COMP1511 focuses on writing programs. Effciency is also important. Often need to consider:
|
|
|
- Ginger Bennett
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Efficiency COMP1511 focuses on writing programs. Effciency is also important. Often need to consider: execution time memory use. A correct but slow program can be useless. Efficiency often depends on the size of the data being processed. Understanding this dependancy lets us predict program performance on larger data Informal exploration in COMP much more in COMP2521 and COMP3121
2 Analysis of Algorithms How can we find out whether a program is efficient or not? empirical approach - run the program, several times with different input sizes and measure the time taken theoretical approach - try to count the number of operations performed by the algorithm on input of size n
3 Linear Search Unordered Array - Code int linear_search(int array[], int length, int x) { for (int i = 0; i < length; i = i + 1) { if (array[i] == x) { return 1; return 0;
4 Linear Search Unordered Array - Informal Analysis Operations: start at first element inspect each element in turn stop when find X or reach end If there are N elements to search: Best case check 1 element Worst case check N elements If in list on average check N/2 elements If not in list check N elements
5 Linear Search Ordered Array - Code int linear_ordered(int array[], int length, int x) { for (int i = 0; i < length; i = i + 1) { if (array[i] == x) { return 1; else if (array[i] > x) { return 0; return 0;
6 Linear Search Ordered Array - Informal Analysis Operations: start at first element inspect each element in turn stop when find X or find value X or reach end If there are N elements to search: Best case check 1 element Worst case check N elements If in list on average check N/2 elements If not in list on average check N/2 elements
7 Binary Search Ordered Array - Code int binary_search(int array[], int length, int x) { int lower = 0; int upper = length - 1; while (lower <= upper) { int mid = (lower + upper)/ 2; if (array[mid] == x) { return 1; else if (array[mid] > x) { upper = mid - 1; else { lower = mid + 1; return 0;
8 Binary Search Ordered Array - Informal Analysis Operations: start with entire array at each step halve the range the element may be in stop when find X or range is empty If there are N elements to search Best case check 1 element Worst case check log2(n)+1 elements If in list on average check log2(n) elements
9 Binary Search Ordered Array - Informal Analysis log2(n) grows very slowly: log2(10) = 3.3 log2(1000) = 10 log2( ) = 20 log2( ) = 30 log2( ) = 40 Physicists estimate atoms in universe: log2(10 80 ) = 240 Binary search all atoms in universe in < 1 microsecond
10 Sorting Aim: rearrange a sequence so it is in non-decreasing order Advantages sorted sequence can be searched efficiently items with equal keys are located together The problem of sorting simple obvious algorithms too slow to sort large sequences better algorithms can sort very large sequences sorting extensively studied and many algorithms proposed. We ll look at one slow obvious algorithm: bubblesort And at one fast algorithm: quicksort We ll assume sorting array of ints. Straight-forward to extend code to handle other types of items (e.g. strings) and other data structures.
11 Bubblesort - Code void bubblesort(int array[], int length) { int swapped = 1; while (swapped) { swapped = 0; for (int i = 1; i < length; i = i + 1) { if (array[i] < array[i - 1]) { int tmp = array[i]; array[i] = array[i - 1]; array[i - 1] = tmp; swapped = 1;
12 Bubblesort - Code Inst void bubblesort(int array[], int length) { int swapped = 1; while (swapped) { swapped = 0; for (int i = 1; i < length; i = i + 1) { if (array[i] < array[i - 1]) { int tmp = array[i]; array[i] = array[i - 1]; array[i - 1] = tmp; swapped = 1;
13 Quicksort - Code void quicksort(int array[], int length) { quicksort1(array, 0, length - 1); void quicksort1(int array[], int lo, int hi) { if (lo >= hi) { return; int p = partition(array, lo, hi); // sort lower part of array quicksort1(array, lo, p); // sort upper part of array quicksort1(array, p + 1, hi);
14 Quicksort Partition - Code int partition(int array[], int lo, int hi) { int i = lo, j = hi; int pivotvalue = array[(lo + hi) / 2]; while (1) { while (array[i] < pivotvalue) { i = i + 1; while (array[j] > pivotvalue) { j = j - 1; if (i >= j) { return j; int temp = array[i]; array[i] = array[j]; array[j] = temp; i = i + 1; j = j - 1; return j;
15 Quicksort and Bubblesort Compared If we instrument quicksort and bubble sort code, we see: Array size (n) bubblesort operations quicksort operations bubblesort is proportional to n 2 quicksort is proportional to nlog 2 (n) if n is small, little difference if n is large, huge difference for large n, you need a good sorting algorithm like quicksort
! Search: find a given item in a list, return the. ! Sort: rearrange the items in a list into some. ! list could be: array, linked list, string, etc.
 Searching & Sorting Week 11 Gaddis: 8, 19.6,19.8 CS 5301 Fall 2014 Jill Seaman 1 Definitions of Search and Sort! Search: find a given item in a list, return the position of the item, or -1 if not found.!
Searching & Sorting Week 11 Gaddis: 8, 19.6,19.8 CS 5301 Fall 2014 Jill Seaman 1 Definitions of Search and Sort! Search: find a given item in a list, return the position of the item, or -1 if not found.!
Algorithm for siftdown(int currentposition) while true (infinite loop) do if the currentposition has NO children then return
 0. How would we write the BinaryHeap siftdown function recursively? [0] 6 [1] [] 15 10 Name: template class BinaryHeap { private: int maxsize; int numitems; T * heap;... [3] [4] [5] [6] 114 0
0. How would we write the BinaryHeap siftdown function recursively? [0] 6 [1] [] 15 10 Name: template class BinaryHeap { private: int maxsize; int numitems; T * heap;... [3] [4] [5] [6] 114 0
! Search: find a given item in a list, return the. ! Sort: rearrange the items in a list into some. ! list could be: array, linked list, string, etc.
 Searching & Sorting Week 11 Gaddis: 8, 19.6,19.8 CS 5301 Spring 2015 Jill Seaman 1 Definitions of Search and Sort! Search: find a given item in a list, return the position of the item, or -1 if not found.!
Searching & Sorting Week 11 Gaddis: 8, 19.6,19.8 CS 5301 Spring 2015 Jill Seaman 1 Definitions of Search and Sort! Search: find a given item in a list, return the position of the item, or -1 if not found.!
! Search: find a given item in a list, return the. ! Sort: rearrange the items in a list into some. ! list could be: array, linked list, string, etc.
 Searching & Sorting Week 11 Gaddis: 8, 19.6,19.8 (8th ed) Gaddis: 8, 20.6,20.8 (9th ed) CS 5301 Fall 2018 Jill Seaman!1 Definitions of Search and Sort! Search: find a given item in a list, return the position
Searching & Sorting Week 11 Gaddis: 8, 19.6,19.8 (8th ed) Gaddis: 8, 20.6,20.8 (9th ed) CS 5301 Fall 2018 Jill Seaman!1 Definitions of Search and Sort! Search: find a given item in a list, return the position
DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS. Sorting algorithms (insertion sort, bubble sort, selection sort)
 DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS Sorting algorithms (insertion sort, bubble sort, selection sort) Summary of the previous lecture Recursion Definition Examples Factorial Fibonacci Hanoi tower Printing of
DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS Sorting algorithms (insertion sort, bubble sort, selection sort) Summary of the previous lecture Recursion Definition Examples Factorial Fibonacci Hanoi tower Printing of
Quicksort. Repeat the process recursively for the left- and rightsub-blocks.
 Quicksort As the name implies, this is the fastest known sorting algorithm in practice. It is excellent for average input but bad for the worst-case input. (you will see later). Basic idea: (another divide-and-conquer
Quicksort As the name implies, this is the fastest known sorting algorithm in practice. It is excellent for average input but bad for the worst-case input. (you will see later). Basic idea: (another divide-and-conquer
CSCI 2170 Algorithm Analysis
 CSCI 2170 Algorithm Analysis Given two solutions (algorithms) for a given problem, which one is better? In computer science, we measure the quality of algorithms in terms of its memory and time efficiency.
CSCI 2170 Algorithm Analysis Given two solutions (algorithms) for a given problem, which one is better? In computer science, we measure the quality of algorithms in terms of its memory and time efficiency.
12/1/2016. Sorting. Savitch Chapter 7.4. Why sort. Easier to search (binary search) Sorting used as a step in many algorithms
 Sorting Savitch Chapter. Why sort Easier to search (binary search) Sorting used as a step in many algorithms Sorting algorithms There are many algorithms for sorting: Selection sort Insertion sort Bubble
Sorting Savitch Chapter. Why sort Easier to search (binary search) Sorting used as a step in many algorithms Sorting algorithms There are many algorithms for sorting: Selection sort Insertion sort Bubble
Sorting Algorithms. + Analysis of the Sorting Algorithms
 Sorting Algorithms + Analysis of the Sorting Algorithms Insertion Sort What if first k elements of array are already sorted? 4, 7, 12, 5, 19, 16 We can shift the tail of the sorted elements list down and
Sorting Algorithms + Analysis of the Sorting Algorithms Insertion Sort What if first k elements of array are already sorted? 4, 7, 12, 5, 19, 16 We can shift the tail of the sorted elements list down and
Ch 5-2. Arrays Part 2
 2014-1 Ch 5-2. Arrays Part 2 March 29, 2014 Advanced Networking Technology Lab. (YU-ANTL) Dept. of Information & Comm. Eng, Graduate School, Yeungnam University, KOREA (Tel : +82-53-810-2497; Fax : +82-53-810-4742
2014-1 Ch 5-2. Arrays Part 2 March 29, 2014 Advanced Networking Technology Lab. (YU-ANTL) Dept. of Information & Comm. Eng, Graduate School, Yeungnam University, KOREA (Tel : +82-53-810-2497; Fax : +82-53-810-4742
Recursion. ! When the initial copy finishes executing, it returns to the part of the program that made the initial call to the function.
 Recursion! A Recursive function is a functions that calls itself.! Recursive functions can be useful in solving problems that can be broken down into smaller or simpler subproblems of the same type.! A
Recursion! A Recursive function is a functions that calls itself.! Recursive functions can be useful in solving problems that can be broken down into smaller or simpler subproblems of the same type.! A
CS 112 Introduction to Computing II. Wayne Snyder Computer Science Department Boston University
 CS 112 Introduction to Computing II Wayne Snyder Department Boston University Today Recursive Sorting Methods and their Complexity: Mergesort Conclusions on sorting algorithms and complexity Next Time:
CS 112 Introduction to Computing II Wayne Snyder Department Boston University Today Recursive Sorting Methods and their Complexity: Mergesort Conclusions on sorting algorithms and complexity Next Time:
DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS
 DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS Fast sorting algorithms Shellsort, Mergesort, Quicksort Summary of the previous lecture Why sorting is needed? Examples from everyday life What are the basic operations in
DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS Fast sorting algorithms Shellsort, Mergesort, Quicksort Summary of the previous lecture Why sorting is needed? Examples from everyday life What are the basic operations in
Sorting & Searching. Hours: 10. Marks: 16
 Sorting & Searching CONTENTS 2.1 Sorting Techniques 1. Introduction 2. Selection sort 3. Insertion sort 4. Bubble sort 5. Merge sort 6. Radix sort ( Only algorithm ) 7. Shell sort ( Only algorithm ) 8.
Sorting & Searching CONTENTS 2.1 Sorting Techniques 1. Introduction 2. Selection sort 3. Insertion sort 4. Bubble sort 5. Merge sort 6. Radix sort ( Only algorithm ) 7. Shell sort ( Only algorithm ) 8.
LECTURE 17. Array Searching and Sorting
 LECTURE 17 Array Searching and Sorting ARRAY SEARCHING AND SORTING Today we ll be covering some of the more common ways for searching through an array to find an item, as well as some common ways to sort
LECTURE 17 Array Searching and Sorting ARRAY SEARCHING AND SORTING Today we ll be covering some of the more common ways for searching through an array to find an item, as well as some common ways to sort
8/2/10. Looking for something COMP 10 EXPLORING COMPUTER SCIENCE. Where is the book Modern Interiors? Lecture 7 Searching and Sorting TODAY'S OUTLINE
 Looking for something COMP 10 EXPLORING COMPUTER SCIENCE Where is the book Modern Interiors? Lecture 7 Searching and Sorting TODAY'S OUTLINE Searching algorithms Linear search Complexity Sorting algorithms
Looking for something COMP 10 EXPLORING COMPUTER SCIENCE Where is the book Modern Interiors? Lecture 7 Searching and Sorting TODAY'S OUTLINE Searching algorithms Linear search Complexity Sorting algorithms
Cosc 241 Programming and Problem Solving Lecture 17 (30/4/18) Quicksort
 1 Cosc 241 Programming and Problem Solving Lecture 17 (30/4/18) Quicksort Michael Albert michael.albert@cs.otago.ac.nz Keywords: sorting, quicksort The limits of sorting performance Algorithms which sort
1 Cosc 241 Programming and Problem Solving Lecture 17 (30/4/18) Quicksort Michael Albert michael.albert@cs.otago.ac.nz Keywords: sorting, quicksort The limits of sorting performance Algorithms which sort
Searching & Sorting. Definitions of Search and Sort. Other forms of Linear Search. Linear Search. Week 11. Gaddis: 8, 19.6,19.8.
 Searching & Sorting Week 11 Gaddis: 8, 19.6,19.8 CS 5301 Fa 2017 Ji Seaman 1 Definitions of Search and Sort Search: find a given item in a ist, return the position of the item, or -1 if not found. Sort:
Searching & Sorting Week 11 Gaddis: 8, 19.6,19.8 CS 5301 Fa 2017 Ji Seaman 1 Definitions of Search and Sort Search: find a given item in a ist, return the position of the item, or -1 if not found. Sort:
Quicksort. The divide-and-conquer strategy is used in quicksort. Below the recursion step is described:
 Quicksort Quicksort is a divide and conquer algorithm. Quicksort first divides a large list into two smaller sub-lists: the low elements and the high elements. Quicksort can then recursively sort the sub-lists.
Quicksort Quicksort is a divide and conquer algorithm. Quicksort first divides a large list into two smaller sub-lists: the low elements and the high elements. Quicksort can then recursively sort the sub-lists.
Merge- and Quick Sort
 Merge- and Quick Sort Merge Sort Quick Sort Exercises Unit 28 1 Merge Sort Merge Sort uses the algorithmic paradigm of divide and conquer: Divide the block into two subblocks of equal size; Merge Sort
Merge- and Quick Sort Merge Sort Quick Sort Exercises Unit 28 1 Merge Sort Merge Sort uses the algorithmic paradigm of divide and conquer: Divide the block into two subblocks of equal size; Merge Sort
Overview of Sorting Algorithms
 Unit 7 Sorting s Simple Sorting algorithms Quicksort Improving Quicksort Overview of Sorting s Given a collection of items we want to arrange them in an increasing or decreasing order. You probably have
Unit 7 Sorting s Simple Sorting algorithms Quicksort Improving Quicksort Overview of Sorting s Given a collection of items we want to arrange them in an increasing or decreasing order. You probably have
ECE 242 Data Structures and Algorithms. Advanced Sorting I. Lecture 16. Prof.
 ECE 242 Data Structures and Algorithms http://www.ecs.umass.edu/~polizzi/teaching/ece242/ Advanced Sorting I Lecture 16 Prof. Eric Polizzi Sorting Algorithms... so far Bubble Sort Selection Sort Insertion
ECE 242 Data Structures and Algorithms http://www.ecs.umass.edu/~polizzi/teaching/ece242/ Advanced Sorting I Lecture 16 Prof. Eric Polizzi Sorting Algorithms... so far Bubble Sort Selection Sort Insertion
Measuring algorithm efficiency
 CMPT 225 Measuring algorithm efficiency Timing Counting Cost functions Cases Best case Average case Worst case Searching Sorting O Notation O notation's mathematical basis O notation classes and notations
CMPT 225 Measuring algorithm efficiency Timing Counting Cost functions Cases Best case Average case Worst case Searching Sorting O Notation O notation's mathematical basis O notation classes and notations
CSE 2123 Sorting. Jeremy Morris
 CSE 2123 Sorting Jeremy Morris 1 Problem Specification: Sorting Given a list of values, put them in some kind of sorted order Need to know: Which order? Increasing? Decreasing? What does sorted order mean?
CSE 2123 Sorting Jeremy Morris 1 Problem Specification: Sorting Given a list of values, put them in some kind of sorted order Need to know: Which order? Increasing? Decreasing? What does sorted order mean?
CS 12 Fall 2003 Solutions for mid-term exam #2
 CS 12 Fall 2003 Solutions for mid-term exam #2 1. (10 points) Compilers and interpreters Provide short answers (a few sentences at most) to the following questions. (a) What is the difference between a
CS 12 Fall 2003 Solutions for mid-term exam #2 1. (10 points) Compilers and interpreters Provide short answers (a few sentences at most) to the following questions. (a) What is the difference between a
Computers in Engineering COMP 208. Where s Waldo? Linear Search. Searching and Sorting Michael A. Hawker
 Computers in Engineering COMP 208 Searching and Sorting Michael A. Hawker Where s Waldo? A common use for computers is to search for the whereabouts of a specific item in a list The most straightforward
Computers in Engineering COMP 208 Searching and Sorting Michael A. Hawker Where s Waldo? A common use for computers is to search for the whereabouts of a specific item in a list The most straightforward
CS125 : Introduction to Computer Science. Lecture Notes #38 and #39 Quicksort. c 2005, 2003, 2002, 2000 Jason Zych
 CS125 : Introduction to Computer Science Lecture Notes #38 and #39 Quicksort c 2005, 2003, 2002, 2000 Jason Zych 1 Lectures 38 and 39 : Quicksort Quicksort is the best sorting algorithm known which is
CS125 : Introduction to Computer Science Lecture Notes #38 and #39 Quicksort c 2005, 2003, 2002, 2000 Jason Zych 1 Lectures 38 and 39 : Quicksort Quicksort is the best sorting algorithm known which is
Searching for Information. A Simple Method for Searching. Simple Searching. Class #21: Searching/Sorting I
 Class #21: Searching/Sorting I Software Design II (CS 220): M. Allen, 26 Feb. 18 Searching for Information Many applications involve finding pieces of information Finding a book in a library or store catalogue
Class #21: Searching/Sorting I Software Design II (CS 220): M. Allen, 26 Feb. 18 Searching for Information Many applications involve finding pieces of information Finding a book in a library or store catalogue
KF5008 Algorithm Efficiency; Sorting and Searching Algorithms;
 KF5008 Algorithm Efficiency; Sorting and Searching Algorithms; Efficiency: Principles An algorithm is a step-by-step procedure for solving a stated problem. The algorithm will be performed by a processor
KF5008 Algorithm Efficiency; Sorting and Searching Algorithms; Efficiency: Principles An algorithm is a step-by-step procedure for solving a stated problem. The algorithm will be performed by a processor
Chapter 17: Sorting Algorithms. 1.1 Description Performance Example: Bubble Sort Bubble Sort Algorithm 5
 Chapter 17: Sorting Algorithms Christian Jacob 1 Bubble Sort 3 1.1 Description 3 1.2 Performance 3 1.3 Example: Bubble Sort 4 1.4 Bubble Sort Algorithm 5 2 Selection Sort 6 2.1 Description 6 2.2 Performance
Chapter 17: Sorting Algorithms Christian Jacob 1 Bubble Sort 3 1.1 Description 3 1.2 Performance 3 1.3 Example: Bubble Sort 4 1.4 Bubble Sort Algorithm 5 2 Selection Sort 6 2.1 Description 6 2.2 Performance
CSCI 2132 Software Development Lecture 18: Implementation of Recursive Algorithms
 Lecture 18 p.1 Faculty of Computer Science, Dalhousie University CSCI 2132 Software Development Lecture 18: Implementation of Recursive Algorithms 17-Oct-2018 Location: Chemistry 125 Time: 12:35 13:25
Lecture 18 p.1 Faculty of Computer Science, Dalhousie University CSCI 2132 Software Development Lecture 18: Implementation of Recursive Algorithms 17-Oct-2018 Location: Chemistry 125 Time: 12:35 13:25
Sorting is ordering a list of objects. Here are some sorting algorithms
 Sorting Sorting is ordering a list of objects. Here are some sorting algorithms Bubble sort Insertion sort Selection sort Mergesort Question: What is the lower bound for all sorting algorithms? Algorithms
Sorting Sorting is ordering a list of objects. Here are some sorting algorithms Bubble sort Insertion sort Selection sort Mergesort Question: What is the lower bound for all sorting algorithms? Algorithms
Sorting. Task Description. Selection Sort. Should we worry about speed?
 Sorting Should we worry about speed? Task Description We have an array of n values in any order We need to have the array sorted in ascending or descending order of values 2 Selection Sort Select the smallest
Sorting Should we worry about speed? Task Description We have an array of n values in any order We need to have the array sorted in ascending or descending order of values 2 Selection Sort Select the smallest
CS 310 Advanced Data Structures and Algorithms
 CS 310 Advanced Data Structures and Algorithms Sorting June 13, 2017 Tong Wang UMass Boston CS 310 June 13, 2017 1 / 42 Sorting One of the most fundamental problems in CS Input: a series of elements with
CS 310 Advanced Data Structures and Algorithms Sorting June 13, 2017 Tong Wang UMass Boston CS 310 June 13, 2017 1 / 42 Sorting One of the most fundamental problems in CS Input: a series of elements with
QuickSort. CIS 15 : Spring 2007
 QuickSort CIS 15 : Spring 2007 Functionalia TEA! HW 1 is DUE FRIDAY 23rd, 11:59 PM Do the BASIC Program First! Turn in Basic Program and Challenges Seperately Today: Binary Search Example QuickSort Submitting
QuickSort CIS 15 : Spring 2007 Functionalia TEA! HW 1 is DUE FRIDAY 23rd, 11:59 PM Do the BASIC Program First! Turn in Basic Program and Challenges Seperately Today: Binary Search Example QuickSort Submitting
Data Structures and Algorithms for Engineers
 0-630 Data Structures and Algorithms for Engineers David Vernon Carnegie Mellon University Africa vernon@cmu.edu www.vernon.eu Data Structures and Algorithms for Engineers 1 Carnegie Mellon University
0-630 Data Structures and Algorithms for Engineers David Vernon Carnegie Mellon University Africa vernon@cmu.edu www.vernon.eu Data Structures and Algorithms for Engineers 1 Carnegie Mellon University
Bubble sort starts with very first two elements, comparing them to check which one is greater.
 Bubble Sorting: Bubble sort is a simple sorting algorithm. This sorting algorithm is comparison-based algorithm in which each pair of adjacent elements is compared and the elements are swapped if they
Bubble Sorting: Bubble sort is a simple sorting algorithm. This sorting algorithm is comparison-based algorithm in which each pair of adjacent elements is compared and the elements are swapped if they
Divide and Conquer Sorting Algorithms and Noncomparison-based
 Divide and Conquer Sorting Algorithms and Noncomparison-based Sorting Algorithms COMP1927 16x1 Sedgewick Chapters 7 and 8 Sedgewick Chapter 6.10, Chapter 10 DIVIDE AND CONQUER SORTING ALGORITHMS Step 1
Divide and Conquer Sorting Algorithms and Noncomparison-based Sorting Algorithms COMP1927 16x1 Sedgewick Chapters 7 and 8 Sedgewick Chapter 6.10, Chapter 10 DIVIDE AND CONQUER SORTING ALGORITHMS Step 1
Search,Sort,Recursion
 Search,Sort,Recursion Searching, Sorting and Recursion Searching Linear Search Inserting into an Array Deleting from an Array Selection Sort Bubble Sort Binary Search Recursive Binary Search Searching
Search,Sort,Recursion Searching, Sorting and Recursion Searching Linear Search Inserting into an Array Deleting from an Array Selection Sort Bubble Sort Binary Search Recursive Binary Search Searching
Sorting. Bubble Sort. Pseudo Code for Bubble Sorting: Sorting is ordering a list of elements.
 Sorting Sorting is ordering a list of elements. Types of sorting: There are many types of algorithms exist based on the following criteria: Based on Complexity Based on Memory usage (Internal & External
Sorting Sorting is ordering a list of elements. Types of sorting: There are many types of algorithms exist based on the following criteria: Based on Complexity Based on Memory usage (Internal & External
Key question: how do we pick a good pivot (and what makes a good pivot in the first place)?
 More on sorting Mergesort (v2) Quicksort Mergesort in place in action 53 2 44 85 11 67 7 39 14 53 87 11 50 67 2 14 44 53 80 85 87 14 87 80 50 29 72 95 2 44 80 85 7 29 39 72 95 Boxes with same color are
More on sorting Mergesort (v2) Quicksort Mergesort in place in action 53 2 44 85 11 67 7 39 14 53 87 11 50 67 2 14 44 53 80 85 87 14 87 80 50 29 72 95 2 44 80 85 7 29 39 72 95 Boxes with same color are
CSE373: Data Structure & Algorithms Lecture 21: More Comparison Sorting. Aaron Bauer Winter 2014
 CSE373: Data Structure & Algorithms Lecture 21: More Comparison Sorting Aaron Bauer Winter 2014 The main problem, stated carefully For now, assume we have n comparable elements in an array and we want
CSE373: Data Structure & Algorithms Lecture 21: More Comparison Sorting Aaron Bauer Winter 2014 The main problem, stated carefully For now, assume we have n comparable elements in an array and we want
Quick-Sort fi fi fi 7 9. Quick-Sort Goodrich, Tamassia
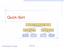 Quick-Sort 7 4 9 6 2 fi 2 4 6 7 9 4 2 fi 2 4 7 9 fi 7 9 2 fi 2 9 fi 9 Quick-Sort 1 Quick-Sort ( 10.2 text book) Quick-sort is a randomized sorting algorithm based on the divide-and-conquer paradigm: x
Quick-Sort 7 4 9 6 2 fi 2 4 6 7 9 4 2 fi 2 4 7 9 fi 7 9 2 fi 2 9 fi 9 Quick-Sort 1 Quick-Sort ( 10.2 text book) Quick-sort is a randomized sorting algorithm based on the divide-and-conquer paradigm: x
Outline. Quadratic-Time Sorting. Linearithmic-Time Sorting. Conclusion. Bubble/Shaker Sort Insertion Sort Odd-Even Sort
 Outline Quadratic-Time Sorting Bubble/Shaker Sort Insertion Sort Odd-Even Sort Linearithmic-Time Sorting Heap Sort Merge Sort Quick Sort Conclusion Check out this link for animation of various sorting
Outline Quadratic-Time Sorting Bubble/Shaker Sort Insertion Sort Odd-Even Sort Linearithmic-Time Sorting Heap Sort Merge Sort Quick Sort Conclusion Check out this link for animation of various sorting
Assignment 4: Question 1b omitted. Assignment 5: Question 1b clarification
 Announcements Assignment 4: Question 1b omitted Assignment 5: Question 1b clarification /* initialize and keep track of the last processed element smaller than pivot; use the mid variable from lecture
Announcements Assignment 4: Question 1b omitted Assignment 5: Question 1b clarification /* initialize and keep track of the last processed element smaller than pivot; use the mid variable from lecture
for (int outercounter = nums.length - 1; outercounter > 0 && swappedthatturn; outercounter --
 /* * A small set of sorting algorithms, written in Java and C++ * Note that they are written by a C++ beginner, may contain mistakes * Or bad habits that have to be avoided * @author Kadir Can Çelik */
/* * A small set of sorting algorithms, written in Java and C++ * Note that they are written by a C++ beginner, may contain mistakes * Or bad habits that have to be avoided * @author Kadir Can Çelik */
Unit Outline. Comparing Sorting Algorithms Heapsort Mergesort Quicksort More Comparisons Complexity of Sorting 2 / 33
 Unit #4: Sorting CPSC : Basic Algorithms and Data Structures Anthony Estey, Ed Knorr, and Mehrdad Oveisi 0W Unit Outline Comparing Sorting Algorithms Heapsort Mergesort Quicksort More Comparisons Complexity
Unit #4: Sorting CPSC : Basic Algorithms and Data Structures Anthony Estey, Ed Knorr, and Mehrdad Oveisi 0W Unit Outline Comparing Sorting Algorithms Heapsort Mergesort Quicksort More Comparisons Complexity
Searching and Sorting
 CS 211 SEARCH & SORT SEARCHING & SORTING Searching and Sorting Searching means that we have some collection of data, and we seek a particular value that might be contained within our collection. We provide
CS 211 SEARCH & SORT SEARCHING & SORTING Searching and Sorting Searching means that we have some collection of data, and we seek a particular value that might be contained within our collection. We provide
8/5/10 TODAY'S OUTLINE. Recursion COMP 10 EXPLORING COMPUTER SCIENCE. Revisit search and sorting using recursion. Recursion WHAT DOES THIS CODE DO?
 8/5/10 TODAY'S OUTLINE Recursion COMP 10 EXPLORING COMPUTER SCIENCE Revisit search and sorting using recursion Binary search Merge sort Lecture 8 Recursion WHAT DOES THIS CODE DO? A function is recursive
8/5/10 TODAY'S OUTLINE Recursion COMP 10 EXPLORING COMPUTER SCIENCE Revisit search and sorting using recursion Binary search Merge sort Lecture 8 Recursion WHAT DOES THIS CODE DO? A function is recursive
What is an algorithm?
 /0/ What is an algorithm? Searching and Sorting (Savitch, Chapter 7.) TOPICS Algorithms Complexity Binary Search Bubble Sort Insertion Sort Selection Sort A finite set of precise instrucons for performing
/0/ What is an algorithm? Searching and Sorting (Savitch, Chapter 7.) TOPICS Algorithms Complexity Binary Search Bubble Sort Insertion Sort Selection Sort A finite set of precise instrucons for performing
LECTURE NOTES ON DATA STRUCTURES THROUGH C
 LECTURE NOTES ON DATA STRUCTURES THROUGH C Revision 4 July 2013 L. V. NARASIMHA PRASAD Professor and Head E. KRISHNARAO PATRO Associate Professor Department of Computer Science and Engineering Shamshabad,Hyderabad
LECTURE NOTES ON DATA STRUCTURES THROUGH C Revision 4 July 2013 L. V. NARASIMHA PRASAD Professor and Head E. KRISHNARAO PATRO Associate Professor Department of Computer Science and Engineering Shamshabad,Hyderabad
Problem. Input: An array A = (A[1],..., A[n]) with length n. Output: a permutation A of A, that is sorted: A [i] A [j] for all. 1 i j n.
![Problem. Input: An array A = (A[1],..., A[n]) with length n. Output: a permutation A of A, that is sorted: A [i] A [j] for all. 1 i j n. Problem. Input: An array A = (A[1],..., A[n]) with length n. Output: a permutation A of A, that is sorted: A [i] A [j] for all. 1 i j n.](/thumbs/84/89326706.jpg) Problem 5. Sorting Simple Sorting, Quicksort, Mergesort Input: An array A = (A[1],..., A[n]) with length n. Output: a permutation A of A, that is sorted: A [i] A [j] for all 1 i j n. 98 99 Selection Sort
Problem 5. Sorting Simple Sorting, Quicksort, Mergesort Input: An array A = (A[1],..., A[n]) with length n. Output: a permutation A of A, that is sorted: A [i] A [j] for all 1 i j n. 98 99 Selection Sort
COMP 250. Lecture 7. Sorting a List: bubble sort selection sort insertion sort. Sept. 22, 2017
 COMP 250 Lecture 7 Sorting a List: bubble sort selection sort insertion sort Sept. 22, 20 1 Sorting BEFORE AFTER 2 2 2 Example: sorting exams by last name Sorting Algorithms Bubble sort Selection sort
COMP 250 Lecture 7 Sorting a List: bubble sort selection sort insertion sort Sept. 22, 20 1 Sorting BEFORE AFTER 2 2 2 Example: sorting exams by last name Sorting Algorithms Bubble sort Selection sort
Sorting. Sorting. Stable Sorting. In-place Sort. Bubble Sort. Bubble Sort. Selection (Tournament) Heapsort (Smoothsort) Mergesort Quicksort Bogosort
 Principles of Imperative Computation V. Adamchik CS 15-1 Lecture Carnegie Mellon University Sorting Sorting Sorting is ordering a list of objects. comparison non-comparison Hoare Knuth Bubble (Shell, Gnome)
Principles of Imperative Computation V. Adamchik CS 15-1 Lecture Carnegie Mellon University Sorting Sorting Sorting is ordering a list of objects. comparison non-comparison Hoare Knuth Bubble (Shell, Gnome)
ECE 242 Data Structures and Algorithms. Advanced Sorting II. Lecture 17. Prof.
 ECE 242 Data Structures and Algorithms http://www.ecs.umass.edu/~polizzi/teaching/ece242/ Advanced Sorting II Lecture 17 Prof. Eric Polizzi Sorting Algorithms... so far Bubble Sort Selection Sort Insertion
ECE 242 Data Structures and Algorithms http://www.ecs.umass.edu/~polizzi/teaching/ece242/ Advanced Sorting II Lecture 17 Prof. Eric Polizzi Sorting Algorithms... so far Bubble Sort Selection Sort Insertion
Sorting. Weiss chapter , 8.6
 Sorting Weiss chapter 8.1 8.3, 8.6 Sorting 5 3 9 2 8 7 3 2 1 4 1 2 2 3 3 4 5 7 8 9 Very many different sorting algorithms (bubblesort, insertion sort, selection sort, quicksort, heapsort, mergesort, shell
Sorting Weiss chapter 8.1 8.3, 8.6 Sorting 5 3 9 2 8 7 3 2 1 4 1 2 2 3 3 4 5 7 8 9 Very many different sorting algorithms (bubblesort, insertion sort, selection sort, quicksort, heapsort, mergesort, shell
DIVIDE AND CONQUER ALGORITHMS ANALYSIS WITH RECURRENCE EQUATIONS
 CHAPTER 11 SORTING ACKNOWLEDGEMENT: THESE SLIDES ARE ADAPTED FROM SLIDES PROVIDED WITH DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS IN C++, GOODRICH, TAMASSIA AND MOUNT (WILEY 2004) AND SLIDES FROM NANCY M. AMATO AND
CHAPTER 11 SORTING ACKNOWLEDGEMENT: THESE SLIDES ARE ADAPTED FROM SLIDES PROVIDED WITH DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS IN C++, GOODRICH, TAMASSIA AND MOUNT (WILEY 2004) AND SLIDES FROM NANCY M. AMATO AND
Data Types. Operators, Assignment, Output and Return Statements
 Pseudocode Reference Sheet rev 4/17 jbo Note: This document has been developed by WeTeach_CS, and is solely based on current study materials and practice tests provided on the TEA website. An official
Pseudocode Reference Sheet rev 4/17 jbo Note: This document has been developed by WeTeach_CS, and is solely based on current study materials and practice tests provided on the TEA website. An official
Sorting. Lecture10: Sorting II. Sorting Algorithms. Performance of Sorting Algorithms
 Sorting (2013F) Lecture10: Sorting II Bohyung Han CSE, POSTECH bhhan@postech.ac.kr Important operation when organizing data Ordering of elements Finding duplicate elements Ranking elements (i.e., n th
Sorting (2013F) Lecture10: Sorting II Bohyung Han CSE, POSTECH bhhan@postech.ac.kr Important operation when organizing data Ordering of elements Finding duplicate elements Ranking elements (i.e., n th
Searches and Sorts. ICT Officers. September 2018
 Searches and Sorts ICT Officers September 2018 1 Searches Searching is a powerful tool that will come up often in the USACO competition. Searching is the process of retrieving information stored within
Searches and Sorts ICT Officers September 2018 1 Searches Searching is a powerful tool that will come up often in the USACO competition. Searching is the process of retrieving information stored within
Sorting and Selection
 Sorting and Selection Introduction Divide and Conquer Merge-Sort Quick-Sort Radix-Sort Bucket-Sort 10-1 Introduction Assuming we have a sequence S storing a list of keyelement entries. The key of the element
Sorting and Selection Introduction Divide and Conquer Merge-Sort Quick-Sort Radix-Sort Bucket-Sort 10-1 Introduction Assuming we have a sequence S storing a list of keyelement entries. The key of the element
Lecture 15: Algorithms. AP Computer Science Principles
 Lecture 15: Algorithms AP Computer Science Principles Algorithm algorithm: precise sequence of instructions to solve a computational problem. Search for a name in a phone s contact list. Sort emails by
Lecture 15: Algorithms AP Computer Science Principles Algorithm algorithm: precise sequence of instructions to solve a computational problem. Search for a name in a phone s contact list. Sort emails by
Algorithmic Analysis. Go go Big O(h)!
 Algorithmic Analysis Go go Big O(h)! 1 Corresponding Book Sections Pearson: Chapter 6, Sections 1-3 Data Structures: 4.1-4.2.5 2 What is an Algorithm? Informally, any well defined computational procedure
Algorithmic Analysis Go go Big O(h)! 1 Corresponding Book Sections Pearson: Chapter 6, Sections 1-3 Data Structures: 4.1-4.2.5 2 What is an Algorithm? Informally, any well defined computational procedure
Programming challenges in C++
 Programming challenges in C++ 7. Using functions and improving sorting algorithms Nacho Iborra IES San Vicente This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution- NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0
Programming challenges in C++ 7. Using functions and improving sorting algorithms Nacho Iborra IES San Vicente This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution- NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0
CS 137 Part 8. Merge Sort, Quick Sort, Binary Search. November 20th, 2017
 CS 137 Part 8 Merge Sort, Quick Sort, Binary Search November 20th, 2017 This Week We re going to see two more complicated sorting algorithms that will be our first introduction to O(n log n) sorting algorithms.
CS 137 Part 8 Merge Sort, Quick Sort, Binary Search November 20th, 2017 This Week We re going to see two more complicated sorting algorithms that will be our first introduction to O(n log n) sorting algorithms.
Slide Set 18. for ENCM 339 Fall 2017 Section 01. Steve Norman, PhD, PEng
 Slide Set 18 for ENCM 339 Fall 2017 Section 01 Steve Norman, PhD, PEng Electrical & Computer Engineering Schulich School of Engineering University of Calgary December 2017 ENCM 339 Fall 2017 Section 01
Slide Set 18 for ENCM 339 Fall 2017 Section 01 Steve Norman, PhD, PEng Electrical & Computer Engineering Schulich School of Engineering University of Calgary December 2017 ENCM 339 Fall 2017 Section 01
Chapter 10 - Notes Applications of Arrays
 Chapter - Notes Applications of Arrays I. List Processing A. Definition: List - A set of values of the same data type. B. Lists and Arrays 1. A convenient way to store a list is in an array, probably a
Chapter - Notes Applications of Arrays I. List Processing A. Definition: List - A set of values of the same data type. B. Lists and Arrays 1. A convenient way to store a list is in an array, probably a
SCJ2013 Data Structure & Algorithms. Bubble Sort. Nor Bahiah Hj Ahmad & Dayang Norhayati A. Jawawi
 SCJ2013 Data Structure & Algorithms Bubble Sort Nor Bahiah Hj Ahmad & Dayang Norhayati A. Jawawi 1 Bubble Sort Sorting activities for Bubble: Go through multiple passes over the array. In every pass: Compare
SCJ2013 Data Structure & Algorithms Bubble Sort Nor Bahiah Hj Ahmad & Dayang Norhayati A. Jawawi 1 Bubble Sort Sorting activities for Bubble: Go through multiple passes over the array. In every pass: Compare
COP 3337 Test 3. private int minimumposition(int from) { Part 1: Selection Sort
 COP 3337 Test 3 NAME Part 1: Selection Sort The SelectionSorter class implements a selection sort on an array of strings. It is missing the minimumposition() method that returns the index position of the
COP 3337 Test 3 NAME Part 1: Selection Sort The SelectionSorter class implements a selection sort on an array of strings. It is missing the minimumposition() method that returns the index position of the
Introduction. Sorting. Definitions and Terminology: Program efficiency. Sorting Algorithm Analysis. 13. Sorting. 13. Sorting.
 Sorting Introduction Slides. Table of Contents. Introduction 3. Bubblesort 4. Bubblesort Complexity 5. Bubblesort Complexity (cont) 6. Selection Sort 7. Selection Sort Complexity 8. Duplex Selection Sort
Sorting Introduction Slides. Table of Contents. Introduction 3. Bubblesort 4. Bubblesort Complexity 5. Bubblesort Complexity (cont) 6. Selection Sort 7. Selection Sort Complexity 8. Duplex Selection Sort
Searching & Sorting. Definitions of Search and Sort. Other forms of Linear Search. Linear Search. Week 11. Gaddis: 8, 19.6,19.8. CS 5301 Spring 2017
 Searching & Sorting Week 11 Gaddis: 8, 19.6,19.8 CS 5301 Spring 2017 Ji Seaman 1 Definitions of Search and Sort Search: find a given item in a ist, return the position of the item, or -1 if not found.
Searching & Sorting Week 11 Gaddis: 8, 19.6,19.8 CS 5301 Spring 2017 Ji Seaman 1 Definitions of Search and Sort Search: find a given item in a ist, return the position of the item, or -1 if not found.
CS Sorting Terms & Definitions. Comparing Sorting Algorithms. Bubble Sort. Bubble Sort: Graphical Trace
 CS 704 Introduction to Data Structures and Software Engineering Sorting Terms & Definitions Internal sorts holds all data in RAM External sorts use Files Ascending : Low to High Descending : High to Low
CS 704 Introduction to Data Structures and Software Engineering Sorting Terms & Definitions Internal sorts holds all data in RAM External sorts use Files Ascending : Low to High Descending : High to Low
First Swedish Workshop on Multi-Core Computing MCC 2008 Ronneby: On Sorting and Load Balancing on Graphics Processors
 First Swedish Workshop on Multi-Core Computing MCC 2008 Ronneby: On Sorting and Load Balancing on Graphics Processors Daniel Cederman and Philippas Tsigas Distributed Computing Systems Chalmers University
First Swedish Workshop on Multi-Core Computing MCC 2008 Ronneby: On Sorting and Load Balancing on Graphics Processors Daniel Cederman and Philippas Tsigas Distributed Computing Systems Chalmers University
ECE 242 Fall 13 Exam I Profs. Wolf and Tessier
 ECE 242 Fall 13 Exam I Profs. Wolf and Tessier Name: ID Number: Maximum Achieved Question 1 16 Question 2 24 Question 3 18 Question 4 18 Question 5 24 Total 100 This exam is closed book, closed notes.
ECE 242 Fall 13 Exam I Profs. Wolf and Tessier Name: ID Number: Maximum Achieved Question 1 16 Question 2 24 Question 3 18 Question 4 18 Question 5 24 Total 100 This exam is closed book, closed notes.
Sorting. Quicksort analysis Bubble sort. November 20, 2017 Hassan Khosravi / Geoffrey Tien 1
 Sorting Quicksort analysis Bubble sort November 20, 2017 Hassan Khosravi / Geoffrey Tien 1 Quicksort analysis How long does Quicksort take to run? Let's consider the best and the worst case These differ
Sorting Quicksort analysis Bubble sort November 20, 2017 Hassan Khosravi / Geoffrey Tien 1 Quicksort analysis How long does Quicksort take to run? Let's consider the best and the worst case These differ
Computer Science Foundation Exam
 Computer Science Foundation Exam December 18, 015 Section I B COMPUTER SCIENCE NO books, notes, or calculators may be used, and you must work entirely on your own. SOLUTION Question # Max Pts Category
Computer Science Foundation Exam December 18, 015 Section I B COMPUTER SCIENCE NO books, notes, or calculators may be used, and you must work entirely on your own. SOLUTION Question # Max Pts Category
Sorting. CSE 143 Java. Insert for a Sorted List. Insertion Sort. Insertion Sort As A Card Game Operation. CSE143 Au
 CSE 43 Java Sorting Reading: Ch. 3 & Sec. 7.3 Sorting Binary search is a huge speedup over sequential search But requires the list be sorted Slight Problem: How do we get a sorted list? Maintain the list
CSE 43 Java Sorting Reading: Ch. 3 & Sec. 7.3 Sorting Binary search is a huge speedup over sequential search But requires the list be sorted Slight Problem: How do we get a sorted list? Maintain the list
CSE 143. Two important problems. Searching and Sorting. Review: Linear Search. Review: Binary Search. Example. How Efficient Is Linear Search?
 Searching and Sorting [Chapter 9, pp. 402-432] Two important problems Search: finding something in a set of data Sorting: putting a set of data in order Both very common, very useful operations Both can
Searching and Sorting [Chapter 9, pp. 402-432] Two important problems Search: finding something in a set of data Sorting: putting a set of data in order Both very common, very useful operations Both can
ITEC2620 Introduction to Data Structures
 ITEC2620 Introduction to Data Structures Lecture 5a Recursive Sorting Algorithms Overview Previous sorting algorithms were O(n 2 ) on average For 1 million records, that s 1 trillion operations slow! What
ITEC2620 Introduction to Data Structures Lecture 5a Recursive Sorting Algorithms Overview Previous sorting algorithms were O(n 2 ) on average For 1 million records, that s 1 trillion operations slow! What
Sorting. CPSC 259: Data Structures and Algorithms for Electrical Engineers. Hassan Khosravi
 CPSC 259: Data Structures and Algorithms for Electrical Engineers Sorting Textbook Reference: Thareja first edition: Chapter 14: Pages 586-606 Thareja second edition: Chapter 14: Pages 424-456 Hassan Khosravi
CPSC 259: Data Structures and Algorithms for Electrical Engineers Sorting Textbook Reference: Thareja first edition: Chapter 14: Pages 586-606 Thareja second edition: Chapter 14: Pages 424-456 Hassan Khosravi
Structured programming
 Exercises 9 Version 1.0, 13 December, 2016 Table of Contents 1. Remainders from lectures.................................................... 1 1.1. What is a pointer?.......................................................
Exercises 9 Version 1.0, 13 December, 2016 Table of Contents 1. Remainders from lectures.................................................... 1 1.1. What is a pointer?.......................................................
Algorithm efficiency can be measured in terms of: Time Space Other resources such as processors, network packets, etc.
 Algorithms Analysis Algorithm efficiency can be measured in terms of: Time Space Other resources such as processors, network packets, etc. Algorithms analysis tends to focus on time: Techniques for measuring
Algorithms Analysis Algorithm efficiency can be measured in terms of: Time Space Other resources such as processors, network packets, etc. Algorithms analysis tends to focus on time: Techniques for measuring
DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS
 DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS Fast sorting algorithms Heapsort, Radixsort Summary of the previous lecture Fast sorting algorithms Shellsort Mergesort Quicksort Why these algorithm is called FAST? What
DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS Fast sorting algorithms Heapsort, Radixsort Summary of the previous lecture Fast sorting algorithms Shellsort Mergesort Quicksort Why these algorithm is called FAST? What
Elementary Sorting Algorithms
 Elementary Sorting Algorithms COMP1927 16x1 Sedgewick Chapter 6 WARM UP EXERCISE: HANDSHAKE PROBLEM In a room of n people, how many different handshakes are possible? 0 + 1 + 2 + + (n-1) Using Maths formula:
Elementary Sorting Algorithms COMP1927 16x1 Sedgewick Chapter 6 WARM UP EXERCISE: HANDSHAKE PROBLEM In a room of n people, how many different handshakes are possible? 0 + 1 + 2 + + (n-1) Using Maths formula:
DESIGN AND ANALYSIS OF ALGORITHMS UNIT I INTRODUCTION
 1 DESIGN AND ANALYSIS OF ALGORITHMS UNIT I INTRODUCTION Objectives Explain what the use of algorithm is Describe the fundamentals of algorithmic problem solving Understand how to calculate the complexity
1 DESIGN AND ANALYSIS OF ALGORITHMS UNIT I INTRODUCTION Objectives Explain what the use of algorithm is Describe the fundamentals of algorithmic problem solving Understand how to calculate the complexity
Priority Queues (Heaps)
 Priority Queues (Heaps) 1 Priority Queues Many applications require that we process records with keys in order, but not necessarily in full sorted order. Often we collect a set of items and process the
Priority Queues (Heaps) 1 Priority Queues Many applications require that we process records with keys in order, but not necessarily in full sorted order. Often we collect a set of items and process the
ECE 2574: Data Structures and Algorithms - Basic Sorting Algorithms. C. L. Wyatt
 ECE 2574: Data Structures and Algorithms - Basic Sorting Algorithms C. L. Wyatt Today we will continue looking at sorting algorithms Bubble sort Insertion sort Merge sort Quick sort Common Sorting Algorithms
ECE 2574: Data Structures and Algorithms - Basic Sorting Algorithms C. L. Wyatt Today we will continue looking at sorting algorithms Bubble sort Insertion sort Merge sort Quick sort Common Sorting Algorithms
Sorting. CSC 143 Java. Insert for a Sorted List. Insertion Sort. Insertion Sort As A Card Game Operation CSC Picture
 CSC 43 Java Sorting Reading: Sec. 9.3 Sorting Binary search is a huge speedup over sequential search But requires the list be sorted Slight Problem: How do we get a sorted list? Maintain the list in sorted
CSC 43 Java Sorting Reading: Sec. 9.3 Sorting Binary search is a huge speedup over sequential search But requires the list be sorted Slight Problem: How do we get a sorted list? Maintain the list in sorted
Searching an Array: Linear and Binary Search. 21 July 2009 Programming and Data Structure 1
 Searching an Array: Linear and Binary Search 21 July 2009 Programming and Data Structure 1 Searching Check if a given element (key) occurs in the array. Two methods to be discussed: If the array elements
Searching an Array: Linear and Binary Search 21 July 2009 Programming and Data Structure 1 Searching Check if a given element (key) occurs in the array. Two methods to be discussed: If the array elements
QuickSort
 QuickSort 7 4 9 6 2 2 4 6 7 9 4 2 2 4 7 9 7 9 2 2 9 9 1 QuickSort QuickSort on an input sequence S with n elements consists of three steps: n n n Divide: partition S into two sequences S 1 and S 2 of about
QuickSort 7 4 9 6 2 2 4 6 7 9 4 2 2 4 7 9 7 9 2 2 9 9 1 QuickSort QuickSort on an input sequence S with n elements consists of three steps: n n n Divide: partition S into two sequences S 1 and S 2 of about
C/C++ Programming Lecture 18 Name:
 . The following is the textbook's code for a linear search on an unsorted array. //***************************************************************** // The searchlist function performs a linear search
. The following is the textbook's code for a linear search on an unsorted array. //***************************************************************** // The searchlist function performs a linear search
9/10/12. Outline. Part 5. Computational Complexity (2) Examples. (revisit) Properties of Growth-rate functions(1/3)
 Outline Part 5. Computational Complexity (2) Complexity of Algorithms Efficiency of Searching Algorithms Sorting Algorithms and Their Efficiencies CS 200 Algorithms and Data Structures 1 2 (revisit) Properties
Outline Part 5. Computational Complexity (2) Complexity of Algorithms Efficiency of Searching Algorithms Sorting Algorithms and Their Efficiencies CS 200 Algorithms and Data Structures 1 2 (revisit) Properties
CS 261 Data Structures. Big-Oh Analysis: A Review
 CS 261 Data Structures Big-Oh Analysis: A Review Big-Oh: Purpose How can we characterize the runtime or space usage of an algorithm? We want a method that: doesn t depend upon hardware used (e.g., PC,
CS 261 Data Structures Big-Oh Analysis: A Review Big-Oh: Purpose How can we characterize the runtime or space usage of an algorithm? We want a method that: doesn t depend upon hardware used (e.g., PC,
Lecture 6 Sorting and Searching
 Lecture 6 Sorting and Searching Sorting takes an unordered collection and makes it an ordered one. 1 2 3 4 5 6 77 42 35 12 101 5 1 2 3 4 5 6 5 12 35 42 77 101 There are many algorithms for sorting a list
Lecture 6 Sorting and Searching Sorting takes an unordered collection and makes it an ordered one. 1 2 3 4 5 6 77 42 35 12 101 5 1 2 3 4 5 6 5 12 35 42 77 101 There are many algorithms for sorting a list
Sorting. Order in the court! sorting 1
 Sorting Order in the court! sorting 1 Importance of sorting Sorting a list of values is a fundamental task of computers - this task is one of the primary reasons why people use computers in the first place
Sorting Order in the court! sorting 1 Importance of sorting Sorting a list of values is a fundamental task of computers - this task is one of the primary reasons why people use computers in the first place
CS302 - Data Structures using C++
 CS302 - Data Structures using C++ Topic: Recursion - Examples Kostas Alexis CS302 - Data Structures using C++ Topic: The Binary Search Kostas Alexis The Binary Search Assumes and exploits that the input
CS302 - Data Structures using C++ Topic: Recursion - Examples Kostas Alexis CS302 - Data Structures using C++ Topic: The Binary Search Kostas Alexis The Binary Search Assumes and exploits that the input
MPATE-GE 2618: C Programming for Music Technology. Unit 4.2
 MPATE-GE 2618: C Programming for Music Technology Unit 4.2 Quiz 1 results (out of 25) Mean: 19.9, (standard deviation = 3.9) Equivalent to 79.1% (SD = 15.6) Median: 21.5 High score: 24 Low score: 13 Pointer
MPATE-GE 2618: C Programming for Music Technology Unit 4.2 Quiz 1 results (out of 25) Mean: 19.9, (standard deviation = 3.9) Equivalent to 79.1% (SD = 15.6) Median: 21.5 High score: 24 Low score: 13 Pointer
(8-2) Arrays II H&K Chapter 7. Instructor - Andrew S. O Fallon CptS 121 (February 28, 2018) Washington State University
 (8-2) Arrays II H&K Chapter 7 Instructor - Andrew S. O Fallon CptS 121 (February 28, 2018) Washington State University Array Searching (1) ots of motivating problems Find a name in the phone book Find
(8-2) Arrays II H&K Chapter 7 Instructor - Andrew S. O Fallon CptS 121 (February 28, 2018) Washington State University Array Searching (1) ots of motivating problems Find a name in the phone book Find
Lecture 7: Searching and Sorting Algorithms
 Reading materials Dale, Joyce, Weems:Dale, Joyce, Weems: 10.1-10.5 OpenDSA: 11 (Sorting) and 13 (Searching) Liang (10): 7 (for searching and quadratic sorts), 25 (comprehensive edition only) Contents 1
Reading materials Dale, Joyce, Weems:Dale, Joyce, Weems: 10.1-10.5 OpenDSA: 11 (Sorting) and 13 (Searching) Liang (10): 7 (for searching and quadratic sorts), 25 (comprehensive edition only) Contents 1
CSE373: Data Structure & Algorithms Lecture 18: Comparison Sorting. Dan Grossman Fall 2013
 CSE373: Data Structure & Algorithms Lecture 18: Comparison Sorting Dan Grossman Fall 2013 Introduction to Sorting Stacks, queues, priority queues, and dictionaries all focused on providing one element
CSE373: Data Structure & Algorithms Lecture 18: Comparison Sorting Dan Grossman Fall 2013 Introduction to Sorting Stacks, queues, priority queues, and dictionaries all focused on providing one element
