RAII and Smart Pointers. Ali Malik
|
|
|
- Della Underwood
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 RAII and Smart Pointers Ali Malik
2 Game Plan Recap Conversion Operators RAII Smart Pointers
3 Recap
4 Initialisation: Initialisation vs Assignment Transforms an object s initial junk data into valid data. Assignment: Replaces existing valid data with other valid data.
5 Constructors Normal Constructor: What you are used to! Copy Constructor Initialise an instance of a type to be a copy of another instance Copy Assignment Not a constructor Assign an instance of a type to be a copy of another instance
6 The Rule of Three If you implement a copy constructor, assignment operator, or destructor, you should implement the others, as well
7 Conversion Operators
8 Conversion Operators Let you define how a class can be converted to other types. For example, we could define a conversion of the MyVector to a bool to be false if the vector is empty and true otherwise.
9 Converting to Type works by overloading the Type() operator. Doesn t have a return value. Conversion Operators class MyClass { public: operator Type() { // return something of type Type } }
10 Conversion Operators An example defining a bool conversion for MyVector : class MyVector { public: operator bool() { return empty(); } }; MyVector v; if(v) { cout << v[0] << endl; }
11 RAII
12 Resource Let s first talk about the abstraction of a resource. We will look at file opening and closing in C as a case study.
13 C File I/O To read a file in C, you need to: 1. Open the file with fopen 2. Read data using fgets 3. Close the open file with fclose If a programmer doesn t remember to close an open file, bad things happen (memory leaks, crashes etc.)
14 C File I/O You can think of this as a resource. What is a resource? Anything that exists in limited supply. Something you have to acquire and release. Examples: memory, open files, sockets etc.
15 C File I/O To read a file in C, you need to: 1. Open the file with fopen 2. Read data using fgets 3. Close the open file with fclose If a programmer doesn t remember to close an open file, bad things happen (memory leaks, crashes etc.)
16 C File I/O To read a file in C, you need to: 1. Open the file with fopen // acquire 2. Read data using fgets 3. Close the open file with fclose If a programmer doesn t remember to close an open file, bad things happen (memory leaks, crashes etc.)
17 C File I/O To read a file in C, you need to: 1. Open the file with fopen // acquire 2. Read data using fgets 3. Close the open file with fclose // release If a programmer doesn t remember to close an open file, bad things happen (memory leaks, crashes etc.)
18 Other examples of resources: Resources Acquire Release Files fopen fclose Memory new, new[] delete, delete[] Locks lock, try_lock unlock Sockets socket close
19 RAII Resource Acquisition Is Initialisation
20 RAII A modern C++ idiom. When you initialize an object, it should already have acquired any resources it needs (in the constructor). When an object goes out of scope, it should release every resource it is using (using the destructor).
21 RAII Key points: There should never be a half-ready or half-dead object. When an object is created, it should be in a ready state. When an object goes out of scope, it should release its resources.
22 RAII Key points: There should never be a half-ready or half-dead object. When an object is created, it should be in a ready state. When an object goes out of scope, it should release its resources. The user shouldn t have to do anything more.
23 How does C File I/O violate RAII? C File I/O void printfile(const char* name) { // acquire file resource FILE* f = fopen(name, "r"); // print contents of f } // release file resource fclose(f);
24 How does C File I/O violate RAII? C File I/O void printfile(const char* name) { // acquire file resource FILE* f = fopen(name, "r"); // print contents of f } // release file resource fclose(f);
25 How does C File I/O violate RAII? C File I/O void printfile(const char* name) { // acquire file resource FILE* f = fopen(name, "r"); // print contents of f // release file resource? }
26 How does C File I/O violate RAII? C File I/O void printfile(const char* name) { // acquire file resource FILE* f = fopen(name, "r"); } // print contents of f // release file resource? f goes out of scope, but doesn t release its resources.
27 C File I/O What would be an RAII friendly solution for C File I/O?
28 C File I/O + RAII class FileObj { public: FILE* ptr; FileObj(char* name) : ptr(fopen(name, "r") {} }; ~FileObj() { fclose(ptr); }
29 C File I/O Our new printfile method would look like: void printfile(const char* name) { // initialization will acquire resources FileObj fobj(name); // print contents of f } // FileObj destructor will release resources
30 In fact, you have already been using RAII! For example: C File I/O You can create an ifstream and it will open the file When the ifstream goes out of scope, its destructor closes the file. Don t actually need to call the.close() method.
31 RAII - An Aside RAII is a bad name for the concept. "The best example of why I shouldn't be in marketing" "I didn't have a good day when I named that" Bjarne Stroustrup, still unhappy with the name RAII in 2012
32 A better name is probably: RAII - An Aside Constructor Acquires, Destructor Releases or Scope Based Resource Management
33 Smart Pointers
34 Smart Pointers What is another thing that violates RAII? Raw Pointers and heap allocation!
35 Smart Pointers Calls to new acquire resource (memory). Calls to delete release resource. But this is not automatically done when the pointers go out of scope.
36 Smart Pointers But this is not automatically done when the pointers go out of scope: void rawptrfn() { // acquire memory resource Node* n = new Node; } // manually release memory delete n;
37 Smart Pointers But this is not automatically done when the pointers go out of scope: void rawptrfn() { // acquire memory resource Node* n = new Node; } // manually release memory delete n; If we forget this, we leak memory.
38 Smart Pointers What would be an RAII solution to this? Have a class that Allocates the memory when initialized Frees the memory when destructor is called Allows access to underlying pointer
39 Let s plan and write this up: Smart Pointers Smart Pointers (RAIIPtr_unique.pro)
40 First we make a smart pointer Smart Pointers SmartPtr<int> x; resource Data (heap)
41 Smart Pointers We then make a copy of our smart pointer SmartPtr<int> y; resource SmartPtr<int> x; resource Data (heap)
42 Smart Pointers When y goes out of scope, it deletes the heap data SmartPtr<int> y; resource SmartPtr<int> x; resource Data (heap)
43 Smart Pointers This leaves x pointing at deallocated data SmartPtr<int> x; resource
44 Smart Pointers If we dereference x or its destructor calls delete, we crash SmartPtr<int> x; resource
45 Smart Pointers If we dereference x or its destructor calls delete, we crash SmartPtr<int> x; resource
46 Smart Pointers Have to be careful when copying an RAII object Don t want two objects thinking they both exclusively own a resource
47 Smart Pointers C++ already has built-in smart pointers. std::unique_ptr std::shared_ptr std::weak_ptr
48 unique_ptr Similar to what we wrote earlier Uniquely own its resource and deletes it when the object is destroyed Cannot be copied! { std::unique_ptr<int> p(new int); // Use p } // Freed!
49 shared_ptr Resource can be stored by any number of shared_ptrs Deleted when none of them point to it { std::shared_ptr<int> p1(new int); // Use p1 { std::shared_ptr<int> p2 = p1; // Use p1 and p2 } // Use p1 } // Freed!
50 How are these implemented? shared_ptr Reference counting! Store an int that keeps track of the number currently referencing that data Gets incremented in copy constructor/copy assignment Gets decremented in destructor or when overwritten with copy assignment Frees the resource when reference count hits 0
51 Smart Pointers See Course Reader pg. 351 onwards for details. Let s plan and write this up: Smart Pointers (RAIIPtr_shared.pro)
52 Used to deal with circular references of shared_ptr Read documentation to learn more! weak_ptr
53 Next Time Final Topics
54
Pointers. Developed By Ms. K.M.Sanghavi
 Pointers Developed By Ms. K.M.Sanghavi Memory Management : Dynamic Pointers Linked List Example Smart Pointers Auto Pointer Unique Pointer Shared Pointer Weak Pointer Memory Management In order to create
Pointers Developed By Ms. K.M.Sanghavi Memory Management : Dynamic Pointers Linked List Example Smart Pointers Auto Pointer Unique Pointer Shared Pointer Weak Pointer Memory Management In order to create
CSE 333 Lecture smart pointers
 CSE 333 Lecture 14 -- smart pointers Hal Perkins Paul G. Allen School of Computer Science & Engineering University of Washington Administrivia New exercise out today, due Wednesday morning Exam Friday
CSE 333 Lecture 14 -- smart pointers Hal Perkins Paul G. Allen School of Computer Science & Engineering University of Washington Administrivia New exercise out today, due Wednesday morning Exam Friday
CSE 333 Lecture smart pointers
 CSE 333 Lecture 14 -- smart pointers Hal Perkins Department of Computer Science & Engineering University of Washington Administrivia Midterm Friday - Review in sections this week - Closed book; topic list
CSE 333 Lecture 14 -- smart pointers Hal Perkins Department of Computer Science & Engineering University of Washington Administrivia Midterm Friday - Review in sections this week - Closed book; topic list
Homework 4. Any questions?
 CSE333 SECTION 8 Homework 4 Any questions? STL Standard Template Library Has many pre-build container classes STL containers store by value, not by reference Should try to use this as much as possible
CSE333 SECTION 8 Homework 4 Any questions? STL Standard Template Library Has many pre-build container classes STL containers store by value, not by reference Should try to use this as much as possible
C++ Smart Pointers. CSE 333 Autumn 2018
 C++ Smart Pointers CSE 333 Autumn 2018 Instructor: Hal Perkins Teaching Assistants: Tarkan Al-Kazily Renshu Gu Trais McGaha Harshita Neti Thai Pham Forrest Timour Soumya Vasisht Yifan Xu Administriia New
C++ Smart Pointers CSE 333 Autumn 2018 Instructor: Hal Perkins Teaching Assistants: Tarkan Al-Kazily Renshu Gu Trais McGaha Harshita Neti Thai Pham Forrest Timour Soumya Vasisht Yifan Xu Administriia New
04-17 Discussion Notes
 04-17 Discussion Notes PIC 10B Spring 2018 1 RAII RAII is an acronym for the idiom Resource Acquisition is Initialization. What is meant by resource acquisition is initialization is that a resource should
04-17 Discussion Notes PIC 10B Spring 2018 1 RAII RAII is an acronym for the idiom Resource Acquisition is Initialization. What is meant by resource acquisition is initialization is that a resource should
Smart Pointers. Some slides from Internet
 Smart Pointers Some slides from Internet 1 Part I: Concept Reference: Using C++11 s Smart Pointers, David Kieras, EECS Department, University of Michigan C++ Primer, Stanley B. Lippman, Jesee Lajoie, Barbara
Smart Pointers Some slides from Internet 1 Part I: Concept Reference: Using C++11 s Smart Pointers, David Kieras, EECS Department, University of Michigan C++ Primer, Stanley B. Lippman, Jesee Lajoie, Barbara
CS 241 Honors Memory
 CS 241 Honors Memory Ben Kurtovic Atul Sandur Bhuvan Venkatesh Brian Zhou Kevin Hong University of Illinois Urbana Champaign February 20, 2018 CS 241 Course Staff (UIUC) Memory February 20, 2018 1 / 35
CS 241 Honors Memory Ben Kurtovic Atul Sandur Bhuvan Venkatesh Brian Zhou Kevin Hong University of Illinois Urbana Champaign February 20, 2018 CS 241 Course Staff (UIUC) Memory February 20, 2018 1 / 35
Lecture 15a Persistent Memory & Shared Pointers
 Lecture 15a Persistent Memory & Shared Pointers Dec. 5 th, 2017 Jack Applin, Guest Lecturer 2017-12-04 CS253 Fall 2017 Jack Applin & Bruce Draper 1 Announcements PA9 is due today Recitation : extra help
Lecture 15a Persistent Memory & Shared Pointers Dec. 5 th, 2017 Jack Applin, Guest Lecturer 2017-12-04 CS253 Fall 2017 Jack Applin & Bruce Draper 1 Announcements PA9 is due today Recitation : extra help
CSCI-1200 Data Structures Fall 2011 Lecture 24 Garbage Collection & Smart Pointers
 CSCI-1200 Data Structures Fall 2011 Lecture 24 Garbage Collection & Smart Pointers Review from Lecture 23 Basic exception mechanisms: try/throw/catch Functions & exceptions, constructors & exceptions Today
CSCI-1200 Data Structures Fall 2011 Lecture 24 Garbage Collection & Smart Pointers Review from Lecture 23 Basic exception mechanisms: try/throw/catch Functions & exceptions, constructors & exceptions Today
COMP6771 Advanced C++ Programming
 1.. COMP6771 Advanced C++ Programming Week 5 Part Two: Dynamic Memory Management 2016 www.cse.unsw.edu.au/ cs6771 2.. Revisited 1 #include 2 3 struct X { 4 X() { std::cout
1.. COMP6771 Advanced C++ Programming Week 5 Part Two: Dynamic Memory Management 2016 www.cse.unsw.edu.au/ cs6771 2.. Revisited 1 #include 2 3 struct X { 4 X() { std::cout
Assertions and Exceptions
 CS 247: Software Engineering Principles Assertions and Exceptions Reading: Eckel, Vol. 2 Ch. 1 Exception Handling U Waterloo CS247 (Spring 2017) p.1/32 Defensive Programming The question isn t whether
CS 247: Software Engineering Principles Assertions and Exceptions Reading: Eckel, Vol. 2 Ch. 1 Exception Handling U Waterloo CS247 (Spring 2017) p.1/32 Defensive Programming The question isn t whether
C++ Programming Lecture 7 Software Engineering Group
 C++ Programming Lecture 7 Software Engineering Group Philipp D. Schubert Contents 1. Template metaprogramming 2. Variadic template arguments 3. Smart pointer Template metaprogramming Template metaprogramming
C++ Programming Lecture 7 Software Engineering Group Philipp D. Schubert Contents 1. Template metaprogramming 2. Variadic template arguments 3. Smart pointer Template metaprogramming Template metaprogramming
CSCI-1200 Data Structures Spring 2017 Lecture 27 Garbage Collection & Smart Pointers
 CSCI-1200 Data Structures Spring 2017 Lecture 27 Garbage Collection & Smart Pointers Announcements Please fill out your course evaluations! Those of you interested in becoming an undergraduate mentor for
CSCI-1200 Data Structures Spring 2017 Lecture 27 Garbage Collection & Smart Pointers Announcements Please fill out your course evaluations! Those of you interested in becoming an undergraduate mentor for
G52CPP C++ Programming Lecture 16
 G52CPP C++ Programming Lecture 16 Dr Jason Atkin http://www.cs.nott.ac.uk/~jaa/cpp/ g52cpp.html 1 Last Lecture Casting static cast dynamic cast const cast reinterpret cast Implicit type conversion 2 How
G52CPP C++ Programming Lecture 16 Dr Jason Atkin http://www.cs.nott.ac.uk/~jaa/cpp/ g52cpp.html 1 Last Lecture Casting static cast dynamic cast const cast reinterpret cast Implicit type conversion 2 How
Memory Leak. C++: Memory Problems. Memory Leak. Memory Leak. Pointer Ownership. Memory Leak
 Memory Leak C++ Memory Problems or When Good Memory Goes Bad A bug in a program that prevents it from freeing up memory that it no longer needs. As a result, the program grabs more and more memory until
Memory Leak C++ Memory Problems or When Good Memory Goes Bad A bug in a program that prevents it from freeing up memory that it no longer needs. As a result, the program grabs more and more memory until
COMP6771 Advanced C++ Programming
 1.... COMP6771 Advanced C++ Programming Week 5 Part One: Exception Handling 2016 www.cse.unsw.edu.au/ cs6771 2.... Memory Management & Exception Handling.1 Part I: Exception Handling Exception objects
1.... COMP6771 Advanced C++ Programming Week 5 Part One: Exception Handling 2016 www.cse.unsw.edu.au/ cs6771 2.... Memory Management & Exception Handling.1 Part I: Exception Handling Exception objects
Vector and Free Store (Pointers and Memory Allocation)
 DM560 Introduction to Programming in C++ Vector and Free Store (Pointers and Memory Allocation) Marco Chiarandini Department of Mathematics & Computer Science University of Southern Denmark [Based on slides
DM560 Introduction to Programming in C++ Vector and Free Store (Pointers and Memory Allocation) Marco Chiarandini Department of Mathematics & Computer Science University of Southern Denmark [Based on slides
Object-Oriented Programming for Scientific Computing
 Object-Oriented Programming for Scientific Computing Smart Pointers and Constness Ole Klein Interdisciplinary Center for Scientific Computing Heidelberg University ole.klein@iwr.uni-heidelberg.de Summer
Object-Oriented Programming for Scientific Computing Smart Pointers and Constness Ole Klein Interdisciplinary Center for Scientific Computing Heidelberg University ole.klein@iwr.uni-heidelberg.de Summer
Intermediate C++ 1/83
 Intermediate C++ 1/83 Sections I. Memory Management Basics II. The C++ Standard Library III. Casting IV. Resource Management: RAII 2/83 I. Memory Management Basics 1. Checking for memory leaks 2. Pass
Intermediate C++ 1/83 Sections I. Memory Management Basics II. The C++ Standard Library III. Casting IV. Resource Management: RAII 2/83 I. Memory Management Basics 1. Checking for memory leaks 2. Pass
Chapter 17 vector and Free Store. Bjarne Stroustrup
 Chapter 17 vector and Free Store Bjarne Stroustrup www.stroustrup.com/programming Overview Vector revisited How are they implemented? Pointers and free store Allocation (new) Access Arrays and subscripting:
Chapter 17 vector and Free Store Bjarne Stroustrup www.stroustrup.com/programming Overview Vector revisited How are they implemented? Pointers and free store Allocation (new) Access Arrays and subscripting:
Engineering Robust Server Software
 Engineering Robust Server Software Exceptions Exceptions Handling problems: exceptions C++ Java temp-and-swap RAII Smart Pointers finally specifications finalizers (and why they are not what you need for
Engineering Robust Server Software Exceptions Exceptions Handling problems: exceptions C++ Java temp-and-swap RAII Smart Pointers finally specifications finalizers (and why they are not what you need for
05-01 Discussion Notes
 05-01 Discussion Notes PIC 10B Spring 2018 1 Exceptions 1.1 Introduction Exceptions are used to signify that a function is being used incorrectly. Once an exception is thrown, it is up to the programmer
05-01 Discussion Notes PIC 10B Spring 2018 1 Exceptions 1.1 Introduction Exceptions are used to signify that a function is being used incorrectly. Once an exception is thrown, it is up to the programmer
Chapter 17 vector and Free Store
 Chapter 17 vector and Free Store Bjarne Stroustrup www.stroustrup.com/programming Overview Vector revisited How are they implemented? Pointers and free store Allocation (new) Access Arrays and subscripting:
Chapter 17 vector and Free Store Bjarne Stroustrup www.stroustrup.com/programming Overview Vector revisited How are they implemented? Pointers and free store Allocation (new) Access Arrays and subscripting:
Consider the program...
 Smart Pointers Consider the program... When the scope of foo is entered storage for pointer x is created The new allocates storage on the heap class X {... When the scope foo is left, the storage for x
Smart Pointers Consider the program... When the scope of foo is entered storage for pointer x is created The new allocates storage on the heap class X {... When the scope foo is left, the storage for x
Chapter 17 vector and Free Store
 Chapter 17 vector and Free Store Hartmut Kaiser hkaiser@cct.lsu.edu http://www.cct.lsu.edu/~hkaiser/fall_2010/csc1253.html Slides adapted from: Bjarne Stroustrup, Programming Principles and Practice using
Chapter 17 vector and Free Store Hartmut Kaiser hkaiser@cct.lsu.edu http://www.cct.lsu.edu/~hkaiser/fall_2010/csc1253.html Slides adapted from: Bjarne Stroustrup, Programming Principles and Practice using
CS93SI Handout 04 Spring 2006 Apr Review Answers
 CS93SI Handout 04 Spring 2006 Apr 6 2006 Review Answers I promised answers to these questions, so here they are. I'll probably readdress the most important of these over and over again, so it's not terribly
CS93SI Handout 04 Spring 2006 Apr 6 2006 Review Answers I promised answers to these questions, so here they are. I'll probably readdress the most important of these over and over again, so it's not terribly
CSE 333 Lecture smart pointers
 CSE 333 Lecture 13 -- smart pointers Steve Gribble Department of Computer Science & Engineering University of Washington Administrivia HW2 is due on Thursday! - check out the discussion board for a few
CSE 333 Lecture 13 -- smart pointers Steve Gribble Department of Computer Science & Engineering University of Washington Administrivia HW2 is due on Thursday! - check out the discussion board for a few
Object-Oriented Programming for Scientific Computing
 Object-Oriented Programming for Scientific Computing Dynamic Memory Management Ole Klein Interdisciplinary Center for Scientific Computing Heidelberg University ole.klein@iwr.uni-heidelberg.de 2. Mai 2017
Object-Oriented Programming for Scientific Computing Dynamic Memory Management Ole Klein Interdisciplinary Center for Scientific Computing Heidelberg University ole.klein@iwr.uni-heidelberg.de 2. Mai 2017
Pointers! Arizona State University 1
 Pointers! CSE100 Principles of Programming with C++, Fall 2018 (based off Chapter 10 slides by Pearson) Ryan Dougherty Arizona State University http://www.public.asu.edu/~redoughe/ Arizona State University
Pointers! CSE100 Principles of Programming with C++, Fall 2018 (based off Chapter 10 slides by Pearson) Ryan Dougherty Arizona State University http://www.public.asu.edu/~redoughe/ Arizona State University
Arrays. Returning arrays Pointers Dynamic arrays Smart pointers Vectors
 Arrays Returning arrays Pointers Dynamic arrays Smart pointers Vectors To declare an array specify the type, its name, and its size in []s int arr1[10]; //or int arr2[] = {1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8}; arr2 has 8
Arrays Returning arrays Pointers Dynamic arrays Smart pointers Vectors To declare an array specify the type, its name, and its size in []s int arr1[10]; //or int arr2[] = {1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8}; arr2 has 8
Vector and Free Store (Vectors and Arrays)
 DM560 Introduction to Programming in C++ Vector and Free Store (Vectors and Arrays) Marco Chiarandini Department of Mathematics & Computer Science University of Southern Denmark [Based on slides by Bjarne
DM560 Introduction to Programming in C++ Vector and Free Store (Vectors and Arrays) Marco Chiarandini Department of Mathematics & Computer Science University of Southern Denmark [Based on slides by Bjarne
COMP322 - Introduction to C++ Lecture 10 - Overloading Operators and Exceptions
 COMP322 - Introduction to C++ Lecture 10 - Overloading Operators and Exceptions Dan Pomerantz School of Computer Science 19 March 2012 Overloading operators in classes It is useful sometimes to define
COMP322 - Introduction to C++ Lecture 10 - Overloading Operators and Exceptions Dan Pomerantz School of Computer Science 19 March 2012 Overloading operators in classes It is useful sometimes to define
Pointers, Dynamic Data, and Reference Types
 Pointers, Dynamic Data, and Reference Types Review on Pointers Reference Variables Dynamic Memory Allocation The new operator The delete operator Dynamic Memory Allocation for Arrays 1 C++ Data Types simple
Pointers, Dynamic Data, and Reference Types Review on Pointers Reference Variables Dynamic Memory Allocation The new operator The delete operator Dynamic Memory Allocation for Arrays 1 C++ Data Types simple
a data type is Types
 Pointers Class 2 a data type is Types Types a data type is a set of values a set of operations defined on those values in C++ (and most languages) there are two flavors of types primitive or fundamental
Pointers Class 2 a data type is Types Types a data type is a set of values a set of operations defined on those values in C++ (and most languages) there are two flavors of types primitive or fundamental
Project. C++: Smart Pointers. The Plan. Announcement. Memory Leak. Pointer Ownership. Today: STL 1 Wednesday: STL 2 Thursday: Smart Pointers
 Project C++: Smart Pointers Takeaway submitted. Next submission: Nim Oct 26 th Remember: okay to change framework Make sure all games work with framework Memory checks Your program should do proper memory
Project C++: Smart Pointers Takeaway submitted. Next submission: Nim Oct 26 th Remember: okay to change framework Make sure all games work with framework Memory checks Your program should do proper memory
CSCI-1200 Data Structures Spring 2018 Lecture 25 Garbage Collection & Smart Pointers
 CSCI-1200 Data Structures Spring 2018 Lecture 25 Garbage Collection & Smart Pointers Announcements Please fill out your course evaluations! Those of you interested in becoming an undergraduate mentor for
CSCI-1200 Data Structures Spring 2018 Lecture 25 Garbage Collection & Smart Pointers Announcements Please fill out your course evaluations! Those of you interested in becoming an undergraduate mentor for
vector and Free Store
 vector and Free Store Abstract Vector is not just the most useful standard container, it is also provides examples of some of the most important/powerful/interesting implementation techniques. In this
vector and Free Store Abstract Vector is not just the most useful standard container, it is also provides examples of some of the most important/powerful/interesting implementation techniques. In this
Modern C++ for Computer Vision and Image Processing. Igor Bogoslavskyi
 Modern C++ for Computer Vision and Image Processing Igor Bogoslavskyi Outline Using pointers Pointers are polymorphic Pointer this Using const with pointers Stack and Heap Memory leaks and dangling pointers
Modern C++ for Computer Vision and Image Processing Igor Bogoslavskyi Outline Using pointers Pointers are polymorphic Pointer this Using const with pointers Stack and Heap Memory leaks and dangling pointers
Lecture 2, September 4
 Lecture 2, September 4 Intro to C/C++ Instructor: Prashant Shenoy, TA: Shashi Singh 1 Introduction C++ is an object-oriented language and is one of the most frequently used languages for development due
Lecture 2, September 4 Intro to C/C++ Instructor: Prashant Shenoy, TA: Shashi Singh 1 Introduction C++ is an object-oriented language and is one of the most frequently used languages for development due
Reminder: compiling & linking
 Reminder: compiling & linking source file 1 object file 1 source file 2 compilation object file 2 library object file 1 linking (relocation + linking) load file source file N object file N library object
Reminder: compiling & linking source file 1 object file 1 source file 2 compilation object file 2 library object file 1 linking (relocation + linking) load file source file N object file N library object
Abstract. Vector. Overview. Building from the ground up. Building from the ground up 1/8/10. Chapter 17 vector and Free Store
 Chapter 17 vector and Free Store Bjarne Stroustrup www.stroustrup.com/programming Abstract Vector is not just the most useful standard container, it is also provides examples of some of the most important/powerful/
Chapter 17 vector and Free Store Bjarne Stroustrup www.stroustrup.com/programming Abstract Vector is not just the most useful standard container, it is also provides examples of some of the most important/powerful/
Programming in C and C++
 Programming in C and C++ 5. C++: Overloading, Namespaces, and Classes Dr. Neel Krishnaswami University of Cambridge (based on notes from and with thanks to Anil Madhavapeddy, Alan Mycroft, Alastair Beresford
Programming in C and C++ 5. C++: Overloading, Namespaces, and Classes Dr. Neel Krishnaswami University of Cambridge (based on notes from and with thanks to Anil Madhavapeddy, Alan Mycroft, Alastair Beresford
G52CPP C++ Programming Lecture 17
 G52CPP C++ Programming Lecture 17 Dr Jason Atkin http://www.cs.nott.ac.uk/~jaa/cpp/ g52cpp.html 1 Last Lecture Exceptions How to throw (return) different error values as exceptions And catch the exceptions
G52CPP C++ Programming Lecture 17 Dr Jason Atkin http://www.cs.nott.ac.uk/~jaa/cpp/ g52cpp.html 1 Last Lecture Exceptions How to throw (return) different error values as exceptions And catch the exceptions
Ch. 12: Operator Overloading
 Ch. 12: Operator Overloading Operator overloading is just syntactic sugar, i.e. another way to make a function call: shift_left(42, 3); 42
Ch. 12: Operator Overloading Operator overloading is just syntactic sugar, i.e. another way to make a function call: shift_left(42, 3); 42
CSE 333. Lecture 11 - constructor insanity. Hal Perkins Paul G. Allen School of Computer Science & Engineering University of Washington
 CSE 333 Lecture 11 - constructor insanity Hal Perkins Paul G. Allen School of Computer Science & Engineering University of Washington Administrivia Exercises: - New exercise out today, due Monday morning
CSE 333 Lecture 11 - constructor insanity Hal Perkins Paul G. Allen School of Computer Science & Engineering University of Washington Administrivia Exercises: - New exercise out today, due Monday morning
Laboratorio di Tecnologie dell'informazione. Ing. Marco Bertini
 Laboratorio di Tecnologie dell'informazione Ing. Marco Bertini bertini@dsi.unifi.it http://www.dsi.unifi.it/~bertini/ Resource Management Memory, auto_ptr and RAII The most commonly used resource in
Laboratorio di Tecnologie dell'informazione Ing. Marco Bertini bertini@dsi.unifi.it http://www.dsi.unifi.it/~bertini/ Resource Management Memory, auto_ptr and RAII The most commonly used resource in
G52CPP C++ Programming Lecture 20
 G52CPP C++ Programming Lecture 20 Dr Jason Atkin http://www.cs.nott.ac.uk/~jaa/cpp/ g52cpp.html 1 Wrapping up Slicing Problem Smart pointers More C++ things Exams 2 The slicing problem 3 Objects are not
G52CPP C++ Programming Lecture 20 Dr Jason Atkin http://www.cs.nott.ac.uk/~jaa/cpp/ g52cpp.html 1 Wrapping up Slicing Problem Smart pointers More C++ things Exams 2 The slicing problem 3 Objects are not
COMP 2355 Introduction to Systems Programming
 COMP 2355 Introduction to Systems Programming Christian Grothoff christian@grothoff.org http://grothoff.org/christian/ 1 Today Class syntax, Constructors, Destructors Static methods Inheritance, Abstract
COMP 2355 Introduction to Systems Programming Christian Grothoff christian@grothoff.org http://grothoff.org/christian/ 1 Today Class syntax, Constructors, Destructors Static methods Inheritance, Abstract
Midterm Review. PIC 10B Spring 2018
 Midterm Review PIC 10B Spring 2018 Q1 What is size t and when should it be used? A1 size t is an unsigned integer type used for indexing containers and holding the size of a container. It is guarenteed
Midterm Review PIC 10B Spring 2018 Q1 What is size t and when should it be used? A1 size t is an unsigned integer type used for indexing containers and holding the size of a container. It is guarenteed
Laboratorio di Tecnologie dell'informazione
 Laboratorio di Tecnologie dell'informazione Ing. Marco Bertini marco.bertini@unifi.it http://www.micc.unifi.it/bertini/ Resource Management Memory, smart pointers and RAII Resource management The most
Laboratorio di Tecnologie dell'informazione Ing. Marco Bertini marco.bertini@unifi.it http://www.micc.unifi.it/bertini/ Resource Management Memory, smart pointers and RAII Resource management The most
Laboratorio di Tecnologie dell'informazione
 Laboratorio di Tecnologie dell'informazione Ing. Marco Bertini marco.bertini@unifi.it http://www.micc.unifi.it/bertini/ Resource Management Memory, smart pointers and RAII Resource management The most
Laboratorio di Tecnologie dell'informazione Ing. Marco Bertini marco.bertini@unifi.it http://www.micc.unifi.it/bertini/ Resource Management Memory, smart pointers and RAII Resource management The most
CMSC 341 Lecture 7 Lists
 CMSC 341 Lecture 7 Lists Today s Topics Linked Lists vs Arrays Nodes Using Linked Lists Supporting Actors (member variables) Overview Creation Traversal Deletion UMBC CMSC 341 Lists 2 Linked Lists vs Arrays
CMSC 341 Lecture 7 Lists Today s Topics Linked Lists vs Arrays Nodes Using Linked Lists Supporting Actors (member variables) Overview Creation Traversal Deletion UMBC CMSC 341 Lists 2 Linked Lists vs Arrays
The issues. Programming in C++ Common storage modes. Static storage in C++ Session 8 Memory Management
 Session 8 Memory Management The issues Dr Christos Kloukinas City, UoL http://staff.city.ac.uk/c.kloukinas/cpp (slides originally produced by Dr Ross Paterson) Programs manipulate data, which must be stored
Session 8 Memory Management The issues Dr Christos Kloukinas City, UoL http://staff.city.ac.uk/c.kloukinas/cpp (slides originally produced by Dr Ross Paterson) Programs manipulate data, which must be stored
Classes and Pointers: Some Peculiarities
 Classes and Pointers: Some Peculiarities Dr. Mardé Helbig Dr. Mardé Helbig, COS 110 1 Issues with Destructor ~ void print Which method is the constructor? How is the constructor different from other methods?
Classes and Pointers: Some Peculiarities Dr. Mardé Helbig Dr. Mardé Helbig, COS 110 1 Issues with Destructor ~ void print Which method is the constructor? How is the constructor different from other methods?
A Crash Course in (Some of) Modern C++
 CMPT 373 Software Development Methods A Crash Course in (Some of) Modern C++ Nick Sumner wsumner@sfu.ca With material from Bjarne Stroustrup & Herb Sutter C++ was complicated/intimidating Pointers Arithmetic
CMPT 373 Software Development Methods A Crash Course in (Some of) Modern C++ Nick Sumner wsumner@sfu.ca With material from Bjarne Stroustrup & Herb Sutter C++ was complicated/intimidating Pointers Arithmetic
CS
 CS 1666 www.cs.pitt.edu/~nlf4/cs1666/ Programming in C++ First, some praise for C++ "It certainly has its good points. But by and large I think it s a bad language. It does a lot of things half well and
CS 1666 www.cs.pitt.edu/~nlf4/cs1666/ Programming in C++ First, some praise for C++ "It certainly has its good points. But by and large I think it s a bad language. It does a lot of things half well and
A brief introduction to C++
 A brief introduction to C++ Rupert Nash r.nash@epcc.ed.ac.uk 13 June 2018 1 References Bjarne Stroustrup, Programming: Principles and Practice Using C++ (2nd Ed.). Assumes very little but it s long Bjarne
A brief introduction to C++ Rupert Nash r.nash@epcc.ed.ac.uk 13 June 2018 1 References Bjarne Stroustrup, Programming: Principles and Practice Using C++ (2nd Ed.). Assumes very little but it s long Bjarne
G52CPP C++ Programming Lecture 13
 G52CPP C++ Programming Lecture 13 Dr Jason Atkin http://www.cs.nott.ac.uk/~jaa/cpp/ g52cpp.html 1 Last lecture Function pointers Arrays of function pointers Virtual and non-virtual functions vtable and
G52CPP C++ Programming Lecture 13 Dr Jason Atkin http://www.cs.nott.ac.uk/~jaa/cpp/ g52cpp.html 1 Last lecture Function pointers Arrays of function pointers Virtual and non-virtual functions vtable and
Heap Arrays and Linked Lists. Steven R. Bagley
 Heap Arrays and Linked Lists Steven R. Bagley Recap Data is stored in variables Can be accessed by the variable name Or in an array, accessed by name and index Variables and arrays have a type Create our
Heap Arrays and Linked Lists Steven R. Bagley Recap Data is stored in variables Can be accessed by the variable name Or in an array, accessed by name and index Variables and arrays have a type Create our
Fast Introduction to Object Oriented Programming and C++
 Fast Introduction to Object Oriented Programming and C++ Daniel G. Aliaga Note: a compilation of slides from Jacques de Wet, Ohio State University, Chad Willwerth, and Daniel Aliaga. Outline Programming
Fast Introduction to Object Oriented Programming and C++ Daniel G. Aliaga Note: a compilation of slides from Jacques de Wet, Ohio State University, Chad Willwerth, and Daniel Aliaga. Outline Programming
CS201 Some Important Definitions
 CS201 Some Important Definitions For Viva Preparation 1. What is a program? A program is a precise sequence of steps to solve a particular problem. 2. What is a class? We write a C++ program using data
CS201 Some Important Definitions For Viva Preparation 1. What is a program? A program is a precise sequence of steps to solve a particular problem. 2. What is a class? We write a C++ program using data
Unit III Virtual Functions. Developed By Ms. K.M.Sanghavi
 Unit III Virtual Functions Developed By Ms. K.M.Sanghavi Topics Pointers- indirection Operators Memory Management: new and delete : Slide 23-24 / (Covered In Unit I Too) Accessing Arrays using pointers
Unit III Virtual Functions Developed By Ms. K.M.Sanghavi Topics Pointers- indirection Operators Memory Management: new and delete : Slide 23-24 / (Covered In Unit I Too) Accessing Arrays using pointers
Smart Pointers in C++11
 Smart Pointers in C++11 Karl Stratos 1 Background 1.1 Pointers When we write T x to create an instance x of type T, we allocate the amount of memory required for T and names it as x. We can reference (i.e.,
Smart Pointers in C++11 Karl Stratos 1 Background 1.1 Pointers When we write T x to create an instance x of type T, we allocate the amount of memory required for T and names it as x. We can reference (i.e.,
Separate Compilation Model
 Separate Compilation Model Recall: For a function call to compile, either the function s definition or declaration must appear previously in the same file. Goal: Compile only modules affected by recent
Separate Compilation Model Recall: For a function call to compile, either the function s definition or declaration must appear previously in the same file. Goal: Compile only modules affected by recent
C++ Primer. CS 148 Autumn
 C++ Primer CS 148 Autumn 2018-2019 1 Who is this for? If you are taking this class and are not familiar with some of the features of C++, then this guide is for you. In other words, if any of these words
C++ Primer CS 148 Autumn 2018-2019 1 Who is this for? If you are taking this class and are not familiar with some of the features of C++, then this guide is for you. In other words, if any of these words
Introduction to C++ Part II. Søren Debois. Department of Theoretical Computer Science IT University of Copenhagen. September 12th, 2005
 Introduction to C++ Part II Søren Debois Department of Theoretical Computer Science IT University of Copenhagen September 12th, 2005 Søren Debois (Theory, ITU) Introduction to C++ September 12th, 2005
Introduction to C++ Part II Søren Debois Department of Theoretical Computer Science IT University of Copenhagen September 12th, 2005 Søren Debois (Theory, ITU) Introduction to C++ September 12th, 2005
Topics. Constructor. Constructors
 Topics 1) How can we initialize an object when it's created? 2) How can we do things when an object is destroyed? 3) How can we write functions with different parameters? Slides #11 - Text 7.6-7.7 Constructors
Topics 1) How can we initialize an object when it's created? 2) How can we do things when an object is destroyed? 3) How can we write functions with different parameters? Slides #11 - Text 7.6-7.7 Constructors
These are notes for the third lecture; if statements and loops.
 These are notes for the third lecture; if statements and loops. 1 Yeah, this is going to be the second slide in a lot of lectures. 2 - Dominant language for desktop application development - Most modern
These are notes for the third lecture; if statements and loops. 1 Yeah, this is going to be the second slide in a lot of lectures. 2 - Dominant language for desktop application development - Most modern
Introduction to Linked Lists. Introduction to Recursion Search Algorithms CS 311 Data Structures and Algorithms
 Introduction to Linked Lists Introduction to Recursion Search Algorithms CS 311 Data Structures and Algorithms Lecture Slides Friday, September 25, 2009 Glenn G. Chappell Department of Computer Science
Introduction to Linked Lists Introduction to Recursion Search Algorithms CS 311 Data Structures and Algorithms Lecture Slides Friday, September 25, 2009 Glenn G. Chappell Department of Computer Science
1. Write the number of the definition on the right next to the term it defines. (a) copy 4
 CS 7B - Fall 2017 - Final Exam Solutions (in-class portion). Write your responses to following questions on this paper, or attach extra, as needed. sentences where appropriate and write out code using
CS 7B - Fall 2017 - Final Exam Solutions (in-class portion). Write your responses to following questions on this paper, or attach extra, as needed. sentences where appropriate and write out code using
377 Student Guide to C++
 377 Student Guide to C++ c Mark Corner January 21, 2004 1 Introduction In this course you will be using the C++ language to complete several programming assignments. Up to this point we have only provided
377 Student Guide to C++ c Mark Corner January 21, 2004 1 Introduction In this course you will be using the C++ language to complete several programming assignments. Up to this point we have only provided
CS201- Introduction to Programming Current Quizzes
 CS201- Introduction to Programming Current Quizzes Q.1 char name [] = Hello World ; In the above statement, a memory of characters will be allocated 13 11 12 (Ans) Q.2 A function is a block of statements
CS201- Introduction to Programming Current Quizzes Q.1 char name [] = Hello World ; In the above statement, a memory of characters will be allocated 13 11 12 (Ans) Q.2 A function is a block of statements
double d0, d1, d2, d3; double * dp = new double[4]; double da[4];
![double d0, d1, d2, d3; double * dp = new double[4]; double da[4]; double d0, d1, d2, d3; double * dp = new double[4]; double da[4];](/thumbs/91/107167668.jpg) All multiple choice questions are equally weighted. You can generally assume that code shown in the questions is intended to be syntactically correct, unless something in the question or one of the answers
All multiple choice questions are equally weighted. You can generally assume that code shown in the questions is intended to be syntactically correct, unless something in the question or one of the answers
INITIALISING POINTER VARIABLES; DYNAMIC VARIABLES; OPERATIONS ON POINTERS
 INITIALISING POINTER VARIABLES; DYNAMIC VARIABLES; OPERATIONS ON POINTERS Pages 792 to 800 Anna Rakitianskaia, University of Pretoria INITIALISING POINTER VARIABLES Pointer variables are declared by putting
INITIALISING POINTER VARIABLES; DYNAMIC VARIABLES; OPERATIONS ON POINTERS Pages 792 to 800 Anna Rakitianskaia, University of Pretoria INITIALISING POINTER VARIABLES Pointer variables are declared by putting
Financial computing with C++
 Financial Computing with C++, Lecture 6 - p1/24 Financial computing with C++ LG Gyurkó University of Oxford Michaelmas Term 2015 Financial Computing with C++, Lecture 6 - p2/24 Outline Linked lists Linked
Financial Computing with C++, Lecture 6 - p1/24 Financial computing with C++ LG Gyurkó University of Oxford Michaelmas Term 2015 Financial Computing with C++, Lecture 6 - p2/24 Outline Linked lists Linked
Chapter 9: Pointers. Copyright 2015, 2012, 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., Publishing as Addison-Wesley All rights reserved.
 Chapter 9: Pointers 9.1 Getting the Address of a Variable Getting the Address of a Variable Each variable in program is stored at a unique address Use address operator & to get address of a variable: int
Chapter 9: Pointers 9.1 Getting the Address of a Variable Getting the Address of a Variable Each variable in program is stored at a unique address Use address operator & to get address of a variable: int
Chapter 9: Getting the Address of a Variable. Something Like Pointers: Arrays. Pointer Variables 8/23/2014. Getting the Address of a Variable
 Chapter 9: Pointers 9.1 Getting the Address of a Variable Getting the Address of a Variable Each variable in program is stored at a unique address Use address operator & to get address of a variable: int
Chapter 9: Pointers 9.1 Getting the Address of a Variable Getting the Address of a Variable Each variable in program is stored at a unique address Use address operator & to get address of a variable: int
Vectors of Pointers to Objects. Vectors of Objects. Vectors of unique ptrs C++11. Arrays of Objects
 Vectors of Objects As we have mentioned earlier, you should almost always use vectors instead of arrays. If you need to keep track of persons (objects of class Person), you must decide what to store in
Vectors of Objects As we have mentioned earlier, you should almost always use vectors instead of arrays. If you need to keep track of persons (objects of class Person), you must decide what to store in
Implementing Abstractions
 Implementing Abstractions Pointers A pointer is a C++ variable that stores the address of an object. Given a pointer to an object, we can get back the original object. Can then read the object's value.
Implementing Abstractions Pointers A pointer is a C++ variable that stores the address of an object. Given a pointer to an object, we can get back the original object. Can then read the object's value.
C++ is Evolving. std::array
 C++ is Evolving C++ is an evolving language. A committee of the ISO (International Organization for Standards) ratifies proposed changes to C++. New standards have been released every few years. In this
C++ is Evolving C++ is an evolving language. A committee of the ISO (International Organization for Standards) ratifies proposed changes to C++. New standards have been released every few years. In this
Heap Arrays. Steven R. Bagley
 Heap Arrays Steven R. Bagley Recap Data is stored in variables Can be accessed by the variable name Or in an array, accessed by name and index a[42] = 35; Variables and arrays have a type int, char, double,
Heap Arrays Steven R. Bagley Recap Data is stored in variables Can be accessed by the variable name Or in an array, accessed by name and index a[42] = 35; Variables and arrays have a type int, char, double,
Written by John Bell for CS 342, Spring 2018
 Advanced OO Concepts Written by John Bell for CS 342, Spring 2018 Based on chapter 3 of The Object-Oriented Thought Process by Matt Weisfeld, with additional material from other sources. Constructors Constructors
Advanced OO Concepts Written by John Bell for CS 342, Spring 2018 Based on chapter 3 of The Object-Oriented Thought Process by Matt Weisfeld, with additional material from other sources. Constructors Constructors
6. Pointers, Structs, and Arrays. March 14 & 15, 2011
 March 14 & 15, 2011 Einführung in die Programmierung Introduction to C/C++, Tobias Weinzierl page 1 of 47 Outline Recapitulation Pointers Dynamic Memory Allocation Structs Arrays Bubble Sort Strings Einführung
March 14 & 15, 2011 Einführung in die Programmierung Introduction to C/C++, Tobias Weinzierl page 1 of 47 Outline Recapitulation Pointers Dynamic Memory Allocation Structs Arrays Bubble Sort Strings Einführung
The vector Class and Memory Management Chapter 17. Bjarne Stroustrup Lawrence "Pete" Petersen Walter Daugherity Fall 2007
 The vector Class and Memory Management Chapter 17 Bjarne Stroustrup Lawrence "Pete" Petersen Walter Daugherity Fall 2007 Abstract Vector is not just the most useful standard container, it is also provides
The vector Class and Memory Management Chapter 17 Bjarne Stroustrup Lawrence "Pete" Petersen Walter Daugherity Fall 2007 Abstract Vector is not just the most useful standard container, it is also provides
Chapter 18 Vectors and Arrays [and more on pointers (nmm) ] Bjarne Stroustrup
![Chapter 18 Vectors and Arrays [and more on pointers (nmm) ] Bjarne Stroustrup Chapter 18 Vectors and Arrays [and more on pointers (nmm) ] Bjarne Stroustrup](/thumbs/74/69971210.jpg) Chapter 18 Vectors and Arrays [and more on pointers (nmm) ] Bjarne Stroustrup www.stroustrup.com/programming Abstract arrays, pointers, copy semantics, elements access, references Next lecture: parameterization
Chapter 18 Vectors and Arrays [and more on pointers (nmm) ] Bjarne Stroustrup www.stroustrup.com/programming Abstract arrays, pointers, copy semantics, elements access, references Next lecture: parameterization
Programmazione. Prof. Marco Bertini
 Programmazione Prof. Marco Bertini marco.bertini@unifi.it http://www.micc.unifi.it/bertini/ Resource Management Memory, smart pointers and RAII Resource management The most commonly used resource in C++
Programmazione Prof. Marco Bertini marco.bertini@unifi.it http://www.micc.unifi.it/bertini/ Resource Management Memory, smart pointers and RAII Resource management The most commonly used resource in C++
dynamically allocated memory char* x = new char; int* x = new int[n]; ???...?
![dynamically allocated memory char* x = new char; int* x = new int[n]; ???...? dynamically allocated memory char* x = new char; int* x = new int[n]; ???...?](/thumbs/74/71153925.jpg) dynamically allocated memory char* x = new char; yields a memory address 1. allocates memory for a char 2. declares a pointer to a char 3. sets pointer to memory address x pointer? memory (1 byte) int*
dynamically allocated memory char* x = new char; yields a memory address 1. allocates memory for a char 2. declares a pointer to a char 3. sets pointer to memory address x pointer? memory (1 byte) int*
An Introduction to C++
 An Introduction to C++ Introduction to C++ C++ classes C++ class details To create a complex type in C In the.h file Define structs to store data Declare function prototypes The.h file serves as the interface
An Introduction to C++ Introduction to C++ C++ classes C++ class details To create a complex type in C In the.h file Define structs to store data Declare function prototypes The.h file serves as the interface
Variables, Memory and Pointers
 Variables, Memory and Pointers A variable is a named piece of memory The name stands in for the memory address int num; Variables, Memory and Pointers When a value is assigned to a variable, it is stored
Variables, Memory and Pointers A variable is a named piece of memory The name stands in for the memory address int num; Variables, Memory and Pointers When a value is assigned to a variable, it is stored
Quiz Start Time: 09:34 PM Time Left 82 sec(s)
 Quiz Start Time: 09:34 PM Time Left 82 sec(s) Question # 1 of 10 ( Start time: 09:34:54 PM ) Total Marks: 1 While developing a program; should we think about the user interface? //handouts main reusability
Quiz Start Time: 09:34 PM Time Left 82 sec(s) Question # 1 of 10 ( Start time: 09:34:54 PM ) Total Marks: 1 While developing a program; should we think about the user interface? //handouts main reusability
Data Structures and Algorithms for Engineers
 04-630 Data Structures and Algorithms for Engineers David Vernon Carnegie Mellon University Africa vernon@cmu.edu www.vernon.eu Data Structures and Algorithms for Engineers 1 Carnegie Mellon University
04-630 Data Structures and Algorithms for Engineers David Vernon Carnegie Mellon University Africa vernon@cmu.edu www.vernon.eu Data Structures and Algorithms for Engineers 1 Carnegie Mellon University
A Generic Non-intrusive Smart Pointer Implementation
 A Generic Non-intrusive Smart Pointer Implementation Anthony Williams 13th March 2001 1 Background I started writing an article about resource management using Resource Acquisition Is Initialisation (RAII),
A Generic Non-intrusive Smart Pointer Implementation Anthony Williams 13th March 2001 1 Background I started writing an article about resource management using Resource Acquisition Is Initialisation (RAII),
static CS106L Spring 2009 Handout #21 May 12, 2009 Introduction
 CS106L Spring 2009 Handout #21 May 12, 2009 static Introduction Most of the time, you'll design classes so that any two instances of that class are independent. That is, if you have two objects one and
CS106L Spring 2009 Handout #21 May 12, 2009 static Introduction Most of the time, you'll design classes so that any two instances of that class are independent. That is, if you have two objects one and
Recap: Pointers. int* int& *p &i &*&* ** * * * * IFMP 18, M. Schwerhoff
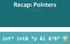 Recap: Pointers IFMP 18, M. Schwerhoff int* int& *p &i &*&* ** * * * * A 0 A 1 A 2 A 3 A 4 A 5 A 0 A 1 A 2 A 3 A 4 A 5 5 i int* p; A 0 A 1 A 2 A 3 A 4 A 5 5 i p int* p; p = &i; A 0 A 1 A 2 A 3 A 4 A 5
Recap: Pointers IFMP 18, M. Schwerhoff int* int& *p &i &*&* ** * * * * A 0 A 1 A 2 A 3 A 4 A 5 A 0 A 1 A 2 A 3 A 4 A 5 5 i int* p; A 0 A 1 A 2 A 3 A 4 A 5 5 i p int* p; p = &i; A 0 A 1 A 2 A 3 A 4 A 5
C++ Programming Lecture 7 Software Engineering Group
 C++ Programming Lecture 7 Software Engineering Group Philipp D. Schubert Contents 1. Template metaprogramming 2. Variadic template arguments 3. Smart pointer Template metaprogramming Template metaprogramming
C++ Programming Lecture 7 Software Engineering Group Philipp D. Schubert Contents 1. Template metaprogramming 2. Variadic template arguments 3. Smart pointer Template metaprogramming Template metaprogramming
No littering! Bjarne Stroustrup. Morgan Stanley, Columbia University
 No littering! Bjarne Stroustrup Morgan Stanley, Columbia University www.stroustrup.com Executive summary We now offer complete type- and resource-safety No memory corruption No resource leaks No garbage
No littering! Bjarne Stroustrup Morgan Stanley, Columbia University www.stroustrup.com Executive summary We now offer complete type- and resource-safety No memory corruption No resource leaks No garbage
COMP6771 Advanced C++ Programming
 1. COMP6771 Advanced C++ Programming Week 9 Multithreading (continued) 2016 www.cse.unsw.edu.au/ cs6771 2. So Far Program Workflows: Sequential, Parallel, Embarrassingly Parallel Memory: Shared Memory,
1. COMP6771 Advanced C++ Programming Week 9 Multithreading (continued) 2016 www.cse.unsw.edu.au/ cs6771 2. So Far Program Workflows: Sequential, Parallel, Embarrassingly Parallel Memory: Shared Memory,
C++ 8. Constructors and Destructors
 8. Constructors and Destructors C++ 1. When an instance of a class comes into scope, the function that executed is. a) Destructors b) Constructors c) Inline d) Friend 2. When a class object goes out of
8. Constructors and Destructors C++ 1. When an instance of a class comes into scope, the function that executed is. a) Destructors b) Constructors c) Inline d) Friend 2. When a class object goes out of
377 Student Guide to C++
 377 Student Guide to C++ c Mark Corner, edited by Emery Berger January 23, 2006 1 Introduction C++ is an object-oriented language and is one of the most frequently used languages for development due to
377 Student Guide to C++ c Mark Corner, edited by Emery Berger January 23, 2006 1 Introduction C++ is an object-oriented language and is one of the most frequently used languages for development due to
