1 Background
Background. Virtual Memory (2/2) Demand Paging Example. First-In-First-Out (FIFO) Algorithm. Page Replacement Algorithms. Performance of Demand Paging
 Virtual Memory (/) Background Page Replacement Allocation of Frames Thrashing Background Virtual memory separation of user logical memory from physical memory. Only part of the program needs to be in memory
Virtual Memory (/) Background Page Replacement Allocation of Frames Thrashing Background Virtual memory separation of user logical memory from physical memory. Only part of the program needs to be in memory
CS370 Operating Systems
 CS370 Operating Systems Colorado State University Yashwant K Malaiya Spring 2018 L20 Virtual Memory Slides based on Text by Silberschatz, Galvin, Gagne Various sources 1 1 Questions from last time Page
CS370 Operating Systems Colorado State University Yashwant K Malaiya Spring 2018 L20 Virtual Memory Slides based on Text by Silberschatz, Galvin, Gagne Various sources 1 1 Questions from last time Page
Optimal Algorithm. Replace page that will not be used for longest period of time Used for measuring how well your algorithm performs
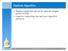 Optimal Algorithm Replace page that will not be used for longest period of time Used for measuring how well your algorithm performs page 1 Least Recently Used (LRU) Algorithm Reference string: 1, 2, 3,
Optimal Algorithm Replace page that will not be used for longest period of time Used for measuring how well your algorithm performs page 1 Least Recently Used (LRU) Algorithm Reference string: 1, 2, 3,
CS6401- Operating System UNIT-III STORAGE MANAGEMENT
 UNIT-III STORAGE MANAGEMENT Memory Management: Background In general, to rum a program, it must be brought into memory. Input queue collection of processes on the disk that are waiting to be brought into
UNIT-III STORAGE MANAGEMENT Memory Management: Background In general, to rum a program, it must be brought into memory. Input queue collection of processes on the disk that are waiting to be brought into
1. Background. 2. Demand Paging
 COSC4740-01 Operating Systems Design, Fall 2001, Byunggu Yu Chapter 10 Virtual Memory 1. Background PROBLEM: The entire process must be loaded into the memory to execute limits the size of a process (it
COSC4740-01 Operating Systems Design, Fall 2001, Byunggu Yu Chapter 10 Virtual Memory 1. Background PROBLEM: The entire process must be loaded into the memory to execute limits the size of a process (it
Memory Management. Virtual Memory. By : Kaushik Vaghani. Prepared By : Kaushik Vaghani
 Memory Management Virtual Memory By : Kaushik Vaghani Virtual Memory Background Page Fault Dirty Page / Dirty Bit Demand Paging Copy-on-Write Page Replacement Objectives To describe the benefits of a virtual
Memory Management Virtual Memory By : Kaushik Vaghani Virtual Memory Background Page Fault Dirty Page / Dirty Bit Demand Paging Copy-on-Write Page Replacement Objectives To describe the benefits of a virtual
Lecture 17. Edited from slides for Operating System Concepts by Silberschatz, Galvin, Gagne
 Lecture 17 Edited from slides for Operating System Concepts by Silberschatz, Galvin, Gagne Page Replacement Algorithms Last Lecture: FIFO Optimal Page Replacement LRU LRU Approximation Additional-Reference-Bits
Lecture 17 Edited from slides for Operating System Concepts by Silberschatz, Galvin, Gagne Page Replacement Algorithms Last Lecture: FIFO Optimal Page Replacement LRU LRU Approximation Additional-Reference-Bits
Chapters 9 & 10: Memory Management and Virtual Memory
 Chapters 9 & 10: Memory Management and Virtual Memory Important concepts (for final, projects, papers) addressing: physical/absolute, logical/relative/virtual overlays swapping and paging memory protection
Chapters 9 & 10: Memory Management and Virtual Memory Important concepts (for final, projects, papers) addressing: physical/absolute, logical/relative/virtual overlays swapping and paging memory protection
Page Replacement. 3/9/07 CSE 30341: Operating Systems Principles
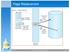 Page Replacement page 1 Page Replacement Algorithms Want lowest page-fault rate Evaluate algorithm by running it on a particular string of memory references (reference string) and computing the number
Page Replacement page 1 Page Replacement Algorithms Want lowest page-fault rate Evaluate algorithm by running it on a particular string of memory references (reference string) and computing the number
CS420: Operating Systems
 Virtual Memory James Moscola Department of Physical Sciences York College of Pennsylvania Based on Operating System Concepts, 9th Edition by Silberschatz, Galvin, Gagne Background Code needs to be in memory
Virtual Memory James Moscola Department of Physical Sciences York College of Pennsylvania Based on Operating System Concepts, 9th Edition by Silberschatz, Galvin, Gagne Background Code needs to be in memory
Virtual Memory. CSCI 315 Operating Systems Design Department of Computer Science
 Virtual Memory CSCI 315 Operating Systems Design Department of Computer Science Notice: The slides for this lecture have been largely based on those from an earlier edition of the course text Operating
Virtual Memory CSCI 315 Operating Systems Design Department of Computer Science Notice: The slides for this lecture have been largely based on those from an earlier edition of the course text Operating
Page Replacement Chap 21, 22. Dongkun Shin, SKKU
 Page Replacement Chap 21, 22 1 Virtual Memory Concept Virtual memory Concept A technique that allows the execution of processes that are not completely in memory Partition each user s program into multiple
Page Replacement Chap 21, 22 1 Virtual Memory Concept Virtual memory Concept A technique that allows the execution of processes that are not completely in memory Partition each user s program into multiple
Chapter 8: Main Memory. Operating System Concepts 8th Edition
 Chapter 8: Main Memory Operating System Concepts 8th Edition Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne 2009 Chapter 8: Memory Management Background Swapping Contiguous Memory Allocation Paging Structure of the Page
Chapter 8: Main Memory Operating System Concepts 8th Edition Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne 2009 Chapter 8: Memory Management Background Swapping Contiguous Memory Allocation Paging Structure of the Page
Operating Systems. Overview Virtual memory part 2. Page replacement algorithms. Lecture 7 Memory management 3: Virtual memory
 Operating Systems Lecture 7 Memory management : Virtual memory Overview Virtual memory part Page replacement algorithms Frame allocation Thrashing Other considerations Memory over-allocation Efficient
Operating Systems Lecture 7 Memory management : Virtual memory Overview Virtual memory part Page replacement algorithms Frame allocation Thrashing Other considerations Memory over-allocation Efficient
Principles of Operating Systems
 Principles of Operating Systems Lecture 21-23 - Virtual Memory Ardalan Amiri Sani (ardalan@uci.edu) [lecture slides contains some content adapted from previous slides by Prof. Nalini Venkatasubramanian,
Principles of Operating Systems Lecture 21-23 - Virtual Memory Ardalan Amiri Sani (ardalan@uci.edu) [lecture slides contains some content adapted from previous slides by Prof. Nalini Venkatasubramanian,
UNIT - IV. What is virtual memory?
 UNIT - IV Virtual Memory Demand Paging Process creation Page Replacement Allocation of frames Thrashing- File Concept - Access Methods Directory Structure File System Mounting File Sharing Protection.
UNIT - IV Virtual Memory Demand Paging Process creation Page Replacement Allocation of frames Thrashing- File Concept - Access Methods Directory Structure File System Mounting File Sharing Protection.
Addresses in the source program are generally symbolic. A compiler will typically bind these symbolic addresses to re-locatable addresses.
 1 Memory Management Address Binding The normal procedures is to select one of the processes in the input queue and to load that process into memory. As the process executed, it accesses instructions and
1 Memory Management Address Binding The normal procedures is to select one of the processes in the input queue and to load that process into memory. As the process executed, it accesses instructions and
Virtual Memory - Overview. Programmers View. Virtual Physical. Virtual Physical. Program has its own virtual memory space.
 Virtual Memory - Overview Programmers View Process runs in virtual (logical) space may be larger than physical. Paging can implement virtual. Which pages to have in? How much to allow each process? Program
Virtual Memory - Overview Programmers View Process runs in virtual (logical) space may be larger than physical. Paging can implement virtual. Which pages to have in? How much to allow each process? Program
Page Replacement Algorithms
 Page Replacement Algorithms MIN, OPT (optimal) RANDOM evict random page FIFO (first-in, first-out) give every page equal residency LRU (least-recently used) MRU (most-recently used) 1 9.1 Silberschatz,
Page Replacement Algorithms MIN, OPT (optimal) RANDOM evict random page FIFO (first-in, first-out) give every page equal residency LRU (least-recently used) MRU (most-recently used) 1 9.1 Silberschatz,
Swapping. Operating Systems I. Swapping. Motivation. Paging Implementation. Demand Paging. Active processes use more physical memory than system has
 Swapping Active processes use more physical memory than system has Operating Systems I Address Binding can be fixed or relocatable at runtime Swap out P P Virtual Memory OS Backing Store (Swap Space) Main
Swapping Active processes use more physical memory than system has Operating Systems I Address Binding can be fixed or relocatable at runtime Swap out P P Virtual Memory OS Backing Store (Swap Space) Main
Chapter 6: Demand Paging
 ADRIAN PERRIG & TORSTEN HOEFLER ( 5-006-00 ) Networks and Operating Systems Chapter 6: Demand Paging Source: http://redmine.replicant.us/projects/replicant/wiki/samsunggalaxybackdoor If you miss a key
ADRIAN PERRIG & TORSTEN HOEFLER ( 5-006-00 ) Networks and Operating Systems Chapter 6: Demand Paging Source: http://redmine.replicant.us/projects/replicant/wiki/samsunggalaxybackdoor If you miss a key
CS 3733 Operating Systems:
 CS 3733 Operating Systems: Topics: Virtual Memory (SGG, Chapter 09) Instructor: Dr. Dakai Zhu Department of Computer Science @ UTSA 1 Reminders Assignment 3: due March 30, 2018 (mid-night)! Part I: fixed
CS 3733 Operating Systems: Topics: Virtual Memory (SGG, Chapter 09) Instructor: Dr. Dakai Zhu Department of Computer Science @ UTSA 1 Reminders Assignment 3: due March 30, 2018 (mid-night)! Part I: fixed
Topics: Virtual Memory (SGG, Chapter 09) CS 3733 Operating Systems
 Topics: Virtual Memory (SGG, Chapter 09) 9.1-9.7 CS 3733 Operating Systems Instructor: Dr. Turgay Korkmaz Department Computer Science The University of Texas at San Antonio Office: NPB 3.330 Phone: (210)
Topics: Virtual Memory (SGG, Chapter 09) 9.1-9.7 CS 3733 Operating Systems Instructor: Dr. Turgay Korkmaz Department Computer Science The University of Texas at San Antonio Office: NPB 3.330 Phone: (210)
CS370 Operating Systems
 CS370 Operating Systems Colorado State University Yashwant K Malaiya Fall 2016 Lecture 32 Virtual Memory Slides based on Text by Silberschatz, Galvin, Gagne Various sources 1 1 Questions for you What is
CS370 Operating Systems Colorado State University Yashwant K Malaiya Fall 2016 Lecture 32 Virtual Memory Slides based on Text by Silberschatz, Galvin, Gagne Various sources 1 1 Questions for you What is
ADRIAN PERRIG & TORSTEN HOEFLER Networks and Operating Systems ( ) Chapter 6: Demand Paging
 ADRIAN PERRIG & TORSTEN HOEFLER Networks and Operating Systems (5-006-00) Chapter 6: Demand Paging http://redmine.replicant.us/projects/replicant/wiki/samsunggalaxybackdoor (0) # Inverted page table One
ADRIAN PERRIG & TORSTEN HOEFLER Networks and Operating Systems (5-006-00) Chapter 6: Demand Paging http://redmine.replicant.us/projects/replicant/wiki/samsunggalaxybackdoor (0) # Inverted page table One
Virtual Memory. Reading: Silberschatz chapter 10 Reading: Stallings. chapter 8 EEL 358
 Virtual Memory Reading: Silberschatz chapter 10 Reading: Stallings chapter 8 1 Outline Introduction Advantages Thrashing Principal of Locality VM based on Paging/Segmentation Combined Paging and Segmentation
Virtual Memory Reading: Silberschatz chapter 10 Reading: Stallings chapter 8 1 Outline Introduction Advantages Thrashing Principal of Locality VM based on Paging/Segmentation Combined Paging and Segmentation
VII. Memory Management
 VII. Memory Management 1 Intended Schedule Date Lecture Hand out Submission 0 20.04. Introduction to Operating Systems Course registration 1 27.04. Systems Programming using C (File Subsystem) 1. Assignment
VII. Memory Management 1 Intended Schedule Date Lecture Hand out Submission 0 20.04. Introduction to Operating Systems Course registration 1 27.04. Systems Programming using C (File Subsystem) 1. Assignment
instruction is 6 bytes, might span 2 pages 2 pages to handle from 2 pages to handle to Two major allocation schemes
 Allocation of Frames How should the OS distribute the frames among the various processes? Each process needs minimum number of pages - at least the minimum number of pages required for a single assembly
Allocation of Frames How should the OS distribute the frames among the various processes? Each process needs minimum number of pages - at least the minimum number of pages required for a single assembly
Basic Memory Management
 Basic Memory Management CS 256/456 Dept. of Computer Science, University of Rochester 10/15/14 CSC 2/456 1 Basic Memory Management Program must be brought into memory and placed within a process for it
Basic Memory Management CS 256/456 Dept. of Computer Science, University of Rochester 10/15/14 CSC 2/456 1 Basic Memory Management Program must be brought into memory and placed within a process for it
Basic Memory Management. Basic Memory Management. Address Binding. Running a user program. Operating Systems 10/14/2018 CSC 256/456 1
 Basic Memory Management Program must be brought into memory and placed within a process for it to be run Basic Memory Management CS 256/456 Dept. of Computer Science, University of Rochester Mono-programming
Basic Memory Management Program must be brought into memory and placed within a process for it to be run Basic Memory Management CS 256/456 Dept. of Computer Science, University of Rochester Mono-programming
Memory Management. Disclaimer: some slides are adopted from book authors slides with permission 1
 Memory Management Disclaimer: some slides are adopted from book authors slides with permission 1 Demand paging Concepts to Learn 2 Abstraction Virtual Memory (VM) 4GB linear address space for each process
Memory Management Disclaimer: some slides are adopted from book authors slides with permission 1 Demand paging Concepts to Learn 2 Abstraction Virtual Memory (VM) 4GB linear address space for each process
Page Replacement Chap 21, 22. Dongkun Shin, SKKU
 Page Replacement Chap 21, 22 1 Virtual Memory Concept Virtual memory Concept A technique that allows the execution of processes that are not completely in memory Partition each user s program into multiple
Page Replacement Chap 21, 22 1 Virtual Memory Concept Virtual memory Concept A technique that allows the execution of processes that are not completely in memory Partition each user s program into multiple
Memory Management. To improve CPU utilization in a multiprogramming environment we need multiple programs in main memory at the same time.
 Memory Management To improve CPU utilization in a multiprogramming environment we need multiple programs in main memory at the same time. Basic CPUs and Physical Memory CPU cache Physical memory
Memory Management To improve CPU utilization in a multiprogramming environment we need multiple programs in main memory at the same time. Basic CPUs and Physical Memory CPU cache Physical memory
Memory Management and Protection
 Part IV Memory Management and Protection Sadeghi, Cubaleska RUB 2008-09 Course Operating System Security Memory Management and Protection Main Memory Virtual Memory Roadmap of Chapter 4 Main Memory Background
Part IV Memory Management and Protection Sadeghi, Cubaleska RUB 2008-09 Course Operating System Security Memory Management and Protection Main Memory Virtual Memory Roadmap of Chapter 4 Main Memory Background
Memory Management Outline. Operating Systems. Motivation. Paging Implementation. Accessing Invalid Pages. Performance of Demand Paging
 Memory Management Outline Operating Systems Processes (done) Memory Management Basic (done) Paging (done) Virtual memory Virtual Memory (Chapter.) Motivation Logical address space larger than physical
Memory Management Outline Operating Systems Processes (done) Memory Management Basic (done) Paging (done) Virtual memory Virtual Memory (Chapter.) Motivation Logical address space larger than physical
Memory Management. Disclaimer: some slides are adopted from book authors slides with permission 1
 Memory Management Disclaimer: some slides are adopted from book authors slides with permission 1 Recap Paged MMU: Two main Issues Translation speed can be slow TLB Table size is big Multi-level page table
Memory Management Disclaimer: some slides are adopted from book authors slides with permission 1 Recap Paged MMU: Two main Issues Translation speed can be slow TLB Table size is big Multi-level page table
Virtual Memory. ICS332 Operating Systems
 Virtual Memory ICS332 Operating Systems Virtual Memory Allow a process to execute while not completely in memory Part of the address space is kept on disk So far, we have assumed that the full address
Virtual Memory ICS332 Operating Systems Virtual Memory Allow a process to execute while not completely in memory Part of the address space is kept on disk So far, we have assumed that the full address
CS370 Operating Systems
 CS370 Operating Systems Colorado State University Yashwant K Malaiya Fall 2016 Lecture 33 Virtual Memory Slides based on Text by Silberschatz, Galvin, Gagne Various sources 1 1 FAQ How does the virtual
CS370 Operating Systems Colorado State University Yashwant K Malaiya Fall 2016 Lecture 33 Virtual Memory Slides based on Text by Silberschatz, Galvin, Gagne Various sources 1 1 FAQ How does the virtual
Memory Management. Disclaimer: some slides are adopted from book authors slides with permission 1
 Memory Management Disclaimer: some slides are adopted from book authors slides with permission 1 CPU management Roadmap Process, thread, synchronization, scheduling Memory management Virtual memory Disk
Memory Management Disclaimer: some slides are adopted from book authors slides with permission 1 CPU management Roadmap Process, thread, synchronization, scheduling Memory management Virtual memory Disk
현재이이미지를표시할수없습니다. Chapter 9: Virtual Memory
 현재이이미지를표시할수없습니다. Chapter 9: Virtual Memory Objectives To describe the benefits of a virtual memory system To explain the concepts of demand paging, page-replacement algorithms, and allocation of page frames
현재이이미지를표시할수없습니다. Chapter 9: Virtual Memory Objectives To describe the benefits of a virtual memory system To explain the concepts of demand paging, page-replacement algorithms, and allocation of page frames
Memory management, part 2: outline. Operating Systems, 2017, Danny Hendler and Amnon Meisels
 Memory management, part 2: outline 1 Page Replacement Algorithms Page fault forces choice o which page must be removed to make room for incoming page? Modified page must first be saved o unmodified just
Memory management, part 2: outline 1 Page Replacement Algorithms Page fault forces choice o which page must be removed to make room for incoming page? Modified page must first be saved o unmodified just
Memory management, part 2: outline
 Memory management, part 2: outline Page replacement algorithms Modeling PR algorithms o Working-set model and algorithms Virtual memory implementation issues 1 Page Replacement Algorithms Page fault forces
Memory management, part 2: outline Page replacement algorithms Modeling PR algorithms o Working-set model and algorithms Virtual memory implementation issues 1 Page Replacement Algorithms Page fault forces
MEMORY MANAGEMENT/1 CS 409, FALL 2013
 MEMORY MANAGEMENT Requirements: Relocation (to different memory areas) Protection (run time, usually implemented together with relocation) Sharing (and also protection) Logical organization Physical organization
MEMORY MANAGEMENT Requirements: Relocation (to different memory areas) Protection (run time, usually implemented together with relocation) Sharing (and also protection) Logical organization Physical organization
!! What is virtual memory and when is it useful? !! What is demand paging? !! When should pages in memory be replaced?
 Chapter 10: Virtual Memory Questions? CSCI [4 6] 730 Operating Systems Virtual Memory!! What is virtual memory and when is it useful?!! What is demand paging?!! When should pages in memory be replaced?!!
Chapter 10: Virtual Memory Questions? CSCI [4 6] 730 Operating Systems Virtual Memory!! What is virtual memory and when is it useful?!! What is demand paging?!! When should pages in memory be replaced?!!
Chapter 9: Virtual Memory
 Chapter 9: Virtual Memory Multiprogramming Memory Management so far 1. Dynamic Loading The main Program gets loaded into memory Routines are stored in Relocatable Load format on disk As main program (or
Chapter 9: Virtual Memory Multiprogramming Memory Management so far 1. Dynamic Loading The main Program gets loaded into memory Routines are stored in Relocatable Load format on disk As main program (or
ECE 7650 Scalable and Secure Internet Services and Architecture ---- A Systems Perspective. Part I: Operating system overview: Memory Management
 ECE 7650 Scalable and Secure Internet Services and Architecture ---- A Systems Perspective Part I: Operating system overview: Memory Management 1 Hardware background The role of primary memory Program
ECE 7650 Scalable and Secure Internet Services and Architecture ---- A Systems Perspective Part I: Operating system overview: Memory Management 1 Hardware background The role of primary memory Program
Virtual Memory B: Objec5ves
 Virtual Memory B: Objec5ves Benefits of a virtual memory system" Demand paging, page-replacement algorithms, and allocation of page frames" The working-set model" Relationship between shared memory and
Virtual Memory B: Objec5ves Benefits of a virtual memory system" Demand paging, page-replacement algorithms, and allocation of page frames" The working-set model" Relationship between shared memory and
PAGE REPLACEMENT. Operating Systems 2015 Spring by Euiseong Seo
 PAGE REPLACEMENT Operating Systems 2015 Spring by Euiseong Seo Today s Topics What if the physical memory becomes full? Page replacement algorithms How to manage memory among competing processes? Advanced
PAGE REPLACEMENT Operating Systems 2015 Spring by Euiseong Seo Today s Topics What if the physical memory becomes full? Page replacement algorithms How to manage memory among competing processes? Advanced
Chapter 8 Virtual Memory
 Chapter 8 Virtual Memory Contents Hardware and control structures Operating system software Unix and Solaris memory management Linux memory management Windows 2000 memory management Characteristics of
Chapter 8 Virtual Memory Contents Hardware and control structures Operating system software Unix and Solaris memory management Linux memory management Windows 2000 memory management Characteristics of
Memory Management Virtual Memory
 Background; key issues Memory Management Virtual Memory Memory allocation schemes Virtual memory Memory management design and implementation issues 1 Remember Basic OS structures: intro in historical order
Background; key issues Memory Management Virtual Memory Memory allocation schemes Virtual memory Memory management design and implementation issues 1 Remember Basic OS structures: intro in historical order
CS370 Operating Systems
 CS370 Operating Systems Colorado State University Yashwant K Malaiya Fall 2017 Lecture 21 Main Memory Slides based on Text by Silberschatz, Galvin, Gagne Various sources 1 1 FAQ Why not increase page size
CS370 Operating Systems Colorado State University Yashwant K Malaiya Fall 2017 Lecture 21 Main Memory Slides based on Text by Silberschatz, Galvin, Gagne Various sources 1 1 FAQ Why not increase page size
Chapter 4 Memory Management
 Chapter 4 Memory Management 4.1 Basic memory management 4.2 Swapping 4.3 Virtual memory 4.4 Page replacement algorithms 4.5 Modeling page replacement algorithms 4.6 Design issues for paging systems 4.7
Chapter 4 Memory Management 4.1 Basic memory management 4.2 Swapping 4.3 Virtual memory 4.4 Page replacement algorithms 4.5 Modeling page replacement algorithms 4.6 Design issues for paging systems 4.7
Even in those cases where the entire program is needed, it may not all be needed at the same time (such is the case with overlays, for example).
 Chapter 10 VIRTUAL MEMORY In Chapter 9, we discussed various memory-management strategies used in computer systems. All these strategies have the same goal: to keep many processes in memory simultaneously
Chapter 10 VIRTUAL MEMORY In Chapter 9, we discussed various memory-management strategies used in computer systems. All these strategies have the same goal: to keep many processes in memory simultaneously
CSE 4/521 Introduction to Operating Systems. Lecture 15 Virtual Memory I (Background, Demand Paging) Summer 2018
 CSE 4/521 Introduction to Operating Systems Lecture 15 Virtual Memory I (Background, Demand Paging) Summer 2018 Overview Objective: To describe the benefits of a virtual memory system. To explain the concept
CSE 4/521 Introduction to Operating Systems Lecture 15 Virtual Memory I (Background, Demand Paging) Summer 2018 Overview Objective: To describe the benefits of a virtual memory system. To explain the concept
Memory Management. Chapter 4 Memory Management. Multiprogramming with Fixed Partitions. Ideally programmers want memory that is.
 Chapter 4 Memory Management Ideally programmers want memory that is Memory Management large fast non volatile 4.1 Basic memory management 4.2 Swapping 4.3 Virtual memory 4.4 Page replacement algorithms
Chapter 4 Memory Management Ideally programmers want memory that is Memory Management large fast non volatile 4.1 Basic memory management 4.2 Swapping 4.3 Virtual memory 4.4 Page replacement algorithms
Operating System - Virtual Memory
 Operating System - Virtual Memory Virtual memory is a technique that allows the execution of processes which are not completely available in memory. The main visible advantage of this scheme is that programs
Operating System - Virtual Memory Virtual memory is a technique that allows the execution of processes which are not completely available in memory. The main visible advantage of this scheme is that programs
Virtual Memory CHAPTER CHAPTER OBJECTIVES. 8.1 Background
 Virtual Memory 8 CHAPTER In Chapter 7, we discussed various memory-management strategies used in computer systems. All these strategies have the same goal: to keep many processes in memory simultaneously
Virtual Memory 8 CHAPTER In Chapter 7, we discussed various memory-management strategies used in computer systems. All these strategies have the same goal: to keep many processes in memory simultaneously
Practice Exercises 449
 Practice Exercises 449 Kernel processes typically require memory to be allocated using pages that are physically contiguous. The buddy system allocates memory to kernel processes in units sized according
Practice Exercises 449 Kernel processes typically require memory to be allocated using pages that are physically contiguous. The buddy system allocates memory to kernel processes in units sized according
Basic Page Replacement
 Basic Page Replacement 1. Find the location of the desired page on disk 2. Find a free frame: - If there is a free frame, use it - If there is no free frame, use a page replacement algorithm to select
Basic Page Replacement 1. Find the location of the desired page on disk 2. Find a free frame: - If there is a free frame, use it - If there is no free frame, use a page replacement algorithm to select
Operating Systems. No. 9 ศร ณย อ นทโกส ม Sarun Intakosum
 Operating Systems No. 9 ศร ณย อ นทโกส ม Sarun Intakosum 1 Virtual-Memory Management 2 Background Virtual memory separation of user logical memory from physical memory. Only part of the program needs to
Operating Systems No. 9 ศร ณย อ นทโกส ม Sarun Intakosum 1 Virtual-Memory Management 2 Background Virtual memory separation of user logical memory from physical memory. Only part of the program needs to
Chapter 8 Virtual Memory
 Operating Systems: Internals and Design Principles Chapter 8 Virtual Memory Seventh Edition William Stallings Modified by Rana Forsati for CSE 410 Outline Principle of locality Paging - Effect of page
Operating Systems: Internals and Design Principles Chapter 8 Virtual Memory Seventh Edition William Stallings Modified by Rana Forsati for CSE 410 Outline Principle of locality Paging - Effect of page
Virtual Memory: Page Replacement. CSSE 332 Operating Systems Rose-Hulman Institute of Technology
 Virtual Memory: Page Replacement CSSE 332 Operating Systems Rose-Hulman Institute of Technology Announcements Project E & presentation are due Wednesday Team reflections due Monday, May 19 The need for
Virtual Memory: Page Replacement CSSE 332 Operating Systems Rose-Hulman Institute of Technology Announcements Project E & presentation are due Wednesday Team reflections due Monday, May 19 The need for
Chapter 8: Main Memory Chapter 9: Virtual Memory. Operating System Concepts 9th Edition
 Chapter 8: Main Memory Chapter 9: Virtual Memory Dr Prabhaker Mateti, CEG 4350 edition This collection is the combined edition of slides for Chapters 8 and 9 of SG, with several slides deleted or modified.
Chapter 8: Main Memory Chapter 9: Virtual Memory Dr Prabhaker Mateti, CEG 4350 edition This collection is the combined edition of slides for Chapters 8 and 9 of SG, with several slides deleted or modified.
Chapter 4 Memory Management. Memory Management
 Chapter 4 Memory Management 4.1 Basic memory management 4.2 Swapping 4.3 Virtual memory 4.4 Page replacement algorithms 4.5 Modeling page replacement algorithms 4.6 Design issues for paging systems 4.7
Chapter 4 Memory Management 4.1 Basic memory management 4.2 Swapping 4.3 Virtual memory 4.4 Page replacement algorithms 4.5 Modeling page replacement algorithms 4.6 Design issues for paging systems 4.7
Virtual Memory Management
 Virtual Memory Management CS-3013 Operating Systems Hugh C. Lauer (Slides include materials from Slides include materials from Modern Operating Systems, 3 rd ed., by Andrew Tanenbaum and from Operating
Virtual Memory Management CS-3013 Operating Systems Hugh C. Lauer (Slides include materials from Slides include materials from Modern Operating Systems, 3 rd ed., by Andrew Tanenbaum and from Operating
Chapter 8 Virtual Memory
 Operating Systems: Internals and Design Principles Chapter 8 Virtual Memory Seventh Edition William Stallings Operating Systems: Internals and Design Principles You re gonna need a bigger boat. Steven
Operating Systems: Internals and Design Principles Chapter 8 Virtual Memory Seventh Edition William Stallings Operating Systems: Internals and Design Principles You re gonna need a bigger boat. Steven
VIRTUAL MEMORY READING: CHAPTER 9
 VIRTUAL MEMORY READING: CHAPTER 9 9 MEMORY HIERARCHY Core! Processor! Core! Caching! Main! Memory! (DRAM)!! Caching!! Secondary Storage (SSD)!!!! Secondary Storage (Disk)! L cache exclusive to a single
VIRTUAL MEMORY READING: CHAPTER 9 9 MEMORY HIERARCHY Core! Processor! Core! Caching! Main! Memory! (DRAM)!! Caching!! Secondary Storage (SSD)!!!! Secondary Storage (Disk)! L cache exclusive to a single
