Local Search and Constraint Reasoning. CS 510 Lecture 3 October 6, 2009
|
|
|
- August Little
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Warm Up A* Exercise In groups, draw the tree that A* builds to find a path from Oradea to Bucharest marking g, h, and f for each node. Use straight-line distance as h(n) In what order are the nodes expanded? What is the path found?
2 Local Search and Constraint Reasoning CS 510 Lecture 3 October 6, 2009
3 Reminder Project proposal : due next week before class (mail me a pdf) send draft of project proposal after class to peer review partners send feedback to partners on proposal by thursday night
4 Reminder Midterm : 2 weeks from today (Oct 20) Will cover book, lectures, readings Ch 1-3, , 5-6, 17.6 Open book/note (not open device) Practice [2.2, 2.5, 3.1, 3.8, 4.1, 4.2, 4.4, 5.5b, 5.6, 6.2, 6.3abc, 17.9, 17.13]
5 Overview Local Search (Hill climbing, simulated annealing, genetic algorithms) Constraint Reasoning (Constraint Satisfaction problems (CSP), constraint optimization (COP), Distributed COP Project groups Paper discussion
6 Local Search In many optimization problems, the path to the goal is irrelevant; the goal state itself is the solution State space = set of "complete" configurations Find configuration satisfying constraints, e.g., n- queens In such cases, we can use local search algorithms keep a single "current" state, try to improve it
7 Example: n-queens Put n queens on an n n board with no two queens on the same row, column, or diagonal
8 Hill-Climbing Search "Like climbing Everest in thick fog with amnesia"
9 Hill-climbing search Problem: depending on initial state, can get stuck in local maxima
10 Hill-climbing search 8-queens problem h = number of pairs of queens that are attacking each other, either directly or indirectly h = 17 for the above state
11 Hill-climbing search 8-queens problem A local minimum with h=1
12 Annealing in Metallurgy Remove crystal dislocations in metal Heat the material - cause atoms to become unstuck from position Then slowly cool, atoms wander try to find configurations with lower energy
13 Simulate this process to escape local minima Replace solution with nearby solution How nearby depends on temperature Heat - nearly random solution Slowly cool - gradually improve
14 Simulated annealing search Idea: escape local maxima by allowing some "bad" moves but gradually decrease their frequency
15 Properties of Simulated annealing search One can prove: If T decreases slowly enough, then simulated annealing search will find a global optimum with probability approaching 1 Widely used in VLSI layout, airline scheduling, etc
16 Local beam search Keep track of k states rather than just one Start with k randomly generated states At each iteration, all the successors of all k states are generated If any one is a goal state, stop; else select the k best successors from the complete list and repeat.
17 Genetic Algorithms A successor state is generated by combining two parent states Start with k randomly generated states (population) A state is represented as a string over a finite alphabet (often a string of 0s and 1s) Evaluation function (fitness function). Higher values for better states. Produce the next generation of states by selection, crossover, and mutation
18 Genetic algorithms Fitness function: number of non-attacking pairs of queens (min = 0, max = 8 7/2 = 28) 24/( ) = 31% 23/( ) = 29% etc
19 Genetic algorithms
20 Constraint Reasoning
21 Constraint Satisfaction Problem (CSP) Variables: V1,V2,V3...with domains D1, D2, D3 Constraints: Set of allowed value pairs V1 not equal V2 = {(red,blue),(green, blue,(green, red)} Solution: Assign values to variables that satisfy all constraints V1=red, V2=blue, V3=green V1 = = D1={red, green} V2 D2={blue,red} V3 D3={green}
22 3SAT as CSP xi are variables values are true and false Constraints expressed in conjunctive normal form ex 1: (x1 v x2 v x3) ^ (~x1 v ~x2 v ~x3) ^ (~x1 v x2 v ~x3) ex 2: (x1 v ~x2) ^ (~x1 v ~x2) ^ (~x1 v ~x2)
23 Class Exercise Formulate the 4 queens problem as a CSP variables values constraints
24 What if no solution? Or multiple solutions? If no solution, minimize broken constraints? If multiple solutions, some solutions may be preferred Gives rise to the Constraint Optimization Problem
25 Constraint Optimization Constraints have degrees of violation (or degrees of satisfaction) Goal is to minimize violation (or maximize satisfaction) Significantly generalizes CSPs
26 Constraint Optimization Problem (COP) Given: Variables (x1,x2,...,xn) Finite, discrete domains (D1,D2,...,Dn) Foreach xi, xj: Valued constraint function fij: Di x Dj N
27 Constraint Optimization(COP) Goal: Find complete solution: an assignment A that minimizes F(A) where F(A) = Sum(fij(di,dj), xi di, xj dj in A Example: di dj f(di,dj) F(A)= F(A)=6 1 2 F(A)=
28 Example: Map Coloring Variables WA, NT, Q, NSW, V, SA, T Domains Di = {red,green,blue} Constraints: adjacent regions must have different colors e.g., WA NT, or (WA,NT) in {(red,green), (red,blue),(green,red), (green,blue), (blue,red),(blue,green)}
29 Examples: Map Coloring Solutions are complete and consistent assignments, e.g., WA = red, NT = green,q = red,nsw = green,v = red,sa = blue,t = green
30 Constraint Graph Binary CSP: each constraint relates two variables Constraint graph: nodes are variables, arcs are constraints
31 CSP as search Initial State: Empty assignment {} Successor Function: Assign value to an unassigned variable Goal Test: Complete assignment that does not violate any constraints Path Cost: Constant for each step
32 Backtracking Search Basically DFS Map coloring (no adjacent regions the same color)
33 Improving efficiency General-purpose heuristics can give huge gains in speed: Which variable should be assigned next? In what order should its values be tried? Can we detect inevitable failure early?
34 Most Constrained Variable Most constrained variable: choose the variable with the fewest legal values a.k.a. minimum remaining values (MRV) heuristic
35 Most Constraining Variable Tie-breaker among most constrained variables Most constraining variable: Choose the variable with the most constraints on remaining variables
36 Least constraining variable assignment Given a variable, choose the least constraining value: the one that rules out the fewest values in the remaining variables Combining these heuristics makes 1000 queens possible (as opposed to about 25)
37 Forward Checking Idea: Keep track of remaining legal values for unassigned variables Terminate search when any variable has no legal values
38 Forward Checking Idea: Keep track of remaining legal values for unassigned variables Terminate search when any variable has no legal values
39 Constraint Propagation Forward checking propagates information from assigned to unassigned variables, but doesn't provide early detection for all failures: NT and SA cannot both be blue! Constraint propagation repeatedly enforces constraints locally
40 Arc Consistency Simplest form of propagation makes each arc consistent X Y is consistent iff for every value x of X there is some allowed y
41 Arc Consistency Simplest form of propagation makes each arc consistent X Y is consistent iff for every value x of X there is some allowed y If X loses a value, neighbors of X must be rechecked
42 Arc Consistency Simplest form of propagation makes each arc consistent X Y is consistent iff for every value x of X there is some allowed y If X loses a value, neighbors of X must be rechecked Detects failures quicker than forward checking
43 Local Search for CSPs Hill-climbing, simulated annealing typically work with "complete" states, i.e., all variables assigned To apply to CSPs: allow states with unsatisfied constraints operators reassign variable values Variable selection: randomly select any conflicted variable Value selection by min-conflicts heuristic: choose value that violates the fewest constraints i.e., hill-climb with h(n) = total number of violated constraints
44 Example: 4 Queens States: 4 queens in 4 columns (4 4 = 256 states) Actions: move queen in column Goal test: no attacks Evaluation: h(n) = number of attacks Given random initial state, can solve n-queens in almost constant time for arbitrary n with high probability (e.g., n = 10,000,000)
45 Distributed Optimization Problem How do a set of agents optimize over a set of alternatives that have varying degrees of global quality? Examples allocating resources constructing schedules planning activities Difficulties No global control/knowledge Localized communication Quality guarantees required Limited Time 45
46 Interesting Research Questions How to evaluate performance? Cycles, CBR, CCC, etc? How much distribution counts? OptAPO? Local approximations of optimization How to apply DCR to new domains? More flexible DCOP? multiply constrained, resource constraints? Privacy? 46
47 Privacy in Constraint Optimization Common model for automated coordination Assign values to variables, subject to constraints Problems Constraints may be personal or proprietary Current algorithms not designed for privacy NP-hard! 47
48 Eucalyptus Grower Supply Chain Bundled leaves Transport Company Gas Packed leaves Distributor Corn Farmer Bundled corn Transport Company Packed leaves Alcohol Shipping Company Bundled corn Need to coordinate when to send and how much Wholesaler Tanked alcohol Retailer 48
49 Algs: Asynchronous Backtracking (ABT) Not DCOP, constraint satisfaction Agents form communication/priority chain Pass down tentative assignments (ok? messages) If value inconsistent with higher agents, change Pass up violations (nogood messages) nogoods causes higher agents to change value All happens concurrently 49
50 Synchronous Branch and Bound (SynchBB) Simulate branch and bound in distributed environment Messages sent in predefined, sequential order First agent sends a partial solution (one variable) Next agent adds variable, evaluates If < bound (best complete solution cost), send on If > bound, try new values If all values tried, backtrack 50
51 Synchronous Iterative Deepening (SynchID) Simulates iterative deepening First agent picks value, sends it and cost limit (initially 0) to next agent Next agent tries to find value under limit If succeed, pass on values, limit to next agent If fail, backtrack up and increase the limit 51
52 Adopt (Asynchronous Optimization) Agents organized in tree, not chain, constraints between ancestors/descendants not siblings When agents receive messages choose value with min cost send VALUE message to descendants send COST message to parents send THRESHOLD message to child 52
53 DPOP (Dynamic Pseudotree) Same tree as Adopt, but sequential Dynamic programming/variable elimination approach Each agent sends only one message up (with constraint information) and then one message down (with value information) 53
54 Project Groups (Stacey) and (Dan and Brian) (Balaji and Huiqing) and (Melissa, Anya, and Yiannis) (Raffi, Lenrik, and Andrew) and (Kevin) Alexis, Olufunke, and Rich 54
55 Discussion: PageRank and Eigenvalues Create matrix whose values aij are the number of backlinks into page i from page j divided by number of forward links of page j. a14 = 1 link from page 4/2 total links from page 4 = 1/2 To get page rank find eigenvector Ax=lambda(x) where lambda =1 (eigenvalue) 55
56 Discussion: PageRank and Eigenvalues To get page rank find eigenvector Ax=lambda(x) where lambda =1 (eigenvalue) A [ ] = [ ] All multiples of eigenvectors are eigenvectors (normalize to fraction) [12/31 4/31 9/31 6/31] 56
57 Page Rank Have to add in E to fix link problems Vector [ ] for democratic E or [x 0 0 0] for specific E rank now c(a + E x 1)R = R still looking for an eigenvector just more complex one 57
58 Iterating Rank R0 = [ ] R1 = df R0 R1 = [ ] d = R1 = R1 + [ ] v = sqrt(v1 2 + v vn 2 ) delta = [ ]
59 Is PageRank Admissible? How does the type of search talked about here connect with the other search algorithms we ve studied?
60 Customized PageRank Where does google customize pagerank today? What are the pitfalls of this? 60
Constraint Satisfaction Problems
 Constraint Satisfaction Problems Chapter 5 Section 1 3 Constraint Satisfaction 1 Outline Constraint Satisfaction Problems (CSP) Backtracking search for CSPs Local search for CSPs Constraint Satisfaction
Constraint Satisfaction Problems Chapter 5 Section 1 3 Constraint Satisfaction 1 Outline Constraint Satisfaction Problems (CSP) Backtracking search for CSPs Local search for CSPs Constraint Satisfaction
Constraint Satisfaction Problems. A Quick Overview (based on AIMA book slides)
 Constraint Satisfaction Problems A Quick Overview (based on AIMA book slides) Constraint satisfaction problems What is a CSP? Finite set of variables V, V 2,, V n Nonempty domain of possible values for
Constraint Satisfaction Problems A Quick Overview (based on AIMA book slides) Constraint satisfaction problems What is a CSP? Finite set of variables V, V 2,, V n Nonempty domain of possible values for
CS W4701 Artificial Intelligence
 CS W4701 Artificial Intelligence Fall 2013 Chapter 6: Constraint Satisfaction Problems Jonathan Voris (based on slides by Sal Stolfo) Assignment 3 Go Encircling Game Ancient Chinese game Dates back At
CS W4701 Artificial Intelligence Fall 2013 Chapter 6: Constraint Satisfaction Problems Jonathan Voris (based on slides by Sal Stolfo) Assignment 3 Go Encircling Game Ancient Chinese game Dates back At
Constraint Satisfaction Problems Part 2
 Constraint Satisfaction Problems Part 2 Deepak Kumar October 2017 CSP Formulation (as a special case of search) State is defined by n variables x 1, x 2,, x n Variables can take on values from a domain
Constraint Satisfaction Problems Part 2 Deepak Kumar October 2017 CSP Formulation (as a special case of search) State is defined by n variables x 1, x 2,, x n Variables can take on values from a domain
What is Search For? CSE 473: Artificial Intelligence. Example: N-Queens. Example: N-Queens. Example: Map-Coloring 4/7/17
 CSE 473: Artificial Intelligence Constraint Satisfaction Dieter Fox What is Search For? Models of the world: single agent, deterministic actions, fully observed state, discrete state space Planning: sequences
CSE 473: Artificial Intelligence Constraint Satisfaction Dieter Fox What is Search For? Models of the world: single agent, deterministic actions, fully observed state, discrete state space Planning: sequences
Constraint Satisfaction Problems (CSPs)
 1 Hal Daumé III (me@hal3.name) Constraint Satisfaction Problems (CSPs) Hal Daumé III Computer Science University of Maryland me@hal3.name CS 421: Introduction to Artificial Intelligence 7 Feb 2012 Many
1 Hal Daumé III (me@hal3.name) Constraint Satisfaction Problems (CSPs) Hal Daumé III Computer Science University of Maryland me@hal3.name CS 421: Introduction to Artificial Intelligence 7 Feb 2012 Many
CSE 473: Artificial Intelligence
 CSE 473: Artificial Intelligence Constraint Satisfaction Luke Zettlemoyer Multiple slides adapted from Dan Klein, Stuart Russell or Andrew Moore What is Search For? Models of the world: single agent, deterministic
CSE 473: Artificial Intelligence Constraint Satisfaction Luke Zettlemoyer Multiple slides adapted from Dan Klein, Stuart Russell or Andrew Moore What is Search For? Models of the world: single agent, deterministic
Week 8: Constraint Satisfaction Problems
 COMP3411/ 9414/ 9814: Artificial Intelligence Week 8: Constraint Satisfaction Problems [Russell & Norvig: 6.1,6.2,6.3,6.4,4.1] COMP3411/9414/9814 18s1 Constraint Satisfaction Problems 1 Outline Constraint
COMP3411/ 9414/ 9814: Artificial Intelligence Week 8: Constraint Satisfaction Problems [Russell & Norvig: 6.1,6.2,6.3,6.4,4.1] COMP3411/9414/9814 18s1 Constraint Satisfaction Problems 1 Outline Constraint
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall 2008
 CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall 2008 Lecture 4: CSPs 9/9/2008 Dan Klein UC Berkeley Many slides over the course adapted from either Stuart Russell or Andrew Moore 1 1 Announcements Grading questions:
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall 2008 Lecture 4: CSPs 9/9/2008 Dan Klein UC Berkeley Many slides over the course adapted from either Stuart Russell or Andrew Moore 1 1 Announcements Grading questions:
Announcements. CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall Large Scale: Problems with A* What is Search For? Example: N-Queens
 CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall 2008 Announcements Grading questions: don t panic, talk to us Newsgroup: check it out Lecture 4: CSPs 9/9/2008 Dan Klein UC Berkeley Many slides over the course adapted
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall 2008 Announcements Grading questions: don t panic, talk to us Newsgroup: check it out Lecture 4: CSPs 9/9/2008 Dan Klein UC Berkeley Many slides over the course adapted
Lecture 6: Constraint Satisfaction Problems (CSPs)
 Lecture 6: Constraint Satisfaction Problems (CSPs) CS 580 (001) - Spring 2018 Amarda Shehu Department of Computer Science George Mason University, Fairfax, VA, USA February 28, 2018 Amarda Shehu (580)
Lecture 6: Constraint Satisfaction Problems (CSPs) CS 580 (001) - Spring 2018 Amarda Shehu Department of Computer Science George Mason University, Fairfax, VA, USA February 28, 2018 Amarda Shehu (580)
Constraint Satisfaction
 Constraint Satisfaction Philipp Koehn 1 October 2015 Outline 1 Constraint satisfaction problems (CSP) examples Backtracking search for CSPs Problem structure and problem decomposition Local search for
Constraint Satisfaction Philipp Koehn 1 October 2015 Outline 1 Constraint satisfaction problems (CSP) examples Backtracking search for CSPs Problem structure and problem decomposition Local search for
Constraint Satisfaction Problems
 Last update: February 25, 2010 Constraint Satisfaction Problems CMSC 421, Chapter 5 CMSC 421, Chapter 5 1 Outline CSP examples Backtracking search for CSPs Problem structure and problem decomposition Local
Last update: February 25, 2010 Constraint Satisfaction Problems CMSC 421, Chapter 5 CMSC 421, Chapter 5 1 Outline CSP examples Backtracking search for CSPs Problem structure and problem decomposition Local
Informed search algorithms. Chapter 4
 Informed search algorithms Chapter 4 Material Chapter 4 Section 1 - Exclude memory-bounded heuristic search 3 Outline Best-first search Greedy best-first search A * search Heuristics Local search algorithms
Informed search algorithms Chapter 4 Material Chapter 4 Section 1 - Exclude memory-bounded heuristic search 3 Outline Best-first search Greedy best-first search A * search Heuristics Local search algorithms
Constraint Satisfaction Problems
 Constraint Satisfaction Problems Chapter 5 Chapter 5 1 Outline CSP examples Backtracking search for CSPs Problem structure and problem decomposition Local search for CSPs Chapter 5 2 Constraint satisfaction
Constraint Satisfaction Problems Chapter 5 Chapter 5 1 Outline CSP examples Backtracking search for CSPs Problem structure and problem decomposition Local search for CSPs Chapter 5 2 Constraint satisfaction
10/11/2017. Constraint Satisfaction Problems II. Review: CSP Representations. Heuristic 1: Most constrained variable
 //7 Review: Constraint Satisfaction Problems Constraint Satisfaction Problems II AIMA: Chapter 6 A CSP consists of: Finite set of X, X,, X n Nonempty domain of possible values for each variable D, D, D
//7 Review: Constraint Satisfaction Problems Constraint Satisfaction Problems II AIMA: Chapter 6 A CSP consists of: Finite set of X, X,, X n Nonempty domain of possible values for each variable D, D, D
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Spring Announcements
 CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Spring 2006 Lecture 4: CSPs 9/7/2006 Dan Klein UC Berkeley Many slides over the course adapted from either Stuart Russell or Andrew Moore Announcements Reminder: Project
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Spring 2006 Lecture 4: CSPs 9/7/2006 Dan Klein UC Berkeley Many slides over the course adapted from either Stuart Russell or Andrew Moore Announcements Reminder: Project
Material. Thought Question. Outline For Today. Example: Map-Coloring EE562 ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE FOR ENGINEERS
 EE562 ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE FOR ENGINEERS Lecture 6, 4/20/2005 University of Washington, Department of Electrical Engineering Spring 2005 Instructor: Professor Jeff A. Bilmes Material Read all of chapter
EE562 ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE FOR ENGINEERS Lecture 6, 4/20/2005 University of Washington, Department of Electrical Engineering Spring 2005 Instructor: Professor Jeff A. Bilmes Material Read all of chapter
Announcements. CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall Reminder: CSPs. Today. Example: 3-SAT. Example: Boolean Satisfiability.
 CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall 2008 Lecture 5: CSPs II 9/11/2008 Announcements Assignments: DUE W1: NOW P1: Due 9/12 at 11:59pm Assignments: UP W2: Up now P2: Up by weekend Dan Klein UC Berkeley
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall 2008 Lecture 5: CSPs II 9/11/2008 Announcements Assignments: DUE W1: NOW P1: Due 9/12 at 11:59pm Assignments: UP W2: Up now P2: Up by weekend Dan Klein UC Berkeley
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall 2008
 CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall 2008 Lecture 5: CSPs II 9/11/2008 Dan Klein UC Berkeley Many slides over the course adapted from either Stuart Russell or Andrew Moore 1 1 Assignments: DUE Announcements
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall 2008 Lecture 5: CSPs II 9/11/2008 Dan Klein UC Berkeley Many slides over the course adapted from either Stuart Russell or Andrew Moore 1 1 Assignments: DUE Announcements
Constraint Satisfaction Problems
 Revised by Hankui Zhuo, March 14, 2018 Constraint Satisfaction Problems Chapter 5 Chapter 5 1 Outline CSP examples Backtracking search for CSPs Problem structure and problem decomposition Local search
Revised by Hankui Zhuo, March 14, 2018 Constraint Satisfaction Problems Chapter 5 Chapter 5 1 Outline CSP examples Backtracking search for CSPs Problem structure and problem decomposition Local search
Example: Map-Coloring. Constraint Satisfaction Problems Western Australia. Example: Map-Coloring contd. Outline. Constraint graph
 Example: Map-Coloring Constraint Satisfaction Problems Western Northern erritory ueensland Chapter 5 South New South Wales asmania Variables, N,,, V, SA, Domains D i = {red,green,blue} Constraints: adjacent
Example: Map-Coloring Constraint Satisfaction Problems Western Northern erritory ueensland Chapter 5 South New South Wales asmania Variables, N,,, V, SA, Domains D i = {red,green,blue} Constraints: adjacent
Constraint Satisfaction Problems
 Constraint Satisfaction Problems Chapter 5 Chapter 5 1 Outline CSP examples Backtracking search for CSPs Problem structure and problem decomposition Local search for CSPs Chapter 5 2 Constraint satisfaction
Constraint Satisfaction Problems Chapter 5 Chapter 5 1 Outline CSP examples Backtracking search for CSPs Problem structure and problem decomposition Local search for CSPs Chapter 5 2 Constraint satisfaction
Australia Western Australia Western Territory Northern Territory Northern Australia South Australia South Tasmania Queensland Tasmania Victoria
 Constraint Satisfaction Problems Chapter 5 Example: Map-Coloring Western Northern Territory South Queensland New South Wales Tasmania Variables WA, NT, Q, NSW, V, SA, T Domains D i = {red,green,blue} Constraints:
Constraint Satisfaction Problems Chapter 5 Example: Map-Coloring Western Northern Territory South Queensland New South Wales Tasmania Variables WA, NT, Q, NSW, V, SA, T Domains D i = {red,green,blue} Constraints:
Artificial Intelligence
 Artificial Intelligence Dr Ahmed Rafat Abas Computer Science Dept, Faculty of Computers and Informatics, Zagazig University arabas@zu.edu.eg http://www.arsaliem.faculty.zu.edu.eg/ Informed search algorithms
Artificial Intelligence Dr Ahmed Rafat Abas Computer Science Dept, Faculty of Computers and Informatics, Zagazig University arabas@zu.edu.eg http://www.arsaliem.faculty.zu.edu.eg/ Informed search algorithms
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence
 CS 188: Artificial Intelligence CSPs II + Local Search Prof. Scott Niekum The University of Texas at Austin [These slides based on those of Dan Klein and Pieter Abbeel for CS188 Intro to AI at UC Berkeley.
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence CSPs II + Local Search Prof. Scott Niekum The University of Texas at Austin [These slides based on those of Dan Klein and Pieter Abbeel for CS188 Intro to AI at UC Berkeley.
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall 2011
 CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall 2011 Lecture 5: CSPs II 9/8/2011 Dan Klein UC Berkeley Multiple slides over the course adapted from either Stuart Russell or Andrew Moore 1 Today Efficient Solution
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall 2011 Lecture 5: CSPs II 9/8/2011 Dan Klein UC Berkeley Multiple slides over the course adapted from either Stuart Russell or Andrew Moore 1 Today Efficient Solution
Announcements. CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall 2010
 Announcements Project 1: Search is due Monday Looking for partners? After class or newsgroup Written 1: Search and CSPs out soon Newsgroup: check it out CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall 2010 Lecture
Announcements Project 1: Search is due Monday Looking for partners? After class or newsgroup Written 1: Search and CSPs out soon Newsgroup: check it out CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall 2010 Lecture
Announcements. CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Spring Today. A* Review. Consistency. A* Graph Search Gone Wrong
 CS 88: Artificial Intelligence Spring 2009 Lecture 4: Constraint Satisfaction /29/2009 John DeNero UC Berkeley Slides adapted from Dan Klein, Stuart Russell or Andrew Moore Announcements The Python tutorial
CS 88: Artificial Intelligence Spring 2009 Lecture 4: Constraint Satisfaction /29/2009 John DeNero UC Berkeley Slides adapted from Dan Klein, Stuart Russell or Andrew Moore Announcements The Python tutorial
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence. Recap: Search
 CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Lecture 4 and 5: Constraint Satisfaction Problems (CSPs) Pieter Abbeel UC Berkeley Many slides from Dan Klein Recap: Search Search problem: States (configurations of the
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Lecture 4 and 5: Constraint Satisfaction Problems (CSPs) Pieter Abbeel UC Berkeley Many slides from Dan Klein Recap: Search Search problem: States (configurations of the
Informed Search. Best-first search. Greedy best-first search. Intelligent Systems and HCI D7023E. Romania with step costs in km
 Informed Search Intelligent Systems and HCI D7023E Lecture 5: Informed Search (heuristics) Paweł Pietrzak [Sec 3.5-3.6,Ch.4] A search strategy which searches the most promising branches of the state-space
Informed Search Intelligent Systems and HCI D7023E Lecture 5: Informed Search (heuristics) Paweł Pietrzak [Sec 3.5-3.6,Ch.4] A search strategy which searches the most promising branches of the state-space
EE562 ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE FOR ENGINEERS
 EE562 ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE FOR ENGINEERS Lecture 4, 4/11/2005 University of Washington, Department of Electrical Engineering Spring 2005 Instructor: Professor Jeff A. Bilmes Today: Informed search algorithms
EE562 ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE FOR ENGINEERS Lecture 4, 4/11/2005 University of Washington, Department of Electrical Engineering Spring 2005 Instructor: Professor Jeff A. Bilmes Today: Informed search algorithms
Constraint Satisfaction Problems. Chapter 6
 Constraint Satisfaction Problems Chapter 6 Office hours Office hours for Assignment 1 (ASB9810 in CSIL): Sep 29th(Fri) 12:00 to 13:30 Oct 3rd(Tue) 11:30 to 13:00 Late homework policy You get four late
Constraint Satisfaction Problems Chapter 6 Office hours Office hours for Assignment 1 (ASB9810 in CSIL): Sep 29th(Fri) 12:00 to 13:30 Oct 3rd(Tue) 11:30 to 13:00 Late homework policy You get four late
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Spring Announcements
 CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Spring 2010 Lecture 4: A* wrap-up + Constraint Satisfaction 1/28/2010 Pieter Abbeel UC Berkeley Many slides from Dan Klein Announcements Project 0 (Python tutorial) is due
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Spring 2010 Lecture 4: A* wrap-up + Constraint Satisfaction 1/28/2010 Pieter Abbeel UC Berkeley Many slides from Dan Klein Announcements Project 0 (Python tutorial) is due
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall 2011
 Announcements Project 1: Search is due next week Written 1: Search and CSPs out soon Piazza: check it out if you haven t CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall 2011 Lecture 4: Constraint Satisfaction 9/6/2011
Announcements Project 1: Search is due next week Written 1: Search and CSPs out soon Piazza: check it out if you haven t CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall 2011 Lecture 4: Constraint Satisfaction 9/6/2011
Spezielle Themen der Künstlichen Intelligenz
 Spezielle Themen der Künstlichen Intelligenz 2. Termin: Constraint Satisfaction Dr. Stefan Kopp Center of Excellence Cognitive Interaction Technology AG A Recall: Best-first search Best-first search =
Spezielle Themen der Künstlichen Intelligenz 2. Termin: Constraint Satisfaction Dr. Stefan Kopp Center of Excellence Cognitive Interaction Technology AG A Recall: Best-first search Best-first search =
Informed search algorithms. (Based on slides by Oren Etzioni, Stuart Russell)
 Informed search algorithms (Based on slides by Oren Etzioni, Stuart Russell) The problem # Unique board configurations in search space 8-puzzle 9! = 362880 15-puzzle 16! = 20922789888000 10 13 24-puzzle
Informed search algorithms (Based on slides by Oren Etzioni, Stuart Russell) The problem # Unique board configurations in search space 8-puzzle 9! = 362880 15-puzzle 16! = 20922789888000 10 13 24-puzzle
ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE (CS 370D)
 Princess Nora University Faculty of Computer & Information Systems ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE (CS 370D) (CHAPTER-6) CONSTRAINT SATISFACTION PROBLEMS Outline What is a CSP CSP applications Backtracking search
Princess Nora University Faculty of Computer & Information Systems ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE (CS 370D) (CHAPTER-6) CONSTRAINT SATISFACTION PROBLEMS Outline What is a CSP CSP applications Backtracking search
Constraint Satisfaction Problems
 Constraint Satisfaction Problems Berlin Chen Department of Computer Science & Information Engineering National Taiwan Normal University References: 1. S. Russell and P. Norvig. Artificial Intelligence:
Constraint Satisfaction Problems Berlin Chen Department of Computer Science & Information Engineering National Taiwan Normal University References: 1. S. Russell and P. Norvig. Artificial Intelligence:
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence
 CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Constraint Satisfaction Problems II Instructors: Dan Klein and Pieter Abbeel University of California, Berkeley [These slides were created by Dan Klein and Pieter Abbeel
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Constraint Satisfaction Problems II Instructors: Dan Klein and Pieter Abbeel University of California, Berkeley [These slides were created by Dan Klein and Pieter Abbeel
CS 343: Artificial Intelligence
 CS 343: Artificial Intelligence Constraint Satisfaction Problems Prof. Scott Niekum The University of Texas at Austin [These slides are based on those of Dan Klein and Pieter Abbeel for CS188 Intro to
CS 343: Artificial Intelligence Constraint Satisfaction Problems Prof. Scott Niekum The University of Texas at Austin [These slides are based on those of Dan Klein and Pieter Abbeel for CS188 Intro to
Announcements. Reminder: CSPs. Today. Example: N-Queens. Example: Map-Coloring. Introduction to Artificial Intelligence
 Introduction to Artificial Intelligence 22.0472-001 Fall 2009 Lecture 5: Constraint Satisfaction Problems II Announcements Assignment due on Monday 11.59pm Email search.py and searchagent.py to me Next
Introduction to Artificial Intelligence 22.0472-001 Fall 2009 Lecture 5: Constraint Satisfaction Problems II Announcements Assignment due on Monday 11.59pm Email search.py and searchagent.py to me Next
What is Search For? CS 188: Artificial Intelligence. Constraint Satisfaction Problems
 CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Constraint Satisfaction Problems What is Search For? Assumptions about the world: a single agent, deterministic actions, fully observed state, discrete state space Planning:
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Constraint Satisfaction Problems What is Search For? Assumptions about the world: a single agent, deterministic actions, fully observed state, discrete state space Planning:
Outline. Best-first search
 Outline Best-first search Greedy best-first search A* search Heuristics Local search algorithms Hill-climbing search Beam search Simulated annealing search Genetic algorithms Constraint Satisfaction Problems
Outline Best-first search Greedy best-first search A* search Heuristics Local search algorithms Hill-climbing search Beam search Simulated annealing search Genetic algorithms Constraint Satisfaction Problems
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence. What is Search For? Constraint Satisfaction Problems. Constraint Satisfaction Problems
 CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Constraint Satisfaction Problems Constraint Satisfaction Problems N variables domain D constraints x 1 x 2 Instructor: Marco Alvarez University of Rhode Island (These slides
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Constraint Satisfaction Problems Constraint Satisfaction Problems N variables domain D constraints x 1 x 2 Instructor: Marco Alvarez University of Rhode Island (These slides
Announcements. Homework 1: Search. Project 1: Search. Midterm date and time has been set:
 Announcements Homework 1: Search Has been released! Due Monday, 2/1, at 11:59pm. On edx online, instant grading, submit as often as you like. Project 1: Search Has been released! Due Friday 2/5 at 5pm.
Announcements Homework 1: Search Has been released! Due Monday, 2/1, at 11:59pm. On edx online, instant grading, submit as often as you like. Project 1: Search Has been released! Due Friday 2/5 at 5pm.
Constraint Satisfaction Problems
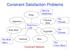 Constraint Satisfaction Problems Soup Must be Hot&Sour Appetizer Pork Dish Total Cost < $30 Chicken Dish Vegetable No Peanuts No Peanuts Not Both Spicy Seafood Rice Constraint Network Not Chow Mein 1 Formal
Constraint Satisfaction Problems Soup Must be Hot&Sour Appetizer Pork Dish Total Cost < $30 Chicken Dish Vegetable No Peanuts No Peanuts Not Both Spicy Seafood Rice Constraint Network Not Chow Mein 1 Formal
Announcements. Homework 4. Project 3. Due tonight at 11:59pm. Due 3/8 at 4:00pm
 Announcements Homework 4 Due tonight at 11:59pm Project 3 Due 3/8 at 4:00pm CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Constraint Satisfaction Problems Instructor: Stuart Russell & Sergey Levine, University of California,
Announcements Homework 4 Due tonight at 11:59pm Project 3 Due 3/8 at 4:00pm CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Constraint Satisfaction Problems Instructor: Stuart Russell & Sergey Levine, University of California,
CS 771 Artificial Intelligence. Constraint Satisfaction Problem
 CS 771 Artificial Intelligence Constraint Satisfaction Problem Constraint Satisfaction Problems So far we have seen a problem can be solved by searching in space of states These states can be evaluated
CS 771 Artificial Intelligence Constraint Satisfaction Problem Constraint Satisfaction Problems So far we have seen a problem can be solved by searching in space of states These states can be evaluated
Review Adversarial (Game) Search ( ) Review Constraint Satisfaction ( ) Please review your quizzes and old CS-271 tests
 Review Agents (2.1-2.3) Mid-term Review Chapters 2-6 Review State Space Search Problem Formulation (3.1, 3.3) Blind (Uninformed) Search (3.4) Heuristic Search (3.5) Local Search (4.1, 4.2) Review Adversarial
Review Agents (2.1-2.3) Mid-term Review Chapters 2-6 Review State Space Search Problem Formulation (3.1, 3.3) Blind (Uninformed) Search (3.4) Heuristic Search (3.5) Local Search (4.1, 4.2) Review Adversarial
Constraint Satisfaction. AI Slides (5e) c Lin
 Constraint Satisfaction 4 AI Slides (5e) c Lin Zuoquan@PKU 2003-2018 4 1 4 Constraint Satisfaction 4.1 Constraint satisfaction problems 4.2 Backtracking search 4.3 Constraint propagation 4.4 Local search
Constraint Satisfaction 4 AI Slides (5e) c Lin Zuoquan@PKU 2003-2018 4 1 4 Constraint Satisfaction 4.1 Constraint satisfaction problems 4.2 Backtracking search 4.3 Constraint propagation 4.4 Local search
Local Search and Optimization Chapter 4. Mausam (Based on slides of Padhraic Smyth, Stuart Russell, Rao Kambhampati, Raj Rao, Dan Weld )
 Local Search and Optimization Chapter 4 Mausam (Based on slides of Padhraic Smyth, Stuart Russell, Rao Kambhampati, Raj Rao, Dan Weld ) 1 Outline Local search techniques and optimization Hill-climbing
Local Search and Optimization Chapter 4 Mausam (Based on slides of Padhraic Smyth, Stuart Russell, Rao Kambhampati, Raj Rao, Dan Weld ) 1 Outline Local search techniques and optimization Hill-climbing
Iterative improvement algorithms. Today. Example: Travelling Salesperson Problem. Example: n-queens
 Today See Russell and Norvig, chapters 4 & 5 Local search and optimisation Constraint satisfaction problems (CSPs) CSP examples Backtracking search for CSPs 1 Iterative improvement algorithms In many optimization
Today See Russell and Norvig, chapters 4 & 5 Local search and optimisation Constraint satisfaction problems (CSPs) CSP examples Backtracking search for CSPs 1 Iterative improvement algorithms In many optimization
Constraint Satisfaction Problems
 Constraint Satisfaction Problems Tuomas Sandholm Carnegie Mellon University Computer Science Department [Read Chapter 6 of Russell & Norvig] Constraint satisfaction problems (CSPs) Standard search problem:
Constraint Satisfaction Problems Tuomas Sandholm Carnegie Mellon University Computer Science Department [Read Chapter 6 of Russell & Norvig] Constraint satisfaction problems (CSPs) Standard search problem:
Constraint Satisfaction Problems
 Constraint Satisfaction Problems CE417: Introduction to Artificial Intelligence Sharif University of Technology Spring 2013 Soleymani Course material: Artificial Intelligence: A Modern Approach, 3 rd Edition,
Constraint Satisfaction Problems CE417: Introduction to Artificial Intelligence Sharif University of Technology Spring 2013 Soleymani Course material: Artificial Intelligence: A Modern Approach, 3 rd Edition,
CS 4100 // artificial intelligence
 CS 4100 // artificial intelligence instructor: byron wallace Constraint Satisfaction Problems Attribution: many of these slides are modified versions of those distributed with the UC Berkeley CS188 materials
CS 4100 // artificial intelligence instructor: byron wallace Constraint Satisfaction Problems Attribution: many of these slides are modified versions of those distributed with the UC Berkeley CS188 materials
What is Search For? CS 188: Artificial Intelligence. Example: Map Coloring. Example: N-Queens. Example: N-Queens. Constraint Satisfaction Problems
 CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Constraint Satisfaction Problems What is Search For? Assumptions about the world: a single agent, deterministic actions, fully observed state, discrete state space Planning:
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Constraint Satisfaction Problems What is Search For? Assumptions about the world: a single agent, deterministic actions, fully observed state, discrete state space Planning:
Outline. Best-first search
 Outline Best-first search Greedy best-first search A* search Heuristics Local search algorithms Hill-climbing search Beam search Simulated annealing search Genetic algorithms Constraint Satisfaction Problems
Outline Best-first search Greedy best-first search A* search Heuristics Local search algorithms Hill-climbing search Beam search Simulated annealing search Genetic algorithms Constraint Satisfaction Problems
Beyond Classical Search: Local Search. CMPSCI 383 September 23, 2011
 Beyond Classical Search: Local Search CMPSCI 383 September 23, 2011 1 Today s lecture Local Search Hill-climbing Simulated annealing Local beam search Genetic algorithms Genetic programming Local search
Beyond Classical Search: Local Search CMPSCI 383 September 23, 2011 1 Today s lecture Local Search Hill-climbing Simulated annealing Local beam search Genetic algorithms Genetic programming Local search
2006/2007 Intelligent Systems 1. Intelligent Systems. Prof. dr. Paul De Bra Technische Universiteit Eindhoven
 test gamma 2006/2007 Intelligent Systems 1 Intelligent Systems Prof. dr. Paul De Bra Technische Universiteit Eindhoven debra@win.tue.nl 2006/2007 Intelligent Systems 2 Informed search and exploration Best-first
test gamma 2006/2007 Intelligent Systems 1 Intelligent Systems Prof. dr. Paul De Bra Technische Universiteit Eindhoven debra@win.tue.nl 2006/2007 Intelligent Systems 2 Informed search and exploration Best-first
Local Search and Optimization Chapter 4. Mausam (Based on slides of Padhraic Smyth, Stuart Russell, Rao Kambhampati, Raj Rao, Dan Weld )
 Local Search and Optimization Chapter 4 Mausam (Based on slides of Padhraic Smyth, Stuart Russell, Rao Kambhampati, Raj Rao, Dan Weld ) 1 2 Outline Local search techniques and optimization Hill-climbing
Local Search and Optimization Chapter 4 Mausam (Based on slides of Padhraic Smyth, Stuart Russell, Rao Kambhampati, Raj Rao, Dan Weld ) 1 2 Outline Local search techniques and optimization Hill-climbing
Announcements. CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Spring Today. Example: Map-Coloring. Example: Cryptarithmetic.
 CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Spring 2010 Lecture 5: CSPs II 2/2/2010 Pieter Abbeel UC Berkeley Many slides from Dan Klein Announcements Project 1 due Thursday Lecture videos reminder: don t count on
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Spring 2010 Lecture 5: CSPs II 2/2/2010 Pieter Abbeel UC Berkeley Many slides from Dan Klein Announcements Project 1 due Thursday Lecture videos reminder: don t count on
Local Search and Optimization Chapter 4. Mausam (Based on slides of Padhraic Smyth, Stuart Russell, Rao Kambhampati, Raj Rao, Dan Weld )
 Local Search and Optimization Chapter 4 Mausam (Based on slides of Padhraic Smyth, Stuart Russell, Rao Kambhampati, Raj Rao, Dan Weld ) 1 2 Outline Local search techniques and optimization Hill-climbing
Local Search and Optimization Chapter 4 Mausam (Based on slides of Padhraic Smyth, Stuart Russell, Rao Kambhampati, Raj Rao, Dan Weld ) 1 2 Outline Local search techniques and optimization Hill-climbing
CS 380: Artificial Intelligence Lecture #4
 CS 380: Artificial Intelligence Lecture #4 William Regli Material Chapter 4 Section 1-3 1 Outline Best-first search Greedy best-first search A * search Heuristics Local search algorithms Hill-climbing
CS 380: Artificial Intelligence Lecture #4 William Regli Material Chapter 4 Section 1-3 1 Outline Best-first search Greedy best-first search A * search Heuristics Local search algorithms Hill-climbing
Space of Search Strategies. CSE 573: Artificial Intelligence. Constraint Satisfaction. Recap: Search Problem. Example: Map-Coloring 11/30/2012
 /0/0 CSE 57: Artificial Intelligence Constraint Satisfaction Daniel Weld Slides adapted from Dan Klein, Stuart Russell, Andrew Moore & Luke Zettlemoyer Space of Search Strategies Blind Search DFS, BFS,
/0/0 CSE 57: Artificial Intelligence Constraint Satisfaction Daniel Weld Slides adapted from Dan Klein, Stuart Russell, Andrew Moore & Luke Zettlemoyer Space of Search Strategies Blind Search DFS, BFS,
Constraint Satisfaction. CS 486/686: Introduction to Artificial Intelligence
 Constraint Satisfaction CS 486/686: Introduction to Artificial Intelligence 1 Outline What are Constraint Satisfaction Problems (CSPs)? Standard Search and CSPs Improvements Backtracking Backtracking +
Constraint Satisfaction CS 486/686: Introduction to Artificial Intelligence 1 Outline What are Constraint Satisfaction Problems (CSPs)? Standard Search and CSPs Improvements Backtracking Backtracking +
Today. CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall Example: Boolean Satisfiability. Reminder: CSPs. Example: 3-SAT. CSPs: Queries.
 CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall 2007 Lecture 5: CSPs II 9/11/2007 More CSPs Applications Tree Algorithms Cutset Conditioning Today Dan Klein UC Berkeley Many slides over the course adapted from either
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall 2007 Lecture 5: CSPs II 9/11/2007 More CSPs Applications Tree Algorithms Cutset Conditioning Today Dan Klein UC Berkeley Many slides over the course adapted from either
Informed search algorithms. Chapter 4
 Informed search algorithms Chapter 4 Outline Best-first search Greedy best-first search A * search Heuristics Memory Bounded A* Search Best-first search Idea: use an evaluation function f(n) for each node
Informed search algorithms Chapter 4 Outline Best-first search Greedy best-first search A * search Heuristics Memory Bounded A* Search Best-first search Idea: use an evaluation function f(n) for each node
Artificial Intelligence
 Artificial Intelligence Local Search Vibhav Gogate The University of Texas at Dallas Some material courtesy of Luke Zettlemoyer, Dan Klein, Dan Weld, Alex Ihler, Stuart Russell, Mausam Systematic Search:
Artificial Intelligence Local Search Vibhav Gogate The University of Texas at Dallas Some material courtesy of Luke Zettlemoyer, Dan Klein, Dan Weld, Alex Ihler, Stuart Russell, Mausam Systematic Search:
Reading: Chapter 6 (3 rd ed.); Chapter 5 (2 nd ed.) For next week: Thursday: Chapter 8
 Constraint t Satisfaction Problems Reading: Chapter 6 (3 rd ed.); Chapter 5 (2 nd ed.) For next week: Tuesday: Chapter 7 Thursday: Chapter 8 Outline What is a CSP Backtracking for CSP Local search for
Constraint t Satisfaction Problems Reading: Chapter 6 (3 rd ed.); Chapter 5 (2 nd ed.) For next week: Tuesday: Chapter 7 Thursday: Chapter 8 Outline What is a CSP Backtracking for CSP Local search for
Games and Adversarial Search II Alpha-Beta Pruning (AIMA 5.3)
 Games and Adversarial Search II Alpha-Beta Pruning (AIMA 5.) Some slides adapted from Richard Lathrop, USC/ISI, CS 7 Review: The Minimax Rule Idea: Make the best move for MAX assuming that MIN always replies
Games and Adversarial Search II Alpha-Beta Pruning (AIMA 5.) Some slides adapted from Richard Lathrop, USC/ISI, CS 7 Review: The Minimax Rule Idea: Make the best move for MAX assuming that MIN always replies
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Spring Today
 CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Spring 2006 Lecture 7: CSPs II 2/7/2006 Dan Klein UC Berkeley Many slides from either Stuart Russell or Andrew Moore Today More CSPs Applications Tree Algorithms Cutset
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Spring 2006 Lecture 7: CSPs II 2/7/2006 Dan Klein UC Berkeley Many slides from either Stuart Russell or Andrew Moore Today More CSPs Applications Tree Algorithms Cutset
Chapter 6 Constraint Satisfaction Problems
 Chapter 6 Constraint Satisfaction Problems CS5811 - Artificial Intelligence Nilufer Onder Department of Computer Science Michigan Technological University Outline CSP problem definition Backtracking search
Chapter 6 Constraint Satisfaction Problems CS5811 - Artificial Intelligence Nilufer Onder Department of Computer Science Michigan Technological University Outline CSP problem definition Backtracking search
Announcements. CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Spring Production Scheduling. Today. Backtracking Search Review. Production Scheduling
 CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Spring 2009 Lecture : Constraint Satisfaction 2/3/2009 Announcements Project 1 (Search) is due tomorrow Come to office hours if you re stuck Today at 1pm (Nick) and 3pm
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Spring 2009 Lecture : Constraint Satisfaction 2/3/2009 Announcements Project 1 (Search) is due tomorrow Come to office hours if you re stuck Today at 1pm (Nick) and 3pm
Introduction to Artificial Intelligence 2 nd semester 2016/2017. Chapter 4: Beyond Classical Search
 Introduction to Artificial Intelligence 2 nd semester 2016/2017 Chapter 4: Beyond Classical Search Mohamed B. Abubaker Palestine Technical College Deir El-Balah 1 Outlines local search algorithms and optimization
Introduction to Artificial Intelligence 2 nd semester 2016/2017 Chapter 4: Beyond Classical Search Mohamed B. Abubaker Palestine Technical College Deir El-Balah 1 Outlines local search algorithms and optimization
Recap: Search Problem. CSE 473: Artificial Intelligence. Space of Search Strategies. Constraint Satisfaction. Example: N-Queens 4/9/2012
 CSE 473: Artificial Intelligence Constraint Satisfaction Daniel Weld Slides adapted from Dan Klein, Stuart Russell, Andrew Moore & Luke Zettlemoyer Recap: Search Problem States configurations of the world
CSE 473: Artificial Intelligence Constraint Satisfaction Daniel Weld Slides adapted from Dan Klein, Stuart Russell, Andrew Moore & Luke Zettlemoyer Recap: Search Problem States configurations of the world
Gradient Descent. 1) S! initial state 2) Repeat: Similar to: - hill climbing with h - gradient descent over continuous space
 Local Search 1 Local Search Light-memory search method No search tree; only the current state is represented! Only applicable to problems where the path is irrelevant (e.g., 8-queen), unless the path is
Local Search 1 Local Search Light-memory search method No search tree; only the current state is represented! Only applicable to problems where the path is irrelevant (e.g., 8-queen), unless the path is
Constraint Satisfaction Problems
 Constraint Satisfaction Problems Robert Platt Northeastern University Some images and slides are used from: 1. AIMA What is a CSP? The space of all search problems states and actions are atomic goals are
Constraint Satisfaction Problems Robert Platt Northeastern University Some images and slides are used from: 1. AIMA What is a CSP? The space of all search problems states and actions are atomic goals are
Outline. Best-first search. Greedy best-first search A* search Heuristics Local search algorithms
 Outline Best-first search Greedy best-first search A* search Heuristics Local search algorithms Hill-climbing search Beam search Simulated annealing search Genetic algorithms Constraint Satisfaction Problems
Outline Best-first search Greedy best-first search A* search Heuristics Local search algorithms Hill-climbing search Beam search Simulated annealing search Genetic algorithms Constraint Satisfaction Problems
DIT411/TIN175, Artificial Intelligence. Peter Ljunglöf. 30 January, 2018
 DIT411/TIN175, Artificial Intelligence Chapter 7: Constraint satisfaction problems CHAPTER 7: CONSTRAINT SATISFACTION PROBLEMS DIT411/TIN175, Artificial Intelligence Peter Ljunglöf 30 January, 2018 1 TABLE
DIT411/TIN175, Artificial Intelligence Chapter 7: Constraint satisfaction problems CHAPTER 7: CONSTRAINT SATISFACTION PROBLEMS DIT411/TIN175, Artificial Intelligence Peter Ljunglöf 30 January, 2018 1 TABLE
Lars Schmidt-Thieme, Information Systems and Machine Learning Lab (ISMLL), University of Hildesheim, Germany, Course on Artificial Intelligence,
 Course on Artificial Intelligence, winter term 2012/2013 0/35 Artificial Intelligence Artificial Intelligence 3. Constraint Satisfaction Problems Lars Schmidt-Thieme Information Systems and Machine Learning
Course on Artificial Intelligence, winter term 2012/2013 0/35 Artificial Intelligence Artificial Intelligence 3. Constraint Satisfaction Problems Lars Schmidt-Thieme Information Systems and Machine Learning
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence
 CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Constraint Satisfaction Problems II and Local Search Instructors: Sergey Levine and Stuart Russell University of California, Berkeley [These slides were created by Dan Klein
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Constraint Satisfaction Problems II and Local Search Instructors: Sergey Levine and Stuart Russell University of California, Berkeley [These slides were created by Dan Klein
ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE. Informed search
 INFOB2KI 2017-2018 Utrecht University The Netherlands ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE Informed search Lecturer: Silja Renooij These slides are part of the INFOB2KI Course Notes available from www.cs.uu.nl/docs/vakken/b2ki/schema.html
INFOB2KI 2017-2018 Utrecht University The Netherlands ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE Informed search Lecturer: Silja Renooij These slides are part of the INFOB2KI Course Notes available from www.cs.uu.nl/docs/vakken/b2ki/schema.html
Solving Problems: Intelligent Search
 Solving Problems: Intelligent Search Instructor: B. John Oommen Chancellor s Professor Fellow: IEEE; Fellow: IAPR School of Computer Science, Carleton University, Canada The primary source of these notes
Solving Problems: Intelligent Search Instructor: B. John Oommen Chancellor s Professor Fellow: IEEE; Fellow: IAPR School of Computer Science, Carleton University, Canada The primary source of these notes
Lecture 18. Questions? Monday, February 20 CS 430 Artificial Intelligence - Lecture 18 1
 Lecture 18 Questions? Monday, February 20 CS 430 Artificial Intelligence - Lecture 18 1 Outline Chapter 6 - Constraint Satisfaction Problems Path Consistency & Global Constraints Sudoku Example Backtracking
Lecture 18 Questions? Monday, February 20 CS 430 Artificial Intelligence - Lecture 18 1 Outline Chapter 6 - Constraint Satisfaction Problems Path Consistency & Global Constraints Sudoku Example Backtracking
CS 4100/5100: Foundations of AI
 CS 4100/5100: Foundations of AI Constraint satisfaction problems 1 Instructor: Rob Platt r.platt@neu.edu College of Computer and information Science Northeastern University September 5, 2013 1 These notes
CS 4100/5100: Foundations of AI Constraint satisfaction problems 1 Instructor: Rob Platt r.platt@neu.edu College of Computer and information Science Northeastern University September 5, 2013 1 These notes
Constraint Satisfaction Problems. slides from: Padhraic Smyth, Bryan Low, S. Russell and P. Norvig, Jean-Claude Latombe
 Constraint Satisfaction Problems slides from: Padhraic Smyth, Bryan Low, S. Russell and P. Norvig, Jean-Claude Latombe Standard search problems: State is a black box : arbitrary data structure Goal test
Constraint Satisfaction Problems slides from: Padhraic Smyth, Bryan Low, S. Russell and P. Norvig, Jean-Claude Latombe Standard search problems: State is a black box : arbitrary data structure Goal test
CS 331: Artificial Intelligence Local Search 1. Tough real-world problems
 CS 331: Artificial Intelligence Local Search 1 1 Tough real-world problems Suppose you had to solve VLSI layout problems (minimize distance between components, unused space, etc.) Or schedule airlines
CS 331: Artificial Intelligence Local Search 1 1 Tough real-world problems Suppose you had to solve VLSI layout problems (minimize distance between components, unused space, etc.) Or schedule airlines
Adopt Algorithm for Distributed Constraint Optimization
 Adopt Algorithm for Distributed Constraint Optimization Pragnesh Jay Modi Information Sciences Institute & Department of Computer Science University of Southern California http://www.isi.edu/~modi Distributed
Adopt Algorithm for Distributed Constraint Optimization Pragnesh Jay Modi Information Sciences Institute & Department of Computer Science University of Southern California http://www.isi.edu/~modi Distributed
Lecture Plan. Best-first search Greedy search A* search Designing heuristics. Hill-climbing. 1 Informed search strategies. Informed strategies
 Lecture Plan 1 Informed search strategies (KA AGH) 1 czerwca 2010 1 / 28 Blind vs. informed search strategies Blind search methods You already know them: BFS, DFS, UCS et al. They don t analyse the nodes
Lecture Plan 1 Informed search strategies (KA AGH) 1 czerwca 2010 1 / 28 Blind vs. informed search strategies Blind search methods You already know them: BFS, DFS, UCS et al. They don t analyse the nodes
Constraint Satisfaction Problems
 Constraint Satisfaction Problems In which we see how treating states as more than just little black boxes leads to the invention of a range of powerful new search methods and a deeper understanding of
Constraint Satisfaction Problems In which we see how treating states as more than just little black boxes leads to the invention of a range of powerful new search methods and a deeper understanding of
Discussion Section Week 1
 Discussion Section Week 1 Intro Course Project Information Constraint Satisfaction Problems Sudoku Backtracking Search Example Heuristics for guiding Search Example Intro Teaching Assistant Junkyu Lee
Discussion Section Week 1 Intro Course Project Information Constraint Satisfaction Problems Sudoku Backtracking Search Example Heuristics for guiding Search Example Intro Teaching Assistant Junkyu Lee
Constraints. CSC 411: AI Fall NC State University 1 / 53. Constraints
 CSC 411: AI Fall 2013 NC State University 1 / 53 Constraint satisfaction problems (CSPs) Standard search: state is a black box that supports goal testing, application of an evaluation function, production
CSC 411: AI Fall 2013 NC State University 1 / 53 Constraint satisfaction problems (CSPs) Standard search: state is a black box that supports goal testing, application of an evaluation function, production
Artificial Intelligence Constraint Satisfaction Problems
 Artificial Intelligence Constraint Satisfaction Problems Recall Search problems: Find the sequence of actions that leads to the goal. Sequence of actions means a path in the search space. Paths come with
Artificial Intelligence Constraint Satisfaction Problems Recall Search problems: Find the sequence of actions that leads to the goal. Sequence of actions means a path in the search space. Paths come with
Local Search for CSPs
 Local Search for CSPs Alan Mackworth UBC CS CSP February, 0 Textbook. Lecture Overview Domain splitting: recap, more details & pseudocode Local Search Time-permitting: Stochastic Local Search (start) Searching
Local Search for CSPs Alan Mackworth UBC CS CSP February, 0 Textbook. Lecture Overview Domain splitting: recap, more details & pseudocode Local Search Time-permitting: Stochastic Local Search (start) Searching
Informed Search. Dr. Richard J. Povinelli. Copyright Richard J. Povinelli Page 1
 Informed Search Dr. Richard J. Povinelli Copyright Richard J. Povinelli Page 1 rev 1.1, 9/25/2001 Objectives You should be able to explain and contrast uniformed and informed searches. be able to compare,
Informed Search Dr. Richard J. Povinelli Copyright Richard J. Povinelli Page 1 rev 1.1, 9/25/2001 Objectives You should be able to explain and contrast uniformed and informed searches. be able to compare,
AI Fundamentals: Constraints Satisfaction Problems. Maria Simi
 AI Fundamentals: Constraints Satisfaction Problems Maria Simi Constraints satisfaction LESSON 3 SEARCHING FOR SOLUTIONS Searching for solutions Most problems cannot be solved by constraint propagation
AI Fundamentals: Constraints Satisfaction Problems Maria Simi Constraints satisfaction LESSON 3 SEARCHING FOR SOLUTIONS Searching for solutions Most problems cannot be solved by constraint propagation
Example: Map coloring
 Today s s lecture Local Search Lecture 7: Search - 6 Heuristic Repair CSP and 3-SAT Solving CSPs using Systematic Search. Victor Lesser CMPSCI 683 Fall 2004 The relationship between problem structure and
Today s s lecture Local Search Lecture 7: Search - 6 Heuristic Repair CSP and 3-SAT Solving CSPs using Systematic Search. Victor Lesser CMPSCI 683 Fall 2004 The relationship between problem structure and
Outline. Informed Search. Recall: Uninformed Search. An Idea. Heuristics Informed search techniques More on heuristics Iterative improvement
 Outline Informed Search ECE457 Applied Artificial Intelligence Fall 2007 Lecture #3 Heuristics Informed search techniques More on heuristics Iterative improvement Russell & Norvig, chapter 4 Skip Genetic
Outline Informed Search ECE457 Applied Artificial Intelligence Fall 2007 Lecture #3 Heuristics Informed search techniques More on heuristics Iterative improvement Russell & Norvig, chapter 4 Skip Genetic
Artificial Intelligence
 Artificial Intelligence Informed Search and Exploration Chapter 4 (4.3 4.6) Searching: So Far We ve discussed how to build goal-based and utility-based agents that search to solve problems We ve also presented
Artificial Intelligence Informed Search and Exploration Chapter 4 (4.3 4.6) Searching: So Far We ve discussed how to build goal-based and utility-based agents that search to solve problems We ve also presented
