2.3 Flow Control. Flow-Of-Control. If-Else: Leap Year. If-Else
|
|
|
- Winifred Holland
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Flow-Of-Control 2.3 Flow Control Flow-of-control. Sequence of statements that are actually executed in a program. Conditionals and loops: enable us to harness power of the computer. statement 1 boolean 1 statement 2 statement 3 statement 1 boolean 2 statement 2 Copyright 2004, FoxTrot by Bill Amend, statement 4 statement 3 straight-line flow-of-control flow-of-control with conditionals and loops Introduction to Computer Science Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne 2 If-Else If-Else: Leap Year The if-else statement is a common branching structure. Check boolean condition. If, execute some statements. Otherwise, execute other statements. If-else example: print informative text. Different operation is performed depending on value of variable. if isleapyear is, then print " is a " otherwise, print " isn't a " if (boolean expression) statement1 else statement2 if-else syntax can be a block of statements statement1 boolean expression statement2 System.out.println(year); if (isleapyear) { System.out.println(" is a "); else { System.out.println(" isn't a "); System.out.println("leap year"); if-else flow chart 3 4
2 Oblivious Sorting While Loops Read in 3 integers and rearrange ascending order. public class Sort3 { The while loop is a common repetition structure. Check loop-continuation condition. Execute a sequence of statements. Repeat. int A = Integer.parseInt(args[0]); int B = Integer.parseInt(args[1]); int C = Integer.parseInt(args[2]); read in 3 integers swap A and B if (B < A) { int t = B; B = A; A = t; if (C < B) { int t = C; C = B; B = t; if (B < A) { int t = B; B = A; A = t; System.out.println(A + " " + B + " " + C); % java Sort while (boolean expression) statement; while loop syntax loop-continuation condition boolean expression statement body Puzzle 1: sort 4 integers with 5 compare-exchanges. Puzzle 2: sort 6 integers with 12. % java Sort while loop flow chart 5 6 While Loops: Powers of Two While Loops: Newton-Raphson Method While loop example: print powers of 2. Increment i from 1 to 6 by 1. How might we implement Math.sqrt? Goal: compute the square root of c. Double N each time. i N i <= 6 Initialize t = c. Replace t with the average of t and c / t. int i = 0; int N = 1; while (i <= 6) { System.out.println(N); i = i + 1; N = 2 * N; a block statement Click for demo % java Powers Repeat until t = c / t, up to desired precision. public class Sqrt { double EPSILON = 1E-15; double c = Double.parseDouble(args[0]); double t = c; while (Math.abs(t - c/t) > t*epsilon) { t = (c/t + t) / 2.0; error tolerance System.out.println(t); % java Sqrt Copyright 2004, Sidney Harris 15 decimal digits of accuracy in 5 iterations 7 8
3 While Loops: Newton-Raphson Method For Loops Newton-Raphson method explained. The for loop is another common repetition structure. Goal: find root of function f(x). Initialize variable. Ex: f(x) = x 2 - c Start with estimate t 0. Draw line tangent to curve at x= t i. Set t i+1 to be x-coordinate where line hits x-axis. Repeat until desired precision. Check loop-continuation condition. Execute sequence of statements. Increment variable. Repeat. for (init; boolean; update) statement; initialization update Applications and extensions. for loop syntax Find the roots of a differentiable function of one variable. Find the roots of a function of several variables. boolean expression statement Optimize a twice differentiable function: find where derivative = 0. Optimize a function subject to constraints. loop-continuation condition body for loop flow chart 9 10 For Loops: Subdivisions of a Ruler For Loops: Subdivisions of a Ruler Create subdivision of a ruler. Initialize ruler to the empty string. For each value i = 1 to N. Sandwich two copies of the ruler on either side of i. Observation. Program produces 2 N 1 integers. Loops can produce a huge amount of output! String ruler = " "; for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++) { ruler = ruler + i + ruler; System.out.println(ruler); Java code i ruler % java Ruler 1 1 % java Ruler % java Ruler % java Ruler % java Ruler 100 Exception in thread "main" java.lang.outofmemoryerror 11 12
4 Nesting Conditionals and Loops Nested If-Else Conditionals enable you to do one of 2 N sequences of operations with N lines of code. Loops enable you to do something N times using only 2 lines of code. Nesting conditionals within conditionals. Ex: Pay a certain tax rate depending on income level. if (a0 > 0) System.out.print(0); if (a1 > 0) System.out.print(1); if (a2 > 0) System.out.print(2); if (a3 > 0) System.out.print(3); if (a4 > 0) System.out.print(4); if (a5 > 0) System.out.print(5); if (a6 > 0) System.out.print(6); if (a7 > 0) System.out.print(7); if (a8 > 0) System.out.print(8); if (a9 > 0) System.out.print(9); double sum = 0.0; for (int i = 1; i <= 1024; i++) sum = sum / i; computes 1/1 + 1/ /1024 double rate; if (income < 47450) rate = 0.22; else if (income < ) rate = 0.25; else if (income < ) rate = 0.28; else if (income < ) rate = 0.33; else rate = 0.35; Income Rate 0-47,450 22% 47, ,650 25% 114, ,700 28% 174, ,950 33% 1024 possible results, depending on input graduated income tax calculation 311,950-35% More sophisticated programs. Nest conditionals within conditionals. Nest loops within loops. Nest conditionals within loops within loops Gambler's Ruin Library Functions: Math.random Gambler starts with $stake and places $1 even bets until going broke or reaching $goal. What are the chances of winning? How many bets will it take? Cash One approach: numerical simulation. Flip digital coins and see what happens. Repeat and compute statistics. goal = 16 stake = 7 Math.random generates number between 0 and 1. How is Math.random implemented? Linear feedback shift register? Cosmic rays? User doesn't need to know details. User doesn't want to know details. Caveats. "Random" numbers are not really random. Don't use for crypto or Internet gambling! Check assumptions about library function before using. Time One simulation of the gambler's ruin problem. $
5 Gambler's Ruin Simulation and Analysis public class Gambler { int stake = Integer.parseInt(args[0]); int goal = Integer.parseInt(args[1]); int N = Integer.parseInt(args[2]); int wins = 0; // repeat simulation N times for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) { // do gambler's ruin simulation int t = stake; while (t > 0 && t < goal) { // flip coin and update if (Math.random() < 0.5) t++; else t--; if (t == goal) wins++; System.out.println(wins + " wins of " + N); stake goal N % java Gambler wins of 1000 % java Gambler wins of 1000 % java Gambler wins of 100 Fact: Probability of winning = stake goal. Fact: Expected number of bets = stake desired gain. Ex: 20% chance of turning $500 into $2500, but expect to make one million $1 bets. These two facts can be proved mathematically; for more complex scenarios, computer simulation is often the best plan of attack. takes a few minutes Debugging a Program: Syntax Errors Debugging a Program: Semantic Errors Given an integer N, compute its prime factorization. Application: break RSA cryptosystem. 168 = Semantic error: legal but wrong Java program. Use "System.out.println" method to identify problem. Syntax error: illegal Java program. Compiler error messages help locate problem. Eventually, a file named Factors.class. public class Factors1 { long N = Long.parseLong(args[0]) for (i = 0; i < N; i++) { while (N % i == 0) System.out.print(i + " ") N = N / i Check if i is a factor. public class Factors2 { long N = Long.parseLong(args[0]); for (long i = 2; i < N; i++) { while (N % i == 0) System.out.print(i + " "); N = N / i; No output (17) or infinite loop (49) Check if i is a factor. Does not compile 19 20
6 Debugging a Program: Performance Errors Debugging a Program: Success Performance error: correct program but too slow. Use profiling to discover bottleneck. Devise better algorithm. If N has a factor, it has one less than or equal to its square root. Many fewer iterations of for loop. public class Factors { long N = Long.parseLong(args[0]); public class Factors3 { long N = Long.parseLong(args[0]); for (long i = 2; i <= N; i++) { while (N % i == 0) { System.out.print(i + " "); N = N / i; Too slow for large N (999,999,937) Check if i is a factor. Check if i is a factor. for (long i = 2; i <= N / i; i++) { while (N % i == 0) { System.out.print(i + " "); N = N / i; if (N > 1) System.out.println(N); else System.out.println(); Special case: biggest factor occurs once Debugging a Program: Analysis Debugging a Program How big an integer can I factor? % java Factors % java Factors Debug: cyclic process of editing, compiling, and fixing errors. Always a logical explanation. What would the machine do? Say it to the teddy bear. largest factor % java Factors minutes You will make many mistakes as you write programs. It's normal. Digits i <= N seconds 9 77 seconds i <= N / i i * i <= N "As soon as we started programming, we found out to our surprise that it wasn't as easy to get programs right as we had thought. I can remember the exact when I realized that a large part of my life from then on was going to be spent in finding mistakes in my own programs." -Maurice Wilkes hours 0.21 seconds 0.16 seconds years millennia 4.5 seconds 157 seconds 2.7 seconds 92 seconds "If I had 8 hours to chop down a tree, I would spend 6 hours sharpening an axe." - Anonymous estimated 23 24
7 Etymology and Entomology of Computer "Bug" Flow Of Control Summary Flow of control. Sequence of statements that are actually executed in a program. Flow-Of-Control Description Examples Straight-line programs Conditionals Loops All statements are executed in the order given. Certain statements are executed depending on the values of certain variables. Certain statements are executed repeatedly until certain conditions are met. if if-else while for do-while Reference: Grace Hopper Admiral, US Navy Conditionals and loops. Simple, but powerful tools. Enables us to harness power of the computer U.S.S. Grace Murray Hopper "A ship in port is safe, but that is not what ships are built for. I want all the youngsters to sail out to sea and be good ships." - Grace Hopper 27
Lecture 3: Loops. While Loops. While Loops: Newton-Raphson Method. While Loops: Powers of Two
 While Loops Lecture 3: Loops The while loop is a common repetition structure. Check loop-continuation condition. Execute a sequence of statements. Repeat. while (boolean expression) statement; while loop
While Loops Lecture 3: Loops The while loop is a common repetition structure. Check loop-continuation condition. Execute a sequence of statements. Repeat. while (boolean expression) statement; while loop
Lecture 3: Loops. While Loops. While Loops: Powers of Two. While Loops: Newton-Raphson Method
 While Loops Lecture : Loops The while loop is a common repetition structure. Check loop-continuation condition. Execute a sequence of statements. Repeat. while (boolean expression) statement; while loop
While Loops Lecture : Loops The while loop is a common repetition structure. Check loop-continuation condition. Execute a sequence of statements. Repeat. while (boolean expression) statement; while loop
! Sequence of statements that are actually executed in a program. ! Conditionals and loops: enable us to choreograph control flow.
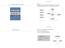 Control Flow 1.3 Conditionals and Loops Control flow.! Sequence of statements that are actually executed in a program.! Conditionals and loops: enable us to choreograph control flow. statement 1 boolean
Control Flow 1.3 Conditionals and Loops Control flow.! Sequence of statements that are actually executed in a program.! Conditionals and loops: enable us to choreograph control flow. statement 1 boolean
1.3 Conditionals and Loops
 A Foundation for Programming 1.3 Conditionals and Loops any program you might want to write objects functions and modules graphics, sound, and image I/O arrays conditionals and loops Math primitive data
A Foundation for Programming 1.3 Conditionals and Loops any program you might want to write objects functions and modules graphics, sound, and image I/O arrays conditionals and loops Math primitive data
1.3 Conditionals and Loops
 1 1.3 Conditionals and Loops any program you might want to write objects functions and modules graphics, sound, and image I/O arrays conditionals and loops to infinity and beyond Math primitive data types
1 1.3 Conditionals and Loops any program you might want to write objects functions and modules graphics, sound, and image I/O arrays conditionals and loops to infinity and beyond Math primitive data types
1.3 Conditionals and Loops
 .3 Conditionals and Loops Introduction to Programming in Java: An Interdisciplinary Approach Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne Copyright 2008 February 04, 2008 0:00 AM A Foundation for Programming A Foundation
.3 Conditionals and Loops Introduction to Programming in Java: An Interdisciplinary Approach Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne Copyright 2008 February 04, 2008 0:00 AM A Foundation for Programming A Foundation
1.3 Conditionals and Loops
 A Foundation for Programming 1.3 Conditionals and Loops any program you might want to write objects functions and modules graphics, sound, and image I/O arrays conditionals and loops Math primitive data
A Foundation for Programming 1.3 Conditionals and Loops any program you might want to write objects functions and modules graphics, sound, and image I/O arrays conditionals and loops Math primitive data
1.3 Conditionals and Loops. 1.3 Conditionals and Loops. Conditionals and Loops
 1.3 Conditionals and Loops any program you might want to write objects functions and modules graphics, sound, and image I/O arrays conditionals and loops Math primitive data types text I/O assignment statements
1.3 Conditionals and Loops any program you might want to write objects functions and modules graphics, sound, and image I/O arrays conditionals and loops Math primitive data types text I/O assignment statements
1.3 Conditionals and Loops
 1.3 Conditionals and Loops Introduction to Programming in Java: An Interdisciplinary Approach Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne Copyright 2002 2010 15/1/2013 22:16:24 A Foundation for Programming any program
1.3 Conditionals and Loops Introduction to Programming in Java: An Interdisciplinary Approach Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne Copyright 2002 2010 15/1/2013 22:16:24 A Foundation for Programming any program
CS 112 Introduction to Programming
 CS 112 Introduction to Programming (Spring 2012) Lecture #5: Conditionals and Loops Zhong Shao Department of Computer Science Yale University Office: 314 Watson http://flint.cs.yale.edu/cs112 Acknowledgements:
CS 112 Introduction to Programming (Spring 2012) Lecture #5: Conditionals and Loops Zhong Shao Department of Computer Science Yale University Office: 314 Watson http://flint.cs.yale.edu/cs112 Acknowledgements:
3. Conditionals & Loops
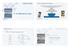 Context: basic building blocks for programming any program you might want to write objects functions and modules graphics, sound, and image I/O arrays conditionals and loops conditionals loops Math primitive
Context: basic building blocks for programming any program you might want to write objects functions and modules graphics, sound, and image I/O arrays conditionals and loops conditionals loops Math primitive
3. Conditionals & Loops
 COMPUTER SCIENCE S E D G E W I C K / W A Y N E 3. Conditionals & Loops Section 1.3 http://introcs.cs.princeton.edu Context: basic building blocks for programming any program you might want to write objects
COMPUTER SCIENCE S E D G E W I C K / W A Y N E 3. Conditionals & Loops Section 1.3 http://introcs.cs.princeton.edu Context: basic building blocks for programming any program you might want to write objects
3. Conditionals and loops
 COMPUTER SCIENCE S E D G E W I C K / W A Y N E 3. Conditionals and loops Section 1.3 http://introcs.cs.princeton.edu COMPUTER SCIENCE S E D G E W I C K / W A Y N E 3. Conditionals & Loops Conditionals:
COMPUTER SCIENCE S E D G E W I C K / W A Y N E 3. Conditionals and loops Section 1.3 http://introcs.cs.princeton.edu COMPUTER SCIENCE S E D G E W I C K / W A Y N E 3. Conditionals & Loops Conditionals:
I/O (cont) and Program Development. Standard Audio. A Foundation for Programming. Crash Course in Sound
 A Foundation for Programming I/O (cont) and Program Development any program you might want to write objects functions and modules graphics, sound, and image I/O arrays conditionals and loops what you've
A Foundation for Programming I/O (cont) and Program Development any program you might want to write objects functions and modules graphics, sound, and image I/O arrays conditionals and loops what you've
Program Development. Program Development. A Foundation for Programming. Program Development
 Program Development Program Development Ada Lovelace Introduction to Programming in Java: An Interdisciplinary Approach Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne Copyright 2008 February 11, 2010 8:48 AM 2 A Foundation
Program Development Program Development Ada Lovelace Introduction to Programming in Java: An Interdisciplinary Approach Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne Copyright 2008 February 11, 2010 8:48 AM 2 A Foundation
TESTING AND DEBUGGING
 TESTING AND DEBUGGING zombie[1] zombie[3] Buuuuugs zombie[4] zombie[2] zombie[5] zombie[0] Fundamentals of Computer Science I Outline Debugging Types of Errors Syntax Errors Semantic Errors Logic Errors
TESTING AND DEBUGGING zombie[1] zombie[3] Buuuuugs zombie[4] zombie[2] zombie[5] zombie[0] Fundamentals of Computer Science I Outline Debugging Types of Errors Syntax Errors Semantic Errors Logic Errors
A Foundation for Programming
 Program Development Introduction to Programming in Java: An Interdisciplinary Approach Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne Copyright 2002 2010 2/17/11 7:35 AM! A Foundation for Programming any program you
Program Development Introduction to Programming in Java: An Interdisciplinary Approach Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne Copyright 2002 2010 2/17/11 7:35 AM! A Foundation for Programming any program you
! Widely available. ! Widely used. ! Variety of automatic checks for mistakes in programs. ! Embraces full set of modern abstractions. Caveat.
 Why Java? Lecture 2: Intro to Java Java features.! Widely available.! Widely used.! Variety of automatic checks for mistakes in programs.! Embraces full set of modern abstractions. Caveat.! No perfect
Why Java? Lecture 2: Intro to Java Java features.! Widely available.! Widely used.! Variety of automatic checks for mistakes in programs.! Embraces full set of modern abstractions. Caveat.! No perfect
Lecture 2: Intro to Java
 Why Java? Lecture 2: Intro to Java Java features. Widely available. Widely used. Variety of automatic checks for mistakes in programs. Embraces full set of modern abstractions. 2 Why Java? Why Java? Java
Why Java? Lecture 2: Intro to Java Java features. Widely available. Widely used. Variety of automatic checks for mistakes in programs. Embraces full set of modern abstractions. 2 Why Java? Why Java? Java
Lecture 2: Intro to Java
 Why Programming? Lecture 2: Intro to Java Idealized computer. "Please simulate the motion of a system of N heavenly bodies, subject to Newton's laws of motion and gravity." Prepackaged software solutions.
Why Programming? Lecture 2: Intro to Java Idealized computer. "Please simulate the motion of a system of N heavenly bodies, subject to Newton's laws of motion and gravity." Prepackaged software solutions.
Review. Primitive Data Types & Variables. String Mathematical operators: + - * / % Comparison: < > <= >= == int, long float, double boolean char
 Review Primitive Data Types & Variables int, long float, double boolean char String Mathematical operators: + - * / % Comparison: < > = == 1 1.3 Conditionals and Loops Introduction to Programming in
Review Primitive Data Types & Variables int, long float, double boolean char String Mathematical operators: + - * / % Comparison: < > = == 1 1.3 Conditionals and Loops Introduction to Programming in
More on variables, arrays, debugging
 More on variables, arrays, debugging zombie[1] zombie[3] Buuuuugs zombie[4] zombie[2] zombie[5] zombie[0] Fundamentals of Computer Science Keith Vertanen Variables revisited Scoping Arrays revisited Overview
More on variables, arrays, debugging zombie[1] zombie[3] Buuuuugs zombie[4] zombie[2] zombie[5] zombie[0] Fundamentals of Computer Science Keith Vertanen Variables revisited Scoping Arrays revisited Overview
Debugging [continued]
![Debugging [continued] Debugging [continued]](/thumbs/92/109562294.jpg) Debugging [continued] Admiral Grace Murray Hopper http://www.history.navy.mil/photos/images/h96000/h96566kc.htm 1 2 Debugging Your Program Debugging: Where we left off Debugging Your Program. [summary]
Debugging [continued] Admiral Grace Murray Hopper http://www.history.navy.mil/photos/images/h96000/h96566kc.htm 1 2 Debugging Your Program Debugging: Where we left off Debugging Your Program. [summary]
Debugging [continued]
![Debugging [continued] Debugging [continued]](/thumbs/93/114063657.jpg) 1 Debugging [continued] Admiral Grace Murray Hopper http://www.history.navy.mil/photos/images/h96000/h96566kc.htm 2 Debugging Your Program Debugging Your Program. [summary] 1. Edit the program (type in
1 Debugging [continued] Admiral Grace Murray Hopper http://www.history.navy.mil/photos/images/h96000/h96566kc.htm 2 Debugging Your Program Debugging Your Program. [summary] 1. Edit the program (type in
Learning Outcomes for this week. Inf1-OP. A Foundation for Programming. A Foundation for Programming
 Learning Outcomes for this week Inf1-OP Conditionals and Loops 1 Perdita Stevens, adapting earlier version by Ewan Klein School of Informatics January 9, 2016 Use if and if-else statements to execute a
Learning Outcomes for this week Inf1-OP Conditionals and Loops 1 Perdita Stevens, adapting earlier version by Ewan Klein School of Informatics January 9, 2016 Use if and if-else statements to execute a
1.1 Your First Program
 Why Programming? 1.1 Your First Program Why programming? Need to tell computer what you want it to do. Naive ideal. Natural language instructions. Please simulate the motion of these heavenly bodies, subject
Why Programming? 1.1 Your First Program Why programming? Need to tell computer what you want it to do. Naive ideal. Natural language instructions. Please simulate the motion of these heavenly bodies, subject
1.1 Your First Program
 1.1 Your First Program 1 Why Programming? Why programming? Need to tell computer what you want it to do. Naive ideal. Natural language instructions. Please simulate the motion of these heavenly bodies,
1.1 Your First Program 1 Why Programming? Why programming? Need to tell computer what you want it to do. Naive ideal. Natural language instructions. Please simulate the motion of these heavenly bodies,
1.1 Your First Program
 1.1 Your First Program Introduction to Programming in Java: An Interdisciplinary Approach Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne Copyright 2002 2010 5/20/2013 9:37:22 AM Why Programming? Why programming? Need
1.1 Your First Program Introduction to Programming in Java: An Interdisciplinary Approach Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne Copyright 2002 2010 5/20/2013 9:37:22 AM Why Programming? Why programming? Need
Outline. 1 If Statement. 2 While Statement. 3 For Statement. 4 Nesting. 5 Applications. 6 Other Conditional and Loop Constructs 2 / 19
 Control Flow 1 / 19 Outline 1 If Statement 2 While Statement 3 For Statement 4 Nesting 5 Applications 6 Other Conditional and Loop Constructs 2 / 19 If Statement Most computations require different actions
Control Flow 1 / 19 Outline 1 If Statement 2 While Statement 3 For Statement 4 Nesting 5 Applications 6 Other Conditional and Loop Constructs 2 / 19 If Statement Most computations require different actions
1.1 Your First Program
 Why Programming? 1.1 Your First Program Why programming? Need to tell computer what you want it to do. Naive ideal. Natural language instructions. Please simulate the motion of N heavenly bodies, subject
Why Programming? 1.1 Your First Program Why programming? Need to tell computer what you want it to do. Naive ideal. Natural language instructions. Please simulate the motion of N heavenly bodies, subject
Condi(onals and Loops
 Condi(onals and Loops 1 Review Primi(ve Data Types & Variables int, long float, double boolean char String Mathema(cal operators: + - * / % Comparison: < > = == 2 A Founda(on for Programming any program
Condi(onals and Loops 1 Review Primi(ve Data Types & Variables int, long float, double boolean char String Mathema(cal operators: + - * / % Comparison: < > = == 2 A Founda(on for Programming any program
1.1 Your First Program
 Why Programming? 1.1 Your First Program Why programming? Need to tell computer what to do. Please simulate the motion of N heavenly bodies, subject to Newton s laws of motion and gravity. Prepackaged software
Why Programming? 1.1 Your First Program Why programming? Need to tell computer what to do. Please simulate the motion of N heavenly bodies, subject to Newton s laws of motion and gravity. Prepackaged software
1.1 Your First Program
 1.1 Your First Program Introduction to Programming in Java: An Interdisciplinary Approach Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne Copyright 2002 2010 1/29/11 6:37 AM! Why Programming? Why programming? Need to
1.1 Your First Program Introduction to Programming in Java: An Interdisciplinary Approach Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne Copyright 2002 2010 1/29/11 6:37 AM! Why Programming? Why programming? Need to
1.1 Your First Program
 Why Programming? Idealized computer. "Please simulate the motion of a system of N heavenly bodies, subject to Newton's laws of motion and gravity." 1.1 Your First Program Prepackaged software solutions.
Why Programming? Idealized computer. "Please simulate the motion of a system of N heavenly bodies, subject to Newton's laws of motion and gravity." 1.1 Your First Program Prepackaged software solutions.
Conditionals, Loops, and Style
 Conditionals, Loops, and Style yes x > y? no max = x; max = y; http://xkcd.com/292/ Fundamentals of Computer Science Keith Vertanen Copyright 2013 Control flow thus far public class ArgsExample public
Conditionals, Loops, and Style yes x > y? no max = x; max = y; http://xkcd.com/292/ Fundamentals of Computer Science Keith Vertanen Copyright 2013 Control flow thus far public class ArgsExample public
1/16/12. CS 112 Introduction to Programming. A Foundation for Programming. (Spring 2012) Lecture #4: Built-in Types of Data. The Computer s View
 1/16/12 A Foundation for Programming CS 112 Introduction to Programming (Spring 2012) any program you might want to write Lecture #4: Built-in Types of Data objects Zhong Shao methods and classes graphics,
1/16/12 A Foundation for Programming CS 112 Introduction to Programming (Spring 2012) any program you might want to write Lecture #4: Built-in Types of Data objects Zhong Shao methods and classes graphics,
CONDITIONAL EXECUTION
 CONDITIONAL EXECUTION yes x > y? no max = x; max = y; logical AND logical OR logical NOT &&! Fundamentals of Computer Science I Outline Conditional Execution if then if then Nested if then statements Comparisons
CONDITIONAL EXECUTION yes x > y? no max = x; max = y; logical AND logical OR logical NOT &&! Fundamentals of Computer Science I Outline Conditional Execution if then if then Nested if then statements Comparisons
Conditionals, Loops, and Style. Control flow thus far. if statement. Control flow. Common branching statement Evaluate a boolean expression
 Conditionals, Loops, and Style Control flow thus far yes no x > y? max = x; max = y; public class ArgsExample time 0 String product = args[0]; time 1 int qty = Integer.parseInt(args[1]); time 2 double
Conditionals, Loops, and Style Control flow thus far yes no x > y? max = x; max = y; public class ArgsExample time 0 String product = args[0]; time 1 int qty = Integer.parseInt(args[1]); time 2 double
Unit 1 Lesson 4. Introduction to Control Statements
 Unit 1 Lesson 4 Introduction to Control Statements Essential Question: How are control loops used to alter the execution flow of a program? Lesson 4: Introduction to Control Statements Objectives: Use
Unit 1 Lesson 4 Introduction to Control Statements Essential Question: How are control loops used to alter the execution flow of a program? Lesson 4: Introduction to Control Statements Objectives: Use
CS112 Lecture: Repetition Statements
 CS112 Lecture: Repetition Statements Objectives: Last revised 2/18/05 1. To explain the general form of the java while loop 2. To introduce and motivate the java do.. while loop 3. To explain the general
CS112 Lecture: Repetition Statements Objectives: Last revised 2/18/05 1. To explain the general form of the java while loop 2. To introduce and motivate the java do.. while loop 3. To explain the general
Tutorials. Inf1-OP. Learning Outcomes for this week. A Foundation for Programming. Conditionals and Loops 1
 Tutorials Inf1-OP Conditionals and Loops 1 Volker Seeker, adapting earlier version by Perdita Stevens and Ewan Klein Start this week please let the ITO know if you need to switch tutorial groups. Labs
Tutorials Inf1-OP Conditionals and Loops 1 Volker Seeker, adapting earlier version by Perdita Stevens and Ewan Klein Start this week please let the ITO know if you need to switch tutorial groups. Labs
CONDITIONAL EXECUTION
 CONDITIONAL EXECUTION yes x > y? no max = x; max = y; logical AND logical OR logical NOT &&! Fundamentals of Computer Science I Outline Conditional Execution if then if then Nested if then statements Comparisons
CONDITIONAL EXECUTION yes x > y? no max = x; max = y; logical AND logical OR logical NOT &&! Fundamentals of Computer Science I Outline Conditional Execution if then if then Nested if then statements Comparisons
Computer Programming I - Unit 5 Lecture page 1 of 14
 page 1 of 14 I. The while Statement while, for, do Loops Note: Loop - a control structure that causes a sequence of statement(s) to be executed repeatedly. The while statement is one of three looping statements
page 1 of 14 I. The while Statement while, for, do Loops Note: Loop - a control structure that causes a sequence of statement(s) to be executed repeatedly. The while statement is one of three looping statements
Java. Programming: Chapter Objectives. Why Is Repetition Needed? Chapter 5: Control Structures II. Program Design Including Data Structures
 Chapter 5: Control Structures II Java Programming: Program Design Including Data Structures Chapter Objectives Learn about repetition (looping) control structures Explore how to construct and use count-controlled,
Chapter 5: Control Structures II Java Programming: Program Design Including Data Structures Chapter Objectives Learn about repetition (looping) control structures Explore how to construct and use count-controlled,
AP CS Unit 3: Control Structures Notes
 AP CS Unit 3: Control Structures Notes The if and if-else Statements. These statements are called control statements because they control whether a particular block of code is executed or not. Some texts
AP CS Unit 3: Control Structures Notes The if and if-else Statements. These statements are called control statements because they control whether a particular block of code is executed or not. Some texts
COMP-202 Unit 4: Programming With Iterations. CONTENTS: The while and for statements
 COMP-202 Unit 4: Programming With Iterations CONTENTS: The while and for statements Introduction (1) Suppose we want to write a program to be used in cash registers in stores to compute the amount of money
COMP-202 Unit 4: Programming With Iterations CONTENTS: The while and for statements Introduction (1) Suppose we want to write a program to be used in cash registers in stores to compute the amount of money
Chapter 4 Introduction to Control Statements
 Introduction to Control Statements Fundamentals of Java: AP Computer Science Essentials, 4th Edition 1 Objectives 2 How do you use the increment and decrement operators? What are the standard math methods?
Introduction to Control Statements Fundamentals of Java: AP Computer Science Essentials, 4th Edition 1 Objectives 2 How do you use the increment and decrement operators? What are the standard math methods?
AP Programming - Chapter 6 Lecture
 page 1 of 21 The while Statement, Types of Loops, Looping Subtasks, Nested Loops I. The while Statement Note: Loop - a control structure that causes a sequence of statement(s) to be executed repeatedly.
page 1 of 21 The while Statement, Types of Loops, Looping Subtasks, Nested Loops I. The while Statement Note: Loop - a control structure that causes a sequence of statement(s) to be executed repeatedly.
CSCI 135 Exam #0 Fundamentals of Computer Science I Fall 2013
 CSCI 135 Exam #0 Fundamentals of Computer Science I Fall 2013 Name: This exam consists of 7 problems on the following 6 pages. You may use your single- side hand- written 8 ½ x 11 note sheet during the
CSCI 135 Exam #0 Fundamentals of Computer Science I Fall 2013 Name: This exam consists of 7 problems on the following 6 pages. You may use your single- side hand- written 8 ½ x 11 note sheet during the
Sequence structure. The computer executes java statements one after the other in the order in which they are written. Total = total +grade;
 Control Statements Control Statements All programs could be written in terms of only one of three control structures: Sequence Structure Selection Structure Repetition Structure Sequence structure The
Control Statements Control Statements All programs could be written in terms of only one of three control structures: Sequence Structure Selection Structure Repetition Structure Sequence structure The
COMP-202 Unit 4: Programming with Iterations
 COMP-202 Unit 4: Programming with Iterations Doing the same thing again and again and again and again and again and again and again and again and again... CONTENTS: While loops Class (static) variables
COMP-202 Unit 4: Programming with Iterations Doing the same thing again and again and again and again and again and again and again and again and again... CONTENTS: While loops Class (static) variables
Repetition Structures
 Repetition Structures Chapter 5 Fall 2016, CSUS Introduction to Repetition Structures Chapter 5.1 1 Introduction to Repetition Structures A repetition structure causes a statement or set of statements
Repetition Structures Chapter 5 Fall 2016, CSUS Introduction to Repetition Structures Chapter 5.1 1 Introduction to Repetition Structures A repetition structure causes a statement or set of statements
Condition-Controlled Loop. Condition-Controlled Loop. If Statement. Various Forms. Conditional-Controlled Loop. Loop Caution.
 Repetition Structures Introduction to Repetition Structures Chapter 5 Spring 2016, CSUS Chapter 5.1 Introduction to Repetition Structures The Problems with Duplicate Code A repetition structure causes
Repetition Structures Introduction to Repetition Structures Chapter 5 Spring 2016, CSUS Chapter 5.1 Introduction to Repetition Structures The Problems with Duplicate Code A repetition structure causes
Java Methods. Lecture 8 COP 3252 Summer May 23, 2017
 Java Methods Lecture 8 COP 3252 Summer 2017 May 23, 2017 Java Methods In Java, the word method refers to the same kind of thing that the word function is used for in other languages. Specifically, a method
Java Methods Lecture 8 COP 3252 Summer 2017 May 23, 2017 Java Methods In Java, the word method refers to the same kind of thing that the word function is used for in other languages. Specifically, a method
You have seen abstractions in many places, lets consider them from the ground up.
 CS1706 Intro to Object Oriented Dev II - Fall 04 Announcements Week 10 Project 2 due 11/01 Material Interfaces Anonymous classes Lets see abstractions... You have seen abstractions in many places, lets
CS1706 Intro to Object Oriented Dev II - Fall 04 Announcements Week 10 Project 2 due 11/01 Material Interfaces Anonymous classes Lets see abstractions... You have seen abstractions in many places, lets
Debugging [continued]
![Debugging [continued] Debugging [continued]](/thumbs/89/98091015.jpg) Debugging [continued] Admiral Grace Murray Hopper http://www.history.navy.mil/photos/images/h96000/h96566kc.htm 1 2 Debugging Your Program Debugging: Performance Errors Debugging Your Program. [summary]
Debugging [continued] Admiral Grace Murray Hopper http://www.history.navy.mil/photos/images/h96000/h96566kc.htm 1 2 Debugging Your Program Debugging: Performance Errors Debugging Your Program. [summary]
CS112 Lecture: Loops
 CS112 Lecture: Loops Objectives: Last revised 3/11/08 1. To introduce some while loop patterns 2. To introduce and motivate the java do.. while loop 3. To review the general form of the java for loop.
CS112 Lecture: Loops Objectives: Last revised 3/11/08 1. To introduce some while loop patterns 2. To introduce and motivate the java do.. while loop 3. To review the general form of the java for loop.
CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I
 Repetition CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University Course website: www.csc.villanova.edu/~map/1051/ Some slides in this
Repetition CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University Course website: www.csc.villanova.edu/~map/1051/ Some slides in this
School of Computer Science CPS109 Course Notes 6 Alexander Ferworn Updated Fall 15. CPS109 Course Notes 6. Alexander Ferworn
 CPS109 Course Notes 6 Alexander Ferworn Unrelated Facts Worth Remembering Use metaphors to understand issues and explain them to others. Look up what metaphor means. Table of Contents Contents 1 ITERATION...
CPS109 Course Notes 6 Alexander Ferworn Unrelated Facts Worth Remembering Use metaphors to understand issues and explain them to others. Look up what metaphor means. Table of Contents Contents 1 ITERATION...
Definite Loops. Computer Science S-111 Harvard University David G. Sullivan, Ph.D. Using a Variable for Counting
 Unit 2, Part 2 Definite Loops Computer Science S-111 Harvard University David G. Sullivan, Ph.D. Using a Variable for Counting Let's say that we're using a variable i to count the number of times that
Unit 2, Part 2 Definite Loops Computer Science S-111 Harvard University David G. Sullivan, Ph.D. Using a Variable for Counting Let's say that we're using a variable i to count the number of times that
CS 112 Introduction to Programming
 CS 112 Introduction to Programming (Spring 2012) Lecture #8: More on Conditional & Loop Zhong Shao Department of Computer Science Yale University Office: 314 Watson http://flint.cs.yale.edu/cs112 Acknowledgements:
CS 112 Introduction to Programming (Spring 2012) Lecture #8: More on Conditional & Loop Zhong Shao Department of Computer Science Yale University Office: 314 Watson http://flint.cs.yale.edu/cs112 Acknowledgements:
Chapter 4: Control structures. Repetition
 Chapter 4: Control structures Repetition Loop Statements After reading and studying this Section, student should be able to Implement repetition control in a program using while statements. Implement repetition
Chapter 4: Control structures Repetition Loop Statements After reading and studying this Section, student should be able to Implement repetition control in a program using while statements. Implement repetition
Flow of Control of Program Statements CS 112 Introduction to Programming. Basic if Conditional Statement Basic Test: Relational Operators
 Flow of Control of Program Statements CS 112 Introduction to Programming (Spring 2012) q Java provides two types of program flow of control statements: decision statements, or conditional statements: decide
Flow of Control of Program Statements CS 112 Introduction to Programming (Spring 2012) q Java provides two types of program flow of control statements: decision statements, or conditional statements: decide
1.4 Arrays. A Foundation for Programming. Arrays. Many Variables of the Same Type. This lecture. Store and manipulate huge quantities of data.
 A Foundation for Programming 1.4 Arrays any program you might want to write objects functions and modules graphics, sound, and image I/O arrays store and manipulate huge quantities of data conditionals
A Foundation for Programming 1.4 Arrays any program you might want to write objects functions and modules graphics, sound, and image I/O arrays store and manipulate huge quantities of data conditionals
Repetition with for loops
 Repetition with for loops So far, when we wanted to perform a task multiple times, we have written redundant code: System.out.println( Building Java Programs ); // print 5 blank lines System.out.println(
Repetition with for loops So far, when we wanted to perform a task multiple times, we have written redundant code: System.out.println( Building Java Programs ); // print 5 blank lines System.out.println(
Chapter 7. Iteration. 7.1 Multiple assignment
 Chapter 7 Iteration 7.1 Multiple assignment You can make more than one assignment to the same variable; effect is to replace the old value with the new. int bob = 5; System.out.print(bob); bob = 7; System.out.println(bob);
Chapter 7 Iteration 7.1 Multiple assignment You can make more than one assignment to the same variable; effect is to replace the old value with the new. int bob = 5; System.out.print(bob); bob = 7; System.out.println(bob);
2.3 Recursion. Overview. Greatest Common Divisor. Greatest Common Divisor. What is recursion? When one function calls itself directly or indirectly.
 Overview 2.3 Recursion What is recursion? When one function calls itself directly or indirectly. Why learn recursion? New mode of thinking. Powerful programming paradigm. Many computations are naturally
Overview 2.3 Recursion What is recursion? When one function calls itself directly or indirectly. Why learn recursion? New mode of thinking. Powerful programming paradigm. Many computations are naturally
CSC 1051 Villanova University. CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I. Course website:
 Repetition CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University Course website: www.csc.villanova.edu/~map/1051/ Some slides in this
Repetition CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University Course website: www.csc.villanova.edu/~map/1051/ Some slides in this
AP Computer Science Unit 3. Programs
 AP Computer Science Unit 3. Programs For most of these programs I m asking that you to limit what you print to the screen. This will help me in quickly running some tests on your code once you submit them
AP Computer Science Unit 3. Programs For most of these programs I m asking that you to limit what you print to the screen. This will help me in quickly running some tests on your code once you submit them
Running Time. Analytic Engine. Charles Babbage (1864) how many times do you have to turn the crank?
 4.1 Performance Introduction to Programming in Java: An Interdisciplinary Approach Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne Copyright 2008 March 30, 2009 7:37 tt Running Time As soon as an Analytic Engine exists,
4.1 Performance Introduction to Programming in Java: An Interdisciplinary Approach Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne Copyright 2008 March 30, 2009 7:37 tt Running Time As soon as an Analytic Engine exists,
2.3 Recursion. Overview. Greatest Common Divisor. Greatest Common Divisor. What is recursion? When one function calls itself directly or indirectly.
 Overview 2.3 Recursion What is recursion? When one function calls itself directly or indirectly. Why learn recursion? New mode of thinking. Powerful programming paradigm. Many computations are naturally
Overview 2.3 Recursion What is recursion? When one function calls itself directly or indirectly. Why learn recursion? New mode of thinking. Powerful programming paradigm. Many computations are naturally
Chapter 4: Control structures
 Chapter 4: Control structures Repetition Loop Statements After reading and studying this Section, student should be able to Implement repetition control in a program using while statements. Implement repetition
Chapter 4: Control structures Repetition Loop Statements After reading and studying this Section, student should be able to Implement repetition control in a program using while statements. Implement repetition
STUDENT LESSON A12 Iterations
 STUDENT LESSON A12 Iterations Java Curriculum for AP Computer Science, Student Lesson A12 1 STUDENT LESSON A12 Iterations INTRODUCTION: Solving problems on a computer very often requires a repetition of
STUDENT LESSON A12 Iterations Java Curriculum for AP Computer Science, Student Lesson A12 1 STUDENT LESSON A12 Iterations INTRODUCTION: Solving problems on a computer very often requires a repetition of
IT 1033: Fundamentals of Programming Loops
 IT 1033: Fundamentals of Programming Loops Budditha Hettige Department of Computer Science Repetitions: Loops A loop is a sequence of instruction s that is continually repeated until a certain condition
IT 1033: Fundamentals of Programming Loops Budditha Hettige Department of Computer Science Repetitions: Loops A loop is a sequence of instruction s that is continually repeated until a certain condition
1.4 Arrays. A Foundation for Programming. Many Variables of the Same Type. Arrays. !!! any program you might want to write
 A Foundation for Programming 1.4 Arrays any program you might want to write objects functions and modules graphics, sound, and image I/O arrays store and manipulate huge quantities of data conditionals
A Foundation for Programming 1.4 Arrays any program you might want to write objects functions and modules graphics, sound, and image I/O arrays store and manipulate huge quantities of data conditionals
2.3 Recursion. Overview. Mathematical Induction. What is recursion? When one function calls itself directly or indirectly.
 2.3 Recursion Overview Mathematical Induction What is recursion? When one function calls itself directly or indirectly. Why learn recursion? New mode of thinking. Powerful programming paradigm. Many computations
2.3 Recursion Overview Mathematical Induction What is recursion? When one function calls itself directly or indirectly. Why learn recursion? New mode of thinking. Powerful programming paradigm. Many computations
Lesson 39: Conditionals #3 (W11D4)
 Lesson 39: Conditionals #3 (W11D4) Balboa High School Michael Ferraro October 29, 2015 1 / 29 Do Now In order to qualify for a $50k loan, the following conditions must be met: Your annual income must be
Lesson 39: Conditionals #3 (W11D4) Balboa High School Michael Ferraro October 29, 2015 1 / 29 Do Now In order to qualify for a $50k loan, the following conditions must be met: Your annual income must be
COMP Flow of Control: Branching 2. Yi Hong May 19, 2015
 COMP 110-001 Flow of Control: Branching 2 Yi Hong May 19, 2015 Review if else Q1: Write a program that Reads an integer from user Prints Even if the integer is even Otherwise, prints Odd Boolean expression
COMP 110-001 Flow of Control: Branching 2 Yi Hong May 19, 2015 Review if else Q1: Write a program that Reads an integer from user Prints Even if the integer is even Otherwise, prints Odd Boolean expression
C212 Early Evaluation Exam Mon Feb Name: Please provide brief (common sense) justifications with your answers below.
 C212 Early Evaluation Exam Mon Feb 10 2014 Name: Please provide brief (common sense) justifications with your answers below. 1. What is the type (and value) of this expression: 5 * (7 + 4 / 2) 2. What
C212 Early Evaluation Exam Mon Feb 10 2014 Name: Please provide brief (common sense) justifications with your answers below. 1. What is the type (and value) of this expression: 5 * (7 + 4 / 2) 2. What
Michele Van Dyne Museum 204B CSCI 136: Fundamentals of Computer Science II, Spring
 Michele Van Dyne Museum 204B mvandyne@mtech.edu http://katie.mtech.edu/classes/csci136 CSCI 136: Fundamentals of Computer Science II, Spring 2016 1 Review of Java Basics Data Types Arrays NEW: multidimensional
Michele Van Dyne Museum 204B mvandyne@mtech.edu http://katie.mtech.edu/classes/csci136 CSCI 136: Fundamentals of Computer Science II, Spring 2016 1 Review of Java Basics Data Types Arrays NEW: multidimensional
Chapter 4 Lab. Loops and Files. Objectives. Introduction
 Chapter 4 Lab Loops and Files Objectives Be able to convert an algorithm using control structures into Java Be able to write a while loop Be able to write a do-while loop Be able to write a for loop Be
Chapter 4 Lab Loops and Files Objectives Be able to convert an algorithm using control structures into Java Be able to write a while loop Be able to write a do-while loop Be able to write a for loop Be
Recap: Assignment as an Operator CS 112 Introduction to Programming
 Recap: Assignment as an Operator CS 112 Introduction to Programming q You can consider assignment as an operator, with a (Spring 2012) lower precedence than the arithmetic operators First the expression
Recap: Assignment as an Operator CS 112 Introduction to Programming q You can consider assignment as an operator, with a (Spring 2012) lower precedence than the arithmetic operators First the expression
CONTENTS: While loops Class (static) variables and constants Top Down Programming For loops Nested Loops
 COMP-202 Unit 4: Programming with Iterations Doing the same thing again and again and again and again and again and again and again and again and again... CONTENTS: While loops Class (static) variables
COMP-202 Unit 4: Programming with Iterations Doing the same thing again and again and again and again and again and again and again and again and again... CONTENTS: While loops Class (static) variables
(Refer Slide Time: 1:27)
 Data Structures and Algorithms Dr. Naveen Garg Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi Lecture 1 Introduction to Data Structures and Algorithms Welcome to data
Data Structures and Algorithms Dr. Naveen Garg Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi Lecture 1 Introduction to Data Structures and Algorithms Welcome to data
true false Imperative Programming III, sections , 3.0, 3.9 Introductory Programming Control flow of programs While loops: generally Loops
 Introductory Programming Imperative Programming III, sections 3.6-3.8, 3.0, 3.9 Anne Haxthausen a IMM, DTU 1. Loops (while, do, for) (sections 3.6 3.8) 2. Overview of Java s (learnt so far) 3. Program
Introductory Programming Imperative Programming III, sections 3.6-3.8, 3.0, 3.9 Anne Haxthausen a IMM, DTU 1. Loops (while, do, for) (sections 3.6 3.8) 2. Overview of Java s (learnt so far) 3. Program
COMPUTER SCIENCE. 4. Arrays. Section 1.4.
 COMPUTER SCIENCE S E D G E W I C K / W A Y N E 4. Arrays Section 1.4 http://introcs.cs.princeton.edu Basic building blocks for programming any program you might want to write objects functions and modules
COMPUTER SCIENCE S E D G E W I C K / W A Y N E 4. Arrays Section 1.4 http://introcs.cs.princeton.edu Basic building blocks for programming any program you might want to write objects functions and modules
Object-Oriented Programming
 Object-Oriented Programming Java Syntax Program Structure Variables and basic data types. Industry standard naming conventions. Java syntax and coding conventions If Then Else Case statements Looping (for,
Object-Oriented Programming Java Syntax Program Structure Variables and basic data types. Industry standard naming conventions. Java syntax and coding conventions If Then Else Case statements Looping (for,
! New mode of thinking. ! Powerful programming paradigm. ! Mergesort, FFT, gcd. ! Linked data structures.
 Overview 2.3 Recursion What is recursion? When one function calls itself directly or indirectly. Why learn recursion? New mode of thinking. Powerful programming paradigm. Many computations are naturally
Overview 2.3 Recursion What is recursion? When one function calls itself directly or indirectly. Why learn recursion? New mode of thinking. Powerful programming paradigm. Many computations are naturally
Basic computer skills such as using Windows, Internet Explorer, and Microsoft Word. Chapter 1 Introduction to Computers, Programs, and Java
 Basic computer skills such as using Windows, Internet Explorer, and Microsoft Word Chapter 1 Introduction to Computers, Programs, and Java Chapter 2 Primitive Data Types and Operations Chapter 3 Selection
Basic computer skills such as using Windows, Internet Explorer, and Microsoft Word Chapter 1 Introduction to Computers, Programs, and Java Chapter 2 Primitive Data Types and Operations Chapter 3 Selection
Repetition, Looping. While Loop
 Repetition, Looping Last time we looked at how to use if-then statements to control the flow of a program. In this section we will look at different ways to repeat blocks of statements. Such repetitions
Repetition, Looping Last time we looked at how to use if-then statements to control the flow of a program. In this section we will look at different ways to repeat blocks of statements. Such repetitions
The keyword list thus far: The Random class. Generating "Random" Numbers. Topic 16
 Topic 16 Creating Correct Programs "It is a profoundly erroneous truism, repeated by all the copybooks, and by eminent people when they are making speeches, that we should cultivate the habit of thinking
Topic 16 Creating Correct Programs "It is a profoundly erroneous truism, repeated by all the copybooks, and by eminent people when they are making speeches, that we should cultivate the habit of thinking
APCS-AB: Java. Recursion in Java December 12, week14 1
 APCS-AB: Java Recursion in Java December 12, 2005 week14 1 Check point Double Linked List - extra project grade Must turn in today MBCS - Chapter 1 Installation Exercises Analysis Questions week14 2 Scheme
APCS-AB: Java Recursion in Java December 12, 2005 week14 1 Check point Double Linked List - extra project grade Must turn in today MBCS - Chapter 1 Installation Exercises Analysis Questions week14 2 Scheme
2.3 Recursion 7/23/2015 3:06:35 PM
 3 Recursion Introduction to Programming in Java: An Interdisciplinary Approach Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne Copyright 2002 2010 7/23/2015 3:06:35 PM Factorial The factorial of a positive integer N
3 Recursion Introduction to Programming in Java: An Interdisciplinary Approach Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne Copyright 2002 2010 7/23/2015 3:06:35 PM Factorial The factorial of a positive integer N
CS 112 Introduction to Programming
 CS 112 Introduction to Programming (Spring 2012) Lecture #7: Variable Scope, Constants, and Loops Zhong Shao Department of Computer Science Yale University Office: 314 Watson http://flint.cs.yale.edu/cs112
CS 112 Introduction to Programming (Spring 2012) Lecture #7: Variable Scope, Constants, and Loops Zhong Shao Department of Computer Science Yale University Office: 314 Watson http://flint.cs.yale.edu/cs112
All copyrights reserved - KV NAD, Aluva. Dinesh Kumar Ram PGT(CS) KV NAD Aluva
 All copyrights reserved - KV NAD, Aluva Dinesh Kumar Ram PGT(CS) KV NAD Aluva Overview Looping Introduction While loops Syntax Examples Points to Observe Infinite Loops Examples using while loops do..
All copyrights reserved - KV NAD, Aluva Dinesh Kumar Ram PGT(CS) KV NAD Aluva Overview Looping Introduction While loops Syntax Examples Points to Observe Infinite Loops Examples using while loops do..
Topic 16. battle -they are strictly limited in number, they require fresh horses, and must only be made at decisive moments." -Alfred North Whitehead
 Topic 16 Creating Correct Programs "It is a profoundly erroneous truism, repeated by all the copybooks, and by eminent people when they are making speeches, that we should cultivate the habit of thinking
Topic 16 Creating Correct Programs "It is a profoundly erroneous truism, repeated by all the copybooks, and by eminent people when they are making speeches, that we should cultivate the habit of thinking
Warmup : Name that tune!
 Warmup : Name that tune! Write, using a loop, Java code to print the lyrics to the song 99 Bottles of Beer on the Wall 99 bottles of beer on the wall. 99 bottles of beer. Take one down, pass it around,
Warmup : Name that tune! Write, using a loop, Java code to print the lyrics to the song 99 Bottles of Beer on the Wall 99 bottles of beer on the wall. 99 bottles of beer. Take one down, pass it around,
Algorithms. Abdelghani Bellaachia, CSCI 1121 Page: 1
 Algorithms 1. Objectives... 2 2. Design You Solution... 2 3. Structure of an algorithm:... 3 4. Pseudocode:... 4 5. Example... 5 6. Selection or Conditional Execution... 8 7. Looping or Iteration... 9
Algorithms 1. Objectives... 2 2. Design You Solution... 2 3. Structure of an algorithm:... 3 4. Pseudocode:... 4 5. Example... 5 6. Selection or Conditional Execution... 8 7. Looping or Iteration... 9
Module 2: Choice and Iteration
 Module 2: Choice and Iteration Ron K. Cytron * Department of Computer Science and Engineering * Washington University in Saint Louis Thanks to Alan Waldman for comments that improved these slides Prepared
Module 2: Choice and Iteration Ron K. Cytron * Department of Computer Science and Engineering * Washington University in Saint Louis Thanks to Alan Waldman for comments that improved these slides Prepared
Introduction to the Java Basics: Control Flow Statements
 Lesson 3: Introduction to the Java Basics: Control Flow Statements Repetition Structures THEORY Variable Assignment You can only assign a value to a variable that is consistent with the variable s declared
Lesson 3: Introduction to the Java Basics: Control Flow Statements Repetition Structures THEORY Variable Assignment You can only assign a value to a variable that is consistent with the variable s declared
