INTELLIGENCE PLUS CHARACTER - THAT IS THE GOAL OF TRUE EDUCATION UNIT-I
|
|
|
- Steven Barrett
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 UNIT-I 1. List and explain the functional units of a computer with a neat diagram 2. Explain the computer levels of programming languages 3. a) Explain about instruction formats b) Evaluate the arithmetic statement X= A+ (B*C) +D using zero, one, two, three address instructions 4. Explain basic computer organization with a neat diagram 5. Explain different types of primary memory(ram & ROM) 6. Draw the internal linear and 2-D configuration of 8 X 2 ROM chip. Explain 7. Explain I/O subsystem organization and interfacing 8. a) Explain types of assembly language instructions b) Explain various addressing modes 9. Describe a simple computer architecture 10. Describe a simple instruction set architecture INTELLIGENCE PLUS CHARACTER - THAT IS THE GOAL OF TRUE EDUCATION
2 UNIT-II 1. (a) Explain interrupt cycle with flow chart. (b) Describe general branch and call/return instructions 2. (a) Draw and explain about the instruction cycle state diagram. (b) Describe various arithmetic and logical instruction set operations 3. (a) Explain data transfer and manipulation instructions. (b) A relative mode branch type of instruction is stored in memory at an address equivalent to decimal 750. The branch is made to an address equivalent to decimal 500. (i) What should be the value of the relative address field of the instruction (in decimal)? (ii) Determine the relative address value in binary using 12 bits. (iii) Determine the binary value in PC after the fetch phase and calculate the binary value of 500. Then show that the binary value in PC plus the relative address calculated in part (ii) is equal to the binary value of (a) Explain the different types of addressing modes with examples. (b) An instruction is stored at location 300 with its address field at locations 301. The address field has the value 400. A processor register R1 contains the number 200. Evaluate the effective address if the addressing mode of the instruction is: (i) Immediate. (ii) Direct. (iii) Register indirect. (iv) Index with R1 as the index register. 5. Draw the flowchart for Booth s algorithm for multiplication of signed 2 s complement numbers and explain with an example. 6. Convert the following numerical expression into reverse polish notation and show the stack operations for evaluating the numerical result: (3+4)*(10*(2+6) +8). 7. What is an addressing mode? A two word instruction is stored in memory at an address designated by symbol. The address field of the instruction (Stored at ) is designated by the symbol. The operand used during the execution of the instruction is stored at an address symbolized by Z. An index register contains the value. State how Z is calculated from the 8. (a) List the sequence of micro operations needed to execute the following instructions: (1) LDA (2) BSA (3) ISZ (4) BUN (b) What is an interrupt? Explain about interrupt cycle in detail. 9. List the essential steps required in performing division operation on floating point numbers. Explain them in detail 10. (a) Write short notes on array multiplier. (b) Explain the operation of restoring division with flow chart. 11. (a) Explain addition and subtraction algorithm for floating-point data. (b) Explain division algorithm for floating-point data. 12. (a) Explain the Booth s algorithm with flow chart. (b) Show the contents of register A, E, Q and SC during the process of multiplication of two signed binary numbers (multiplicand) and (multiplier). 13. (a) Explain the hardware implementation of unsigned binary multiplication. (b) Perform multiplication of unsigned numbers 1101 and (a) Explain the hardware for signed 2 s complement addition and subtraction. (b) Perform the following in 2 s complement form: (i) (+28)10 + (+15)10 (ii) (+28)10 + (-15)10 (iii) (-28)10 + (+15)10(iv) (-28)10 + (-15) (a) Explain the floating point addition and subtraction with flow chart. (b) Show how the following floating point operations are performed (where significants are truncated to 4 decimal digits) (i) ( X 102) X ( X 101) (ii) ( X 103) ( X 105) 16. (a) Explain the operation of BCD adder with the help of diagram. (b)explain mantissa overflow, mantissa underflow, exponent overflow and exponent underflow. "Striving for success without hard work is like trying to harvest where you haven t planted."
3 UNIT-III 1. (a) What are register transfer languages? (b) Draw and explain the bus structure for the data transfer between various registers and the common bus. 2. (a) Draw and explain how to construct a bus line using three state buffers. (b) How to multiply & divide a number by 2 using shift operations, give an example 3. (a) Explain about arithmetical, logical and shift micro operations. (b) Show that the statement A 4. (a) Design a 4 bit combinational circuit decrementer using four full-adder circuits. (b) The following transfer statements specify a memory. Explain the memory operation in each case: (i) R2 (ii) M[AR] (iii) R5 5. (a) Explain the operation of 4-bit adder-subtractor with example. (b) Give hardware implementations to perform logic and shift operations. 6. (a) With a neat sketch explain the 4 bit combinational circuit shifter. (b) Starting from an initial value of R = , determine the sequence of binary values in R after logical shift left, followed by a circular shift-right, followed by a logical shift right and a circular shift-left. 7. A digital computer has a common bus system for 16 registers of 32 bits each. The bus is constructed with multiplexers. (i) How many selection inputs are there in each multiplexer? (ii) What size of multiplexers are needed? (iii) How many multiplexers are there in the bus? 8. Draw and explain the microprogram sequencer for a control memory 9. Write short notes on the following: (a) Hardwired control. (b) Microprogrammed control 10. Discuss in detail the design of control unit with block diagram. 11. (a) Explain with the help of diagram the selection of address for control memory. (b) Discuss in brief about the applications of microprogramming 12. Explain mapping techniques to convert an operation to a micro routine address in control memory. "You may never know what results come of your action, but if you do nothing there will be no result."
4 UNIT-IV 1. a) Discuss the memory hierarchy in a computer system with regard to speed, size and cost. b) What is the need for cache memory? Explain direct mapped cache organization. 2. a) Explain memory hierarchy in detail. b) Explain the concept of content addressable memory. How the time for read/write operation is minimized in associative memory? 3. Explain the concept of virtual address and physical address. 4. a) What is cache memory? Explain its operation. b) Brief out the hardware organization of associate memory 5. a) With a block diagram explain about associative memory and also explain the match logic, read operation and write operation. b) Define RAM and how many RAM chips are needed to provide a memory capacity of 2048 bytes. 6. The access time of a cache memory is 100 ns and that of main memory is 1000 ns. It is estimated that 80% of the memory requests are for read and the remaining 20% are for write. The hit ratio for read accesses only is 0.9. A write-through procedure is used. (a) What is the average access time of the system considering only memory read cycles? (b) What is the average access time of the system for both read and write requests? 7. a) The access time of the main memory is 700 ns and the access time of the cache memory is 100 ns. The hit ratio for the read access is only 0.8. What is the average access time of the system considering only memory read cycles? b) Explain memory address map. 8. To construct a memory unit with capacity of 4096 bytes, only 128 x 8 RAM chips are available, how many of them are used to get the memory capacity. If so how many address lines are needed to access the memory and how many lines are needed to access each chip 9. a) Discuss the various I/O interfacing techniques. b) Discuss the programmed I/O. 10. With a neat diagram, describe DMA transfer in a computer system 11. What is the advantage of priority interrupt over non priority interrupt? Explain the use of mask register. 12. a) What is DMA? Explain the transfer of data from memory to I/O device with the help of a flow chart. b) Explain the limitations in programmed I/O and interrupt driven I/O. 13. What is an I/O interface? Describe methods to implement the same with two examples 14. a) Explain the methods of priority resolution for interrupts. b) Explain handshaking in asynchronous data transfer. 15. Explain the interrupt priority system using daisy chain. 16. a) Explain in detail the strobe control method of asynchronous data transfer. b) Draw block diagram of typical daisy-chain priority interrupt scheme and explain its operation. "Learn from the mistakes of others... you can't live long enough to make them all yourselves!!"
5 UNIT-V 1. (a) What is pipeline? Explain. (b) Explain arithmetic pipeline. 2. A nonpipeline system takes 50 ns to process a task. The same task can be processed in a 6 segment pipeline with a clock cycle of 10 ns. Determine the speed up ratio of the pipeline for 100 tasks. What is the maximum speed up that can be achieved 3. Explain the following with neat sketches: (a) Parallel processing. (b) Arithmetic pipeline. 4. (a) What is pipeline? Explain space-time diagram for pipeline. (b) Explain pipeline for floating point addition and subtraction. 5. Classify the pipeline processors and explain them in detail 6. What is the Flynn s classification of the computer system? Explain in detail. 7. (a) Explain serial arbitration logic. (b) Give short notes on the system bus. 8. (a) Give a short note on SISD and SIMD multiprocessing. (b) List out the types of multiprocessing. Explain. 9. What are the various physical forms available for establishing an interconnection network? Explain 10. (a) Explain the hardware organization for four stage instruction pipeline. (b) What is a data hazard? 11. Discuss in detail about inter processor communication and synchronization 12. (a) Compare communication costs in multicomputer and multiprocessor systems. (b) Explain about Amdahl s law. 13. (a) Explain the functioning of omega switching network with a neat sketch. (b) In 8 x 8 omega switching network how many stages are there and in each stage how many switches are there. 14. (a) Explain the process of arithmetic pipelining with an example. (b) Explain the terms data dependencies, hardware interlock and operand forwarding techniques 15. (a) What do you mean by bus arbitration? (b) Explain the serial arbitration technique with the help of a neat diagram. State 16. advantages and disadvantages 17. (a) Explain with the help of a neat sketch how a time shared bus inter connection system for multiple processors provide a common communication path connecting all of the functional units. (b) Draw the sketch and explain the multiprocessor with unidirectional buses. 18. (a) Explain the inter processor communication using message passing. (b) How does message transfer system function? 19. (a) Explain the Interprocessor communication. (b) Write in detail about Interprocessor arbitration. 20. (a) Differentiate tightly coupled and loosely coupled multiprocessors according to hardware. (b) Explain the functioning of omega switching network with a neat sketch. "Books are as useful to a stupid person as a mirror is useful to a blind person."
PART A (22 Marks) 2. a) Briefly write about r's complement and (r-1)'s complement. [8] b) Explain any two ways of adding decimal numbers.
![PART A (22 Marks) 2. a) Briefly write about r's complement and (r-1)'s complement. [8] b) Explain any two ways of adding decimal numbers. PART A (22 Marks) 2. a) Briefly write about r's complement and (r-1)'s complement. [8] b) Explain any two ways of adding decimal numbers.](/thumbs/96/128058841.jpg) Set No. 1 IV B.Tech I Semester Supplementary Examinations, March - 2017 COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE & ORGANIZATION (Common to Electronics & Communication Engineering and Electronics & Time: 3 hours Max. Marks:
Set No. 1 IV B.Tech I Semester Supplementary Examinations, March - 2017 COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE & ORGANIZATION (Common to Electronics & Communication Engineering and Electronics & Time: 3 hours Max. Marks:
Course Description: This course includes concepts of instruction set architecture,
 Computer Architecture Course Title: Computer Architecture Full Marks: 60+ 20+20 Course No: CSC208 Pass Marks: 24+8+8 Nature of the Course: Theory + Lab Credit Hrs: 3 Course Description: This course includes
Computer Architecture Course Title: Computer Architecture Full Marks: 60+ 20+20 Course No: CSC208 Pass Marks: 24+8+8 Nature of the Course: Theory + Lab Credit Hrs: 3 Course Description: This course includes
JNTUWORLD. 1. Discuss in detail inter processor arbitration logics and procedures with necessary diagrams? [15]
![JNTUWORLD. 1. Discuss in detail inter processor arbitration logics and procedures with necessary diagrams? [15] JNTUWORLD. 1. Discuss in detail inter processor arbitration logics and procedures with necessary diagrams? [15]](/thumbs/96/128058746.jpg) Code No: 09A50402 R09 Set No. 2 1. Discuss in detail inter processor arbitration logics and procedures with necessary diagrams? [15] 2. (a) Discuss asynchronous serial transfer concept? (b) Explain in
Code No: 09A50402 R09 Set No. 2 1. Discuss in detail inter processor arbitration logics and procedures with necessary diagrams? [15] 2. (a) Discuss asynchronous serial transfer concept? (b) Explain in
2 MARKS Q&A 1 KNREDDY UNIT-I
 2 MARKS Q&A 1 KNREDDY UNIT-I 1. What is bus; list the different types of buses with its function. A group of lines that serves as a connecting path for several devices is called a bus; TYPES: ADDRESS BUS,
2 MARKS Q&A 1 KNREDDY UNIT-I 1. What is bus; list the different types of buses with its function. A group of lines that serves as a connecting path for several devices is called a bus; TYPES: ADDRESS BUS,
CHETTINAD COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY COMPUTER ARCHITECURE- III YEAR EEE-6 TH SEMESTER 16 MARKS QUESTION BANK UNIT-1
 CHETTINAD COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY COMPUTER ARCHITECURE- III YEAR EEE-6 TH SEMESTER 16 MARKS QUESTION BANK UNIT-1 Data representation: (CHAPTER-3) 1. Discuss in brief about Data types, (8marks)
CHETTINAD COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY COMPUTER ARCHITECURE- III YEAR EEE-6 TH SEMESTER 16 MARKS QUESTION BANK UNIT-1 Data representation: (CHAPTER-3) 1. Discuss in brief about Data types, (8marks)
MaanavaN.Com CS1202 COMPUTER ARCHITECHTURE
 DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK SUB CODE / SUBJECT: CS1202/COMPUTER ARCHITECHTURE YEAR / SEM: II / III UNIT I BASIC STRUCTURE OF COMPUTER 1. What is meant by the stored program
DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK SUB CODE / SUBJECT: CS1202/COMPUTER ARCHITECHTURE YEAR / SEM: II / III UNIT I BASIC STRUCTURE OF COMPUTER 1. What is meant by the stored program
COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND ARCHITECTURE
 Page 1 1. Which register store the address of next instruction to be executed? A) PC B) AC C) SP D) NONE 2. How many bits are required to address the 128 words of memory? A) 7 B) 8 C) 9 D) NONE 3. is the
Page 1 1. Which register store the address of next instruction to be executed? A) PC B) AC C) SP D) NONE 2. How many bits are required to address the 128 words of memory? A) 7 B) 8 C) 9 D) NONE 3. is the
Computer Organisation CS303
 Computer Organisation CS303 Module Period Assignments 1 Day 1 to Day 6 1. Write a program to evaluate the arithmetic statement: X=(A-B + C * (D * E-F))/G + H*K a. Using a general register computer with
Computer Organisation CS303 Module Period Assignments 1 Day 1 to Day 6 1. Write a program to evaluate the arithmetic statement: X=(A-B + C * (D * E-F))/G + H*K a. Using a general register computer with
UNIT I BASIC STRUCTURE OF COMPUTERS Part A( 2Marks) 1. What is meant by the stored program concept? 2. What are the basic functional units of a
 UNIT I BASIC STRUCTURE OF COMPUTERS Part A( 2Marks) 1. What is meant by the stored program concept? 2. What are the basic functional units of a computer? 3. What is the use of buffer register? 4. Define
UNIT I BASIC STRUCTURE OF COMPUTERS Part A( 2Marks) 1. What is meant by the stored program concept? 2. What are the basic functional units of a computer? 3. What is the use of buffer register? 4. Define
SYLLABUS. osmania university CHAPTER - 1 : REGISTER TRANSFER LANGUAGE AND MICRO OPERATION CHAPTER - 2 : BASIC COMPUTER
 Contents i SYLLABUS osmania university UNIT - I CHAPTER - 1 : REGISTER TRANSFER LANGUAGE AND MICRO OPERATION Difference between Computer Organization and Architecture, RTL Notation, Common Bus System using
Contents i SYLLABUS osmania university UNIT - I CHAPTER - 1 : REGISTER TRANSFER LANGUAGE AND MICRO OPERATION Difference between Computer Organization and Architecture, RTL Notation, Common Bus System using
CS6303-COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE UNIT I OVERVIEW AND INSTRUCTIONS PART A
 CS6303-COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE UNIT I OVERVIEW AND INSTRUCTIONS 1. Define Computer Architecture 2. Define Computer H/W 3. What are the functions of control unit? 4. 4.Define Interrupt 5. What are the uses
CS6303-COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE UNIT I OVERVIEW AND INSTRUCTIONS 1. Define Computer Architecture 2. Define Computer H/W 3. What are the functions of control unit? 4. 4.Define Interrupt 5. What are the uses
SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE) UNIT-I
 SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road 517583 QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE) Subject with Code : CO (16MC802) Year & Sem: I-MCA & I-Sem Course & Branch: MCA Regulation:
SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road 517583 QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE) Subject with Code : CO (16MC802) Year & Sem: I-MCA & I-Sem Course & Branch: MCA Regulation:
SRM ARTS AND SCIENCE COLLEGE SRM NAGAR, KATTANKULATHUR
 SRM ARTS AND SCIENCE COLLEGE SRM NAGAR, KATTANKULATHUR 603203 DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE & APPLICATIONS LESSON PLAN (207-208) Course / Branch : M.Sc CST Total Hours : 50 Subject Name : Computer Architecture
SRM ARTS AND SCIENCE COLLEGE SRM NAGAR, KATTANKULATHUR 603203 DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE & APPLICATIONS LESSON PLAN (207-208) Course / Branch : M.Sc CST Total Hours : 50 Subject Name : Computer Architecture
DC57 COMPUTER ORGANIZATION JUNE 2013
 Q2 (a) How do various factors like Hardware design, Instruction set, Compiler related to the performance of a computer? The most important measure of a computer is how quickly it can execute programs.
Q2 (a) How do various factors like Hardware design, Instruction set, Compiler related to the performance of a computer? The most important measure of a computer is how quickly it can execute programs.
UNIT I DATA REPRESENTATION, MICRO-OPERATIONS, ORGANIZATION AND DESIGN
 UNIT I DATA REPRESENTATION, MICRO-OPERATIONS, ORGANIZATION AND DESIGN Data representation: Data types, complements, fixed point representation, floating-point representation, other binary codes, error
UNIT I DATA REPRESENTATION, MICRO-OPERATIONS, ORGANIZATION AND DESIGN Data representation: Data types, complements, fixed point representation, floating-point representation, other binary codes, error
QUESTION BANK UNIT-I. 4. With a neat diagram explain Von Neumann computer architecture
 UNIT-I 1. Write the basic functional units of computer? (Nov/Dec 2014) 2. What is a bus? What are the different buses in a CPU? 3. Define multiprogramming? 4.List the basic functional units of a computer?
UNIT-I 1. Write the basic functional units of computer? (Nov/Dec 2014) 2. What is a bus? What are the different buses in a CPU? 3. Define multiprogramming? 4.List the basic functional units of a computer?
COA. Prepared By: Dhaval R. Patel Page 1. Q.1 Define MBR.
 Q.1 Define MBR. MBR( Memory buffer register) A Memory Buffer Register (MBR) is the register in a computers processor that stores the data being transferred to and from the devices It allowing the processor
Q.1 Define MBR. MBR( Memory buffer register) A Memory Buffer Register (MBR) is the register in a computers processor that stores the data being transferred to and from the devices It allowing the processor
2. (a) Compare the characteristics of a floppy disk and a hard disk. (b) Discuss in detail memory interleaving. [8+7]
![2. (a) Compare the characteristics of a floppy disk and a hard disk. (b) Discuss in detail memory interleaving. [8+7] 2. (a) Compare the characteristics of a floppy disk and a hard disk. (b) Discuss in detail memory interleaving. [8+7]](/thumbs/96/127320205.jpg) Code No: A109211202 R09 Set No. 2 1. (a) Explain the purpose of the following registers: i. IR ii. PC iii. MDR iv. MAR. (b) Explain with an example the steps in subtraction of two n-digit unsigned numbers.
Code No: A109211202 R09 Set No. 2 1. (a) Explain the purpose of the following registers: i. IR ii. PC iii. MDR iv. MAR. (b) Explain with an example the steps in subtraction of two n-digit unsigned numbers.
Computer organization and architecture UNIT-I 2 MARKS
 Computer organization and architecture UNIT-I 1. What are the functional units? 2. what is meant by input unit? 3. What is meant by memory unit? 4. What are the operations in ALU? 5. What is meant by output
Computer organization and architecture UNIT-I 1. What are the functional units? 2. what is meant by input unit? 3. What is meant by memory unit? 4. What are the operations in ALU? 5. What is meant by output
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK
 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK SUBJECT : CS6303 / COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE SEM / YEAR : VI / III year B.E. Unit I OVERVIEW AND INSTRUCTIONS Part A Q.No Questions BT Level
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK SUBJECT : CS6303 / COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE SEM / YEAR : VI / III year B.E. Unit I OVERVIEW AND INSTRUCTIONS Part A Q.No Questions BT Level
Honorary Professor Supercomputer Education and Research Centre Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore
 COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND ARCHITECTURE V. Rajaraman Honorary Professor Supercomputer Education and Research Centre Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore T. Radhakrishnan Professor of Computer Science
COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND ARCHITECTURE V. Rajaraman Honorary Professor Supercomputer Education and Research Centre Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore T. Radhakrishnan Professor of Computer Science
CS2253 COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND ARCHITECTURE 1 KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY
 CS2253 COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND ARCHITECTURE 1 KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY QUESTION BANK Sub. Code & Name: CS2253 Computer organization and architecture Year/Sem
CS2253 COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND ARCHITECTURE 1 KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY QUESTION BANK Sub. Code & Name: CS2253 Computer organization and architecture Year/Sem
Pipeline and Vector Processing 1. Parallel Processing SISD SIMD MISD & MIMD
 Pipeline and Vector Processing 1. Parallel Processing Parallel processing is a term used to denote a large class of techniques that are used to provide simultaneous data-processing tasks for the purpose
Pipeline and Vector Processing 1. Parallel Processing Parallel processing is a term used to denote a large class of techniques that are used to provide simultaneous data-processing tasks for the purpose
DHANALAKSHMI SRINIVASAN INSTITUTE OF RESEARCH AND TECHNOLOGY. Department of Computer science and engineering
 DHANALAKSHMI SRINIVASAN INSTITUTE OF RESEARCH AND TECHNOLOGY Department of Computer science and engineering Year :II year CS6303 COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE Question Bank UNIT-1OVERVIEW AND INSTRUCTIONS PART-B
DHANALAKSHMI SRINIVASAN INSTITUTE OF RESEARCH AND TECHNOLOGY Department of Computer science and engineering Year :II year CS6303 COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE Question Bank UNIT-1OVERVIEW AND INSTRUCTIONS PART-B
PIPELINE AND VECTOR PROCESSING
 PIPELINE AND VECTOR PROCESSING PIPELINING: Pipelining is a technique of decomposing a sequential process into sub operations, with each sub process being executed in a special dedicated segment that operates
PIPELINE AND VECTOR PROCESSING PIPELINING: Pipelining is a technique of decomposing a sequential process into sub operations, with each sub process being executed in a special dedicated segment that operates
Instruction Register. Instruction Decoder. Control Unit (Combinational Circuit) Control Signals (These signals go to register) The bus and the ALU
 Hardwired and Microprogrammed Control For each instruction, the control unit causes the CPU to execute a sequence of steps correctly. In reality, there must be control signals to assert lines on various
Hardwired and Microprogrammed Control For each instruction, the control unit causes the CPU to execute a sequence of steps correctly. In reality, there must be control signals to assert lines on various
SAE5C Computer Organization and Architecture. Unit : I - V
 SAE5C Computer Organization and Architecture Unit : I - V UNIT-I Evolution of Pentium and Power PC Evolution of Computer Components functions Interconnection Bus Basics of PCI Memory:Characteristics,Hierarchy
SAE5C Computer Organization and Architecture Unit : I - V UNIT-I Evolution of Pentium and Power PC Evolution of Computer Components functions Interconnection Bus Basics of PCI Memory:Characteristics,Hierarchy
Darshan Institute of Engineering & Technology for Diploma Studies Unit - 1
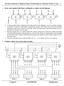 Darshan Institute of Engineering & Technology for Diploma Studies Unit - 1 1. Draw and explain 4 bit binary arithmetic or adder circuit diagram. A binary parallel adder is digital function that produces
Darshan Institute of Engineering & Technology for Diploma Studies Unit - 1 1. Draw and explain 4 bit binary arithmetic or adder circuit diagram. A binary parallel adder is digital function that produces
csitnepal Unit 3 Basic Computer Organization and Design
 Unit 3 Basic Computer Organization and Design Introduction We introduce here a basic computer whose operation can be specified by the resister transfer statements. Internal organization of the computer
Unit 3 Basic Computer Organization and Design Introduction We introduce here a basic computer whose operation can be specified by the resister transfer statements. Internal organization of the computer
TYPICAL QUESTIONS & ANSWERS
 TYPICAL QUESTIONS & ANSWERS PART-I Each Question carries 2 marks. OBJECTIVE TYPE QUESTIONS Choose the correct or best alternative in the following: Q.1 In Reverse Polish notation, expression A*B+C*D is
TYPICAL QUESTIONS & ANSWERS PART-I Each Question carries 2 marks. OBJECTIVE TYPE QUESTIONS Choose the correct or best alternative in the following: Q.1 In Reverse Polish notation, expression A*B+C*D is
1. Draw general diagram of computer showing different logical components (3)
 Tutorial 1 1. Draw general diagram of computer showing different logical components (3) 2. List at least three input devices (1.5) 3. List any three output devices (1.5) 4. Fill the blank cells of the
Tutorial 1 1. Draw general diagram of computer showing different logical components (3) 2. List at least three input devices (1.5) 3. List any three output devices (1.5) 4. Fill the blank cells of the
COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND ARCHITECTURE
 COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND ARCHITECTURE For COMPUTER SCIENCE COMPUTER ORGANIZATION. SYLLABUS AND ARCHITECTURE Machine instructions and addressing modes, ALU and data-path, CPU control design, Memory interface,
COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND ARCHITECTURE For COMPUTER SCIENCE COMPUTER ORGANIZATION. SYLLABUS AND ARCHITECTURE Machine instructions and addressing modes, ALU and data-path, CPU control design, Memory interface,
CHAPTER 4 MARIE: An Introduction to a Simple Computer
 CHAPTER 4 MARIE: An Introduction to a Simple Computer 4.1 Introduction 177 4.2 CPU Basics and Organization 177 4.2.1 The Registers 178 4.2.2 The ALU 179 4.2.3 The Control Unit 179 4.3 The Bus 179 4.4 Clocks
CHAPTER 4 MARIE: An Introduction to a Simple Computer 4.1 Introduction 177 4.2 CPU Basics and Organization 177 4.2.1 The Registers 178 4.2.2 The ALU 179 4.2.3 The Control Unit 179 4.3 The Bus 179 4.4 Clocks
QUESTION BANK CS2252 MICROPROCESSOR AND MICROCONTROLLERS
 FATIMA MICHAEL COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY Senkottai Village, Madurai Sivagangai Main Road, Madurai -625 020 QUESTION BANK CS2252 MICROPROCESSOR AND MICROCONTROLLERS UNIT 1 - THE 8085 AND 8086
FATIMA MICHAEL COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY Senkottai Village, Madurai Sivagangai Main Road, Madurai -625 020 QUESTION BANK CS2252 MICROPROCESSOR AND MICROCONTROLLERS UNIT 1 - THE 8085 AND 8086
COMPUTER ORGANIZATION
 COMPUTER ORGANIZATION INDEX UNIT-II PPT SLIDES Srl. No. Module as per Session planner Lecture No. PPT Slide No. 1. Register Transfer language 2. Register Transfer Bus and memory transfers 3. Arithmetic
COMPUTER ORGANIZATION INDEX UNIT-II PPT SLIDES Srl. No. Module as per Session planner Lecture No. PPT Slide No. 1. Register Transfer language 2. Register Transfer Bus and memory transfers 3. Arithmetic
Computer Organization
 A Text Book of Computer Organization and Architecture Prof. JATINDER SINGH Director, GGI, Dhaliwal Er. AMARDEEP SINGH M.Tech (IT) AP&HOD, Deptt.of CSE, SVIET, Banur Er. GURJEET SINGH M.Tech (CSE) Head,
A Text Book of Computer Organization and Architecture Prof. JATINDER SINGH Director, GGI, Dhaliwal Er. AMARDEEP SINGH M.Tech (IT) AP&HOD, Deptt.of CSE, SVIET, Banur Er. GURJEET SINGH M.Tech (CSE) Head,
COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE AND ORGANIZATION Register Transfer and Micro-operations 1. Introduction A digital system is an interconnection of digital
 Register Transfer and Micro-operations 1. Introduction A digital system is an interconnection of digital hardware modules that accomplish a specific information-processing task. Digital systems vary in
Register Transfer and Micro-operations 1. Introduction A digital system is an interconnection of digital hardware modules that accomplish a specific information-processing task. Digital systems vary in
M. Sc (CS) (II Semester) Examination, Subject: Computer System Architecture Paper Code: M.Sc-CS-203. Time: Three Hours] [Maximum Marks: 60
![M. Sc (CS) (II Semester) Examination, Subject: Computer System Architecture Paper Code: M.Sc-CS-203. Time: Three Hours] [Maximum Marks: 60 M. Sc (CS) (II Semester) Examination, Subject: Computer System Architecture Paper Code: M.Sc-CS-203. Time: Three Hours] [Maximum Marks: 60](/thumbs/87/96339673.jpg) M. Sc (CS) (II Semester) Examination, 2012-13 Subject: Computer System Architecture Paper Code: M.Sc-CS-203 Time: Three Hours] [Maximum Marks: 60 Note: Question Number 1 is compulsory. Answer any four
M. Sc (CS) (II Semester) Examination, 2012-13 Subject: Computer System Architecture Paper Code: M.Sc-CS-203 Time: Three Hours] [Maximum Marks: 60 Note: Question Number 1 is compulsory. Answer any four
PESIT Bangalore South Campus
 INTERNAL ASSESSMENT TEST III Date : 21/11/2017 Max Marks : 40 Subject & Code : Computer Organization (15CS34) Semester : III (A & B) Name of the faculty: Mrs. Sharmila Banu Time : 11.30 am 1.00 pm Answer
INTERNAL ASSESSMENT TEST III Date : 21/11/2017 Max Marks : 40 Subject & Code : Computer Organization (15CS34) Semester : III (A & B) Name of the faculty: Mrs. Sharmila Banu Time : 11.30 am 1.00 pm Answer
PREPARED BY: S.SAKTHI, AP/IT
 CHETTINAD COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF EIE CS6303 COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE (5 th semester)-regulation 2013 16 MARKS QUESTION BANK WITH ANSWER KEY UNIT I OVERVIEW & INSTRUCTIONS 1. Explain
CHETTINAD COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF EIE CS6303 COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE (5 th semester)-regulation 2013 16 MARKS QUESTION BANK WITH ANSWER KEY UNIT I OVERVIEW & INSTRUCTIONS 1. Explain
 EASWARI ENGINEERING COLLEGE DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION QUESTION BANK - V SEMESTER ECE EC2304 MICROPROCESSORS AND MICROCONTROLLERS UNIT I 1. When the 8086 processor is in minimum mode and
EASWARI ENGINEERING COLLEGE DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION QUESTION BANK - V SEMESTER ECE EC2304 MICROPROCESSORS AND MICROCONTROLLERS UNIT I 1. When the 8086 processor is in minimum mode and
s complement 1-bit Booth s 2-bit Booth s
 ECE/CS 552 : Introduction to Computer Architecture FINAL EXAM May 12th, 2002 NAME: This exam is to be done individually. Total 6 Questions, 100 points Show all your work to receive partial credit for incorrect
ECE/CS 552 : Introduction to Computer Architecture FINAL EXAM May 12th, 2002 NAME: This exam is to be done individually. Total 6 Questions, 100 points Show all your work to receive partial credit for incorrect
LOW-COST SIMD. Considerations For Selecting a DSP Processor Why Buy The ADSP-21161?
 LOW-COST SIMD Considerations For Selecting a DSP Processor Why Buy The ADSP-21161? The Analog Devices ADSP-21161 SIMD SHARC vs. Texas Instruments TMS320C6711 and TMS320C6712 Author : K. Srinivas Introduction
LOW-COST SIMD Considerations For Selecting a DSP Processor Why Buy The ADSP-21161? The Analog Devices ADSP-21161 SIMD SHARC vs. Texas Instruments TMS320C6711 and TMS320C6712 Author : K. Srinivas Introduction
1. Define Peripherals. Explain I/O Bus and Interface Modules. Peripherals: Input-output device attached to the computer are also called peripherals.
 1. Define Peripherals. Explain I/O Bus and Interface Modules. Peripherals: Input-output device attached to the computer are also called peripherals. A typical communication link between the processor and
1. Define Peripherals. Explain I/O Bus and Interface Modules. Peripherals: Input-output device attached to the computer are also called peripherals. A typical communication link between the processor and
-COMPUTER ARCillTECTURE. Time : Three hours. -Maximum Marks : 100. AU parts of a question (a, b, etc.) should be answered at one place.
 S'09 : 6 FN : CP 406 ( 1451) -COMPUTER ARCillTECTURE Time : Three hours -Maximum Marks : 100 A!Jswer FIVE questions, taking ANY TWO from Group A, _ANY TWO from Group B and ALL from. Group C. - AU parts
S'09 : 6 FN : CP 406 ( 1451) -COMPUTER ARCillTECTURE Time : Three hours -Maximum Marks : 100 A!Jswer FIVE questions, taking ANY TWO from Group A, _ANY TWO from Group B and ALL from. Group C. - AU parts
EC 6504 MICROPROCESSOR AND MICROCONTROLLER
 DEPARTMENTOFELECTRONICS&COMMUNICATIONENGINEERING EC 6504 MICROPROCESSOR AND MICROCONTROLLER UNIT I THE 8086 MICROPROCESSOR PARTA 1. What is microprocessor? What is the difference between a MP and CPU?
DEPARTMENTOFELECTRONICS&COMMUNICATIONENGINEERING EC 6504 MICROPROCESSOR AND MICROCONTROLLER UNIT I THE 8086 MICROPROCESSOR PARTA 1. What is microprocessor? What is the difference between a MP and CPU?
Chapter 4. Operations on Data
 Chapter 4 Operations on Data 1 OBJECTIVES After reading this chapter, the reader should be able to: List the three categories of operations performed on data. Perform unary and binary logic operations
Chapter 4 Operations on Data 1 OBJECTIVES After reading this chapter, the reader should be able to: List the three categories of operations performed on data. Perform unary and binary logic operations
UNIT - I: COMPUTER ARITHMETIC, REGISTER TRANSFER LANGUAGE & MICROOPERATIONS
 UNIT - I: COMPUTER ARITHMETIC, REGISTER TRANSFER LANGUAGE & MICROOPERATIONS (09 periods) Computer Arithmetic: Data Representation, Fixed Point Representation, Floating Point Representation, Addition and
UNIT - I: COMPUTER ARITHMETIC, REGISTER TRANSFER LANGUAGE & MICROOPERATIONS (09 periods) Computer Arithmetic: Data Representation, Fixed Point Representation, Floating Point Representation, Addition and
REGISTER TRANSFER LANGUAGE
 REGISTER TRANSFER LANGUAGE The operations executed on the data stored in the registers are called micro operations. Classifications of micro operations Register transfer micro operations Arithmetic micro
REGISTER TRANSFER LANGUAGE The operations executed on the data stored in the registers are called micro operations. Classifications of micro operations Register transfer micro operations Arithmetic micro
VETRI VINAYAHA COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY THOTTIAM DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING B.
 VETRI VINAYAHA COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY THOTTIAM 621215 DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING B.E SIXTH SEMESTER CS6303- COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE (Regulation 2013) UNIT I OVERVIEW&INSTRUCTIONS
VETRI VINAYAHA COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY THOTTIAM 621215 DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING B.E SIXTH SEMESTER CS6303- COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE (Regulation 2013) UNIT I OVERVIEW&INSTRUCTIONS
Blog -
 . Instruction Codes Every different processor type has its own design (different registers, buses, microoperations, machine instructions, etc) Modern processor is a very complex device It contains Many
. Instruction Codes Every different processor type has its own design (different registers, buses, microoperations, machine instructions, etc) Modern processor is a very complex device It contains Many
Total No. of Questions :09] [Total No. of Pages : 02. II/IV B.Tech. DEGREE EXAMINATIONS, NOV/DEC Second Semester CSE/IT DBMS
![Total No. of Questions :09] [Total No. of Pages : 02. II/IV B.Tech. DEGREE EXAMINATIONS, NOV/DEC Second Semester CSE/IT DBMS Total No. of Questions :09] [Total No. of Pages : 02. II/IV B.Tech. DEGREE EXAMINATIONS, NOV/DEC Second Semester CSE/IT DBMS](/thumbs/95/125615636.jpg) CSE/IT 224 (CR) Total No. of Questions :09] [Total No. of Pages : 02 Time: Three Hours II/IV B.Tech. DEGREE EXAMINATIONS, NOV/DEC- 2015 Second Semester CSE/IT DBMS Answer Question NO.1 Compulsory Answer
CSE/IT 224 (CR) Total No. of Questions :09] [Total No. of Pages : 02 Time: Three Hours II/IV B.Tech. DEGREE EXAMINATIONS, NOV/DEC- 2015 Second Semester CSE/IT DBMS Answer Question NO.1 Compulsory Answer
S.R.M. INSTITUTE OF SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY SCHOOL OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING
 S.R.M. INSTITUTE OF SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY SCHOOL OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK Subject Code : EC307 Subject Name : Microprocessor and Interfacing Year & Sem : III Year, V Sem
S.R.M. INSTITUTE OF SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY SCHOOL OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK Subject Code : EC307 Subject Name : Microprocessor and Interfacing Year & Sem : III Year, V Sem
UNIT-III REGISTER TRANSFER LANGUAGE AND DESIGN OF CONTROL UNIT
 UNIT-III 1 KNREDDY UNIT-III REGISTER TRANSFER LANGUAGE AND DESIGN OF CONTROL UNIT Register Transfer: Register Transfer Language Register Transfer Bus and Memory Transfers Arithmetic Micro operations Logic
UNIT-III 1 KNREDDY UNIT-III REGISTER TRANSFER LANGUAGE AND DESIGN OF CONTROL UNIT Register Transfer: Register Transfer Language Register Transfer Bus and Memory Transfers Arithmetic Micro operations Logic
b) Write basic performance equation.
 1. a) What is use of buffers? Ans: The Buffer Register prevents the high speed processor from being locked to a slow I/O device during a sequence of data transfer or reduces speed mismatch between faster
1. a) What is use of buffers? Ans: The Buffer Register prevents the high speed processor from being locked to a slow I/O device during a sequence of data transfer or reduces speed mismatch between faster
Computer Architecture
 Computer Architecture Lecture 1: Digital logic circuits The digital computer is a digital system that performs various computational tasks. Digital computers use the binary number system, which has two
Computer Architecture Lecture 1: Digital logic circuits The digital computer is a digital system that performs various computational tasks. Digital computers use the binary number system, which has two
Computer Organization (Autonomous)
 Computer Organization (Autonomous) UNIT II Sections - A & D Prepared by Anil Kumar Prathipati, Asst. Prof., Dept. of CSE. SYLLABUS Basic Computer Organization and Design: Instruction codes Stored Program
Computer Organization (Autonomous) UNIT II Sections - A & D Prepared by Anil Kumar Prathipati, Asst. Prof., Dept. of CSE. SYLLABUS Basic Computer Organization and Design: Instruction codes Stored Program
UNIT-II. Part-2: CENTRAL PROCESSING UNIT
 Page1 UNIT-II Part-2: CENTRAL PROCESSING UNIT Stack Organization Instruction Formats Addressing Modes Data Transfer And Manipulation Program Control Reduced Instruction Set Computer (RISC) Introduction:
Page1 UNIT-II Part-2: CENTRAL PROCESSING UNIT Stack Organization Instruction Formats Addressing Modes Data Transfer And Manipulation Program Control Reduced Instruction Set Computer (RISC) Introduction:
3. Which of the following is volatile? [ ] A) Bubble memory B) RAM C) ROM D) Magneticdisk
![3. Which of the following is volatile? [ ] A) Bubble memory B) RAM C) ROM D) Magneticdisk 3. Which of the following is volatile? [ ] A) Bubble memory B) RAM C) ROM D) Magneticdisk](/thumbs/89/98061154.jpg) Code No: 05210505 Set No. 1 JAWAHARLAL NEHRU TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY HYDERABAD III B.Tech. II Sem. II Mid-Term Examinations, April 2009 COMPUTER ORGANIZATION Objective Exam Name: Hall Ticket No. Answer
Code No: 05210505 Set No. 1 JAWAHARLAL NEHRU TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY HYDERABAD III B.Tech. II Sem. II Mid-Term Examinations, April 2009 COMPUTER ORGANIZATION Objective Exam Name: Hall Ticket No. Answer
VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE. SRM Nagar, Kattankulathur DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE ENGINEERING
 VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE SRM Nagar, Kattankulathur-603 203 DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE ENGINEERING EC6504 MICROPROCESSOR AND MICROCONTROLLER YEAR / SEMESTER: II / IV ACADEMIC YEAR: 2015-2016 (EVEN
VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE SRM Nagar, Kattankulathur-603 203 DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE ENGINEERING EC6504 MICROPROCESSOR AND MICROCONTROLLER YEAR / SEMESTER: II / IV ACADEMIC YEAR: 2015-2016 (EVEN
G GLOSSARY. Terms. Figure G-0. Table G-0. Listing G-0.
 G GLOSSARY Figure G-0. Table G-0. Listing G-0. Terms Autobuffering Unit (ABU). (See I/O processor and DMA) Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU). This part of a processing element performs arithmetic and logic operations
G GLOSSARY Figure G-0. Table G-0. Listing G-0. Terms Autobuffering Unit (ABU). (See I/O processor and DMA) Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU). This part of a processing element performs arithmetic and logic operations
Chapter 5. Computer Architecture Organization and Design. Computer System Architecture Database Lab, SANGJI University
 Chapter 5. Computer Architecture Organization and Design Computer System Architecture Database Lab, SANGJI University Computer Architecture Organization and Design Instruction Codes Computer Registers
Chapter 5. Computer Architecture Organization and Design Computer System Architecture Database Lab, SANGJI University Computer Architecture Organization and Design Instruction Codes Computer Registers
Computer organization by G. Naveen kumar, Asst Prof, C.S.E Department 1
 Pipelining and Vector Processing Parallel Processing: The term parallel processing indicates that the system is able to perform several operations in a single time. Now we will elaborate the scenario,
Pipelining and Vector Processing Parallel Processing: The term parallel processing indicates that the system is able to perform several operations in a single time. Now we will elaborate the scenario,
Class Notes. Dr.C.N.Zhang. Department of Computer Science. University of Regina. Regina, SK, Canada, S4S 0A2
 Class Notes CS400 Part VI Dr.C.N.Zhang Department of Computer Science University of Regina Regina, SK, Canada, S4S 0A2 C. N. Zhang, CS400 83 VI. CENTRAL PROCESSING UNIT 1 Set 1.1 Addressing Modes and Formats
Class Notes CS400 Part VI Dr.C.N.Zhang Department of Computer Science University of Regina Regina, SK, Canada, S4S 0A2 C. N. Zhang, CS400 83 VI. CENTRAL PROCESSING UNIT 1 Set 1.1 Addressing Modes and Formats
4 Operations On Data 4.1. Foundations of Computer Science Cengage Learning
 4 Operations On Data 4.1 Foundations of Computer Science Cengage Learning Objectives After studying this chapter, the student should be able to: List the three categories of operations performed on data.
4 Operations On Data 4.1 Foundations of Computer Science Cengage Learning Objectives After studying this chapter, the student should be able to: List the three categories of operations performed on data.
Unit II Basic Computer Organization
 1. Define the term. Internal Organization-The internal organization of a digital system is defined by the sequence of microoperations it performs on data stored in its registers. Program- A program is
1. Define the term. Internal Organization-The internal organization of a digital system is defined by the sequence of microoperations it performs on data stored in its registers. Program- A program is
BASIC COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND DESIGN
 1 BASIC COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND DESIGN Instruction Codes Computer Registers Computer Instructions Timing and Control Instruction Cycle Memory Reference Instructions Input-Output and Interrupt Complete
1 BASIC COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND DESIGN Instruction Codes Computer Registers Computer Instructions Timing and Control Instruction Cycle Memory Reference Instructions Input-Output and Interrupt Complete
Chapter 4. MARIE: An Introduction to a Simple Computer
 Chapter 4 MARIE: An Introduction to a Simple Computer Chapter 4 Objectives Learn the components common to every modern computer system. Be able to explain how each component contributes to program execution.
Chapter 4 MARIE: An Introduction to a Simple Computer Chapter 4 Objectives Learn the components common to every modern computer system. Be able to explain how each component contributes to program execution.
Latches. IT 3123 Hardware and Software Concepts. Registers. The Little Man has Registers. Data Registers. Program Counter
 IT 3123 Hardware and Software Concepts Notice: This session is being recorded. CPU and Memory June 11 Copyright 2005 by Bob Brown Latches Can store one bit of data Can be ganged together to store more
IT 3123 Hardware and Software Concepts Notice: This session is being recorded. CPU and Memory June 11 Copyright 2005 by Bob Brown Latches Can store one bit of data Can be ganged together to store more
UNIT - V MEMORY P.VIDYA SAGAR ( ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR) Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, VBIT
 UNIT - V MEMORY P.VIDYA SAGAR ( ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR) contents Memory: Introduction, Random-Access memory, Memory decoding, ROM, Programmable Logic Array, Programmable Array Logic, Sequential programmable
UNIT - V MEMORY P.VIDYA SAGAR ( ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR) contents Memory: Introduction, Random-Access memory, Memory decoding, ROM, Programmable Logic Array, Programmable Array Logic, Sequential programmable
Data Representation and Architecture Modeling Year 1 Exam preparation
 1 BINARY SYSTEM Data Representation and Architecture Modeling Year 1 Exam preparation 1 Binary system you need to be able to understand and convert numbers between the following different notations: decimal
1 BINARY SYSTEM Data Representation and Architecture Modeling Year 1 Exam preparation 1 Binary system you need to be able to understand and convert numbers between the following different notations: decimal
Digital System Design Using Verilog. - Processing Unit Design
 Digital System Design Using Verilog - Processing Unit Design 1.1 CPU BASICS A typical CPU has three major components: (1) Register set, (2) Arithmetic logic unit (ALU), and (3) Control unit (CU) The register
Digital System Design Using Verilog - Processing Unit Design 1.1 CPU BASICS A typical CPU has three major components: (1) Register set, (2) Arithmetic logic unit (ALU), and (3) Control unit (CU) The register
CHAPTER 5 Basic Organization and Design Outline Instruction Codes Computer Registers Computer Instructions Timing and Control Instruction Cycle
 CS 224: Computer Organization S.KHABET CHAPTER 5 Basic Organization and Design Outline Instruction Codes Computer Registers Computer Instructions Timing and Control Instruction Cycle Memory Reference Instructions
CS 224: Computer Organization S.KHABET CHAPTER 5 Basic Organization and Design Outline Instruction Codes Computer Registers Computer Instructions Timing and Control Instruction Cycle Memory Reference Instructions
MICROPROCESSORS & MICRO CONTROLLER COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK
 KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK SUBJECT CODE: EC1257 SUBJECT NAME: MICROPROCESSOR AND MICROCONTROLLER YEAR : II IT SEM : IV UNIT I THE 8085 MICROPROCESSOR
KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK SUBJECT CODE: EC1257 SUBJECT NAME: MICROPROCESSOR AND MICROCONTROLLER YEAR : II IT SEM : IV UNIT I THE 8085 MICROPROCESSOR
Register Transfer and Micro-operations
 Register Transfer Language Register Transfer Bus Memory Transfer Micro-operations Some Application of Logic Micro Operations Register Transfer and Micro-operations Learning Objectives After reading this
Register Transfer Language Register Transfer Bus Memory Transfer Micro-operations Some Application of Logic Micro Operations Register Transfer and Micro-operations Learning Objectives After reading this
SRI VIDYA COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY,VIRUDHUNAGAR
 Year/sem: 02/04 Academic Year: 2014-2015 (even) UNIT II THE 8086 SYSTEM BUS STRUCTURE PART A 1. What are the three groups of signals in 8086? The 8086 signals are categorized in three groups. They are:
Year/sem: 02/04 Academic Year: 2014-2015 (even) UNIT II THE 8086 SYSTEM BUS STRUCTURE PART A 1. What are the three groups of signals in 8086? The 8086 signals are categorized in three groups. They are:
,1752'8&7,21. Figure 1-0. Table 1-0. Listing 1-0.
 ,1752'8&7,21 Figure 1-0. Table 1-0. Listing 1-0. The ADSP-21065L SHARC is a high-performance, 32-bit digital signal processor for communications, digital audio, and industrial instrumentation applications.
,1752'8&7,21 Figure 1-0. Table 1-0. Listing 1-0. The ADSP-21065L SHARC is a high-performance, 32-bit digital signal processor for communications, digital audio, and industrial instrumentation applications.
MARIE: An Introduction to a Simple Computer
 MARIE: An Introduction to a Simple Computer Outline Learn the components common to every modern computer system. Be able to explain how each component contributes to program execution. Understand a simple
MARIE: An Introduction to a Simple Computer Outline Learn the components common to every modern computer system. Be able to explain how each component contributes to program execution. Understand a simple
RISC Processors and Parallel Processing. Section and 3.3.6
 RISC Processors and Parallel Processing Section 3.3.5 and 3.3.6 The Control Unit When a program is being executed it is actually the CPU receiving and executing a sequence of machine code instructions.
RISC Processors and Parallel Processing Section 3.3.5 and 3.3.6 The Control Unit When a program is being executed it is actually the CPU receiving and executing a sequence of machine code instructions.
Chapter 4. MARIE: An Introduction to a Simple Computer. Chapter 4 Objectives. 4.1 Introduction. 4.2 CPU Basics
 Chapter 4 Objectives Learn the components common to every modern computer system. Chapter 4 MARIE: An Introduction to a Simple Computer Be able to explain how each component contributes to program execution.
Chapter 4 Objectives Learn the components common to every modern computer system. Chapter 4 MARIE: An Introduction to a Simple Computer Be able to explain how each component contributes to program execution.
ASSIGNMENT-1 M.Sc. DEGREE EXAMINATION, MAY 2018 (First Year) INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY Basics of Information Technology
 ASSIGNMENT-1 () Basics of Information Technology (DMSIT01) Q1) Discuss in detail about IT support at different organizational levels. Q2) Explain about hierarchy of computers. Q3) Discuss different categories
ASSIGNMENT-1 () Basics of Information Technology (DMSIT01) Q1) Discuss in detail about IT support at different organizational levels. Q2) Explain about hierarchy of computers. Q3) Discuss different categories
Unit 1. Chapter 3 Top Level View of Computer Function and Interconnection
 Unit 1 Chapter 3 Top Level View of Computer Function and Interconnection Program Concept Hardwired systems are inflexible General purpose hardware can do different tasks, given correct control signals
Unit 1 Chapter 3 Top Level View of Computer Function and Interconnection Program Concept Hardwired systems are inflexible General purpose hardware can do different tasks, given correct control signals
Roll No TCS 402/TIT 402
 Roll No TCS 402/TIT 402 Mid Term Examination March 2016 B.Tech (IV Semester) Computer Organization Time: Two (2) Hrs. Maximum Marks: 60 NOTE: (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) This question paper contains three questions
Roll No TCS 402/TIT 402 Mid Term Examination March 2016 B.Tech (IV Semester) Computer Organization Time: Two (2) Hrs. Maximum Marks: 60 NOTE: (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) This question paper contains three questions
DSP Platforms Lab (AD-SHARC) Session 05
 University of Miami - Frost School of Music DSP Platforms Lab (AD-SHARC) Session 05 Description This session will be dedicated to give an introduction to the hardware architecture and assembly programming
University of Miami - Frost School of Music DSP Platforms Lab (AD-SHARC) Session 05 Description This session will be dedicated to give an introduction to the hardware architecture and assembly programming
UPY14602-DIGITAL ELECTRONICS AND MICROPROCESSORS Lesson Plan
 UPY14602-DIGITAL ELECTRONICS AND MICROPROCESSORS Lesson Plan UNIT I - NUMBER SYSTEMS AND LOGIC GATES Introduction to decimal- Binary- Octal- Hexadecimal number systems-inter conversions-bcd code- Excess
UPY14602-DIGITAL ELECTRONICS AND MICROPROCESSORS Lesson Plan UNIT I - NUMBER SYSTEMS AND LOGIC GATES Introduction to decimal- Binary- Octal- Hexadecimal number systems-inter conversions-bcd code- Excess
ASSEMBLY LANGUAGE MACHINE ORGANIZATION
 ASSEMBLY LANGUAGE MACHINE ORGANIZATION CHAPTER 3 1 Sub-topics The topic will cover: Microprocessor architecture CPU processing methods Pipelining Superscalar RISC Multiprocessing Instruction Cycle Instruction
ASSEMBLY LANGUAGE MACHINE ORGANIZATION CHAPTER 3 1 Sub-topics The topic will cover: Microprocessor architecture CPU processing methods Pipelining Superscalar RISC Multiprocessing Instruction Cycle Instruction
ECE 341 Midterm Exam
 ECE 341 Midterm Exam Time allowed: 90 minutes Total Points: 75 Points Scored: Name: Problem No. 1 (10 points) For each of the following statements, indicate whether the statement is TRUE or FALSE: (a)
ECE 341 Midterm Exam Time allowed: 90 minutes Total Points: 75 Points Scored: Name: Problem No. 1 (10 points) For each of the following statements, indicate whether the statement is TRUE or FALSE: (a)
omputer Design Concept adao Nakamura
 omputer Design Concept adao Nakamura akamura@archi.is.tohoku.ac.jp akamura@umunhum.stanford.edu 1 1 Pascal s Calculator Leibniz s Calculator Babbage s Calculator Von Neumann Computer Flynn s Classification
omputer Design Concept adao Nakamura akamura@archi.is.tohoku.ac.jp akamura@umunhum.stanford.edu 1 1 Pascal s Calculator Leibniz s Calculator Babbage s Calculator Von Neumann Computer Flynn s Classification
The ALU consists of combinational logic. Processes all data in the CPU. ALL von Neuman machines have an ALU loop.
 CS 320 Ch 10 Computer Arithmetic The ALU consists of combinational logic. Processes all data in the CPU. ALL von Neuman machines have an ALU loop. Signed integers are typically represented in sign-magnitude
CS 320 Ch 10 Computer Arithmetic The ALU consists of combinational logic. Processes all data in the CPU. ALL von Neuman machines have an ALU loop. Signed integers are typically represented in sign-magnitude
ECE 341 Final Exam Solution
 ECE 341 Final Exam Solution Time allowed: 110 minutes Total Points: 100 Points Scored: Name: Problem No. 1 (10 points) For each of the following statements, indicate whether the statement is TRUE or FALSE.
ECE 341 Final Exam Solution Time allowed: 110 minutes Total Points: 100 Points Scored: Name: Problem No. 1 (10 points) For each of the following statements, indicate whether the statement is TRUE or FALSE.
Computer Organization
 Computer Organization It describes the function and design of the various units of digital computers that store and process information. It also deals with the units of computer that receive information
Computer Organization It describes the function and design of the various units of digital computers that store and process information. It also deals with the units of computer that receive information
 Part A Questions 1. What is an ISP? ISP stands for Instruction Set Processor. This unit is simply called as processor which executes machine instruction and coordinates the activities of other units..
Part A Questions 1. What is an ISP? ISP stands for Instruction Set Processor. This unit is simply called as processor which executes machine instruction and coordinates the activities of other units..
Computer Organization and Design
 CSE211 Computer Organization and Design Lecture : 3 Tutorial: 1 Practical: 0 Credit: 4 KIDS Labs 1 Unit 1 : Basics of Digital Electronics Introduction Logic Gates Flip Flops Decoder Encoder Multiplexers
CSE211 Computer Organization and Design Lecture : 3 Tutorial: 1 Practical: 0 Credit: 4 KIDS Labs 1 Unit 1 : Basics of Digital Electronics Introduction Logic Gates Flip Flops Decoder Encoder Multiplexers
AC58/AT58/AC106/AT106 COMPUTER ORGANIZATION DEC 2015
 Q.2 a. With the help of diagram, explain the different functional units of a Computer. (6) A computer consists of five functionally independent main parts: input, memory, arithmetic and logic, output,
Q.2 a. With the help of diagram, explain the different functional units of a Computer. (6) A computer consists of five functionally independent main parts: input, memory, arithmetic and logic, output,
Computer Architecture and Organization: L04: Micro-operations
 Computer Architecture and Organization: L4: Micro-operations By: A. H. Abdul Hafez Abdul.hafez@hku.edu.tr, ah.abdulhafez@gmail.com, hafez@research.iiit.ac.in 1 Outlines 1. Arithmetic microoperation 2.
Computer Architecture and Organization: L4: Micro-operations By: A. H. Abdul Hafez Abdul.hafez@hku.edu.tr, ah.abdulhafez@gmail.com, hafez@research.iiit.ac.in 1 Outlines 1. Arithmetic microoperation 2.
(+A) + ( B) + (A B) (B A) + (A B) ( A) + (+ B) (A B) + (B A) + (A B) (+ A) (+ B) + (A - B) (B A) + (A B) ( A) ( B) (A B) + (B A) + (A B)
 COMPUTER ARITHMETIC 1. Addition and Subtraction of Unsigned Numbers The direct method of subtraction taught in elementary schools uses the borrowconcept. In this method we borrow a 1 from a higher significant
COMPUTER ARITHMETIC 1. Addition and Subtraction of Unsigned Numbers The direct method of subtraction taught in elementary schools uses the borrowconcept. In this method we borrow a 1 from a higher significant
Computer Architecture
 http://www.bsccsit.com/ Computer Architecture CSC. 201 Third Semester Prepared By: Arjun Singh Saud Special thanks to Mr. Arjun Singh Saud for providing this valuable note! Chapter 1 Data representation
http://www.bsccsit.com/ Computer Architecture CSC. 201 Third Semester Prepared By: Arjun Singh Saud Special thanks to Mr. Arjun Singh Saud for providing this valuable note! Chapter 1 Data representation
M. C. A. (Second Semester) Theory Examination,
 M. C. A. (Second Semester) Theory Examination, 2010-11 COMPUTER ORGANIZATION Time: 3 Hours} [Total Marks: 100 Note: This paper is in three Sections. Section-A carries 20 marks. ',Section-B carries 30 marks
M. C. A. (Second Semester) Theory Examination, 2010-11 COMPUTER ORGANIZATION Time: 3 Hours} [Total Marks: 100 Note: This paper is in three Sections. Section-A carries 20 marks. ',Section-B carries 30 marks
COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE AND ORGANIZATION. Operation Add Magnitudes Subtract Magnitudes (+A) + ( B) + (A B) (B A) + (A B)
 Computer Arithmetic Data is manipulated by using the arithmetic instructions in digital computers. Data is manipulated to produce results necessary to give solution for the computation problems. The Addition,
Computer Arithmetic Data is manipulated by using the arithmetic instructions in digital computers. Data is manipulated to produce results necessary to give solution for the computation problems. The Addition,
Microprocessor Micro Syllabus BSc. CSIT, IOST, TU. Microprocessor
 Microprocessor Micro Syllabus BSc. CSIT, IOST, TU Microprocessor Course Title: Microprocessor Full Marks: 60 + 20 + 20 Course No: CSC162 Pass Marks: 24 + 8 + 8 Nature of the Course: Theory + Lab Credit
Microprocessor Micro Syllabus BSc. CSIT, IOST, TU Microprocessor Course Title: Microprocessor Full Marks: 60 + 20 + 20 Course No: CSC162 Pass Marks: 24 + 8 + 8 Nature of the Course: Theory + Lab Credit
