CIS 500 Software Foundations Fall December 6
|
|
|
- Estella Allison
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CIS 500 Software Foundations Fall 2006 December 6
2 Administrivia
3 Administrivia No recitations this week Extra office hours will be posted to the class mailing list Exam: Wednesday, Dec 20, 9 11 Location: Towne 313 (not here!) Coverage: Chapters 1 to 19, 22, and 23 of TAPL, excluding 12 and 15.6, plus reading knowledge of basic OCaml Hints: The exam is extremely likely to include... at least one question that is very similar to a homework problem from the past month at least one problem taken verbatim from a one-star exercise in TAPL at least one problem involving proofs at least one problem from chapter 22 and/or 23 (universal and existential types) but nothing too complicated
4 Existential Types
5 Motivation If universal quantifiers are useful in programming, then what about existential quantifiers?
6 Motivation If universal quantifiers are useful in programming, then what about existential quantifiers? Rough intuition: Terms with universal types are functions from types to terms. Terms with existential types are pairs of a type and a term.
7 Concrete Intuition Existential types describe simple modules: An existentially typed value is introduced by pairing a type with a term, written {*S,t}. (The star avoids syntactic confusion with ordinary pairs.) A value {*S,t} of type { X,T} is a module with one (hidden) type component and one term component. Example: p = {*Nat, {a=5, f=λx:nat. succ(x)}} has type { X, {a:x, f:x X}} The type component of p is Nat, and the value component is a record containing a field a of type X and a field f of type X X, for some X (namely Nat).
8 The same package p = {*Nat, {a=5, f=λx:nat. succ(x)}} also has type { X, {a:x, f:x Nat}}, since its right-hand component is a record with fields a and f of type X and X Nat, for some X (namely Nat). This example shows that there is no automatic ( best ) way to guess the type of an existential package. The programmer has to say what is intended. We re-use the ascription notation for this: p = {*Nat, {a=5, f=λx:nat. succ(x)}} as { X, {a:x, f:x X}} p1 = {*Nat, {a=5, f=λx:nat. succ(x)}} as { X, {a:x, f:x Nat}} This gives us the introduction rule for existentials: Γ t 2 : [X U]T 2 Γ {*U,t 2 } as { X,T 2 } : { X,T 2 } (T-Pack)
9 Different representations... Note that this rule permits packages with different hidden types to inhabit the same existential type. Example: p2 = {*Nat, 0} as { X,X} p3 = {*Bool, true} as { X,X}
10 Different representations... Note that this rule permits packages with different hidden types to inhabit the same existential type. Example: p2 = {*Nat, 0} as { X,X} p3 = {*Bool, true} as { X,X} More useful example: p4 = {*Nat, {a=0, f=λx:nat. succ(x)}} as { X, {a:x, f:x Nat}} p5 = {*Bool, {a=true, f=λx:bool. 0}} as { X, {a:x, f:x Nat}}
11 Exercise... Here are three more variations on the same theme: p6 = {*Nat, {a=0, f=λx:nat. succ(x)}} as { X, {a:x, f:x X}} p7 = {*Nat, {a=0, f=λx:nat. succ(x)}} as { X, {a:x, f:nat X}} p8 = {*Nat, {a=0, f=λx:nat. succ(x)}} as { X, {a:nat, f:nat Nat}} In what ways are these less useful than p4 and p5? p4 = {*Nat, {a=0, f=λx:nat. succ(x)}} as { X, {a:x, f:x Nat}} p5 = {*Bool, {a=true, f=λx:bool. 0}} as { X, {a:x, f:x Nat}}
12 The elimination form for existentials Intuition: If an existential package is like a module, then eliminating (using) such a package should correspond to open or import. I.e., we should be able to use the components of the module, but the identity of the type component should be held abstract. Γ t 1 : { X,T 12 } Γ, X, x:t 12 t 2 : T 2 Γ let {X,x}=t 1 in t 2 : T 2 (T-Unpack) Example: if p4 = {*Nat, {a=0, f=λx:nat. succ(x)}} as { X,{a:X,f:X Nat}} then let {X,x} = p4 in (x.f x.a) has type Nat (and evaluates to 1).
13 Abstraction However, if we try to use the a component of p4 as a number, typechecking fails: p4 = {*Nat, {a=0, f=λx:nat. succ(x)}} as { X,{a:X,f:X Nat}} let {X,x} = p4 in (succ x.a) = Error: argument of succ is not a number This failure makes good sense, since we saw that another package with the same existential type as p4 might use Bool or anything else as its representation type. Γ t 1 : { X,T 12 } Γ, X, x:t 12 t 2 : T 2 Γ let {X,x}=t 1 in t 2 : T 2 (T-Unpack)
14 Computation The computation rule for existentials is also straightforward: let {X,x}=({*T 11,v 12 } as T 1 ) in t 2 [X T 11 ][x v 12 ]t 2 (E-UnpackPack)
15 Example: Abstract Data Types counteradt = {*Nat, {new = 1, get = λi:nat. i, inc = λi:nat. succ(i)}} as { Counter, {new: Counter, get: Counter Nat, inc: Counter Counter}}; let {Counter,counter} = counteradt in counter.get (counter.inc counter.new);
16 Representation independence We can substitute another implementation of counters without affecting the code that uses counters: counteradt = {*{x:nat}, {new = {x=1}, get = λi:{x:nat}. i.x, inc = λi:{x:nat}. {x=succ(i.x)}}} as { Counter, {new: Counter, get: Counter Nat, inc: Counter Counter}};
17 Cascaded ADTs We can use the counter ADT to define new ADTs that use counters in their internal representations: let {Counter,counter} = counteradt in let {FlipFlop,flipflop} = {*Counter, {new = counter.new, read = λc:counter. iseven (counter.get c), toggle = λc:counter. counter.inc c, reset = λc:counter. counter.new}} as { FlipFlop, {new: FlipFlop, read: FlipFlop Bool, toggle: FlipFlop FlipFlop, reset: FlipFlop FlipFlop}} i flipflop.read (flipflop.toggle (flipflop.toggle flipflop.new));
18 Existential Objects Counter = { X, {state:x, methods: {get:x Nat, inc:x X}}}; c = {*Nat, {state = 5, methods = {get = λx:nat. x, inc = λx:nat. succ(x)}}} as Counter; let {X,body} = c in body.methods.get(body.state);
19 Existential objects: invoking methods More generally, we can define a little function that sends the get message to any counter: sendget = λc:counter. let {X,body} = c in body.methods.get(body.state);
20 Invoking the inc method of a counter object is a little more complicated. If we simply do the same as for get, the typechecker complains let {X,body} = c in body.methods.inc(body.state); = Error: Scoping error! because the type variable X appears free in the type of the body of the let. Indeed, what we ve written doesn t make intuitive sense either, since the result of the inc method is a bare internal state, not an object.
21 To satisfy both the typechecker and our informal understanding of what invoking inc should do, we must take this fresh internal state and repackage it as a counter object, using the same record of methods and the same internal state type as in the original object: c1 = let {X,body} = c in {*X, {state = body.methods.inc(body.state), methods = body.methods}} as Counter; More generally, to send the inc message to a counter, we can write: sendinc = λc:counter. let {X,body} = c in {*X, {state = body.methods.inc(body.state), methods = body.methods}} as Counter;
22 Objects vs. ADTs The examples of ADTs and objects that we have seen in the past few slides offer a revealing way to think about the differences between classical ADTs and objects. Both can be represented using existentials With ADTs, each existential package is opened as early as possible (at creation time) With objects, the existential package is opened as late as possible (at method invocation time) These differences in style give rise to the well-known pragmatic differences between ADTs and objects: ADTs support binary operations objects support multiple representations
23 A full-blown existential object model What we ve done so far is to give an account of object-style encapsulation in terms of existential types. To give a full model of all the core OO features we have discussed before, some significant work is required. In particular, we must add: subtyping (and bounded quantification ) type operators ( higher-order subtyping )
24 Recap... Where we ve been
25 What is software foundations? Software foundations (a.k.a. theory of programming languages ) is the study of the meaning of programs. A main goal is finding ways to describe program behaviors that are both precise and abstract.
26 Why study software foundations? To be able to prove specific facts about particular programs (i.e., program verification) Important in some domains (safety-critical systems, hardware design, inner loops of key algorithms,...), but currently very difficult and expensive. We have not said much about this in the course. To develop intuitions for informal reasoning about programs To prove general facts about all the programs in a given programming language (e.g., safety or security properties) To understand language features (and their interactions) deeply and develop principles for better language design PL as the materials science of computer science...
27 What I hope you got out of the course A more sophisticated perspective on programs, programming languages, and the activity of programming How to view programs and whole languages as formal, mathematical objects How to make and prove rigorous claims about them Detailed study of a range of basic language features Deep intuitions about key language properties such as type safety Familiarity with today s best tools for language design, description, and analysis Programming languages are everywhere. Most software designers are at some point language designers!
28 Overview In this course, we concentrated on operational semantics and type systems. Part O: Background A taste of OCaml Functional programming style Part I: Basics Inductive definitions and proofs Operational semantics The lambda-calculus Evaluator implementation in OCaml
29 Part II: Type systems Simple types Type safety preservation and progress Formal description of a variety of basic language features (records, variants, lists, casting,...) References Exceptions Subtyping Metatheory of subtyping (subtyping and typechecking algorithms) Polymorphism (universal and existential types) Part III: Object-oriented features (case studies) A simple imperative object model An direct formalization of core Java
30 What next?
31 The rest of TAPL Several more core topics are covered in the second half of TAPL. Recursive types (including a rigorous treatment of induction and co-induction) More on parametric polymorphism (universal and existential types) Bounded quantification Refinement of the imperative object model ML-style type inference Type operators Higher-order bounded quantification A purely functional object model
32 The Research Literature With this course under your belt, you are ready to directly address research papers in programming languages. This is a big area, and each sub-area has its own special techniques and notations, but you now have pretty much all the basic intuitions needed to understand these on your own.
33 The End
Administrivia. Existential Types. CIS 500 Software Foundations Fall December 6. Administrivia. Motivation. Motivation
 CIS 500 Software Foundations Fall 2006 Administrivia December 6 Administrivia No recitations this week Extra office hours will be posted to the class mailing list Exam: Wednesday, Dec 20, 9 11 Location:
CIS 500 Software Foundations Fall 2006 Administrivia December 6 Administrivia No recitations this week Extra office hours will be posted to the class mailing list Exam: Wednesday, Dec 20, 9 11 Location:
CIS 500 Software Foundations Fall December 4
 CIS 500 Software Foundations Fall 2006 December 4 Administrivia Homework 11 Homework 11 is currently due on Friday. Should we make it due next Monday instead? More on Evaluation Contexts Progress for FJ
CIS 500 Software Foundations Fall 2006 December 4 Administrivia Homework 11 Homework 11 is currently due on Friday. Should we make it due next Monday instead? More on Evaluation Contexts Progress for FJ
Lambda Calculi With Polymorphism
 Resources: The slides of this lecture were derived from [Järvi], with permission of the original author, by copy & x = 1 let x = 1 in... paste or by selection, annotation, or rewording. [Järvi] is in turn
Resources: The slides of this lecture were derived from [Järvi], with permission of the original author, by copy & x = 1 let x = 1 in... paste or by selection, annotation, or rewording. [Järvi] is in turn
Lambda Calculi With Polymorphism
 Resources: The slides of this lecture were derived from [Järvi], with permission of the original author, by copy & x = 1 let x = 1 in... paste or by selection, annotation, or rewording. [Järvi] is in turn
Resources: The slides of this lecture were derived from [Järvi], with permission of the original author, by copy & x = 1 let x = 1 in... paste or by selection, annotation, or rewording. [Järvi] is in turn
Type Systems. Parametric Polymorphism. 1. Recall Let-Polymorphism. 1. Recall Let-Polymorphism. Lecture 9 Dec. 15th, 2004 Sebastian Maneth
 Today Parametric Polymorphism Type Systems Lecture 9 Dec. 15th, 2004 Sebastian Maneth 1. Recall Let-Polymorphism 4. System F-sub 5. Properties of F-sub http://lampwww.epfl.ch/teaching/typesystems/2004
Today Parametric Polymorphism Type Systems Lecture 9 Dec. 15th, 2004 Sebastian Maneth 1. Recall Let-Polymorphism 4. System F-sub 5. Properties of F-sub http://lampwww.epfl.ch/teaching/typesystems/2004
Part III. Chapter 15: Subtyping
 Part III Chapter 15: Subtyping Subsumption Subtype relation Properties of subtyping and typing Subtyping and other features Intersection and union types Subtyping Motivation With the usual typing rule
Part III Chapter 15: Subtyping Subsumption Subtype relation Properties of subtyping and typing Subtyping and other features Intersection and union types Subtyping Motivation With the usual typing rule
Goal. CS152: Programming Languages. Lecture 15 Parametric Polymorphism. What the Library Likes. What The Client Likes. Start simpler.
 Goal Understand what this interface means and why it matters: CS152: Programming Languages Lecture 15 Parametric Polymorphism Dan Grossman Spring 2011 type a mylist; val mt_list : a mylist val cons : a
Goal Understand what this interface means and why it matters: CS152: Programming Languages Lecture 15 Parametric Polymorphism Dan Grossman Spring 2011 type a mylist; val mt_list : a mylist val cons : a
Lecture 13: Subtyping
 Lecture 13: Subtyping Polyvios Pratikakis Computer Science Department, University of Crete Type Systems and Programming Languages Pratikakis (CSD) Subtyping CS546, 2018-2019 1 / 15 Subtyping Usually found
Lecture 13: Subtyping Polyvios Pratikakis Computer Science Department, University of Crete Type Systems and Programming Languages Pratikakis (CSD) Subtyping CS546, 2018-2019 1 / 15 Subtyping Usually found
CS152: Programming Languages. Lecture 11 STLC Extensions and Related Topics. Dan Grossman Spring 2011
 CS152: Programming Languages Lecture 11 STLC Extensions and Related Topics Dan Grossman Spring 2011 Review e ::= λx. e x e e c v ::= λx. e c τ ::= int τ τ Γ ::= Γ, x : τ (λx. e) v e[v/x] e 1 e 1 e 1 e
CS152: Programming Languages Lecture 11 STLC Extensions and Related Topics Dan Grossman Spring 2011 Review e ::= λx. e x e e c v ::= λx. e c τ ::= int τ τ Γ ::= Γ, x : τ (λx. e) v e[v/x] e 1 e 1 e 1 e
CS 565: Programming Languages. Spring 2008 Tu, Th: 16:30-17:45 Room LWSN 1106
 CS 565: Programming Languages Spring 2008 Tu, Th: 16:30-17:45 Room LWSN 1106 Administrivia Who am I? Course web page http://www.cs.purdue.edu/homes/peugster/cs565spring08/ Office hours By appointment Main
CS 565: Programming Languages Spring 2008 Tu, Th: 16:30-17:45 Room LWSN 1106 Administrivia Who am I? Course web page http://www.cs.purdue.edu/homes/peugster/cs565spring08/ Office hours By appointment Main
Subsumption. Principle of safe substitution
 Recap on Subtyping Subsumption Some types are better than others, in the sense that a value of one can always safely be used where a value of the other is expected. Which can be formalized as by introducing:
Recap on Subtyping Subsumption Some types are better than others, in the sense that a value of one can always safely be used where a value of the other is expected. Which can be formalized as by introducing:
Part III Chapter 15: Subtyping
 Part III Chapter 15: Subtyping Subsumption Subtype relation Properties of subtyping and typing Subtyping and other features Intersection and union types Subtyping Motivation With the usual typing rule
Part III Chapter 15: Subtyping Subsumption Subtype relation Properties of subtyping and typing Subtyping and other features Intersection and union types Subtyping Motivation With the usual typing rule
What Is Computer Science? The Scientific Study of Computation. Expressing or Describing
 What Is Computer Science? The Scientific Study of Computation CMPSCI 630: Programming Languages Introduction Spring 2009 (with thanks to Robert Harper) Expressing or Describing Automating Understanding
What Is Computer Science? The Scientific Study of Computation CMPSCI 630: Programming Languages Introduction Spring 2009 (with thanks to Robert Harper) Expressing or Describing Automating Understanding
Subtyping. Lecture 13 CS 565 3/27/06
 Subtyping Lecture 13 CS 565 3/27/06 Polymorphism Different varieties of polymorphism: Parametric (ML) type variables are abstract, and used to encode the fact that the same term can be used in many different
Subtyping Lecture 13 CS 565 3/27/06 Polymorphism Different varieties of polymorphism: Parametric (ML) type variables are abstract, and used to encode the fact that the same term can be used in many different
Review. CS152: Programming Languages. Lecture 11 STLC Extensions and Related Topics. Let bindings (CBV) Adding Stuff. Booleans and Conditionals
 Review CS152: Programming Languages Lecture 11 STLC Extensions and Related Topics e ::= λx. e x ee c v ::= λx. e c (λx. e) v e[v/x] e 1 e 2 e 1 e 2 τ ::= int τ τ Γ ::= Γ,x : τ e 2 e 2 ve 2 ve 2 e[e /x]:
Review CS152: Programming Languages Lecture 11 STLC Extensions and Related Topics e ::= λx. e x ee c v ::= λx. e c (λx. e) v e[v/x] e 1 e 2 e 1 e 2 τ ::= int τ τ Γ ::= Γ,x : τ e 2 e 2 ve 2 ve 2 e[e /x]:
Programming Languages Fall 2014
 Programming Languages Fall 2014 Lecture 7: Simple Types and Simply-Typed Lambda Calculus Prof. Liang Huang huang@qc.cs.cuny.edu 1 Types stuck terms? how to fix it? 2 Plan First I For today, we ll go back
Programming Languages Fall 2014 Lecture 7: Simple Types and Simply-Typed Lambda Calculus Prof. Liang Huang huang@qc.cs.cuny.edu 1 Types stuck terms? how to fix it? 2 Plan First I For today, we ll go back
CSE 505 Graduate PL. Fall 2013
 CSE 505 Graduate PL Fall 2013 Goals Since Day 1 Develop tools to rigorously study what programs mean. semantics equivalence, termination, determinism,... Develop tools for studying program behavior! inductive
CSE 505 Graduate PL Fall 2013 Goals Since Day 1 Develop tools to rigorously study what programs mean. semantics equivalence, termination, determinism,... Develop tools for studying program behavior! inductive
CIS 500 Software Foundations Fall October 2
 CIS 500 Software Foundations Fall 2006 October 2 Preliminaries Homework Results of my email survey: There was one badly misdesigned (PhD) problem and a couple of others that were less well thought through
CIS 500 Software Foundations Fall 2006 October 2 Preliminaries Homework Results of my email survey: There was one badly misdesigned (PhD) problem and a couple of others that were less well thought through
COSE212: Programming Languages. Lecture 0 Course Overview
 COSE212: Programming Languages Lecture 0 Course Overview Hakjoo Oh 2017 Fall Hakjoo Oh COSE212 2017 Fall, Lecture 0 September 4, 2017 1 / 9 Basic nformation nstructor: Hakjoo Oh TAs: Position: Assistant
COSE212: Programming Languages Lecture 0 Course Overview Hakjoo Oh 2017 Fall Hakjoo Oh COSE212 2017 Fall, Lecture 0 September 4, 2017 1 / 9 Basic nformation nstructor: Hakjoo Oh TAs: Position: Assistant
Chapter 22: Type Reconstruction (Type Inference)
 Chapter 22: Type Reconstruction (Type Inference) Calculating a Principal Type for a Term Constraint based Typing Unification and Principle Types Extension with let-polymorphism Type Variables and Type
Chapter 22: Type Reconstruction (Type Inference) Calculating a Principal Type for a Term Constraint based Typing Unification and Principle Types Extension with let-polymorphism Type Variables and Type
Type Systems. Pierce Ch. 3, 8, 11, 15 CSE
 Type Systems Pierce Ch. 3, 8, 11, 15 CSE 6341 1 A Simple Language ::= true false if then else 0 succ pred iszero Simple untyped expressions Natural numbers encoded as succ succ
Type Systems Pierce Ch. 3, 8, 11, 15 CSE 6341 1 A Simple Language ::= true false if then else 0 succ pred iszero Simple untyped expressions Natural numbers encoded as succ succ
Resources: The slides of this lecture were derived from [Järvi], with permission of the original author, by copy & x = 1 let x = 1 in...
![Resources: The slides of this lecture were derived from [Järvi], with permission of the original author, by copy & x = 1 let x = 1 in... Resources: The slides of this lecture were derived from [Järvi], with permission of the original author, by copy & x = 1 let x = 1 in...](/thumbs/79/79820018.jpg) Resources: The slides of this lecture were derived from [Järvi], with permission of the original author, by copy & x = 1 let x = 1 in... paste or by selection, annotation, or rewording. [Järvi] is in turn
Resources: The slides of this lecture were derived from [Järvi], with permission of the original author, by copy & x = 1 let x = 1 in... paste or by selection, annotation, or rewording. [Järvi] is in turn
The Untyped Lambda Calculus
 Resources: The slides of this lecture were derived from x = 1 [Järvi], with permission of the original author, by copy & let x = 1 in... paste or by selection, annotation, or rewording. [Järvi] is in turn
Resources: The slides of this lecture were derived from x = 1 [Järvi], with permission of the original author, by copy & let x = 1 in... paste or by selection, annotation, or rewording. [Järvi] is in turn
Programming with Math and Logic
 .. Programming with Math and Logic an invitation to functional programming Ed Morehouse Wesleyan University The Plan why fp? terms types interfaces The What and Why of Functional Programming Computing
.. Programming with Math and Logic an invitation to functional programming Ed Morehouse Wesleyan University The Plan why fp? terms types interfaces The What and Why of Functional Programming Computing
Type Systems Winter Semester 2006
 Type Systems Winter Semester 2006 Week 9 December 13 December 13, 2006 - version 1.0 Plan PREVIOUSLY: unit, sequencing, let, pairs, sums TODAY: 1. recursion 2. state 3.??? NEXT: exceptions? NEXT: polymorphic
Type Systems Winter Semester 2006 Week 9 December 13 December 13, 2006 - version 1.0 Plan PREVIOUSLY: unit, sequencing, let, pairs, sums TODAY: 1. recursion 2. state 3.??? NEXT: exceptions? NEXT: polymorphic
Polymorphic lambda calculus Princ. of Progr. Languages (and Extended ) The University of Birmingham. c Uday Reddy
 06-02552 Princ. of Progr. Languages (and Extended ) The University of Birmingham Spring Semester 2016-17 School of Computer Science c Uday Reddy2016-17 Handout 6: Polymorphic Type Systems 1. Polymorphic
06-02552 Princ. of Progr. Languages (and Extended ) The University of Birmingham Spring Semester 2016-17 School of Computer Science c Uday Reddy2016-17 Handout 6: Polymorphic Type Systems 1. Polymorphic
More Lambda Calculus and Intro to Type Systems
 More Lambda Calculus and Intro to Type Systems Plan Heavy Class Participation Thus, wake up! Lambda Calculus How is it related to real life? Encodings Fixed points Type Systems Overview Static, Dyamic
More Lambda Calculus and Intro to Type Systems Plan Heavy Class Participation Thus, wake up! Lambda Calculus How is it related to real life? Encodings Fixed points Type Systems Overview Static, Dyamic
CS-XXX: Graduate Programming Languages. Lecture 9 Simply Typed Lambda Calculus. Dan Grossman 2012
 CS-XXX: Graduate Programming Languages Lecture 9 Simply Typed Lambda Calculus Dan Grossman 2012 Types Major new topic worthy of several lectures: Type systems Continue to use (CBV) Lambda Caluclus as our
CS-XXX: Graduate Programming Languages Lecture 9 Simply Typed Lambda Calculus Dan Grossman 2012 Types Major new topic worthy of several lectures: Type systems Continue to use (CBV) Lambda Caluclus as our
COS 320. Compiling Techniques
 Topic 5: Types COS 320 Compiling Techniques Princeton University Spring 2016 Lennart Beringer 1 Types: potential benefits (I) 2 For programmers: help to eliminate common programming mistakes, particularly
Topic 5: Types COS 320 Compiling Techniques Princeton University Spring 2016 Lennart Beringer 1 Types: potential benefits (I) 2 For programmers: help to eliminate common programming mistakes, particularly
Simple Unification-based Type Inference for GADTs
 Simple Unification-based Type Inference for GADTs Stephanie Weirich University of Pennsylvania joint work with Dimitrios Vytiniotis, Simon Peyton Jones and Geoffrey Washburn Overview Goal: Add GADTs to
Simple Unification-based Type Inference for GADTs Stephanie Weirich University of Pennsylvania joint work with Dimitrios Vytiniotis, Simon Peyton Jones and Geoffrey Washburn Overview Goal: Add GADTs to
Types. Type checking. Why Do We Need Type Systems? Types and Operations. What is a type? Consensus
 Types Type checking What is a type? The notion varies from language to language Consensus A set of values A set of operations on those values Classes are one instantiation of the modern notion of type
Types Type checking What is a type? The notion varies from language to language Consensus A set of values A set of operations on those values Classes are one instantiation of the modern notion of type
Second-Order Type Systems
 #1 Second-Order Type Systems Homework 5 Summary Student : 37.9704 Student : 44.4466 ORIGINAL : 50.2442 Student : 50.8275 Student : 50.8633 Student : 50.9181 Student : 52.1347 Student : 52.1633 Student
#1 Second-Order Type Systems Homework 5 Summary Student : 37.9704 Student : 44.4466 ORIGINAL : 50.2442 Student : 50.8275 Student : 50.8633 Student : 50.9181 Student : 52.1347 Student : 52.1633 Student
Formal Systems and their Applications
 Formal Systems and their Applications Dave Clarke (Dave.Clarke@cs.kuleuven.be) Acknowledgment: these slides are based in part on slides from Benjamin Pierce and Frank Piessens 1 Course Overview Introduction
Formal Systems and their Applications Dave Clarke (Dave.Clarke@cs.kuleuven.be) Acknowledgment: these slides are based in part on slides from Benjamin Pierce and Frank Piessens 1 Course Overview Introduction
CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages
 CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages Lambda Calculus CMSC 330 1 Programming Language Features Many features exist simply for convenience Multi-argument functions foo ( a, b, c ) Use currying
CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages Lambda Calculus CMSC 330 1 Programming Language Features Many features exist simply for convenience Multi-argument functions foo ( a, b, c ) Use currying
Lecture 15 CIS 341: COMPILERS
 Lecture 15 CIS 341: COMPILERS Announcements HW4: OAT v. 1.0 Parsing & basic code generation Due: March 28 th No lecture on Thursday, March 22 Dr. Z will be away Zdancewic CIS 341: Compilers 2 Adding Integers
Lecture 15 CIS 341: COMPILERS Announcements HW4: OAT v. 1.0 Parsing & basic code generation Due: March 28 th No lecture on Thursday, March 22 Dr. Z will be away Zdancewic CIS 341: Compilers 2 Adding Integers
Types and Programming Languages. Lecture 6. Normalization, references, and exceptions
 Types and Programming Languages Lecture 6. Normalization, references, and exceptions Xiaojuan Cai cxj@sjtu.edu.cn BASICS Lab, Shanghai Jiao Tong University Fall, 2016 Coming soon One more language features:
Types and Programming Languages Lecture 6. Normalization, references, and exceptions Xiaojuan Cai cxj@sjtu.edu.cn BASICS Lab, Shanghai Jiao Tong University Fall, 2016 Coming soon One more language features:
Recitation 6: System F and Existential Types : Foundations of Programming Languages
 Recitation 6: System F and Existential Types 15-312: Foundations of Programming Languages Serena Wang, Charles Yuan February 21, 2018 We saw how to use inductive and coinductive types last recitation.
Recitation 6: System F and Existential Types 15-312: Foundations of Programming Languages Serena Wang, Charles Yuan February 21, 2018 We saw how to use inductive and coinductive types last recitation.
(Refer Slide Time: 4:00)
 Principles of Programming Languages Dr. S. Arun Kumar Department of Computer Science & Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi Lecture - 38 Meanings Let us look at abstracts namely functional
Principles of Programming Languages Dr. S. Arun Kumar Department of Computer Science & Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi Lecture - 38 Meanings Let us look at abstracts namely functional
Introduction to Axiomatic Semantics
 Introduction to Axiomatic Semantics Meeting 10, CSCI 5535, Spring 2009 Announcements Homework 3 due tonight Homework 2 is graded 13 (mean), 14 (median), out of 21 total, but Graduate class: final project
Introduction to Axiomatic Semantics Meeting 10, CSCI 5535, Spring 2009 Announcements Homework 3 due tonight Homework 2 is graded 13 (mean), 14 (median), out of 21 total, but Graduate class: final project
Simply-Typed Lambda Calculus
 #1 Simply-Typed Lambda Calculus #2 Back to School What is operational semantics? When would you use contextual (small-step) semantics? What is denotational semantics? What is axiomatic semantics? What
#1 Simply-Typed Lambda Calculus #2 Back to School What is operational semantics? When would you use contextual (small-step) semantics? What is denotational semantics? What is axiomatic semantics? What
Operational Semantics. One-Slide Summary. Lecture Outline
 Operational Semantics #1 One-Slide Summary Operational semantics are a precise way of specifying how to evaluate a program. A formal semantics tells you what each expression means. Meaning depends on context:
Operational Semantics #1 One-Slide Summary Operational semantics are a precise way of specifying how to evaluate a program. A formal semantics tells you what each expression means. Meaning depends on context:
The design of a programming language for provably correct programs: success and failure
 The design of a programming language for provably correct programs: success and failure Don Sannella Laboratory for Foundations of Computer Science School of Informatics, University of Edinburgh http://homepages.inf.ed.ac.uk/dts
The design of a programming language for provably correct programs: success and failure Don Sannella Laboratory for Foundations of Computer Science School of Informatics, University of Edinburgh http://homepages.inf.ed.ac.uk/dts
Types and Programming Languages. Lecture 5. Extensions of simple types
 Types and Programming Languages Lecture 5. Extensions of simple types Xiaojuan Cai cxj@sjtu.edu.cn BASICS Lab, Shanghai Jiao Tong University Fall, 2016 Coming soon Simply typed λ-calculus has enough structure
Types and Programming Languages Lecture 5. Extensions of simple types Xiaojuan Cai cxj@sjtu.edu.cn BASICS Lab, Shanghai Jiao Tong University Fall, 2016 Coming soon Simply typed λ-calculus has enough structure
The Lambda Calculus. 27 September. Fall Software Foundations CIS 500. The lambda-calculus. Announcements
 CIS 500 Software Foundations Fall 2004 27 September IS 500, 27 September 1 The Lambda Calculus IS 500, 27 September 3 Announcements Homework 1 is graded. Pick it up from Cheryl Hickey (Levine 502). We
CIS 500 Software Foundations Fall 2004 27 September IS 500, 27 September 1 The Lambda Calculus IS 500, 27 September 3 Announcements Homework 1 is graded. Pick it up from Cheryl Hickey (Levine 502). We
The Untyped Lambda Calculus
 Resources: The slides of this lecture were derived from [Järvi], with permission of the original author, by copy & x = 1 let x = 1 in... paste or by selection, annotation, or rewording. [Järvi] is in turn
Resources: The slides of this lecture were derived from [Järvi], with permission of the original author, by copy & x = 1 let x = 1 in... paste or by selection, annotation, or rewording. [Järvi] is in turn
CIS 500 Software Foundations Fall September 25
 CIS 500 Software Foundations Fall 2006 September 25 The Lambda Calculus The lambda-calculus If our previous language of arithmetic expressions was the simplest nontrivial programming language, then the
CIS 500 Software Foundations Fall 2006 September 25 The Lambda Calculus The lambda-calculus If our previous language of arithmetic expressions was the simplest nontrivial programming language, then the
Introduction to dependent types in Coq
 October 24, 2008 basic use of the Coq system In Coq, you can play with simple values and functions. The basic command is called Check, to verify if an expression is well-formed and learn what is its type.
October 24, 2008 basic use of the Coq system In Coq, you can play with simple values and functions. The basic command is called Check, to verify if an expression is well-formed and learn what is its type.
Chapter 13: Reference. Why reference Typing Evaluation Store Typings Safety Notes
 Chapter 13: Reference Why reference Typing Evaluation Store Typings Safety Notes References Computational Effects Also known as side effects. A function or expression is said to have a side effect if,
Chapter 13: Reference Why reference Typing Evaluation Store Typings Safety Notes References Computational Effects Also known as side effects. A function or expression is said to have a side effect if,
Note that in this definition, n + m denotes the syntactic expression with three symbols n, +, and m, not to the number that is the sum of n and m.
 CS 6110 S18 Lecture 8 Structural Operational Semantics and IMP Today we introduce a very simple imperative language, IMP, along with two systems of rules for evaluation called small-step and big-step semantics.
CS 6110 S18 Lecture 8 Structural Operational Semantics and IMP Today we introduce a very simple imperative language, IMP, along with two systems of rules for evaluation called small-step and big-step semantics.
The Untyped Lambda Calculus
 Resources: The slides of this lecture were derived from [Järvi], with permission of the original author, by copy & x = 1 let x = 1 in... paste or by selection, annotation, or rewording. [Järvi] is in turn
Resources: The slides of this lecture were derived from [Järvi], with permission of the original author, by copy & x = 1 let x = 1 in... paste or by selection, annotation, or rewording. [Järvi] is in turn
On to Objects. CIS 500 Software Foundations Fall November 20. A Change of Pace. Case study: object-oriented programming
 CIS 500 Software Foundations Fall 2006 On to Objects November 20 A Change of Pace We ve spent the semester developing tools for defining and reasoning about a variety of programming language features.
CIS 500 Software Foundations Fall 2006 On to Objects November 20 A Change of Pace We ve spent the semester developing tools for defining and reasoning about a variety of programming language features.
Lambda Calculus. Type Systems, Lectures 3. Jevgeni Kabanov Tartu,
 Lambda Calculus Type Systems, Lectures 3 Jevgeni Kabanov Tartu, 13.02.2006 PREVIOUSLY ON TYPE SYSTEMS Arithmetical expressions and Booleans Evaluation semantics Normal forms & Values Getting stuck Safety
Lambda Calculus Type Systems, Lectures 3 Jevgeni Kabanov Tartu, 13.02.2006 PREVIOUSLY ON TYPE SYSTEMS Arithmetical expressions and Booleans Evaluation semantics Normal forms & Values Getting stuck Safety
Programming Languages Assignment #7
 Programming Languages Assignment #7 December 2, 2007 1 Introduction This assignment has 20 points total. In this assignment, you will write a type-checker for the PolyMinML language (a language that is
Programming Languages Assignment #7 December 2, 2007 1 Introduction This assignment has 20 points total. In this assignment, you will write a type-checker for the PolyMinML language (a language that is
Lecture 9: Typed Lambda Calculus
 Advanced Topics in Programming Languages Spring Semester, 2012 Lecture 9: Typed Lambda Calculus May 8, 2012 Lecturer: Mooly Sagiv Scribe: Guy Golan Gueta and Shachar Itzhaky 1 Defining a Type System for
Advanced Topics in Programming Languages Spring Semester, 2012 Lecture 9: Typed Lambda Calculus May 8, 2012 Lecturer: Mooly Sagiv Scribe: Guy Golan Gueta and Shachar Itzhaky 1 Defining a Type System for
Recursive Types and Subtyping
 Recursive Types and Subtyping #1 One-Slide Summary Recursive types (e.g., list) make the typed lambda calculus as powerful as the untyped lambda calculus. If is a subtype of then any expression of type
Recursive Types and Subtyping #1 One-Slide Summary Recursive types (e.g., list) make the typed lambda calculus as powerful as the untyped lambda calculus. If is a subtype of then any expression of type
Mutable References. Chapter 1
 Chapter 1 Mutable References In the (typed or untyped) λ-calculus, or in pure functional languages, a variable is immutable in that once bound to a value as the result of a substitution, its contents never
Chapter 1 Mutable References In the (typed or untyped) λ-calculus, or in pure functional languages, a variable is immutable in that once bound to a value as the result of a substitution, its contents never
Programming Language Features. CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages. Turing Completeness. Turing Machine.
 CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages Lambda Calculus Programming Language Features Many features exist simply for convenience Multi-argument functions foo ( a, b, c ) Ø Use currying or tuples
CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages Lambda Calculus Programming Language Features Many features exist simply for convenience Multi-argument functions foo ( a, b, c ) Ø Use currying or tuples
CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages
 CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages Lambda Calculus CMSC 330 1 Programming Language Features Many features exist simply for convenience Multi-argument functions foo ( a, b, c ) Ø Use currying
CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages Lambda Calculus CMSC 330 1 Programming Language Features Many features exist simply for convenience Multi-argument functions foo ( a, b, c ) Ø Use currying
Type Systems. Today. 1. Organizational Matters. 1. Organizational Matters. Lecture 1 Oct. 20th, 2004 Sebastian Maneth. 1. Organizational Matters
 Today Type Systems 1. Organizational Matters 2. What is this course about? 3. Where do types come from? 4. Def. of the small language Expr. Its syntax and semantics. Lecture 1 Oct. 20th, 2004 Sebastian
Today Type Systems 1. Organizational Matters 2. What is this course about? 3. Where do types come from? 4. Def. of the small language Expr. Its syntax and semantics. Lecture 1 Oct. 20th, 2004 Sebastian
CS422 - Programming Language Design
 1 CS422 - Programming Language Design Elements of Functional Programming Grigore Roşu Department of Computer Science University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign 2 The two languages that we defined so far
1 CS422 - Programming Language Design Elements of Functional Programming Grigore Roşu Department of Computer Science University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign 2 The two languages that we defined so far
Comp 411 Principles of Programming Languages Lecture 7 Meta-interpreters. Corky Cartwright January 26, 2018
 Comp 411 Principles of Programming Languages Lecture 7 Meta-interpreters Corky Cartwright January 26, 2018 Denotational Semantics The primary alternative to syntactic semantics is denotational semantics.
Comp 411 Principles of Programming Languages Lecture 7 Meta-interpreters Corky Cartwright January 26, 2018 Denotational Semantics The primary alternative to syntactic semantics is denotational semantics.
This is already grossly inconvenient in present formalisms. Why do we want to make this convenient? GENERAL GOALS
 1 THE FORMALIZATION OF MATHEMATICS by Harvey M. Friedman Ohio State University Department of Mathematics friedman@math.ohio-state.edu www.math.ohio-state.edu/~friedman/ May 21, 1997 Can mathematics be
1 THE FORMALIZATION OF MATHEMATICS by Harvey M. Friedman Ohio State University Department of Mathematics friedman@math.ohio-state.edu www.math.ohio-state.edu/~friedman/ May 21, 1997 Can mathematics be
Types for References, Exceptions and Continuations. Review of Subtyping. Γ e:τ τ <:σ Γ e:σ. Annoucements. How s the midterm going?
 Types for References, Exceptions and Continuations Annoucements How s the midterm going? Meeting 21, CSCI 5535, Spring 2009 2 One-Slide Summary Review of Subtyping If τ is a subtype of σ then any expression
Types for References, Exceptions and Continuations Annoucements How s the midterm going? Meeting 21, CSCI 5535, Spring 2009 2 One-Slide Summary Review of Subtyping If τ is a subtype of σ then any expression
Tracing Ambiguity in GADT Type Inference
 Tracing Ambiguity in GADT Type Inference ML Workshop 2012, Copenhagen Jacques Garrigue & Didier Rémy Nagoya University / INRIA Garrigue & Rémy Tracing ambiguity 1 Generalized Algebraic Datatypes Algebraic
Tracing Ambiguity in GADT Type Inference ML Workshop 2012, Copenhagen Jacques Garrigue & Didier Rémy Nagoya University / INRIA Garrigue & Rémy Tracing ambiguity 1 Generalized Algebraic Datatypes Algebraic
Type Checking and Type Inference
 Type Checking and Type Inference Principles of Programming Languages CSE 307 1 Types in Programming Languages 2 Static Type Checking 3 Polymorphic Type Inference Version: 1.8 17:20:56 2014/08/25 Compiled
Type Checking and Type Inference Principles of Programming Languages CSE 307 1 Types in Programming Languages 2 Static Type Checking 3 Polymorphic Type Inference Version: 1.8 17:20:56 2014/08/25 Compiled
Objects as Session-Typed Processes
 Objects as Session-Typed Processes Stephanie Balzer and Frank Pfenning Computer Science Department, Carnegie Mellon University AGERE! 2015 The essence of object-orientation 2 The essence of object-orientation
Objects as Session-Typed Processes Stephanie Balzer and Frank Pfenning Computer Science Department, Carnegie Mellon University AGERE! 2015 The essence of object-orientation 2 The essence of object-orientation
Typed Lambda Calculus and Exception Handling
 Typed Lambda Calculus and Exception Handling Dan Zingaro zingard@mcmaster.ca McMaster University Typed Lambda Calculus and Exception Handling p. 1/2 Untyped Lambda Calculus Goal is to introduce typing
Typed Lambda Calculus and Exception Handling Dan Zingaro zingard@mcmaster.ca McMaster University Typed Lambda Calculus and Exception Handling p. 1/2 Untyped Lambda Calculus Goal is to introduce typing
CS3110 Spring 2017 Lecture 9 Inductive proofs of specifications
 CS3110 Spring 2017 Lecture 9 Inductive proofs of specifications Robert Constable 1 Lecture Plan 1. Repeating schedule of remaining five problem sets and prelim. 2. Comments on tautologies and the Coq logic.
CS3110 Spring 2017 Lecture 9 Inductive proofs of specifications Robert Constable 1 Lecture Plan 1. Repeating schedule of remaining five problem sets and prelim. 2. Comments on tautologies and the Coq logic.
Hoare Logic. COMP2600 Formal Methods for Software Engineering. Rajeev Goré
 Hoare Logic COMP2600 Formal Methods for Software Engineering Rajeev Goré Australian National University Semester 2, 2016 (Slides courtesy of Ranald Clouston) COMP 2600 Hoare Logic 1 Australian Capital
Hoare Logic COMP2600 Formal Methods for Software Engineering Rajeev Goré Australian National University Semester 2, 2016 (Slides courtesy of Ranald Clouston) COMP 2600 Hoare Logic 1 Australian Capital
CS-XXX: Graduate Programming Languages. Lecture 22 Class-Based Object-Oriented Programming. Dan Grossman 2012
 CS-XXX: Graduate Programming Languages Lecture 22 Class-Based Object-Oriented Programming Dan Grossman 2012 PL Issues for OOP? OOP lets you: 1. Build some extensible software concisely 2. Exploit an intuitive
CS-XXX: Graduate Programming Languages Lecture 22 Class-Based Object-Oriented Programming Dan Grossman 2012 PL Issues for OOP? OOP lets you: 1. Build some extensible software concisely 2. Exploit an intuitive
Contents. Chapter 1 SPECIFYING SYNTAX 1
 Contents Chapter 1 SPECIFYING SYNTAX 1 1.1 GRAMMARS AND BNF 2 Context-Free Grammars 4 Context-Sensitive Grammars 8 Exercises 8 1.2 THE PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE WREN 10 Ambiguity 12 Context Constraints in Wren
Contents Chapter 1 SPECIFYING SYNTAX 1 1.1 GRAMMARS AND BNF 2 Context-Free Grammars 4 Context-Sensitive Grammars 8 Exercises 8 1.2 THE PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE WREN 10 Ambiguity 12 Context Constraints in Wren
Introduction to Functional Programming in Haskell 1 / 56
 Introduction to Functional Programming in Haskell 1 / 56 Outline Why learn functional programming? The essence of functional programming What is a function? Equational reasoning First-order vs. higher-order
Introduction to Functional Programming in Haskell 1 / 56 Outline Why learn functional programming? The essence of functional programming What is a function? Equational reasoning First-order vs. higher-order
Symmetry in Type Theory
 Google May 29th, 2012 What is Symmetry? Definition Symmetry: Two or more things that initially look distinct, may actually be instances of a more general underlying principle. Why do we care? Simplicity.
Google May 29th, 2012 What is Symmetry? Definition Symmetry: Two or more things that initially look distinct, may actually be instances of a more general underlying principle. Why do we care? Simplicity.
More Lambda Calculus and Intro to Type Systems
 More Lambda Calculus and Intro to Type Systems #1 One Slide Summary The lambda calculus is a model of computation or a programming language that is as expressive as a Turing machine. The lambda calculus
More Lambda Calculus and Intro to Type Systems #1 One Slide Summary The lambda calculus is a model of computation or a programming language that is as expressive as a Turing machine. The lambda calculus
Assistant for Language Theory. SASyLF: An Educational Proof. Corporation. Microsoft. Key Shin. Workshop on Mechanizing Metatheory
 SASyLF: An Educational Proof Assistant for Language Theory Jonathan Aldrich Robert J. Simmons Key Shin School of Computer Science Carnegie Mellon University Microsoft Corporation Workshop on Mechanizing
SASyLF: An Educational Proof Assistant for Language Theory Jonathan Aldrich Robert J. Simmons Key Shin School of Computer Science Carnegie Mellon University Microsoft Corporation Workshop on Mechanizing
CSc 372. Comparative Programming Languages. 2 : Functional Programming. Department of Computer Science University of Arizona
 1/37 CSc 372 Comparative Programming Languages 2 : Functional Programming Department of Computer Science University of Arizona collberg@gmail.com Copyright c 2013 Christian Collberg 2/37 Programming Paradigms
1/37 CSc 372 Comparative Programming Languages 2 : Functional Programming Department of Computer Science University of Arizona collberg@gmail.com Copyright c 2013 Christian Collberg 2/37 Programming Paradigms
Reasoning About Programs Panagiotis Manolios
 Reasoning About Programs Panagiotis Manolios Northeastern University February 26, 2017 Version: 100 Copyright c 2017 by Panagiotis Manolios All rights reserved. We hereby grant permission for this publication
Reasoning About Programs Panagiotis Manolios Northeastern University February 26, 2017 Version: 100 Copyright c 2017 by Panagiotis Manolios All rights reserved. We hereby grant permission for this publication
Supplementary Notes on Recursive Types
 Supplementary Notes on Recursive Types 15-312: Foundations of Programming Languages Frank Pfenning Lecture 13 October 8, 2002 In the last two lectures we have seen two critical concepts of programming
Supplementary Notes on Recursive Types 15-312: Foundations of Programming Languages Frank Pfenning Lecture 13 October 8, 2002 In the last two lectures we have seen two critical concepts of programming
Z Notation. June 21, 2018
 Z Notation June 21, 2018 1 Definitions There are many different ways to introduce an object in a Z specification: declarations, abbreviations, axiomatic definitions, and free types. Keep in mind that the
Z Notation June 21, 2018 1 Definitions There are many different ways to introduce an object in a Z specification: declarations, abbreviations, axiomatic definitions, and free types. Keep in mind that the
HOL DEFINING HIGHER ORDER LOGIC LAST TIME ON HOL CONTENT. Slide 3. Slide 1. Slide 4. Slide 2 WHAT IS HIGHER ORDER LOGIC? 2 LAST TIME ON HOL 1
 LAST TIME ON HOL Proof rules for propositional and predicate logic Safe and unsafe rules NICTA Advanced Course Forward Proof Slide 1 Theorem Proving Principles, Techniques, Applications Slide 3 The Epsilon
LAST TIME ON HOL Proof rules for propositional and predicate logic Safe and unsafe rules NICTA Advanced Course Forward Proof Slide 1 Theorem Proving Principles, Techniques, Applications Slide 3 The Epsilon
Chapter 11 :: Functional Languages
 Chapter 11 :: Functional Languages Programming Language Pragmatics Michael L. Scott Copyright 2016 Elsevier 1 Chapter11_Functional_Languages_4e - Tue November 21, 2017 Historical Origins The imperative
Chapter 11 :: Functional Languages Programming Language Pragmatics Michael L. Scott Copyright 2016 Elsevier 1 Chapter11_Functional_Languages_4e - Tue November 21, 2017 Historical Origins The imperative
Fundamentals and lambda calculus. Deian Stefan (adopted from my & Edward Yang s CSE242 slides)
 Fundamentals and lambda calculus Deian Stefan (adopted from my & Edward Yang s CSE242 slides) Logistics Assignments: Programming assignment 1 is out Homework 1 will be released tomorrow night Podcasting:
Fundamentals and lambda calculus Deian Stefan (adopted from my & Edward Yang s CSE242 slides) Logistics Assignments: Programming assignment 1 is out Homework 1 will be released tomorrow night Podcasting:
Programming Language Pragmatics
 Chapter 10 :: Functional Languages Programming Language Pragmatics Michael L. Scott Historical Origins The imperative and functional models grew out of work undertaken Alan Turing, Alonzo Church, Stephen
Chapter 10 :: Functional Languages Programming Language Pragmatics Michael L. Scott Historical Origins The imperative and functional models grew out of work undertaken Alan Turing, Alonzo Church, Stephen
Last class. CS Principles of Programming Languages. Introduction. Outline
 Last class CS6848 - Principles of Programming Languages Principles of Programming Languages V. Krishna Nandivada IIT Madras Interpreters A Environment B Cells C Closures D Recursive environments E Interpreting
Last class CS6848 - Principles of Programming Languages Principles of Programming Languages V. Krishna Nandivada IIT Madras Interpreters A Environment B Cells C Closures D Recursive environments E Interpreting
Higher-Order Intensional Type Analysis. Stephanie Weirich Cornell University
 Higher-Order Intensional Type Analysis Stephanie Weirich Cornell University Reflection A style of programming that supports the run-time discovery of program information. What does this code do? How is
Higher-Order Intensional Type Analysis Stephanie Weirich Cornell University Reflection A style of programming that supports the run-time discovery of program information. What does this code do? How is
Pierce Ch. 3, 8, 11, 15. Type Systems
 Pierce Ch. 3, 8, 11, 15 Type Systems Goals Define the simple language of expressions A small subset of Lisp, with minor modifications Define the type system of this language Mathematical definition using
Pierce Ch. 3, 8, 11, 15 Type Systems Goals Define the simple language of expressions A small subset of Lisp, with minor modifications Define the type system of this language Mathematical definition using
The Substitution Model
 The Substitution Model Prof. Clarkson Fall 2017 Today s music: Substitute by The Who Review Previously in 3110: simple interpreter for expression language abstract syntax tree (AST) evaluation based on
The Substitution Model Prof. Clarkson Fall 2017 Today s music: Substitute by The Who Review Previously in 3110: simple interpreter for expression language abstract syntax tree (AST) evaluation based on
CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages
 CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages Type Systems, Names and Binding CMSC 330 - Spring 2013 1 Topics Covered Thus Far! Programming languages Ruby OCaml! Syntax specification Regular expressions
CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages Type Systems, Names and Binding CMSC 330 - Spring 2013 1 Topics Covered Thus Far! Programming languages Ruby OCaml! Syntax specification Regular expressions
Topic 3: Propositions as types
 Topic 3: Propositions as types May 18, 2014 Propositions as types We have seen that the main mathematical objects in a type theory are types. But remember that in conventional foundations, as based on
Topic 3: Propositions as types May 18, 2014 Propositions as types We have seen that the main mathematical objects in a type theory are types. But remember that in conventional foundations, as based on
Functional Programming. Big Picture. Design of Programming Languages
 Functional Programming Big Picture What we ve learned so far: Imperative Programming Languages Variables, binding, scoping, reference environment, etc What s next: Functional Programming Languages Semantics
Functional Programming Big Picture What we ve learned so far: Imperative Programming Languages Variables, binding, scoping, reference environment, etc What s next: Functional Programming Languages Semantics
A Type System for Functional Traversal-Based Aspects
 A Type System for Functional Traversal-Based Aspects Bryan Chadwick College of Computer & Information Science Northeastern University, 360 Huntington Avenue Boston, Massachusetts 02115 USA chadwick@ccs.neu.edu
A Type System for Functional Traversal-Based Aspects Bryan Chadwick College of Computer & Information Science Northeastern University, 360 Huntington Avenue Boston, Massachusetts 02115 USA chadwick@ccs.neu.edu
Lecture slides & distribution files:
 Type Theory Lecture slides & distribution files: http://www.cs.rhul.ac.uk/home/zhaohui/ttlectures.html Zhaohui Luo Department of Computer Science Royal Holloway, University of London April 2011 2 Type
Type Theory Lecture slides & distribution files: http://www.cs.rhul.ac.uk/home/zhaohui/ttlectures.html Zhaohui Luo Department of Computer Science Royal Holloway, University of London April 2011 2 Type
CS4215 Programming Language Implementation. Martin Henz
 CS4215 Programming Language Implementation Martin Henz Thursday 26 January, 2012 2 Chapter 4 The Language simpl In this chapter, we are exting the language epl in order to provide a more powerful programming
CS4215 Programming Language Implementation Martin Henz Thursday 26 January, 2012 2 Chapter 4 The Language simpl In this chapter, we are exting the language epl in order to provide a more powerful programming
Meeting14:Denotations
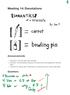 Meeting14:Denotations Announcements Homework 3 due next week Friday at 6:00pm Reminder: 5-minute feedback discussion with Sean is part of the assignment ("interview light") Talk (with me, with the class
Meeting14:Denotations Announcements Homework 3 due next week Friday at 6:00pm Reminder: 5-minute feedback discussion with Sean is part of the assignment ("interview light") Talk (with me, with the class
CSCI-GA Scripting Languages
 CSCI-GA.3033.003 Scripting Languages 12/02/2013 OCaml 1 Acknowledgement The material on these slides is based on notes provided by Dexter Kozen. 2 About OCaml A functional programming language All computation
CSCI-GA.3033.003 Scripting Languages 12/02/2013 OCaml 1 Acknowledgement The material on these slides is based on notes provided by Dexter Kozen. 2 About OCaml A functional programming language All computation
The Essence of Reynolds
 The Essence of Reynolds 3. State and Abstraction Uday S. Reddy 1 1 University of Birmingham POPL, 2014 John C. Reynolds, 1935-2013 Emmy Noether, 1882-1935 According to Mac Lane, she emphasized the importance
The Essence of Reynolds 3. State and Abstraction Uday S. Reddy 1 1 University of Birmingham POPL, 2014 John C. Reynolds, 1935-2013 Emmy Noether, 1882-1935 According to Mac Lane, she emphasized the importance
Paradigms of computer programming
 Paradigms of computer programming Louv1.1x and Louv1.2x form a two-course sequence Together they teach programming as a unified discipline that covers all programming languages Second-year university level:
Paradigms of computer programming Louv1.1x and Louv1.2x form a two-course sequence Together they teach programming as a unified discipline that covers all programming languages Second-year university level:
λ calculus is inconsistent
 Content Rough timeline COMP 4161 NICTA Advanced Course Advanced Topics in Software Verification Gerwin Klein, June Andronick, Toby Murray λ Intro & motivation, getting started [1] Foundations & Principles
Content Rough timeline COMP 4161 NICTA Advanced Course Advanced Topics in Software Verification Gerwin Klein, June Andronick, Toby Murray λ Intro & motivation, getting started [1] Foundations & Principles
Lecture 5 - Axiomatic semantics
 Program Verification March 2014 Lecture 5 - Axiomatic semantics Lecturer: Noam Rinetzky Scribes by: Nir Hemed 1.1 Axiomatic semantics The development of the theory is contributed to Robert Floyd, C.A.R
Program Verification March 2014 Lecture 5 - Axiomatic semantics Lecturer: Noam Rinetzky Scribes by: Nir Hemed 1.1 Axiomatic semantics The development of the theory is contributed to Robert Floyd, C.A.R
7. Introduction to Denotational Semantics. Oscar Nierstrasz
 7. Introduction to Denotational Semantics Oscar Nierstrasz Roadmap > Syntax and Semantics > Semantics of Expressions > Semantics of Assignment > Other Issues References > D. A. Schmidt, Denotational Semantics,
7. Introduction to Denotational Semantics Oscar Nierstrasz Roadmap > Syntax and Semantics > Semantics of Expressions > Semantics of Assignment > Other Issues References > D. A. Schmidt, Denotational Semantics,
