Performance Study of a Compiler/Hardware Approach to Embedded Systems Security
|
|
|
- Brian Jordan
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Performance Study of a Compiler/Hardware Approach to Embedded Systems Security Kripashankar Mohan, Bhagi Narahari, Rahul Simha, Paul Ott 1, Alok Choudhary, and Joe Zambreno 2 1 The George Washington University, Washington, DC Northwestern University, Evanston, IL Abstract. Trusted software execution, prevention of code and data tampering, authentication, and providing a secure environment for software are some of the most important security challenges in the design of embedded systems. This short paper evaluates the performance of a hardware/software co-design methodology for embedded software protection. Secure software is created using a secure compiler that inserts hidden codes into the executable code which are then validated dynamically during execution by a reconfigurable hardware component constructed from Field Programmable Gate Array (FPGA) technology. While the overall approach has been described in other papers, this paper focuses on security-performance tradeoffs and the effect of using compiler optimizations in such an approach. Our results show that the approach provides software protection with modest performance penalty and hardware overhead. 1 Introduction The primary goal of software protection is to reduce the risk from hackers who compromise software applications or the execution environment that runs applications. Our approach to this problem has been described in an earlier paper [1]. In this approach, bit sequences are inserted into the executable by the compiler that are then checked by supporting hardware during execution. The idea is that, if the code has been tampered, the sequence will be affected, thereby enabling the hardware to detect a modification. At this point, the hardware component can halt the processor. Observe that the compiler can instrument executables with hidden codes in several ways. The most direct approach is to simply add codewords to the executable. However, this has the disadvantage that the resulting executable may not execute on processors without the supporting hardware, and may be easily detected by an attacker. Our approach is to employ the freedom that the compiler has in allocating registers. Because there are many choices in allocating This work is supported in part by Grant CCR from the National Science Foundation. P. Kantor et al. (Eds.): ISI 2005, LNCS 3495, pp , c Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg 2005
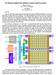
2 544 K. Mohan et al. registers, compilers can use these choices to represent binary codes that can then be extracted by the hardware. And because the register allocation is a valid one, the executable will run on processors that do not perform any checking. The hardware support is needed so that the checking is itself not compromised, as is possible with software checking methods [10]. While it is generally expensive to build custom hardware support for this type of run-time checking, Field Programming Gate Array (FPGA) technology provides an attractive alternative. These programmable fabrics are today available with many commercial processors, and can easily be configured to perform the kind of checking during runtime. Because FPGA s are usually on-chip, and because they can be optimized to perform simple computations, they are also space and time efficient. Thus, the combination of compiler and FPGA technology makes the whole approach worthy of investigation. The purpose of this paper is to explore the performance of this approach. Several factors can affect performance when actively checking an executable at runtime. The computation time in the FPGA depends on the lengths of the codes, their spread across the executable and how often the checking is performed. In particular, we consider the lengths of basic blocks and simple compiler techniques such as loop unrolling. We find that, overall, the approach imposes a modest penalty. At the same time, we find that loop-unrolling provides negligible performance benefit, thereby suggesting that other compiler techniques will be needed to further reduce the performance overhead. Because a complete survey of software protection and security-driven compilation is presented in some of our earlier work [1, 9], we refer the reader to these papers for reviews of related work. 2 The Compiler/Hardware Approach Figure 1 depicts the overall system architecture using our earlier approach [1]. The right side of Figure 1 shows a processor and FGPA on a single chip. As instructions stream into the chip, the FGPA secure component extracts the register information and uses the stream of registers to extract the hidden sequences, which are then checked. All the checking is performed by the FPGA itself. To see how this works, consider a sample program as shown in Figure 2. The code on the left shows the output of standard compilation, before our register encoding is performed. The compiler approach replaces the standard register allocation algorithm with one that embeds keys. We use an even-numbered register to encode a 0 (zero) from the binary key, and an odd-numbered register to encode a 1 (one). This process continues until all the available definition registers of the basic block are assigned according to the key. The reverse process is performed in the FPGA. In this paper, we consider two fundamental ways in which an embedded bitsequence can be used. In the first method, the extracted bit sequence is compared against a pre-stored key in the FPGA. This, however, requires addressing the problem of key distribution. For systems in which such distribution or storage is
3 Performance Study of a Compiler/Hardware 545 Fig. 1. System architecture not possible, a simpler (albeit less secure) approach can be used. In this case, the bit-sequence is compared against a specific (say, the first) opcode in the basic block. The overall technique relies on the fact that, when the code is tampered with, the bit sequence will be disrupted with high probability. Consider, for example, the second flavor mentioned above. In Figure 2, the opcode of the first instruction of a basic block yields a key of Since the first bit of the key is 1 the register assigned to the first instruction is R1. From the use-def and def-use chain of the registers, the instructions that depend on the first instruction s register R1 are updated. In the second instruction, register R1 is once again chosen, as the bit value is 1 and the register is also redefined. An even register R0 is chosen for the fourth instruction from the available even registers, since the third bit of the key is 0. This register s use locations are then updated. This process continues until all the registers are modified based on the key chosen. A modified program with a new register sequence is thus obtained. For the above example, Figure 2 shows the result. How is tampered code detected? Consider an insertion of instructions. Clearly, any instruction that uses registers is likely to disrupt the bit sequence with high Fig. 2. Register encoding example with key
4 546 K. Mohan et al. probability, and will therefore be detected. Although not discussed here, it is easy to select opcodes that are at a fixed distance away, so that any insertion or deletion of instructions will result in a different opcode being checked, and therefore in failing the test. The security of a program can be increased by using private keys instead of opcodes of the instructions. This includes additional performance overhead of storing the keys in FPGA but can be tuned to meet the security objectives. Note that processors with caches will need to allow FPGA to probe the cache to fetch instructions of the encrypted basic blocks that span across multiple cache blocks. 3 Experimental Analysis 3.1 Experimental Framework Our experimental framework uses the gcc cross-compiler targeting the ARM instruction set. The register allocation pass, the data flow analysis, loop unrolling and code generation pass of GCC were modified to incorporate the registerencoding scheme. The output of the compiler consists of the encrypted ARM executable and a description file for the FPGA. The FPGA is simulated using the Simplescalar toolset [8]. The FPGA is placed between L1 cache and the main memory. It has access to the cache controller and can probe the cache. We assume that there is no L2 Cache. The FPGA is configured like a Virtex-II XC2V8000 component which is an ARM1020E type processor running at a chosen clock speed of 150 Mhz but with a processor clock rate of 300 MHz. The size of the on-board memory is 3MB with a memory access delay of 2 processor cycle (1 FPGA Cycle) and delay for comparing values is 2 processor cycles. The L1 cache is configured with 16 sets with the block size and associativity of cache being 32 and 64 respectively. The cache follows the Least Recently Used policy with a cache hit latency of one cycle. Main memory access latency is 15 and 2 cycles for the first and rest of the data respectively. The width of the FPGA operator is 8 bytes, nonsequential access latency being 10 cycles and sequential access latency being 10 cycles respectively. The FPGA validates each cache block that is being fetched from the main memory and placed into the L1 cache. 3.2 Benchmarks Diverse benchmarks such as Susan (an image recognition package for Magnetic Resonance Images), Dijkstra (the well-known shortest path algorithm), Fast Fourier Transform, Rijndael (the AES encryption/decryption algorithm) and Patricia (a trie data structure) are used. We study the effect on overall system performance using basic blocks of varying lengths for purposes of encoding the bit sequences. The results are normalized to the performance of unencrypted case as shown in Figure 3 (left side). The overall performance for most of the benchmarks is within 78% of the unencrypted case. Benchmarks Patricia and
5 Performance Study of a Compiler/Hardware 547 Fig. 3. Performance as a function of encryption of varying basic block lengths before(left side) and after(right side) performing loop unrolling on the benchmarks. (25%, 50%, 75% and 100% basic blocks are encrypted) Dijkstra suffered a penalty of above 23%. This is because of instruction cache misses that occur in the FPGA that incur high cache miss penalty. Benchmarks Rijndael and FFT performed the best. Dijkstra suffered higher penalty due to large number of looping instructions being committed and it also runs longer. The effect of loop unrolling on the performance of the benchmarks was studied by selecting the basic blocks with longer instruction count. The main purpose of performing loop unrolling on the benchmarks is to increase the code size thereby increasing the number of instructions in the basic block, so that keys of greater length can be embedded into them. Further loop unrolling reduces loop overheads such as index variable maintenance and control hazards in pipelines, increases the number of statements in basic block to optimize and also improves the effectiveness of other optimizations such as common-subexpression elimination, software pipelining, etc. But its disadvantage is that the unrolled version of the code is larger than the rolled version, thereby having a negative impact on the performance on effectiveness of instruction cache. The effect of loop unrolling on the benchmarks is shown in Figure 3 (right side). The optimization had little effect on Susan and Rijndael benchmarks. FFT suffered a 0.1% decrease in performance but performance of both computationally intensive Dijkstra and Patricia benchmarks is increased by nearly 3%. This shows that loop-unrolling provides negligible performance benefit, thereby suggesting that other compiler techniques will be needed to reduce the performance overhead. The security of the program is increased by loop unrolling, as the key length is increased since
6 548 K. Mohan et al. more number of registers are now available to embed keys due to the increase in code size. 4 Conclusions and Future work Because embedded processors constitute an overwhelming share (above 90%) of the processor market, and because embedded devices are easily accessible to hackers, security has now become an important objective in the design of embedded systems. Pure-software approaches may not stop the determined hacker and pure-hardware approaches require expensive custom hardware. A combined compiler-fpga approach offers the advantages of both at a fraction of the cost, while also offering backward-compatibility. The purpose of this paper was to study the performance of this approach using some well-known benchmarks, and to examine the effect of some compiler optimizations. References 1. Zambreno, J., Choudhary, A., Simha, R., Narahari, B., Memon, A.: SAFE-OPS: A Compiler/ Architecture Approach to Embedded Software Security. ACM Transactions on Embedded Computing. 2. Chang, H., Atallah, M.: Protecting software code by guards. Proceedings of the ACM Workshop on Security and Privacy in Digital Rights Management. (2000) Collberg, C., Thomborson, C., and Low, D.: A taxonomy of obfuscating transformations. Dept of Computer Science, University of Auckland. Tech. Rep. 148 (1997). 4. Daeman, J. Rijmen, V.: The block cipher Rijndael. In Smart Card Research and Applications. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol Springer-Verlag (2000) Dallas Semiconductor: Features, advantages, and benefits of button-based security. available at 6. Gobioff, H., Smith, S., Tygar, D., Yee, B.: Smart cards in hostile environments. Proceedings of 2nd USENIX Workshop on Electronic Commerce. (1996) Necula, G.: Proof-carrying code. Proceedings of the 24th ACM SIGPLAN-SIGACT Symposium on Principles of Programming Languagers. (1997) Todd Austin, Eric Larson, Dan Ernst.: SimpleScalar: An Infrastructure for Computer System Modeling. IEEE Computer. (February 2002). 9. Simha, R., Narahari, B., Choudhary, A., Zambreno, J.: An overview of securitydriven compilation. Workshop on New Horizons in Compiler Analysis and Optimizations, Bangalore, India, (Dec 2004). 10. Wurster, G., Oorschot, P., Somayaji, A.: A generic attack on checksummingbased software tamper resistance. IEEE Symp. Security and Privacy, Oakland, CA (2005).
CODESSEAL: Compiler/FPGA Approach to Secure Applications
 CODESSEAL: Compiler/FPGA Approach to Secure Applications Olga Gelbart 1, Paul Ott 1, Bhagirath Narahari 1, Rahul Simha 1, Alok Choudhary 2, and Joseph Zambreno 2 1 The George Washington University, Washington,
CODESSEAL: Compiler/FPGA Approach to Secure Applications Olga Gelbart 1, Paul Ott 1, Bhagirath Narahari 1, Rahul Simha 1, Alok Choudhary 2, and Joseph Zambreno 2 1 The George Washington University, Washington,
Flexible Software Protection Using Hardware/Software Codesign Techniques
 Flexible Software Protection Using Hardware/Software Codesign Techniques Abstract A strong level of trust in the software running on an embedded processor is a prerequisite for its widespread deployment
Flexible Software Protection Using Hardware/Software Codesign Techniques Abstract A strong level of trust in the software running on an embedded processor is a prerequisite for its widespread deployment
SAFE-OPS: An Approach to Embedded Software Security
 SAFE-OPS: An Approach to Embedded Software Security JOSEPH ZAMBRENO and ALOK CHOUDHARY Northwestern University RAHUL SIMHA and BHAGI NARAHARI The George Washington University and NASIR MEMON Polytechnic
SAFE-OPS: An Approach to Embedded Software Security JOSEPH ZAMBRENO and ALOK CHOUDHARY Northwestern University RAHUL SIMHA and BHAGI NARAHARI The George Washington University and NASIR MEMON Polytechnic
SAFE-OPS: A Compiler/Architecture Approach to Embedded Software Security
 SAFE-OPS: A Compiler/Architecture Approach to Embedded Software Security JOSEPH ZAMBRENO and ALOK CHOUDHARY Northwestern University and RAHUL SIMHA and BHAGI NARAHARI The George Washington University and
SAFE-OPS: A Compiler/Architecture Approach to Embedded Software Security JOSEPH ZAMBRENO and ALOK CHOUDHARY Northwestern University and RAHUL SIMHA and BHAGI NARAHARI The George Washington University and
High-Performance Software Protection Using Reconfigurable Architectures
 High-Performance Software Protection Using Reconfigurable Architectures JOSEPH ZAMBRENO, STUDENT MEMBER, IEEE, DAN HONBO, STUDENT MEMBER, IEEE, ALOK CHOUDHARY, FELLOW, IEEE, RAHUL SIMHA, MEMBER, IEEE,
High-Performance Software Protection Using Reconfigurable Architectures JOSEPH ZAMBRENO, STUDENT MEMBER, IEEE, DAN HONBO, STUDENT MEMBER, IEEE, ALOK CHOUDHARY, FELLOW, IEEE, RAHUL SIMHA, MEMBER, IEEE,
Secure Execution with Components from Untrusted Foundries
 Secure Execution with Components from Untrusted Foundries Rahul Simha Bhagirath Narahari Department of Computer Science The George Washington University Washington, DC 20052 {simha, narahari}@gwu.edu Joseph
Secure Execution with Components from Untrusted Foundries Rahul Simha Bhagirath Narahari Department of Computer Science The George Washington University Washington, DC 20052 {simha, narahari}@gwu.edu Joseph
Security Applications
 1. Introduction Security Applications Abhyudaya Chodisetti Paul Wang Lee Garrett Smith Cryptography applications generally involve a large amount of processing. Thus, there is the possibility that these
1. Introduction Security Applications Abhyudaya Chodisetti Paul Wang Lee Garrett Smith Cryptography applications generally involve a large amount of processing. Thus, there is the possibility that these
Exploiting On-Chip Data Transfers for Improving Performance of Chip-Scale Multiprocessors
 Exploiting On-Chip Data Transfers for Improving Performance of Chip-Scale Multiprocessors G. Chen 1, M. Kandemir 1, I. Kolcu 2, and A. Choudhary 3 1 Pennsylvania State University, PA 16802, USA 2 UMIST,
Exploiting On-Chip Data Transfers for Improving Performance of Chip-Scale Multiprocessors G. Chen 1, M. Kandemir 1, I. Kolcu 2, and A. Choudhary 3 1 Pennsylvania State University, PA 16802, USA 2 UMIST,
Architecture Tuning Study: the SimpleScalar Experience
 Architecture Tuning Study: the SimpleScalar Experience Jianfeng Yang Yiqun Cao December 5, 2005 Abstract SimpleScalar is software toolset designed for modeling and simulation of processor performance.
Architecture Tuning Study: the SimpleScalar Experience Jianfeng Yang Yiqun Cao December 5, 2005 Abstract SimpleScalar is software toolset designed for modeling and simulation of processor performance.
Exploring Area/Delay Tradeoffs in an AES FPGA Implementation
 Exploring Area/Delay Tradeoffs in an AES FPGA Implementation Joseph Zambreno, David Nguyen, and Alok Choudhary Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Northwestern University Evanston, IL 60208,
Exploring Area/Delay Tradeoffs in an AES FPGA Implementation Joseph Zambreno, David Nguyen, and Alok Choudhary Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Northwestern University Evanston, IL 60208,
Journal of Global Research in Computer Science A UNIFIED BLOCK AND STREAM CIPHER BASED FILE ENCRYPTION
 Volume 2, No. 7, July 2011 Journal of Global Research in Computer Science RESEARCH PAPER Available Online at www.jgrcs.info A UNIFIED BLOCK AND STREAM CIPHER BASED FILE ENCRYPTION Manikandan. G *1, Krishnan.G
Volume 2, No. 7, July 2011 Journal of Global Research in Computer Science RESEARCH PAPER Available Online at www.jgrcs.info A UNIFIED BLOCK AND STREAM CIPHER BASED FILE ENCRYPTION Manikandan. G *1, Krishnan.G
Fast implementation and fair comparison of the final candidates for Advanced Encryption Standard using Field Programmable Gate Arrays
 Kris Gaj and Pawel Chodowiec Electrical and Computer Engineering George Mason University Fast implementation and fair comparison of the final candidates for Advanced Encryption Standard using Field Programmable
Kris Gaj and Pawel Chodowiec Electrical and Computer Engineering George Mason University Fast implementation and fair comparison of the final candidates for Advanced Encryption Standard using Field Programmable
An update on Scalable Implementation of Primitives for Homomorphic EncRyption FPGA implementation using Simulink Abstract
 An update on Scalable Implementation of Primitives for Homomorphic EncRyption FPGA implementation using Simulink David Bruce Cousins, Kurt Rohloff, Chris Peikert, Rick Schantz Raytheon BBN Technologies,
An update on Scalable Implementation of Primitives for Homomorphic EncRyption FPGA implementation using Simulink David Bruce Cousins, Kurt Rohloff, Chris Peikert, Rick Schantz Raytheon BBN Technologies,
Increasing Instruction-Level Parallelism with Instruction Precomputation
 Increasing Instruction-Level Parallelism with Instruction Precomputation Joshua J. Yi, Resit Sendag, and David J. Lilja Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Minnesota Supercomputing Institute
Increasing Instruction-Level Parallelism with Instruction Precomputation Joshua J. Yi, Resit Sendag, and David J. Lilja Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Minnesota Supercomputing Institute
Trace Driven Simulation of GDSF# and Existing Caching Algorithms for Web Proxy Servers
 Proceeding of the 9th WSEAS Int. Conference on Data Networks, Communications, Computers, Trinidad and Tobago, November 5-7, 2007 378 Trace Driven Simulation of GDSF# and Existing Caching Algorithms for
Proceeding of the 9th WSEAS Int. Conference on Data Networks, Communications, Computers, Trinidad and Tobago, November 5-7, 2007 378 Trace Driven Simulation of GDSF# and Existing Caching Algorithms for
Automatic compilation framework for Bloom filter based intrusion detection
 Automatic compilation framework for Bloom filter based intrusion detection Dinesh C Suresh, Zhi Guo*, Betul Buyukkurt and Walid A. Najjar Department of Computer Science and Engineering *Department of Electrical
Automatic compilation framework for Bloom filter based intrusion detection Dinesh C Suresh, Zhi Guo*, Betul Buyukkurt and Walid A. Najjar Department of Computer Science and Engineering *Department of Electrical
Implementation of Full -Parallelism AES Encryption and Decryption
 Implementation of Full -Parallelism AES Encryption and Decryption M.Anto Merline M.E-Commuication Systems, ECE Department K.Ramakrishnan College of Engineering-Samayapuram, Trichy. Abstract-Advanced Encryption
Implementation of Full -Parallelism AES Encryption and Decryption M.Anto Merline M.E-Commuication Systems, ECE Department K.Ramakrishnan College of Engineering-Samayapuram, Trichy. Abstract-Advanced Encryption
An Efficient Web Cache Replacement Policy
 In the Proc. of the 9th Intl. Symp. on High Performance Computing (HiPC-3), Hyderabad, India, Dec. 23. An Efficient Web Cache Replacement Policy A. Radhika Sarma and R. Govindarajan Supercomputer Education
In the Proc. of the 9th Intl. Symp. on High Performance Computing (HiPC-3), Hyderabad, India, Dec. 23. An Efficient Web Cache Replacement Policy A. Radhika Sarma and R. Govindarajan Supercomputer Education
FAULT DETECTION IN THE ADVANCED ENCRYPTION STANDARD. G. Bertoni, L. Breveglieri, I. Koren and V. Piuri
 FAULT DETECTION IN THE ADVANCED ENCRYPTION STANDARD G. Bertoni, L. Breveglieri, I. Koren and V. Piuri Abstract. The AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) is an emerging private-key cryptographic system. Performance
FAULT DETECTION IN THE ADVANCED ENCRYPTION STANDARD G. Bertoni, L. Breveglieri, I. Koren and V. Piuri Abstract. The AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) is an emerging private-key cryptographic system. Performance
Lossless Compression using Efficient Encoding of Bitmasks
 Lossless Compression using Efficient Encoding of Bitmasks Chetan Murthy and Prabhat Mishra Department of Computer and Information Science and Engineering University of Florida, Gainesville, FL 326, USA
Lossless Compression using Efficient Encoding of Bitmasks Chetan Murthy and Prabhat Mishra Department of Computer and Information Science and Engineering University of Florida, Gainesville, FL 326, USA
VLSI ARCHITECTURE FOR NANO WIRE BASED ADVANCED ENCRYPTION STANDARD (AES) WITH THE EFFICIENT MULTIPLICATIVE INVERSE UNIT
 VLSI ARCHITECTURE FOR NANO WIRE BASED ADVANCED ENCRYPTION STANDARD (AES) WITH THE EFFICIENT MULTIPLICATIVE INVERSE UNIT K.Sandyarani 1 and P. Nirmal Kumar 2 1 Research Scholar, Department of ECE, Sathyabama
VLSI ARCHITECTURE FOR NANO WIRE BASED ADVANCED ENCRYPTION STANDARD (AES) WITH THE EFFICIENT MULTIPLICATIVE INVERSE UNIT K.Sandyarani 1 and P. Nirmal Kumar 2 1 Research Scholar, Department of ECE, Sathyabama
Parallel and Pipeline Processing for Block Cipher Algorithms on a Network-on-Chip
 Parallel and Pipeline Processing for Block Cipher Algorithms on a Network-on-Chip Yoon Seok Yang, Jun Ho Bahn, Seung Eun Lee, and Nader Bagherzadeh Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science
Parallel and Pipeline Processing for Block Cipher Algorithms on a Network-on-Chip Yoon Seok Yang, Jun Ho Bahn, Seung Eun Lee, and Nader Bagherzadeh Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science
A Run-Time Reconfigurable Architecture for Embedded Program Flow Verification
 A Run-Time Reconfigurable Architecture for Embedded Program Flow Verification Joseph ZAMBRENO, Tanathil ANISH and Alok CHOUDHARY 1 Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Northwestern University
A Run-Time Reconfigurable Architecture for Embedded Program Flow Verification Joseph ZAMBRENO, Tanathil ANISH and Alok CHOUDHARY 1 Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Northwestern University
Threshold-Based Markov Prefetchers
 Threshold-Based Markov Prefetchers Carlos Marchani Tamer Mohamed Lerzan Celikkanat George AbiNader Rice University, Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering ELEC 525, Spring 26 Abstract In this
Threshold-Based Markov Prefetchers Carlos Marchani Tamer Mohamed Lerzan Celikkanat George AbiNader Rice University, Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering ELEC 525, Spring 26 Abstract In this
Reducing Power Consumption for High-Associativity Data Caches in Embedded Processors
 Reducing Power Consumption for High-Associativity Data Caches in Embedded Processors Dan Nicolaescu Alex Veidenbaum Alex Nicolau Dept. of Information and Computer Science University of California at Irvine
Reducing Power Consumption for High-Associativity Data Caches in Embedded Processors Dan Nicolaescu Alex Veidenbaum Alex Nicolau Dept. of Information and Computer Science University of California at Irvine
Improving the Database Logging Performance of the Snort Network Intrusion Detection Sensor
 -0- Improving the Database Logging Performance of the Snort Network Intrusion Detection Sensor Lambert Schaelicke, Matthew R. Geiger, Curt J. Freeland Department of Computer Science and Engineering University
-0- Improving the Database Logging Performance of the Snort Network Intrusion Detection Sensor Lambert Schaelicke, Matthew R. Geiger, Curt J. Freeland Department of Computer Science and Engineering University
Storage Efficient Hardware Prefetching using Delta Correlating Prediction Tables
 Storage Efficient Hardware Prefetching using Correlating Prediction Tables Marius Grannaes Magnus Jahre Lasse Natvig Norwegian University of Science and Technology HiPEAC European Network of Excellence
Storage Efficient Hardware Prefetching using Correlating Prediction Tables Marius Grannaes Magnus Jahre Lasse Natvig Norwegian University of Science and Technology HiPEAC European Network of Excellence
A Lost Cycles Analysis for Performance Prediction using High-Level Synthesis
 A Lost Cycles Analysis for Performance Prediction using High-Level Synthesis Bruno da Silva, Jan Lemeire, An Braeken, and Abdellah Touhafi Vrije Universiteit Brussel (VUB), INDI and ETRO department, Brussels,
A Lost Cycles Analysis for Performance Prediction using High-Level Synthesis Bruno da Silva, Jan Lemeire, An Braeken, and Abdellah Touhafi Vrije Universiteit Brussel (VUB), INDI and ETRO department, Brussels,
Evaluation of Branch Prediction Strategies
 1 Evaluation of Branch Prediction Strategies Anvita Patel, Parneet Kaur, Saie Saraf Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Rutgers University 2 CONTENTS I Introduction 4 II Related Work 6 III
1 Evaluation of Branch Prediction Strategies Anvita Patel, Parneet Kaur, Saie Saraf Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Rutgers University 2 CONTENTS I Introduction 4 II Related Work 6 III
6.857 L17. Secure Processors. Srini Devadas
 6.857 L17 Secure Processors Srini Devadas 1 Distributed Computation Example: Distributed Computation on the Internet (SETI@home, etc.) Job Dispatcher Internet DistComp() { x = Receive(); result = Func(x);
6.857 L17 Secure Processors Srini Devadas 1 Distributed Computation Example: Distributed Computation on the Internet (SETI@home, etc.) Job Dispatcher Internet DistComp() { x = Receive(); result = Func(x);
COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND DESI
 COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND DESIGN 5 Edition th The Hardware/Software Interface Chapter 4 The Processor 4.1 Introduction Introduction CPU performance factors Instruction count Determined by ISA and compiler
COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND DESIGN 5 Edition th The Hardware/Software Interface Chapter 4 The Processor 4.1 Introduction Introduction CPU performance factors Instruction count Determined by ISA and compiler
Efficient Hardware Realization of Advanced Encryption Standard Algorithm using Virtex-5 FPGA
 IJCSNS International Journal of Computer Science and Network Security, VOL.9 No.9, September 2009 59 Efficient Hardware Realization of Advanced Encryption Standard Algorithm using Virtex-5 FPGA Muhammad
IJCSNS International Journal of Computer Science and Network Security, VOL.9 No.9, September 2009 59 Efficient Hardware Realization of Advanced Encryption Standard Algorithm using Virtex-5 FPGA Muhammad
Adapted from instructor s supplementary material from Computer. Patterson & Hennessy, 2008, MK]
![Adapted from instructor s supplementary material from Computer. Patterson & Hennessy, 2008, MK] Adapted from instructor s supplementary material from Computer. Patterson & Hennessy, 2008, MK]](/thumbs/80/82108809.jpg) Lecture 17 Adapted from instructor s supplementary material from Computer Organization and Design, 4th Edition, Patterson & Hennessy, 2008, MK] SRAM / / Flash / RRAM / HDD SRAM / / Flash / RRAM/ HDD SRAM
Lecture 17 Adapted from instructor s supplementary material from Computer Organization and Design, 4th Edition, Patterson & Hennessy, 2008, MK] SRAM / / Flash / RRAM / HDD SRAM / / Flash / RRAM/ HDD SRAM
Developing a Data Driven System for Computational Neuroscience
 Developing a Data Driven System for Computational Neuroscience Ross Snider and Yongming Zhu Montana State University, Bozeman MT 59717, USA Abstract. A data driven system implies the need to integrate
Developing a Data Driven System for Computational Neuroscience Ross Snider and Yongming Zhu Montana State University, Bozeman MT 59717, USA Abstract. A data driven system implies the need to integrate
Utilizing Concurrency: A New Theory for Memory Wall
 Utilizing Concurrency: A New Theory for Memory Wall Xian-He Sun (&) and Yu-Hang Liu Illinois Institute of Technology, Chicago, USA {sun,yuhang.liu}@iit.edu Abstract. In addition to locality, data access
Utilizing Concurrency: A New Theory for Memory Wall Xian-He Sun (&) and Yu-Hang Liu Illinois Institute of Technology, Chicago, USA {sun,yuhang.liu}@iit.edu Abstract. In addition to locality, data access
Combining In-Transit Buffers with Optimized Routing Schemes to Boost the Performance of Networks with Source Routing
 Combining In-Transit Buffers with Optimized Routing Schemes to Boost the Performance of Networks with Source Routing Jose Flich 1,PedroLópez 1, Manuel. P. Malumbres 1, José Duato 1,andTomRokicki 2 1 Dpto.
Combining In-Transit Buffers with Optimized Routing Schemes to Boost the Performance of Networks with Source Routing Jose Flich 1,PedroLópez 1, Manuel. P. Malumbres 1, José Duato 1,andTomRokicki 2 1 Dpto.
An Analysis of Delay Based PUF Implementations on FPGA
 An Analysis of Delay Based PUF Implementations on FPGA Sergey Morozov, Abhranil Maiti, and Patrick Schaumont Virginia Tech, Blacksburg, VA 24061, USA {morozovs,abhranil,schaum}@vt.edu Abstract. Physical
An Analysis of Delay Based PUF Implementations on FPGA Sergey Morozov, Abhranil Maiti, and Patrick Schaumont Virginia Tech, Blacksburg, VA 24061, USA {morozovs,abhranil,schaum}@vt.edu Abstract. Physical
Improving Data Access Efficiency by Using Context-Aware Loads and Stores
 Improving Data Access Efficiency by Using Context-Aware Loads and Stores Alen Bardizbanyan Chalmers University of Technology Gothenburg, Sweden alenb@chalmers.se Magnus Själander Uppsala University Uppsala,
Improving Data Access Efficiency by Using Context-Aware Loads and Stores Alen Bardizbanyan Chalmers University of Technology Gothenburg, Sweden alenb@chalmers.se Magnus Själander Uppsala University Uppsala,
The Impact of Instruction Compression on I-cache Performance
 Technical Report CSE-TR--97, University of Michigan The Impact of Instruction Compression on I-cache Performance I-Cheng K. Chen Peter L. Bird Trevor Mudge EECS Department University of Michigan {icheng,pbird,tnm}@eecs.umich.edu
Technical Report CSE-TR--97, University of Michigan The Impact of Instruction Compression on I-cache Performance I-Cheng K. Chen Peter L. Bird Trevor Mudge EECS Department University of Michigan {icheng,pbird,tnm}@eecs.umich.edu
On the Interplay of Loop Caching, Code Compression, and Cache Configuration
 On the Interplay of Loop Caching, Code Compression, and Cache Configuration Marisha Rawlins and Ann Gordon-Ross* Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Florida, Gainesville, FL
On the Interplay of Loop Caching, Code Compression, and Cache Configuration Marisha Rawlins and Ann Gordon-Ross* Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Florida, Gainesville, FL
CryptoManiac: Application Specific Architectures for Cryptography. Overview
 : Application Specific Architectures for Cryptography Lisa Wu, Chris Weaver, Todd Austin {wul,chriswea,taustin}@eecs.umich.edu Overview Goal - fast programmable cryptographic processing Fast : efficient
: Application Specific Architectures for Cryptography Lisa Wu, Chris Weaver, Todd Austin {wul,chriswea,taustin}@eecs.umich.edu Overview Goal - fast programmable cryptographic processing Fast : efficient
instruction fetch memory interface signal unit priority manager instruction decode stack register sets address PC2 PC3 PC4 instructions extern signals
 Performance Evaluations of a Multithreaded Java Microcontroller J. Kreuzinger, M. Pfeer A. Schulz, Th. Ungerer Institute for Computer Design and Fault Tolerance University of Karlsruhe, Germany U. Brinkschulte,
Performance Evaluations of a Multithreaded Java Microcontroller J. Kreuzinger, M. Pfeer A. Schulz, Th. Ungerer Institute for Computer Design and Fault Tolerance University of Karlsruhe, Germany U. Brinkschulte,
Parallel FIR Filters. Chapter 5
 Chapter 5 Parallel FIR Filters This chapter describes the implementation of high-performance, parallel, full-precision FIR filters using the DSP48 slice in a Virtex-4 device. ecause the Virtex-4 architecture
Chapter 5 Parallel FIR Filters This chapter describes the implementation of high-performance, parallel, full-precision FIR filters using the DSP48 slice in a Virtex-4 device. ecause the Virtex-4 architecture
A Novel FPGA Implementation of AES-128 using Reduced Residue of Prime Numbers based S-Box
 IJCSNS International Journal of Computer Science and Network Security, VOL.9 No.9, September 2009 305 A Novel FPGA Implementation of AES-128 using Reduced Residue of Prime Numbers based S-Box Muhammad
IJCSNS International Journal of Computer Science and Network Security, VOL.9 No.9, September 2009 305 A Novel FPGA Implementation of AES-128 using Reduced Residue of Prime Numbers based S-Box Muhammad
Reducing Instruction Fetch Cost by Packing Instructions into Register Windows
 Reducing Instruction Fetch Cost by Packing Instructions into Register Windows Stephen Hines, Gary Tyson, David Whalley Computer Science Dept. Florida State University November 14, 2005 ➊ Introduction Reducing
Reducing Instruction Fetch Cost by Packing Instructions into Register Windows Stephen Hines, Gary Tyson, David Whalley Computer Science Dept. Florida State University November 14, 2005 ➊ Introduction Reducing
Covert Communication with Authentication via Software Programs Using Invisible ASCII Codes --- A New Approach
 Covert Communication with Authentication via Software Programs Using Invisible ASCII Codes --- A New Approach I-Shi Lee Dept. of Computer Science, National Chiao Tung University, Hsinchu, Taiwan 30010
Covert Communication with Authentication via Software Programs Using Invisible ASCII Codes --- A New Approach I-Shi Lee Dept. of Computer Science, National Chiao Tung University, Hsinchu, Taiwan 30010
Dynamic Memory Management in the Loci Framework
 Dynamic Memory Management in the Loci Framework Yang Zhang and Edward A. Luke Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Mississippi State University, Mississippi State, MS 39762, USA {fz15, luke}@cse.msstate.edu
Dynamic Memory Management in the Loci Framework Yang Zhang and Edward A. Luke Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Mississippi State University, Mississippi State, MS 39762, USA {fz15, luke}@cse.msstate.edu
Algorithms to Watermark Software Through Register Allocation
 Algorithms to Watermark Software Through Register Allocation William Zhu and Clark Thomborson Department of Computer Sciences, University of Auckland, Auckland, New Zealand fzhu009@ec.auckland.ac.nz, cthombor@cs.auckland.ac.nz
Algorithms to Watermark Software Through Register Allocation William Zhu and Clark Thomborson Department of Computer Sciences, University of Auckland, Auckland, New Zealand fzhu009@ec.auckland.ac.nz, cthombor@cs.auckland.ac.nz
Performance and Overhead in a Hybrid Reconfigurable Computer
 Performance and Overhead in a Hybrid Reconfigurable Computer Osman Devrim Fidanci 1, Dan Poznanovic 2, Kris Gaj 3, Tarek El-Ghazawi 1, Nikitas Alexandridis 1 1 George Washington University, 2 SRC Computers
Performance and Overhead in a Hybrid Reconfigurable Computer Osman Devrim Fidanci 1, Dan Poznanovic 2, Kris Gaj 3, Tarek El-Ghazawi 1, Nikitas Alexandridis 1 1 George Washington University, 2 SRC Computers
Memory Performance Characterization of SPEC CPU2006 Benchmarks Using TSIM1
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Physics Procedia 33 (2012 ) 1029 1035 2012 International Conference on Medical Physics and Biomedical Engineering Memory Performance Characterization of SPEC CPU2006
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Physics Procedia 33 (2012 ) 1029 1035 2012 International Conference on Medical Physics and Biomedical Engineering Memory Performance Characterization of SPEC CPU2006
Supporting Multithreading in Configurable Soft Processor Cores
 Supporting Multithreading in Configurable Soft Processor Cores Roger Moussali, Nabil Ghanem, and Mazen A. R. Saghir Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering American University of Beirut P.O.
Supporting Multithreading in Configurable Soft Processor Cores Roger Moussali, Nabil Ghanem, and Mazen A. R. Saghir Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering American University of Beirut P.O.
Efficient Self-Reconfigurable Implementations Using On-Chip Memory
 10th International Conference on Field Programmable Logic and Applications, August 2000. Efficient Self-Reconfigurable Implementations Using On-Chip Memory Sameer Wadhwa and Andreas Dandalis University
10th International Conference on Field Programmable Logic and Applications, August 2000. Efficient Self-Reconfigurable Implementations Using On-Chip Memory Sameer Wadhwa and Andreas Dandalis University
Enhancing Security of Improved RC4 Stream Cipher by Converting into Product Cipher
 Enhancing Security of Improved RC4 Stream Cipher by Converting into Product Cipher Nishith Sinha Mallika Chawda Kishore Bhamidipati Assistant Professor ABSTRACT RC4 is one of the most widely used stream
Enhancing Security of Improved RC4 Stream Cipher by Converting into Product Cipher Nishith Sinha Mallika Chawda Kishore Bhamidipati Assistant Professor ABSTRACT RC4 is one of the most widely used stream
Understanding The Effects of Wrong-path Memory References on Processor Performance
 Understanding The Effects of Wrong-path Memory References on Processor Performance Onur Mutlu Hyesoon Kim David N. Armstrong Yale N. Patt The University of Texas at Austin 2 Motivation Processors spend
Understanding The Effects of Wrong-path Memory References on Processor Performance Onur Mutlu Hyesoon Kim David N. Armstrong Yale N. Patt The University of Texas at Austin 2 Motivation Processors spend
Comparison of the Hardware Performance of the AES Candidates Using Reconfigurable Hardware
 Comparison of the Hardware Performance of the AES Candidates Using Reconfigurable Hardware Master s Thesis Pawel Chodowiec MS CpE Candidate, ECE George Mason University Advisor: Dr. Kris Gaj, ECE George
Comparison of the Hardware Performance of the AES Candidates Using Reconfigurable Hardware Master s Thesis Pawel Chodowiec MS CpE Candidate, ECE George Mason University Advisor: Dr. Kris Gaj, ECE George
Performance Analysis of AES Algorithm on MPC Processor
 Send Orders for Reprints to reprints@benthamscience.ae 2248 The Open Cybernetics & Systemics Journal, 2015, 9, 2248-2253 Performance Analysis of AES Algorithm on MPC Processor Open Access Gao Haifeng 1,
Send Orders for Reprints to reprints@benthamscience.ae 2248 The Open Cybernetics & Systemics Journal, 2015, 9, 2248-2253 Performance Analysis of AES Algorithm on MPC Processor Open Access Gao Haifeng 1,
Limiting the Number of Dirty Cache Lines
 Limiting the Number of Dirty Cache Lines Pepijn de Langen and Ben Juurlink Computer Engineering Laboratory Faculty of Electrical Engineering, Mathematics and Computer Science Delft University of Technology
Limiting the Number of Dirty Cache Lines Pepijn de Langen and Ben Juurlink Computer Engineering Laboratory Faculty of Electrical Engineering, Mathematics and Computer Science Delft University of Technology
UML-Based Design Flow and Partitioning Methodology for Dynamically Reconfigurable Computing Systems
 UML-Based Design Flow and Partitioning Methodology for Dynamically Reconfigurable Computing Systems Chih-Hao Tseng and Pao-Ann Hsiung Department of Computer Science and Information Engineering, National
UML-Based Design Flow and Partitioning Methodology for Dynamically Reconfigurable Computing Systems Chih-Hao Tseng and Pao-Ann Hsiung Department of Computer Science and Information Engineering, National
Multi-Level Encryption Framework
 Multi-Level Encryption Framework Ahmad Habboush Faculty of Computer and Information Technology Jerash University Jerash, Jordan Abstract Multi-level encryption approaches are becoming more popular as they
Multi-Level Encryption Framework Ahmad Habboush Faculty of Computer and Information Technology Jerash University Jerash, Jordan Abstract Multi-level encryption approaches are becoming more popular as they
Automatic Counterflow Pipeline Synthesis
 Automatic Counterflow Pipeline Synthesis Bruce R. Childers, Jack W. Davidson Computer Science Department University of Virginia Charlottesville, Virginia 22901 {brc2m, jwd}@cs.virginia.edu Abstract The
Automatic Counterflow Pipeline Synthesis Bruce R. Childers, Jack W. Davidson Computer Science Department University of Virginia Charlottesville, Virginia 22901 {brc2m, jwd}@cs.virginia.edu Abstract The
Computer Organization & Assembly Language Programming
 Computer Organization & Assembly Language Programming CSE 2312-002 (Fall 2011) Lecture 5 Memory Junzhou Huang, Ph.D. Department of Computer Science and Engineering Fall 2011 CSE 2312 Computer Organization
Computer Organization & Assembly Language Programming CSE 2312-002 (Fall 2011) Lecture 5 Memory Junzhou Huang, Ph.D. Department of Computer Science and Engineering Fall 2011 CSE 2312 Computer Organization
Exploration of Cache Coherent CPU- FPGA Heterogeneous System
 Exploration of Cache Coherent CPU- FPGA Heterogeneous System Wei Zhang Department of Electronic and Computer Engineering Hong Kong University of Science and Technology 1 Outline ointroduction to FPGA-based
Exploration of Cache Coherent CPU- FPGA Heterogeneous System Wei Zhang Department of Electronic and Computer Engineering Hong Kong University of Science and Technology 1 Outline ointroduction to FPGA-based
Exploiting Forwarding to Improve Data Bandwidth of Instruction-Set Extensions
 Exploiting Forwarding to Improve Data Bandwidth of Instruction-Set Extensions Ramkumar Jayaseelan, Haibin Liu, Tulika Mitra School of Computing, National University of Singapore {ramkumar,liuhb,tulika}@comp.nus.edu.sg
Exploiting Forwarding to Improve Data Bandwidth of Instruction-Set Extensions Ramkumar Jayaseelan, Haibin Liu, Tulika Mitra School of Computing, National University of Singapore {ramkumar,liuhb,tulika}@comp.nus.edu.sg
An Efficient Storage Mechanism to Distribute Disk Load in a VoD Server
 An Efficient Storage Mechanism to Distribute Disk Load in a VoD Server D.N. Sujatha 1, K. Girish 1, K.R. Venugopal 1,andL.M.Patnaik 2 1 Department of Computer Science and Engineering University Visvesvaraya
An Efficient Storage Mechanism to Distribute Disk Load in a VoD Server D.N. Sujatha 1, K. Girish 1, K.R. Venugopal 1,andL.M.Patnaik 2 1 Department of Computer Science and Engineering University Visvesvaraya
Encryption / decryption system. Fig.1. Block diagram of Hummingbird
 801 Lightweight VLSI Design of Hybrid Hummingbird Cryptographic Algorithm NIKITA ARORA 1, YOGITA GIGRAS 2 12 Department of Computer Science, ITM University, Gurgaon, INDIA 1 nikita.0012@gmail.com, 2 gigras.yogita@gmail.com
801 Lightweight VLSI Design of Hybrid Hummingbird Cryptographic Algorithm NIKITA ARORA 1, YOGITA GIGRAS 2 12 Department of Computer Science, ITM University, Gurgaon, INDIA 1 nikita.0012@gmail.com, 2 gigras.yogita@gmail.com
SDACCEL DEVELOPMENT ENVIRONMENT. The Xilinx SDAccel Development Environment. Bringing The Best Performance/Watt to the Data Center
 SDAccel Environment The Xilinx SDAccel Development Environment Bringing The Best Performance/Watt to the Data Center Introduction Data center operators constantly seek more server performance. Currently
SDAccel Environment The Xilinx SDAccel Development Environment Bringing The Best Performance/Watt to the Data Center Introduction Data center operators constantly seek more server performance. Currently
Guided Prefetching Based on Runtime Access Patterns
 Guided Prefetching Based on Runtime Access Patterns Jie Tao 1, Georges Kneip 2, and Wolfgang Karl 2 1 Steinbuch Center for Computing Forschungszentrum Karlsruhe Karlsruhe Institute of Technology, Germany
Guided Prefetching Based on Runtime Access Patterns Jie Tao 1, Georges Kneip 2, and Wolfgang Karl 2 1 Steinbuch Center for Computing Forschungszentrum Karlsruhe Karlsruhe Institute of Technology, Germany
Minimum Area Cost for a 30 to 70 Gbits/s AES Processor
 Minimum Area Cost for a 30 to 70 Gbits/s AE Processor Alireza Hodjat and Ingrid Verbauwhede Electrical Engineering Department University of California, Los Angeles {ahodjat, ingrid} @ ee.ucla.edu Abstract
Minimum Area Cost for a 30 to 70 Gbits/s AE Processor Alireza Hodjat and Ingrid Verbauwhede Electrical Engineering Department University of California, Los Angeles {ahodjat, ingrid} @ ee.ucla.edu Abstract
Compiler-Assisted Memory Encryption for Embedded Processors
 Compiler-Assisted Memory Encryption for Embedded Processors Vijay Nagarajan, Rajiv Gupta, and Arvind Krishnaswamy University of Arizona, Dept. of Computer Science, Tucson, AZ 85721 {vijay,gupta,arvind}@cs.arizona.edu
Compiler-Assisted Memory Encryption for Embedded Processors Vijay Nagarajan, Rajiv Gupta, and Arvind Krishnaswamy University of Arizona, Dept. of Computer Science, Tucson, AZ 85721 {vijay,gupta,arvind}@cs.arizona.edu
Hardware Implementation of Cryptosystem by AES Algorithm Using FPGA
 Available Online at www.ijcsmc.com International Journal of Computer Science and Mobile Computing A Monthly Journal of Computer Science and Information Technology ISSN 2320 088X IMPACT FACTOR: 6.017 IJCSMC,
Available Online at www.ijcsmc.com International Journal of Computer Science and Mobile Computing A Monthly Journal of Computer Science and Information Technology ISSN 2320 088X IMPACT FACTOR: 6.017 IJCSMC,
Chapter 7 The Potential of Special-Purpose Hardware
 Chapter 7 The Potential of Special-Purpose Hardware The preceding chapters have described various implementation methods and performance data for TIGRE. This chapter uses those data points to propose architecture
Chapter 7 The Potential of Special-Purpose Hardware The preceding chapters have described various implementation methods and performance data for TIGRE. This chapter uses those data points to propose architecture
DECENTRALIZED ATTRIBUTE-BASED ENCRYPTION AND DATA SHARING SCHEME IN CLOUD STORAGE
 DECENTRALIZED ATTRIBUTE-BASED ENCRYPTION AND DATA SHARING SCHEME IN CLOUD STORAGE ABSTRACT We propose a Multi-Authority Attribute-Based Encryption (ABE) system. In our system, any party can become an authority
DECENTRALIZED ATTRIBUTE-BASED ENCRYPTION AND DATA SHARING SCHEME IN CLOUD STORAGE ABSTRACT We propose a Multi-Authority Attribute-Based Encryption (ABE) system. In our system, any party can become an authority
Saving Register-File Leakage Power by Monitoring Instruction Sequence in ROB
 Saving Register-File Leakage Power by Monitoring Instruction Sequence in ROB Wann-Yun Shieh * and Hsin-Dar Chen Department of Computer Science and Information Engineering Chang Gung University, Taiwan
Saving Register-File Leakage Power by Monitoring Instruction Sequence in ROB Wann-Yun Shieh * and Hsin-Dar Chen Department of Computer Science and Information Engineering Chang Gung University, Taiwan
Donn Morrison Department of Computer Science. TDT4255 Memory hierarchies
 TDT4255 Lecture 10: Memory hierarchies Donn Morrison Department of Computer Science 2 Outline Chapter 5 - Memory hierarchies (5.1-5.5) Temporal and spacial locality Hits and misses Direct-mapped, set associative,
TDT4255 Lecture 10: Memory hierarchies Donn Morrison Department of Computer Science 2 Outline Chapter 5 - Memory hierarchies (5.1-5.5) Temporal and spacial locality Hits and misses Direct-mapped, set associative,
Demand fetching is commonly employed to bring the data
 Proceedings of 2nd Annual Conference on Theoretical and Applied Computer Science, November 2010, Stillwater, OK 14 Markov Prediction Scheme for Cache Prefetching Pranav Pathak, Mehedi Sarwar, Sohum Sohoni
Proceedings of 2nd Annual Conference on Theoretical and Applied Computer Science, November 2010, Stillwater, OK 14 Markov Prediction Scheme for Cache Prefetching Pranav Pathak, Mehedi Sarwar, Sohum Sohoni
A SIMPLE 1-BYTE 1-CLOCK RC4 DESIGN AND ITS EFFICIENT IMPLEMENTATION IN FPGA COPROCESSOR FOR SECURED ETHERNET COMMUNICATION
 A SIMPLE 1-BYTE 1-CLOCK RC4 DESIGN AND ITS EFFICIENT IMPLEMENTATION IN FPGA COPROCESSOR FOR SECURED ETHERNET COMMUNICATION Abstract In the field of cryptography till date the 1-byte in 1-clock is the best
A SIMPLE 1-BYTE 1-CLOCK RC4 DESIGN AND ITS EFFICIENT IMPLEMENTATION IN FPGA COPROCESSOR FOR SECURED ETHERNET COMMUNICATION Abstract In the field of cryptography till date the 1-byte in 1-clock is the best
Improving Reconfiguration Speed for Dynamic Circuit Specialization using Placement Constraints
 Improving Reconfiguration Speed for Dynamic Circuit Specialization using Placement Constraints Amit Kulkarni, Tom Davidson, Karel Heyse, and Dirk Stroobandt ELIS department, Computer Systems Lab, Ghent
Improving Reconfiguration Speed for Dynamic Circuit Specialization using Placement Constraints Amit Kulkarni, Tom Davidson, Karel Heyse, and Dirk Stroobandt ELIS department, Computer Systems Lab, Ghent
Incremental Reconfiguration for Pipelined Applications
 Incremental Reconfiguration for Pipelined Applications Herman Schmit Dept. of ECE, Carnegie Mellon University Pittsburgh, PA 15213 Abstract This paper examines the implementation of pipelined applications
Incremental Reconfiguration for Pipelined Applications Herman Schmit Dept. of ECE, Carnegie Mellon University Pittsburgh, PA 15213 Abstract This paper examines the implementation of pipelined applications
Simulation on Agent-based Onion Routing Network *
 National Research Council Canada Institute for Information Technology Conseil national de recherches Canada Institut de technologie de l'information Simulation on Agent-based Onion Routing Network * Song,
National Research Council Canada Institute for Information Technology Conseil national de recherches Canada Institut de technologie de l'information Simulation on Agent-based Onion Routing Network * Song,
2 Application Support via Proxies Onion Routing can be used with applications that are proxy-aware, as well as several non-proxy-aware applications, w
 Onion Routing for Anonymous and Private Internet Connections David Goldschlag Michael Reed y Paul Syverson y January 28, 1999 1 Introduction Preserving privacy means not only hiding the content of messages,
Onion Routing for Anonymous and Private Internet Connections David Goldschlag Michael Reed y Paul Syverson y January 28, 1999 1 Introduction Preserving privacy means not only hiding the content of messages,
Security in sensors, an important requirement for embedded systems
 Security in sensors, an important requirement for embedded systems Georg Sigl Institute for Security in Information Technology Technical University Munich sigl@tum.de Fraunhofer AISEC Institute for Applied
Security in sensors, an important requirement for embedded systems Georg Sigl Institute for Security in Information Technology Technical University Munich sigl@tum.de Fraunhofer AISEC Institute for Applied
Cache Side Channel Attacks on Intel SGX
 Cache Side Channel Attacks on Intel SGX Princeton University Technical Report CE-L2017-001 January 2017 Zecheng He Ruby B. Lee {zechengh, rblee}@princeton.edu Department of Electrical Engineering Princeton
Cache Side Channel Attacks on Intel SGX Princeton University Technical Report CE-L2017-001 January 2017 Zecheng He Ruby B. Lee {zechengh, rblee}@princeton.edu Department of Electrical Engineering Princeton
Compiler-in-the-Loop Design Space Exploration Framework for Energy Reduction in Horizontally Partitioned Cache Architectures
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON COMPUTER-AIDED DESIGN OF INTEGRATED CIRCUITS AND SYSTEMS, VOL. 28, NO. 3, MARCH 2009 461 Compiler-in-the-Loop Design Space Exploration Framework for Energy Reduction in Horizontally
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON COMPUTER-AIDED DESIGN OF INTEGRATED CIRCUITS AND SYSTEMS, VOL. 28, NO. 3, MARCH 2009 461 Compiler-in-the-Loop Design Space Exploration Framework for Energy Reduction in Horizontally
Computer Sciences Department
 Computer Sciences Department SIP: Speculative Insertion Policy for High Performance Caching Hongil Yoon Tan Zhang Mikko H. Lipasti Technical Report #1676 June 2010 SIP: Speculative Insertion Policy for
Computer Sciences Department SIP: Speculative Insertion Policy for High Performance Caching Hongil Yoon Tan Zhang Mikko H. Lipasti Technical Report #1676 June 2010 SIP: Speculative Insertion Policy for
Separating Access Control Policy, Enforcement, and Functionality in Extensible Systems. Robert Grimm University of Washington
 Separating Access Control Policy, Enforcement, and Functionality in Extensible Systems Robert Grimm University of Washington Extensions Added to running system Interact through low-latency interfaces Form
Separating Access Control Policy, Enforcement, and Functionality in Extensible Systems Robert Grimm University of Washington Extensions Added to running system Interact through low-latency interfaces Form
Improving Instruction Locality with Just-In-Time Code Layout
 The following paper was originally published in the Proceedings of the USENIX Windows NT Workshop Seattle, Washington, August 1997 Improving Instruction Locality with Just-In-Time Code Layout J. Bradley
The following paper was originally published in the Proceedings of the USENIX Windows NT Workshop Seattle, Washington, August 1997 Improving Instruction Locality with Just-In-Time Code Layout J. Bradley
Outline. Exploiting Program Parallelism. The Hydra Approach. Data Speculation Support for a Chip Multiprocessor (Hydra CMP) HYDRA
 CS 258 Parallel Computer Architecture Data Speculation Support for a Chip Multiprocessor (Hydra CMP) Lance Hammond, Mark Willey and Kunle Olukotun Presented: May 7 th, 2008 Ankit Jain Outline The Hydra
CS 258 Parallel Computer Architecture Data Speculation Support for a Chip Multiprocessor (Hydra CMP) Lance Hammond, Mark Willey and Kunle Olukotun Presented: May 7 th, 2008 Ankit Jain Outline The Hydra
Privacy-Preserving Computation with Trusted Computing via Scramble-then-Compute
 Privacy-Preserving Computation with Trusted Computing via Scramble-then-Compute Hung Dang, Anh Dinh, Ee-Chien Chang, Beng Chin Ooi School of Computing National University of Singapore The Problem Context:
Privacy-Preserving Computation with Trusted Computing via Scramble-then-Compute Hung Dang, Anh Dinh, Ee-Chien Chang, Beng Chin Ooi School of Computing National University of Singapore The Problem Context:
The extreme Adaptive DSP Solution to Sensor Data Processing
 The extreme Adaptive DSP Solution to Sensor Data Processing Abstract Martin Vorbach PACT XPP Technologies Leo Mirkin Sky Computers, Inc. The new ISR mobile autonomous sensor platforms present a difficult
The extreme Adaptive DSP Solution to Sensor Data Processing Abstract Martin Vorbach PACT XPP Technologies Leo Mirkin Sky Computers, Inc. The new ISR mobile autonomous sensor platforms present a difficult
Power Protocol: Reducing Power Dissipation on Off-Chip Data Buses
 Power Protocol: Reducing Power Dissipation on Off-Chip Data Buses K. Basu, A. Choudhary, J. Pisharath ECE Department Northwestern University Evanston, IL 60208, USA fkohinoor,choudhar,jayg@ece.nwu.edu
Power Protocol: Reducing Power Dissipation on Off-Chip Data Buses K. Basu, A. Choudhary, J. Pisharath ECE Department Northwestern University Evanston, IL 60208, USA fkohinoor,choudhar,jayg@ece.nwu.edu
Using a Victim Buffer in an Application-Specific Memory Hierarchy
 Using a Victim Buffer in an Application-Specific Memory Hierarchy Chuanjun Zhang Depment of lectrical ngineering University of California, Riverside czhang@ee.ucr.edu Frank Vahid Depment of Computer Science
Using a Victim Buffer in an Application-Specific Memory Hierarchy Chuanjun Zhang Depment of lectrical ngineering University of California, Riverside czhang@ee.ucr.edu Frank Vahid Depment of Computer Science
Jazz: A Tool for Demand-Driven Structural Testing
 Jazz: A Tool for Demand-Driven Structural Testing J. Misurda, J. A. Clause, J. L. Reed, P. Gandra, B. R. Childers, and M. L. Soffa Department of Computer Science University of Pittsburgh Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania
Jazz: A Tool for Demand-Driven Structural Testing J. Misurda, J. A. Clause, J. L. Reed, P. Gandra, B. R. Childers, and M. L. Soffa Department of Computer Science University of Pittsburgh Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania
Research Statement. Yehuda Lindell. Dept. of Computer Science Bar-Ilan University, Israel.
 Research Statement Yehuda Lindell Dept. of Computer Science Bar-Ilan University, Israel. lindell@cs.biu.ac.il www.cs.biu.ac.il/ lindell July 11, 2005 The main focus of my research is the theoretical foundations
Research Statement Yehuda Lindell Dept. of Computer Science Bar-Ilan University, Israel. lindell@cs.biu.ac.il www.cs.biu.ac.il/ lindell July 11, 2005 The main focus of my research is the theoretical foundations
Language and Compiler Support for Out-of-Core Irregular Applications on Distributed-Memory Multiprocessors
 Language and Compiler Support for Out-of-Core Irregular Applications on Distributed-Memory Multiprocessors Peter Brezany 1, Alok Choudhary 2, and Minh Dang 1 1 Institute for Software Technology and Parallel
Language and Compiler Support for Out-of-Core Irregular Applications on Distributed-Memory Multiprocessors Peter Brezany 1, Alok Choudhary 2, and Minh Dang 1 1 Institute for Software Technology and Parallel
High Performance Single-Chip FPGA Rijndael Algorithm Implementations
 High Performance Single-Chip FPGA Rijndael Algorithm Implementations Máire McLoone and J.V McCanny DSiP TM Laboratories, School of Electrical and Electronic Engineering, The Queen s University of Belfast,
High Performance Single-Chip FPGA Rijndael Algorithm Implementations Máire McLoone and J.V McCanny DSiP TM Laboratories, School of Electrical and Electronic Engineering, The Queen s University of Belfast,
Implementation of Stronger S-Box for Advanced Encryption Standard
 The International Journal Of Engineering And Science (IJES) Volume 3 Issue 12 December - 2014 Pages 39-47 ISSN (e): 2319 1813 ISSN (p): 2319 1805 Implementation of Stronger S-Box for Advanced Encryption
The International Journal Of Engineering And Science (IJES) Volume 3 Issue 12 December - 2014 Pages 39-47 ISSN (e): 2319 1813 ISSN (p): 2319 1805 Implementation of Stronger S-Box for Advanced Encryption
Performance of tournament predictors In the last lecture, we saw the design of the tournament predictor used by the Alpha
 Performance of tournament predictors In the last lecture, we saw the design of the tournament predictor used by the Alpha 21264. The Alpha s predictor is very successful. On the SPECfp 95 benchmarks, there
Performance of tournament predictors In the last lecture, we saw the design of the tournament predictor used by the Alpha 21264. The Alpha s predictor is very successful. On the SPECfp 95 benchmarks, there
Improving Data Cache Performance via Address Correlation: An Upper Bound Study
 Improving Data Cache Performance via Address Correlation: An Upper Bound Study Peng-fei Chuang 1, Resit Sendag 2, and David J. Lilja 1 1 Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Minnesota Supercomputing
Improving Data Cache Performance via Address Correlation: An Upper Bound Study Peng-fei Chuang 1, Resit Sendag 2, and David J. Lilja 1 1 Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Minnesota Supercomputing
CACHE-CONSCIOUS ALLOCATION OF POINTER- BASED DATA STRUCTURES
 CACHE-CONSCIOUS ALLOCATION OF POINTER- BASED DATA STRUCTURES Angad Kataria, Simran Khurana Student,Department Of Information Technology Dronacharya College Of Engineering,Gurgaon Abstract- Hardware trends
CACHE-CONSCIOUS ALLOCATION OF POINTER- BASED DATA STRUCTURES Angad Kataria, Simran Khurana Student,Department Of Information Technology Dronacharya College Of Engineering,Gurgaon Abstract- Hardware trends
A Low Power and High Speed MPSOC Architecture for Reconfigurable Application
 ISSN (Online) : 2319-8753 ISSN (Print) : 2347-6710 International Journal of Innovative Research in Science, Engineering and Technology Volume 3, Special Issue 3, March 2014 2014 International Conference
ISSN (Online) : 2319-8753 ISSN (Print) : 2347-6710 International Journal of Innovative Research in Science, Engineering and Technology Volume 3, Special Issue 3, March 2014 2014 International Conference
